Al-Balqa Applied University
|
|
|
- Dina Caldwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COURSE PLAN FIRST: BASIC INFORMATION College College : Medicine Department : Basic Medical Sciences Course Course Title : Musculoskeletal Systems and Skin Course Code : Credit Hours : 5 Prerequisite : None Instructor Name : Nabil Khouri Course coordinator and other staff members as per subject. Office No. : Dean Office Tel (Ext) : nkhori@bau.edu.jo Office Hours : Sunday through Thursday 9-11am Class Times Building Day Start Time End Time Room No. Lecture Hall Complex Sunday, Monday, Tuesday Wednesday & Thursday 8:00 12:00 2 Text Books ANATOMY:. 1. Clinical Anatomy for Medical Students. By R.S. Snell, Latest edition. 2. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. K.L. Moore, et al. Latest Edition. 3. Basic Histology, by L. Carlos Junqueira. Latest edition. 4. Before we are born. By K.L. Moore and T.V.N. Persaud, Latest edition. 5. Grants Atlas of Anatomy or any other good colored Atlas of Human Anatomy. BIOCHEMISTRY: 1. Biochemistry by Campbell & Farrell,latest edition 2. Lippincott s Illustrated Reviews Biochemistry, latest edition PHYSIOLOGY: 1. Textbook of Medical Physiology, by Guyton and Hall, 13 th edition, Review of Medical Physiology, by William F. Ganong, 23 th edition, PATHOLOGY: Basic Pathology, by Kumar, Cotran and Robbins, Latest edition. PHARMACOLOGY: 1
2 Lipincott s Illustrated Reviews: Pharmacology, Latest edition. COMMUNITY MEDICINE: Supplementary Departmental handouts. SECOND: PROFESSIONAL INFORMATION COURSE DESCRIPTION The goal of this integrated course is to provide the medical student with multi disciplinary detailed information about bones, joints, and muscles of the human body with emphasis on heir group s distribution, orientation and their attachments. In addition, the skin as an organ and the associated structures and contents of soft tissues and organs will be discussed. Finally, the related clinical and pathological manifestations of diseases of the Musculo-skeletal system and skin will be discussed. COURSE OBJECTIVES By the end of this course, students are expected to understand and describe: 1. The anatomy and histology of the human body skeletal system including bone types, External features, location and orientation with emphasis on muscular attachments. 2. The histological aspects of bone types and their cellular components and organization. 3. The vertebral column at different levels with emphasis on their parts, positions and the inter-vertebral discs and alignments. 4. The anatomy and histology of the muscular system as individual and muscle groups. Naming of muscles and their relations with their specific distribution within the body with emphasis on their individual and group actions, nerve and blood supply. 5. The histology of skin and identify the macroscopic and microscopic features of the skin and subcutaneous tissues. 6. The normal development and the congenital abnormalities of the musculo- skeletal system 7. The pathogenesis of osteoporosis, osteomalacia and rickts 8. Different types of arthritis (including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and crystal induced arthritis) and osteomyelitis 9. The main types of the skeletal muscle diseases. 10. The pathological changes that occur in the skin, and the etiology, pathogenesis and pathologic features of selected major diseases of the skin. 11. The mechanism of muscle contraction. 12. The mechanism of action, pharmacokenetics and therapeutic use and adverse effects of drugs that affect the musculo-skeletal system and the skin. 13. The metabolism and the biochemical and molecular basis of diseases affecting muscles and bones 14. The biochemical processes of normal skin and subcutaneous tissues. 15. The epidemiology and control of the common injuries that may affect the human musculo-skeletal and skin The pathogenesis and pathological features of infections and diseases that affect bones, joints, 2
3 muscles, soft tissue and the skin. 17. The commensally and pathogenic microbes affecting the skin, subcutaneous tissue and musculoskeletal system. COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES 1) Knowledge and Understanding a. The Anatomical structures of Muscolo-skeletal system, the development of the system, and its histology. b. The Anatomical structures of the skin, its development, and its histology. c. The nature, functions, physiologic roles and mechanisms of action of muscles and their mechanism of action and the nervous and hormone regulation and. d. The Pathogenesis, morphological changes and complications of diseases affecting the Muscolo-skeletal system. e. The use of drugs in diagnosis for the treatment of various disorders of this system 2) Professional Skills The student should be able to differentiate the different Muscolo-skeletal disorders. 3) Competences (Transferable skill and attributes) The student should be able to differentiate the different investigations required for each Muscoloskeletal system disorders No COURSE SYLLABUS Title of Lectures (1 st.week) Learning Objectives 0 Introductory case presentation for Muscolo-skeletal system.(multidisciplinary) 1 Overview of the components of the MSS. (Anatomy 1) 2&3 Skull bones and temporomandibular joint 1. Understand the general outline of the Muscolo-skeletal Module. 2. Be familiar with the modalities of teaching throughout the course. 3. Acknowledge the important relation between normal and abnormal Muscolo-skeletal structure and function. 4. Appreciate the importance of basic medical sciences in clinical application. 1. Discuss the components and functions of the MSS. 2. Describe the relation between bones and skeletal muscles in producing body movements. 3. Identify the major regions and compartments of upper and lower limbs. 4. Contrast the structural and functional classification of joints and identify factors that determine the degree of movement at a joint. 5. Describe the components of the synovial joints and give examples from the upper and lower limbs. 1. Identify and name the bones of the skull. 2. Identify the major regions of the skull. 3
