ACUTE AND CHRONIC OSTEOMYELITIS
|
|
|
- Rodger Dennis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ACUTE AND CHRONIC OSTEOMYELITIS
2 DEFINITION Inflammation of the bone caused by an infecting organism
3 HISTORY In the early 1900 s about 20% of patients with osteomyelitis died and patients who survived had significant morbidity.
4 Introduction- Oldest known evidence of osteomyelitis fractured spine of dimetrodon permian reptile million years ago Hippocrates BC infection after fracture Nelaton credited with introducing the term osteomyelitis in
5 INTRODUCTION The key to successful management is early diagnosis and appropriate surgical and antimicrobial treatment. A multi disciplinary approach is required, involving an orthopaedic surgeon, an infectious disease specialist, and a plastic surgeon in complex cases with significant soft tissue loss.
6 CLASSIFICATION 1) The duration - acute, subacute and chronic 2) Mechanism of infection exogenous or hematogenous 3) The type of host response to the infection- pyogenic or non pyogenic
7 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS Most common type of bone infection, usually seen in children Decrease in incidence, could be due to higher standard of living and improved hygiene. Bimodal distribution- younger than 2 years, and 8-12 years More common in males
8 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS- CAUSES Caused by a bacteraemia Bacteriological seeding of bone generally is associated with other factors such as localized trauma, chronic illness, malnutrition or an inadequate immune system.
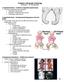
9 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY In children the infection generally involves the metaphyses of rapidly growing long bones Bacterial seeding leads to an inflammatory reaction which can cause local ischaemic necrosis of bone and subsequent abscess formation
10 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY As the abscess enlarges, intramedullary pressure increases causing cortical ischaemia, which may allow purulent material to escape through the cortex into the subperoisteal space.
11
12 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY A subperisoteal abscess then develops If left untreated this process eventually results in extensive sequetra formation and chronic osteomyelitis
13 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY In children younger than 2 years, blood vessels cross the physis, thus epiphysis may be involved Limb shortening or angular deformity may occur
14 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Joint may be involved in some caseship joint most common, especially for intraarticular physes- proximal humerus,radial neck, distal fibula Metaphysis has relatively fewer phagocytic cells than the physis or diaphysis, hence more infection here
15 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY In children older than 2 years the physis effectively acts as a barrier to the spread of a metaphyseal abscess Metaphyseal cortex thicker, hence diaphysis more at risk After physes are closed acute hematogenous osteomyelitis is much less common
16 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY After the physes are closed, infection can extend directly from the metaphysis into the epiphysis and involve the joint Septic arthritis resulting from acute hematogenous osteomyelitis generally is seen only in infants and adults.
17 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS MICROBIAL PATTERN Staphylococcus aureus most common in older children and adults Gram negative bacteria- increasing trend- vertebral Pseudomonas most common in intravenous drug abusers Salmonella in sicke cell Fungal infections in chronically ill patients on long term intravenous therapy.
18 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS MICROBIAL PATTERN Infants- staph aureus most common but group B streptococcus and gram negative coliforms Prematures staph aureus andgram negative organisms Hemophilus influenzae primarily in children 6 months to 4 years old, incidence decreased dramatically by
19 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS MICROBIAL PATTERN Ngetich, 2002 found that of children presenting with haematogenous osteomyelitis in Kenyatta national hospital the commonest isolated organism was staphylococcus aureus accounting for 29 (60.4%)of the cases, 15 (60%) of these were MRSA strains
20 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS DIAGNOSIS History and physical examination Fever and malaise Pain and local tenderness Sweliing Compartment syndrome in children
21 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS DIAGNOSIS Laboratory tests White blood cell count Erythrocyte sedimentation rate C-reactive protein checked very 2-3 days post treatment initiation Aspiration for suspected abscess
22 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS DIAGNOSIS Plain radiographs Technetium-99m bone scan +/- MRI
23 RADIOGRAPHS Soft tissue swelling Periosteal reaction Bony destruction (10-12 days)
24 BONE SCAN Can confirm diagnosis hrs after onset
25 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS TREATMENT Surgery and antibiotic treatment are complementary, in some cases antibiotics alone may cure the disease. Choice of antibiotics is based on the highest bacteriocidal activity, the least toxicity and the lowest cost
26 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS TREATMENT Nade s 5 principles of treatment 1. An appropriate antibiotic is effective before pus formation 2. Antibiotics do not sterilize avascular tissues or abscesses and such areas require surgical removal
27 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS TREATMENT- NADES PRINCIPLES 3. If such removal is effective, antibiotics should prevent their reformation and primary wound closure should be safe 4. Surgery should not damage already ischaemic bone and soft tissue 5. Antibiotics should be continued after surgery
28 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS TREATMENT The two main indications for surgery in acute hematogenous osteomyelitis are: 1. The presence of an abscess requiring drainage 2. Failure of the patient to improve despite appropriate intravenous antibiotic treatment
29 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS TREATMENT- SURGERY The objective of surgery is to drain any abscess cavity and remove all non viable or necrotic tissue Subperiosteal abscess in an infant-several small holes drilled through the cortex into the medullary canal If intramedullary pus is found, a small window of bone is removed Skin is closed loosely over drains and the limb splinted
30 ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS TREATMENT Generally a 6 week course of intravenous antibiotics is given Orthopedic and infectious disease followup is continued for at least 1 year
31 SUBACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS More insidious onset and lacks severity of symptoms Indolent course hence diagnosis delayed for more than two weeks.
