Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Bromodeoxyuridine
|
|
|
- Roger Snow
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kateřina Náměstková, Zuzana Šimonová, Eva Syková Behavioural Brain Research Bromodeoxyuridine : Doublecortin : DCX Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein : GFAP Trace eye blink conditioning 1 Volume 163 : pp , , a compound that is structurally similar to thymidine, one of the building blocks of DNA. gets incorporated into DNA instead of thymidine. Deoxyribose sugar Phosphate A : Adenine T : Thymine G : Guanine 3 C : Cytosine Bromodeoxyuridine 4 Thymidine Daughter DNA Strand DCX, a component of the microtubule cytoskeleton, is one such molecule which are involved specifically in neuronal path-finding and movement. Parental DNA Strand DCX is associated with migration of neuronal precursors during development of the nervous system. Therefore, measuring the cells with indicates how many cells are replicating. Therefore, measuring the cells with DCX indicates newborn neurons. 5 6
2 Neurons Astrocyte Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is an intermediate filament protein. In the central nervous system, GFAP is expressed in astrocytes and but not in other glial cells. Corneal Air Puff Elicits Eyeblink Response Corneal Air Puff Given with Tone Tone Given Alone Elicits Eyeblink Response Microglial cell Therefore, measuring the cells with GFAP indicates astrocyte. 7 (tone) CS (air puff) US Time Trace 8 on off on off Hippocampus is an important structure for spatial learning and memory. Inner blade hilus Outer blade New neurons are continuously born in the granular cell layer of the hippocampus throughout life in a number mammalian species, including humans. (Altman and Das, 1965; van Praag H et al., 1999; Brown JP et al., 2003) Newborn cells can be detected by labeling with [ 3 H] thymidine or. Neuronal phenotype can be determined by using various neuronal markers such as doublecortin (DCX). 9 Copyright 2001 by Allyn & Bacon 10 Several conditions influence the rate of proliferation and the survival and function of the newborn cells During aging Exposure to stress Antidepressant Tx Physical activity Enrich environment Some task of hippocampusdependent learning Suppress granule cell proliferation (Gould E and Tanapat P, 1999) Promote proliferation and survival (Malberg JE and Duman RS, 2003; Stressful experiences Duman RS et al., 2001; Malberg JE et al., 2000) Corticosterone levels Suppress proliferation (Gould E and Tanapat P, 1999; Duman RS et al., 2001) Basal levels of corticosterone may influence proliferation throughout the entire lifespan.
3 In the study of Gould E and Tanapat P (1999) In the first 2-postnatal weeks old rats Chronic application of several classes of antidepressants (including selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitor : fluoxetine) Low levels of corticosterone that are accompanied by a stress hyporesponsive period a high rate of granular cell proliferation Age Basal levels of corticosterone 13 Rate of proliferation Expression of the trophic factor BDNF Rate of granular cell proliferation (Malberg JE et al., 2000) Physical activity also up-regulates the transcription of BDNF gene and to be additive to antidepressant treatment. (Neeper SA et al., ; Russo-Neustadt AA et al., 2000) Hippocampus-dependent learning as short as 4 days in the Morris water maze (MWM) Acquisition of 800 trials of a trace eye blink conditioning Animal exposed to an enriched environment for 8 weeks Voluntary wheel running for 30 days Number of surviving cells (Gould E et al., 1999) Performance in the hippocampus-dependent spatial learning in the Morris water maze (Nilsson M et al., 1999; van Praag H et al., 1999) Presumably due to the contribution of newborn cells to hippocampus formation Objectives of this study Physical activity Morris water maze task = Stressful component To investigate whether spatial learning in the Morris water maze (MWM) will affect the proliferation of granule cells in the hippocampus of adult rats. Affect the proliferation of granular cells in the hippocampus of adult rats. To investigate the effects of antidepressant treatment with fluoxetine on the change in proliferative response to the MWM task
4 Animals 3-month-old male Wistar rats ( g) Housed under standard conditions, 2-3 per cage Maintained on a 12 h light and dark cycle Study were approved by the ethical committee (Institute of Experiment Medicine, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic) Rats were randomly assigned to 4 groups and then underwent 15 days of 4 different treatments. Control group (C) 1.5 ml saline (i.p.) Water maze group (WM) Saline MWM Fluoxetine group (F) 5 mg/kg Fluoxetine (i.p.) Fluoxetine treated and Water maze group (FWM) Fluoxetine MWM Experimental schedule Sacrificed Morris Water Maze 3-month-old rats i.p. injection - C group - WM group - F group Treatment 15 days - FWM group 8 hr 16 hr Day 1 Day 15 Day Tissue processing and immunohistochemistry Rats swim in a pool of water to find a hidden platform. Rats were exposed to 4 trial / day with an intertrial interval of 60 sec. For each trial, rat was placed in a random quadrant of the tank. Provided 60 sec to locate and mount the platform. Latency to reach the platform, was recorded. 22 camera Morris Water Maze Light Day Invisible platform Invisible platform platform Invisible platform 23 Cold water (22 ± 2 C) 24
5 Tissue processing and immunohistochemistry 4% paraformaldehyde Add Primary Antibody Mouse monoclonal directed against 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine Doublecortin Goat anti-doublecortin C-18 GFAP Cy3-conjugated rabbit anti-rat GFAP 40 μm thick coronal sections Peroxidase immunohistochemistry Add Secondary Antibody After saturation sucrose Peroxidase-conjugated rabbit anti-mouse (goat) IgG, visualized by DAB Doublecortin 25 Vectastain Elite ABC kit 26 Add Primary Antibody Mouse monoclonal directed against 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine Doublecortin Goat anti-doublecortin C-18 GFAP Cy3-conjugated rabbit anti-rat GFAP Images and cell counting Microscope (63x) Indirect immunofluorescence Alexa Flour 594 (488) -conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG Add Secondary Antibody Coronal brain sections Count cells every 6 th section Separately count in GCL and in hilus DCX cells count in 3 sections from each animal Doublecortin Alexa Flour 488-conjugated donkey anti-goat IgG Number of cells and DCX cells Statistical analyses Photomicrographs of a rat hippocampus stained with anti- (newborn cell) Number of cells and DCX cells expressed as mean ± S.E.M. / hippocampus in a slice Comparisons between groups using Student s t-test Statistical significance P
