RESISTANCE TO ANTIBIOTICS. A. Some scary statistics. B. Nature of genotypic alterations drug resistance
|
|
|
- Shonda Lambert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IV. RESISTANCE T ANTIBITICS A. Some scary statistics B. Nature of genotypic alterations drug resistance 1. Spontaneous mutations a) is the origin of resistance b) occurs in low frequency 1/10 6-1/10 8 and is unrelated to contact with an antibiotic c) mutations rarely complete resistance d) an infection can contain organisms e) selection process is important in increasing the small numbers of drug resistant mutants that appear 2. Transformation a) uptake of genetic material coding for resistance by a sensitive bacterium donated by a resistant bacterium on lysis b) may be how Strep. pneumoniae became resistant to penicillins 3. Transduction a) important especially with the gram-positive and especially of clinical importance with the Staph b) during lysogeny a phage can pick up randomly or selectively bits of genetic pieces and/or plasmids coding for resistance which are then donated to a sensitive cell when infected by the phage 4. Conjugation a) resistant determinants located on a plasmid plasmid = nonessential, self-replicating element composed of a circular piece of double stranded DNA; is independent from chromosomal DNA R factor = a plasmid coding for resistance and conjugation Transposon = genes coding for resistance with insertion sequences at either end - can "jump" from plasmid to chromosome and between plasmids e.g., TEM gene coding for β-lactamase b) R-factor is transferred during mating to drug sensitive recipient cells c) R-factor can be split into two determinants, (1) a resistance transfer factor (RTF) coding for pilus formation and, (2) a resistance determinant; Staph lack RTF and R-factor is transferred mainly by transduction d) dangers of conjugation: i. gram-negative enteric bacteria can transfer R-factor by conjugation to same or even different genera ii. plasmids usually carry genes determining resistance to multiple antimicrobials iii. bacteria can contain multiple plasmids iv. greater than 50% of GI tract inhabitants are capable of transferring R- factor and they may serve as a reservoir of R factors e) modifying factors i. R transfer is under genetic control, however; a repressor for R transfer normally limits the process ii. microbes carrying R-factor may be at a selective disadvantage in an antibiotic free environment which also limits the significance of this process 13
2 C. Mechanisms of Ab resistance 1. conversion of active drug to inactive derivative - e.g. hydrolysis of penicillins and cephalosporins by β-lactamases; usually plasmid born S S 3 R C NH C R C NH 2 C N 3 C N C 2 R C a penicillin a cephalosporin a) e.g. β-lactamases i. gram-positive bacteria β-lactamases 1. inducible 2. excreted 3. will lower extracellular antibiotic concentration 4. most gram(+) do not make β-lactamases 5. Staph. aureus makes a narrow spectrum β-lactamase with high affinity for most penicillins. It is usually called a "penicillinase." 6. penicillinase has a high Km for penicillinase resistant penicillins and for some cephalosporins ii. gram-negative bacteria β-lactamases 1. constitutive or inducible 2. not excreted but located in periplasmic space 3. keep intracellular antibiotic concentrations low 4. don't affect extracellular antibiotic concentrations 5. > 20 known enzymes which vary in Km for different β-lactam antibiotics; some have broad specificity, e.g. Enterobacter and Klebsiella β-lactamases 6. plasmid-encoded β-lactamases a. produced by S. aureus (gm+), H. influenzae, N. gonorrhoeae, Salmonella, Shigella, E. coli, Klebsiella b. generally inhibited by the available β-lactamase inhibitors 7. chromosomally encoded (usually inducible) (Group 1 in table) a. produced by Enterobacter, Citrobacter, and Pseudomomas, Serratia, Morganella, Providencia b. not generally inhibited by the available -lactamase inhibitors c.is a cephalosporinase 14
3 b) e.g. acetyl transferases - inactivation of chloramphenicol 2 N H C H NH C 2 H Cl 2 acetyltransferase is an inducible enzyme in some gram-positive and constitutive in some gram-negative c) other enzymes, e.g. transformation of aminoglycoside antibiotics; free H - groups on sugars can be acetylated, phosphorylated, or adenylated; enzymes are coded for on plasmids 2. modification of drug-sensitive site - via mutation; usually seen with drugs affecting protein synthesis e.g. streptomycin - subtle changes in protein component of 30s ribosomal subunit may prevent streptomycin from binding e.g. rifamycin - altered DNA dependent RNA polymerase prevents binding e.g. β-lactams - alteration in penicillin binding protein (PBP) which can result in conformational changes on the binding site thus decreasing antibiotic affinity. The amount of PBP can also be decreased. 3. loss of bacterial cell permeability e.g. β-lactams - change in porin proteins results in decreased permeability; Pseudomonas is infamous for porin exclusion 4. enhanced efflux e.g. tetracyclines; multidrug efflux pumps are increasingly important in resistance; may be broad spectrum efflux pumps 5. enhancement of alternate metabolic pathway to avoid inhibited pathway; e.g., sulfa drugs where microbes synthesize enough PABA to overcome block in folate synthesis 6. absence of autolytic enzymes e.g. β-lactams - tolerant cells lack autolysins C. Therapeutic Control of Drug Resistance 1. give the proper antibiotic a) is it necessary? b) is pathogen sensitive? c) will drug get to site of infection? d) is antibiotic unnecessarily toxic (risk vs. benefit) - decreases compliance? e) is antibiotic expensive (cost vs. risk of infection) - decreases compliance? 2. give high antibiotic loading doses - e.g. a one-time STAT dose 3. simultaneous therapy with unrelated (MA) antibiotics 4. use only when necessary - antibiotics in animal feeds? 5. randomly use different antibiotics - rotation 6. patient compliance to complete course of therapy 7. concentration dependent killing vs time dependent killing 15
4 a) b) c) 16
5 8. the concept of mutant selection window a) 17
6 V. ANTIBITICS INHIBITRY BACTERIAL CELL WALL BISYNTHESIS A. PENICILLINS 1. Introduction a) still most widely prescribed and useful group of Abs b) are potent, nontoxic, and have fairly broad spectrum with use of β-lactamase inhibitors 2. Chemistry R C NH * * C N cysteine S 3 C 3 C 2 H valine a) Structure/Activity Relationships considerations 3. Production 1. need conformation, intact β-lactam ring 2. can modify 5-membered ring and replace R groups Fleming, P. notatum Flory and Chain international cooperation with U.S. and England mainly using P. chrysogenum England - Beecham developed process for forming 6-APA which lead to commercial development of semisynthetic derivatives 18
7 4. General Properties of Penicillins a) stability in stomach acid varies; Pen G is labile and has low bioavailability so is only rarely used orally; amoxicillin has high stability and bioavailability and is only used orally. b) susceptibility to Gram + β-lactamses (penicillinase) varies; Pen G, Pen V, amox, ampi are very susceptible but modification of side chain can lead to penicillinase resistance, e.g. dicloxacillin (a "penicillinase resistant penicillin") c) susceptibility to Gram ( ) β-lactamases highly susceptible except ticarcillin and piperacillin d) bacteriocidal e) allergy This is considered the "major determinant" of penicillin allergy. The "minor determinants" are a variety of other penicillin breakdown products. 1) immediate - urticaria, pruritus, shock; occurs within 60 min - ~.01% (for Pen G); 1g E mediated and directed against minor determinants 2) accelerated - rash; occurs within 72 h - common (5-10% of treated); 1g M and 1g E directed against major determinant 3) late - fever, urticaria; occurs > 72 h rare; 1g M and 1g E 19
