Skin disorders. Seborrhoeic dermatitis Search date February 2007 Juan Jorge Manriquez and Pablo Uribe ...
|
|
|
- Richard Brown
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Search date February 27 Juan Jorge Manriquez and Pablo Uribe ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: affects at least 1 3% of the population. Malassezia (Pityrosporum) ovale is thought to be the causative organism, and causes inflammation involving T cells and complement. tends to relapse after treatment. METHODS AND OUTCOMES: We conducted a systematic review and aimed to answer the following clinical questions: What are the effects of topical treatments for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp in adults? What are the effects of topical treatments for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face and body in adults? We searched: Medline, Embase, The Cochrane Library and other important databases up to February 26 (BMJ Clinical Evidence reviews are updated periodically, please check our website for the most up-to-date version of this review). We included harms alerts from relevant organisations such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the UK Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA). RESULTS: We found nine systematic reviews, RCTs, or observational studies that met our inclusion criteria. We performed a GRADE evaluation of the quality of evidence for interventions. CONCLUSIONS: In this systematic review we present information relating to the effectiveness and safety of the following interventions: bifonazole, emollients, ketoconazole, lithium succinate, selenium sulphide, tar shampoo, terbinafine, and topical steroids (betamethasone valerate, clobetasol propionate, clobetasone butyrate, hydrocortisone, mometasone furate). QUESTIONS What are the effects of topical treatments for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp in adults? What are the effects of topical treatments for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face and body in adults? TOPICAL TREATMENTS FOR SEBORRHOEIC DER- MATITIS OF SCALP Beneficial Ketoconazole Likely to be beneficial Bifonazole Corticosteroids (topical) (hydrocortisone, betamethasone valerate, clobetasone butyrate, mometasone furoate, clobetasol propionate)* Selenium sulphide Tar shampoo INTERVENTIONS Likely to be beneficial Bifonazole Corticosteroids (topical) (hydrocortisone, betamethasone valerate, clobetasone butyrate, mometasone furoate, clobetasol propionate; short term episodic treatment in adults)* Unknown effectiveness Emollients Lithium succinate Selenium sulphide Terbinafine Unknown effectiveness Terbinafine TOPICAL TREATMENTS FOR SEBORRHOEIC DER- MATITIS OF FACE OR BODY Beneficial Ketoconazole To be covered in future updates Combination agents Oral antifungal agents Topical calcineurin inhibitors Footnote *Based on consensus. Key points affects at least 1 3% of the population and causes red patches with greasy scales on the face, chest, skin flexures, and scalp. The cause of seborrhoeic dermatitis is unknown. Malassezia yeasts are considered to have an important role producing an inflammatory reaction involving T cells and complement. Known risk factors include immunodeficiency, neurological or cardiac disease, and alcoholic pancreatitis. In this review, however, we deal with treatment in immunocompetent adults who have no known predisposing conditions. tends to relapse after treatment. In adults with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp, antifungal preparations containing ketoconazole improve symptoms compared with placebo. Bifonazole and selenium sulphide are also likely to be effective, but we don't know whether terbinafine is beneficial as no studies have been found. BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 27. All rights reserved Clinical Evidence 27;7:1713
2 There is consensus that topical corticosteroids are effective in treating seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp in adults, although no studies have been found. Tar shampoo may reduce scalp dandruff and redness compared with placebo. In adults with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face and body, short courses of topical corticosteroids are considered to be effective if used episodically, although no studies have been found that assessed this. Ketoconazole cream or gel and bifonazole cream may improve skin symptoms compared with placebo. We don't know whether terbinafine or selenium sulphide are also beneficial as no studies have been found. We don't know whether emollients or topical lithium succinate improve lesions compared with no treatment. DEFINITION INCIDENCE/ PREVALENCE occurs in areas of the skin with a rich supply of sebaceous glands and manifests as red, sharply marginated lesions with greasy looking scales. On the face it mainly affects the medial aspect of the eyebrows, the area between the eyebrows, and the nasolabial folds. It may also affect the skin on the chest (commonly presternal) and the flexures. On the scalp it manifests as dry, flaking desquamation (dandruff) or yellow, greasy scaling with erythema. Dandruff is a lay term commonly used in the context of mild seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp. However, any scalp condition that produces scales could be labelled as dandruff. There is also an infantile variant, commonly affecting the scalp, flexures, and genital area, but this infantile variant seems to have a different pathogenesis than adult seborrhoeic dermatitis. Common differential diagnoses for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp are psoriasis, eczema (see review on atopic eczema), and tinea capitis (see table 1, p 9 ). is estimated to affect around 1 3% of the general population. [1] However, this is likely to be an underestimate because people do not tend to seek medical advice for mild dandruff. AETIOLOGY/ The cause of seborrhoeic dermatitis is unknown and seems to be a multifactorial disease. Malassezia RISK FACTORS yeasts, a genus classified in seven species, are considered to have an important role in seborrhoeic dermatitis producing an inflammatory reaction involving T cells and complement. Conditions that have been reported to predispose to seborrhoeic dermatitis include human immunodeficiency virus, [2] neurological conditions such as Parkinson's disease, neuronal damage such as facial nerve palsy, [3] spinal injury, [4] ischaemic heart disease, [5] and alcoholic pancreatitis. [6] In this review, we deal with treatment in immunocompetent adults who have no known predisposing conditions. PROGNOSIS is a chronic condition that tends to flare and remit spontaneously, and is [1] [7] prone to recurrence after treatment. AIMS OF To reduce the symptoms and signs of seborrhoeic dermatitis with minimal adverse effects. Most INTERVENTION therapeutic options aim to reduce colonisation with Malassezia spp and reduce inflammation, although they tend to palliate rather than cure. OUTCOMES METHODS Severity of symptoms, including itching, scale, and erythema; adverse effects of treatment. BMJ Clinical Evidence search and appraisal February 27. Most authors have used the term dandruff to mean seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp. If there was any doubt about the diagnosis the study was excluded. The following databases were used to identify studies for this systematic review: Medline 1966 to February 27, Embase 198 to February 27, and The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Clinical Trials 27, Issue 1. Additional searches were carried out using these websites: NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD) for Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE) and Health Technology Assessment (HTA), Turning Research into Practice (TRIP), and National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). Abstracts of the studies retrieved from the initial search were assessed by an information specialist. Selected studies were then sent to the author for additional assessment, using predetermined criteria to identify relevant studies. Study design criteria for evaluation in this review were: published systematic reviews and RCTs in any language. RCTs had to be double blinded and contain 2 or more individuals. Trials of less than 4 weeks' duration had to have at least 9% follow up; trials lasting 4 weeks or longer had to have at least 8% follow up. Trials of less than 1 week were excluded. We use a regular surveillance protocol to capture harms alerts from organisations such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the UK Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA), which are added to the reviews as required. We have performed a GRADE evaluation of the quality of evidence for interventions included in this review (see table, p 11 ). BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 27. All rights reserved
3 QUESTION What are the effects of topical treatments for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp in adults? OPTION KETOCONAZOLE SCALP PREPARATIONS Compared with placebo Ketoconazole shampoo is more effective than placebo at improving scalp symptoms such as scaling, itching, redness, and dandruff at 4 weeks in people with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp (moderatequality evidence). Ketoconazole shampoo versus placebo: We found no systematic reviews. We found five RCTs ranging in size from 2 to 246 participants. [8] [9] [1] [11] [12] All found improvements in symptoms with ketoconazole 2% shampoo after 4 weeks compared with placebo (see table 2, p 1 ). Ketoconazole shampoo versus placebo: Four of the five RCTs reported that there were no adverse effects of treatment. [8] [9] [1] [11] The fifth RCT reported one instance of scalp tenderness that was probably related to ketoconazole treatment. [12] OPTION BIFONAZOLE SCALP PREPARATIONS Compared with placebo Bifonazole shampoo may be more effective than placebo at improving symptoms such as scaling and pruritus, and overall symptom severity at six weeks in people with seborrhoea or seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp (low-quality evidence). Bifonazole shampoo versus placebo: We found no systematic review. We found one RCT which compared bifonazole 1% shampoo versus placebo. [13] It found that bifonazole 1% shampoo significantly improved scalp symptoms (severity of scaling, pruritus, and overall severity graded by a clinician on a 3 point scale from = none to 3 = severe) compared with placebo after 6 weeks (51 people with seborrhoea or seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp; scaling: P =.1; pruritus: P =.8; overall severity: P =.12). Bifonazole shampoo versus placebo: The RCT reported no major side effects. [13] OPTION SELENIUM SULPHIDE SCALP PREPARATIONS Compared with placebo Selenium sulphide shampoo is more effective than placebo at reducing dandruff, and at increasing response to treatment at 29 days, in people with moderate to severe dandruff (moderate-quality evidence). Selenium sulphide shampoo versus placebo: We found no systematic reviews. We found one RCT which compared three treatments randomised in a 2 : 2 : 1 ratio: selenium sulphide 2.5% shampoo (1 people); ketoconazole 2% shampoo (97 people); and placebo (49 people). [11] It found significantly greater reductions in mean adherent dandruff scores (determined by visual examination of six scalp areas, in which = none and 9 1 = severe/heavy) with selenium sulphide shampoo compared with placebo over 29 days (people with moderate to severe dandruff; percentage reduction in adherent dandruff scores from baseline: 66.7% with selenium sulphide v 44.5% with placebo; P value not reported). It also found that significantly more people responded to treatment (global improvement of completely cleared, excellent, or good) with selenium sulphide shampoo than with placebo at 29 days (AR for responding to treatment: 54.7% with selenium sulphide v 28.6% with placebo; P =.4). BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 27. All rights reserved.... 3
