Conserved properties of dentate gyrus neurogenesis across postnatal development revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing
|
|
|
- Emma Collins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Resource In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Conserved properties of dentate gyrus neurogenesis across postnatal development revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing Hannah Hochgerner 1,2, Amit Zeisel 1,2, Peter Lönnerberg 1,2 and Sten Linnarsson 1,2 * 1 Division of Molecular Neurobiology, Dept. of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden. 2 Science for Life Laboratory, Solna, Sweden. Hannah Hochgerner and Amit Zeisel contributed equally to this work. * sten.linnarsson@ki.se Nature Neuroscience Nature America Inc., part of Springer Nature. All rights reserved.
2
3 Supplementary Figure 1 Overview of sampling and technical details for Data sets A C. (a) Schematic over the dentate gyrus granule layer emergence and maintained neurogenesis through development, as in Fig. 1a, with sampling timepoints indicated for each dataset. (b), (d), (f) Distribution of cell-type frequency in each dataset. Circle area represents fraction of positive cells, per sampling age, normalized by cell-type. Dashed box indicates time points sampled in the hgfap:gfp reporter mouse, by FACS on GFP+ cells. (c), (e), (g) Technical specifications of the datasets. Single-cell barplots for number of molecules (left) and genes (right), arranged by cluster. tsne visualizations of each dataset (compare Fig. 1, Suppl. Fig. 5, Fig. 5), are colored by number of genes (grey-low, red-high).
4 Supplementary Figure 2 Cajal Retzius cells (CR) in the marginal zone of the dentate gyrus. (a) t-sne visualization of Dataset A (see Fig. 1). Cells are stained for expression of genes enriched in the Cajal-Retzius population (grey, low; red, high). (b) Allen Mouse Brain Atlas images of known Cajal-Retzius cell marker Reln (encoding reelin, co-expressed in hilus GABAergic neurons), and more specific genes identified in our dataset Lhx1 and Lhx5, across postnatal development and the adult. Scale bars represent 200μm. Image credit: Allen Institute. (c) Validation of Reln+/Lhx1+ Cajal-Retzius cells (outlined by solid circles) at ages P10, P16, P24 and P37, representative images from hybridizations on six sections in two mice per time point. Higher density of Cajal-Retzius cells along the marginal zone (dashed line) observed in younger ages. Co-expression of Reln/Lhx1 is preserved also in the adolescent. Left panel: Overview dentate gyrus, localization of Cajal-Retzius cells to the marginal zone. Middle panel: Zoom-in on area outlined by solid rectangle in left panel, spanning marginal zone (dashed line), molecular layer and granule layer (between solid outlines). Right panel: detailed view, zoom-in on area outlined by solid square in left panel. Scale bars represent 200μm (left panel) and 50μm (zoom-ins, middle and right panels). (d) Distribution of Cajal-Retzius cells in single-cell data from Dataset A (left) and B (right), across ages, shows enrichment in earlier postnatal time points.
5 Supplementary Figure 3 Early neurogenesis markers. t-sne visualization of Dataset A (as in Fig. 1), cells are stained for expression of consecutive markers of early neurogenesis. Grey - low expression, red - high expression.
6 Supplementary Figure 4 Mutual KNN graph of early neurogenesis, without nipc-specific genes. Analysis of astrocytes and early neurogenesis clusters (Radial Glia-like (n=165), nipc (n=88), Neuroblast 1 (n=97) and 2 (n=777)) with nipc-specific genes removed (see Methods, as in Fig. 2e-f). Nodes represent cells (total n=1127 cells), edges connect mutual nearest neighbors. (a) Cells stained by cluster annotations as in Fig. 1d. nipcs fall along a trajectory between Radial Glia-like and Neuroblast 1. (b) Mutual KNN graph stained by gene expression: progenitor genes (top), cell-cycle genes (middle), neurogenic genes (bottom) (grey, not expressed; red, expressed; compare Fig. 2f). Line indicates the divide of nipcs by distance from Radial Glia-like or Neuroblast 1 (as in Fig 2e).