32 SUBACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS CLINICAL FEATURES The indolent course of subacute osteomyelitis is due to: increased host resistance decreased bacterial virulence administration of antibiotics before the onset of symptoms Systemic signs and symptoms are minimal Temperature is only mildly elevated Mild to moderate pain
33 SUBACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS INVESTIGATIONS White blood cell counts are generally normal ESR is elevated in only 50% of patients Blood cultures are usually negative Plain radiographs and bone scans generally are positive
34 SUBACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS INVESTIGATIONS S. Aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis are the predominant organisms identified in subacute osteomyelitis
35 SUBACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS BRODIE ABSCESS Localized form of subacute osteomyelitis occuring most commonly in the long bones of the lower extremeties Intermittent pain of long duration is most times the presenting compliant, along with tenderness over the affected area
36 BRODIE ABSCESS
37 SUBACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS BRODIE ABSCESS On plain radiographs appears as a lytic lesion with a rim of sclerotic bone S aureus is cultured in 50% of patients and in 20% the culture is negative The condition requires open biopsy with curetage to make the diagnosis The wound should be closed loosely over a drain
38 SUBACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS GLEDHILL CLASSIFICATION
39 SUBACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITIS TREATMENT Biopsy and curettage followed by treatment with appropriate antibiotics for all lesions that seem to be aggressive For lesions that seem to be a simple abscess in the epiphysis or metaphysis biopsy is not recommended- IV antibiotics for 48 hrs followed by a 6 week course of oral antibiotics
40 CHRONIC OSTEOMYELITIS Hallmark is infected dead bone within a compromised soft tissue envelope The infected foci within the bone are surrounded by sclerotic, relatively avascular bone covered by a thickened periosteum and scarred muscle and subcutaneous tissue
41 COM Sinus track cultures usually do not corelate with cultures obtained at bone biopsy
42 COM IN KNH 2008-= = = = = 53
43 CLASSIFICATION OF COM
44 ANATOMICAL CLASSIFICATION
45 CLASSIFICATION OF COM
46 DIAGNOSIS COM Based on Clinical laboratory and imaging studies
47 CLINICAL EVALUATION COM Skin and soft tissue integrity Tenderness Bone stability Neurovascular status of limb Presence of sinus
48 LABORATORY COM Erythrocyte sedimentation rate C reactive protein WBC count only elevated in 35% Biopsy for histological and microbiological evaluation Staphyloccocus species Anaerobes and gram negative bacilli
49 ORGANISMS IN COM Girasi, 1981 found that the commonest organisms found at the orthopaedic unit at Kenyatta national hospital, then in kabete was staphylococcus aureus which was resistant to penicillin and ampicillin
50 IMAGING STUDIES IN COM Plain X rays Cortical destruction Periosteal reaction Sequestra Sinography
51 SINOGRAPHY
52 IMAGING - Isotopic bone scanning more useful in acute than in chronic osteomyelitis Gallium scans increased uptake in areas where leucocytes and bacteria accumulate. Normal scan excludes osteomyelitis
53 COM IMAGING CT Scan Identifying sequestra Definition of cortical bone and surrounding soft tissues
54 COM IMAGING MRI Shows margins of bone and soft tissue oedema Evaluate recurrence of infection after 1 year Rim sign- well defined rim of high signal intensity surrounding the focus of active disease Sinus tracks and cellulitis
55 TREATMENT OF COM Surgical treatment mainstay Sequestrectomy Resection of scarred and infected bone and soft tissue Radical debridement Resection margins >5mm
56 SURGICAL TREATMENT OF COM Adequate debridement leaves a dead space that needs to be managed to avoid recurrence, or bony instability Skin grafts, Muscle and myocutaneous flaps Free bone transfer Papineau technique Hyperbaric oxygen therapy Vacuum dressing
57 TREATMENT OF COM Antibiotic duration is controversial 6 week is the traditional duration 1 week IV, 6 weeks of oral therapy Antibiotic polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) beads as a temporary filler of dead space Biodegradable antibiotic delivery system
58 RESECTION OR EXCISION FOR COM Resection of a segment of affected bone may be necessary to control infection With techniques of bone and soft tissue transport, massive resections can be performed and reconstructed without significant disability.
59 RESECTION OR EXCISION FOR COM
60 AMPUTATION FOR OSTEOMYELITIS Amputation indications include Arterial insufficiency Major nerve paralysis Non functional limb-stiffness, contracture Malignant change Prevalence of maliganacy arising from COM reported as 0.2 to 1.6% of cases. Most are squamous cell carcinoma, also reticulum cell carcinoma,fibrosarcoma
61 SCLEROSING OSTEOMYELITIS OF GARRE Bone is thickened and distended, but abscesses and sequestra are absent. Cause unknown Thought to caused by a low grade, possibly anaerobic bacterium
62 SCLEROSING OSTEOMYELITIS OF GARRE
63 REFERENCES Canale Terry and Beaty James (2007) Campbell s Operative Orthopaedics, Philadelphia, Mosby Ben Mbonye-Girasi (1981) Mode of Presentation and End results of Management of Haematogenous Osteomyelitis at the Orthopaedic Unit Kenyatta National Hospital over a Five Year Period. Nairobi : unpublished masters in medicine project, School of Medicine, University of Nairobi Issac K Ngetich (2002) A Study of Haematogenous Osteomyelitis in Children in Kenyatta National Hospital Kenya. Nairobi : unpublished masters in medicine project, School of Medicine, University of Nairobi Lewis R P, Sutter V L and Finegold S M (1978) Bone Infections Involving Anaerobic Bacteria. Baltimore pub med PMID
OSTEOMYELITIS. If it occurs in adults, then the axial skeleton is the usual site.
 OSTEOMYELITIS Introduction Osteomyelitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process of the bone and its structures secondary to infection with pyogenic organisms. Pathophysiology Osteomyelitis may be
OSTEOMYELITIS Introduction Osteomyelitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process of the bone and its structures secondary to infection with pyogenic organisms. Pathophysiology Osteomyelitis may be
Osteomyelitis in infancy and childhood: A clinical and diagnostic overview M. Mearadji
 Osteomyelitis in infancy and childhood: A clinical and diagnostic overview M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Introduction Osteomyelitis is a relative common disease in infancy
Osteomyelitis in infancy and childhood: A clinical and diagnostic overview M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Introduction Osteomyelitis is a relative common disease in infancy
Prof Oluwadiya KS FMCS (Orthop) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon / Associate Professor Division of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Department of Surgery
 Prof Oluwadiya KS FMCS (Orthop) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon / Associate Professor Division of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Department of Surgery College of Health Sciences Ladoke Akintola University
Prof Oluwadiya KS FMCS (Orthop) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon / Associate Professor Division of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Department of Surgery College of Health Sciences Ladoke Akintola University
BONE AND JOINT INFECTION. Dr.Jónás Zoltán Dept.of Orthopaedics
 BONE AND JOINT INFECTION Dr.Jónás Zoltán Dept.of Orthopaedics www.ortopedia.dote.hu Order of verbal exams: The students are able to register for the exam on the Neptun system. The students pick two titles,
BONE AND JOINT INFECTION Dr.Jónás Zoltán Dept.of Orthopaedics www.ortopedia.dote.hu Order of verbal exams: The students are able to register for the exam on the Neptun system. The students pick two titles,
Acute Osteomyelitis: similar to septic arthritis but up to 40% may be afebrile swelling overlying the bone & tenderness
 Osteomyelitis / Bone and Joint Infections Bone infections in children are usually from haematogenous bacterial seeding to a single joint, usually the lower limbs, but may be multifocal. Approximately 10%
Osteomyelitis / Bone and Joint Infections Bone infections in children are usually from haematogenous bacterial seeding to a single joint, usually the lower limbs, but may be multifocal. Approximately 10%
ESPID New Bone and Joint Infection Guidelines
 ESPID New Bone and Joint Infection Guidelines Theoklis Zaoutis, MD, MSCE Professor of Pediatrics and Epidemiology Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Chief, Division of Infectious
ESPID New Bone and Joint Infection Guidelines Theoklis Zaoutis, MD, MSCE Professor of Pediatrics and Epidemiology Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Chief, Division of Infectious
OBJECTIVE INFECTION OF BONE AND JOINT CONTENT. Case. Case. Make diagnosis and treatment in bone and joint sepsis
 INFECTION OF BONE AND JOINT ธนพจน จ นทร น ม ภาคว ชาออร โธป ด กส โรงพยาบาลรามาธ บด OBJECTIVE Make diagnosis and treatment in bone and joint sepsis Prevent complications i from disease and treatment Use
INFECTION OF BONE AND JOINT ธนพจน จ นทร น ม ภาคว ชาออร โธป ด กส โรงพยาบาลรามาธ บด OBJECTIVE Make diagnosis and treatment in bone and joint sepsis Prevent complications i from disease and treatment Use
Osteomieliti STEOMIE
 OsteomielitiSTEOMIE Osteomyelitis is the inflammation of bone caused by pyogenic organisms. Major sources of infection: - haematogenous spread - tracking from adjacent foci of infection - direct inoculation
OsteomielitiSTEOMIE Osteomyelitis is the inflammation of bone caused by pyogenic organisms. Major sources of infection: - haematogenous spread - tracking from adjacent foci of infection - direct inoculation
Topics. Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities. Detection of Infection. Role of Imaging in Extremity Infection. Detection of Infection
 Topics Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities Nuttaya Pattamapaspong M.D. Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Role of imaging in extremity infection
Topics Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities Nuttaya Pattamapaspong M.D. Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Role of imaging in extremity infection
Management of Acute Haematogenous Osteomyelitis. SAPOS ICL 2017 Anthony Robertson
 Management of Acute Haematogenous Osteomyelitis SAPOS ICL 2017 Anthony Robertson Diagnosis Diagnosis RED FLAGS: Nunn, Rollinson;; SAMJ 2007 Acute hip pain in a child Infant with loss of movement in a limb
Management of Acute Haematogenous Osteomyelitis SAPOS ICL 2017 Anthony Robertson Diagnosis Diagnosis RED FLAGS: Nunn, Rollinson;; SAMJ 2007 Acute hip pain in a child Infant with loss of movement in a limb
Osteomyelitis (Inflammation of the Bone and Bone Marrow) Basics
 Osteomyelitis (Inflammation of the Bone and Bone Marrow) Basics OVERVIEW Sudden (acute) or long-term (chronic) inflammation of bone and its associated soft-tissue elements of bone marrow, endosteum (lining
Osteomyelitis (Inflammation of the Bone and Bone Marrow) Basics OVERVIEW Sudden (acute) or long-term (chronic) inflammation of bone and its associated soft-tissue elements of bone marrow, endosteum (lining
Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections
 Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections Objectives How do you to diagnose, classify and manage DFI? How do you diagnose
Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections Objectives How do you to diagnose, classify and manage DFI? How do you diagnose
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 2.417, ISSN: , Volume 3, Issue 11, December 2015
 MANAGEMENT OF PATHOLOGICAL FRACTURE SHAFT HUMERUS SECONDARY TO BACTERIAL OSTEOMYELITIS: A CASE REPORT DR. NARENDRA SINGH KUSHWAHA* DR.SHAH WALIULLAH** DR.VINEET KUMAR*** DR.VINEET SHARMA**** *Asst. Professor,
MANAGEMENT OF PATHOLOGICAL FRACTURE SHAFT HUMERUS SECONDARY TO BACTERIAL OSTEOMYELITIS: A CASE REPORT DR. NARENDRA SINGH KUSHWAHA* DR.SHAH WALIULLAH** DR.VINEET KUMAR*** DR.VINEET SHARMA**** *Asst. Professor,
Abscess. A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body.
 Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Special Imaging MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTION. Special Imaging. Special Imaging. 18yr old male pt What is it? Additional Imaging
 MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTION Additional Imaging May assist in diagnosis and, possibly, treatment Help create the picture May help differentiate from neoplasia 18yr old male pt What is it? Lymphoma Ewings
MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTION Additional Imaging May assist in diagnosis and, possibly, treatment Help create the picture May help differentiate from neoplasia 18yr old male pt What is it? Lymphoma Ewings
BONES & JOINTS INFECTION BONE TUMOURS
 BONES & JOINTS INFECTION BONE TUMOURS IMPORTANT SERIOUS CONSEQUENCE PLEASE DON T MISS!! EARLY DIAGNOSIS & PROPER TREATMENT HOW?? AWARE of THEIR EXISTENCE (Knowledge) PREPARE for THEIR OCCURRENCE A HIGH
BONES & JOINTS INFECTION BONE TUMOURS IMPORTANT SERIOUS CONSEQUENCE PLEASE DON T MISS!! EARLY DIAGNOSIS & PROPER TREATMENT HOW?? AWARE of THEIR EXISTENCE (Knowledge) PREPARE for THEIR OCCURRENCE A HIGH
Osteomyelitis: What tests I believe; When is a debridement a debridement?
