What are the Inhalant drugs?
|
|
|
- Vernon Cunningham
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Why and why not? Advantages: - Less systemic toxicity - More rapid onset of medication - Delivery to target of action - Higher concentrations available in the lung Disadvantages: - Time and effort consuming - Limitation of delivery device
2 What are the Inhalant drugs? Antiallergic agents Budesonide Cromolyn sodium Bronchodilators Ventolin nebules (βagonist) Bricanyl solution (βagonist) Atrovert nebulizer solution (anticholinergic)
3 Inhalant drugs Mucolytic agents Acetein (Acetylcysteine) Mistabron (Mesna) Antimicrobials Tobramycin Pentamidine Ribavirin Amphotericin
4 Inhalant drugs Immune modulators Cyclosporine Interferon α Interferon γ Vaso-active Prostacyclin Nitric oxide
5 Inhalant drugs Anesthetics Other Opioids Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor Surfactant Interleukin II Gene therapy vectors
6 Regions of Drug absorption in the Pulomonary Epithelium
7 Respiratory tract characteristics Large surface area, good vascularization, immense capacity for solute exchange, ultra-thinness of the pulmonary epithelium Conducting region : Nasal cavity, nasopharynx, bronchi, bronchioles Respiratory region : respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts and sacs
8 Particle Size MMAD: mass median aerodynamic diameter MMAD <1μm: exhaled MMAD 1~5μm: target MMAD >5μm: oropharynx Strict control of MMAD of the particles ensures the reproducibility of aerosol deposition and retention.
9 Ideal Particle Size optimal airway deposition
10 Particle Size
11 Device for Inhalation Therapy Selections of device include: 1.Nebulizer: small volume, large volume, ultrasonic, pneumatic 2.Metered dose inhaler, MDI 3.Dry powder inhaler, DPI
12 Metered-dose inhalers A liquid propellant A metering valve that dispenses a constant volume of a solution or suspension of the drug in the propellant. Inhalation technique is critical for optimal drug delivery Actuating a MDI out of synchrony may cause negligible lower airway delivery Mainly oropharyngeal deposition Protein denaturation
13 Dry powder inhalers No propellant Breath-activated, and patient coordination is not as important an issue. The drug is formulated in a filler and contained in a capsule that is placed in the device and punctured to release the powder. Proteins and macromolecules are more stable in dry powder form, this approach has been preferred for delivery of these compounds by the inhalational route
14 Nebulizers Patient cooperation and coordination is not as critical Commercially available nebulizers deliver 12% to 20% of the nebulized dose into the bronchial tree. Heterogeneous drops Protein denaturation
15 Nebulizers
16 AEROSOLS Are pressured dosage forms containing one or more active ingredients which upon actuation emit a fine dispersion of liquid and/or solid materials in gaseous medium The term Pressurized package is commonly used when referring to the aerosol container or completed product. Pressure is applied to the aerosol system through the use of one or more liquefied or gaseous propellants.
17 Aerosol Similarity with other dosage form: Formulation Product stability Therapeutic efficacy However they differ from most other dosage form: Dependence upon the function of the container Valve assembly Propellant, the added component
18 Pressurized package Pressure is applied to the aerosol system through the use of one or more propellants. Upon activation of the valve assembly of the aerosol, it is the pressure exerted by the propellant which forces the contents of the package out through the opening of the valve. The physical form of the emitted is dependent upon the formulation of the product and and the type of valve employed
19 AEROSOLS Aerosol packaging refers to products packaged in a pressurized container having a valve that permits controlled product release as required. - Depending on the formulation, the valve system and the means of pressurizing, aerosols can be designed to release product in forms ranging from fine mists to heavy pastes. - Usages: Personal care products(perfumes, shaving creams, deodorants, and hair sprays), household products (polishes, cleaners, and room fresheners), smaller market portions(paints, automotive products, and insect sprays), food(limited). - The advantage of aerosols: their ability to disperse product into much finer particles that stayed suspended in the air for a much longer time than was available from other systems.
20 AEROSOLS Aerosol Propellants. -A typical aerosol product has a liquid phase and a vapor phase The liquid phase: contains the product to be expelled. The vapor phase: at an increased pressure and will force the product up the dip tube and expel it through the nozzle whenever the valve is opened. - The product typically occupies about 75%, but never more than 92.5%, of the available space. - Well-designed aerosol containers will deliver 95% or better of the contained product.
21 AEROSOLS Figure 5.14 In a two-phase aerosol, the propellant is dissolved in the product. In a three-phase system, the propellant forms a separate layer
22
23 Aerosol Aerosol product may be design to expel their content as a Fine mist Coarse wet or dry spray Steady stream or Stable or fast breaking foams. The physical form for a given aerosol is based on the intended use of the product. Eg.for inhalation therapy ( treatment of asthma)the particles shall be an the form of fine liquid mist or finely divided small particles.
24 Aerosol Particles less than 6 μm will reach respiratory bronchioles and less than 2 μm will reach alveolar ducts and alveoli. Particle size for dermatological spray would be more coarse.
25 AEROSOLS Aerosols used to provide an airborne mist are termed space sprays. Examples: room disinfectants, room deodorizers, and space insecticides. Aerosols intended to carry the active ingredient to a surface are termed Surface sprays or surface coatings. Examples: dermatologic aerosols, pharmaceutical aerosols, as personal deodorant sprays, cosmetic hair lacquers and sprays, perfumes and cologne sprays, shaving lathers, toothpaste, surface pesticide sprays, paint sprays and others.
26 Advantages of the Aerosol Dosage Forms 1. A portion of medication may be easily withdrawn from the package without contamination or exposure to the remaining material. 2. Hermetic character, the aerosol container protects medicinal agents from atmospheric oxygen, moisture and even from light. 3. Topical medication may be applied in a uniform, thin layer to the skin, without touching the affected area thus, reducing irritation. 4. By proper formulation and valve control, the physical form and the particles size of the emitted product may be controlled which may contribute to the efficacy of a drug. Example: the fine controlled mist of an inhalant aerosol. Through the use of metered valves, dosage may be controlled. 5. Aerosol application is clean process, requiring little or no wash-up by the user.
27 The Aerosol Principle As aerosol formulation consists of 2 components: 1. The product concentrate is the active ingredient of the aerosol combined with the required adjuncts, such as antioxidants, surface-active agents, and solvents, to prepare a stable and efficacious product. 2. The propellant when the propellant is a liquefied gas or a mixture of liquefied gases, it frequently serves the dual role of propellant and solvent or vehicle for the product concentrate. In some aerosols non liquefied compressed gases such as carbon dioxide, nitrogen and nitrous oxide are used as propellants
28 Aerosol components Propellants: 1. Halogenated derivative of hydrocarbons Trichloromonofluoromethane; Dichlorodifluoromethane; Dichlorotetrafluoroethane; Chloropentafluoroethane; Monochlorodifluoroethane; Octafluorocyclobutane 2. Low molecular weight hydrocarbons: butane, pentane 3. Compressed gas 28 Carbon dioxide, Nitrogen, Nitrous oxide
29 Test for propellants Vapour pressure Density Gas chromatography test for purity Moisture, halogen, non-volatile residue
30 Aerosol Container and Valve Assembly The effectiveness of the aerosol depends on: 1. proper combination of formulation, 2. container 3. valve assembly. The formulation must not chemically interact with the container or valve components to avoid unstability of the formulation. The container and the valve must be capable of withstanding the pressure required by the product It must be corrosive resistant Valve must contribute to the form of the product to be emitted.