6 Photomicrographs of a rat hippocampus stained with anti-dcx (newborn neuron) From Photomicrographs Show GFAP processes forming a basket around only some of the cells in the cluster of cells. Survival of newborn cells is likely to be successful when I. Stimulating substances diffusing from the blood stream II. Impulses from the functional neuronal network Both are delivered through the astrocytic syncytium Sub-granular zone astrocytes are the primary precursors of the D cells that differentiate into neuron. Syková E et al. study (2002) Learning deficits in aged rats are related to the disorganization of astrocytic processes and the loss of extracellular matrix in the hippocampus. SGL astrocytes Dark cells (Doetsch F. Curr 35 Opin Genet Dev 2003; 13: ) 36
7 Effects of the treatments on the number of cells per hippocampus in one slice (mean ± S.E.M.) Immunohistochemical staining for DCX to determine the number of cells differentiating into new neurons born during approximately the last 14 days preceding sacrifice. The time period when newborn cells show this early neuronal marker. * p < ** p < 0.01 Effects of the treatments on the number of cell and DCX cells per hippocampus in one slice (mean ± S.E.M.) * p > 0.05 Learning curves of the 2 groups of animals that underwent the MWM learning task (WM and FWM) Suggest that fluoxetine treatment increases proliferation but not the differentiation and survival of newborn neurons. Supporting for this results In the work of Shors et al. (2002) Blocking neurogenesis with cytostatic Spatial learning performance in the water maze Trace eye blink and fear conditioning intact impaired Present study Shows that spatial learning acquisition trials in the MWM and fluoxetine treatment affect the rate of cell proliferation in the neurogenic region. Complex stimulation and learning in the MWM for 15 days Suggested that the acquisition of spatial memory in the water maze may be a task that requires only a small percentage of new neurons. 41 Down-regulation of granular cell proliferation 42
8 has been considered as a factor that positively influences the generation of new neurons in adulthood. Hippocampus-dependent learning of temporal or spatial events Present results contradict previous study In an experiment done by Lemaire et al. (2000) 5 days of spatial task learning in the MWM Rate of proliferation Survival of newborn cells There are important differences between the studies I. Length of exposure to the MWM task this study 15 days Lemaire et al. study 5 days Morris water maze task = Spatial learning Physical activity Stressful component II. injection after the training before the training The motivation for finding the location of the hidden platform is to escape from a life-threatening situation in a unpleasant environment of cold water The different results of the two studies suggest that Prolonged exposure to a stressful experience Benefit from proliferation factors (such as physical activity) Results in this study can be compared to van Praag et al. study van Praag et al. study (1999) Mice were divided into 2 groups and underwent 12 days of training (inject everyday) only to swimming water maze acquisition 47 48
9 Result in the van Praag et al. study (1999) Number of labeled cells was not different between two groups. Down-regulating effect of stress was probably masked by a normal rate of neurogenesis prior to the decline in the proliferative rate during the water maze training.? First question Further study In this study have not examined the survival of newborn cells for an extended period of time. It would be of interest to see if the combination of fluoxetine and learning in MWM would change the number of surviving cells 4 weeks after labeling Second question? Mechanism of action of stressful learning combined with fluoxetine on the rate of neurogenesis. This study Show the negative effect of long-term exposure to the MWM on the proliferation of new neurons. To be a potential substrate for new learning capacity 51 Speaker : Mr. Nattapon Sookprasert SIPS/M
Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex?
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 107 (2006) No. 1, p. 71 80 71) Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex? Šimonová Z., Dutt J. Department of Neuroscience of the Institute
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 107 (2006) No. 1, p. 71 80 71) Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex? Šimonová Z., Dutt J. Department of Neuroscience of the Institute
Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing. Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2
 ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models. From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Hippocampal Pyramidal Neuron of Mice and Rats Figure 1 Open Field Apparatus Open Field Behavior
Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Hippocampal Pyramidal Neuron of Mice and Rats Figure 1 Open Field Apparatus Open Field Behavior
Learning enhances adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal formation
 Learning enhances adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal formation Elizabeth Gould 1, Anna Beylin 1, Patima Tanapat 1, Alison Reeves 1 and Tracey J. Shors 2 1 Department of Psychology, Princeton University,
Learning enhances adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal formation Elizabeth Gould 1, Anna Beylin 1, Patima Tanapat 1, Alison Reeves 1 and Tracey J. Shors 2 1 Department of Psychology, Princeton University,
Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2+ cells in different brain regions.
 Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05772 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental figure 1. Enrichment facilitates learning. a. Images showing a home cage and a cage used for environmental enrichment (EE). For EE up to
doi: 10.1038/nature05772 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental figure 1. Enrichment facilitates learning. a. Images showing a home cage and a cage used for environmental enrichment (EE). For EE up to
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by
 Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
BRAIN RESEARCH XX (2006) XXX XXX. available at
 BRES-35047; No. of pages: 12; 4C: 6 BRAIN RESEARCH XX (2006) XXX XXX available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainres Research Report Selective serotonin depletion does not regulate
BRES-35047; No. of pages: 12; 4C: 6 BRAIN RESEARCH XX (2006) XXX XXX available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainres Research Report Selective serotonin depletion does not regulate
Inhibiting the microglia activation improves the spatial memory and adult neurogenesis in rat hippocampus during 48 h of sleep deprivation
 Wadhwa et al. Journal of Neuroinflammation (2017) 14:222 DOI 10.1186/s12974-017-0998-z RESEARCH Open Access Inhibiting the microglia activation improves the spatial memory and adult neurogenesis in rat
Wadhwa et al. Journal of Neuroinflammation (2017) 14:222 DOI 10.1186/s12974-017-0998-z RESEARCH Open Access Inhibiting the microglia activation improves the spatial memory and adult neurogenesis in rat
The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females
 The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females Samantha Pavlock (Medical Student) Pradeep Bhide and Deirdre McCarthy (Faculty
The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females Samantha Pavlock (Medical Student) Pradeep Bhide and Deirdre McCarthy (Faculty
Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis of individual mice during maze learning. a,
 Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain. - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function
 Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (21): ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (21): ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Inhibition of convulsive status epilepticus-induced abnormal neurogenesis by sodium valproate. Peng Wu 1, Yue Hu 1, Xiujuan Li 1, Min
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (21): ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Inhibition of convulsive status epilepticus-induced abnormal neurogenesis by sodium valproate. Peng Wu 1, Yue Hu 1, Xiujuan Li 1, Min
Dr Francis A. Olaolorun Report on ISN/CAEN category 1A August 2016 research grant Home institution: Host institution:
 Dr Francis. Olaolorun Report on ISN/CEN category 1 ugust 2016 research grant Home institution: Neuroscience Unit, Department of Veterinary natomy, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria. Host institution:
Dr Francis. Olaolorun Report on ISN/CEN category 1 ugust 2016 research grant Home institution: Neuroscience Unit, Department of Veterinary natomy, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria. Host institution:
Short-Term But Not Long-Term Exercise Ameliorates Depressive Behavior in Mice
 Short-Term But Not Long-Term Exercise Ameliorates Depressive Behavior in Mice Hiroki Yashima, Aya Matsushita, Ken-ichi Kinoshita, Yoshikage Muroi, and Toshiaki Ishii ABSTRACT Objective Voluntary exercise
Short-Term But Not Long-Term Exercise Ameliorates Depressive Behavior in Mice Hiroki Yashima, Aya Matsushita, Ken-ichi Kinoshita, Yoshikage Muroi, and Toshiaki Ishii ABSTRACT Objective Voluntary exercise
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS
 TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Running Rescues Defective Adult Neurogenesis by Shortening the Length of the Cell Cycle of Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells STEFANO FARIOLI VECCHIOLI, a ANDREA MATTERA, a LAURA
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Running Rescues Defective Adult Neurogenesis by Shortening the Length of the Cell Cycle of Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells STEFANO FARIOLI VECCHIOLI, a ANDREA MATTERA, a LAURA
Exercising Our Minds: Effects of Exercise on Brain Structure & Function
 Public Lecture Exercising Our Minds: Effects of Exercise on Brain Structure & Function Dr. Brian R. Christie Division of Medical Sciences, University of Victoria Cellular and Physiological Sciences, UBC
Public Lecture Exercising Our Minds: Effects of Exercise on Brain Structure & Function Dr. Brian R. Christie Division of Medical Sciences, University of Victoria Cellular and Physiological Sciences, UBC
THE EFFECTS OF bfgf TREATMENT IN THE AGED BRAIN FOLLOWING TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY
 Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2010 THE EFFECTS OF bfgf TREATMENT IN THE AGED BRAIN FOLLOWING TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Michael Zeigler Virginia
Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2010 THE EFFECTS OF bfgf TREATMENT IN THE AGED BRAIN FOLLOWING TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Michael Zeigler Virginia
Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - -
 BRAIN PLASTICITY Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - - Recently, it was found that new neurons and glial cells are born in specific brain regions - reorganization. Brain plasticity occurs
BRAIN PLASTICITY Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - - Recently, it was found that new neurons and glial cells are born in specific brain regions - reorganization. Brain plasticity occurs
BRAIN PLASTICITY. Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - -
 BRAIN PLASTICITY Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - - Recently, it was found that new neurons and glial cells are born in specific brain regions - reorganization. Brain plasticity occurs
BRAIN PLASTICITY Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - - Recently, it was found that new neurons and glial cells are born in specific brain regions - reorganization. Brain plasticity occurs
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Information. Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease. Supplementary Figures S1-10
 Supplementary Information Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease Christine Grienberger 1 *, Nathalie L. Rochefort 1 *, Helmuth Adelsberger 1, Horst A. Henning
Supplementary Information Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease Christine Grienberger 1 *, Nathalie L. Rochefort 1 *, Helmuth Adelsberger 1, Horst A. Henning
Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus
 Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus Gerd Kempermann 1,2, Sebastian Jessberger 2, Barbara Steiner 2 and Golo Kronenberg 1,3 1 Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin-Buch,
Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus Gerd Kempermann 1,2, Sebastian Jessberger 2, Barbara Steiner 2 and Golo Kronenberg 1,3 1 Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin-Buch,
The Timing of Differentiation of Adult Hippocampal Neurons Is Crucial for Spatial Memory
 The Timing of Differentiation of Adult Hippocampal Neurons Is Crucial for Spatial Memory PLoS BIOLOGY Stefano Farioli-Vecchioli 1[, Daniele Saraulli 2,3[, Marco Costanzi 2,3[, Simone Pacioni 4[, Irene
The Timing of Differentiation of Adult Hippocampal Neurons Is Crucial for Spatial Memory PLoS BIOLOGY Stefano Farioli-Vecchioli 1[, Daniele Saraulli 2,3[, Marco Costanzi 2,3[, Simone Pacioni 4[, Irene
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus
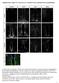 Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Environmental influences on brain and behaviour
 Environmental influences on brain and behaviour Abdul H. Mohammed Dept. of Neurotec Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden IBRO African Neuroscience School, Nairobi, 2005 Environmental interventions affecting
Environmental influences on brain and behaviour Abdul H. Mohammed Dept. of Neurotec Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden IBRO African Neuroscience School, Nairobi, 2005 Environmental interventions affecting
Behavioral and Pharmacological Evaluation of a Selectively Bred Mouse Model of Home Cage Hyperactivity
 Behav Genet (214) 44:516 534 DOI 1.17/s1519-14-9667-5 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Behavioral and Pharmacological Evaluation of a Selectively Bred Mouse Model of Home Cage Hyperactivity Petra Majdak Paula J. Bucko
Behav Genet (214) 44:516 534 DOI 1.17/s1519-14-9667-5 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Behavioral and Pharmacological Evaluation of a Selectively Bred Mouse Model of Home Cage Hyperactivity Petra Majdak Paula J. Bucko
17β-ESTRADIOL, BUT NOT ESTRONE, INCREASES HIPPOCAMPAL NEUROGENESIS AND ACTIVATION OF NEW GRANULE NEURONS IN RESPONSE
 17β-ESTRADIOL, BUT NOT ESTRONE, INCREASES HIPPOCAMPAL NEUROGENESIS AND ACTIVATION OF NEW GRANULE NEURONS IN RESPONSE TO SPATIAL MEMORY IN ADULT FEMALE RATS by ROBYN ELIZABETH STEWART B.Sc., Acadia University,
17β-ESTRADIOL, BUT NOT ESTRONE, INCREASES HIPPOCAMPAL NEUROGENESIS AND ACTIVATION OF NEW GRANULE NEURONS IN RESPONSE TO SPATIAL MEMORY IN ADULT FEMALE RATS by ROBYN ELIZABETH STEWART B.Sc., Acadia University,
GFP/Iba1/GFAP. Brain. Liver. Kidney. Lung. Hoechst/Iba1/TLR9!
 Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Ophthalmology, Radiation Oncology,
 Supporting Online Material Journal: Nature Neuroscience Article Title: Corresponding Author: All Authors: Affiliations: Tanycytes of the Hypothalamic Median Eminence Form a Diet- Responsive Neurogenic
Supporting Online Material Journal: Nature Neuroscience Article Title: Corresponding Author: All Authors: Affiliations: Tanycytes of the Hypothalamic Median Eminence Form a Diet- Responsive Neurogenic
Chapter 6: Hippocampal Function In Cognition. From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Chapter 6: Hippocampal Function In Cognition From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Grid Cell The Hippocampus Serves a Role in Multimodal Information Processing and Memory
Chapter 6: Hippocampal Function In Cognition From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Grid Cell The Hippocampus Serves a Role in Multimodal Information Processing and Memory
TITLE: A Rat Model of Sytemic Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer to Evaluate and Treat Chemobrain
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0736 TITLE: A Rat Model of Sytemic Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer to Evaluate and Treat Chemobrain PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kevin C.E. Little, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0736 TITLE: A Rat Model of Sytemic Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer to Evaluate and Treat Chemobrain PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kevin C.E. Little, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
University of Groningen. New neurons in the adult brain van der Borght, Karin
 University of Groningen New neurons in the adult brain van der Borght, Karin IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen New neurons in the adult brain van der Borght, Karin IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Spatial Learning Depends on Both the Addition and Removal of New Hippocampal Neurons
 PLoS BIOLOGY Spatial Learning Depends on Both the Addition and Removal of New Hippocampal Neurons David Dupret 1,2, Annabelle Fabre 1,2,Màtè Dàniel Döbrössy 1,2, Aude Panatier 1,2, José Julio Rodríguez
PLoS BIOLOGY Spatial Learning Depends on Both the Addition and Removal of New Hippocampal Neurons David Dupret 1,2, Annabelle Fabre 1,2,Màtè Dàniel Döbrössy 1,2, Aude Panatier 1,2, José Julio Rodríguez
Additive effects of physical exercise and environmental enrichment on adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE published: 10 November 2009 doi: 10.3389/neuro.22.002.2009 Additive effects of physical exercise and environmental enrichment on adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice Klaus Fabel
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE published: 10 November 2009 doi: 10.3389/neuro.22.002.2009 Additive effects of physical exercise and environmental enrichment on adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice Klaus Fabel
Short-Term Environmental Enrichment Enhances Adult Neurogenesis, Vascular Network and Dendritic Complexity in the Hippocampus of Type 1 Diabetic Mice
 Short-Term Environmental Enrichment Enhances Adult Neurogenesis, Vascular Network and Dendritic Complexity in the Hippocampus of Type 1 Diabetic Mice Juan Beauquis 1, Paulina Roig 1, Alejandro F. De Nicola
Short-Term Environmental Enrichment Enhances Adult Neurogenesis, Vascular Network and Dendritic Complexity in the Hippocampus of Type 1 Diabetic Mice Juan Beauquis 1, Paulina Roig 1, Alejandro F. De Nicola
Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury
 Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury Bridgette Semple Ph.D. Postdoctoral Fellow, Noble Laboratory Department of Neurological Surgery, UCSF Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury
Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury Bridgette Semple Ph.D. Postdoctoral Fellow, Noble Laboratory Department of Neurological Surgery, UCSF Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury
Untangling the Influences of Voluntary Running, Environmental Complexity, Social Housing and Stress on Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis
 Untangling the Influences of Voluntary Running, Environmental Complexity, Social Housing and Stress on Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis Catherine-Alexandra Grégoire, David Bonenfant, Adalie Le Nguyen, Anne
Untangling the Influences of Voluntary Running, Environmental Complexity, Social Housing and Stress on Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis Catherine-Alexandra Grégoire, David Bonenfant, Adalie Le Nguyen, Anne
Repeated Social Defeat Stress Induces Neuroinflammation and Impairs Hippocampal Neurogenesis That Differentially Regulate Mood and Cognition
 Repeated Social Defeat Stress Induces Neuroinflammation and Impairs Hippocampal Neurogenesis That Differentially Regulate Mood and Cognition Anzela Niraula, Graduate Student Associate Neuroscience Graduate
Repeated Social Defeat Stress Induces Neuroinflammation and Impairs Hippocampal Neurogenesis That Differentially Regulate Mood and Cognition Anzela Niraula, Graduate Student Associate Neuroscience Graduate
Adrenalectomy-induced neuronal degeneration : development of a novel animal model of cognitive dysfuntion and neurogenic treatment strategies
 University of Lethbridge Research Repository OPUS Theses http://opus.uleth.ca Arts and Science, Faculty of 2010 Adrenalectomy-induced neuronal degeneration : development of a novel animal model of cognitive
University of Lethbridge Research Repository OPUS Theses http://opus.uleth.ca Arts and Science, Faculty of 2010 Adrenalectomy-induced neuronal degeneration : development of a novel animal model of cognitive
University of Groningen. New neurons in the adult brain van der Borght, Karin
 University of Groningen New neurons in the adult brain van der Borght, Karin IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen New neurons in the adult brain van der Borght, Karin IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis as Target for the Treatment of Depression
 CNS & Neurological Disorders - Drug Targets, 2007, 6, 205-218 205 Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis as Target for the Treatment of Depression Michael R. Drew *,1,2 and Rene Hen 1,2,3 1 Center for Neurobiology