8 4) incidence - 5% show (+) reaction with skin test using penicilloyl polylysine (Prepen ) 50-70% of (+) have clinical Sx on amin. of penicillins - mostly rash <1% of (+) have serious reaction; overall incidence is about <.02%, <.0014% death semisynthetic show reactions; oral show reactions relative to parenteral doses but an allergy to one penicillin means that the patient would be assumed to have a problem with any penicillin allergy to penicillin does not necessarily mean allergy to cephalosporins but cross reactivity does occur (~10%); rule: if patient has serious reaction to a penicillin, don't give any beta lactam except aztreonam ampicillin 9.5% allergy; this is due, in part, to the chemical nature of ampicillin, i.e. not all ampicillin induced rashes are true penicillin allergies. Amoxicillin has a somewhat lower incidence densensitization protocols can be employed if infection requires penicillin therapy for an allergic patient a rare interstitial nephritis is sometimes seen which may be a type of allergic reaction 5) skin testing - is useful but an imperfect test (see above) commercial PrePen can better predict rashes than anaphylaxis a pharmacist can make up a mixture of "minor determinants" that will better predict more serious reactions but this is rarely done 6) precautions on penicillin allergy a) ask about prior reactions b) ask about the type of allergic reaction (i.e. symptoms of anaphylaxis) c) don't give a cephalosporin to a patient who has had an anaphylactic or other serious reaction to a penicillin d) skin testing may be helpful if a penicillin is clearly needed e) a desensitization protocol (small repetitive increasing doses of a penicillin) can be used if a penicillin is clearly needed. Go to the literature to find a good protocol. Patient probably needs to be hospitalized. f) toxicity some rare toxicity with high dose IV-therapy; diarrhea (ampicillin); neurotox; seizures; nephrotox; hemolytic anemia pseudomembranous colitis and bacterial overgrowth with the broad spectrum agents; generally the safest group of antibiotics, however g) absorption orally - varies with the drug used 20
9 for Pen G, T 1/2 =.7h oral absorption Pen G 15-30% Pen V 60% ampicillin 30-50% amoxicillin 70-80% h) distribution - high in kidney (>70%), low in cerebrospinal fluid (except when inflammation is present) i) metabolism and serum protein binding and excretion not significant [>80% excreted unchanged] Pen G - 65% bound phenoxymethyl - 75% bound ampicillin - 25% bound methicillin - 38% bound oxacillin - 80% bound cloxacillin - 95% (but binding is not tight so that these differences are not very important greater than 70% via kidneys and is rapid; must adjust dose in renal failure j) Probenecid - inhibits tubular secretion of organic acids (most pens and cephs) which results in increased β-lactam blood levels (~2 x). 21
10 TABLE 1 - Properties of Penicillins Type of penicillin Structure ral absorption 1. "Natural: Penicillin G 2 poor Routes of admin. IV, IM Penicillin V % P 2. Amino Ampicillin 30-50% P, IV, IM NH 2 Amoxicillin H 70-90% P NH 2 3. Penicillinase resistant Nafcillin poor IV, IM C 2 H 5 xacillin poor IV, IM Cl N 3 Dicloxacillin Cl N 3 good P 4. Extended spectrum Carbenicillin (indanyl) C 2 H K P Ticarcillin S poor IV, IM C 2 H Piperacillin 3 2 N N C NH poor IV, IM 22
11 TABLE 2 - Antimicrobial Spectrum of Penicillins Penicillin Type Staph β- lactamase (penicillinase) resistance Gram( ) β-lactamase resistance spectrum Penicillin G no no Gm(+) and some neisseria IV Penicillin V no no " " mild GM(=) infections e.g. strep throat Ampicillin no no Gm(+) and some gm( ) IV, IM Amoxicillin no no " " oral use for mild infections use Nafcillin yes no staph IV, IM xacillin yes no " IV, IM Dicloxacillin yes no " P Carbenicillin (indanyl) no ± mild UTI involving pseudomonas Ticarcillin no ± Pseudomonas* and also some Enterobacteriaceae Piperacillin no better than ticar Pseudomonas* and also some Enterobacteriaceae P IV, IM IV, IM *Pseudomonas often elaborate group 1 beta lactamases (cephalosporinase) which will not hydrolyze ticarand piperacillin (i.e. ticar and pip can be effective for pseudomonas infections). TABLE 3 - Combination Products with β-lactamase inhibitors resistance to Staph β-lactamase resistance to Gram( ) β-lactamase* spectrum amoxicillin/clavulonic acid (Agumentin ) yes yes broad P ampicillin/sulbactam (Unisyn ) yes yes broad IM, IV ticarcillin/clavulonic acid (Timentin ) yes yes broad IM, IV piperacillin/tazobactam (Zosyn ) yes yes broad IM, IV *note: the type 1 β-lactamase of Pseudomonas is not inhibited by the available β-lactamase inhibitors but ticar and pip are not usually hydrolyzed so they can be used. use 5. More detail on penicillins on UW formulary 23
12 a) Penicillin G - (mainly IV use) 1) spectrum a. gram-positive cocci i. Strep. pyogenes (Group A, beta hemolytic strep) causes strep throat, scarlet fever, erisiphelis and necrotizing faciitis. S. pyrogenes generally sens. - usually don't even test. ii. Streptococcus pneumoniae - now resistance to penicillins is a problem, resistance is due to altered PBPs. (UW = ~ 20% resistant) The most common agent in otitis media (middle ear infection) (~ 35%) and community acquired pneumonia. (~ 50-80%) A very important pathogen. iii. Anaerobic strep. - sensitive iv. S. viridans - usually sens. v. Enterococcus faecalis Enterococcus faecium often resistant and need heroic treatments E. faecium is the most difficult to treat. At UW most strains are resistant to pen G and vanco. vi. Staph - almost all are now resistant b. gram-positive rods i. Clostridium - usually sens. e.g. C. tetani, C. perfringens but C. difficile is resistant c. gram-negative cocci i. Neisseria meningitidis - often sensitive ii. Neisseria gonorrhoeae - no longer agent of choice for this infection due to acquisition of plasmids coding for TEM-1 beta lactamases. d. gram-negative rods - mostly resistant i. Enterobacteriaeae - E. Coli, Salmonella, Shigella, Serratia, Enterobacter, Klebsiella, Proteus - all resistant ii. Pseudomonas - resistant iii. Hemophilus - resistant e. Treponema pallidum - sens. 2) Indications - penicillin G (IV) a. meningococcal meningitis and septicemia b. clostridial infections (not C. difficile) c. listeria infections d. serious streptococcal infections (but strep pneumoniae can be resistant) e. neurosyphilis b) Procaine Pen G Crysticillin Apothecon; Wyeillin Wyeth (IM use) 1) equimolar mix of Pen G and Procaine = insol salt. 2) peak blood levels in about 2 h. and persist for about 24 h. 3) use: gonorrhea, 4.8 MU 1 M plus 1 g Probenecid (this is now not a regimen of first choice due to increased resistance) c) Benzathine Pen G Bicillin Wyeth (IM use) 24
13 1) N-N-dibenzylethylenediamine pen G; longest acting of all penicillins 2) levels persist for days but are low not good for gonorrhea but K for syphilis 3) good for rheumatic fever prophylaxis and strep. throat treatment d) Pen V (P use) - 60% absorbed, acid stable, but food still interferes with absorption somewhat best given 1/2h ac or 2-3h pc use: mild infections, not useful for gonorrhea, Neisseria, or syphilis indications: for mild to moderate URI caused by strep, for scarlet fever, for erysipelas, for strep pyrogenes (strep throat) e) Penicillinase - resistant penicillins -- semisynthetic 1) nafcillin and dicloxacillin a. should be reserved for Staph infections b. dicloxacillin is the P drug of choice here c. methicillin resistant staph (MRS) are resistant due to altered penicillin binding proteins (PBPs). MRS will be usually resistant to all beta lactams,; vancomycin plus an aminoglycoside may be needed. 6. Amino Penicillins a) Ampicillin (mainly used IV now) NH 2 C 1) A minor chemical modification broader spectrum; still P'ase sens.; penetrates porins in gram-negative bacteria because it is a relatively polar molecule 2) Spectrum a. Gram-positive - similar to Pen G but sl. less active. Exception = Enterococcus faecalis which is generally more sensitive to ampicillin, nevertheless is often used in combination with an aminoglycoside for E. faecalis b. Gram-negative - active here where Pen G and Pen V are not - these agents penetrate Gm (-) cell wall. For example, the following are often sensitive: E. coli - causes >90% of all acute, uncomplicated urinary tract infections - resistance is on the increase due to β-lactamase production Proteus mirabilis - causes 60-70% of all proteus infections - is urinary tract invader Proteus vulgaris, Morganella morganii, Providencia sp. and Citrobacter are resistant to ampicillin and are more difficult to treat Salmonella - typhoid, gasteroenteritis, bacteremia (resistance to ampicillin is ) Shigella - alternate to TMP-SMX Neisseria meningitidis sens. unless pencillinase producer Neisseria gonorrhoeae 3.5 g stat dose is convenient, but effectiveness is due to penicillinase producers. No longer agent of first choice here. H. influenza - common cause of otitis media in children, and bacterial meningitis in children, other = pneumonia, etc., epiglotitis; effective-ness of ampicillin is decreasing due to β-lactamases 25
