A Guide for Patients with Hip and Groin Pain. By - Rob Lawton & Ajay Malviya. Overview
|
|
|
- Emory Dickerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 A Guide for Patients with Hip and Groin Pain By - Rob Lawton & Ajay Malviya Overview - Introduction - Hip Anatomy - Is the pain coming from the hip joint? - Intra-articular causes of hip pain o Impingement o Dysplasia o Arthritis - Extra articular causes of hip pain o Trochanteric Pain Syndrome o Snapping Hip Syndromes o Deep Gluteal Pain Syndrome o Adductor Tendinopathy & Pubic Symphysitis o Sports Injuries - Conclusions - References Introduction The following is written for patients who are being investigated by their doctor for pain in or around the hip joint. It is not an exhaustive explanation of all hip problems, but an introduction to common causes of hip pain and how they are diagnosed. Many people have relatives or friends who have undergone a hip replacement. This is a successful treatment for chronic hip joint pain, such as that caused by osteoarthritis, where the internal cartilage lining of the joint has been worn away.
3 However, no replacement joint so far developed is as good as a well functioning natural joint and all replacement joints have a risk of wearing out, especially in younger and active patients, who may then need a replacement of the replacement. Replacement of a replacement joint is termed revision surgery and is more technically demanding for the surgeon and more risky for the patient than initial replacement of a natural hip. Hence modern philosophy in the management of hip problems is to identify symptoms early, to see if anything can be done repair the joint and/or prevent further damage in order to relieve symptoms and slow down the progress to arthritis, preserving the patient s natural joint for as long as possible. Key-hole surgery (arthroscopy) to repair and reshape the inside of the hip joint, and bone realignment (osteotomy) to change the orientation of the socket or thigh bone are the main techniques used to protect and preserve the natural hip joint. Hip Anatomy You probably know that the hip is a ball and socket joint. What you may not know is that the hip socket also has a soft cartilage rim, called the labrum. This rim makes the socket slightly deeper, helps to keep the ball shaped head of the femur (thigh bone) in the acetabulum (socket), and also keeps the joint lubricating fluid in place. Fig 1a. Diagram of the right hip ball and socket joint, with the head of the femur dislocated to reveal the articular joint surfaces.
4 Fig 1b. Schematic axial representation (as if the patient is lying down on their back and the hip joint is viewed from below) of the left hip joint, showing femoral head, acetabulum, anterior acetabular labrum and articular cartilage. Often the first sign of a problem with the hip is a tear in the cartilage rim (labral tear), which it thought to allow the lubricating fluid to leak out. Without lubricating fluid, the joint is more vulnerable to wear and tear damage that leads to arthritis.
5 The joint reacts by making more fluid, which causes swelling and pain. The torn labrum can also click or catch (although most commonly clicking around the hip joint is due to tendons outside the hip, rather than anything inside the hip joint itself). Fig 2 a. Axial view of normal labral function producing a seal at that helps keep synovial fluid (joint lubricating fluid) in position when the cartilage is loaded. Fig. 2b. Axial view of labral tear at junction between labrum and acetabulum, which allows synovial fluid to escape. Fig. 2c. Lack of lubricating synovial fluid results in altered loading of articular cartilage during weight-bearing activities.
6 Not all people have the same type of hip anatomy. There is natural variation in both the shape and orientation of the femoral head and neck and in the shape and orientation of the acetabulum. The commonest variations are referred to as cam when the femoral head is shaped like slightly more oval than a perfect sphere; Pincer, where the socket is slightly deeper so that the rim of the socket can pinch the neck of the femur and dysplasia where the socket is shallow. Pincer pathology can also occur when the socket is not particularly deeper, but not orientated in the ideal direction, typically pointing slightly too far backwards, termed retroversion. In some cases these variations may be a result of childhood hip disorders such as slipped upper femoral epiphysis (SUFE), Perthes Disease or childhood dysplasia. Fig. 3 a. Normal AP pelvis x-ray and axial schematic view of normal hip. Fig. 3b. X- ray of bilateral cam deformities and axial schematic of cam deformity.
7 Fig. 3 c. AP diagram and X Ray of acetabular retroversion causing pincer type impingement. Cross-over of the anterior and posterior walls is illustrated in the diagram and x-ray. Increased anterior coverage is shown in the axial schematic representation. Fig. 3 d. Axial schematic representation of a mixed impingement with pincer increased acetabular coverage and femoral cam deformity.
8 Fig 3 e. X ray of bilateral hip dysplasia, with reduced superior bony coverage in the superior weight-bearing zone illustrated by the orange segment of the left hip. The axial schematic representation illustrates the typical finding of a shallow acetabulum and a thickened hypertrophic labrum. Interestingly, the reasons for this degree of variation may be related to evolution. Running mammals have more oval shaped hips that move well forwards and back, but not as much from side to side or in rotation. Swimming and climbing mammals have rounder hips with a shallow socket that move well in all directions. Human hips are somewhere in between. Some studies have reported a higher proportion of cam shaped hips among athletes than the general population and it may be that a cam shape is advantageous for running. The hip shape we develop as adults is probably related to a combination of our genes and our activities during growth. However, considerable variation is seen, even among asymptomatic individuals, and more research is needed before we can be sure about the reasons for observed variations. Fig. 4. Horse and walrus femora (thigh bones) showing variation in femoral head (hip ball) shape. The asymmetric more barrel shaped head of the horse femur on the left (a) is typical of running mammals. This shape is more common in nature and is similar to a cam hip in humans. It allows the hip to moves more forwards and backwards than in rotation. The more symmetrical and spherical head shape of the walrus femur on the right (b) is less common in nature and is seen in climbing and swimming mammals whose hips have more multidirectional rotation. (1)
9 Is the pain coming from the hip joint? Pain arising from the hip joint itself is most commonly experienced in the groin. However, pain in the buttock, side of the hip (trochanteric region) and knee are also common. The pain can radiate down the thigh or upwards into the lower back. Several conditions can cause pain in similar areas, such as pinched nerves in the lower back or buttock, herniae in the groin and muscle or tendon problems. As it can be difficult to work out exactly where the pain is coming from in addition to clinical examination, xrays and CT/MRI scans your doctor may suggest an injection of local anaesthetic into the hip joint itself to see if this relieves your symptoms. If an injection helps, that is an indication that the problem lies in the hip joint and surgery may help. If the injection makes no difference, then it is unlikely that surgery will help, and it is better to keep investigating to find the real cause of the problem. Fig. 5. Location of pain related to hip joint. Anterior groin shown in blue, lateral or trochanteric shown in red, posterior, buttock, gluteal pain shown in orange. (2)
10 Intra-articular causes of hip and groin pain 1. Impingement Impingement is a clinical syndrome, where mismatch between the shape of the ball and socket cause pinching of the labrum in certain movements. Commonly, the head of the femur is not perfectly round (cam), and as it squeezes into the socket it pinches the labrum. Impingement can also be due to the rim of the socket overhanging if it is slightly too deep (pincer), or pointing slightly backwards (retroversion). The third type of impingement is a combination of both cam and pincer types, termed mixed. If the process of pinching at the rim of joint continues, damage can spread to the articular cartilage inside of the hip causing arthritis. Fig. 6 a. Axial view of cam impingement. Impingement occurs as aspherical femoral head or an overhanging bony acetabular rim pinches the soft acetabular labrum against the bony acetabular rim when the hip is moved into certain positions (6b). Typically when the hip is flexed forwards and rotated inwards.
