ISPUB.COM. M Duvic, E Olsen PURPOSE OF REVISION
|
|
|
- Bertram Sherman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 International Society of Cutaneous Lymphoma (ISCL) and the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) revisions to the staging and classification of mycosis fungoides and M Duvic, E Olsen Citation M Duvic, E Olsen.. The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3. DOI: /80e Abstract Madeleine Duvic, MD, is Professor of Internal Medicine and Dermatology, and Deputy Chairman of the Department of Dermatology at The University of Texas, M. D. Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas. She is a founding member of the United States Cutaneous Lymphoma Consortium (USCLC), a Board member of the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphoma, and also serves as Director of The Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic at MD Anderson Cancer Center. Dr. Duvic has also served on the Board of Directors of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD). standardized response criteria and endpoints for MF and SS (in progress). She is a founder and current President of the United States Consortium for Cutaneous Lymphomas (USCCL), a multidisciplinary group whose mission is to enhance patient care through a national registry of patients with cutaneous lymphoma and collaborative clinical trials. She has authored over 90 original articles and is the editor of two textbooks. Dr. Olsen is currently on the Board of Directors of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) and Deputy Chair of the AAD Patient Advocacy Task Force. She is certified in Internal Medicine and Dermatology. She has been a principal and co-principal investigator on numerous clinical trials studying the immunology of T-cell mediated disorders and skin cancers, as well as clinical drug development and translational research in T-cell lymphomas, melanoma, and various skin cancers. A prolific author, she has written manuscripts, book chapters, abstracts, and over 300 peer-reviewed journal articles. She is co-author on a recent book on Retinoids and Carotenoids in Dermatology. As background to the following educational activity, this brief review will discuss the International Society of Cutaneous Lymphoma (ISCL) and the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) revisions to the staging and classification of mycosis fungoides and Dr. Olsen is Professor of Dermatology and Oncology at Duke University Medical Center and the founder and Director of the Duke Cutaneous Lymphoma Research and Treatment Center. She is a Past President, SecretaryTreasurer and member of the Board of Directors of the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas (ISCL) and has chaired the ISCL initiatives on the revisions to 1) the staging and classification of Mycosis Fungoides (MF) and Sezary Syndrome (SS) (published in Blood 2007) and 2) DOI: /80e PURPOSE OF REVISION The Mycosis Fungoides Cooperative Group (MFCG) developed a staging system for CTCL 1 designed for the particular clinical findings in the mycosis fungoides (MF)/ Sézary syndrome (SS) subtypes and based on the TNM (tumor-node-metastasis) classification advocated by the International Union Against Cancer (UICC) 2 and American Joint Committee on Cancer. 3 This classification and staging system was modified in conjunction with the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and the Veteran's Administration (VA) Hospital and published in of 6
2 The updated International Society of Cutaneous Lymphoma (ISCL)/ European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) staging and classification applies to MF and SS and has maintained the major components of the MFCG system to allow for continued comparison of patient outcomes within both systems. 5 WHO/EORTC considers SS to be a separate entity from cases that otherwise meet the criteria for SS but has been preceded by clinically typical MF. 6 PURPOSED CHANGES TO T CLASSIFICATION In both the original MFCG 4 and the revised staging system 5, the T1 skin rating is defined as papules, patches, and/or plaques covering less than 10% body surface area (BSA) and T2 skin rating is defined as patches and/or plaques covering 10% or more BSA (Table 1). Figure 1 For skin, plaque indicates any size skin lesion that is elevated or indurated. Presence or absence of scale, crusting, and/or poikiloderma should be noted. Histologic features such as folliculotropism or large-cell transformation (> 25% large cells), CD30 or CD30, and clinical features such as ulceration are important to document. For skin, tumor indicates at least one 1-cm diameter solid or nodular lesion with evidence of depth and/or vertical growth. Note total number of lesions, total volume of lesions, largest size lesion, and region of body involved. Also note if histologic evidence of large-cell transformation has occurred. Phenotyping for CD30 is encouraged. For node, abnormal peripheral lymph node(s) indicates any palpable peripheral node that on physical examination is firm, irregular, clustered, fixed or 1.5 cm or larger in diameter. Minimal nodal groups examined on physical examination should include cervical, supraclavicular, epitrochlear, axillary, and inguinal. Central nodes, which are not generally amenable to pathologic assessment, are not currently considered in the nodal classification unless used to establish N3 histopathologically. For viscera, spleen and liver may be diagnosed by imaging criteria. For blood, Sézary cells are defined as lymphocytes with hyperconvoluted cerebriform nuclei. If Sézary cells are not able to be used to determine tumor burden for B2, then one of the following modified ISCL criteria along with a positive clonal rearrangement of the TCR may be used instead: (1) expanded CD4 or CD3 cells with CD4/CD8 ratio of 10 or more, (2) expanded CD4 cells with abnormal immunophenotype including loss of CD7 or CD26. # A T-cell clone is defined by PCR or Southern blot analysis of the T-cell receptor gene. TNMB STAGES * For skin, patch indicates any size skin lesion without significant elevation or induration. Presence/absence of hypo- or hyperpigmentation, scale, crusting, and/or poikiloderma should be noted. 2 of 6 In the classification published by the MFCG, 1% BSA was defined as equal to the palmar surface of the hand. 1 but it has since been determined that the palm and fingers of the patient s hand is a better approximation of 1% BSA. 5 Another method of determining BSA is to estimate the percentage of skin involvement in each of 12 regions of the body (each with a relative assigned percent BSA 7 multiplying this number by the percentage of the BSA for that particular region and adding up the regional percentages to obtain the total BSA involved with MF/SS.
3 Figure 2 Figure 1. Regional percent body surface area (BSA) in the adult corroborated by an imaging study (computed tomography [CT] ± 18 F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography [FDG-PET] or by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (in cases where patients may be allergic to contrast dye) or ultrasound prior to biopsy. Because a biopsy of a clinically abnormal node is not always done at initial staging, the revised ISCL/EORTC classification has added a new category, the Nx node rating, to facilitate capture of at least this clinical information. PATHOLOGY OF LYMPH NODES The MFCG originally required that a diagnosis of tumorstage disease include at least 3 tumors, 8 but this was changed to one or more tumors in the final MFCG staging system. 4 The proposed ISCL/EORTC classification revision retains the requirement of at least one tumor ( 1.5 cm in diameter) for the definition of T3. 5 Whether there should be a minimum histologic depth of infiltrate to distinguish plaque from tumor in order to corroborate this important assignment of T stage based on a single lesion has not been yet been determined. There is currently no distinction in the updated staging system for subclassifying T4 based on varying degrees of induration, erythema, or scale. The ISCL/EORTC recommends tracking folliculotropic MF and large-cell transformation to determine if either warrants an advance in stage. Folliculotropic MF has been shown to be associated with a worse prognosis than expected for clinical stage and is considered equivalent to T3 tumors REVISIONS TO THE N (NODE) CLASSIFICATION The ISCL/EORTC revision defines clinically abnormal peripheral nodes as 1.5 cm or larger in the longest transverse diameter or any palpable peripheral node, regardless of size, that on physical examination is firm, irregular, clustered, or fixed. These clinically enlarged or abnormal nodes should be 3 of 6 The two main histopathologic grading systems for lymph nodes in MF/SS are the NCI/VA classification system, 12 first proposed by Matthews and Gazdar, 13 and the Dutch System 14 (Table 2). The major difference between these classification systems resides in the criteria used to define abnormal lymphocytes. 14 Specifically, the NCI/VA system, 12 although it defines abnormal (neoplastic) cells as small (6-10 µm) or large (> 11.5 µm) cells with cerebriform, irregularly folded, hyperconvoluted nuclei (ie, Sézary cells), does not use the size of cells but instead uses the relative numbers of such cells in the paracortex of the lymph node for the LN0-2 definition. The Dutch system uses the diameter of the cerebriform cells (> 7.5 µm) to define abnormal (neoplastic) cells, and if present, this constitutes early involvement (grade 2). 14 N1 and N2 ratings can be further classified into 2 subgroups: N1a and N2a (clone negative) and N1b and N2b (clone positive). 5 It is hoped that by capturing this information longitudinally, it can be determined if there is a similar prognosis of patients with and without clonal involvement and between N2b and N3.. Prognosis in MF/SS is clearly related to partially or completely effaced nodal architecture as defined by either the NCI-VA (LN4) or Dutch (grade 3/4) grading system, 15 and continues to define the N3 node rating in the updated ISCL/EORTC staging system.
