Rheumatoid Arthritis and Tuberculous Arthritis: Differentiating MRI Features
|
|
|
- Stewart Damon Chambers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choi et al. MRI of Rheumatoid and Tuberculous Arthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Jung-Ah Choi 1,2 Sung Hye Koh 3 Sung-Hwan Hong 2 Yong Hwan Koh 2 Ja-Young Choi 2 Heung Sik Kang 1,2 Choi JA, Koh SH, Hong SH, Koh YH, Choi JY, Kang HS Keywords: arthritis, MRI, rheumatoid arthritis, tuberculosis, tuberculous arthritis DOI: /AJR Received November 25, 2008; accepted after revision January 9, Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, 300 Gumi-dong, Bundang-gu, Seongnam, Gyeongi-Do, , Korea. Address correspondence to H. S. Kang (kanghs@radcom.snu.ac.kr). 2 Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. 3 Department of Radiology, Hallym Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University School of Medicine, Pyeongchon, Gyeongi-Do, Korea. AJR 2009; 193: X/09/ American Roentgen Ray Society Rheumatoid Arthritis and Tuberculous Arthritis: Differentiating MRI Features OBJECTIVE. The purpose of our study was to determine the MRI findings of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and tuberculous arthritis, with emphasis on differential diagnostic features. MATERIALS AND METHODS. MR images of 63 joints in 62 patients with clinically or pathologically proven RA (36 joints in 35 patients) or tuberculous arthritis (27 joints in 27 patients) were evaluated retrospectively with regard to pattern and degree of synovial thickening, size of bone erosions, rim enhancement at bone erosions, degree of bone marrow and periarticular soft-tissue edema, and presence and number of extraarticular cystic masses. MRI findings were compared between RA and tuberculous arthritis by statistical analysis using kappa statistics, the Mann-Whitney U test, linear-by-linear association, and the chi-square test. RESULTS. Nonuniform and greater degree of synovial thickening was more frequent in RA (p < 0.01); the thicker the synovial membrane, the greater the likelihood of RA (p < 0.01). Bone erosions of tuberculous arthritis were larger (p < 0.01), and the likelihood of tuberculous arthritis increased proportionally to the increment of size of the bone erosions (p < 0.01). Rim enhancement at bone erosion was more frequent in tuberculous arthritis (p < 0.01). Extraarticular cystic masses were more frequently seen and more numerous in tuberculous arthritis (p < 0.01). CONCLUSION. Uniform synovial thickening, large size of bone erosion, rim enhancement at site of bone erosion, and extraarticular cystic masses were more frequent and more numerous in tuberculous arthritis. MRI may be helpful in the differentiation between RA and tuberculous arthritis. T uberculous arthritis is generally a monoarticular disease that typically involves the spine or largeand medium-sized joints, such as the hip and knee. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is usually a symmetric polyarticular disease with common involvement of peripheral joints. However, RA may also manifest as a monoarticular disease and persist in such a fashion for a long time [1]. RA and tuberculous arthritis may have similar clinical characteristics, consisting of a chronic course with periarticular soft-tissue swelling [2], as well as similar radiologic findings, such as periarticular osteoporosis, bone erosion, and presence of joint effusion, rendering differential diagnosis difficult [2]. Actually, there have been reports of cases in which tuberculous arthritis was misdiagnosed as RA or juvenile RA [3 5]. The value of MRI has been advocated in each of the two diseases because of its superior soft-tissue contrast and its ability to depict changes in cartilage, liga- ments, and synovial tissue, especially in the evaluation of early changes [6, 7]. With MRI, both diseases have been reported to reveal heterogeneous low signal intensity in the joint because of rice bodies, cartilage fragments, and hemorrhage [8, 9]. Furthermore, the distinction by virtue of the number of joints involved does not always hold true because early asymmetric oligoarticular involvement of RA is not rare [10], and polyarticular involvement in tuberculous arthritis has been reported [11]. Although there has been a report comparing RA and tuberculous arthritis of the knee using MRI [12], this report compared a limited number of cases and only cases involving the knee; therefore, a comprehensive investigation of MRI in those two articular diseases, especially comparing the MRI findings of the two diseases, has not been undertaken to our knowledge. The purpose of this study was to determine MRI findings of RA and tuberculous AJR:193, November
2 Choi et al. arthritis with special emphasis on findings that allow their differentiation. Materials and Methods Subjects and MRI MR images of 63 joints in 62 patients (32 female and 30 male; age range, 4 76 years) that were clinically and pathologically diagnosed as either RA (36 cases in 35 patients) or tuberculous arthritis (27 cases in 27 patients) were evaluated. The cases were retrieved retrospectively by a computer-based database program that searched on patients by final diagnosis of RA or tuberculous arthritis during a period from October 1998 to September Medical records were reviewed, and all patients had undergone MRI because of monoarticular disease with joint manifestation for the first time with symptom durations varying from 3 to 40 months, so the clinician had no prior knowledge of the disease of the patient. Final diagnoses were made on the basis of clinical history, physical examinations, radiographic survey, synovial biopsy, culture, tuberculosis polymerase chain reaction, and serologic studies. The study design was approved by our institutional review board; informed consent was not required at the time of study. MRI was performed with various MR units, including 1- and 1.5-T scanners, but in all patients, spin-echo T1-weighted (TR range/te range, /10 30) and fast spin-echo T2-weighted (2,500 4,500/60 108) images with or without fat suppression, along with gadolinium-enhanced spin-echo T1-weighted images were acquired [13, 14]. Although imaging planes were variable, at least two orthogonal plane images were available, including transverse images in all patients. The field of view varied from to mm and the matrix from to ; various coils were used, including wrist, shoulder, knee, head, and body surface coils. Analysis of MR Images MR images were analyzed retrospectively and independently by three experienced musculoskeletal radiologists without prior information about patient history, findings of other imaging studies, and final diagnosis. MR images were analyzed regarding the following findings: uniformity and degree of synovial thickening, size of and enhancement around bone erosion, degree of marrow edema, degree of soft-tissue edema, and the presence of extraarticular cystic masses. One of the three observers determined the number of extraarticular cystic masses, which were defined as any cystic masses located outside the joint regardless of their contiguity with the joint. The degree of synovial thickening after IV gadolinium administration was TABLE 1: Age and Sex Distribution of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Tuberculous Arthritis Characteristic Tuberculous Arthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis Total No. of Patients Mean Age (y) classified into four grades according to the maximal thickness of enhancing synovium: grade 0, 0~3 mm; grade 1, 3.1~6 mm; grade 2, 6.1~9 mm; and grade 3, > 9 mm. Uniform synovial thickening was considered to be present when the maximal thickness of synovium measured