14 Not effective for most other Gm (-) pathogens, e.g. - Pseudomonas - sepsis, particularly a problem with burn and immunosuppressed patients; UTI - Enterobacter - occasional cause of UTI and sepsis; difficult to treat - Klebsiella - pneumonia, UTI - Serratia - pneumonia, UTI, sepsis, endocarditis 3) Distribution - similar to Pen G, but larger amount secreted via bile and is conc. in intestine have incidence of diarrhea and problems with super infection in G.I. tract. (Note: high gut concentrations may be an advantage for sensitive Shigella, Salmonella infections.) 4) Adverse effects - secreted in bile and diarrhea and GI overgrowth with Candida is a problem; risk of pseudomembranous colitis with ampicillin and all β-lactams having a broad spectrum. 5) Allergy % get some type of allergic reaction. Question - Does reaction to ampi. mean allergic to penicillin? Answer - maybe not but is difficult to distinguish true Pen. allergy from ampicillin allergy. Macropapular rash is usually seen vs. urticaria in true penicillin allergy. macropapular 1. nonimmunologic - no (+) skin test for penicillin 2. start at 4 days after initiation of drug 3. on trunk at first 4. associated with viral infections esp. mono 5. dose related 6. doesn't usually itch 7. mechanism? 8. can continue drug and readminister but often chart is labeled "allergic to penicillin" urticarial 1. onset in <1 day 2. itch "hives" 3. true allergic reaction to penicillin - don't give again b) Amoxicillin H C NH R NH 2 1) oral only 2) better oral drug than ampicillin - T1/2, flow in bile less diarrhea, food doesn't affect absorption much 3) TID dosing or high dose BID 4) not as good for gut infections as ampicillin, e.g. Shigellosis 5) indications a. ear, nose, throat - Strep. pneumoniae, Strep. pyogenes, H. flu (res. is problem) 26
15 b. genitourinary - E. coli, Proteus, Enterococcus faecalis c. soft tissue - Strep., H. flu (resistance is a problem) d. prophylaxis of endocarditis in dental patients d) Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid Augmentin Glaxo and now generic products 2 H N clavulanic acid 1) The presence of clavulanic acid extends the spectrum to include β-lactamase producing microorganisms including the important pediatric pathogen Moraxella catarrhalis (causes otitis media, URI, LRI). B. catarrhalis usually produces β- lactamase. Also pick up Staph (not agent of choice), Bacteriodes, some Klebsiella, some Enterobacter and β-lactamase producing H. influenzae 2) Available in tablet and suspension form. TID or BID dosing in 250 mg, 500 mg and 825 mg tablets. Each contain 125 mg of clavulanic acid so the tablets cannot be interchanged, i.e. 2 x 250 mg 1 x 500 mg 3) Clavulanic acid does not inhibit all β-lactamases; e.g. not Group 1 (more later). 4) Indications a. lower respiratory infection - including β-lactamases producing H. flu and M. cat. b. otitis media - Strep. pneumoniae, H. flu., M. cat. c. skin - Staph., Strep., E. coli d. UTI - Klebsiella, Enterobacter, E. coli e) Ampicillin and sulbactam Unasyn Roerig S 3 3 N H C Na sulbactam 1) β-lactamase inhibitor plus ampicillin 2) For intravenous use; same spectrum as Augmentin. 3) Excellent activity against anaerobes f) Broad spectrum penicillins used primarily for Pseudomonas infections or mixed infections involving Pseudomonas or emperic therapy. Useful for anaerobic infections also. 1) General Points a. have electron withdrawing group on α-amino function. This allows better penetration of drug into Pseudomonas, and related pathogens (e.g. Serratia, Citrobacter). b. these agents are more resistant to hydrolysis by chromosomally mediated beta lactamases (often elaborated by Pseudomonas, Serratia, Citrobacter, Acinetobacter, Morganella) i.e. Group 1 β-lactamases (cephalosporinase) 27
16 Aside: These beta lactamases are not inhibited by clavulanic acid or sulbactam or tazobactam c. combination of these anti pseudomonas penicillins and clavulanic acid or tazobactam (e.g. Timentin or Zosyn) are no more effective than Ticarcillin or Piperacillin alone for Pseudomonas but may be useful for mixed infections involving Pseudomonas and one or more plasmid mediated beta lactamase producing pathogens. d. these agents will still be inactivated by penicillinases and some plasmid mediated beta lactamases unless an inhibition is present 2) Ticarcillin plus clavulanic acid, Timentin. This is better for mixed infections involving Pseudomonas. Indications: a. septicemia β-lactamase producing Klebsiella, Staph., Strep., Pseudomonas b. lower respiratory β-lactamase producing Staph., H. flu., Klebsiella c. bone Staph. d. skin Klebsiella, E. coli, Staph. e. UTI E. coli, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Citrobacter, Enterobacter, Senatia, Staph. f. genitourinary Enterobacter, Staph., E. coli, Staph. epi g. intra abdominal Bacteriodes, E. coli, Klebsiella h. Pseudomonas in combination with aminoglycoside 3) Piperacillin Pipracil Lederle a. more potent against Gm (-) bacteria than Ticarcillin. Active against Klebsiella. b. may be more potent against Pseudomonas c. dose 4-20 g/day IV d. used for mixed infections, presumptive therapy, and for Pseudomonas infections e. bile and renal excretion, therefore no dose adjustment needed in renal failure 4) Piperacillin plus Tazobactam Zosyn Lederle H H H N H H 2 C 3 S N N N Tazobactam better for mixed infections involving Pseudomonas 5) Carbenicillin indanyl ester orally absorbed and used for mild Pseudomonas UTI. 28
STRUCTURE OF COMMONLY USED PENICILLINS
 PENICILLINS Alice Prince I. CHEMISTRY A basic structure of penicillins consists of a nucleus with three components: a thiazolidine ring, a β-lactam ring and a side chain. The side chain determines, in
PENICILLINS Alice Prince I. CHEMISTRY A basic structure of penicillins consists of a nucleus with three components: a thiazolidine ring, a β-lactam ring and a side chain. The side chain determines, in
AXITAB-CV TAB. COMPOSITION :
 AXITAB-CV TAB. COMPOSITION : Each film coated tablet contains: Cefuroxime Axetil I.P. Eq. to Anhydrous 500mg. Potassium Clavulanate Diluted I.P. Eq. to Clavulanic Acid 125mg DESCRIPTION : Cefuroxime Axetil
AXITAB-CV TAB. COMPOSITION : Each film coated tablet contains: Cefuroxime Axetil I.P. Eq. to Anhydrous 500mg. Potassium Clavulanate Diluted I.P. Eq. to Clavulanic Acid 125mg DESCRIPTION : Cefuroxime Axetil
College of Pharmacy Advanced Clinical Pharmacology Spring 2013 Semester. Antibiotics PCN. Danita 1 Dee Narciso Pharm D
 College of Pharmacy Advanced Clinical Pharmacology Spring 2013 Semester Antibiotics PCN Danita 1 Dee Narciso Pharm D 2 Objectives Recognize the signs and symptoms of infection Become familiar with antibiotics
College of Pharmacy Advanced Clinical Pharmacology Spring 2013 Semester Antibiotics PCN Danita 1 Dee Narciso Pharm D 2 Objectives Recognize the signs and symptoms of infection Become familiar with antibiotics
ZINEX. Composition Each tablet contains Cefuroxime (as axetil) 250 or 500 mg
 ZINEX Composition Each tablet contains Cefuroxime (as axetil) 250 or 500 mg Tablets Action Cefuroxime axetil owes its bactericidal activity to the parent compound cefuroxime. Cefuroxime is a well-characterized
ZINEX Composition Each tablet contains Cefuroxime (as axetil) 250 or 500 mg Tablets Action Cefuroxime axetil owes its bactericidal activity to the parent compound cefuroxime. Cefuroxime is a well-characterized
Development of C sporins. Beta-lactam antibiotics - Cephalosporins. Second generation C sporins. Targets - PBP s
 Beta-lactam antibiotics - Cephalosporins Development of C sporins Targets - PBP s Activity - Cidal - growing organisms (like the penicillins) Principles of action - Affinity for PBP s Permeability properties
Beta-lactam antibiotics - Cephalosporins Development of C sporins Targets - PBP s Activity - Cidal - growing organisms (like the penicillins) Principles of action - Affinity for PBP s Permeability properties
Aminoglycosides. Not orally absorbed. Interact with negatively charged lipopolysaccharide on Gram- cell wall. Aminoglycoside properties
 Aminoglycosides Tobramycin Kanamycin H2N Gentamicin Amikacin NHCOCHCH2CH2NH2 OH Aminoglycosides made of linked sugars. Decorated with many OH and NH2 groups, which render these compounds positively charged
Aminoglycosides Tobramycin Kanamycin H2N Gentamicin Amikacin NHCOCHCH2CH2NH2 OH Aminoglycosides made of linked sugars. Decorated with many OH and NH2 groups, which render these compounds positively charged
Aciphin Ceftriaxone Sodium
 Aciphin Ceftriaxone Sodium Only for the use of Medical Professionals Description Aciphin is a bactericidal, long-acting, broad spectrum, parenteral cephalosporin preparation, active against a wide range
Aciphin Ceftriaxone Sodium Only for the use of Medical Professionals Description Aciphin is a bactericidal, long-acting, broad spectrum, parenteral cephalosporin preparation, active against a wide range
Amoxitid 125 Suspension Each teaspoonful (5 ml) contains Amoxicillin (as trihydrate) 125 mg.