31 AEROSOL SYSTEMS SPACE AEROSOLS usually operate at pressures between 30 to 40 psig (pounds per square inch gauge) at 70 0 F and may contain as much as 85% propellant SURFACE AEROLSOLS commonly contain 30 to 70% propellant with pressures between 25 to 55 psig at 70 0 F FOAM AEROSOLS usually operate between 35 and 55 psig at 70 0 F and may contain only 6 to 10% propellant
32 AEROSOL SYSTEMS TWO PHASE SYSTEM = comprised (1) the liquid phase propellant and product concentrate (2) the vapor phase THREE PHASE SYSTEM = comprised (1) layer of water immiscible liquid propellant, (2) layer of highly aqueous product concentrate, and (3) vapor pressure COMPRESSED GAS SYSTEM = compressed rather liquefied, gases may be used to pressure aerosols. The pressure of the compressed gas contained in the headspace of the aerosol container forces the product concentrate up the dip tube and out of the valve Examples: Nitrogen; carbon dioxide; nitrous oxide
33 Containers 1. Glass, uncoated or plastic coated 2. Metal, including tinplated steel, aluminum, and stainless steel 3. Plastics The selection of containers for an aerosol product is based on 1. Its adaptability to production methods 2. Compatibility with formulation components 3. Ability to sustain the pressure intended for the product 4. The interest in design and aesthetic appeal on the part of the manufacturer, and 5. Cost
34 VALVE ASSEMBLY The function of the valve assembly is to permit the expulsion of the contents of the can in the desired form, at the desired rate, and, in the case of metered valve, in the proper amount or dose. The materials used in the manufacture of valves must be inert and approved. Among the materials used in making valve parts are plastic, rubber, aluminum, and stainless steel.
35 Actuators Actuators: is the fitting attached to an aerosol valve stem, which when depressed or moved, open the valve, and directs the spray containing the drug preparation to the desired area.
36 Parts of Aerosol Valve Actuator Stem Gasket Spring Mounting cup Housing Dip tube The actuator is the button which the user presses to activate the valve assembly for the emission of the product. The stem supports the actuator and delivers the formulation in the proper form to the chamber of the actuat The gasket, placed snugly with the stem, serves to prevent leakage of the formulation when the valve is in closed position The spring holds the gasket in place and also is the mechanism by which the actuator retracts when pressure is released, thereby returning the valve to the closed position The mounting cup, which is attached to the aerosol can or container, serves to hold the valve in place. The housing, located directly below the mounting cup, serves as the link between the dip tube and the stem and actuator. With the stem, its orifice helps to determine the delivery rate and the form in which the product is emitted. The dip tube, which extends from the housing down into the product, serves to bring the formulation from the container to the valve.
37 Valve Cup :- typically constructed from tinplated steel, or aluminium. Outer Gasket :- this is the seal between the valve cup and the aerosol can. Valve Housing :- contains the valve stem, spring and inner gasket. Valve Stem :- in effect, the tap through which the product flows. Inner Gasket :- covers the hole in the valve stem. Valve Spring :- usually stainless steel. Dip Tube :- allows the liquid to enter the valve. Actuator (not shown) :- fits onto the valve stem.
38 Aerosol valve
39
40
41
42 HOW AEROSOLS ARE FILLED These all have to be assembled, and this is achieved using automatic filling machinery which can operate at speeds in excess of 400 cans per minute. For conventional aerosols the key steps in the filling process are:- 1. Start with an empty aerosol container. This will be made of tinplate or aluminium, or perhaps glass. The capacity of the container will be greater than that which is declared on the pack. 2. The product, usually in the form of a liquid, is now added. This contains all the active ingredients, except for the propellant. The volume of liquid is very carefully controlled to ensure that it conforms with Weights & Measures legislation. 3. The Aerosol valve is now fitted (crimped) to the can. This is a very critical operation and the crimping machinery has to be carefully set up to ensure that the can / valve seal does not leak.
43
44 Where a 'small' actuator is to be used, this will be fitted on to the valve before it is crimped onto the can. The propellant is now injected under pressure, through the valve. The propellant may be in the form of a liquified gas, or a compressed gas. If a liquified gas is used it will exist as both a liquid, and vapour in the aerosol can head space. The volume of liquid in the can will increase. If a compressed gas is used, it will usually only be in the head space, above the liquid in the can, and there will be little or no increase in liquid volume. Again, the volume of liquid is very carefully controlled to ensure that it conforms with Weights & Measures legislation.the aerosol is now in a pressurised state due to the addition of the propellant. The cans are now immersed in a water bath at 50 C to check for any leaks. Any cans that leak are rejected. If a large, or special, actuator is required it is fitted now. Where necessary, a dust cap is also fitted. Finally the can will be date / batch coded, and shrink wrapped or boxed as required.
45 Testing the Filled Containers Container is tested under various environmental conditions 1. Leaks 2. Weakness in the valve assembly or container 3. Proper function s of the valve 4. The valve discharge rate - determine by discharging a portion of the contents of a previously weighed aerosol during a given period of time, and calculating, by the difference in weight, the grams of contents discharged per unit of time. 5. Particle size distribution of the spray 6. For accuracy and reproducibility of dosage when using metered valves
46 Sample Products SALBUTAMOL LIBRENTIN INHALER
47 Aerosol characteristics: Particle size distribution Uniformity of dose for metered valve Delivery rate Wetness and temperature of the spray Spray pattern Velocity of spray Foam density Fluid viscosity 47
48 Extractable substances Leaching of extractable from plastic components into the formulation is a potential serious problem. Extractable include: antioxidants, plasticizers, monomers, nitrosamine, vulcanization accelerators, etc., should be identified and minimized. The composition and the quality of materials used in the manufacturing of the valve components must be carefully selected and controlled. Their compatibility with formulation components should be well established to minimize change in the medication delivery, leak rate, impurity profile of the drug product over time ربيع الثاني 1432
49 Containers: Made of glass, plastic or metal as stainless steel, aluminum, tin. Extractable or leachable and particulates on the internal surfaces of containers should be controlled. Manufacturing process controls usually include: monitoring of proper formulation and propellant fill weight and pressure testing, leak testing, and valve function testing of the finished aerosol. 49
50 Aerosols Topical Aerosols Aerosols packages for topical use on the skin which include: Antiinfectives: Povidone - iodine, Tolnaftate Adrenocortical steroids: Betamethasone and Triamcinolone Acetonide Local anesthetic: Dibucaine hydrochloride Vaginal and Rectal Aerosols Aerosols foams are commercially available containing estrogenic substances and contraceptives agents. Example: ProctoFoam - contains pramoxine hydrochloride - use to relieve inflammatory anorectal disorder
51 Topical Aerosols Delivery rate and delivered amount Only perform these tests on containers fitted with continuous valves. Procedure: Select not less than 4 aerosol containers, weigh, actuate each valve for 5 seconds, weigh each container again. Calculate the average delivery rate in g per second, for each container. Calculate the total weight loss from the container. This is the delivered amount. 51
52 Pressure test Only perform this test on topical aerosols fitted with continuous valves. Select 4 aerosol containers, determine the pressure in each container by placing a calibrated pressure gauge on the valve stem. 52
53 53 Leakage Test Only perform on topical aerosols fitted with continuous valves. Select 12 aerosol containers, weigh each container, mg W 1, allow to stand in upright position at temp. 25 C for not less than 3 days, weigh again each container, record the weight, mg as W 2, calculate the leakage rate mg/year. 365x(24/t) (W1-w2)
54 Flame extension test The product is sprayed for 4 seconds into a flame, the extension of the flame is measured by a ruler. Spray pattern test By spraying the content of the container on a rotating paper impregnated with a dye solution, coloured spots are produced Homogeneity of the colour indicates a homogenous spray pattern. 54
55 Uniformity of dosage units The test is required for aerosols fitted with dose-metered valves, metered dose inhaler and dry powder inhalers. The drug content of at last 9 of the 10 doses collected from one inhaler, are between 75% and 125% of label claim, and none is outside the range of 65% to 135% of the label claim. If the contents of not more than 3 doses are outside the range of 75% to 125%, but within the range of 65% to 135% of label claim, select 2 additional inhalers and follow the procedure for analyzing 10 doses from each. The requirements are met if not more than 3 results, out of the 30 values, lie outside the range of 75% to 125% of label claim and none is outside the range of 65%to 135% of label claim. 55
56 Particle size The particle or droplet size distribution in the spray discharged from metered-dose inhalers or from dry powder inhalers are important characteristics used in judging inhaler performance. 56
57 Inhaler aerosol ربيع الثاني 1432
58 INHALANTS Are drugs or combinations of drugs that by virtue of their high vapor pressure can be carried by an air current into the nasal passage where they exert their effect. The device in which they are administered is termed an inhaler. Examples: 1. Amyl Nitrite Inhalant - treatment of anginal pain 2. Propylhexedrine Inhalant - nasal decongestant
59 INHALATIONS Inhalations are drugs or solutions of drugs administered by the nasal or oral respiratory route. A widely used instrument capable of producing fine particles for inhalation therapy is the NEBULIZERS. When volatile medication is added to the water in the chamber, the medication is volatilizes and also inhaled by the patient, HUMIDIFIERS will be used.
