4/14/2017. Disclosures. Peripheral Nerve Imaging: Lumbosacral plexus MRI. No relevant financial relationship to disclose
|
|
|
- Hilary Skinner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Peripheral Nerve Imaging: Lumbosacral plexus MRI Disclosures No relevant financial relationship to disclose Sarah E. Stilwill M.D.- MSK Radiology Division, University of Utah Avneesh Chhabra M.D. Chief of MSK Radiology Division, UT Southwestern R. Kent Sanders M.D. MSK Radiology, North Canyon Medical Center Idaho Megan K Mills M.D. - MSK Radiology Division, University of Utah Importance of imaging the LS Plexus Importance of imaging the LS Plexus Often clinically difficult to tease out spine related abnormalities vs LS plexus pathology Often clinically difficult to tease out spine related abnormalities vs LS plexus pathology MR Neurography has dramatically improved ways of accurately diagnosing exact location, type, extent and cause of the peripheral plexopathy Chhabra et all. MRN: Past, present and future. AJR 2011; 197: Sag T2 Chhabra et all. MRN: Past, present and future. AJR 2011; 197: What is the Lumbosacral plexus? What is the Lumbosacral plexus? Coalescence of the ventral rami of the lumbar and sacral spinal nerve roots forming the lumbrosacral trunk Wikipedia 1
2 What is the Lumbosacral plexus? Coalescence of the ventral rami of the lumbar and sacral spinal nerve roots forming the lumbrosacral trunk Specifically L4-S3 nerves --> LS Plexus What is the Lumbosacral plexus? Coalescence of the ventral rami of the lumbar and sacral spinal nerve roots forming the lumbrosacral trunk Specifically L4-S3 nerves --> LS Plexus Provides motor and sensory innervation to most structures of the pelvis and lower extremities R Femoral Neuropathy Soltados et al. High Resolution 3T MRN of the LS Plexus. Radiographics 2013; What is the Lumbosacral plexus? Educational Objectives Coalescence of the ventral rami of the lumbar and sacral spinal nerve roots forming the lumbrosacral trunk Specifically L4-S3 nerves --> LS Plexus Provides motor and sensory innervation to most structures of the pelvis and lower extremities Very susceptible to traumatic, inflammatory, metabolic, and neoplastic processes Amyloid Review our institutions imaging protocol Cor T1 FS PG Dr. Chhabra Chhabra SSR 2017 Educational Objectives Review our institutions imaging protocol Review normal nerve anatomy Educational Objectives Review our institutions imaging protocol Review normal nerve anatomy Recognize key imaging findings of LS plexus pathology Chhabra SSR 2017 Chhabra SSR
3 Combination of 2D and 3D techniques 1.5T and 3T 3T better SNR, can get thinner slices and MIP recons Combination of 2D and 3D techniques 1.5T and 3T 3T better SNR, can get thinner slices and MIP recons Axial T1 and T2 FS/ SPAIR Cor T1 and / SPAIR Combination of 2D and 3D techniques 1.5T and 3T 3T better SNR, can get thinner slices and MIP recons Axial T1 and T2 FS/ SPAIR Cor T1 and / SPAIR Contrast for tumors and infection >>> inflammation Combination of 2D and 3D techniques 1.5T and 3T 3T better SNR, can get thinner slices and MIP recons Axial T1 and T2 FS/ SPAIR Cor T1 and / SPAIR Contrast for tumors and infection >>> inflammation Future: DWI/DTI sequences Cor T 1 FS PC Dr. Chhabra Zhao L et al. Diffusion-Weighted MR Neurography of Extremity Nerves With Unidirectional Motion-Probing Gradients at 3 T: Feasibility Study. AJR, 2013 vol 200, No 5. Combination of 2D and 3D techniques 1.5T and 3T 3T better SNR, can get thinner slices and MIP recons Axial T1 and T2 FS/ SPAIR Cor T1 and / SPAIR Contrast for tumors and infection >>> inflammation Future: DWI/DTI sequences PSIF??? Selective nerve imaging 2D or 3D Coronal STIR - useful for LS plexus nerve size and signal with excellent contrast resolution for depicting pathology. Great for internal nerve architecture. 3D SPACE 3