4 (TMJ) (Anatomy 2&3) 4&5 Vertebral column I & II. (Anatomy 4&5) 6 Bones of the upper limb (Anatomy 6) 3. Describe the major foramina in the skull. 4. Describe how a fetal skull differs from the adult skull. 5. Explain the function of the fontanels. 6. Describe the components of TMJ. 7. List the ligaments associated with TM joint and their attachment. 1. Describe the regions and curvatures of the vertebral column and the number of vertebrae in each region. 2. Describe the basic components of a typical vertebrae and their function. 3. Identify and recognize the differences between cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae. 4. Describe and classify the joints associated with the vertebral column. 5. Describe the location and general function of ligaments. 6. Name the true back muscles and understand their relative positions and actions. 7. Understand the relationships of neural structures and meninges to the vertebral column, including the points of exit of spinal nerves 1. List the bones of the upper limb (shoulder girdle, arm, forearm, and hand bones). 2. Describe the structure, relationships and function of the upper limb bones. 3. Identify the surface anatomy of the upper limb bones. 7 Bones of the lower limb. (Anatomy 7) 8 Joints of the upper limb I (Anatomy 8) 9 Joints of the upper limb II (Anatomy 9) 1. List the bones of the lower limb (pelvic girdle, thigh, leg, and foot bones). 2. Describe the structure, relationships and function of the lower limb bones. 3. Identify the surface anatomy of the lower limb bones. 4. Describe the arches of the foot. 1. Describe the sternoclavicular and acromioclavicular joints 2. Describe the type and the components of the shoulder joint. 3. List the ligaments associated with the shoulder joint and their attachment. 4. Describe the muscles acting on the shoulder joint according to the type and movement they perform. 5. Describe the major palpable bony prominences of the shoulder joint. 1. Describe the type and the components of the elbow, and wrist and hand joints. 2. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. 3. Describe the bursas in relation to these joints. 4. Describe the stability of the elbow and wrist joints. 5. List the muscles acting on the wrist joint according to the type and movement they perform. 6. Describe the bursas in relation to these joints. 7. Describe the major palpable bony prominences of the elbow and wrist joints. 4
5 10 Joints of lower limb I (Anatomy 10) 11 Joints of the lower limb II (Anatomy 11) 12 Bone remodeling (Physiology 1) 13 Vessels of the upper limb (Anatomy 12) 14 Nerves of the upper limbs (Anatomy13) (2 nd.week) 15 Muscles of the shoulder and axilla (Anatomy14) 1. Describe the sacroiliac joint. 2. Describe the structure of the lesser and greater sciatic foramina. 3. Describe the components of the hip joint. 4. List the ligaments associated with the hip joint and their attachment. 5. Describe the muscles acting on the hip joint according to the type and movement they perform. 6. Describe the bursas in relation to the hip joint. 7. Describe the stability of the hip joint. 8. Describe the blood supply and nerve supply of the hip joint. 9. Describe the major palpable bony prominences of the hip joint. 10. Describe the joints of the foot. 1. Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. 2. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. 3. List the muscles acting on these joints according to the type and movement they perform. 4. Describe the bursas in relation to these joints. 5. Describe the stability of these joints. 6. Describe the major palpable bony prominences of these joints. Describe Bone remodeling Deposition of Bone by the Osteoblasts. Resorption of Bone Function of the Osteoclasts. How osteoclast stimulated Bone deposition and resorption are normally in equilibrium Value of Continual Bone Remodeling Control of the Rate of Bone Deposition by Bone Stress. 1. Describe the organization of upper limb blood vessels. 2. Describe the major course, branches, and supply areas of the upper limb blood vessels. 3. Describe the innervation of the upper limb vessels. 1. Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the upper limb. 2. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the upper limb. 3. Give a general description of a peripheral nerve lesion. 1. List the muscles that are attached to the scapula. 2. Describe the attachments and the action of the above-mentioned muscles and their nerve supply. 3. Discuss the inter-muscular spaces related to the scapula and their contents. 4. List the rotator cuff muscles. 5. Define the axilla. 6. Describe the boundaries and borders of the axilla. 7. List the contents of the axilla and relations. 5
6 16 Biochemistry of Muscles, Bone and connective tissue. (Biochemistry 1) 17 Muscle relaxants (Pharmacology1) 18 Physiology of Muscle sensory receptors (Physiology 2) 19 Muscles of arm and forearm and cubital fossa (anatomy 15) 20 Muscles of the hand (Anatomy 16) 21 M Sensory & Motor Innervation of the Muscle Spindle, General properties of reflexes & monosynaptic reflex (Physiology 3) 1. Describe the biochemical structure of muscles, bone tissue, the collagen matrix and the hydroxyapatite cement. 2. List bone matrix proteins and describe their function 3. Describe the formation of hydroxyapatite. 4. Understand the role of alkaline phosphatase, calcium and phosphate and vitamin D in bone formation and remodeling 5. Review calcium and phosphate homeostasis 1. Review the transmission process at the neuromuscular endplate and the points at which drugs can modify this process. 2. Compare the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of non-depolarizing and the depolarizing neuromuscular blockers.. 3. Describe the main indications, major adverse effects and drug interaction of non-depolarizing and depolarizing neuromuscular blockers. 1. Anterior Motor Neurons and interneurons and their role 2. Describe the Renshaw Cells and its role in inhibitory signals effects to surrounding motor neurons 3. Discuss multi-segmental connections 4. Discuss the types of Muscle sensory receptors including Muscle spindle and Golgi tendon organs 5. Describe the physiological role and structure of muscle spindle including nuclear bag muscle fibers and nuclear chain fibers 6. Discuss sensory innervations of the muscle spindle including type Ia fiber and type II fiber 7. Describing Motor innervations of the muscle spindle 8. Explain the types of gamma motor neurons static & Dynamic gamma motor neurons 1. List the muscles that are attached to the arm and forearm. 2. Describe the attachments and the action of the above-mentioned muscle and their nerve supply. 3. Describe the cubital fossa. 4. List the content of the cubital fossa. Understand the clinical importance of the cubital fossa 1. Describe the carpal tunnel and the flexor and extensor retinacula and the structures passing in relation to the retinacula. 2. Describe the snuffbox. 3. Describe the movement of the fingers. 4. List the muscles acting on the fingers. 1. Describe what will happen when the muscle is stretched by 10 Kg? Explain the continuous discharge of the muscle spindles (tonic discharge) under normal conditions 2. Discuss muscle reflexes and Muscle reflex arc components 3. Discuss General properties of reflexes 4. Discuss the types of muscle reflexes 5. Discuss first muscle stretch reflex or monosynaptic reflex including neuronal 6
