2004 Health Press Ltd.
|
|
|
- Jerome Todd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Eczema and Contact Dermatitis John Berth-Jones Consultant Dermatologist University Hospitals Coventry and Warwickshire NHS Trust, Coventry, UK Eunice Tan Specialist Registrar in Dermatology Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals Norwich, UK Howard I Maibach Professor of Dermatology University of California San Francisco, USA HEALTH PRESS Oxford
3 Fast Facts Eczema and Contact Dermatitis First published April 2004 Text 2004 John Berth-Jones, Eunice Tan, Howard I Maibach 2004 in this edition Health Press Limited Health Press Limited, Elizabeth House, Queen Street, Abingdon, Oxford OX14 3JR, UK Tel: +44 (0) Fax: +44 (0) Book orders can be placed by telephone or via the website. For regional distributors or to order via the website, please go to: For telephone orders, please call (UK) or (North America, toll free). Fast Facts is a trademark of Health Press Limited. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the express permission of the publisher. The rights of John Berth-Jones, Eunice Tan and Howard I Maibach to be identified as the authors of this work have been asserted in accordance with the Copyright, Designs & Patents Act 1988 Sections 77 and 78. The publisher and the authors have made every effort to ensure the accuracy of this book, but cannot accept responsibility for any errors or omissions. Registered names, trademarks, etc. used in this book, even when not marked as such, are not to be considered unprotected by law. A CIP catalogue record for this title is available from the British Library. ISBN Berth-Jones, J (John) Fast Facts Eczema and Contact Dermatitis John Berth-Jones, Eunice Tan, Howard I Maibach Medical illustrations by Dee McLean, London, UK. Typesetting and page layout by Zed, Oxford, UK. Printed by Fine Print (Services) Ltd, Oxford, UK. Printed with vegetable inks on fully biodegradable and recyclable paper manufactured from sustainable forests. Low chlorine Sustainable forests
4 Introduction 5 Allergic contact dermatitis 9 Irritant contact dermatitis 23 Atopic eczema 33 Photosensitive eczema 50 Seborrheic eczema 58 Hand and foot eczema 65 Other forms of eczema 73 Future trends 85 Sources of further information 89 Index 91
5
6 Introduction Eczema (also known as dermatitis) encompasses many common and important skin diseases. These affect patients of all ages. They include atopic eczema the intensely itchy and distressing disease seen mainly in infancy and childhood through industrial contact dermatitis a major source of handicap and time lost from work in the adult population to asteatotic eczema the itchy dry skin associated with aging. Indeed, there can be few people who are not affected by some form of eczema at some point in their lives. Largely because of the high incidence of eczema, physicians in many different medical disciplines are regularly involved in its management. This text is intended to help by familiarizing the non-dermatologist reader with the etiology, diagnosis and treatment of the various forms of this disease. The different types of eczema have such diverse etiologies that it is not immediately obvious what they have in common. They all share a range of clinical and histological features. They are characterized, in the acute phase, by itching and erythema. Sometimes, especially on the hands and feet, vesicles or bullae may appear. Dryness, excoriation, exudation, edema, induration, scaling, lichenification and fissuring develop later. Lichenification, a sign of chronic inflammation, is a thickening of the skin initially manifested by a subtle accentuation of surface markings and progressing to marked induration and roughening of the skin surface. The histological features of eczema include edema of the epidermis (often called spongiosis), which may progress to vesicle or bulla formation, and inflammation of the dermis (infiltration with lymphocytes and macrophages). The histological appearances of normal and eczematous skin are shown in Figures 1 and 2, respectively. A good starting point in the classification of eczema/dermatitis is the definition of two groups: endogenous, meaning the eczema is not believed to be due to contributing factors outside of the body exogenous, meaning outside influences have a significant contributory role. 5
7 Fast Facts Eczema and Contact Dermatitis Epidermis Stratum corneum (keratin layer) Stratum granulosum (granular cell layer) Stratum spinosum (prickle cell layer) Dermo-epidermal junction (basement membrane) Dermis Stratum basale (basal layer) Papillary dermis Blood vessels Reticular dermis 6 Figure 1 Histological appearance of normal skin. Photomicrograph reproduced courtesy of Dr N Bajallan, George Eliot Hospital, Nuneaton, UK.