7
8 Supplementary Figure 5 Time-resolved dentate gyrus Data set B and characterization of hgfap:gfp reporter mice. (a) t-sne visualization of all 2303 cells, colored and labeled by cluster names. (b) Heatmap of 17 clusters from 2303 cells (all sampled time points), by their top marker genes (526 genes), expression normalized by gene. Barplots on top show sampling age source. (c) Dendrogram and correlation heatmap of clusters. (d) t-sne visualization (as in (a)). Cells are colored by sampling age and experiment source (hgfap:gfp sorted by FACS). Dashed box indicates astrocytes and clusters in early neurogenesis. (e) t-sne visualization (as in (a)) with cells contributed by FACS are colored light green, cells expressing at least one molecule of Gfap or Cdk1 are encircled as indicated. Dashed circles outline populations that contain GFP+ cells, and are labeled by cluster name. (f) Analysis of clusters containing GFP+ cells. GFP expression is not restricted to Gfap+ cells or progenitor populations. Left: Contribution of GFP+ cells to each cluster, in percent. Line shows total contribution of GFP+ cells to the dataset (5.2%). Left center: Percentage of all cells expressing at least one molecule Gfap, per cluster. Right center: Percentage of GFP+ cells expressing at least one molecule Gfap, per cluster. Right: Percentage of all cells expressing at least one molecule Cdk1, per cluster. (g) Immunohistochemistry of hgfap:gfp mouse dentate gyrus, stained with antibodies against GFP, GFAP, Aldoc (astrocytes) and Pdgfra (OPCs), representative images from stainings in two mice. Left panel: Overview of denate gyrus. Right panel: zoom-in, coexpression of respective markers indicated by arrowheads. Scale bars represent 200μm (left) and 50μm (zoom-ins, right).
9 Supplementary Figure 6 Markers of neurogenesis, maturation, and Notch-signaling. t-sne visualization of Dataset A (as in Fig. 1d), cells stained for expression of markers of early neurogenesis (Calb2), granule cell maturation (Fxyd7-Icam5), and Notch-signaling related genes (Notch1, Notch2, Dner, Dlk2, Jag1). Grey, low expression; red, high expression.
10 Supplementary Figure 7 Overview of dentate gyrus Data set C, spanning perinatal, juvenile, and adult neurogenesis. (a) t-sne visualization of all 24,185 cells, colored and labeled by cluster names, sampled from perinatal (E16.5-P5), juvenile (P18-23) and adult (P ) mice. (b) Dendrogram and correlation heatmap of Dataset C clusters. (c) Heatmap of 24 clusters from 24,185 cells (all sampled time points), represented by their top marker genes (756 genes), expression normalized by gene. Barplots on top show sampling age source.
11 Supplementary Figure 8 Suggested model of cell types involved in perinatal and adult dentate neurogenesis. Both in perinatal and adult neurogenesis we propose distinct initiation clusters (radial glia and radial glia-like; size of circle symbolizes frequency), and convergence of the maturation process.
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain. - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function
 Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, Jeremy Miller Scientist I
 Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, 2013 Jeremy Miller Scientist I jeremym@alleninstitute.org Outline 1. Brief introduction to previous WGCNA studies in brain 2.
Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, 2013 Jeremy Miller Scientist I jeremym@alleninstitute.org Outline 1. Brief introduction to previous WGCNA studies in brain 2.
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral training.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
Nature Neuroscience doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of viral injections.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation. Reading: BCP Chapter 23
 Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Fig. S1. Upregulation of K18 and K14 mrna levels during ectoderm specification of hescs. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of mrna levels of OCT4
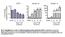 Fig. S1. Upregulation of K18 and K14 mrna levels during ectoderm specification of hescs. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of mrna levels of OCT4 (n=3 independent differentiation experiments for each
Fig. S1. Upregulation of K18 and K14 mrna levels during ectoderm specification of hescs. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of mrna levels of OCT4 (n=3 independent differentiation experiments for each
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. MADM labeling of thalamic clones.
 Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2275
 Supplementary Figure S1. The presence of MeCP2 in enriched primary glial cultures from rat or mouse brains is not neuronal. Western blot analysis of protein extracts from (a) rat glial and neuronal cultures.
Supplementary Figure S1. The presence of MeCP2 in enriched primary glial cultures from rat or mouse brains is not neuronal. Western blot analysis of protein extracts from (a) rat glial and neuronal cultures.
Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis of individual mice during maze learning. a,
 Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Ophthalmology, Radiation Oncology,
 Supporting Online Material Journal: Nature Neuroscience Article Title: Corresponding Author: All Authors: Affiliations: Tanycytes of the Hypothalamic Median Eminence Form a Diet- Responsive Neurogenic
Supporting Online Material Journal: Nature Neuroscience Article Title: Corresponding Author: All Authors: Affiliations: Tanycytes of the Hypothalamic Median Eminence Form a Diet- Responsive Neurogenic
label the basement membrane). Different fixation methods of EB-perfused P8 mice to optimize the combination
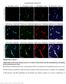 Supplementary Figure 1 Optimization of the tissue fixation protocol to combine EB perfusion and IB4 endothelial tip cell staining in the postnatal mouse brain. a-l Labeling of EB-perfused P8 mice with
Supplementary Figure 1 Optimization of the tissue fixation protocol to combine EB perfusion and IB4 endothelial tip cell staining in the postnatal mouse brain. a-l Labeling of EB-perfused P8 mice with
Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing. Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2
 ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0150-0 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent homeostasis Michelle C.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0150-0 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent homeostasis Michelle C.
GFP/Iba1/GFAP. Brain. Liver. Kidney. Lung. Hoechst/Iba1/TLR9!
 Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Supplementary Information
 1 Supplementary Information A role for primary cilia in glutamatergic synaptic integration of adult-orn neurons Natsuko Kumamoto 1,4,5, Yan Gu 1,4, Jia Wang 1,4, Stephen Janoschka 1,2, Ken-Ichi Takemaru
1 Supplementary Information A role for primary cilia in glutamatergic synaptic integration of adult-orn neurons Natsuko Kumamoto 1,4,5, Yan Gu 1,4, Jia Wang 1,4, Stephen Janoschka 1,2, Ken-Ichi Takemaru
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Broad Integration of Expression Maps and Co-Expression Networks Compassing Novel Gene Functions in the Brain
 Supplementary Information Broad Integration of Expression Maps and Co-Expression Networks Compassing Novel Gene Functions in the Brain Yuko Okamura-Oho a, b, *, Kazuro Shimokawa c, Masaomi Nishimura b,
Supplementary Information Broad Integration of Expression Maps and Co-Expression Networks Compassing Novel Gene Functions in the Brain Yuko Okamura-Oho a, b, *, Kazuro Shimokawa c, Masaomi Nishimura b,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-b signaling Randolph S. Ashton, Anthony Conway, Chinmay Pangarkar, Jamie Bergen, Kwang-Il Lim, Priya Shah, Mina
Supplementary Information Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-b signaling Randolph S. Ashton, Anthony Conway, Chinmay Pangarkar, Jamie Bergen, Kwang-Il Lim, Priya Shah, Mina
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Hey! The major concepts discussed relative to neural crest cell migration apply to cell migration
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Hey! The major concepts discussed relative to neural crest cell migration apply to cell migration
Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1:
 Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1: Representative FACS data showing Concurrent Brain cell type Acquisition using either Percoll PLUS (top row) or myelin removal beads (bottom two rows). Debris
Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1: Representative FACS data showing Concurrent Brain cell type Acquisition using either Percoll PLUS (top row) or myelin removal beads (bottom two rows). Debris
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1.
 Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs.
 Supplementary Figure 1 RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs. (a) Schematic representation of the tumor and cell types used for the study. HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell cancer; NSCLC, non-small
Supplementary Figure 1 RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs. (a) Schematic representation of the tumor and cell types used for the study. HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell cancer; NSCLC, non-small
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus
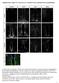 Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Wednesday (Oct 18) 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Wednesday (Oct 18) 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop
Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Supplementary Figure 1 Cytokine receptors on developing thymocytes that can potentially signal Runx3d expression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cytokine receptors on developing thymocytes that can potentially signal Runx3d expression. (a) Characterization of c-independent SP8 cells. Stainings for maturation markers (top)
Supplementary Figure 1 Cytokine receptors on developing thymocytes that can potentially signal Runx3d expression. (a) Characterization of c-independent SP8 cells. Stainings for maturation markers (top)
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencemag.org/content/355/6332/eaai8478/suppl/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Decoupling genetics, lineages, and microenvironment in IDH-mutant gliomas by single-cell RNA-seq Andrew S. Venteicher,
www.sciencemag.org/content/355/6332/eaai8478/suppl/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Decoupling genetics, lineages, and microenvironment in IDH-mutant gliomas by single-cell RNA-seq Andrew S. Venteicher,
OSVZ progenitors of human and ferret neocortex are epithelial-like and
 OSVZ progenitors of human and ferret neocortex are epithelial-like and expand by integrin signaling Simone A Fietz, Iva Kelava, Johannes Vogt, Michaela Wilsch-Bräuninger, Denise Stenzel, Jennifer L Fish,
OSVZ progenitors of human and ferret neocortex are epithelial-like and expand by integrin signaling Simone A Fietz, Iva Kelava, Johannes Vogt, Michaela Wilsch-Bräuninger, Denise Stenzel, Jennifer L Fish,
Supporting Information. Calculation of the relative contributions of myocyte proliferation, stem cell. Supporting Information Fig 1 (page 9)
 Supporting Information Table of contents Calculation of the relative contributions of myocyte proliferation, stem cell differentiation and cardioprotection (page 2) Supporting Information Fig 1 (page 9)
Supporting Information Table of contents Calculation of the relative contributions of myocyte proliferation, stem cell differentiation and cardioprotection (page 2) Supporting Information Fig 1 (page 9)
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the
 Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of dnscs.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
PBZ FT01_PBZ FT01_TZ FT01_NZ. interface zone (I) tumor zone (TZ) necrotic zone (NZ)
 Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ SUPPLEMENTRY FLES ndividuals factor map (P) FT_ FT_ FT_ Dim (.%) Dim (.%) >% peripheral brain zone () around % interface zone () FT
Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ SUPPLEMENTRY FLES ndividuals factor map (P) FT_ FT_ FT_ Dim (.%) Dim (.%) >% peripheral brain zone () around % interface zone () FT
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity
 Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Mnemonic representations of transient stimuli and temporal sequences in the rodent hippocampus in vitro
 Supplementary Material Mnemonic representations of transient stimuli and temporal sequences in the rodent hippocampus in vitro Robert. Hyde and en W. Strowbridge Mossy ell 1 Mossy ell Mossy ell 3 Stimulus
Supplementary Material Mnemonic representations of transient stimuli and temporal sequences in the rodent hippocampus in vitro Robert. Hyde and en W. Strowbridge Mossy ell 1 Mossy ell Mossy ell 3 Stimulus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Human cerebral cortex development from pluripotent stem cells to functional excitatory synapses Yichen Shi 1,2, Peter Kirwan 1,2, James Smith 1,2, Hugh P.C. Robinson 3 and Frederick
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Human cerebral cortex development from pluripotent stem cells to functional excitatory synapses Yichen Shi 1,2, Peter Kirwan 1,2, James Smith 1,2, Hugh P.C. Robinson 3 and Frederick
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu
 Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0110-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0110-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 2 3 4 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Supplementary Table S1. Brain Tumors used in the study Code Tumor Classification Age Gender HuTuP51 Glioblastoma 57 Male HuTuP52 Glioblastoma 53 Male
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 2 3 4 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Supplementary Table S1. Brain Tumors used in the study Code Tumor Classification Age Gender HuTuP51 Glioblastoma 57 Male HuTuP52 Glioblastoma 53 Male
Supplementary Information
 Nature Immunology doi:1.138/ni.2477 Supplementary Information Capillary and arteriolar pericytes attract innate leukocytes exiting through venules and instruct them with pattern recognition and motility
Nature Immunology doi:1.138/ni.2477 Supplementary Information Capillary and arteriolar pericytes attract innate leukocytes exiting through venules and instruct them with pattern recognition and motility
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplemental Information. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Controls. Monocyte Differentiation. into Dendritic Cells versus Macrophages
 Immunity, Volume 47 Supplemental Information Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Controls Monocyte Differentiation into Dendritic Cells versus Macrophages Christel Goudot, Alice Coillard, Alexandra-Chloé Villani,
Immunity, Volume 47 Supplemental Information Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Controls Monocyte Differentiation into Dendritic Cells versus Macrophages Christel Goudot, Alice Coillard, Alexandra-Chloé Villani,
mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons
 Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma.
 Fig S1 CD4 Fibronectin EpCM CD8 CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma. Fluorescently-labeled CD4 (CMFD, green) and CD8 (Hoechst, yellow) T cells were added to a human lung
Fig S1 CD4 Fibronectin EpCM CD8 CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma. Fluorescently-labeled CD4 (CMFD, green) and CD8 (Hoechst, yellow) T cells were added to a human lung
TGF-β Signaling Regulates Neuronal C1q Expression and Developmental Synaptic Refinement
 Supplementary Information Title: TGF-β Signaling Regulates Neuronal C1q Expression and Developmental Synaptic Refinement Authors: Allison R. Bialas and Beth Stevens Supplemental Figure 1. In vitro characterization
Supplementary Information Title: TGF-β Signaling Regulates Neuronal C1q Expression and Developmental Synaptic Refinement Authors: Allison R. Bialas and Beth Stevens Supplemental Figure 1. In vitro characterization
mm Distance (mm)
 b a Magnet Illumination Coverslips MPs Objective 2575 µm 1875 µm 1575 µm 1075 µm 875 µm 545 µm 20µm 2 3 0.5 0.3mm 1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Field Induction (Gauss) 1.5 0 5 10 15 20 Distance
b a Magnet Illumination Coverslips MPs Objective 2575 µm 1875 µm 1575 µm 1075 µm 875 µm 545 µm 20µm 2 3 0.5 0.3mm 1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Field Induction (Gauss) 1.5 0 5 10 15 20 Distance
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Electroporation of a stable form of β-catenin causes masses protruding into the IV ventricle. HH12 chicken embryos were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Electroporation of a stable form of β-catenin causes masses protruding into the IV ventricle. HH12 chicken embryos were electroporated with β- Catenin S33Y in PiggyBac expression
Supplementary Figure 1. Electroporation of a stable form of β-catenin causes masses protruding into the IV ventricle. HH12 chicken embryos were electroporated with β- Catenin S33Y in PiggyBac expression
Supplemental Table S1
 Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
TEB. Id4 p63 DAPI Merge. Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge
 a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
Neurogenesis and its Association to Epileptogenesis in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
 Neurogenesis and its Association to Epileptogenesis in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Vanessa Marques Donegá Cover page: Figure adapted from Siebzehnrubl FA. and Blumcke I., 2008 Supervisor: Dr. P.N.E. de Graan
Neurogenesis and its Association to Epileptogenesis in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Vanessa Marques Donegá Cover page: Figure adapted from Siebzehnrubl FA. and Blumcke I., 2008 Supervisor: Dr. P.N.E. de Graan
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
The neuron. Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex
 The neuron Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex Discovery of the neuron (A) Reticularist Doctrine (B) Neuron Doctrine Exception.GAP JUNCTIONS between neurons Neuronal shape Dendrites
The neuron Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex Discovery of the neuron (A) Reticularist Doctrine (B) Neuron Doctrine Exception.GAP JUNCTIONS between neurons Neuronal shape Dendrites
Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC
 1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
ANAT3231: lectures overview
 ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
Neocortex Zbtb20 / NFIA / Sox9
 Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
Supplemental Information. Planarian Epidermal Stem Cells Respond. to Positional Cues to Promote Cell-Type Diversity
 Developmental Cell, Volume 4 Supplemental Information Planarian Epidermal Stem Cells Respond to Positional Cues to Promote Cell-Type Diversity Omri Wurtzel, Isaac M. Oderberg, and Peter W. Reddien Supplemental