4 Selenium sulphide shampoo versus placebo: The RCT reported infrequent adverse events with selenium sulphide shampoo, including pruritus or burning sensation of the scalp (3 people), eruption near the hair line (1 person), psoriasis (1 person), lightening/bleaching of hair colour (2 people), orange staining of the scalp (1 person), and a chemical taste during shampooing (1 person). [11] OPTION TAR SHAMPOO Compared with placebo Tar shampoo is more effective than placebo at improving dandruff and redness at 29 days in people with seborrhoeic dermatitis or dandruff (moderate-quality evidence). For GRADE evaluation of seborrhoeic dermatitis, see table, p 11. OPTION Tar shampoo versus placebo: We found no systematic reviews. We found one RCT which compared tar shampoo (4% coal tar) versus placebo. [12] It found that, compared with placebo, tar shampoo significantly improved both dandruff (dandruff score, assessed by a technician by multiplying size of affected area by severity; size of affected area scored from = 1% to 4 = > 7%; severity scored from 1 = small flakes resembling a white powder to 5 = flakes adhering to the scalp as white or yellow plates) and redness (graded by a clinician on a 5 point scale from = none to 4 = very severe) after 29 days (111 people with seborrhoeic dermatitis or dandruff; mean reduction in dandruff score from baseline: 31 with tar shampoo v 19 with placebo, P <.1; mean difference in redness from baseline: 1.2 with tar shampoo v.6 with placebo, P <.5). There was no significant difference in scaling or area of seborrhoeic dermatitis after 29 days between tar shampoo and placebo. Tar shampoo versus placebo: The RCT reported no major adverse events. [12] TOPICAL CORTICOSTEROIDS (HYDROCORTISONE, BETAMETHASONE VALERATE, CLO- BETASONE BUTYRATE, MOMETASONE FUROATE, CLOBETASOL PROPIONATE) We found no direct information about whether topical corticosteroids (hydrocortisone, betamethasone valerate, clobetasone butyrate, mometasone furoate, or clobetasol propionate) are better than no active treatment for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp in adults. There is consensus that topical corticosteroids are effective in treating seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp in adults. Topical corticosteroids versus placebo: We found no systematic review or RCTs comparing topical corticosteroids (hydrocortisone, betamethasone valerate, clobetasone butyrate, mometasone furoate, or clobetasol propionate) versus placebo for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp in adults. Topical corticosteroids versus placebo: We found no RCTs. Although no systematic reviews or RCTs were identified, there is consensus that topical corticosteroids are effective in treating seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp in adults. Betamethasone valerate scalp application in a lotion or mousse is routinely used in practice by dermatologists. OPTION TERBINAFINE SCALP PREPARATIONS We found no direct information about whether terbinafine is better than no active treatment in adults with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp. Terbinafine versus placebo: We found no systematic review or RCTs (see comment below). Terbinafine versus placebo: We found no RCTs (see comment below). BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 27. All rights reserved.... 4
5 QUESTION Terbinafine versus placebo: Terbinafine is not manufactured as a scalp preparation in the UK and is not known to be available worldwide. What are the effects of topical treatments for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face and body in adults? OPTION KETOCONAZOLE Compared with placebo Ketoconazole may be more effective than placebo at increasing the number of people successfully treated, and at improving symptoms such as erythema, scaling, papules, and pruritus, at 4 weeks (lowquality evidence). Ketoconazole versus placebo: We found no systematic review. We found two small RCTs that compared ketoconazole 2% cream versus placebo [8] [14] and one large RCT that compared ketoconazole 2% gel versus placebo. [15] The first small RCT found that ketoconazole 2% cream improved symptoms (according to a composite clinical score in which 8 sites were graded for erythema, scaling, papules, and pruritus; range not given) compared with placebo after 4 weeks (37 people with seborrhoeic dermatitis; reduction in approximate mean sum of symptom scores from baseline [see comment below]: 19 with ketoconazole cream v 13 with placebo; P value not reported). [14] The second small RCT compared ketoconazole 2% cream plus ketoconazole 2% shampoo versus placebo. [8] It found that ketoconazole 2% cream improved facial symptoms (severity of symptoms graded on a 4 point scale from = none to 3 = severe) compared with placebo after 4 weeks (2 people with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face, with or without seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp, chest, or back [see comment below]; AR for improving by at least one symptom grade from baseline: 9% [9/1] with ketoconazole v % [/1] with placebo; P value not reported). [8]. The third large RCT compared a once daily 2 week course of ketoconazole 2% gel versus placebo (vehicle gel) in people with seborrhoeic dermatitis. [15] Successful treatment was defined as both an erythema and scaling score of (none) if the baseline score was 2 or less (moderate) or a score of 1 or less (mild) if the baseline score was 3 (severe) based on a 4 point scale for erythema and scaling, and an Investigator's Global Assessment score of (clear) or 1 (almost clear), based on a 5 point scale measured at day 28. The RCT found that a significantly greater proportion of subjects were successfully treated with ketoconazole 2% gel compared with placebo after 4 weeks (459 people with seborrhoeic dermatitis; percentage of subjects successfully treated, intention to treat analysis: 25.3% [58/229] with ketoconazole v 13.9% [32/23] with placebo; P value =.14). [15] Ketoconazole versus placebo: Two of the RCTs reported that there were no adverse effects of treatment. [8] [14] One RCT found that there were mild or moderate adverse effects similarly distributed between treatment groups. [15] The RCT reported that treatment related adverse effects in 1% or more of subjects were application site burning (2.6% with ketoconazole gel v 2.6% with placebo gel), erythema (1.7% v 1.3%), and application site reaction (.4% v 1.7%; between group statistical analysis not reported). [15] Ketoconazole versus placebo: Approximate mean scores were extracted from graphs because data were not tabulated. [14] Of the 2 people with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face, 16 (8%) also had seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp, seven (35%) had chest involvement, and five (25%) had back involvement. [8] OPTION BIFONAZOLE Compared with placebo Bifonazole cream may be more effective than placebo at improving symptoms and response to treatment at 4 weeks in people with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face (low-quality evidence). Bifonazole versus placebo: We found no systematic review. We found one RCT which compared bifonazole 1% cream versus placebo. [16] It found that significantly more people responded to treatment (global improvement graded on a 4 point scale from = no improvement or worsening to 3 = healing) with bifonazole compared with placebo at 4 weeks (1 people with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face; AR for healing: 16/37 [43%] with bifonazole v 1/43 [23%] with placebo; AR for improvement: 2/37 [54%] BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 27. All rights reserved.... 5
6 OPTION with bifonazole v 26/43 [61%] with placebo; AR for treatment failure: 1/37 [3%] with bifonazole v 7/43 [16%] with placebo; overall P value =.44; P values for individual outcomes not reported). Bifonazole versus placebo: The RCT reported more minor adverse effects of treatment (including itch, burning, tightness, erythema, papules, and scaling) with bifonazole than with placebo (5/5 [1%] with bifonazole v 2/5 [4%] with placebo; P value not reported). [16]. TOPICAL CORTICOSTEROIDS (HYDROCORTISONE, BETAMETHASONE VALERATE, CLO- BETASONE BUTYRATE, MOMETASONE FUROATE, CLOBETASOL PROPIONATE) We found no direct information about whether topical corticosteroids (hydrocortisone, betamethasone valerate, clobetasone butyrate, mometasone furoate, or clobetasol propionate) are better than no active treatment for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp in adults.there is consensus that short courses of topical corticosteroids used episodically are effective in treating seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face and body in adults. Topical corticosteroids versus placebo: We found no systematic review or RCTs comparing topical corticosteroids (hydrocortisone, betamethasone valerate, clobetasone butyrate, mometasone furoate, or clobetasol propionate) versus placebo in adults with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face and body. Topical corticosteroids versus placebo: We found no RCTs. Although we found no RCTs of topical corticosteroids in adults with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face or body, consensus regards their use as effective. It is current practice to use short courses of topical corticosteroids episodically in seborrhoeic dermatitis. Affected areas of the body are treated with short courses of potent topical corticosteroids (betamethasone valerate [.1%], mometasone furoate [.1%]) while the face is treated with short courses of moderate (clobetasone butyrate [.5%]) or low potency (hydrocortisone [1%]) corticosteroids. OPTION EMOLLIENTS We found no direct information about whether emollients are better than no active treatment in adults with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face and body. Emollients versus no treatment: We found no systematic review or RCTs of sufficient quality comparing emollients versus no treatment in adults with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face and body. Emollients versus no treatment: We found no RCTs. OPTION LITHIUM SUCCINATE Compared with placebo Lithium succinate cream may be more effective than placebo at improving overall clinical impression, severity of redness, scaling, and greasiness in adults with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face and body (very low-quality evidence). Lithium succinate versus placebo: We found no systematic review or RCTs of sufficient quality comparing lithium succinate versus placebo in adults with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face and body (see comment below). Lithium succinate versus placebo: We found no RCTs of sufficient quality. BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 27. All rights reserved.... 6