4 Figure 3 The assessment of blood tumor burden in MF/SS in the current staging assessment is based on morphologic features of the neoplastic cells alone (eg, Sézary cell counts). 19 Blood flow cytometry offers an alternate objective means of identifying and quantifying these neoplastic lymphocytes in the blood. The populations of CD4CD26- or CD4CD7cells or V beta subtype measured by flow can be used to identify the population of SS cells. EVALUATION AND STAGING OF THE PATIENT WITH MF/SS REVISION TO M CLASSIFICATION To be considered as having visceral disease (stage IVb), documentation of involvement by only one organ outside the skin, nodes, or blood is needed. The ISCL/EORTC considers splenomegaly as visceral disease, even without biopsy confirmation, when it is (a) unequivocally present on physical exam and (b) documented radiographically by either enlargement. 5, The staging of MF/SS according to the TNMB system implies that an appropriate evaluation of the 4 TNMB systems has been performed. The recommended workup is detailed in Table 3 below. Figure 4 Liver disease may be suspected by physical examination, abnormal liver function tests, or radiologic tests (CT, FDGPET, liver/spleen scan) but should be confirmed by liver biopsy. 16 The ISCL/EORTC recommends performance of a bone marrow biopsy in patients who have B2 blood involvement or unexplained hematologic abnormalities. If lung abnormalities or other suggestions of extracutaneous lymphomatous involvement, besides splenomegaly, are found on radiographic examination, pathological assessment is recommended before ascribing this to visceral involvement with MF/SS. REVISIONS TO THE B (BLOOD) RATING The ISCL/EORTC has simplified and clarified the definitions of B to B2. B remains 5% or less Sézary cells. B2 is now defined as a clonal rearrangement of the TCR in the blood and either 1.0 K/µL or more Sézary cells or one of the 2 criteria outlined by the ISCL, 17 that is, (1) increased CD4 or CD3 cells with CD4/CD8 of 10 or more or (2) increase in CD4 cells with an abnormal phenotype ( 40% CD4 18 /CD7 or 30% CD4 /CD26 has been suggested ). B1 is defined as more than 5% Sézary cells and either less than 1.0 K/µL absolute Sézary cells, absence of a clonal rearrangement of the TCR, or both. 4 of 6 CONCLUSIONS Although the ISCL/EORTC revisions to the staging and classification of MF and SS further narrows and defines the variables involved, it does not provide a finite staging
5 system that inherently incorporates all potential prognostic factors. References 1. Lamberg SI, Diamond EL, Lorincz AL, et al. Mycosis fungoides cooperative study. Arch Dermatol 1975; 111: Harmer MH. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. 1978; 3rd ed. Geneva, Switzerland UICC International Union Against Cancer. 3. Oliver HB, Carr DT, Rubin P, et al. American Joint Committee on Cancer: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 1978; 1st ed. Chicago, IL Whiting Press. 4. Bunn PA and Lamberg SI. Report of the committee on staging and classification of cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Cancer Treat Rep 1979; 63: Olsen E, Vonderheid E, Pimpinelli N, Willemze R, Kim Y, Knobler R et al. Revisions to the staging and classification of mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome: a proposal of the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas (ISCL) and the Cutaneous Lymphoma Task Force of the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Blood. 2007;110: Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood 2005; 105: Lund CC and Browder NC. The estimation of areas of burns. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1944; 79: Lamberg SI, Green SB, Byar DP, et al. Clinical staging for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Ann Int Med 1984; 100: Bonta MD, Tannous ZS, Demierre M-F, Gonzalez E, Harris NL, Duncan LM. Rapidly progressing mycosis fungoides presenting as follicular mucinosis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2000; 43: Gilliam AC, Lessin SR, Wilson DM, Salhany KE. 5 of 6 Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides with large cell transformation presenting as dissecting cellulitis of the scalp. J Cutan Pathol 1997; 24: van Doorn R, Scheffer E, Willemze R. Follicular mycosis fungoides, a distinct disease entity with or without associated follicular mucinosis. Arch Dermatol 2002; 138: Sausville EA, Worsham GF, Matthews MJ, et al. Histologic assessment of lymph nodes in mycosis fungoides/sézary syndrome (cutaneous T-cell lymphoma): clinical correlations and prognostic import of a new classification system. Human Pathol 1985; 16: Clendenning WE and Rappaport HW. Report of the committee on pathology of cutaneous T cell lymphomas. Cancer Treat Report 1979; 63: Scheffer E, Meijer CJLM, van Vloten WA. Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy and lymph node involvement in mycosis fungoides. Cancer 1980; 45: Vonderheid EC, Diamond LW, van Vloten WA, et al. Lymph node classification systems in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: evidence for the utility of the working formulation of non-hodgkin's lymphomas for clinical usage. Cancer 1994; 73: Huberman MS, Bunn PA, Matthews MJ, et al. Hepatic involvement in the cutaneous T-cell lymphomas: results of percutaneous biopsy and peritoneoscopy. Cancer 1980; 45: Vonderheid EC, Bernengo MG, Burg G, et al. Update on erythrodermic cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: report of the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas. J Am Acad Dermatol 2002; 46: Vonderheid EC and Bernengo MG. The Sézary syndrome: hematologic criteria. Hematol Oncol Clin N Amer 2003; 17: Vonderheid EC, Pena J, Nowell P. Sézary cell counts in erythrodermic cutaneous T cell lymphoma: implications for prognosis and staging. Leuk Lymphoma 2006; 47:
6 Author Information Madeleine Duvic, M.D. Division of Internal Medicine, Department of Dermatology, The University of Texas, M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Elise Olsen, M.D. Department of Dermatology and Oncology, Department of Dermatology, Duke University Medical Center 6 of 6
Sezary Syndrome(SS) and other malignancies. Hernani Cualing MD Hematopathologist IHCFLOW Lab
 Sezary Syndrome(SS) and other malignancies Hernani Cualing MD Hematopathologist IHCFLOW Lab Disclosures IHCFLOW Laboratory:consultant and director NEOGENOMICS: contract consultant USF: contract reviewer
Sezary Syndrome(SS) and other malignancies Hernani Cualing MD Hematopathologist IHCFLOW Lab Disclosures IHCFLOW Laboratory:consultant and director NEOGENOMICS: contract consultant USF: contract reviewer
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging. Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology
 Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
ISPUB.COM. Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Long-term Management with Low Dose Methotrexate. S Parker INTRODUCTION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Long-term Management with Low Dose S Parker Citation S Parker.. The Internet Journal of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Long-term Management with Low Dose S Parker Citation S Parker.. The Internet Journal of
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2010 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Benner, Marchina Frederika Title: Cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferations
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2010 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Benner, Marchina Frederika Title: Cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferations
Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology
 Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology Agenda Overview of cutaneous T and B- cell lymphomas Diagnosis, Staging, Prognosis
Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology Agenda Overview of cutaneous T and B- cell lymphomas Diagnosis, Staging, Prognosis
Classification of Cutaneous T cell Lymphomas (CTCLs) Hernani Cualing, MD
 Classification of Cutaneous T cell Lymphomas (CTCLs) Hernani Cualing, MD Pathology and Cell Biology, USF IFLOW, Inc. CTCL, MF, and Sézary syndrome In 1806, mycosis fungoides (MF) was first described 1
Classification of Cutaneous T cell Lymphomas (CTCLs) Hernani Cualing, MD Pathology and Cell Biology, USF IFLOW, Inc. CTCL, MF, and Sézary syndrome In 1806, mycosis fungoides (MF) was first described 1
