SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Meagan Taylor
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 doi: /nature13908 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1: Families in this study (.xlsx) All families included in the study are listed. For each family, we show: the genders of the probands and the unaffected sibling; the centers that sequenced the family; the collection the family is from (Methods); the SFARI database ids of the sequenced probands and siblings (for example, p1 and s1 are the proband and the sibling of family 13416); the race of the parents; the verbal and non- verbal IQ of the proband; and the ages of the parents at the birth dates of their children. Also included are the number of identified de novo LGDs, missense and synonymous mutations in the sequenced children. Supplementary Table 2: All de novo events (.xlsx) All de novo variants identified in the study are listed. For each observed de novo event, we list: family (familyid: SFARI family identifier) and child affected status and gender (inchild: pm male proband; pf female proband; sm male sibling; and sf female sibling); genomic location (location) and the type of the variant (variant, like substitutions (sub), insertions (ins) or deletions (del); see the supplement of Iossifov et al. Neuron 74, (2012) for details of the nomenclature); representation of the variant in the VCF standard format (vcfvariant); parental genome from which the mutation originates when we could so determine (fromparent); gene target (effectgene) and the effect type (effecttype); genotype confidence scores from the common pipeline (strong, weak or not called when the common pipeline missed the variant) over the data from the three sequencing centers and the validation status: valid for the successfully validated variants and missing for the variants that have not been validated (CSHL, YALE, UW). 1
2 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CSHL strong LGDs strong non LGDs strong non coding weak LGDs weak non LGDs weak non coding strong LGDs strong non LGDs strong non coding weak LGDs weak non LGDs weak non coding UW strong LGDs strong non LGDs strong non coding weak LGDs weak non LGDs weak non coding strong LGDs strong non LGDs strong non coding weak LGDs weak non LGDs weak non coding YALE strong LGDs strong non LGDs strong non coding weak LGDs weak non LGDs weak non coding strong LGDs strong non LGDs strong non coding weak LGDs weak non LGDs weak non coding Supplementary Table 3: Experimental validation in the 40X target The results of the experimental validation of de novo variants in the well- covered 40X target are tabulated for the each of the sequencing centers. Variants are classified by their type (substitutions or indels) and by the confidence assigned by the common pipeline (strong or weak). Each attempted validation either verifies the variant (verified), rejects the variant (rejected), or fails (failed validation). 2
3 RESEARCH Groups of X events Role Group Distance prb gene 3, sib gene 2, prb 100,000 3, sib 100,000 2, prb 10,000 3, sib 10,000 2, prb , sib , prb 100 3, sib 100 2, prb 10 3, sib 10 2, prb 5 3, sib 5 2, prb 1 3, sib 1 2, Supplementary Table 4: Multiple de novo events The de novo events are grouped if found in the same child and appear near to each other. The table lists the number of groups of various sizes in probands and in siblings under different definitions of near. In the first two lines, the events are grouped if they are in the same gene; in the following lines, the events are grouped if they are closer than the specified (Group Distance) genomic distance. The number of groups of given size is shown in columns 1, 2, 3 and 4. Supplementary Table 5: De novo substitution mutations (.xlsx) Each de novo substitution is characterized by the parental nucleotide (From) and the novel nucleotide (column headers). The Observed substitution counts section shows the number of observed de novo substitution split by from and to nucleotides. The Opportunity sections shows the number of Mendelian genotypes in children for the given From allele at nearly fixed loci (at most one alternative allele allowed). The Rates section shows per- base- per- generation rate of substitutions. Supplementary Table 6: Properties of mutational classes in SSC child types (.xlsx) We show various properties of the mutation- child- types. We define mutation- child- type to refer to a set of events of a certain mutational type (e.g. missense or LGD) in children of a certain type (e.g. male affecteds or unaffected siblings). We grouped 3
4 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION children into seven types: unaffected siblings, probands, affected females, affected males, affected males with low nviq (<90), affected girls plus low nviq boys, and affected males with high nviq. We partitioned mutations into three types: LGDs, missense, and synonymous. For each mutation- child- type we show: 1. Details of 40X- based rate and ascertainment- differential computation, including: the number of children included in the 40X analysis (quads only); total length of 40X target; number of de novo mutation- child- type events in the 40X target; estimated rate and its standard deviation; estimated ascertainment differential, and its standard deviation and a p- value of the ascertainment differential. 2. Total number of children, total number of events, and the number of gene targets. 3. The number of recurrent genes and the number of recurrent events. 4. The expected number of recurrent genes under gene length- based null model and p value of the observer number of recurrent genes. 5. Details of the target size estimation including: proportion of events in the target and the approximate number of contributory events; target size estimated with a 95% CI. 6. Observed and expected overlaps with the eight gene classes defined in Table 1 and p- values computed by comparing the observed and expected number. Expectations are based on the gene length- based null model. 7. Observed and expected overlaps with all the other mutation- child- types. The expectation and the p- value are based on the gene length null model. De novo variants shared between siblings and de novo mutations occurring in the same gene in the same child are removed prior to testing for overlaps. We only tested for overlap between two mutation- child- types with distinct sets of children. Supplementary Table 7: Numbers of mutations by gene and type (.xlsx) All genes included within SeqCap EZ Human Exome Library v2.0 (Roche NimbleGen) are listed within the table. Total coding region length in nucleotides (predicted by RefSeq) is displayed in column B, whereas the length represented within the actual capture reagent is shown in column C. Gene sets (columns D K) are as defined in Table 1; the presence of a 1 in these columns indicates that the gene falls within the particular class. Columns L AC tabulate de novo (dnv) events of specific classes (LGD, missense or synonymous) that fall within the specified child cohorts: all probands (prb); male probands (prbm); male probands with nviq<90 (prbml); male probands with nviq 90 (prbmh); all female probands (prbf); and unaffected siblings (sib). 4