7 We found one crossover RCT (3 people with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face and/or the trunk) which compared lithium succinate 8% cream versus placebo. [17] It found that lithium succinate significantly improved symptoms (graded on a 1 mm scale on severity of redness, scaling, greasiness, and overall clinical impression of the condition) compared with placebo (results not pre-crossover). However, these results should be interpreted with caution because of the potential for persistence of effects after crossover. The RCT also had a high withdrawal rate (37%) and it is not clear whether the analyses were conducted on an intention to treat basis. Withdrawals were due to non-compliance (2 people with lithium succinate, 3 with placebo), local stinging sensation and erythema (1 person with lithium succinate, 2 with placebo), worsening of acne vulgaris (1 person with lithium succinate, 1 with placebo), or resolution of lesions (1 person, group not reported). OPTION SELENIUM SULPHIDE We found no direct information about whether selenium sulphide is better than no active treatment in adults with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face and body. Selenium sulphide versus placebo: We found no systematic review or RCTs. Selenium sulphide versus placebo: We found no RCTs. OPTION TERBINAFINE We found no direct information about whether terbinafine is better than no active treatment in adults with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face and body. Terbinafine versus placebo: We found no systematic review or RCTs. Terbinafine versus placebo: We found no RCTs. GLOSSARY Low-quality evidence Further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate. Moderate-quality evidence Further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate. Very low-quality evidence Any estimate of effect is very uncertain. SUBSTANTIVE CHANGES Ketoconazole (under question on topical treatments for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face and body in adults) One large RCT added comparing ketoconazole gel versus placebo; [15] benefits and harms data enhanced, recategorised from Unknown effectiveness to Beneficial. Selenium sulphide (under question on topical treatments for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp in adults) Evidence re-evaluated, recategorised from Beneficial to Likely to be beneficial. REFERENCES 1. Gupta AK, Bluhm R, Cooper EA.. Dermatol Clin 23;21: [PubMed] 2. Berger RS. Cutaneous manifestations of early human immunodeficiency virus exposure. J Am Acad Dermatol 1988;19: [PubMed] 3. Bettley FR, Marten RH. Unilateral seborrhoeic dermatitis following a nerve lesion. Arch Dermatol 1956;73: Wilson CL, Walshe M. Incidence of seborrhoeic dermatitis in spinal injury patients. Br J Dermatol 1988;119(suppl 33): Tager A. in acute cardiac disease. Br J Dermatol 1964;76: [PubMed] 6. Barba A, Piubello W, Vantini I, et al. Skin lesions in chronic alcoholic pancreatitis. Dermatologica 1982;164: [PubMed] 7. Rook et al. Textbook of Dermatology, 6th ed. Blackwell and Synergy: Green CA, Farr PM, Shuster S. Treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis with ketoconazole: II. Response of seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face, scalp and trunk to topical ketoconazole. Br J Dermatol 1987;116: [PubMed] 9. Carr MM, Pryce DM, Ive FA. Treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis with ketoconazole: I. Response of seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp to topical ketoconazole. Br J Dermatol 1987;116: [PubMed] 1. Berger R, Mills OH. Double blind placebo-controlled trial of ketoconazole 2% shampoo in the treatment of moderate to severe dandruff. Adv Ther 199;7: Danby FW, Maddin WS, Margesson LJ. A randomised, double-blind, placebocontrolled trial of ketoconazole 2% shampoo versus selenium sulfide 2.5% shampoo in the treatment of moderate to severe dandruff. J Am Acad Dermatol 1993;29: [PubMed] BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 27. All rights reserved.... 7
8 12. Davies DB, Boorman GC, Shuttleworth D. Comparative efficacy of shampoos containing coal tar (4.% w/w; Tarmed TM ), coal tar (4.% w/w) plus ciclopirox olamine (1.% w/w; Tarmed TM AF) and ketoconazole (2.% w/w; Nizoral ) for the treatment of dandruff/seborrhoeic dermatitis. J Dermatol Treat 1999;1: Segal R, David A, Ingber R, et al. Treatment with bifonazole shampoo for seborrhoea and seborrhoeic dermatitis: a randomised, double blind study. Acta Derm Venereol (Stockh) 1992;72: Skinner RB, Noah PW, Taylor RM, et al. Double-blind treatment of seborrheic dermatitis cream with 2% ketoconazole cream. J Am Acad Dermatol 1985;12: [PubMed] 15. Elewski B, Ling MR, Phillips TJ. Efficacy and safety of a new once-daily topical ketoconazole 2% gel in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis: a phase III trial. J Drugs Dermatol 26;5: [PubMed] 16. Zienicke H, Korting HC, Braun-Falco O, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of bifonazole 1% cream and the corresponding base preparation in the treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis. Mycoses 1993;36: [PubMed] 17. Cuelenaere C, De Bersaques J, Kint A. Use of topical lithium succinate in the treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis. Dermatology 1992;184: [PubMed] Juan Jorge Manríquez Unidad Docente Asociada de Dermatologia School of Medicine, Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile Santiago Chile Pablo Uribe Unidad Docente Asociada de Dermatologia School of Medicine, Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile Santiago Chile Competing interests: JM and PU declare that they have no competing interests. Disclaimer The information contained in this publication is intended for medical professionals. Categories presented in Clinical Evidence indicate a judgement about the strength of the evidence available to our contributors prior to publication and the relevant importance of benefit and harms. We rely on our contributors to confirm the accuracy of the information presented and to adhere to describe accepted practices. Readers should be aware that professionals in the field may have different opinions. Because of this and regular advances in medical research we strongly recommend that readers' independently verify specified treatments and drugs including manufacturers' guidance. Also, the categories do not indicate whether a particular treatment is generally appropriate or whether it is suitable for a particular individual. Ultimately it is the readers' responsibility to make their own professional judgements, so to appropriately advise and treat their patients. To the fullest extent permitted by law, BMJ Publishing Group Limited and its editors are not responsible for any losses, injury or damage caused to any person or property (including under contract, by negligence, products liability or otherwise) whether they be direct or indirect, special, incidental or consequential, resulting from the application of the information in this publication. BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 27. All rights reserved.... 8
9 TABLE 1 Differential diagnoses for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp (see text). Diagnosis Psoriasis Eczema (atopic and contact dermatitis) Tinea capitis Distinguishing features Prominent erythema Tendency for hair line involvement More prominent silver scale Presence of psoriasis elsewhere (skin, nails, joints) Atopic dermatitis: General skin examination History Contact dermatitis: Distribution of eczema History Microscopy Fungal culture of scalp scrapings BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 27. All rights reserved
10 [8] [9] [1] TABLE 2 RCTs comparing ketoconazole shampoo versus placebo for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp (see antifungal scalp preparations, p 3 ). [11] [12] Trial details Ketoconazole (2% shampoo plus 2% cream) v placebo Crossover RCT comparing ketoconazole 2% shampoo v placebo (shampoo base without ketoconazole) Ketoconazole 2% shampoo v placebo (shampoo base without ketoconazole) Ketoconazole 2% shampoo v selenium sulphide 2.5% shampoo v placebo Ketoconazole 2% shampoo v coal tar 4.% plus ciclopirox olamine 1% shampoo v placebo VAS = visual analogue scale. Ref [8] [9] [1] [11] [12] Participants 2 people with seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face: 8% had seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp, 35% had chest involvement, and 25% had back involvement 2 people (16 male, 4 female) with either dandruff or seborrhoeic dermatitis (no distinction made between these; proportion with seborrhoeic dermatitis not reported) 53 people with moderate to severe dandruff, 28 [52.8%] of whom had seborrhoeic dermatitis 246 people with moderate to severe dandruff 163 people with seborrhoeic dermatitis or dandruff Outcome Clinician rated scalp scaling ( = none to 3 = severe): AR for improvement in scaling at 4 weeks: 86% (6/7) with ketoconazole v % (/9) with placebo (P value not reported) Participant rated scalp scaling (1 mm VAS from = none to 1 = severe): Scalp scaling improved significantly more at 4 weeks with ketoconazole than with placebo (scores shown graphically; P <.5) Participant rated scalp itching and scaling (1 mm VAS from = none to 1 = "worst ever"): Approximate median change in itch score at 4 weeks: 2 with ketoconazole v +8 with placebo (P value not reported) Approximate median change in scale score at 4 weeks: 2 with ketoconazole v +15 with placebo (P value not reported) (Median scores pre crossover approximated from graphs) Adherent dandruff score (six scalp areas assessed; = no scaling to 1 = extremely severe scaling): Mean change in score at day 15: 12 with ketoconazole v 7 with placebo (P <.5) Mean change in score at day 29: 19 with ketoconazole v 13 with placebo (P <.5) Response to treatment (global evaluation of completely cleared, excellent, or good): AR for responding to treatment at day 29: 78.6% (22/28) with ketoconazole v 37.5% (9/24) with placebo (P =.4) Adherent dandruff score (six scalp areas assessed; = none and 9 1 = severe/heavy): % Reduction in mean score from baseline at 29 days: 73.% with ketoconazole v 44.5% with placebo (P value not reported) Response to treatment (global evaluation of completely cleared, excellent, or good): AR for responding to treatment at day 29: 64.9% with ketoconazole v 28.6% with placebo (P <.1) Clinician rated scaling and redness ( = none to 4 = very severe): Mean reduction in scale score at 29 days: 1.2 with ketoconazole v.3 with placebo (P <.1) Mean reduction in redness score at 29 days: 1.3 with ketoconazole v.5 with placebo (P <.1) Area of scalp affected by seborrhoeic dermatitis: No significant difference between ketoconazole and placebo at 29 days (area and P value not reported). BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 27. All rights reserved.... 1
11 TABLE Important outcomes Number of studies (participants) GRADE evaluation of interventions for seborrhoeic dermatitis, adverse effects Outcome Comparison Type of evidence What are the effects of topical treatments for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp in adults? [8] [9] [1] 5 (52) Ketoconazole shampoo v 4 1 [11] [12] placebo 1 (51) [13] Bifonazole v placebo (246) [11] 1 (111) [12] Selenium sulphide v placebo Tar shampoo v placebo 4 4 Quality 1 1 Consistency Directness Effect size GRADE Moderate Low Moderate Moderate Comment Quality point deducted for incomplete reporting of results Quality points deducted for sparse data and incomplete reporting of results Quality point deducted for incomplete reporting of results Quality point deducted for sparse data What are the effects of topical treatments for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the face and body in adults? [8] [14] 3 (516) Ketoconazole v placebo (1) [15] 1 (3) [17] Bifonazole cream v placebo Lithium succinate cream v placebo Low Low Very low Quality point deducted for incomplete reporting of results. Directness point deducted for no direct comparison between groups in two RCTs Quality points deducted for sparse data and incomplete reporting of results Quality points deducted for sparse data, incomplete reporting of results, no intention-to-treat analysis, poor follow-up, and uncertainty about results Type of evidence: 4 = RCT; 2 = Observational; 1 = Non-analytical/expert opinion. Consistency: similarity of results across studies. Directness: generalisability of population or outcomes. Effect size: based on relative risk or odds ratio. BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 27. All rights reserved
Skin disorders. Seborrhoeic dermatitis Search date April 2010 Luigi Naldi ...