Developmental Cell, Volume 4 Supplemental Information Planarian Epidermal Stem Cells Respond to Positional Cues to Promote Cell-Type Diversity Omri Wurtzel, Isaac M. Oderberg, and Peter W. Reddien Supplemental
Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane
 Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane potential recorded from POMC neurons following treatment with
Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane potential recorded from POMC neurons following treatment with
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Illustration of the working of network-based SVM to confidently predict a new (and now confirmed) ASD gene. Gene CTNND2 s brain network neighborhood that enabled its prediction by
Supplementary Figure 1 Illustration of the working of network-based SVM to confidently predict a new (and now confirmed) ASD gene. Gene CTNND2 s brain network neighborhood that enabled its prediction by
Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols
 Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols used to differentiate mouse ESCs. (b) Representative
Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols used to differentiate mouse ESCs. (b) Representative
ANAT3231: lectures overview
 ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
a 0,8 Figure S1 8 h 12 h y = 0,036x + 0,2115 y = 0,0366x + 0,206 Labeling index Labeling index ctrl shrna Time (h) Time (h) ctrl shrna S G2 M G1
 (GFP+ BrdU+)/GFP+ Labeling index Labeling index Figure S a, b, y =,x +, y =,x +,,,,,,,, Time (h) - - Time (h) c d S G M G h M G S G M G S G h Time of BrdU injection after electroporation (h) M G S G M
(GFP+ BrdU+)/GFP+ Labeling index Labeling index Figure S a, b, y =,x +, y =,x +,,,,,,,, Time (h) - - Time (h) c d S G M G h M G S G M G S G h Time of BrdU injection after electroporation (h) M G S G M
Supplementary Figure 1. Chimeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) Chimeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears.
 Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
Supplemental Information. Genomic Characterization of Murine. Monocytes Reveals C/EBPb Transcription. Factor Dependence of Ly6C Cells
 Immunity, Volume 46 Supplemental Information Genomic Characterization of Murine Monocytes Reveals C/EBPb Transcription Factor Dependence of Ly6C Cells Alexander Mildner, Jörg Schönheit, Amir Giladi, Eyal
Immunity, Volume 46 Supplemental Information Genomic Characterization of Murine Monocytes Reveals C/EBPb Transcription Factor Dependence of Ly6C Cells Alexander Mildner, Jörg Schönheit, Amir Giladi, Eyal
marker. DAPI labels nuclei. Flies were 20 days old. Scale bar is 5 µm. Ctrl is
 Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Nos is detected in glial cells in both control and GFAP R79H transgenic flies (arrows), but not in deletion mutant Nos Δ15 animals. Repo is a glial cell marker. DAPI labels
Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Nos is detected in glial cells in both control and GFAP R79H transgenic flies (arrows), but not in deletion mutant Nos Δ15 animals. Repo is a glial cell marker. DAPI labels
20 2 Stomach Fig. 2.1 An illustration showing different patterns of the myenteric plexus peculiar to the regions in the guinea-pig stomach stained wit
 Stomach 2 The stomach is unique in that ICC have a different distribution in proximal and distal regions of the same organ. ICC-CM and ICC-LM are densely distributed throughout the thick circular and longitudinal
Stomach 2 The stomach is unique in that ICC have a different distribution in proximal and distal regions of the same organ. ICC-CM and ICC-LM are densely distributed throughout the thick circular and longitudinal
Cell Birth and Death. Chapter Three
 Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplemental Data Figure S1 Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells.