8 Introduction Epidermis Edema Dermis Lymphocytes and macrophages Figure 2 Histological appearance of eczematous skin. Edema develops between the keratinocytes in the epidermis (spongiosis), the epidermis thickens (acanthosis) and inflammatory cells infiltrate the dermis. Photomicrograph reproduced courtesy of Dr N Bajallan, George Eliot Hospital, Nuneaton, UK. 7
9 Fast Facts Eczema and Contact Dermatitis TABLE 1 Classification of eczema/dermatitis Endogenous Atopic Seborrheic Discoid/nummular Pompholyx Venous Asteatotic (eczema craquelé) Juvenile plantar dermatosis Erythroderma Exogenous Allergic Irritant Photosensitive An example of this classification is given in Table 1. In reality, the situation may not be so simple, and eczema commonly has a mixed etiology. For example, atopic eczema may be aggravated by exposure to irritants or by allergy to topical medications. Traditionally, endogenous dermatitis was given the term eczema and exogenous dermatitis was termed dermatitis. Indeed, in an industrial setting the term dermatitis is often viewed as indicating a condition resulting from occupational exposure to irritants and may be seen as a diagnosis associated with litigation. However, the terms dermatitis and eczema are now used interchangeably. Eczema is derived from the Greek word meaning to boil and refers to the itching and heating of the skin and to the appearance of small blisters. Dermatitis simply means inflammation of the skin. 8
10 1 Allergic contact dermatitis Epidemiology Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is seen predominantly in adults and is less common in children and the elderly. This age distribution is probably due more to patterns of exposure to potential allergens than to any constitutional changes in the immune system. The most common form of contact allergy is nickel sensitivity (Figure 1.1), which probably affects at least 10% of women. Figure 1.1 Nickel dermatitis caused, in this case, by contact with metal earrings. Pathophysiology The development of ACD requires two phases. The first is a sensitization phase during which contact with the allergen results in the development of a specific immune response. This sensitization process may occur rapidly after brief contact with the allergen but often follows years of repeated contact. Once sensitization has occurred, subsequent contact results in the second phase of the reaction the elicitation phase. This is a delayed (type IV) hypersensitivity reaction (Figure 1.2) which gives rise to the dermatitis at the site of contact. The delay between contact and the development of dermatitis in sensitized individuals is typically hours, but reactions may occasionally develop within a few hours, or a longer delay of a week or more may be observed. 9
11 Fast Facts Eczema and Contact Dermatitis Step 1 Step 2 Antigen Class II MHC Langerhans' cell T-cell receptor Accessory activating mechanism CD4+ T-cell Step 3 Activated T-lymphocytes IL-2 receptor Daughter T-cells IL-1 IL-2 Recruitment of inflammatory cells Cytokines: -interferon Chemotactic factors IL-2 Tumor necrosis factor α 10 Figure 1.2 Cell-mediated immune (type IV) reaction. In step 1 the antigen is taken up by antigen-presenting cells (e.g. Langerhans cells in the skin), processed and bound to class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC). In step 2, these complexes migrate to the paracortical area of the draining lymph node via the afferent lymphatics. The MHC and antigen are recognized by T-cell receptors on CD4+ T-cells. In step 3, interleukin-1 (IL-1) is released by the antigen-presenting cell. The T-cells secrete IL-2, express IL-2 receptors and proliferate. Daughter T-cells, including memory cells, are generated. On reexposure to the same antigen, the memory T-cell recognizes the antigen after it has been processed in steps 1 and 2. T-lymphocytes become activated and secrete cytokines, which induce the components of inflammation.
12 2 Irritant contact dermatitis Epidemiology Irritant contact dermatitis is a common form of contact dermatitis, accounting for up to 75% of exogenous dermatitis. Those who work in constant contact with oils or solvents and those who have their hands constantly in water or detergent are particularly vulnerable. People in certain occupations, such as nurses, hairdressers and those who work in engineering, are therefore the most frequently affected. Irritants are also encountered at home, so people who spend their days looking after young families often develop irritant hand dermatitis. Individuals with a history of atopic eczema, even in childhood, seem to remain sensitive to the development of irritant dermatitis of the hands, and this may become a real problem if they enter the wrong employment. In an industrial setting, irritant dermatitis should be largely preventable in all but the most vulnerable individuals. Work should be planned in such a way that constant or repeated exposure to irritants is minimized by using the least irritant materials possible, by installing appropriate shielding and by use of protective gloves and clothing. Inadequate care is often exposed when several employees working on the same task all develop dermatitis; this is the subject of much litigation. Pathophysiology Irritant dermatitis results from physical or chemical damage to the skin. In contrast to allergic dermatitis, the mechanism is not primarily immunologic, and inflammation develops as a secondary event. Chemical damage to the skin can be caused by acids, alkalis, detergents, solvents, antiseptics, adhesives and industrial oils used for cooling or lubrication. Physical causes include friction, contact with abrasive powders and heat. All individuals will develop dermatitis if exposed to these irritants with sufficient intensity, although there is considerable variation between individuals in the amount of exposure required. Dermatitis most commonly develops as a result of repeated mild 23
13 Fast Facts Eczema and Contact Dermatitis exposure which has a cumulative effect, but acute reactions are also seen, caused by a single intense exposure to the irritant. Clinical presentation Acute irritant contact dermatitis develops as a result of a single overwhelming exposure to an irritant or caustic chemical or a series of brief chemical or physical contacts (Figure 2.1). This response may be enhanced by occlusion. There is immediate stinging or burning. The initial reaction is usually limited to the area of contact. The most frequently affected sites are the finger webs and dorsa of the hands, especially under rings. The clinical features range from transient erythema or chapping to edema, inflammation, pain, vesiculation and, in severe cases, exudation, bullae and necrosis. Cumulative irritant contact dermatitis develops as a result of repeated chemical or physical insults (Figure 2.2). The dorsal aspects of the hands (Figure 2.3), finger webs, face and eyelids are the most frequently affected sites. Initially there are localized patches of dry, slightly inflamed, chapped skin. Painful fissures may develop on the palms and Clinically apparent disease Impairment Subclinical disease Irritant contact dermatitis caused by exposure to irritant at sufficient dose and concentration Exposure to subirritant dose of the same chemical or physical agent Time 24 Figure 2.1 Acute irritant contact dermatitis.