 AMOXITID Composition Amoxitid 250 Capsules Each capsule contains Amoxicillin (as trihydrate) 250 mg. Capsules & Suspension Amoxitid 500 Capsules Each capsule contains Amoxicillin (as trihydrate) 500 mg.
AMOXITID Composition Amoxitid 250 Capsules Each capsule contains Amoxicillin (as trihydrate) 250 mg. Capsules & Suspension Amoxitid 500 Capsules Each capsule contains Amoxicillin (as trihydrate) 500 mg.
Anaerobes Bacteroides species, Clostridium species (Note: most strains of C.difficile are resistant).
 CEFIXON Composition Each vial contains 1 g Ceftriaxone (as sodium). Vial Action The bactericidal activity of Ceftriaxone results from inhibition of cell wall Synthesis. Ceftriaxone has a high degree of
CEFIXON Composition Each vial contains 1 g Ceftriaxone (as sodium). Vial Action The bactericidal activity of Ceftriaxone results from inhibition of cell wall Synthesis. Ceftriaxone has a high degree of
Other β-lactam. A. Carbapenems:
 A. Carbapenems: Other β-lactam Carbapenems are synthetic β-lactam antibiotics Differ in structure from the penicillins in that the sulfur atom of the thiazolidine ring. Imipenem, meropenem, doripenem,
A. Carbapenems: Other β-lactam Carbapenems are synthetic β-lactam antibiotics Differ in structure from the penicillins in that the sulfur atom of the thiazolidine ring. Imipenem, meropenem, doripenem,
life-threatening infections
 Vancomycin Vancomycin has become increasingly important in the treatment of life-threatening infections. MRSA infections. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) infections Enterococcal
Vancomycin Vancomycin has become increasingly important in the treatment of life-threatening infections. MRSA infections. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) infections Enterococcal
Ceftomax TM S (Cefoperazone Sodium plus Sulbactam Sodium Injection)
 COMPOSITION Ceftomax TM S (Cefoperazone Sodium plus Sulbactam Sodium Injection) CEFTOMAX - S Injection 1.5 gm Each vial contains: Cefoperazone Sodium equivalent to Cefoperazone IP. 1,000 mg Sulbactam Sodium
COMPOSITION Ceftomax TM S (Cefoperazone Sodium plus Sulbactam Sodium Injection) CEFTOMAX - S Injection 1.5 gm Each vial contains: Cefoperazone Sodium equivalent to Cefoperazone IP. 1,000 mg Sulbactam Sodium
Antibacterials and Antivirals
 Structure of a Bacterium: Antibacterials and Antivirals Capsule: protective layer made up of proteins, sugars and lipids Cell wall: provides the bacteria with its shape and structure Cell membrane: permeable
Structure of a Bacterium: Antibacterials and Antivirals Capsule: protective layer made up of proteins, sugars and lipids Cell wall: provides the bacteria with its shape and structure Cell membrane: permeable
PHARMACOLOGY II. Dr Shariq Syed Associate Professor AIKTC, SoP
 PHARMACOLOGY II Dr Shariq Syed Associate Professor AIKTC, SoP INTRODUCTION TO BACTERIA! INTRODUCTION TO BACTERIA! THEY COME IN DIFFERENT SHAPES ANTIMICROBIAL SITES OF ACTION SULPHONAMIDES 1930, Physician/researcher
PHARMACOLOGY II Dr Shariq Syed Associate Professor AIKTC, SoP INTRODUCTION TO BACTERIA! INTRODUCTION TO BACTERIA! THEY COME IN DIFFERENT SHAPES ANTIMICROBIAL SITES OF ACTION SULPHONAMIDES 1930, Physician/researcher
PENICILLIN V POTASSIUM - penicillin v potassium tablet, film coated Aurobindo Pharma Limited
 PENICILLIN V POTASSIUM - penicillin v potassium tablet, film coated To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of penicillin V potassium and other antibacterial
PENICILLIN V POTASSIUM - penicillin v potassium tablet, film coated To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of penicillin V potassium and other antibacterial
PACKAGE INSERT USP ANTIBIOTIC
 Pr AMPICILLIN for Injection USP ANTIBIOTIC ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Ampicillin has a broad spectrum of bactericidal activity against many gram-positive and gramnegative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria.
Pr AMPICILLIN for Injection USP ANTIBIOTIC ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Ampicillin has a broad spectrum of bactericidal activity against many gram-positive and gramnegative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria.
Anti-Microbial Drugs
 Name: Date: Monday March 7 th 2011 Class: I "Pharmacology Anti-Microbial Drugs Lecture 5 د. حيدر الشكرجي Macrolides: Anti-Microbial Drugs Erythromycin was the 1 st of macrolides to find clinical application,
Name: Date: Monday March 7 th 2011 Class: I "Pharmacology Anti-Microbial Drugs Lecture 5 د. حيدر الشكرجي Macrolides: Anti-Microbial Drugs Erythromycin was the 1 st of macrolides to find clinical application,
NOVACEF Tablets (Cefuroxime axetil)
 Published on: 6 Oct 2016 NOVACEF Tablets (Cefuroxime axetil) Composition NOVACEF 250 Tablets Each film-coated tablet contains: Cefuroxime Axetil, IP, equivalent to Cefuroxime. 250 mg NOVACEF 500 Tablets
Published on: 6 Oct 2016 NOVACEF Tablets (Cefuroxime axetil) Composition NOVACEF 250 Tablets Each film-coated tablet contains: Cefuroxime Axetil, IP, equivalent to Cefuroxime. 250 mg NOVACEF 500 Tablets
Cefuroxime iv Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th September 2010
 Cefuroxime iv Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the
Cefuroxime iv Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the
MAGNEX Injection (Sulbactam Sodium/Cefoperazone Sodium 1:1)
 MAGNEX Injection (Sulbactam Sodium/Cefoperazone Sodium 1:1) 1. NAME OF MEDICINAL PRODUCT MAGNEX 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Sulbactam sodium/cefoperazone sodium combination is available
MAGNEX Injection (Sulbactam Sodium/Cefoperazone Sodium 1:1) 1. NAME OF MEDICINAL PRODUCT MAGNEX 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Sulbactam sodium/cefoperazone sodium combination is available
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE REPUBLIC OF BELARUS. Patient Information Leaflet
 No. 851 of August 19, 2014 КЛС No. 10 of July 31, 2014 Invented trade name: Cefosulbactam MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE REPUBLIC OF BELARUS Patient Information Leaflet CEFOSULBACTAM (ЦЕФОСУЛЬБАКТАМ) Powder
No. 851 of August 19, 2014 КЛС No. 10 of July 31, 2014 Invented trade name: Cefosulbactam MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE REPUBLIC OF BELARUS Patient Information Leaflet CEFOSULBACTAM (ЦЕФОСУЛЬБАКТАМ) Powder
Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th September 2010
 Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the European
Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the European
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors. Ass Prof. Dr. Naza M. Ali 15 Nov 2018 Lec 8
 Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Ass Prof. Dr. Naza M. Ali 15 Nov 2018 Lec 8 These drugs selectively inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. The selectivity is due to the differences between bacterial and human
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Ass Prof. Dr. Naza M. Ali 15 Nov 2018 Lec 8 These drugs selectively inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. The selectivity is due to the differences between bacterial and human
Tetracyclines Chloramphenicol Aminoglycosides Macrolides
 Protein synthesis inhibitors Antimicrobial protein synthesis inhibitors Joseph K. Ritter, PhD Assoc. Prof Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology MSB Room 536 jritter@mail2.vcu.edu 828-1022 Tetracyclines
Protein synthesis inhibitors Antimicrobial protein synthesis inhibitors Joseph K. Ritter, PhD Assoc. Prof Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology MSB Room 536 jritter@mail2.vcu.edu 828-1022 Tetracyclines
University of Alberta Hospital Antibiogram for 2007 and 2008 Division of Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology
 University of Alberta Hospital Antibiogram for 2007 and 2008 Division of Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology This material is supported in part by unrestricted educational
University of Alberta Hospital Antibiogram for 2007 and 2008 Division of Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology This material is supported in part by unrestricted educational
CEFADUR Tablet (Cefadroxil)
 Published on: 23 Sep 2014 CEFADUR Tablet (Cefadroxil) Composition CEFADUR-500 Each Film-coated tablet contains Cefadroxil IP equivalent to Cefadroxil anhydrous...500 CEFADUR 125 DT Each dispersible uncoated
Published on: 23 Sep 2014 CEFADUR Tablet (Cefadroxil) Composition CEFADUR-500 Each Film-coated tablet contains Cefadroxil IP equivalent to Cefadroxil anhydrous...500 CEFADUR 125 DT Each dispersible uncoated
Penicillin VK Official FDA information, side effects and uses.