11 Fig. 6 c & d. Repeated impaction of the cam against the labrum and acetabular rim can result in a labral tear at the junction between the labrum and the acetabular rim, and bony oedema and/or cyst formation in the cam lesion on the femoral neck as shown on the axial MRI in Fig 6c and in the axial schematic in Fig 6d. Eventually this process leads to damage to the articular cartilage, which may start to peel away from the chondro- labral junction (junction between the labrum and cartilage). Non-operative treatment for Impingement The role of non-operative treatment is often underestimated. Physiotherapy in particular is very important. If the muscles around the hips get tight or weak, then they can cause the pelvis to tilt, making any pinching problems or socket problems worse. Core stability exercises to make sure the hip ball is always well centred in the socket are important (and also form an important part of recovery after surgery).
12 If you have never done any specific exercises for the hips, then this is always recommended as the first step, as any sports that only exercise the hips in one direction (like running which moves the hips mainly forwards and back, and not side to side) can result in muscles being out of balance, making the symptoms worse. Physiotherapy focuses on strengthening the small but important muscles that keep the hip joint well centered in the socket and the spine stable above the pelvis, rather than big muscles that are used for running and jumping, which may be so strong and overdeveloped they are over powering the smaller important stabilising muscles. Surgery for Impingement The aim of surgery is to reshape the bones so that no more pinching of the labrum happens. This can be done either by open, or key-hole surgery (hip arthroscopy). To perform hip arthroscopy traction is used to partially dislocate the hip joint, just enough to insert a narrow camera and specialised instruments into the joint. Typically two to four small incisions are made. The areas of bone that are pinching the labrum are removed and the labrum is repaired or smoothed off (debridement). If impingement is being caused by retroversion of the socket (socket pointing backwards and rim overhanging) it may be possible to address this from inside the joint using arthroscopy, however, if the orientation of the whole socket needs to be adjusted it may be necessary to perform an osteotomy as in dysplasia below. Fig. 7 a. Intra operative fluoroscopy (x-rays) of arthroscopic re-shaping of femoral cam deformity (osteochondroplasty). The area of bone removed superiorly is highlighted in blue. However, as symptoms are most commonly experienced when the hip is flexed, it is also very important to reshape the anterior portion of the cam, which is brought into contact with the rim of the socket when the hip is flexed forwards (highlighted in red). The surgeon can check during the operation that enough bone has been removed by moving
13 the hip around to test that there is enough clearance. Fig 7b. Intra-operative photographs of arthroscopic reshaping of femoral cam deformity Fig 7 c. Intra-operative photographs of arthroscopic debridement of a labral tear using a radiofrequency probe to smooth way the torn fragments.
14 Fig 7 d. Intra-operative photographs of arthroscopic labral repair using suture anchors to refix the torn labrum to the bony rim of the acetabulum. Traction is applied to distract the joint and create space for specialized instruments. 2. Dysplasia Dysplasia is a condition where the hip socket is too shallow or is pointing in the wrong direction. This results in not enough bony support in the weight-bearing zone of the hip and too much pressure falling on the rim (labrum), which can become torn or damaged. Many patients with shallow hips have excellent hip mobility and flexibility as the shallow socket allows more movement. However, the hip muscles have to work harder to keep the hip in the socket and many patients experience muscle fatigue and aching. When the hip socket is shallow the weigh bearing area is smaller and over time the wear and tear concentrated in a small area can result in early arthritis. Non-operative treatment for Dysplasia Often the symptoms of dysplasia are due to instability and physiotherapy exercises to strengthen the muscles that make sure the hip ball is well centred in the socket can help. Surgery for Dysplasia Surgery for dysplasia can depend on how shallow the socket is. In milder forms, key-hole surgery to repair the labrum and tighten the capsule can improve
15 symptoms of instability and has been shown to have good short and medium term results in some patients. When the socket is very shallow, key-hole surgery is no-longer recommended. In these cases Peri-acetabular Osteotomy is advised. This involves cutting around the socket (acetabulum), rotating it into the best possible position and fixing it in place with screws. Peri-acetabular means around the acetabulum and osteotomy comes from osteo, meaning bone and otomy meaning cutting. So translated literally the operation means: Around the acetabulum bone cutting. This has been shown to have good medium and long-term results. Fig. 8 a & b. Periacetabular osteotomy (PAO) is a technique that rotates the acetabulum around the head of the femur, providing more bony support where it is needed. This improves stability and increases the superior weight-bearing cartilage zone. Fig. 8d shows the initial position on intraoperative fluoroscopy (xrays). Many patients with dysplasia are referred because labral damage has been picked up on an MRI scan. However, the reason for this damage is the shallow socket. The important thing is to address the instability, which is the cause of the labral damage. Ideally this is by making the socket deeper and increasing the weight bearing area of the hip, which will take the pressure off the labrum and allow it to heal. Fig. 9 a. Pelvic X-ray of bilateral hip dysplasia illustrating the shallow socket and reduced bony support for the ball (femoral head) in the superior weight bearing part of the hip socket (orange zone). This increases the pressure on a small area of cartilage and on the labrum. Fig. 9 b. Shows increased size of the weight-bearing zone achieved by rotation of
16 the acetabulum. The screws for initial stabilization remain in position. In Fig. 9 c the bony cuts in the pelvis have healed and the screws have been removed 3. Arthritis Once there is established damage to the weight bearing cartilage surfaces inside the joint, this is referred to as osteoarthritis, or sometimes just as arthritis. If this has happened and the surfaces of the joint are already worn it is unfortunately not possible to repair the surface of the joint. In this situation is important to consider the options carefully as the outcome of joint preservation surgery is less predictable. In the very early stages of arthritis hip preservation techniques may slow the progression. However, past a critical point hip preservation techniques can no longer help and in some cases can make symptoms worse. It can sometimes be difficult to judge exactly how advanced the arthritic changes are before surgery. To minimize surprises we encourage a detailed discussion of expectations before surgery in every case. For some patients hip replacement may be the best option. Fig 10a. Xray of the pelvis showing joint space narrowing, osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis and cysts, the cardinal features of osteoarthritis.