Eczema & Dermatitis Clinical features: Histopathological features: Classification:
 Eczema & Dermatitis Eczema is an inflammatory reactive pattern of skin to many and different stimuli characterized by itching, redness, scaling and clustered papulovesicles. Eczema and dermatitis are synonymous
Eczema & Dermatitis Eczema is an inflammatory reactive pattern of skin to many and different stimuli characterized by itching, redness, scaling and clustered papulovesicles. Eczema and dermatitis are synonymous
Gastroenterology Second edition
 Clinical drawings for your patients Patient Pictures books are: PATI ENT PICTU RES Patient Pictures time-saving books for doctors and nurses. Use them when describing medical conditions and treatments
Clinical drawings for your patients Patient Pictures books are: PATI ENT PICTU RES Patient Pictures time-saving books for doctors and nurses. Use them when describing medical conditions and treatments
Fast Facts: Multiple Sclerosis
 Fast Facts Fast Facts: Multiple Sclerosis George D Perkin and Jerry S Wolinsky Second edition 2006 Health Press Ltd. www.fastfacts.com Fast Facts Fast Facts: Multiple Sclerosis Second edition George D
Fast Facts Fast Facts: Multiple Sclerosis George D Perkin and Jerry S Wolinsky Second edition 2006 Health Press Ltd. www.fastfacts.com Fast Facts Fast Facts: Multiple Sclerosis Second edition George D
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
 Obstructive Sleep Apnea by Barbara Phillips MD MSPH and Matthew T Naughton MD FRACP Epidemiology and risk factors 7 Clinical presentation 13 Medical complications 22 Diagnosis 40 Medical management 50
Obstructive Sleep Apnea by Barbara Phillips MD MSPH and Matthew T Naughton MD FRACP Epidemiology and risk factors 7 Clinical presentation 13 Medical complications 22 Diagnosis 40 Medical management 50
2010 Health Press Ltd.
 Fast Facts Fast Facts: Asthma Third edition Stephen T Holgate MD DSc FRCP FMedSci MRC Clinical Professor of Immunopharmacology School of Medicine Southampton General Hospital Southampton, UK Jo Douglass
Fast Facts Fast Facts: Asthma Third edition Stephen T Holgate MD DSc FRCP FMedSci MRC Clinical Professor of Immunopharmacology School of Medicine Southampton General Hospital Southampton, UK Jo Douglass
2004 Health Press Ltd.
 ... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
Eczema. By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University
 Eczema By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University Dermatitis= Eczema =Spongiosis Eczema Atopic Seborrheic Contact Allergic Irritant Nummular Asteatotic Stasis Neurodermatitis/Lichen Simplex
Eczema By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University Dermatitis= Eczema =Spongiosis Eczema Atopic Seborrheic Contact Allergic Irritant Nummular Asteatotic Stasis Neurodermatitis/Lichen Simplex
Allergic versus Contact
 Allergic versus Contact Dermatitis Julie Sterbank, DO Assistant Clinical Professor Allergy/Immunology MetroHealth Medical Center/Case Western Reserve University Disclosure I have no financial disclosures
Allergic versus Contact Dermatitis Julie Sterbank, DO Assistant Clinical Professor Allergy/Immunology MetroHealth Medical Center/Case Western Reserve University Disclosure I have no financial disclosures
Fast Facts: Ovarian Cancer
 Fast Facts Fast Facts: Ovarian Cancer Christina Fotopoulou MD PhD Consultant Gynaecological Oncologist Queen Charlotte s and Chelsea Hospital London, UK Thomas J Herzog MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Fast Facts Fast Facts: Ovarian Cancer Christina Fotopoulou MD PhD Consultant Gynaecological Oncologist Queen Charlotte s and Chelsea Hospital London, UK Thomas J Herzog MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Dermatitis. Occupational aspects of management
 Dermatitis Occupational aspects of management Evidence-based guidance for healthcare professionals Introduction This leaflet summarises the findings from a review of the published scientific literature
Dermatitis Occupational aspects of management Evidence-based guidance for healthcare professionals Introduction This leaflet summarises the findings from a review of the published scientific literature
Dermatology elective for yr. 5. Natta Rajatanavin, MD. Div. of dermatology Dep. Of Medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol University 23 rd Feb 2015
 Dermatology elective for yr. 5 Natta Rajatanavin, MD. Div. of dermatology Dep. Of Medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol University 23 rd Feb 2015 How to diagnosis and manage eczema and psoriasis. Objectives
Dermatology elective for yr. 5 Natta Rajatanavin, MD. Div. of dermatology Dep. Of Medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol University 23 rd Feb 2015 How to diagnosis and manage eczema and psoriasis. Objectives
My Algorithm. Questions to ask. Do you or your family have a history of?... Allergic rhinitis, Sensitive skin, Asthma Skin Cancer
 Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM Associate Professor, Temple University School of Podiatric Medicine My Algorithm Inflammatory Skin Disorder on Feet Family hx, clinical exam, look at hands! Defined plaques: Psoriasis
Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM Associate Professor, Temple University School of Podiatric Medicine My Algorithm Inflammatory Skin Disorder on Feet Family hx, clinical exam, look at hands! Defined plaques: Psoriasis
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Identifying the causes of contact dermatitis
 Identifying the causes of contact Jones R, Horn H M. Identifying the causes of contact. Practitioner 2014;258 (1772)27-31 Dr Ruth Jones MRCP ST3 Dermatology Dr Helen M. Horn MD FRCP Associate Specialist
Identifying the causes of contact Jones R, Horn H M. Identifying the causes of contact. Practitioner 2014;258 (1772)27-31 Dr Ruth Jones MRCP ST3 Dermatology Dr Helen M. Horn MD FRCP Associate Specialist
The Integumentary System. Chapter 6
 The Integumentary System Chapter 6 What is the integumentary system? skin hair nails glands blood vessels sensory receptors What is your skin made of? 3 layers epidermis (outside) dermis (middle) subcutaneous
The Integumentary System Chapter 6 What is the integumentary system? skin hair nails glands blood vessels sensory receptors What is your skin made of? 3 layers epidermis (outside) dermis (middle) subcutaneous
Gynaecological oncology
 PATI ENT PICTU RES Patient Pictures Clinical drawings for your patients Patient Pictures books are: time-saving books for doctors and nurses. Use them when describing medical conditions and treatments
PATI ENT PICTU RES Patient Pictures Clinical drawings for your patients Patient Pictures books are: time-saving books for doctors and nurses. Use them when describing medical conditions and treatments
Clinical Anatomy. of the Eye SECOND EDITION
 Clinical Anatomy of the Eye SECOND EDITION, ~ Clinical Anatomy of he Eye SECOND EDITION RichardS. Snell, M.D., Ph.D. Emeritus Professor of Anatomy, The George Washington School of Medicine and Health Sciences,
Clinical Anatomy of the Eye SECOND EDITION, ~ Clinical Anatomy of he Eye SECOND EDITION RichardS. Snell, M.D., Ph.D. Emeritus Professor of Anatomy, The George Washington School of Medicine and Health Sciences,
A*STAR skin examination protocol
 A*STAR skin examination protocol Professor Carsten Flohr Chair in Dermatology and Population Science & Consultant Dermatologist Unit for Population-Based Dermatology Research St John s Institute of Dermatology
A*STAR skin examination protocol Professor Carsten Flohr Chair in Dermatology and Population Science & Consultant Dermatologist Unit for Population-Based Dermatology Research St John s Institute of Dermatology
Genitourinary medicine
 PATIENT PICTURES Clinical drawings for your patients Genitourinary medicine by Simon E Barton and Antony Newell Illustrated by Dee McLean Series Editor: J Richard Smith HEALTH PRESS PATIENT PICTURES Clinical
PATIENT PICTURES Clinical drawings for your patients Genitourinary medicine by Simon E Barton and Antony Newell Illustrated by Dee McLean Series Editor: J Richard Smith HEALTH PRESS PATIENT PICTURES Clinical
GLOVE ALLERGIES AND HAND HEALTH
 GLOVE ALLERGIES AND HAND HEALTH INTRODUCTION Skin conditions caused by chemical, physical or biological agents in the workplace are common among disposable glove wearers in the industrial sector. Understanding
GLOVE ALLERGIES AND HAND HEALTH INTRODUCTION Skin conditions caused by chemical, physical or biological agents in the workplace are common among disposable glove wearers in the industrial sector. Understanding
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
Update on emollients
 Update on emollients Amal Mhanna, MD Pediatric Dermatologist Clemenceau Medical Center Disclosure: I was a member of an advisory board y for J&J and received honoraria. Emollients and moisturizers are
Update on emollients Amal Mhanna, MD Pediatric Dermatologist Clemenceau Medical Center Disclosure: I was a member of an advisory board y for J&J and received honoraria. Emollients and moisturizers are
Contact Dermatitis Challenges for the General Dermatologist. Susan Nedorost, MD
 Contact Dermatitis Challenges for the General Dermatologist Susan Nedorost, MD Contact Dermatitis: Challenges for the General Dermatologist Disclosure Statement I, Susan Nedorost, MD, do not have any relevant
Contact Dermatitis Challenges for the General Dermatologist Susan Nedorost, MD Contact Dermatitis: Challenges for the General Dermatologist Disclosure Statement I, Susan Nedorost, MD, do not have any relevant
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Body Membranes & Skin
 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
B. Incorrect! The ectoderm does not produce the dermis. C. Incorrect! The dermis is derived from the mesoderm.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
Erectile dysfunction
 Clinical drawings for your patients Patient Pictures books are: time-saving books for doctors and nurses. Use them when describing medical conditions and treatments to your patients. easy to photocopy.
Clinical drawings for your patients Patient Pictures books are: time-saving books for doctors and nurses. Use them when describing medical conditions and treatments to your patients. easy to photocopy.
CHAPTER 1. Eczema Basics
 CHAPTER 1 Eczema Basics Definition Eczema is an inflammatory skin condition, characterised by ichtyosis (dry skin), erythema (redness), excoriation (interruption of the skin), scratching lesions, lichenification
CHAPTER 1 Eczema Basics Definition Eczema is an inflammatory skin condition, characterised by ichtyosis (dry skin), erythema (redness), excoriation (interruption of the skin), scratching lesions, lichenification
A Resource Kit for Career Counsellors
 A Resource Kit for Career Counsellors Occupational Dermatology Research and Education Centre www.occderm.asn.au/skinatwork 2 About this kit The Skin @ Work education kit aims to raise awareness of a potential
A Resource Kit for Career Counsellors Occupational Dermatology Research and Education Centre www.occderm.asn.au/skinatwork 2 About this kit The Skin @ Work education kit aims to raise awareness of a potential
Fast Facts. Fast Facts: Osteoarthritis. Philip G Conaghan and Leena Sharma Health Press Ltd.
 Fast Facts Fast Facts: Osteoarthritis Philip G Conaghan and Leena Sharma Fast Facts Fast Facts: Osteoarthritis Philip G Conaghan MB BS PhD FRACP FRCP Professor of Musculoskeletal Medicine University of
Fast Facts Fast Facts: Osteoarthritis Philip G Conaghan and Leena Sharma Fast Facts Fast Facts: Osteoarthritis Philip G Conaghan MB BS PhD FRACP FRCP Professor of Musculoskeletal Medicine University of
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9
 Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Fast Facts. Fast Facts: Contraception. Ailsa E Gebbie and Katharine O Connell White Third edition Health Press Ltd.
 Fast Facts Fast Facts: Contraception Ailsa E Gebbie and Katharine O Connell White Third edition Fast Facts Fast Facts: Contraception Third edition Ailsa E Gebbie MB ChB FRCOG FFSRH Consultant Gynecologist
Fast Facts Fast Facts: Contraception Ailsa E Gebbie and Katharine O Connell White Third edition Fast Facts Fast Facts: Contraception Third edition Ailsa E Gebbie MB ChB FRCOG FFSRH Consultant Gynecologist
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis
 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis The Integument Means Covering Composed: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands The Integument Thickness 1.5 4 mm (or more) Weight 9 11
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis The Integument Means Covering Composed: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands The Integument Thickness 1.5 4 mm (or more) Weight 9 11
This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur.
 Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings
 Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings List the four types of epithelial or connective membranes. The epithelial cutaneous includes your and is exposed to the. Its function is to. An example is..
Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings List the four types of epithelial or connective membranes. The epithelial cutaneous includes your and is exposed to the. Its function is to. An example is..
Skin and Body Membranes
 4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
Psoriasis Case presentation 2 Ahmad is 50 years old male came to the on call dermatologist with a 3 day history of feeling generally unwell and
 Psoriasis Case presentation 2 Ahmad is 50 years old male came to the on call dermatologist with a 3 day history of feeling generally unwell and redness of all skin associated with de-sequamation scaling.
Psoriasis Case presentation 2 Ahmad is 50 years old male came to the on call dermatologist with a 3 day history of feeling generally unwell and redness of all skin associated with de-sequamation scaling.
ATOPIC ECZEMA. What are the aims of this leaflet?