 Page 1 of 10 A to Z Drug List Drugs by Condition Drugs by Class Side Effects Dosage Pregnancy New Drugs Pipeline Images Professional Information Consumer FDA > Penicillin VK Relat Penicillin VK Generic
Page 1 of 10 A to Z Drug List Drugs by Condition Drugs by Class Side Effects Dosage Pregnancy New Drugs Pipeline Images Professional Information Consumer FDA > Penicillin VK Relat Penicillin VK Generic
Streptococci facultative anaerobe
 THE GENUS STREPTOCOCCUS The genus Streptococcus obtains Gram-positive cocci, nonmotile, nonsporeforming, arranged mostly in chains or in pairs. Most species are facultative anaerobes. Some of streptococci
THE GENUS STREPTOCOCCUS The genus Streptococcus obtains Gram-positive cocci, nonmotile, nonsporeforming, arranged mostly in chains or in pairs. Most species are facultative anaerobes. Some of streptococci
Rapid and progressive necrosis of the tissue underlying epidermis (cellulitis)
 Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION APO-PEN-VK
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION APO-PEN-VK Penicillin V Potassium (Potassium Phenoxymethyl Penicillin) Tablets USP 500,000 i.u. (300 mg) Antibiotic Powder for suspension USP 500,000 i.u./5 Ml (300 mg/5 ml) Powder
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION APO-PEN-VK Penicillin V Potassium (Potassium Phenoxymethyl Penicillin) Tablets USP 500,000 i.u. (300 mg) Antibiotic Powder for suspension USP 500,000 i.u./5 Ml (300 mg/5 ml) Powder
Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia
 Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia George Samonis MD, PhD Medical Oncologist Infectious Diseases Specialist Professor of Medicine The University of Crete, Heraklion,, Crete, Greece
Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia George Samonis MD, PhD Medical Oncologist Infectious Diseases Specialist Professor of Medicine The University of Crete, Heraklion,, Crete, Greece
FAROBACT 200 Tablets (Faropenem)
 Published on: 10 Jul 2014 FAROBACT Tablets (Faropenem) Composition FAROBACT Tablets Each film-coated tablet contains: Faropenem Sodium equivalent to Faropenem... Dosage Form Oral tablet Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics
Published on: 10 Jul 2014 FAROBACT Tablets (Faropenem) Composition FAROBACT Tablets Each film-coated tablet contains: Faropenem Sodium equivalent to Faropenem... Dosage Form Oral tablet Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics
Macrolides, Clindamycin & Ketolides Polymyxins
 Macrolides, Clindamycin & Ketolides Polymyxins Kwan Soo Ko Macrolides - Erythromycin - Azithromycin - Clarithromycin Lincosamides - Lincomycin - Clindamycin Unrelated chemically But, many similar biological
Macrolides, Clindamycin & Ketolides Polymyxins Kwan Soo Ko Macrolides - Erythromycin - Azithromycin - Clarithromycin Lincosamides - Lincomycin - Clindamycin Unrelated chemically But, many similar biological
Elements for a Public Summary
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Rapenin (phenoxymethylpenicillin potassium) is indicated for the treatment of infections caused by penicillin-sensitive bacteria.
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Rapenin (phenoxymethylpenicillin potassium) is indicated for the treatment of infections caused by penicillin-sensitive bacteria.
Cefuroxime sodium equivalent to Cefuroxime 250 mg, 750 mg and 1.5 g Powder for Injection
 Cefuroxime-AFT Cefuroxime sodium equivalent to Cefuroxime 250 mg, 750 mg and 1.5 g Powder for Injection Presentation CEFUROXIME-AFT 250 mg contains Cefuroxime sodium equivalent to Cefuroxime 250 mg. CEFUROXIME-AFT
Cefuroxime-AFT Cefuroxime sodium equivalent to Cefuroxime 250 mg, 750 mg and 1.5 g Powder for Injection Presentation CEFUROXIME-AFT 250 mg contains Cefuroxime sodium equivalent to Cefuroxime 250 mg. CEFUROXIME-AFT
ROSOBAC-1GM / ROSOBAC-FORT
 ROSOBAC-1GM / ROSOBAC-FORT ROSOBAC - 1GM. COMPOSITION : Each vial contains Sterile Cefoperazone Sodium IP Eq. to Anhydrous Cefoperazone - Sterile Sulbactam Sodium USP Eq. to Anhydrous Sulbactam - ROSOBAC
ROSOBAC-1GM / ROSOBAC-FORT ROSOBAC - 1GM. COMPOSITION : Each vial contains Sterile Cefoperazone Sodium IP Eq. to Anhydrous Cefoperazone - Sterile Sulbactam Sodium USP Eq. to Anhydrous Sulbactam - ROSOBAC
Antibiotic Resistance Pattern of Blood and CSF Culture Isolates At NHLS Academic Laboratories (2005)
 Antibiotic Resistance Pattern of Blood and CSF Culture Isolates At NHLS Academic Laboratories (2005) Streptococcus pneumoniae (SP) Blood Culture Isolates Penicillin intermediate Penicillin Cefotaxime 336
Antibiotic Resistance Pattern of Blood and CSF Culture Isolates At NHLS Academic Laboratories (2005) Streptococcus pneumoniae (SP) Blood Culture Isolates Penicillin intermediate Penicillin Cefotaxime 336
For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory CEFTUM TABLETS. Cefuroxime Axetil Tablets IP 125/250/500mg
 For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory CEFTUM TABLETS Cefuroxime Axetil Tablets IP 125/250/500mg QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION CEFTUM TABLETS 125
For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory CEFTUM TABLETS Cefuroxime Axetil Tablets IP 125/250/500mg QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION CEFTUM TABLETS 125
Severe β-lactam allergy. Alternative (use for mild-moderate β-lactam allergy) therapy
 Recommended Empirical Antibiotic Regimens for MICU Patients Notes: The antibiotic regimens shown are general guidelines and should not replace clinical judgment. Always assess for antibiotic allergies.
Recommended Empirical Antibiotic Regimens for MICU Patients Notes: The antibiotic regimens shown are general guidelines and should not replace clinical judgment. Always assess for antibiotic allergies.
