Rapid evolution of highly variable competitive abilities in a key phytoplankton species
|
|
|
- Christal Manning
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTARY Brief Communication INFORMATION In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Rapid evolution of highly variable competitive abilities in a key phytoplankton species Lennart T. Bach 1 *, Kai T. Lohbeck 1,2, Thorsten B. H. Reusch 1 and Ulf Riebesell 1 1 GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, Kiel, Germany. 2 Present address: Department of Marine Sciences, University of Gothenburg, Göteborg, Sweden. * lbach@geomar.de Nature Ecology & Evolution Macmillan Publishers Limited, part of Springer Nature. All rights reserved.
2 1 Title: Rapid evolution of highly variable competitive abilities in a key phytoplankton species 2 3 Supplementary Tables Table S1. Summary of the statistical analysis. The statistical analysis was conducted as 2x2 factorial design with the fixed factors selection and complex environment, in combination with a sub-replication (n=3) at the level of independent long-term lineages, permitting to compare lineages (=replicates) within treatment combinations (the final abundance was log-transformed to meet the prerequisites of parametric statistical testing (i.e. variance homogeneity, normal distribution of residuals)). Neither the main factors of the complex environment (complex) nor the selection environment (select) or the interaction of both (complex*select) had a significant influence on E. huxleyi final abundance after 26 days in the complex environments. In contrast, the variation among replicates within treatment combinations, assessed as random factor nested in complex*select had a significant effect on the final abundance (P=0.001). The affiliation to a particular lineage explained 43.9 % of the variance between lineages after 26 days in the complex environments. 17 Nested analysis traditional least square variance component by nested factor MS df F P Var component % of total complex nested[complex,select]&random select residual complex*select total nested[complex,select]&random residual
3 Table S2. Microzooplankton abundance. Microzooplankton populations (mostly ciliates) were distinguished from other particles based on FSC-A and FL3-A/FL2-A (red/orange) fluorescence signal strength using the Cytosense imaging flow cytometer (Cytobuoy) which is specifically designed for the quantification of plankton in natural samples. The microzooplankton population in the cytogram had a slightly elevated red/orange fluorescence ratio and could therefore be distinguished from other particles. The population was photographed during the measurement to reassure that the particles in the gated population were ciliates. It should be kept in mind, however, that the gated population may only represent part of the microzooplankton present in the microcosms. Organisms with other scatter and fluorescence properties may have co-existed but not been included in the designated microzooplankton gate. Nevertheless, these measurements support our statement that microzooplankton grazers were present in all microcosms (see main text). Please note that the measurement is time consuming (10 minutes per sample) so that we could not determine the abundances in all 60 replicates on every sampling day. All abundances are given in cells ml -1. Day of experiment Environment Selection line Replicate Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control
4 Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA
5 34 OA OA OA OA Table S3. Copepod abundance at the end of the experiment. Copepods were sampled on the last day of the experiment (day 26). Therefore, 550 ml of microcosm volume were filtered with a 55 µm (mesh size) net while emptying the bottles. The individuals collected on the net were transferred into 30 ml beakers and conserved with Lugol solution (1%) until quantification with a Leica stereomicroscope in a Bogorov chamber. Copepodites and smaller copepods (<1 mm) were identified mostly as Pseudocalanus acuspes or Oithona similis. Larger copepods (>1 mm) were mostly Pseudocalanus acuspes or Temora longicornis. All abundances are shown in individuals L -1. Environment Selection line Replicate Nauplii Copepodites Smaller copepods Larger copepods control control control control control control control control control control control control control control control control control control control control control
6 43 control control control control control control control control control OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA OA Supplementary Figures
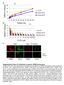
7 Figure S1. Development of abundance and relative fluorescence of the 10 lineages during the 26 days challenge experiment. (A, B) Abundance. (C, D) Relative fluorescence. Each line represents the mean development of one lineage (average of triplicate incubations). Visualization of standard deviations were omitted to maintain clarity. Please note that standard deviations on days 12 and 26 are shown in the bar charts of Fig. 1C, D. Cool and warm colours show control and OA lineages, respectively. Subplots on the left (A, C) and on the right (B, D) show the developments in the control and the OA environment, respectively.
8 Figure S2. Initial growth rate vs. final abundance relationship. E. huxleyi growth rate at the beginning (average of days 0 4) of the experiment in the complex environment vs. E. huxleyi cell abundance at the last day (day 26) in the complex environment. µ was calculated as: (ln(t 4 )-ln(t 0 ))/4, where t 0 and t 4 are E. huxleyi cell abundances on day 0 and day 4, respectively. The figure legend shows the selection environment (first term) and the test environment (second term). For example, control->oa refers to lineages that were cultured for 1700 generations in the simplified control environment and then transferred into the complex OA environment. The positive correlation underlines that high growth rates at the onset of a bloom largely determined peak abundance 1.
9 Figure S3. Fitness of E. huxleyi lineages in the simplified environment in relation to final abundance or growth in the complex environment. Growth rates of the 10 E. huxleyi lineages in the simplified laboratory experiment after 1600 generations 2,3 (x-axis) vs. (A) cell abundance of the lineages after 26 days in the complex environments or vs. (B) growth rates of the lineages in the complex environments at the beginning of the experiment (days 0 4) where all lineages were growing exponentially (see Fig. S1). The figure legend shows the simplified selection environment (first term) and the test environment (second term). For example, control->oa refers to lineages that were cultured in the simplified control environment but growth rates were tested in the OA environment. The test environment was a simplified one in case of the growth rate data taken from the Lohbeck and Schlüter et al studies 2,3 (x-axis) or a complex environment for the experiments
10 73 presented here (y-axis). Neither of the two correlations is significant (p>>0.05), demonstrating that 74 growth rates determined in the simplified environment are poor indicators for growth rate and 75 bloom intensity in a complex environment. (Please note that Schlüter et al.8 determined growth rates 76 in the simplified test environment after 1600 generations of selection in the simplified environment 77 whereas the experiment in the complex test environment (this study) was performed after generations of selection in the simplified environment. Thus, it is important to keep in mind that the 79 correlations shown here include a 100 generations mismatch.) Figure S4. Experimental design. Step A: E. huxleyi cells were collected in Norway (Raunefjord) 82 and transported to Kiel, Germany. Step B: A single genotype was isolated from the E. huxleyi 83 assemblage. Five control and five OA lineages were established from this genotype and grown 84 exponentially for 3 years in semi-continuous batch cultures under simplified laboratory conditions2 85 (the selection environment). Step C: Natural plankton assemblages were collected after 3 months of 86 growth in a control and an OA mesocosm and split in 30 microcosms, respectively. (Step D) The 87 OA-adapted and control E. huxleyi lineages were incubated in the OA-acclimated and control
11 88 microcosms and attached to a plankton wheel for 26 days (i.e. the experiment in the complex 89 environments). The objective of the experiment in the complex experiment was to assess whether 90 adaptive evolution to a common stressor (in this case OA) in a simple laboratory environment is 91 associated with equivalent fitness gains in a complex natural environment Figure S5. Gating strategy in the flow cytometer analysis. (A) Population I could be distinguished 94 best from electronic noise on the FL3-A vs. FL4-A plot. (B) Several phytoplankton populations and 95 E. huxleyi were gated on the SSC-A vs. FL3-A plot. Plots (C) and (D) illustrate the differences in 96 forward scatter (FSC-A) and side scatter (SSC-A) characteristics of the E. huxleyi population. E. 97 huxleyi was close to, and in some samples indistinguishable from, population III on the FSC-A 98 channel but there was never overlap with any other populations when using the SSC-A channel for 99 gating.