CNS & Neurological Disorders - Drug Targets, 2007, 6, 205-218 205 Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis as Target for the Treatment of Depression Michael R. Drew *,1,2 and Rene Hen 1,2,3 1 Center for Neurobiology
Neurogenesis and its Association to Epileptogenesis in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
 Neurogenesis and its Association to Epileptogenesis in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Vanessa Marques Donegá Cover page: Figure adapted from Siebzehnrubl FA. and Blumcke I., 2008 Supervisor: Dr. P.N.E. de Graan
Neurogenesis and its Association to Epileptogenesis in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Vanessa Marques Donegá Cover page: Figure adapted from Siebzehnrubl FA. and Blumcke I., 2008 Supervisor: Dr. P.N.E. de Graan
Citation for published version (APA): Martina-Mamber, C. E. (2014). GFAP as an understudy in adult neurogenesis. 's-hertogenbosch: Boxpress.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) GFAP as an understudy in adult neurogenesis Mamber, C.E. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Martina-Mamber, C. E. (2014). GFAP as an understudy
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) GFAP as an understudy in adult neurogenesis Mamber, C.E. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Martina-Mamber, C. E. (2014). GFAP as an understudy
Cell Birth and Death. Chapter Three
 Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
Experimental stroke leads to increased generation of new
 Enriched Environment Increases Neural Stem/Progenitor Cell Proliferation and Neurogenesis in the Subventricular Zone of Stroke-Lesioned Adult Rats Mila Komitova, MD; Bengt Mattsson, BSc; Barbro B. Johansson,
Enriched Environment Increases Neural Stem/Progenitor Cell Proliferation and Neurogenesis in the Subventricular Zone of Stroke-Lesioned Adult Rats Mila Komitova, MD; Bengt Mattsson, BSc; Barbro B. Johansson,
ErbB4 migrazione I parte. 3- ErbB4- NRG1
 ErbB4 migrazione I parte 3- ErbB4- NRG1 1 In rodent brains postnatal neuronal migration is evident in three main areas: the cerebellum (CB), the hippocampus (Hipp) and the rostral migratory stream (RMS).
ErbB4 migrazione I parte 3- ErbB4- NRG1 1 In rodent brains postnatal neuronal migration is evident in three main areas: the cerebellum (CB), the hippocampus (Hipp) and the rostral migratory stream (RMS).
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
Learning and Memory. The Case of H.M.
 Learning and Memory Learning deals with how experience changes the brain Memory refers to how these changes are stored and later reactivated The Case of H.M. H.M. suffered from severe, intractable epilepsy
Learning and Memory Learning deals with how experience changes the brain Memory refers to how these changes are stored and later reactivated The Case of H.M. H.M. suffered from severe, intractable epilepsy
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of dnscs.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Conserved properties of dentate gyrus neurogenesis across postnatal development revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Resource https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0056-2 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Conserved properties of dentate gyrus neurogenesis across postnatal development
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Resource https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0056-2 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Conserved properties of dentate gyrus neurogenesis across postnatal development
Region-Dependent and Stage-Specific Effects of Stress, Environmental Enrichment, and Antidepressant Treatment on Hippocampal Neurogenesis
 HIPPOCAMPUS 00:00 00 (2013) Region-Dependent and Stage-Specific Effects of Stress, Environmental Enrichment, and Antidepressant Treatment on Hippocampal Neurogenesis Arnaud Tanti, 1,2 * Willy-Paul Westphal,
HIPPOCAMPUS 00:00 00 (2013) Region-Dependent and Stage-Specific Effects of Stress, Environmental Enrichment, and Antidepressant Treatment on Hippocampal Neurogenesis Arnaud Tanti, 1,2 * Willy-Paul Westphal,
Long-term administration of ginsenoside Rh 1 enhances learning and memory by promoting cell survival in the mouse hippocampus
 234 Long-term administration of ginsenoside Rh 1 enhances learning and memory by promoting cell survival in the mouse hippocampus JINGANG HOU, JIANJIE XUE, MIRA LEE, JIAOJIAO YU and CHANGKEUN SUNG Department
234 Long-term administration of ginsenoside Rh 1 enhances learning and memory by promoting cell survival in the mouse hippocampus JINGANG HOU, JIANJIE XUE, MIRA LEE, JIAOJIAO YU and CHANGKEUN SUNG Department
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung
 IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
Soluble Lutein (Lutemax2020 ) Prevents Retinal Damage in Streptozotocin (STZ)- induced Diabetic Rats
 Soluble Lutein (Lutemax2020 ) Prevents Retinal Damage in Streptozotocin (STZ)- induced Diabetic Rats Vijaya Juturu, Ph.D., F.A.C.N. OmniActive Health Technologies, Inc. Morristown, NJ Acknowledgements
Soluble Lutein (Lutemax2020 ) Prevents Retinal Damage in Streptozotocin (STZ)- induced Diabetic Rats Vijaya Juturu, Ph.D., F.A.C.N. OmniActive Health Technologies, Inc. Morristown, NJ Acknowledgements
Prolonged Seizures Increase Proliferating Neuroblasts in the Adult Rat Subventricular Zone Olfactory Bulb Pathway
 The Journal of Neuroscience, April 15, 2002, 22(8):3174 3188 Prolonged Seizures Increase Proliferating Neuroblasts in the Adult Rat Subventricular Zone Olfactory Bulb Pathway Jack M. Parent, 1 Vivian V.
The Journal of Neuroscience, April 15, 2002, 22(8):3174 3188 Prolonged Seizures Increase Proliferating Neuroblasts in the Adult Rat Subventricular Zone Olfactory Bulb Pathway Jack M. Parent, 1 Vivian V.
 a Control IgG Intestine c Testis b Thymus 1 3 2 S S 2 1 3 4 4 Figure S1 The wild-type mouse (C57BL/6J) organs (intestine, thymus and testis) were frozen in liquid nitrogen and sectioned at 5 µm on a cryostat.
a Control IgG Intestine c Testis b Thymus 1 3 2 S S 2 1 3 4 4 Figure S1 The wild-type mouse (C57BL/6J) organs (intestine, thymus and testis) were frozen in liquid nitrogen and sectioned at 5 µm on a cryostat.