Infective endocarditis
 Infective endocarditis Today's lecture is about infective endocarditis, the Dr started the lecture by asking what are the most common causative agents of infective endocarditis? 1-Group A streptococci
Infective endocarditis Today's lecture is about infective endocarditis, the Dr started the lecture by asking what are the most common causative agents of infective endocarditis? 1-Group A streptococci
Antibiotics and Ribosomes as Drug Targets
 Antibiotics and Ribosomes as Drug Targets www.biochemj.org/bj/330/0581/bj3300581.htm Professor Vassie Ware Bioscience in the 21 st Century November 5, 2012 PERSPECTIVE Widespread use of antibiotics after
Antibiotics and Ribosomes as Drug Targets www.biochemj.org/bj/330/0581/bj3300581.htm Professor Vassie Ware Bioscience in the 21 st Century November 5, 2012 PERSPECTIVE Widespread use of antibiotics after
Cefuroxime (as sodium)
 Cefuroxime (as sodium) Zinacef Powder for Injection Antibacterial PRODUCT DESCRIPTION Cefuroxime (as sodium) (Zinacef ) 250mg Powder for Injection: Each white to faintly yellow powder to which appropriate
Cefuroxime (as sodium) Zinacef Powder for Injection Antibacterial PRODUCT DESCRIPTION Cefuroxime (as sodium) (Zinacef ) 250mg Powder for Injection: Each white to faintly yellow powder to which appropriate
Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics. Question No. 1 of 10. Question. Feedback. Question
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics No. 1 of 10 1. An effective chemotherapeutic drug should have. (A) Low therapeutic index (B) More toxicity (C) Selective toxicity (D) Mutation inducing properties
Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics No. 1 of 10 1. An effective chemotherapeutic drug should have. (A) Low therapeutic index (B) More toxicity (C) Selective toxicity (D) Mutation inducing properties
CEFPROZIL FOR ORAL SUSPENSION USP 125 mg/5 ml and 250 mg/5 ml. Rx Only
 CEFPROZIL FOR ORAL SUSPENSION USP 125 mg/5 ml and 250 mg/5 ml Rx Only To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefprozil for oral suspension and other antibacterial
CEFPROZIL FOR ORAL SUSPENSION USP 125 mg/5 ml and 250 mg/5 ml Rx Only To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefprozil for oral suspension and other antibacterial
CEFPROZIL FOR ORAL SUSPENSION USP 125 mg/5 ml and 250 mg/5 ml. Rx only
 CEFPROZIL FOR ORAL SUSPENSION USP 125 mg/5 ml and 250 mg/5 ml Rx only To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefprozil for oral suspension and other antibacterial
CEFPROZIL FOR ORAL SUSPENSION USP 125 mg/5 ml and 250 mg/5 ml Rx only To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefprozil for oral suspension and other antibacterial
Overcoming the PosESBLities of Enterobacteriaceae Resistance
 Overcoming the PosESBLities of Enterobacteriaceae Resistance Review of current treatment options Jamie Reed, PharmD Pharmacy Grand Rounds August 28, 2018 Rochester, MN 2018 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure No
Overcoming the PosESBLities of Enterobacteriaceae Resistance Review of current treatment options Jamie Reed, PharmD Pharmacy Grand Rounds August 28, 2018 Rochester, MN 2018 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure No
Vancomycin. A bactericidal drug which acts by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Active only against gram-positive bacteria, particularly staphylococci.
 Vancomycin A bactericidal drug which acts by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Active only against gram-positive bacteria, particularly staphylococci. Used IV in treating endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant
Vancomycin A bactericidal drug which acts by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Active only against gram-positive bacteria, particularly staphylococci. Used IV in treating endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant
Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate
 Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate Professor of Pharmacy & Associate Member of Medicine, UBC
Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate Professor of Pharmacy & Associate Member of Medicine, UBC
Vancomycin Orion , Version 2 Public Summary of the Risk Management Plan
 Vancomycin Orion 18.1.2016, Version 2 Public Summary of the Risk Management Plan VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary Vancomycin Orion is intravenously administered glycopeptide antibiotic. It is indicated
Vancomycin Orion 18.1.2016, Version 2 Public Summary of the Risk Management Plan VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary Vancomycin Orion is intravenously administered glycopeptide antibiotic. It is indicated
The Streptococci. Diverse collection of cocci. Gram-positive Chains or pairs significant pathogens
 The Streptococci Diverse collection of cocci. Gram-positive Chains or pairs significant pathogens Strong fermenters Facultative anaerobes Non-motile Catalase Negative 1 Classification 1 2 Classification
The Streptococci Diverse collection of cocci. Gram-positive Chains or pairs significant pathogens Strong fermenters Facultative anaerobes Non-motile Catalase Negative 1 Classification 1 2 Classification
1. Which of the following statements concerning Plasmodium vivax is TRUE?
 1 Microm 301 Final Exam 2012 Practice Questions and Key 1. Which of the following statements concerning Plasmodium vivax is TRUE? A. It infects all stages of erythrocytes (immature, mature, and senescent).
1 Microm 301 Final Exam 2012 Practice Questions and Key 1. Which of the following statements concerning Plasmodium vivax is TRUE? A. It infects all stages of erythrocytes (immature, mature, and senescent).
Foundations in Microbiology
 Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 18 Cocci of Medical Importance Chapter 18 2 Cocci of Interest Staphylococcus aureus S. epidermidis, S. hominis, S. capitis S. saprophyticus Streptococcus
Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 18 Cocci of Medical Importance Chapter 18 2 Cocci of Interest Staphylococcus aureus S. epidermidis, S. hominis, S. capitis S. saprophyticus Streptococcus
Urinary Tract Infections: From Simple to Complex. Adriane N Irwin, MS, PharmD, BCACP Clinical Assistant Professor Ambulatory Care October 25, 2014
 Urinary Tract Infections: From Simple to Complex Adriane N Irwin, MS, PharmD, BCACP Clinical Assistant Professor Ambulatory Care October 25, 2014 Learning Objectives Develop empiric antimicrobial treatment
Urinary Tract Infections: From Simple to Complex Adriane N Irwin, MS, PharmD, BCACP Clinical Assistant Professor Ambulatory Care October 25, 2014 Learning Objectives Develop empiric antimicrobial treatment
Cefadroxil for Oral Suspension USP 250 mg/5 ml and 500 mg/5 ml
 Cefadroxil for Oral Suspension USP 250 mg/5 ml and 500 mg/5 ml Rx only To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefadroxil for oral suspension and other antibacterial
Cefadroxil for Oral Suspension USP 250 mg/5 ml and 500 mg/5 ml Rx only To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefadroxil for oral suspension and other antibacterial
Gram-Negative rods Introduction to
 Lec 5 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Gram-Negative rods Introduction to Enterobacteriaceae Characteristics: جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان Small gram-negative rods (2-5 by 0.5 microns) Most motile with peritrichous
Lec 5 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Gram-Negative rods Introduction to Enterobacteriaceae Characteristics: جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان Small gram-negative rods (2-5 by 0.5 microns) Most motile with peritrichous
MERREM IV. meropenem PRODUCT INFORMATION COOH CH 3
 MERREM IV meropenem PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF THE DRUG Meropenem, as meropenem trihydrate. DESCRIPTION Structural Formula: HO H 3 C O COOH H N S H H H H CH 3 H NH CON(CH 3 ) 2. 3H2 O CAS Number: 119478-56-7
MERREM IV meropenem PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF THE DRUG Meropenem, as meropenem trihydrate. DESCRIPTION Structural Formula: HO H 3 C O COOH H N S H H H H CH 3 H NH CON(CH 3 ) 2. 3H2 O CAS Number: 119478-56-7
Mesporin TM. Ceftriaxone sodium. Rapid onset, sustained action, for a broad spectrum of infections
 Ceftriaxone sodium Rapid onset, sustained action, for a broad spectrum of infections 1, 2, 3 Antibiotic with a broad spectrum of activity Broad spectrum of activity against gram-positive* and gram-negative
Ceftriaxone sodium Rapid onset, sustained action, for a broad spectrum of infections 1, 2, 3 Antibiotic with a broad spectrum of activity Broad spectrum of activity against gram-positive* and gram-negative
Adenium Biotech. Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes
 Adenium Biotech Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes Board of Directors: - Stephan Christgau, PhD, chairman,
Adenium Biotech Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes Board of Directors: - Stephan Christgau, PhD, chairman,
PATHOGENICITY OF MICROORGANISMS
 PATHOGENICITY OF MICROORGANISMS Some microorganisms are : 1- Harmless microorganism, as normal flora 2- Harmfull microorganism, as pathogenic. A pathogenic microorganism is defined as one that causes or
PATHOGENICITY OF MICROORGANISMS Some microorganisms are : 1- Harmless microorganism, as normal flora 2- Harmfull microorganism, as pathogenic. A pathogenic microorganism is defined as one that causes or
COOH CH 2 COOH N O C CONH H
 SUPRAX CEFIXIME TABLETS USP, 400 mg Rx only To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Suprax (cefixime) Tablets and other antibacterial drugs, Suprax should
SUPRAX CEFIXIME TABLETS USP, 400 mg Rx only To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Suprax (cefixime) Tablets and other antibacterial drugs, Suprax should
Cases in employees. Cases. Day of onset (July)
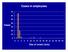 Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
GenRx AMOXYCILLIN POWDER FOR SUSPENSION
 NAME OF THE MEDICINE Amoxycillin (as amoxycillin trihydrate). GenRx AMOXYCILLIN POWDER FOR SUSPENSION Chemical name: (2S,5R,6R)-6[(R)-2-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4- thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic
NAME OF THE MEDICINE Amoxycillin (as amoxycillin trihydrate). GenRx AMOXYCILLIN POWDER FOR SUSPENSION Chemical name: (2S,5R,6R)-6[(R)-2-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4- thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic
Cefuroxime (as sodium)
 Cefuroxime (as sodium) Zinacef Powder for Injection Antibacterial PRODUCT DESCRIPTION Cefuroxime (as sodium) (Zinacef ) 250mg Powder for Injection: Each white to faintly yellow powder to which appropriate
Cefuroxime (as sodium) Zinacef Powder for Injection Antibacterial PRODUCT DESCRIPTION Cefuroxime (as sodium) (Zinacef ) 250mg Powder for Injection: Each white to faintly yellow powder to which appropriate
Choosing an appropriate antimicrobial agent. 3) the spectrum of potential pathogens
 Choosing an appropriate antimicrobial agent Consider: 1) the host 2) the site of infection 3) the spectrum of potential pathogens 4) the likelihood that these pathogens are resistant to antimicrobial agents
Choosing an appropriate antimicrobial agent Consider: 1) the host 2) the site of infection 3) the spectrum of potential pathogens 4) the likelihood that these pathogens are resistant to antimicrobial agents
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
The color of drug powder in the dry powder state is white to off-white. After reconstitution, it turns to a red suspension.