 9:10 9:20 am The Infection Algorithm: Beating the Spread Better Than Vegas Odds Makers William C. McGarvey, MD Osteomyelitis: What tests I believe; When is a debridement a debridement? Osteomyelitis bone
9:10 9:20 am The Infection Algorithm: Beating the Spread Better Than Vegas Odds Makers William C. McGarvey, MD Osteomyelitis: What tests I believe; When is a debridement a debridement? Osteomyelitis bone
Mohammad Ashraf. - Bahaa Najjar. - Mousa Al-Abbadi. 1 P a g e
 - 4 - Mohammad Ashraf - Bahaa Najjar - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Fractures (cont d). Healing of fractures: There are a lot of factors determine the proper healing of the fracture. For example: Displaced
- 4 - Mohammad Ashraf - Bahaa Najjar - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Fractures (cont d). Healing of fractures: There are a lot of factors determine the proper healing of the fracture. For example: Displaced
Chapter 19 Hidradenitis Suppurativa
 1 Chapter 19 Hidradenitis Suppurativa Peter Nthumba Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic, recurrent, painful inflammatory skin disease, first described in 1833 by a French surgeon. Verneuil, another French
1 Chapter 19 Hidradenitis Suppurativa Peter Nthumba Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic, recurrent, painful inflammatory skin disease, first described in 1833 by a French surgeon. Verneuil, another French
Types of bone/joint infections. Bone and Joint Infections. Septic Arthritis. Pathogenesis. Pathogenesis. Bacterial arthritis: predisposing factors
 Bone and Joint Infections Types of bone/joint infections Arthritis (infective/septic) Osteomyelitis Prosthetic bone and joint infections Septic Arthritis Common destructive athroplasty Mono-articular Poly-articular
Bone and Joint Infections Types of bone/joint infections Arthritis (infective/septic) Osteomyelitis Prosthetic bone and joint infections Septic Arthritis Common destructive athroplasty Mono-articular Poly-articular
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida
 Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
a Total Hip Prosthesis by Clostridum perfringens. A Case Report
 Haematogenous Infection of a Total Hip Prosthesis by Clostridum perfringens. A Case Report CHAPTER 5 CHAPTER 5 5.1. Introduction In orthopaedic surgery, an infection of a prosthesis is a very serious,
Haematogenous Infection of a Total Hip Prosthesis by Clostridum perfringens. A Case Report CHAPTER 5 CHAPTER 5 5.1. Introduction In orthopaedic surgery, an infection of a prosthesis is a very serious,
STAGING, BIOPSY AND NATURAL HISTORY OF TUMORS SCOTT D WEINER MD
 STAGING, BIOPSY AND NATURAL HISTORY OF TUMORS SCOTT D WEINER MD WHAT DO YOU DO WHEN THIS SHOWS UP IN YOUR OFFICE? besides panicking KEY PRINCIPLE!!! Reactive zone is the edema, neovascularity and inflammation
STAGING, BIOPSY AND NATURAL HISTORY OF TUMORS SCOTT D WEINER MD WHAT DO YOU DO WHEN THIS SHOWS UP IN YOUR OFFICE? besides panicking KEY PRINCIPLE!!! Reactive zone is the edema, neovascularity and inflammation
Surgical Management of Osteomyelitis & Infected Hardware. Michael L. Sganga, DPM Orthopedics New England Natick, MA
 Surgical Management of Osteomyelitis & Infected Hardware Michael L. Sganga, DPM Orthopedics New England Natick, MA Disclosures None relevant to the content of this material Overview Implants Timing Tenants
Surgical Management of Osteomyelitis & Infected Hardware Michael L. Sganga, DPM Orthopedics New England Natick, MA Disclosures None relevant to the content of this material Overview Implants Timing Tenants
Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections
 Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections Christophe Van de Wiele, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Orthopedic prostheses: world market 1996 Prosthetic
Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections Christophe Van de Wiele, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Orthopedic prostheses: world market 1996 Prosthetic
Tibial Nonunions: Should I Tackle and How
 Tibial Nonunions: Should I Tackle and How Frank R. Avilucea, MD Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati Medical Center Disclosures Journal Reviewer Journal of Bone
Tibial Nonunions: Should I Tackle and How Frank R. Avilucea, MD Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati Medical Center Disclosures Journal Reviewer Journal of Bone
Case Report Acute Haematogenous Metacarpal Osteomyelitis in Children: A Case Report and Review of Literature
 Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2011, Article ID 674820, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/674820 Case Report Acute Haematogenous Metacarpal Osteomyelitis in Children: A Case Report and Review of Literature
Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2011, Article ID 674820, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/674820 Case Report Acute Haematogenous Metacarpal Osteomyelitis in Children: A Case Report and Review of Literature
Introduction. Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment
 Diabetic Foot Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment Epidemiology DM largest cause of neuropathy in N.A. 1 million DM patients in Canada Half don t know Foot ulcerations is
Diabetic Foot Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment Epidemiology DM largest cause of neuropathy in N.A. 1 million DM patients in Canada Half don t know Foot ulcerations is
Buruli ulcer disease. Epidemiology and transmission l Clinical manifestations and diagnosis l Treatment. Chapter 2
 Epidemiology and transmission l Clinical manifestations and diagnosis l Treatment Chapter 2 KEY POINTS Buruli ulcer is an infection caused by an organism called Mycobacterium ulcerans that lives in the
Epidemiology and transmission l Clinical manifestations and diagnosis l Treatment Chapter 2 KEY POINTS Buruli ulcer is an infection caused by an organism called Mycobacterium ulcerans that lives in the
34 th Annual Meeting of the European Bone and Joint Infection Society (EBJIS)
 34 th Annual Meeting of the European Bone and Joint Infection Society (EBJIS) 10-12 September 2015 Estoril, Portugal Free Paper: #135 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THREE BIOABSORBABLE ANTIBIOTIC CARRIERS IN CHRONIC
34 th Annual Meeting of the European Bone and Joint Infection Society (EBJIS) 10-12 September 2015 Estoril, Portugal Free Paper: #135 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THREE BIOABSORBABLE ANTIBIOTIC CARRIERS IN CHRONIC
Case report. Open Access. Abstract
 Open Access Case report Primary sternal osteomyelitis in a 40 days old infant: a case report and review of the literature Nikolaos S Pettas 1 *, Alexandros P Apostolopoulos 2 *, Ioannis Flieger 3 and Omiros
Open Access Case report Primary sternal osteomyelitis in a 40 days old infant: a case report and review of the literature Nikolaos S Pettas 1 *, Alexandros P Apostolopoulos 2 *, Ioannis Flieger 3 and Omiros
Interesting Case Series. Pyogenic (Suppurative) Flexor Tenosynovitis: Assessment and Management
 Interesting Case Series Pyogenic (Suppurative) Flexor Tenosynovitis: Assessment and Management Renee L. Barry, BS a,nicholass.adams,md a,b, and Matthew D. Martin, MD a,b,c a Michigan State University College
Interesting Case Series Pyogenic (Suppurative) Flexor Tenosynovitis: Assessment and Management Renee L. Barry, BS a,nicholass.adams,md a,b, and Matthew D. Martin, MD a,b,c a Michigan State University College
Pressure Injury Complications: Diagnostic Dilemmas
 Pressure Injury Complications: Diagnostic Dilemmas Aimée D. Garcia, MD, CWS, FACCWS Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Geriatrics Section Baylor College of Medicine Medical Director, Wound Clinic
Pressure Injury Complications: Diagnostic Dilemmas Aimée D. Garcia, MD, CWS, FACCWS Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Geriatrics Section Baylor College of Medicine Medical Director, Wound Clinic
Treatment of infection
 Clinica Ortopedica e Traumatologica Università degli Studi di Pavia Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Chairman: Prof. F. Benazzo Goals: - Healing of infection - Healing of fracture - Try to keep
Clinica Ortopedica e Traumatologica Università degli Studi di Pavia Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Chairman: Prof. F. Benazzo Goals: - Healing of infection - Healing of fracture - Try to keep
Pott s Puffy Tumor. Shahad Almohanna 15/1/2018
 Pott s Puffy Tumor Shahad Almohanna R2 15/1/2018 Definition First described in 1760 by Sir Percival Pott. s he originally suggested that trauma of the frontal bone was causative for this lesion, but later,
Pott s Puffy Tumor Shahad Almohanna R2 15/1/2018 Definition First described in 1760 by Sir Percival Pott. s he originally suggested that trauma of the frontal bone was causative for this lesion, but later,
Osteomyelitis Categories of Osteomyelitis
 Osteomyelitis 2017 David Mushatt, M.D., M.P.H.&T.M. Associate Professor of Medicine Chief, Tulane Adult Infectious Diseases Section Categories of Osteomyelitis Acute vs. Chronic Vertebral Diabetic foot
Osteomyelitis 2017 David Mushatt, M.D., M.P.H.&T.M. Associate Professor of Medicine Chief, Tulane Adult Infectious Diseases Section Categories of Osteomyelitis Acute vs. Chronic Vertebral Diabetic foot
-> Education -> Excellence
 Quality Conference 5/2557 Extravasations: Event -> Education -> Excellence รศ.นพ. รว ศ เร องตระก ล สาขาว ชาก มารศ ลยศาสตร ภาควชาศลยศาสตร Extravasations: Event 1. Thrombophlebitis - superficial vein 2.
Quality Conference 5/2557 Extravasations: Event -> Education -> Excellence รศ.นพ. รว ศ เร องตระก ล สาขาว ชาก มารศ ลยศาสตร ภาควชาศลยศาสตร Extravasations: Event 1. Thrombophlebitis - superficial vein 2.
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Wounds and Infections: Wound Management From the ID Physician Standpoint. Alena Klochko, MD Orlando VA Medical Center Infectious Disease Department
 Wounds and Infections: Wound Management From the ID Physician Standpoint Alena Klochko, MD Orlando VA Medical Center Infectious Disease Department Objectives Distinguish between colonization, critical
Wounds and Infections: Wound Management From the ID Physician Standpoint Alena Klochko, MD Orlando VA Medical Center Infectious Disease Department Objectives Distinguish between colonization, critical
SEPTIC ARTHRITIS. Dr Ahmed Husam Al Ahmed Rheumatologist SYRIA. University of Science and technology Hospital Sanaa Yemen 18/Dec/2014
 SEPTIC ARTHRITIS Dr Ahmed Husam Al Ahmed Rheumatologist SYRIA University of Science and technology Hospital Sanaa Yemen 18/Dec/2014 Objectives be able to define Septic Arthritis know what factors predispose
SEPTIC ARTHRITIS Dr Ahmed Husam Al Ahmed Rheumatologist SYRIA University of Science and technology Hospital Sanaa Yemen 18/Dec/2014 Objectives be able to define Septic Arthritis know what factors predispose
CIERNY CLASSIFICATION CIERNY CLASSIFICATION. Classification of Infection according to Severity LAUTENBACH CLASSIFICATION OF MUSCULO SKELETAL INFECTION
 CIERNY CLASSIFICATION Classification of Infection according to Severity E E G LAUTENBACH Division of Orthopaedics Faculty of Health Sciences August 2008 University of Texas staging system for adult osteomyelitis
CIERNY CLASSIFICATION Classification of Infection according to Severity E E G LAUTENBACH Division of Orthopaedics Faculty of Health Sciences August 2008 University of Texas staging system for adult osteomyelitis
Assessment of limping child (beware the child who does not weight bear at all):
 Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline Acutely Limping Child and Septic Arthritis Assessment of limping child (beware the child who does not weight bear at all): History Careful history of any significant
Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline Acutely Limping Child and Septic Arthritis Assessment of limping child (beware the child who does not weight bear at all): History Careful history of any significant
7th CL Davis Diagnostic Pathology Symposium Diagnostic Orthopaedic Pathology Reno, NV October 19, 2007
 7th CL Davis Diagnostic Pathology Symposium Diagnostic Orthopaedic Pathology Reno, NV October 19, 2007 Roy R. Pool, DVM, PhD Professor of Pathology, Texas A&M Department Veterinary Pathobiology Director
7th CL Davis Diagnostic Pathology Symposium Diagnostic Orthopaedic Pathology Reno, NV October 19, 2007 Roy R. Pool, DVM, PhD Professor of Pathology, Texas A&M Department Veterinary Pathobiology Director
Morbidity & Mortality Conference Downstate Medical Center. Daniel Kaufman, MD
 Morbidity & Mortality Conference Downstate Medical Center University Case Presentation Hospital of Brooklyn Daniel Kaufman, MD Necrotizing Fasciitis and Soft- Tissue Infections Necrotizing Fasciitis Deep
Morbidity & Mortality Conference Downstate Medical Center University Case Presentation Hospital of Brooklyn Daniel Kaufman, MD Necrotizing Fasciitis and Soft- Tissue Infections Necrotizing Fasciitis Deep
Infection. Arthrocentesis: Cell count Differential Culture. Infection and associated microorganism(s) confirmed
 Painful joint History and examination Radiograph of affected joint Erythrocyte sedimentation rate C-reactive protein Infection No infection suspected Arthrocentesis: Cell count Differential Culture Stop
Painful joint History and examination Radiograph of affected joint Erythrocyte sedimentation rate C-reactive protein Infection No infection suspected Arthrocentesis: Cell count Differential Culture Stop
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SKELETAL TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN
 PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SKELETAL TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN DR.JANANI SANKAR SENIOR CONSULTANT - PEDIATRICS DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS & PEDIATRIC ORTHOPEDICS KANCHI KAMAKOTI CHILDS TRUST HOSPITAL CHENNAI,
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SKELETAL TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN DR.JANANI SANKAR SENIOR CONSULTANT - PEDIATRICS DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS & PEDIATRIC ORTHOPEDICS KANCHI KAMAKOTI CHILDS TRUST HOSPITAL CHENNAI,
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children
 Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
P-1 (Former P-1) Are pediatric patients on oral or intravenous steroids at an increased risk of developing septic arthritis?
 Pediatrics Prevention P-1 (Former P-1) Are pediatric patients on oral or intravenous steroids at an increased risk of developing septic arthritis? RESEARCHED BY: Muhammad Amin Chinoy MD, Pakistan Literature:
Pediatrics Prevention P-1 (Former P-1) Are pediatric patients on oral or intravenous steroids at an increased risk of developing septic arthritis? RESEARCHED BY: Muhammad Amin Chinoy MD, Pakistan Literature:
Stage Protocol in the Management of Infection Following Plating of the Tibia
 Stage Protocol in the Management of Infection Following Plating of the Tibia Nazri MY a, AS Halim b a Department of Orthopaedics, Traumatology and Rehabilitation, Kulliyyah of Medicine, International Islamic
Stage Protocol in the Management of Infection Following Plating of the Tibia Nazri MY a, AS Halim b a Department of Orthopaedics, Traumatology and Rehabilitation, Kulliyyah of Medicine, International Islamic
CASE STUDY: PRO-DENSE Injectable Regenerative Graft Used to Backfill a Bone Cavity Following Resection of a Giant Cell Tumor
 : PRO-DENSE Used to Backfill a Bone Cavity Following Resection of a Giant Cell Tumor Contributed by: Matthew J. Seidel, MD* Lauren A. Schwartz, NP Scottsdale, AZ *Dr. Seidel is a paid consultant for Wright
: PRO-DENSE Used to Backfill a Bone Cavity Following Resection of a Giant Cell Tumor Contributed by: Matthew J. Seidel, MD* Lauren A. Schwartz, NP Scottsdale, AZ *Dr. Seidel is a paid consultant for Wright
6/18/2014. John K. Midturi, DO, MPH June 5 th, 2014
 John K. Midturi, DO, MPH June 5 th, 2014 Heterogeneous disease Disease of antiquity Evolved from disease of high mortality disease with high morbidity One of the most difficult infections to treat Thomas
John K. Midturi, DO, MPH June 5 th, 2014 Heterogeneous disease Disease of antiquity Evolved from disease of high mortality disease with high morbidity One of the most difficult infections to treat Thomas
Pathophysiology and Etiology
 Sinusitis Pathophysiology and Etiology Sinusitis is inflammation of the mucosa of one or more sinuses. It can be either acute chronic. Chronic sinusitis is diagnosed if symptoms are present for more than
Sinusitis Pathophysiology and Etiology Sinusitis is inflammation of the mucosa of one or more sinuses. It can be either acute chronic. Chronic sinusitis is diagnosed if symptoms are present for more than
PSOAS ABSCESS. Dr Noman Ullah Wazir
 PSOAS ABSCESS Dr Noman Ullah Wazir Psoas Major muscle The psoas major is a long fusiform muscle located on the side of the lumbar region of the vertebral column and brim of the lesser pelvis. Psoas Major
PSOAS ABSCESS Dr Noman Ullah Wazir Psoas Major muscle The psoas major is a long fusiform muscle located on the side of the lumbar region of the vertebral column and brim of the lesser pelvis. Psoas Major
MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN. Dr Caren Landes Alder Hey Children s NHS Foundation Trust Liverpool
 MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN Dr Caren Landes Alder Hey Children s NHS Foundation Trust Liverpool MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS Common and uncommon infections Common and uncommon presentations Imaging
MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN Dr Caren Landes Alder Hey Children s NHS Foundation Trust Liverpool MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS Common and uncommon infections Common and uncommon presentations Imaging
Definitions and criteria
 Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
PATHWAY #4 DIABETIC FOOT DISORDERS VOLUME 45, NUMBER 5, SEPTEMBER/OCTOBER 2006 S 29
 PATHWAY #4 DIABETIC FOOT DISORDERS VOLUME 45, NUMBER 5, SEPTEMBER/OCTOBER 2006 S 29 be present. Hospitalization is required to treat the infection as well as systemic sequelae. Patients with poor vascular
PATHWAY #4 DIABETIC FOOT DISORDERS VOLUME 45, NUMBER 5, SEPTEMBER/OCTOBER 2006 S 29 be present. Hospitalization is required to treat the infection as well as systemic sequelae. Patients with poor vascular
Moath Darweesh. Zaid Emad. Anas Abu -Humaidan
 3 Moath Darweesh Zaid Emad Anas Abu -Humaidan Introduction: First two lectures we talked about acute and chronic meningitis, which is considered an emergency situation. If you remember, CSF examination
3 Moath Darweesh Zaid Emad Anas Abu -Humaidan Introduction: First two lectures we talked about acute and chronic meningitis, which is considered an emergency situation. If you remember, CSF examination
Clinical Case. ! 2am: Call from Surgeon, Ballarat Hospital. ! Suspicion of Necrotizing Fasciitis: ! Need of HBOT?
 Clinical Case! 2am: Call from Surgeon, Ballarat Hospital! Suspicion of Necrotizing Fasciitis:! 59y, Police Officer, diabetic, overweight! 4pm: pain in right arm! 8pm: pain worsening " ED! HD instability
Clinical Case! 2am: Call from Surgeon, Ballarat Hospital! Suspicion of Necrotizing Fasciitis:! 59y, Police Officer, diabetic, overweight! 4pm: pain in right arm! 8pm: pain worsening " ED! HD instability
General surgery department of SGMU Lecturer ass. Khilgiyaev R.H. Anaerobic infection. Gas gangrene
 Anaerobic infection Gas gangrene Anaerobic bacteria Anaerobic bacteria are the most numerous inhabitants of the normal gastrointestinal tract, including the mouth Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium The
Anaerobic infection Gas gangrene Anaerobic bacteria Anaerobic bacteria are the most numerous inhabitants of the normal gastrointestinal tract, including the mouth Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium The
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
Assesment by MRI in the diagnosing of osteomyelitis in children
 Assesment by MRI in the diagnosing of osteomyelitis in children Poster No.: C-1295 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Teixidor Viñas, J. L. Ribó, J. muxart, J. Blanch, L. Riaza ;
Assesment by MRI in the diagnosing of osteomyelitis in children Poster No.: C-1295 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Teixidor Viñas, J. L. Ribó, J. muxart, J. Blanch, L. Riaza ;
TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS OF PATELLA: A CASE REPORT Babu B. Hundekar 1
 TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS OF PATELLA: A Babu B. Hundekar 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Babu B. Hundekar. Tuberculous Osteomyelitis of Patella: A Case Report. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences
TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS OF PATELLA: A Babu B. Hundekar 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Babu B. Hundekar. Tuberculous Osteomyelitis of Patella: A Case Report. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences
Balgrist Shoulder Course 2017
 Diagnosis and Management of Infection in Revision Shoulder Arthroplasty Joseph P. Iannotti MD, PhD Maynard Madden Professor and Chairman Orthopaedic and Rheumatologic Institute Cleveland Clinic Conflict
Diagnosis and Management of Infection in Revision Shoulder Arthroplasty Joseph P. Iannotti MD, PhD Maynard Madden Professor and Chairman Orthopaedic and Rheumatologic Institute Cleveland Clinic Conflict
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
Surgical interventions in chronic osteomyelitis
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 50-54 Surgical interventions in chronic osteomyelitis Shrestha BK 1, Rajbhandary T 2, Bijukachhe B 2, Banskota AK 3 1 Associate Professor,
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 50-54 Surgical interventions in chronic osteomyelitis Shrestha BK 1, Rajbhandary T 2, Bijukachhe B 2, Banskota AK 3 1 Associate Professor,
TREATMENT OF ACUTE OSTEOMYELITIS IN CHILDHOOD
 TREATMENT OF ACUTE OSTEOMYELITIS IN CHILDHOOD W. G. COLE, R. E. DALZIEL, S. LEITL From The Royal Children s Hospital, Melbourne A protocol of treatment for acute haematogenous osteomyelitis has been evaluated
TREATMENT OF ACUTE OSTEOMYELITIS IN CHILDHOOD W. G. COLE, R. E. DALZIEL, S. LEITL From The Royal Children s Hospital, Melbourne A protocol of treatment for acute haematogenous osteomyelitis has been evaluated
Disclosures. Orthopedic infections. Case 1. Pen Barnes MBBS PhD. Clinical Associate Professor Departments of Medicine Pathology and Orthopedics OHSU
 Orthopedic infections Disclosures Pen Barnes MBBS PhD I have nothing to disclose Clinical Associate Professor Departments of Medicine Pathology and Orthopedics OHSU Case 1 48 year old woman presents to
Orthopedic infections Disclosures Pen Barnes MBBS PhD I have nothing to disclose Clinical Associate Professor Departments of Medicine Pathology and Orthopedics OHSU Case 1 48 year old woman presents to
Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection
 Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection Defense Mechanisms Three lines of defense protect the body against foreign invasion: Physical or surface barriers Inflammation Immune response Inflammation Non-specific
Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection Defense Mechanisms Three lines of defense protect the body against foreign invasion: Physical or surface barriers Inflammation Immune response Inflammation Non-specific
Chronic Ear Disease. Daekeun Joo Resident Lecture Series 11/18/09
 Chronic Ear Disease Daekeun Joo Resident Lecture Series 11/18/09 ETD URIs Viral-induced damage to ET lining resulting in decreased mucociliary clearance Viral invasion of ME mucosa results in inflamm Reflux
Chronic Ear Disease Daekeun Joo Resident Lecture Series 11/18/09 ETD URIs Viral-induced damage to ET lining resulting in decreased mucociliary clearance Viral invasion of ME mucosa results in inflamm Reflux
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida
 Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT
 TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP JOINT Occurrence-15% of all osteo articular tuber culosis Next common after spinal TB AETIO PATHOGENESIS Most common cause Mycobacterium tuberculosis
TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP JOINT Occurrence-15% of all osteo articular tuber culosis Next common after spinal TB AETIO PATHOGENESIS Most common cause Mycobacterium tuberculosis
ACUTE PAEDIATRIC EAR PRESENTATIONS PROF IAIN BRUCE PAEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGIST & ADULT OTOLOGIST
 www.manchesterchildrensent.com ACUTE PAEDIATRIC EAR PRESENTATIONS PROF IAIN BRUCE PAEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGIST & ADULT OTOLOGIST A CHILD WITH EARACHE UNCOMPLICATED AOM ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA Acute otitis media
www.manchesterchildrensent.com ACUTE PAEDIATRIC EAR PRESENTATIONS PROF IAIN BRUCE PAEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGIST & ADULT OTOLOGIST A CHILD WITH EARACHE UNCOMPLICATED AOM ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA Acute otitis media
INFECTION & INFLAMMATION IMAGING
 INFECTION & INFLAMMATION IMAGING Radiopharmaceutical Drug Interactions & Other Interesting Case Studies MICHELLE RUNDIO, CNMT NCT MBA PCI NUCLEAR IN-111 WHITE BLOOD CELL IMAGING Interactions, Imaging Parameters
INFECTION & INFLAMMATION IMAGING Radiopharmaceutical Drug Interactions & Other Interesting Case Studies MICHELLE RUNDIO, CNMT NCT MBA PCI NUCLEAR IN-111 WHITE BLOOD CELL IMAGING Interactions, Imaging Parameters
USE OF ANTIBIOTIC CEMENT SPACERS/BEADS IN TREATMENT OF MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS AT A.I.C. KIJABE HOSPITAL
 Research article USE OF ANTIBIOTIC CEMENT SPACERS/BEADS IN TREATMENT OF MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS AT A.I.C. KIJABE HOSPITAL G.C. Mwangi, MBChB, COSECSA Resident Orthopaedics, A.I.C. Kijabe Hospital, P.O.
Research article USE OF ANTIBIOTIC CEMENT SPACERS/BEADS IN TREATMENT OF MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS AT A.I.C. KIJABE HOSPITAL G.C. Mwangi, MBChB, COSECSA Resident Orthopaedics, A.I.C. Kijabe Hospital, P.O.
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 5 Basic Surgical Procedures Key Points 2 5.1 Wound Management Many important procedures can be performed under local anesthesia and do not require a surgical specialist
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 5 Basic Surgical Procedures Key Points 2 5.1 Wound Management Many important procedures can be performed under local anesthesia and do not require a surgical specialist
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell
 Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Objectives. The ability to demonstrate knowledge of the following:
 Objectives The ability to demonstrate knowledge of the following: Bone and joints infections presentation Assessment and work up for bone and joint infections Differential diagnosis for bone and joint
Objectives The ability to demonstrate knowledge of the following: Bone and joints infections presentation Assessment and work up for bone and joint infections Differential diagnosis for bone and joint
Open Fractures. Ria Dindial. Photo courtesy pic2fly.com
 Open Fractures Ria Dindial Photo courtesy pic2fly.com CLINICAL PEARL TYPE WOUND DESCRIPTION OTHER CRITERIA I < 1cm (puncture wounds) - II 1-10 cm - IIIA >10 cm, coverage available Segmental fractures,
Open Fractures Ria Dindial Photo courtesy pic2fly.com CLINICAL PEARL TYPE WOUND DESCRIPTION OTHER CRITERIA I < 1cm (puncture wounds) - II 1-10 cm - IIIA >10 cm, coverage available Segmental fractures,
Prolonged infection at the tibial bone tunnel after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
 Fukushima J. Med. Sci., Vol. 63, No. 2, 2017 [Case Report] Prolonged infection after ACL Reconstruction 121 Prolonged infection at the tibial bone tunnel after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
Fukushima J. Med. Sci., Vol. 63, No. 2, 2017 [Case Report] Prolonged infection after ACL Reconstruction 121 Prolonged infection at the tibial bone tunnel after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
TUBERCULOSIS OF THE RIB IN A 20 MONTH S OLD BOY
 CASE REPORT TUBERCULOSIS OF THE RIB IN A 20 MONTH S OLD BOY El Mouhtadi Aghoutane, Tarik Salama, Redouane El Fezzazi Pediatric surgery department, Kadi Ayyad University, Marrakech, Morocco Abstract Primary
CASE REPORT TUBERCULOSIS OF THE RIB IN A 20 MONTH S OLD BOY El Mouhtadi Aghoutane, Tarik Salama, Redouane El Fezzazi Pediatric surgery department, Kadi Ayyad University, Marrakech, Morocco Abstract Primary
ORIGINAL ARTICLES. Haematogenous pyogenic bone and joint sepsis reducing avoidable morbidity. Methods. T Nunn, P Rollinson
 Haematogenous pyogenic bone and joint sepsis reducing avoidable morbidity T Nunn, P Rollinson Background and objectives. Delayed presentation of haematogenous bone and joint sepsis is common in our childhood
Haematogenous pyogenic bone and joint sepsis reducing avoidable morbidity T Nunn, P Rollinson Background and objectives. Delayed presentation of haematogenous bone and joint sepsis is common in our childhood
Case Report Sacral Emphysematous Osteomyelitis Caused by Escherichia coli after Arthroscopy of the Knee
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1961287, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1961287 Case Report Sacral Emphysematous Osteomyelitis Caused by Escherichia coli after Arthroscopy of
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1961287, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1961287 Case Report Sacral Emphysematous Osteomyelitis Caused by Escherichia coli after Arthroscopy of
Introduction. Paronychia. Hand Infections. Eponychium. Paronychia 1/26/2015. INFECTIONS OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY Mark Rekant M.D.
 Introduction INFECTIONS OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY Mark Rekant M.D. Thomas Jefferson University Philadelphia Hand Center South Jersey Hand Center Hand infections are frequent Taking into account the countless
Introduction INFECTIONS OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY Mark Rekant M.D. Thomas Jefferson University Philadelphia Hand Center South Jersey Hand Center Hand infections are frequent Taking into account the countless
Use of Vacuum-assisted Wound Closure to Manage Limb Wounds in Patients Suffering from Acute Necrotizing Fasciitis
 Original Article Use of Vacuum-assisted Wound Closure to Manage Limb Wounds in Patients Suffering from Acute Necrotizing Fasciitis Wen-Shyan Huang, Shang-Chin Hsieh, Chun-Sheng Hsieh, Jen-Yu Schoung and
Original Article Use of Vacuum-assisted Wound Closure to Manage Limb Wounds in Patients Suffering from Acute Necrotizing Fasciitis Wen-Shyan Huang, Shang-Chin Hsieh, Chun-Sheng Hsieh, Jen-Yu Schoung and
Power to Transform Outcomes
 CASE STUDIES CASE STUDY Courtesy of Dr Parihar Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Center for Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction, Mangal Anand Hospital, Mumbai, India Clinical particulars 42-year-old female
CASE STUDIES CASE STUDY Courtesy of Dr Parihar Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Center for Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction, Mangal Anand Hospital, Mumbai, India Clinical particulars 42-year-old female
MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR. Physician-in-Chief, AIRP. Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging
 ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
Case Report Sequential MR Images and Radiographs of Epiphyseal Osteomyelitis in the Distal Femur of an Infant
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2013, Article ID 672815, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/672815 Case Report Sequential MR Images and Radiographs of Epiphyseal Osteomyelitis in the Distal Femur
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2013, Article ID 672815, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/672815 Case Report Sequential MR Images and Radiographs of Epiphyseal Osteomyelitis in the Distal Femur
Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Case Report Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report MihirDesai* and Shivanand Bandekar Department of Orthopedics, Goa Medical College, Goa, India *Corresponding
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Case Report Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report MihirDesai* and Shivanand Bandekar Department of Orthopedics, Goa Medical College, Goa, India *Corresponding
A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Keywords: Tubercular osteomyelitis, Extrapulmonary, Sequestrectomy
 Orthopaedics Case Report International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 5, Issue 4, July-Aug 2017 Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. PRIMARY TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS
Orthopaedics Case Report International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 5, Issue 4, July-Aug 2017 Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. PRIMARY TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS
Management of infected custom mega prosthesis by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gudaru K et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Dec;3(12):3874-3878 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20151459
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gudaru K et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Dec;3(12):3874-3878 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20151459
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Vascular and Parameningeal Infections of the Head and Neck
 Vascular and Parameningeal Infections of the Head and Neck Kevin B. Laupland, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor Departments of Medicine, Critical Care Medicine, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, and
Vascular and Parameningeal Infections of the Head and Neck Kevin B. Laupland, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor Departments of Medicine, Critical Care Medicine, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, and
EWMA Educational Development Programme. Curriculum Development Project. Education Module. Wound Infection
 EWMA Educational Development Programme Curriculum Development Project Education Module Wound Infection Latest revision: February 2014 ABOUT THE EWMA EDUCATIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME The Programme is designed
EWMA Educational Development Programme Curriculum Development Project Education Module Wound Infection Latest revision: February 2014 ABOUT THE EWMA EDUCATIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME The Programme is designed
Cierny-Mader classification of chronic osteomyelitis: Preoperative evaluation with cross-sectional imaging
 Cierny-Mader classification of chronic osteomyelitis: Preoperative evaluation with cross-sectional imaging Poster No.: C-590 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal Authors:
Cierny-Mader classification of chronic osteomyelitis: Preoperative evaluation with cross-sectional imaging Poster No.: C-590 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal Authors:
6/23/2017. What do you see? skull fracture
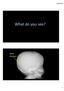 What do you see? skull fracture 1 Head CT On soft tissue windows, posterior soft tissues swelling and hemorrhage, no definite evidence of fracture Head CT On bone windows, fracture now seen subjacent to
What do you see? skull fracture 1 Head CT On soft tissue windows, posterior soft tissues swelling and hemorrhage, no definite evidence of fracture Head CT On bone windows, fracture now seen subjacent to
Case. 5 year old with 2 weeks leg pain and now refusing to walk + Fevers, lower leg swelling, warmth Denies and history of trauma or wounds
 Case 5 year old with 2 weeks leg pain and now refusing to walk + Fevers, lower leg swelling, warmth Denies and history of trauma or wounds Exam I: Swelling over entire tibia extending to foot P: Tenderness
Case 5 year old with 2 weeks leg pain and now refusing to walk + Fevers, lower leg swelling, warmth Denies and history of trauma or wounds Exam I: Swelling over entire tibia extending to foot P: Tenderness
CHAPTER 22 Haematogenous Osteomyelitis and Septic Arthritis
 CHAPTER 22 Haematogenous Osteomyelitis and Septic Arthritis Donald E. Meier Bankole S. Rouma Haematogenous Osteomyelitis Haematogenous osteomyelitis (HO) is a common and devastating problem for children
CHAPTER 22 Haematogenous Osteomyelitis and Septic Arthritis Donald E. Meier Bankole S. Rouma Haematogenous Osteomyelitis Haematogenous osteomyelitis (HO) is a common and devastating problem for children
Hand and wrist emergencies
 Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
Crush Injury. Professeur D. MATHIEU. Medicine
 Crush Injury Professeur D. MATHIEU Department of Critical Care and Hyperbaric Medicine University Hospital of Lille - France Definitions Crush Injury An injury sustained when a body part is subjected to
Crush Injury Professeur D. MATHIEU Department of Critical Care and Hyperbaric Medicine University Hospital of Lille - France Definitions Crush Injury An injury sustained when a body part is subjected to