4 (Axial and Coronal) T1 non FS-key sequences for peri-neural and intermuscular fat plane evaluation, chronic fatty muscle atrophy, bone marrow signal and Met-hgb blood products (Axial and Coronal) T1 non FS-key sequences for peri-neural and intermuscular fat plane evaluation, chronic fatty muscle atrophy, bone marrow signal and Met-hgb blood products Axial T2 FS +/- SPAIR -2D images provide detailed fascicular depiction of the lumbrosacral plexus nerve roots and their peripheral branches, size, course and caliber - Mainstay sequence Axial T2 FS +/- SPAIR -2D images provide detailed fascicular depiction of the lumbrosacral plexus nerve roots and their peripheral branches, size, course and caliber - Mainstay sequence MR Evaluation of Peripheral Nerves Normal MR Evaluation of Peripheral Nerves Abnormal Normal nerves intermediate signal on T1 WI and intermed/slightly inc signal on T2WI Similar size to adjacent arteries / vessels, with a decrease in size distally Normal fascicular pattern on both T2 >> T1 Smooth, continuous morphology, + preserved perineural fat No enhancement Abnormal nerves are hyperintense on T2 WI Focal or diffusely enlarged, larger than adjacent arteries Abnormal fascicular pattern--> enlarged and/or disrupted fascicles Irregular, focal or diffuse deviations, +/- nerve discontinuty, + effacement of peri-neural fat planes + Enhancement in tumors and infections 2/2 disruption of BBB 4
5 MR Evaluation of Peripheral Nerves Abnormal Proximal Cords Abnormal nerves are hyperintense on T2 WI Focal or diffusely enlarged, larger than adjacent arteries Abnormal fascicular pattern--> enlarged and/or disrupted fascicles Irregular, focal or diffuse deviations, +/- nerve discontinuty, + effacement of peri-neural fat planes + Enhancement in tumors and infections 2/2 disruption of BBB SA Lateral SAG T2 FS Posterior Medial Lumbosacral Plexus: Anatomy Overview LS Trunk- L4-S3 Nerves to know: Lateral femoral cutaneous (L2-3) Obturator (L2-4) mostly L3 Femoral (L2-4) mostly L4 Sciatic Nerve (L4-S3) Common Peroneal (L4-S2) mostly L5 Tibial (L4-S3) mostly S1 Pudendal (S2-4) plexus really the medial inferior sacral plex. at sciatic notch. Proximal sacral nerves larger than distal. Lumbosacral Plexus: L3-S1 nerve course Lumbosacral Plexus: L3-S1 nerve course L4 L5 Ax T1 at L4/L5 Ax T1 at L5/S1 Lumbosacral Plexus: L3-S1 nerve course Lumbosacral Plexus: L3-S1 nerve course Ax Ax T1 T1 at at L5/S1 Sacrum- L5 along sacral alae Ax T1 sciatic notch 5
6 Lumbosacral Plexus: L3-S1 nerve course Lumbosacral Plexus: L3-S1 nerve course Obturator nerve ( L2-L4) --> innervates external obturator, adductor muscles Femoral nerve ( L2-L4) --> innervates iliacus, pectineus, prox anterior thigh muscles Sciatic nerve ( L4-S1) --> via peroneal and tibial nerve components inervates leg muscles Ax T1 sciatic notch MR Case Based Review of LS Plexus Pathology Intrinsic neuropathy Acute vs chronic Focal vs Diffuse Tumor /Tumor like lesions NF/Neurofibromatosis Perineuroma Lymphoma Inflammatory Radiation plexitis/ plexopathy CIDP Trauma Intrinsic Neuropathies: Focal Acute 36 YOF awoke with sciatica following colon surgery Intrinsic Neuropathies: Focal Acute Intrinsic Neuropathies: Focal Acute 36 YOF awoke with sciatica following colon surgery 36 YOF awoke with sciatica following colon surgery Edematous sciatic nerve + Perineural edema No denervation change yet = Acute 6
7 Intrinsic Neuropathies: Focal Acute 36 YOF awoke with sciatica following colon surgery Intrinsic Neuropathies: Acute on Chronic 26 yo F with Myesenthia Gravis and L4/L5 radiculopathy on exam Cor T1 FS PG Edematous sciatic nerve + Perineural edema No denervation change yet = Acute + Enhancement 2/2 stretch injury Intrinsic Neuropathies: Acute on Chronic 26 yo F with Myesenthia Gravis and L4/L5 radiculopathy on exam Intrinsic Neuropathies: Acute on Chronic 26 yo F with Myesenthia Gravis and L4/L5 radiculopathy on exam Subtle asymmetrically enlarged and edematous L4 lateral branch and L5 nerves at L5/S1 Acute denervation edema in gluteus minimus muscle with enlargement of the coursing gluteal nerves Enlarged and edematous sciatic nerve Intrinsic Neuropathies: Acute on Chronic 26 yo F with Myesenthia Gravis and L4/L5 radiculopathy on exam Intrinsic Neuropathies: Acute Femoral Gluteus minimus and glut medius muscle innervation --> Superior gluteal nerve (NR L4-S1) 37 yo M found down + bilateral femoral neuropathy and rhabdomyolysis 7