Cholinergic Modification of Neurogenesis and Gliosis Improves the Memory of A PPswe/PSEN1dE9 Alzheimer s Disease Model Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet
 Journal of Alzheimer s Disease 56 (2017) 1 23 DOI 10.3233/JAD-160761 IOS Press 1 Cholinergic Modification of Neurogenesis and Gliosis Improves the Memory of A PPswe/PSEN1dE9 Alzheimer s Disease Model Mice
Journal of Alzheimer s Disease 56 (2017) 1 23 DOI 10.3233/JAD-160761 IOS Press 1 Cholinergic Modification of Neurogenesis and Gliosis Improves the Memory of A PPswe/PSEN1dE9 Alzheimer s Disease Model Mice
Adrenal steroid receptor immunoreactivity in cells born in the adult rat dentate gyrus
 342 Bruin Research, 611 (1993) 342-346 Elsevier Science Publishers B.V. BRES 25656 Adrenal steroid receptor immunoreactivity in cells born in the adult rat dentate gyrus Heather A. Cameron, Catherine S.
342 Bruin Research, 611 (1993) 342-346 Elsevier Science Publishers B.V. BRES 25656 Adrenal steroid receptor immunoreactivity in cells born in the adult rat dentate gyrus Heather A. Cameron, Catherine S.
Address: Department of Biomedical Genetics, University of Rochester Medical Center, 601 Elmwood Avenue, Rochester, NY 14642, USA.
 Journal of Biology BioMed Central Research article CNS progenitor cells and oligodendrocytes are targets of chemotherapeutic agents in vitro and in vivo Joerg Dietrich, Ruolan Han, Yin Yang, Margot Mayer-Pröschel
Journal of Biology BioMed Central Research article CNS progenitor cells and oligodendrocytes are targets of chemotherapeutic agents in vitro and in vivo Joerg Dietrich, Ruolan Han, Yin Yang, Margot Mayer-Pröschel
EFFECTS OF CHRONIC ANTIDEPRESSANT COADMINISTRATION ON ACQUISITION, MEMORY CONSOLIDATION, AND NEUROGENESIS AFTER REPEATED
 EFFECTS OF CHRONIC ANTIDEPRESSANT COADMINISTRATION ON ACQUISITION, MEMORY CONSOLIDATION, AND NEUROGENESIS AFTER REPEATED LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE ADMINISTRATION by ANDREW JUSTIN TARR Bachelor of Arts, 2003 University
EFFECTS OF CHRONIC ANTIDEPRESSANT COADMINISTRATION ON ACQUISITION, MEMORY CONSOLIDATION, AND NEUROGENESIS AFTER REPEATED LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE ADMINISTRATION by ANDREW JUSTIN TARR Bachelor of Arts, 2003 University
Songbirds, Steroids, and Adult Neurogenesis. Brad Walters Biological Sciences Lehigh University September, 2008
 Songbirds, Steroids, and Adult Neurogenesis Brad Walters Biological Sciences Lehigh University September, 2008 Songbirds, steroids, and neurogenesis Some tissues regenerate well 1 2 3 4 http://flickr.com/photos/museumoflondon/2392340925/
Songbirds, Steroids, and Adult Neurogenesis Brad Walters Biological Sciences Lehigh University September, 2008 Songbirds, steroids, and neurogenesis Some tissues regenerate well 1 2 3 4 http://flickr.com/photos/museumoflondon/2392340925/
Enhanced Adult Neurogenesis and Angiogenesis and Altered Affective Behaviors in Mice Overexpressing Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor 120
 14522 The Journal of Neuroscience, December 31, 2008 28(53):14522 14536 Neurobiology of Disease Enhanced Adult Neurogenesis and Angiogenesis and Altered Affective Behaviors in Mice Overexpressing Vascular
14522 The Journal of Neuroscience, December 31, 2008 28(53):14522 14536 Neurobiology of Disease Enhanced Adult Neurogenesis and Angiogenesis and Altered Affective Behaviors in Mice Overexpressing Vascular
Early Life Effects on Hypothalamic Circuitry. By: The Mystery Gang
 Early Life Effects on Hypothalamic Circuitry By: The Mystery Gang Hypothalamic Circuits Controlling Energy Balance ARH (Arcuate nucleus of the Hypothalamus) Subgroup of Neurons 1: coexpress Neuropeptide
Early Life Effects on Hypothalamic Circuitry By: The Mystery Gang Hypothalamic Circuits Controlling Energy Balance ARH (Arcuate nucleus of the Hypothalamus) Subgroup of Neurons 1: coexpress Neuropeptide
Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, Jeremy Miller Scientist I
 Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, 2013 Jeremy Miller Scientist I jeremym@alleninstitute.org Outline 1. Brief introduction to previous WGCNA studies in brain 2.
Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, 2013 Jeremy Miller Scientist I jeremym@alleninstitute.org Outline 1. Brief introduction to previous WGCNA studies in brain 2.
