KIDNEY HEALTH. Kidney Masses and Localized Kidney Tumors: A Patient Guide
|
|
|
- Quentin Anderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 KIDNEY HEALTH Kidney Masses and Localized Kidney Tumors: A Patient Guide
2 Table of Contents Kidney & Adrenal Health Committee Renal Mass Committee Patient Story Introduction: I have a kidney mass What do I do now?... 3 GET THE FACTS What do the Kidneys do? What is a Kidney Mass? What do we Know about Kidney Cancer? What Causes a Kidney Mass? What are the Symptoms of a Kidney Mass? GET DIAGNOSED How is my Kidney Mass Diagnosed? What does Tumor Grade and Stage Mean?... 6 GET TREATED Active Surveillance Partial Nephrectomy Radical Nephrectomy Ablation Care Management AFTER TREATMENT Managing After Kidney Mass Treatment QUESTIONS TO ASK YOUR DOCTOR... 8 GLOSSARY... 9 CHAIR Kenneth Ogan, MD Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta, GA PANEL MEMBERS Raymond J. Leveillee, MD, FRCS-G Bethesda Hospital East Boynton Beach, FL Vitaly Margulis, MD The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center Dallas, TX Viraj Master, MD, PhD Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta, GA Brian Matlaga, MD Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine The James Buchanan Brady Urological Institute Baltimore, Maryland About the Urology Care Foundation.... [back cover] 2
3 Mike Sweigart s Story Mike Sweigart, is the Chief Deputy Tax Commissioner for Gwinnet County in Atlanta, Georgia. In December 2016, he was diagnosed with a stage 2 renal tumor. Mike had an aortic aneurysm and was being treated when his renal tumor was found. At the time, Mike said he didn t have any symptoms. Unless his tumor had gotten bigger or more advanced, Mike s doctor said he may never have had symptoms. Mike had an open partial nephrectomy to treat his cancer. His doctor said it would be the best way to save his kidney function. Mike says he has been fortunate because he has not had any side effects from his treatment. I was able to get back to work three weeks later, he says. Mike says he has been seeing his doctor regularly and is looking forward to a good prognosis at this six-month check-up. I recommend anyone dealing with this cancer have frank talks with their provider about what treatment option will work best, he urges. Introduction: I have a Kidney Mass What do I do now? Your doctor has just given you the news that there is a growth in your kidney. What is it and what does this mean for you? Our kidneys main job is to filter our blood. Sometimes we develop masses (growths or tumors) inside our kidneys. Some of these growths are cancerous, many are not. You must have your mass checked out to learn if it is cancerous or not. Don t delay getting treatment. There are many different options for treatment, and usually more choices for an early diagnosis. Your medical team is there to help you. They can help you learn more about the pros and cons of treatments. This guide will tell you about localized kidney masses and the steps that you can take if one forms in your body. 3
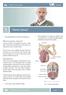
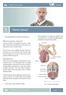
4 GET THE FACTS What do the Kidneys do? What is a Kidney Mass? Our kidneys serve many purposes, but they mainly do the following: Detoxify (clean) our blood Balance fluids Maintain electrolyte levels (e.g., sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, acid) Remove waste (as urine) Make hormones that help keep our blood pressure stable, make red blood cells and keep our bones strong A tumor, or mass, is an abnormal growth in the body. A kidney mass, or tumor, is an abnormal growth in the kidney. Some kidney masses are benign (not cancerous) and some are malignant (cancerous). One in four kidney masses are benign. Smaller masses are more likely to be benign. Larger masses are more likely to be cancerous. Some tumors can be slow to grow while some can be aggressive. Aggressive tumors usually form, grow and spread very quickly. Most kidney growths (about 40%) are small, localized masses. Localized means that the tumor has not spread out from where it first started. The main classes of tumors are: Renal Cell Carcinomas (RCC). These are the most common malignant kidney tumors. They are found in the lining of the small tubes in the kidney. RCC may form as a single tumor within a kidney or as two or more tumors in one kidney. Benign kidney tumors. About 20% of tumors removed from kidneys are benign. There are about nine named tumors in this class. Some can grow quite large but they are almost always non-cancerous and do not spread to other organs. Wilms tumor. Wilms tumors almost always occur in children and are rarely found in adults. 4 * All words that appear in blue are explained in the glossary.
5 What do we Know about Kidney Cancer? There will be close to 65,000 new cases of kidney cancer in the U.S. in Of those cases, nearly 15,000 people will likely die from the disease. More of those who die will be men. Kidney cancer is more common in African Americans, American Indians and Alaskan Native people. You can get kidney cancer at any age but it is more common in older people (those greater than 75 years old). The earlier kidney cancer is diagnosed the better your chances of survival. What Causes a Kidney Mass? There is no known cause for developing a kidney mass. But, there are a number of things that can increase your risk for kidney tumors such as: Smoking (men smokers have a higher risk than women smokers) Obesity, poor diet Family history of high blood pressure Being on kidney dialysis Workplace exposure to chlorinated chemicals Heredity What are the Symptoms of a Kidney Mass? Most kidney masses have no symptoms in the early stages. However, if there are symptoms, they will most likely be: Hematuria (blood in urine) Flank pain between the ribs and hips Low back pain on one side (not caused by injury) and that does not go away Loss of appetite Weight loss not caused by dieting Fever that is not caused by an infection and does not go away Anemia (low red blood cell count) GET DIAGNOSED Over half of kidney masses are found by chance. Often they are found during generic screening or when you see a doctor about some other problem. If your regular doctor thinks you may have kidney disease they might send you to a urologist. A urologist is a doctor who specializes in the urinary system. How is my Kidney Mass Diagnosed? There are no routine laboratory tests to find kidney masses. Your healthcare provider may use many tests and procedures to make a diagnosis. Here are some tests and procedures that you might expect: Physical exam and history Basic or complete metabolic panel (CMP), also called a blood chemistry Complete Blood Count (CBC) to check for certain substances Urinalysis to check for infection, blood and protein in urine Kidney function tests to check how well the kidneys are working. They show if the kidneys are getting rid of waste the right way. Ultrasound exams take pictures of your kidneys and organs. CT scan and MRI for diagnosing and staging localized kidney masses Bone Scan and Chest X-Ray to find out if the cancer has spread Kidney mass biopsy: A biopsy may be done to find out what type of tumor you have. A biopsy is when cells or tiny parts of an organ are removed and studied. A pathologist views the sample under a microscope. Findings can tell if the tumor started in another part of your body or if it started in the kidney. A biopsy may also tell if there is an infection such as an abscess. 5
6 What does Tumor Grade and Stage Mean? T1 T2 A tumor grade tells how aggressive the cancer cells are. A tumor stage tells how much the cancer has spread. The grades 1 through 4 show increasing severity with 1 being the lowest level and 4 the highest. A higher grade and more advanced stage usually come with larger tumor size and more aggressive tumors. Tumor size helps in assessing risk for cancer developing. Kidney cancer is staged using the tumor node metastases (TNM) system. T tells us the size of the main (primary) tumor and whether it has grown into nearby areas. 6 o T1: Tumor 7.0 cm (about 2.8 inches) or less, only in the kidney o T1a: Tumor 4.0 cm (about 1.6 inches) or less, only in the kidney o T1b: Tumor cm, only in the kidney o T2: Tumor greater than 7.0 cm, only in kidney o T2a: Tumor greater than 7.0 cm and less than 10.0 cm, only in the kidney o T2b: Tumor greater than 10 cm (about 3.9 inches), only in the kidney o T3: Tumor grows into major veins but not into the adrenal gland and not beyond Gerota s fascia o T4: Tumor reaches beyond Gerota s fascia (including the adrenal gland). This is not a localized tumor. N tells us how much it has spread to nearby (regional) lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are small bean-sized collections of immune system cells. o N0: No regional lymph node metastasis o N1: Metastasis in regional lymph node(s) M tells us about metastasis ¾ whether the cancer has spread (metastasized) to other parts of the body. Spread is most common to the lungs, bones, liver, brain, and far off lymph nodes. o M0: No distant metastasis o M1: Distant metastasis Stage I and II tumors include cancers of any size that are only inside the kidney. Stage III tumors are either locally invasive (T3) or involve lymph nodes (N1). This is cancer that is only found within the kidney organ. Stage IV tumors have spread beyond the kidney into organs nearby (T4) or distant metastases (M1). T3 T3b T4 T4b
7 GET TREATED Have an open and frank talk with your healthcare team about your treatment choices. The main goal in treating kidney masses is to protect kidney function where possible. This is especially important for patients with only one kidney or some other kidney disease. For some, surgery will never be needed. For others, surgery may be the best choice. Your doctor may recommend one of four treatment choices. These are: Active surveillance Partial nephrectomy Radical nephrectomy Renal tumor ablation Radical Nephrectomy During a radical nephrectomy, the whole kidney is removed. This is done if your kidney tumor shows signs of becoming cancerous or is very large. Your body can function well with one kidney if the other is removed. Surgery for both types of nephrectomy can be done by laparoscopy. During laparoscopy, your surgeon makes a very small hole in your abdomen and threads a thin, lighted tube to the site to look at the kidney. If your lymph nodes are affected, your surgeon will examine the node for staging. Active Surveillance For active surveillance, your provider will see you at intervals for tests and imaging (taking pictures of inside your body). Active surveillance is considered for small masses less than 3 cm (about 1.2 inches) in size. The goal is to prevent progression and avoid potential risks and negative effects of other treatments. Your visits will be every 3-, 6- or 12-month intervals as necessary. Chest x-rays will be done, as well as CT scans and ultrasounds as indicated. How often you see your provider will depend on tumor size and stage. Partial Nephrectomy Nephrectomy means removal of the kidney. Partial nephrectomy means that the doctor removes the tumor and/or diseased part of the kidney and leaves the healthy part. If your tumor is at T1a stage (4cm or less) your doctor may recommend a partial nephrectomy. A partial nephrectomy can also be done for larger tumors. A doctor will do a biopsy of the tumor to see if it shows signs of getting worse. Ablation If your tumor is small (T1a mass less than 3 cm in size), your surgeon may consider ablation. Ablation destroys the tumor with extreme heat or cold. Your doctor will do a biopsy before ablation so a pathologist can look closely at the tumor cells to see if there is cancer. Cryoablation (cold ablation) is when very cold gases are passed to the tumor through a probe that destroy the tumor cells. Radiofrequency ablation (hot ablation) is when a thin, needle-like probe is placed through the skin to reach the tumor. An electric current is passed through the tip of the probe. This heats the tumor and destroys the cells. Care Management Your healthcare team is likely to have several different medical professionals such as a radiologist, urologist, neurologist, a pathologist and a medical oncologist. These specialists will work with you to consider all your choices and discuss the risks and benefits of treatment. You should have a urologist to help coordinate evaluation, counseling and care management. Genetic counseling might also be recommended if you have a family history of kidney tumors. 7