60 Common Inhaled Steroids
REFERENCES OVERVIEW ADVANTAGES AEROSOLS. Aerosols. and Foams
 COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of Monash University pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968
COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of Monash University pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968
NEBULIZERS, METERED DOSE INHALERS, AND DRY POWDER INHALERS
 NEBULIZERS, METERED DOSE INHALERS, AND DRY POWDER INHALERS Douglas S. Gardenhire, Ed.D, RRT-NPS MODULE 1 Manipulate Small Volume Nebulizers by Order or Protocol 1 Objectives for Module 1 At the end of
NEBULIZERS, METERED DOSE INHALERS, AND DRY POWDER INHALERS Douglas S. Gardenhire, Ed.D, RRT-NPS MODULE 1 Manipulate Small Volume Nebulizers by Order or Protocol 1 Objectives for Module 1 At the end of
PREMIXES FOR MEDICATED FEEDING STUFFS FOR VETERINARY USE. Praeadmixta ad alimenta medicata ad usum veterinarium. Effervescent powders
 Preparations for inhalation administered in or with water or another suitable liquid. They may also be swallowed directly. They are presented as single-dose or multidose preparations. Where applicable,
Preparations for inhalation administered in or with water or another suitable liquid. They may also be swallowed directly. They are presented as single-dose or multidose preparations. Where applicable,
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON THE PHARMACEUTICAL QUALITY OF INHALATION AND NASAL PRODUCTS
 European Medicines Agency Inspections London, 16 February 2005 Doc Ref.: EMEA/CHMP/QWP/49313/2005 corr. COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON THE PHARMACEUTICAL QUALITY OF
European Medicines Agency Inspections London, 16 February 2005 Doc Ref.: EMEA/CHMP/QWP/49313/2005 corr. COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON THE PHARMACEUTICAL QUALITY OF
Formulation Considerations for Inhaled Products
 Formulation Considerations for Inhaled Products Formulation Considerations of Inhaled Products Inhalation Therapy Nebulizers and Formulations Dry Powder Inhalers and Formulations Metered Dose Inhalers
Formulation Considerations for Inhaled Products Formulation Considerations of Inhaled Products Inhalation Therapy Nebulizers and Formulations Dry Powder Inhalers and Formulations Metered Dose Inhalers
Device Change Management for Inhaled Products. Loy Britto, Ph.D. GlaxoSmithKline ISAM Congress Munich 2015
 Device Change Management for Inhaled Products Loy Britto, Ph.D. GlaxoSmithKline ISAM Congress Munich 2015 Topics to be covered Update on ISO/TC 084/WG 15: Guidelines for development of drug products- Quality
Device Change Management for Inhaled Products Loy Britto, Ph.D. GlaxoSmithKline ISAM Congress Munich 2015 Topics to be covered Update on ISO/TC 084/WG 15: Guidelines for development of drug products- Quality
All About Aerosols. Jim Hammer Pharmasol Corporation
 All About Aerosols Jim Hammer Pharmasol Corporation Purpose of this presentation Many formulating chemists are comfortable making liquids, creams, lotions, and gels, but when it comes to aerosols, there
All About Aerosols Jim Hammer Pharmasol Corporation Purpose of this presentation Many formulating chemists are comfortable making liquids, creams, lotions, and gels, but when it comes to aerosols, there
Hazardous Substances
 1 9 x Which strains and pollutants is the lung subject to while working? x How do possible strains and pollutants affect us? 2 9 Potential danger Aerosols are extremely fine AIRBORNE particles as solid
1 9 x Which strains and pollutants is the lung subject to while working? x How do possible strains and pollutants affect us? 2 9 Potential danger Aerosols are extremely fine AIRBORNE particles as solid
CSPA AEROSOL GUIDE NINTH EDITION TABLE OF CONTENTS. SECTION B INTRODUCTION: CSPA Aerosol Products Division Committees
 SECTION A : AEROSOL GUIDE -- 9 th EDITION CD INTRODUCTION A1 A2 SECTION B INTRODUCTION: CSPA Aerosol Products Division Committees Rosters for Aerosol Products Division Committees -- September 2009 B1 B6
SECTION A : AEROSOL GUIDE -- 9 th EDITION CD INTRODUCTION A1 A2 SECTION B INTRODUCTION: CSPA Aerosol Products Division Committees Rosters for Aerosol Products Division Committees -- September 2009 B1 B6
Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: CARE AND USE OF NEBULIZER AND INTERMITTENT POSITIVE PRESSURE BREATHING DEVICE
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 421 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: CARE AND USE OF NEBULIZER AND INTERMITTENT POSITIVE PRESSURE
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 421 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: CARE AND USE OF NEBULIZER AND INTERMITTENT POSITIVE PRESSURE
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer
 Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
GRAPEVINE DISEASES. Formulation Information & Adjuvants. Online Guide To. Virginia Tech
 Online Guide To GRAPEVINE DISEASES Virginia Tech Formulation Information & Adjuvants Ashley L. Myers Grape Pathology Extension Specialist, Department of Plant Pathology, Physiology, and Weed Sciences,
Online Guide To GRAPEVINE DISEASES Virginia Tech Formulation Information & Adjuvants Ashley L. Myers Grape Pathology Extension Specialist, Department of Plant Pathology, Physiology, and Weed Sciences,
Respiratory Therapy. Medical/Scientific/General Background
 Respiratory Therapy Medical/Scientific/General Background Marketing Europe Dr. Rainer Jakobs PMM Europe 1 Dr. Rainer Jakobs, PMM Europe RT Medical/Scientific/General Background 2 Dr. Rainer Jakobs, PMM
Respiratory Therapy Medical/Scientific/General Background Marketing Europe Dr. Rainer Jakobs PMM Europe 1 Dr. Rainer Jakobs, PMM Europe RT Medical/Scientific/General Background 2 Dr. Rainer Jakobs, PMM
Investigations into Domestic Household Aerosols Air Freshener and body spray
 ILASS Europe 2010, 23rd Annual Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Brno, Czech Republic, September 2010 Investigations into Domestic Household Aerosols Air Freshener and body spray R.A.