 Seborrhoeic Search date April 21 Luigi Naldi.................................................. ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: Seborrhoeic affects at least 1% of the population. Malassezia (Pityrosporum) ovale
Seborrhoeic Search date April 21 Luigi Naldi.................................................. ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: Seborrhoeic affects at least 1% of the population. Malassezia (Pityrosporum) ovale
FACTSHEET ADULT SEBORRHOEIC DERMATITIS. What is seborrhoeic dermatitis? Who gets and why? What does it look like?
 What is seborrhoeic dermatitis? Sebhorrhoeic dermatitis is a common scaly rash that often affects the face, scalp and chest but it can affect other areas. Dermatitis is another word for eczema. Seborrhoeic
What is seborrhoeic dermatitis? Sebhorrhoeic dermatitis is a common scaly rash that often affects the face, scalp and chest but it can affect other areas. Dermatitis is another word for eczema. Seborrhoeic
forniture parafarmaceutiche
 User's Manual forniture parafarmaceutiche CONTENTS forniture parafarmaceutiche Dermatitis of the Scalp Seborrheic Dermatitis Treatments Atopshield Lotion The mechanism of action of Atopshield Lotion Indications
User's Manual forniture parafarmaceutiche CONTENTS forniture parafarmaceutiche Dermatitis of the Scalp Seborrheic Dermatitis Treatments Atopshield Lotion The mechanism of action of Atopshield Lotion Indications
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Seborrheic Dermatitis
 Diagnosis And Treatment Of Seborrheic Dermatitis 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 Diagnosis And Treatment Of Seborrheic Seborrheic dermatitis Diagnosis. Your doctor will likely be able to determine whether you have seborrheic
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Seborrheic Dermatitis 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 Diagnosis And Treatment Of Seborrheic Seborrheic dermatitis Diagnosis. Your doctor will likely be able to determine whether you have seborrheic
TCIs are only available on prescription and are usually started by a dermatology specialist.
 (TCIs) What are topical calcineurin inhibitors? Topical calcineurin inhibitors are treatments that alter the immune system and have been developed for controlling eczema. There are two types available:
(TCIs) What are topical calcineurin inhibitors? Topical calcineurin inhibitors are treatments that alter the immune system and have been developed for controlling eczema. There are two types available:
Dupixent (dupilumab)
 Dupixent (dupilumab) Line(s) of Business: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration Effective Date: TBD POLICY A. INDICATIONS The indications below including FDA-approved indications and compendial uses are considered
Dupixent (dupilumab) Line(s) of Business: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration Effective Date: TBD POLICY A. INDICATIONS The indications below including FDA-approved indications and compendial uses are considered
KEY MESSAGES. Psoriasis patients are more prone to cardiovascular diseases, stroke, lymphoma and non-melanoma skin cancers, and increased mortality.
 KEY MESSAGES Psoriasis is a genetically determined, systemic immune-mediated chronic inflammatory disease that affects primarily the skin and joints. Psoriasis Vulgaris is characterised by well-demarcated
KEY MESSAGES Psoriasis is a genetically determined, systemic immune-mediated chronic inflammatory disease that affects primarily the skin and joints. Psoriasis Vulgaris is characterised by well-demarcated
(5). (1, 5) Table 1:Appearance and location of dandruff, psoriasis and seborrhoeic dermatitis
 A-Dandruff(pityriasis capitis) 1-Dandruff is a chronic relapsing condition of the scalp which respond to treatment, but return when the treatment is stopped (1). Increased cell turnover rate (twice the
A-Dandruff(pityriasis capitis) 1-Dandruff is a chronic relapsing condition of the scalp which respond to treatment, but return when the treatment is stopped (1). Increased cell turnover rate (twice the
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Technology Appraisals and Guidance Information Services Static List Review (SLR) Title and TA publication number of static topic: Final decision: TA82;
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Technology Appraisals and Guidance Information Services Static List Review (SLR) Title and TA publication number of static topic: Final decision: TA82;
Medication Policy Manual. Topic: Dupixent, dupilumab Date of Origin: March 10, Committee Approval: March 10, 2017 Next Review Date: May 2018
 Independent licensees of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru493 Topic: Dupixent, dupilumab Date of Origin: March 10, 2017 Committee Approval: March 10, 2017
Independent licensees of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru493 Topic: Dupixent, dupilumab Date of Origin: March 10, 2017 Committee Approval: March 10, 2017
Literature Scan: Topical Corticosteroids. Month/Year of Review: March 2015 Date of Last Review: March 2013 Source Document: OSU College of Pharmacy
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
15 minute eczema consultation
 THERAPY WORKSHOP 15 minute eczema consultation History Current treatments Examination Treatment Plan Written action plan Soap substitute/bath oil Antiseptic baths Emollients Topical steroids Other treatments
THERAPY WORKSHOP 15 minute eczema consultation History Current treatments Examination Treatment Plan Written action plan Soap substitute/bath oil Antiseptic baths Emollients Topical steroids Other treatments
Seborrheic dermatitis. What is SEBORRHEIC DERMATITIS? This is a common condition which affects 1-3 % of individuals.
 750 West Broadway Suite 905 - Vancouver BC V5Z 1H8 Phone: 604.283.9299 Fax: 604.648.9003 Email: vancouveroffice@donovanmedical.com Web: www.donovanmedical.com Seborrheic dermatitis What is SEBORRHEIC DERMATITIS?
750 West Broadway Suite 905 - Vancouver BC V5Z 1H8 Phone: 604.283.9299 Fax: 604.648.9003 Email: vancouveroffice@donovanmedical.com Web: www.donovanmedical.com Seborrheic dermatitis What is SEBORRHEIC DERMATITIS?
Pharmacologic Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis
 J KMA Pharmacotherapeutics Pharmacologic Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis Chun Wook Park, MD Department of Dermatology, Hallym University College of Medicine E mail : dermap@paran.com J Korean Med Assoc
J KMA Pharmacotherapeutics Pharmacologic Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis Chun Wook Park, MD Department of Dermatology, Hallym University College of Medicine E mail : dermap@paran.com J Korean Med Assoc
Eczema. By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University
 Eczema By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University Dermatitis= Eczema =Spongiosis Eczema Atopic Seborrheic Contact Allergic Irritant Nummular Asteatotic Stasis Neurodermatitis/Lichen Simplex
Eczema By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University Dermatitis= Eczema =Spongiosis Eczema Atopic Seborrheic Contact Allergic Irritant Nummular Asteatotic Stasis Neurodermatitis/Lichen Simplex
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Technology Appraisals and Guidance Information Services Static List Review (SLR) report Title and TA publication number of static topic: Final decision:
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Technology Appraisals and Guidance Information Services Static List Review (SLR) report Title and TA publication number of static topic: Final decision:
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level
 Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
Clearance in vulvar lichen sclerosus: a realistic treatment endpoint or a chimera?
