ErbB4 migrazione I parte. 3- ErbB4- NRG1
|
|
|
- Kristin Marshall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ErbB4 migrazione I parte 3- ErbB4- NRG1 1
2 In rodent brains postnatal neuronal migration is evident in three main areas: the cerebellum (CB), the hippocampus (Hipp) and the rostral migratory stream (RMS). A small number of neurons also complete their migration into the hypothalamus (Hyp) at around the time of birth. Initiation of neuronal migration The initiation of neuronal migration is regulated by a combination of motogenic (for example, migration-inducing activity, MIA, secreted by glial tubes surrounding the neuronal chains), chemoattractive (such as netrin and deleted in colorectal carcinoma, DCC) and chemorepulsive (for example, SLIT and ROBO) signals. Arrows indicate the direction of migration away from the subventricular zone towards the rostral migratory stream. 2
3 Maintenance of neuronal migration Neuroblasts migrate as chains, sliding along each other. Maintenance of chain migration is dependent on the continued motogenic activity of migrationinducing activity (MIA, orange), neuregulin 1 ErbB4 interactions (both purple), adhesion mediated by the polysialated form of neuronal cell adhesion molecule (PSA-NCAM, yellow) and extracellular matrix (ECM) integrin signalling (blue). Arrows indicate the direction of migration towards the olfactory bulb. The expression of the ErbB receptors in the RMS and SVZ of the forebrain of postnatal day (P) 11 and adult rats was determined using in situ hybridization P11 adult 3
4 1, anterior olfactory nucleus, dorsal; 2, anterior olfactory nucleus, ventral; 3, RMS; 4, corpus callosum; 5, SVZ; 6, lateral ventricle; 7, striatum In situ hybridization: quali informazioni ne traggo? Quali altre analisi posso effettuare? at P11, ErbB4 is expressed at high levels in the RMS and remains detectable in these cells as they migrate into the OB expression persists in granule neurons in the mature OB, but at reduced levels ErbB4 is also expressed in scattered cells in the striatum. in adults, ErbB4-specific hybridization in the RMS were lower than in P11 rats PSA-NCAM migrating neuroblast marker GFAP + glial cell marker immunohystochemistry: quali informazioni ne traggo? 4
5 near-perfect colocalization of ErbB4 and PSA-NCAM in the adult RMS, indicating that this receptor was expressed by the migrating neuroblast subpopulation. ErbB4 was also detected in a small subset of GFAP + glial cells dispersed in the RMS 1, anterior olfactory nucleus, dorsal; 2, anterior olfactory nucleus, ventral; 3, RMS; 4, corpus callosum; 5, SVZ; 6, lateral ventricle; 7, striatum the type I and II isoforms were detected at low levels in the stream both at P11 and in the adult and were also observed in the anterior lining of the ventricle at P11 5
6 1, anterior olfactory nucleus, dorsal; 2, anterior olfactory nucleus, ventral; 3, RMS; 4, corpus callosum; 5, SVZ; 6, lateral ventricle; 7, striatum the type III form was expressed at high levels in the RMS at P11 and was particularly noticeable in the regions surrounding the RMS, including in the anterior olfactory nucleus, in the internal granule cell layer as well as in the mitral cell and glomerular layers in the OB in the adult, the type III isoform was detected in the same regions, but at reduced levels 1, anterior olfactory nucleus, dorsal; 2, anterior olfactory nucleus, ventral; 3, RMS; 4, corpus callosum; 5, SVZ; 6, lateral ventricle; 7, striatum NRG2 was present at very low levels in the stream and at high levels in the internal granule cell, external plexiform and glomerular layers of the OB at P11 and in the adult. 6
7 These studies showed that: - ErbB4 is expressed by the migrating neuroblasts and at least some of the proliferating precursors of the SVZ - multiple potential ligands are located in the forebrain region, where they may influence neuroblast proliferation, migration and differentiation through ErbB4 Conditional knock-outs inactivate a gene only in specific tissues and at certain times during development and life. Cre-lox technology Promoter element Cre Cre a site-specific recombinase enzyme from the P1 phage. Recognises a 34bp DNA sequence loxp = Cre Your gene of interest is flanked by 34 bp loxp sites (floxed). Where CRE recombinase is expressed at least once Cre Cre Gene between loxp sites is removed 7
8 CONDITIONAL DELETION OF ErbB4 lines of conditional null mice were generated that lacked ErbB4 expression in the CNS to evaluate the role of this receptor in the SVZ and RMS mice in which the second exon of the gene ErbB4 was flanked by loxp sites were mated with transgenic mice that expressed Cre recombinase under the control of either the human GFAP (hgfap) promoter or the rat nestin promoter and enhancer to maximize the number of cells with a complete loss of ErbB4 function, they mated the mice carrying loxp sites (ErbB4 lox ) with the mice carrying Cre recombinase in a background that is heterozygous with respect to the null allele of ErbB4 (Gassmann). Promoter element Cre IRES GFP SV40 p(a) hgfap rat nestin ErbB4 II exon floxed Erbb4 lox/lox Erbb4 lox/- nestin-cre In situ hybridization using a probe specific to Erbb4 exon 2 did not detect any cells in either the RMS or the OB of P12 Erbb4 lox/- nestin-cre or Erbb4 lox/- hgfap-cre mice 8