less than two times the minimal thickness after IV gadolinium administration. Size of the largest bone erosion in longest diameter was documented. The size of the bone erosions was classified into five grades: grade 0, no erosion; grade 1, < 6 mm; grade 2, 6~10 mm; grade 3, 11~15 mm; and grade 4, > 15 mm on T1-weighted images. Enhancement around bone erosion was determined on gadolinium-enhanced images as either present or absent. The number of erosions was not counted. Bone marrow edema was classified into four grades after calculation of the extent of marrow edema for the joint as ([maximal distance from articular margin to outer margin of signal change of bone marrow on sagittal or coronal image / maximal diameter of articular surface on axial image] 100[%]) into the following four grades: grade 0, no edema; grade 1, 1~25%; grade 2, 26~50%; and grade 3, > 50%. Soft-tissue edema was classified into three grades after measuring the maximal vertical distance from the outer margin of joint capsule to the outer margin of periarticular soft-tissue edema on coronal or sagittal image as follows: grade 0, no edema; grade 1, 0.1~1 cm; and grade 2, > 1 cm. No. of Patients Mean Age (y) No. of Patients Mean Age (y) Female Male Total no. of patients Median age (y) Age range (y) TABLE 2: Distribution of Locations of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Tuberculous Arthritis Location Rheumatoid Arthritis (%) Tuberculous Arthritis (%) Total (%) Shoulder 2 (5.6) 0 (0) 2 (3.2) Elbow 7 (19.4) 2 (7.4) 9 (14.3) Wrist 12 (33.3) 4 (14.8) 16 (25.4) Hip 0 (0) 4 (14.8) 4 (6.3) Knee 11 (30.6) 13 (48.1) 24 (38.1) Ankle 4 (11.1) 4 (14.8) 8 (12.7) Total 36 (100) 27 (100) 63 (100) Note Data are numbers of cases (%). Bone marrow and soft-tissue edema were evaluated on T2-weighted sequences. Statistical Analysis Statistical analysis was performed using a commercially available software (SPSS for Windows, version ). Using kappa statistics, interobserver agreement was evaluated for uniformity of synovial thickening, degree of synovial thickening, rim enhancement around bone erosions, bone marrow edema, soft-tissue edema, and the presence of extraarticular cystic masses. Interobserver agreement was considered poor for kappa values equal to or less than 0.200, fair for values of , moderate for values of , substantial for values of , or almost perfect for values of If the kappa value of an item was less than 0.2 in one or more pairs between the three observers, the item was considered to be improper for use as an objective sign for differential evaluation of the joint [15, 16]. The Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparing two groups for the degree of synovial thickening, size of bone erosion, and bone marrow edema. Linear-by-linear association was calculated for the statistically significant items for evaluation of likelihood. The chi-square test was used for comparing two groups for nonuniform synovial thickening, rim enhancement of bone erosion, and presence of extraarticular cystic mass. A 1348 AJR:193, November 2009
3 MRI of Rheumatoid and Tuberculous Arthritis p value of 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance. Results The mean age of the 62 patients was 43.3 years (45 years for those with RA and 42 years for those with tuberculous arthritis; median age, 44.5 years). The distribution by age and sex and the location of the evaluated joints of both RA and tuberculous arthritis groups are listed in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. The case of a 4-year-old patient represented juvenile RA. The results of kappa statistics for evaluation of interobserver agreement are summarized in Table 3. Interobserver agreement was generally moderate. The kappa value of interobserver agreement for the degree of soft-tissue edema was less than in one pair and less than in all three pairs between the three observers. Thus, the degree of soft-tissue edema was eliminated from further statistical analysis. The results of image analysis for uneven synovial thickening, the degree of synovial thickening, the size of bone erosion, the presence of rim enhancement along the erosions, the degree of bone marrow edema, the degree of soft-tissue edema, and the presence and number of extraarticular cystic masses are listed in Table 4. The results of comparison between the two groups using mean values of all data sets created by the three observers by statistical analysis for each item are summarized in Table 5. Because the degree of synovial thickening and size of bone erosion were statistically significant in differentiation of the two diseases and classified into grades (i.e., quantified), linear-by-linear association was calculated for evaluation of trend for both items (Table 5). Nonuniform synovial thickening was noted in 72.2%, 86.1%, and 80.6% of RA cases by three independent observers (Figs. 1 3) and in 44.4%, 55.6%, and 44.4% of tuberculous arthritis cases, whereas uniform synovial thickening was observed in 27.8%, 13.9%, and 19.4% of RA and in 55.6%, 44.4%, and 55.6% of tuberculous arthritis (Figs. 4 7). Therefore, nonuniform synovial thickening was more frequent in RA than in tuberculous arthritis (p < 0.01). Grade 0 synovial thickening was evident in 55.6%, 44.4%, and 44.4% of tuberculous arthritis cases (Fig. 4) and in 27.8%, 16.7%, and 27.8% of RA. In contrast, grade 3 synovial thickening was noted in 44.4%, 22.2%, and 36.1% of RA cases (Figs. 3 and 8) and in TABLE 3: Kappa Statistics for Evaluation of Interobserver Agreement Feature Evaluated Observers 1 vs 2 Observers 2 vs 3 Observers 3 vs 1 Uneven synovial thickening Degree of synovial thickening Size of bone erosion Rim enhancement of erosion Bone marrow edema Soft-tissue edema Extraarticular cystic mass TABLE 4: Comparison of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Tuberculous Arthritis on MRI by Three Independent Observers Grade Observer 1 Observer 2 Observer 3 RA (%) TB (%) RA (%) TB (%) RA (%) TB (%) Uneven synovial thickening Yes 26 (72.2) 12 (44.4) 31 (86.1) 15 (55.6) 29 (80.6) 12 (44.4) No 10 (27.8) 15 (55.6) 5 (13.9) 12 (44.4) 7 (19.4) 15 (55.6) Degree of synovial thickening 0 10 (27.8) 15 (55.6) 6 (16.7) 12 (44.4) 10 (27.8) 12 (44.4) 1 3 (8.3) 6 (22.2) 7 (19.4) 10 (37.0) 6 (16.7) 4 (14.8) 2 7 (19.4) 4 (14.8) 15 (41.7) 3 (11.1) 7 (19.4) 7 (25.9) 3 16 (44.4) 2 (7.4) 8 (22.2) 2 (7.4) 13 (36.1) 4 (14.8) Size of bone erosion 0 11 (30.6) 2 (7.4) 13 (36.1) 3 (11.1) 12 (33.3) 2 (7.4) 1 4 (11.1) 2 (7.4) 7 (19.4) 1 (3.7) 0 (0) 1 (3.7) 2 9 (25.0) 2 (7.4) 2 (5.6) 7 (25.9) 13 (36.1) 2 (7.4) 3 5 (13.9) 7 (25.9) 6 (16.7) 9 (33.3) 9 (25.0) 10 (37.0) 4 7 (19.4) 14 (51.9) 3 (8.3) 6 (22.2) 2 (5.6) 12 (44.4) Rim enhancement of erosion Yes 5 (13.9) 14 (51.9) 2 (5.6) 18 (66.7) 4 (11.1) 21(77.8) No 31 (86.1) 13 (48.1) 34 (94.4) 9 (33.3) 32 (88.9) 6 (22.2) Bone marrow edema 0 13 (36.1) 6 (22.2) 19 (52.8) 7 (25.9) 16 (44.4) 4 (14.8) 1 6 (16.7) 5 (18.5) 3 (8.3) 2 (7.4) 2 (5.6) 4 (14.8) 2 2 (5.5) 0 (0.0) 5 (13.9) 6 (22.2) 5 (13.9) 4 (14.8) 3 15 (41.7) 16 (59.3) 9 (25.0) 12 (44.4) 13 (36.1) 15 (55.6) Soft-tissue edema 0 13 (36.1) 10 (37.0) 29 (80.6) 16 (59.3) 13 (36.1) 8 (29.6) 1 10 (27.8) 9 (33.3) 3 (8.3) 11 (40.7) 9 (25.0) 7 (25.9) 2 13 (36.1) 8 (29.6) 4 (11.1) 0 (0) 14 (38.9) 12 (44.4) Extraarticular cystic mass Yes 6 (16.7) 21(77.8) 7 (19.4) 19 (70.4) 7 (19.4) 21(77.8) No 30 (83.3) 6 (22.2) 29 (80.6) 8 (29.6) 29 (80.6) 6 (22.2) Note Data are numbers of cases (%). RA = rheumatoid arthritis, TB = tuberculous arthritis. AJR:193, November
4 Choi et al. 7.4%, 7.4%, and 14.8% of tuberculous arthritis. Therefore, the involved synovial membrane in RA generally was thicker than in tuberculous arthritis (p < 0.01). The p value of linear-by-linear association of degree of synovial thickening was less than 0.01; therefore, the thicker the synovial membrane, the more likely the diagnosis of RA. With regard to the presence of bone erosions, bone erosions were observed in 48.1%, 88.9%, and 92.6% of tuberculous arthritis cases (Fig. 4) and in 69.4%, 63.9%, and TABLE 5: Comparison of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Tuberculous Arthritis by Mean Data of Three Sets of Three Observers and Linear-by-Linear Association (Trend) Mean Data a Comparison Result p Linear-by-Linear Association Uneven synovial thickening RA > TB < 0.01 Degree of synovial thickening RA > TB < 0.01 < 0.01 Size of bone erosion RA < TB < 0.01 > 0.05 Rim enhancement of bone erosion RA < TB < 0.01 Degree of bone marrow edema NS Extraarticular cystic mass RA < TB < 0.01 Note Dash ( ) indicates not applicable. NS = not significant. a (Each case of observers ) / 3. Fig year-old woman with rheumatoid arthritis. Fat-saturated, gadolinium-enhanced sagittal T1- weighted MR image of knee shows uneven and thick (grade 2 in all observers) synovium (arrows). Fig year-old girl with rheumatoid arthritis. Fatsaturated axial T1-weighted image of elbow shows uneven and thick (grade 2 in all observers) synovial hypertrophy (arrows). More markedly thickened synovium in olecranon fossa and surrounding radial neck is probably due to synovial redundancy. 66.7% of RA cases. Furthermore, the size of bone erosions was greater in tuberculous arthritis than in RA (p < 0.01). The p value of linear association of the size of the bone erosion was greater than Rim enhancement around bone erosions was more frequent in tuberculous arthritis (51.9%, 66.7%, and 77.8%) (Figs. 4 and 6) than in RA (13.9%, 5.6%, and 11.1%), and the difference was statistically significant (p < 0.01). Grade 3 bone marrow edema was noted in 59.3%, 44.4%, and 55.6% of tuberculous arthritis cases by the three observers (Figs. 5 and 7), and in 41.7%, 25.0%, and 36.1% of RA (Fig. 3). The difference of marrow edema in the two groups was not clinically significant (p > 0.05). Extraarticular cystic masses were more frequent in tuberculous arthritis (Figs. 5 7) than in RA, and the difference was statistically significant (p < 0.01). Fig year-old woman with rheumatoid arthritis. Fat-saturated, gadolinium-enhanced sagittal T1- weighted image of ankle shows uneven and thick (grade 3 in all observers) synovial enhancement (arrow) and extensive bone marrow enhancement (grade 3 in all observers, arrowheads) of calcaneus. A B Fig year-old man with tuberculous arthritis. A and B, Unenhanced (A) and contrast-enhanced (B) axial T1-weighted images of knee show rim enhancement of bone erosions (arrowheads, B) at medial tibial plateau AJR:193, November 2009
5 MRI of Rheumatoid and Tuberculous Arthritis Fig year-old woman with tuberculous arthritis. Fat-saturated, gadolinium-enhanced sagittal T1- weighted image of elbow shows even synovial thickening (grade 1 in two observers and grade 0 in one observer, arrowhead) of elbow joint with bone marrow enhancement (grade 3 in all observers). Cystic mass, possibly resulting from expansion of joint capsule, with rim enhancement is seen at anteroinferior portion of radial neck (arrow). Fig year-old woman with tuberculous arthritis of ankle. Fat-saturated gadoliniumenhanced sagittal T1-weighted image shows even and thin (grade 1) synovial thickening of ankle and intertarsal joint. Subchondral bone marrow shows heterogeneous enhancement (arrowheads, grade 3 in two observers and grade 2 in one observer). Cold abscess at posterior aspect of ankle (arrows) shows even thin rim enhancement and faint softtissue enhancement. Discussion Monoarticular disease is most commonly caused by an infectious disease process but can also be of noninfectious origin, such as metabolic or immunologic. In some cases, it is difficult to differentiate the origin of a monoarticular disease [17]. Differential diagnoses include infectious arthritides, such as pyogenic or tuberculous arthritis, or noninfectious diseases, such as synovial osteochondromatosis, pigmented villonodular synovitis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and hemophilic arthropathy, among many others. Appropriate treatment after accurate diagnosis is crucial for good prognosis and preservation of joint function; final pathologic diagnosis usually requires culture of synovial fluid or synovial biopsy or both. RA is a chronic inflammatory arthritis, affecting about 1% of the population worldwide [6], that leads to cartilage and bone destruction and eventually to loss of function. Tuberculous arthritis is second in frequency to spinal involvement by tuberculosis; osteoarticular tuberculosis is estimated to occur in 1.5 3% of patients with musculoskeletal tuberculosis [18]. The incidence of extrapulmonary tuberculosis has been increasing over the past decades because of increasing travel and immigration; an increasing number of elderly, chronically ill, or immunosuppressed patients; and an increasing number of patients with AIDS [17]. Both RA and tuberculous arthritis may have not only similar clinical manifestations, but also similar radiographic findings, such as periarticular osteopenia, marginal erosions with relatively late sparing of the joint space, and increased joint effusion, which may render differential diagnosis difficult in some cases [2, 19]. Grossly, both RA and tuberculous arthritis have chronic inflammatory hypertrophied synovium. However, on microscopic examination, the synovium of RA shows infiltration by plasma cells and lymphocytes with or without lymphoid follicles and fibrin deposits often seen close to the synovial lining or within the stroma [20], whereas the synovium in tuberculous arthritis contains necrotic and fibrinlike material, caseous areas, and collections of leukocytes and mononuclear phagocytes [2]. RA consists of articular manifestations of a disease of immunoregulatory dysfunction that are linked by complex processes. In addition to lymphocytes and plasma cells, many different cells, as Fig year-old woman with tuberculous arthritis and combined tenosynovitis and cold abscess. Fatsaturated gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted axial scan shows even and thin (grade 0 in three observers) enhancement in synovium of wrist and tendon sheath (arrowheads) associated with rim enhancement of fluid collection (arrows) at volar aspect of radius. Bone marrow (grade 3) and soft-tissue edema (grade 1 in two observers and grade 2 in one observer) adjacent to synovium show heterogeneous enhancement. Fig year-old man with rheumatoid arthritis. Fat-saturated gadolinium-enhanced coronal T1-weighted image of wrist shows ovoid mass formation of synovium (arrowheads) at distal radioulnar joint level. well as their variable products (cytokines), contribute to the disease process. Lymphocytes, plasma cells, and a large number of plump luxuriant cells in the synovium of RA produce bulky, hypervascular, proliferative lesions, almost resembling a tumor, in response to the proliferative factors generated AJR:193, November
6 Choi et al. by the activated immune response. In fact, synovial tissue taken from a rheumatoid knee may weigh up to 500 g or more, in contrast to synovium in a normal knee, which in total usually weighs less than 5 g [9]. In our patients, synovial thickness in RA was variable in the joint space. Prominent thickening, even mass formation of more than 1 cm, was frequently seen at sites of synovial redundancy (Fig. 8) or at sites with more capacious space in a joint in RA (Figs. 1 3 and 8). This may be explained by the fact that sufficient space allows more room for tissue accumulation in joints without an immediate increase in pressure or displacement of other tissue, permitting bulky proliferative growth [9]. In contrast, tuberculous arthritis is characterized by synovial inflammation and formation of granulation tissue that are accompanied by immune responses with no proliferative factor, so thick and uneven or bulky proliferation of synovium and bone erosion, which are seen more frequently in RA, are usually not seen in tuberculous arthritis. Instead, even and relatively thin synovium and rim enhancement are observed in tuberculous arthritis. Bone change of RA occurs after proliferative pannus extension over the cartilage and cartilaginous destruction by enzymatic, phagocytic, and mechanical processes. But in tuberculous arthritis, cartilaginous destruction is associated with phagocytic and vascular processes without involvement of proteolytic enzymes [2, 4]. Bone erosion is seen not only after cartilaginous erosion but also after detachment of cartilage due to insinuation of granulation tissue between cartilage and subchondral bone [2]. Nonperipheral subchondral bone erosion was more frequent in tuberculous arthritis in our study, which may have occurred because of this subchondral extension of pannus (Figs. 4 and 7). Intercondylar widening of the distal femur, which was reported by Bohrer [21] to be due to entering of the synovium from the patella, was not seen in our study; instead, intercondylar erosion at the attachment site of the cruciate ligament was frequently seen, especially more frequently in tuberculous arthritis (Fig. 4) than in RA in our study. This may have been due to pannus of the synovial membrane enveloping the cruciate ligaments attaching to the intercondylar area of the knee; in tuberculous arthritis, the tendency toward subchondral extension of granulation tissue and caseation necrosis may have contributed further to the intercondylar erosion, which may explain the larger size of erosions in our study. Extraarticular cold abscess in tuberculous arthritis may also be attributed to nonenzymatic processes [22, 23]. On MRI, a cold abscess is seen as a cystic mass with even, thin rim enhancement, usually not accompanied by prominent surrounding edema (Figs. 6 and 7). Sometimes the differentiation between abscess in tuberculous arthritis and fluid collections in bursa and other extraarticular cystic lesions in RA, such as Baker s cysts, is difficult [6]. In our study, extraarticular cystic mass was more frequently seen in tuberculous arthritis (Figs. 5 7) than in RA, and cases with more than two cystic masses were observed only in tuberculous arthritis. Both tuberculous arthritis and RA are accompanied by bone marrow edema, which is due to increased vascular flow and increased vascular permeability of bone marrow [24]. In our study, the difference of bone marrow edema in RA and tuberculous arthritis was not clinically significant. Our study has several limitations. Different joints were assessed for the two diseases, and the numbers of joint were not matched for the two diseases for example, a large number of wrists were imaged in RA patients, which may have introduced a bias. However, despite the lack of statistical comparison, comparing grossly just the knees and the ankles, of which the number are approximately closely matched, the differences seem to remain according to the two diseases (Figs. 1, 3, 4, and 6). Because of the retrospective nature of the study, the sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values of each finding could not be determined. Also, the use of different MRI parameters and different field-strength scanners is another limitation of this study. However, from the results of our study, we may conclude that uneven and thick synovial proliferation was more frequently seen in RA, whereas, even and thin synovium, large bone erosions, rim enhancement around bone erosion, and extraarticular cystic masses were more frequently seen in tuberculous arthritis. Although findings evaluated in this study show some degree of overlap in both RA and tuberculous arthritis, evaluation with MRI may be helpful in differentiation between RA and tuberculous arthritis. References 1. Resnick D. Rheumatoid arthritis. In: Resnick D, ed. Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders, 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2002: Resnick D. Osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, and soft tissue infection: organisms. In: Resnick D, ed. Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders, 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 1995: Schuchmann L, Pernice W, Hufschmidt C, Adler CP. Tuberculous arthritis: a rare, but important differential diagnosis in juvenile chronic arthritis [in German]. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd 1991; 139: Tsuduki E, Kawada H, Takeda Y, et al. A case of multiple bone and joint tuberculosis which had been misdiagnosed as the rheumatoid arthritis and treated with prednisolone for eleven months [in Japanese]. Kekkaku 2002; 77: Al-Matar MJ, Cabral DA, Petty RE. Isolated tuberculous monoarthritis mimicking oligoarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2001; 28: Winalski CS, Palmer WE, Rosenthal DI, Weissman BN. Magnetic resonance imaging of rheumatoid arthritis. Radiol Clin North Am 1996; 34: De Vuyst D, Vanhoenacker F, Gielen J, Bernaerts A, De Schepper AM. Imaging features of musculoskeletal tuberculosis. Eur Radiol 2003; 13: Schultz E, Richterman I, Dorfman HD. Case report 739: Tuberculous arthritis of knee. Skeletal Radiol 1992; 21: Harris ED Jr. In: Kelly WN, Harris ED Jr, Ruddy S, Sledge CB, eds. Etiology and pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 1993: Harris ED Jr. Clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis. In: Kelly WN, Harris ED Jr, Ruddy S, Sledge CB, eds. Textbook of rheumatology, 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 1993: Valdazo J-P, Perez-Ruiz F, Albarracin A, et al. Tuberculous arthritis: report of a case with multiple joint involvement and periarticular tuberculous abscesses. J Rheumatol 1990; 17: Lim YS, Park JM, Shin KH, et al. Tuberculous arthritis and monoarticular rheumatoid arthritis in the knee: differential diagnosis using MR imaging [in Korean]. J Korean Radiol Soc 1999; 41: Adam G, Dammer M, Bohndorf K, Christoph R, Fenke F, Guenther RW. Rheumatoid arthritis of the knee: value of gadopentetate dimeglumineenhanced MR imaging. AJR 1991; 156: König H, Sieper J, Wolf KJ. Rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation of hypervascular and fibrous pannus with dynamic MR imaging enhanced with Gd- DTPA. Radiology 1990; 176: Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977; 33: Volk M, Strotzer M, Lenhart M, et al. Time-resolved contrast-enhanced MR angiography of renal artery stenosis: diagnostic accuracy and inter AJR:193, November 2009
7 MRI of Rheumatoid and Tuberculous Arthritis observer variability. AJR 2000; 174: Rutten MJCM, Van den Berg JC, Van den Hoogen FHJ, Lemmens JAM. Nontuberculous mycobacterial bursitis and arthritis of the shoulder. Skeletal Radiol 1998; 27: Dhillon MS, Sharma S, Gill SS, et al. Tuberculosis of the bones and joints of the foot: an analysis of 22 cases. Foot Ankle Int 1993; 14: Versfeld GA, Solomon A. A diagnostic approach FOR YOUR INFORMATION to tuberculosis of bones and joint. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1982; 64: Rosai J. Bone and joints. In: Rosai J, ed. Ackerman s surgical pathology, 8th ed. St. Louis, MO: Mosby, 1996: Bohrer SP. Tuberculous synovitis with widening of the intercondylar notch of the femur. Br J Radiol 1969; 42: Kang HS, Yeon KM. Differentiation between tuberculosis and pyogenic spondylitis: MR imaging characteristics of paraspinal mass [in Korean]. J Korean Radiol Soc 1996; 34: Yao DC, Sartoris DJ. Musculoskeletal tuberculosis. Radiol Clin North Am 1995; 33: Hopkins KL, Li KC, Bergman G. Gadolinium- DTPA-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of musculoskeletal infectious processes. Skeletal Radiol 1995; 24: Realize Your Potential with AJR Integrative Imaging Each quarterly issue of AJR Integrative Imaging offers you a series of peer-reviewed learning opportunities, many with CME credit, which will challenge and enhance your diagnostic and treatment skills. Whether it is the printed version or the online version, AJR Integrative Imaging is an important tool for your professional development. For more information or the latest issue of AJR Integrative Imaging, visit AJR:193, November
MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis
 CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 2000, 45
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Pictorial Essay Magnetic Resonance Related Disorders Uetani, Masataka; Hashmi, Rashid; N Hayashi, Kuniaki Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 2000, 45
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Pictorial Essay Magnetic Resonance Related Disorders Uetani, Masataka; Hashmi, Rashid; N Hayashi, Kuniaki Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 2000, 45
Topics. Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities. Detection of Infection. Role of Imaging in Extremity Infection. Detection of Infection
 Topics Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities Nuttaya Pattamapaspong M.D. Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Role of imaging in extremity infection
Topics Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities Nuttaya Pattamapaspong M.D. Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Role of imaging in extremity infection
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas
 ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS
 February 2002 Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS Amy Gillis, Harvard Medical School Year III 47 year old female Our Patient Right hip pain since age 20 No history of trauma Diagnosed with DJD of R hip
February 2002 Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS Amy Gillis, Harvard Medical School Year III 47 year old female Our Patient Right hip pain since age 20 No history of trauma Diagnosed with DJD of R hip
2 A B Fig. 1. Lateral tibial condyle fracture with joint effusion in a 35-year-old man. Sagittal T2-weighted MRI shows a large amount of effusion
 1 2 1 1 1 2 A B Fig. 1. Lateral tibial condyle fracture with joint effusion in a 35-year-old man. Sagittal T2-weighted MRI shows a large amount of effusion (between arrowheads) in the suprapatellar pouch,
1 2 1 1 1 2 A B Fig. 1. Lateral tibial condyle fracture with joint effusion in a 35-year-old man. Sagittal T2-weighted MRI shows a large amount of effusion (between arrowheads) in the suprapatellar pouch,
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE. Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV. Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
 MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
of the lumbar facet joints there
 Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
ISPUB.COM. Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay. P Chudgar INTRODUCTION SPINE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after competition
 Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
Figuring out the "fronds"-synovial proliferative disorders of the knee.
 Figuring out the "fronds"-synovial proliferative disorders of the knee. Poster No.: C-1209 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Sivasubramanian; Tamil Nadu/IN Keywords: Imaging sequences,
Figuring out the "fronds"-synovial proliferative disorders of the knee. Poster No.: C-1209 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Sivasubramanian; Tamil Nadu/IN Keywords: Imaging sequences,
Extra-spinal musculoskeletal manifestations of mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) infection: A review of radiological findings
 Extra-spinal musculoskeletal manifestations of mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) infection: A review of radiological findings Poster No.: P-0118 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: I. Anwar,
Extra-spinal musculoskeletal manifestations of mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) infection: A review of radiological findings Poster No.: P-0118 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: I. Anwar,
Synovial hemangioma of the suprapatellar bursa
 Synovial hemangioma of the suprapatellar bursa Poster No.: P-0040 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. YESILDAG, S. Keskin, H. Kalkan, S. Kucuksen, U. Kerimoglu; Konya/TR
Synovial hemangioma of the suprapatellar bursa Poster No.: P-0040 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. YESILDAG, S. Keskin, H. Kalkan, S. Kucuksen, U. Kerimoglu; Konya/TR
Gout. Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives. Crystal associated arthropathies. Clinical Stages of Gout 07/06/60
 Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
Contiguous Spinal Metastasis Mimicking Infectious Spondylodiscitis 감염성척추염과유사하게보였던연속적척추전이의증례
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.73.6.408 감염성척추염과유사하게보였던연속적척추전이의증례 Chul-Min Lee, MD 1, Seunghun Lee, MD 1 *, Jiyoon Bae, MD 2 1 Department of Radiology,
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.73.6.408 감염성척추염과유사하게보였던연속적척추전이의증례 Chul-Min Lee, MD 1, Seunghun Lee, MD 1 *, Jiyoon Bae, MD 2 1 Department of Radiology,
Lipoma Arborescens of Subacromial-subdeltoid Bursa: Ultrasonographic Findings
 C A S E R E P O R T Lipoma Arborescens of Subacromial-subdeltoid Bursa: Ultrasonographic Findings Amelia Bargiela*, Esther Rodriguez, Rafaela Soler The present study describes the ultrasound findings of
C A S E R E P O R T Lipoma Arborescens of Subacromial-subdeltoid Bursa: Ultrasonographic Findings Amelia Bargiela*, Esther Rodriguez, Rafaela Soler The present study describes the ultrasound findings of
Rheumatoid Arthritis 2. Inflammatory Diseases. Definition. Imaging Signs
 Rheumatoid Arthritis 2 Definition " Epidemiology Affects 2% of the population Peak incidence (diagnosis) in 4th and 5th decades Women affected 3 4 times more often than men Increased familial incidence
Rheumatoid Arthritis 2 Definition " Epidemiology Affects 2% of the population Peak incidence (diagnosis) in 4th and 5th decades Women affected 3 4 times more often than men Increased familial incidence
Brain Atrophy. Brain Atrophy
 Aging Central Nervous System Processes Age related brain atrophy Non-age related brain atrophy Cerebrovascular disease Cerebral infarction Hypertensive hemorrhage Carotid artery stenosis and occlusion
Aging Central Nervous System Processes Age related brain atrophy Non-age related brain atrophy Cerebrovascular disease Cerebral infarction Hypertensive hemorrhage Carotid artery stenosis and occlusion
Ultrasound in Rheumatology
 Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
Case 27 Clinical Presentation
 53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (4), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (4), Page 2294-2300 Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Ultrasonography in Diagnosis and Follow Up Rheumatoid Arthritis in Hand and Wrist
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (4), Page 2294-2300 Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Ultrasonography in Diagnosis and Follow Up Rheumatoid Arthritis in Hand and Wrist
Patient #1. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis. 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour
 Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
Role of Imaging in Management of Hemophilic Patients
 Pediatric Imaging Ng et al. Imaging of Hemophilic Patients W. H. Ng 1 W. C. W. Chu 1 M. K. Shing 2 W. W. M. Lam 1 K. W. Chik 2 C. K. Li 2 C. K. Li 3 S. C. Ling 3 Ng WH, Chu WCW, Shing MK, et al. Received
Pediatric Imaging Ng et al. Imaging of Hemophilic Patients W. H. Ng 1 W. C. W. Chu 1 M. K. Shing 2 W. W. M. Lam 1 K. W. Chik 2 C. K. Li 2 C. K. Li 3 S. C. Ling 3 Ng WH, Chu WCW, Shing MK, et al. Received
Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures
 Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Outline Hip Joint Native hip
Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Outline Hip Joint Native hip
Candida Parapsilosis Arthritis Involving the Ankle in a Diabetes Patient: A Case Report 1
 Candida Parapsilosis Arthritis Involving the Ankle in a Diabetes Patient: A Case Report 1 Jinkyeong Sung, M.D., Kyung Ah Chun, M.D. Candida parapsilosis is a rare opportunistic fungal pathogen of the musculoskeletal
Candida Parapsilosis Arthritis Involving the Ankle in a Diabetes Patient: A Case Report 1 Jinkyeong Sung, M.D., Kyung Ah Chun, M.D. Candida parapsilosis is a rare opportunistic fungal pathogen of the musculoskeletal
Indian Journal of Medical Research and Pharmaceutical Sciences August 2015; 2(8) ISSN: ISSN: Impact Factor (PIF): 2.672
 CASE REPORT OF TUBERCULOUS SUBDELTOID BURSITIS WITH RICE BODIES Dr. Jhatoth Venkateshwarlu*, Dr. Tandra Venkateshwararao, Dr. K. Ramkumar Reddy, Dr. K.Venkatswamy, Dr. M.Sudhir MS Orthopaedics, Associate
CASE REPORT OF TUBERCULOUS SUBDELTOID BURSITIS WITH RICE BODIES Dr. Jhatoth Venkateshwarlu*, Dr. Tandra Venkateshwararao, Dr. K. Ramkumar Reddy, Dr. K.Venkatswamy, Dr. M.Sudhir MS Orthopaedics, Associate
Knee: Cruciate Ligaments
 72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT
 TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP JOINT Occurrence-15% of all osteo articular tuber culosis Next common after spinal TB AETIO PATHOGENESIS Most common cause Mycobacterium tuberculosis
TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP JOINT Occurrence-15% of all osteo articular tuber culosis Next common after spinal TB AETIO PATHOGENESIS Most common cause Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Post-injury painful and locked knee
 H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies
 Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
The Acute Calcific Prevertebral Tendinitis : Report of Two Cases
 The Acute Calcific Prevertebral Tendinitis : Report of Two Cases Asian Spine Journal Vol. 4, No. 2, pp 123~127, 2010 doi:10.4184/asj.2010.4.2.123 Dong-Eun Shin 1, Chang-Soo Ahn 2, Jung-Pil Choi 1 1 Department
The Acute Calcific Prevertebral Tendinitis : Report of Two Cases Asian Spine Journal Vol. 4, No. 2, pp 123~127, 2010 doi:10.4184/asj.2010.4.2.123 Dong-Eun Shin 1, Chang-Soo Ahn 2, Jung-Pil Choi 1 1 Department
Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A
 Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Assessing Cervical Spinal Canal Compression
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition
 Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition Firestein, G ISBN-13: 9781437717389 Table of Contents VOLUME I STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BONE,
Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition Firestein, G ISBN-13: 9781437717389 Table of Contents VOLUME I STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BONE,
Disclosures. Ultrasonography. Conventional radiography (XR) Magnetic resonance imaging. Conventional CT 10/27/2013
 What I can see in my gout patient that I couldn t before: the role of advanced imaging in gout diagnosis and monitoring Disclosures ND is supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand I have
What I can see in my gout patient that I couldn t before: the role of advanced imaging in gout diagnosis and monitoring Disclosures ND is supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand I have
Urgent Cases and Foreign Bodies
 Urgent Cases and Foreign Bodies Catherine J. Brandon, MD, MS University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI, USA Introduction: Patients added on to the schedule from the emergency department or as urgent add-on
Urgent Cases and Foreign Bodies Catherine J. Brandon, MD, MS University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI, USA Introduction: Patients added on to the schedule from the emergency department or as urgent add-on
triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
MRI Findings of Subcutaneous Epidermal Cysts: Emphasis on the Presence of Rupture
 MRI Findings of Subcutaneous Epidermal Cysts Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C D E M N E U T R Y L I M C I G O F I N G Sung Hwan Hong 1 Hye Won Chung 2 Ja-Young Choi 1 Young Hwan Koh 1 Jung-h
MRI Findings of Subcutaneous Epidermal Cysts Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C D E M N E U T R Y L I M C I G O F I N G Sung Hwan Hong 1 Hye Won Chung 2 Ja-Young Choi 1 Young Hwan Koh 1 Jung-h
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint. Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital
 Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach
 Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1
 CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Survey of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Features in the Musculoskeletal System
 J HK Coll Radiol 2002;5:63-68 PL Munk, LO Marchinkow, WC Torreggiani, MJ Lee PICTORIAL ESSAY Rheumatoid Arthritis: Survey of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Features in the Musculoskeletal System PL Munk, LO
J HK Coll Radiol 2002;5:63-68 PL Munk, LO Marchinkow, WC Torreggiani, MJ Lee PICTORIAL ESSAY Rheumatoid Arthritis: Survey of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Features in the Musculoskeletal System PL Munk, LO
Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis
 Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis JIA is the most common rheumatic disease in childhood and a major cause of chronic disability. Etiology: Unknown, but may
Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis JIA is the most common rheumatic disease in childhood and a major cause of chronic disability. Etiology: Unknown, but may
Wrist and Ankle MRI of Patients With Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Identification of Unsuspected Multicompartmental Tenosynovitis and Arthritis
 Pediatric Imaging Original Research Javadi et al. Wrist and nkle MRI of Patients With Juvenile Idiopathic rthritis Pediatric Imaging Original Research Sanaz Javadi 1 J. Herman Kan 1 Robert C. Orth 1 Marietta
Pediatric Imaging Original Research Javadi et al. Wrist and nkle MRI of Patients With Juvenile Idiopathic rthritis Pediatric Imaging Original Research Sanaz Javadi 1 J. Herman Kan 1 Robert C. Orth 1 Marietta
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
MRI IN NONOSSEOUS ABNORMALITIES OF THE FOREFOOT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW
 MRI IN NONOSSEOUS ABNORMALITIES OF THE FOREFOOT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW I Delgado, P Melloni, M Veintemillas, R Valls, M Vilagran, A Valera UDIAT. Sabadell (Barcelona). Spain. PURPOSE To catalog the wide spectrum
MRI IN NONOSSEOUS ABNORMALITIES OF THE FOREFOOT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW I Delgado, P Melloni, M Veintemillas, R Valls, M Vilagran, A Valera UDIAT. Sabadell (Barcelona). Spain. PURPOSE To catalog the wide spectrum
Manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis: epidural pannus and atlantoaxial subluxation resulting in basilar invagination.
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Rehabilitation Medicine Faculty Papers Department of Rehabilitation Medicine 1-1-2012 Manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis: epidural
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Rehabilitation Medicine Faculty Papers Department of Rehabilitation Medicine 1-1-2012 Manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis: epidural
MRI of Bucket-Handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1
 MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis of the Axial Joints: A Systematic Review of the Diagnostic Accuracy and Predictive Value of Conventional MRI
 Pediatric Imaging Review Munir et al. MRI for Diagnosis of JIA in the Axial Joints Pediatric Imaging Review Sohaib Munir 1 Kedar Patil 2 Elka Miller 3 Elizabeth Uleryk 3 Marinka Twilt 3 Lynn Spiegel 3
Pediatric Imaging Review Munir et al. MRI for Diagnosis of JIA in the Axial Joints Pediatric Imaging Review Sohaib Munir 1 Kedar Patil 2 Elka Miller 3 Elizabeth Uleryk 3 Marinka Twilt 3 Lynn Spiegel 3
Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies
 Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Bilateral Shoulder Pain
 HR J Bilateral Shoulder Pain, p. 64-69 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Bilateral Shoulder Pain Musculoskeletal Eirini D. Savva, Rafaela M. Smarlamaki, Foteini I. Terezaki Department of Radiology, University
HR J Bilateral Shoulder Pain, p. 64-69 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Bilateral Shoulder Pain Musculoskeletal Eirini D. Savva, Rafaela M. Smarlamaki, Foteini I. Terezaki Department of Radiology, University
MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia
 MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia discuss the most common normal variants in the pediatric knee that may simulate pathology
MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia discuss the most common normal variants in the pediatric knee that may simulate pathology
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls
 MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
Meniscal Tears: Role of Axial MRI Alone and in Combination with Other Imaging Planes
 Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain
 Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
MRI of Cartilage. D. BENDAHAN (PhD)
 MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
Radiologic Pathologic Correlation of Intraosseous Lipomas. Tim Propeck 1, Mary Anne Bullard 1, John Lin 1, Kei Doi 2, William Martel 1
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORAL HEAD AND NECK
 908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot. Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine
 MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine Disclosures Under contract with Lippincott Williams and Wilkins (LWW)
MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine Disclosures Under contract with Lippincott Williams and Wilkins (LWW)
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients
 Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
Lumbar Actinomycosis: A Case Report 1
 Lumbar Actinomycosis: A Case Report 1 Min Hee Lee, M.D., Jang Gyu Cha, M.D., Eun Ju Choo, M.D. 2, Kyeong Cheon Jung, M.D. 3, Jai Soung Park, M.D., Sung-Il Park, M.D., Sang Hyun Paik, M.D., Hae Kyung Lee,
Lumbar Actinomycosis: A Case Report 1 Min Hee Lee, M.D., Jang Gyu Cha, M.D., Eun Ju Choo, M.D. 2, Kyeong Cheon Jung, M.D. 3, Jai Soung Park, M.D., Sung-Il Park, M.D., Sang Hyun Paik, M.D., Hae Kyung Lee,
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms.
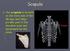 The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
The role of CT and MRI in evaluation of Osteoid Oteoma
 The role of CT and MRI in evaluation of Osteoid Oteoma Elene Iordanishvili Tbilisi Sate Medical University Instructor: Prof. Dr. Ketevan Kotetishvili Department of Physics Georgian Technical University
The role of CT and MRI in evaluation of Osteoid Oteoma Elene Iordanishvili Tbilisi Sate Medical University Instructor: Prof. Dr. Ketevan Kotetishvili Department of Physics Georgian Technical University
Magnetic resonance imaging of ulnar nerve abscess in leprosy: a case report
 Lepr Rev (2006) 77, 381 385 CASE REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of ulnar nerve abscess in leprosy: a case report SMRITI HARI, SUBRAMANIAN SUBRAMANIAN & RAJU SHARMA Department of Radiodiagnosis, All
Lepr Rev (2006) 77, 381 385 CASE REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of ulnar nerve abscess in leprosy: a case report SMRITI HARI, SUBRAMANIAN SUBRAMANIAN & RAJU SHARMA Department of Radiodiagnosis, All
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Ultrasound of the Knee
 Ultrasound of the Knee Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties: Elsevier Advisory
Ultrasound of the Knee Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties: Elsevier Advisory
patients with rheumatoid arthritis
 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: -11 SCINTIFIC PAPRS Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University Hospital, Leiden, The Netherlands G J Kieft J L Bloem H M Kroon Department of Rheumatology,
Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: -11 SCINTIFIC PAPRS Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University Hospital, Leiden, The Netherlands G J Kieft J L Bloem H M Kroon Department of Rheumatology,
Pott disease (spinal tuberculosis): MR and CT imaging
 Pott disease (spinal tuberculosis): MR and CT imaging Poster No.: C-1422 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. Beretis, K. Giannaki, M. Fasoula, D. Kypriotis, T. Dagla, T.-P. Mantzouranis;
Pott disease (spinal tuberculosis): MR and CT imaging Poster No.: C-1422 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. Beretis, K. Giannaki, M. Fasoula, D. Kypriotis, T. Dagla, T.-P. Mantzouranis;
FieldStrength. Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
Clinical and Imaging Findings of Musculoskeletal Melioidosis in the Right Hip: A Case Report 우측대퇴부에서발생한근골격계유비저의임상적, 영상학적소견 : 증례보고
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 J Korean Soc Radiol 2018;78(3):212-219 https://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2018.78.3.212 Clinical and Imaging Findings of Musculoskeletal Melioidosis in the Right
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 J Korean Soc Radiol 2018;78(3):212-219 https://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2018.78.3.212 Clinical and Imaging Findings of Musculoskeletal Melioidosis in the Right
When Pads of Fat are a Welcome Sight: Fat Pads in Acute Musculoskeletal Imaging
 When Pads of Fat are a Welcome Sight: Fat Pads in Acute Musculoskeletal Imaging Poster No.: C-2444 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Zakhary 1, M. Adix 2, C. Yablon
When Pads of Fat are a Welcome Sight: Fat Pads in Acute Musculoskeletal Imaging Poster No.: C-2444 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Zakhary 1, M. Adix 2, C. Yablon
The mandibular condyle fracture is a common mandibular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Synovial Disorders
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Synovial Disorders Poster No.: P-0036 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. Arkun, S. Orguc, M. ARGIN ; Izmir/TR, Istanbul/TR Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Synovial Disorders Poster No.: P-0036 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. Arkun, S. Orguc, M. ARGIN ; Izmir/TR, Istanbul/TR Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review.
 Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Radiography is typically the first imaging study in evaluation for arthritis. On radiographs, one critical assessment is differentiating inflammatory
 Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, use the Radiology Reprints form at the end of this article.
Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, use the Radiology Reprints form at the end of this article.
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review.
 Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Monophasic Synovial Carcinoma of knee joint- A Case Report and Review of Literature
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.5 March. (2018), PP 13-17 www.iosrjournals.org Monophasic Synovial Carcinoma of knee
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.5 March. (2018), PP 13-17 www.iosrjournals.org Monophasic Synovial Carcinoma of knee
Sonographic appearance of chronic inflammatory rheumatism
 Sonographic appearance of chronic inflammatory rheumatism Poster No.: C-2237 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Elfattach, F. Houari, O. Addou, M. Maaroufi, S. Tizniti ; 1 1 1 1 2
Sonographic appearance of chronic inflammatory rheumatism Poster No.: C-2237 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Elfattach, F. Houari, O. Addou, M. Maaroufi, S. Tizniti ; 1 1 1 1 2
Radiological Reasoning: Acutely Painful Swollen Finger. Musculoskeletal Imaging Chew and Richardson Benign-Appearing Bone Mass.
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Chew and Richardson Benign-Appearing Bone Mass AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY This Radiological Reasoning article is available for SAM credit and CME credits
Musculoskeletal Imaging Chew and Richardson Benign-Appearing Bone Mass AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY This Radiological Reasoning article is available for SAM credit and CME credits
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines
 Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
MRI Features of Lyme Arthritis in Children
 Pediatric Imaging Ecklund et al. MRI of Lyme Arthritis in Children Kirsten Ecklund 1 Sigella Vargas 1 David Zurakowski 2 Robert P. Sundel 3 Ecklund K, Vargas S, Zurakowski D, Sundel RP Received June 30,
Pediatric Imaging Ecklund et al. MRI of Lyme Arthritis in Children Kirsten Ecklund 1 Sigella Vargas 1 David Zurakowski 2 Robert P. Sundel 3 Ecklund K, Vargas S, Zurakowski D, Sundel RP Received June 30,
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST
 MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST Wrist Instability Dissociative Pattern apparent on routine radiographs Non-dissociative Stress / positional radiographs Dynamic fluoroscopy during stress Arthrography MRI / MR arthrography
MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST Wrist Instability Dissociative Pattern apparent on routine radiographs Non-dissociative Stress / positional radiographs Dynamic fluoroscopy during stress Arthrography MRI / MR arthrography
Synovial Hemangioma of the elbow: An uncommon lesion to be considered
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 7 Number 2 Synovial Hemangioma of the elbow: An uncommon lesion to be considered A Mohammadi, M Rosa, D Wolfson Citation A Mohammadi, M Rosa, D Wolfson.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 7 Number 2 Synovial Hemangioma of the elbow: An uncommon lesion to be considered A Mohammadi, M Rosa, D Wolfson Citation A Mohammadi, M Rosa, D Wolfson.
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Giant-cell tumor of the tendon sheath: when must we suspect it?
 Giant-cell tumor of the tendon sheath: when must we suspect it? Poster No.: C-0538 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Santos Montón, J. M. Alonso Sánchez, D. C. Cuellar, P. A. Chaparro
Giant-cell tumor of the tendon sheath: when must we suspect it? Poster No.: C-0538 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Santos Montón, J. M. Alonso Sánchez, D. C. Cuellar, P. A. Chaparro
Case Study. Your Diagnosis?
 Case Study 35 year old man twisted his ankle while playing and was surgically for treated for ankle sprain for instability symptoms 2 years. Increasing pain around the ankle and pain present all the time
Case Study 35 year old man twisted his ankle while playing and was surgically for treated for ankle sprain for instability symptoms 2 years. Increasing pain around the ankle and pain present all the time
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review
 Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Musculoskeletal Imaging What to order? Brian Cole, MD
 Musculoskeletal Imaging What to order? Brian Cole, MD my background: 1994 University of Illinois 1998 MD University of Illinois College of Medicine 1999-2003 Diagnostic Radiology Mayo Clinic 2004 Fellowship
Musculoskeletal Imaging What to order? Brian Cole, MD my background: 1994 University of Illinois 1998 MD University of Illinois College of Medicine 1999-2003 Diagnostic Radiology Mayo Clinic 2004 Fellowship
Unilateral Sacroiliitis: Differential Diagnosis Between Infectious Sacroiliitis and Spondyloarthritis Based on MRI Findings
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kang et al. Use of MRI to Differentiate Infectious Sacroiliitis From Spondyloarthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Yusuhn Kang 1 Sung Hwan Hong Ji
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kang et al. Use of MRI to Differentiate Infectious Sacroiliitis From Spondyloarthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Yusuhn Kang 1 Sung Hwan Hong Ji
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging
 Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
Radiologic Finding of Failed Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
 Radiologic Finding of Failed Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Liu, Wei Chiang 1, M.D., Sang-Ho Lee 2, M.D., Won Gyu Choi 2, M.D., Dong-Yeob Lee 2, M.D., Sung Suk Paeng 3, M.D., Amy Kwon 4, Ph.D. Department
Radiologic Finding of Failed Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Liu, Wei Chiang 1, M.D., Sang-Ho Lee 2, M.D., Won Gyu Choi 2, M.D., Dong-Yeob Lee 2, M.D., Sung Suk Paeng 3, M.D., Amy Kwon 4, Ph.D. Department