2/9 MATERIALS AND METHODS. Central
 Annals of Clinical Pathology Research Article Flow Cytometric Criteria for Lymph Node Ratings and Staging of Mycosis Fungoides and Sézary Syndrome Eric C. Vonderheid 1 *, J. Steve Hou 2, and Robert Bigler
Annals of Clinical Pathology Research Article Flow Cytometric Criteria for Lymph Node Ratings and Staging of Mycosis Fungoides and Sézary Syndrome Eric C. Vonderheid 1 *, J. Steve Hou 2, and Robert Bigler
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: Updated results from a single center
 Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: Updated results from a single center Madeleine Duvic, MD Professor and Deputy Chairman Blanche Bender Professor in Cancer Research Departments
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: Updated results from a single center Madeleine Duvic, MD Professor and Deputy Chairman Blanche Bender Professor in Cancer Research Departments
Sézary syndrome presenting with leonine facies ajd_560
 285..288 Australasian Journal of Dermatology (2009) 50, 285 288 doi: 10.1111/j.1440-0960.2009.00560.x CASE REPORT Sézary syndrome presenting with leonine facies ajd_560 Shano Nassem, 1 Rajesh Kashyap,
285..288 Australasian Journal of Dermatology (2009) 50, 285 288 doi: 10.1111/j.1440-0960.2009.00560.x CASE REPORT Sézary syndrome presenting with leonine facies ajd_560 Shano Nassem, 1 Rajesh Kashyap,
Cluster of differentiation (CD) markers in erythrodermic patients: A case series study
 Original Article Cluster of differentiation (CD) markers in erythrodermic patients: A case series study Fariba Ghalamkarpour, MD Faranak Niknafs, MD Shima Younespour, PhD Skin Research Center, Shahid Beheshti
Original Article Cluster of differentiation (CD) markers in erythrodermic patients: A case series study Fariba Ghalamkarpour, MD Faranak Niknafs, MD Shima Younespour, PhD Skin Research Center, Shahid Beheshti
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
ISPUB.COM. Bexarotene in Tumor stage Mycosis Fungoides. R Talpur, M Duvic INITIAL PRESENTATION TREATMENT COURSE INTRODUCTION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Bexarotene in Tumor stage Mycosis Fungoides R Talpur, M Duvic Citation R Talpur, M Duvic. Bexarotene in Tumor stage Mycosis Fungoides. The
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Bexarotene in Tumor stage Mycosis Fungoides R Talpur, M Duvic Citation R Talpur, M Duvic. Bexarotene in Tumor stage Mycosis Fungoides. The
Los Angeles Radiological Society 62 nd Annual Midwinter Radiology Conference January 31, 2010
 Los Angeles Radiological Society 62 nd Annual Midwinter Radiology Conference January 31, 2010 Self Assessment Module on Nuclear Medicine and PET/CT Case Review FDG PET/CT IN LYMPHOMA AND MELANOMA Submitted
Los Angeles Radiological Society 62 nd Annual Midwinter Radiology Conference January 31, 2010 Self Assessment Module on Nuclear Medicine and PET/CT Case Review FDG PET/CT IN LYMPHOMA AND MELANOMA Submitted
SWOG ONCOLOGY RESEARCH PROFESSIONAL (ORP) MANUAL RESPONSE ASSESSMENT LYMPHOMA CHAPTER 11B REVISED: SEPTEMBER 2016
 LYMPHOMA Definitions of Response According to Non Hodgkin s Lymphoma (NHL) Criteria Listed below is the new NCI Lymphoma criteria for evaluation and endpoint definitions for Non Hodgkin s Lymphoma response
LYMPHOMA Definitions of Response According to Non Hodgkin s Lymphoma (NHL) Criteria Listed below is the new NCI Lymphoma criteria for evaluation and endpoint definitions for Non Hodgkin s Lymphoma response
Translating Evidence into Practice: Primary Cutaneous Melanoma Guidelines. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
 American Academy of Dermatology 2018 Annual Meeting San Diego, CA, February 17, 2018 Translating Evidence into Practice: Primary Cutaneous Melanoma Guidelines. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Christopher Bichakjian,
American Academy of Dermatology 2018 Annual Meeting San Diego, CA, February 17, 2018 Translating Evidence into Practice: Primary Cutaneous Melanoma Guidelines. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Christopher Bichakjian,
A rare clinical presentation of non Hodgkin Lymphoma as multiple neurofibromas with review of literature
 Original article A rare clinical presentation of non Hodgkin Lymphoma as multiple neurofibromas with review of literature Dr.C.R.Sirajunnisa Begum, Professor 1, Dr. Ira Bharadhwaj, Professor 1, Dr. Lavanya,
Original article A rare clinical presentation of non Hodgkin Lymphoma as multiple neurofibromas with review of literature Dr.C.R.Sirajunnisa Begum, Professor 1, Dr. Ira Bharadhwaj, Professor 1, Dr. Lavanya,
Sézary syndrome. Diagnosis and staging
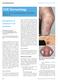 CME DERMATOLOGY Clinical Medicine 2012, Vol 12, No 2: 160 4 Edited by Clive B Archer, consultant dermatologist and lead for Medical Education, St John s Institute of Dermatology, Guy s and St Thomas NHS
CME DERMATOLOGY Clinical Medicine 2012, Vol 12, No 2: 160 4 Edited by Clive B Archer, consultant dermatologist and lead for Medical Education, St John s Institute of Dermatology, Guy s and St Thomas NHS
Subject Index. Dry desquamation, see Skin reactions, radiotherapy
 Subject Index Actinic keratosis disseminated disease 42 surgical excision 42 AIDS, see Kaposi s sarcoma Amifostine, skin reaction prophylaxis 111 Basal cell carcinoma, superficial X-ray therapy Bowen s
Subject Index Actinic keratosis disseminated disease 42 surgical excision 42 AIDS, see Kaposi s sarcoma Amifostine, skin reaction prophylaxis 111 Basal cell carcinoma, superficial X-ray therapy Bowen s
Lymphoma of the Skin Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Lymphoma of the Skin Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can
Lymphoma of the Skin Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can
Disclosures. Advisory Board. Consultant. Investigator. MiRagen, Actelion, Celgene, Therakos. Mindera
 Cutaneous Lymphomas Christiane Querfeld, MD, PhD Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Program City of Hope ~ How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Symposium March 10 13, 2017 Disclosures Advisory Board
Cutaneous Lymphomas Christiane Querfeld, MD, PhD Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Program City of Hope ~ How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Symposium March 10 13, 2017 Disclosures Advisory Board
ISPUB.COM. Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides and Lymphomatoid Papulosis. E Kim PHYSICAL FINDINGS INTRODUCTION INITIAL PRESENTATION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides and Lymphomatoid Papulosis E Kim Citation E Kim. Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides and Lymphomatoid Papulosis E Kim Citation E Kim. Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides
clinical recommendations
 19 (Supplement 2): ii72 ii76, 2008 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn095 Primary cutaneous lymphoma: ESMO Clinical Recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up R. Dummer 1 & M. Dreyling 2 On behalf of the
19 (Supplement 2): ii72 ii76, 2008 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn095 Primary cutaneous lymphoma: ESMO Clinical Recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up R. Dummer 1 & M. Dreyling 2 On behalf of the
Case Report A Severe Case of Lymphomatoid Papulosis Type E Successfully Treated with Interferon-Alfa 2a
 Hindawi Case Reports in Dermatological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 3194738, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3194738 Case Report A Severe Case of Lymphomatoid Papulosis Type E Successfully Treated
Hindawi Case Reports in Dermatological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 3194738, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3194738 Case Report A Severe Case of Lymphomatoid Papulosis Type E Successfully Treated
Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma
 Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma Laura B. Pincus, MD Co-Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic Associate Professor Dermatology and Pathology University of California, San Francisco I HAVE NO RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma Laura B. Pincus, MD Co-Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic Associate Professor Dermatology and Pathology University of California, San Francisco I HAVE NO RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
Mycosis Fungoides, then and now Have we travelled?
 USCAP 103 rd Annual Meeting 2014 American Society of Dermatopathology Companion Meeting Mycosis Fungoides, then and now Have we travelled? Vijaya B. Reddy, MD, MBA Professor of Pathology Rush University
USCAP 103 rd Annual Meeting 2014 American Society of Dermatopathology Companion Meeting Mycosis Fungoides, then and now Have we travelled? Vijaya B. Reddy, MD, MBA Professor of Pathology Rush University
Primary cutaneous lymphomas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up
 Annals of Oncology 24 (Supplement 6): vi149 vi154, 2013 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdt242 Published online 17 July 2013 Primary cutaneous lymphomas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and
Annals of Oncology 24 (Supplement 6): vi149 vi154, 2013 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdt242 Published online 17 July 2013 Primary cutaneous lymphomas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and
Clusterin Expression Correlates With Stage and Presence of Large Cells in Mycosis Fungoides
 Anatomic Pathology / Clusterin Expression in Mycosis Fungoides Clusterin Expression Correlates With Stage and Presence of Large Cells in Mycosis Fungoides Pranil Chandra, DO, 1 Jose A. Plaza, MD, 2,4 Zhuang
Anatomic Pathology / Clusterin Expression in Mycosis Fungoides Clusterin Expression Correlates With Stage and Presence of Large Cells in Mycosis Fungoides Pranil Chandra, DO, 1 Jose A. Plaza, MD, 2,4 Zhuang
Bone Marrow Histopathologic and Molecular Staging in Epidermotropic T-Cell Lymphomas
 Hematopathology / BONE MARROW STAGING IN CUTANEOUS T-CELL LYMPHOMA Bone Marrow Histopathologic and Molecular Staging in Epidermotropic T-Cell Lymphomas Vincent Sibaud, MD, 1,2 Marie Beylot-Barry, MD, PhD,
Hematopathology / BONE MARROW STAGING IN CUTANEOUS T-CELL LYMPHOMA Bone Marrow Histopathologic and Molecular Staging in Epidermotropic T-Cell Lymphomas Vincent Sibaud, MD, 1,2 Marie Beylot-Barry, MD, PhD,
Mycosis Fungoides Presentation in Emergency
 The Open Emergency Medicine Journal, 2011, 4, 17-21 17 Mycosis Fungoides Presentation in Emergency Asaad Shujaa*,1 and M. Owais Suriya 2 Open Access Department of Emergency Medicine College of Medicine,
The Open Emergency Medicine Journal, 2011, 4, 17-21 17 Mycosis Fungoides Presentation in Emergency Asaad Shujaa*,1 and M. Owais Suriya 2 Open Access Department of Emergency Medicine College of Medicine,
WORKUP. USEFUL IN SELECTED CASES: PET-CT scan Bone marrow biopsy
 DIAGNOSIS a WORKUP ESSENTIAL: Review of all slides with at least one paraffin lock representative of the tum should e done y a pathologist with expertise in the diagnosis of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma.
DIAGNOSIS a WORKUP ESSENTIAL: Review of all slides with at least one paraffin lock representative of the tum should e done y a pathologist with expertise in the diagnosis of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma.
Dermatology nurses often serve as the primary
 Gelling Your Dermatology Nursing Practice A Practical Guide for Managing the Treatment of Mycosis Fungoides Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma With Mechlorethamine Gel Sue A. McCann, Allister Benjamin Chase, Marianne
Gelling Your Dermatology Nursing Practice A Practical Guide for Managing the Treatment of Mycosis Fungoides Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma With Mechlorethamine Gel Sue A. McCann, Allister Benjamin Chase, Marianne
performed to help sway the clinician in what the appropriate diagnosis is, which can substantially alter the treatment of management.
 Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
CUTANEOUS T-CELL LYMPHOMA PROFORMA
 STATE OF KUWAIT MINISTRY OF HEALTH AS AD ALHAMAD DERMATOLOGY CENTER ALSABAH HOSPITAL دولة الكویت وزارة الصحة مرآز أسعد الحمد للا مراض الجلدیة مستشفى الصباح بسم االله الرحمن الرحيم CUTANEOUS TCELL LYMPHOMA
STATE OF KUWAIT MINISTRY OF HEALTH AS AD ALHAMAD DERMATOLOGY CENTER ALSABAH HOSPITAL دولة الكویت وزارة الصحة مرآز أسعد الحمد للا مراض الجلدیة مستشفى الصباح بسم االله الرحمن الرحيم CUTANEOUS TCELL LYMPHOMA
Primary cutaneous large cell lymphoma CD30+: a case-based review
 Case-based review Primary cutaneous large cell lymphoma CD30+: a case-based review Anna Campanati 1 Katia Giuliodori 1 Emanuela Martina 1 Luca Conocchiari 1 Giulia Ganzetti 1 Gaia Goteri 2 Annamaria Offidani
Case-based review Primary cutaneous large cell lymphoma CD30+: a case-based review Anna Campanati 1 Katia Giuliodori 1 Emanuela Martina 1 Luca Conocchiari 1 Giulia Ganzetti 1 Gaia Goteri 2 Annamaria Offidani
See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
 Clinical Policy: Vorinostat (Zolinza) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.83 Effective Date: 10.01.18 Last Review Date: 07.13.18 Line of Business: Oregon Health Plan Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end
Clinical Policy: Vorinostat (Zolinza) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.83 Effective Date: 10.01.18 Last Review Date: 07.13.18 Line of Business: Oregon Health Plan Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end
A Review of Survival in Mycosis Fungoides
 A Review of Survival in Mycosis Fungoides Robin T. Vollmer, MD From the VA and Duke University Medical Centers, Durham, NC. Key Words: Mycosis fungoides; Survival; Hazard function; Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
A Review of Survival in Mycosis Fungoides Robin T. Vollmer, MD From the VA and Duke University Medical Centers, Durham, NC. Key Words: Mycosis fungoides; Survival; Hazard function; Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Clinical Study The Influence of the Coexpression of CD4 and CD8 in Cutaneous Lesions on Prognosis of Mycosis Fungoides: A Preliminary Study
 Skin Cancer, Article ID 624143, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/624143 Clinical Study The Influence of the Coexpression of CD4 and CD8 in Cutaneous Lesions on Prognosis of Mycosis Fungoides: A Preliminary
Skin Cancer, Article ID 624143, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/624143 Clinical Study The Influence of the Coexpression of CD4 and CD8 in Cutaneous Lesions on Prognosis of Mycosis Fungoides: A Preliminary
Granulomatous Slack Skin with an unusually aggressive course due to the subsequent development of a CD30-positive Large Cell Lymphoma
 Granulomatous Slack Skin with an unusually aggressive course due to the subsequent development of a CD30-positive Large Cell Lymphoma Alexandra Papoudou-Bai 1, Eleni Kapsali 2, Ioannis Kostas-Agnantis
Granulomatous Slack Skin with an unusually aggressive course due to the subsequent development of a CD30-positive Large Cell Lymphoma Alexandra Papoudou-Bai 1, Eleni Kapsali 2, Ioannis Kostas-Agnantis
CD30+ Lymphoproliferative Disorders Associated with Longstanding Mycosis Fungoides
 Case Report DOI: 10.6003/jtad.16102c5 CD30+ Lymphoproliferative Disorders Associated with Longstanding Mycosis Fungoides Esra Adışen, 1 MD, Özlem Erdem, 2 MD, Mehmet Ali Gürer, 1 MD Address: 1 Gazi University
Case Report DOI: 10.6003/jtad.16102c5 CD30+ Lymphoproliferative Disorders Associated with Longstanding Mycosis Fungoides Esra Adışen, 1 MD, Özlem Erdem, 2 MD, Mehmet Ali Gürer, 1 MD Address: 1 Gazi University
Instructions for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Post-HSCT Data (Form 2113)
 Instructions for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Post-HSCT Data (Form 2113) This section of the CIBMTR Forms Instruction Manual is intended to be a resource for completing the CLL Post-HSCT Data Form. E-mail
Instructions for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Post-HSCT Data (Form 2113) This section of the CIBMTR Forms Instruction Manual is intended to be a resource for completing the CLL Post-HSCT Data Form. E-mail
Case Scenario 1 Worksheet. Primary Site C44.4 Morphology 8743/3 Laterality 0 Stage/ Prognostic Factors
 CASE SCENARIO 1 9/10/13 HISTORY: Patient is a 67-year-old white male and presents with lesion located 4-5cm above his right ear. The lesion has been present for years. No lymphadenopathy. 9/10/13 anterior
CASE SCENARIO 1 9/10/13 HISTORY: Patient is a 67-year-old white male and presents with lesion located 4-5cm above his right ear. The lesion has been present for years. No lymphadenopathy. 9/10/13 anterior
Radiographic Assessment of Response An Overview of RECIST v1.1
 Radiographic Assessment of Response An Overview of RECIST v1.1 Stephen Liu, MD Georgetown University May 15 th, 2015 Presentation Objectives To understand the purpose of RECIST guidelines To describe the
Radiographic Assessment of Response An Overview of RECIST v1.1 Stephen Liu, MD Georgetown University May 15 th, 2015 Presentation Objectives To understand the purpose of RECIST guidelines To describe the
Abstract. Hematopathology / FLOW CYTOMETRIC DNA PLOIDY ANALYSIS IN SÉZARY SYNDROME
 Hematopathology / FLOW CYTOMETRIC DNA PLOIDY ANALYSIS IN SÉZARY SYNDROME Flow Cytometric DNA Ploidy Analysis of Peripheral Blood From Patients With Sézary Syndrome Detection of Aneuploid Neoplastic T Cells
Hematopathology / FLOW CYTOMETRIC DNA PLOIDY ANALYSIS IN SÉZARY SYNDROME Flow Cytometric DNA Ploidy Analysis of Peripheral Blood From Patients With Sézary Syndrome Detection of Aneuploid Neoplastic T Cells
Collaborative Stage for TNM 7 - Revised 12/02/2009 [ Schema ]
![Collaborative Stage for TNM 7 - Revised 12/02/2009 [ Schema ] Collaborative Stage for TNM 7 - Revised 12/02/2009 [ Schema ]](/thumbs/82/86783199.jpg) CS Tumor Size Collaborative Stage for TNM 7 - Revised 12/02/2009 [ Schema ] Note: the specific tumor size as documented in the medical record. If the ONLY information regarding tumor size is the physician's
CS Tumor Size Collaborative Stage for TNM 7 - Revised 12/02/2009 [ Schema ] Note: the specific tumor size as documented in the medical record. If the ONLY information regarding tumor size is the physician's
Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders
 Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders Definition A spectrum of related conditions originating from transformed or activated CD30-positive T-lymphocytes May coexist in individual
Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders Definition A spectrum of related conditions originating from transformed or activated CD30-positive T-lymphocytes May coexist in individual
Renaissance of Low-Dose Radiotherapy Concepts for Cutaneous Lymphomas
 Review Article DOI: 10.1159/000470845 Received: February 06, 2017 Accepted: March 13, 2017 Published online: April 6, 2017 Renaissance of Low-Dose Radiotherapy Concepts for Cutaneous Lymphomas Bouthaina
Review Article DOI: 10.1159/000470845 Received: February 06, 2017 Accepted: March 13, 2017 Published online: April 6, 2017 Renaissance of Low-Dose Radiotherapy Concepts for Cutaneous Lymphomas Bouthaina
LYMPHOMA DIAGNOSIS and PROGNOSIS. LC Lim Dept of Hematology Singapore General Hospital
 LYMPHOMA DIAGNOSIS and PROGNOSIS LC Lim Dept of Hematology Singapore General Hospital OUTLINE Accurate diagnosis Define subtype : WHO classification Staging : Defines extent of involvement Prognosis Determining
LYMPHOMA DIAGNOSIS and PROGNOSIS LC Lim Dept of Hematology Singapore General Hospital OUTLINE Accurate diagnosis Define subtype : WHO classification Staging : Defines extent of involvement Prognosis Determining
The Lymphomas. An overview..
 The Lymphomas An overview.. Peter Anglin MD, FRCPC, MBA Stronach Regional Cancer Centre Newmarket, ON The lymphomas are an important part of the history of medicine 1666 Magpighi publishes first recorded
The Lymphomas An overview.. Peter Anglin MD, FRCPC, MBA Stronach Regional Cancer Centre Newmarket, ON The lymphomas are an important part of the history of medicine 1666 Magpighi publishes first recorded
MALIGNANT MELANOMA. Dr D. Tenea Department of Dermatology University of Pretoria
 MALIGNANT MELANOMA Dr D. Tenea Department of Dermatology University of Pretoria BACKGROUND History MM. of the skin is a malignant neoplasm of the epidermal melanocytes The incidence rates show considerable
MALIGNANT MELANOMA Dr D. Tenea Department of Dermatology University of Pretoria BACKGROUND History MM. of the skin is a malignant neoplasm of the epidermal melanocytes The incidence rates show considerable
Increase of DC-LAMP+ mature dendritic cell subsets in dermatopathic lymphadenitis of mycosis fungoides
 Increase of DC-LAMP+ mature dendritic cell subsets in dermatopathic lymphadenitis of mycosis fungoides Kotaro TADA 1,2, Toshihisa HAMADA 1, Kenji ASAGOE 3, Hiroshi UMEMURA 1, Kazuko MIZUNO-IKEDA 1, Yumi
Increase of DC-LAMP+ mature dendritic cell subsets in dermatopathic lymphadenitis of mycosis fungoides Kotaro TADA 1,2, Toshihisa HAMADA 1, Kenji ASAGOE 3, Hiroshi UMEMURA 1, Kazuko MIZUNO-IKEDA 1, Yumi
OBSERVATION. Psoralen Plus Long-Wave UV-A (PUVA) and Bexarotene Therapy
 OBSERVATION Psoralen Plus Long-Wave UV-A (PUVA) and Bexarotene Therapy An Effective and Synergistic Combined Adjunct to Therapy for Patients With Advanced Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma Karen S. McGinnis, MD;
OBSERVATION Psoralen Plus Long-Wave UV-A (PUVA) and Bexarotene Therapy An Effective and Synergistic Combined Adjunct to Therapy for Patients With Advanced Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma Karen S. McGinnis, MD;
NON HODGKINS LYMPHOMA: INDOLENT Updated June 2015 by Dr. Manna (PGY-5 Medical Oncology Resident, University of Calgary)
 NON HODGKINS LYMPHOMA: INDOLENT Updated June 2015 by Dr. Manna (PGY-5 Medical Oncology Resident, University of Calgary) Reviewed by Dr. Michelle Geddes (Staff Hematologist, University of Calgary) and Dr.
NON HODGKINS LYMPHOMA: INDOLENT Updated June 2015 by Dr. Manna (PGY-5 Medical Oncology Resident, University of Calgary) Reviewed by Dr. Michelle Geddes (Staff Hematologist, University of Calgary) and Dr.
STUDY. fungoides (FMF) is an uncommon
 STUDY Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides Single-Center Study and Systematic Review Julia S. Lehman, MD; Robert H. Cook-Norris, MD; Brent R. Weed, MD; Roger H. Weenig, MD; Lawrence E. Gibson, MD; Amy L.
STUDY Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides Single-Center Study and Systematic Review Julia S. Lehman, MD; Robert H. Cook-Norris, MD; Brent R. Weed, MD; Roger H. Weenig, MD; Lawrence E. Gibson, MD; Amy L.
When Do I Consider Myself Cured?
 The Melanoma Patient Symposium - Science to Survivorship When Do I Consider Myself Cured? 26 September 2009 Jeffrey E. Gershenwald, MD, FACS Professor of Surgery, Dept. of Surgical Oncology Professor,
The Melanoma Patient Symposium - Science to Survivorship When Do I Consider Myself Cured? 26 September 2009 Jeffrey E. Gershenwald, MD, FACS Professor of Surgery, Dept. of Surgical Oncology Professor,
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE IN THE HEAD & NECK
 LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE IN THE HEAD & NECK Like other parts of the body, the head and neck contains lymph nodes (commonly called glands). Which form part of the overall Lymphatic Drainage system of the body.
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE IN THE HEAD & NECK Like other parts of the body, the head and neck contains lymph nodes (commonly called glands). Which form part of the overall Lymphatic Drainage system of the body.
A middle-aged man with self-healing papulonecrotic lesions over the trunk and proximal limbs
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2011) 19, 30-34 Case Report A middle-aged man with self-healing papulonecrotic lesions over the trunk and proximal limbs JC Chan, N Trendell-Smith, CK Yeung Lymphomatoid
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2011) 19, 30-34 Case Report A middle-aged man with self-healing papulonecrotic lesions over the trunk and proximal limbs JC Chan, N Trendell-Smith, CK Yeung Lymphomatoid
Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS
 Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS CS Tumor Size Tumor size is the diameter of the tumor, not the depth or thickness of the tumor. Chest x-ray shows 3.5 cm mass; the pathology report
Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS CS Tumor Size Tumor size is the diameter of the tumor, not the depth or thickness of the tumor. Chest x-ray shows 3.5 cm mass; the pathology report
Synthetic hypericin (SGX301; VIMRxyn) for cutaneous T cell lymphoma, unspecified
 NIHR Innovation Observatory Evidence Briefing: May 2017 Synthetic hypericin (SGX301; VIMRxyn) for cutaneous T cell lymphoma, unspecified NIHRIO (HSRIC) ID: 10761 NICE ID: 8375 LAY SUMMARY Cutaneous T cell
NIHR Innovation Observatory Evidence Briefing: May 2017 Synthetic hypericin (SGX301; VIMRxyn) for cutaneous T cell lymphoma, unspecified NIHRIO (HSRIC) ID: 10761 NICE ID: 8375 LAY SUMMARY Cutaneous T cell
Lymphatic system component
 Introduction Lymphatic system component Statistics Overview Lymphoma Non Hodgkin s Lymphoma Non- Hodgkin's is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system. It is estimated to be the sixth most
Introduction Lymphatic system component Statistics Overview Lymphoma Non Hodgkin s Lymphoma Non- Hodgkin's is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system. It is estimated to be the sixth most
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
 HEMATOPATHOLOGY Original Article Mantle Cell Lymphoma Morphologic Findings in Bone Marrow Involvement JAY WASMAN, MD, 1 NANCY S. ROSENTHAL, MD,' AND DIANE C. FARHI, MD 2 Although mantle cell lymphoma (MCL),
HEMATOPATHOLOGY Original Article Mantle Cell Lymphoma Morphologic Findings in Bone Marrow Involvement JAY WASMAN, MD, 1 NANCY S. ROSENTHAL, MD,' AND DIANE C. FARHI, MD 2 Although mantle cell lymphoma (MCL),
Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: An Entry From Thomson Gale's Gale Encyclopedia Of Cancer, 2nd Ed. [HTML] [Digital]
![Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: An Entry From Thomson Gale's Gale Encyclopedia Of Cancer, 2nd Ed. [HTML] [Digital] Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: An Entry From Thomson Gale's Gale Encyclopedia Of Cancer, 2nd Ed. [HTML] [Digital]](/thumbs/80/80529096.jpg) Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: An Entry From Thomson Gale's Gale Encyclopedia Of Cancer, 2nd Ed. [HTML] [Digital] By Michelle, M.S., J.D. Johnson;Rebecca, PhD Frey READ ONLINE If searched for a ebook Cutaneous
Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: An Entry From Thomson Gale's Gale Encyclopedia Of Cancer, 2nd Ed. [HTML] [Digital] By Michelle, M.S., J.D. Johnson;Rebecca, PhD Frey READ ONLINE If searched for a ebook Cutaneous
During past decades, because of the lack of knowledge
 Staging and Classification of Lymphoma Ping Lu, MD In 2004, new cases of non-hodgkin s in the United States were estimated at 54,370, representing 4% of all cancers and resulting 4% of all cancer deaths,
Staging and Classification of Lymphoma Ping Lu, MD In 2004, new cases of non-hodgkin s in the United States were estimated at 54,370, representing 4% of all cancers and resulting 4% of all cancer deaths,