 CEFACLOR- cefaclor for suspension Avadel Pharmaceuticals (USA), Inc. Cefaclor for Oral Suspension, USP Rx Only To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Cefaclor
CEFACLOR- cefaclor for suspension Avadel Pharmaceuticals (USA), Inc. Cefaclor for Oral Suspension, USP Rx Only To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Cefaclor
FISAMOX Amoxycillin (as amoxycillin sodium) Powder for Injection
 FISAMOX Amoxycillin (as amoxycillin sodium) Powder for Injection PRODUCT INFORMATION DESCRIPTION FISAMOX (amoxycillin sodium) has the chemical name of d-(-)-a-amino-p-hydroxybenzylpenicillin sodium. Amoxycillin
FISAMOX Amoxycillin (as amoxycillin sodium) Powder for Injection PRODUCT INFORMATION DESCRIPTION FISAMOX (amoxycillin sodium) has the chemical name of d-(-)-a-amino-p-hydroxybenzylpenicillin sodium. Amoxycillin
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
 Frank Lowy Protein Synthesis Inhibitors This lecture discusses a diverse group of antibiotics that are grouped together because they all have a common mechanism of action they are protein synthesis inhibitors.
Frank Lowy Protein Synthesis Inhibitors This lecture discusses a diverse group of antibiotics that are grouped together because they all have a common mechanism of action they are protein synthesis inhibitors.
Beta-lactamase production should have no effect on Azithromycin activity.
 AZIMEX Composition Azimex 250 Capsules Each capsule contains Azithromycin (as dihydrate) 250 mg Capsules Azimex 500 mg Capsules Each capsule contains Azithromycin (as dihydrate) 500 mg Action Azithromycin
AZIMEX Composition Azimex 250 Capsules Each capsule contains Azithromycin (as dihydrate) 250 mg Capsules Azimex 500 mg Capsules Each capsule contains Azithromycin (as dihydrate) 500 mg Action Azithromycin
List of teams: Practice question: Which of the following individuals was among the first to recognize the importance of handwashing?
 List of teams: 1. Group 1 - Room 304 - Dr. Dobkin 2. Group 2 - Room 306 - Dr. Yin 3. Group 3 - Room 308 - Dr. Lowy 4. Group 4 - Room 310 - Dr. Neu 5. Group 5 - Room 316 - Dr. Prince 6. Group 6 - Room 320
List of teams: 1. Group 1 - Room 304 - Dr. Dobkin 2. Group 2 - Room 306 - Dr. Yin 3. Group 3 - Room 308 - Dr. Lowy 4. Group 4 - Room 310 - Dr. Neu 5. Group 5 - Room 316 - Dr. Prince 6. Group 6 - Room 320
APO-AMOXYCILLIN CAPSULES
 APO-AMOXYCILLIN CAPSULES NAME OF THE MEDICINE Amoxycillin (as amoxycillin trihydrate) Chemical Name: (2S,5R,6R)-6[(R)-2-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4- thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic
APO-AMOXYCILLIN CAPSULES NAME OF THE MEDICINE Amoxycillin (as amoxycillin trihydrate) Chemical Name: (2S,5R,6R)-6[(R)-2-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4- thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic
.3H 2. Page 1 of 13. SUPRAX CEFIXIME FOR ORAL SUSPENSION, USP 100 mg/5 ml Rx only
 Page 1 of 13 SUPRAX CEFIXIME FOR ORAL SUSPENSION, USP 100 mg/5 ml Rx only To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Suprax (cefixime) for Oral Suspension and
Page 1 of 13 SUPRAX CEFIXIME FOR ORAL SUSPENSION, USP 100 mg/5 ml Rx only To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Suprax (cefixime) for Oral Suspension and
WARNING: TENDON EFFECTS and EXACERBATION OF MYASTHENIA GRAVIS
 DECLESAU (dergrafloxacin) tablets, for oral use DECLESAU (dergrafloxacin) injection, solution for intravenous use WARNING: TENDON EFFECTS and EXACERBATION OF MYASTHENIA GRAVIS Fluoroquinolones, including
DECLESAU (dergrafloxacin) tablets, for oral use DECLESAU (dergrafloxacin) injection, solution for intravenous use WARNING: TENDON EFFECTS and EXACERBATION OF MYASTHENIA GRAVIS Fluoroquinolones, including
MCQ S. 1. Which of the following could be given to someone who had an allergy to sulphonamides previously:
 MCQ S 1. Which of the following could be given to someone who had an allergy to sulphonamides previously: a) Acetazolamide b) Frusemide c) Bumetanide d) Pyrimethamine e) Diazoxide 2. Which of the following
MCQ S 1. Which of the following could be given to someone who had an allergy to sulphonamides previously: a) Acetazolamide b) Frusemide c) Bumetanide d) Pyrimethamine e) Diazoxide 2. Which of the following
Chapter 19. Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacteria. Staphylococcus & Streptococcus
 Chapter 19 Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacteria Staphylococcus & Streptococcus Staphylococcus Normal members of every human's microbiota Can be opportunistic pathogens Facultative anaerobes Cells occur in
Chapter 19 Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacteria Staphylococcus & Streptococcus Staphylococcus Normal members of every human's microbiota Can be opportunistic pathogens Facultative anaerobes Cells occur in
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET. Each vial contains 263 mg, 789 mg or g of cefuroxime sodium, equivalent to 250 mg, 750 mg or 1.5 g of cefuroxime.
