Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease
|
|
|
- Horatio Ray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thorax (1966), 21, 230. Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease DEWI DAVIES From Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Notts Rheumatoid nodules in the lung, in the absence of exposure to mineral dust, are uncommon. Noonan, Taylor, and Engleman (1963) stated that up to that time only 13 microscopically proved cases had been reported. They added one of their own, and since then other proved cases have been added by Dumas, Gregory, and Ozer (1963), Yates (1963), Mattingly (1964, two cases), and Hindle and Yates (1965). These figures underestimate considerably the frequency of such nodules because thoracotomy or post-mortem examination are often not done. Locke (1963), for example, reported six cases, all without histological proof. Necrosis is a regular feature of such nodules, and it is not surprising that they cavitate at times. Such cases have been recorded by Sieniewicz, Martin, Moore, and Miller (1962), Dumas et al. (1963), Locke (1963), Thomson (1963), Yates (1963), and Mattingly (1964). It is also recognized that nodules may disappear from lung radiographs (Sieniewicz et al., 1962). This may be due to seepage of virtually all the material in the nodule into the bronchial tree and its elimination in this way. These nodules usually lie subpleurally, and there is some doubt as to whether they arise in the pleura or from the underlying parenchyma. Because of their location it is not surprising that they are sometimes accompanied by pleural changes. The classical serous effusion of rheumatoid disease, which usually occurs in the absence of parenchymal shadowing, may be expected as an occasional complication. Such a case was recorded by Sieniewicz et al. (1962). In their other case they noted a localized pleural reaction over the nodule. At thoracotomy this was found to be a pleural exudate which peeled off easily to reveal full description of the fluid was not given, and it was postulated that the effusion was due to lymphatic obstruction. However, as the fluid was not chyle, this is not a reasonable explanation: it seems more likely that the effusion was formed by the leakage of necrotic material from one or more nodules into the pleura. From this evidence on the way the nodules behave, the next complication to be expected is that a freer communication should become established between the bronchial tree and the pleura through a cavitated necrotic nodule. Such a case with a sterile pyopneumothorax was described by Hindle and Yates (1965), and another is now added. CASE REPORT CASE 1 This patient, born in 1929, was a housewife and secretary and had not been exposed to mineral dust. In September 1961 she developed arthritis involving the hands, wrists, knees, and feet. A radiograph of the chest in October 1961 showed no abnormality. After a few months, treatment with prednisolone was started and has been continued since in variable dosage. Troublesome symptoms continued and she was admitted to hospital in November She had active polyarthritis but no subcutaneous nodules. She was also found to have an extensive pleural rub over the left chest. The radiograph showed pleural shadowing over the periphery of the lower half of the left lung, denser at the base (Fig. 1). The erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 20 mm. in one hour (Westergren) and the serum differential agglutination test was negative on two occasions and doubtfully positive on one. The Mantoux test was positive at a dilution of 1 in 10,000. Chloroquine was added to the treatment and continued for several months. Her general condition and an opening into a necrotic nodule. It was evident that the nodule had ruptured through the visceral arthritis improved slowly, and this improvement has been maintained since. The pleura but had become sealed off by the exudate. pleural rub persisted. In February 1963 aspiration produced a small quantity A related complication may have occurred in a of thick pus from the pleural cavity. It contained a case described by Thomson (1963) in which few pus cells, but tubercle bacilli and other organisms nodular lung lesions, one of which was cavitated, were not seen or grown. A needle biopsy of the were accompanied by a chyliform effusion. A parietal pleura showed fibrous tissue infiltrated with 230
2 FIG. 2. Case 1. Chest radiograph, January 1965, shows a collection of air and fluid in the lower and lateralpart of the left pleural cavity; the upper part of the lung is adherent. FIG. 1. Case 1. Chest radiograph, November 1962, shows pleural shadowing over the periphery of the lower half of the left lung.
3 232 Dewi Davies chronic inflammatory cells, without specific features. The pleural rub persisted until June She was kept under observation and there was no significant clinical or radiological change until January The radiograph then showed a collection of air and fluid in the lower and lateral part of the left pleural cavity, the upper part of the lung being adherent (Fig. 2). She felt quite well, had a mild cough and scanty mucopurulent sputum, and had noticed slight pain in the left chest a month earlier. The arthritis was under good control and she was taking prednisolone, 7 5 mg. daily. When admitted to hospital she had low-grade fever. The haemoglobin was 10-4 g. per 100 ml., the white blood count normal, and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate 50 mm. in one hour (Westergren). The serum gave positive latex fixation and differential agglutination tests. The vital capacity was 2x4 1. and the F.E.V.1.o 2-2 litres. The electrocardiogram was normal. An intercostal tube was inserted into the left pleural cavity and connected to an underwater seal. The material draining from the pleura was collected in an intermediate bottle. This was thick pus, and about 100 ml. collected in the first day. It contained polymorphs, but no organisms or fungi were found in it. Its glucose content was 13 mg./ 100 ml. A needle biopsy of the parietal pleura showed muscle and thickened pleura with no active inflammation. The fluid in the tube dipping into the underwater seal bottle continued- to swing, and a little pus continued to drain. Suction caused the fluid in the tube to stop swinging, but produced no continued leak of air. When suction was discontinued, swinging reappeared in a few hours. It was evident that a small leak was continuing from the lung and that the pleura would not obliterate. The intercostal tube was removed after 10 days, and the pleural air pocket then grew almost to its previous size. It was then possible to suggest what had been happening. At some time after October 1961 she had developed a probable rheumatoid lung nodule which by November 1962 became necrotic and leaked sterile pus into the pleural cavity. The development of a pyopneumothorax about January 1965 was due either to the rupture of the nodule into the bronchial tree as well or to the establishment of a freer communication between the bronchial tree and the pleural cavity through the necrotic nodule. Tomograms confirmed the presence of a nodule underlying the thickened visceral pleura, and this contained a small cavity (Fig. 3). At thoracotomy in March 1965 an extrapleural strip was done and the empyema cavity was opened. It contained a little straw-coloured fluid and purulent debris. When the latter was rubbed off the visceral pleura a small air leak was visible, and the underlying lung in the area was nodular and granular. The empyema was excised together with a wedge of underlying adherent lung from the lower lobe. The lung was oversewn and the chest closed with tube drainage. Her progress since then has been satisfactory. FIG. 3. Case 1. Tomogram showing a nodule underlying the thickened visceralpleura. The resected specimen was reported on as follows: The specimen consists of a piece of pleura, both visceral and parietal layers, 10 cm. in diameter, with a wedge of lung tissue, 4 x 3 cm., adherent to it. The pleura is thickened and near the lung tissue it shows infiltration by pale yellow material. The lung contains a necrotic nodule, 2 cm. in diameter, which has ruptured into the pleura. Microscopically the sections show a typical rheumatoid nodule situated in the lung tissue, which has ruptured into the pleural cavity. The surrounding lung tissue shows chronic collapse and fibrosis with two small rheumatoid nodules outside and separate from the large nodule. These small nodules appear to be originating in the walls of bronchioles. RHEUMATOID PNEUMOCONIOSIS In contrast to the rarity of the type of rheumatoid lung nodules discussed above, rheumatoid pneumoconiosis is common in people exposed to mineral dust, especially coal-miners. Caplan (quoted by Mattingly, 1964) has recorded about 600 cases, and I have recognized over 70 cases in hospitals serving, in the main, a population of
4 Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease about 200,000 in a coal-mining area. In most of these the radiographic evidence of dust accumulation in the lungs is slight or absent, in contrast to the findings in the ordinary form of progressive massive fibrosis. Even so, exposure to dust has a marked synergistic effect on the development of the lung nodules, and it often makes the lungs more vulnerable to the manifestations of the rheumatoid process than the joints. Only about 50% of my patients with rheumatoid pneumoconiosis suffered from or developed arthritis during observation. It is now commonplace to diagnose this condition in the absence of arthritis on the basis of the radiographic appearance of the nodules, and support is often (but not always) given by positive tests for rheumatoid factor in the serum. On the other hand, rheumatoid lung nodules of the first type described above are not being recognized in the absence of arthritis, but pleural effusions are (Ward, 1961). The presence of rheumatoid factor in the serum of people with diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis without arthritis is also becoming increasingly recognized (Turner-Warwick and Doniach, 1965). Serous pleural effusions do occur in patients with rheumatoid pneumoconiosis (Ward, 1961; Caplan, Payne, and Withey, 1962). Cavitation of the nodules is common. Other nodules wax and wane in size, probably due to intermittent seepage of their contents into the bronchial tree. The establishment of a bronchopleural fistula through a necrotic nodule has not so far been recorded, but a case in which this appears to have happened is now described. CASE REPORT 233 CASE 2 This patient, born in 1903, was a coal-miner from 1918 until 1945, when he developed pain in the right chest and was found to have clinical and radiological evidence of a right pleural effusion. Apart from sputum tests for tubercle bacilli (which were negative), no other investigations were done. The pleural shadowing decreased, but after nine months pleural thickening was still considered to be present. He was then discharged from observation. The radiographs have not been preserved. He remained well until he developed rheumatoid arthritis in 1953, the wrists and fingers being mainly involved. The arthritis has remained active since that time, but he has not developed any subcutaneous nodules. FIG. 4. Case 2. Chest radiograph shows nodular lesions in both lungs, with more extensive shadowing and pleural calcification in the lower half of the right lung.
5 234 ~~.~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~... Dewi Davies When first seen in 1958 the chest radiograph (Fig. 4) showed category 1 simple pneumoconiosis. There were five fairly discrete round lesions in the right upper lobe, the largest 2-5 cm. in diameter. In the lower half of the right lung there was more extensive parenchymal shadowing with scattered pleural calcification in the lower third. There was also thickening of the pleura laterally and in the lesser fissure. Lateral films and tomograms showed that the opacity in the lower half was due to lobulated nodules in the anterior basal segment and a discrete nodule 2 cm. in diameter in the apical segment of the shrunken I lower lobe. All the pleural calcification was in the region of the middle lobe, which did not contain any obvious nodules (Fig. 5). The left lung contained four nodules, the largest 1 cm. in diameter. A film taken in 1954 was traced. It differed in that the nodules on the left were smaller and those in the _ right upper lobe were fewer and vaguer in outline. There was rather less pleural calcification. He was kept under occasional observation and his _ sputum was repeatedly examined for tubercle bacilli. The nodules in the left lung became a little larger and those on the right tended to vary in size and to agglomerate. A little further increase in calcification occurred at the right base (Fig. 6). In April 1963, when there was little change in his FIG. 6- Case 2 Chest radiograph shows increased general condition, he stated that he had been coughing pleural calcification at right base. up a little blood on occasion for some months. The chest radiograph showed the development of a fairly FIG. 5. Case 2. Right lateral radiograph shows nodular opacities in upper lobe, apical segment, and anterior FIG. 7. Case2 Chest radiograph shows an irregular basal segment of lower lobe. The pleural calcification cavity with fluid level at the right base and a lies over the middle lobe area. redis.tibution of the pleural calcification.
6 Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease large irregular cavity at the right base, approximately 5 cm. in diameter and containing a fluid level (Fig. 7). The other striking feature was the redistribution and agglomeration of the pleural calcification. The lateral film showed that the round lesions in the right lower lobe, which had previously increased in size, were much smaller. The fluid level, however, was anterior and the calcified pleura had become displaced backwards from behind the sternal shadow. These findings were supported by tomography, which also failed to demonstrate cavitation in the parenchyma. It was concluded that he had developed a localized pyopneumothorax over the surface of the right middle lobe, and it seemed probable that this was caused by softening and rupture of a nodule from the anterior basal segment of the lower lobe into the bronchial tree and pleura. The striking shift in the pleural calcification demonstrated clearly that the cavity was in the pleura and not in the lung. Tubercle bacilli were grown from one sputum specimen taken at this time. The organism was sensitive to streptomycin, para-aminosalicylic acid, and isoniazid. The tuberculin skin test and the serum latex fixation test were positive. He was treated with antituberculosis drugs. Bleeding soon ceased and tubercle bacilli were not again found in the sputum. By November 1963 the radiograph no longer showed cavitation and the calcification was returning towards its former distribution. His progress since has been satisfactory. DISCUSSION This man's pleural effusion, which developed in 1945 and resulted in considerable pleural calcification, could have been tuberculous or rheumatoid in origin. That it developed eight years before the appearance of arthritis is against a rheumatoid aetiology. If it were tuberculous, the finding of tubercle bacilli in the sputum after the development of a bronchopleural fistula could well be explained by a release of organisms from the old pleural caseous debris. There is good evidence that viable bacilli can remain in such situations for many years. The alternative explanation is that the rheumatoid nodules had become infected by the tubercle bacillus. There is good pathological evidence that this does occur (Gough, Rivers, and Seal, 1955), though clinically this is an uncommon complication. SUMMARY The behaviour of nodular lung lesions in people with rheumatoid arthritis without exposure to mineral dust is reviewed. Such nodules often cavitate and occasionally disappear. Pleural complications also occur. A patient who developed a sterile pyopneumothorax due to softening and rupture of a rheumatoid nodule is described. Rheumatoid pneumoconiotic lung nodules are fairly common in coal-miners even in the absence of arthritis. Cavitation is a frequent feature. The case of a patient in whom such lesions were complicated by a localized pyopneumothorax is recorded. Case 1 was originally under the care of Dr. F. W. A. Turnbull and Dr. J. Sharp. I am indebted to them for referring her and for much information. I am also indebted to Mr. J. S. A. Linton for the findings at operation and to Dr. A. MacFarlane for histological reports. REFERENCES 235 Caplan, A., Payne, R. B., and Withey, J. L. (1962). A broader concept of Caplan's syndrome related to rheumatoid factors. Thorax, 17, 205. Dumas, L. W., Gregory, R. L., and Ozer, F. L. (1963). Case of rheumatoid lung with cavity formation. Brit. med. J., 1, 383. Gough, J., Rivers, D., and Seal, R. M. E. (1955). Pathological studies of modified pneumoconiosis in coal-miners with rheumatoid arthritis (Caplan's syndrome). Thorax, 10, 9. Hindle, W., and Yates, D. A. H. (1965). Pyopneumothorax complicating rheumatoid lung disease. Ann. rheum. Dis., 24, 57. Locke, G. B. (1963). Rheumatoid lung. Clin. Radiol., 14, 43. Mattingly, S. (1964). Review article: The lungs and rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. phys. Med., 7, 185. Noonan, C. D., Taylor, F. B., and Engleman, E. P. (1963). Nodular rheumatoid disease of the lung with cavitation. Arthr. and Rheum. 6, 232. Sieniewicz, D. J., Martin, J. R., Moore, S., and Miller, A. (1962). Rheumatoid nodules in the lung. J. Canad. Ass. Radiol., 13, 73. Thomson, W. N. (1963). Pulmonary changes in collagen diseases. Clin. Radiol., 14, 451. Turner-Warwick, M., and Doniach, D. (1965). Auto-antibody studies in interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. Brit. med. J., 1, 886. Ward, R. (1961). Pleural effusion and rheumatoid disease. Lancet, 2, Yates, D. A. H. (1963). Clinical report: Cavitation of a rheumatoid lung nodule. Ann. phys. Med., 7, 105.
Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid
 British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1973, 30, 396-401 Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid pneu moconiosis DEWI DAVI ES Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Nottinghamshire Davies, D. (1973). British
British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1973, 30, 396-401 Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid pneu moconiosis DEWI DAVI ES Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Nottinghamshire Davies, D. (1973). British
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
A BROADER CONCEPT OF CAPLAN'S SYNDROME RELATED TO RHEUMATOID FACTORS
 Thorax (1962), 17, 205. A BROADER CONCEPT OF CAPLAN'S SYNDROME RELATED TO RHEUMATOID FACTORS BY A. CAPLAN, R. B. PAYNE, AND J. L. WITHEY From the Cardiff Pneumoconiosis Medical Panel and the Department
Thorax (1962), 17, 205. A BROADER CONCEPT OF CAPLAN'S SYNDROME RELATED TO RHEUMATOID FACTORS BY A. CAPLAN, R. B. PAYNE, AND J. L. WITHEY From the Cardiff Pneumoconiosis Medical Panel and the Department
Rheumatoid pneumoconiosis
 Thorax (1967), 22, 525. Rheumatoid pneumoconiosis A study in colliery populations in the East Midlands coalfield DAVID C. LINDARS' AND DEWI DAVIES From the East Midlands Chest X-ray Unit, National Coal
Thorax (1967), 22, 525. Rheumatoid pneumoconiosis A study in colliery populations in the East Midlands coalfield DAVID C. LINDARS' AND DEWI DAVIES From the East Midlands Chest X-ray Unit, National Coal
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
Empyema in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 181 Empyema in rheumatoid arthritis P. A. DIEPPE From the Brompton Hospital, Fulham Road, London Dieppe, P. A. (1975). Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases, 34, 181. Empyema in
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 181 Empyema in rheumatoid arthritis P. A. DIEPPE From the Brompton Hospital, Fulham Road, London Dieppe, P. A. (1975). Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases, 34, 181. Empyema in
PULMONARY RESECTION FOR TUBERCULOSIS
 Thorax (1951), 6, 375. PULMONARY RESECTION FOR TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN BY COLIN A. ROSS From Shotley Bridge Hospital and Poole Sanatorium (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JULY 9, 1951) The literature concerning
Thorax (1951), 6, 375. PULMONARY RESECTION FOR TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN BY COLIN A. ROSS From Shotley Bridge Hospital and Poole Sanatorium (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JULY 9, 1951) The literature concerning
Tuberculosis: The Essentials
 Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Lung folding simulating peripheral pulmonary
 Thorax, 1980, 35, 936-940 Lung folding simulating peripheral pulmonary neoplasm (Blesovsky's syndrome) C R PAYNE, P JAQUES, AND I From the Brompton Hospital, London H KERR ABSTRACT Six cases are reported
Thorax, 1980, 35, 936-940 Lung folding simulating peripheral pulmonary neoplasm (Blesovsky's syndrome) C R PAYNE, P JAQUES, AND I From the Brompton Hospital, London H KERR ABSTRACT Six cases are reported
Table 2: Outcomes measured. Table 1: Intrapleural alteplase instillation therapy protocol
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Intrapleural F brinolytic Therapy with Alteplase in Empyema Thoracis in Children conducted in the Department of Pediatric critical care and Pulmonology unit at our institution
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Intrapleural F brinolytic Therapy with Alteplase in Empyema Thoracis in Children conducted in the Department of Pediatric critical care and Pulmonology unit at our institution
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
Tuberculosis - clinical forms. Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA
 Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
Case Report Ruptured Hydatid Cyst with an Unusual Presentation
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2011, Article ID 730604, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/730604 Case Report Ruptured Hydatid Cyst with an Unusual Presentation Deepak Puri, Amit Kumar Mandal, Harinder Pal Kaur,
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2011, Article ID 730604, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/730604 Case Report Ruptured Hydatid Cyst with an Unusual Presentation Deepak Puri, Amit Kumar Mandal, Harinder Pal Kaur,
SYNDROME) BY. these instances they are considered as possibly " rheumatoid " in origin. The inflammation was
 Thorax (1955), 10, 9. PATHOLOGICAL STUDIES OF MODIFIED PNEUMOCONIOSIS IN COAL-MINERS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (CAPLAN'S SYNDROME) BY J. GOUGH, D. RIVERS, AND R. M. E. SEAL From the Department of Pathology
Thorax (1955), 10, 9. PATHOLOGICAL STUDIES OF MODIFIED PNEUMOCONIOSIS IN COAL-MINERS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (CAPLAN'S SYNDROME) BY J. GOUGH, D. RIVERS, AND R. M. E. SEAL From the Department of Pathology
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
Idiopathic progressive pulmonary fibrosis
 Thorax (1975), 30, 316. Idiopathic progressive pulmonary fibrosis DEWI DAVIES, J. S. CROWTHER, and ANDREW MacFARLANE Ransom Hospital, Mansfield Davies, D, Crowther, J. S., and MacFarlane, A. (1975). Thorax,
Thorax (1975), 30, 316. Idiopathic progressive pulmonary fibrosis DEWI DAVIES, J. S. CROWTHER, and ANDREW MacFARLANE Ransom Hospital, Mansfield Davies, D, Crowther, J. S., and MacFarlane, A. (1975). Thorax,
TUBERCULOUS PERICARDIAL EFFUSION
 BY S. SUZMAN From the Cardiographic Department, Guy's Hospital Received June 22, 1942 Tuberculous pericardial effusion is not common; and so the case described is of interest on account of the patient's
BY S. SUZMAN From the Cardiographic Department, Guy's Hospital Received June 22, 1942 Tuberculous pericardial effusion is not common; and so the case described is of interest on account of the patient's
Empyema due to Klebsiella pneumoniae
 Thorax (1967), 22, 170. Empyema due to Klebsiella pneumoniae J. M. REID, R. S. BARCLAY, J. G. STEVENSON, T. M. WELSH, AND N. McSWAN From thle Cardio-thoracic Unit, Mearnskirk Hospital, Renifrewshire Three
Thorax (1967), 22, 170. Empyema due to Klebsiella pneumoniae J. M. REID, R. S. BARCLAY, J. G. STEVENSON, T. M. WELSH, AND N. McSWAN From thle Cardio-thoracic Unit, Mearnskirk Hospital, Renifrewshire Three
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT
 How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD
 TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
LUNG CANCER IN COAL-MINERS
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1959, 16, 318. LUNG CANCER IN COAL-MINERS BY R. ABBEY SMITH Fronm the Thoracic Surgical Unit, King Edward VII Memorial Chest Hospital, Warwick (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION NOVEMBER
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1959, 16, 318. LUNG CANCER IN COAL-MINERS BY R. ABBEY SMITH Fronm the Thoracic Surgical Unit, King Edward VII Memorial Chest Hospital, Warwick (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION NOVEMBER
Pneumothorax. Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms
 Pneumothorax Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms Traumatic pneumothorax Penetrating chest trauma Common secondary to bullet or knife penetration Chest tube
Pneumothorax Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms Traumatic pneumothorax Penetrating chest trauma Common secondary to bullet or knife penetration Chest tube
LUNG RESECTION FOR TUBERCULOSIS IN THE ARMY
 216 LUNG RESECTION FOR TUBERCULOSIS IN THE ARMY A REPORT ON 61 CASES BY Lieut.-Colonel S. E. LARGE, M.B.E., M.B., M.R.C.P., D.p.iI. Captain A. N. LAIRD, M.B., Ch.B. Royal Army Medical Corps AND G. KENT
216 LUNG RESECTION FOR TUBERCULOSIS IN THE ARMY A REPORT ON 61 CASES BY Lieut.-Colonel S. E. LARGE, M.B.E., M.B., M.R.C.P., D.p.iI. Captain A. N. LAIRD, M.B., Ch.B. Royal Army Medical Corps AND G. KENT
CARDIAC HYPERTROPHY IN COALWORKERS' PNEUMOCONIOSIS BY W. R. L. JAMES and ARTHUR J. THOMAS
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1956, 13, 24. CARDIAC HYPERTROPHY IN COALWORKERS' PNEUMOCONIOSIS BY W. R. L. JAMES and ARTHUR J. THOMAS Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff, and Llandough Hospital, the United
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1956, 13, 24. CARDIAC HYPERTROPHY IN COALWORKERS' PNEUMOCONIOSIS BY W. R. L. JAMES and ARTHUR J. THOMAS Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff, and Llandough Hospital, the United
APICAL SEGMENT OF THE LOWER LOBE IN RESECTIONS FOR BRONCHIECTASIS
 Thorax (1955), 10, 137. THE LATE RESULTS OF THE CONSERVATION OF THE APICAL SEGMENT OF THE LOWER LOBE IN RESECTIONS FOR BRONCHIECTASIS BY E. HOFFMAN From the Regional Thoracic Surgery Centre, Shotley Bridge
Thorax (1955), 10, 137. THE LATE RESULTS OF THE CONSERVATION OF THE APICAL SEGMENT OF THE LOWER LOBE IN RESECTIONS FOR BRONCHIECTASIS BY E. HOFFMAN From the Regional Thoracic Surgery Centre, Shotley Bridge
A 50-year-old male with fever, cough, dyspnoea, chest pain, weight loss and night sweats
 Petru Emil Muntean muntean.petruemil@yahoo.com Pulmonology, Spitalul Clinic Judetean Mures, Targu Mures, Romania. A 50-year-old male with fever, cough, dyspnoea, chest pain, weight loss and night sweats
Petru Emil Muntean muntean.petruemil@yahoo.com Pulmonology, Spitalul Clinic Judetean Mures, Targu Mures, Romania. A 50-year-old male with fever, cough, dyspnoea, chest pain, weight loss and night sweats
Destructive pulmonary disease due to mixed anaerobic infection
 Thorax (1970), 25, 41. Destructive pulmonary disease due to mixed anaerobic infection 0. SERIKI, A. ADEYOKUNNU, T. 0. DE LA CRUZ Departments of Paediatrics and Surgery, University College Hospital, Ibadan,
Thorax (1970), 25, 41. Destructive pulmonary disease due to mixed anaerobic infection 0. SERIKI, A. ADEYOKUNNU, T. 0. DE LA CRUZ Departments of Paediatrics and Surgery, University College Hospital, Ibadan,
380 Annals New York Academy of Sciences
 11. A PRELIMINARY STUDY OF OBSERVER VARIATION IN THE CLASSIFICATION OF RADIOGRAPHS OF ASBESTOS- EXPOSED WORKERS AND THE RELATION OF PATHOLOGY AND X-RAY APPEARANCES A. Caplan," J. C. Gilson,t K. F. W. Hinson,$
11. A PRELIMINARY STUDY OF OBSERVER VARIATION IN THE CLASSIFICATION OF RADIOGRAPHS OF ASBESTOS- EXPOSED WORKERS AND THE RELATION OF PATHOLOGY AND X-RAY APPEARANCES A. Caplan," J. C. Gilson,t K. F. W. Hinson,$
RHEUMATOID PNEUMOCONIOSIS (CAPLAN'S SYNDROME) IN AN ASBESTOS WORKER
 Thorax (1961), 16, 372. RHEUMATOID PNEUMOCONIOSIS (CAPLAN'S SYNDROME) IN AN ASBESTOS WORKER BY W. G. TELLESSON From the Randwick Chest Hospital, Sydney, A ustralia The association of certain features in
Thorax (1961), 16, 372. RHEUMATOID PNEUMOCONIOSIS (CAPLAN'S SYNDROME) IN AN ASBESTOS WORKER BY W. G. TELLESSON From the Randwick Chest Hospital, Sydney, A ustralia The association of certain features in
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations
 Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
THE RELATION BETWEEN LEFT ATRIAL HYPERTENSION
 Thorax (1960), 15, 54. THE RELATION BETWEEN LEFT ATRIAL HYPERTENSION AND LYMPHATIC DISTENSION IN LUNG BIOPSIES BY DONALD HEATH AND PETER HICKEN From the Department of Pathology, University of Birmingham
Thorax (1960), 15, 54. THE RELATION BETWEEN LEFT ATRIAL HYPERTENSION AND LYMPHATIC DISTENSION IN LUNG BIOPSIES BY DONALD HEATH AND PETER HICKEN From the Department of Pathology, University of Birmingham
Empyema and ruptured lung abscess in adults'
 Thorax (1964), 19, 492. Empyema and ruptured lung abscess in adults' ROWAN NICKS From the Thoracic Surgical Unit, Page Chest Pavilion, Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Melbourne This brief annotation concerns
Thorax (1964), 19, 492. Empyema and ruptured lung abscess in adults' ROWAN NICKS From the Thoracic Surgical Unit, Page Chest Pavilion, Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Melbourne This brief annotation concerns
weeks after starting " prednisone," showed a titre of The blood urea was 25 mg. per 100 ml.
 Thorax (1957), 12, 352. RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY J. R. EDGE AND A. G. RICKARDS From High Carley Hospital, Ulverston, and the Royal Infirmary, Lancaster Since the original reports of Ellman (1947) and Ellman
Thorax (1957), 12, 352. RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY J. R. EDGE AND A. G. RICKARDS From High Carley Hospital, Ulverston, and the Royal Infirmary, Lancaster Since the original reports of Ellman (1947) and Ellman
CHEST DRAIN PROTOCOL
 CHEST DRAIN PROTOCOL Rationale The pleural membranes have an important role in effective lung expansion. The visceral pleura is a thin, smooth, serous membrane covering the surface of the lungs and is
CHEST DRAIN PROTOCOL Rationale The pleural membranes have an important role in effective lung expansion. The visceral pleura is a thin, smooth, serous membrane covering the surface of the lungs and is
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES
 PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
UERMMMC Department of Radiology. Basic Chest Radiology
 UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
CT Manifestations of Late Sequelae in Patients with Tuberculous Pleuritis
 CT Manifestations of Late Sequelae in Patients with Tuberculous Pleuritis T uberculous pleuritis remains one of the major causes of pleural effusion with an incidence ranging from as high as 86% in a population
CT Manifestations of Late Sequelae in Patients with Tuberculous Pleuritis T uberculous pleuritis remains one of the major causes of pleural effusion with an incidence ranging from as high as 86% in a population
Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT
 Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT Poster No.: C-2488 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. J. Martín Sánchez, J. M. Fernandez 1 1
Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT Poster No.: C-2488 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. J. Martín Sánchez, J. M. Fernandez 1 1
A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma
 August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW. Financial Conflicts of Interest. Question #1: Question #1 (Cont.): None. Christopher H. Fanta, M.D.
 PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs
 The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
General History. 林陳 珠 Female 69 years old 住院期間 : ~ Chief Complaint : sudden loss of conscious 5 minutes in the morning.
 General History 林陳 珠 Female 69 years old 住院期間 : 93.5.8~93.5.15 Chief Complaint : sudden loss of conscious for 2-52 5 minutes in the morning. General History DM under regular medical control for 10 years.
General History 林陳 珠 Female 69 years old 住院期間 : 93.5.8~93.5.15 Chief Complaint : sudden loss of conscious for 2-52 5 minutes in the morning. General History DM under regular medical control for 10 years.
FOR A FURTHER REPORT ON LUNG RESECTION PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS
 Thorax (1952), 7, 3 10. A FURTHER REPORT ON LUNG RESECTION PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY FOR B. J. BlCKFORD, F. RONALD EDWARDS, J. R. ESPLEN, J. G. GIFFORD, AND 0. F. THOMAS Fraom the Thoracic Suirgical Service
Thorax (1952), 7, 3 10. A FURTHER REPORT ON LUNG RESECTION PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY FOR B. J. BlCKFORD, F. RONALD EDWARDS, J. R. ESPLEN, J. G. GIFFORD, AND 0. F. THOMAS Fraom the Thoracic Suirgical Service
RESECTION OF TUBERCULOUS STRICTURES OF THE MAIN BRONCHI IN THREE CASES
 Thorax (1955), 10, 229. RESECTION OF TUBERCULOUS STRICTURES OF THE MAIN BRONCHI IN THREE CASES BY J. W. JACKSON, P. H. JONES, AND T. HOLMES SELLORS From the London Chest and Harefield Hospitals (RECEIVED
Thorax (1955), 10, 229. RESECTION OF TUBERCULOUS STRICTURES OF THE MAIN BRONCHI IN THREE CASES BY J. W. JACKSON, P. H. JONES, AND T. HOLMES SELLORS From the London Chest and Harefield Hospitals (RECEIVED
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
 A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
FROM THE WIGAN AREA OF LANCASHIRE
 Brit. J. indtistr. Med., 1963, 20, 118. DUST AND FIBROSIS IN THE LUNGS OF COAL-WORKERS FROM THE WIGAN AREA OF LANCASHIRE BY R. SPINK* and G. NAGELSCHMIDT From the Department ofpathology, Wigan Royal Infirmary,
Brit. J. indtistr. Med., 1963, 20, 118. DUST AND FIBROSIS IN THE LUNGS OF COAL-WORKERS FROM THE WIGAN AREA OF LANCASHIRE BY R. SPINK* and G. NAGELSCHMIDT From the Department ofpathology, Wigan Royal Infirmary,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Perfusing chemotherapy by percutaneous lung puncture holing for pulmonary tuberculoma a ten-year single center experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Perfusing chemotherapy by percutaneous lung puncture holing for pulmonary tuberculoma a ten-year single center experience Shu-Hua Yang 1*, Ping Zhan 2*, Hui-Huan Mao 1, Xu-Dong Shi 3,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Perfusing chemotherapy by percutaneous lung puncture holing for pulmonary tuberculoma a ten-year single center experience Shu-Hua Yang 1*, Ping Zhan 2*, Hui-Huan Mao 1, Xu-Dong Shi 3,
Right lung. -fissures:
 -Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
-Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
Pleural Empyema Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Pleural Empyema Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 03/19/2010 History Teenager with persistent fever and cough. Pneumonia diagnosed 1 week ago. Diagnosis Pleural Empyema Additional Clinical Surgery-Clear fluid with
Pleural Empyema Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 03/19/2010 History Teenager with persistent fever and cough. Pneumonia diagnosed 1 week ago. Diagnosis Pleural Empyema Additional Clinical Surgery-Clear fluid with
CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY
 Thorax (1947), 2, 58 CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY Leeds Cavernous haemangiomata of the lung are rare, and a survey of the French, American, and English literature on the subject has revealed only
Thorax (1947), 2, 58 CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY Leeds Cavernous haemangiomata of the lung are rare, and a survey of the French, American, and English literature on the subject has revealed only
THE CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT OF THE TENSION LESIONS OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL PNEUMONIA IN INFANCY
 Thorax (1960), 15, 233. THE CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT OF THE TENSION LESIONS OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL PNEUMONIA IN INFANCY BY JAMES S. DAVIDSON From the Royal Infirmary, Bradford (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION APRIL
Thorax (1960), 15, 233. THE CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT OF THE TENSION LESIONS OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL PNEUMONIA IN INFANCY BY JAMES S. DAVIDSON From the Royal Infirmary, Bradford (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION APRIL
BRONCHOPULMONARY CARCINOMA
 J. clin. Path. (1960), 13, 425. THE DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF PLEURAL BIOPSY IN BRONCHOPULMONARY CARCINOMA BY WALTER PAGEL AND SUSAN GOLDFARB From the Department of Pathology, Clare Hall Hospital, Herts (RECEIVED
J. clin. Path. (1960), 13, 425. THE DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF PLEURAL BIOPSY IN BRONCHOPULMONARY CARCINOMA BY WALTER PAGEL AND SUSAN GOLDFARB From the Department of Pathology, Clare Hall Hospital, Herts (RECEIVED
Dana Alrafaiah. - Moayyad Al-Shafei. -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 - 6 - Dana Alrafaiah - Moayyad Al-Shafei -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb 1 P a g e Quick recap: Both lungs have an apex, base, mediastinal and costal surfaces, anterior and posterior borders. The right lung,
- 6 - Dana Alrafaiah - Moayyad Al-Shafei -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb 1 P a g e Quick recap: Both lungs have an apex, base, mediastinal and costal surfaces, anterior and posterior borders. The right lung,
HISTOPLASMOSIS (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION APRIL 6, 1960) was not confirmed by culture. This patient was in
 Thorax (1960), 15, 204. A REPORT OF 12 SELECTED CASES OF PULMONARY HISTOPLASMOSIS BY ALEX SALIBA AND OREN A. BEATTY From District Two State Tuberculosis Hospital, Louisville, Kentucky, U.S.A. (RECEIVED
Thorax (1960), 15, 204. A REPORT OF 12 SELECTED CASES OF PULMONARY HISTOPLASMOSIS BY ALEX SALIBA AND OREN A. BEATTY From District Two State Tuberculosis Hospital, Louisville, Kentucky, U.S.A. (RECEIVED
David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David E. Griffith, MD March 13, 2015 TB for Pulmonologist March 13, 2015 Phoenix, AZ EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David E. Griffith, MD March 13, 2015 TB for Pulmonologist March 13, 2015 Phoenix, AZ EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
CASE REPORTS. Inflammatory Polyp of the Bronchus. V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D.
 CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
Pneumothorax and Chest Tube Problems
 Pneumothorax and Chest Tube Problems Pneumothorax Definition Air accumulation in the pleural space with secondary lung collapse Sources Visceral pleura Ruptured esophagus Chest wall defect Gas-forming
Pneumothorax and Chest Tube Problems Pneumothorax Definition Air accumulation in the pleural space with secondary lung collapse Sources Visceral pleura Ruptured esophagus Chest wall defect Gas-forming
Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 118. Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis R. H. ELLIS From the Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Pulmonary aspergillosis can be divided conveniently into two main types, allergic
Thorax (1965), 20, 118. Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis R. H. ELLIS From the Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Pulmonary aspergillosis can be divided conveniently into two main types, allergic
Science & Technologies
 A GIANT LIVER HYDATIDE CYST SIMULTANEOUSLY PERFORATED TO PERITONEAL AND PLEURAL CAVITIES A RARE CASE REPORT. Ivan P. Novakov Department of Special Surgery; Medical University - Plovdiv Abstract. Background.
A GIANT LIVER HYDATIDE CYST SIMULTANEOUSLY PERFORATED TO PERITONEAL AND PLEURAL CAVITIES A RARE CASE REPORT. Ivan P. Novakov Department of Special Surgery; Medical University - Plovdiv Abstract. Background.
empyema and lung abscess exceedingly difficult; every physician will agree that
 August, 1938 THE DIAGNOSIS OF EMi~PYEMA 251 THE DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF EMPYEMA. By R. R. TRAIL, M.A., M.D., F.R.C.P. (Physician, Royal Chest Hospital and Papworth Village Settlement.) Few diseases
August, 1938 THE DIAGNOSIS OF EMi~PYEMA 251 THE DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF EMPYEMA. By R. R. TRAIL, M.A., M.D., F.R.C.P. (Physician, Royal Chest Hospital and Papworth Village Settlement.) Few diseases
The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax
 Respiratory 131 The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a relatively common presentation in patients under the age of 40 years (approximately, 85% of patients are younger than 40 years).
Respiratory 131 The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a relatively common presentation in patients under the age of 40 years (approximately, 85% of patients are younger than 40 years).
Pneumothorax lecture no. 3
 Pneumothorax lecture no. 3 Is accumulation of air in a pleural space or accumulation of extra pulmonary air within the chest, Is uncommon during childhood, may result from external trauma, iatrogenic,
Pneumothorax lecture no. 3 Is accumulation of air in a pleural space or accumulation of extra pulmonary air within the chest, Is uncommon during childhood, may result from external trauma, iatrogenic,
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis. Dr: Salah Ahmed
 Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Pulmonary aspergiliomas treated with corticosteroids
 Thorax (1972), 27, 156. Pulmonary aspergiliomas treated with corticosteroids DEWI DAVIES and ALAN R. SOMNER Ransom Hospital, Mansfield and the Chest Clinic, Wallsend-on-Tyne The development of an aspergilloma
Thorax (1972), 27, 156. Pulmonary aspergiliomas treated with corticosteroids DEWI DAVIES and ALAN R. SOMNER Ransom Hospital, Mansfield and the Chest Clinic, Wallsend-on-Tyne The development of an aspergilloma
GEOFFREY H. Leeds WOOLER. The coronary ligament surrounds the bare area of
 Thorax (1956), 11, 21 1. SUBPHRENIC ABSCESS BY GEOFFREY H. Leeds The term subphrenic abscess denotes infection occurring in the region bounded by the diaphragm above, and by the transverse meso-colon,
Thorax (1956), 11, 21 1. SUBPHRENIC ABSCESS BY GEOFFREY H. Leeds The term subphrenic abscess denotes infection occurring in the region bounded by the diaphragm above, and by the transverse meso-colon,
TREATMENT OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY THORA- COPLASTY IN PATIENTS OVER 50 YEARS OF AGE
 Thorax (1954), 9, 2 1. TREATMENT OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY THORA- COPLASTY IN PATIENTS OVER 50 YEARS OF AGE BY PETER BEACONSFIELD, H. S. COULTHARD, AND F. G. KERGIN From the Toronto Hospital for the
Thorax (1954), 9, 2 1. TREATMENT OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY THORA- COPLASTY IN PATIENTS OVER 50 YEARS OF AGE BY PETER BEACONSFIELD, H. S. COULTHARD, AND F. G. KERGIN From the Toronto Hospital for the
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION
 CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
THORACIC CHORDOMA. G. G. CROWE AND P. B. LL. MULDOON From City General Hospital, Stoke-on-Trent
 Thorax (1951), 6, 403. THORACIC CHORDOMA BY G. G. CROWE AND P. B. LL. MULDOON From City General Hospital, Stoke-on-Trent (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION AUGUST 22, 1951) Remnants of the notochord sometimes become
Thorax (1951), 6, 403. THORACIC CHORDOMA BY G. G. CROWE AND P. B. LL. MULDOON From City General Hospital, Stoke-on-Trent (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION AUGUST 22, 1951) Remnants of the notochord sometimes become
Yellow nails, lymphoedema, and pleural effusions
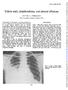 Thorax (1966), 21, 247. Yellow nails, lymphoedema, and pleural effusions PETER A. From Westminster Hospital, The purpose of this paper is to draw attention to a new syndrome and to describe three examples
Thorax (1966), 21, 247. Yellow nails, lymphoedema, and pleural effusions PETER A. From Westminster Hospital, The purpose of this paper is to draw attention to a new syndrome and to describe three examples
10/17/2016. Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology. Objectives. Techniques
 Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Lung manifestations in leptospirosis
 Lung manifestations in leptospirosis S. C. POH and C. S. SOH Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Thorax (1970), 25, 751. Two cases of leptospirosis presenting with cough and haemoptysis are described, together
Lung manifestations in leptospirosis S. C. POH and C. S. SOH Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Thorax (1970), 25, 751. Two cases of leptospirosis presenting with cough and haemoptysis are described, together
Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Pleural syndrome Tuberculous pleurisy
 Pleural syndrome Tuberculous pleurisy Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Pleural effusion: Findings of fluid between
Pleural syndrome Tuberculous pleurisy Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Pleural effusion: Findings of fluid between
Persistent Spontaneous Pneumothorax for Four Years: A Case Report
 303) Persistent Spontaneous Pneumothorax for Four Years: A Case Report Mizuno Y., Iwata H., Shirahashi K., Matsui M., Takemura H. Department of General and Cardiothoracic Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine,
303) Persistent Spontaneous Pneumothorax for Four Years: A Case Report Mizuno Y., Iwata H., Shirahashi K., Matsui M., Takemura H. Department of General and Cardiothoracic Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine,
Lung Cancer Resection
 Lung Cancer Resection Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your health care provider may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer.
Lung Cancer Resection Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your health care provider may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer.
Patient History 1. Patient History 2. Social History. The Role of Surgery in the Management of TB. Reynard McDonald, MD & Paul Bolanowski, MD
 Patient History 1 The Role of Surgery in the Management of TB Reynard McDonald, MD & Paul Bolanowski, MD September 16, 2010 42 y/o AA male was initially diagnosed with pansensitive pulmonary TB in 1986
Patient History 1 The Role of Surgery in the Management of TB Reynard McDonald, MD & Paul Bolanowski, MD September 16, 2010 42 y/o AA male was initially diagnosed with pansensitive pulmonary TB in 1986
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
A recurrent empyema with peripheral bronchopleural fistulas treated by retrograde bronchial sealing with Gore Tex plugs: a case report
 Case Report A recurrent empyema with peripheral bronchopleural fistulas treated by retrograde bronchial sealing with Gore Tex plugs: a case report Jin-Young Ahn 1, Dohun Kim 2, Jong-Myeon Hong 2, Si-Wook
Case Report A recurrent empyema with peripheral bronchopleural fistulas treated by retrograde bronchial sealing with Gore Tex plugs: a case report Jin-Young Ahn 1, Dohun Kim 2, Jong-Myeon Hong 2, Si-Wook
Atypical radiologic appearances of pulmonary tuberculosis in non-hiv adult patients
 Atypical radiologic appearances of pulmonary tuberculosis in non-hiv adult patients Poster No.: R-0200 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. N. Jeon, K. Bae, M. J. Park Keywords:
Atypical radiologic appearances of pulmonary tuberculosis in non-hiv adult patients Poster No.: R-0200 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. N. Jeon, K. Bae, M. J. Park Keywords:
Critical Care Monitoring. Indications. Pleural Space. Chest Drainage. Chest Drainage. Potential space. Contains fluid lubricant
 Critical Care Monitoring Indications 1-2- 2 Pleural Space Potential space Contains fluid lubricant Can fill with air, blood, plasma, serum, lymph, pus 3 1 Pleural Space Problems when contain abnormal substances:
Critical Care Monitoring Indications 1-2- 2 Pleural Space Potential space Contains fluid lubricant Can fill with air, blood, plasma, serum, lymph, pus 3 1 Pleural Space Problems when contain abnormal substances:
Lung cancer in patients with chronic empyema
 Lung cancer in patients with chronic empyema Poster No.: P-0025 Congress: ESTI 2015 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: Y. Lee, C.-K. Park; Guri/KR Keywords: Neoplasia, Biopsy, PET-CT, CT, Thorax, Lung DOI:
Lung cancer in patients with chronic empyema Poster No.: P-0025 Congress: ESTI 2015 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: Y. Lee, C.-K. Park; Guri/KR Keywords: Neoplasia, Biopsy, PET-CT, CT, Thorax, Lung DOI:
Pleural Effusion. Exudative pleural effusion - Involve an increase in capillary permeability and impaired pleural fluid resorption
 Pleural Effusion Definition of pleural effusion Accumulation of fluid between the pleural layers Epidemiology of pleural effusion Estimated prevalence of pleural effusion is 320 cases per 100,000 people
Pleural Effusion Definition of pleural effusion Accumulation of fluid between the pleural layers Epidemiology of pleural effusion Estimated prevalence of pleural effusion is 320 cases per 100,000 people
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping. Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington
 Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
Let s Talk TB A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year
 A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year Barry Rabinovitch, MD, FRCP(C) Author Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD co-author and Series Editor Barry Rabinovitch is an assistant
A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year Barry Rabinovitch, MD, FRCP(C) Author Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD co-author and Series Editor Barry Rabinovitch is an assistant
Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1966, 41, 402. Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children An analysis of 40 cases CONSTANCE M. DAVIS From the Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital and Alder Hey Children's Hospital, Liverpool
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1966, 41, 402. Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children An analysis of 40 cases CONSTANCE M. DAVIS From the Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital and Alder Hey Children's Hospital, Liverpool
Chest X rays and Case Studies. No disclosures. Outline 5/31/2018. Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital
 Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer
 Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your doctor may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer. The
Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your doctor may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer. The
TOTAL THYROIDECTOMY FOR HEART FAILURE:
 TOTAL THYROIDECTOMY FOR HEART FAILURE: AN UNUSUAL CASE BY From the Medical and Surgical Units, University College Hospital Received May 15, 1941 Congestive cardiac failure associated with thyrotoxicosis
TOTAL THYROIDECTOMY FOR HEART FAILURE: AN UNUSUAL CASE BY From the Medical and Surgical Units, University College Hospital Received May 15, 1941 Congestive cardiac failure associated with thyrotoxicosis
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis
 Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
Mushroom worker's lung
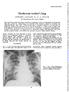 Mushroom worker's lung EDWARD JACKSON, K. M. A. WELCH The Royal Hospital, West Street, Sheffield Thorax (1970), 25, 25. Two cases of an acute chest illness occurring in mushroom workers are described.
Mushroom worker's lung EDWARD JACKSON, K. M. A. WELCH The Royal Hospital, West Street, Sheffield Thorax (1970), 25, 25. Two cases of an acute chest illness occurring in mushroom workers are described.
Tuberculosis. By: Shefaa Q aqa
 Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
Pneumonia, Pleurisy, Lung cancer
 Pneumonia, Pleurisy, Lung cancer Pneumonia is an infection of lung parenchyma, which leads to inflammation and exudates filling air spaces with fluid (consolidation). This leads to reduced lung compliance
Pneumonia, Pleurisy, Lung cancer Pneumonia is an infection of lung parenchyma, which leads to inflammation and exudates filling air spaces with fluid (consolidation). This leads to reduced lung compliance
Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings
 Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings Poster No.: C-2067 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. M. Almeida, N. Antunes, C. Leal, L. Figueiredo ; Lisboa/PT,
Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings Poster No.: C-2067 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. M. Almeida, N. Antunes, C. Leal, L. Figueiredo ; Lisboa/PT,
Pulmonary TB aspects
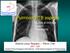 Pulmonary TB aspects Nodule & infiltrate Cavern Pneumonia Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Nodules and infiltrates
Pulmonary TB aspects Nodule & infiltrate Cavern Pneumonia Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Nodules and infiltrates