5 RESEARCH Prb. vs. Proband Sibling Proband Sib. p- Gene Group only only & Sibling Neither Value FMRP-associated targets of de novo LGDs in probands targets of de novo missense in probands all genes , Supplementary Table 8: Compound non- synonymous hits in targets from quad families The Supplementary Table hows the numbers of genes hit by two rare nonsynonymous variants, one inherited from the mother and one inherited from the father (compound hit). Since each parent carries an affected allele, the compound hit can be in proband only, in the unaffected sibling only, in both proband and sibling, or in neither of the children. We report either all compound hits or only those in three sets of genes: FMRP- associated genes, genes affected by de novo LGDs in probands, and genes affected by de novo missense variants in probands. The p- values are calculated under the null model assuming that the probability of a compound hit in a proband only is the same as the probability of a compound hit in a sibling only. Supplementary Table 9: Gene targets of recurrent mutation in coding regions (.xlsx) Genes with recurrent mutations (defined here as two independent missense and/or severe de novo events) are ranked based on a per- gene model (O Roak et al., Science 338, , 2012). The term severe as used here refers to LGDs plus all coding mutations that are neither synonymous nor missense, such as frame- preserving small indels and mutations that remove start or stop codons. Genes with recurrent hits that were rejected by this model are indicated by asterisks (*). Supplementary Table 10: UW sequencing protocols (.xlsx) SSC families processed by the UW group are listed by family ID and the version of capture and sequencing protocols used. If previously published, the corresponding study is referenced: O'Roak, B. J. et al., Nat Genet 43, (2011), or O'Roak, B. J. et al., Nature 485, (2012). Families new to this study are indicated accordingly. 5
6 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CSHL strong LGDs strong non LGDs strong non coding weak LGDs weak non LGDs weak non coding strong LGDs strong non LGDs strong non coding weak LGDs weak non LGDs weak non coding UW strong LGDs strong non LGDs strong non coding weak LGDs weak non LGDs weak non coding strong LGDs strong non LGDs strong non coding weak LGDs weak non LGDs weak non coding YALE strong LGDs strong non LGDs strong non coding weak LGDs weak non LGDs weak non coding strong LGDs strong non LGDs strong non coding weak LGDs weak non LGDs weak non coding Supplementary Table 11: Validation summary by center (.docx) The results of the experimental validation of de novo variants in the well- covered are tabulated for the each of the sequencing centers. Variants are classified by their type ( or ) and by the confidence assigned by the common pipeline (strong or weak). Each attempted validation either verifies the variant (verified), rejects the variant (rejected), or fails (failed validation). 6
7 RESEARCH Supplementary Table 12: Data agreement (.docx) We intentionally had a number of families sequenced independently in more than one sequencing center (Extended Data Fig. 1). For the three centers, we show the agreement of the results of the common pipeline of the families sequenced independently at the two centers. Variants are classified by their type ( of ) and by the confidence assigned by the common pipeline (strong or weak). Not called labels are used for variants identified in one dataset but not in the other. Description of genes Median length p-val Selected based on length 2,175 Selected uniformly 1,335 Hit by LGDs in probands 2, Hit by LGDs in siblings 2, Hit by missense in proband 2, Hit by missense in sibling 2, Hit by synonymous (sib + prb) 2, Supplementary Table 13: Median gene lengths Median gene lengths of simulated and genes sets and genes hit by different types of mutations. The first line shows the median gene lengths if genes are selected with probability proportional to their length. The second line shows the median gene length if genes are randomly selected independent of their length. The lines following show the median gene lengths of genes hit by de novo LGDs in probands, LGDs in siblings, missense in probands, missense in siblings, and synonymous mutations in probands or siblings. In addition, we show the empirical p- values of the observed median lengths under the gene- length based null model. The p- values were computed by selecting the same number of random genes (proportional to their length) and recording the number of times (out of 10,000 attempts) that the median lengths of selected genes were larger than those observed. 7
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. PCA for ancestry in SNV data.
 Supplementary Figure 1 PCA for ancestry in SNV data. (a) EIGENSTRAT principal-component analysis (PCA) of SNV genotype data on all samples. (b) PCA of only proband SNV genotype data. (c) PCA of SNV genotype
Supplementary Figure 1 PCA for ancestry in SNV data. (a) EIGENSTRAT principal-component analysis (PCA) of SNV genotype data on all samples. (b) PCA of only proband SNV genotype data. (c) PCA of SNV genotype
SCALPEL MICRO-ASSEMBLY APPROACH TO DETECT INDELS WITHIN EXOME-CAPTURE DATA. Giuseppe Narzisi, PhD Schatz Lab
 SCALPEL MICRO-ASSEMBLY APPROACH TO DETECT INDELS WITHIN EXOME-CAPTURE DATA Giuseppe Narzisi, PhD Schatz Lab November 14, 2013 Micro-Assembly Approach to detect INDELs 2 Outline Scalpel micro-assembly pipeline
SCALPEL MICRO-ASSEMBLY APPROACH TO DETECT INDELS WITHIN EXOME-CAPTURE DATA Giuseppe Narzisi, PhD Schatz Lab November 14, 2013 Micro-Assembly Approach to detect INDELs 2 Outline Scalpel micro-assembly pipeline
TOWARDS ACCURATE GERMLINE AND SOMATIC INDEL DISCOVERY WITH MICRO-ASSEMBLY. Giuseppe Narzisi, PhD Bioinformatics Scientist
 TOWARDS ACCURATE GERMLINE AND SOMATIC INDEL DISCOVERY WITH MICRO-ASSEMBLY Giuseppe Narzisi, PhD Bioinformatics Scientist July 29, 2014 Micro-Assembly Approach to detect INDELs 2 Outline 1 Detecting INDELs:
TOWARDS ACCURATE GERMLINE AND SOMATIC INDEL DISCOVERY WITH MICRO-ASSEMBLY Giuseppe Narzisi, PhD Bioinformatics Scientist July 29, 2014 Micro-Assembly Approach to detect INDELs 2 Outline 1 Detecting INDELs:
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Illustrative example of ptdt using height The expected value of a child s polygenic risk score (PRS) for a trait is the average of maternal and paternal PRS values. For example,
Supplementary Figure 1 Illustrative example of ptdt using height The expected value of a child s polygenic risk score (PRS) for a trait is the average of maternal and paternal PRS values. For example,
The contribution of de novo coding mutations to autism spectrum disorder
 doi:10.1038/nature13908 The contribution of de novo coding mutations to autism spectrum disorder Ivan Iossifov 1 *, Brian J. O Roak,3 *, Stephan J. Sanders 4,5 *, Michael Ronemus 1 *, Niklas Krumm, Dan
doi:10.1038/nature13908 The contribution of de novo coding mutations to autism spectrum disorder Ivan Iossifov 1 *, Brian J. O Roak,3 *, Stephan J. Sanders 4,5 *, Michael Ronemus 1 *, Niklas Krumm, Dan
Variant Classification. Author: Mike Thiesen, Golden Helix, Inc.