12 Figure S6. Temporal development of ph. Blue and red lines show the average development of 5 control and 5 OA lineages, respectively. Shaded areas represent ± 1 standard deviations. ph was calibrated to the free scale with certified seawater standard as described by Bach et al 4. The slight ph increase over time was most likely due to autotrophic biomass build-up in the course of the experiment. Please note that the 10 lineages were accustomed to ph drift within this range as they experienced the same degree of ph drift in the semi-continuous batch culture during the laboratory adaptation phase in the simplified environments 2, Supplementary references 1. Riebesell, U. et al. Nat. Geosci. 10, (2017). 2. Lohbeck, K. T., Riebesell, U. & Reusch, T. B. H. Nat. Geosci. 5, (2012). 3. Schlüter, L., Lohbeck, K. T., Gröger, J. P., Riebesell, U. & Reusch, T. B. H. Sci. Adv. 2, e (2016). 4. Bach, L. T., Bauke, C., Meier, K. J. S., Riebesell, U. & Schulz, K. G. Biogeosciences 9, (2012).
EOSC Biology 3. Zooplankton Measurements
 EOSC 473-573 Biology 3 Zooplankton Measurements Zooplankton Biomass and Abundance Two Quantitative Procedures: Biomass Determination (mg C per m 3 or per m 2 ) Abundance (# individuals per m 3 or per m
EOSC 473-573 Biology 3 Zooplankton Measurements Zooplankton Biomass and Abundance Two Quantitative Procedures: Biomass Determination (mg C per m 3 or per m 2 ) Abundance (# individuals per m 3 or per m
Meaning-based guidance of attention in scenes as revealed by meaning maps
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters DOI: 1.138/s41562-17-28- In the format provided by the authors and unedited. -based guidance of attention in scenes as revealed by meaning maps John M. Henderson 1,2 *
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters DOI: 1.138/s41562-17-28- In the format provided by the authors and unedited. -based guidance of attention in scenes as revealed by meaning maps John M. Henderson 1,2 *
Ocean acidification effects on plankton communities, ecosystem structure and carbon cycling
 Ocean acidification effects on plankton communities, ecosystem structure and carbon cycling Monika Winder Department of Ecology, Environment and Plant Sciences Stockholm University What does a more acidic
Ocean acidification effects on plankton communities, ecosystem structure and carbon cycling Monika Winder Department of Ecology, Environment and Plant Sciences Stockholm University What does a more acidic
Global diversity patterns of marine phytoplankton and zooplankton
 AIV presentation 14/10/05 Claude Loverdo Sakina Ayata Global diversity patterns of marine phytoplankton and zooplankton X.Irigoien, J.Huisman and R.P.Harris Nature 429, 863-867 (2004) Presentation's overview
AIV presentation 14/10/05 Claude Loverdo Sakina Ayata Global diversity patterns of marine phytoplankton and zooplankton X.Irigoien, J.Huisman and R.P.Harris Nature 429, 863-867 (2004) Presentation's overview
Farmington Bay Report Corixid Predation on Brine Shrimp Dr. Gary E. Belovsky March 20, 2005
 Farmington Bay Report Corixid Predation on Brine Shrimp Dr. Gary E. Belovsky March 20, 2005 This report deals with preliminary studies of phytoplankton and corixid predation on brine shrimp conducted in
Farmington Bay Report Corixid Predation on Brine Shrimp Dr. Gary E. Belovsky March 20, 2005 This report deals with preliminary studies of phytoplankton and corixid predation on brine shrimp conducted in
Primary Productivity and Lake Health: Examination of Phytoplankton Growth Rate Regulations in Keuka Lake via Short-term Microcosm Experiments
 Primary Productivity and Lake Health: Examination of Phytoplankton Growth Rate Regulations in Keuka Lake via Short-term Microcosm Experiments Extended Abstract Rochester Academy of Sciences Student Scientific
Primary Productivity and Lake Health: Examination of Phytoplankton Growth Rate Regulations in Keuka Lake via Short-term Microcosm Experiments Extended Abstract Rochester Academy of Sciences Student Scientific
Biogeosciences Discussions
 Biogeosciences Discuss., 9, C6311 C6319, 2012 www.biogeosciences-discuss.net/9/c6311/2012/ Author(s) 2012. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. Biogeosciences Discussions
Biogeosciences Discuss., 9, C6311 C6319, 2012 www.biogeosciences-discuss.net/9/c6311/2012/ Author(s) 2012. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. Biogeosciences Discussions
Concentration Estimation from Flow Cytometry Exosome Data Protocol
 Concentration Estimation from Flow Cytometry Exosome Data Protocol 1. STANDARD CURVE Create a standard curve for the target exosome by plotting the mean fluorescence (y axis) against the protein concentration
Concentration Estimation from Flow Cytometry Exosome Data Protocol 1. STANDARD CURVE Create a standard curve for the target exosome by plotting the mean fluorescence (y axis) against the protein concentration
A simple and rapid flow cytometry-based assay to identify a competent embryo prior to embryo transfer.