 DOI: 10.1111/jdv.14516 JEADV SHORT REPORT Clearance in vulvar lichen sclerosus: a realistic treatment endpoint or a chimera? A. Borghi,* A. Virgili, S. Minghetti, G. Toni, M. Corazza Dipartimento di Scienze
DOI: 10.1111/jdv.14516 JEADV SHORT REPORT Clearance in vulvar lichen sclerosus: a realistic treatment endpoint or a chimera? A. Borghi,* A. Virgili, S. Minghetti, G. Toni, M. Corazza Dipartimento di Scienze
Time to Learn. 6 th March 2018 Dr. Shirin Chakera GPwSI Integrated Dermatology Service
 Time to Learn 6 th March 2018 Dr. Shirin Chakera GPwSI Integrated Dermatology Service The Red Face Rosacea Acne Seborrhoeic eczema eczema Psoriasis Slapped cheek syndrome Fungal infection Erysipelas...
Time to Learn 6 th March 2018 Dr. Shirin Chakera GPwSI Integrated Dermatology Service The Red Face Rosacea Acne Seborrhoeic eczema eczema Psoriasis Slapped cheek syndrome Fungal infection Erysipelas...
Elements for a Public Summary
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology is intended for the treatment of: Steroid responsive dermatoses such as psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis of the hairy regions,
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology is intended for the treatment of: Steroid responsive dermatoses such as psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis of the hairy regions,
QUESTIONS What are the effects of interventions at the end of life in people with delirium caused by underlying terminal illness?...
 at the end of life Search date February 29 Paul Keeley ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: is common in the last weeks of life, occurring in 26% to 44% of people with advanced cancer in hospital, and in up to 88% of
at the end of life Search date February 29 Paul Keeley ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: is common in the last weeks of life, occurring in 26% to 44% of people with advanced cancer in hospital, and in up to 88% of
QUESTIONS What are the effects of interventions to reduce symptoms of acute infective sore throat?... 3
 Search date September 213 Tim Kenealy ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: About 1% of people present to primary healthcare services with sore throat each year. The causative organisms of sore throat may be bacteria
Search date September 213 Tim Kenealy ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: About 1% of people present to primary healthcare services with sore throat each year. The causative organisms of sore throat may be bacteria
Using Your ESP* in Pharmacy: How to Improve Treatment Adherence and Patient Outcomes in Psoriasis (*Expanded Scope of Practice)
 Using Your ESP* in Pharmacy: How to Improve Treatment Adherence and Patient Outcomes in Psoriasis (*Expanded Scope of Practice) Patient Case Study in Psoriasis Patient Case Study in Psoriasis William Smith,
Using Your ESP* in Pharmacy: How to Improve Treatment Adherence and Patient Outcomes in Psoriasis (*Expanded Scope of Practice) Patient Case Study in Psoriasis Patient Case Study in Psoriasis William Smith,
PHARMACY PRACTICE I PHCY280 (2 CREDITS); PHCY280L (1CREDIT) SUMMER Christy Mary Sam
 PHARMACY PRACTICE I PHCY280 (2 CREDITS); PHCY280L (1CREDIT) SUMMER 2014-15 1 Christy Mary Sam COMMUNICATION SKILLS Communication is the process involved with the exchange of any kind of information between
PHARMACY PRACTICE I PHCY280 (2 CREDITS); PHCY280L (1CREDIT) SUMMER 2014-15 1 Christy Mary Sam COMMUNICATION SKILLS Communication is the process involved with the exchange of any kind of information between
The role of the practice nurse in managing psoriasis in primary care
 The role of the practice nurse in managing psoriasis in primary care Item type Authors Publisher Journal Article Buckley, David Nursing in General Practice Nursing in general practice Downloaded 16-Sep-2016
The role of the practice nurse in managing psoriasis in primary care Item type Authors Publisher Journal Article Buckley, David Nursing in General Practice Nursing in general practice Downloaded 16-Sep-2016
GROUP 15 TOPICAL PREPARATIONS
 - 105 - GROUP 15 15.1 DERMATOLOGICAL PREPARATIONS 15.1.1 TOPICAL ANTIFUNGALS CLOTRIMAZOLE Indication: Treatment of susceptible fungal infections, dermatophytoses, superficial mycoses, and cutaneous candidiasis
- 105 - GROUP 15 15.1 DERMATOLOGICAL PREPARATIONS 15.1.1 TOPICAL ANTIFUNGALS CLOTRIMAZOLE Indication: Treatment of susceptible fungal infections, dermatophytoses, superficial mycoses, and cutaneous candidiasis
CLINICAL REPORT MATERIALS AND METHODS
 Acta Derm Venereol 2013; 93: 557 561 CLINICAL REPORT Proactive Treatment of Adult Facial Seborrhoeic Dermatitis with 0.1% Tacrolimus Ointment: Randomized, Double-blind, Vehicle-controlled, Multi-centre
Acta Derm Venereol 2013; 93: 557 561 CLINICAL REPORT Proactive Treatment of Adult Facial Seborrhoeic Dermatitis with 0.1% Tacrolimus Ointment: Randomized, Double-blind, Vehicle-controlled, Multi-centre
QUESTIONS What are the effects of empirical treatments for otitis externa?... 4
 Search date October 213 Daniel Hajioff and Samuel Mackeith ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: is thought to affect 1% of people at some stage, and can present in acute, chronic, or necrotising forms. may be associated
Search date October 213 Daniel Hajioff and Samuel Mackeith ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: is thought to affect 1% of people at some stage, and can present in acute, chronic, or necrotising forms. may be associated
Psoriasis the latest recommendations for management: where can primary care make a real difference?
 Dermatology Psoriasis the latest recommendations for management: where can primary care make a real difference? Dr Stephen Kownacki Executive chair, Primary Care Dermatology Society (PCDS) This session
Dermatology Psoriasis the latest recommendations for management: where can primary care make a real difference? Dr Stephen Kownacki Executive chair, Primary Care Dermatology Society (PCDS) This session
RECLASSIFICATION SUBMISSION. EUMOVATE Eczema and Dermatitis Cream. (Clobetasone butyrate 0.05%) From Prescription Only Medicine
 RECLASSIFICATION SUBMISSION EUMOVATE Eczema and Dermatitis Cream (Clobetasone butyrate 0.05%) From Prescription Only Medicine To Pharmacist Only Medicine NOVEMBER 2000 MEETING PART A 1. International non-proprietary
RECLASSIFICATION SUBMISSION EUMOVATE Eczema and Dermatitis Cream (Clobetasone butyrate 0.05%) From Prescription Only Medicine To Pharmacist Only Medicine NOVEMBER 2000 MEETING PART A 1. International non-proprietary
Month/Year of Review: January 2015 Date of Last Review: January 2010
 Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights
Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights
Staying A- Head in Pediatric Dermatology:
 Staying A- Head in Pediatric Dermatology: Common Scalp and Hair Diagnoses Matt Grisham, MD Greenville Health System Post-Graduate Seminar April 20, 2016 I have no financial disclosures or conflicts of
Staying A- Head in Pediatric Dermatology: Common Scalp and Hair Diagnoses Matt Grisham, MD Greenville Health System Post-Graduate Seminar April 20, 2016 I have no financial disclosures or conflicts of
Clinical Evidence. A BMJ database of the very best evidence for effective health care
 Clinical Evidence A BMJ database of the very best evidence for effective health care Myleen Oosthuizen Academic Information Service School for Health Sciences What is Clinical Evidence? An international
Clinical Evidence A BMJ database of the very best evidence for effective health care Myleen Oosthuizen Academic Information Service School for Health Sciences What is Clinical Evidence? An international
New Medicine Report. Pimecrolimus. RED- Hospital only Date of Last Revision 6 th March 2003
 New Medicine Report Document Status Pimecrolimus Reviewed by Suffolk D&T RED- Hospital only Date of Last Revision 6 th March 2003 Approved Name Pimecrolimus Trade Name Elidel Manufacturer Novartis Legal
New Medicine Report Document Status Pimecrolimus Reviewed by Suffolk D&T RED- Hospital only Date of Last Revision 6 th March 2003 Approved Name Pimecrolimus Trade Name Elidel Manufacturer Novartis Legal
The safety and effectiveness of Dupixent in pediatric patients have not been established (1).
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.90.30 Subject: Dupixent Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Dupixent Description Dupixent
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.90.30 Subject: Dupixent Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Dupixent Description Dupixent
Steroid use in managing your child s Atopic Eczema
 Steroid use in managing your child s Atopic Eczema Clinical Nurse Specialist for Paediatric Dermatology (01284) 713575 Step up step down approach: Addressograph Severe Call your General Practitioner (GP)
Steroid use in managing your child s Atopic Eczema Clinical Nurse Specialist for Paediatric Dermatology (01284) 713575 Step up step down approach: Addressograph Severe Call your General Practitioner (GP)
See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
 Clinical Policy: (Dupixent) Reference Number: CP.HNMC.208 Effective Date: 04.11.17 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Medicaid Medi-Cal Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy
Clinical Policy: (Dupixent) Reference Number: CP.HNMC.208 Effective Date: 04.11.17 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Medicaid Medi-Cal Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy
This is a repository copy of Treatment of severe, chronic hand eczema. Results from a UK-wide survey..