 ATOPIC ECZEMA What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about atopic eczema. It tells you what it is, what causes it, what can be done about it, and where
ATOPIC ECZEMA What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about atopic eczema. It tells you what it is, what causes it, what can be done about it, and where
Clinico Pathological Test SCPA605-Essential Pathology
 Clinico Pathological Test SCPA605-Essential Pathology Somphong Narkpinit, M.D. Department of Pathogbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University e-mail : somphong.nar@mahidol.ac.th Pathogenesis of allergic
Clinico Pathological Test SCPA605-Essential Pathology Somphong Narkpinit, M.D. Department of Pathogbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University e-mail : somphong.nar@mahidol.ac.th Pathogenesis of allergic
BOHRF BOHRF BOHRF BOHRF
 Occupational Contact Dermatitis and Urticaria A Guide for General Practitioners and Practice Nurses March 2010 British Occupational Health Research Foundat ion This leaflet summarises the key evidence
Occupational Contact Dermatitis and Urticaria A Guide for General Practitioners and Practice Nurses March 2010 British Occupational Health Research Foundat ion This leaflet summarises the key evidence
eczema the basics 2EE6E629CEA25112ABD0B8EB Eczema The Basics 1 / 6
 Eczema The Basics 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Eczema The Basics Eczema is a group of conditions that cause inflammation of the skin. Typically, eczema causes skin to become itchy, red, and dry -- even cracked and
Eczema The Basics 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Eczema The Basics Eczema is a group of conditions that cause inflammation of the skin. Typically, eczema causes skin to become itchy, red, and dry -- even cracked and
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1
 Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin Homework. (Skin is the largest organ in the body)
 Skin Homework (Skin is the largest organ in the body) This homework is following the information in the Louise Tucker book so the answers should be easy to find. 1 Label the Cross Section of Skin below:
Skin Homework (Skin is the largest organ in the body) This homework is following the information in the Louise Tucker book so the answers should be easy to find. 1 Label the Cross Section of Skin below:
Your Skin. Section 14.2 Your Skin, Hair, and Nails
 Your Skin The skin covers and protects the body from injury, infection, and water loss. The skin also helps to regulate body temperature and gathers information from the environment. Protection The skin
Your Skin The skin covers and protects the body from injury, infection, and water loss. The skin also helps to regulate body temperature and gathers information from the environment. Protection The skin
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Eleventh Edition. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide
 Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
Integumentary System. 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1
 Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
Integumentary System
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
PROTECT YOURSELF FROM TYPE I ALLERGIES.
 PROTECT YOURSELF FROM TYPE I ALLERGIES. 1 PROTECT YOURSELF FROM TYPE I ALLERGIES. Occasionally wearing glove products can cause issues with the health of our skin. This predominantly manifests itself in
PROTECT YOURSELF FROM TYPE I ALLERGIES. 1 PROTECT YOURSELF FROM TYPE I ALLERGIES. Occasionally wearing glove products can cause issues with the health of our skin. This predominantly manifests itself in
ESTABLISHING A PATCH TEST CLINIC
 ESTABLISHING A PATCH TEST CLINIC A RESOURCE MANUAL DORMER LABORATORIES INC. North American Distributors Chemotechnique Patch Tests & Accessories www.dormer.com 91 Kelfield Street # 5 Toronto, ON M9W 5A3
ESTABLISHING A PATCH TEST CLINIC A RESOURCE MANUAL DORMER LABORATORIES INC. North American Distributors Chemotechnique Patch Tests & Accessories www.dormer.com 91 Kelfield Street # 5 Toronto, ON M9W 5A3
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Invest Dermatol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 April 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Invest Dermatol. 2013 October ; 133(10): 2311 2314. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.239. Mechanisms of contact sensitization offer insights
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Invest Dermatol. 2013 October ; 133(10): 2311 2314. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.239. Mechanisms of contact sensitization offer insights
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition)
 Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
OCCUPATIONAL CONTACT DERMATITIS IN A TERTIARY CARE CENTRE EPIDEMIOLOGY, CLINICAL PROFILE AND PATCH TEST EVALUATION
 OCCUPATIONAL CONTACT DERMATITIS IN A TERTIARY CARE CENTRE EPIDEMIOLOGY, CLINICAL PROFILE AND PATCH TEST EVALUATION DONE BY : Dr.Ragini Rajan Final year Post Graduate MD(DVL) Govt.Stanley Medical College,
OCCUPATIONAL CONTACT DERMATITIS IN A TERTIARY CARE CENTRE EPIDEMIOLOGY, CLINICAL PROFILE AND PATCH TEST EVALUATION DONE BY : Dr.Ragini Rajan Final year Post Graduate MD(DVL) Govt.Stanley Medical College,
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Introduction CHAPTER 1. Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction OVERVIEW The clinical features of skin lesions are related to the underlying pathological processes. Broadly skin conditions fall into three clinical groups: (a) those with a well-defined
CHAPTER 1 Introduction OVERVIEW The clinical features of skin lesions are related to the underlying pathological processes. Broadly skin conditions fall into three clinical groups: (a) those with a well-defined
Skin is a complex organ, but by understanding its structure and function it becomes easier to create skin that is Reborn Beautiful.
 SKIN SCIENCE Skin is a complex organ, but by understanding its structure and function it becomes easier to create skin that is Reborn Beautiful. Dr. Des Fernandes Copyright 2016 Environ Skin Care (Pty)
SKIN SCIENCE Skin is a complex organ, but by understanding its structure and function it becomes easier to create skin that is Reborn Beautiful. Dr. Des Fernandes Copyright 2016 Environ Skin Care (Pty)
Unit 4 The Integumentary System
 Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Hypersensitivity Reactions
 Color code: Important in red Extra in blue Hypersensitivity Reactions For team error adjustments, click here Objectives To know that hypersensitivity reactions are over and excessive immune responses that
Color code: Important in red Extra in blue Hypersensitivity Reactions For team error adjustments, click here Objectives To know that hypersensitivity reactions are over and excessive immune responses that
Is it allergy? Debbie Shipley
 Is it allergy? Debbie Shipley Topics Food Allergy and Eczema Hand Eczema and Patch Testing Urticaria Tackling Allergy Gell and Coombs classification Skin conditions with possible allergic component Allergy
Is it allergy? Debbie Shipley Topics Food Allergy and Eczema Hand Eczema and Patch Testing Urticaria Tackling Allergy Gell and Coombs classification Skin conditions with possible allergic component Allergy
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY
 CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
Chapter 5. Integumentary System 5-1
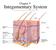 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Commonly Coded Conditions in Dermatology
 Commonly Coded Conditions in Dermatology No part of this presentation may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means (graphically, electronically, or mechanically, including photocopying,
Commonly Coded Conditions in Dermatology No part of this presentation may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means (graphically, electronically, or mechanically, including photocopying,
Integumentary System. Packet #12
 Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest
 Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest Overview & Learning Objectives Review the cardinal signs/symptoms of acute inflammation Review the histological features of acute inflammation
Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest Overview & Learning Objectives Review the cardinal signs/symptoms of acute inflammation Review the histological features of acute inflammation
Introduction to Immunopathology
 MICR2209 Introduction to Immunopathology Dr Allison Imrie 1 Allergy and Hypersensitivity Adaptive immune responses can sometimes be elicited by antigens not associated with infectious agents, and this
MICR2209 Introduction to Immunopathology Dr Allison Imrie 1 Allergy and Hypersensitivity Adaptive immune responses can sometimes be elicited by antigens not associated with infectious agents, and this
Skin cancer awareness for non-healthcare professionals
 Skin cancer awareness for non-healthcare professionals UV21577 A/505/3590 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy,
Skin cancer awareness for non-healthcare professionals UV21577 A/505/3590 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy,
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
2013 Health Press Ltd.
 Fast Facts Fast Facts: Asthma Fourth edition Stephen T Holgate MD DSc FRCP FMedSci MRC Clinical Professor of Immunopharmacology School of Medicine Southampton General Hospital Southampton, UK Jo A Douglass
Fast Facts Fast Facts: Asthma Fourth edition Stephen T Holgate MD DSc FRCP FMedSci MRC Clinical Professor of Immunopharmacology School of Medicine Southampton General Hospital Southampton, UK Jo A Douglass
DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY. Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations
 DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Epidermal Layers ECM Structure Dermis Structure Skin
DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Epidermal Layers ECM Structure Dermis Structure Skin
The Integumentary System: An Overview
 The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
Introduction. Skin and Body Membranes. Cutaneous Membranes Skin 9/14/2017. Classification of Body Membranes. Classification of Body Membranes
 Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS D R S H O AI B R AZ A
 HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS D R S H O AI B R AZ A HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS Are exaggerated immune response upon antigenic stimulation Individuals who have been previously exposed to an antigen are said
HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS D R S H O AI B R AZ A HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS Are exaggerated immune response upon antigenic stimulation Individuals who have been previously exposed to an antigen are said
Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function.
 Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Integumentary System Skin, hair, and nails. Skin: Epidermis: outer layer. Dermis: also called corium, or true skin. Subcutaneous fascia: innermost layer. Integumentary Glands Sudoriferous:
Integumentary System Integumentary System Skin, hair, and nails. Skin: Epidermis: outer layer. Dermis: also called corium, or true skin. Subcutaneous fascia: innermost layer. Integumentary Glands Sudoriferous:
1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) i. Organ of the Integument. Connective Tissues. Epithelial Tissues
 Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Ex. 7: Integumentary
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
The EASI scoring system uses a defined process to grade the severity of the signs of eczema and the extent affected:
 How to Use EASI The EASI scoring system uses a defined process to grade the severity of the signs of eczema and the extent affected: 1. Select a body region Four body regions are considered separately:
How to Use EASI The EASI scoring system uses a defined process to grade the severity of the signs of eczema and the extent affected: 1. Select a body region Four body regions are considered separately:
Overview of the Lymphoid System
 Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Fast Facts: Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
 Fast Facts Fast Facts: Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Mary O Brien MD FRCP Consultant Medical Oncologist The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust London, UK Benjamin Besse MD PhD Thoracic Cancer Unit, Head Department
Fast Facts Fast Facts: Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Mary O Brien MD FRCP Consultant Medical Oncologist The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust London, UK Benjamin Besse MD PhD Thoracic Cancer Unit, Head Department
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Skin (Integument) Consists of two major regions 1. Epidermis superficial region 2. Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia) deepest region Subcutaneous layer deep to
The Integumentary System Skin (Integument) Consists of two major regions 1. Epidermis superficial region 2. Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia) deepest region Subcutaneous layer deep to
Food allergies and eczema
 Department of Dermatology Food allergies and eczema Information for parents and carers Eczema, also known as atopic eczema or atopic dermatitis, is a skin condition that causes inflammation and irritation.
Department of Dermatology Food allergies and eczema Information for parents and carers Eczema, also known as atopic eczema or atopic dermatitis, is a skin condition that causes inflammation and irritation.
THERE IS A GROUP OF PAtients. Defining Urticarial Dermatitis. A Subset of Dermal Hypersensitivity Reaction Pattern
 STUDY Defining Urticarial Dermatitis A Subset of Dermal Hypersensitivity Reaction Pattern Steven Kossard, FACD; Ian Hamann, FACD; Barbara Wilkinson, BSc Background: Urticarial dermatitis may represent
STUDY Defining Urticarial Dermatitis A Subset of Dermal Hypersensitivity Reaction Pattern Steven Kossard, FACD; Ian Hamann, FACD; Barbara Wilkinson, BSc Background: Urticarial dermatitis may represent
Skin lesions & Abrasions
 Skin lesions & Abrasions What Are Skin Lesions? A skin lesion is a part of the skin that has an abnormal growth or appearance compared to the skin around it Types of Skin Lesions Two types of skin lesions
Skin lesions & Abrasions What Are Skin Lesions? A skin lesion is a part of the skin that has an abnormal growth or appearance compared to the skin around it Types of Skin Lesions Two types of skin lesions
CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM I. OBJECTIVES A. Label a diagram of a cross section of the skin B. Differentiate between the two types of skin glands C. Identify six functions of the skin D. Provide the
CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM I. OBJECTIVES A. Label a diagram of a cross section of the skin B. Differentiate between the two types of skin glands C. Identify six functions of the skin D. Provide the
Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Bio40C schedule Lecture Immune system Lab Quiz 2 this week; bring a scantron! Study guide on my website (see lab assignments) Extra credit Critical thinking questions at end of chapters 5 pts/chapter Due
Bio40C schedule Lecture Immune system Lab Quiz 2 this week; bring a scantron! Study guide on my website (see lab assignments) Extra credit Critical thinking questions at end of chapters 5 pts/chapter Due
The hands in health and disease of individuals with filaggrin loss-of-function mutations: clinical reflections on the hand eczema phenotype
 Contact Dermatitis Review Article COD Contact Dermatitis The hands in health and disease of individuals with filaggrin loss-of-function mutations: clinical reflections on the hand eczema phenotype Jeanette
Contact Dermatitis Review Article COD Contact Dermatitis The hands in health and disease of individuals with filaggrin loss-of-function mutations: clinical reflections on the hand eczema phenotype Jeanette
1. Erythema. 2. Edema/papulation. 3. Excoriation 4. Lichenification
 How to Use EASI The EASI scoring system uses a defined process to grade the severity of the signs of eczema and the extent affected: 1. Select a body region Four body regions are considered separately:
How to Use EASI The EASI scoring system uses a defined process to grade the severity of the signs of eczema and the extent affected: 1. Select a body region Four body regions are considered separately:
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
Contact dermatitis Pathomechanism and understanding of disease in clinical setting
 Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2011, Vol-7, No-4, 70-77 Review Contact dermatitis Pathomechanism and understanding of disease in clinical setting M. Mathur 1 S. Kumari 2 1 Professor 2 Senior
Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2011, Vol-7, No-4, 70-77 Review Contact dermatitis Pathomechanism and understanding of disease in clinical setting M. Mathur 1 S. Kumari 2 1 Professor 2 Senior
It s all in your hands: Preventing hand dermatitis. Introduction 3/5/2018. Hand hygiene is a cornerstone of effective infection control, but
 It s all in your hands: Preventing hand dermatitis Monica Herrera MHA, CDMP Introduction Hand hygiene is a cornerstone of effective infection control, but Hand sanitization and gloving are essential if
It s all in your hands: Preventing hand dermatitis Monica Herrera MHA, CDMP Introduction Hand hygiene is a cornerstone of effective infection control, but Hand sanitization and gloving are essential if
11/8/2012. Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Skin = Integument = Cutaneous Membrane. The Structure of Skin. Epidermis
 Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
ICHTHYOSIS. What are the aims of this leaflet?
 ICHTHYOSIS What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about ichthyosis. It will tell you what it is, the types of ichthyosis, what can be done about it,
ICHTHYOSIS What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about ichthyosis. It will tell you what it is, the types of ichthyosis, what can be done about it,
The skin acts as a protective barrier against a number of hazards within our environment. These hazards can be:
 The skin acts as a protective barrier against a number of hazards within our environment. These hazards can be: chemical, e.g: acids, alkalis, solvents, cutting, or soluble oils; biological,e.g: bacteria,plant
The skin acts as a protective barrier against a number of hazards within our environment. These hazards can be: chemical, e.g: acids, alkalis, solvents, cutting, or soluble oils; biological,e.g: bacteria,plant
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Barrier Function and Microbiotic Dysbiosis in Atopic Dermatitis. Mike Levin Division of asthma and allergy Department of paediatrics
 Barrier Function and Microbiotic Dysbiosis in Atopic Dermatitis Mike Levin Division of asthma and allergy Department of paediatrics Eczema / dermatitis is an inflammatory skin reaction Atopic Phototoxic
Barrier Function and Microbiotic Dysbiosis in Atopic Dermatitis Mike Levin Division of asthma and allergy Department of paediatrics Eczema / dermatitis is an inflammatory skin reaction Atopic Phototoxic
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System. Integumentary System. Page 1
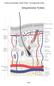 Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