 A simple and rapid flow cytometry-based assay to identify a competent embryo prior to embryo transfer. Eva Pallinger 1, Zoltan Bognar 2,5,7, Jozsef Bodis 3,4,7, Timea Csabai 2,5,7, Nelli Farkas 6 Krisztina
A simple and rapid flow cytometry-based assay to identify a competent embryo prior to embryo transfer. Eva Pallinger 1, Zoltan Bognar 2,5,7, Jozsef Bodis 3,4,7, Timea Csabai 2,5,7, Nelli Farkas 6 Krisztina
University of Groningen. The origin of DMS(P)cies Kwint, Richard Leendert Jan
 University of Groningen The origin of DMS(P)cies Kwint, Richard Leendert Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen The origin of DMS(P)cies Kwint, Richard Leendert Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
148 0#7 y VV h y å &>%30%%2% (1983)
 148 0#7 y VV h y å &>%30%%2% (1983) constant or "saturated") has been frequently observed in laboratory studies (CORNER et al. 1972, FROST 1972). Saturation of ingestion rate has also been observed for
148 0#7 y VV h y å &>%30%%2% (1983) constant or "saturated") has been frequently observed in laboratory studies (CORNER et al. 1972, FROST 1972). Saturation of ingestion rate has also been observed for
Grazing Indices of Zooplankton on Phytoplankton in the San Juan Channel in Jordan Omoto. University of Washington and Friday Harbor Labs
 Grazing Indices of Zooplankton on Phytoplankton in the San Juan Channel in 216 Jordan Omoto University of Washington and Friday Harbor Labs PEF Ocean 492 Email: jdomoto@uw.edu Keywords: phytoplankton,
Grazing Indices of Zooplankton on Phytoplankton in the San Juan Channel in 216 Jordan Omoto University of Washington and Friday Harbor Labs PEF Ocean 492 Email: jdomoto@uw.edu Keywords: phytoplankton,
Feeding Measurements
 Feeding Measurements Measures of Feeding Rates (or specific mortality rate) Clearance Rate Concept Clearance Rate (F) = Volume cleared of prey pred -1 time -1 predator prey A consumer may have different
Feeding Measurements Measures of Feeding Rates (or specific mortality rate) Clearance Rate Concept Clearance Rate (F) = Volume cleared of prey pred -1 time -1 predator prey A consumer may have different
Zooplankton. Fall 2006
 Zooplankton Fall 2006 Plankton Classification Plankton Holoplankton Meroplankton Plankton Classification Picoplankton (0.2 2 µm) Plankton Nanoplankton (2-20 µm) Microplankton (20-200 µm) Mesoplankton (200-2000
Zooplankton Fall 2006 Plankton Classification Plankton Holoplankton Meroplankton Plankton Classification Picoplankton (0.2 2 µm) Plankton Nanoplankton (2-20 µm) Microplankton (20-200 µm) Mesoplankton (200-2000
Nature Protocols: doi: /nprot Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Traditional electronic gating strategy for analysing cell death based on A5-FITC and 7-AAD. a, Flow cytometry analysis showing the traditional two-stage electronic gating strategy
Supplementary Figure 1 Traditional electronic gating strategy for analysing cell death based on A5-FITC and 7-AAD. a, Flow cytometry analysis showing the traditional two-stage electronic gating strategy
The unconstrained evolution of fast and efficient antibiotic-resistant bacterial genomes
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. VOLUME: ARTICLE NUMBER: 5 The unconstrained evolution of fast and efficient antibiotic-resistant bacterial genomes Carlos Reding-Roman, Mark Hewlett,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. VOLUME: ARTICLE NUMBER: 5 The unconstrained evolution of fast and efficient antibiotic-resistant bacterial genomes Carlos Reding-Roman, Mark Hewlett,
ab Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Cell culture
 Version 1 Last updated 14 March 2018 ab228564 Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Cell culture For the measurement of human exosomes in cell culture. This product is for research use only
Version 1 Last updated 14 March 2018 ab228564 Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Cell culture For the measurement of human exosomes in cell culture. This product is for research use only
Microplastic ingestion: the role of taste
 Microplastic ingestion: the role of taste Renske Vroom 1,2, Claudia Halsband 1, Ellen Besseling 2, Bart Koelmans 2 1 Akvaplan-niva, Fram Centre, Tromsø, Norway 2 Wageningen University and Research Centre,
Microplastic ingestion: the role of taste Renske Vroom 1,2, Claudia Halsband 1, Ellen Besseling 2, Bart Koelmans 2 1 Akvaplan-niva, Fram Centre, Tromsø, Norway 2 Wageningen University and Research Centre,
Is sedimentation of copepod faecal pellets determined by cyclopoids? Evidence from enclosed ecosystems
 Is sedimentation of copepod faecal pellets determined by cyclopoids? Evidence from enclosed ecosystems CAMILLA SVENSEN* AND JENS C. NEJSTGAARD NORWEGIAN COLLEGE OF FISHERY SCIENCE, UNIVERSITY OF TROMSØ,
Is sedimentation of copepod faecal pellets determined by cyclopoids? Evidence from enclosed ecosystems CAMILLA SVENSEN* AND JENS C. NEJSTGAARD NORWEGIAN COLLEGE OF FISHERY SCIENCE, UNIVERSITY OF TROMSØ,
d e f Spatiotemporal quantification of subcellular ATP levels in a single HeLa cell during changes in morphology Supplementary Information
 Ca 2+ level (a. u.) Area (a. u.) Normalized distance Normalized distance Center Edge Center Edge Relative ATP level Relative ATP level Supplementary Information Spatiotemporal quantification of subcellular
Ca 2+ level (a. u.) Area (a. u.) Normalized distance Normalized distance Center Edge Center Edge Relative ATP level Relative ATP level Supplementary Information Spatiotemporal quantification of subcellular
Trade off-based zooplankton feeding strategies in a global model
 Trade off-based zooplankton feeding strategies in a global model Fi Prowe 1,2 Ken Andersen 2 Andy Visser 2 Thomas Kiørboe 2 Bei Su 1 Markus Pahlow 1 Andreas Oschlies 1 1 GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean
Trade off-based zooplankton feeding strategies in a global model Fi Prowe 1,2 Ken Andersen 2 Andy Visser 2 Thomas Kiørboe 2 Bei Su 1 Markus Pahlow 1 Andreas Oschlies 1 1 GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean
Principles of Experimental Design
 Principles of Experimental Design Bret Hanlon and Bret Larget Department of Statistics University of Wisconsin Madison November 15, 2011 Designing Experiments 1 / 31 Experimental Design Many interesting
Principles of Experimental Design Bret Hanlon and Bret Larget Department of Statistics University of Wisconsin Madison November 15, 2011 Designing Experiments 1 / 31 Experimental Design Many interesting
Principles of Experimental Design
 Principles of Experimental Design Bret Hanlon and Bret Larget Department of Statistics University of Wisconsin Madison November 15, 2011 Designing Experiments 1 / 31 Experimental Design Many interesting
Principles of Experimental Design Bret Hanlon and Bret Larget Department of Statistics University of Wisconsin Madison November 15, 2011 Designing Experiments 1 / 31 Experimental Design Many interesting
Cervical Cancer Surgery:
 Cervical Cancer Surgery: Basic Information 1. What is being measured? 2. Why is it being measured? 3. How is the indicator defined? The proportion of cervical cancer patients who received surgery. Surgery
Cervical Cancer Surgery: Basic Information 1. What is being measured? 2. Why is it being measured? 3. How is the indicator defined? The proportion of cervical cancer patients who received surgery. Surgery
Marine Life. Plankton and Primary Production
 Marine Life Plankton and Primary Production Marine Plankton Key Ideas Drifting, floating and weakly swimming plants and animals - mainly in sunlit portion of ocean Phytoplankton Plankton make up more well
Marine Life Plankton and Primary Production Marine Plankton Key Ideas Drifting, floating and weakly swimming plants and animals - mainly in sunlit portion of ocean Phytoplankton Plankton make up more well
Zooplankton Chapters 6-8 in Miller for more details. 1. Crustaceans- include shrimp, copepods, euphausiids ("krill")
 I. Major Groups Zooplankton Chapters 6-8 in Miller for more details Heterotrophs consume organic matter rather than manufacturing it, as do autotrophs. Zooplankton can be: herbivores carnivores (several
I. Major Groups Zooplankton Chapters 6-8 in Miller for more details Heterotrophs consume organic matter rather than manufacturing it, as do autotrophs. Zooplankton can be: herbivores carnivores (several
Effect of Acartia grazing on the size distribution of phytoplankton in Academy Bay, Galapagos
 Effect of Acartia grazing on the size distribution of phytoplankton in Academy Bay, Galapagos Jonathan Herzog University of Washington School of Oceanography 1 NON-TECHNICAL SUMMARY The goal of this experiment
Effect of Acartia grazing on the size distribution of phytoplankton in Academy Bay, Galapagos Jonathan Herzog University of Washington School of Oceanography 1 NON-TECHNICAL SUMMARY The goal of this experiment
Electronic Supporting Information for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supporting Information for Microfluidic-enabled quantitative measurements of insulin
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supporting Information for Microfluidic-enabled quantitative measurements of insulin
Experimental Studies. Statistical techniques for Experimental Data. Experimental Designs can be grouped. Experimental Designs can be grouped
 Experimental Studies Statistical techniques for Experimental Data Require appropriate manipulations and controls Many different designs Consider an overview of the designs Examples of some of the analyses
Experimental Studies Statistical techniques for Experimental Data Require appropriate manipulations and controls Many different designs Consider an overview of the designs Examples of some of the analyses
Response of bacterioplankton activity in an Arctic fjord system to elevated pco 2 : results from a mesocosm perturbation study
 Biogeosciences, 1, 297 314, 213 www.biogeosciences.net/1/297/213/ doi:1.5194/bg-1-297-213 Author(s) 213. CC Attribution 3. License. Biogeosciences Response of bacterioplankton activity in an Arctic fjord
Biogeosciences, 1, 297 314, 213 www.biogeosciences.net/1/297/213/ doi:1.5194/bg-1-297-213 Author(s) 213. CC Attribution 3. License. Biogeosciences Response of bacterioplankton activity in an Arctic fjord
In vitro human regulatory T cell suppression assay
 Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, in vitro suppression assay and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell suppression assay Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of
Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, in vitro suppression assay and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell suppression assay Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of
Zooplankton Grazing and Secondary Production in the Indian Ocean
 Zooplankton Grazing and Secondary Production in the Indian Ocean Michael Landry Integrative Oceanography Division Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego SIBER Workshop
Zooplankton Grazing and Secondary Production in the Indian Ocean Michael Landry Integrative Oceanography Division Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego SIBER Workshop
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a
 Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Maintenance of coelomic fluid ph in sea urchins exposed to elevated CO 2 : the role of body cavity epithelia and stereom dissolution
 Marine Biology Supplementary Online Resource For: Maintenance of coelomic fluid ph in sea urchins exposed to elevated CO 2 : the role of body cavity epithelia and stereom dissolution Wiebke C. Holtmann
Marine Biology Supplementary Online Resource For: Maintenance of coelomic fluid ph in sea urchins exposed to elevated CO 2 : the role of body cavity epithelia and stereom dissolution Wiebke C. Holtmann
Supplemental material: Interference between number magnitude and parity: Discrete representation in number processing
 Krajcsi, Lengyel, Laczkó: Interference between number and parity Supplemental material 1/7 Supplemental material: Interference between number magnitude and parity: Discrete representation in number processing
Krajcsi, Lengyel, Laczkó: Interference between number and parity Supplemental material 1/7 Supplemental material: Interference between number magnitude and parity: Discrete representation in number processing
Annual boom bust cycles of polar phytoplankton biomass revealed by space-based lidar
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NGEO2861 Annual boom bust cycles of polar phytoplankton biomass revealed by space-based lidar Michael J. Behrenfeld,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NGEO2861 Annual boom bust cycles of polar phytoplankton biomass revealed by space-based lidar Michael J. Behrenfeld,
Danish Institute for Fisheries Research, Kavalergården 6, DK-2920 Charlottenlund, Denmark
 Seasonal changes in food quantity and quality for the development and egg production of the common North Sea copepods Temora longicornis and Pseudocalanus elongatus 1) Marja Koski, 1) Jörg Dutz and ) Wim
Seasonal changes in food quantity and quality for the development and egg production of the common North Sea copepods Temora longicornis and Pseudocalanus elongatus 1) Marja Koski, 1) Jörg Dutz and ) Wim
ab Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Cell Culture (CD63 / CD81)
 Version 1 Last updated 26 September 2018 ab239682 Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Cell Culture (CD63 / For the isolation and analysis of exosome from cell culture. This product is
Version 1 Last updated 26 September 2018 ab239682 Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Cell Culture (CD63 / For the isolation and analysis of exosome from cell culture. This product is
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Lipid peroxidation causes endosomal antigen release for cross-presentation Ilse Dingjan 1, Daniëlle RJ Verboogen 1, Laurent M Paardekooper 1, Natalia H Revelo 1, Simone P Sittig
Supplementary information Lipid peroxidation causes endosomal antigen release for cross-presentation Ilse Dingjan 1, Daniëlle RJ Verboogen 1, Laurent M Paardekooper 1, Natalia H Revelo 1, Simone P Sittig
Gladstone Institutes, University of California (UCSF), San Francisco, USA
 Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Ovarian Cancer Prevalence:
 Ovarian Cancer Prevalence: Basic Information 1. What is being measured? 2. Why is it being measured? The prevalence of ovarian cancer, ICD-10 C56 Prevalence is an indicator of the burden of cancer and
Ovarian Cancer Prevalence: Basic Information 1. What is being measured? 2. Why is it being measured? The prevalence of ovarian cancer, ICD-10 C56 Prevalence is an indicator of the burden of cancer and
ab Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Plasma
 Version 1 Last updated 25 May 2018 ab228565 Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Plasma For the isolation/detection of exosomes from human plasma, urine or cell culture media. This product
Version 1 Last updated 25 May 2018 ab228565 Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Plasma For the isolation/detection of exosomes from human plasma, urine or cell culture media. This product
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.aal4326/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structure of a eukaryotic voltage-gated sodium channel at near-atomic resolution Huaizong Shen, Qiang Zhou, Xiaojing
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.aal4326/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structure of a eukaryotic voltage-gated sodium channel at near-atomic resolution Huaizong Shen, Qiang Zhou, Xiaojing
Combining dialysis and dilution techniques to estimate gross growth rate of phytoplankton and grazing by micro- and mesozooplankton in situ
 Arch. Hydrobiol. 167 1 4 403 419 Stuttgart, September 2006 Combining dialysis and dilution techniques to estimate gross growth rate of phytoplankton and grazing by micro- and mesozooplankton in situ Herwig
Arch. Hydrobiol. 167 1 4 403 419 Stuttgart, September 2006 Combining dialysis and dilution techniques to estimate gross growth rate of phytoplankton and grazing by micro- and mesozooplankton in situ Herwig
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
Zooplankton community structure and size spectra linked to phytoplankton and hydrographic features on the Faroe Shelf in spring
 Zooplankton community structure and size spectra linked to phytoplankton and hydrographic features on the Faroe Shelf in spring Sólvá Jacobsen, Eilif Gaard, Karin M. H. Larsen, Sólvá K. Eliasen Faroe Islands
Zooplankton community structure and size spectra linked to phytoplankton and hydrographic features on the Faroe Shelf in spring Sólvá Jacobsen, Eilif Gaard, Karin M. H. Larsen, Sólvá K. Eliasen Faroe Islands
Biodiversity Study & Biomass Analysis
 PR072 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Biodiversity Study & Biomass Analysis Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE-403) think proteins!
PR072 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Biodiversity Study & Biomass Analysis Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE-403) think proteins!
RAG Rating Indicator Values
 Technical Guide RAG Rating Indicator Values Introduction This document sets out Public Health England s standard approach to the use of RAG ratings for indicator values in relation to comparator or benchmark
Technical Guide RAG Rating Indicator Values Introduction This document sets out Public Health England s standard approach to the use of RAG ratings for indicator values in relation to comparator or benchmark
Chapter 8 Statistical Principles of Design. Fall 2010
 Chapter 8 Statistical Principles of Design Fall 2010 Experimental Design Many interesting questions in biology involve relationships between response variables and one or more explanatory variables. Biology
Chapter 8 Statistical Principles of Design Fall 2010 Experimental Design Many interesting questions in biology involve relationships between response variables and one or more explanatory variables. Biology
Gene expression scaled by distance to the genome replication site. Ying et al. Supporting Information. Contents. Supplementary note I p.
 Gene expression scaled by distance to the genome replication site Ying et al Supporting Information Contents Supplementary note I p. 2 Supplementary note II p. 3-5 Supplementary note III p. 5-7 Supplementary
Gene expression scaled by distance to the genome replication site Ying et al Supporting Information Contents Supplementary note I p. 2 Supplementary note II p. 3-5 Supplementary note III p. 5-7 Supplementary
Plankton Lab 11/14 Integrated Science 1 Redwood High School Name: Period:
 Plankton Lab 11/14 Integrated Science 1 Redwood High School Period: Introduction Plankton (which comes from the Greek word for drifting) are often defined as organisms that float at or near the surface
Plankton Lab 11/14 Integrated Science 1 Redwood High School Period: Introduction Plankton (which comes from the Greek word for drifting) are often defined as organisms that float at or near the surface
Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h)
 Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h) after feeding. A small slice (~5-1 mm 3 ) was taken
Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h) after feeding. A small slice (~5-1 mm 3 ) was taken
Additional File 3. Description of methods used for co-localization analysis and additional co-localization figures.
 Additional File 3. Description of methods used for co-localization analysis and additional co-localization figures. Methods. In order to determine the interaction between EGFR and F-actin, four independent
Additional File 3. Description of methods used for co-localization analysis and additional co-localization figures. Methods. In order to determine the interaction between EGFR and F-actin, four independent
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.2109
 HIV 1 Infects Multipotent Progenitor Cells Causing Cell Death and Establishing Latent Cellular Reservoirs Christoph C. Carter, Adewunmi Onafuwa Nuga, Lucy A. M c Namara, James Riddell IV, Dale Bixby, Michael
HIV 1 Infects Multipotent Progenitor Cells Causing Cell Death and Establishing Latent Cellular Reservoirs Christoph C. Carter, Adewunmi Onafuwa Nuga, Lucy A. M c Namara, James Riddell IV, Dale Bixby, Michael
Estimating the Grazing Impact of Marine Micro-zooplankton *
 Marine Biology 67, 283-288 (1982) MARINE BIOLOGY 9 Springer-Verlag 1982 Estimating the Grazing Impact of Marine Micro-zooplankton * M. R. Landry and R. P. Hassett School of Oceanography, WB-10, University
Marine Biology 67, 283-288 (1982) MARINE BIOLOGY 9 Springer-Verlag 1982 Estimating the Grazing Impact of Marine Micro-zooplankton * M. R. Landry and R. P. Hassett School of Oceanography, WB-10, University
QA 605 WINTER QUARTER ACADEMIC YEAR
 Instructor: Office: James J. Cochran 117A CAB Telephone: (318) 257-3445 Hours: e-mail: URL: QA 605 WINTER QUARTER 2006-2007 ACADEMIC YEAR Tuesday & Thursday 8:00 a.m. 10:00 a.m. Wednesday 8:00 a.m. noon
Instructor: Office: James J. Cochran 117A CAB Telephone: (318) 257-3445 Hours: e-mail: URL: QA 605 WINTER QUARTER 2006-2007 ACADEMIC YEAR Tuesday & Thursday 8:00 a.m. 10:00 a.m. Wednesday 8:00 a.m. noon
CRITICAL EVALUATION OF BIOMEDICAL LITERATURE
 Chapter 9 CRITICAL EVALUATION OF BIOMEDICAL LITERATURE M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. INTRODUCTION Reviewing the Biomedical Literature poses a
Chapter 9 CRITICAL EVALUATION OF BIOMEDICAL LITERATURE M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. INTRODUCTION Reviewing the Biomedical Literature poses a
pro-b large pre-b small pre-b CCCP (µm) Rag1 -/- ;33.C9HCki
 a TMRM FI (Median) b TMRM FI (Median) c 20 15 10 5 0 8 6 4 2 0 pro-b large pre-b small pre-b 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 TMRM (nm) pro-b large pre-b small pre-b 0 1 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 CCCP (mm)
a TMRM FI (Median) b TMRM FI (Median) c 20 15 10 5 0 8 6 4 2 0 pro-b large pre-b small pre-b 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 TMRM (nm) pro-b large pre-b small pre-b 0 1 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 CCCP (mm)
Simulated coal spill causes mortality and growth inhibition in tropical marine organisms
 Simulated coal spill causes mortality and inhibition in tropical marine organisms Kathryn L. E. Berry 1,2,3,4*, Mia O. Hoogenboom 1,4, Florita Flores 2, Andrew P. Negri 2 1 College of Marine and Environmental
Simulated coal spill causes mortality and inhibition in tropical marine organisms Kathryn L. E. Berry 1,2,3,4*, Mia O. Hoogenboom 1,4, Florita Flores 2, Andrew P. Negri 2 1 College of Marine and Environmental
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig 1. Comparison of sub-samples on the first two principal components of genetic variation. TheBritishsampleisplottedwithredpoints.The sub-samples of the diverse sample
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig 1. Comparison of sub-samples on the first two principal components of genetic variation. TheBritishsampleisplottedwithredpoints.The sub-samples of the diverse sample
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Genetic labeling of microglia Male and female 2-3 month-old CreERT2;R26-tdTomato mice or CreERT2;R26-tdTomato;Iba1-eGFP transgenic mice were treated with 1x, 2x (48 h apart), or
Supplementary Figure 1 Genetic labeling of microglia Male and female 2-3 month-old CreERT2;R26-tdTomato mice or CreERT2;R26-tdTomato;Iba1-eGFP transgenic mice were treated with 1x, 2x (48 h apart), or
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of myelin fragments in the aging brain (a) Electron microscopy on corpus callosum is shown for a 18-month-old wild type mice. Myelin fragments (arrows) were detected
Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of myelin fragments in the aging brain (a) Electron microscopy on corpus callosum is shown for a 18-month-old wild type mice. Myelin fragments (arrows) were detected
MICROPLANKTON ECOLOGY: AN EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH. M.D.,- University Of Hamburg, FRG, 1973 Dr.med., University Of Hamburg, FRG, 1973
 ESTUARINE MICROPLANKTON ECOLOGY: AN EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH by ANNETTE SPIES M.D.,- University Of Hamburg, FRG, 1973 Dr.med., University Of Hamburg, FRG, 1973 A THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF
ESTUARINE MICROPLANKTON ECOLOGY: AN EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH by ANNETTE SPIES M.D.,- University Of Hamburg, FRG, 1973 Dr.med., University Of Hamburg, FRG, 1973 A THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF
GAFCHROMIC DOSIMETRY MEDIA TYPE MD-V3
 GAFCHROMIC DOSIMETRY MEDIA TYPE MD-V3 WARNING: Store below 25ºC Store away from radiation sources Avoid exposure of film to sunlight Handle film carefully, creasing may cause damage Do not expose to temperatures
GAFCHROMIC DOSIMETRY MEDIA TYPE MD-V3 WARNING: Store below 25ºC Store away from radiation sources Avoid exposure of film to sunlight Handle film carefully, creasing may cause damage Do not expose to temperatures
Extracellular vesicles are transferred from melanocytes to keratinocytes after UVA irradiation
 Supplementary material; Title; Extracellular vesicles are transferred from melanocytes to keratinocytes after UVA irradiation Authors; Petra Wäster 1, Ida Eriksson 1, Linda Vainikka 1, Inger Rosdahl 2,
Supplementary material; Title; Extracellular vesicles are transferred from melanocytes to keratinocytes after UVA irradiation Authors; Petra Wäster 1, Ida Eriksson 1, Linda Vainikka 1, Inger Rosdahl 2,
Pearson r = P (one-tailed) = n = 9
 8F4-Specific Lysis, % 1 UPN1 UPN3 8 UPN7 6 Pearson r =.69 UPN2 UPN5 P (one-tailed) =.192 4 UPN8 n = 9 2 UPN9 UPN4 UPN6 5 1 15 2 25 8 8F4, % Max MFI Supplementary Figure S1. AML samples UPN1-UPN9 show variable
8F4-Specific Lysis, % 1 UPN1 UPN3 8 UPN7 6 Pearson r =.69 UPN2 UPN5 P (one-tailed) =.192 4 UPN8 n = 9 2 UPN9 UPN4 UPN6 5 1 15 2 25 8 8F4, % Max MFI Supplementary Figure S1. AML samples UPN1-UPN9 show variable
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Mass Spectrometry Imaging Shows Cocaine and Methylphenidate have Opposite Effects on Major Lipids in Drosophila Brain Mai H. Philipsen *, Nhu T. N. Phan *, John S. Fletcher *, Per
Supporting Information Mass Spectrometry Imaging Shows Cocaine and Methylphenidate have Opposite Effects on Major Lipids in Drosophila Brain Mai H. Philipsen *, Nhu T. N. Phan *, John S. Fletcher *, Per
DIVERSITY AND ABUNDANCE OF ZOOPLANKTON IN CORAL COMMUNITIES AT KO SAK, CHONBURI PROVINCE FOLLOWING THE 2010 CORAL BLEACHING EVENT
 I_I0030 1 DIVERSITY AND ABUNDANCE OF ZOOPLANKTON IN CORAL COMMUNITIES AT KO SAK, CHONBURI PROVINCE FOLLOWING THE 2010 CORAL BLEACHING EVENT Arporn Sompaonoi,* Sittiporn Pengsakun, Wanlaya Klinthong, Makamas
I_I0030 1 DIVERSITY AND ABUNDANCE OF ZOOPLANKTON IN CORAL COMMUNITIES AT KO SAK, CHONBURI PROVINCE FOLLOWING THE 2010 CORAL BLEACHING EVENT Arporn Sompaonoi,* Sittiporn Pengsakun, Wanlaya Klinthong, Makamas
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
Flow Cytometry Based Exosome Detection and Analysis Using the ZE5 Cell Analyzer
 Flow Cytometry ased Exosome Detection and nalysis Using the ZE5 Cell nalyzer Yasha Talaga, Elizabeth Dreskin, Joyce Lee io-rad Laboratories, Inc. 2000 lfred Nobel Drive, Hercules C 94547 Flow Cytometry
Flow Cytometry ased Exosome Detection and nalysis Using the ZE5 Cell nalyzer Yasha Talaga, Elizabeth Dreskin, Joyce Lee io-rad Laboratories, Inc. 2000 lfred Nobel Drive, Hercules C 94547 Flow Cytometry
Dietary shifts in the copepod Temora longicornis during spring: evidence from stable isotope signatures, fatty acid biomarkers and feeding experiments
 JOURNAL OF PLANKTON RESEARCH j VOLUME 31 j NUMBER 1 j PAGES 45 60 j 2009 Dietary shifts in the copepod Temora longicornis during spring: evidence from stable isotope signatures, fatty acid biomarkers and
JOURNAL OF PLANKTON RESEARCH j VOLUME 31 j NUMBER 1 j PAGES 45 60 j 2009 Dietary shifts in the copepod Temora longicornis during spring: evidence from stable isotope signatures, fatty acid biomarkers and
IS THE CONDITION AND GROWTH OF EARLY LIFE STAGES OF NORTHERN ANCHOVY RELATED TO THE BIOCHEMICAL CLIMATOLOGY OF THE NORTHERN CALIFORNIA CURRENT?
 IS THE CONDITION AND GROWTH OF EARLY LIFE STAGES OF NORTHERN ANCHOVY RELATED TO THE BIOCHEMICAL CLIMATOLOGY OF THE NORTHERN CALIFORNIA CURRENT? Jessica A. Miller 1, William T. Peterson 2, Louise Copeman
IS THE CONDITION AND GROWTH OF EARLY LIFE STAGES OF NORTHERN ANCHOVY RELATED TO THE BIOCHEMICAL CLIMATOLOGY OF THE NORTHERN CALIFORNIA CURRENT? Jessica A. Miller 1, William T. Peterson 2, Louise Copeman
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis
 Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
Flow Cytometry. What is flow cytometry?
 Flow Cytometry Flow Cytometry What is flow cytometry? Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence
Flow Cytometry Flow Cytometry What is flow cytometry? Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence
MMCS Turkey Flu Pandemic Project
 MMCS Turkey Flu Pandemic Project This is a group project with 2 people per group. You can chose your own partner subject to the constraint that you must not work with the same person as in the banking
MMCS Turkey Flu Pandemic Project This is a group project with 2 people per group. You can chose your own partner subject to the constraint that you must not work with the same person as in the banking
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Method Comparison Report Semi-Annual 1/5/2018
 Method Comparison Report Semi-Annual 1/5/2018 Prepared for Carl Commissioner Regularatory Commission 123 Commission Drive Anytown, XX, 12345 Prepared by Dr. Mark Mainstay Clinical Laboratory Kennett Community
Method Comparison Report Semi-Annual 1/5/2018 Prepared for Carl Commissioner Regularatory Commission 123 Commission Drive Anytown, XX, 12345 Prepared by Dr. Mark Mainstay Clinical Laboratory Kennett Community
Optimization of the Fuse-It-mRNA Protocol for L929 Cells in the µ-plate 24 Well
 Optimization of the Fuse-It-mRNA Protocol for L929 Cells in the µ-plate 24 Well 1. General Information... 1 2. Background... 1 3. Material and Equipment Required... 2 4. Experimental Procedure and Results...
Optimization of the Fuse-It-mRNA Protocol for L929 Cells in the µ-plate 24 Well 1. General Information... 1 2. Background... 1 3. Material and Equipment Required... 2 4. Experimental Procedure and Results...
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1. Quantity of phosphorus spared via phospholipid substitutions by picocyanobacteria. (1 6 P atoms cell -1 )* (% of P in DNA) Synechococcus WH812.7 ±.1 15 ± 2 Synechococcus WH783 2.7
Supplementary Table 1. Quantity of phosphorus spared via phospholipid substitutions by picocyanobacteria. (1 6 P atoms cell -1 )* (% of P in DNA) Synechococcus WH812.7 ±.1 15 ± 2 Synechococcus WH783 2.7
COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate. bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic
 COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic mucus SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES AND FIGURES Tables S1 S8, page 1 and separate
COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic mucus SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES AND FIGURES Tables S1 S8, page 1 and separate
Chapter 3: Describing Relationships
 Chapter 3: Describing Relationships Objectives: Students will: Construct and interpret a scatterplot for a set of bivariate data. Compute and interpret the correlation, r, between two variables. Demonstrate
Chapter 3: Describing Relationships Objectives: Students will: Construct and interpret a scatterplot for a set of bivariate data. Compute and interpret the correlation, r, between two variables. Demonstrate
ILC1 and ILC3 isolation and culture Following cell sorting, we confirmed that the recovered cells belonged to the ILC1, ILC2 and
 Supplementary Methods and isolation and culture Following cell sorting, we confirmed that the recovered cells belonged to the, ILC2 and subsets. For this purpose we performed intracellular flow cytometry
Supplementary Methods and isolation and culture Following cell sorting, we confirmed that the recovered cells belonged to the, ILC2 and subsets. For this purpose we performed intracellular flow cytometry
Plankton Identification Activity
 Plankton Identification Credit: Erin B. Gordon, Stoneham High School. Prepared for the New Bedford Oceanarium s WOW Mobile Curriculum in 2006 Objectives Students will be able to: Explain the various types
Plankton Identification Credit: Erin B. Gordon, Stoneham High School. Prepared for the New Bedford Oceanarium s WOW Mobile Curriculum in 2006 Objectives Students will be able to: Explain the various types
Figure S1. In vitro drug combinations Growth inhibition assays performed on BE(2)-C neuroblastoma cell line using Alamar Blue after 72 h incubation
 Figure S1. In vitro drug combinations Growth inhibition assays performed on BE(2)-C neuroblastoma cell line using Alamar Blue after 72 h incubation with a range of concentrations of chemotherapy agents
Figure S1. In vitro drug combinations Growth inhibition assays performed on BE(2)-C neuroblastoma cell line using Alamar Blue after 72 h incubation with a range of concentrations of chemotherapy agents
BIOL 458 BIOMETRY Lab 7 Multi-Factor ANOVA
 BIOL 458 BIOMETRY Lab 7 Multi-Factor ANOVA PART 1: Introduction to Factorial ANOVA ingle factor or One - Way Analysis of Variance can be used to test the null hypothesis that k or more treatment or group
BIOL 458 BIOMETRY Lab 7 Multi-Factor ANOVA PART 1: Introduction to Factorial ANOVA ingle factor or One - Way Analysis of Variance can be used to test the null hypothesis that k or more treatment or group
Structured models for dengue epidemiology
 Structured models for dengue epidemiology submitted by Hannah Woodall for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy of the University of Bath Department of Mathematical Sciences September 24 COPYRIGHT Attention
Structured models for dengue epidemiology submitted by Hannah Woodall for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy of the University of Bath Department of Mathematical Sciences September 24 COPYRIGHT Attention
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Rates of different mutation types in CRC.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Rates of different mutation types in CRC. (a) Stratification by mutation type indicates that C>T mutations occur at a significantly greater rate than other types. (b) As for the
Supplementary Figure 1 Rates of different mutation types in CRC. (a) Stratification by mutation type indicates that C>T mutations occur at a significantly greater rate than other types. (b) As for the
Supporting Information. Lysine Propionylation to Boost Proteome Sequence. Coverage and Enable a Silent SILAC Strategy for
 Supporting Information Lysine Propionylation to Boost Proteome Sequence Coverage and Enable a Silent SILAC Strategy for Relative Protein Quantification Christoph U. Schräder 1, Shaun Moore 1,2, Aaron A.
Supporting Information Lysine Propionylation to Boost Proteome Sequence Coverage and Enable a Silent SILAC Strategy for Relative Protein Quantification Christoph U. Schräder 1, Shaun Moore 1,2, Aaron A.
Temporal and vertical dynamics of phytoplankton net growth in Castle Lake, California
 Journal of Plankton Research Vol.21 no.2 pp.373 385, 1999 Temporal and vertical dynamics of phytoplankton net growth in Castle Lake, California Pirjo S.Huovinen 1, Michael T.Brett 2 and Charles R.Goldman
Journal of Plankton Research Vol.21 no.2 pp.373 385, 1999 Temporal and vertical dynamics of phytoplankton net growth in Castle Lake, California Pirjo S.Huovinen 1, Michael T.Brett 2 and Charles R.Goldman
Unit 7 Comparisons and Relationships
 Unit 7 Comparisons and Relationships Objectives: To understand the distinction between making a comparison and describing a relationship To select appropriate graphical displays for making comparisons
Unit 7 Comparisons and Relationships Objectives: To understand the distinction between making a comparison and describing a relationship To select appropriate graphical displays for making comparisons
A Method to Determine in situ Zooplankton Grazing Rates on Natural Particle Assemblages
 A Method to Determine in situ Zooplankton Grazing Rates on Natural Particle Assemblages By: M. R. Roman and Parke A. Rublee Roman, M.R. and P.A. Rublee. 1981. A method to determine in situ zooplankton
A Method to Determine in situ Zooplankton Grazing Rates on Natural Particle Assemblages By: M. R. Roman and Parke A. Rublee Roman, M.R. and P.A. Rublee. 1981. A method to determine in situ zooplankton
Zooplankton Migration Patterns at Scotton Landing: Behavioral Adaptations written by Lauren Zodl, University of Delaware
 Zooplankton Migration Patterns at Scotton Landing: Behavioral Adaptations written by Lauren Zodl, University of Delaware Summary: Zooplankton have evolved specific migration patterns that increase their
Zooplankton Migration Patterns at Scotton Landing: Behavioral Adaptations written by Lauren Zodl, University of Delaware Summary: Zooplankton have evolved specific migration patterns that increase their
Phytoplankton Cell Size Reduction in Response to Warming Mediated by Nutrient Limitation
 Phytoplankton Cell Size Reduction in Response to Warming Mediated by Nutrient Limitation Kalista Higini Peter, Ulrich Sommer* GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, Kiel, Germany Abstract Shrinking
Phytoplankton Cell Size Reduction in Response to Warming Mediated by Nutrient Limitation Kalista Higini Peter, Ulrich Sommer* GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, Kiel, Germany Abstract Shrinking
Model building with craft materials Presented to grade 4; appropriate for grades K 12 with age appropriate modifications
 Unit: Lesson 1: Oceans of Energy Plankton Summary: In this lesson, students are introduced to phytoplankton and zooplankton as the oceans primary producers and consumers. Lesson includes two activities:
Unit: Lesson 1: Oceans of Energy Plankton Summary: In this lesson, students are introduced to phytoplankton and zooplankton as the oceans primary producers and consumers. Lesson includes two activities:
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis!
 Factors Affecting Photosynthesis! Temperature Eppley (1972) Light Sverdrup s Critical Depth Model Nutrients Limitations Uptake Kinetics Temperature! The oceans vary much less than the land does, both seasonally
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis! Temperature Eppley (1972) Light Sverdrup s Critical Depth Model Nutrients Limitations Uptake Kinetics Temperature! The oceans vary much less than the land does, both seasonally
EFFECTIVE NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF COMPLIANCE WITH THE BALLAST WATER MANAGEMENT CONVENTION
 EFFECTIVE NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF COMPLIANCE WITH THE BALLAST WATER MANAGEMENT CONVENTION A project financed by the Federal German Maritime and Hydrographic Agency Project Status Informal
EFFECTIVE NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF COMPLIANCE WITH THE BALLAST WATER MANAGEMENT CONVENTION A project financed by the Federal German Maritime and Hydrographic Agency Project Status Informal
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
The algal osmolyte DMSP as a microzooplankton grazing deterrent in laboratory and field studies
 The algal osmolyte DMSP as a microzooplankton grazing deterrent in laboratory and field studies KERRI A. FREDRICKSON* AND SUZANNE L. STROM SHANNON POINT MARINE CENTER, WESTERN WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY, ANACORTES,
The algal osmolyte DMSP as a microzooplankton grazing deterrent in laboratory and field studies KERRI A. FREDRICKSON* AND SUZANNE L. STROM SHANNON POINT MARINE CENTER, WESTERN WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY, ANACORTES,