 Variant Classification Author: Mike Thiesen, Golden Helix, Inc. Overview Sequencing pipelines are able to identify rare variants not found in catalogs such as dbsnp. As a result, variants in these datasets
Variant Classification Author: Mike Thiesen, Golden Helix, Inc. Overview Sequencing pipelines are able to identify rare variants not found in catalogs such as dbsnp. As a result, variants in these datasets
Lecture 20. Disease Genetics
 Lecture 20. Disease Genetics Michael Schatz April 12 2018 JHU 600.749: Applied Comparative Genomics Part 1: Pre-genome Era Sickle Cell Anaemia Sickle-cell anaemia (SCA) is an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying
Lecture 20. Disease Genetics Michael Schatz April 12 2018 JHU 600.749: Applied Comparative Genomics Part 1: Pre-genome Era Sickle Cell Anaemia Sickle-cell anaemia (SCA) is an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying
Sequencing studies implicate inherited mutations in autism
 NEWS Sequencing studies implicate inherited mutations in autism BY EMILY SINGER 23 JANUARY 2013 1 / 5 Unusual inheritance: Researchers have found a relatively mild mutation in a gene linked to Cohen syndrome,
NEWS Sequencing studies implicate inherited mutations in autism BY EMILY SINGER 23 JANUARY 2013 1 / 5 Unusual inheritance: Researchers have found a relatively mild mutation in a gene linked to Cohen syndrome,
De Novo Gene Disruptions in Children on the Autistic Spectrum
 Article De Novo Gene Disruptions in Children on the Autistic Spectrum Ivan Iossifov, 1,6 Michael Ronemus, 1,6 Dan Levy, 1 Zihua Wang, 1 Inessa Hakker, 1 Julie Rosenbaum, 1 Boris Yamrom, 1 Yoon-ha Lee,
Article De Novo Gene Disruptions in Children on the Autistic Spectrum Ivan Iossifov, 1,6 Michael Ronemus, 1,6 Dan Levy, 1 Zihua Wang, 1 Inessa Hakker, 1 Julie Rosenbaum, 1 Boris Yamrom, 1 Yoon-ha Lee,
Illuminating the genetics of complex human diseases
 Illuminating the genetics of complex human diseases Michael Schatz Sept 27, 2012 Beyond the Genome @mike_schatz / #BTG2012 Outline 1. De novo mutations in human diseases 1. Autism Spectrum Disorder 2.
Illuminating the genetics of complex human diseases Michael Schatz Sept 27, 2012 Beyond the Genome @mike_schatz / #BTG2012 Outline 1. De novo mutations in human diseases 1. Autism Spectrum Disorder 2.
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Illustration of the working of network-based SVM to confidently predict a new (and now confirmed) ASD gene. Gene CTNND2 s brain network neighborhood that enabled its prediction by
Supplementary Figure 1 Illustration of the working of network-based SVM to confidently predict a new (and now confirmed) ASD gene. Gene CTNND2 s brain network neighborhood that enabled its prediction by
Reducing INDEL calling errors in whole genome and exome sequencing data.
 Reducing INDEL calling errors in whole genome and exome sequencing data. Han Fang November 8, 2014 CSHL Biological Data Science Meeting Acknowledgments Lyon Lab Yiyang Wu Jason O Rawe Laura J Barron Max
Reducing INDEL calling errors in whole genome and exome sequencing data. Han Fang November 8, 2014 CSHL Biological Data Science Meeting Acknowledgments Lyon Lab Yiyang Wu Jason O Rawe Laura J Barron Max
Variant Detection & Interpretation in a diagnostic context. Christian Gilissen
 Variant Detection & Interpretation in a diagnostic context Christian Gilissen c.gilissen@gen.umcn.nl 28-05-2013 So far Sequencing Johan den Dunnen Marja Jakobs Ewart de Bruijn Mapping Victor Guryev Variant
Variant Detection & Interpretation in a diagnostic context Christian Gilissen c.gilissen@gen.umcn.nl 28-05-2013 So far Sequencing Johan den Dunnen Marja Jakobs Ewart de Bruijn Mapping Victor Guryev Variant
TADA: Analyzing De Novo, Transmission and Case-Control Sequencing Data
 TADA: Analyzing De Novo, Transmission and Case-Control Sequencing Data Each person inherits mutations from parents, some of which may predispose the person to certain diseases. Meanwhile, new mutations
TADA: Analyzing De Novo, Transmission and Case-Control Sequencing Data Each person inherits mutations from parents, some of which may predispose the person to certain diseases. Meanwhile, new mutations
CITATION FILE CONTENT/FORMAT
 CITATION For any resultant publications using please cite: Matthew A. Field, Vicky Cho, T. Daniel Andrews, and Chris C. Goodnow (2015). "Reliably detecting clinically important variants requires both combined
CITATION For any resultant publications using please cite: Matthew A. Field, Vicky Cho, T. Daniel Andrews, and Chris C. Goodnow (2015). "Reliably detecting clinically important variants requires both combined
Advance Your Genomic Research Using Targeted Resequencing with SeqCap EZ Library
 Advance Your Genomic Research Using Targeted Resequencing with SeqCap EZ Library Marilou Wijdicks International Product Manager Research For Life Science Research Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures.
Advance Your Genomic Research Using Targeted Resequencing with SeqCap EZ Library Marilou Wijdicks International Product Manager Research For Life Science Research Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures.
Supplementary Figure 1: Classification scheme for non-synonymous and nonsense germline MC1R variants. The common variants with previously established
 Supplementary Figure 1: Classification scheme for nonsynonymous and nonsense germline MC1R variants. The common variants with previously established classifications 1 3 are shown. The effect of novel missense
Supplementary Figure 1: Classification scheme for nonsynonymous and nonsense germline MC1R variants. The common variants with previously established classifications 1 3 are shown. The effect of novel missense
Congenital Heart Disease How much of it is genetic?
 Congenital Heart Disease How much of it is genetic? Stephen Robertson Curekids Professor of Paediatric Genetics Dunedin School of Medicine University of Otago Congenital Heart Disease The most common survivable
Congenital Heart Disease How much of it is genetic? Stephen Robertson Curekids Professor of Paediatric Genetics Dunedin School of Medicine University of Otago Congenital Heart Disease The most common survivable
Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
 LETTER doi:10.1038/nature10945 De novo mutations revealed by whole-exome sequencing are strongly associated with autism Stephan J. Sanders 1, Michael T. Murtha 1, Abha R. Gupta 2 *, John D. Murdoch 1 *,
LETTER doi:10.1038/nature10945 De novo mutations revealed by whole-exome sequencing are strongly associated with autism Stephan J. Sanders 1, Michael T. Murtha 1, Abha R. Gupta 2 *, John D. Murdoch 1 *,
Using large-scale human genetic variation to inform variant prioritization in neuropsychiatric disorders
 Using large-scale human genetic variation to inform variant prioritization in neuropsychiatric disorders Kaitlin E. Samocha Hurles lab, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute ACGS Summer Scientific Meeting 27
Using large-scale human genetic variation to inform variant prioritization in neuropsychiatric disorders Kaitlin E. Samocha Hurles lab, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute ACGS Summer Scientific Meeting 27
De novo mutational profile in RB1 clarified using a mutation rate modeling algorithm
 Aggarwala et al. BMC Genomics (2017) 18:155 DOI 10.1186/s12864-017-3522-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access De novo mutational profile in RB1 clarified using a mutation rate modeling algorithm Varun Aggarwala
Aggarwala et al. BMC Genomics (2017) 18:155 DOI 10.1186/s12864-017-3522-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access De novo mutational profile in RB1 clarified using a mutation rate modeling algorithm Varun Aggarwala
Supplementary Information. Data Identifies FAN1 at 15q13.3 as a Susceptibility. Gene for Schizophrenia and Autism
 Supplementary Information A Scan-Statistic Based Analysis of Exome Sequencing Data Identifies FAN1 at 15q13.3 as a Susceptibility Gene for Schizophrenia and Autism Iuliana Ionita-Laza 1,, Bin Xu 2, Vlad