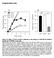 Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
F-actin VWF Vinculin. F-actin. Vinculin VWF
 a F-actin VWF Vinculin b F-actin VWF Vinculin Supplementary Fig. 1. WPBs in HUVECs are located along stress fibers and at focal adhesions. (a) Immunofluorescence images of f-actin (cyan), VWF (yellow),
a F-actin VWF Vinculin b F-actin VWF Vinculin Supplementary Fig. 1. WPBs in HUVECs are located along stress fibers and at focal adhesions. (a) Immunofluorescence images of f-actin (cyan), VWF (yellow),
Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse
 Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Supplementary information. Nkx2.1 regulates the generation of telencephalic astrocytes during embryonic
 Supplementary information Nkx2.1 regulates the generation of telencephalic astrocytes during embryonic development Shilpi Minocha 1*, Delphine Valloton 1*, Yvan Arsenijevic 2, Jean-René Cardinaux 3, Raffaella
Supplementary information Nkx2.1 regulates the generation of telencephalic astrocytes during embryonic development Shilpi Minocha 1*, Delphine Valloton 1*, Yvan Arsenijevic 2, Jean-René Cardinaux 3, Raffaella
Supplementary Figure 1: Features of IGLL5 Mutations in CLL: a) Representative IGV screenshot of first
 Supplementary Figure 1: Features of IGLL5 Mutations in CLL: a) Representative IGV screenshot of first intron IGLL5 mutation depicting biallelic mutations. Red arrows highlight the presence of out of phase
Supplementary Figure 1: Features of IGLL5 Mutations in CLL: a) Representative IGV screenshot of first intron IGLL5 mutation depicting biallelic mutations. Red arrows highlight the presence of out of phase
Supplementary Information. Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease. Supplementary Figures S1-10
 Supplementary Information Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease Christine Grienberger 1 *, Nathalie L. Rochefort 1 *, Helmuth Adelsberger 1, Horst A. Henning
Supplementary Information Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease Christine Grienberger 1 *, Nathalie L. Rochefort 1 *, Helmuth Adelsberger 1, Horst A. Henning
Astroglia induce neurogenesis from adult neural stem cells
 Astroglia induce neurogenesis from adult neural stem cells Hongjun Song*, Charles F. Stevens* & Fred H. Gage * Molecular Neurobiology Laboratory, Howard Hughes Medical Institute at the Salk Institute,
Astroglia induce neurogenesis from adult neural stem cells Hongjun Song*, Charles F. Stevens* & Fred H. Gage * Molecular Neurobiology Laboratory, Howard Hughes Medical Institute at the Salk Institute,
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS
 TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Brain Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Directs the Transition from Stem Cells to Mature Neurons During Postnatal/Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis VANESA NIETO-ESTÉVEZ, a,b CARLOS O.
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Brain Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Directs the Transition from Stem Cells to Mature Neurons During Postnatal/Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis VANESA NIETO-ESTÉVEZ, a,b CARLOS O.
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a
 Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
Environmental influences on brain and behaviour
 Environmental influences on brain and behaviour Abdul H. Mohammed Dept. of Neurotec Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden IBRO African Neuroscience School, Nairobi, 2005 Environmental interventions affecting
Environmental influences on brain and behaviour Abdul H. Mohammed Dept. of Neurotec Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden IBRO African Neuroscience School, Nairobi, 2005 Environmental interventions affecting
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
CD3 coated cover slips indicating stimulatory contact site, F-actin polymerization and
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES FIGURE S1. Detection of MCs. A, Schematic representation of T cells stimulated on anti- CD3 coated cover slips indicating stimulatory contact site, F-actin polymerization and microclusters.
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES FIGURE S1. Detection of MCs. A, Schematic representation of T cells stimulated on anti- CD3 coated cover slips indicating stimulatory contact site, F-actin polymerization and microclusters.
Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is
 Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is not co-expressed in DCLK1-positive tuft cells. Scale
Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is not co-expressed in DCLK1-positive tuft cells. Scale
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN
 UNC-6/Netrin mediates dendritic self-avoidance Cody J. Smith 1, Joseph D. Watson 1,4,5, Miri K. VanHoven 2, Daniel A. Colón-Ramos 3 and David M. Miller III 1,4,6 1 Department of Cell and Developmental
UNC-6/Netrin mediates dendritic self-avoidance Cody J. Smith 1, Joseph D. Watson 1,4,5, Miri K. VanHoven 2, Daniel A. Colón-Ramos 3 and David M. Miller III 1,4,6 1 Department of Cell and Developmental
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3631
 Supplementary Figure 1 SPT analyses of Zap70 at the T cell plasma membrane. (a) Total internal reflection fluorescent (TIRF) excitation at 64-68 degrees limits single molecule detection to 100-150 nm above
Supplementary Figure 1 SPT analyses of Zap70 at the T cell plasma membrane. (a) Total internal reflection fluorescent (TIRF) excitation at 64-68 degrees limits single molecule detection to 100-150 nm above
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex?
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 107 (2006) No. 1, p. 71 80 71) Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex? Šimonová Z., Dutt J. Department of Neuroscience of the Institute
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 107 (2006) No. 1, p. 71 80 71) Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex? Šimonová Z., Dutt J. Department of Neuroscience of the Institute
Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63.
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