7 22 Metabolic disorders and clinical biochemistry of muscle and bone (Biochemistry 2) 23 Diseases of skeletal muscles (Pathology 1) 24 Sensory & Motor Innervation of the Muscle Spindle General properties of reflexes & monosynaptic reflex (Physiology 4 ) 25 Vessels of the lower limb. (Anatomy 17) 26 Diseases of the bone (Pathology 2) Midterm Exam 30% Circuitry, clinical applications 1. Discuss the markers for bone formation and resorption and their clinical use in diagnosis 2. Describe the molecular basis of : Duchene Muscular Dystrophy, 3. Glycogen storage diseases of muscle, Muscle mitochondrial diseases, 4. Osteogenesis imperfecta and Ehlar Danlos syndromes 1. List the main types of the skeletal muscle diseases. 2. Discuss the two main types of muscle atrophy. 3. Discuss the main inflammatory myopathies. 4. Discuss muscular dystrophy. 5. Understand the pathogenesis and pathological features of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. 1.Describing the Golgi tendon organ and Golgi Tendon reflex (second type) 2. Discuss third type of Muscle stretch reflex the Flexor reflex and withdrawal reflex including: A. the neuronal mechanism of the flexor reflex B. the reciprocal inhibition and reciprocal innervations Explaining the neuronal mechanism of the crossed extensor reflex 4. Describe the general characteristics of withdrawal reflex including the intensity of stimuli, the site of stimulation, fractionation and occlusion 5. Describe how muscle spindle system stabilizes body position during tense action, Myogram and its relation to muscle 1. Describe the major arteries of the lower limb. 2. Describe the deep and superficial veins of the lower limb. 3. Describe the topographical relationships of the arteries and veins of the lower limb. 4. Describe the lymphatic vessels of the lower limb. 1. Describe Paget s disease of bone 2. Describe the pathogenesis and pathologic features of osteomyelities. 3. Describe Osteoporosis, osteomalacia and rickets, Third week 27 & 28 Nerves of the lower limb (Anatomy 18 & 19) 1. The structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. 2. The course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the lower limb. 3. A general description of a peripheral nerve lesion. 29 Anti-rheumatoid drug 1. List the indications to use antirheumatoid drugs in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. 7
8 (Pharmacology 2) 30 Muscles of gluteal region (Anatomy 20) 31 Muscles of thigh (Anatomy 21) 32 Arthritis (Pathology 3) 33 Bone, soft tissue and skin tumors (Pathology 4) 34 Muscles of leg and popliteal fossa (Anatomy 22) 35 Muscles of the foot Anatomy 23 4 th week 2. Describe the concept of disease-modifying agents. 3. Describe the mechanism of action, toxic effect and contraindications of drugs used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. List the muscles of the gluteal region. Describe the attachments of the gluteal region muscles and their nerve supply. Describe the greater and lesser sciatic foramina and their contents. 1. List the muscles of the thigh. 2. Describe the femoral triangle. 3. Describe the femoral sheath and its contents. 4. Describe the attachments of the thigh muscles and their nerve supply. 1. Describe different types of arthritis (including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and crystal induced arthritis) 1. Describe and list the types of skin and soft tissue tumors 2. Understand the importance of cytological and histological features of soft tissue tumors in identifying type and behavior 3. Describe bone tumors. 4. Understand the classification of bone tumors 1. List the muscles of the leg. 2. Describe the attachments of the leg muscles and their nerve supply. 3. Describe the popliteal fossa. 4. List the content of the popliteal fossa. 5. Understand the clinical importance of the popliteal fossa. 1. Describe the movement of the toes. 2. List the muscles acting on the toes. 3. Describe the flexor and extensor retinacula and the structures passing in relation to them. 4. Describe the retinacula which are related to the foot and the structures passing in relation to the retinacula. 5. Describe the four muscle layers of the foot. 36 Histology of the MSS Anatomy & 38 Skin and its appendages I & II (Anatomy 25& 26) 1. Describe the normal bone histology including cellular and sub-cellular structure. 2. Describe the compact and spongy bone histological structure. 3. Describe the bone formation (a) endochondral and (b) intramembranous ossification and compare these two processes. 4. Identify the general times (a) of formation of primary and (b) of formation of secondary ossification centers, and (c) of fusion of such centers with each other. 5. Describe the muscle histology. 1. Describe briefly the development of the integumentary system. 2. Describe the layers of the epidermis. 3. Describe structure of the dermis. 8
9 39 & 40 Development of the MSS I & II. (Anatomy and histology Embryology 27 & 28) 41 Anaerobes and clostridium perfrenges and Gas gangrene Microbiology 1 42 Description of types of skin tactile Receptors Physiology 5 43 Drugs of non-infective skin conditions (Pharmacology 3) 44 Fungal infections of the skin Microbiology 2 45 Epidemiology of MSS diseases and injuries. (Community Medicine, Public Health 1) 46 Viral infections of the skin. (Microbiology 3) 47 Drugs of non-infective skin conditions (Pharmacology4) 4. Compare the structure and distribution of hair follicles, nails, sebaceous and sweat glands. 5. Explain bases of skin color. 1. Describe the development of skull, limbs, and vertebral column. 2. Describe the development of the skeletal muscles. 3. Identify the components of a somite and the adult derivatives of each component. 4. Explain the process of development of the limbs. 5. Explain limbs rotation 6. Describe the development of the motor and sensory nerves of the limbs 7. Discuss related congenital anomalies. 1. Interrelations among skin tactile sensations of Touch, Pressure, and Vibration 2. Description of types of skin tactile Receptors. free nerve endings, Meissner s corpuscle, Merkel discs, hair end-organ or free nerve ending of root hair plexus, Ruffini s endings, Pacinian corpuscles, 3. Types of functions of skin, muscle and bone Mechanoreceptors (Touch / pressure / position) I. Types of muscle and joint Proprioceptors & Position Sensory Receptors II. Types of skin tactile receptors 1. Describe anti-inflammatory topical corticosteroid drugs, the tar compounds and keratolytic drugs. 1. Describe the fungi that infect the skin and subcutaneous tissue, their identification and control (Dermatophytes, Candida spp., and Mycetoma agents). 2. Describe the fungi that infect the skin, their clinical classification, their identification and prevention (cutaneous, subcutaneous and apportunistics infection). 1. Define: Epidemiology of MSS diseases and injuries. 2. Distinguish between harm, risk and hazard. 3. Identify the human, situational and environmental risk factors of accidents and Injuries. 4. Explain the factors that influence Osteoporosis and its prevention. 1. Explain morphology and pathogenesis as well as diagnostic procedures of viruses infecting skin. 2. Describe the Herpesviruses and childhood exanthens. 1. Describe anti-inflammatory topical corticosteroid drugs, the tar compounds and keratolytic drugs. 9
10 48 Pacinian corpuscle as representative of skin sensory receptors (Physiology 6) 49 Parasitic infecting the skin. (Microbiology4) 50 Topical antimicrobial drugs Pharmacology 5 51 Drugs of Non-inflammatory skin conditions (Pharmacology 6) Transmission of Tactile Signals in skin peripheral nerve fibers Pacinian corpuscle as representative of skin sensory receptors Sensory Transduction in skin Pacinian corpuscle Loewenstein's experiments with the Pacinian corpuscle Maximum Pacinian corpuscle Receptor Potential amplitude Relation of the Pacinian corpuscle Receptor Potential to Action Potentials 1. Discuss the parasites that infect the skin ( Scabes Leishmania and Onchocerca, loaloa, and cutaneous larva migrans). 2. Briefly describe the life cycle, pathogenicity, control and prevention of each parasite. 1. Describe antibacterial agents, antifungal agents, antiviral agents and ectoparasitic ones 1. Describe drugs employed in the treatment of acne, psoriasis affecting pigmentation. Acne preparations. Drugs for psoriasis. Antipruritic agents. 2. Trichogenic agents. 3. Antiseborrhea agents. 52 Bacterial infections of the skin. Microbiology 5 53 Acute inflammatory dermatoses (Pathology 5) 1. Describe the cultural characteristics of skin and pathogenesis of skin commensals and pathogens 2. Describe the dermatologic manifestations of Diphtheroids, Staphylococci, Streptococci, Actinomyces israelii, Propionobacterium acnes, Mycobacteria ) 3. Explain pathogens of wound infection, methods of specimen collection for proper diagnosis, and laboratory diagnosis. 1. Define etiology, pathogenesis and pathologic features of urticaria, acute eczema, acne vulgaris and pathologic features of panniculitis. 10
11 Final Exam ( Theory + Practical ) = 70 % PRACTICAL LABORATORY SESSIONS No Title Objectives 1 Anatomy Lab 1 1. Identify the components of the vertebral column. 2. Identify the parts of each vertebra. 3. Identify bony features of the vertebral column in X-rays. 4. Identify the vertebral column ligaments and joints. 5. Identify the back muscles. 6. Identify the skull bones, structures, and regions. 7. Identify the components of TMJ. 2 Anatomy Lab 2 1. Identify different parts of each bone in the upper limb. 2. Identify the features of the upper limb bones in X-rays. 3. Identify the components of upper limb joints. 4. Identify different parts of each bone in the lower limb. 5. Identify the features of the lower limb bones in X-rays. 6. Identify the components of the lower limb joints. 3 Anatomy Lab 3 1. Identify the muscles of the upper limb. 2. Identify the upper limb vessels and nerves. 3. Identify the components of the axilla and cubital fossa. 4 Anatomy Lab 4 1. Identify the muscles of the lower limb. 2. Identify the lower limb vessels and nerves. 3. Identify the components of the femoral triangle, femoral canal, and popliteal fossa. Histology Lab 1 1. Identify the following: a. Thick skin and thin skin. b. The layers of epidermis. c. Components of the dermis. d. Epidermal derivatives. 2. Review the histology of the bone and muscles. 11
12 6 Pathology Lab 1 -Describe the morphology of the following soft tissue tumors Lipoma and liposarcoma Fibromatosis Malignant fibrous histiocytoma High grade sarcoma Describe the main morphological features of the different types of skin tumors SCC BCC Melanoma Describe the morphology of the following bone tumors Osteochondroma Osteosarcoma Chondrosarcoma Ewing,s sarcoma Giant cell tumor Metastatic carcinoma 7 Pathology Lab 2 Describe the main morphological features of the different types of arthritis RA OA Gout and pseudogout Describe the morphology of the following Osteomyelitis Paget,s disease of bone Describe the main morphological features of the following skin dermatoses Dermatitis and urticaria Erythema multiform Psoriasis Lichen planus Pimphigus vulgaris 12
13 Bullous pemphegoid 8 Microbiology Lab 1 Wound Culture Describe types: Describe specimen collection methods Lists the most common aerobic and anaerobic organisms causing the infection and their laboratory identification. COURSE LEARNING RESOURCES Lectures, Labs, clinical case discussion, video sessions and seminars. ONLINE RESOURCES {Write some useful websites related to the course and other material that help students to complete the course successfully.} This system is taught by more than one staff member that represent one of the basic medical education discipline. Each staff is free to give online links to the students as learning resources. ASSESSMANT TOOLS )Write assessment tools that will be used to test students ability to understand the course material and gain the skills and competencies stated in learning outcomes ASSESSMENT TOOLS % Midterm theory in-course exam (Online) 30 Practical final (Online) 20 Final theory end-course exam (Online) 50 TOTAL MARKS 100 THIRD: COURSE RULES ATTENDANCE RULES Attendance and participation are extremely important, and the usual University rules will apply. Attendance will be recorded for each class. Absence of 10% will result in a first written warning. Absence of 15% of the course will result in a second warning. Absence of 20% or more will result in forfeiting the course and the student will not be permitted to 13
14 attend the final examination. Should a student encounter any special circumstances (i.e. medical or personal), he/she is encouraged to discuss this with the instructor and written proof will be required to delete any absences from his/her attendance records. The use of the Mobile Devices, Laptops, etc. During Class, unexpected noises and movement automatically divert and capture people's attention, which means you are affecting everyone s learning experience if your cell phone, laptop, etc. makes noise or is visually distracting during class. For this reason, students are required to turn off their mobile devices and close their laptops during class. RADING SYSTEM Example: *Percentages are according to the number of students who passed the exam. REMARKS {The instructor can add any comments and directives such as the attendance policy and topics related to ethics}. COURSE COORDINATOR Course Coordinator: Dr. Riadh Ramadani - Department of Basic Sciences Signature: Signature: Date: Date: 14
MSS and Integument System
 Time Table/Week 1 - Sun- 17 to 21-9-2017 MSS and Integument System Time Sun 17/9 Mon 18/9 Tue 19/9 Wed 20/9 Thur 21/9 8:00-9:30 Introductory Presentation (ll participants) Overview of the omponents of
Time Table/Week 1 - Sun- 17 to 21-9-2017 MSS and Integument System Time Sun 17/9 Mon 18/9 Tue 19/9 Wed 20/9 Thur 21/9 8:00-9:30 Introductory Presentation (ll participants) Overview of the omponents of
Lab: Histology of Bone and Cartilage
 WEEK 1 Time/Date Monday, October 8 Tuesday, October 9 Wednesday, October 10 Thursday, October 11 Friday, October 12 1. 2. PHARMACOLOGY 1. PATHOLOGY 2. CELL BIOLOGY/PHYSIO 4. CELL BIOLOGY/PHYSIO Concepts
WEEK 1 Time/Date Monday, October 8 Tuesday, October 9 Wednesday, October 10 Thursday, October 11 Friday, October 12 1. 2. PHARMACOLOGY 1. PATHOLOGY 2. CELL BIOLOGY/PHYSIO 4. CELL BIOLOGY/PHYSIO Concepts
COURSE OUTLINE. Dean s Review:
 Fall 2015 24TBiology 141 24TAnatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Virginia Garden Program Head: Virginia Garden Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall 2014 24TBIOLOGY
Fall 2015 24TBiology 141 24TAnatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Virginia Garden Program Head: Virginia Garden Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall 2014 24TBIOLOGY
Virginia Western Community College BIO 141 Human Anatomy and Physiology I
 BIO 141 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Prerequisites BIO 101 or high school Biology within the past 5 years; an ENG 111 placement recommendation, co-enrollment in ENF 3/ENG 111, or successful completion
BIO 141 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Prerequisites BIO 101 or high school Biology within the past 5 years; an ENG 111 placement recommendation, co-enrollment in ENF 3/ENG 111, or successful completion
CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science
 CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science Anatomy and Physiology I - Biology 203 4 Credit Hours CATALOG DESCRIPTION
CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science Anatomy and Physiology I - Biology 203 4 Credit Hours CATALOG DESCRIPTION
Block 2 VIRGINIA CAMPUS Musculoskeletal System 2018
 WEEK 1 Time/Date Monday, October 15 Tuesday, October 16 Wednesday, October 17 Thursday, October 18 Friday, October 19 1. CELL BIOLOGY/PHYSIO 1. ANATOMY 2-3. CELL BIOLOGY/PHYSIO 6. CELL BIOLOGY/PHYSIO 8:00
WEEK 1 Time/Date Monday, October 15 Tuesday, October 16 Wednesday, October 17 Thursday, October 18 Friday, October 19 1. CELL BIOLOGY/PHYSIO 1. ANATOMY 2-3. CELL BIOLOGY/PHYSIO 6. CELL BIOLOGY/PHYSIO 8:00
Anatomy I ANAT 301. Course Description
 Anatomy I ANAT 301 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the osteomyoarticular system and peripheral nervous system, with
Anatomy I ANAT 301 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the osteomyoarticular system and peripheral nervous system, with
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives
 Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
2012/13 Batch Locomotion Module - Year 1
 2012/13 Batch Locomotion Module - Year 1 FINAL document Updated on January 2014 Concept Objective Time T/L activity General consideration 2012-1/SBM-2/1 Department a. Introduction to limbs and limb girdles
2012/13 Batch Locomotion Module - Year 1 FINAL document Updated on January 2014 Concept Objective Time T/L activity General consideration 2012-1/SBM-2/1 Department a. Introduction to limbs and limb girdles
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS
 BASICS LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS LECTURE TOPIC: ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Read the textbook: Ch. 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go To: Web Site > Folder: AnatTerm > A25terms09.pdf. Download the file &
BASICS LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS LECTURE TOPIC: ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Read the textbook: Ch. 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go To: Web Site > Folder: AnatTerm > A25terms09.pdf. Download the file &
Course Syllabus. Musculoskeletal system & Skin. Course Name:
 . The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center Course Syllabus Course Name: Musculoskeletal system & Skin 1 Course title Musculoskeletal system & Skin 2 Course number 3 Credit hours
. The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center Course Syllabus Course Name: Musculoskeletal system & Skin 1 Course title Musculoskeletal system & Skin 2 Course number 3 Credit hours
Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education
 Date Adopted: July 1, 1998 Date Reviewed: December 1, 1999 Date Revised: 1999, 2007, 2011 Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education Representing Alabama s Public Two-Year College System Jefferson State
Date Adopted: July 1, 1998 Date Reviewed: December 1, 1999 Date Revised: 1999, 2007, 2011 Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education Representing Alabama s Public Two-Year College System Jefferson State
Integumentary and Musculoskeletal Systems COM Fall 2016
 Integumentary and Musculoskeletal Systems COM 511 - Fall 2016 Weeks Date Time Title Faculty Week 1 Monday, 10/31/16 8:00-9:00 am CP: Skin Rashes, Papules, and Macules Sharma Monday, 10/31/16 9:00-10:00
Integumentary and Musculoskeletal Systems COM 511 - Fall 2016 Weeks Date Time Title Faculty Week 1 Monday, 10/31/16 8:00-9:00 am CP: Skin Rashes, Papules, and Macules Sharma Monday, 10/31/16 9:00-10:00
December 3, Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow?
 December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
Lab # 2: Spinal Cord & Nerves, Reflexes and General Senses. A & P II Spring, 2014
 Lab # 2: Spinal Cord & Nerves, Reflexes and General Senses A & P II Spring, 2014 Objectives Be able to identify specified spinal cord structures and spinal nerves on models Be familiar with spinal nerve
Lab # 2: Spinal Cord & Nerves, Reflexes and General Senses A & P II Spring, 2014 Objectives Be able to identify specified spinal cord structures and spinal nerves on models Be familiar with spinal nerve
Topic list for the Anatomy end-semester exam of the First semester Academic year 2018/2019, Autumn term
 University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
School of Pharmacy and Health Sciences
 School of Pharmacy and Health Sciences SEMESTER: Summer 2017 COURSE: HAN 1321: Human Anatomy I LECTURER : Nyaribo Cyprian Mose CLASS DAYS/TIME: Monday/Wednesday (9:00-10:40 and 1:20-3:00pm) CLASS VENUE:
School of Pharmacy and Health Sciences SEMESTER: Summer 2017 COURSE: HAN 1321: Human Anatomy I LECTURER : Nyaribo Cyprian Mose CLASS DAYS/TIME: Monday/Wednesday (9:00-10:40 and 1:20-3:00pm) CLASS VENUE:
Course Specifications
 Cairo University Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy Course Specifications Course title: Human Anatomy and Embryology (1 st year) (Code): ANA-101 Department offering the course: Anatomy Department
Cairo University Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy Course Specifications Course title: Human Anatomy and Embryology (1 st year) (Code): ANA-101 Department offering the course: Anatomy Department
High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following about the skeletal system is true? Question #01 A. There are two types
High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following about the skeletal system is true? Question #01 A. There are two types
Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord
 Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
FUNDEMENTALS OF ANATOMY. TBD TBD
 Course Details FUNDEMENTALS OF ANATOMY Course Title Fundamentals of Anatomy Course Number BIOL 160 Department Anatomy Credit Hours 4 Grading Type Letter Course Director Sushama Rich M.D. Director s Email
Course Details FUNDEMENTALS OF ANATOMY Course Title Fundamentals of Anatomy Course Number BIOL 160 Department Anatomy Credit Hours 4 Grading Type Letter Course Director Sushama Rich M.D. Director s Email
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
8. Radiology: Radiological Features of Bone and Joint Infection. Study from: Alhashli note
 PROBLEM 1 (SHOULDER PAIN) Anatomy of The Shoulder Region Bone of Upper Limbs: 399 402 Clinical Box: 404-405 Scapulo-Humeral Muscles: 419 Joints of Upper Limbs: 465 471 Axioappendicular Muscles: 414 419
PROBLEM 1 (SHOULDER PAIN) Anatomy of The Shoulder Region Bone of Upper Limbs: 399 402 Clinical Box: 404-405 Scapulo-Humeral Muscles: 419 Joints of Upper Limbs: 465 471 Axioappendicular Muscles: 414 419
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Spinal Cord Anatomy Protective structures: Vertebral column and the meninges protect the spinal cord and provide physical stability. a. Dura mater, b. Arachnoid,
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Spinal Cord Anatomy Protective structures: Vertebral column and the meninges protect the spinal cord and provide physical stability. a. Dura mater, b. Arachnoid,
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p.
 General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
Acknowledgments Figure Credits List of Clinical Blue Boxes Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p.
 Preface p. ix Acknowledgments p. xi Figure Credits p. xv List of Clinical Blue Boxes p. xix Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p. 2 Regional Anatomy p. 2 Systemic
Preface p. ix Acknowledgments p. xi Figure Credits p. xv List of Clinical Blue Boxes p. xix Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p. 2 Regional Anatomy p. 2 Systemic
Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for
 Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
UNIT 1: CELLS, SKIN, & SENSORY ORGANS
 Anatomy UNIT 1: CELLS, SKIN, & SENSORY ORGANS Section 1.1: Intro to Anatomy Section 1.2: Cell & Skin Anatomy Section 1.3: Sensory Organs Learning Objectives Compare ic and regional anatomy Evaluate the
Anatomy UNIT 1: CELLS, SKIN, & SENSORY ORGANS Section 1.1: Intro to Anatomy Section 1.2: Cell & Skin Anatomy Section 1.3: Sensory Organs Learning Objectives Compare ic and regional anatomy Evaluate the
Definition of anatomy 1 Questions 5
 Contents Chapter 1: Introduction 1 5 Definition of anatomy 1 Questions 5 Chapter 2: Skeletal System 6 74 Skeleton 6 Skeletal system 8 Bones of superior extremity 12 Articulated skeleton of hand 17 Clinical
Contents Chapter 1: Introduction 1 5 Definition of anatomy 1 Questions 5 Chapter 2: Skeletal System 6 74 Skeleton 6 Skeletal system 8 Bones of superior extremity 12 Articulated skeleton of hand 17 Clinical
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
Chp. 6: Bones and Skeletal Tissue Student Worksheet. 1. The skeletal system is composed of bones,,, and.
 Chp. 6: Bones and Skeletal Tissue Student Worksheet 1. The skeletal system is composed of bones,,, and. 2. What are 5 functions of the skeletal system? 3. Besides osseous tissue (connective tissue with
Chp. 6: Bones and Skeletal Tissue Student Worksheet 1. The skeletal system is composed of bones,,, and. 2. What are 5 functions of the skeletal system? 3. Besides osseous tissue (connective tissue with
Human Anatomy. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13)
 Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System
 Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System Kyle E. Rarey, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology and Otolaryngology University of Florida College of Medicine Outline of Presentation Vertebral Column Upper
Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System Kyle E. Rarey, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology and Otolaryngology University of Florida College of Medicine Outline of Presentation Vertebral Column Upper
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
PNS and ANS Flashcards
 1. Name several SOMATIC SENSES Light touch (being touched by a feather), heat, cold, vibration, pressure, pain are SOMATIC SENSES. 2. What are proprioceptors; and how is proprioception tested? PROPRIOCEPTORS
1. Name several SOMATIC SENSES Light touch (being touched by a feather), heat, cold, vibration, pressure, pain are SOMATIC SENSES. 2. What are proprioceptors; and how is proprioception tested? PROPRIOCEPTORS
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION. The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include:
 Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Department of Anatomy ESI-PGIMSR, Joka, Kolkata
 Teaching Schedule - 2016-2017, 1st MBBS Date and Day Time Topic Name/ Group 8-9 Orientation, Introduction to theoretical aspects of Practical SC 3.10.2016 Anatomy, Tools of Trade - Anatomical Nomenclature-
Teaching Schedule - 2016-2017, 1st MBBS Date and Day Time Topic Name/ Group 8-9 Orientation, Introduction to theoretical aspects of Practical SC 3.10.2016 Anatomy, Tools of Trade - Anatomical Nomenclature-
COURSE-SPECIFIC GRADE CALCULATION Advanced notification of any changes will be provided to the student.
 Piedmont Technical College Course Information Sheet Course Title: Human Anatomy and Physiology I Course Prefix/Number: BIO 210 COURSE-SPECIFIC GRADE CALCULATION Advanced notification of any changes will
Piedmont Technical College Course Information Sheet Course Title: Human Anatomy and Physiology I Course Prefix/Number: BIO 210 COURSE-SPECIFIC GRADE CALCULATION Advanced notification of any changes will
The Skeletal System. Dr. Naim Kittana. Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted from the text book
The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted from the text book
LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS. Please check with the LCC bookstore for the required texts for this class.
 LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS SPECIAL NOTE: This brief syllabus is not intended to be a legal contract. A full syllabus will be distributed to students at the first class session. TEXT AND SUPPLEMENTARY
LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS SPECIAL NOTE: This brief syllabus is not intended to be a legal contract. A full syllabus will be distributed to students at the first class session. TEXT AND SUPPLEMENTARY
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Human Skeletal System Glossary
 Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
The Skeletal System. Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab. Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted
The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted
Updated: Page 1 of 6
 A. Academic Division: Health Sciences B. Discipline: Science MASTER SYLLABUS 2019-2020 C. Course Number and Title: BIOL2751 Human Anatomy & Physiology I D. Course Coordinator: Jeff Taylor, MS Assistant
A. Academic Division: Health Sciences B. Discipline: Science MASTER SYLLABUS 2019-2020 C. Course Number and Title: BIOL2751 Human Anatomy & Physiology I D. Course Coordinator: Jeff Taylor, MS Assistant
7/10/18. Introduction. Integumentary System. Physiology. Anatomy. Structure of the Skin. Epidermis
 Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Red Comet. Anatomy. *This course is recommended for grades UNIT 1: CELLS, SKIN, & SENSORY ORGANS. (Time Estimate for Content Study 15 hours)
 Red Comet Anatomy In this course students will explore the anatomy or structure of the human body. In addition to learning anatomical terminology, students will study and the main systems of the body including
Red Comet Anatomy In this course students will explore the anatomy or structure of the human body. In addition to learning anatomical terminology, students will study and the main systems of the body including
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Course Syllabus Anatomy and Physiology I BIOL 2401
 Course Syllabus Anatomy and Physiology I BIOL 2401 Semester with Course Reference Number (CRN) Instructor contact information (phone number and email address) Fall 2012 (August 27 December 16) 22167 Dr.
Course Syllabus Anatomy and Physiology I BIOL 2401 Semester with Course Reference Number (CRN) Instructor contact information (phone number and email address) Fall 2012 (August 27 December 16) 22167 Dr.
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System. Introduction. Membranes
 Slide 1 Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System Slide 2 Introduction Skin often reveals our inner workings and general health In most manual therapies, the skin is primary interface with
Slide 1 Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System Slide 2 Introduction Skin often reveals our inner workings and general health In most manual therapies, the skin is primary interface with
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves mediate reactions to environmental changes. B. The spinal cord has several functions. 1. It processes reflexes. 2. It is
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves mediate reactions to environmental changes. B. The spinal cord has several functions. 1. It processes reflexes. 2. It is
Course Information Physical Therapy in Orthopedics. Saddam Kanaan, PT, PhD Sakher Obaidat, PT; Terez Kabboushi, PT
 Jordan University of Science and Technology Faculty of Applied Medical Sciences Department of Rehabilitation Sciences First Semester 2013-2014, Course Syllabus Course Title Course Number PT 341 Instructor
Jordan University of Science and Technology Faculty of Applied Medical Sciences Department of Rehabilitation Sciences First Semester 2013-2014, Course Syllabus Course Title Course Number PT 341 Instructor
Rama Nada. - Mousa Al-Abbadi. 1 P a g e
 - 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
- 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
Introductory Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 KNES 200 Kinesiology Program/University Studies. Course Outline
 Introductory Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 KNES 200 Kinesiology Program/University Studies Course Outline COURSE IMPLEMENTATION DATE: Pre 1998 OUTLINE EFFECTIVE DATE: September 2018 COURSE OUTLINE REVIEW
Introductory Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 KNES 200 Kinesiology Program/University Studies Course Outline COURSE IMPLEMENTATION DATE: Pre 1998 OUTLINE EFFECTIVE DATE: September 2018 COURSE OUTLINE REVIEW
Training the Clinical Anatomy Trainer Level 2 Teaching Objectives
 Training the Clinical Anatomy Trainer Level 2 Presentations o Large group teaching o Small group teaching Prosection-based teaching Osteology teaching Surface anatomy Innovative teaching Conceptual teaching
Training the Clinical Anatomy Trainer Level 2 Presentations o Large group teaching o Small group teaching Prosection-based teaching Osteology teaching Surface anatomy Innovative teaching Conceptual teaching
Chapter 7 Skeletal System. Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions.
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions. support protection muscle attachment - movement blood production
Chapter 7 Skeletal System Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions. support protection muscle attachment - movement blood production
Chapter 13. The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Cord Protection. Meninges. Together with brain forms the CNS Functions
 Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity
 Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity I. Peripheral nervous system A. PNS links CNS to the body B. Sensory: the afferent division C. Motor: the efferent division D. Ganglia: collections of cell bodies in
Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity I. Peripheral nervous system A. PNS links CNS to the body B. Sensory: the afferent division C. Motor: the efferent division D. Ganglia: collections of cell bodies in
Skeletal System. By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr.
 Skeletal System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Learning Outcomes Describe the parts of a long
Skeletal System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Learning Outcomes Describe the parts of a long
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle)
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Anatomy 2 nd Paper. Past Papers
 Anatomy 2 nd Paper Past Papers September 2010 April 2010 September 2009 April 2009 September 2008 April 2008 September 2007 April 2007 September 2006 May 2006 September 2005 April 2005 September 2004 April
Anatomy 2 nd Paper Past Papers September 2010 April 2010 September 2009 April 2009 September 2008 April 2008 September 2007 April 2007 September 2006 May 2006 September 2005 April 2005 September 2004 April
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
What type of tissue is this
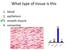 What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense
 The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 Introduction... 2 Muscle Spindles and Golgi Tendon Organs... 3 Gamma Drive... 5 Three Spinal Reflexes...