 This is a repository copy of Treatment of severe, chronic hand eczema. Results from a UK-wide survey.. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/104211/ Version: Accepted
This is a repository copy of Treatment of severe, chronic hand eczema. Results from a UK-wide survey.. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/104211/ Version: Accepted
Keywords: Psoriasis vulgaris Zinc pyrithione Betamethasone dipropionate
 CLINICAL EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF A COMBINED FORMULATION OF ZINC PYRITHIONE 0.25% AND BETAMETHASONE DIPROPIONATE MICRONIZED 0.05% IN THE TREATMENT OF MILD TO MODERATE PLAQUE PSORIASIS. Abstract Background
CLINICAL EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF A COMBINED FORMULATION OF ZINC PYRITHIONE 0.25% AND BETAMETHASONE DIPROPIONATE MICRONIZED 0.05% IN THE TREATMENT OF MILD TO MODERATE PLAQUE PSORIASIS. Abstract Background
Comparative efficacy of topical mometasone furoate 0.1% cream vs topical tacrolimus 0.03% ointment in the treatment of atopic dermatitis
 Original Article Comparative efficacy of topical mometasone furoate 0.1% cream vs topical tacrolimus 0.03% ointment in the treatment of atopic dermatitis Md Alauddin Khan *, Lubna Khondker **, Dilshad
Original Article Comparative efficacy of topical mometasone furoate 0.1% cream vs topical tacrolimus 0.03% ointment in the treatment of atopic dermatitis Md Alauddin Khan *, Lubna Khondker **, Dilshad
Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy Treatment (Ultraviolet A [PUVA] and B [UBV])
![Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy Treatment (Ultraviolet A [PUVA] and B [UBV]) Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy Treatment (Ultraviolet A [PUVA] and B [UBV])](/thumbs/89/99382632.jpg) Origination: 09/27/07 Revised: 08/2/17 Annual Review: 11/2/17 Purpose: To provide Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy Treatment (PUVA and UBV) guidelines for the Medical Department staff to reference when
Origination: 09/27/07 Revised: 08/2/17 Annual Review: 11/2/17 Purpose: To provide Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy Treatment (PUVA and UBV) guidelines for the Medical Department staff to reference when
Vulval dermatoses. Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough
 Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Eucrisa. Eucrisa (crisaborole) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.90.25 Subject: Eucrisa Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Eucrisa Description Eucrisa
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.90.25 Subject: Eucrisa Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Eucrisa Description Eucrisa
Drug Class Literature Scan: Topical Antipsoriatics
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Prescribing Information
 Prescribing Information Pr DERMOVATE Cream (clobetasol propionate cream, USP) Pr DERMOVATE Ointment (clobetasol propionate ointment, USP) Topical corticosteroid TaroPharma Preparation Date: A Division
Prescribing Information Pr DERMOVATE Cream (clobetasol propionate cream, USP) Pr DERMOVATE Ointment (clobetasol propionate ointment, USP) Topical corticosteroid TaroPharma Preparation Date: A Division
The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis
 Dermatology The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis The image to the left shows an image of skin cells and the proteins which
Dermatology The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis The image to the left shows an image of skin cells and the proteins which
NIZORAL (KETOCONAZOLE) 2% SHAMPOO DESCRIPTION
 NIZORAL (KETOCONAZOLE) 2% SHAMPOO DESCRIPTION NIZORAL (ketoconazole) 2% Shampoo is a red-orange liquid for topical application, containing the broad spectrum synthetic antifungal agent ketoconazole in
NIZORAL (KETOCONAZOLE) 2% SHAMPOO DESCRIPTION NIZORAL (ketoconazole) 2% Shampoo is a red-orange liquid for topical application, containing the broad spectrum synthetic antifungal agent ketoconazole in
Guselkumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis [ID1075]
![Guselkumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis [ID1075] Guselkumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis [ID1075]](/thumbs/83/87872235.jpg) Guselkumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis [ID1075] Thank you for agreeing to give us your organisation s views on this technology and its possible use in the NHS. You can provide a unique
Guselkumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis [ID1075] Thank you for agreeing to give us your organisation s views on this technology and its possible use in the NHS. You can provide a unique
CENTENE PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS NEW DRUG REVIEW 3Q17 July August
 BRAND NAME Dupixent GENERIC NAME dupilumab MANUFACTURER Regeneron DATE OF APPROVAL March 28, 2017 PRODUCT LAUNCH DATE First week of April 2017 REVIEW TYPE Review type 1 (RT1): New Drug Review Full review
BRAND NAME Dupixent GENERIC NAME dupilumab MANUFACTURER Regeneron DATE OF APPROVAL March 28, 2017 PRODUCT LAUNCH DATE First week of April 2017 REVIEW TYPE Review type 1 (RT1): New Drug Review Full review
Eucrisa. Eucrisa (crisaborole) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Eucrisa Page: 1 of 7 Last Review Date: June 22, 2018 Eucrisa Description Eucrisa (crisaborole)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Eucrisa Page: 1 of 7 Last Review Date: June 22, 2018 Eucrisa Description Eucrisa (crisaborole)
Texas Children's Hospital Dermatology Service PCP Referral Guidelines- Atopic Dermatitis (AD)
 Diagnosis: ATOPIC DERMATITIS (AD) Texas Children's Hospital Dermatology Service PCP Referral Guidelines- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) PATIENT ADVICE: Unfortunately, there is no cure for atopic dermatitis, so
Diagnosis: ATOPIC DERMATITIS (AD) Texas Children's Hospital Dermatology Service PCP Referral Guidelines- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) PATIENT ADVICE: Unfortunately, there is no cure for atopic dermatitis, so
Dermatology elective for yr. 5. Natta Rajatanavin, MD. Div. of dermatology Dep. Of Medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol University 23 rd Feb 2015
 Dermatology elective for yr. 5 Natta Rajatanavin, MD. Div. of dermatology Dep. Of Medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol University 23 rd Feb 2015 How to diagnosis and manage eczema and psoriasis. Objectives
Dermatology elective for yr. 5 Natta Rajatanavin, MD. Div. of dermatology Dep. Of Medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol University 23 rd Feb 2015 How to diagnosis and manage eczema and psoriasis. Objectives
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Psoriasis: the management of psoriasis 1.1 Short title Psoriasis 2 The remit The Department of Health has asked NICE: 'to produce
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Psoriasis: the management of psoriasis 1.1 Short title Psoriasis 2 The remit The Department of Health has asked NICE: 'to produce
(minutes for web publishing)
 Dermatology Subcommittee of the Pharmacology and Therapeutics Advisory Committee (PTAC) Meeting held on 20 October 2017 (minutes for web publishing) Dermatology Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance
Dermatology Subcommittee of the Pharmacology and Therapeutics Advisory Committee (PTAC) Meeting held on 20 October 2017 (minutes for web publishing) Dermatology Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance
Derm quiz. Go to this link: goo.gl/forms/kchrhmtzl3vfnlv52. bit.ly/2a8asoy. Scan the QR code with your phone
 Dermatology quiz Derm quiz Go to this link: goo.gl/forms/kchrhmtzl3vfnlv52 OR bit.ly/2a8asoy OR Scan the QR code with your phone Contents Childhood rashes Pigmented lesions Sun damage Pityriasis References
Dermatology quiz Derm quiz Go to this link: goo.gl/forms/kchrhmtzl3vfnlv52 OR bit.ly/2a8asoy OR Scan the QR code with your phone Contents Childhood rashes Pigmented lesions Sun damage Pityriasis References
Brodalumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis [ID878]
![Brodalumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis [ID878] Brodalumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis [ID878]](/thumbs/82/85279721.jpg) Brodalumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis [ID878] Thank you for agreeing to give us your organisation s views on this technology and its possible use in the NHS. You can provide a unique
Brodalumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis [ID878] Thank you for agreeing to give us your organisation s views on this technology and its possible use in the NHS. You can provide a unique
UnitedHealthcare Pharmacy Clinical Pharmacy Programs
 UnitedHealthcare Pharmacy Clinical Pharmacy Programs Program Number 2017 P 2116-3 Program Prior Authorization/Medical Necessity Medications Dupixent (dupilumab) P&T Approval Date 1/2017, 5/2017, 7/2017
UnitedHealthcare Pharmacy Clinical Pharmacy Programs Program Number 2017 P 2116-3 Program Prior Authorization/Medical Necessity Medications Dupixent (dupilumab) P&T Approval Date 1/2017, 5/2017, 7/2017
Novan Announces Promising Clinical Results with SB414
 Novan Announces Promising Clinical Results with SB414 In the recently completed Phase 1b trial for atopic dermatitis, clinical efficacy measures were highly correlated with critical and disease-relevant
Novan Announces Promising Clinical Results with SB414 In the recently completed Phase 1b trial for atopic dermatitis, clinical efficacy measures were highly correlated with critical and disease-relevant
Treatment of Pityriasis Versicolor. A Comparative Study of Topical 4% Potassium Hydroxide Solution Versus 1% Clotrimazole Solution
 British Journal of Medicine & Medical Research 3(4): 2317-2324, 2013 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org Treatment of Pityriasis Versicolor. A Comparative Study of Topical 4% Potassium Hydroxide
British Journal of Medicine & Medical Research 3(4): 2317-2324, 2013 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org Treatment of Pityriasis Versicolor. A Comparative Study of Topical 4% Potassium Hydroxide
Types of Skin Infections
 Anatomy of Skin Types of Skin Infections Bacterial Impetigo Folliculitis Acne Fungal /Parasitic Tinea Pedis Tinea Cruris Tinea Versicolor Tinea Corporis Toenail fungus Allergic/Irritation conditions Dermatitis
Anatomy of Skin Types of Skin Infections Bacterial Impetigo Folliculitis Acne Fungal /Parasitic Tinea Pedis Tinea Cruris Tinea Versicolor Tinea Corporis Toenail fungus Allergic/Irritation conditions Dermatitis
7/13/09. Definition. Infections Due to Malassezia. Case Report 1. Case Report 1 (cont.) Case Report 1 (cont.)