Melanoma Update: 8th Edition of AJCC Staging System
 Melanoma Update: 8th Edition of AJCC Staging System Rosalie Elenitsas, M.D. Professor of Dermatology Director, Dermatopathology University of Pennsylvania DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY None
Melanoma Update: 8th Edition of AJCC Staging System Rosalie Elenitsas, M.D. Professor of Dermatology Director, Dermatopathology University of Pennsylvania DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY None
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL)
 Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Accepted Article. Unusual involvement in mycosis fungoides: Duodenal papilla. Álvaro Andrés Gómez Venegas, Rómulo Darío Vargas Rubio
 Accepted Article Unusual involvement in mycosis fungoides: Duodenal papilla Álvaro Andrés Gómez Venegas, Rómulo Darío Vargas Rubio DOI: 10.17235/reed.2015.3831/2015 Link: PDF Please cite this article as:
Accepted Article Unusual involvement in mycosis fungoides: Duodenal papilla Álvaro Andrés Gómez Venegas, Rómulo Darío Vargas Rubio DOI: 10.17235/reed.2015.3831/2015 Link: PDF Please cite this article as:
Plasma cell myeloma (multiple myeloma)
 Plasma cell myeloma (multiple myeloma) Common lymphoid neoplasm, present at old age (70 years average) Remember: plasma cells are terminally differentiated B-lymphocytes that produces antibodies. B-cells
Plasma cell myeloma (multiple myeloma) Common lymphoid neoplasm, present at old age (70 years average) Remember: plasma cells are terminally differentiated B-lymphocytes that produces antibodies. B-cells
Chapter 2 Staging of Breast Cancer
 Chapter 2 Staging of Breast Cancer Zeynep Ozsaran and Senem Demirci Alanyalı 2.1 Introduction Five decades ago, Denoix et al. proposed classification system (tumor node metastasis [TNM]) based on the dissemination
Chapter 2 Staging of Breast Cancer Zeynep Ozsaran and Senem Demirci Alanyalı 2.1 Introduction Five decades ago, Denoix et al. proposed classification system (tumor node metastasis [TNM]) based on the dissemination
Clinical Trial Outcomes
 l Recent clinical evidence for topical mechlorethamine in mycosis fungoides Mycosis fungoides (MF) is a rare, potentially life-threatening cutaneous T-cell lymphoma characterized by cutaneous homing of
l Recent clinical evidence for topical mechlorethamine in mycosis fungoides Mycosis fungoides (MF) is a rare, potentially life-threatening cutaneous T-cell lymphoma characterized by cutaneous homing of
Research Article Characteristics of Primary Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma in Iran: A 10-Year Retrospective Study
 International Scholarly Research Notices, Article ID 820921, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/820921 Research Article Characteristics of Primary Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma in Iran: A 10-Year Retrospective
International Scholarly Research Notices, Article ID 820921, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/820921 Research Article Characteristics of Primary Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma in Iran: A 10-Year Retrospective
CASE 15 Patient: A 41-year-old Thai female Chief Compliant: Generalized papulovesicular rash for 1 month Present Illness: She presented with a 1-week
 CASE 15 Patient: A 41-year-old Thai female Chief Compliant: Generalized papulovesicular rash for 1 month Present Illness: She presented with a 1-week history of the generalized asymptomatic erythematous
CASE 15 Patient: A 41-year-old Thai female Chief Compliant: Generalized papulovesicular rash for 1 month Present Illness: She presented with a 1-week history of the generalized asymptomatic erythematous
Research Article Flow Cytometric Analysis of T, B, and NK Cells Antigens in Patients with Mycosis Fungoides
 Immunology Research Volume 2015, Article ID 856340, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/856340 Research Article Flow Cytometric Analysis of T, B, and NK Cells Antigens in Patients with Mycosis Fungoides
Immunology Research Volume 2015, Article ID 856340, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/856340 Research Article Flow Cytometric Analysis of T, B, and NK Cells Antigens in Patients with Mycosis Fungoides
AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th Edition. Prostate Chapter 58. Executive Committee, AJCC. Professor and Director, Duke Prostate Center
 AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th Edition Prostate Chapter 58 Judd W Moul, MD, FACS Executive Committee, AJCC Professor and Director, Duke Prostate Center Duke University Durham, North Carolina Validating science.
AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th Edition Prostate Chapter 58 Judd W Moul, MD, FACS Executive Committee, AJCC Professor and Director, Duke Prostate Center Duke University Durham, North Carolina Validating science.
Lugano classification: Role of PET-CT in lymphoma follow-up
 CAR Educational Exhibit: ID 084 Lugano classification: Role of PET-CT in lymphoma follow-up Charles Nhan 4 Kevin Lian MD Charlotte J. Yong-Hing MD FRCPC Pete Tonseth 3 MD FRCPC Department of Diagnostic
CAR Educational Exhibit: ID 084 Lugano classification: Role of PET-CT in lymphoma follow-up Charles Nhan 4 Kevin Lian MD Charlotte J. Yong-Hing MD FRCPC Pete Tonseth 3 MD FRCPC Department of Diagnostic
Burkitt lymphoma. Sporadic Endemic in Africa associated with EBV Translocations involving MYC gene on chromosome 8
 Heme 8 Burkitt lymphoma Sporadic Endemic in Africa associated with EBV Translocations involving MYC gene on chromosome 8 Most common is t(8;14) Believed to be the fastest growing tumor in humans!!!! Morphology
Heme 8 Burkitt lymphoma Sporadic Endemic in Africa associated with EBV Translocations involving MYC gene on chromosome 8 Most common is t(8;14) Believed to be the fastest growing tumor in humans!!!! Morphology
1) Title: Cutaneous lymphoma in Japan: a nationwide study of 1,733 patients.
 1) Title: Cutaneous lymphoma in Japan: a nationwide study of 1,733 patients. 2) The short running title: Cutaneous lymphoma in Japan. 3) Toshihisa Hamada and Keiji Iwatsuki 4) Departments of Dermatology,
1) Title: Cutaneous lymphoma in Japan: a nationwide study of 1,733 patients. 2) The short running title: Cutaneous lymphoma in Japan. 3) Toshihisa Hamada and Keiji Iwatsuki 4) Departments of Dermatology,
PET-imaging: when can it be used to direct lymphoma treatment?
 PET-imaging: when can it be used to direct lymphoma treatment? Luca Ceriani Nuclear Medicine and PET-CT centre Oncology Institute of Southern Switzerland Bellinzona Disclosure slide I declare no conflict
PET-imaging: when can it be used to direct lymphoma treatment? Luca Ceriani Nuclear Medicine and PET-CT centre Oncology Institute of Southern Switzerland Bellinzona Disclosure slide I declare no conflict
Lymphoma co existing with Tuberculosis granulomatous
 Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 90 (2017) 265-270 EISSN 2392-2192 SHORT COMMUNICATION Lymphoma co existing with Tuberculosis granulomatous Madeeha Subhan 1, *, Waleed Sadiq 2 1 Ayub
Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 90 (2017) 265-270 EISSN 2392-2192 SHORT COMMUNICATION Lymphoma co existing with Tuberculosis granulomatous Madeeha Subhan 1, *, Waleed Sadiq 2 1 Ayub
King s Research Portal
 King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.10.025 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Boonk, S. E., Zoutman,
King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.10.025 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Boonk, S. E., Zoutman,
Fig. 3.1 Fig Past history: She was previously healthy and not taking any medication.