Conditional p53 Deletion Promotes Adult Neurogenesis and Improves the Acquisition and Clearance of Contextual Fear Memory
 Conditional p53 Deletion Promotes Adult Neurogenesis and Improves the Acquisition and Clearance of Contextual Fear Memory by Xiaochen Hu A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree
Conditional p53 Deletion Promotes Adult Neurogenesis and Improves the Acquisition and Clearance of Contextual Fear Memory by Xiaochen Hu A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree
Soft-diet feeding inhibits adult ne Title hippocampus of mice. Yamamoto, T; Hirayama, A; Hosoe, N; Author(s) Hirano, S
 Soft-diet feeding inhibits adult ne Title hippocampus of mice Yamamoto, T; Hirayama, A; Hosoe, N; Author(s) Hirano, S Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/1081 Right
Soft-diet feeding inhibits adult ne Title hippocampus of mice Yamamoto, T; Hirayama, A; Hosoe, N; Author(s) Hirano, S Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/1081 Right
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-b signaling Randolph S. Ashton, Anthony Conway, Chinmay Pangarkar, Jamie Bergen, Kwang-Il Lim, Priya Shah, Mina
Supplementary Information Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-b signaling Randolph S. Ashton, Anthony Conway, Chinmay Pangarkar, Jamie Bergen, Kwang-Il Lim, Priya Shah, Mina
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Diagram of BBB and brain chips.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diagram of BBB and brain chips. (a) Schematic of the BBB Chip demonstrates the 3 parts of the chip, Top PDMS channel, membrane and Bottom PDMS channel; (b) Image of 2 BBB Chips,
Supplementary Figure 1 Diagram of BBB and brain chips. (a) Schematic of the BBB Chip demonstrates the 3 parts of the chip, Top PDMS channel, membrane and Bottom PDMS channel; (b) Image of 2 BBB Chips,
STRESS INHIBITS THE PROLIFERATION OF GRANULE CELL PRECURSORS IN THE DEVELOPING DENTATE GYRUS
 Pergamon Int[ J[ Devl Neuroscience\ Vol[ 05\ No[ 2:3\ pp[ 124Ð128\ 0887 Þ 0887 ISDN[ Published by Elsevier Science Ltd All rights reserved[ Printed in Great Britain 9625Ð4637:87,08[99 9[99 PII ] S9625Ð4637"87#99918ÐX
Pergamon Int[ J[ Devl Neuroscience\ Vol[ 05\ No[ 2:3\ pp[ 124Ð128\ 0887 Þ 0887 ISDN[ Published by Elsevier Science Ltd All rights reserved[ Printed in Great Britain 9625Ð4637:87,08[99 9[99 PII ] S9625Ð4637"87#99918ÐX
Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive
 The Journal of Neuroscience, May 12, 2010 30(19):6635 6645 6635 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Severe Early Life Stress Hampers Spatial Learning and Neurogenesis, but Improves Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity
The Journal of Neuroscience, May 12, 2010 30(19):6635 6645 6635 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Severe Early Life Stress Hampers Spatial Learning and Neurogenesis, but Improves Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity
BRAIN REJUVENATION HOW TO KEEP BRAIN STEM CELLS HAPPY
 BRAIN REJUVENATION HOW TO KEEP BRAIN STEM CELLS HAPPY Natalia Surzenko, PhD Research Assistant Professor UNC Chapel Hill Nutrition Research Institute October 13, 2015 MY JOURNEY Tallinn, Estonia Aiken,
BRAIN REJUVENATION HOW TO KEEP BRAIN STEM CELLS HAPPY Natalia Surzenko, PhD Research Assistant Professor UNC Chapel Hill Nutrition Research Institute October 13, 2015 MY JOURNEY Tallinn, Estonia Aiken,
2 3 Carbon Compounds. Proteins. Proteins
 2 3 Carbon Compounds Proteins Proteins Proteins are macromolecules that contain nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Proteins are polymers of molecules called amino acids. There are 20 amino acids,
2 3 Carbon Compounds Proteins Proteins Proteins are macromolecules that contain nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Proteins are polymers of molecules called amino acids. There are 20 amino acids,
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Supplementary Fig. 1
 PDK1-dependent quenching of TACE shedding activity in prion and Alzheimer s diseases Mathéa Pietri, Caroline Dakowski, Samia Hannaoui, Aurélie Alleaume-Butaux, Julia Hernandez-Rapp, Audrey Ragagnin, Sophie
PDK1-dependent quenching of TACE shedding activity in prion and Alzheimer s diseases Mathéa Pietri, Caroline Dakowski, Samia Hannaoui, Aurélie Alleaume-Butaux, Julia Hernandez-Rapp, Audrey Ragagnin, Sophie
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1 Treatment with both Sema6D and Plexin-A1 sirnas induces the phenotype essentially identical to that induced by treatment with Sema6D sirna alone or Plexin-A1 sirna alone. (a,b) The cardiac tube
Figure S1 Treatment with both Sema6D and Plexin-A1 sirnas induces the phenotype essentially identical to that induced by treatment with Sema6D sirna alone or Plexin-A1 sirna alone. (a,b) The cardiac tube
Neurons vs. glia. Traditionally, glia have been viewed as passive cells that help to maintain the function of neurons.
 GLIA Neurons vs. glia The defining characteristic of a neuron is its ability to transmit rapid electrical signals in the form of action potentials. All other neural cells that lack this property are broadly
GLIA Neurons vs. glia The defining characteristic of a neuron is its ability to transmit rapid electrical signals in the form of action potentials. All other neural cells that lack this property are broadly
The Potential Effect of Caffeine and Nicotine Co-administration on the Induction of Alzheimer s disease
 The Potential Effect of Caffeine and Nicotine Co-administration on the Induction of Alzheimer s disease Azza A Ali *, Hebatalla I Ahmed * Hanan A Abd El-Samea ** Ebtehal El-Demerdash *** * Pharmacology
The Potential Effect of Caffeine and Nicotine Co-administration on the Induction of Alzheimer s disease Azza A Ali *, Hebatalla I Ahmed * Hanan A Abd El-Samea ** Ebtehal El-Demerdash *** * Pharmacology
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Multiple memory trace theory Duncan, 1949
 Neurobiology of Learning and Memory Prof. Stephan Anagnostaras Lecture 5: Memory Consolidation Multiple memory trace theory Duncan, 1949 McGaugh, 2 Squire: retention of TV shows after ECS At least 2 kinds
Neurobiology of Learning and Memory Prof. Stephan Anagnostaras Lecture 5: Memory Consolidation Multiple memory trace theory Duncan, 1949 McGaugh, 2 Squire: retention of TV shows after ECS At least 2 kinds
Paternal physical exercise improves spatial learning ability by enhancing hippocampal neuroplasticity in male pups born from obese maternal rats