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET CEFUROXIME FOR INJECTION 1. Product Name Cefuroxime for injection, 250mg, 750 mg, 1.5 g, powder for injection. 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Each vial contains 263
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET CEFUROXIME FOR INJECTION 1. Product Name Cefuroxime for injection, 250mg, 750 mg, 1.5 g, powder for injection. 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Each vial contains 263
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis. Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017
 320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
Issues Abx request. Sneezing w/ post- nasal d/c & redness mucous membranes Throat. Chest px w/ coughing, difficulty breathing
 Week 5 Magic Bullets URTI + Pneumonia Presenting Sx Cough, sore throat & runny nose Aches & pains all over Shivers & fevers Respiratory Viruses Viruses causing flu Influenza A/B/C (orthomyxovirus) Respiratory
Week 5 Magic Bullets URTI + Pneumonia Presenting Sx Cough, sore throat & runny nose Aches & pains all over Shivers & fevers Respiratory Viruses Viruses causing flu Influenza A/B/C (orthomyxovirus) Respiratory
ICU Volume 11 - Issue 3 - Autumn Series
 ICU Volume 11 - Issue 3 - Autumn 2011 - Series Impact of Pharmacokinetics of Antibiotics in ICU Clinical Practice Introduction The efficacy of a drug is mainly dependent on its ability to achieve an effective
ICU Volume 11 - Issue 3 - Autumn 2011 - Series Impact of Pharmacokinetics of Antibiotics in ICU Clinical Practice Introduction The efficacy of a drug is mainly dependent on its ability to achieve an effective
Page 1 of 21. Adult Patients and Pediatric Patients Dosage Guidelines for Cefuroxime Axetil Tablets USP. Infection
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Cefuroxime Axetil Tablets USP safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Cefuroxime
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Cefuroxime Axetil Tablets USP safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Cefuroxime
Streptococcus pyogenes
 Streptococcus pyogenes From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Streptococcus pyogenes S. pyogenes bacteria at 900x magnification. Scientific classification Kingdom: Eubacteria Phylum: Firmicutes Class: Cocci
Streptococcus pyogenes From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Streptococcus pyogenes S. pyogenes bacteria at 900x magnification. Scientific classification Kingdom: Eubacteria Phylum: Firmicutes Class: Cocci
Rapid identification and resistance assessment: The future is mass spectrometry
 Rapid identification and resistance assessment: The future is mass spectrometry Dr Sanmarié Schlebusch Director of Microbiology Mater Pathology Brisbane Outline Introduction Plug and play Pre-prep and
Rapid identification and resistance assessment: The future is mass spectrometry Dr Sanmarié Schlebusch Director of Microbiology Mater Pathology Brisbane Outline Introduction Plug and play Pre-prep and
Chapter 15. Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Chapter 15 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity I. Entry of a Microorganism into the Host A. Portals of Entry 1. Mucous Membranes Conjunctiva, respiratory, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary tracts Important
Chapter 15 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity I. Entry of a Microorganism into the Host A. Portals of Entry 1. Mucous Membranes Conjunctiva, respiratory, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary tracts Important
Laboratory CLSI M100-S18 update. Paul D. Fey, Ph.D. Associate Professor/Associate Director Josh Rowland, M.T. (ASCP) State Training Coordinator
 Nebraska Public Health Laboratory 2008 CLSI M100-S18 update Paul D. Fey, Ph.D. Associate Professor/Associate Director Josh Rowland, M.T. (ASCP) State Training Coordinator Agenda Discuss 2008 M100- S18
Nebraska Public Health Laboratory 2008 CLSI M100-S18 update Paul D. Fey, Ph.D. Associate Professor/Associate Director Josh Rowland, M.T. (ASCP) State Training Coordinator Agenda Discuss 2008 M100- S18
ZOSUL Injection (Cefoperazone Sodium + Sulbactam Sodium) Cefoperazone Sodium Plus Sulbactam Sodium Injection Zosul
 Published on: 10 Jul 2014 ZOSUL Injection (Cefoperazone Sodium + Sulbactam Sodium) Cefoperazone Sodium Plus Sulbactam Sodium Injection Zosul Composition ZOSUL Injection 1.0 g Each vial contains: Cefoperazone
Published on: 10 Jul 2014 ZOSUL Injection (Cefoperazone Sodium + Sulbactam Sodium) Cefoperazone Sodium Plus Sulbactam Sodium Injection Zosul Composition ZOSUL Injection 1.0 g Each vial contains: Cefoperazone
Overview of Translation (2) Protein Synthesis Inhibitors. Overview of Translation (3) Lecture Outline. Overview of Translation (1)
 Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Macrolides - Lincosamides Aminoglycosides Tetracyclines Chloramphenicol Streptogramins Oxazolidinones Overview of Translation (2) Initiation trna + AA binds translation elongation
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Macrolides - Lincosamides Aminoglycosides Tetracyclines Chloramphenicol Streptogramins Oxazolidinones Overview of Translation (2) Initiation trna + AA binds translation elongation
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students. Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile.. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile.. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products,
Translocation Studies Mid-Term Review (MTR) Meeting Marseille, France
 Marie Curie Actions Research Training Networks (RTN) Translocation Studies Mid-Term Review (MTR) Meeting Marseille, France F. Vidal-Aroca, M.G.P. Page and J. Dreier Background Deteriorating situation regarding
Marie Curie Actions Research Training Networks (RTN) Translocation Studies Mid-Term Review (MTR) Meeting Marseille, France F. Vidal-Aroca, M.G.P. Page and J. Dreier Background Deteriorating situation regarding
Cefazolin Injection, USP in GALAXY Container (PL 2040 Plastic)
 Cefazolin Injection, USP in GALAXY Container (PL 2040 Plastic) To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Cefazolin Injection, USP and other antibacterial drugs,
Cefazolin Injection, USP in GALAXY Container (PL 2040 Plastic) To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Cefazolin Injection, USP and other antibacterial drugs,
PREVENTIVE MEDICINE - LABORATORY
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2014 vol. 118, no. 3 PREVENTIVE MEDICINE - LABORATORY ORIGINAL PAPERS CLINICAL EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY ON THE INCIDENCE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI INFECTIONS IN THE CANCER PATIENTS
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2014 vol. 118, no. 3 PREVENTIVE MEDICINE - LABORATORY ORIGINAL PAPERS CLINICAL EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY ON THE INCIDENCE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI INFECTIONS IN THE CANCER PATIENTS
Sep Oct Nov Dec Total
 LB PAGE 2 LB PAGE 3 Sep Oct Nov Dec 2007 2007 2007 2007 Total Repeat Information Total Repeats 35 15 17 9 76 Repeat Rate 6.01% 0.17% 1.12% 0.39% 2.07% Repeat Chemistry 25 0 2 0 27 Repeat Extraction 1 0
LB PAGE 2 LB PAGE 3 Sep Oct Nov Dec 2007 2007 2007 2007 Total Repeat Information Total Repeats 35 15 17 9 76 Repeat Rate 6.01% 0.17% 1.12% 0.39% 2.07% Repeat Chemistry 25 0 2 0 27 Repeat Extraction 1 0
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
 Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Macrolides - Lincosamides Aminoglycosides Tetracyclines Chloramphenicol Oxazolidinones Streptogramins Lecture Outline Description of protein synthesis - translation Antibiotics
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Macrolides - Lincosamides Aminoglycosides Tetracyclines Chloramphenicol Oxazolidinones Streptogramins Lecture Outline Description of protein synthesis - translation Antibiotics
Beta-lactamase production should have no effect on Azithromycin activity.
 AZIMEX Composition Azimex 250 Capsules Each capsule contains Azithromycin (as dihydrate) 250 mg Capsules & Powder Azimex 500 mg Capsules Each capsule contains Azithromycin (as dihydrate) 500 mg Azimex
AZIMEX Composition Azimex 250 Capsules Each capsule contains Azithromycin (as dihydrate) 250 mg Capsules & Powder Azimex 500 mg Capsules Each capsule contains Azithromycin (as dihydrate) 500 mg Azimex
Phenoxymethylpenicillin-AFT AFT Pharmaceuticals Pty. Ltd
 Phenoxymethylpenicillin-AFT AFT Pharmaceuticals Pty. Ltd Name of the medicine Phenoxymethylpenicillin-AFT, powder for oral liquid, contains phenoxymethylpenicillin as the potassium salt. Phenoxymethylpenicillin
Phenoxymethylpenicillin-AFT AFT Pharmaceuticals Pty. Ltd Name of the medicine Phenoxymethylpenicillin-AFT, powder for oral liquid, contains phenoxymethylpenicillin as the potassium salt. Phenoxymethylpenicillin
MICHIGAN MEDICINE GUIDELINES FOR TREATMENT OF URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN ADULTS
 When to Order a Urine Culture: Asymptomatic bacteriuria is often treated unnecessarily, and accounts for a substantial burden of unnecessary antimicrobial use. National guidelines recommend against testing
When to Order a Urine Culture: Asymptomatic bacteriuria is often treated unnecessarily, and accounts for a substantial burden of unnecessary antimicrobial use. National guidelines recommend against testing
2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Cefaclor 250mg/5ml Suspension Keftid 250mg/5ml Suspension 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Per 5ml Cefaclor Monohydrate Ph.
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Cefaclor 250mg/5ml Suspension Keftid 250mg/5ml Suspension 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Per 5ml Cefaclor Monohydrate Ph.
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS. Each tablet contains phenoxymethylpenicillin 250 mg (as phenoxymethylpenicillin potassium).
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Phenoxymethylpenicillin, 250mg, Film-coated Tablets 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each tablet contains phenoxymethylpenicillin
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Phenoxymethylpenicillin, 250mg, Film-coated Tablets 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each tablet contains phenoxymethylpenicillin
Bacteriemia and sepsis
 Bacteriemia and sepsis Case 1 An 80-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by his son, who noted that his father had become lethargic and has decreased urination over the past 4 days. The patient
Bacteriemia and sepsis Case 1 An 80-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by his son, who noted that his father had become lethargic and has decreased urination over the past 4 days. The patient
Adults and Adolescents (13 years and older) Pharyngitis/tonsillitis (mild to moderate) 500 mg. every 12 hours. (mild to moderate) every 12 hours
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CEFUROXIME AXETIL TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CEFUROXIME
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CEFUROXIME AXETIL TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CEFUROXIME