 Case 3 A 41-year-old Thai female from Bangkok Chief compliant: Erythematous patch at left thigh for 2 months Present illness: The patient presented with a 10- year history of erythematous patch on her
Case 3 A 41-year-old Thai female from Bangkok Chief compliant: Erythematous patch at left thigh for 2 months Present illness: The patient presented with a 10- year history of erythematous patch on her
category cm0. Category will ensure it T1 melanoma. 68 Retinoblastoma
 AJCC 8 th Edition Chapter 1 Principles of Cancer Staging: Node Status Not Required in Rare Circumstances Clinical Staging, cn Category For some cancer sites in which lymph node involvement is rare, patients
AJCC 8 th Edition Chapter 1 Principles of Cancer Staging: Node Status Not Required in Rare Circumstances Clinical Staging, cn Category For some cancer sites in which lymph node involvement is rare, patients
MEASUREMENT OF EFFECT SOLID TUMOR EXAMPLES
 MEASUREMENT OF EFFECT SOLID TUMOR EXAMPLES Although response is not the primary endpoint of this trial, subjects with measurable disease will be assessed by standard criteria. For the purposes of this
MEASUREMENT OF EFFECT SOLID TUMOR EXAMPLES Although response is not the primary endpoint of this trial, subjects with measurable disease will be assessed by standard criteria. For the purposes of this
ACHIEVING EXCELLENCE IN ABSTRACTING: LYMPHOMA
 ACHIEVING EXCELLENCE IN ABSTRACTING: LYMPHOMA ACHIEVING EXCELLENCE IN ABSTRACTING LYMPHOMA Recoding Audit Performed in 2009 260 cases audited 17 data items audited per case 4420 possible discrepancies
ACHIEVING EXCELLENCE IN ABSTRACTING: LYMPHOMA ACHIEVING EXCELLENCE IN ABSTRACTING LYMPHOMA Recoding Audit Performed in 2009 260 cases audited 17 data items audited per case 4420 possible discrepancies
ISPUB.COM. Advanced Stage CTCL, PTCL with Cutaneous Involvement. J Messenger, P Porcu INTRODUCTION INITIAL PRESENTATION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Advanced Stage CTCL, PTCL with Cutaneous Involvement J Messenger, P Porcu Citation J Messenger, P Porcu. Advanced Stage CTCL, PTCL with Cutaneous
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Advanced Stage CTCL, PTCL with Cutaneous Involvement J Messenger, P Porcu Citation J Messenger, P Porcu. Advanced Stage CTCL, PTCL with Cutaneous
Michael T. Tetzlaff MD, PhD
 American Joint Cancer Committee (AJCC) staging system for primary cutaneous melanoma (8 th Edition) and principles of sentinel lymph node evaluation Emphasis on concise and accurate reporting of primary
American Joint Cancer Committee (AJCC) staging system for primary cutaneous melanoma (8 th Edition) and principles of sentinel lymph node evaluation Emphasis on concise and accurate reporting of primary
Evaluation of Lung Cancer Response: Current Practice and Advances
 Evaluation of Lung Cancer Response: Current Practice and Advances Jeremy J. Erasmus I have no financial relationships, arrangements or affiliations and this presentation will not include discussion of
Evaluation of Lung Cancer Response: Current Practice and Advances Jeremy J. Erasmus I have no financial relationships, arrangements or affiliations and this presentation will not include discussion of
Radiology- Pathology Conference 4/29/2012. Lymph Nodes. John McGrath
 Radiology- Pathology Conference 4/29/2012 Lymph Nodes John McGrath 1 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2012 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 24 Case 1: 51 year-old male
Radiology- Pathology Conference 4/29/2012 Lymph Nodes John McGrath 1 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2012 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 24 Case 1: 51 year-old male
47. Melanoma of the Skin
 1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
Talk to Your Doctor. Fact Sheet
 Talk to Your Doctor Hearing the words you have skin cancer is overwhelming and would leave anyone with a lot of questions. If you have been diagnosed with Stage I or II cutaneous melanoma with no apparent
Talk to Your Doctor Hearing the words you have skin cancer is overwhelming and would leave anyone with a lot of questions. If you have been diagnosed with Stage I or II cutaneous melanoma with no apparent
1. Written information to patient /GP: fax ASAP to GP & offer copy of consultation letter.
 Skin Cancer follow up guidelines If NEW serious diagnosis given: 1. Written information to patient /GP: fax ASAP to GP & offer copy of consultation letter. 2. Free prescription information details. 3.
Skin Cancer follow up guidelines If NEW serious diagnosis given: 1. Written information to patient /GP: fax ASAP to GP & offer copy of consultation letter. 2. Free prescription information details. 3.
Management of Neck Metastasis from Unknown Primary
 Management of Neck Metastasis from Unknown Primary.. Definition Histologic evidence of malignancy in the cervical lymph node (s) with no apparent primary site of original tumour Diagnosis after a thorough
Management of Neck Metastasis from Unknown Primary.. Definition Histologic evidence of malignancy in the cervical lymph node (s) with no apparent primary site of original tumour Diagnosis after a thorough
Cervical Cancer: 2018 FIGO Staging
 Cervical Cancer: 2018 FIGO Staging Jonathan S. Berek, MD, MMS Laurie Kraus Lacob Professor Stanford University School of Medicine Director, Stanford Women s Cancer Center Senior Scientific Advisor, Stanford
Cervical Cancer: 2018 FIGO Staging Jonathan S. Berek, MD, MMS Laurie Kraus Lacob Professor Stanford University School of Medicine Director, Stanford Women s Cancer Center Senior Scientific Advisor, Stanford
Clinical and Histopathological Spectrum of Mycosis Fungoides
 Awad Hasan Al-Tarawneh, MD, Jordan Board* Background: Early diagnosis of mycosis fungoides is essential but difficult and can be easily missed because it mimics many inflammatory skin diseases both clinically
Awad Hasan Al-Tarawneh, MD, Jordan Board* Background: Early diagnosis of mycosis fungoides is essential but difficult and can be easily missed because it mimics many inflammatory skin diseases both clinically
Interhospital Dermatology Conference 2013
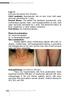 Case 21 A 50-year-old woman from Chonburi. Chief complaint: Asymptomatic rash on neck, trunk, both upper and lower extremities for 2 years. Present illness: The patient has developed asymptomatic scaly
Case 21 A 50-year-old woman from Chonburi. Chief complaint: Asymptomatic rash on neck, trunk, both upper and lower extremities for 2 years. Present illness: The patient has developed asymptomatic scaly
Melanoma Case Scenario 1
 Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C.
 Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies. Patricia Aoun MD MPH
 Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
Staging Colorectal Cancer
 Staging Colorectal Cancer CT is recommended as the initial staging scan for colorectal cancer to assess local extent of the disease and to look for metastases to the liver and/or lung Further imaging for
Staging Colorectal Cancer CT is recommended as the initial staging scan for colorectal cancer to assess local extent of the disease and to look for metastases to the liver and/or lung Further imaging for
Lymph Node Enlargement in Dogs & Cats A Swelling Not to Be Ignored!
 Lymph Node Enlargement in Dogs & Cats A Swelling Not to Be Ignored! A common clinical scenario I encounter is a pet referred to me for evaluation of enlarged lymph nodes. Parents may incidentally discover
Lymph Node Enlargement in Dogs & Cats A Swelling Not to Be Ignored! A common clinical scenario I encounter is a pet referred to me for evaluation of enlarged lymph nodes. Parents may incidentally discover
Cancer of Unknown Primary (CUP)
 Cancer of Unknown Primary (CUP) Pathways and Guidelines V1.0 London Cancer September 2013 The following pathways and guidelines document has been compiled by the London Cancer CUP technical subgroup and
Cancer of Unknown Primary (CUP) Pathways and Guidelines V1.0 London Cancer September 2013 The following pathways and guidelines document has been compiled by the London Cancer CUP technical subgroup and