 Definition Infections Due to Malassezia Various species of Malassezia cause both opportunistic, superficial infections and occasionally systemic infections Common superficial infections include: Pityriasis
Definition Infections Due to Malassezia Various species of Malassezia cause both opportunistic, superficial infections and occasionally systemic infections Common superficial infections include: Pityriasis
See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
 Policy: Atopic Dermatitis and Topical Antipsoriatics Reference Number: TCHP.PHAR.18004 Effective Date: 01.01.18 Last Review Date: 10.12.18 Line of Business: Oregon Health Plan Revision Log See Important
Policy: Atopic Dermatitis and Topical Antipsoriatics Reference Number: TCHP.PHAR.18004 Effective Date: 01.01.18 Last Review Date: 10.12.18 Line of Business: Oregon Health Plan Revision Log See Important
Skin disorders. Basal cell carcinoma December 2009 Anthony Ormerod, Sanjay Rajpara, and Fiona Craig ...
 December 29 Anthony Ormerod, Sanjay Rajpara, and Fiona Craig.................................................. ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: (BCC) is the most common form of skin cancer, predominantly affecting
December 29 Anthony Ormerod, Sanjay Rajpara, and Fiona Craig.................................................. ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: (BCC) is the most common form of skin cancer, predominantly affecting
RELEVANT DISCLOSURES ATOPIC DERMATITIS / ECZEMA MANAGING ECZEMA IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN
 RELEVANT DISCLOSURES MANAGING ECZEMA IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN Advisory board member - MEDA (Elidel), Speaking honoraria Bayer (Advantan) Advisory board, consultant, speaker: Pfizer, Abbvie, Janssen, Elli
RELEVANT DISCLOSURES MANAGING ECZEMA IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN Advisory board member - MEDA (Elidel), Speaking honoraria Bayer (Advantan) Advisory board, consultant, speaker: Pfizer, Abbvie, Janssen, Elli
Original Article. Skin Appendage Disord 2015;1: DOI: /
 Original Article Received: June 12, 2015 Accepted: August 11, 2015 Published online: October 17, 2015 Noncorticosteroid Combination Shampoo versus 1% Ketoconazole Shampoo for the Management of Mild-to-Moderate
Original Article Received: June 12, 2015 Accepted: August 11, 2015 Published online: October 17, 2015 Noncorticosteroid Combination Shampoo versus 1% Ketoconazole Shampoo for the Management of Mild-to-Moderate
EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF CLOBETASOL PROPIONATE SHAMPOO IN THERAPY OF PSORIASIS OF THE SCALP
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Platonova et al. SJIF Impact Factor 2.786 Volume 4, Issue 04, 238-246. Research Article ISSN 2278 4357 EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF CLOBETASOL PROPIONATE
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Platonova et al. SJIF Impact Factor 2.786 Volume 4, Issue 04, 238-246. Research Article ISSN 2278 4357 EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF CLOBETASOL PROPIONATE
Dermclinic
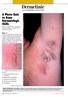 Dermclinic /Dermclinic A Photo Quiz to Hone Dermatologic Skills DAVID L. KAPLAN, MD Series Editor University of Missouri Kansas City, University of Kansas Case 1: Upon his return from a summer visit to
Dermclinic /Dermclinic A Photo Quiz to Hone Dermatologic Skills DAVID L. KAPLAN, MD Series Editor University of Missouri Kansas City, University of Kansas Case 1: Upon his return from a summer visit to
FACTSHEET CICLOSPORIN. Introduction. How does ciclosporin work? When is ciclosporin used?
 Introduction Ciclosporin is a potent immunosuppressant drug that requires supervision by a specialised doctor such as a dermatologist. It was originally used to prevent organ rejection in transplant patients.
Introduction Ciclosporin is a potent immunosuppressant drug that requires supervision by a specialised doctor such as a dermatologist. It was originally used to prevent organ rejection in transplant patients.
Psoriasis is a lifelong condition, with onset
 THERAPEUTICS FOR THE CLINICIAN Clobetasol Propionate Lotion in the Treatment of Moderate to Severe Plaque-Type Psoriasis Jacques Decroix, MD; Henrik Pres, MD; Nicolaï Tsankov, MD; Michel Poncet, PhD; Stéphanie
THERAPEUTICS FOR THE CLINICIAN Clobetasol Propionate Lotion in the Treatment of Moderate to Severe Plaque-Type Psoriasis Jacques Decroix, MD; Henrik Pres, MD; Nicolaï Tsankov, MD; Michel Poncet, PhD; Stéphanie
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Review proposal of NICE guidance no. 82; on the use of pimecrolimus and tacrolimus for atopic eczema Provisional matrix
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Review proposal of NICE guidance no. 82; on the use of pimecrolimus and tacrolimus for atopic eczema Provisional matrix
This PDF is available for free download from a site hosted by Medknow Publications
 Net Study Comparison of clinical efficacy of topical tazarotene.1% cream with topical clobetasol propionate.5% cream in chronic plaque psoriasis: A double-blind, randomized, right-left comparison study
Net Study Comparison of clinical efficacy of topical tazarotene.1% cream with topical clobetasol propionate.5% cream in chronic plaque psoriasis: A double-blind, randomized, right-left comparison study
Study selection Study designs of evaluations included in the review Diagnosis.
 Diagnosis and treatment of worker-related musculoskeletal disorders of the upper extremity: epicondylitis Chapell R, Bruening W, Mitchell M D, Reston J T, Treadwell J R Authors' objectives The objectives
Diagnosis and treatment of worker-related musculoskeletal disorders of the upper extremity: epicondylitis Chapell R, Bruening W, Mitchell M D, Reston J T, Treadwell J R Authors' objectives The objectives
Difference Between Seborrheic Dermatitis and Psoriasis
 Difference Between Seborrheic Dermatitis and Psoriasis www.differencebetween.com Key Difference Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Psoriasis Dermatological conditions are perhaps the most worrisome diseases in the
Difference Between Seborrheic Dermatitis and Psoriasis www.differencebetween.com Key Difference Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Psoriasis Dermatological conditions are perhaps the most worrisome diseases in the
PSORIASIS BEST PRACTICE IN MANAGEMENT
 PSORIASIS BEST PRACTICE IN MANAGEMENT Objectives Discuss pathology of psoriasis Review types of psoriasis Review triggers and factors affecting disease severity Common comorbidity review Review first and
PSORIASIS BEST PRACTICE IN MANAGEMENT Objectives Discuss pathology of psoriasis Review types of psoriasis Review triggers and factors affecting disease severity Common comorbidity review Review first and
Teledermatology Paediatric eczema. Dr Carolyn Charman Consultant Dermatologist Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital
 Teledermatology Paediatric eczema Dr Carolyn Charman Consultant Dermatologist Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital NHS e-referral teledermatology Rapid access to diagnosis / management advice from local integrated
Teledermatology Paediatric eczema Dr Carolyn Charman Consultant Dermatologist Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital NHS e-referral teledermatology Rapid access to diagnosis / management advice from local integrated
Scottish Medicines Consortium
 Scottish Medicines Consortium imiquimod 5% cream (Aldara) No. (385/07) Meda Pharmaceuticals Ltd 04 April 2008 The Scottish Medicines Consortium has completed its assessment of the above product and advises
Scottish Medicines Consortium imiquimod 5% cream (Aldara) No. (385/07) Meda Pharmaceuticals Ltd 04 April 2008 The Scottish Medicines Consortium has completed its assessment of the above product and advises
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Review Proposal of NICE Technology Appraisal no. 81; on the frequency of application of topical Provisional matrix of consultees
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Review Proposal of NICE Technology Appraisal no. 81; on the frequency of application of topical Provisional matrix of consultees
Topical Immunomodulator Step Therapy Program
 Topical Immunomodulator Step Therapy Program Policy Number: 5.01.557 Last Review: 8/2017 Origination: 7/2013 Next Review: 8/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) BCBSKC will provide
Topical Immunomodulator Step Therapy Program Policy Number: 5.01.557 Last Review: 8/2017 Origination: 7/2013 Next Review: 8/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) BCBSKC will provide
Identifying and managing dermatologic toxicities associated with EGFR-inhibitor therapy. An educational resource for healthcare professionals
 Identifying and managing dermatologic toxicities associated with EGFR-inhibitor therapy An educational resource for healthcare professionals What to expect from EGFR-inhibitor therapy The goal of EGFR-inhibitor
Identifying and managing dermatologic toxicities associated with EGFR-inhibitor therapy An educational resource for healthcare professionals What to expect from EGFR-inhibitor therapy The goal of EGFR-inhibitor
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. Flutarzole 0,05% w/w cream, Fluticasone propionate
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Flutarzole 0,05% w/w cream, Fluticasone propionate 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT 1.1. Trade name Flutarzole 1.2. Composition Active substance: Fluticasone
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Flutarzole 0,05% w/w cream, Fluticasone propionate 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT 1.1. Trade name Flutarzole 1.2. Composition Active substance: Fluticasone
Learning Circle: Jan 26, 2011 Childhood Eczema
 Learning Circle: Jan 26, 2011 Childhood Eczema Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, UBC Department of Paediatrics Associate Member, UBC Department of Dermatology
Learning Circle: Jan 26, 2011 Childhood Eczema Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, UBC Department of Paediatrics Associate Member, UBC Department of Dermatology
STUDY. 1% Pimecrolimus, 0.005% Calcipotriol, and 0.1% Betamethasone in the Treatment of Intertriginous Psoriasis
 STUDY 1% Pimecrolimus, 0.005% Calcipotriol, and 0.1% Betamethasone in the Treatment of Intertriginous Psoriasis A Double-blind, Randomized Controlled Study Alexander Kreuter, MD; Anna Sommer, MD; Julia
STUDY 1% Pimecrolimus, 0.005% Calcipotriol, and 0.1% Betamethasone in the Treatment of Intertriginous Psoriasis A Double-blind, Randomized Controlled Study Alexander Kreuter, MD; Anna Sommer, MD; Julia
A case of rosacea fulminans in a pregnant woman
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2018) 26, 122-126 Views and Practice A case of rosacea fulminans in a pregnant woman JE Seol, SH Park, JU Kim, GJ Cho, SH Moon, H Kim Introduction Rosacea fulminans (RF)
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2018) 26, 122-126 Views and Practice A case of rosacea fulminans in a pregnant woman JE Seol, SH Park, JU Kim, GJ Cho, SH Moon, H Kim Introduction Rosacea fulminans (RF)
Atopic dermatitis: tacrolimus vs. topical corticosteroid use
 Atopic dermatitis: tacrolimus vs. topical corticosteroid use Langa Y, BPharm Van der Merwe E, BPharm, MSc (Pharmacology) Correspondence to: Elsabe van der Merwe, e-mail: elsabev@medikredit.co.za Keywords:
Atopic dermatitis: tacrolimus vs. topical corticosteroid use Langa Y, BPharm Van der Merwe E, BPharm, MSc (Pharmacology) Correspondence to: Elsabe van der Merwe, e-mail: elsabev@medikredit.co.za Keywords:
Involving patients in research experiences from the eczema priority setting partnership
 Involving patients in research experiences from the eczema priority setting partnership Professor Kim Thomas, Deputy Director Centre of Evidence Based Dermatology Aims What is a Priority Setting Partnership
Involving patients in research experiences from the eczema priority setting partnership Professor Kim Thomas, Deputy Director Centre of Evidence Based Dermatology Aims What is a Priority Setting Partnership
If looking for a book Psoriasis Cure: Treatments, Natural Remedies and Best Home Managements (Skin Disease, Skin Problems, Skin Diseases and
 Psoriasis Cure: Treatments, Natural Remedies And Best Home Managements (Skin Disease, Skin Problems, Skin Diseases And Disorders Book 1) By Jeff Kennedy READ ONLINE If looking for a book Psoriasis Cure:
Psoriasis Cure: Treatments, Natural Remedies And Best Home Managements (Skin Disease, Skin Problems, Skin Diseases And Disorders Book 1) By Jeff Kennedy READ ONLINE If looking for a book Psoriasis Cure:
Atopic dermatitis Tacrolimus vs topical corticosteroid use
 Atopic dermatitis Tacrolimus vs topical corticosteroid use Yolande Langa, BPharm Elsabé van der Merwe, BPharm; MSc (Pharmacology) Abstract Atopic dermatitis (AD), the dermatologic manifestation of the
Atopic dermatitis Tacrolimus vs topical corticosteroid use Yolande Langa, BPharm Elsabé van der Merwe, BPharm; MSc (Pharmacology) Abstract Atopic dermatitis (AD), the dermatologic manifestation of the
Lead team presentation
 Lead team presentation Dupilumab for treating adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis [ID1048] 1 st Appraisal Committee meeting Committee B Chair: Amanda Adler Lead team: Diar Fattah, Danielle
Lead team presentation Dupilumab for treating adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis [ID1048] 1 st Appraisal Committee meeting Committee B Chair: Amanda Adler Lead team: Diar Fattah, Danielle
Tinea Incognito Incorrect Initial Diagnosis. Case Series Presentation with Emphasis on the Mycological Examination
 CASE SERIES DERMATOLOGY // INTERNAL MEDICINE Tinea Incognito Incorrect Initial Diagnosis. Case Series Presentation with Emphasis on the Mycological Examination Anca Chiriac 1,2,3, Piotr Brzezinski 4, Cristian
CASE SERIES DERMATOLOGY // INTERNAL MEDICINE Tinea Incognito Incorrect Initial Diagnosis. Case Series Presentation with Emphasis on the Mycological Examination Anca Chiriac 1,2,3, Piotr Brzezinski 4, Cristian
I n order to give the best care to patients and families,
 286 ARCHIMEDES Towards evidence based medicine for paediatricians Edited by Bob Phillips... I n order to give the best care to patients and families, paediatricians need to integrate the highest quality
286 ARCHIMEDES Towards evidence based medicine for paediatricians Edited by Bob Phillips... I n order to give the best care to patients and families, paediatricians need to integrate the highest quality
1 / 5. الابط في الحبيبي التقرن نظير=- parakeratosis Axillary granular
 1 / 5 الابط في الحبيبي التقرن نظير=- parakeratosis Axillary granular Axillary Granular manifesting cutaneous parakeratosis antiperspirants agents. sweating, granular Granular parakeratosis, and, folds.
1 / 5 الابط في الحبيبي التقرن نظير=- parakeratosis Axillary granular Axillary Granular manifesting cutaneous parakeratosis antiperspirants agents. sweating, granular Granular parakeratosis, and, folds.
Area Drug and Therapeutics Committee Prescribing Supplement No 3 November 2003
 Area Drug and Therapeutics Committee Prescribing Supplement No 3 In this issue Drugs currently being considered by the SMC advice due on 8 December 2003. SMC Notice of meeting: Patient power Making a Difference,
Area Drug and Therapeutics Committee Prescribing Supplement No 3 In this issue Drugs currently being considered by the SMC advice due on 8 December 2003. SMC Notice of meeting: Patient power Making a Difference,
Psoriasis. What is Psoriasis? What causes psoriasis? Medical Topics Psoriasis
 1 Psoriasis What is Psoriasis? Psoriasis is a long standing inflammatory non-contagious skin disease which waxes and wanes with triggering factors. There is a genetic predisposition in psoriasis. Internationally,
1 Psoriasis What is Psoriasis? Psoriasis is a long standing inflammatory non-contagious skin disease which waxes and wanes with triggering factors. There is a genetic predisposition in psoriasis. Internationally,
Prescribing Information. Taro-Clobetasol. Taro-Clobetasol
 Prescribing Information Pr Taro-Clobetasol Clobetasol Propionate Cream USP, 0.05% w/w Pr Taro-Clobetasol Clobetasol Propionate Ointment USP, 0.05% w/w Therapeutic Classification Topical corticosteroid
Prescribing Information Pr Taro-Clobetasol Clobetasol Propionate Cream USP, 0.05% w/w Pr Taro-Clobetasol Clobetasol Propionate Ointment USP, 0.05% w/w Therapeutic Classification Topical corticosteroid
An Update on Topical Therapy for Atopic Dermatitis
 An Update on Topical Therapy for Atopic Dermatitis Amy S. Paller, M.D. Professor and Chair of Dermatology Professor of Pediatrics Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, Illinois Disclosures
An Update on Topical Therapy for Atopic Dermatitis Amy S. Paller, M.D. Professor and Chair of Dermatology Professor of Pediatrics Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, Illinois Disclosures
Tinea: Head to Toe A dermatophyte tour of human skin. Tour de Tinea Head to Toe. Tips for Tinea Head to Toe. Psoriasis. Non-inflammatory Tinea Capitis
 Tinea: Head to Toe A dermatophyte tour of human skin Renee Howard, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Dermatology, UCSF Tour de Tinea Head to Toe Tips for Tinea Head to Toe Capitis Faciei Corporis Pedis
Tinea: Head to Toe A dermatophyte tour of human skin Renee Howard, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Dermatology, UCSF Tour de Tinea Head to Toe Tips for Tinea Head to Toe Capitis Faciei Corporis Pedis
Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children
 May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
Rashes in the elderly
 Clinical practice 29 Rashes in the elderly In this article we aim to highlight some of the commoner skin conditions one might expect to see in an elderly population, their typical features and treatments.
Clinical practice 29 Rashes in the elderly In this article we aim to highlight some of the commoner skin conditions one might expect to see in an elderly population, their typical features and treatments.
Clinical Trial Report Synopsis
 Clinical Trial Report Synopsis A phase 2a, proof of concept trial, testing twice daily application of LEO 124249 ointment 30 mg/g in the treatment of mild to moderate inverse psoriasis Design of trial:
Clinical Trial Report Synopsis A phase 2a, proof of concept trial, testing twice daily application of LEO 124249 ointment 30 mg/g in the treatment of mild to moderate inverse psoriasis Design of trial:
