Sacrum and Pelvic. Lecture 7. Please check our Editing File.
|
|
|
- Bernard Parker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sacrum and Pelvic Lecture 7 Please check our Editing File. هذا العمل ال يغني عن المصدر األساسي للمذاكرة و م ن ي ت و ك ل ع ل ى ا لل ه ف و هو { {ح س بووه
2 Objectives Describe the bony structures of the pelvis. Describe in detail the hip bone, the sacrum, and the coccyx. Describe the boundaries of the pelvic inlet and outlet. Identify the structures forming the Pelvic Wall. Identify the articulations of the bony pelvis. List the major differences between the male and female pelvis. List the different types of female pelvis. Text in BLUE was found only in the boys slides Text in PINK was found only in the girls slides Text in RED is considered important Text in GREY is considered extra notes
3 Bony Pelvis From team 436
4 Bony Pelvis, Functions: The skeleton of the pelvis is a basin- shaped ring of bones with holes in its walls that connect the vertebral column (Trunk) to both femora (lower extremities). Its Primary Functions are: Bears the weight of the upper body when sitting and standing the most important function. Transfers that weight from the axial skeleton to the lower appendicular skeleton when standing and walking. Provides attachments and withstands the forces of the powerful muscles of locomotion (movement) and posture. Its Secondary Functions are: Contains and Protects the pelvic and abdominopelvic viscera (inferior parts of the urinary tracts, internal reproductive organs) Provides attachment for external reproductive organs and associated muscles and membranes.
5 Pelvic Girdle : Compared to the Pectoral Girdle, the pelvic girdle is Larger, heavier, and stronger. The total weight of the upper body rests on the pelvis. Composed of: Two hip (coxal) bones Important to know the difference between: Hip Bone : Each one is a large irregular bone. Formed of three bones: Ilium (superior) Ischium (inferior posterior) Pubis (inferior anterior) They are joined at a deep socket (Acetabulum)* During childhood, these sections are separate bones, joined by Y shaped cartilage. During puberty, they fuse together to form a single bone. Bony Pelvis : hip bones, sacrum and coccyx. Pelvic girdle: only the two hip bones. *Acetabulum: The socket of the hip bone, into which the head of the femur fits.
6 Ilium It is the Upper Flattened Part of the hip bone. The Inner surface has: Iliac Fossa (forms false pelvis). Smooth Auricular surface ( for articulation with the sacrum). Rough Iliopectinial (Arcuate) Line: Runs downwards & forwards. It separates between the False & the True pelvis Iliac Crest: An important anatomical landmark below the *waist. It runs between the Anterior and Posterior Superior Iliac Spines. Below are the corresponding Anterior and Posterior Inferior Iliac Spines. (Total 4 spines) *Waist: body below the ribs and above the hips It Possesses: *Medial view It has: two surfaces: The Outer Surface: rough and has three Gluteal Lines *Lateral view Outer surface: called "Gluteal surface" because it has 3 gluteal lines, which serves as an attachment for gluteal muscles,(maximus,medius,minimus).
7 Forms the Anterior & Inferior part of the hip bone. It is composed of: - Body; bears the Pubic Crest and Pubic Tubercle. -Two pubic Rami; Superior & Inferior. They bound the Obturator Foramen, which is closed partially by the obturator membrane. leaving the obturator canal for passing of blood vessels & nerves into the thigh Pubis (3parts) Body The greater and lower sciatic notches are separated by the ischial spine
8 Ischium: Forms the Posterior & inferior part of the hip bone Ischial Tuberosity: A roughened area that receives العظمة الي نجلس عليها body weight in sitting Ischial Spine: Superior to the tuberosity, it is important landmark in pregnant women. (obstetrics) Greater sciatic notch. Allow sciatic nerve & vessels to pass from the pelvis to the thigh. Lesser sciatic notch. allow vessels & nerves to pass from pelvic to *perinium. In Living patients: Greater Sciatic Foramen Lesser Sciatic Foramen *The distance between two spines help us know weather the women will have a normal birth or not. *Extra:The perinium
9 -The outer surface articulates at the acetabulum with the head of the femur. Articulations of hip bone symphysis pubis: -a secondary cartilaginous joint between the two pubic bones Sacroiliac joints: -strong synovial joints, between the auricular surfaces of both iliac bones and the sacrum -transmit the weight of the body from vertebral column to the bony pelvis Hip joints:
10 Sacrum And Coccyx: *Sacrum: -A single wedge shaped bone. -Consist of Five rudimentary vertebraeبدائية fused together. -The anterior and posterior surfaces possess on each side four Sacral Foramina. Coccyx: - Consists of four vertebrae fused together forming a single Triangular piece. *Dorsal surface(posterior): rough & ridge Pelvic surface(anteriorly): relatively smooth -The fused vertebral foramina form the *Sacral Canal. -Its lower limit is the Sacral Hiatus. Sacral promontory: 1) The anterior and upper margin.(represent the body of the first sacral vertebrae) 2) It is tilted forward forming the lumbosacral angle. *Sacral Canal: The cauda equina, pass through the canal to send their dorsal and ventral rami through the corresponding sacral foramina.
11 Articulation Of Sacrum 1)Lumbosacral joint: The upper border articulates with the 5th lumbar vertebra. 2) Sacrococcygeal joint: The inferior part articulates with the Coccyx. 3) Sacroiliac joints: Lateral articulation with both hip bones. These joints + pubic symphysis form the bony pelvis; by joining the sacrum and the hip bones together
12 Foramina in Body pelvis The holes of the basin are called foramina. Only in girls slides Anterior sacral foramina The important foramina in the bony pelvis include: Greater and lesser sciatic foramina Obturator foramen These are present on the anterior surface of the sacrum (which forms the posterior surface of the bony pelvis) Through these foramina pass the anterior rami of the sacral spinal nerves. These are the major foramina of the pelvis. In the bony pelvis, they are present as greater and lesser sciatic notches but by the attachment of sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments, these notches are converted to respective foramina. Each lateral wall of the pelvis has a large hole, called the obturator foramen. In living subjects, this hole is closed by the obturator membrane except for a small opening, which represents the obturator canal. Through these foramina various structures enter and leave the pelvis. Obturator nerve passes through this small opening.
13 Orientation of the Pelvis It is the Correct Position of the bony pelvis relative to the trunk (in the anatomical position): 1.The Anterior Superior iliac spine and the front of the Symphysis pubis (The pubic tubercles) are in the same vertical plane.. 2.The coccyx and the upper margin of the pubic symphysis are in the same horizontal plane. 3.The axis of the pelvic cavity running through the central point of the inlet and the outlet, almost parallels the curvature of the sacrum. In this position: The anterior surface of the Sacrum is directed forward and downward while the pelvic surface of symphysis pubis faces upward and backward.
14 Fractures of the Bony Pelvis Only in girl s slides The weakest parts of the bony pelvis are: Pubic rami Acetabula Region of sacroiliac joint Alae of the ilium Pelvic Fractures can result from direct trauma to the pelvic bones as occurs in car accidents or by forces transmitted to these bones from the lower limbs during falls on the feet. Pelvic fractures may cause injury to the pelvic soft tissues, blood vessels, nerves and organs.
15 Subdivision of the bony pelvis The bony pelvis is divided into two parts by the Pelvic Brim. Posteriorly: Sacral Promontory The brim is formed Only in girl s slides Laterally: Iliopectineal line Anteriorly : Symphysis pubis. Above the pelvic brim lies the False Pelvis, which is not of much clinical importance. Below the brim is the True Pelvis
16 False Pelvis (Greater pelvis) Lies superior to the pelvic brim. Enclosed by the Fossae of the iliac bones Forms the inferior region of the abdominal cavity. Houses the Inferior abdominal organs True Pelvis (lesser pelvis) Lies inferior to the pelvic brim. Encloses the pelvic cavity. Contains the pelvic organs. It has : Inlet Outlet Pelvic walls
17 True Pelvis (pelvic inlet and outlet) Bounded by: Pelvic Inlet (pelvic brim) 1-Sacral promontory 2- Symphysis pubes 3- iliopectineal lines Pelvic outlet 1- Tip of Coccyx 2- Ischial tuberosities 3- Pubic arches
18 Pelvic Walls This slide is only in males lecture - Formed by bones and ligaments - Lined with muscles, and covered with fascia Piriformis muscle Anterior wall Posterior wall Lateral wall - Posterior surfaces of bodies of pubic bones - Pubic rami - Symphysis pubes - Sacrum and coccyx - Piriformis muscles, and their covering of parietal pelvic fascia - hip bone below the pelvic inlet (pelvic brim) -Obturator membrane - Sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments -Obturator internus muscle and covering fascia
19 Mostly the iliac fossa The deeper it is the smaller the cavity Bony pelvis Male Female General structure Thick & heavy Thin, Smaller & lighter False (major) pelvis Deep Shallow True (lesser) pelvis Narrow & Deep Wide & Shallow Pelvic inlet Heart shaped Oval or Rounded Pelvic outlet Small Larger Pubic arch Narrow Wide subpubic angle Acute angle obtuse angle Obturator foramen Round Oval Acetabulum Large Small Auricular surface. Sacrum articulates with 3 vertebrae, is fixed Sacrum articulates with 2 vertebrae Ischial tuberosities Turned in Everted Differences between the male and female pelvis Because of the everted tuberosity The other 3 vertebrae are only bound by ligaments, during pregnancy, the ligaments relax and the sacrum moves backwards Ischial spines Shorter and farther apart Wide= roomer Pelvic cavity Less, small Wide for normal birth Doctor s notes Male s slides only Females slides only
20 Differences between the male and female sacrum Male Difference Female Longer Length Shorter Narrower Breadth Wider More curved Curvature Less curved
21 Forensic Medicine and Bony Pelvis For identification of human skeletal remains, the bony pelvis is of prime focus of attention because sexual differences are clearly visible. Even parts of the pelvis are useful in making a diagnosis of sex.
22 Types of Obstetrical Female Pelvis (1)Gynaecoid: the typical female type. (2)Anthropoid: long, narrow, and oval shaped.(between Male & Female pelvic) (3)Android: funnel shaped with contracted outlet. (It causes hazards to normal vaginal delivery) (close to male pelvic) (4)Platypelloid: wide, flattened at the brim, with forward promontory. (Transverse is wider than usual)
23 summary: (Cartilaginous joint) (synovial joint)
24 summary: Foramina in Bony Pelvis: foramina Location importance (4)Sacral foramina Greater and lesser sciatic foramina (2)On anterior surface of the sacrum (2)On posterior surface of the sacrum Above and below the Ischial Spine *Which separates between them Passes through them the anterior & posterior rami of the sacral spinal nerves allow sciatic nerve & vessels to pass from pelvis to thigh (Greater) & perinium (Lesser) Obturator foramen the large hole on each lateral wall of the pelvis Obturator nerve passes through it
25 Questions 1) Which of the following is a secondary function of the Pelvic girdle? a) Bears weight of upper body while sitting b) Provides attachments & endures the forces of the muscles of locomotion and posture. c) Provides attachment for external reproductive organs 2) The Iliac crest of Ilium: a) Runs between the Anterior and Posterior Superior Iliac Spines. b) Runs between the lateral and medial superior iliac spines c) Runs between the anterior and posterior inferior iliac spines 3) pubis bone bounds the: a) Iliac fossa b) Obturator foramen c) acetabulum 4) How many types of articulations does the hip bone have? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 5) the lumbosacral joint is articulation between: a) Sacrum and L3 vertebra b) Upper border of Sacrum and L5 vertebra c) Sacrum and coccyx 6) The weakest part of the pelvis is: a) Acetabula b) Pubic bone c) Ischium 7) The bony pelvis of the male is: a) Thick & Heavy b) Thin, Smaller & lighter c) Same as female 8) which type of female pelvis is likely to cause hazards during normal vagina delivery? a) Gynaecoid b) Android c) Platypelloid Answers: 1. C 2. A 3. B 4. C 5. B 6. A 7. A 8. B
26 Lamia Abdullah Alkuwaiz (Team Leader) Rawan Mohammad Alharbi Abeer Alabduljabbar Afnan Abdulaziz Almustafa Ahad Algrain Alanoud Almansour Albandari Alshaye AlFhadah abdullah alsaleem Arwa Alzahrani Dana Abdulaziz Alrasheed Dimah Khalid Alaraifi Ghada Alhaidari Ghada Almuhanna Ghaida Alsanad Hadeel Khalid Awartani Haifa Alessa Khulood Alwehabi Layan Hassan Alwatban Lojain Azizalrahman Lujain Tariq AlZaid Maha Barakah Majd Khalid AlBarrak Norah Alharbi Nouf Alotaibi Noura Mohammed Alothaim Rahaf Turki Alshammari Reham Alhalabi Rinad Musaed Alghoraiby Sara Alsultan Shahad Alzahrani Wafa Alotaibi Wejdan Fahad Albadrani Wjdan AlShamry Team Members Faisal Fahad Alsaif (Team Leader) Abdulaziz Al dukhayel Fahad Alfaiz Akram Alfandi Saad Aloqile Saleh Almoaiqel Abdulaziz Alabdulkareem Abdullah Almeaither Yazeed Aldossari Muath Alhumood Abdulrahman Almotairi Abdulelah Aldossari Abdulrahman Alduhayyim Hamdan Aldossari Mohammed Alomar Abdulrahman Aldawood Saud Alghufaily Hassan Aloraini Khalid Almutairi Abdulmajeed Alwardi Abdulrahman Alageel Rayyan Almousa Sultan Alfuhaid Ali Alammari Fahad alshughaithry Fayez Ghiyath Aldarsouni Mohammed Alquwayfili Abduljabbar Al-yamani Sultan Al-nasser Majed Aljohani Zeyad Al-khenaizan Mohammed Nouri Abdulaziz Al-drgam Fahad Aldhowaihy Omar alyabis
PELVIS & SACRUM Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama
 PELVIS & SACRUM Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Learning Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the bony structures of the pelvis. Describe in detail
PELVIS & SACRUM Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Learning Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the bony structures of the pelvis. Describe in detail
Joints. Lecture 11. Please check our Editing File.
 Joints Lecture 11 }و ﻣ ﻦ ﻳ ﺘ ﻮ ﻛﻞ ﻋ ﻠ ﻰ اﻟﻠﻪ ﻓ ﻬ ﻮ ﺣ ﺴ ﺒ ﻪ { Please check our Editing File. ھﺬا اﻟﻌﻤﻞ ﻻ ﯾﻐﻨﻲ ﻋﻦ اﻟﻤﺼﺪر اﻷﺳﺎﺳﻲ ﻟﻠﻤﺬاﻛﺮة Objectives Define the term Joint. Describe the classification of 3
Joints Lecture 11 }و ﻣ ﻦ ﻳ ﺘ ﻮ ﻛﻞ ﻋ ﻠ ﻰ اﻟﻠﻪ ﻓ ﻬ ﻮ ﺣ ﺴ ﺒ ﻪ { Please check our Editing File. ھﺬا اﻟﻌﻤﻞ ﻻ ﯾﻐﻨﻲ ﻋﻦ اﻟﻤﺼﺪر اﻷﺳﺎﺳﻲ ﻟﻠﻤﺬاﻛﺮة Objectives Define the term Joint. Describe the classification of 3
Mediastinum. Lecture 5. Please check our Editing File. ھذا العمل لا یغني عن المصدر الا ساسي للمذاكرة
 Mediastinum Lecture 5 Please check our Editing File. ھذا العمل لا یغني عن المصدر الا ساسي للمذاكرة Objectives At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate
Mediastinum Lecture 5 Please check our Editing File. ھذا العمل لا یغني عن المصدر الا ساسي للمذاكرة Objectives At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate
Skeletal Muscles SECOND LECTURE. Please check our Editing File BEFORE studying this lecture
 Skeletal Muscles SECOND LECTURE } و م ن ي ت و ك ل ع ل ى ا لل ه ف ه و ح س ب ه { هذا العمل ال يغني عن المصدر األساسي للمذاكرة Please check our Editing File BEFORE studying this lecture Guide: Text in BLUE
Skeletal Muscles SECOND LECTURE } و م ن ي ت و ك ل ع ل ى ا لل ه ف ه و ح س ب ه { هذا العمل ال يغني عن المصدر األساسي للمذاكرة Please check our Editing File BEFORE studying this lecture Guide: Text in BLUE
Muscles involved in respiration
 Muscles involved in respiration Lecture 1 Please check our Editing File. ھﺬا اﻟﻌﻤﻞ ﻻ ﯾﻐﻨﻲ ﻋﻦ اﻟﻤﺼﺪر اﻷﺳﺎﺳﻲ ﻟﻠﻤﺬاﻛﺮة Objectives Describe the components of the thoracic cage and their articulations. Describe
Muscles involved in respiration Lecture 1 Please check our Editing File. ھﺬا اﻟﻌﻤﻞ ﻻ ﯾﻐﻨﻲ ﻋﻦ اﻟﻤﺼﺪر اﻷﺳﺎﺳﻲ ﻟﻠﻤﺬاﻛﺮة Objectives Describe the components of the thoracic cage and their articulations. Describe
Skeletal System Module 13: The Pelvic Girdle and Pelvis
 OpenStax-CNX module: m47993 1 Skeletal System Module 13: The Pelvic Girdle and Pelvis Donna Browne Based on The Pelvic Girdle and Pelvis by OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed
OpenStax-CNX module: m47993 1 Skeletal System Module 13: The Pelvic Girdle and Pelvis Donna Browne Based on The Pelvic Girdle and Pelvis by OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed
Slide Read the tables it is about the difference between male & female pelvis.
 I didn t include the slides, this is only what the doctor read or said because he skipped a lot of things because we took it previously, very important to go back to the slides (*there is an edited version)
I didn t include the slides, this is only what the doctor read or said because he skipped a lot of things because we took it previously, very important to go back to the slides (*there is an edited version)
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax
 Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Lecture 6 Please check our Editing File. ھذا العمل لا یغني عن المصدر الا ساسي للمذاكرة Objectives 1- Identify the bones of the thoracic cage. 2- Identify superficial soft
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Lecture 6 Please check our Editing File. ھذا العمل لا یغني عن المصدر الا ساسي للمذاكرة Objectives 1- Identify the bones of the thoracic cage. 2- Identify superficial soft
The os coxae or hip bone consists of three flat bones, ilium, ischium and pubis, which fuse together to form the acetabulum.
 The os coxae The os coxae or hip bone consists of three flat bones, ilium, ischium and pubis, which fuse together to form the acetabulum. The ilium extends from the acetabulum upwards forming the lateral
The os coxae The os coxae or hip bone consists of three flat bones, ilium, ischium and pubis, which fuse together to form the acetabulum. The ilium extends from the acetabulum upwards forming the lateral
Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 14.January.2014 Tuesday
 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 14.January.2014 Tuesday Sexual differences are related mainly 1. Heavier build and larger muscles of most men 2. Adaptation of the pelvis (particularly the lesser pelvis) in women
Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 14.January.2014 Tuesday Sexual differences are related mainly 1. Heavier build and larger muscles of most men 2. Adaptation of the pelvis (particularly the lesser pelvis) in women
LAB Notes#1. Ahmad Ar'ar. Eslam
 LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
Anatomy & Physiology Pelvic Girdles 10.1 General Information
 Anatomy & Physiology Pelvic Girdles 10.1 General Information ICan2Ed, Inc. In human anatomy, the pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of. The area of the body that is between the abdomen
Anatomy & Physiology Pelvic Girdles 10.1 General Information ICan2Ed, Inc. In human anatomy, the pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of. The area of the body that is between the abdomen
C. Bones of the Pelvic Girdle
 C. Bones of the Pelvic Girdle 1. 2 coxal bones (a.k.a hip bones): -bony pelvis is made up of hip bones, sacrum, & coccyx -pelvic bones are large & heavy & attach to the axial skeleton via sacrum/coccyx
C. Bones of the Pelvic Girdle 1. 2 coxal bones (a.k.a hip bones): -bony pelvis is made up of hip bones, sacrum, & coccyx -pelvic bones are large & heavy & attach to the axial skeleton via sacrum/coccyx
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
First practical session. Bones of the gluteal region
 First practical session 2017 Bones of the gluteal region The Hip bone The hip bone is made of: 1 The ilium: superior in position 2 The ischium:postero-inferior in position 3 The pubis: antero-inferior
First practical session 2017 Bones of the gluteal region The Hip bone The hip bone is made of: 1 The ilium: superior in position 2 The ischium:postero-inferior in position 3 The pubis: antero-inferior
Figure 7: Bones of the lower limb
 BONES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton is composed of the 126 bones of the appendages and the pectoral and pelvic girdles, which attach the limbs to the axial skeleton. Although the
BONES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton is composed of the 126 bones of the appendages and the pectoral and pelvic girdles, which attach the limbs to the axial skeleton. Although the
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil khouri
 Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings
 Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
NERVOUS SYSTEM. Text in pink was only found in the girls slides. Text in blue was only found in the boys slides. Text in red is considered important
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Text in pink was only found in the girls slides Text in blue was only found in the boys slides Text in red is considered important The Dr. s comments in class are written in green Please
NERVOUS SYSTEM Text in pink was only found in the girls slides Text in blue was only found in the boys slides Text in red is considered important The Dr. s comments in class are written in green Please
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax
 Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
The Lower Limb. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
Bones of Lower Limb. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Bones of Lower Limb Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Bones of the lower limb Hip Bone Made up of 3 bones: 1) Ilium (flat), superior in position 2) Ischium (L), postero-inferior
Bones of Lower Limb Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Bones of the lower limb Hip Bone Made up of 3 bones: 1) Ilium (flat), superior in position 2) Ischium (L), postero-inferior
Gluteal Region and Back of Thigh
 Gluteal Region and Back of Thigh Musculoskeletal block- Anatomy-lecture 14 Editing file Objectives Know contents of gluteal region: 1. Groups of Glutei muscles and small muscles (Lateral Rotators). 2.
Gluteal Region and Back of Thigh Musculoskeletal block- Anatomy-lecture 14 Editing file Objectives Know contents of gluteal region: 1. Groups of Glutei muscles and small muscles (Lateral Rotators). 2.
Skeletal System. It s all about the bones!!!
 Skeletal System It s all about the bones!!! The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=icwllrqkv cg&list=plzile25upgebvru0jneppcabh0fhktgt Q 1. FYI 5
Skeletal System It s all about the bones!!! The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=icwllrqkv cg&list=plzile25upgebvru0jneppcabh0fhktgt Q 1. FYI 5
Ureters, Urinary Bladder & Urethra
 Ureters, Urinary Bladder & Urethra Please check our Editing File هذا العمل ال يغني عن المصدر األساسي للمذاكرة Lecture 2 } و م ن ي ت و ك ع ل ا لل ه ف ه و ح س ب ه { Objectives o Describe the course of ureter
Ureters, Urinary Bladder & Urethra Please check our Editing File هذا العمل ال يغني عن المصدر األساسي للمذاكرة Lecture 2 } و م ن ي ت و ك ع ل ا لل ه ف ه و ح س ب ه { Objectives o Describe the course of ureter
Introduction to Anatomy. Dr. Maher Hadidi. Tala Ar ar. Mar/10th/2013
 Sheet Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Tala Ar ar 15 Mar/10th/2013 Lower limb The skeleton of the lower limb is the lower appendicular skeleton which consists of 2 parts: 1- Pelvic girdle. 2- Bones
Sheet Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Tala Ar ar 15 Mar/10th/2013 Lower limb The skeleton of the lower limb is the lower appendicular skeleton which consists of 2 parts: 1- Pelvic girdle. 2- Bones
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 8 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 203) 1. The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones that form: i. two pectoral (shoulder) girdles two upper limbs i one pelvic
Chapter 8 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 203) 1. The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones that form: i. two pectoral (shoulder) girdles two upper limbs i one pelvic
Chapter 8. The Appendicular Skeleton. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Appendicular Skeleton Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Allows us
Chapter 8 The Appendicular Skeleton Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Allows us
ORIENTING TO BISECTED SPECIMENS ON THE PELVIS PRACTICAL
 ORIENTING TO BISECTED SPECIMENS ON THE PELVIS PRACTICAL The Pelvis is just about as complicated as head and neck and considerably more mysterious. You have to be able to visualize (imagine) the underlying
ORIENTING TO BISECTED SPECIMENS ON THE PELVIS PRACTICAL The Pelvis is just about as complicated as head and neck and considerably more mysterious. You have to be able to visualize (imagine) the underlying
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure Sectioned spinous process. Interspinous.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone).
 It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone). Pubis Acetabulum Ana (242 ) The three constituent of bones of the hip
It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone). Pubis Acetabulum Ana (242 ) The three constituent of bones of the hip
Chapter 8B. The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton. The Appendicular Skeleton. Clavicle. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
Lecture 10 Arteries and veins of the upper limb
 Lecture 10 Arteries and veins of the upper limb 1. Identify the Subclavian, axillary, brachial (deep and superficial), radial and ulnar arteries and superficial/deep palmar arches 2. Describe the major
Lecture 10 Arteries and veins of the upper limb 1. Identify the Subclavian, axillary, brachial (deep and superficial), radial and ulnar arteries and superficial/deep palmar arches 2. Describe the major
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
The Appendicular Skeleton
 8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
ANATOMY (7). INTRODUCTION TO THE PELVIS. MOHAMMAD ALLOUH. BNB. 1 P a g e
 ANATOMY (7). INTRODUCTION TO THE PELVIS. MOHAMMAD ALLOUH. BNB 1 P a g e Introduction to the Pelvis: Pelvic Wall & Pelvic Cavity pelvis (L, basin, sink ), is The region of the trunk that lies inferoposterior
ANATOMY (7). INTRODUCTION TO THE PELVIS. MOHAMMAD ALLOUH. BNB 1 P a g e Introduction to the Pelvis: Pelvic Wall & Pelvic Cavity pelvis (L, basin, sink ), is The region of the trunk that lies inferoposterior
The Axial Skeleton Hyoid Bone. Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 7 The Axial and Appendicular Skeleton Lecture 14
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 7 The Axial and Appendicular Skeleton Lecture 14 1 Axial Skeleton Hyoid bone Bones of the orbit Paranasal sinuses Infantile skull Vertebral column
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 7 The Axial and Appendicular Skeleton Lecture 14 1 Axial Skeleton Hyoid bone Bones of the orbit Paranasal sinuses Infantile skull Vertebral column
Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton
 Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear ossicles Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones upper & lower limbs
Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear ossicles Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones upper & lower limbs
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
 The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
Main Menu. Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
Bones of Thorax (Rib Cage)
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
Muscles Of The Back. Musculoskeletal block- Anatomy-lecture 3. Editing file
 Muscles Of The Back Musculoskeletal block- Anatomy-lecture 3 Editing file Objectives At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Distinguish between the different groups of back muscles. Compare
Muscles Of The Back Musculoskeletal block- Anatomy-lecture 3 Editing file Objectives At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Distinguish between the different groups of back muscles. Compare
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
Muscles involved in respiration
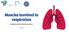 Muscles involved in respiration Respiratory block-anatomy-lecture 1 Editing file Objectives Describe the components of the thoracic cage and their articulations. Describe in brief the respiratory movements.
Muscles involved in respiration Respiratory block-anatomy-lecture 1 Editing file Objectives Describe the components of the thoracic cage and their articulations. Describe in brief the respiratory movements.
Axial skeleton bones and markings
 Axial skeleton bones and markings Skull Cranial bones Frontal x 1 Supraorbital foramen Occipital x 1 Foramen magnum Occipital condyles Superior nuchal line Inferior nuchal line Anterior cranial fossa External
Axial skeleton bones and markings Skull Cranial bones Frontal x 1 Supraorbital foramen Occipital x 1 Foramen magnum Occipital condyles Superior nuchal line Inferior nuchal line Anterior cranial fossa External
Table 2. First Generated List of Expert Responses. Likert-Type Scale. Category or Criterion. Rationale or Comments (1) (2) (3) (4)
 Table 2. First Generated List of Expert Responses. Likert-Type Scale Category or Criterion Anatomical Structures and Features Skeletal Structures and Features (1) (2) (3) (4) Rationale or Comments 1. Bones
Table 2. First Generated List of Expert Responses. Likert-Type Scale Category or Criterion Anatomical Structures and Features Skeletal Structures and Features (1) (2) (3) (4) Rationale or Comments 1. Bones
human anatomy 2015 lecture four Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB. Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Gluteal Region Cutaneous nerve supply of (Gluteal region) 1. Lateral cutaneous
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Gluteal Region Cutaneous nerve supply of (Gluteal region) 1. Lateral cutaneous
NOTES FROM GUTMAN LECTURE 10/26 Use this outline to study from. As you go through Gutman s lecture, fill in the topics.
 NOTES FROM GUTMAN LECTURE 10/26 Use this outline to study from. As you go through Gutman s lecture, fill in the topics. Anatomy above the arcuate line Skin Camper s fascia Scarpa s fascia External oblique
NOTES FROM GUTMAN LECTURE 10/26 Use this outline to study from. As you go through Gutman s lecture, fill in the topics. Anatomy above the arcuate line Skin Camper s fascia Scarpa s fascia External oblique
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL
 Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
ANATOMY TEAM GLUTEAL REGION & BACK OF THIGH
 ANATOMY TEAM GLUTEAL REGION & BACK OF THIGH OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to identify and discuss: Contents of gluteal region: Groups of Glutei muscles and small muscles
ANATOMY TEAM GLUTEAL REGION & BACK OF THIGH OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to identify and discuss: Contents of gluteal region: Groups of Glutei muscles and small muscles
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM
 AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
Muscles of the lower extremities. Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis
 Hip Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis The terms hip and pelvis are frequently used interchangeably, but strictly speaking, the pelvis is a girdle of bones and the hip is a joint. The pelvis consists of The sacrum
Hip Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis The terms hip and pelvis are frequently used interchangeably, but strictly speaking, the pelvis is a girdle of bones and the hip is a joint. The pelvis consists of The sacrum
CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower extremities and the shoulder and hip girdles. B. The appendicular skeleton functions primarily
CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower extremities and the shoulder and hip girdles. B. The appendicular skeleton functions primarily
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206. AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Clavicle. Clavicle. Pectoral girdles. Scapula. Scapula.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Pectoral girdles 4 Clavicle Scapula 2 2 Clavicle Scapula Humerus 2 Humerus Upper limbs 60 Radius 2 Ulna Carpal bones Metacarpal
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Pectoral girdles 4 Clavicle Scapula 2 2 Clavicle Scapula Humerus 2 Humerus Upper limbs 60 Radius 2 Ulna Carpal bones Metacarpal
VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
Inferior Pelvic Border
 Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
Bony framework of the vertebral column Structure of the vertebral column
 5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System
 BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System Objectives Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton. Distinguish between the cranium and facial skeleton. Locate and name the bones of the skull and
BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System Objectives Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton. Distinguish between the cranium and facial skeleton. Locate and name the bones of the skull and
UROGENITAL SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department UROGENITAL SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistance Professor of Anatomy &embryology PELVIS Learning Objectives 1. Bony pelvis, its joints and
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department UROGENITAL SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistance Professor of Anatomy &embryology PELVIS Learning Objectives 1. Bony pelvis, its joints and
Located more distal and anterior together with Trapezoid, anterior to scaphoid Trapezium rarely to be fractured.
 The hand The hand consists of the 3 groups: Proximal part: carpals bones (8) Middle part: metacarpal bones (5) Distal part: fingers or phalanges bones (3 for each finger except for the thumb just 2 bones).
The hand The hand consists of the 3 groups: Proximal part: carpals bones (8) Middle part: metacarpal bones (5) Distal part: fingers or phalanges bones (3 for each finger except for the thumb just 2 bones).
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
The Appendicular Skeleton
 8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton Learning Outcomes 8-1 Identify the bones
8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton Learning Outcomes 8-1 Identify the bones
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System
 Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Spring Written By: J. E. Sutton. Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV.
 Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
Dana Alrafaiah. - Amani Nofal. - Ahmad Alsalman. 1 P a g e
 - 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
- 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
PRE-LAB EXERCISES. Before we get started, look up the definitions of these common bone marking terms: Canal: Condyle: Facet: Fissure:
 1 PRE-LAB EXERCISES When studying the skeletal system, the bones are often sorted into two broad categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. This lab focuses on the appendicular skeleton,
1 PRE-LAB EXERCISES When studying the skeletal system, the bones are often sorted into two broad categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. This lab focuses on the appendicular skeleton,
Pelvic Girdle
 ARTICULATIONS OF LOWER EXTREMITY Pages 429-437 Pelvic Girdle formed by connection of the hip bones and the sacrum Sacroiliac Joints compound joints synovial joint - anterior, between the auricular surfaces
ARTICULATIONS OF LOWER EXTREMITY Pages 429-437 Pelvic Girdle formed by connection of the hip bones and the sacrum Sacroiliac Joints compound joints synovial joint - anterior, between the auricular surfaces
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint. Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa
 The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
Dr.Israa H. Mohsen. Lecture 5. The vertebral column
 Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
Bony Anatomy. Femur. Femoral Head Femoral Neck Greater Trochanter Lesser Trochanter Intertrochanteric Crest Intertrochanteric Line Gluteal Tuberosity
 Hip Anatomy Bony Anatomy Femur Femoral Head Femoral Neck Greater Trochanter Lesser Trochanter Intertrochanteric Crest Intertrochanteric Line Gluteal Tuberosity Bony Anatomy Pelvic Girdle Acetabulum 3 bones
Hip Anatomy Bony Anatomy Femur Femoral Head Femoral Neck Greater Trochanter Lesser Trochanter Intertrochanteric Crest Intertrochanteric Line Gluteal Tuberosity Bony Anatomy Pelvic Girdle Acetabulum 3 bones
The Lower Limb. Sevda LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD.PhD.
 The Lower Limb Sevda LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD.PhD. The Lower Limb The bones of the lower limb form the inferior part of the appendicular skeleton the organ of locomotion for bearing the weight of body stronger
The Lower Limb Sevda LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD.PhD. The Lower Limb The bones of the lower limb form the inferior part of the appendicular skeleton the organ of locomotion for bearing the weight of body stronger
Perineum. done by : zaid al-ghnaneem
 Perineum done by : zaid al-ghnaneem Hello everyone, this sheet will talk about 2 nd Lecture which is Perineum but there are some slides and info from 1 st Lecture. Everything included Slides + Pics Let
Perineum done by : zaid al-ghnaneem Hello everyone, this sheet will talk about 2 nd Lecture which is Perineum but there are some slides and info from 1 st Lecture. Everything included Slides + Pics Let
Vertebral Column. Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions. Cervical
 Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
Chapter 8 Outline. Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton
 Chapter 8 Outline Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton Figure 8.1 Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral Girdle Clavicle
Chapter 8 Outline Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton Figure 8.1 Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral Girdle Clavicle
8 THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
 CHAPTER 8 THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON 293 8 THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON Figure 8.1 Dancer The appendicular skeleton consists of the upper and lower limb bones, the bones of the hands and feet, and the bones
CHAPTER 8 THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON 293 8 THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON Figure 8.1 Dancer The appendicular skeleton consists of the upper and lower limb bones, the bones of the hands and feet, and the bones
THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE
 THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE Osteology of the Vertebral Column Bone Description vertebra Notes a vertebra
THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE Osteology of the Vertebral Column Bone Description vertebra Notes a vertebra
Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes. border of the superior ramus. inferolaterally from the pubic symphysis
 Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes pubis an angulated bone the forms the anterior part of the pelvis one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its forms 1/5
Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes pubis an angulated bone the forms the anterior part of the pelvis one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its forms 1/5
2. The vertebral arch is composed of pedicles (projecting from the body) and laminae (uniting arch posteriorly).
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES)
 Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
10/12/2010. Upper Extremity. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle. Clavicle (collarbone) Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton
 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton The primary function is movement It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton The primary function is movement It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW MSAK101-I Session 1 Learning Objectives: 1. Define
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW MSAK101-I Session 1 Learning Objectives: 1. Define
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME
 TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME Background: Skeletal remains are important pieces of evidence. The flesh, muscle, and organs of a victim rapidly decompose; however, the victim s skeleton
TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME Background: Skeletal remains are important pieces of evidence. The flesh, muscle, and organs of a victim rapidly decompose; however, the victim s skeleton
Appendicular Skeleton. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College
 Appendicular Skeleton Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College Pectoral girdle clavicle scapula Upper limb brachium antebrachium carpus manus Pelvic girdle oscoxae Lower limb femoral region
Appendicular Skeleton Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College Pectoral girdle clavicle scapula Upper limb brachium antebrachium carpus manus Pelvic girdle oscoxae Lower limb femoral region
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Professor of Anatomy &embryology Perineum It is the diamond-shaped lower end of the trunk
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Professor of Anatomy &embryology Perineum It is the diamond-shaped lower end of the trunk
To classify the joints relative to structure & shape
 To classify the joints relative to structure & shape To describe the anatomy of the hip joint To describe the ankle joint To memorize their blood & nerve supply JOINTS: Joints are sites where skeletal
To classify the joints relative to structure & shape To describe the anatomy of the hip joint To describe the ankle joint To memorize their blood & nerve supply JOINTS: Joints are sites where skeletal
Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh. Razi kittaneh. Maher hadidi
 1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
Bony ypelvis. Composition: formed by coccyx, and their articulations Two portions
 Pelvis Bony ypelvis Composition: formed by paired hip bones, sacrum, coccyx, and their articulations Two portions Greater pelvis Lesser pelvis Terminal line ( pelvic inlet): formed by promontory of sacrum,
Pelvis Bony ypelvis Composition: formed by paired hip bones, sacrum, coccyx, and their articulations Two portions Greater pelvis Lesser pelvis Terminal line ( pelvic inlet): formed by promontory of sacrum,
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
Chapter 7: Skeletal System
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