ILASS Europe 2010, 23rd Annual Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Brno, Czech Republic, September 2010 Investigations into Domestic Household Aerosols Air Freshener and body spray R.A.
Metered Dose Inhaler Technology
 Metered Dose Inhaler Technology Edited by Tol S. Purewal and David J. W. Grant Interpharm Press, Inc. Buffalo Grove, Illinois Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 1 T. S. Purewal Definition of the Metered Dose Inhaler
Metered Dose Inhaler Technology Edited by Tol S. Purewal and David J. W. Grant Interpharm Press, Inc. Buffalo Grove, Illinois Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 1 T. S. Purewal Definition of the Metered Dose Inhaler
Achieving Optimal Particle Size Distribution in Inhalation Therapy
 Achieving Optimal Particle Size Distribution in Inhalation Therapy By Bob Bruno Inhalation therapy has proven to be an effective method of administering a number of pharmaceuticals for more than a century.
Achieving Optimal Particle Size Distribution in Inhalation Therapy By Bob Bruno Inhalation therapy has proven to be an effective method of administering a number of pharmaceuticals for more than a century.
Appendix M: Device Technique
 Nursing Care of Dyspnea: The 6th Vital Sign in Individuals with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Appendix M: Device Technique Medications: Inhalation Devices Medications come in many forms.
Nursing Care of Dyspnea: The 6th Vital Sign in Individuals with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Appendix M: Device Technique Medications: Inhalation Devices Medications come in many forms.
Paper No.: 13 Paper Title: Food Additives Module 2. Functional Classification of Food Additives
 Paper No.: 13 Paper Title: Food Additives Module 2. Functional Classification of Food Additives 2.1 Introduction According to the Food Protection Committee of the Food and Nutrition Board, food additives
Paper No.: 13 Paper Title: Food Additives Module 2. Functional Classification of Food Additives 2.1 Introduction According to the Food Protection Committee of the Food and Nutrition Board, food additives
Metered dose Alternative technologies
 FACT SHEET 14 Aerosols UNEP Ozone Secretariat UNEP Ozone Secretariat Background Workshop Material for on HFC HFC Workshop, management: 2015 technical issues Bangkok, 20 and 21 April 2015 1. Description
FACT SHEET 14 Aerosols UNEP Ozone Secretariat UNEP Ozone Secretariat Background Workshop Material for on HFC HFC Workshop, management: 2015 technical issues Bangkok, 20 and 21 April 2015 1. Description
Metering Valve Design and Material Selection; How can this be chosen to maximize product performance?
 Metering Valve Design and Material Selection; How can this be chosen to maximize product performance? B. Grosjean Medical Plastics 2007 Inhalation Devices for Medicine Delivery 2007, 1-2 October 2007,
Metering Valve Design and Material Selection; How can this be chosen to maximize product performance? B. Grosjean Medical Plastics 2007 Inhalation Devices for Medicine Delivery 2007, 1-2 October 2007,
COMPARISON OF THE RESPIRABLE FRACTION FROM THREE DIFERENT DPI DEVICES
 COMPARISON OF THE RESPIRABLE FRACTION FROM THREE DIFERENT DPI DEVICES Miriam Sanz Cermeño and Helena Maria Cabral Marques UCTF, Faculdade de Farmácia, Universidade de Lisboa, PORTUGAL 1. Introduction Inhalation
COMPARISON OF THE RESPIRABLE FRACTION FROM THREE DIFERENT DPI DEVICES Miriam Sanz Cermeño and Helena Maria Cabral Marques UCTF, Faculdade de Farmácia, Universidade de Lisboa, PORTUGAL 1. Introduction Inhalation
905 UNIFORMITY OF DOSAGE UNITS
 Change to read: 905 UNIFORMITY OF DOSAGE UNITS [ NOTE In this chapter, unit and dosage unit are synonymous. ] To ensure the consistency of dosage units, each unit in a batch should have a drug substance
Change to read: 905 UNIFORMITY OF DOSAGE UNITS [ NOTE In this chapter, unit and dosage unit are synonymous. ] To ensure the consistency of dosage units, each unit in a batch should have a drug substance
Understanding cascade impaction and its importance for inhaler testing
 Understanding cascade impaction and its importance for inhaler testing Mark Copley, Technical Sales Manager Inhalation product development is an important area of activity for the pharmaceutical sector.
Understanding cascade impaction and its importance for inhaler testing Mark Copley, Technical Sales Manager Inhalation product development is an important area of activity for the pharmaceutical sector.
Laboratory Pesticide Formulations, Labels, and Safety
 1 Laboratory Pesticide Formulations, Labels, and Safety I. Pesticide Formulations Pesticides are rarely used in their pure form (technical grade). They are processed into a usable form for direct application.
1 Laboratory Pesticide Formulations, Labels, and Safety I. Pesticide Formulations Pesticides are rarely used in their pure form (technical grade). They are processed into a usable form for direct application.
HARD TWO-PIECE HPMC CAPSULES FOR PHARMACEUTICAL APPLICATIONS IN INHALATION
 HARD TWO-PIECE HPMC CAPSULES FOR PHARMACEUTICAL APPLICATIONS IN INHALATION 2 3 QUALICAPS HISTORY Over one hundred years of experience in the manufacturing and filling of hard two-piece capsules Qualicaps
HARD TWO-PIECE HPMC CAPSULES FOR PHARMACEUTICAL APPLICATIONS IN INHALATION 2 3 QUALICAPS HISTORY Over one hundred years of experience in the manufacturing and filling of hard two-piece capsules Qualicaps
Aerosol Delivery Devices
 Aerosol Delivery Devices Judy Bielenda LRRT Respiratory Therapy Clinical Specialist Pediatric Asthma Education Coordinator University of Michigan C.S. Mott Children s and Von Voigtlander Women s Hospital
Aerosol Delivery Devices Judy Bielenda LRRT Respiratory Therapy Clinical Specialist Pediatric Asthma Education Coordinator University of Michigan C.S. Mott Children s and Von Voigtlander Women s Hospital
OPTIMISATION OF SALBUTAMOL SUSPENSION AS METERED DOSE INHALATION (MDI) AND COMPARISON WITH A MARKETED MDI SUSPENSION
 Khale & Bajaj, IJPSR, 2011; Vol. 2(2): 391-403 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2011), Vol. 2, Issue 2 (Research Article) Received on 11 October, 2010; received in revised form 12 November, 2010; accepted 18 January,
Khale & Bajaj, IJPSR, 2011; Vol. 2(2): 391-403 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2011), Vol. 2, Issue 2 (Research Article) Received on 11 October, 2010; received in revised form 12 November, 2010; accepted 18 January,
FORMULATION CHOICE. How and why they are chosen. Dr Andy Fowles On behalf of ECPA Specification Expert Group
 FORMULATION CHOICE How and why they are chosen Dr Andy Fowles On behalf of ECPA Specification Expert Group Topics Why formulate? How to identify formulation options Drivers Principle formulation type overview
FORMULATION CHOICE How and why they are chosen Dr Andy Fowles On behalf of ECPA Specification Expert Group Topics Why formulate? How to identify formulation options Drivers Principle formulation type overview
Material Safety Data Sheet:
 Date Updated: 05-2013 Material Safety Data Sheet: sspions PDMS 1. Product and Company Information PRODUCT NAME: sspions PDMS CHEMICAL NAME: single Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (sspions) dispersed
Date Updated: 05-2013 Material Safety Data Sheet: sspions PDMS 1. Product and Company Information PRODUCT NAME: sspions PDMS CHEMICAL NAME: single Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (sspions) dispersed
PARENTERAL PREPARATIONS
 PARENTERAL PREPARATIONS INTRODUCTION Parenteral (Gk, para enteron, beside the intestine) dosage forms differ from all other drug dosage forms, because they are injected directly into body tissue through
PARENTERAL PREPARATIONS INTRODUCTION Parenteral (Gk, para enteron, beside the intestine) dosage forms differ from all other drug dosage forms, because they are injected directly into body tissue through
Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
Chapter 7, Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration Caution: Administering medications is business Always
 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Chapter 7, Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration Caution: Administering medications is business Always take appropriate Standard measures
1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Chapter 7, Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration Caution: Administering medications is business Always take appropriate Standard measures
Citation for published version (APA): Westerman, E. M. (2009). Studies on antibiotic aerosols for inhalation in cystic fibrosis s.n.