8 AFTER TREATMENT Make sure that you stay in touch with your healthcare provider and keep follow-up appointments as directed. These check-ups are important to watch for re-growth of tumors. After initial treatment, your doctor may perform many of the same tests used to diagnose the kidney mass. Keep copies of your records with you in a binder so that you have them if you change healthcare providers. Consider placing the following in the binder: Copies of pathology reports from all of your biopsies and procedures Copies of imaging test results (CT or MRI scans, etc.) Copies of your treatment summaries Contact information for the healthcare providers who treat you A healthy lifestyle is important. If you smoke now, quit smoking. Limit your alcohol intake. Eat a balanced diet, with lots of green leafy vegetables and occasional fatty fish. Exercise and try to keep your weight within recommended limits. QUESTIONS TO ASK YOUR DOCTOR Do I have kidney cancer? What is the stage and grade of my cancer and what does that mean? Has the mass spread anywhere else? Is the mass likely to grow or spread some more? Do I need other tests before we can decide on treatment? What are my treatment choices? Which treatment should I choose, and why? What should I expect after the procedure? Will I have a lot of pain? How will my pain be managed? Will I be cured after treatment? What are the chances that the mass will return after treatment? What risks or side effects should I expect from treatment? For how long? What can I do to keep my kidneys functioning in a healthy manner? What should I do to get myself ready for treatment? What will we do if the treatment doesn t work? Can you recommend another urologist for a second opinion? What more can I do to protect my health? How often will I need to have checkups after treatment? How long will I need to stay in the hospital? Following surgery, will I need additional treatments? 8
9 GLOSSARY ABLATION Destroys the tumor with extreme heat or cold ACTIVE SURVEILLANCE Patients see their doctor at regular intervals to assess a mass for progression; recommended treatment for small kidney masses less than 3cm (about 1.2 inches) BASIC OR COMPLETE METABOLIC PANEL (CMP) Used to evaluate organ function and check for certain conditions BENIGN A mass that is not cancerous BIOPSY A small piece of body tissue is removed and examined to find out if disease is present, what may cause it, or how advanced a disease may be BONE SCAN A test where a very small amount of a radioactive substance, called a tracer, is injected into a vein; areas where too much or too little tracer is absorbed by the body may indicate cancer COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT (CBC) Checks for certain substances. If amounts are higher or lower than normal, that may be a sign of disease. CRYOABLATION A treatment to kill cancer cells with extreme cold passed through a probe to destroy the tumor CT SCAN A procedure that uses both x-rays and computer technology to produce detailed images of the body HEMATURIA Blood in the urine LAPAROSCOPY A form of surgery where the surgeon passes a thin, lighted tube through a small cut in the belly to look at the organs inside the abdomen and pelvis LOCALIZED MASS A mass that is confined to one area of the organ MALIGNANT A mass that is cancerous. MASS An abnormal growth METASTASIS Cancer cells have broken away from where they first formed, traveled through the blood or lymph system, and formed new tumors in other parts of the body MRI SCAN Magnetic resonance imaging uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the organs and tissues within the body NEPHRECTOMY The removal of the kidney PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY The removal of part of the kidney PHYSICAL EXAM AND HISTORY Checks body and asks questions about health and family; health habits, past illnesses and treatments will also be discussed RADICAL NEPHRECTOMY The complete removal of the kidney. RADIOFREQUENCY ABLATION The use of radio waves to heat and destroy abnormal cells TUMOR An abnormal growth TUMOR GRADE How quickly a tumor is likely to grow and spread TUMOR STAGE The size of cancer and how much it has spread into nearby lymph nodes or to other parts of the body ULTRASOUND The use of high-frequency sound waves to produce images of structures within the body URINALYSIS Checks for infection, blood and protein in your urine 9
10 10 NOTES
11 NOTES 11
12 ABOUT THE UROLOGY CARE FOUNDATION The Urology Care Foundation is the world s leading urologic foundation and the official foundation of the American Urological Association. We provide information for those actively managing their urologic health and those ready to make health changes. Our information is based on the American Urological Association resources and is reviewed by medical experts. To learn more, visit the Urology Care Foundation s website, UrologyHealth.org/UrologicConditions or go to UrologyHealth.org/FindAUrologist to find a doctor near you. DISCLAIMER This information is not a tool for self-diagnosis or a substitute for professional medical advice. It is not to be used or relied on for that purpose. Please talk to your urologists or health care provider about your health concerns. Always consult a health care provider before you start or stop any treatments, including medications. For copies of printed materials about Bladder Cancer and other urologic conditions, visit UrologyHealth.org/Order or call For more information, contact: 1000 Corporate Boulevard, Linthicum, MD UrologyHealth.org For copies of other printed material and other urologic conditions, visit Urology Care Foundation
Introduction. Growths in the prostate can be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer).
 This information was taken from urologyhealth.org. Feel free to explore their website to learn more. Another trusted website with good information is the national comprehensive cancer network (nccn.org).
This information was taken from urologyhealth.org. Feel free to explore their website to learn more. Another trusted website with good information is the national comprehensive cancer network (nccn.org).
General information about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
Cancer , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. ocf80101 Last reviewed: 06/08/2016 1
 Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
General Information Key Points
 The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Male Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated September 29,2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/male-breast-treatment-pdq
The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Male Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated September 29,2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/male-breast-treatment-pdq
Kidney Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Kidney Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be noticed,
Kidney Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be noticed,
PROSTATE CANCER CONTENT CREATED BY. Learn more at
 PROSTATE CANCER CONTENT CREATED BY Learn more at www.health.harvard.edu TALK WITH YOUR DOCTOR Table of Contents Ask your doctor about screening and treatment options. WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? 4 WATCHFUL
PROSTATE CANCER CONTENT CREATED BY Learn more at www.health.harvard.edu TALK WITH YOUR DOCTOR Table of Contents Ask your doctor about screening and treatment options. WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? 4 WATCHFUL
BLADDER CANCER CONTENT CREATED BY. Learn more at
 BLADDER CANCER CONTENT CREATED BY Learn more at www.health.harvard.edu TALK TO YOUR DOCTOR Table of Contents WHAT IS BLADDER CANCER? 4 TYPES OF BLADDER CANCER 5 GRADING AND STAGING 8 TREATMENT OVERVIEW
BLADDER CANCER CONTENT CREATED BY Learn more at www.health.harvard.edu TALK TO YOUR DOCTOR Table of Contents WHAT IS BLADDER CANCER? 4 TYPES OF BLADDER CANCER 5 GRADING AND STAGING 8 TREATMENT OVERVIEW
Bladder Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Bladder Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Bladder Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Esophageal Cancer. Source: National Cancer Institute
 Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer forms in the tissues that line the esophagus, or the long, hollow tube that connects the mouth and stomach. Food and drink pass through the esophagus to be digested.
Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer forms in the tissues that line the esophagus, or the long, hollow tube that connects the mouth and stomach. Food and drink pass through the esophagus to be digested.
How is primary breast cancer treated?
 How is primary breast cancer treated? The treatment team This information is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. It is written by Breast Cancer Care,
How is primary breast cancer treated? The treatment team This information is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. It is written by Breast Cancer Care,
GUIDELINES ON RENAL CELL CANCER
 20 G. Mickisch (chairman), J. Carballido, S. Hellsten, H. Schulze, H. Mensink Eur Urol 2001;40(3):252-255 Introduction is characterised by a constant rise in incidence over the last 50 years, with a predominance
20 G. Mickisch (chairman), J. Carballido, S. Hellsten, H. Schulze, H. Mensink Eur Urol 2001;40(3):252-255 Introduction is characterised by a constant rise in incidence over the last 50 years, with a predominance
Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer
 Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
Chapter 2. Understanding My Diagnosis
 Chapter 2. Understanding My Diagnosis With contributions from Nancy L. Brown, Ph.D.,Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute; and Patrick Swift, M.D., Alta Bates Comprehensive Cancer Program o Facts
Chapter 2. Understanding My Diagnosis With contributions from Nancy L. Brown, Ph.D.,Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute; and Patrick Swift, M.D., Alta Bates Comprehensive Cancer Program o Facts
Esophageal cancer. What is esophageal cancer? Esophageal cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the esophagus.
 Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer What is esophageal cancer? What are risk factors? Signs and symptoms Tests for esophageal cancer Stages of esophageal cancer Treatment options What is esophageal cancer?
Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer What is esophageal cancer? What are risk factors? Signs and symptoms Tests for esophageal cancer Stages of esophageal cancer Treatment options What is esophageal cancer?
Your Guide to Prostate Cancer
 Your Guide to Prostate Cancer If you face a diagnosis of prostate cancer, what s next? We can help. A prostate cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming. The good news is that while prostate cancer can be serious,
Your Guide to Prostate Cancer If you face a diagnosis of prostate cancer, what s next? We can help. A prostate cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming. The good news is that while prostate cancer can be serious,
BLADDER HEALTH. Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Patient Guide
 BLADDER HEALTH Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Patient Guide Table of Contents Bladder Cancer Expert Panel Mike's Story: A Patient Story.... Introduction.... GET THE FACTS What is bladder cancer?....
BLADDER HEALTH Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Patient Guide Table of Contents Bladder Cancer Expert Panel Mike's Story: A Patient Story.... Introduction.... GET THE FACTS What is bladder cancer?....
Pancreatic Cancer (1 of 5)
 i If you need your information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact Customer Care on 0800 374 208 or send an email to: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk You are entitled
i If you need your information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact Customer Care on 0800 374 208 or send an email to: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk You are entitled
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect
 Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect For women with vaginal cancer What is the vagina? The vagina is a hollow canal that connects the cervix and the uterus to the outside. of the body. When a woman gives
Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect For women with vaginal cancer What is the vagina? The vagina is a hollow canal that connects the cervix and the uterus to the outside. of the body. When a woman gives
Kidneys and Kidney Disease
 Learn About Kidneys and Kidney Disease www.kidney.org Know Your Kidneys Where are they? Your two kidneys are under the lower ribs in the back of the body above the waist. They are about the size of your
Learn About Kidneys and Kidney Disease www.kidney.org Know Your Kidneys Where are they? Your two kidneys are under the lower ribs in the back of the body above the waist. They are about the size of your
BOWEL CANCER. Causes of bowel cancer
 A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated.
 How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. How is primary breast cancer treated? Part 1 the treatment
How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. How is primary breast cancer treated? Part 1 the treatment
Cervical Cancer. Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year.
 Cervical Cancer Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. Most cases of cervical cancer can be prevented by getting regular
Cervical Cancer Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. Most cases of cervical cancer can be prevented by getting regular
Breast Cancer Task Force of the Greater Miami Valley A collaborative effort of health care professionals and breast cancer survivors in the Greater
 Breast Cancer Task Force of the Greater Miami Valley A collaborative effort of health care professionals and breast cancer survivors in the Greater Dayton Area Last Updated Fall 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Breast Cancer Task Force of the Greater Miami Valley A collaborative effort of health care professionals and breast cancer survivors in the Greater Dayton Area Last Updated Fall 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix.
 Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where
Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where
Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide
 Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide Breast Cancer - Understanding Your Pathology Report Pathology Reports can be overwhelming. They contain scientific terms that are unfamiliar and might be a bit
Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide Breast Cancer - Understanding Your Pathology Report Pathology Reports can be overwhelming. They contain scientific terms that are unfamiliar and might be a bit
Wilms' tumor most often occurs in just one kidney, though it can sometimes be found in both kidneys at the same time.
 Wilms' Tumor Wilms' tumor is a rare kidney cancer that primarily affects children. Also known as nephroblastoma, Wilms' tumor is the most common cancer of the kidneys in children. Wilms' tumor most often
Wilms' Tumor Wilms' tumor is a rare kidney cancer that primarily affects children. Also known as nephroblastoma, Wilms' tumor is the most common cancer of the kidneys in children. Wilms' tumor most often
Screening tests. When you need them and when you don t
 Screening tests When you need them and when you don t S creening tests help doctors look for diseases when you don t have symptoms. The tests can Screenings find problems early, when they are easier to
Screening tests When you need them and when you don t S creening tests help doctors look for diseases when you don t have symptoms. The tests can Screenings find problems early, when they are easier to
Vaginal Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Vaginal Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Vaginal Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time.
 Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
Questions to ask before you have a kidney removed for kidney cancer
 Questions to ask before you have a kidney removed for kidney cancer Updated March 11, 2011 If you have a small kidney cancer (less than 7 cm.), you have several treatment options available to you. These
Questions to ask before you have a kidney removed for kidney cancer Updated March 11, 2011 If you have a small kidney cancer (less than 7 cm.), you have several treatment options available to you. These
Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinomas (UTUCs)
 Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinomas (UTUCs) Part II: UTUC Treatment Options November 14, 2017 Moderated by: Presented by: Gary D. Steinberg, MD University of Chicago Medical Center Ahmad Shabsigh, MD Ohio
Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinomas (UTUCs) Part II: UTUC Treatment Options November 14, 2017 Moderated by: Presented by: Gary D. Steinberg, MD University of Chicago Medical Center Ahmad Shabsigh, MD Ohio
Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer starts in your cells. Cells are the building blocks of your tissues. Tissues make up the organs of your
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer starts in your cells. Cells are the building blocks of your tissues. Tissues make up the organs of your
If You Have Head or Neck Cancer
 EASY READING If You Have Head or Neck Cancer What is head and neck cancer? Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the head and neck can have many names. It depends on where the cancer
EASY READING If You Have Head or Neck Cancer What is head and neck cancer? Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the head and neck can have many names. It depends on where the cancer
A VIDEO SERIES. living WELL. with kidney failure KIDNEY TRANSPLANT
 A VIDEO SERIES living WELL with kidney failure KIDNEY TRANSPLANT Contents 2 Introduction 3 What will I learn? 5 Who is on my healthcare team? 6 What is kidney failure? 6 What treatments are available
A VIDEO SERIES living WELL with kidney failure KIDNEY TRANSPLANT Contents 2 Introduction 3 What will I learn? 5 Who is on my healthcare team? 6 What is kidney failure? 6 What treatments are available
Quick Facts about Bile Duct Cancer
 Quick Facts about Bile Duct Cancer What is the bile duct? The bile duct is a thin tube, about 10 centimetres to 15 centimetres long, that carries a fluid called bile from the liver and gallbladder to the
Quick Facts about Bile Duct Cancer What is the bile duct? The bile duct is a thin tube, about 10 centimetres to 15 centimetres long, that carries a fluid called bile from the liver and gallbladder to the
Breast Cancer. Common kinds of breast cancer are
 Breast Cancer A breast is made up of three main parts: glands, ducts, and connective tissue. The glands produce milk. The ducts are passages that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which
Breast Cancer A breast is made up of three main parts: glands, ducts, and connective tissue. The glands produce milk. The ducts are passages that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which
Kidney Cancer Patient Handbook
 Page 1 of 15 Kidney Cancer Patient Handbook Urology and Institute for Prostate and Urologic Cancers Contents Welcome to Urology and Institute for Prostate and Urologic Cancers... 2 Your Care Team... 3
Page 1 of 15 Kidney Cancer Patient Handbook Urology and Institute for Prostate and Urologic Cancers Contents Welcome to Urology and Institute for Prostate and Urologic Cancers... 2 Your Care Team... 3
Soft Tissue Sarcoma Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Soft Tissue Sarcoma Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can
Soft Tissue Sarcoma Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can
What Is Barrett s Esophagus?
 What Is Barrett s Esophagus? Having Barrett s esophagus means the cells lining the esophagus (the tube that links the mouth and the stomach) have changed into types of intestinal cells that are not normal
What Is Barrett s Esophagus? Having Barrett s esophagus means the cells lining the esophagus (the tube that links the mouth and the stomach) have changed into types of intestinal cells that are not normal
Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Small Cell Lung Cancer Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) affects 15% of all lung cancer patients. SCLC is the most aggressive type of lung cancer. It may be treated with chemotherapy and radiation. SCLC has
Small Cell Lung Cancer Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) affects 15% of all lung cancer patients. SCLC is the most aggressive type of lung cancer. It may be treated with chemotherapy and radiation. SCLC has
Renal Cancer. By Jamie Calderwood
 Renal Cancer By Jamie Calderwood ("Kidney Cancer")*1 ("What are the different types of kidney mass?")*2 What is it? Renal cancer is more commonly known as kidney cancer. Wilms tumor Another name for kidney
Renal Cancer By Jamie Calderwood ("Kidney Cancer")*1 ("What are the different types of kidney mass?")*2 What is it? Renal cancer is more commonly known as kidney cancer. Wilms tumor Another name for kidney
What is Thyroid Cancer?
 Thyroid Cancer What is Thyroid Cancer? The thyroid is a gland at the base of the throat near the trachea (windpipe). It is shaped like a butterfly, with a right lobe and a left lobe. The isthmus, a thin
Thyroid Cancer What is Thyroid Cancer? The thyroid is a gland at the base of the throat near the trachea (windpipe). It is shaped like a butterfly, with a right lobe and a left lobe. The isthmus, a thin
Different Types of Cancer
 Different Types of Cancer Cancer can originate almost anywhere in the body. Sarcomas (connective tissue) Ø arise from cells found in the supporting tissues of the body such as bone, cartilage, fat, connective
Different Types of Cancer Cancer can originate almost anywhere in the body. Sarcomas (connective tissue) Ø arise from cells found in the supporting tissues of the body such as bone, cartilage, fat, connective
Testing for. Prostate Cancer
 Testing for Prostate Cancer Who this booklet is for: This booklet is to help men who do not have any symptoms decide if they want to be tested. Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find
Testing for Prostate Cancer Who this booklet is for: This booklet is to help men who do not have any symptoms decide if they want to be tested. Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find
Symptoms, Diagnosis and Classification
 Patient Information English 2 Symptoms, Diagnosis and Classification The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. Signs and symptoms Blood in the urine is the most common symptom when a bladder tumour
Patient Information English 2 Symptoms, Diagnosis and Classification The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. Signs and symptoms Blood in the urine is the most common symptom when a bladder tumour
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
Penis Cancer. What is penis cancer? Symptoms. Patient Information. Pagina 1 / 9. Patient Information - Penis Cancer
 Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Diagnosis and Classification of Prostate Cancer
 Patient Information English 32 Diagnosis and Classification of Prostate Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. prostate biopsy is the only test that can confirm a prostate cancer diagnosis.
Patient Information English 32 Diagnosis and Classification of Prostate Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. prostate biopsy is the only test that can confirm a prostate cancer diagnosis.
GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMOR. cancer that affects the digestive system
 Understanding GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMOR cancer that affects the digestive system GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMOR About This Guide This guide will: Help you understand gastrointestinal stromal tumor
Understanding GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMOR cancer that affects the digestive system GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMOR About This Guide This guide will: Help you understand gastrointestinal stromal tumor
ARE YOU AT INCREASED RISK FOR CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE?
 ARE YOU AT INCREASED RISK FOR CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE? www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease
ARE YOU AT INCREASED RISK FOR CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE? www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease
What Your Kidneys Do
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What Your Kidneys Do And what happens with kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia. 3. Know the common causes of kidney
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What Your Kidneys Do And what happens with kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia. 3. Know the common causes of kidney
Penis Cancer. What is penis cancer? Symptoms. Patient Information. Pagina 1 / 9. Patient Information - Penis Cancer
 Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Lung cancer rates among Southeast
X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Lung cancer rates among Southeast
Patient Information. Prostate Tissue Ablation. High Intensity Focused Ultrasound for
 High Intensity Focused Ultrasound for Prostate Tissue Ablation Patient Information CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sell by or on the order of a physician CONTENT Introduction... 3 The prostate...
High Intensity Focused Ultrasound for Prostate Tissue Ablation Patient Information CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sell by or on the order of a physician CONTENT Introduction... 3 The prostate...
Prostate Cancer Awareness - Prevention, Symptoms and. Treatment
 Quality Assurance Lunch and Learn Sessions: Prostate Cancer Awareness - Prevention, Symptoms and What s wrong with my prostate? Treatment??? Sponsored by the Chief Engineer s Team and Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance Lunch and Learn Sessions: Prostate Cancer Awareness - Prevention, Symptoms and What s wrong with my prostate? Treatment??? Sponsored by the Chief Engineer s Team and Quality Assurance
Gastric (Stomach) Cancer
 Gastric (Stomach) Cancer Gastric cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining of the stomach. The stomach is a J-shaped organ in the upper abdomen. It is part of the digestive
Gastric (Stomach) Cancer Gastric cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining of the stomach. The stomach is a J-shaped organ in the upper abdomen. It is part of the digestive
BLADDER HEALTH. Painful Bladder AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
 BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
Breast Cancer. American Cancer Society
 Breast Cancer American Cancer Society Reviewed February 2017 What we ll be talking about How common is breast cancer? What is breast cancer? What causes it? What are the risk factors? Can breast cancer
Breast Cancer American Cancer Society Reviewed February 2017 What we ll be talking about How common is breast cancer? What is breast cancer? What causes it? What are the risk factors? Can breast cancer
Quick facts about gallbladder cancer
 Quick facts about gallbladder cancer What is the gallbladder? Princess Margaret The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located under right side of the liver. The gallbladder concentrates and stores
Quick facts about gallbladder cancer What is the gallbladder? Princess Margaret The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located under right side of the liver. The gallbladder concentrates and stores
PROSTATE HEALTH. Non-metastatic CastrationResistant Prostate Cancer. (nmcrpc) Patient Guide
 PROSTATE HEALTH Non-metastatic CastrationResistant Prostate Cancer (nmcrpc) Patient Guide Table of Contents Prostate Health Committee Introduction Introduction.... 3 GET THE FACTS How Does the Prostate
PROSTATE HEALTH Non-metastatic CastrationResistant Prostate Cancer (nmcrpc) Patient Guide Table of Contents Prostate Health Committee Introduction Introduction.... 3 GET THE FACTS How Does the Prostate
What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells.
 Cancer Biology What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells. What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells.
Cancer Biology What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells. What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells.
Thoracic Diagnostic Assessment Program. Patient information for. Last revised: November
 Thoracic Diagnostic Assessment Program Patient information for Last revised: November 2016 1 A list of your tests and appointments Diagnostic tests 2 3 4 Specialist appointments Doctor: Specialty: Notes:
Thoracic Diagnostic Assessment Program Patient information for Last revised: November 2016 1 A list of your tests and appointments Diagnostic tests 2 3 4 Specialist appointments Doctor: Specialty: Notes:
This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated.
 A-Z of medical words This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated. Absorption: once your food has been broken down,
A-Z of medical words This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated. Absorption: once your food has been broken down,
Kidney Biopsy. Table of Contents. Test Overview. Why It Is Done. Test Overview. Why It Is Done. How to Prepare. How It Is Done.
 Kidney Biopsy Table of Contents Test Overview Why It Is Done How to Prepare How It Is Done Results What Affects the Test? Test Overview The two kidneys {IMAGE LINK 1} are found on either side of the spine,
Kidney Biopsy Table of Contents Test Overview Why It Is Done How to Prepare How It Is Done Results What Affects the Test? Test Overview The two kidneys {IMAGE LINK 1} are found on either side of the spine,
Diagnosis and classification
 Patient Information English 2 Diagnosis and classification The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. Signs and symptoms Blood in the urine is the most common symptom when a bladder tumour is present.
Patient Information English 2 Diagnosis and classification The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. Signs and symptoms Blood in the urine is the most common symptom when a bladder tumour is present.
Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology. Report. Key Questions. Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help:
 Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report Key Questions Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help: Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report 1. Is this
Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report Key Questions Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help: Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report 1. Is this
Pancreas transplants. What you need to know. Information for patients Sheffield Kidney Institute (Renal Unit)
 Pancreas transplants What you need to know Information for patients Sheffield Kidney Institute (Renal Unit) page 2 of 16 What is the pancreas and why is it transplanted? The pancreas is part of the digestive
Pancreas transplants What you need to know Information for patients Sheffield Kidney Institute (Renal Unit) page 2 of 16 What is the pancreas and why is it transplanted? The pancreas is part of the digestive
Esophageal Cancer. What is esophageal cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Esophageal cancer may not
Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Esophageal cancer may not
A VIDEO SERIES. living WELL. with kidney failure WHAT IS KIDNEY FAILURE?
 A VIDEO SERIES living WELL with kidney failure WHAT IS KIDNEY FAILURE? Contents 2 Introduction 11 What is a kidney transplant? 3 What will I learn? 12 What role do diet and medi- 5 Who is on my 7 healthcare
A VIDEO SERIES living WELL with kidney failure WHAT IS KIDNEY FAILURE? Contents 2 Introduction 11 What is a kidney transplant? 3 What will I learn? 12 What role do diet and medi- 5 Who is on my 7 healthcare
w This information leaflet contains basic information Basic Information on Kidney and Ureteral Stones What is a stone? Patient Information Go Online
 Patient Information English Basic Information on Kidney and Ureteral Stones The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is a stone? right kidney left kidney A stone is a hard, solid mass that
Patient Information English Basic Information on Kidney and Ureteral Stones The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is a stone? right kidney left kidney A stone is a hard, solid mass that
Rhabdomyosarcoma Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Rhabdomyosarcoma Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Rhabdomyosarcoma Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging of Ewing Tumors
 Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging of Ewing Tumors Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging of Ewing Tumors Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer)
 Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
SAMPLE. Do Not Reproduce. Breast Lumps & Breast Cancer. Breast Lumps. Breast Cancer. Treatment. Signs, Symptoms, and Causes. Signs and Symptoms
 Breast Lumps & Breast Cancer Feeling a lump in a breast can be scary. For a lot of women, the first thought is cancer. The good news is that 80% to 90% of breast lumps are not cancer. If you feel a lump
Breast Lumps & Breast Cancer Feeling a lump in a breast can be scary. For a lot of women, the first thought is cancer. The good news is that 80% to 90% of breast lumps are not cancer. If you feel a lump
AN INFORMATION LEAFLET
 LAPAROSCOPIC NEPHRECTOMY AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Website: www.stockport.nhs.uk Tameside: 0161 922 6696/6698 Website: www.tameside.nhs.uk
LAPAROSCOPIC NEPHRECTOMY AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Website: www.stockport.nhs.uk Tameside: 0161 922 6696/6698 Website: www.tameside.nhs.uk
Bladder Cancer Canada November 21st, Bladder Cancer 2018: A brighter light at the end of the cystoscope
 Bladder Cancer Canada November 21st, 2018 Bladder Cancer 2018: A brighter light at the end of the cystoscope Chris Morash MD FRCSC Associate Professor, University of Ottawa Head, Urological Oncology Bladder
Bladder Cancer Canada November 21st, 2018 Bladder Cancer 2018: A brighter light at the end of the cystoscope Chris Morash MD FRCSC Associate Professor, University of Ottawa Head, Urological Oncology Bladder
What Your Kidneys Do and What Happens When They Fail
 Patient Education Chapter 2 Page 1 What Your Kidneys Do and What Happens When They Fail Objectives: 1. Understand basic kidney functions. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some treatments used for it.
Patient Education Chapter 2 Page 1 What Your Kidneys Do and What Happens When They Fail Objectives: 1. Understand basic kidney functions. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some treatments used for it.
BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION
 BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION The bladder is the balloon like organ located in the pelvis that stores and empties urine. Urine is produced by the kidneys, is conducted to the bladder by the ureters,
BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION The bladder is the balloon like organ located in the pelvis that stores and empties urine. Urine is produced by the kidneys, is conducted to the bladder by the ureters,
Bile Duct Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Bile Duct Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Bile Duct Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
[A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
![[A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE] [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]](/thumbs/88/117127924.jpg) 2013 COLORECTAL SURGERY GROUP Dr. Carl J. Brown Dr. Ahmer A. Karimuddin Dr. P. Terry Phang Dr. Manoj J. Raval Authored by Jennifer Lee A cartoon about colonoscopies. 1 [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
2013 COLORECTAL SURGERY GROUP Dr. Carl J. Brown Dr. Ahmer A. Karimuddin Dr. P. Terry Phang Dr. Manoj J. Raval Authored by Jennifer Lee A cartoon about colonoscopies. 1 [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
Treating localised prostate cancer using freezing (cryotherapy) needles in a targeted area of the prostate
 Issue date April 2012 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services NICE interventional procedures guidance advises the NHS on when and how new procedures can be used in clinical
Issue date April 2012 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services NICE interventional procedures guidance advises the NHS on when and how new procedures can be used in clinical
What is endometrial cancer?
 Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
Patient Education Kidney Early Education Program (KEEP) Chapter 2 bjectives: Overview 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms
 Patient Education (KEEP) Chapter 2 What Your Kidneys Do And what happens when they fail Objectives: 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some ways to treat it. 3. Know the
Patient Education (KEEP) Chapter 2 What Your Kidneys Do And what happens when they fail Objectives: 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some ways to treat it. 3. Know the
Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors
 Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Overview Ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer are
Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Overview Ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer are
Attachment #2 Overview of Follow-up
 Attachment #2 Overview of Follow-up Provided below is a general overview of follow-up and this may vary based on specific patient or cancer characteristics. Of note, Labs and imaging can be performed closer
Attachment #2 Overview of Follow-up Provided below is a general overview of follow-up and this may vary based on specific patient or cancer characteristics. Of note, Labs and imaging can be performed closer
What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen).
 What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen). It is a very common cancer in men; some cancers grow very slowly,
What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen). It is a very common cancer in men; some cancers grow very slowly,
What is Thyroid Cancer? Here are four types of thyroid cancer:
 What is Thyroid Cancer? Thyroid cancer is a group of malignant tumors that originate from the thyroid gland. The thyroid is a gland in the front of the neck. The thyroid gland absorbs iodine from the bloodstream
What is Thyroid Cancer? Thyroid cancer is a group of malignant tumors that originate from the thyroid gland. The thyroid is a gland in the front of the neck. The thyroid gland absorbs iodine from the bloodstream
Getting A New Pancreas: Facts About Pancreas Transplants
 Released October 1, 2003 Revised December 2006 Revised March 2012 Revised July 2017 Getting A New Pancreas: Facts About Pancreas Transplants Authors Yolanda Becker, MD Nadey Hakim, MD, PhD Kathleen Lake,
Released October 1, 2003 Revised December 2006 Revised March 2012 Revised July 2017 Getting A New Pancreas: Facts About Pancreas Transplants Authors Yolanda Becker, MD Nadey Hakim, MD, PhD Kathleen Lake,
Blood pressure and kidney disease
 Blood pressure and High blood pressure is the second most common cause of. Your heart pumps your blood through tubes (blood vessels) called arteries and veins. When your blood moves through the blood vessels,
Blood pressure and High blood pressure is the second most common cause of. Your heart pumps your blood through tubes (blood vessels) called arteries and veins. When your blood moves through the blood vessels,
HEPATIC METASTASES. We can state 3 types of metastases depending on their treatment options:
 HEPATIC METASTASES 1. Definition Metastasis means the spread of cancer. Cancerous cells can separate from the primary tumor and enter the bloodstream or the lymphatic system (the one that produces, stores,
HEPATIC METASTASES 1. Definition Metastasis means the spread of cancer. Cancerous cells can separate from the primary tumor and enter the bloodstream or the lymphatic system (the one that produces, stores,
ADVICE TO PATIENTS REQUESTING PSA MEASUREMENT FREQUENTLY-ASKED QUESTIONS
 The British Association of Urological Surgeons 35-43 Lincoln s Inn Fields London WC2A 3PE Phone: Fax: Website: E-mail: +44 (0)20 7869 6950 +44 (0)20 7404 5048 www.baus.org.uk admin@baus.org.uk ADVICE TO
The British Association of Urological Surgeons 35-43 Lincoln s Inn Fields London WC2A 3PE Phone: Fax: Website: E-mail: +44 (0)20 7869 6950 +44 (0)20 7404 5048 www.baus.org.uk admin@baus.org.uk ADVICE TO
LIVING WITH. Understanding Your Treatment Options 1510
 Get the Support You Need Having prostate cancer can be hard to cope with. But you don t have to keep your feelings to yourself. Talk with family and friends. Try a prostate cancer support group. Sharing
Get the Support You Need Having prostate cancer can be hard to cope with. But you don t have to keep your feelings to yourself. Talk with family and friends. Try a prostate cancer support group. Sharing
What is Testicular cancer?
 Testicular Cancer What is Testicular cancer? Testicular cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles. The testicles are 2 egg-shaped glands located inside the
Testicular Cancer What is Testicular cancer? Testicular cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles. The testicles are 2 egg-shaped glands located inside the
After Adrenal Cancer Treatment
 After Adrenal Cancer Treatment Living as a Cancer Survivor For many people, cancer treatment often raises questions about next steps as a survivor. Lifestyle Changes After Treatment for Adrenal Cancer
After Adrenal Cancer Treatment Living as a Cancer Survivor For many people, cancer treatment often raises questions about next steps as a survivor. Lifestyle Changes After Treatment for Adrenal Cancer
Information for. Patients with an Abnormal Lung X-ray
 Information for Patients with an Abnormal Lung X-ray Some of the materials in this resource were adapted with permission from: Understanding Lung Cancer, Juravinski Cancer Centre, Hamilton Health Sciences,
Information for Patients with an Abnormal Lung X-ray Some of the materials in this resource were adapted with permission from: Understanding Lung Cancer, Juravinski Cancer Centre, Hamilton Health Sciences,
The prostate can be affected by three conditions that may cause problems for men as they get older.
 The Prostate Gland The Prostate gland specific to males only, located in the pelvis between the bladder and rectum. It is about the shape and size of a walnut or satsuma and gets bigger as you get older.
The Prostate Gland The Prostate gland specific to males only, located in the pelvis between the bladder and rectum. It is about the shape and size of a walnut or satsuma and gets bigger as you get older.