Supplementary Information A Scan-Statistic Based Analysis of Exome Sequencing Data Identifies FAN1 at 15q13.3 as a Susceptibility Gene for Schizophrenia and Autism Iuliana Ionita-Laza 1,, Bin Xu 2, Vlad
1. Create a mutation rate table from intergenic SNPs for all possible trinucleotide to trinucleotide changes
 1. Create a mutation rate table from intergenic SNPs for all possible trinucleotide to trinucleotide changes ATCGGCTGG ATCGACTGG CCTAGCTAA CCTGGCTAA CTCACCGGA CTCACTGGA Change AAA ACA AAA AGA AAA ATA AAC
1. Create a mutation rate table from intergenic SNPs for all possible trinucleotide to trinucleotide changes ATCGGCTGG ATCGACTGG CCTAGCTAA CCTGGCTAA CTCACCGGA CTCACTGGA Change AAA ACA AAA AGA AAA ATA AAC
MULTIFACTORIAL DISEASES. MG L-10 July 7 th 2014
 MULTIFACTORIAL DISEASES MG L-10 July 7 th 2014 Genetic Diseases Unifactorial Chromosomal Multifactorial AD Numerical AR Structural X-linked Microdeletions Mitochondrial Spectrum of Alterations in DNA Sequence
MULTIFACTORIAL DISEASES MG L-10 July 7 th 2014 Genetic Diseases Unifactorial Chromosomal Multifactorial AD Numerical AR Structural X-linked Microdeletions Mitochondrial Spectrum of Alterations in DNA Sequence
To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank
 Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
How many disease-causing variants in a normal person? Matthew Hurles
 How many disease-causing variants in a normal person? Matthew Hurles Summary What is in a genome? What is normal? Depends on age What is a disease-causing variant? Different classes of variation Final
How many disease-causing variants in a normal person? Matthew Hurles Summary What is in a genome? What is normal? Depends on age What is a disease-causing variant? Different classes of variation Final
LTA Analysis of HapMap Genotype Data
 LTA Analysis of HapMap Genotype Data Introduction. This supplement to Global variation in copy number in the human genome, by Redon et al., describes the details of the LTA analysis used to screen HapMap
LTA Analysis of HapMap Genotype Data Introduction. This supplement to Global variation in copy number in the human genome, by Redon et al., describes the details of the LTA analysis used to screen HapMap
Introduction to genetic variation. He Zhang Bioinformatics Core Facility 6/22/2016
 Introduction to genetic variation He Zhang Bioinformatics Core Facility 6/22/2016 Outline Basic concepts of genetic variation Genetic variation in human populations Variation and genetic disorders Databases
Introduction to genetic variation He Zhang Bioinformatics Core Facility 6/22/2016 Outline Basic concepts of genetic variation Genetic variation in human populations Variation and genetic disorders Databases
Rare Variant Burden Tests. Biostatistics 666
 Rare Variant Burden Tests Biostatistics 666 Last Lecture Analysis of Short Read Sequence Data Low pass sequencing approaches Modeling haplotype sharing between individuals allows accurate variant calls
Rare Variant Burden Tests Biostatistics 666 Last Lecture Analysis of Short Read Sequence Data Low pass sequencing approaches Modeling haplotype sharing between individuals allows accurate variant calls
Problem 3: Simulated Rheumatoid Arthritis Data
 Problem 3: Simulated Rheumatoid Arthritis Data Michael B Miller Michael Li Gregg Lind Soon-Young Jang The plan
Problem 3: Simulated Rheumatoid Arthritis Data Michael B Miller Michael Li Gregg Lind Soon-Young Jang The plan
Computational Systems Biology: Biology X
 Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#4:(October-0-4-2010) Cancer and Signals 1 2 1 2 Evidence in Favor Somatic mutations, Aneuploidy, Copy-number changes and LOH
Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#4:(October-0-4-2010) Cancer and Signals 1 2 1 2 Evidence in Favor Somatic mutations, Aneuploidy, Copy-number changes and LOH
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Rates of different mutation types in CRC.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Rates of different mutation types in CRC. (a) Stratification by mutation type indicates that C>T mutations occur at a significantly greater rate than other types. (b) As for the
Supplementary Figure 1 Rates of different mutation types in CRC. (a) Stratification by mutation type indicates that C>T mutations occur at a significantly greater rate than other types. (b) As for the
Single-strand DNA library preparation improves sequencing of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) cancer DNA
 www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials 2016 Single-strand DNA library preparation improves sequencing of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) DNA Supplementary Materials
www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials 2016 Single-strand DNA library preparation improves sequencing of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) DNA Supplementary Materials
What can genetic studies tell us about ADHD? Dr Joanna Martin, Cardiff University
 What can genetic studies tell us about ADHD? Dr Joanna Martin, Cardiff University Outline of talk What do we know about causes of ADHD? Traditional family studies Modern molecular genetic studies How can
What can genetic studies tell us about ADHD? Dr Joanna Martin, Cardiff University Outline of talk What do we know about causes of ADHD? Traditional family studies Modern molecular genetic studies How can
Statistics Assignment 11 - Solutions
 Statistics 44.3 Assignment 11 - Solutions 1. Samples were taken of individuals with each blood type to see if the average white blood cell count differed among types. Eleven individuals in each group were
Statistics 44.3 Assignment 11 - Solutions 1. Samples were taken of individuals with each blood type to see if the average white blood cell count differed among types. Eleven individuals in each group were
Whole Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of Anaplastic Meningioma. Patrick Tarpey Cancer Genome Project Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
 Whole Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of Anaplastic Meningioma Patrick Tarpey Cancer Genome Project Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Outline Anaplastic meningioma compared to other cancers Whole genomes
Whole Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of Anaplastic Meningioma Patrick Tarpey Cancer Genome Project Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Outline Anaplastic meningioma compared to other cancers Whole genomes
Supplementary Figure 1: Features of IGLL5 Mutations in CLL: a) Representative IGV screenshot of first
 Supplementary Figure 1: Features of IGLL5 Mutations in CLL: a) Representative IGV screenshot of first intron IGLL5 mutation depicting biallelic mutations. Red arrows highlight the presence of out of phase
Supplementary Figure 1: Features of IGLL5 Mutations in CLL: a) Representative IGV screenshot of first intron IGLL5 mutation depicting biallelic mutations. Red arrows highlight the presence of out of phase
Analysis with SureCall 2.1
 Analysis with SureCall 2.1 Danielle Fletcher Field Application Scientist July 2014 1 Stages of NGS Analysis Primary analysis, base calling Control Software FASTQ file reads + quality 2 Stages of NGS Analysis
Analysis with SureCall 2.1 Danielle Fletcher Field Application Scientist July 2014 1 Stages of NGS Analysis Primary analysis, base calling Control Software FASTQ file reads + quality 2 Stages of NGS Analysis
The Inheritance of Complex Traits
 The Inheritance of Complex Traits Differences Among Siblings Is due to both Genetic and Environmental Factors VIDEO: Designer Babies Traits Controlled by Two or More Genes Many phenotypes are influenced
The Inheritance of Complex Traits Differences Among Siblings Is due to both Genetic and Environmental Factors VIDEO: Designer Babies Traits Controlled by Two or More Genes Many phenotypes are influenced
Dr Rick Tearle Senior Applications Specialist, EMEA Complete Genomics Complete Genomics, Inc.
 Dr Rick Tearle Senior Applications Specialist, EMEA Complete Genomics Topics Overview of Data Processing Pipeline Overview of Data Files 2 DNA Nano-Ball (DNB) Read Structure Genome : acgtacatgcattcacacatgcttagctatctctcgccag
Dr Rick Tearle Senior Applications Specialist, EMEA Complete Genomics Topics Overview of Data Processing Pipeline Overview of Data Files 2 DNA Nano-Ball (DNB) Read Structure Genome : acgtacatgcattcacacatgcttagctatctctcgccag
Non-Mendelian inheritance
 Non-Mendelian inheritance Focus on Human Disorders Peter K. Rogan, Ph.D. Laboratory of Human Molecular Genetics Children s Mercy Hospital Schools of Medicine & Computer Science and Engineering University
Non-Mendelian inheritance Focus on Human Disorders Peter K. Rogan, Ph.D. Laboratory of Human Molecular Genetics Children s Mercy Hospital Schools of Medicine & Computer Science and Engineering University
RACP Congress 2017 Genetics of Intellectual Disability and Autism: Past Present and Future 9 th May 2017
 RACP Congress 2017 Genetics of Intellectual Disability and Autism: Past Present and Future 9 th May 2017 Why causation? Explanation for family Prognosis Recurrence risk and reproductive options Guide medical
RACP Congress 2017 Genetics of Intellectual Disability and Autism: Past Present and Future 9 th May 2017 Why causation? Explanation for family Prognosis Recurrence risk and reproductive options Guide medical
MEDICAL GENOMICS LABORATORY. Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of NF1 Only (NF1-NG)
 Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of NF1 Only (NF1-NG) Ordering Information Acceptable specimen types: Fresh blood sample (3-6 ml EDTA; no time limitations associated with receipt)
Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of NF1 Only (NF1-NG) Ordering Information Acceptable specimen types: Fresh blood sample (3-6 ml EDTA; no time limitations associated with receipt)
Supplementary note: Comparison of deletion variants identified in this study and four earlier studies
 Supplementary note: Comparison of deletion variants identified in this study and four earlier studies Here we compare the results of this study to potentially overlapping results from four earlier studies
Supplementary note: Comparison of deletion variants identified in this study and four earlier studies Here we compare the results of this study to potentially overlapping results from four earlier studies
November 9, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD,
 Fast detection of de-novo copy number variants from case-parent SNP arrays identifies a deletion on chromosome 7p14.1 associated with non-syndromic isolated cleft lip/palate Samuel G. Younkin 1, Robert
Fast detection of de-novo copy number variants from case-parent SNP arrays identifies a deletion on chromosome 7p14.1 associated with non-syndromic isolated cleft lip/palate Samuel G. Younkin 1, Robert
Pedigree Construction Notes
 Name Date Pedigree Construction Notes GO TO à Mendelian Inheritance (http://www.uic.edu/classes/bms/bms655/lesson3.html) When human geneticists first began to publish family studies, they used a variety
Name Date Pedigree Construction Notes GO TO à Mendelian Inheritance (http://www.uic.edu/classes/bms/bms655/lesson3.html) When human geneticists first began to publish family studies, they used a variety
5/2/18. After this class students should be able to: Stephanie Moon, Ph.D. - GWAS. How do we distinguish Mendelian from non-mendelian traits?
 corebio II - genetics: WED 25 April 2018. 2018 Stephanie Moon, Ph.D. - GWAS After this class students should be able to: 1. Compare and contrast methods used to discover the genetic basis of traits or
corebio II - genetics: WED 25 April 2018. 2018 Stephanie Moon, Ph.D. - GWAS After this class students should be able to: 1. Compare and contrast methods used to discover the genetic basis of traits or
The role of sex-differential biology in risk for autism spectrum disorder
 Werling Biology of Sex Differences (2016) 7:58 DOI 10.1186/s13293-016-0112-8 REVIEW The role of sex-differential biology in risk for autism spectrum disorder Donna M. Werling Open Access Abstract Autism
Werling Biology of Sex Differences (2016) 7:58 DOI 10.1186/s13293-016-0112-8 REVIEW The role of sex-differential biology in risk for autism spectrum disorder Donna M. Werling Open Access Abstract Autism
An Introduction to Quantitative Genetics I. Heather A Lawson Advanced Genetics Spring2018
 An Introduction to Quantitative Genetics I Heather A Lawson Advanced Genetics Spring2018 Outline What is Quantitative Genetics? Genotypic Values and Genetic Effects Heritability Linkage Disequilibrium
An Introduction to Quantitative Genetics I Heather A Lawson Advanced Genetics Spring2018 Outline What is Quantitative Genetics? Genotypic Values and Genetic Effects Heritability Linkage Disequilibrium
NGS Types of gene dossier applications UKGTN can evaluate
 NGS Types of gene dossier applications UKGTN can evaluate Jo Whittaker on behalf of the Genetic Test Evaluation Working Group & UKGTN Project team NGS used in a number of ways Replacement technology for
NGS Types of gene dossier applications UKGTN can evaluate Jo Whittaker on behalf of the Genetic Test Evaluation Working Group & UKGTN Project team NGS used in a number of ways Replacement technology for
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 8 Questions
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 8 Questions Linkage Analysis Question Question 8.1 Affected members of the pedigree above have an autosomal dominant disorder, and cytogenetic analyses using conventional
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 8 Questions Linkage Analysis Question Question 8.1 Affected members of the pedigree above have an autosomal dominant disorder, and cytogenetic analyses using conventional
Neuropsychiatric Disease Working Group Plan June 14, 2016 NHGRI Centers for Common Disease Genomics Program
 Neuropsychiatric Disease Working Group Plan June 14, 2016 NHGRI Centers for Common Disease Genomics Program Disease/Phenotype As its inaugural CCDG project, the Neuropsychiatric Working Group (NWG) proposes
Neuropsychiatric Disease Working Group Plan June 14, 2016 NHGRI Centers for Common Disease Genomics Program Disease/Phenotype As its inaugural CCDG project, the Neuropsychiatric Working Group (NWG) proposes
Strength of functional signature correlates with effect size in autism
 Ballouz and Gillis Genome Medicine (217) 9:64 DOI 1.1186/s1373-17-455-8 RESEARCH Open Access Strength of functional signature correlates with effect size in autism Sara Ballouz and Jesse Gillis * Abstract
Ballouz and Gillis Genome Medicine (217) 9:64 DOI 1.1186/s1373-17-455-8 RESEARCH Open Access Strength of functional signature correlates with effect size in autism Sara Ballouz and Jesse Gillis * Abstract
SFARI Gene 2.0 User Guide
 1 SFARI Gene 2.0 User Guide This document is designed to acquaint the new user with SFARI Gene release 4.0, an integrated resource for autism research, and to provide enough information to allow the user
1 SFARI Gene 2.0 User Guide This document is designed to acquaint the new user with SFARI Gene release 4.0, an integrated resource for autism research, and to provide enough information to allow the user
Mendelian & Complex Traits. Quantitative Imaging Genomics. Genetics Terminology 2. Genetics Terminology 1. Human Genome. Genetics Terminology 3
 Mendelian & Complex Traits Quantitative Imaging Genomics David C. Glahn, PhD Olin Neuropsychiatry Research Center & Department of Psychiatry, Yale University July, 010 Mendelian Trait A trait influenced
Mendelian & Complex Traits Quantitative Imaging Genomics David C. Glahn, PhD Olin Neuropsychiatry Research Center & Department of Psychiatry, Yale University July, 010 Mendelian Trait A trait influenced
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
AVENIO ctdna Analysis Kits The complete NGS liquid biopsy solution EMPOWER YOUR LAB
 Analysis Kits The complete NGS liquid biopsy solution EMPOWER YOUR LAB Analysis Kits Next-generation performance in liquid biopsies 2 Accelerating clinical research From liquid biopsy to next-generation
Analysis Kits The complete NGS liquid biopsy solution EMPOWER YOUR LAB Analysis Kits Next-generation performance in liquid biopsies 2 Accelerating clinical research From liquid biopsy to next-generation
Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3. Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented in our
 1 2 Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3 Mutations 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented
1 2 Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3 Mutations 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented
SNPrints: Defining SNP signatures for prediction of onset in complex diseases
 SNPrints: Defining SNP signatures for prediction of onset in complex diseases Linda Liu, Biomedical Informatics, Stanford University Daniel Newburger, Biomedical Informatics, Stanford University Grace
SNPrints: Defining SNP signatures for prediction of onset in complex diseases Linda Liu, Biomedical Informatics, Stanford University Daniel Newburger, Biomedical Informatics, Stanford University Grace
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Country distribution of GME samples and designation of geographical subregions.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Country distribution of GME samples and designation of geographical subregions. GME samples collected across 20 countries and territories from the GME. Pie size corresponds to the
Supplementary Figure 1 Country distribution of GME samples and designation of geographical subregions. GME samples collected across 20 countries and territories from the GME. Pie size corresponds to the
Functional analysis of DNA variants
 Functional analysis of DNA variants GS011143, Introduction to Bioinformatics The University of Texas GSBS program, Fall 2012 Ken Chen, Ph.D. Department of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology UT MD
Functional analysis of DNA variants GS011143, Introduction to Bioinformatics The University of Texas GSBS program, Fall 2012 Ken Chen, Ph.D. Department of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology UT MD
Prevalence and clinical implications of BRCA1/2 germline mutations in Chinese women with breast cancer Yuntao Xie M.D., Ph.D.
 Prevalence and clinical implications of BRCA1/2 germline mutations in Chinese women with breast cancer Yuntao Xie M.D., Ph.D. Hereditary Cancer Center, Peking University Cancer Hospital 1 Breast cancer
Prevalence and clinical implications of BRCA1/2 germline mutations in Chinese women with breast cancer Yuntao Xie M.D., Ph.D. Hereditary Cancer Center, Peking University Cancer Hospital 1 Breast cancer
Structural Variation and Medical Genomics
 Structural Variation and Medical Genomics Andrew King Department of Biomedical Informatics July 8, 2014 You already know about small scale genetic mutations Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) Deletions,
Structural Variation and Medical Genomics Andrew King Department of Biomedical Informatics July 8, 2014 You already know about small scale genetic mutations Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) Deletions,
Assessing Laboratory Performance for Next Generation Sequencing Based Detection of Germline Variants through Proficiency Testing
 Assessing Laboratory Performance for Next Generation Sequencing Based Detection of Germline Variants through Proficiency Testing Karl V. Voelkerding, MD Professor of Pathology University of Utah Medical
Assessing Laboratory Performance for Next Generation Sequencing Based Detection of Germline Variants through Proficiency Testing Karl V. Voelkerding, MD Professor of Pathology University of Utah Medical
A framework for the interpretation of de novo mutation in human disease
 A framework for the interpretation of de novo mutation in human disease The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
A framework for the interpretation of de novo mutation in human disease The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
PERSONALIZED GENETIC REPORT CLIENT-REPORTED DATA PURPOSE OF THE X-SCREEN TEST
 INCLUDED IN THIS REPORT: REVIEW OF YOUR GENETIC INFORMATION RELEVANT TO ENDOMETRIOSIS PERSONAL EDUCATIONAL INFORMATION RELEVANT TO YOUR GENES INFORMATION FOR OBTAINING YOUR ENTIRE X-SCREEN DATA FILE PERSONALIZED
INCLUDED IN THIS REPORT: REVIEW OF YOUR GENETIC INFORMATION RELEVANT TO ENDOMETRIOSIS PERSONAL EDUCATIONAL INFORMATION RELEVANT TO YOUR GENES INFORMATION FOR OBTAINING YOUR ENTIRE X-SCREEN DATA FILE PERSONALIZED
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions
 Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
A guide to understanding variant classification
 White paper A guide to understanding variant classification In a diagnostic setting, variant classification forms the basis for clinical judgment, making proper classification of variants critical to your
White paper A guide to understanding variant classification In a diagnostic setting, variant classification forms the basis for clinical judgment, making proper classification of variants critical to your
Chapter 1 : Genetics 101
 Chapter 1 : Genetics 101 Understanding the underlying concepts of human genetics and the role of genes, behavior, and the environment will be important to appropriately collecting and applying genetic
Chapter 1 : Genetics 101 Understanding the underlying concepts of human genetics and the role of genes, behavior, and the environment will be important to appropriately collecting and applying genetic
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Joensuu H, Wardelmann E, Sihto H, et al. Effect of KIT and PDGFRA mutations on survival in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors treated with adjuvant imatinib: an
Supplementary Online Content Joensuu H, Wardelmann E, Sihto H, et al. Effect of KIT and PDGFRA mutations on survival in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors treated with adjuvant imatinib: an
Dan Koller, Ph.D. Medical and Molecular Genetics
 Design of Genetic Studies Dan Koller, Ph.D. Research Assistant Professor Medical and Molecular Genetics Genetics and Medicine Over the past decade, advances from genetics have permeated medicine Identification
Design of Genetic Studies Dan Koller, Ph.D. Research Assistant Professor Medical and Molecular Genetics Genetics and Medicine Over the past decade, advances from genetics have permeated medicine Identification
Interrogation of rare functional variation within bipolar disorder and suicidal behavior cohorts
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2018 Interrogation of rare functional variation within bipolar disorder and suicidal behavior cohorts Eric Thayne Monson University
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2018 Interrogation of rare functional variation within bipolar disorder and suicidal behavior cohorts Eric Thayne Monson University
Using the Bravo Liquid-Handling System for Next Generation Sequencing Sample Prep
 Using the Bravo Liquid-Handling System for Next Generation Sequencing Sample Prep Tom Walsh, PhD Division of Medical Genetics University of Washington Next generation sequencing Sanger sequencing gold
Using the Bravo Liquid-Handling System for Next Generation Sequencing Sample Prep Tom Walsh, PhD Division of Medical Genetics University of Washington Next generation sequencing Sanger sequencing gold
SVIM: Structural variant identification with long reads DAVID HELLER MAX PLANCK INSTITUTE FOR MOLECULAR GENETICS, BERLIN JUNE 2O18, SMRT LEIDEN
 SVIM: Structural variant identification with long reads DAVID HELLER MAX PLANCK INSTITUTE FOR MOLECULAR GENETICS, BERLIN JUNE 2O18, SMRT LEIDEN Structural variation (SV) Variants larger than 50bps Affect
SVIM: Structural variant identification with long reads DAVID HELLER MAX PLANCK INSTITUTE FOR MOLECULAR GENETICS, BERLIN JUNE 2O18, SMRT LEIDEN Structural variation (SV) Variants larger than 50bps Affect
Home Brewed Personalized Genomics
 Home Brewed Personalized Genomics The Quest for Meaningful Analysis Results of a 23andMe Exome Pilot Trio of Myself, Wife, and Son February 22, 2013 Gabe Rudy, Vice President of Product Development Exome
Home Brewed Personalized Genomics The Quest for Meaningful Analysis Results of a 23andMe Exome Pilot Trio of Myself, Wife, and Son February 22, 2013 Gabe Rudy, Vice President of Product Development Exome
Mendelian Inheritance. Jurg Ott Columbia and Rockefeller Universities New York
 Mendelian Inheritance Jurg Ott Columbia and Rockefeller Universities New York Genes Mendelian Inheritance Gregor Mendel, monk in a monastery in Brünn (now Brno in Czech Republic): Breeding experiments
Mendelian Inheritance Jurg Ott Columbia and Rockefeller Universities New York Genes Mendelian Inheritance Gregor Mendel, monk in a monastery in Brünn (now Brno in Czech Republic): Breeding experiments
AVENIO family of NGS oncology assays ctdna and Tumor Tissue Analysis Kits
 AVENIO family of NGS oncology assays ctdna and Tumor Tissue Analysis Kits Accelerating clinical research Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has the ability to interrogate many different genes and detect
AVENIO family of NGS oncology assays ctdna and Tumor Tissue Analysis Kits Accelerating clinical research Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has the ability to interrogate many different genes and detect
Quantitative genetics: traits controlled by alleles at many loci
 Quantitative genetics: traits controlled by alleles at many loci Human phenotypic adaptations and diseases commonly involve the effects of many genes, each will small effect Quantitative genetics allows
Quantitative genetics: traits controlled by alleles at many loci Human phenotypic adaptations and diseases commonly involve the effects of many genes, each will small effect Quantitative genetics allows
Genetic Approaches to Alcoholism, Alcohol Abuse Susceptibility, and Therapeutic Response. Ray White Verona March
 Genetic Approaches to Alcoholism, Alcohol Abuse Susceptibility, and Therapeutic Response Ray White Verona March 18. 2008 Craig Venter Genome 2,810,000,000 bases, 7.5-fold coverage 3,213,401 SNPs 85% in
Genetic Approaches to Alcoholism, Alcohol Abuse Susceptibility, and Therapeutic Response Ray White Verona March 18. 2008 Craig Venter Genome 2,810,000,000 bases, 7.5-fold coverage 3,213,401 SNPs 85% in
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 An example of the gene-term-disease network automatically generated by Phenolyzer web server for 'autism'. The largest word represents the user s input term, Autism. The pink round
Supplementary Figure 1 An example of the gene-term-disease network automatically generated by Phenolyzer web server for 'autism'. The largest word represents the user s input term, Autism. The pink round
Statistical power and significance testing in large-scale genetic studies
 STUDY DESIGNS Statistical power and significance testing in large-scale genetic studies Pak C. Sham 1 and Shaun M. Purcell 2,3 Abstract Significance testing was developed as an objective method for summarizing
STUDY DESIGNS Statistical power and significance testing in large-scale genetic studies Pak C. Sham 1 and Shaun M. Purcell 2,3 Abstract Significance testing was developed as an objective method for summarizing
Supplementary Figure 1. Estimation of tumour content
 Supplementary Figure 1. Estimation of tumour content a, Approach used to estimate the tumour content in S13T1/T2, S6T1/T2, S3T1/T2 and S12T1/T2. Tissue and tumour areas were evaluated by two independent
Supplementary Figure 1. Estimation of tumour content a, Approach used to estimate the tumour content in S13T1/T2, S6T1/T2, S3T1/T2 and S12T1/T2. Tissue and tumour areas were evaluated by two independent
MEDICAL GENOMICS LABORATORY. Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Panel by Next-Gen Sequencing (PNT-NG)
 Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Panel by Next-Gen Sequencing (PNT-NG) Ordering Information Acceptable specimen types: Blood (3-6ml EDTA; no time limitations associated with receipt) Saliva (OGR-575 DNA Genotek;
Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Panel by Next-Gen Sequencing (PNT-NG) Ordering Information Acceptable specimen types: Blood (3-6ml EDTA; no time limitations associated with receipt) Saliva (OGR-575 DNA Genotek;
JULY 21, Genetics 101: SCN1A. Katie Angione, MS CGC Certified Genetic Counselor CHCO Neurology
 JULY 21, 2018 Genetics 101: SCN1A Katie Angione, MS CGC Certified Genetic Counselor CHCO Neurology Disclosures: I have no financial interests or relationships to disclose. Objectives 1. Review genetic
JULY 21, 2018 Genetics 101: SCN1A Katie Angione, MS CGC Certified Genetic Counselor CHCO Neurology Disclosures: I have no financial interests or relationships to disclose. Objectives 1. Review genetic
Genome Wide Variant Analysis of Simplex Autism Families with an Integrative Clinical-Bioinformatics Pipeline
 Genome Wide Variant Analysis of Simplex Autism Families with an Integrative Clinical-Bioinformatics Pipeline Laura T. Jiménez-Barrón 1,5, Jason A. O Rawe 1,2, Yiyang Wu 1,2, Margaret Yoon 1, Han Fang 1,
Genome Wide Variant Analysis of Simplex Autism Families with an Integrative Clinical-Bioinformatics Pipeline Laura T. Jiménez-Barrón 1,5, Jason A. O Rawe 1,2, Yiyang Wu 1,2, Margaret Yoon 1, Han Fang 1,
Parental age and autism: Population data from NJ
 Parental age and autism: Population data from NJ Introduction While the cause of autism is not known, current research suggests that a combination of genetic and environmental factors may be involved.
Parental age and autism: Population data from NJ Introduction While the cause of autism is not known, current research suggests that a combination of genetic and environmental factors may be involved.
6/12/2018. Disclosures. Clinical Genomics The CLIA Lab Perspective. Outline. COH HopeSeq Heme Panels
 Clinical Genomics The CLIA Lab Perspective Disclosures Raju K. Pillai, M.D. Hematopathologist / Molecular Pathologist Director, Pathology Bioinformatics City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, CA
Clinical Genomics The CLIA Lab Perspective Disclosures Raju K. Pillai, M.D. Hematopathologist / Molecular Pathologist Director, Pathology Bioinformatics City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, CA
Concurrent Practical Session ACMG Classification
 Variant Effect Prediction Training Course 6-8 November 2017 Prague, Czech Republic Concurrent Practical Session ACMG Classification Andreas Laner / Anna Benet-Pagès 1 Content 1. Background... 3 2. Aim
Variant Effect Prediction Training Course 6-8 November 2017 Prague, Czech Republic Concurrent Practical Session ACMG Classification Andreas Laner / Anna Benet-Pagès 1 Content 1. Background... 3 2. Aim
Clinical evaluation of microarray data
 Clinical evaluation of microarray data David Amor 19 th June 2011 Single base change Microarrays 3-4Mb What is a microarray? Up to 10 6 bits of Information!! Highly multiplexed FISH hybridisations. Microarray
Clinical evaluation of microarray data David Amor 19 th June 2011 Single base change Microarrays 3-4Mb What is a microarray? Up to 10 6 bits of Information!! Highly multiplexed FISH hybridisations. Microarray
Pedigree Analysis Why do Pedigrees? Goals of Pedigree Analysis Basic Symbols More Symbols Y-Linked Inheritance
 Pedigree Analysis Why do Pedigrees? Punnett squares and chi-square tests work well for organisms that have large numbers of offspring and controlled mating, but humans are quite different: Small families.
Pedigree Analysis Why do Pedigrees? Punnett squares and chi-square tests work well for organisms that have large numbers of offspring and controlled mating, but humans are quite different: Small families.
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Brain magnetic resonance imaging in patient 9 at age 3.6 years.
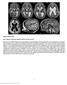 Supplementary Figure 1 Brain magnetic resonance imaging in patient 9 at age 3.6 years. (a d) Axial T2-weighted images show a marked degree of ventriculomegaly. Note the diencephalic mesencephalic junction
Supplementary Figure 1 Brain magnetic resonance imaging in patient 9 at age 3.6 years. (a d) Axial T2-weighted images show a marked degree of ventriculomegaly. Note the diencephalic mesencephalic junction
Burning debate: What s the best way to nab real autism genes?
 OPINION, VIEWPOINT Burning debate: What s the best way to nab real autism genes? BY BRIAN O'ROAK 27 JUNE 2017 Over the past 10 years researchers have made tremendous progress in understanding the genetic
OPINION, VIEWPOINT Burning debate: What s the best way to nab real autism genes? BY BRIAN O'ROAK 27 JUNE 2017 Over the past 10 years researchers have made tremendous progress in understanding the genetic
Integrated Model of De Novo and Inherited Genetic Variants Yields Greater Power to Identify Risk Genes
 Integrated Model of De Novo and Inherited Genetic Variants Yields Greater Power to Identify Risk Genes Xin He 1, Stephan J. Sanders 2, Li Liu 3, Silvia De Rubeis 4,5, Elaine T. Lim 6,7, James S. Sutcliffe
Integrated Model of De Novo and Inherited Genetic Variants Yields Greater Power to Identify Risk Genes Xin He 1, Stephan J. Sanders 2, Li Liu 3, Silvia De Rubeis 4,5, Elaine T. Lim 6,7, James S. Sutcliffe
Non-parametric methods for linkage analysis
 BIOSTT516 Statistical Methods in Genetic Epidemiology utumn 005 Non-parametric methods for linkage analysis To this point, we have discussed model-based linkage analyses. These require one to specify a
BIOSTT516 Statistical Methods in Genetic Epidemiology utumn 005 Non-parametric methods for linkage analysis To this point, we have discussed model-based linkage analyses. These require one to specify a
Genome. Institute. GenomeVIP: A Genomics Analysis Pipeline for Cloud Computing with Germline and Somatic Calling on Amazon s Cloud. R. Jay Mashl.
 GenomeVIP: the Genome Institute at Washington University A Genomics Analysis Pipeline for Cloud Computing with Germline and Somatic Calling on Amazon s Cloud R. Jay Mashl October 20, 2014 Turnkey Variant
GenomeVIP: the Genome Institute at Washington University A Genomics Analysis Pipeline for Cloud Computing with Germline and Somatic Calling on Amazon s Cloud R. Jay Mashl October 20, 2014 Turnkey Variant
ARTICLE RESEARCH. Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
 Extended Data Figure 6 Annotation of drivers based on clinical characteristics and co-occurrence patterns. a, Putative drivers affecting greater than 10 patients were assessed for enrichment in IGHV mutated
Extended Data Figure 6 Annotation of drivers based on clinical characteristics and co-occurrence patterns. a, Putative drivers affecting greater than 10 patients were assessed for enrichment in IGHV mutated
Recurrence rates provide evidence for sex-differential, familial genetic liability for autism spectrum disorders in multiplex families and twins
 Werling and Geschwind Molecular Autism (2015) 6:27 DOI 10.1186/s13229-015-0004-5 RESEARCH Open Access Recurrence rates provide evidence for sex-differential, familial genetic liability for autism spectrum
Werling and Geschwind Molecular Autism (2015) 6:27 DOI 10.1186/s13229-015-0004-5 RESEARCH Open Access Recurrence rates provide evidence for sex-differential, familial genetic liability for autism spectrum
Title:Exome sequencing helped the fine diagnosis of two siblings afflicted with atypical Timothy syndrome (TS2)
 Author's response to reviews Title:Exome sequencing helped the fine diagnosis of two siblings afflicted with atypical Timothy syndrome (TS2) Authors: Sebastian Fröhler (Sebastian.Froehler@mdc-berlin.de)
Author's response to reviews Title:Exome sequencing helped the fine diagnosis of two siblings afflicted with atypical Timothy syndrome (TS2) Authors: Sebastian Fröhler (Sebastian.Froehler@mdc-berlin.de)
MEDICAL GENOMICS LABORATORY. Non-NF1 RASopathy panel by Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of SPRED1 (NNP-NG)
 Non-NF1 RASopathy panel by Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of SPRED1 (NNP-NG) Ordering Information Acceptable specimen types: Blood (3-6ml EDTA; no time limitations associated with
Non-NF1 RASopathy panel by Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of SPRED1 (NNP-NG) Ordering Information Acceptable specimen types: Blood (3-6ml EDTA; no time limitations associated with
Estimating genetic variation within families
 Estimating genetic variation within families Peter M. Visscher Queensland Institute of Medical Research Brisbane, Australia peter.visscher@qimr.edu.au 1 Overview Estimation of genetic parameters Variation
Estimating genetic variation within families Peter M. Visscher Queensland Institute of Medical Research Brisbane, Australia peter.visscher@qimr.edu.au 1 Overview Estimation of genetic parameters Variation