 University of Groningen Studies on antibiotic aerosols for inhalation in cystic fibrosis Westerman, Elisabeth Mechteld IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
University of Groningen Studies on antibiotic aerosols for inhalation in cystic fibrosis Westerman, Elisabeth Mechteld IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
Division 1 Introduction to Advanced Prehospital Care
 Division 1 Introduction to Advanced Prehospital Care Chapter 7 Intravenous Access and Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration Topics Aseptic Technique Medication
Division 1 Introduction to Advanced Prehospital Care Chapter 7 Intravenous Access and Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration Topics Aseptic Technique Medication
Process Drift and it s Resolution in the Manufacture of Drug Products. MDI s and DPI s Metered Dose Inhalations and Dry Powder Inhalations
 Process Drift and it s Resolution in the Manufacture of Drug Products MDI s and DPI s Metered Dose Inhalations and Dry Powder Inhalations Ed Warner, Merck MMD December 2, 2010 PQRI-FDA Workshop on Process
Process Drift and it s Resolution in the Manufacture of Drug Products MDI s and DPI s Metered Dose Inhalations and Dry Powder Inhalations Ed Warner, Merck MMD December 2, 2010 PQRI-FDA Workshop on Process
How can I benefit most from my COPD medications?
 Fact Sheet: COPD Medications and Delivery Devices How can I benefit most from my COPD medications? COPD medications can improve your symptoms. By taking the right medication at the right time, you can
Fact Sheet: COPD Medications and Delivery Devices How can I benefit most from my COPD medications? COPD medications can improve your symptoms. By taking the right medication at the right time, you can
I. Subject: Medication Delivery by Metered Dose Inhaler (MDI)
 I. Subject: Medication Delivery by Metered Dose Inhaler (MDI) II. Policy: Aerosol medication administration by metered dose inhaler will be performed upon a physician's order by Respiratory Therapy personnel.
I. Subject: Medication Delivery by Metered Dose Inhaler (MDI) II. Policy: Aerosol medication administration by metered dose inhaler will be performed upon a physician's order by Respiratory Therapy personnel.
GE Healthcare Life Sciences. Quality matters. Whatman TM filters for air monitoring
 GE Healthcare Life Sciences Quality matters Whatman TM filters for air monitoring Quality matters Why does quality matter? Particulate testing Examples include PM 10 & PM 2.5 particulate monitoring. Quality
GE Healthcare Life Sciences Quality matters Whatman TM filters for air monitoring Quality matters Why does quality matter? Particulate testing Examples include PM 10 & PM 2.5 particulate monitoring. Quality
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
EduCare Knowledge & Skill Assessment Medication I Routes
 EduCare Knowledge & Skill Assessment Medication I Routes Employee Name Date Demonstration/Skill Assessment Oral (O) Pass Fail 1. Wash your hands; apply gloves. 2. Perform the 3 safety checks on the Simple
EduCare Knowledge & Skill Assessment Medication I Routes Employee Name Date Demonstration/Skill Assessment Oral (O) Pass Fail 1. Wash your hands; apply gloves. 2. Perform the 3 safety checks on the Simple
AEROSOL THERAPY: THE PRACTICALITIES
 AEROSOL THERAPY: THE PRACTICALITIES Lester I. Harrison, PhD Section Head, Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 3M Pharmaceuticals, 3M Center 270-3S-05, St. Paul, MN, USA 55144 liharrison@mmm.com Introduction: Horses,
AEROSOL THERAPY: THE PRACTICALITIES Lester I. Harrison, PhD Section Head, Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 3M Pharmaceuticals, 3M Center 270-3S-05, St. Paul, MN, USA 55144 liharrison@mmm.com Introduction: Horses,
LECTURE 10. PACKAGING TECHNOLOGY
 LECTURE 10. PACKAGING TECHNOLOGY The increasing demand for fresh and quality packaged food, consumer convenience and manufacturers concern for longer shelf life of the food products is driving the market
LECTURE 10. PACKAGING TECHNOLOGY The increasing demand for fresh and quality packaged food, consumer convenience and manufacturers concern for longer shelf life of the food products is driving the market
Anaesthetic and respiratory equipment Nebulizing systems and components
 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 27427 Third edition 2013-12-15 Anaesthetic and respiratory equipment Nebulizing systems and components Matériel d anesthésie et de réanimation
Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 27427 Third edition 2013-12-15 Anaesthetic and respiratory equipment Nebulizing systems and components Matériel d anesthésie et de réanimation
Q. What are metered-dose inhalers? A. These are devices that dispense medicines directly into the lungs, in the form of a mist or aerosol in a
 1 2 Q. What are metered-dose inhalers? A. These are devices that dispense medicines directly into the lungs, in the form of a mist or aerosol in a specific dosage. In an MDI, the medicine is suspended
1 2 Q. What are metered-dose inhalers? A. These are devices that dispense medicines directly into the lungs, in the form of a mist or aerosol in a specific dosage. In an MDI, the medicine is suspended
Delivering Aerosol Medication in ICU
 Delivering Aerosol Medication in ICU 18th Aug 2017 Lau Chee Lan Pharmacist HCTM PPUKM ASMIC 2017 Aerosol Therapy Part of the treatment for a variety of respiratory disease * asthma and chronic obstructive
Delivering Aerosol Medication in ICU 18th Aug 2017 Lau Chee Lan Pharmacist HCTM PPUKM ASMIC 2017 Aerosol Therapy Part of the treatment for a variety of respiratory disease * asthma and chronic obstructive
Chapter 7. Principles of Pharmacology
 Chapter 7 Principles of Pharmacology Introduction Administering medications is a serious business. Medications may alleviate pain and improve patient s well-being. Used inappropriately, may cause harm
Chapter 7 Principles of Pharmacology Introduction Administering medications is a serious business. Medications may alleviate pain and improve patient s well-being. Used inappropriately, may cause harm
A. Incorrect! The alveolus is where gas exchange takes place. B. Correct! Surfactant is the lipid-rich material that permits lung inflation.
 Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
A PRACTICAL GUIDE TO nebulization
 A PRACTICAL GUIDE TO nebulization therapy a initiative This book is based on sources believed to be reliable in providing information that is complete and generally in accordance with the standards accepted
A PRACTICAL GUIDE TO nebulization therapy a initiative This book is based on sources believed to be reliable in providing information that is complete and generally in accordance with the standards accepted
Selection and Optimization of the Sample Introduction System
 Selection and Optimization of the Sample Introduction System Geoff Tyler*, Lisa Goldstone, Odile Hirsch* Jobin Yvon, Inc., 3880 Park Avenue, Edison, NJ 08820 * Jobin Yvon SAS, 16-18, rue du Canal, 91165
Selection and Optimization of the Sample Introduction System Geoff Tyler*, Lisa Goldstone, Odile Hirsch* Jobin Yvon, Inc., 3880 Park Avenue, Edison, NJ 08820 * Jobin Yvon SAS, 16-18, rue du Canal, 91165
Drug/Device Combination Products: Bioequivalence
 Drug/Device Combination Products: Bioequivalence Three stories:. The story of Nasal and Inhalation Product BE 2. The story of the Generic Auto-Injector 3. The story of User Interface Considerations Bioequivalence
Drug/Device Combination Products: Bioequivalence Three stories:. The story of Nasal and Inhalation Product BE 2. The story of the Generic Auto-Injector 3. The story of User Interface Considerations Bioequivalence
15 cm Reservoir Tubing. 210 cm Tubing
 12 Aerosol Therapy nebulisers AEROSOL THERAPY MICRO MIST SMALL VOLUME NEBULISER The MICRO MIST small volume nebuliser is designed for performance and economy and can be used for hand-held or in-line treatments.
12 Aerosol Therapy nebulisers AEROSOL THERAPY MICRO MIST SMALL VOLUME NEBULISER The MICRO MIST small volume nebuliser is designed for performance and economy and can be used for hand-held or in-line treatments.
FAO SPECIFICATIONS FAO PLANT PROTECTION PRODUCTS. ZINEB Zinc ethylenebisdithiocarbamate
 AGP: CP/82 FAO SPECIFICATIONS FAO PLANT PROTECTION PRODUCTS ZINEB Zinc ethylenebisdithiocarbamate FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS Rome, 1979 DISCLAIMER 1 FAO specifications are
AGP: CP/82 FAO SPECIFICATIONS FAO PLANT PROTECTION PRODUCTS ZINEB Zinc ethylenebisdithiocarbamate FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS Rome, 1979 DISCLAIMER 1 FAO specifications are
Identification of crystalline forms suitable for inhalation in drug discovery
 Identification of crystalline forms suitable for inhalation in drug discovery Valentina Diana Di Lallo Chiesi Farmaceutici - Corporate R&D Preclinical Analytics & Early Formulations Department Crystallization:
Identification of crystalline forms suitable for inhalation in drug discovery Valentina Diana Di Lallo Chiesi Farmaceutici - Corporate R&D Preclinical Analytics & Early Formulations Department Crystallization:
Ultrasonic Humidifiers and Nebulisers
 Ultrasonic Humidifiers and Nebulisers for Medical Institutions DP100 NF EN ISO 13485 0459 SYST AM DP100, a n Container Ê Stands upright : convenient for preparing the session. Ê With simple and quick connector.
Ultrasonic Humidifiers and Nebulisers for Medical Institutions DP100 NF EN ISO 13485 0459 SYST AM DP100, a n Container Ê Stands upright : convenient for preparing the session. Ê With simple and quick connector.
Element B1 / 3 Target Organs and Systems
 / 3 Target Organs and Systems Target Organs / Target Systems (Specified toxic substance exerts its effects) Target organs Liver Lungs Kidneys Brain Skin Bladder Eyes Target Organs / Target Systems Substances
/ 3 Target Organs and Systems Target Organs / Target Systems (Specified toxic substance exerts its effects) Target organs Liver Lungs Kidneys Brain Skin Bladder Eyes Target Organs / Target Systems Substances
Recommendations for Aerosol Applications of Silicone-Based Materials
 Recommendations for Aerosol Applications of Silicone-Based Materials September 2001 Revised March 2018 This document provides information and recommendations relevant to formulating aerosol products containing
Recommendations for Aerosol Applications of Silicone-Based Materials September 2001 Revised March 2018 This document provides information and recommendations relevant to formulating aerosol products containing
INFORMATION TOPIC: II-5 OR DEMONSTRATION: II-5. DOSAGE, MEASUREMENTS, AND DRUG FORMS (Lesson Title) OBJECTIVES THE STUDENT WILL BE ABLE TO:
 LESSON PLAN: 5 COURSE TITLE: UNIT: II MEDICATION TECHNICIAN GENERAL PRINCIPLES SCOPE OF UNIT: This unit includes medication terminology, dosage, measurements, drug forms, transcribing physician s orders,
LESSON PLAN: 5 COURSE TITLE: UNIT: II MEDICATION TECHNICIAN GENERAL PRINCIPLES SCOPE OF UNIT: This unit includes medication terminology, dosage, measurements, drug forms, transcribing physician s orders,
8/13/11. RSPT 1410 Humidity & Aerosol Therapy Part 3. Humidification Equipment. Aerosol Therapy
 1 RSPT 1410 Humidity & Aerosol Therapy Part 3 Wilkins: Chapter 35, p. 775-799 Cairo: Chapter 4, p. 88-143 2 Humidification Equipment A humidifier is a device that adds molecular liquid (e.g. water vapor)
1 RSPT 1410 Humidity & Aerosol Therapy Part 3 Wilkins: Chapter 35, p. 775-799 Cairo: Chapter 4, p. 88-143 2 Humidification Equipment A humidifier is a device that adds molecular liquid (e.g. water vapor)
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals
 Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p.
 Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS. Tablets
 March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
FAIRFIELD SCHOOL HEALTH PROGRAM. PROCEDURE: Administration of Oral, Topical or Inhalant Medications by Principals and Teachers
 FAIRFIELD SCHOOL HEALTH PROGRAM PROCEDURE: Administration of Oral, Topical or Inhalant Medications by Principals and Teachers 1. Obtain key Access to all stored medications is limited to persons authorized
FAIRFIELD SCHOOL HEALTH PROGRAM PROCEDURE: Administration of Oral, Topical or Inhalant Medications by Principals and Teachers 1. Obtain key Access to all stored medications is limited to persons authorized
Challenges in Nonclinical Development of Inhalation Drug Products
 Challenges in Nonclinical Development of Inhalation Drug Products Luqi Pei, Ph.D. Senior Pharmacologist DPARP, CDER August 6, 2015 Rockville, MD Disclaimer This speech reflects the views of the speaker
Challenges in Nonclinical Development of Inhalation Drug Products Luqi Pei, Ph.D. Senior Pharmacologist DPARP, CDER August 6, 2015 Rockville, MD Disclaimer This speech reflects the views of the speaker
PHARMACEUTICS I صيدالنيات 1 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION
 PHARMACEUTICS I صيدالنيات 1 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION 1 PHARMACEUTICS Pharmaceutics is the science of dosage form design. The general area of study concerned with the formulation, manufacture, stability, and
PHARMACEUTICS I صيدالنيات 1 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION 1 PHARMACEUTICS Pharmaceutics is the science of dosage form design. The general area of study concerned with the formulation, manufacture, stability, and
TENOFOVIR TABLETS: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010)
 June 2010 TENOFOVIR TABLETS: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
June 2010 TENOFOVIR TABLETS: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (June 2010) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
INSTRUCTIONS FOR CLEANING, DISINFECTION AND STERILIZATION OF DFS INSTRUMENTS
 Preparation (cleaning, disinfection and sterilization) of reusable rotating dental instruments General principles All instruments must be cleaned, disinfected and sterilized before each use; this applies
Preparation (cleaning, disinfection and sterilization) of reusable rotating dental instruments General principles All instruments must be cleaned, disinfected and sterilized before each use; this applies
Savillex Technical Note C-Flow 700d PFA Concentric Nebulizer for ICP-OES
 Savillex Technical Note C-Flow 700d PFA Concentric Nebulizer for ICP-OES Summary The Savillex C-Flow 700d (C700d) is a concentric PFA nebulizer designed specifically for ICP-OES, combining extreme matrix
Savillex Technical Note C-Flow 700d PFA Concentric Nebulizer for ICP-OES Summary The Savillex C-Flow 700d (C700d) is a concentric PFA nebulizer designed specifically for ICP-OES, combining extreme matrix
TOWN OF FAIRFIELD HEALTH DEPARTMENT PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING
 TOWN OF FAIRFIELD HEALTH DEPARTMENT PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING PROGRAM: School Health APPROVED BY: Board of Health POLICY: Nebulizer Therapy DATE: 5-10-93 PROCEDURE: a) Nebulizer Therapy With Non-oxygenated
TOWN OF FAIRFIELD HEALTH DEPARTMENT PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING PROGRAM: School Health APPROVED BY: Board of Health POLICY: Nebulizer Therapy DATE: 5-10-93 PROCEDURE: a) Nebulizer Therapy With Non-oxygenated
PRODUCT: BLAZEBRAKE FIRE RATED EXPANDING FOAM
 ISSUE: 1 DATE OF ISSUE: 27/1/09 Page 1 of 5 SECTION 1: IDENTIFICATION OF THE MATERIAL AND SUPPLIER Product Name: BLAZEBRAKE FIRE RATED EXPANDING FOAM Manufacturer s Product Code: FRF700 Other Names: None
ISSUE: 1 DATE OF ISSUE: 27/1/09 Page 1 of 5 SECTION 1: IDENTIFICATION OF THE MATERIAL AND SUPPLIER Product Name: BLAZEBRAKE FIRE RATED EXPANDING FOAM Manufacturer s Product Code: FRF700 Other Names: None
University of Groningen. Technology in practice Lexmond, Anne
 University of Groningen Technology in practice Lexmond, Anne IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Technology in practice Lexmond, Anne IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
MASCOU FLUIDS 2017 CATALOG HIGH-GRADE QUALITY TAPPING AND CUTTING FLUIDS!
