For more information about how to cite these materials visit
|
|
|
- Rosanna Baker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Author(s): Michael Hortsch, Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: We have reviewed this material in accordance with U.S. Copyright Law and have tried to maximize your ability to use, share, and adapt it. The citation key on the following slide provides information about how you may share and adapt this material. Copyright holders of content included in this material should contact with any questions, corrections, or clarification regarding the use of content. For more information about how to cite these materials visit Any medical information in this material is intended to inform and educate and is not a tool for self-diagnosis or a replacement for medical evaluation, advice, diagnosis or treatment by a healthcare professional. Please speak to your physician if you have questions about your medical condition. Viewer discretion is advised: Some medical content is graphic and may not be suitable for all viewers.
2 Citation Key for more information see: Use + Share + Adapt { Content the copyright holder, author, or law permits you to use, share and adapt. } Public Domain Government: Works that are produced by the U.S. Government. (17 USC 105) Public Domain Expired: Works that are no longer protected due to an expired copyright term. Public Domain Self Dedicated: Works that a copyright holder has dedicated to the public domain. Creative Commons Zero Waiver Creative Commons Attribution License Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike License Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike License GNU Free Documentation License Make Your Own Assessment { Content Open.Michigan believes can be used, shared, and adapted because it is ineligible for copyright. } Public Domain Ineligible: Works that are ineligible for copyright protection in the U.S. (17 USC 102(b)) *laws in your jurisdiction may differ { Content Open.Michigan has used under a Fair Use determination. } Fair Use: Use of works that is determined to be Fair consistent with the U.S. Copyright Act. (17 USC 107) *laws in your jurisdiction may differ Our determination DOES NOT mean that all uses of this 3rd-party content are Fair Uses and we DO NOT guarantee that your use of the content is Fair. To use this content you should do your own independent analysis to determine whether or not your use will be Fair.
3 Histology of the Respiratory Tract M1 Cardiovascular/Respiratory Sequence Michael Hortsch, Ph.D. Fall 2008
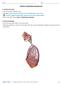
4 Objectives Respiratory Tract Histology: Know the general functions of the respiratory system and the overall organization of the respiratory tree Identify the histological features of the nasal cavity, the vocal cords and the trachea Know the cellular components of the respiratory epithelium and their functional importance Be able to recognize olfactory epithelium and know how it differs from regular respiratory epithelium Identify bronchi, bronchiole, terminal bronchiole, respiratory bronchiole, alveolar ducts and sacs and know their distinct histological features Be able to recognize Clara cells and know their functional significance Understand the structural organization of alveoli, including the air-blood barrier and alveolar pores Know the cellular components of the alveolar tissue and their individual functions and be able to recognize them Understand the organization of the intrapulmonary blood circulation and recognize its different parts
5 Major Functions of the Respiratory System: 1. Air conditioning (air warming, humidifying and filtering) 2. Oxygen/carbon dioxide exchange Minor Functions of the Respiratory System: 1. Perception of smell 2. Phonation 3. Endocrine functions, conversion of Angiotensin I into II
6 Cast of a human bronchial tree Cell and Tissue Biology A Textbook of Histology; 6 th edition; 1988; Weiss, Urban & Schwarzenberg Fig
7 Arborization of Image of respiratory tree arborization removed respiratory tree Original Image: Wheater s Functional Histology; 5 th edition, 2006, Young, Lowe, Stevens and Heath; Churchill Livingstone Elsevier Fig. 12.1
8 Histology A Text and Atlas; 5 th edition, 2006, Ross and Pawlina, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins Fig 19.1 Histological changes along the respiratory tree
9 Histological features of the nasal cavity Human Histology, 2 nd edition, 1997, Stevens and Lowe, Mosby Fig 10.4
10 Nasal venous sinuses warm the incoming air Wheater s Functional Histology; 4 th edition, 2000, Young and Heath; Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; Fig 12.3
11 Transition from stratified squamous epithelium to the respiratory epithelium at the laryngeal ventricle Color Atlas of Basic Histology; 1993; Berman; Appelton and Lange, Fig 14-3
12 Resident cells of the respiratory epithelium
13 Color Atlas of Basic Histology; 1993; Berman; Appelton and Lange; Fig 14-8 Light micrograph of the respiratory epithelium/mucosa
14 Basic Histology Text & Atlas; 10 th edition, 2003; Junqueira and Carneiro, Lange McGraw-Hill; Fig top Scanning EM of the respiratory epithelium G = goblet cell
15 Transmission EM of a respiratory epithelium Cell and Tissue Ultrastructure A Functional Perspective; 1993; Cross and Mercer, Freeman and Co.; page 305
16 Diagram of the olfactory epithelium Dr. Thomas Caceci, Wikipedia Original Image: Human Histology, 1 st edition, 1992, Stevens and Lowe, Grower Medical Publishing, Fig. 9.5
17 Light micrograph of olfactory epithelium (note the absence of goblet cells) Color Textbook of Histology; 2 nd edition, 1994; Gartner and Hiatt; Williams and Wilkins; Plate 12.1, Fig. 1
18 Light micrograph of olfactory epithelium (note the absence of goblet cells) Color Textbook of Histology; 2 nd edition, 1994; Gartner and Hiatt; Williams and Wilkins; Plate 12.1, Fig. 2
19 True vocal cords are not lines by a respiratory epithelium, but rather by a stratified nonkeratinized squamous epithelium. Histology A Text and Atlas; 5 th edition, 2006, Ross and Pawlina, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; Fig 19.4
20 Source Undetermined
21 Color Atlas of Basic Histology; 1993; Berman; Appelton and Lange, Fig 14-2 Two types of glands are found in the lamina propria of the laryngeal and tracheal respiratory epithelium: Serous and mucus producing glands
22 Trachealis muscle (smooth muscle) Human Histology, 1 st edition, 1992, Stevens and Lowe, Grower Medical Publishing, Fig 9.8 Trachea with C-shaped hyaline cartilage ring
23 Light micrograph of a smaller bronchus Color Atlas of Basic Histology; 1993; Berman; Appelton and Lange Fig 14-10
24 Higher magnification of a bronchial wall Color Atlas of Basic Histology; 1993; Berman; Appelton and Lange; Fig 14-11
25 Color Atlas of Basic Histology; 1993; Berman; Appelton and Lange; Fig Bronchiole (note the appearance of more abundant smooth muscle). This muscle layer is causally involved in asthma.
26 Image of Max Clara removed Transmission EM of bronchiolar epithelium with a Clara cell in the center. Clara cells are abundant, domeshaped secretory cells in the terminal bronchioles. Netter s Essential Histology; 2008; Ovalle and Nahirney; Elsevier; page 346 Max Clara (1937) Zeitschr. mikro.-anat. Forsch. 41: M. Clara (1937) Zeitschr. Mikr0.-anat. Forschung 41:
27 Histology A Text and Atlas; 5 th edition, 2006, Ross and Pawlina, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; Fig Clara cells are not ciliated and secrete protective proteins. They have an extensive smooth ER that is involved in the detoxification of inhaled substances. Furthermore, they act as progenitor/stem cells for ciliated and non-ciliated bronchiolar epithelial cells. Clara cell image: Basic Histology Text & Atlas; 10 th edition, 2003; Junqueira and Carneiro, Lange McGraw-Hill; Fig 17-12
28 Clara cells in a terminal bronchiole Clara cells Respiratory bronchiole Terminal bronchiole Clara cells Basic Histology Text & Atlas by Junqueira and Carneiro; 10 th edition, 2003; Lange McGraw-Hill Modified from Fig 17-18
29 Transition Terminal bronchiole from the conducting to Alveolus the respiratory Respiratory bronchiole portion of the respiratory Patrick J. Lynch (wikimedia) tract Original Image: Human Histology, 1 st edition, 1992, Stevens and Lowe, Grower Medical Publishing ; Fig 9.12a
30 Color Atlas of Basic Histology, 1993, Berman, Appelton and Lange, Fig Transition from the terminal (TB) to the respiratory bronchiole (RB)
31 Structure of a respiratory bronchiole and an alveolar duct Color Atlas of Basic Histology, 1993, Berman, Appelton and Lange, Fig 14-16
32 Color Atlas of Basic Histology, 1993, Berman, Appelton and Lange, Fig Alveolar ducts branch further into alveolar sacs and single alveoli
33 Scanning EM of alveolar space Color Atlas of Histology, 1992, Erlandsen and Magney, Mosby Book, Fig 17-20
34 Color Atlas of Basic Histology, 1993, Berman, Appelton and Lange, Fig Light micrograph of alveolar wall
35 Cell and Tissue Ultrastructure A Functional Perspective, 1993, Cross and Mercer, Freeman and Co., Fig Scanning EM of an alveolus demonstrates holes in the alveolar wall.
36 Image of Pores of Kohn removed Image of Hans Kohn removed Original Images: Human Histology, 1 st edition, 1992, Stevens and Lowe, Grower Medical Publishing, Fig 9.14 Structure of the interalveolar septum with Pores of Kohn (allow collateral ventilation)
37 Human Histology, 2 nd edition, 1997, Stevens and Lowe, Mosby, Fig Destruction of alveolar organization in emphysema patient
38 Image of air-blood barrier removed Original Image: Human Histology, 1 st edition, 1992, Stevens and Lowe, Grower Medical Publishing, Fig 9.14 Air-blood barrier in the interalveolar septum
39 Fused basal lamina The air-blood barrier consists of three different components, two cellular and one acellular. Type I pneumocyte layer Endothelial layer Basic Histology Text & Atlas, 10 th edition, 2003, Junqueira and Carneiro, Lange McGraw-Hill, Fig The endothelial, as well as the type I pneumocyte layer are sealed by tight junctions.
40 Capillary system in the alveolar septa. Mammalian Histology-B408; Department of Biological Sciences; University of Delaware. Produced by Roger C. Wagner and Fred E. Hossler
41 Transmission EM of air-blood barrier Gas exchange occurs by diffusion across the alveolar wall, which on average is only 0.1 to 1.5 µm thick. The red arrows mark tight junctions Histology A Text and Atlas, 5 th edition, 2006, Ross and Pawlina, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Fig 19.19
42 Basic Histology Text & Atlas, 10 th edition, 2003, Junqueira and Carneiro, Lange McGraw-Hill, Fig Type II pneumocytes are secretory cells, which produce a protein-lipid secretion product, called surfactant. Composition of surfactant: Lipids (90%) Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), Phosphatidylglycerol, Cholesterol Proteins (10%) Plasma proteins, Surfactant proteins A, B, C and D
43 Lamellar bodies constitute the secretory vesicles of type II pneumocytes. Infants born before 30 weeks of gestation often are unable to produce sufficient quantities of surfactant, a situation known as Infant respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). Basic Histology Text & Atlas, 10 th edition, 2003, Junqueira and Carneiro, Lange McGraw-Hill, Fig 17-26
44 Pulmonary macrophages or dust cells Cell and Tissue Ultrastructure A Functional Perspective, 1993, Cross and Mercer, Freeman and Co., Page 317
45 Color Atlas of Basic Histology, 1993, Berman, Appelton and Lange, Fig Light micrograph of pulmonary macrophages
46 Pulmonary macrophage from a non-smoker Pulmonary macrophage from a smoker Color Atlas of Histology, 1992, Erlandsen and Magney, Mosby Book, Figs and 17-16
47 Intrapulmonary Blood Circulation Image of pulmonary blood flow removed Original Image: Netter s Essential Histology, 2008, Ovalle and Nahirney, Elsevier, page 347 Bronchial arteries and Pulmonary arteries travel together along the bronchiolar system, Pulmonary veins are usually not associated with the lower branches of the bronchiolar system Pulmonary arteries supply deoxygenated blood. Bronchial arteries supply oxygenated blood. After oxygenation in the capillary plexuses, blood is drained by Pulmonary veins.
48 Michigan Medical Histology Slide Collection Pulmonary arteries are large and relatively thinwalled. They are associated with the bronchiolar tree.
49 Michigan Medical Histology Slide Collection Bronchial arteries are much smaller and considering their size have a thicker wall. They also accompany the branches of the bronchiolar tree.
50 Michigan Medical Histology Slide Collection Pulmonary veins collect blood from both Pulmonary arteries and Bronchial arteries. They are usually not associated with bronchioles.
51 Histology A Text and Atlas; 5 th edition, 2006, Ross and Pawlina, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins Fig 19.1 Histological changes along the respiratory tree
52 Additional Source Information for more information see: Slide 6: Cell and Tissue Biology A Textbook of Histology, 6 th edition, 1988, Weiss, Urban & Schwarzenberg Fig Slide 8: Histology A Text and Atlas; 5 th edition, 2006, Ross and Pawlina, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins Fig 19.1 Slide 9: Human Histology, 2 nd edition, 1997, Stevens and Lowe, Mosby Fig 10.4 Slide 10: Wheater s Functional Histology, 4 th edition, 2000, Young and Heath, Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, Fig 12.3 Slide 11: Color Atlas of Basic Histology, 1993, Berman, Appelton and Lange, Fig 14-3 Slide 12: Cell and Tissue Biology A Textbook of Histology, 6 th edition, 1988, Weiss, Urban & Schwarzenberg, Fog Slide 13: Color Atlas of Basic Histology, 1993, Berman, Appelton and Lange, Fig 14-8 Slide 14: Basic Histology Text & Atlas, 10 th edition, 2003, Junqueira and Carneiro, Lange McGraw-Hill, Fig top Slide 15: Cell and Tissue Ultrastructure A Functional Perspective, 1993, Cross and Mercer, Freeman and Co., page 305 Slide 16: Bowman Wikipedia, Dr. Thomas Caceci, Slide 17: Color Textbook of Histology, 2 nd edition, 1994, Gartner and Hiatt, Williams and Wilkins, Plate 12.1, Fig. 1 Slide 18: Color Textbook of Histology, 2 nd edition, 1994, Gartner and Hiatt, Williams and Wilkins, Plate 12.1, Fig. 2 Slide 19: Histology A Text and Atlas, 5 th edition, 2006, Ross and Pawlina, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Fig 19.4 Slide 20: Source Undetermined Slide 21: Color Atlas of Basic Histology, 1993, Berman, Appelton and Lange, Fig 14-2 Slide 22: Human Histology, 1 st edition, 1992, Stevens and Lowe, Grower Medical Publishing, Fig 9.8 Slide 23: Color Atlas of Basic Histology, 1993, Berman, Appelton and Lange, Fig Slide 24: Color Atlas of Basic Histology, 1993, Berman, Appelton and Lange, Fig Slide 25: Color Atlas of Basic Histology, 1993, Berman, Appelton and Lange, Fig Slide 26: Netter s Essential Histology, 2008, Ovalle and Nahirney, Elsevier, page 346; M. Clara (1937) Zeitschr. Mikr0.-anat. Forschung 41: Slide 27: Histology A Text and Atlas, 5 th edition, 2006, Ross and Pawlina, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Fig 19.12; Clara cell image: Basic Histology Text & Atlas; 10 th edition, 2003; Junqueira and Carneiro, Lange McGraw-Hill; Fig Slide 28: Basic Histology Text & Atlas by Junqueira and Carneiro, 10 th edition, 2003, Lange McGraw-Hill Modified from Fig Slide 29: Patrick J. Lynch, Wikimedia, CC: BY Slide 30: Color Atlas of Basic Histology, 1993, Berman, Appelton and Lange, Fig Slide 31: Color Atlas of Basic Histology, 1993, Berman, Appelton and Lange, Fig Slide 32: Color Atlas of Basic Histology, 1993, Berman, Appelton and Lange, Fig Slide 33: Color Atlas of Histology, 1992, Erlandsen and Magney, Mosby Book, Fig 17-20
53 Slide 34: Color Atlas of Basic Histology, 1993, Berman, Appelton and Lange, Fig Slide 35: Cell and Tissue Ultrastructure A Functional Perspective, 1993, Cross and Mercer, Freeman and Co., Fig Slide 36: Human Histology, 1 st edition, 1992, Stevens and Lowe, Grower Medical Publishing, Fig 9.14; The photo of Hans Kohn is used with permission from Kohn s granddaughter Dr. Ruth Anna Putnam, not relicensed for distribution Slide 37: Human Histology, 2 nd edition, 1997, Stevens and Lowe, Mosby, Fig Slide 38: Human Histology, 1 st edition, 1992, Stevens and Lowe, Grower Medical Publishing, Fig 9.14 Slide 39: Basic Histology Text & Atlas, 10 th edition, 2003, Junqueira and Carneiro, Lange McGraw-Hill, Fig Slide 40: Mammalian Histology-B408, ; Department of Biological Sciences, University of Delaware. Produced by Roger C. Wagner and Fred E. Hossler Slide 41: Histology A Text and Atlas, 5 th edition, 2006, Ross and Pawlina, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Fig Slide 42: Basic Histology Text & Atlas, 10 th edition, 2003, Junqueira and Carneiro, Lange McGraw-Hill, Fig Slide 43: Basic Histology Text & Atlas, 10 th edition, 2003, Junqueira and Carneiro, Lange McGraw-Hill, Fig Slide 44: Cell and Tissue Ultrastructure A Functional Perspective, 1993, Cross and Mercer, Freeman and Co., Page 317 Slide 45: Color Atlas of Basic Histology, 1993, Berman, Appelton and Lange, Fig Slide 46: Color Atlas of Histology, 1992, Erlandsen and Magney, Mosby Book, Figs and Slide 47: Netter s Essential Histology, 2008, Ovalle and Nahirney, Elsevier, page 347 Slide 48: Michigan Medical Histology Slide Collection Slide 49: Michigan Medical Histology Slide Collection Slide 50: Michigan Medical Histology Slide Collection Slide 51: Histology A Text and Atlas, 5 th edition, 2006, Ross and Pawlina, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins Fig 19.1
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Prachi Agarwal M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Prachi Agarwal M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Thomas Sisson, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: Thomas Sisson, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Kathleen A. Stringer, Pharm. D, 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Kathleen A. Stringer, Pharm. D, 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung
 Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung Color code: Important Extra & Doctor notes Editing file Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe:
Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung Color code: Important Extra & Doctor notes Editing file Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe:
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Includes : - the lung - a system of tube
 FYH - ERDS 1 Includes : - the lung - a system of tube Divided into 2 principal regions : - conducting portion : nasal cavity, nasopharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles & terminal bronchioles -
FYH - ERDS 1 Includes : - the lung - a system of tube Divided into 2 principal regions : - conducting portion : nasal cavity, nasopharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles & terminal bronchioles -
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Lec #2 histology. Bronchioles:
 Lec #2 histology. Last lecture we talked about the upper respiratory tract histology, this one is about the lower part histology. We will discuss the histology of: -bronchioles -respiratory bronchioles
Lec #2 histology. Last lecture we talked about the upper respiratory tract histology, this one is about the lower part histology. We will discuss the histology of: -bronchioles -respiratory bronchioles
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Jonathan Trobe, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Author: Jonathan Trobe, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Arno Kumagai, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Arno Kumagai, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory System. Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
7/12/2012. Respiratory system. Respiratory Response to Toxic Injury (Lung) Ninth Industrial Toxicology and Pathology Short Course.
 Ninth Industrial Toxicology and Pathology Short Course 23 27 July, 2012 Contemporary Concepts in Target Organ Toxicologic Pathology Respiratory system Respiratory Response to Toxic Injury (Lung) Eric Wheeldon
Ninth Industrial Toxicology and Pathology Short Course 23 27 July, 2012 Contemporary Concepts in Target Organ Toxicologic Pathology Respiratory system Respiratory Response to Toxic Injury (Lung) Eric Wheeldon
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): John G. Younger, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): John G. Younger, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Michael Heung, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Michael Heung, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
Histology and development of the respiratory system
 Histology and development of the respiratory system Árpád Dobolyi Semmelweis University, Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Outline of the lecture 1. Structure of the trachea 2. Histology
Histology and development of the respiratory system Árpád Dobolyi Semmelweis University, Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Outline of the lecture 1. Structure of the trachea 2. Histology
I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous
 I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous Epithelium b. Nasal Cartilages 1) Nasal Cavity Pseudostratified
I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous Epithelium b. Nasal Cartilages 1) Nasal Cavity Pseudostratified
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Michael Hortsch, Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Michael Hortsch, Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
SCPA602 Respiratory System
 SCPA602 Respiratory System Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives
SCPA602 Respiratory System Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives
Respiratory System. Organization of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Chapter 16. Respiratory System
 Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The respiratory system has multiple organs, we will begin with the nose and nasal cavity.
 Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, D.M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License:
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, D.M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License:
Lecture Overview. Respiratory System. Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition. Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11
 Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
2402 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 1 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I nt r oduc t i on TextBook Readings Pages 830 through 845. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 1 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I nt r oduc t i on TextBook Readings Pages 830 through 845. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Silas P. Norman, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Silas P. Norman, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
MH1001 Larynx, Monkey, H&E
 MH1001 Larynx, Monkey, H&E - False vocal fold : ciliated pseuodostratified columnar epithelium - True vocal fold : nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium vocalis muscle, vocal ligament - Thyroid
MH1001 Larynx, Monkey, H&E - False vocal fold : ciliated pseuodostratified columnar epithelium - True vocal fold : nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium vocalis muscle, vocal ligament - Thyroid
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab
 Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
The Respiratory System. Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb
 The Respiratory System Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb Objectives (lecture + practical) 1. Identify the conduction part of the respiratory tract and analyze the function of each segment 2. Identify
The Respiratory System Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb Objectives (lecture + practical) 1. Identify the conduction part of the respiratory tract and analyze the function of each segment 2. Identify
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Rachel Glick, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Rachel Glick, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
Development of Respiratory System. Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra
 Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Rachel Glick, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Rachel Glick, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
 Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 10 Respiratory System 1 Anatomy & Physiology Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 10 Respiratory System 1 Anatomy & Physiology Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models.
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND THORAX A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models. Nasal cavity Pharynx (fare-rinks) B. Lower respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1)
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND THORAX A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models. Nasal cavity Pharynx (fare-rinks) B. Lower respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1)
Respiratory System. BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College
 Respiratory System BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Respiration Ventilation of lungs Gas exchange between air/bld and bld/tissue Use of oxygen in cellular respiration
Respiratory System BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Respiration Ventilation of lungs Gas exchange between air/bld and bld/tissue Use of oxygen in cellular respiration
Lab Activity 27. Anatomy of the Respiratory System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Author(s): Rockefeller A. Oteng, M.D., University of Michigan
 Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: Pulmonary Embolism Part 2 (2012) Author(s): Rockefeller A. Oteng, M.D., University of Michigan License: Unless otherwise noted, this material
Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: Pulmonary Embolism Part 2 (2012) Author(s): Rockefeller A. Oteng, M.D., University of Michigan License: Unless otherwise noted, this material
Ch16: Respiratory System
 Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Rajesh Mangrulkar, M.D., 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Rajesh Mangrulkar, M.D., 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems
 Name Date Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Multiple Choice. Please make your best selection. 1. Respiration is the process of: (a) Sucking air into the lungs (b) Converting glucose into
Name Date Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Multiple Choice. Please make your best selection. 1. Respiration is the process of: (a) Sucking air into the lungs (b) Converting glucose into
Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function. Histology = study of tissues
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Objectives. Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology. Function of the Lungs/Heart. The lung is for gas exchange. Failure of the Lungs/Heart
 Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, D.M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License:
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, D.M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License:
Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems
 Name Date Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Multiple Choice. Please make your best selection. 1. Respiration is the process of: (a) Sucking air into the lungs (b) Converting glucose into
Name Date Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Multiple Choice. Please make your best selection. 1. Respiration is the process of: (a) Sucking air into the lungs (b) Converting glucose into
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
General Human Histology. The Respiratory System
 General Human Histology Lecture 5 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Respiratory System The respiratory system includes the lungs and a system of tubes that link the sites of gas exchange with the external
General Human Histology Lecture 5 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Respiratory System The respiratory system includes the lungs and a system of tubes that link the sites of gas exchange with the external
The Respiratory System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
Karachi King s College of Nursing
 Karachi King s College of Nursing Badil Dass Lecturer Respiratory system Respiratory System Respiratory system consist of: Nose Pharynx (Throat) Larynx (Voice Box) Trachea (Wind Pipe) Bronchi Bronchioles
Karachi King s College of Nursing Badil Dass Lecturer Respiratory system Respiratory System Respiratory system consist of: Nose Pharynx (Throat) Larynx (Voice Box) Trachea (Wind Pipe) Bronchi Bronchioles
2. List seven functions performed by the respiratory system?
 The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System
 C h a p t e r 24 The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
C h a p t e r 24 The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals
 Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
NAME PER DATE. membrane
 NAME PER DATE Chapter 9, Section 1 Review Matching: 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae 6. epiglottis 7. larynx 8. mediastinum 9. nares 10. olfactory
NAME PER DATE Chapter 9, Section 1 Review Matching: 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae 6. epiglottis 7. larynx 8. mediastinum 9. nares 10. olfactory
Respiratory System Functions. Respiratory System Organization. Respiratory System Organization
 Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Bio 104 Respiratory System 81
 81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
The Human Respiration System
 The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System
 CHAPTER 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System Sagittal Section of Upper Airway Fig. 1-1. Sagittal section of upper airway. Structure of the Nose Fig. 1-2. Structure of the nose. Sagittal
CHAPTER 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System Sagittal Section of Upper Airway Fig. 1-1. Sagittal section of upper airway. Structure of the Nose Fig. 1-2. Structure of the nose. Sagittal
Basic Histology. By Mrs. Bailey
 Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