9 Altered RMS in conditional mutants of ErbB4 The mid-rms was labeled with antibodies to PSA-NCAM, which mark neuroblasts that are typically organized as clusters of chains Erbb4 lox/+ hgfap-cre the PSA-NCAM + cells in the mutant mice formed fragmented chains that did not have the normal interdigitated and contiguous appearance Integrity of glial tubes is disrupted in the RMS after ErbB4 deletion to determine how these gross morphological differences were reflected at the cellular level, electron microscopic ultrastructural analyses was carried out using 1.0-µm-thick sections of the RMS. The close apposition of migrating cells (A cells) and the glial-like cells (B1, B2) that normally ensheath them was greatly reduced in the mice the loss of ErbB4 seems to disrupt the characteristic 'glial tube' organization found in the normal adult RMS 9
10 Erbb4 lox/+ hgfap-cre Erbb4 lox/+ hgfap-cre Deficits in the orientation and organization of neuroblast migration in the RMS of ErbB4-deficient mice Deficits in the orientation and organization of neuroblast migration in the RMS of ErbB4- deficient mice Erbb4 lox/+ hgfap-cre Erbb4 lox/+ hgfap-cre 10
11 NRG1 isoforms Type I/II-NRG1 Type III-NRG1 N Ig Ig Ig C EGF EGF MMP EGF EGF EGF MMP EGF?? CRD CRD CRD C C N N Paracrine (shed/secreted) Juxtacrine (contact dependent) (modified from Falls, 2003) the expression of types I and type III NRG1 isoforms in the stream suggested that they could modulate neuroblast migration through ErbB4 by potentially serving as permissive guidance cues, chemotropic agents or motogens Quale saggio si può fare per valutare l affinità nei confronti di un certo substrato? 11
12 the expression of types I and type III NRG1 isoforms in the stream suggested that they could modulate neuroblast migration through ErbB4 by potentially serving as permissive guidance cues, chemotropic agents or motogens to determine if these isoforms provided a permissive substratum for migration, CMTMR-labeled SVZ explants were placed in between adjacent strips of COS cells expressing NRG1 type I and control (mock-transfected) cells or adjacent strips of COS cells expressing NRG1 type III and control cells Control SVZ cells prefer to migrate on the NRG1 type III substrate KO the substrate preference of the neuroblasts migrating out of the SVZ explant was evaluated SVZ cells had a strong preference for COS cells expressing NRG1 type III, but not for mock-transfected cells or COS cells expressing NRG1 type I KO KO NRG1-III NRG1-I NRG1 type III at the cell surface may provide a permissive, guidance substratum for neuroblast migration towards the OB 12
ErbB4 migrazione II parte
 ErbB4 migrazione II parte Control SVZ cells prefer to migrate on the NRG1 type III substrate the substrate preference of the neuroblasts migrating out of the SVZ explant was evaluated SVZ cells had a strong
ErbB4 migrazione II parte Control SVZ cells prefer to migrate on the NRG1 type III substrate the substrate preference of the neuroblasts migrating out of the SVZ explant was evaluated SVZ cells had a strong
Receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB4 modulates neuroblast migration and placement in the adult forebrain
 Receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB4 modulates neuroblast migration and placement in the adult forebrain E S Anton 1,8, H T Ghashghaei 1,8, Janet L Weber 2, Corey McCann 1, Tobias M Fischer 2, Isla D Cheung
Receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB4 modulates neuroblast migration and placement in the adult forebrain E S Anton 1,8, H T Ghashghaei 1,8, Janet L Weber 2, Corey McCann 1, Tobias M Fischer 2, Isla D Cheung
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain. - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function
 Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches
 During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches Two mayor forms of neuronal migration: Radial and Tangential Leber & Sanes, 95 How do young neurons actually
During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches Two mayor forms of neuronal migration: Radial and Tangential Leber & Sanes, 95 How do young neurons actually
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Wednesday (Oct 18) 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Wednesday (Oct 18) 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop
Neuronal migration in the adult brain: are we there yet?
 Neuronal migration in the adult brain: are we there yet? H. Troy Ghashghaei*, Cary Lai and E. S. Anton* Abstract The generation and targeting of appropriate numbers and types of neurons to where they are
Neuronal migration in the adult brain: are we there yet? H. Troy Ghashghaei*, Cary Lai and E. S. Anton* Abstract The generation and targeting of appropriate numbers and types of neurons to where they are
During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches
 During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches Progenitors are Contained within Unique Domains and Tangentially Fixed. EMBRYO ADULT Migratory Behavior
During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches Progenitors are Contained within Unique Domains and Tangentially Fixed. EMBRYO ADULT Migratory Behavior
SOM Husse et al. Supplementary online material. Synaptotagmin10-Cre, a driver to disrupt clock genes in the SCN
 SOM Husse et al. Supplementary online material Synaptotagmin10-Cre, a driver to disrupt clock genes in the SCN Jana Husse, Xunlei Zhou, Anton Shostak, Henrik Oster and Gregor Eichele SOM Husse et al.,
SOM Husse et al. Supplementary online material Synaptotagmin10-Cre, a driver to disrupt clock genes in the SCN Jana Husse, Xunlei Zhou, Anton Shostak, Henrik Oster and Gregor Eichele SOM Husse et al.,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1.
 Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Seafood Contaminants causing Foodborne Diseases
 Seafood Contaminants causing Foodborne Diseases Bacteria and Viruses Vibrio species Viruses: Norwalk-like (NLV) and Hepatitis A (HAV) Industrial Compounds Mercury Polyclorinated biphenyls (PCBs) Natural
Seafood Contaminants causing Foodborne Diseases Bacteria and Viruses Vibrio species Viruses: Norwalk-like (NLV) and Hepatitis A (HAV) Industrial Compounds Mercury Polyclorinated biphenyls (PCBs) Natural
Brain Development III
 Brain Development III Neural Development In the developing nervous system there must be: 1. The formation of different regions of the brain. 2. The ability of a neuron to differentiate. 3. The ability
Brain Development III Neural Development In the developing nervous system there must be: 1. The formation of different regions of the brain. 2. The ability of a neuron to differentiate. 3. The ability
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Hey! The major concepts discussed relative to neural crest cell migration apply to cell migration
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Hey! The major concepts discussed relative to neural crest cell migration apply to cell migration
Expression of Mutant p53 Proteins Implicates a Lineage Relationship between Neural Stem Cells and Malignant Astrocytic Glioma in a Murine Model
 Article Expression of Mutant p53 Proteins Implicates a Lineage Relationship between Neural Stem Cells and Malignant Astrocytic Glioma in a Murine Model Yuan Wang, 1,2,6 Jiong Yang, 1,2,6 Huarui Zheng,
Article Expression of Mutant p53 Proteins Implicates a Lineage Relationship between Neural Stem Cells and Malignant Astrocytic Glioma in a Murine Model Yuan Wang, 1,2,6 Jiong Yang, 1,2,6 Huarui Zheng,
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus
 Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Supplemental Figure 1. (A) The localization of Cre DNA recombinase in the testis of Cyp19a1-Cre mice was detected by immunohistchemical analyses
 Supplemental Figure 1. (A) The localization of Cre DNA recombinase in the testis of Cyp19a1-Cre mice was detected by immunohistchemical analyses using an anti-cre antibody; testes at 1 week (left panel),
Supplemental Figure 1. (A) The localization of Cre DNA recombinase in the testis of Cyp19a1-Cre mice was detected by immunohistchemical analyses using an anti-cre antibody; testes at 1 week (left panel),
Broad Integration of Expression Maps and Co-Expression Networks Compassing Novel Gene Functions in the Brain
 Supplementary Information Broad Integration of Expression Maps and Co-Expression Networks Compassing Novel Gene Functions in the Brain Yuko Okamura-Oho a, b, *, Kazuro Shimokawa c, Masaomi Nishimura b,
Supplementary Information Broad Integration of Expression Maps and Co-Expression Networks Compassing Novel Gene Functions in the Brain Yuko Okamura-Oho a, b, *, Kazuro Shimokawa c, Masaomi Nishimura b,
The Zinc Finger Transcription Factor Sp8 Regulates the Generation and Diversity of Olfactory Bulb Interneurons
 Neuron 49, 503 516, February 16, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.01.018 The Zinc Finger Transcription Factor Sp8 Regulates the Generation and Diversity of Olfactory Bulb Interneurons
Neuron 49, 503 516, February 16, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.01.018 The Zinc Finger Transcription Factor Sp8 Regulates the Generation and Diversity of Olfactory Bulb Interneurons
Citation for published version (APA): Martina-Mamber, C. E. (2014). GFAP as an understudy in adult neurogenesis. 's-hertogenbosch: Boxpress.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) GFAP as an understudy in adult neurogenesis Mamber, C.E. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Martina-Mamber, C. E. (2014). GFAP as an understudy
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) GFAP as an understudy in adult neurogenesis Mamber, C.E. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Martina-Mamber, C. E. (2014). GFAP as an understudy
Supplementary Figure S1: Pial and periventricular vascular networks and the dual GABA neuron streams of the early embryonic mouse telencephalon
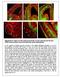 Supplementary Figure S1: Pial and periventricular vascular networks and the dual GABA neuron streams of the early embryonic mouse telencephalon a) The profile of GABA neurons arriving at the pallial-subpallial
Supplementary Figure S1: Pial and periventricular vascular networks and the dual GABA neuron streams of the early embryonic mouse telencephalon a) The profile of GABA neurons arriving at the pallial-subpallial
mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons
 Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse
 Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Development of the Nervous System. Leah Militello, class of 2018
 Development of the Nervous System Leah Militello, class of 2018 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the formation and fate of the neural tube and neural crest including timing and germ layer involved. 2. Describe
Development of the Nervous System Leah Militello, class of 2018 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the formation and fate of the neural tube and neural crest including timing and germ layer involved. 2. Describe
Etv4 BU EMM Etv5 BC MMM UI-M-BH3- Elk1 BC MMM
 Supplementary Tables In situ hybridization probes Genbank Gene Accession Number Clone ID Cat. No Etv1 BC005645 PCR Etv4 BU053662 5062538 EMM1002-5544031 Etv5 BC034680 4036564 MMM1013-7511524 Fev AI876263
Supplementary Tables In situ hybridization probes Genbank Gene Accession Number Clone ID Cat. No Etv1 BC005645 PCR Etv4 BU053662 5062538 EMM1002-5544031 Etv5 BC034680 4036564 MMM1013-7511524 Fev AI876263
9.14 Class 32 Review. Limbic system
 9.14 Class 32 Review Limbic system 1 Lateral view Medial view Brainstem, sagittal section Sensory- Perceptual Motor Behavior Major functional modules of the CNS Motivation Courtesy of MIT Press. Used with
9.14 Class 32 Review Limbic system 1 Lateral view Medial view Brainstem, sagittal section Sensory- Perceptual Motor Behavior Major functional modules of the CNS Motivation Courtesy of MIT Press. Used with
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
A Cxcl12-Cxcr4 Chemokine Signaling Pathway Defines
 Supplemental Data A Cxcl12-Cxcr4 Chemokine Signaling Pathway Defines the Initial Trajectory of Mammalian Motor Axons Ivo Lieberam, Dritan Agalliu, Takashi Nagasawa, Johan Ericson, and Thomas M. Jessell
Supplemental Data A Cxcl12-Cxcr4 Chemokine Signaling Pathway Defines the Initial Trajectory of Mammalian Motor Axons Ivo Lieberam, Dritan Agalliu, Takashi Nagasawa, Johan Ericson, and Thomas M. Jessell
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. MADM labeling of thalamic clones.
 Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Brain homeostasis: VEGF receptor 1 and 2 two unequal brothers in mind
 Cell. Mol. Life Sci. (2013) 70:1705 1725 DOI 10.1007/s00018-013-1279-3 Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences MULTI-AUTHOR REVIEW Brain homeostasis: VEGF receptor 1 and 2 two unequal brothers in mind Ina
Cell. Mol. Life Sci. (2013) 70:1705 1725 DOI 10.1007/s00018-013-1279-3 Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences MULTI-AUTHOR REVIEW Brain homeostasis: VEGF receptor 1 and 2 two unequal brothers in mind Ina
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.
 Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus
 Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus Gerd Kempermann 1,2, Sebastian Jessberger 2, Barbara Steiner 2 and Golo Kronenberg 1,3 1 Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin-Buch,
Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus Gerd Kempermann 1,2, Sebastian Jessberger 2, Barbara Steiner 2 and Golo Kronenberg 1,3 1 Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin-Buch,
Migration of bone marrow progenitor cells in the adult brain of rats and rabbits
 Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.4252/wjsc.v8.i4.136 World J Stem Cells 2016 April 26; 8(4): 136-157 ISSN 1948-0210 (online)
Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.4252/wjsc.v8.i4.136 World J Stem Cells 2016 April 26; 8(4): 136-157 ISSN 1948-0210 (online)
Introduction. Materials and Methods
 4240 The Journal of Neuroscience, May 15, 2003 23(10):4240 4250 Multiple Cell Populations in the Early Postnatal Subventricular Zone Take Distinct Migratory Pathways: A Dynamic Study of Glial and Neuronal
4240 The Journal of Neuroscience, May 15, 2003 23(10):4240 4250 Multiple Cell Populations in the Early Postnatal Subventricular Zone Take Distinct Migratory Pathways: A Dynamic Study of Glial and Neuronal
Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing. Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2
 ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
NG2 + CNS Glial Progenitors Remain Committed to the Oligodendrocyte Lineage in Postnatal Life and following Neurodegeneration
 Article NG2 + CNS Glial Progenitors Remain Committed to the Oligodendrocyte Lineage in Postnatal Life and following Neurodegeneration Shin H. Kang, 1 Masahiro Fukaya, 2,4 Jason K. Yang, 1 Jeffrey D. Rothstein,
Article NG2 + CNS Glial Progenitors Remain Committed to the Oligodendrocyte Lineage in Postnatal Life and following Neurodegeneration Shin H. Kang, 1 Masahiro Fukaya, 2,4 Jason K. Yang, 1 Jeffrey D. Rothstein,
Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN
 UNC-6/Netrin mediates dendritic self-avoidance Cody J. Smith 1, Joseph D. Watson 1,4,5, Miri K. VanHoven 2, Daniel A. Colón-Ramos 3 and David M. Miller III 1,4,6 1 Department of Cell and Developmental
UNC-6/Netrin mediates dendritic self-avoidance Cody J. Smith 1, Joseph D. Watson 1,4,5, Miri K. VanHoven 2, Daniel A. Colón-Ramos 3 and David M. Miller III 1,4,6 1 Department of Cell and Developmental
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information 5-hydroxymethylcytosine-mediated epigenetic dynamics during postnatal neurodevelopment and aging By Keith E. Szulwach 1,8, Xuekun Li 1,8, Yujing Li 1, Chun-Xiao Song 2, Hao Wu
Supplementary Information 5-hydroxymethylcytosine-mediated epigenetic dynamics during postnatal neurodevelopment and aging By Keith E. Szulwach 1,8, Xuekun Li 1,8, Yujing Li 1, Chun-Xiao Song 2, Hao Wu
Cell Birth and Death. Chapter Three
 Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS
 TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Prox1 Is Required for Oligodendrocyte Cell Identity in Adult Neural Stem Cells of the Subventricular Zone : a Institute of Cell Biology, ZMBE, University of M unster, M unster,
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Prox1 Is Required for Oligodendrocyte Cell Identity in Adult Neural Stem Cells of the Subventricular Zone : a Institute of Cell Biology, ZMBE, University of M unster, M unster,
Neocortex Zbtb20 / NFIA / Sox9
 Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI. (a) Gross anatomy of representative spleens from control and T3 SCI mice at 28 days post-injury. (b and c) Hematoxylin and eosin
Supplementary Figure 1 Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI. (a) Gross anatomy of representative spleens from control and T3 SCI mice at 28 days post-injury. (b and c) Hematoxylin and eosin
Malignant Astrocytomas Originate from Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells in a Somatic Tumor Suppressor Mouse Model
 Article Malignant Astrocytomas Originate from Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells in a Somatic Tumor Suppressor Mouse Model Sheila Alcantara Llaguno, 1,4 Jian Chen, 1,4 Chang-Hyuk Kwon, 1,4,5 Erica L. Jackson,
Article Malignant Astrocytomas Originate from Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells in a Somatic Tumor Suppressor Mouse Model Sheila Alcantara Llaguno, 1,4 Jian Chen, 1,4 Chang-Hyuk Kwon, 1,4,5 Erica L. Jackson,
Chapter 11 Development and Diseases
 Chapter 11 Development and Diseases Fertilization Development of the Nervous System Cleavage (Blastula, Gastrula) Neuronal Induction- Neuroblast Formation Cell Migration Axon Growth/Target innervation
Chapter 11 Development and Diseases Fertilization Development of the Nervous System Cleavage (Blastula, Gastrula) Neuronal Induction- Neuroblast Formation Cell Migration Axon Growth/Target innervation
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation. Reading: BCP Chapter 23
 Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Ontogenesis in the CNS neurogenesis during embryonic development
 Ontogenesis in the CNS neurogenesis during embryonic development Formation of the neural tube neural groove neural plate neural groove neural crest notochord neural tube The developing neuroepithelium
Ontogenesis in the CNS neurogenesis during embryonic development Formation of the neural tube neural groove neural plate neural groove neural crest notochord neural tube The developing neuroepithelium
Supplemental Data. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Mesenchymal Progenitors. Controls Osteoblast and Chondrocyte
 Supplemental Data Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Mesenchymal Progenitors Controls Osteoblast and Chondrocyte Differentiation during Vertebrate Skeletogenesis Timothy F. Day, Xizhi Guo, Lisa Garrett-Beal, and
Supplemental Data Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Mesenchymal Progenitors Controls Osteoblast and Chondrocyte Differentiation during Vertebrate Skeletogenesis Timothy F. Day, Xizhi Guo, Lisa Garrett-Beal, and
IL-34 is a tissue-restricted ligand of CSF1R required for the development of Langerhans cells and microglia
 Supplementary Figures IL-34 is a tissue-restricted ligand of CSF1R required for the development of Langerhans cells and microglia Yaming Wang, Kristy J. Szretter, William Vermi, Susan Gilfillan, Cristina
Supplementary Figures IL-34 is a tissue-restricted ligand of CSF1R required for the development of Langerhans cells and microglia Yaming Wang, Kristy J. Szretter, William Vermi, Susan Gilfillan, Cristina
SOPten flox/flox (KO) Pten flox/flox (WT) flox allele 6.0 kb. Pten. Actin. ! allele 2.3 kb. Supplementary Figure S1. Yanagi, et al.
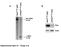 s1 A Pten flox/flox () SOPten flox/flox () flox allele 6. kb B Pten flox/flox () SOPten flox/flox () Pten Actin! allele 2.3 kb Supplementary Figure S1. Yanagi, et al. A B BrdU BrdU positive cells ( ) 3
s1 A Pten flox/flox () SOPten flox/flox () flox allele 6. kb B Pten flox/flox () SOPten flox/flox () Pten Actin! allele 2.3 kb Supplementary Figure S1. Yanagi, et al. A B BrdU BrdU positive cells ( ) 3
Supplementary information. Nkx2.1 regulates the generation of telencephalic astrocytes during embryonic
 Supplementary information Nkx2.1 regulates the generation of telencephalic astrocytes during embryonic development Shilpi Minocha 1*, Delphine Valloton 1*, Yvan Arsenijevic 2, Jean-René Cardinaux 3, Raffaella
Supplementary information Nkx2.1 regulates the generation of telencephalic astrocytes during embryonic development Shilpi Minocha 1*, Delphine Valloton 1*, Yvan Arsenijevic 2, Jean-René Cardinaux 3, Raffaella
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND MOVIE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. (A) Images of nerves stained for GFAP (green), S100 (red) and DAPI
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND MOVIE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. (A) Images of nerves stained for GFAP (green), S100 (red) and DAPI
Glia-independent chains of neuroblasts through the subcortical parenchyma of the adult rabbit brain
 Glia-independent chains of neuroblasts through the subcortical parenchyma of the adult rabbit brain F. Luzzati*, P. Peretto*, P. Aimar, G. Ponti, A. Fasolo*, and L. Bonfanti *Department of Animal and Human
Glia-independent chains of neuroblasts through the subcortical parenchyma of the adult rabbit brain F. Luzzati*, P. Peretto*, P. Aimar, G. Ponti, A. Fasolo*, and L. Bonfanti *Department of Animal and Human
AP VP DLP H&E. p-akt DLP
 A B AP VP DLP H&E AP AP VP DLP p-akt wild-type prostate PTEN-null prostate Supplementary Fig. 1. Targeted deletion of PTEN in prostate epithelium resulted in HG-PIN in all three lobes. (A) The anatomy
A B AP VP DLP H&E AP AP VP DLP p-akt wild-type prostate PTEN-null prostate Supplementary Fig. 1. Targeted deletion of PTEN in prostate epithelium resulted in HG-PIN in all three lobes. (A) The anatomy
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Identification and characterization of neuroblasts in the subventricular zone and rostral migratory stream of the adult human brain
 1534 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2011) 21:1534-1550. 2011 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/11 $ 32.00 www.nature.com/cr npg Identification and characterization of neuroblasts in the subventricular
1534 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2011) 21:1534-1550. 2011 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/11 $ 32.00 www.nature.com/cr npg Identification and characterization of neuroblasts in the subventricular
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP:
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS
 TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Brain Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Directs the Transition from Stem Cells to Mature Neurons During Postnatal/Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis VANESA NIETO-ESTÉVEZ, a,b CARLOS O.
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Brain Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Directs the Transition from Stem Cells to Mature Neurons During Postnatal/Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis VANESA NIETO-ESTÉVEZ, a,b CARLOS O.
Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Tarrytown, New York 10591
 The Journal of Neuroscience, September 1, 2001, 21(17):6706 6717 Infusion of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor into the Lateral Ventricle of the Adult Rat Leads to New Neurons in the Parenchyma of the
The Journal of Neuroscience, September 1, 2001, 21(17):6706 6717 Infusion of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor into the Lateral Ventricle of the Adult Rat Leads to New Neurons in the Parenchyma of the
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70%
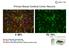 Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Anterior Olfactory Nucleus
 A Anterior Olfactory Nucleus PETER C. BRUNJES, KURT R. ILLIG Department of Psychology, University of Virginia Charlottesville, VA, USA Synonyms Anterior olfactory cortex Definition The primary component
A Anterior Olfactory Nucleus PETER C. BRUNJES, KURT R. ILLIG Department of Psychology, University of Virginia Charlottesville, VA, USA Synonyms Anterior olfactory cortex Definition The primary component
Rat Dlx5 is expressed in the subventricular zone and promotes neuronal differentiation
 ISSN 0100-879X Volume 43 (02) 124-225 February 2010 BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES AND CLINICAL INVESTIGATION Braz J Med Biol Res, February 2010, Volume 43(2) 176-185 Rat Dlx5 is expressed in the subventricular zone
ISSN 0100-879X Volume 43 (02) 124-225 February 2010 BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES AND CLINICAL INVESTIGATION Braz J Med Biol Res, February 2010, Volume 43(2) 176-185 Rat Dlx5 is expressed in the subventricular zone
Nitric Oxide Is a Physiological Inhibitor of Neurogenesis in the Adult Mouse Subventricular Zone and Olfactory Bulb
 The Journal of Neuroscience, January 7, 2004 24(1):85 95 85 Development/Plasticity/Repair Nitric Oxide Is a Physiological Inhibitor of Neurogenesis in the Adult Mouse Subventricular Zone and Olfactory
The Journal of Neuroscience, January 7, 2004 24(1):85 95 85 Development/Plasticity/Repair Nitric Oxide Is a Physiological Inhibitor of Neurogenesis in the Adult Mouse Subventricular Zone and Olfactory
Materiale per uso didattico 1
 BCII - Perroteau - shuttling citoplasma nucleus 1 ERK regulation by scaffolds and anchors 2 Materiale per uso didattico 1 ERK Pathway regulation by feedback loops and phosphatases 3 ERK has more
BCII - Perroteau - shuttling citoplasma nucleus 1 ERK regulation by scaffolds and anchors 2 Materiale per uso didattico 1 ERK Pathway regulation by feedback loops and phosphatases 3 ERK has more
Development of the Nervous System 1 st month
 Development of the Nervous System 1 st month day 1 - fertilization of egg day 6 - uterine implantation day 18 - trilaminar (3-layered) disc (blastoderm, embryo) ectoderm (dorsal) - nervous system and skin
Development of the Nervous System 1 st month day 1 - fertilization of egg day 6 - uterine implantation day 18 - trilaminar (3-layered) disc (blastoderm, embryo) ectoderm (dorsal) - nervous system and skin
Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology
 Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology Each student gets a set of 6 questions, so that each set contains different types of questions and that the set of questions
Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology Each student gets a set of 6 questions, so that each set contains different types of questions and that the set of questions
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE. Thomas Marino, Ph.D.
 BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE Thomas Marino, Ph.D. Development of the Brain I. Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Understand
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE Thomas Marino, Ph.D. Development of the Brain I. Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Understand
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum
 Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Postn MCM Smad2 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad3 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl. Postn MCM. Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl TAC
 A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
4/18/2011. Physiology 67 Lecture on Neural Development
 Physiology 67 Lecture on Neural Development 1 2 3 4 5 6 Neural cell categories After the ectodermal tissue has folded into the neural tube, another series of signaling interactions determine the type of
Physiology 67 Lecture on Neural Development 1 2 3 4 5 6 Neural cell categories After the ectodermal tissue has folded into the neural tube, another series of signaling interactions determine the type of
Young neurons born in the developing or adult brain have to
 Permissive corridor and diffusible gradients direct medial ganglionic eminence cell migration to the neocortex Hynek Wichterle*, Manuel Alvarez-Dolado, Lynda Erskine, and Arturo Alvarez-Buylla *The Rockefeller
Permissive corridor and diffusible gradients direct medial ganglionic eminence cell migration to the neocortex Hynek Wichterle*, Manuel Alvarez-Dolado, Lynda Erskine, and Arturo Alvarez-Buylla *The Rockefeller
Olfactory ensheathing glia
 Olfactory ensheathing glia From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Neuroglia of the brain shown by Golgi's method. Olfactory ensheathing glia (OEG), also known as olfactory ensheathing cells (OECs) or olfactory
Olfactory ensheathing glia From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Neuroglia of the brain shown by Golgi's method. Olfactory ensheathing glia (OEG), also known as olfactory ensheathing cells (OECs) or olfactory
A new role for meninges as a niche for stem/precursor cells with neural differentiation potential during development up to adulthood
 A new role for meninges as a niche for stem/precursor cells with neural differentiation potential during development up to adulthood Francesco Bifari, MD, PhD Mauro Krampera, MD, PhD Ilaria Decimo, PhD
A new role for meninges as a niche for stem/precursor cells with neural differentiation potential during development up to adulthood Francesco Bifari, MD, PhD Mauro Krampera, MD, PhD Ilaria Decimo, PhD
Nature Protocols: doi: /nprot Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of different enzymes on CD13 and CD31 populations.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of different enzymes on CD13 and CD31 populations. Comparison of cortex dissociated for 30 minutes with collagenase/dispase digestion (a) or papain (b). Papain degrades the
Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of different enzymes on CD13 and CD31 populations. Comparison of cortex dissociated for 30 minutes with collagenase/dispase digestion (a) or papain (b). Papain degrades the
Postnatal Neurogenesis and Gliogenesis in the Olfactory Bulb from NG2-Expressing Progenitors of the Subventricular Zone
 10530 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 17, 2004 24(46):10530 10541 Development/Plasticity/Repair Postnatal Neurogenesis and Gliogenesis in the Olfactory Bulb from NG2-Expressing Progenitors of the
10530 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 17, 2004 24(46):10530 10541 Development/Plasticity/Repair Postnatal Neurogenesis and Gliogenesis in the Olfactory Bulb from NG2-Expressing Progenitors of the
Cellular Composition and Three-Dimensional Organization of the Subventricular Germinal Zone in the Adult Mammalian Brain
 The Journal of Neuroscience, July 1, 1997, 17(13):5046 5061 Cellular Composition and Three-Dimensional Organization of the Subventricular Germinal Zone in the Adult Mammalian Brain Fiona Doetsch, 1 Jose
The Journal of Neuroscience, July 1, 1997, 17(13):5046 5061 Cellular Composition and Three-Dimensional Organization of the Subventricular Germinal Zone in the Adult Mammalian Brain Fiona Doetsch, 1 Jose
Netrin 1 contributes to vascular remodeling in the subventricular zone and promotes progenitor emigration after demyelination
 STEM CELLS AND REGENERATION RESEARCH ARTICLE 3107 Development 140, 3107-3117 (2013) doi:10.1242/dev.092999 2013. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Netrin 1 contributes to vascular remodeling in
STEM CELLS AND REGENERATION RESEARCH ARTICLE 3107 Development 140, 3107-3117 (2013) doi:10.1242/dev.092999 2013. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Netrin 1 contributes to vascular remodeling in
Combinations of genetic mutations in the adult neural stem cell compartment determine brain tumour phenotypes
 Manuscript EMBO-2009-71812 Combinations of genetic mutations in the adult neural stem cell compartment determine brain tumour phenotypes Thomas S. Jacques, Alexander Swales, Monika J. Brzozowski, Nico
Manuscript EMBO-2009-71812 Combinations of genetic mutations in the adult neural stem cell compartment determine brain tumour phenotypes Thomas S. Jacques, Alexander Swales, Monika J. Brzozowski, Nico
Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, Jeremy Miller Scientist I
 Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, 2013 Jeremy Miller Scientist I jeremym@alleninstitute.org Outline 1. Brief introduction to previous WGCNA studies in brain 2.
Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, 2013 Jeremy Miller Scientist I jeremym@alleninstitute.org Outline 1. Brief introduction to previous WGCNA studies in brain 2.
Blood Vessels Form a Scaffold for Neuroblast Migration in the Adult Olfactory Bulb
 5976 The Journal of Neuroscience, May 30, 2007 27(22):5976 5980 Brief Communications Blood Vessels Form a Scaffold for Neuroblast Migration in the Adult Olfactory Bulb Serena Bovetti, 1,2 Yi-Chun Hsieh,
5976 The Journal of Neuroscience, May 30, 2007 27(22):5976 5980 Brief Communications Blood Vessels Form a Scaffold for Neuroblast Migration in the Adult Olfactory Bulb Serena Bovetti, 1,2 Yi-Chun Hsieh,
Prolonged Seizures Increase Proliferating Neuroblasts in the Adult Rat Subventricular Zone Olfactory Bulb Pathway
 The Journal of Neuroscience, April 15, 2002, 22(8):3174 3188 Prolonged Seizures Increase Proliferating Neuroblasts in the Adult Rat Subventricular Zone Olfactory Bulb Pathway Jack M. Parent, 1 Vivian V.
The Journal of Neuroscience, April 15, 2002, 22(8):3174 3188 Prolonged Seizures Increase Proliferating Neuroblasts in the Adult Rat Subventricular Zone Olfactory Bulb Pathway Jack M. Parent, 1 Vivian V.
glial cells missing and gcm2 Cell-autonomously Regulate Both Glial and Neuronal
 glial cells missing and gcm2 Cell-autonomously Regulate Both Glial and Neuronal Development in the Visual System of Drosophila Carole Chotard, Wendy Leung and Iris Salecker Supplemental Data Supplemental
glial cells missing and gcm2 Cell-autonomously Regulate Both Glial and Neuronal Development in the Visual System of Drosophila Carole Chotard, Wendy Leung and Iris Salecker Supplemental Data Supplemental
Bio 3411 Midterm Review:
 Bio 3411 Midterm Review: Structure/Development/Systems/ Plastics/Talents/Diseases/Genes Structure General Overview Wednesday October 26, 2011 1 2 THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed, p. 8! THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed,
Bio 3411 Midterm Review: Structure/Development/Systems/ Plastics/Talents/Diseases/Genes Structure General Overview Wednesday October 26, 2011 1 2 THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed, p. 8! THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed,
Coincident generation of pyramidal neurons and protoplasmic astrocytes in neocortical columns
 University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Neurobiology Publications and Presentations Neurobiology 4-4-2012 Coincident generation of pyramidal neurons and protoplasmic astrocytes in
University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Neurobiology Publications and Presentations Neurobiology 4-4-2012 Coincident generation of pyramidal neurons and protoplasmic astrocytes in
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of dnscs.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Synapse Formation. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Synapse Formation Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Midterm Exam Monday, Nov 13 9:30-11:30am Bring a #2 pencil!! 2 Course News Lecture schedule: Mon (Oct 31)
Synapse Formation Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Midterm Exam Monday, Nov 13 9:30-11:30am Bring a #2 pencil!! 2 Course News Lecture schedule: Mon (Oct 31)
Central nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord Collections of cell body and dendrites (grey matter) are called nuclei/nucleus Nucleus can also
 Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Imaging and recording subventricular zone progenitor cells in live tissue of postnatal mice
 Review Article published: 19 July 2010 doi: 10.3389/fnins.2010.00043 Imaging and recording subventricular zone progenitor cells in live tissue of postnatal mice Benjamin Lacar 1,2, Stephanie Z. Young 1,2,
Review Article published: 19 July 2010 doi: 10.3389/fnins.2010.00043 Imaging and recording subventricular zone progenitor cells in live tissue of postnatal mice Benjamin Lacar 1,2, Stephanie Z. Young 1,2,
Environment-dependent fate of implanted neural stem cells in the brain
 Environment-dependent fate of implanted neural stem cells in the brain PhD theses Anita Zádori MD Semmelweis University János Szentágothai Doctoral School of Neurosciences Supervisor: Dr. Emília Madarász
Environment-dependent fate of implanted neural stem cells in the brain PhD theses Anita Zádori MD Semmelweis University János Szentágothai Doctoral School of Neurosciences Supervisor: Dr. Emília Madarász
Visual system invades the endbrain: pathways to striatum and cortex (continued) Why this happened in evolution
 Visual system invades the endbrain: pathways to striatum and cortex (continued) Why this happened in evolution What were the adaptive advantages? Visual information reaching the striatum directly: Advantages
Visual system invades the endbrain: pathways to striatum and cortex (continued) Why this happened in evolution What were the adaptive advantages? Visual information reaching the striatum directly: Advantages
Retinoic acid regulates postnatal neurogenesis in the murine subventricular zone-olfactory bulb pathway
 Research article 2721 Retinoic acid regulates postnatal neurogenesis in the murine subventricular zone-olfactory bulb pathway Tsu-Wei Wang, Helen Zhang and Jack M. Parent* Department of Neurology and Program
Research article 2721 Retinoic acid regulates postnatal neurogenesis in the murine subventricular zone-olfactory bulb pathway Tsu-Wei Wang, Helen Zhang and Jack M. Parent* Department of Neurology and Program
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Neural Stem Cell Niches in Health and Diseases
 Neural Stem Cell Niches in Health and Diseases Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2012, 18, 1755-1783 1755 Ilaria Decimo 1,*,#, Francesco Bifari 2,#, Mauro Krampera 2 and Guido Fumagalli 1, * 1 Department
Neural Stem Cell Niches in Health and Diseases Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2012, 18, 1755-1783 1755 Ilaria Decimo 1,*,#, Francesco Bifari 2,#, Mauro Krampera 2 and Guido Fumagalli 1, * 1 Department
Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation
 Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation Neurulation The cells of the neural tube are NEUROEPITHELIAL CELLS Neural crest cells migrate out of neural tube Neuroepithelial cells are embryonic stem
Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation Neurulation The cells of the neural tube are NEUROEPITHELIAL CELLS Neural crest cells migrate out of neural tube Neuroepithelial cells are embryonic stem
ANAT3231: lectures overview
 ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
Generating Mouse Models of Pancreatic Cancer
 Generating Mouse Models of Pancreatic Cancer Aom Isbell http://www2.massgeneral.org/cancerresourceroom/types/gi/index.asp Spring/Summer 1, 2012 Alexandros Tzatsos, MD PhD Bardeesy Lab: Goals and Objectives
Generating Mouse Models of Pancreatic Cancer Aom Isbell http://www2.massgeneral.org/cancerresourceroom/types/gi/index.asp Spring/Summer 1, 2012 Alexandros Tzatsos, MD PhD Bardeesy Lab: Goals and Objectives
