LRI Children s Hospital
|
|
|
- Bertha Goodman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Atopic Eczema Care LRI Children s Hospital Staff relevant to: Clinical staff working within the UHL Children s Hospital. Team approval date: May 2017 Version: V 4 Revision due: May 2020 Written by: K. Harman, W. Swanson, J. Miller& P. Hickford Trust Ref: C30/ Introduction General Approach to Treatment The Stepped Approach This guideline aims to enable optimal physical, social and emotional development of children with eczema. To improve their quality of life and enhance the family s management skills in treating eczema and in recognizing adverse skin reactions and infection. The management of eczema should be tailored to the individual patient. Emollients should always be used even if the eczema is clear. Other treatments are based on the severity of the condition and are stepped up or down in potency according to response. Mild to moderate topical steroids are adequate in the majority of patients. These can be used long term with minimal side effects. It is important to aim for the lowest potency topical steroid that controls the eczema. Potent or very potent steroids should only be used for short periods and ideally under dermatological advice. 2. Scope This guideline is intended to provide guidance for medical staff, nurses and health care assistants caring for children with eczema. This guideline is also to be used to guide them in supporting the families of children with eczema in managing the condition. Related Documents: UHL Infection Prevention Policy B4/2005 UHL Policy for Consent to Examination or TreatmentA16/2002 UHL Food & Drug Challenge Children s Nursing Guideline. Trust Ref: C10/2010 Page 1 of 11
2 Equality and diversity considerations In recommending skin treatments, healthcare practitioners should be sensitive to the cultural practices of families or carers of children with atopic eczema. For example, if families or carers use olive oil as a skin treatment (which is likely to be harmful to a child s skin) or if they rinse children after bathing (rinsing off the emollients), the reasons for using the recommended treatment and applying it correctly should be explained sensitively. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence 2103 (NICE) 3. Assessment Consider both physical severity and the effect on psychological wellbeing: Be aware that areas of atopic eczema of differing severity can coexist in the same child. If this is the case, each area should be treated independently. During an assessment of psychological and psychosocial wellbeing and quality of life, healthcare professionals should take into account the impact of atopic eczema on parents or carers as well as the child and provide appropriate advice and support. Healthcare professionals should be aware that atopic eczema of any severity, even mild, can have a negative impact on psychological and psychosocial wellbeing and quality of life. This should be taken into account when deciding on treatment strategies. (NICE 2007) Several severity scales are in use: the EASI Score and POEM Score are favoured but table 1 shows a simple classification used by NICE for both severity and wellbeing. Alternatively, the children s dermatology quality of life score is commonly used to measure the impact on daily life. Table 1 NICE 2007 Guidance for the holistic assessment of eczema Skin/Physical Severity Impact on quality of life and psychosocial wellbeing Clear Normal skin, no evidence of active None No impact on quality of life Mild Moderate Severe atopic eczema Areas of dry skin, infrequent itching (with or without small areas of redness) Areas of dry skin, frequent itching, redness (with or without excoriation and localised skin thickening) Widespread areas of dry skin, incessant itching, redness (with or without excoriation, extensive skin thickening, bleeding, oozing, cracking and alteration of pigmentation) Mild Little impact on everyday activities, sleep and psychosocial wellbeing. Moderate Moderate impact on everyday activities and psychosocial wellbeing, frequently disturbed sleep Severe Severe limitation of everyday activities and psychosocial functioning, nightly loss of sleep Page 2 of 11
3 Trigger Factors Identify potential trigger factors including: Irritants Soaps, detergents, swimming and woollen / synthetic clothing* Skin infections Aeroallergens grass, pollen, perfumes and house dust mite Food allergies Contact allergy *Always ask about washing products and stop any soaps or detergents and prescribe soap substitutes. Most emollients can be used as soap substitutes (see below).advise loose cotton clothing to minimise irritation. 3.1 Treatment Emollients (Moisturisers) Every patient is different when it comes to emollient preference and tolerance. Some prefer lighter creams and others greasier ointments. Some find certain products sting and it is often a case of trial and error. There are many emollients available. Table 2 lists some examples. Table 2. Examples of emollients available in UHL. Formulation Examples Comments Creams Epimax cream Balneum plus cream Lighter than ointments so often preferred by patients but not as good for dry skin & contain more preservatives. Better for wet, infected eczema. Ointments Hydromol ointment 50% WSP/50%LP Greasier than creams and better for dry skin. May stick to clothing so sometimes preferred for overnight use only Gels Isomol gel Sits between creams and ointments in terms of greasiness. Other Emollin spray Expensive so only use if circumstances dictate Some children need a combination of emollients for different body sites or time of day e.g. creams during day, greasier ointments at night. Prescribe in large amounts (500g every two weeks) and apply at least twice daily. In infants, suggest they are applied at each nappy change. Smaller quantities can be prescribed to take to nurseries and schools. Page 3 of 11
4 Soap substitutes Most formulary emollients can also be used as soap substitutes. Dermol and Eczmol are soap substitutes containing an antiseptic, useful in patients with recurrent secondary infection. Topical Corticosteroids Concern regarding the use of topical steroids is common, particularly in parents of young children and even healthcare professionals! It is important to emphasise the safety of topical steroids when used correctly and highlight that untreated eczema is often far worse than any potential side effect of the treatment. Ointments are greasier and contain fewer preservatives so are better when the skin is dry and are generally preferred. Some patients prefer creams as they are less greasy. Table 3.Topical Corticosteroids Steroid Potency Steroid Skin/physical severity &Site Mild Hydrocortisone 1% Mild eczema Sensitive body sites including the face and neck Moderate Potent Very Potent Clobetasone butyrate 0.05% (Eumovate) Betamethasone valerate0.025% (Betnovate RD) Fluocinoloneacetonide % (Synalar 1 in 4) Betamethasone valerate0.1% (Betnovate) Fluocinoloneacetonide 0.025% (Synalar) Clobetasolproprionate 0.05% (Dermovate) Moderate eczema Predominantly used on torso &limbs Often used in short bursts to control flares of eczema. Only to be used under dermatological advice. Apply topical steroids once twice daily to the affected areas. Fingertip unit guidance is useful to show how much should be applied. One fingertip unit will cover an area of skin the size of two palms. Page 4 of 11
5 Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors Used second line for treatment of moderate to severe eczema in children aged 2 years and over. Examples include 0.03% tacrolimus (Protopic) ointment and pimecrolimus (Elidel) cream. They do not cause skin atrophy so can be useful adjuncts when children are requiring continuous topical corticosteroids, particularly on the face, neck and flexures. Bandages and Occlusive Medicated Dressings Should not be used first line and are often initiated under dermatology advice Should not be used in the presence of active infection Emollients and/or topical steroids are usually applied to the skin prior to the application of the bandage and are good at treating chronic lichenified (thickened) eczema. Examples include Viscopaste Ichthopaste. Often used for treating limbs but whole body garments can be used under dermatology advice Wet wraps use two layers of bandages with the aim of introducing more moisture with cooling of the skin as the water evaporates. Antihistamines Used when pruritus is a significant problem, particularly at night Used for symptom control but will not treat the underlying eczema Non-sedating antihistamines are often prescribed during the day. Examples include cetirizine and fexofenadine. Sedating antihistamines are often advised to be taken an hour prior to bedtime to aid getting to sleep and to minimise pruritus overnight. Examples include hydroxyzine (no syrup formulation) chlorpheniramine. Page 5 of 11
6 3.2 Infections (Bacterial) Patients and parents/carers should be educated on the signs and symptoms of infected eczema. Painful, weeping or crusted eczema with or without the presence of pustules Yes All suspected areas of infection should be swabbed for culture and sensitivity No No evidence of bacterial infection Localised areas of bacterial infection can be treated with the addition of topical antimicrobials such as fusidic acid 2% More severe infection should be treated with oral flucloxacillin (or erythromycin/clarithromycin if penicillin allergic). Use soap substitutes with antiseptics (Dermol/Eczmol) to reduce the bacterial burden on the skin. In any cases of systemic upset same day assessment by paediatrician or dermatologist is required. 3.3 Infections (Viral) Herpes simplex virus can spread rapidly within an area of eczema Any areas of localised herpes simplex should be promptly treated with oral aciclovir. Consider eczema herpeticum (widespread infection) in rapidly worsening and painful eczema that develops multiple papules, blisters and erosions with systemic upset. Eczema herpeticum involves inpatient admission with systemic acyclovir and same day ophthalmology assessment if there is involvement of the skin around the eyes. 3.4 Food Allergy Food allergy can be associated with eczema particularly in children less than 12 month old. Food allergy should be considered in infants who have early onset moderate to severe eczema not responding to adequate treatment, or if there are immediate type I symptoms after food. Associated gut dysmotiliy and failure to thrive should also raise suspicion of food allergies. Page 6 of 11
7 Patient s diets should not be modified without dietician support. If food allergy is suspected they should be referred to the paediatric allergy service. 3.5 Emollient Application Procedure Initial skin assessment by a qualified competent children s nurse or doctor experienced in skin assessment and application of treatments. Resources needed: Prescribed bath emollients, shampoo, topical steroids and emollients, disposable non-sterile gloves, plastic disposable aprons +/- paste bandages, wet wraps Procedure for Application of Emollient No Action 1 Nurse child in side room wherever possible to maintain privacy and dignity during treatments. 2 Bath child once daily in warm water for10-15 minutes with prescribed bath emollient and soap substitute. Pat dry skin after bath with a clean towel. Consider health and safety: emollients & soap substitutes can make surfaces extremely slippery. 3 Observe skin, compare to initial assessment and document findings in child s records to provide evaluation of care. Note: in Asian, black Caribbean and black African children, atopic eczema can affect the extensor surfaces rather than the flexures Management can be stepped up or down, according to the severity of symptoms 4 Apply a layer of emollient to the skin first in a gentle, downward motion. Never rub up and down as this could trigger itching and block hair follicles. A generous amount should be applied when occlusive dressings are in use. When bandages are not in use, emollients should be applied liberally at least four times daily or as prescribed. If a large tub of emollient is in use it should be removed from the tub with a spatula to prevent bacterial contamination. Emollients should form the basis of atopic eczema management and should always be used, even when the atopic eczema is clear 5 Wait 20 minutes and then apply the prescribed topical steroid to affected areas only, using disposable non-sterile gloves. There are four topical steroid strengths. Ensure you are familiar with the potency of the treatment being applied. Page 7 of 11
8 6 Apply additional treatments if prescribed e.g. Ichthopaste/ Viscopaste bandages or wet wraps, Occlusive therapy on infected skin is contraindicated seek advice 7 Administer antibiotic as prescribed; ensure any requested skin swabs are collected prior to commencement of antibiotic. 8 Provide parents with general management advice for the home environment including: Bedding/clothing Sunblock Nails School/playgroup advice Pets Ensure parents are able to recognize infected eczema and take appropriate action i.e. stop bandaging and obtain advice. 9 Refer to dietician if there are parental or medical concerns about dietary factors. 3.6 Patient Education Adherence to treatment is paramount to clinical improvement and patients and parents/carers should be educated on the following: o How much and how often treatment should be applied o Recognition of infections o Stepped management depending on severity of eczema Consider involving paediatric dermatology nurse specialist to aid patient education and follow-up 3.7 Advice For clinical advice, contact the Dermatology on call service via switchboard or Wendy Swanson Dermatology Nurse Specialist on UHL Ext 6910 or Education and Training The Children s Dermatology Specialist Nurse will offer initial training sessions to all new nurses and health care assistants within the trust induction days and will offer support and training when patients are identified to reinforce this training. Training sessions will also be offered to medical staff within the trust as requested. 5. Monitoring and Audit Criteria Key Performance Indicator Method of Assessment Frequency Lead Page 8 of 11
9 6. Legal Liability Guideline Statement Guidelines issued and approved by the Trust are considered to represent best practice. Staff may only exceptionally depart from any relevant Trust guidelines providing always that such departure is confined to the specific needs of individual circumstances. In healthcare delivery such departure shall only be undertaken where, in the judgement of the responsible healthcare professional it is fully appropriate and justifiable - such decision to be fully recorded in the patient s notes. 7. Equality Statement The Trust recognises the diversity of the local community it serves. Our aim therefore is to provide a safe environment free from discrimination and treat all individuals fairly with dignity and appropriately according to their needs. As part of its development, this policy/guideline and its impact on equality have been reviewed and no detriment was identified. 8. Supporting Documents and Key References Allergy Care Pathway Website. Informative and includes videos of how to apply treatments. Available at Gould D (2001) Childhood eczema. Primary Health Care 11(7)43-50 Holden C et al (2002) Advised best practice for the use of emollients in eczema and other dry skin conditions. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 13, Hughes E & Van Onselen J. (2001) Dermatology Nursing. A Practical Guide Churchill Livingstone. Edinburgh. Long C C et al (1998). A practical guide to topical therapy in children. British Journal of Dermatology.138, Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency. 25 March Aqueous cream: may cause skin irritation. National Eczema Society January Emollients. accessed 11/08/16 National Eczema Society February Topical steroids. accessed 11/08/16 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Atopic Eczema in under 12 s: Diagnosis and Management. NICE Guidance (CG57) NICE (2007) Atopic eczema in children: management of atopic eczema in children from Page 9 of 11
10 birth up to the age of 12 years NICE September Atopic eczema in under 12s. qs44 nice.org.uk/guidance/qs44 Nottingham Support Group for Carers of Children with Eczema. Resource aimed at parents and carers and includes numerous documents on frequently asked questions. Available at: 9. Key Words Atopic Eczema, Eczema, Emollients Author / Lead Officer: Executive Lead Date 2002 C30/2005 & 2007 C116/2007 May 2008 C30/2005 Aug 2009 C30/2005 May 2010 C116/2007 June 2016 C116/2007 DEVELOPMENT AND APPROVAL RECORD FOR THIS DOCUMENT Karen Harman WendySwanson James Miller Simon Robinson Issue Reviewed By Number 1 E Carter P Hickford W Swanson 3 Wendy Swanson REVIEW RECORD Job Title: Cons Dermatologist Children s Nurse Specialist Dermatology registrar Description Of Changes (If Any) May Karen Harman WendySwanso n James Miller Combined medical and nursing guidance C30/2005 & C116/2007 Insertion of NICE equality and diversity & assessment consideration statements Revised to follows current NICE guidance Reference to stepped care plan. Insertion of NICE awareness of darker skin tones eczema sites. Page 10 of 11
11 Removal of cotton mittens, finger nail care and consider scabies advice. Removal of E45 &Balneum bath additive use Updated emollient preparations in line with modern practice and LMSG formulary changes Tabulated and expanded emollient advice Removed outdated advice Tabulated and expanded Corticosteroid advice Removed scalp treatment advice Changed Fucidin strength from 1% to 2% Added topical Calcineurine inhibitors advice Removed K Permanganate baths Expanded anti-histamine advice Highlighted that bandages and occlusive dressings should not be first line use Food allergy section added Removed local information leaflets, now signposted to national websites Addition of health & safety statement regarding slippery surfaces Addition of atopic eczema affecting extensors Addition of continuing emollient application even when eczema is clear Finger-tip guide removed from appendix Addition of occlusive therapy on infected skin is contraindicated Added parent education guidance Added contact numbers for advice References updated Keywords added Page 11 of 11
Clinical guideline Published: 12 December 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg57
 Atopic eczema in under 12s: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 12 December 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg57 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Atopic eczema in under 12s: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 12 December 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg57 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Clinical guideline Published: 12 December 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg57
 Atopic eczema in under 12s: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 12 December 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg57 NICE 2007. All rights reserved. Contents Introduction... 4 Child-centred care...
Atopic eczema in under 12s: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 12 December 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg57 NICE 2007. All rights reserved. Contents Introduction... 4 Child-centred care...
Childhood Eczema Flowchart
 Childhood Eczema Flowchart EXCLUSIONS -Over 15 years of age -Contact dermatitis -Seborrhoeic Eczema -Mild and Moderate Eczema Childhood Eczema Assess Eczema Severity RED FLAGS -Eczema Herpecitum -Severe
Childhood Eczema Flowchart EXCLUSIONS -Over 15 years of age -Contact dermatitis -Seborrhoeic Eczema -Mild and Moderate Eczema Childhood Eczema Assess Eczema Severity RED FLAGS -Eczema Herpecitum -Severe
ATOPIC ECZEMA. What are the aims of this leaflet?
 ATOPIC ECZEMA What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about atopic eczema. It tells you what it is, what causes it, what can be done about it, and where
ATOPIC ECZEMA What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about atopic eczema. It tells you what it is, what causes it, what can be done about it, and where
Atopic Eczema with detail on how to apply wet wraps
 Atopic Eczema with detail on how to apply wet wraps Dr Carol Hlela Consultant Dermatologist Head of Unit, Department of Dermatology, Paediatrics Red Cross Children s Hospital, UCT Red Cross War Memorial
Atopic Eczema with detail on how to apply wet wraps Dr Carol Hlela Consultant Dermatologist Head of Unit, Department of Dermatology, Paediatrics Red Cross Children s Hospital, UCT Red Cross War Memorial
TCIs are only available on prescription and are usually started by a dermatology specialist.
 (TCIs) What are topical calcineurin inhibitors? Topical calcineurin inhibitors are treatments that alter the immune system and have been developed for controlling eczema. There are two types available:
(TCIs) What are topical calcineurin inhibitors? Topical calcineurin inhibitors are treatments that alter the immune system and have been developed for controlling eczema. There are two types available:
15 minute eczema consultation
 THERAPY WORKSHOP 15 minute eczema consultation History Current treatments Examination Treatment Plan Written action plan Soap substitute/bath oil Antiseptic baths Emollients Topical steroids Other treatments
THERAPY WORKSHOP 15 minute eczema consultation History Current treatments Examination Treatment Plan Written action plan Soap substitute/bath oil Antiseptic baths Emollients Topical steroids Other treatments
Dermatology Round Up
 Dermatology Round Up Journal of Family Health Care Live Conference 25 March 2014 Julie Van Onselen Independent Dermatology Nurse, Oxford And Rachael Fagg, Mother Introduction 10.00 10.30hrs: Julie Van
Dermatology Round Up Journal of Family Health Care Live Conference 25 March 2014 Julie Van Onselen Independent Dermatology Nurse, Oxford And Rachael Fagg, Mother Introduction 10.00 10.30hrs: Julie Van
Recommended management of eczema in older patients
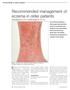 Recommended management of eczema in older patients Victoria Sherman MA, MRCP and Daniel Creamer BSc, MD, FRCP Our series Prescribing in older people gives practical advice for successful management of
Recommended management of eczema in older patients Victoria Sherman MA, MRCP and Daniel Creamer BSc, MD, FRCP Our series Prescribing in older people gives practical advice for successful management of
過敏病科中心. Allergy Centre. Eczema. Allergy Centre 過敏病科中心. Allergy Centre. For enquiries and appointments, please contact us at:
 Allergy Centre 過敏病科中心 Eczema For enquiries and appointments, please contact us at: Allergy Centre 9/F, Li Shu Pui Block Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital 2 Village Road, Happy Valley, Hong Kong Tel: 2835
Allergy Centre 過敏病科中心 Eczema For enquiries and appointments, please contact us at: Allergy Centre 9/F, Li Shu Pui Block Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital 2 Village Road, Happy Valley, Hong Kong Tel: 2835
Steroid use in managing your child s Atopic Eczema
 Steroid use in managing your child s Atopic Eczema Clinical Nurse Specialist for Paediatric Dermatology (01284) 713575 Step up step down approach: Addressograph Severe Call your General Practitioner (GP)
Steroid use in managing your child s Atopic Eczema Clinical Nurse Specialist for Paediatric Dermatology (01284) 713575 Step up step down approach: Addressograph Severe Call your General Practitioner (GP)
ECZEMA. Introduction. Differential diagnoses. Starship Children s Health Clinical Guideline
 Introduction Differential Diagnoses Indications for Admission Inpatient Treatment Flow Chart for Inpatient Care Outpatient Treatment References See also Auckland Regional Clinical Pathways for Eczema (with
Introduction Differential Diagnoses Indications for Admission Inpatient Treatment Flow Chart for Inpatient Care Outpatient Treatment References See also Auckland Regional Clinical Pathways for Eczema (with
Dermatitis (inflammatory skin condition) Nonallergic. dermatitis. Non-atopic eczema (non- IgE mediated)
 Atopic Eczema Dermatitis (inflammatory skin condition) Allergic dermatitis -eczema Nonallergic dermatitis Atopic eczema (IgE mediated) Non-atopic eczema (non- IgE mediated) Pathophysiology of Eczema Allergy
Atopic Eczema Dermatitis (inflammatory skin condition) Allergic dermatitis -eczema Nonallergic dermatitis Atopic eczema (IgE mediated) Non-atopic eczema (non- IgE mediated) Pathophysiology of Eczema Allergy
RELEVANT DISCLOSURES ATOPIC DERMATITIS / ECZEMA MANAGING ECZEMA IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN
 RELEVANT DISCLOSURES MANAGING ECZEMA IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN Advisory board member - MEDA (Elidel), Speaking honoraria Bayer (Advantan) Advisory board, consultant, speaker: Pfizer, Abbvie, Janssen, Elli
RELEVANT DISCLOSURES MANAGING ECZEMA IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN Advisory board member - MEDA (Elidel), Speaking honoraria Bayer (Advantan) Advisory board, consultant, speaker: Pfizer, Abbvie, Janssen, Elli
Learning Circle: Jan 26, 2011 Childhood Eczema
 Learning Circle: Jan 26, 2011 Childhood Eczema Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, UBC Department of Paediatrics Associate Member, UBC Department of Dermatology
Learning Circle: Jan 26, 2011 Childhood Eczema Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, UBC Department of Paediatrics Associate Member, UBC Department of Dermatology
An Everyday Guide to Eczema
 An Everyday Guide to Eczema By Dr. Kristel Polder, Board-Certified Dermatologist Developed in Partnership with Who is affected by eczema? 32 million people in the US 1 in 5 children 1 in 12 adults *www.eczema.org
An Everyday Guide to Eczema By Dr. Kristel Polder, Board-Certified Dermatologist Developed in Partnership with Who is affected by eczema? 32 million people in the US 1 in 5 children 1 in 12 adults *www.eczema.org
Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin
 Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin Co-Management Guidelines To support collaborative care, we have developed guidelines for our community providers to utilize when referring to, and managing patients with,
Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin Co-Management Guidelines To support collaborative care, we have developed guidelines for our community providers to utilize when referring to, and managing patients with,
Volume 2; Number 2 February 2008
 Volume 2; Number 2 February 2008 CONTENTS Page 2 Page 3 Page 3 Page 4 Page 6 New Drug Assessment: Rufinamide (Inovelon) New Drug Assessment: Zoledronic acid infusion (Aclasta) New Drug Assessment: Mesalazine
Volume 2; Number 2 February 2008 CONTENTS Page 2 Page 3 Page 3 Page 4 Page 6 New Drug Assessment: Rufinamide (Inovelon) New Drug Assessment: Zoledronic acid infusion (Aclasta) New Drug Assessment: Mesalazine
Paediatric Eczema. Dr Manjeet Joshi Consultant Dermatologist 16 th May 2012
 Paediatric Eczema Dr Manjeet Joshi Consultant Dermatologist 16 th May 2012 Classification of the principal forms of eczema EXOGENOUS ENDOGENOUS Irritant Allergic contact Photoallergic contact Eczematous
Paediatric Eczema Dr Manjeet Joshi Consultant Dermatologist 16 th May 2012 Classification of the principal forms of eczema EXOGENOUS ENDOGENOUS Irritant Allergic contact Photoallergic contact Eczematous
Texas Children's Hospital Dermatology Service PCP Referral Guidelines- Atopic Dermatitis (AD)
 Diagnosis: ATOPIC DERMATITIS (AD) Texas Children's Hospital Dermatology Service PCP Referral Guidelines- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) PATIENT ADVICE: Unfortunately, there is no cure for atopic dermatitis, so
Diagnosis: ATOPIC DERMATITIS (AD) Texas Children's Hospital Dermatology Service PCP Referral Guidelines- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) PATIENT ADVICE: Unfortunately, there is no cure for atopic dermatitis, so
New Medicine Report. Pimecrolimus. RED- Hospital only Date of Last Revision 6 th March 2003
 New Medicine Report Document Status Pimecrolimus Reviewed by Suffolk D&T RED- Hospital only Date of Last Revision 6 th March 2003 Approved Name Pimecrolimus Trade Name Elidel Manufacturer Novartis Legal
New Medicine Report Document Status Pimecrolimus Reviewed by Suffolk D&T RED- Hospital only Date of Last Revision 6 th March 2003 Approved Name Pimecrolimus Trade Name Elidel Manufacturer Novartis Legal
Dr David Orchard MBBS FACD
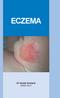 Eczema Dr David Orchard MBBS FACD What is eczema? Eczema is a particular type of inflammatory reaction in the skin. The features include redness, scaling and itch. When it is more severe the skin will
Eczema Dr David Orchard MBBS FACD What is eczema? Eczema is a particular type of inflammatory reaction in the skin. The features include redness, scaling and itch. When it is more severe the skin will
Teledermatology Paediatric eczema. Dr Carolyn Charman Consultant Dermatologist Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital
 Teledermatology Paediatric eczema Dr Carolyn Charman Consultant Dermatologist Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital NHS e-referral teledermatology Rapid access to diagnosis / management advice from local integrated
Teledermatology Paediatric eczema Dr Carolyn Charman Consultant Dermatologist Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital NHS e-referral teledermatology Rapid access to diagnosis / management advice from local integrated
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level
 Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
What are the symptoms of a vulval skin condition?
 Information for you Published in December 2013 Skin conditions of the vulva About this information This information is for you if you want to know about skin conditions affecting the vulva. If you are
Information for you Published in December 2013 Skin conditions of the vulva About this information This information is for you if you want to know about skin conditions affecting the vulva. If you are
Professor Rohan Ameratunga Clinical Immunologist and Allergist Auckland
 Professor Rohan Ameratunga Clinical Immunologist and Allergist Auckland 16:30-17:25 WS #170: Eczema Management 17:35-18:30 WS #182: Eczema Management (Repeated) Managing ECZEMA A/Prof Rohan Ameratunga
Professor Rohan Ameratunga Clinical Immunologist and Allergist Auckland 16:30-17:25 WS #170: Eczema Management 17:35-18:30 WS #182: Eczema Management (Repeated) Managing ECZEMA A/Prof Rohan Ameratunga
Eczema management: how to control the itch
 ATM - Eczema:Layout 1 24/3/11 3:08 PM Page 24 allergytoday skin Eczema management: how to control the itch Eczema is the most common specific skin disorder encountered but it is very poorly managed and
ATM - Eczema:Layout 1 24/3/11 3:08 PM Page 24 allergytoday skin Eczema management: how to control the itch Eczema is the most common specific skin disorder encountered but it is very poorly managed and
Cholestatic jaundice Chronic kidney disease Iron deficiency +/-anaemia. Hepatoma Diabetes Leukaemia
 Pruritis Introduction Pruritis can cause discomfort, frustration, poor sleep, anxiety and depression. Itch may be localised or due to systemic disease. Pruritis in systemic disease is often worse at night.
Pruritis Introduction Pruritis can cause discomfort, frustration, poor sleep, anxiety and depression. Itch may be localised or due to systemic disease. Pruritis in systemic disease is often worse at night.
Dermatology. Women and Children s Services
 Women and Children s Services Dermatology Disclaimer: The recommendations contained in this guideline do not indicate an exclusive course of action, or serve as a standard of medical care. Variations,
Women and Children s Services Dermatology Disclaimer: The recommendations contained in this guideline do not indicate an exclusive course of action, or serve as a standard of medical care. Variations,
Eczema & Dermatitis Clinical features: Histopathological features: Classification:
 Eczema & Dermatitis Eczema is an inflammatory reactive pattern of skin to many and different stimuli characterized by itching, redness, scaling and clustered papulovesicles. Eczema and dermatitis are synonymous
Eczema & Dermatitis Eczema is an inflammatory reactive pattern of skin to many and different stimuli characterized by itching, redness, scaling and clustered papulovesicles. Eczema and dermatitis are synonymous
The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis
 Dermatology The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis The image to the left shows an image of skin cells and the proteins which
Dermatology The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis The image to the left shows an image of skin cells and the proteins which
Contact Allergy Testing (Patch Testing) Information for parents and carers of children up to 12 years of age
 Contact Allergy Testing (Patch Testing) Information for parents and carers of children up to 12 years of age Dermatology Department The aim of this leaflet is to give you information about contact allergy
Contact Allergy Testing (Patch Testing) Information for parents and carers of children up to 12 years of age Dermatology Department The aim of this leaflet is to give you information about contact allergy
Dermatology Literary Review
 Emollients and ageing skin: optimising effectiveness and safety of Nursing, Vol. 25, No.11, pages 596-598. 6 Article outlines the causes of dryness in ageing skin and concludes that emollients are the
Emollients and ageing skin: optimising effectiveness and safety of Nursing, Vol. 25, No.11, pages 596-598. 6 Article outlines the causes of dryness in ageing skin and concludes that emollients are the
What you need to know about ECZEMA
 What you need to know about ECZEMA The Irish Skin Foundation is a national charity with a mission to improve quality of life for people with skin conditions, promote skin health and the prevention of skin
What you need to know about ECZEMA The Irish Skin Foundation is a national charity with a mission to improve quality of life for people with skin conditions, promote skin health and the prevention of skin
What you need to know about ECZEMA
 What you need to know about ECZEMA The Irish Skin Foundation is a national charity with a mission to improve quality of life for people with skin conditions, promote skin health and the prevention of skin
What you need to know about ECZEMA The Irish Skin Foundation is a national charity with a mission to improve quality of life for people with skin conditions, promote skin health and the prevention of skin
SKIN CARE AND PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT OF WORK RELATED DERMATITIS
 SKIN CARE AND PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT OF WORK RELATED DERMATITIS Version No. Date Comments Date Author/s Approved by Amended Approved 1. 10/10/2011 LCP/GC LCP Skin care & prevention of work related dermatitis
SKIN CARE AND PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT OF WORK RELATED DERMATITIS Version No. Date Comments Date Author/s Approved by Amended Approved 1. 10/10/2011 LCP/GC LCP Skin care & prevention of work related dermatitis
Allergy Medications. Antihistamines. are very safe. Although usually taken as tablets, they may be prescribed as a liquid or syrup for young children
 The treatments prescribed for allergy control the symptoms and reactions; they do not cure the condition. However, using treatments as prescribed can show a huge change in a patient s health, mood and
The treatments prescribed for allergy control the symptoms and reactions; they do not cure the condition. However, using treatments as prescribed can show a huge change in a patient s health, mood and
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Technology Appraisals and Guidance Information Services Static List Review (SLR) Title and TA publication number of static topic: Final decision: TA82;
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Technology Appraisals and Guidance Information Services Static List Review (SLR) Title and TA publication number of static topic: Final decision: TA82;
Eczema. By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University
 Eczema By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University Dermatitis= Eczema =Spongiosis Eczema Atopic Seborrheic Contact Allergic Irritant Nummular Asteatotic Stasis Neurodermatitis/Lichen Simplex
Eczema By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University Dermatitis= Eczema =Spongiosis Eczema Atopic Seborrheic Contact Allergic Irritant Nummular Asteatotic Stasis Neurodermatitis/Lichen Simplex
ECZEMA. Introduction. Differential diagnoses. Starship Children s Health Clinical Guideline
 Introduction Differential Diagnoses Indications for Admission Inpatient Treatment Flow Chart for Inpatient Care Outpatient Treatment References Introduction Eczema (also called atopic dermatitis) is characterised
Introduction Differential Diagnoses Indications for Admission Inpatient Treatment Flow Chart for Inpatient Care Outpatient Treatment References Introduction Eczema (also called atopic dermatitis) is characterised
PRIMARY CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD ATOPIC ECZEMA
 PRIMARY CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD ATOPIC ECZEMA INTRODUCTION Atopic Eczema is an inflammatory skin disease categorised by an itchy, erythematous, demarcated rash, which has a predilection for the skin
PRIMARY CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD ATOPIC ECZEMA INTRODUCTION Atopic Eczema is an inflammatory skin disease categorised by an itchy, erythematous, demarcated rash, which has a predilection for the skin
Severe Atopic Dermatitis Management Guideline
 Severe Atopic Dermatitis Management Guideline Severe childhood eczema is a mix of acute and chronic management that often involves acute admission. This CPO pathway covers the acute managementto avoidpotential
Severe Atopic Dermatitis Management Guideline Severe childhood eczema is a mix of acute and chronic management that often involves acute admission. This CPO pathway covers the acute managementto avoidpotential
Constitutional eczema
 Patient information Constitutional eczema What is constitutional eczema? Constitutional eczema, also called atopic eczema, is a form of eczema that mainly occurs in childhood. Eczema usually starts before
Patient information Constitutional eczema What is constitutional eczema? Constitutional eczema, also called atopic eczema, is a form of eczema that mainly occurs in childhood. Eczema usually starts before
Patch testing. Dermatology Department Patient Information Leaflet
 Patch testing Dermatology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about patch testing. It tells you what a patch test is, what is involved
Patch testing Dermatology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about patch testing. It tells you what a patch test is, what is involved
The Sheffield Children s Hospital Dermatology Team Approach
 Atopic eczema The Management of Atopic Eczema1 The Management of Atopic Eczema: The Sheffield Children s Hospital Dermatology Team Approach Contents: Aims and objectives 2 Emollient advice General advice
Atopic eczema The Management of Atopic Eczema1 The Management of Atopic Eczema: The Sheffield Children s Hospital Dermatology Team Approach Contents: Aims and objectives 2 Emollient advice General advice
Primary Care Guidelines for the Management of Atopic Eczema 10/07100
 4 4 w Primary Care Guidelines for the Management of Atopic Eczema 10/07100 1.0 INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVES Primary care manages by far the largest number of patients with atopic eczema, the vast majority
4 4 w Primary Care Guidelines for the Management of Atopic Eczema 10/07100 1.0 INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVES Primary care manages by far the largest number of patients with atopic eczema, the vast majority
Guidelines for the management of paediatric burns
 Guidelines for the management of paediatric burns Are there signs of airway injury? If yes contact anaesthetist! Is burn TBSA >10% If appropriate COOL THE BURN! Heat room. Insert IVC. Obtain FBC, U&,E
Guidelines for the management of paediatric burns Are there signs of airway injury? If yes contact anaesthetist! Is burn TBSA >10% If appropriate COOL THE BURN! Heat room. Insert IVC. Obtain FBC, U&,E
English for Nurses: Eczema Vocabulary allergy allergies be allergic to a bath have a bath to bathe citrus fruits common cool dairy products eczema
 English for Nurses: Eczema Vocabulary allergy allergies be allergic to a bath have a bath to bathe citrus fruits common cool dairy products eczema elbows fingernail a link to link to something make something
English for Nurses: Eczema Vocabulary allergy allergies be allergic to a bath have a bath to bathe citrus fruits common cool dairy products eczema elbows fingernail a link to link to something make something
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 25 August 2004 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta82
 Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus for atopic eczema Technology appraisal guidance Published: 25 August 2004 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta82 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus for atopic eczema Technology appraisal guidance Published: 25 August 2004 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta82 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
MALE GENITAL (PENIS) LICHEN SCLEROSUS
 MALE GENITAL (PENIS) LICHEN SCLEROSUS What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about male genital lichen sclerosus (also known as balanitis xerotica
MALE GENITAL (PENIS) LICHEN SCLEROSUS What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about male genital lichen sclerosus (also known as balanitis xerotica
Food allergies and eczema
 Department of Dermatology Food allergies and eczema Information for parents and carers Eczema, also known as atopic eczema or atopic dermatitis, is a skin condition that causes inflammation and irritation.
Department of Dermatology Food allergies and eczema Information for parents and carers Eczema, also known as atopic eczema or atopic dermatitis, is a skin condition that causes inflammation and irritation.
What is atopic dermatitis?
 What is atopic dermatitis? Complex inflammatory skin disorder intense pruritus cutaneous hyperreactivity immune dysregulation Chronic with exacerbations and remissions Affects all ages, but more common
What is atopic dermatitis? Complex inflammatory skin disorder intense pruritus cutaneous hyperreactivity immune dysregulation Chronic with exacerbations and remissions Affects all ages, but more common
The Itch That Rashes. Sarah D. Cipriano, MD, MPH, MS Resident, Dermatology University of Utah
 The Itch That Rashes Sarah D. Cipriano, MD, MPH, MS Resident, Dermatology University of Utah 1 Conflict of Interest No conflict of interest Will discuss off label use of medications 2 3 Most likely diagnosis?
The Itch That Rashes Sarah D. Cipriano, MD, MPH, MS Resident, Dermatology University of Utah 1 Conflict of Interest No conflict of interest Will discuss off label use of medications 2 3 Most likely diagnosis?
Medication Policy Manual. Topic: Dupixent, dupilumab Date of Origin: March 10, Committee Approval: March 10, 2017 Next Review Date: May 2018
 Independent licensees of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru493 Topic: Dupixent, dupilumab Date of Origin: March 10, 2017 Committee Approval: March 10, 2017
Independent licensees of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru493 Topic: Dupixent, dupilumab Date of Origin: March 10, 2017 Committee Approval: March 10, 2017
Dermatitis. Occupational aspects of management
 Dermatitis Occupational aspects of management Evidence-based guidance for healthcare professionals Introduction This leaflet summarises the findings from a review of the published scientific literature
Dermatitis Occupational aspects of management Evidence-based guidance for healthcare professionals Introduction This leaflet summarises the findings from a review of the published scientific literature
Case studies of children and adults with atopic eczema being treated under the Aron regime
 Case studies of children and adults with atopic eczema being treated under the Prepared by: Parents of patients of Dr Richard Aron (GMC ref no. 3151727) May 2015 Dr Aron s website: www.draron.com Dr Aron
Case studies of children and adults with atopic eczema being treated under the Prepared by: Parents of patients of Dr Richard Aron (GMC ref no. 3151727) May 2015 Dr Aron s website: www.draron.com Dr Aron
A Child with Eczema: A Parent s Guide
 A Child with Eczema: A Parent s Guide What is eczema? Originally the term eczema was used to describe any itchy rash that blistered; now eczema describes skin which is red (inflamed) and intensely itchy.
A Child with Eczema: A Parent s Guide What is eczema? Originally the term eczema was used to describe any itchy rash that blistered; now eczema describes skin which is red (inflamed) and intensely itchy.
MRSA. Meticillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Infection Control Department. Royal Surrey County Hospital. Patient information leaflet
 Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust MRSA Meticillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection Control Department This leaflet has been written to help you understand
Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust MRSA Meticillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection Control Department This leaflet has been written to help you understand
Vulval dermatoses. Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough
 Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Understanding. Atopic Dermatitis. National Jewish Health. An educational health series from
 Understanding Atopic Dermatitis An educational health series from National Jewish Health If you would like further information about National Jewish Health, please write to: National Jewish Health 1400
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis An educational health series from National Jewish Health If you would like further information about National Jewish Health, please write to: National Jewish Health 1400
ECZEMA SOCIETY OF CANADA ATOPIC DERMATITIS: PATIENT INSIGHTS REPORT MILD-TO-MODERATE DISEASE
 ECZEMA SOCIETY OF CANADA ATOPIC DERMATITIS: PATIENT INSIGHTS REPORT MILD-TO-MODERATE DISEASE 1 OVERVIEW OF SURVEY RESULTS INTRODUCTION PATIENT INSIGHTS BY THE NUMBERS: Adult Atopic Dermatitis (AD) In the
ECZEMA SOCIETY OF CANADA ATOPIC DERMATITIS: PATIENT INSIGHTS REPORT MILD-TO-MODERATE DISEASE 1 OVERVIEW OF SURVEY RESULTS INTRODUCTION PATIENT INSIGHTS BY THE NUMBERS: Adult Atopic Dermatitis (AD) In the
PHOTOTHERAPY. With narrowband UVB, the light tubes produce a narrow part of the UVB spectrum. Two wavelengths
 Phototherapy (light therapy) refers to the use of ultraviolet (UV) light to treat moderate to severe eczema in children and adults. Phototherapy is a second-line treatment option that is available at specialist
Phototherapy (light therapy) refers to the use of ultraviolet (UV) light to treat moderate to severe eczema in children and adults. Phototherapy is a second-line treatment option that is available at specialist
Case studies of children and adults with atopic eczema being treated under the Aron regime
 Case studies of children and adults with atopic eczema being treated under the Prepared by: Parents of patients of Dr Richard Aron (GMC ref no. 3151727) May 2015 Dr Aron s website: www.draron.com Dr Aron
Case studies of children and adults with atopic eczema being treated under the Prepared by: Parents of patients of Dr Richard Aron (GMC ref no. 3151727) May 2015 Dr Aron s website: www.draron.com Dr Aron
A Resource Kit for Career Counsellors
 A Resource Kit for Career Counsellors Occupational Dermatology Research and Education Centre www.occderm.asn.au/skinatwork 2 About this kit The Skin @ Work education kit aims to raise awareness of a potential
A Resource Kit for Career Counsellors Occupational Dermatology Research and Education Centre www.occderm.asn.au/skinatwork 2 About this kit The Skin @ Work education kit aims to raise awareness of a potential
Pediatric Dermatology. Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital
 Pediatric Dermatology Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Conflict of interest! No financial conflict of interest! Individual products shown are examples only not a product endorsement Pediatric
Pediatric Dermatology Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Conflict of interest! No financial conflict of interest! Individual products shown are examples only not a product endorsement Pediatric
Assessing the Current Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: Unmet Needs
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
8-year surveillance 2016 Atopic eczema in under 12s (2007) NICE guideline CG57
 8-year 2016 Atopic eczema in under 12s (2007) NICE guideline CG57 Appendix A: decision matrix year Diagnosis 57 01 What criteria should be used to diagnose atopic eczema in children and how do they vary
8-year 2016 Atopic eczema in under 12s (2007) NICE guideline CG57 Appendix A: decision matrix year Diagnosis 57 01 What criteria should be used to diagnose atopic eczema in children and how do they vary
Skin Deep: Or is It? Practical Pearls from a Pediatric Dermatologist
 Skin Deep: Or is It? Practical Pearls from a Pediatric Dermatologist I have no conflicts of interest 6 yo boy referred for AD. On topical HC and food elimination diet s/p topical triamcinolone to body
Skin Deep: Or is It? Practical Pearls from a Pediatric Dermatologist I have no conflicts of interest 6 yo boy referred for AD. On topical HC and food elimination diet s/p topical triamcinolone to body
Food Allergy Testing and Guidelines
 Food Allergy Testing and Guidelines Dr Gosia Skibinska Primary Care Allergy Training Day, 15 th October 2011 Food Allergy Testing and Guidelines Food allergy Testing Guidelines Cases Food Allergy NICE
Food Allergy Testing and Guidelines Dr Gosia Skibinska Primary Care Allergy Training Day, 15 th October 2011 Food Allergy Testing and Guidelines Food allergy Testing Guidelines Cases Food Allergy NICE
Eczema. Most kids get itchy rashes at one time or another. But eczema can be a nuisance that may prompt scratching that makes the problem worse.
 KidsHealth.org The most-visited site devoted to children's health and development Eczema Most kids get itchy rashes at one time or another. But eczema can be a nuisance that may prompt scratching that
KidsHealth.org The most-visited site devoted to children's health and development Eczema Most kids get itchy rashes at one time or another. But eczema can be a nuisance that may prompt scratching that
PRACTICAL ECZEMA & SKIN INFECTION MANAGEMENT IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 PRACTICAL ECZEMA & SKIN INFECTION MANAGEMENT IN GENERAL PRACTICE Debbie Rickard Child Health Nurse Practitioner Capital & Coast DHB CHILDHOOD ECZEMA Affects 15 20% New Zealand school children Preventable
PRACTICAL ECZEMA & SKIN INFECTION MANAGEMENT IN GENERAL PRACTICE Debbie Rickard Child Health Nurse Practitioner Capital & Coast DHB CHILDHOOD ECZEMA Affects 15 20% New Zealand school children Preventable
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter
 Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter Equipment required collect prior to procedure Perform this procedure as an aseptic technique to minimise the risk of introducing Clean the
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter Equipment required collect prior to procedure Perform this procedure as an aseptic technique to minimise the risk of introducing Clean the
CHAPTER 1. Eczema Basics
 CHAPTER 1 Eczema Basics Definition Eczema is an inflammatory skin condition, characterised by ichtyosis (dry skin), erythema (redness), excoriation (interruption of the skin), scratching lesions, lichenification
CHAPTER 1 Eczema Basics Definition Eczema is an inflammatory skin condition, characterised by ichtyosis (dry skin), erythema (redness), excoriation (interruption of the skin), scratching lesions, lichenification
What s Topical About Topicals?
 What s Topical About Topicals? Megha M. Tollefson, MD Associate Professor of Dermatology and Pediatrics July 29, 2017 2015 MFMER 3513105-1 Disclosures None 2015 MFMER 3513105-2 Outline Topical steroids
What s Topical About Topicals? Megha M. Tollefson, MD Associate Professor of Dermatology and Pediatrics July 29, 2017 2015 MFMER 3513105-1 Disclosures None 2015 MFMER 3513105-2 Outline Topical steroids
Management of eczema in infants and children Assoc Prof David Orchard Director, Department of Dermatology Royal Children s Hospital
 Atopic dermatitis definition Management of eczema in infants and children Assoc Prof David Orchard Director, Department of Dermatology Royal Children s Hospital Atopic dermatitis is long lasting (chronic)
Atopic dermatitis definition Management of eczema in infants and children Assoc Prof David Orchard Director, Department of Dermatology Royal Children s Hospital Atopic dermatitis is long lasting (chronic)
Guideline for the Identification and Management of Delirium (Including use of the THINK DELIRIUM Support Tool)
 Guideline for the Identification and Management of Delirium (Including use of the THINK DELIRIUM Support Tool) B27/2009 1. Introduction 1.1 Delirium is a common problem which occurs in about 15-20 out
Guideline for the Identification and Management of Delirium (Including use of the THINK DELIRIUM Support Tool) B27/2009 1. Introduction 1.1 Delirium is a common problem which occurs in about 15-20 out
Sickness and Illness Policy
 Sickness and Illness Policy Children should not be at nursery if they are unwell. If your child becomes unable to stay at nursery, a member of staff will contact the parent or carer, asking them to come
Sickness and Illness Policy Children should not be at nursery if they are unwell. If your child becomes unable to stay at nursery, a member of staff will contact the parent or carer, asking them to come
 ''Can't play with the sand at nursery. I get all scratchy and red and sore. Not fair'' - Sophie ''My teacher helps with my creams when I'm too dry'' - Daniel www.eczemaoutreachscotland.org.uk Dear Early
''Can't play with the sand at nursery. I get all scratchy and red and sore. Not fair'' - Sophie ''My teacher helps with my creams when I'm too dry'' - Daniel www.eczemaoutreachscotland.org.uk Dear Early
Home intravenous and intramuscular antibiotics
 Home intravenous and intramuscular antibiotics Children s Community Nursing Service 0161 206 2370 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. This booklet has been given to you because your
Home intravenous and intramuscular antibiotics Children s Community Nursing Service 0161 206 2370 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. This booklet has been given to you because your
Sickness and Illness Policy
 Sickness and Illness Policy Children should not be at nursery if they are unwell. If your child becomes unable to stay at nursery, a member of staff will contact the parent or carer, asking them to come
Sickness and Illness Policy Children should not be at nursery if they are unwell. If your child becomes unable to stay at nursery, a member of staff will contact the parent or carer, asking them to come
What causes swimmer s ear?
 Swimmer s Ear Affecting the outer ear, swimmer s ear is a painful condition resulting from inflammation, irritation, or infection. These symptoms often occur after water gets trapped in your ear, with
Swimmer s Ear Affecting the outer ear, swimmer s ear is a painful condition resulting from inflammation, irritation, or infection. These symptoms often occur after water gets trapped in your ear, with
Managing Atopic Derma00s: Itching the Night Away. Karol Timmons RN, MS, CPNP Boston Children s Hospital Atopic Derma00s Center
 Managing Atopic Derma00s: Itching the Night Away Karol Timmons RN, MS, CPNP Boston Children s Hospital Atopic Derma00s Center Learning Objec-ves Describe common treatments for atopic derma00s including:
Managing Atopic Derma00s: Itching the Night Away Karol Timmons RN, MS, CPNP Boston Children s Hospital Atopic Derma00s Center Learning Objec-ves Describe common treatments for atopic derma00s including:
Managing Eczema. Eczema Education Series.
 Managing Eczema Eczema Education Series www.eczemahelp.ca Table of Contents Introduction to Eczema Triangle of Control 1 2 Education What is Eczema? What Causes Eczema? Understanding the Disease Impaired
Managing Eczema Eczema Education Series www.eczemahelp.ca Table of Contents Introduction to Eczema Triangle of Control 1 2 Education What is Eczema? What Causes Eczema? Understanding the Disease Impaired
TRIGGERS & TREATMENT OF ATOPIC DERMATITIS COA#PCIA0809 CE Activity provided by PCI Journal
 TRIGGERS & TREATMENT OF ATOPIC DERMATITIS COA#PCIA0809 CE Activity provided by PCI Journal INSTRUCTIONS 1. Read the article. 2. Take the test, record your answers in the test answer section (Section B)
TRIGGERS & TREATMENT OF ATOPIC DERMATITIS COA#PCIA0809 CE Activity provided by PCI Journal INSTRUCTIONS 1. Read the article. 2. Take the test, record your answers in the test answer section (Section B)
Title Management of Impetigo Protocol in MIUs and WICs. Author s job title Professional Lead, Minor Injuries Unit Directorate
 Document Control Title Management of Impetigo Protocol in MIUs and WICs Author Author s job title Professional Lead, Minor Injuries Unit Directorate Department MIU Version Date Issued Status Comment /
Document Control Title Management of Impetigo Protocol in MIUs and WICs Author Author s job title Professional Lead, Minor Injuries Unit Directorate Department MIU Version Date Issued Status Comment /
Clinico Pathological Test SCPA605-Essential Pathology
 Clinico Pathological Test SCPA605-Essential Pathology Somphong Narkpinit, M.D. Department of Pathogbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University e-mail : somphong.nar@mahidol.ac.th Pathogenesis of allergic
Clinico Pathological Test SCPA605-Essential Pathology Somphong Narkpinit, M.D. Department of Pathogbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University e-mail : somphong.nar@mahidol.ac.th Pathogenesis of allergic
Lamellar ichthyosis What Is ichthyosis? Classification of Lamellar Ichthyosis What is Lamellar Ichthyosis? What are the signs?
 Lamellar ichthyosis What Is ichthyosis? Ichthyosis describes dry, thickened, scaly or flaky skin. There are at least 28 different ichthyosis subtypes, which are mainly inherited (have a genetic cause).
Lamellar ichthyosis What Is ichthyosis? Ichthyosis describes dry, thickened, scaly or flaky skin. There are at least 28 different ichthyosis subtypes, which are mainly inherited (have a genetic cause).
miconazole and zinc oxide topical
 miconazole and zinc oxide topical Pronunciation: mye KON a zole and ZINK OX ide TOP ik al Brand: Rash Relief Antifungal, Vusion What is the most important information I should know about miconazole and
miconazole and zinc oxide topical Pronunciation: mye KON a zole and ZINK OX ide TOP ik al Brand: Rash Relief Antifungal, Vusion What is the most important information I should know about miconazole and
Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters
 Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters This leaflet provides you with information and instructions on caring for clients who have an indwelling
Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters This leaflet provides you with information and instructions on caring for clients who have an indwelling
Dermatitis in Hairdressing
 Dermatitis in Hairdressing Copyright All rights reserved by Habia 2007. The text of this publication, or any part thereof, may not be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or
Dermatitis in Hairdressing Copyright All rights reserved by Habia 2007. The text of this publication, or any part thereof, may not be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Technology Appraisals and Guidance Information Services Static List Review (SLR) report Title and TA publication number of static topic: Final decision:
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Technology Appraisals and Guidance Information Services Static List Review (SLR) report Title and TA publication number of static topic: Final decision:
Hand Washing Policy Policy & Procedures Manual March 2018
 Hand Washing Policy Having and encouraging good hygiene practices in early childhood is essential for reducing the risk of cross infection. Helping children to develop appropriate personal hygiene habits
Hand Washing Policy Having and encouraging good hygiene practices in early childhood is essential for reducing the risk of cross infection. Helping children to develop appropriate personal hygiene habits
Eczema and its Management. A Guide for Nurses
 Eczema and its Management A Guide for Nurses Contents Page Contents Introduction 1 What is eczema? 1 Types of Eczema 3 Atopic eczema 3 Seborrhoeic dermatitis 5 Contact dermatitis 6 Gravitational/stasis/varicose
Eczema and its Management A Guide for Nurses Contents Page Contents Introduction 1 What is eczema? 1 Types of Eczema 3 Atopic eczema 3 Seborrhoeic dermatitis 5 Contact dermatitis 6 Gravitational/stasis/varicose
TENA SKINCARE & CLEANSING VERY SPECIAL CARE FOR VERY SPECIAL SKIN
 TENA SKINCARE & CLEANSING VERY SPECIAL CARE FOR VERY SPECIAL SKIN 3-in-1 personal skincare saves time for caregivers and promotes patient skin health Mousse combine three personal skincare products in
TENA SKINCARE & CLEANSING VERY SPECIAL CARE FOR VERY SPECIAL SKIN 3-in-1 personal skincare saves time for caregivers and promotes patient skin health Mousse combine three personal skincare products in
MRSA Positive. An information guide
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION MRSA Positive An information guide MRSA Positive What is MRSA? Staphylococcus aureus is a germ often found on the skin and up the nose of
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION MRSA Positive An information guide MRSA Positive What is MRSA? Staphylococcus aureus is a germ often found on the skin and up the nose of
Allergy occurs when the body's immune system reacts in an unusual way to foods and airborne particles. Allergy can be caused by many substances.
 What is allergy? Allergy occurs when the body's immune system reacts in an unusual way to foods and airborne particles. Allergy can be caused by many substances. How does your baby get allergy? Specific
What is allergy? Allergy occurs when the body's immune system reacts in an unusual way to foods and airborne particles. Allergy can be caused by many substances. How does your baby get allergy? Specific
Skin Problems. Issues for a Child. Skin Problems. Paediatric Palliative Care For Home Based Carers. Common in children with HIV
 Skin Problems Paediatric Palliative Care For Home Based Carers Funded by British High Commission, Pretoria Small Grant Scheme Skin Problems Common in children with HIV Often conditions common in all children
Skin Problems Paediatric Palliative Care For Home Based Carers Funded by British High Commission, Pretoria Small Grant Scheme Skin Problems Common in children with HIV Often conditions common in all children
Atopic Dermatitis Topics discussed
 Dr.F.Shariati Atopic Dermatitis Topics discussed Diagnosis of eczema Incidence Aggravators History and assessment Treatments Clinical Cases Contact details and clinics Eczema = TERMINOLOGY Greek term To
Dr.F.Shariati Atopic Dermatitis Topics discussed Diagnosis of eczema Incidence Aggravators History and assessment Treatments Clinical Cases Contact details and clinics Eczema = TERMINOLOGY Greek term To
Research Review PRODUCT REVIEW. About the Reviewer. Dr Jennifer Pilgrim MB ChB (Otago), FRACP. Atopic eczema
 Research Review PRODUCT REVIEW Methylprednisolone aceponate 0.1% ointment/cream [ADVANTAN ] About the Reviewer Dr Jennifer Pilgrim MB ChB (Otago), FRACP A graduate of Otago University, Dr Jennifer Pilgrim
Research Review PRODUCT REVIEW Methylprednisolone aceponate 0.1% ointment/cream [ADVANTAN ] About the Reviewer Dr Jennifer Pilgrim MB ChB (Otago), FRACP A graduate of Otago University, Dr Jennifer Pilgrim
Latex and Occupational Dermatitis Policy Incorporating Glove Selection
 Latex and Occupational Dermatitis Policy Incorporating Glove Selection DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 3 Ratified by: Risk Management Sub Group Date ratified: 17 July 2013 Name of originator/author: Health
Latex and Occupational Dermatitis Policy Incorporating Glove Selection DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 3 Ratified by: Risk Management Sub Group Date ratified: 17 July 2013 Name of originator/author: Health