 MASCOU FLUIDS 2017 CATALOG HIGH-GRADE QUALITY TAPPING AND CUTTING FLUIDS! AT THE EXCEPTION OF THE, MADE IN GERMANY MASCOU FLUIDS MASCOU-CUT SYNTHETIC EXCEPTIONAL PERFORMANCES! 100 % SYNTHETIC SOLUBLE CUTTING
MASCOU FLUIDS 2017 CATALOG HIGH-GRADE QUALITY TAPPING AND CUTTING FLUIDS! AT THE EXCEPTION OF THE, MADE IN GERMANY MASCOU FLUIDS MASCOU-CUT SYNTHETIC EXCEPTIONAL PERFORMANCES! 100 % SYNTHETIC SOLUBLE CUTTING
CHAPTER-I DRUG CHARACTERIZATION & DOSAGE FORMS
 CHAPTER-I DRUG CHARACTERIZATION & DOSAGE FORMS by: j. jayasutha lecturer department of pharmacy practice Srm college of pharmacy srm university DRUG CHARACTERIZATION: Pre-formulation studies will attempt
CHAPTER-I DRUG CHARACTERIZATION & DOSAGE FORMS by: j. jayasutha lecturer department of pharmacy practice Srm college of pharmacy srm university DRUG CHARACTERIZATION: Pre-formulation studies will attempt
LIQUID PREPARATIONS FOR ORAL USE. Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (November 2007)
 November 2007 LIQUID PREPARATIONS FOR ORAL USE Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (November 2007) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-second WHO Expert Committee on Specifications
November 2007 LIQUID PREPARATIONS FOR ORAL USE Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (November 2007) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-second WHO Expert Committee on Specifications
Title Revision n date
 A. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUE (TLC) 1. SCOPE The method describes the identification of hydrocortisone acetate, dexamethasone, betamethasone, betamethasone 17-valerate and triamcinolone acetonide
A. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUE (TLC) 1. SCOPE The method describes the identification of hydrocortisone acetate, dexamethasone, betamethasone, betamethasone 17-valerate and triamcinolone acetonide
Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration
 1 Chapter 7, Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration 2 Caution: Administering medications is business Always take appropriate Standard measures to reduce your
1 Chapter 7, Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration 2 Caution: Administering medications is business Always take appropriate Standard measures to reduce your
21/03/2011 AEROSOL DEPOSITION AND THE ASSESSMENT OF PULMONARY DRUG DELIVERY. Fundamentals of aerosols
 AEROSOL DEPOSITION AND THE ASSESSMENT OF PULMONARY DRUG DELIVERY AEROSOL DEPOSITION AND THE ASSESSMENT OF PULMONARY DRUG DELIVERY Steve Newman Scientific Consultant Norfolk, UK steve.newman@physics.org
AEROSOL DEPOSITION AND THE ASSESSMENT OF PULMONARY DRUG DELIVERY AEROSOL DEPOSITION AND THE ASSESSMENT OF PULMONARY DRUG DELIVERY Steve Newman Scientific Consultant Norfolk, UK steve.newman@physics.org
Safety Data Sheet. Product Name: DetectX Palladium Screening Fluorescent Detection Kit. Section 1: Identification. Section 2: Hazard(s) Identification
 Safety Data Sheet Revision Date: 17 October 2016 Product Name: DetectX Palladium Screening Fluorescent Detection Kit Section 1: Identification Product Name: DetectX Palladium Screening Fluorescent Detection
Safety Data Sheet Revision Date: 17 October 2016 Product Name: DetectX Palladium Screening Fluorescent Detection Kit Section 1: Identification Product Name: DetectX Palladium Screening Fluorescent Detection
What You Need to Know about Metered-Dose Inhalers and the HFA Propellant
 What You Need to Know about Metered- Inhalers and the HFA Propellant There are a number ways to deliver inhaled medication. They include: Metered-dose inhaler () Metered-dose inhaler with spacer/holding
What You Need to Know about Metered- Inhalers and the HFA Propellant There are a number ways to deliver inhaled medication. They include: Metered-dose inhaler () Metered-dose inhaler with spacer/holding
FAO SPECIFICATIONS FAO PLANT PROTECTION PRODUCTS SULPHUR. FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS Rome, 1973
 AGP: CP/58 FAO SPECIFICATIONS FAO PLANT PROTECTION PRODUCTS SULPHUR FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS Rome, 1973 DISCLAIMER 1 FAO specifications are developed with the basic objective
AGP: CP/58 FAO SPECIFICATIONS FAO PLANT PROTECTION PRODUCTS SULPHUR FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS Rome, 1973 DISCLAIMER 1 FAO specifications are developed with the basic objective
TEST. Directions: Circle the letter indicating whether the following statements are either true ("T") or false ("F").
 TEST Directions: Circle the letter indicating whether the following statements are either true ("T") or false ("F"). T F 1. A closed glass jar of pickles is a closed system. T F 2. Cellular respiration
TEST Directions: Circle the letter indicating whether the following statements are either true ("T") or false ("F"). T F 1. A closed glass jar of pickles is a closed system. T F 2. Cellular respiration
Particle Size and Dust Inhalation
 Pneumoconiosis A disease of the lungs characterized by fibrosis and caused by the chronic inhalation of mineral dusts, especially silica and asbestos. Helen Lang Dept. Geology & Geography West Virginia
Pneumoconiosis A disease of the lungs characterized by fibrosis and caused by the chronic inhalation of mineral dusts, especially silica and asbestos. Helen Lang Dept. Geology & Geography West Virginia
UNIT 2 SOLID AND LIQUID DOSAGE FORMS
 UNIT 2 SOLID AND LIQUID DOSAGE FORMS Solid and Liquid Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Solid Tablets Capsules 2.3 Liquid Advantages of Liquid Disadvantages of Liquid Classification of Liquid Monophasic
UNIT 2 SOLID AND LIQUID DOSAGE FORMS Solid and Liquid Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Solid Tablets Capsules 2.3 Liquid Advantages of Liquid Disadvantages of Liquid Classification of Liquid Monophasic
Medescan Nebuliser Med - S600A Instructions Manual
 Medescan Nebuliser Med - S600A Instructions Manual Please read this guidebook carefully before operating this unit Your Nebuliser is intended for use in the treatment of asthma, COPD and other respiratory
Medescan Nebuliser Med - S600A Instructions Manual Please read this guidebook carefully before operating this unit Your Nebuliser is intended for use in the treatment of asthma, COPD and other respiratory
Physical Pharmacy. Interfacial phenomena. Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department
 Physical Pharmacy Interfacial phenomena Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department 1 Introduction The boundary between two phases is generally described as
Physical Pharmacy Interfacial phenomena Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department 1 Introduction The boundary between two phases is generally described as
Assessment of Human Pharmaceutical Products Registered in Kenya by Route of Administration and Type of Dosage Form
 38 East and Central African Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Vol. 15 (2012) 38-46 Assessment of Human Pharmaceutical Products Registered in Kenya by Route of Administration and Type of Dosage Form N.N.