17 Fig. 10b Intraoperative hip arthroscopy photograph showing changes of osteoarthritis with significant articular cartilage damage on the acetabular side. Fig. 10 c. Hip replacement X Ray. Extra-Articular Causes Of Hip Pain 1. Trochanteric Pain Syndrome Trochanteric pain syndrome is a term used to describe painful conditions around the outer aspect of the hip (See figure 5). It may be caused by inflammation of the trochanteric bursa, gluteus medius or minimus tendinopathy or other inflammatory conditions of the hip. Sometimes overload of the tendons in this area can be due to an underlying problem with the hip joint, such as dysplasia and the hip should be fully assessed to exclude an intra-articular cause. The mainstay of treatment for trochanteric pathology is physiotherapy sometimes combined with injections.
18 Occasionally, key-hole surgery to repair the gluteus tendons or to address bone spurs or inflammation associated with bursitis and tendinopathy are necessary. 2. Snapping Hip Syndrome Most snapping or popping around the hip is due to tendons being pulled tight over a bony protuberance and then releasing. In the hip there are three main types. 1. In external snapping hip, the iliotibial band slips over the outside of the greater trochanter. This can also be a cause of trochanteric pain syndrome. 2. In internal snapping hip, the iliopsoas tendon slips over the ileopectneal eminence in the groin. Fig 11. Extra-articular causes of snapping hip syndrome 3. Intra-articular snapping hip may be due to articular cartilage damage, a loose body or a torn labrum. A full assessment of the hip is recommended to exclude intra-articular causes. Most extra-articular snapping resolves with physiotherapy to stretch and strengthen the
19 tight muscles. Occasionally injections or key hole surgery are required to remove bone spurs or release tendons. For intra-articular causes, surgery may be required. 4. Deep Gluteal Pain Syndrome Patients with this condition present with buttock pain, which may radiate along the back of the thigh. Again it is important to assess the hip fully and exclude intra-articular causes. As the symptoms mimic sciatica, back problems also need to be excluded. This syndrome is commonly caused by pinching of the sciatic nerve, by tight muscles and tendons in the buttock area. It may also be due to piriformis tendonitis, hamstring tendinopathy or inflammation of other tissue in that region. Most of these conditions improve with physiotherapy alone but some patients may require injections. For patients with longstanding problems surgical treatment may be beneficial. The type of surgery would depend on the cause of the problem. 5. Adductor Tendonitis and Pubic Symphisitis Inflammation of adductor tendons can cause groin pain. They are common in runners and athletes and difficult to distinguish from pain arising from hip joint. Once again a full assessment is recommended. Most cases resolve with physiotherapy and/or injections. 6. Sports injuries Avulsion injuries of the tendons around the hip may occur during sports and athletic activities. Specifically, avulsion of the rectus femoris, adductor tendons or hamstring tendons. Surgical repair may be required in some patients. Conclusions Many conditions can cause pain in and around the hip joint in adults. Early and thorough assessment is recommended, particularly in younger adults, to determine the cause and to enable hip preservation surgery to be carried out when indicated.
20 References 1. Hogervorst T. Osteoarthritis: a consequence of evolution? Bone Jt 360 [Internet] Feb 1 [cited 2018 Feb 14];1(1):2 6. Available from: American Academy of Family Physicians. JJ, Furukawa M. American family physician. [Internet]. Vol. 89, American Family Physician. American Academy of Family Physicians; 1970 [cited 2018 Feb 14] p. Available from:
Adolescent Hip Dysplasia
 Adolescent Hip Dysplasia The hip is a "ball-and-socket" joint. In a normal hip, the ball at the upper end of the femur (thighbone) fits firmly into the socket, which is a curved portion of the pelvis called
Adolescent Hip Dysplasia The hip is a "ball-and-socket" joint. In a normal hip, the ball at the upper end of the femur (thighbone) fits firmly into the socket, which is a curved portion of the pelvis called
Hip arthroscopy. Anatomy The hip is functionally a ball and socket joint.
 Hip arthroscopy The term arthroscopy (or keyhole surgery) refers to the viewing of the inside of a joint through a small operating telescope. First described in the 1970s, arthroscopic techniques have
Hip arthroscopy The term arthroscopy (or keyhole surgery) refers to the viewing of the inside of a joint through a small operating telescope. First described in the 1970s, arthroscopic techniques have
Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries. The Hip.
 Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries The Hip INTRODUCTION THE HIP The hip is a ball-and-socket joint. The socket is formed by the acetabulum, which is part
Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries The Hip INTRODUCTION THE HIP The hip is a ball-and-socket joint. The socket is formed by the acetabulum, which is part
Young Adult Hip problems. Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth)
 Young Adult Hip problems Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth) RNOH founded 1837 by William Little 14 year old presenting with limp Knee pain on and off 4 months Limps Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth) The Royal
Young Adult Hip problems Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth) RNOH founded 1837 by William Little 14 year old presenting with limp Knee pain on and off 4 months Limps Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth) The Royal
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) of the Hip 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) of the Hip 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
The Young Adult Hip: FAI. Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California
 The Young Adult Hip: FAI Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California Introduction Femoroacetabular Impingment(FAI) Presentation and Exam Imaging Surgical Management
The Young Adult Hip: FAI Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California Introduction Femoroacetabular Impingment(FAI) Presentation and Exam Imaging Surgical Management
Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Athletes
 Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Athletes John P Salvo, MD Sports Medicine Rothman Institute Philadelphia, PA EATA Annual Meeting January, 2011 Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Anatomy History Physical Exam
Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Athletes John P Salvo, MD Sports Medicine Rothman Institute Philadelphia, PA EATA Annual Meeting January, 2011 Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Anatomy History Physical Exam
Hip Arthroscopy Indications and Latest Techniques
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/hip-arthroscopy-indications-and-latesttechniques/3801/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/hip-arthroscopy-indications-and-latesttechniques/3801/
Thousand Oaks High School AP Research STEM
 Investigating open surgical and arthroscopic surgical treatments and non-surgical alternatives for femoral acetabular impingement and torn acetabular labrum Thousand Oaks High School AP Research STEM 2
Investigating open surgical and arthroscopic surgical treatments and non-surgical alternatives for femoral acetabular impingement and torn acetabular labrum Thousand Oaks High School AP Research STEM 2
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip Sports-related injuries require specialized care to promote optimum healing. Whether you are a weekend jogger or tennis player, a professional soccer player
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip Sports-related injuries require specialized care to promote optimum healing. Whether you are a weekend jogger or tennis player, a professional soccer player
CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE
 Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems?
 What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems? Why is Hip pain so common NOW? Greater awareness More accurate imaging MRI Fashionable?? Geography Arthroscopy used to be OP now FAI! Why is Hip pain so
What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems? Why is Hip pain so common NOW? Greater awareness More accurate imaging MRI Fashionable?? Geography Arthroscopy used to be OP now FAI! Why is Hip pain so
Labral Tears/FAI. Andrew Parker, MD
 Labral Tears/FAI Andrew Parker, MD Athletic Hip Injuries Incidence of hip injuries has increased dramatically over the last decade In part due to better recognition with improved imaging and arthroscopy,
Labral Tears/FAI Andrew Parker, MD Athletic Hip Injuries Incidence of hip injuries has increased dramatically over the last decade In part due to better recognition with improved imaging and arthroscopy,
What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults
 What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery I have no relevant disclosures. 2 1 Most
What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery I have no relevant disclosures. 2 1 Most
A Patient s Guide to Arthroscopy of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Arthroscopy of the Hip Introduction A hip arthroscopy is a procedure where a small video camera attached to a fiberoptic lens is inserted into the hip joint to allow a surgeon to see
A Patient s Guide to Arthroscopy of the Hip Introduction A hip arthroscopy is a procedure where a small video camera attached to a fiberoptic lens is inserted into the hip joint to allow a surgeon to see
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
FAQ s: Hip Arthroscopy with Dr. Boyle
 AUT Millennium, 17 Antares Place Telephone: 09 281 6733 Mairangi Bay, Auckland 0632 Fax: 09 479 3805 www.matthewboyle.co.nz office@matthewboyle.co.nz FAQ s: Hip Arthroscopy with Dr. Boyle What is hip arthroscopy?
AUT Millennium, 17 Antares Place Telephone: 09 281 6733 Mairangi Bay, Auckland 0632 Fax: 09 479 3805 www.matthewboyle.co.nz office@matthewboyle.co.nz FAQ s: Hip Arthroscopy with Dr. Boyle What is hip arthroscopy?
Relieving Hip Pain. Austin W. Chen M.D.
 Relieving Hip Pain Austin W. Chen M.D. A little bit about me From Pittsburgh, PA Undergrad at U. of Notre Dame Medical School and Orthopaedic Surgery Residency at U. of Illinois Chicago Sports Medicine
Relieving Hip Pain Austin W. Chen M.D. A little bit about me From Pittsburgh, PA Undergrad at U. of Notre Dame Medical School and Orthopaedic Surgery Residency at U. of Illinois Chicago Sports Medicine
Periacetabular Osteotomy (PAO)
 Periacetabular Osteotomy (PAO) At the top of your thigh bone, the femur, is a ball shaped structure called the femoral head, which fits in a socket in the pelvis, called the acetabulum. Both of these structures
Periacetabular Osteotomy (PAO) At the top of your thigh bone, the femur, is a ball shaped structure called the femoral head, which fits in a socket in the pelvis, called the acetabulum. Both of these structures
Adult Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD
 Adult Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of Orthopedic Surgery & Pediatrics NYU Langone Medical Center & NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases Overview Adult hip
Adult Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of Orthopedic Surgery & Pediatrics NYU Langone Medical Center & NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases Overview Adult hip
STAIRS. What s Hip: Top 5 Hip Problems in Primary Care. I have no relevant disclosures. Top 5 (or 6) Pathologies. Big 3- Questions to Ask
 I have no relevant disclosures. What s Hip: Top 5 Hip Problems in Primary Care Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery December, 2015
I have no relevant disclosures. What s Hip: Top 5 Hip Problems in Primary Care Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery December, 2015
Stephanie W. Mayer, MD. Director of Child and Young Adult Hip Preservation Sports Medicine Center Children s Hospital Colorado
 Stephanie W. Mayer, MD Director of Child and Young Adult Hip Preservation Sports Medicine Center Children s Hospital Colorado University of Colorado Sports Medicine Assistant Team Physician, Colorado Avalanche
Stephanie W. Mayer, MD Director of Child and Young Adult Hip Preservation Sports Medicine Center Children s Hospital Colorado University of Colorado Sports Medicine Assistant Team Physician, Colorado Avalanche
Hip Preservation Timothy J Sauber MD Orthopaedic Update March 22, 2015 Nemacolin Woodlands Resort
 Hip Preservation Timothy J Sauber MD Orthopaedic Update March 22, 2015 Nemacolin Woodlands Resort Disclosures No disclosures relevant to this topic Objectives Evaluate and recognize common hip pathology
Hip Preservation Timothy J Sauber MD Orthopaedic Update March 22, 2015 Nemacolin Woodlands Resort Disclosures No disclosures relevant to this topic Objectives Evaluate and recognize common hip pathology
Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics)
 Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Northwick Park Hospital 107 Harley Street RSM 16 th September 2010 Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee
Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Northwick Park Hospital 107 Harley Street RSM 16 th September 2010 Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee
A patient s guide to: Arthroscopy of the Hip
 A patient s guide to: Arthroscopy of the Hip Brian J. White MD Assistant Team Physician Denver Nuggets Western Orthopaedics - Denver, Colorado Introduction This is designed to provide you with a better
A patient s guide to: Arthroscopy of the Hip Brian J. White MD Assistant Team Physician Denver Nuggets Western Orthopaedics - Denver, Colorado Introduction This is designed to provide you with a better
Labral Tears / Femoro- Acetabular Impingement / Hip Arthroscopy/THA. Dr Allen Turnbull Hip and Knee Surgery
 Labral Tears / Femoro- Acetabular Impingement / Hip Arthroscopy/THA Hip Anatomy Labrum Fovea Femoral Head Articular Cartilage Ligamentum Teres Labral Tears Function of Labrum Deepens acetabulum by 20%
Labral Tears / Femoro- Acetabular Impingement / Hip Arthroscopy/THA Hip Anatomy Labrum Fovea Femoral Head Articular Cartilage Ligamentum Teres Labral Tears Function of Labrum Deepens acetabulum by 20%
P.O. Box Sierra Park Road Mammoth Lakes, CA Orthopedic Surgery & Sports Medicine
 P.O. Box 660 85 Sierra Park Road Mammoth Lakes, CA 93546 SHOULDER: Instability Dislocation Labral Tears The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body, but to have this amount of motion, it is also
P.O. Box 660 85 Sierra Park Road Mammoth Lakes, CA 93546 SHOULDER: Instability Dislocation Labral Tears The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body, but to have this amount of motion, it is also
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
THE HIP. Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness.
 THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular rim during normal hip range of motion.
 RIM SYNDROME [femoroacetabular impingement] It has been suggested to be a preosteoarthritic mechanism. The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular
RIM SYNDROME [femoroacetabular impingement] It has been suggested to be a preosteoarthritic mechanism. The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular
Non-arthritic anterior hip pain in the younger patient: examination and intervention strategies
 Non-arthritic anterior hip pain in the younger patient: examination and intervention strategies Melodie Kondratek, PT, DScPT, OMPT Bryan Kuhlman, PT, DPT, OMPT Oakland University Orthopedic Spine and Sports
Non-arthritic anterior hip pain in the younger patient: examination and intervention strategies Melodie Kondratek, PT, DScPT, OMPT Bryan Kuhlman, PT, DPT, OMPT Oakland University Orthopedic Spine and Sports
The Focused Hip Examination of the Pre-arthritic, Athletic Patient. Adam Anz, MD Andrews Institute Gulf Breeze, Florida
 The Focused Hip Examination of the Pre-arthritic, Athletic Patient Adam Anz, MD Andrews Institute Gulf Breeze, Florida Correct Diagnosis: - 35% History - 30 % Physical Exam - 30% Plain X-rays - 5% MRI
The Focused Hip Examination of the Pre-arthritic, Athletic Patient Adam Anz, MD Andrews Institute Gulf Breeze, Florida Correct Diagnosis: - 35% History - 30 % Physical Exam - 30% Plain X-rays - 5% MRI
Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016
 Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016 Disclosures No Disclosures to report Questions Does FAI lead to early development of osteoarthritis? Is surgical correction an effective treatment for FAI? Who
Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016 Disclosures No Disclosures to report Questions Does FAI lead to early development of osteoarthritis? Is surgical correction an effective treatment for FAI? Who
HIP ARTHROSCOPY. A Patient s Guide. Guidance prepared on behalf of the International Society for Hip Arthroscopy (
 HIP ARTHROSCOPY A Patient s Guide Guidance prepared on behalf of the International Society for Hip Arthroscopy (www.isha.net) Authors: Singh PJ *, O Donnell JM **, Pritchard MG ** * Nuffield Orthopaedic
HIP ARTHROSCOPY A Patient s Guide Guidance prepared on behalf of the International Society for Hip Arthroscopy (www.isha.net) Authors: Singh PJ *, O Donnell JM **, Pritchard MG ** * Nuffield Orthopaedic
Evaluation of Hip Pain in Adults. Jerry Ahluwalia, M.D. November 13, 2015
 Evaluation of Hip Pain in Adults Jerry Ahluwalia, M.D. November 13, 2015 Objectives Develop a better understanding of the differential diagnosis of hip pain in active young adults Appreciate key points
Evaluation of Hip Pain in Adults Jerry Ahluwalia, M.D. November 13, 2015 Objectives Develop a better understanding of the differential diagnosis of hip pain in active young adults Appreciate key points
Hip Pain in the Athlete: A Diagnostic Challenge
 : A Diagnostic Challenge Matthew Gimre MD Sports Medicine 11 th Annual Sports Medicine Conference Presented June 17, 2017 on: Month day, Year Presented to: Insert relevant presenter information Calibri
: A Diagnostic Challenge Matthew Gimre MD Sports Medicine 11 th Annual Sports Medicine Conference Presented June 17, 2017 on: Month day, Year Presented to: Insert relevant presenter information Calibri
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint. Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa
 The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
A Patient s Guide to Arthroscopy of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Arthroscopy of the Hip 6767 Lake Woodlands Drive, Suite F, The Woodlands, TX 77382 20639 Kuykendahl Road, Suite 200, Spring, TX 77379 The Woodlands & Spring, TX. DISCLAIMER: The information
A Patient s Guide to Arthroscopy of the Hip 6767 Lake Woodlands Drive, Suite F, The Woodlands, TX 77382 20639 Kuykendahl Road, Suite 200, Spring, TX 77379 The Woodlands & Spring, TX. DISCLAIMER: The information
Sports Medicine and Radiology
 Sports Medicine and Radiology The judicious utilization of a thorough history and physical examination and appropriately applied imaging studies will allow for accurate diagnosis and treatment of athletic
Sports Medicine and Radiology The judicious utilization of a thorough history and physical examination and appropriately applied imaging studies will allow for accurate diagnosis and treatment of athletic
A patient guide to Hip Impingement Non-Surgical Management. Mr Sanjeev Patil Miss Louise Duncan Mr Frank Gilroy
 A patient guide to Hip Impingement Non-Surgical Management Mr Sanjeev Patil Miss Louise Duncan Mr Frank Gilroy Contents Page: 1 Cover 2 Contents 3 Hip impingement information 4 Conservative rehabilitation
A patient guide to Hip Impingement Non-Surgical Management Mr Sanjeev Patil Miss Louise Duncan Mr Frank Gilroy Contents Page: 1 Cover 2 Contents 3 Hip impingement information 4 Conservative rehabilitation
Hip Arthroscopy. Christopher J. Utz, MD. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati
 Hip Arthroscopy Christopher J. Utz, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati Disclosures I have no disclosures relevant to this topic. Outline 1. Brief History 2. Review of
Hip Arthroscopy Christopher J. Utz, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati Disclosures I have no disclosures relevant to this topic. Outline 1. Brief History 2. Review of
A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip Iain is a specialist in musculoskeletal imaging and the diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain. This information is provided with the hope that you can
A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip Iain is a specialist in musculoskeletal imaging and the diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain. This information is provided with the hope that you can
HIP INJURY MEDICAL, SCIENTIFIC AND WELFARE COMMITTEE. Lúnasa SLIPPED EPIPHYSIS WHAT IS A SLIPPED FEMORAL EPIPHYSIS?
 HIP INJURY Lúnasa 2013 MEDICAL, SCIENTIFIC AND WELFARE COMMITTEE 1. SLIPPED EPIPHYSIS WHAT IS A SLIPPED FEMORAL EPIPHYSIS? The femoral epiphysis is the ball of the hip joint in a child. In this condition,
HIP INJURY Lúnasa 2013 MEDICAL, SCIENTIFIC AND WELFARE COMMITTEE 1. SLIPPED EPIPHYSIS WHAT IS A SLIPPED FEMORAL EPIPHYSIS? The femoral epiphysis is the ball of the hip joint in a child. In this condition,
Hip Injuries in the Workers Compensation Arena: Diagnosis and Treatment. Joshua S Hornstein, MD TOG Institute
 Hip Injuries in the Workers Compensation Arena: Diagnosis and Treatment Joshua S Hornstein, MD TOG Orthopaedics@Rothman Institute Disclosures No Relevant Disclosures Objectives Basic Anatomy Pathology
Hip Injuries in the Workers Compensation Arena: Diagnosis and Treatment Joshua S Hornstein, MD TOG Orthopaedics@Rothman Institute Disclosures No Relevant Disclosures Objectives Basic Anatomy Pathology
CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT
 SPORTS REHABILITATION CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT A case study and rationale for treatment Written by Joanne Kemp and Kay Crossley, Australia BACKGROUND The hip joint and FAI
SPORTS REHABILITATION CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT A case study and rationale for treatment Written by Joanne Kemp and Kay Crossley, Australia BACKGROUND The hip joint and FAI
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear and tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is
Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear and tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is
UNDERSTANDING ARTHROSCOPY
 UNDERSTANDING ARTHROSCOPY Diagnosing and Treating Your Joint Problem Looking into a Problem Joint Whether you re taking a step or raising your hand, your joints help you move freely. A worn, torn, or injured
UNDERSTANDING ARTHROSCOPY Diagnosing and Treating Your Joint Problem Looking into a Problem Joint Whether you re taking a step or raising your hand, your joints help you move freely. A worn, torn, or injured
Anatomy Your shoulder is made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle).
 Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH
 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH Peter G Gerbino, MD, FACSM Orthopedic Surgeon Monterey Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Monterey, CA TPC, San Diego, 2017 The lecturer has no
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH Peter G Gerbino, MD, FACSM Orthopedic Surgeon Monterey Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Monterey, CA TPC, San Diego, 2017 The lecturer has no
Joints of the lower limb
 Joints of the lower limb 1-Type: Hip joint Synovial ball-and-socket joint 2-Articular surfaces: a- head of femur b- lunate surface of acetabulum Which is deepened by the fibrocartilaginous labrum acetabulare
Joints of the lower limb 1-Type: Hip joint Synovial ball-and-socket joint 2-Articular surfaces: a- head of femur b- lunate surface of acetabulum Which is deepened by the fibrocartilaginous labrum acetabulare
GET HIP! CAPA 2015 Annual Conference WHAT IS HIP? HIP JOINT. Bradford H. Stiles, M.D., FAAFP
 GET HIP! Bradford H. Stiles, M.D., FAAFP WHAT IS HIP? HIP JOINT Synovial ball-and-socket joint Articulation between femoral head and acetabulum Acetabulum formed by the confluence of pelvis bones (ilium,
GET HIP! Bradford H. Stiles, M.D., FAAFP WHAT IS HIP? HIP JOINT Synovial ball-and-socket joint Articulation between femoral head and acetabulum Acetabulum formed by the confluence of pelvis bones (ilium,
hip pathology w mccormick 2017 mccormickortho.com
 hip pathology w mccormick 2017 mccormickortho.com overview classification common hip pathologies FAI GT pain snapping workup treatments sample cases rehabilitation outcomes/complications hip pathology
hip pathology w mccormick 2017 mccormickortho.com overview classification common hip pathologies FAI GT pain snapping workup treatments sample cases rehabilitation outcomes/complications hip pathology
Osteochondritis Dissecans
 Osteochondritis Dissecans Introduction Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) is a problem that affects the knee, mostly at the end of the big bone of the thigh (the femur). A joint surface damaged by OCD doesn't
Osteochondritis Dissecans Introduction Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) is a problem that affects the knee, mostly at the end of the big bone of the thigh (the femur). A joint surface damaged by OCD doesn't
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Bone Bangalore. Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal
 Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Shoulder Instability
 J F de Beer, K van Rooyen, D Bhatia Shoulder Instability INSTABILITY means that the shoulder dislocates completely (dislocation) or partially (subluxation). Anatomy The shoulder consists of a ball (humeral
J F de Beer, K van Rooyen, D Bhatia Shoulder Instability INSTABILITY means that the shoulder dislocates completely (dislocation) or partially (subluxation). Anatomy The shoulder consists of a ball (humeral
SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY
 Página 1 de 6 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "37 - HIP DISLOCATIONS
Página 1 de 6 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "37 - HIP DISLOCATIONS
SURGICAL Technique Guide. Struan H Coleman MD, PhD
 SURGICAL Technique Guide Struan H Coleman MD, PhD THE AUTHOR Struan H. Coleman MD, PhD, specialises in Sports Medicine at Hospital for Special Surgery where he treats orthopedic conditions of the shoulder,
SURGICAL Technique Guide Struan H Coleman MD, PhD THE AUTHOR Struan H. Coleman MD, PhD, specialises in Sports Medicine at Hospital for Special Surgery where he treats orthopedic conditions of the shoulder,
MR Imaging in Athlete s Hip/Pelvis
 MR Imaging in Athlete s Hip/Pelvis Tara Lawrimore, MD FRCPC Department of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School No disclosures MR and Hip Pain in the
MR Imaging in Athlete s Hip/Pelvis Tara Lawrimore, MD FRCPC Department of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School No disclosures MR and Hip Pain in the
Review causes of hip and groin pain in athlete Discuss indications for hip arthroscopy Review, if any, history & physical findings of a patient who
 Review causes of hip and groin pain in athlete Discuss indications for hip arthroscopy Review, if any, history & physical findings of a patient who may benefit from hip arthroscopy Review portal placement
Review causes of hip and groin pain in athlete Discuss indications for hip arthroscopy Review, if any, history & physical findings of a patient who may benefit from hip arthroscopy Review portal placement
Hip Impingement and Arthritis: Preservation vs. Total Hip Arthroplasty. Faculty Disclosures. Objectives 11/17/2017
 Hip Impingement and Arthritis: Preservation vs. Total Hip Arthroplasty Jonathan R. Schiller, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopedics Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University Director, Adolescent
Hip Impingement and Arthritis: Preservation vs. Total Hip Arthroplasty Jonathan R. Schiller, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopedics Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University Director, Adolescent
Hip Arthroscopy Booklet
 Hip Arthroscopy Booklet 2. Hip Anatomy The bones that make up the hip joint are the femur (the thighbone) and the pelvis. At the top end of the femur is a ball called the femoral head. The femoral head
Hip Arthroscopy Booklet 2. Hip Anatomy The bones that make up the hip joint are the femur (the thighbone) and the pelvis. At the top end of the femur is a ball called the femoral head. The femoral head
Many fields are derived from the existing NJR. John Timperley MB ChB FRCS (Ed) DPhil (Oxon) Vice President British Hip Society
 Minimum Dataset for BHS Non Arthropasty Hip Surgery Database Please note: Many fields are derived from the existing NJR John Timperley MB ChB FRCS (Ed) DPhil (Oxon) Vice President British Hip Society 1
Minimum Dataset for BHS Non Arthropasty Hip Surgery Database Please note: Many fields are derived from the existing NJR John Timperley MB ChB FRCS (Ed) DPhil (Oxon) Vice President British Hip Society 1
Welcome to the Royal Orthopaedic Hospital (ROH). For further information please visit
 Produced: Feb2012 Ref: 011/02 Author: Directorate for Large Joints Review: Feb 2014 Royal Orthopaedic Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Hip Arthroscopy Welcome to the Royal Orthopaedic
Produced: Feb2012 Ref: 011/02 Author: Directorate for Large Joints Review: Feb 2014 Royal Orthopaedic Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Hip Arthroscopy Welcome to the Royal Orthopaedic
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Page 1 of 8 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis
Page 1 of 8 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis
3/18/18. Adolescent Hip Injuries. Adolescents with Hip Injuries DISCLOSURES
 Adolescent Hip Injuries Henry Bone Ellis, Jr., MD DFW Sports Medicine Symposium March 24, 2018 DISCLOSURES Royalties and stock options Consulting income Smith and Nephew Other support Research on Osteochondritis
Adolescent Hip Injuries Henry Bone Ellis, Jr., MD DFW Sports Medicine Symposium March 24, 2018 DISCLOSURES Royalties and stock options Consulting income Smith and Nephew Other support Research on Osteochondritis
Shoulder Pathologies
 Shoulder Pathologies In its early stages, AC joint osteoarthritis usually causes pain and tenderness in the front of the shoulder around the joint. The pain is often worse when the arm is brought
Shoulder Pathologies In its early stages, AC joint osteoarthritis usually causes pain and tenderness in the front of the shoulder around the joint. The pain is often worse when the arm is brought
Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX Tel#
 Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX 78240 www.saspine.com Tel# 210-487-7463 PATIENT GUIDE TO SHOULDER INSTABILITY LABRAL (BANKART) REPAIR / CAPSULAR SHIFT WHAT IS
Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX 78240 www.saspine.com Tel# 210-487-7463 PATIENT GUIDE TO SHOULDER INSTABILITY LABRAL (BANKART) REPAIR / CAPSULAR SHIFT WHAT IS
A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
The Hip Joint. Exercises and Injuries
 The Hip Joint Exercises and Injuries Pelvis Abnormalities To appreciate the abnormalities that may occur, picture a box around the pelvis. The two most common situations are: 1.the pelvis is tilted forward
The Hip Joint Exercises and Injuries Pelvis Abnormalities To appreciate the abnormalities that may occur, picture a box around the pelvis. The two most common situations are: 1.the pelvis is tilted forward
The Hip Joint. Shenequia Howard David Rivera
 The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Hip Arthroscopy Procedures
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Hip Arthroscopy Procedures The hip joint is composed of the femur (the thigh bone), and the acetabulum (the socket which is from the three
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Hip Arthroscopy Procedures The hip joint is composed of the femur (the thigh bone), and the acetabulum (the socket which is from the three
The hip: Built for endurance and mobility
 The hip: Built for endurance and mobility The hip joint Some anatomical landmarks Innominate Ilium, pubis, ischium Sacrum Iliac crests Asis Psis Pubic tubercle Acetabulum Femur Head of femur Neck of femur
The hip: Built for endurance and mobility The hip joint Some anatomical landmarks Innominate Ilium, pubis, ischium Sacrum Iliac crests Asis Psis Pubic tubercle Acetabulum Femur Head of femur Neck of femur
Hip Replacement - Anterior
 Hip Replacement - Anterior Anterior hip replacement surgery is an alternative to hip replacements where the surgeon accesses the hip joint from the side or through the buttocks. The anterior procedure
Hip Replacement - Anterior Anterior hip replacement surgery is an alternative to hip replacements where the surgeon accesses the hip joint from the side or through the buttocks. The anterior procedure
SHOULDER IMPINGEMENT / ROTATOR CUFF TENDONITIS / SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS
 SHOULDER IMPINGEMENT / ROTATOR CUFF TENDONITIS / SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS The terms impingement, rotator cuff tendonitis, and subacromial bursitis, all refer to a spectrum of the same condition. Anatomy The
SHOULDER IMPINGEMENT / ROTATOR CUFF TENDONITIS / SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS The terms impingement, rotator cuff tendonitis, and subacromial bursitis, all refer to a spectrum of the same condition. Anatomy The
Femoroacetabular Impingement in the Throwing Athlete. Michael Banffy, MD Sports Medicine, Hip Preservation Kerlan Jobe Institute
 Femoroacetabular Impingement in the Throwing Athlete Michael Banffy, MD Sports Medicine, Hip Preservation Kerlan Jobe Institute Disclosures None Baseball Hip Injuries - Background Abdominal/groin injuries
Femoroacetabular Impingement in the Throwing Athlete Michael Banffy, MD Sports Medicine, Hip Preservation Kerlan Jobe Institute Disclosures None Baseball Hip Injuries - Background Abdominal/groin injuries
SHOULDER INSTABILITY
 SHOULDER INSTABILITY Your shoulder is the most flexible joint in your body, allowing you to throw fastballs, lift a heavy suitcase, scratch your back, and reach in almost any direction. Your shoulder joint
SHOULDER INSTABILITY Your shoulder is the most flexible joint in your body, allowing you to throw fastballs, lift a heavy suitcase, scratch your back, and reach in almost any direction. Your shoulder joint
HIP_CASE 2_OA. Hip Forces. Function of the Hip. Property of VOMPTI, LLC. For Use of Participants Only. No Use or Reproduction Without Consent 1
 HIP_CASE 2_OA Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Eric Magrum DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT 62 yo female AM stiffness Hip pain diffuse, variable ant>lateral>post Gradual onset Tennis
HIP_CASE 2_OA Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Eric Magrum DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT 62 yo female AM stiffness Hip pain diffuse, variable ant>lateral>post Gradual onset Tennis
Shoulder Instability
 Shoulder Instability The shoulder is your body s most flexible joint. It is designed to let the arm move in almost any direction. But this flexibility has a price, making the joint prone to injury. The
Shoulder Instability The shoulder is your body s most flexible joint. It is designed to let the arm move in almost any direction. But this flexibility has a price, making the joint prone to injury. The
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears
 A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Shoulder Instability. Fig 1: Intact labrum and biceps tendon
 Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
Subject: Hip Arthroscopy and Open, Non-Arthroplasty Hip Repair
 02-20000-55 Original Effective Date: 10/15/16 Reviewed: 06/28/18 Revised: 07/15/18 Subject: Hip Arthroscopy and Open, Non-Arthroplasty Hip Repair THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION,
02-20000-55 Original Effective Date: 10/15/16 Reviewed: 06/28/18 Revised: 07/15/18 Subject: Hip Arthroscopy and Open, Non-Arthroplasty Hip Repair THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION,
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Hip Arthroscopy Procedures
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Hip Arthroscopy Procedures The hip joint is composed of the femur (the thigh bone), and the acetabulum (the socket which is from the three
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Hip Arthroscopy Procedures The hip joint is composed of the femur (the thigh bone), and the acetabulum (the socket which is from the three
ANATOMY OF THE HIP JOINT And how it is related to groin pain
 sports radiology ANATOMY OF THE HIP JOINT And how it is related to groin pain Written by Miquel Dalmau-Pastor, Jordi Vega and Pau Golanó, Spain INTRODUCTION Groin pain refers to discomfort in the area
sports radiology ANATOMY OF THE HIP JOINT And how it is related to groin pain Written by Miquel Dalmau-Pastor, Jordi Vega and Pau Golanó, Spain INTRODUCTION Groin pain refers to discomfort in the area
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears
 A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears Sports-related injuries require specialized care to promote optimum healing. Whether you are a weekend jogger or tennis player, a professional soccer player or marathon
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears Sports-related injuries require specialized care to promote optimum healing. Whether you are a weekend jogger or tennis player, a professional soccer player or marathon
A Patient s Guide to Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee
 A Patient s Guide to Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
A Patient s Guide to Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip. William T. Grant, MD
 A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C
A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C
When the patient presents at the GP surgery with Hip pain. Investigations, Input & Referral
 When the patient presents at the GP surgery with Hip pain Investigations, Input & Referral GP with an interest in Pain Management How common is hip pain? Around 450 patients per 100,000 population will
When the patient presents at the GP surgery with Hip pain Investigations, Input & Referral GP with an interest in Pain Management How common is hip pain? Around 450 patients per 100,000 population will
Overview. Overview. Introduction. Introduction Anatomy History Examination Common Disorders. Introduction Anatomy History Examination Common Disorders
 Common Hip Disorders in Figure Skaters 14 th Annual Meeting of Sports Medicine and Science in Figure Skating January 25, 2009 8:15-8:45am Robert J. Dimeff, MD Medical Director of Sports Medicine Overview
Common Hip Disorders in Figure Skaters 14 th Annual Meeting of Sports Medicine and Science in Figure Skating January 25, 2009 8:15-8:45am Robert J. Dimeff, MD Medical Director of Sports Medicine Overview
Pelvis and hip joints: from anatomy to sports trauma
 Pelvis and hip joints: from anatomy to sports trauma Sports Medicine Program, Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel-Aviv University, Israel Iftach Hetsroni, MD Sports Medicine Injuries Service Meir General
Pelvis and hip joints: from anatomy to sports trauma Sports Medicine Program, Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel-Aviv University, Israel Iftach Hetsroni, MD Sports Medicine Injuries Service Meir General
Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis
 Hip Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis The terms hip and pelvis are frequently used interchangeably, but strictly speaking, the pelvis is a girdle of bones and the hip is a joint. The pelvis consists of The sacrum
Hip Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis The terms hip and pelvis are frequently used interchangeably, but strictly speaking, the pelvis is a girdle of bones and the hip is a joint. The pelvis consists of The sacrum
A Guide to Common Ankle Injuries
 A Guide to Common Ankle Injuries Learn About: Common ankle injuries Feet and Ankle Diagnosis and Treatment Ankle exercises Beginning your recovery Frequently asked questions Do s and Don t s Arthroscopy
A Guide to Common Ankle Injuries Learn About: Common ankle injuries Feet and Ankle Diagnosis and Treatment Ankle exercises Beginning your recovery Frequently asked questions Do s and Don t s Arthroscopy
Complex Fractures and Hip Dislocations
 IMAGING OF HIP PAIN Patients may present with acute (< 2 weeks) or chronic hip pain. Acute pain may be related or not related to an acute traumatic event such as fall or trauma from a motor vehicle accident.
IMAGING OF HIP PAIN Patients may present with acute (< 2 weeks) or chronic hip pain. Acute pain may be related or not related to an acute traumatic event such as fall or trauma from a motor vehicle accident.
Evaluation of the Hip
 Evaluation of the Hip Adam Lewno, DO PCSM Fellow, University of Michigan Primary Care Sports Update 2017 Disclosures Financial: None Images: I would like to acknowledge the work of the original owners
Evaluation of the Hip Adam Lewno, DO PCSM Fellow, University of Michigan Primary Care Sports Update 2017 Disclosures Financial: None Images: I would like to acknowledge the work of the original owners
This guideline is structured with clinical indications outlined for each of the following applications: Arthroscopic; Open, non-arthroplasty;
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines: HIP ARTHROSCOPY & OPEN, NON- ARTHROPLASTY HIP REPAIR CPT CODES: Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) Hip Surgery: 29914, 29915, 29916 Hip Surgery Other:
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines: HIP ARTHROSCOPY & OPEN, NON- ARTHROPLASTY HIP REPAIR CPT CODES: Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) Hip Surgery: 29914, 29915, 29916 Hip Surgery Other:
Hip Region. PHTY2020: Lecture
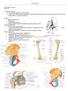 Region PHTY2020: Lecture 2.1 29.02.16 Functional Overview Transfer body weight form trunk to legs Allows leg to adopt numerous positions needed for standing, walking running, stairs, sitting and other
Region PHTY2020: Lecture 2.1 29.02.16 Functional Overview Transfer body weight form trunk to legs Allows leg to adopt numerous positions needed for standing, walking running, stairs, sitting and other
Arthritis of the Shoulder
 Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210827, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210827 Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement Claudio Rafols, Juan
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210827, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210827 Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement Claudio Rafols, Juan