 Original Article es of learning process and memory formation. Active neurogenesis occurs in the hippocampus after birth and hippocampus is the brain area with greatest neuroplasticity (Fuchs and Gould,
Original Article es of learning process and memory formation. Active neurogenesis occurs in the hippocampus after birth and hippocampus is the brain area with greatest neuroplasticity (Fuchs and Gould,
Alcohol Abuse in Mothers during Gravidity and Breastfeeding Brings Changes of Hippocampal Neurons in their Offspring
 103) Alcohol Abuse in Mothers during Gravidity and Breastfeeding Brings Changes of Hippocampal Neurons in their Offspring Milotová M., Riljak V., Jandová K., Langmeier M., Marešová D., Pokorný J., Trojan
103) Alcohol Abuse in Mothers during Gravidity and Breastfeeding Brings Changes of Hippocampal Neurons in their Offspring Milotová M., Riljak V., Jandová K., Langmeier M., Marešová D., Pokorný J., Trojan
Recently, it has been proposed that neurogenesis in the
 Neurogenesis and Helplessness Are Mediated by Controllability in Males But Not in Females Tracey J. Shors, Jason Mathew, Helene M. Sisti, Carol Edgecomb, Steven Beckoff, and Christina Dalla Background:
Neurogenesis and Helplessness Are Mediated by Controllability in Males But Not in Females Tracey J. Shors, Jason Mathew, Helene M. Sisti, Carol Edgecomb, Steven Beckoff, and Christina Dalla Background:
An Introduction to Genetics. 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid
 An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
20: c 2009 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. NeuroReport 2009, 20:
 Developmental neuroscience 371 Intracerebroventricular infusion of cytosine-arabinoside causes prepulse inhibition disruption Benson W.M. Lau a,b,d, Suk-Yu Yau a,b,d, Tatia M.C. Lee b,c, Yick-Pang Ching
Developmental neuroscience 371 Intracerebroventricular infusion of cytosine-arabinoside causes prepulse inhibition disruption Benson W.M. Lau a,b,d, Suk-Yu Yau a,b,d, Tatia M.C. Lee b,c, Yick-Pang Ching
UVicSPACE: Research & Learning Repository
 UVicSPACE: Research & Learning Repository Division of Medical Sciences Faculty Publications Physical Exercise-Induced Adult Neurogenesis: A Good Strategy to Prevent Cognitive Decline in Neurodegenerative
UVicSPACE: Research & Learning Repository Division of Medical Sciences Faculty Publications Physical Exercise-Induced Adult Neurogenesis: A Good Strategy to Prevent Cognitive Decline in Neurodegenerative
Activity-dependent Extrinsic Regulation of Adult Olfactory Bulb and Hippocampal Neurogenesis
 INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON OLFACTION AND TASTE Activity-dependent Extrinsic Regulation of Adult Olfactory Bulb and Hippocampal Neurogenesis Dengke K. Ma, a,b Woon Ryoung Kim, b,c Guo-li Ming, a,b,c and
INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON OLFACTION AND TASTE Activity-dependent Extrinsic Regulation of Adult Olfactory Bulb and Hippocampal Neurogenesis Dengke K. Ma, a,b Woon Ryoung Kim, b,c Guo-li Ming, a,b,c and
Acetylcholine again! - thought to be involved in learning and memory - thought to be involved dementia (Alzheimer's disease)
 Free recall and recognition in a network model of the hippocampus: simulating effects of scopolamine on human memory function Michael E. Hasselmo * and Bradley P. Wyble Acetylcholine again! - thought to
Free recall and recognition in a network model of the hippocampus: simulating effects of scopolamine on human memory function Michael E. Hasselmo * and Bradley P. Wyble Acetylcholine again! - thought to
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
The Effects of Social Environment on Adult Neurogenesis in the Female Prairie Vole
 The Effects of Social Environment on Adult Neurogenesis in the Female Prairie Vole Christie D. Fowler, Yan Liu, Charles Ouimet, Zuoxin Wang Department of Psychology and Program of Neuroscience, Florida
The Effects of Social Environment on Adult Neurogenesis in the Female Prairie Vole Christie D. Fowler, Yan Liu, Charles Ouimet, Zuoxin Wang Department of Psychology and Program of Neuroscience, Florida
Moclobemide up-regulates proliferation of hippocampal progenitor cells in chronically stressed mice 1
 1408 2004, Acta Pharmacologica Sinica Chinese Pharmacological Society Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica Chinese Academy of Sciences http://www.chinaphar.com Moclobemide up-regulates proliferation of
1408 2004, Acta Pharmacologica Sinica Chinese Pharmacological Society Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica Chinese Academy of Sciences http://www.chinaphar.com Moclobemide up-regulates proliferation of
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Hasbi et al. 10.1073/pnas.0903676106 SI Text Drugs. Dopaminergic agonists and antagonists SKF 83959, SKF 83822, dopamine, SCH 22390, and raclopride were purchased from Tocris Bioscience.
Supporting Information Hasbi et al. 10.1073/pnas.0903676106 SI Text Drugs. Dopaminergic agonists and antagonists SKF 83959, SKF 83822, dopamine, SCH 22390, and raclopride were purchased from Tocris Bioscience.
REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
 REGENERATIVE MEDICINE TIMP3 Attenuates the Loss of Neural Stem Cells, Mature Neurons and Neurocognitive Dysfunction in Traumatic Brain Injury STUART L. GIBB, a,b YUHAI ZHAO, c DANIEL POTTER, a,b MICHAEL
REGENERATIVE MEDICINE TIMP3 Attenuates the Loss of Neural Stem Cells, Mature Neurons and Neurocognitive Dysfunction in Traumatic Brain Injury STUART L. GIBB, a,b YUHAI ZHAO, c DANIEL POTTER, a,b MICHAEL
DNA and Histone Methylation in Learning and Memory
 EXPERIMENTAL BIOLOGY ANNUAL MEETING April 2010 DNA and Histone Methylation in Learning and Memory J. David Sweatt Dept of Neurobiology McKnight Brain Institute UAB School of Medicine The Molecular Basis
EXPERIMENTAL BIOLOGY ANNUAL MEETING April 2010 DNA and Histone Methylation in Learning and Memory J. David Sweatt Dept of Neurobiology McKnight Brain Institute UAB School of Medicine The Molecular Basis
GABA from reactive astrocytes impairs memory in mouse models of Alzheimer disease
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION from reactive astrocytes impairs memory in mouse models of Alzheimer disease Seonmi Jo *, Oleg Yarishkin *, Yu Jin Hwang, Ye Eun Chun, Mijeong Park, Dong Ho Woo, Jin Young Bae,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION from reactive astrocytes impairs memory in mouse models of Alzheimer disease Seonmi Jo *, Oleg Yarishkin *, Yu Jin Hwang, Ye Eun Chun, Mijeong Park, Dong Ho Woo, Jin Young Bae,