38 East and Central African Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Vol. 15 (2012) 38-46 Assessment of Human Pharmaceutical Products Registered in Kenya by Route of Administration and Type of Dosage Form N.N.
Glossary of Asthma Terms
 HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab
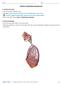 Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
AGP: CP/89 FAO SPECIFICATIONS FOR PLANT PROTECTION PRODUCTS. PHENTHOATE S - a - ethoxycarbonylbenzyl 00-dimethyl phosphorodithioate
 AGP: CP/89 FAO SPECIFICATIONS FOR PLANT PROTECTION PRODUCTS PHENTHOATE S - a - ethoxycarbonylbenzyl 00-dimethyl phosphorodithioate FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS Rome, 1980 DISCLAIMER
AGP: CP/89 FAO SPECIFICATIONS FOR PLANT PROTECTION PRODUCTS PHENTHOATE S - a - ethoxycarbonylbenzyl 00-dimethyl phosphorodithioate FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS Rome, 1980 DISCLAIMER
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
 Date of Issue: October 2006 MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET PRODUCT: SOIL ph TEST KIT NOT CLASSIFIED AS HAZARDOUS ACCORDING TO CRITERIA OF WORKSAFE AUSTRALIA Manufacturer s Name and Address: MANUTEC PTY LTD
Date of Issue: October 2006 MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET PRODUCT: SOIL ph TEST KIT NOT CLASSIFIED AS HAZARDOUS ACCORDING TO CRITERIA OF WORKSAFE AUSTRALIA Manufacturer s Name and Address: MANUTEC PTY LTD
Telephone: Order Desk: Fax:
 Home» Newcastle-Bronchitis Vaccine (B1 Type, B1 Strain; Mass. & Conn. Types) (MERIAL SELECT, INC.) MERIAL SELECT, INC. P.O. DRAWER 2497, GAINESVILLE, GA, 30503 Telephone: 770-536-8787 Order Desk: 770-536-8787
Home» Newcastle-Bronchitis Vaccine (B1 Type, B1 Strain; Mass. & Conn. Types) (MERIAL SELECT, INC.) MERIAL SELECT, INC. P.O. DRAWER 2497, GAINESVILLE, GA, 30503 Telephone: 770-536-8787 Order Desk: 770-536-8787
An update on inhalation devices
 OPTIMIZING INHALED DRUG DELIVERY An update on inhalation devices Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. History of spacers... 1 3. Working of a spacer... 2 4. Advantages of spacer devices... 3 5. Who should
OPTIMIZING INHALED DRUG DELIVERY An update on inhalation devices Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. History of spacers... 1 3. Working of a spacer... 2 4. Advantages of spacer devices... 3 5. Who should
FAO SPECIFICATIONS FAO PLANT PROTECTION PRODUCTS. BROMOPHOS 4-bromo-2,5-dichloropheny1 dimethy1 phosphorothioate
 AGP: CP/70 FAO SPECIFICATIONS FAO PLANT PROTECTION PRODUCTS BROMOPHOS 4-bromo-2,5-dichloropheny1 dimethy1 phosphorothioate FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS Rome, 1977 DISCLAIMER
AGP: CP/70 FAO SPECIFICATIONS FAO PLANT PROTECTION PRODUCTS BROMOPHOS 4-bromo-2,5-dichloropheny1 dimethy1 phosphorothioate FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS Rome, 1977 DISCLAIMER
GE Healthcare Life Sciences. Quality matters. Whatman TM filters for air monitoring
 GE Healthcare Life Sciences Quality matters Whatman TM filters for air monitoring Quality matters Why does quality matter? Particulate testing Examples include PM 10 & PM 2.5 particulate monitoring. Quality
GE Healthcare Life Sciences Quality matters Whatman TM filters for air monitoring Quality matters Why does quality matter? Particulate testing Examples include PM 10 & PM 2.5 particulate monitoring. Quality
Name GLOSSARY. Carrier protein a molecule in the cell membrane that allows materials to pass through it
 2 GLOSSARY Active transport movement of matter into, or out of, a cell which requires energy from the cell; usually this involves movement against the concentration gradient Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
2 GLOSSARY Active transport movement of matter into, or out of, a cell which requires energy from the cell; usually this involves movement against the concentration gradient Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Emulsions. Purpose of emulsions and of emulsification:
 Pharmacist Ghada Hamid Emulsions Emulsion is a dispersion in which the dispersed phase is composed of small globules of a liquid distributed throughout a vehicle in which it is immiscible. The dispersed
Pharmacist Ghada Hamid Emulsions Emulsion is a dispersion in which the dispersed phase is composed of small globules of a liquid distributed throughout a vehicle in which it is immiscible. The dispersed
Apitherapy. Edition 7.0 Date of issue:
 GB Apitherapy Inhalation of aerosol from the hive Inhalation of aerosol from the hive with forced draft Devices for aerosol inhalation therapy Inhalation mixtures Concentrates for mixing with honey Edition
GB Apitherapy Inhalation of aerosol from the hive Inhalation of aerosol from the hive with forced draft Devices for aerosol inhalation therapy Inhalation mixtures Concentrates for mixing with honey Edition
FAO SPECIFICATIONS AND EVALUATIONS FOR AGRICULTURAL PESTICIDES
 FOR AGRICULTURAL PESTICIDES DELTAMETHRIN (S)-α-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (1R,3R)-3-(2,2- dibromovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane carboxylate TABLE OF CONTENTS DELTAMETHRIN Page DISCLAIMER INTRODUCTION 1 PART
FOR AGRICULTURAL PESTICIDES DELTAMETHRIN (S)-α-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (1R,3R)-3-(2,2- dibromovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane carboxylate TABLE OF CONTENTS DELTAMETHRIN Page DISCLAIMER INTRODUCTION 1 PART
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body.
 Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
How to Use Inhaled Medications for Asthma and COPD
 How to Use Inhaled Medications for Asthma and COPD This information is not intended to diagnose health problems or to take the place of medical advice or care you receive from your physician or other health
How to Use Inhaled Medications for Asthma and COPD This information is not intended to diagnose health problems or to take the place of medical advice or care you receive from your physician or other health
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
 MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE SUBSTANCE/PREPARATION AND OF THE COMPANY/UNDERTAKING Product Name: 1,6-HEXANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER CAS No.: 16096-31-4 Brand: Alfa Chemistry Company:
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE SUBSTANCE/PREPARATION AND OF THE COMPANY/UNDERTAKING Product Name: 1,6-HEXANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER CAS No.: 16096-31-4 Brand: Alfa Chemistry Company:
