PNEUMOCONIOSIS IN CHINA-CLAY WORKERS
|
|
|
- Zoe Greene
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1963, 20, 226. PNEUMOCONIOSIS IN CHINA-CLAY WORKERS BY S. WARRAKI and Y. HERANT From Ain-Shams University Hospital and the Ministry of Public Health, U.A.R. (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION OCTOBER 2, 1962) A 70 mm. radiographic survey in 914 workmen exposed to china-clay dust was made in 1959 in an industrial plant in which kaolin deposits are processed for the earthenware industry in Ayyat, United Arab Republic. All were ex-agricultural workers and thus not exposed to any industrial dust hazards. The purpose of the survey was to study the prevalence of pneumoconiosis and active tuberculosis. Fifty subjects were considered to require further investigation and large films were therefore taken which showed the following results: five cases of pneumoconiosis; one case of pneumoconiosis and tuberculosis; and 13 cases of active tuberculosis. Of the five pneumoconiosis cases, two were classified as progressive massive fibrosis (P.M.F.), two as category 3 and one as category 1 simple pneumoconiosis. All had been heavily exposed for 15 years or more. Case records of the pneumoconiosis group are given with follow-up observations for two and a half years. There were no important clinical or radiographic changes except that one of the two patients with P.M.F. died of cor pulmonale. Correlation of the clinical features and radiographic abnormalities was poor. The low prevalence of pneumoconiosis, in spite of the heavy and prolonged exposure, is emphasized. A sample of the airborne dust contained about 2 % of Si02. China-clay or kaolin has long been suspected of majority were ex-agricultural workers from the causing pneumoconiosis. Middleton (1936) suggested that there might be a dust hazard in the china-clay tions before joining the plant. nearby land, and thus not engaged in dusty occupa- industry. McNally and Trostler (1941) reported The factory was built in 1880 by a private company. During the second world war the factory was cases with densely mottled areas in the upper lobes of the lungs among workers in fuller's earth in extended with a considerable increase in the number Illinois. Similar cases have been reported by Bastenier (1950), and by Cavigneaux, Charles, Fuchs, and used. Since 1961 the factory has become the property of workers. No methods of dust suppression were Tara (1950). Thomas (1952) described the findings of of the state, and new measures for dust control have two necropsies; one on a worker in the ball clay been introduced. It is the only factory of its kind in industry, and one on a man who had been engaged in the country for manufacturing chinaware and various refractory materials. Recently, ceramics have grinding china stone, a granite containing china-clay. Kaolinosis is the term given by Lynch and McIver also been produced. (1954), who described the pathological studies in two The china-clay is obtained by digging and is then cases of massive pulmonary fibrosis in kaolin workers in South Carolina. Six cases of pneumoconiosis The processes are all extremely dusty. The final brought to the factory where it is ground and sieved. in kaolin workers were described by Hale, Gough, ground dust is mixed with water to form the moulding clay. The method of washing away the wall of the King, and Nagelschmidt (1956) in Cornwall; two of these died and post-mortem examination showed pit with a high pressure stream of water, as in Cornwall, has not been adopted. large amounts of kaolin dust in the lungs. This report describes six cases of pneumoconiosis discovered during the mass miniature radiographic Methods survey of workers processing kaolin deposits for the earthenware industry in Ayyat, U.A.R. This group A mass miniature radiographic survey was carried of workers was ideal for such a survey since the out in September, 1959, on 914 men working in an 226
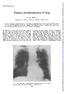
2 PNEUMOCONIOSIS IN CHINA-CLA Y WORKERS industrial plant for processing china-clay deposits. A 70 mm. "Odelca" mirror camera attachment with a four-valve mobile unit was used. The object of the survey was to ascertain the prevalence of pneumoconiosis and active tuberculosis. The total population surveyed was 914. There were no refusals. The periods of exposure at the time of the survey were as follows: less than 10 years, 264 workers; 10 to 15 years, 133; 15 to 20 years, 326 (4 with pneumoconiosis); and more than 20 years, 191 workers (two with pneumoconiosis). The films were read by three observers independently; differences were resolved by discussion and agreement between the readers in conference. Large films (12 x 15 in. (30-48 x cm.)) were taken when at least two of the three observers agreed that the cases were suspect. The 50 cases in which large films were made are categorized (I.L.O. Classification, 1950) in the Table. TABLE Classified from M.M.R. No. Results from Large Films Pneumoconiosis Active Tuberculosis Simple: Category Category Category Complicated The 13 cases of active tuberculosis discovered did not include case 4 (below), which was regarded as a case of pneumoconiosis. In the pneumoconiosis cases, routine medical and industrial histories were taken, a clinical examination was carried out, and sputa were examined for tubercle bacilli. The E.S.R. was measured by the Westergren method. All cases were followed up until April, 1962, except one patient who died in Case Reports Case 1.-M.M.A., aged 57, had worked in grinding for the last 17 years. He had previously been a farmer. He had no symptoms. On clinical examination only a few rhonchi were heard at both bases. The chest radiograph revealed increased bronchovascular markings with dispersed mottling, especially in the right mid-zone peripherally (category 1). Slight mottling was also noticed below the left clavicle. Sputum examination was negative for tubercle bacilli by direct methods and culture. The E.S.R. was 18 mm. in the first hour. He continued with the same job and the last examination in 1962 revealed no marked change. Case 2.-M.A.H., aged 50, worked in grinding and sieving for 15 years, before which he had worked on the land. He complained of mild dyspnoea on exertion and slight mucoid sputum for the last 11 months. Clinical 227 FIG. l.-case 2. Right upper zone showing simple pneumoconiosis (category 3, mixed). examination of the chest and cardiovascular and other systems was negative. A radiograph showed fine light mottling all over both lung fields (category 3, mixed) (Fig. 1). Sputum examination was twice negative for tubercle bacilli by direct smear only. The E.S.R. was 40 mm. in one hour. He worked in the same processes and when last examined in 1962 no important clinical or radiographic change was reported. Case 3.-S.A.B., aged 46, worked in loading of chinaclay, grinding, and sieving for 18 years. He had not previously been engaged in any dusty occupation. He had no complaints and clinical examination was within normal range. A chest radiograph (Fig. 2) showed bilateral diffuse nodular shadows with no accentuation of the bronchovascular markings (category 2, nodular). Sputum was negative for tubercle bacilli by repeated direct smears. The E.S.R. was 30 mm. in the first hour. He continued to work in grinding until the last examination in 1962 when no change was reported. Case 4.-A.E.A., aged 47, had worked at the mill for the last 16 years. Previously he had been an agricultural worker. During the last six months he had noticed that he had anorexia and was easily fatigued with mild dyspnoea on exertion. He also noticed that he had a cough
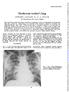
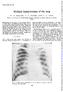
3 228 BRITISH JOURNAL OF INDUSTRIAL MEDICINE FIG. 2.-Case 3. Right upper zone showing simple pneumoconiosis (category 2, nodular). with sputum which he did not have before. Frank blood was coughed up with sputum once. On examination his general condition was less than moderate and a few crepitations were heard over the interscapular region on the left side. A chest radiograph showed a rounded 5 cm. cavity below the left clavicle; both the lung fields showed profuse mottling throughout, particularly in the midzones (category 2A, cavity). Sputum examination was positive for tubercle bacilli both by direct methods and on culture. The E.S.R. was 90 mm. in the first hour. Streptomycin and isoniazid were given in hospital for nine months with great improvement in his general condition and radiographic appearance. The mild dyspnoea was however unaltered. He continued working in the plant as a door-keeper and the last examination in 1962 showed the same findings. The absence of any marked change in the nodulation in the film of the right lung after treatment for tuberculosis is the main reason for regarding this as a case of pneumoconiosis. Case 5.-M.Y.M., aged 54, from the age of 29 worked in the factory in both grinding and sieving. He had had a chronic cough with a little mucoid sputum for the last three years, which was attributed to smoking. Bloodtinged sputum had occurred three times during the last year, and also moderate dyspnoea on exertion. Clinically, FIG. 3.-Case 5. Left upper zone showing areas of consolidation with surrounding nodulation (category 3A). fine rales were heard at both bases. Examination of the heart and other systems was normal. A chest radiograph showed homogeneous non-cavitated shadows in the left parahilar, left infraclavicular, and right apical zones. The rest of the lung fields showed a great deal of very fine mottling (category 3A) (Fig. 3). Sputum examinations for tubercle bacilli were negative by direct examination and on culture. The E.S.R. was 40 mm. in the first hour. He continued with the same job and the last examination in 1962 showed no important change in his clinical or radiographic condition. Case 6.-A.H.M., aged 57, had worked in grinding for the last 22 years. Before this he used to work on the land. He noticed dyspnoea on the least effort, was easily fatigued, and had bouts of lateral chest pain. He raised, on average, one coffee cupful of mucoid sputum daily which was never blood-tinged. Clinical examination showed that he had a temperature of 99 F. (37 2 C.), mild toxaemia, a tachycardia of 110 per minute, mild emphysema, and scattered rhonchi over the chest. The heart was clinically normal and the blood pressure was 140/95 mm.hg. Moderate clubbing of the fingers was noticed. The chest film (Fig. 4) showed a huge dense mass, about 7 cm. in diameter, in each hilum (category 2B). Both masses showed an irregular outline and evidence of
4 PNEUMOCONIOSIS IN CHINA-CLA Y WORKERS FIG. 4.-Case 6. Right mid and upper zone showing large area of consolidation (category 2B). breakdown was noticed. The rest of the lung fields was irregularly and lightly mottled, with areas of focal emphysema. Sputum examination was repeatedly negative for tubercle bacilli by direct methods and on culture. The E.S.R. ranged between 70 and 110 mm. in the first hour. He continued working in the same process for two months in spite of his disabling dyspnoea. From January, 1960, he took to bed with marked weakness and wasting together with episodes of "bronchitis". He died on June 30, 1960, and a diagnosis of cor pulmonale was made. Permission for necropsy was not obtained. Discussion Industrial Hazards.-China-clay is prepared for large-scale use in the pottery industry as an important constituent of chinaware and also in the manufacture of refractory materials. Several processes are carried out in its production but the most dusty ones are grinding and sieving which were done in a closed chamber. Masks were available but were not used by the workers. Chemical analysis of dust samples collected at the mill showed that its chief constituent (83 to 86 %) was potassium aluminium silicate 5.n A (K4 A12 Si2 09); there was only 1 to 20% free silica. Microscopical examination of the same dust showed all particles were below 3 4 microns. The exposure time of the workers diagnosed as having pneumoconiosis varied from 15 to 25 years of 8 hours work daily. No quantitative samples of airborne dust were obtained. The factory was visibly very dusty. Clinical Features.-While no complaint was obtained in two cases, the remaining four men had symptoms. These were mainly dyspnoea on exertion, cough, and slight mucoid sputum of no characteristic colour. In case 6, dyspnoea was marked, and one coffee-cupful of sputum was raised per day. This is a case of progressive massive fibrosis (P. M.F.) with probable cavitation. Repeated blood-tinged sputum occurred in case 5 (P.M.F.), while frank blood-spitting occurred once in case 4 (pneumoconiosis with tuberculosis). Clubbing of the fingers was only noticed in case 6 (P.M.F.). Clinical examination was negative in cases 2, 3, and 5, a few rhonchi on both sides were heard in case 1, and crepitations were present in case 4 who had a tuberculous cavity. The raised E.S.R. in three cases can be partly explained by various degrees of anaemia due to endemic infections of the intestinal and urinary tracts by parasites (schistosomiasis, ancylostomiasis, and amoebiasis) since all the men were ex-landworkers. Sputum examinations were negative for tubercle bacilli in all cases except case 4. Radiographic Examination.-Hale et al. (1956), reporting on china-clay pneumoconiosis in Cornwall, mentioned that lesions were in the form of nodular mottling comparable in appearance to those of silicosis, or P.M.F. as seen in coal-miners' pneumoconiosis. The radiographic patterns observed in the present series conform mostly with those reported by Hale. The mottling was not particularly dense, as described by McNally and Trostler (1941) in workmen exposed to fuller's earth; neither was there any elevation of hilar shadows or strand-like opacities, as described by Geher (1955) and by Barth, Frik, and Scheidemandel (1956) in pneumoconiosis due to aluminium dust. Case 4, whose condition was complicated by tuberculosis, had a nodular type of lesion. The appearance and location of the confluent opacities in cases 5 and 6 were comparable to those of P.M.F. in coal-miners. In these two cases cavitation was not confirmed, though in case 6 there was a suspicion of cavitation on account of the breakdown shown by the postero-anterior radiograph as well as the quantity of sputum. Kilpatrick, Heppleston and Fletcher (1954) reported that cavitation may not be detected in P.M.F. because of the remarkable way in
5 230 BRITISH JOURNAL OF INDUSTRIAL MEDICINE which these cavities may refill completely. A radiograph should thus be taken shortly after the patient has expectorated a large quantity of sputum; also a lateral projection and a tomogram should be done. Moreover, even if cavitation is demonstrated, this cannot be considered tuberculous unless confirmed by bacteriological examination. In our two cases of P.M.F. cavitation was not confirmed, nor were sputum examinations positive for tubercle bacilli. Except for case 6 (P.M.F.), correlation of clinical and radiographic features was poor. This again compares with the slight correlation reported in coal-miners' pneumoconiosis by Higgins and Cochrane (1961). Diagnosis.-Though no histological evidence was available, yet the diagnosis of pneumoconiosis was made on account of the typical radiographic appearances and the long exposure to a very dusty atmosphere. The men were agricultural workers who had not previously worked in a dusty occupation. The composition of the dust was almost pure kaolin, and the free silica content was too low to produce silicosis. Follow-up examinations over two and a half years have shown no progression in the radiographic appearances; this was considered sufficient to exclude any infective cause for the radiological abnormalities. In the two cases with P.M.F., the massive shadows were typical in appearance and distribution, so that the possibility of neoplasm was not considered. This was further substantiated by the subsequent course of these two cases. We wish to acknowledge our indebtedness to Dr. 0. Rifaat, Faculty of Agriculture, Cairo University, for his assistance in particle measurement and the chemical analysis of the dust. REFERENCES Barth, G., Frik, W., and Scheidemandel, H. (1956). Dtsch. med. Wsrhr., 81, Bastenier, H. (1950). Arch. belges Mdd. soc., 8, 81. Cavigneaux, A., Charles, A., Fuchs, S., and Tara, S. (1950). Arch. Mal. prof., 11, 34. Geher, F. (1955). Fortschr. Rontgenstr., 82, 598. Hale, L. W., Gough, J., King, E. J., and Nagelschmidt, G. (1956). Brit. J. industr. Med., 13, 251. Higgins, I. T. T., Cochrane, A. L. (1961). Ibid., 18, 93. Kilpatrick, G. S., Heppleston, A. G., and Fletcher, C. M. (1954). Thorax, 9, 260. Lynch, K. M., and Mclver, F. A. (1954). Amer. J. Path., 30, McNally, W. D., and Trostler, I. S. (1941). J. industr. Hyg., 23, 118. Middleton, E. L. (1936). Lancet, 2, 59. Thomas, R. W. (1952). Ibid., 1, 133. Br J Ind Med: first published as /oem on 1 July Downloaded from on 20 January 2019 by guest. Protected by copyright.
FROM THE WIGAN AREA OF LANCASHIRE
 Brit. J. indtistr. Med., 1963, 20, 118. DUST AND FIBROSIS IN THE LUNGS OF COAL-WORKERS FROM THE WIGAN AREA OF LANCASHIRE BY R. SPINK* and G. NAGELSCHMIDT From the Department ofpathology, Wigan Royal Infirmary,
Brit. J. indtistr. Med., 1963, 20, 118. DUST AND FIBROSIS IN THE LUNGS OF COAL-WORKERS FROM THE WIGAN AREA OF LANCASHIRE BY R. SPINK* and G. NAGELSCHMIDT From the Department ofpathology, Wigan Royal Infirmary,
CARDIAC HYPERTROPHY IN COALWORKERS' PNEUMOCONIOSIS BY W. R. L. JAMES and ARTHUR J. THOMAS
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1956, 13, 24. CARDIAC HYPERTROPHY IN COALWORKERS' PNEUMOCONIOSIS BY W. R. L. JAMES and ARTHUR J. THOMAS Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff, and Llandough Hospital, the United
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1956, 13, 24. CARDIAC HYPERTROPHY IN COALWORKERS' PNEUMOCONIOSIS BY W. R. L. JAMES and ARTHUR J. THOMAS Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff, and Llandough Hospital, the United
punctiform type of coalworkers' In 1958 a stratified random sample of 300 miners and a private census in the Rhondda Fach in Glamorgan
 British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1974, 31, 196-200 Mortality in pneumoconiosis punctiform type of coalworkers' W. E. WATERS1, A. L. COCHRANE, and F. MOORE Medical Research Council's Epidemiology
British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1974, 31, 196-200 Mortality in pneumoconiosis punctiform type of coalworkers' W. E. WATERS1, A. L. COCHRANE, and F. MOORE Medical Research Council's Epidemiology
Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid
 British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1973, 30, 396-401 Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid pneu moconiosis DEWI DAVI ES Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Nottinghamshire Davies, D. (1973). British
British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1973, 30, 396-401 Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid pneu moconiosis DEWI DAVI ES Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Nottinghamshire Davies, D. (1973). British
LUNG CANCER IN COAL-MINERS
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1959, 16, 318. LUNG CANCER IN COAL-MINERS BY R. ABBEY SMITH Fronm the Thoracic Surgical Unit, King Edward VII Memorial Chest Hospital, Warwick (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION NOVEMBER
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1959, 16, 318. LUNG CANCER IN COAL-MINERS BY R. ABBEY SMITH Fronm the Thoracic Surgical Unit, King Edward VII Memorial Chest Hospital, Warwick (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION NOVEMBER
WITH PNEUMOCONIOSIS BY W. R. L. JAMES
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1955, 12, 87. PRIMARY LUNG CANCER IN SOUTH WALES COAL-WORKERS WITH PNEUMOCONIOSIS BY W. R. L. JAMES Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff From the Department ofpathology and
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1955, 12, 87. PRIMARY LUNG CANCER IN SOUTH WALES COAL-WORKERS WITH PNEUMOCONIOSIS BY W. R. L. JAMES Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff From the Department ofpathology and
WITH ISONIAZID BY W. E. MIALL, P. D. OLDHAM, and A. L. COCHRANE
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1954, 11, 186. THE TREATMENT OF COMPLICATED PNEUMOCONIOSIS WITH ISONIAZID BY W. E. MIALL, P. D. OLDHAM, and A. L. COCHRANE From the Medical Research Council Pneumoconiosis Research
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1954, 11, 186. THE TREATMENT OF COMPLICATED PNEUMOCONIOSIS WITH ISONIAZID BY W. E. MIALL, P. D. OLDHAM, and A. L. COCHRANE From the Medical Research Council Pneumoconiosis Research
Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P
 Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P inflammatory disorder of the lung, involving alveolar walls and terminal airways, that is induced, in a susceptible host, by repeated inhalation of a variety of organic agents.
Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P inflammatory disorder of the lung, involving alveolar walls and terminal airways, that is induced, in a susceptible host, by repeated inhalation of a variety of organic agents.
BONE MARROW CHANGES IN SILICOSIS
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1965, 22, 279. BONE MARROW CHANGES IN SILICOSIS BY S. E. WARRAKI*, M. Y. GAMMAL, and A. Y. AWNY From the Chest Unit and Clinical Pathology Department, Ain-Shams University (RECEIVED
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1965, 22, 279. BONE MARROW CHANGES IN SILICOSIS BY S. E. WARRAKI*, M. Y. GAMMAL, and A. Y. AWNY From the Chest Unit and Clinical Pathology Department, Ain-Shams University (RECEIVED
ON THE PREVALENCE OF COAL-WORKERS' PNEUMOCONIOSIS IN THE DUTCH COAL-MINES BY
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1963, 2, 288. EFFECT OF DUST SUPPRESSION MEASURES ON THE PREVALENCE OF COAL-WORKERS' PNEUMOCONIOSIS IN THE DUTCH COAL-MINES BY Ch. A. M. HENDRIKS and H. CLAUS From the Instituut
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1963, 2, 288. EFFECT OF DUST SUPPRESSION MEASURES ON THE PREVALENCE OF COAL-WORKERS' PNEUMOCONIOSIS IN THE DUTCH COAL-MINES BY Ch. A. M. HENDRIKS and H. CLAUS From the Instituut
BYSSINOSIS IN THE COTTON INDUSTRY
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1962, 19, 126. BYSSINOSIS IN THE COTTON INDUSTRY OF EGYPT BY MOSTAFA A. EL BATAWI From the Department of Occupational Health, High Institute of Public Health, Alexandria (RECEIVED
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1962, 19, 126. BYSSINOSIS IN THE COTTON INDUSTRY OF EGYPT BY MOSTAFA A. EL BATAWI From the Department of Occupational Health, High Institute of Public Health, Alexandria (RECEIVED
Miscellanea. Twins with Coal-workers' Pneumoconiosis. Brit. J. industr. Med., I966, 23, 240. pneumoconiosis. Over 200 families have
 Brit. J. industr. Med., I966, 23, 240 Twins with Coal-workers' Pneumoconiosis J. E. M. HUTCHINSON From the Pneumoconiosis Medical Panel, 8I St. Mary's Place, Newcastle upon Tyne As the tuberculous hypothesis
Brit. J. industr. Med., I966, 23, 240 Twins with Coal-workers' Pneumoconiosis J. E. M. HUTCHINSON From the Pneumoconiosis Medical Panel, 8I St. Mary's Place, Newcastle upon Tyne As the tuberculous hypothesis
Significance of irregular opacities in the radiology of coalworkers' pneumoconiosis
 British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1974, 31, 36-44 Significance of irregular opacities in the radiology of coalworkers' pneumoconiosis J. P. LYONS, R. C. RYDER, H. CAMPBELL, W. G. CLARKE, and J. GOUGH
British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1974, 31, 36-44 Significance of irregular opacities in the radiology of coalworkers' pneumoconiosis J. P. LYONS, R. C. RYDER, H. CAMPBELL, W. G. CLARKE, and J. GOUGH
Tuberculosis - clinical forms. Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
THE ROLE OF COAL MINE DUST EXPOSURE IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF PULMONARY EMPHYSEMA
 Ann. occup. Hyg., Vol. 41, Supplement 1, pp. 352-357. 1997 British Occupational Hygiene Society Published by Elsevier Science Ltd Printed in Great Britain 0003-4878/97 $17.00 + 0.00 Inhaled Particles VIII
Ann. occup. Hyg., Vol. 41, Supplement 1, pp. 352-357. 1997 British Occupational Hygiene Society Published by Elsevier Science Ltd Printed in Great Britain 0003-4878/97 $17.00 + 0.00 Inhaled Particles VIII
DIAGNOSIS OF COALWORKERS' PNEUMOCONIOSIS
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1951, 8, 138. THE USE OF STANDARD FILMS IN THE RADIOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS OF COALWORKERS' PNEUMOCONIOSIS BY C. M. FLETCHER and P. D. OLDHAM From the M.R.C. Pneumoconiosis Research (RECEIVED
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1951, 8, 138. THE USE OF STANDARD FILMS IN THE RADIOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS OF COALWORKERS' PNEUMOCONIOSIS BY C. M. FLETCHER and P. D. OLDHAM From the M.R.C. Pneumoconiosis Research (RECEIVED
A study on silicosis among employees of a silica processing factory in the Central Province of Sri Lanka
 A study on silicosis among employees of a silica processing factory in the Central Province of Sri Lanka A D Siribaddana 1, K Wickramasekera 1, W M Palipana 2, M D Peiris 3, B K A Upul 1, K P Senevirathna
A study on silicosis among employees of a silica processing factory in the Central Province of Sri Lanka A D Siribaddana 1, K Wickramasekera 1, W M Palipana 2, M D Peiris 3, B K A Upul 1, K P Senevirathna
A BROADER CONCEPT OF CAPLAN'S SYNDROME RELATED TO RHEUMATOID FACTORS
 Thorax (1962), 17, 205. A BROADER CONCEPT OF CAPLAN'S SYNDROME RELATED TO RHEUMATOID FACTORS BY A. CAPLAN, R. B. PAYNE, AND J. L. WITHEY From the Cardiff Pneumoconiosis Medical Panel and the Department
Thorax (1962), 17, 205. A BROADER CONCEPT OF CAPLAN'S SYNDROME RELATED TO RHEUMATOID FACTORS BY A. CAPLAN, R. B. PAYNE, AND J. L. WITHEY From the Cardiff Pneumoconiosis Medical Panel and the Department
SYNDROME) BY. these instances they are considered as possibly " rheumatoid " in origin. The inflammation was
 Thorax (1955), 10, 9. PATHOLOGICAL STUDIES OF MODIFIED PNEUMOCONIOSIS IN COAL-MINERS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (CAPLAN'S SYNDROME) BY J. GOUGH, D. RIVERS, AND R. M. E. SEAL From the Department of Pathology
Thorax (1955), 10, 9. PATHOLOGICAL STUDIES OF MODIFIED PNEUMOCONIOSIS IN COAL-MINERS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (CAPLAN'S SYNDROME) BY J. GOUGH, D. RIVERS, AND R. M. E. SEAL From the Department of Pathology
LUNG DISEASES DUE TO ORGANIC&INORGANIC DUSTS. Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P
 LUNG DISEASES DUE TO ORGANIC&INORGANIC DUSTS Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P efinition of hypersensitivity pneumonitis(extrinsic allergic alveolitis): Inflammatory disorder of the lung, involving alveolar walls
LUNG DISEASES DUE TO ORGANIC&INORGANIC DUSTS Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P efinition of hypersensitivity pneumonitis(extrinsic allergic alveolitis): Inflammatory disorder of the lung, involving alveolar walls
Radiological changes after withdrawal from asbestos exposure
 British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1979, 36, 23-28 Radiological changes after withdrawal from asbestos exposure M. R. BECKLAKE', F. D. K. LIDDELL1, J. MANFREDA1, AND J. C. McDONALD2 From the 'Department
British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1979, 36, 23-28 Radiological changes after withdrawal from asbestos exposure M. R. BECKLAKE', F. D. K. LIDDELL1, J. MANFREDA1, AND J. C. McDONALD2 From the 'Department
COR PULMONALE IN COAL-WORKER'S PNEUMOCONIOSIS
 COR PULMONALE IN COAL-WORKER'S PNEUMOCONIOSIS From the Institute of Pathology, BY A. L. WELLS* Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff Received September 26, 1953 Attention has been drawn to the occurrence
COR PULMONALE IN COAL-WORKER'S PNEUMOCONIOSIS From the Institute of Pathology, BY A. L. WELLS* Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff Received September 26, 1953 Attention has been drawn to the occurrence
Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Rheumatoid pneumoconiosis
 Thorax (1967), 22, 525. Rheumatoid pneumoconiosis A study in colliery populations in the East Midlands coalfield DAVID C. LINDARS' AND DEWI DAVIES From the East Midlands Chest X-ray Unit, National Coal
Thorax (1967), 22, 525. Rheumatoid pneumoconiosis A study in colliery populations in the East Midlands coalfield DAVID C. LINDARS' AND DEWI DAVIES From the East Midlands Chest X-ray Unit, National Coal
LONG-TERM EFFECTS OF SULPHUR DIOXIDE
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1964, 21, 69. LONG-TERM EFFECTS OF SULPHUR DIOXIDE EXPOSURE IN PULP MILLS BY INGAR 0. SKALPE From the Medical Department, Drammen Municipal Hospital, Drammen, Norway (RECEIVED FOR
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1964, 21, 69. LONG-TERM EFFECTS OF SULPHUR DIOXIDE EXPOSURE IN PULP MILLS BY INGAR 0. SKALPE From the Medical Department, Drammen Municipal Hospital, Drammen, Norway (RECEIVED FOR
Microanalyses of lesions and lymph nodes from coalminers' lungs
 British Journal ofindustrial Medicine 1985;42: 551-555 Microanalyses of lesions and lymph nodes from coalminers' lungs J S CHAPMAN AND V A RUCKLEY From the Institute of Occupational Medicine, Edinburgh
British Journal ofindustrial Medicine 1985;42: 551-555 Microanalyses of lesions and lymph nodes from coalminers' lungs J S CHAPMAN AND V A RUCKLEY From the Institute of Occupational Medicine, Edinburgh
BETWEEN TUBERCULOSIS AND PNEUMOKONIOSIS
 Thorax (1951), 6, 43. A RADIOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TUBERCULOSIS AND PNEUMOKONIOSIS IN COAL MINERS BY From the PneumokQniosis Research Unit (South Wales) of the Medical Research Council
Thorax (1951), 6, 43. A RADIOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TUBERCULOSIS AND PNEUMOKONIOSIS IN COAL MINERS BY From the PneumokQniosis Research Unit (South Wales) of the Medical Research Council
Dr. Heyam Awad Pathology sheet #5 cont. Restrictive lung diseases
 We were talking about the restrictive lung diseases (interstitial lung diseases) and they're:- Fibrosing diseases. Granulomatous diseases. Eosinophilic. smoking related. * Notes:- 1) Cough occur in restrictive
We were talking about the restrictive lung diseases (interstitial lung diseases) and they're:- Fibrosing diseases. Granulomatous diseases. Eosinophilic. smoking related. * Notes:- 1) Cough occur in restrictive
Silicosis and Silicotuberculosis. Dr. Basanta Hazarika Department of pulmonary Medicine PGIMER, Chandigarh
 Silicosis and Silicotuberculosis Dr. Basanta Hazarika Department of pulmonary Medicine PGIMER, Chandigarh Introduction Silicosis, major occupational lung disease Problem in both industrialized and developing
Silicosis and Silicotuberculosis Dr. Basanta Hazarika Department of pulmonary Medicine PGIMER, Chandigarh Introduction Silicosis, major occupational lung disease Problem in both industrialized and developing
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations
 Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1966, 41, 402. Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children An analysis of 40 cases CONSTANCE M. DAVIS From the Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital and Alder Hey Children's Hospital, Liverpool
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1966, 41, 402. Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children An analysis of 40 cases CONSTANCE M. DAVIS From the Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital and Alder Hey Children's Hospital, Liverpool
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
and was tipped into a hopper and fed into a crusher. It then passed through grinding machines and ended up
 British Journal ofindustrial Medicine 1983;40:22-27 Mica pneumoconiosis D DAVIES AND R COTTON From City Hospital, Nottingham NG5 I PB, UK ABSTRACr Two men developed pneumoconiosis after grinding and packing
British Journal ofindustrial Medicine 1983;40:22-27 Mica pneumoconiosis D DAVIES AND R COTTON From City Hospital, Nottingham NG5 I PB, UK ABSTRACr Two men developed pneumoconiosis after grinding and packing
Validation of death certificates in asbestos workers
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1969, 26, 302-307 Validation of death certificates in asbestos workers M. L. NEWHOUSE AND J. C. WAGNER London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine TUC Centenary Institute of
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1969, 26, 302-307 Validation of death certificates in asbestos workers M. L. NEWHOUSE AND J. C. WAGNER London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine TUC Centenary Institute of
Health effects of overexposure to respirable silica dust
 Health effects of overexposure to respirable silica dust Jay Colinet Senior Scientist National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health Silica Dust Control Workshop Elko, Nevada September 28, 2010
Health effects of overexposure to respirable silica dust Jay Colinet Senior Scientist National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health Silica Dust Control Workshop Elko, Nevada September 28, 2010
Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi
 Thorax 1983;38: 373-377 Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi MJ SMITH, KM CITRON From the Cardiothoracic Institute, Brompton Hospital, London ABSTRACT Mycobacterium xenopi
Thorax 1983;38: 373-377 Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi MJ SMITH, KM CITRON From the Cardiothoracic Institute, Brompton Hospital, London ABSTRACT Mycobacterium xenopi
Index No. All five (05) questions should be answered. All questions carry equal marks.
 POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO POSTGRADUATE DIPLOMA IN TUBERCULOSIS & CHEST DISEASES EXAMINATION - MAY 2016 Date :- 4 th May 2016 PAPER I CASE HISTORIES Time :- 9.00 a.m. -11.00
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO POSTGRADUATE DIPLOMA IN TUBERCULOSIS & CHEST DISEASES EXAMINATION - MAY 2016 Date :- 4 th May 2016 PAPER I CASE HISTORIES Time :- 9.00 a.m. -11.00
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
Primary chondrosarcoma of lung
 Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease
 Thorax (1966), 21, 230. Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease DEWI DAVIES From Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Notts Rheumatoid nodules in the lung, in the absence of exposure to mineral dust, are uncommon.
Thorax (1966), 21, 230. Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease DEWI DAVIES From Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Notts Rheumatoid nodules in the lung, in the absence of exposure to mineral dust, are uncommon.
MORTALITY FROM LUNG CANCER IN ASBESTOS WORKERS
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1955,12, 81. MORTALITY FROM LUNG CANCER IN ASBESTOS WORKERS BY RICHARD DOLL From the Statistical Research UInit, Medical Research Council, Lonldon (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION AUGUST
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1955,12, 81. MORTALITY FROM LUNG CANCER IN ASBESTOS WORKERS BY RICHARD DOLL From the Statistical Research UInit, Medical Research Council, Lonldon (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION AUGUST
DISEASE OF LUNGS IN BOILER SCALERS
 DISEASE OF LUNGS IN BOILER SCALERS WITH A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE BY H. E. HARDING, D. L. McRAE TOD AND A. I. G. McLAUGHLIN From the University of Sheffield, Anlaby Road Hospital, Hull,
DISEASE OF LUNGS IN BOILER SCALERS WITH A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE BY H. E. HARDING, D. L. McRAE TOD AND A. I. G. McLAUGHLIN From the University of Sheffield, Anlaby Road Hospital, Hull,
Idiopathic progressive pulmonary fibrosis
 Thorax (1975), 30, 316. Idiopathic progressive pulmonary fibrosis DEWI DAVIES, J. S. CROWTHER, and ANDREW MacFARLANE Ransom Hospital, Mansfield Davies, D, Crowther, J. S., and MacFarlane, A. (1975). Thorax,
Thorax (1975), 30, 316. Idiopathic progressive pulmonary fibrosis DEWI DAVIES, J. S. CROWTHER, and ANDREW MacFARLANE Ransom Hospital, Mansfield Davies, D, Crowther, J. S., and MacFarlane, A. (1975). Thorax,
Peak flow rate in relation to forced expiratory volume in hemp workers
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1971, 28, 159-163 Peak flow rate in relation to forced expiratory volume in hemp workers v v I E. ZUSKIN and F. VALIC Department of Occupational Health, Andrija Stampar School of
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1971, 28, 159-163 Peak flow rate in relation to forced expiratory volume in hemp workers v v I E. ZUSKIN and F. VALIC Department of Occupational Health, Andrija Stampar School of
PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA
 Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
RHEUMATOID PNEUMOCONIOSIS (CAPLAN'S SYNDROME) IN AN ASBESTOS WORKER
 Thorax (1961), 16, 372. RHEUMATOID PNEUMOCONIOSIS (CAPLAN'S SYNDROME) IN AN ASBESTOS WORKER BY W. G. TELLESSON From the Randwick Chest Hospital, Sydney, A ustralia The association of certain features in
Thorax (1961), 16, 372. RHEUMATOID PNEUMOCONIOSIS (CAPLAN'S SYNDROME) IN AN ASBESTOS WORKER BY W. G. TELLESSON From the Randwick Chest Hospital, Sydney, A ustralia The association of certain features in
Mushroom worker's lung
 Mushroom worker's lung EDWARD JACKSON, K. M. A. WELCH The Royal Hospital, West Street, Sheffield Thorax (1970), 25, 25. Two cases of an acute chest illness occurring in mushroom workers are described.
Mushroom worker's lung EDWARD JACKSON, K. M. A. WELCH The Royal Hospital, West Street, Sheffield Thorax (1970), 25, 25. Two cases of an acute chest illness occurring in mushroom workers are described.
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
Diseases of the Lung and Respiratory Tract, Part I. William Bligh-Glover M.D. Department of Anatomy, CWRU
 Diseases of the Lung and Respiratory Tract, Part I William Bligh-Glover M.D. Department of Anatomy, CWRU Educational objectives: Distinguish the types of atelectasis and their etiologies Distinguish the
Diseases of the Lung and Respiratory Tract, Part I William Bligh-Glover M.D. Department of Anatomy, CWRU Educational objectives: Distinguish the types of atelectasis and their etiologies Distinguish the
Edited by: RICHARD LEMEN University of Illinois, School of Public Health, Chicago IL 60680
 DUSTSand DISEASE Edited by: RICHARD LEMEN University of Illinois, School of Public Health, Chicago IL 60680 JOHN M. DEMENT University of North Carolina, School of Public Health, Chapel Hill, NC 27514 1979
DUSTSand DISEASE Edited by: RICHARD LEMEN University of Illinois, School of Public Health, Chicago IL 60680 JOHN M. DEMENT University of North Carolina, School of Public Health, Chapel Hill, NC 27514 1979
DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH MILIARY OPACITIES.
 DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH TO MILIARY OPACITIES. 1 INTRODUCTION The term miliary derives from the radiographic picture of diffuse, discrete, nodular shadows about the size of a millet seed (~2mm). 2 CHEST X-RAY
DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH TO MILIARY OPACITIES. 1 INTRODUCTION The term miliary derives from the radiographic picture of diffuse, discrete, nodular shadows about the size of a millet seed (~2mm). 2 CHEST X-RAY
Occupational Lung Disease in South Africa
 The National Institute for Occupational Health (NIOH) Occupational Lung Disease in South Africa Barry Kistnasamy Started in 1946 (Pneumoconiosis Research Unit) centre of excellence for multidisciplinary
The National Institute for Occupational Health (NIOH) Occupational Lung Disease in South Africa Barry Kistnasamy Started in 1946 (Pneumoconiosis Research Unit) centre of excellence for multidisciplinary
CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY
 Thorax (1947), 2, 58 CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY Leeds Cavernous haemangiomata of the lung are rare, and a survey of the French, American, and English literature on the subject has revealed only
Thorax (1947), 2, 58 CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY Leeds Cavernous haemangiomata of the lung are rare, and a survey of the French, American, and English literature on the subject has revealed only
Insulation workers in Belfast1. 1. Comparison
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1971, 28, 211-216. Insulation workers in Belfast1. 1. Comparison of a random sample with a control population WILLIAM F. M. WALLACE and JEAN H. M. LANGLANDS Department of Physiology,
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1971, 28, 211-216. Insulation workers in Belfast1. 1. Comparison of a random sample with a control population WILLIAM F. M. WALLACE and JEAN H. M. LANGLANDS Department of Physiology,
Pneumoconiosis of shale miners
 Thorax, 1981, 36, 412-418 Pneumoconiosis of shale miners A SEATON, D LAMB, W RHIND BROWN, G SCLARE, AND W G MIDDLETON From the Institue of Occupational Medicine and University Department ofpathology, Edinburgh,
Thorax, 1981, 36, 412-418 Pneumoconiosis of shale miners A SEATON, D LAMB, W RHIND BROWN, G SCLARE, AND W G MIDDLETON From the Institue of Occupational Medicine and University Department ofpathology, Edinburgh,
The Workers Advisers Office (WAO)
 The Workers Advisers Office (WAO) This factsheet has been prepared for general information purposes. It is not a legal document. Please refer to the Workers Compensation Act and the Rehabilitation Services
The Workers Advisers Office (WAO) This factsheet has been prepared for general information purposes. It is not a legal document. Please refer to the Workers Compensation Act and the Rehabilitation Services
Radiological survey of men exposed to asbestos in naval dockyards
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1972, 29, 274-279 Radiological survey of men exposed to asbestos in naval dockyards P. G. HARRIES, F. A. F. MACKENZIE, G. SHEERS, J. H. KEMP, T. P. OLIVER, and D. S. WRIGHT Medical
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1972, 29, 274-279 Radiological survey of men exposed to asbestos in naval dockyards P. G. HARRIES, F. A. F. MACKENZIE, G. SHEERS, J. H. KEMP, T. P. OLIVER, and D. S. WRIGHT Medical
Silicosis in Turkish denim sandblasters
 Occupational Medicine 2006;56:554 558 Published online 4 October 2006 doi:10.1093/occmed/kql094 Silicosis in Turkish denim sandblasters Metin Akgun 1, Arzu Mirici 1, Elif Yilmazel Ucar 1, Mecit Kantarci
Occupational Medicine 2006;56:554 558 Published online 4 October 2006 doi:10.1093/occmed/kql094 Silicosis in Turkish denim sandblasters Metin Akgun 1, Arzu Mirici 1, Elif Yilmazel Ucar 1, Mecit Kantarci
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
Particle Size and Dust Inhalation
 Pneumoconiosis A disease of the lungs characterized by fibrosis and caused by the chronic inhalation of mineral dusts, especially silica and asbestos. Helen Lang Dept. Geology & Geography West Virginia
Pneumoconiosis A disease of the lungs characterized by fibrosis and caused by the chronic inhalation of mineral dusts, especially silica and asbestos. Helen Lang Dept. Geology & Geography West Virginia
Q & A SILICA - THE PROBLEM THAT WON T GO AWAY.
 Silica - the Problem that Won t Go Away! Is Silicosis Serious? Is Silicosis Still a Problem in the 2000's? How Can Silicosis Be Prevented? Why Should Your Company Worry About Silicosis? What is Air Sampling?
Silica - the Problem that Won t Go Away! Is Silicosis Serious? Is Silicosis Still a Problem in the 2000's? How Can Silicosis Be Prevented? Why Should Your Company Worry About Silicosis? What is Air Sampling?
Silicosis in barium miners
 A SEATON, VA RUCKLEY, J ADDISON, W RHIND BROWN Thorax 1986;41:591-595 From the Institute of Occupational Medicine, Edinburgh, and the Medical Boarding Centre (Respiratory Diseases), Department of Health
A SEATON, VA RUCKLEY, J ADDISON, W RHIND BROWN Thorax 1986;41:591-595 From the Institute of Occupational Medicine, Edinburgh, and the Medical Boarding Centre (Respiratory Diseases), Department of Health
RECOGNITION OF NON-OPAQUE FOREIGN
 THE IMPORTANCE OF BRONCHOSCOPY IN THE RECOGNITION OF NON-OPAQUE FOREIGN BODY IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN BY N. ASHERSON, M.A., M.B., B.S., F.R.C.S. Surgeon to the Central London Throat, Nose and Ear Hospital
THE IMPORTANCE OF BRONCHOSCOPY IN THE RECOGNITION OF NON-OPAQUE FOREIGN BODY IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN BY N. ASHERSON, M.A., M.B., B.S., F.R.C.S. Surgeon to the Central London Throat, Nose and Ear Hospital
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax. Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem
 Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
From a pulomonologist s point of view. R Lakshmi Narasimhan
 From a pulomonologist s point of view R Lakshmi Narasimhan History Mining and metallurgy goes back to ancient times Rock cutting and stone carving to build temples also present since a long time in India
From a pulomonologist s point of view R Lakshmi Narasimhan History Mining and metallurgy goes back to ancient times Rock cutting and stone carving to build temples also present since a long time in India
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf
 Indep Rev Jul-Dec 2018;20(7-12) Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf IR-653 Abstract: ILD is a group of diseases affect interstitium of the lung. Repeated insult to the lung cause the interstitium to be damaged. Similarly
Indep Rev Jul-Dec 2018;20(7-12) Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf IR-653 Abstract: ILD is a group of diseases affect interstitium of the lung. Repeated insult to the lung cause the interstitium to be damaged. Similarly
CRYSTALLINE SILICA EMPLOYEE TRAINING
 CRYSTALLINE SILICA EMPLOYEE TRAINING PROGRAM SYNOPSIS: Crystalline silica is a naturally occurring substance used in a wide variety of industries and construction operations such as the production of cement,
CRYSTALLINE SILICA EMPLOYEE TRAINING PROGRAM SYNOPSIS: Crystalline silica is a naturally occurring substance used in a wide variety of industries and construction operations such as the production of cement,
DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE 5 DR HEYAM AWAD FRCPATH
 DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE 5 DR HEYAM AWAD FRCPATH RESTRICTIVE, INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISESAES. FIROSING DISESES. GRANULOMATOUS DISEASES. EOSINOPHILIC. SMOKING RELATED. FIBROSING DISEASES
DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LECTURE 5 DR HEYAM AWAD FRCPATH RESTRICTIVE, INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISESAES. FIROSING DISESES. GRANULOMATOUS DISEASES. EOSINOPHILIC. SMOKING RELATED. FIBROSING DISEASES
INDUSTRIAL DERMATITIS IN THE COAL-MINER*
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1958, 15, 188. INDUSTRIAL DERMATITIS IN THE COAL-MINER* BY 0. P. EDMONDS From the East Midlands Division, National Coal Board (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE 1, 1957) A group of
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1958, 15, 188. INDUSTRIAL DERMATITIS IN THE COAL-MINER* BY 0. P. EDMONDS From the East Midlands Division, National Coal Board (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE 1, 1957) A group of
GEOL 100 (Planet Earth) Topic #6 - Asbestos: The Deadly Mineral? What is Asbestos? What is Asbestos? Uses of Asbestos.
 GEOL 100 (Planet Earth) Topic #6 - Asbestos: The Deadly Mineral? What is Asbestos? Group of highly fibrous silicate minerals that are flexible, strong, heat resistant. Three common varieties: 1) White
GEOL 100 (Planet Earth) Topic #6 - Asbestos: The Deadly Mineral? What is Asbestos? Group of highly fibrous silicate minerals that are flexible, strong, heat resistant. Three common varieties: 1) White
BY W. JONES WILLIAMS. Welsh National School of Medicine, Royal Infirmary, Cardiff. A few general features may be considered before
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1958, 15, 235. THE PATHOLOGY OF THE LUNGS IN FIVE NICKEL WORKERS From the Department of Pathology, BY W. JONES WILLIAMS This investigation is to determine whether there are any
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1958, 15, 235. THE PATHOLOGY OF THE LUNGS IN FIVE NICKEL WORKERS From the Department of Pathology, BY W. JONES WILLIAMS This investigation is to determine whether there are any
Crystalline silica and risk of lung cancer in the potteries
 Occup Environ Med 1998;55:779 785 779 Centre for Occupational Health, Stopford Building, University of Manchester, Oxford Road, Manchester M13 9PT, UK N M Cherry G L Burgess S Turner Department of Occupational
Occup Environ Med 1998;55:779 785 779 Centre for Occupational Health, Stopford Building, University of Manchester, Oxford Road, Manchester M13 9PT, UK N M Cherry G L Burgess S Turner Department of Occupational
SILICOTIC FIBROSIS IN THE LUNGS OF RATS BY E. J. KING, C. V. HARRISON, and DAPHNE ATTYGALLE
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1955, 12, 228. THE EFFECT OF CORTISONE ON ESTABLISHED SILICOTIC FIBROSIS IN THE LUNGS OF RATS BY E. J. KING, C. V. HARRISON, and DAPHNE ATTYGALLE From the Postgraduate Medical School,
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1955, 12, 228. THE EFFECT OF CORTISONE ON ESTABLISHED SILICOTIC FIBROSIS IN THE LUNGS OF RATS BY E. J. KING, C. V. HARRISON, and DAPHNE ATTYGALLE From the Postgraduate Medical School,
THE DUST CONTENT OF THE LUNGS OF HARD-ROCK MINERS AND ITS RELATIONSHIP TO OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE, PATHOLOGICAL AND RADIOLOGICAL FINDINGS
 Ann. occup. Hyg., Vol. 6. Nos. -4. pp. 4 49. 98. OO-4878/8/OO4O-O9SO.O Primed in Great Britain. Pergamon Press Lid. Inhaled Particles V i 98 British Occupational Hygiene Society. THE DUST CONTENT OF THE
Ann. occup. Hyg., Vol. 6. Nos. -4. pp. 4 49. 98. OO-4878/8/OO4O-O9SO.O Primed in Great Britain. Pergamon Press Lid. Inhaled Particles V i 98 British Occupational Hygiene Society. THE DUST CONTENT OF THE
Respiratory ill health among coal miners and telecommunication workers in south Wales
 British Journal of Industrial Medicine 1986;43:177-181 Respiratory ill health among coal miners and telecommunication workers in south Wales M H LLOYD, S J GAULD, AND C A SOUTAR From the Institute of Occupational
British Journal of Industrial Medicine 1986;43:177-181 Respiratory ill health among coal miners and telecommunication workers in south Wales M H LLOYD, S J GAULD, AND C A SOUTAR From the Institute of Occupational
THE RADIOTHERAPEUTIC AND RADIOLOGICAL ASPECTS
 Thorax (1956), 11, 241. THE RADIOTHERAPEUTIC AND RADIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF RADIATION FIBROSIS OF THE LUNGS* BY WILLIAM M. ROSS From Newcastle Regional Hospital Board (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION FEBRUARY 23,
Thorax (1956), 11, 241. THE RADIOTHERAPEUTIC AND RADIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF RADIATION FIBROSIS OF THE LUNGS* BY WILLIAM M. ROSS From Newcastle Regional Hospital Board (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION FEBRUARY 23,
PULMONARY RESECTION FOR TUBERCULOSIS
 Thorax (1951), 6, 375. PULMONARY RESECTION FOR TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN BY COLIN A. ROSS From Shotley Bridge Hospital and Poole Sanatorium (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JULY 9, 1951) The literature concerning
Thorax (1951), 6, 375. PULMONARY RESECTION FOR TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN BY COLIN A. ROSS From Shotley Bridge Hospital and Poole Sanatorium (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JULY 9, 1951) The literature concerning
PNEUMOCONIOSIS DUE TO GRAPHITE DUST
 Thorax (1949), 4, 3 1. PNEUMOCONIOSIS DUE TO GRAPHITE DUST BY S. ROODHOUSE GLOYNE, GEOFFREY MARSHALL, AND CLIFFORD HOYLE From the Brompton Hospital, the London Chest Hospital, and the Institute of Social
Thorax (1949), 4, 3 1. PNEUMOCONIOSIS DUE TO GRAPHITE DUST BY S. ROODHOUSE GLOYNE, GEOFFREY MARSHALL, AND CLIFFORD HOYLE From the Brompton Hospital, the London Chest Hospital, and the Institute of Social
Rheumatoid arthritis in workers exposed to silica in the pottery industry
 Occup Environ Med 2000;57:443 447 443 Centre for Occupational and Environmental Health, Stopford Building, University of Manchester, Oxford Road, Manchester M13 9PT, UK S Turner N Cherry Correspondence
Occup Environ Med 2000;57:443 447 443 Centre for Occupational and Environmental Health, Stopford Building, University of Manchester, Oxford Road, Manchester M13 9PT, UK S Turner N Cherry Correspondence
Fibrosis of lung-an environmental disease?
 J. clin. Path., 31, Suppl. (Roy. Coll. Path.), 12, 158-164 Fibrosis of lung-an environmental disease? P. C. ELMES AND J. C. WAGNER From the MRC Pneumoconiosis Unit, Llandough Hospital, Penarth, Glamorgan
J. clin. Path., 31, Suppl. (Roy. Coll. Path.), 12, 158-164 Fibrosis of lung-an environmental disease? P. C. ELMES AND J. C. WAGNER From the MRC Pneumoconiosis Unit, Llandough Hospital, Penarth, Glamorgan
Multiple hamartomata of the lung
 ".; < ;... *: *. > 6a. ;m_r,:i.: e,:...._'. L w X._w. -... ::.'.'. SQ.B SJ _. *.: : w.... :SW.,. _, :; 81 ej, irsr j2 _.:}:.:,::R o _i :.. Fs be 3.X _1 E!.,f3.-. 1t o. j_ 1\ r?!lfo9x., TRyi 1. 2l, >.,.,,co.qlz
".; < ;... *: *. > 6a. ;m_r,:i.: e,:...._'. L w X._w. -... ::.'.'. SQ.B SJ _. *.: : w.... :SW.,. _, :; 81 ej, irsr j2 _.:}:.:,::R o _i :.. Fs be 3.X _1 E!.,f3.-. 1t o. j_ 1\ r?!lfo9x., TRyi 1. 2l, >.,.,,co.qlz
Radiographic signs of pulmonary embolism and pulmonary infarction
 Thlorax (1973), 28, 198. Radiographic signs of pulmonary embolism and pulmonary infarction S. TALBOT, B. S. WORTHINGTON, and E. J. ROEBUCK General Hospital, Nottingham A comparative analysis of the radiographic
Thlorax (1973), 28, 198. Radiographic signs of pulmonary embolism and pulmonary infarction S. TALBOT, B. S. WORTHINGTON, and E. J. ROEBUCK General Hospital, Nottingham A comparative analysis of the radiographic
weeks after starting " prednisone," showed a titre of The blood urea was 25 mg. per 100 ml.
 Thorax (1957), 12, 352. RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY J. R. EDGE AND A. G. RICKARDS From High Carley Hospital, Ulverston, and the Royal Infirmary, Lancaster Since the original reports of Ellman (1947) and Ellman
Thorax (1957), 12, 352. RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY J. R. EDGE AND A. G. RICKARDS From High Carley Hospital, Ulverston, and the Royal Infirmary, Lancaster Since the original reports of Ellman (1947) and Ellman
polyvinylchloride dust
 Thorax 1983;38:834-839 Clinical studies of workers exposed to polyvinylchloride dust CA SOUTAR, S GAULD From the Institute of Occupational Medicine, Edinburgh ABsTRAcr A previous study showed that exposure
Thorax 1983;38:834-839 Clinical studies of workers exposed to polyvinylchloride dust CA SOUTAR, S GAULD From the Institute of Occupational Medicine, Edinburgh ABsTRAcr A previous study showed that exposure
YES YES YES YES NO NO NO NO YES YES YES YES YES YES YES YES YES YES YES YES NO NO NO NO NO NO NO NO NO NO NO NO YES
 respirator. 1. Do you currently smoke tobacco, or have you smoked tobacco in the last month? 2. Have you ever had any of the following conditions? A. Seizures (fits) B. Diabetes (sugar disease) C. Allergic
respirator. 1. Do you currently smoke tobacco, or have you smoked tobacco in the last month? 2. Have you ever had any of the following conditions? A. Seizures (fits) B. Diabetes (sugar disease) C. Allergic
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT
 How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
RESPIRATOR USE SCREENING QUESTIONNAIRE
 RESPIRATOR USE SCREENING QUESTIONNAIRE Part A. Section 1. Personal Information 1. Today's date: 2. Your name: 3. Your age (to nearest year): 4. Sex (circle one): Male/Female 5. Your height: ft. in. 6.
RESPIRATOR USE SCREENING QUESTIONNAIRE Part A. Section 1. Personal Information 1. Today's date: 2. Your name: 3. Your age (to nearest year): 4. Sex (circle one): Male/Female 5. Your height: ft. in. 6.
ARTERIES IN COALWORKERS
 THE RIGHT VENTRICLE AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN COALWORKERS BY ARTHUR J. THOMAS AND W. R. L. JAMES From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals) and the Department of Pathology, Welsh National
THE RIGHT VENTRICLE AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN COALWORKERS BY ARTHUR J. THOMAS AND W. R. L. JAMES From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals) and the Department of Pathology, Welsh National
Tuberculosis: The Essentials
 Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Silicosis: Radiographic findings and the use of the International Labour Organization Classification 2011
 Silicosis: Radiographic findings and the use of the International Labour Organization Classification 2011 Poster No.: C-1055 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. de Lara Bendahan, C.
Silicosis: Radiographic findings and the use of the International Labour Organization Classification 2011 Poster No.: C-1055 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. de Lara Bendahan, C.
Respiratory Questionnaire
 Respiratory Questionnaire Date: Name: SS#: Sex: M F Height: Weight: DOB: Age: Employer: Department: Job Title: Phone # where you can be reached regarding this questionnaire (include area code): What is
Respiratory Questionnaire Date: Name: SS#: Sex: M F Height: Weight: DOB: Age: Employer: Department: Job Title: Phone # where you can be reached regarding this questionnaire (include area code): What is
SAMPLE OF MEN AND WOMEN IN THE RHONDDA FACH IN 1958
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1961, 18, 93. CHRONIC RESPIRATORY DISEASE IN A RANDOM SAMPLE OF MEN AND WOMEN IN THE RHONDDA FACH IN 1958 BY I. T. T. HIGGINS and A. L. COCHRANE From the Pneumoconiosis Research
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1961, 18, 93. CHRONIC RESPIRATORY DISEASE IN A RANDOM SAMPLE OF MEN AND WOMEN IN THE RHONDDA FACH IN 1958 BY I. T. T. HIGGINS and A. L. COCHRANE From the Pneumoconiosis Research
WORKERS (NON-FOUNDRY)
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1961, 18, 33. THE CAUSES OF DEATH IN IRON AND STEEL WORKERS (NON-FOUNDRY) BY A. I. G. McLAUGHLIN and H. E. HARDING From the Department for Research in Industrial Medicine (Medical
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1961, 18, 33. THE CAUSES OF DEATH IN IRON AND STEEL WORKERS (NON-FOUNDRY) BY A. I. G. McLAUGHLIN and H. E. HARDING From the Department for Research in Industrial Medicine (Medical
ASBESTOS DUST DEPOSITION AND RETENTION IN RATS
 ASBESTOS DUST DEPOSITION AND RETENTION IN RATS J. C. Wagner and J. W. Skidmore Medical Research Couwcil, Pneumoconiosis Research Unit, Llandough Hospital, Penarth, Glamorgan, Great Britain INTRODUCTION
ASBESTOS DUST DEPOSITION AND RETENTION IN RATS J. C. Wagner and J. W. Skidmore Medical Research Couwcil, Pneumoconiosis Research Unit, Llandough Hospital, Penarth, Glamorgan, Great Britain INTRODUCTION
PULMONARY FIBROSIS IN WORKERS EXPOSED
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1961, 18, 10. PULMONARY FIBROSIS IN WORKERS EXPOSED TO FINELY POWDERED ALUMINIUM BY JOHN MITCHELL, G. B. MANNING, M. MOLYNEUX, and RONALD E. LANE From the Nuffield Department of
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1961, 18, 10. PULMONARY FIBROSIS IN WORKERS EXPOSED TO FINELY POWDERED ALUMINIUM BY JOHN MITCHELL, G. B. MANNING, M. MOLYNEUX, and RONALD E. LANE From the Nuffield Department of
PATTERNS OF DISTURBED LUNG FUNCTION IN PATIENTS
 Thorax (1959), 14, 216 PATTERNS OF DISTURBED LUNG FUNCTION IN PATIENTS WITH EMPHYSEMATOUS BULLAE BY COLIN OGILVIE AND MARY CATTERALL From the London Hospital In a previous publication (Ogilvie, 1959) an
Thorax (1959), 14, 216 PATTERNS OF DISTURBED LUNG FUNCTION IN PATIENTS WITH EMPHYSEMATOUS BULLAE BY COLIN OGILVIE AND MARY CATTERALL From the London Hospital In a previous publication (Ogilvie, 1959) an
380 Annals New York Academy of Sciences
 11. A PRELIMINARY STUDY OF OBSERVER VARIATION IN THE CLASSIFICATION OF RADIOGRAPHS OF ASBESTOS- EXPOSED WORKERS AND THE RELATION OF PATHOLOGY AND X-RAY APPEARANCES A. Caplan," J. C. Gilson,t K. F. W. Hinson,$
11. A PRELIMINARY STUDY OF OBSERVER VARIATION IN THE CLASSIFICATION OF RADIOGRAPHS OF ASBESTOS- EXPOSED WORKERS AND THE RELATION OF PATHOLOGY AND X-RAY APPEARANCES A. Caplan," J. C. Gilson,t K. F. W. Hinson,$
PULMONARY ARTERIES IN CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE
 Brit. Heart J., 1963, 25, 583. RIGHT VENTRICULAR HYPERTROPHY AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE BY W. R. L. JAMES AND A. J. THOMAS From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals)
Brit. Heart J., 1963, 25, 583. RIGHT VENTRICULAR HYPERTROPHY AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE BY W. R. L. JAMES AND A. J. THOMAS From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals)
What is Asbestos? GEOL 100 (Planet Earth) Topic #6 - Asbestos: The Deadly Mineral? Uses of Asbestos. Uses of Asbestos - Theater curtains
 GEOL 100 (Planet Earth) Topic #6 - Asbestos: The Deadly Mineral? What is Asbestos?! Group of highly fibrous silicate minerals that are flexible, strong, heat resistant. Three common varieties: 1) White
GEOL 100 (Planet Earth) Topic #6 - Asbestos: The Deadly Mineral? What is Asbestos?! Group of highly fibrous silicate minerals that are flexible, strong, heat resistant. Three common varieties: 1) White