The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 Introduction... 2 Muscle Spindles and Golgi Tendon Organs... 3 Gamma Drive... 5 Three Spinal Reflexes...
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move.
 Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Lesson 6.4 REFLEXES AND PROPRIOCEPTION
 Lesson 6.4 REFLEXES AND PROPRIOCEPTION (a) The Reflex Arc ~ ~ ~ TOPICS COVERED IN THIS LESSON (b) Proprioception and Proprioceptors 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 1 What Are Reflexes? Reflexes
Lesson 6.4 REFLEXES AND PROPRIOCEPTION (a) The Reflex Arc ~ ~ ~ TOPICS COVERED IN THIS LESSON (b) Proprioception and Proprioceptors 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 1 What Are Reflexes? Reflexes
Warm-Up Activity. Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram.
 Warm-Up Activity Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram. Warm-Up 1. What are the 4 types of bones? Give an example of each. 2. Give 3 ways you can tell a female skeleton from a male skeleton.
Warm-Up Activity Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram. Warm-Up 1. What are the 4 types of bones? Give an example of each. 2. Give 3 ways you can tell a female skeleton from a male skeleton.
Structural Support and Movement. Chapter 36
 Structural Support and Movement Chapter 36 Impacts, Issues Pumping Up Muscles Increasing muscle size and strength with drugs such as andro has unwanted side effects and can damage other organ systems 36.1
Structural Support and Movement Chapter 36 Impacts, Issues Pumping Up Muscles Increasing muscle size and strength with drugs such as andro has unwanted side effects and can damage other organ systems 36.1
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
HEAD AND NECK PART 2
 HEAD AND NECK PART 2 INTEGRATED CURRICULUM = Integrate Basic Science and Clinical Training 1- ENT PATIENT EXAM IN ICS COURSE - Today and next week - Review/Preview Anatomy underlying ENT exam 2- NEUROANATOMY/NEUROLOGY
HEAD AND NECK PART 2 INTEGRATED CURRICULUM = Integrate Basic Science and Clinical Training 1- ENT PATIENT EXAM IN ICS COURSE - Today and next week - Review/Preview Anatomy underlying ENT exam 2- NEUROANATOMY/NEUROLOGY
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
PHYS. ED. VCE student worksheets
 HARRY BROOKES ALLEN MUSEUM OF ANATOMY AND PATHOLOGY PHYS. ED. VCE student worksheets PHOTOGRAPHY & FILMING IN THE MUSEUM ARE STRICTLY PROHIBITED Real people have generously donated their bodies so that
HARRY BROOKES ALLEN MUSEUM OF ANATOMY AND PATHOLOGY PHYS. ED. VCE student worksheets PHOTOGRAPHY & FILMING IN THE MUSEUM ARE STRICTLY PROHIBITED Real people have generously donated their bodies so that
Course Syllabus. Dr. Patricia Ashby
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I BIO 201 Course Syllabus Dr. Patricia Ashby Scottsdale Community College office: NS115 phone: 423-6033 email: patricia.ashby@scottsdalecc.edu Meeting Times: Lecture: MTW 7:30-9:30
Human Anatomy and Physiology I BIO 201 Course Syllabus Dr. Patricia Ashby Scottsdale Community College office: NS115 phone: 423-6033 email: patricia.ashby@scottsdalecc.edu Meeting Times: Lecture: MTW 7:30-9:30
Biology 2101 Anatomy and Physiology Lab Syllabus Spring 2016
 Biology 2101 Anatomy and Physiology Lab Syllabus Spring 2016 Instructor: Kerry Walling Office: HS-225J Office phone: 230-3342 Email:kerry.walling@brazosport.edu Alt. Phone: Office Professional Debbie Duncan
Biology 2101 Anatomy and Physiology Lab Syllabus Spring 2016 Instructor: Kerry Walling Office: HS-225J Office phone: 230-3342 Email:kerry.walling@brazosport.edu Alt. Phone: Office Professional Debbie Duncan
JOHN ABBOTT COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I ( AB) COURSE OUTLINE
 JOHN ABBOTT COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I (101-805-AB) COURSE OUTLINE 2012-1 A. GENERAL INFORMATION Program; Intensive Nursing: 180-AO Course Title: Human Anatomy And Physiology I Course Number:
JOHN ABBOTT COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I (101-805-AB) COURSE OUTLINE 2012-1 A. GENERAL INFORMATION Program; Intensive Nursing: 180-AO Course Title: Human Anatomy And Physiology I Course Number:
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
Lab Activity 13. Spinal Cord. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 13 Spinal Cord Portland Community College BI 232 Definitions Tracts: collections of axons in CNS Nerves:collections of axons in PNS Ganglia: collections of neuron cell bodies in PNS Nucleus
Lab Activity 13 Spinal Cord Portland Community College BI 232 Definitions Tracts: collections of axons in CNS Nerves:collections of axons in PNS Ganglia: collections of neuron cell bodies in PNS Nucleus
Skeletal System. Skeleton. Support. Function of Bones. Movement. Protection 10/15/12
 Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Chapter 13. The Nature of Muscle Spindles, Somatic Reflexes, and Posture
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Muscle Spindles, Somatic Reflexes, and Posture Nature of Reflexes A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in the effecter tissue
Chapter 13 The Nature of Muscle Spindles, Somatic Reflexes, and Posture Nature of Reflexes A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in the effecter tissue
Skin. the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight
 Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
Study Guide for Bio 101 Lecture Exam 4
 Study Guide for Bio 101 Lecture Exam 4 Please note that this study guide is a listing of objectives that you are required to master for this course. However, items mentioned in class or in laboratory as
Study Guide for Bio 101 Lecture Exam 4 Please note that this study guide is a listing of objectives that you are required to master for this course. However, items mentioned in class or in laboratory as
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW. VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below.
 SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Introduction Notes (pt 1)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
Musculoskeletal System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
Chapter 14. The Nervous System. The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College
 Chapter 14 The Nervous System The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of: The spinal
Chapter 14 The Nervous System The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of: The spinal
Skeletal Tissues. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