8 Intrinsic Neuropathies: Acute Femoral Intrinsic Neuropathies: Acute Femoral 37 yo M found down + bilateral femoral neuropathy and rhabdomyolysis 37 yo M found down + bilateral femoral neuropathy and rhabdomyolysis Intrinsic Neuropathies: Acute Femoral Intrinsic Neuropathies: Acute Femoral 37 yo M found down + bilateral femoral neuropathy and rhabdomyolysis Iliopsoas myonecrosis 37 yo M found down + bilateral femoral neuropathy and rhabdomyolysis Intrinsic Neuropathies: Acute Femoral Intrinsic Neuropathies: Acute Obturator 55 yo F s/p anterior lumbar fusion with post op adductor weakness 37 yo M found down + bilateral femoral neuropathy and rhabdomyolysis Denervation muscle edema Cor T1 8
9 Intrinsic Neuropathies: Acute Obturator 55 yo F s/p anterior lumbar fusion with post op adductor weakness Intrinsic Neuropathies: Acute Obturator 55 yo F s/p anterior lumbar fusion with post op adductor weakness Cor T1 Cor T1 Denervation edema OE Top 3 Take Home Points: Know the patient s clinical distribution of symptoms Understand the normal course and configuration of the implicated nerves Know the downstream muscle innervation patterns to assist with upstream localization of plexopathy MR Case Based Review of LS Plexus Pathology Intrinsic neuropathy Acute vs chronic Focal vs Diffuse Tumor /Tumor like lesions NF/Neurofibromatosis Perineuroma Lymphoma Inflammatory Radiation plexitis/ plexopathy CIDP Trauma Tumor and Tumor- like Lesions Malignant plexopathy is commonly due to infiltration/ invasion from primary pelvic tumor Prostate cancer, colorectal cancer Tumor and Tumor- like Lesions Malignant plexopathy is commonly due to infiltration/ invasion from primary pelvic tumor Prostate cancer, colorectal cancer Lymphoma, leukemia, melanoma, breast and lung cancer are the most common extra-pelvic primary malignancies to directly invade the LS plexus Mets to the nerves are very rare 9
10 Tumor and Tumor- like Lesions Tumor and Tumor-like Lesions: Neurofibromatosis Malignant plexopathy is commonly due to infiltration/ invasion from primary pelvic tumor Prostate cancer, colorectal cancer Lymphoma, leukemia, melanoma, breast and lung cancer are the most common extra-pelvic primary malignancies to directly invade the LS plexus Mets to the nerves are very rare Intrinsic tumors of the lumbosacral plexus include: PNST/ NF, perineuroma, neurolymphoma 50 yo F NF-1 MIP 45 yo M with NF-1 MR images show manifestations of neurofibromatosis, with more extensive plexiform disease on the left. Tumor and Tumor-like Lesions: Neurofibromatosis Companion tumor cases: Neurofibromatosis and MPNST 50 yo F NF-1 45 yo M with NF-1 35 yo F with NF-1 and diffuse involvement of the BP 40 yo F with NF-1 and MPNST Coronal T1WI C+ FS StatDx MIP Neurofibromas are the most common benign neural tumor to involve the BP and LSP 1/3 of these tumors occur in patients with NF-1; 2/3 s of cases are sporadic Plexiform neurofibromas are pathopneumonic for NF-1, with increased risk of malignant txf Wittenburg KH. Radiographics, Tumor and Tumor like lesions: Perineuroma 35 yo F with sciatica Tumor and Tumor like lesions: Lymphoma 45 yo F with progressive right lower extremity weakness and pain with known Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Dr. Chhabra Dr. Chhabra Cor T1 FS Post contrast Cor T1 FS Post contrast Diffuse nerve enlargement with Iso T1, hyper on T2, avid homogeneous enhancement, with prominent enlarged fasicular pattern Fat planes preserved, no muscle invasion Rodrigues JF et al. Acta Neuropathol Mar; 123 (3): Wadhwa V et al.skeletal Radiology, 2012, V 41, I7, Loss of fascicular architecture Difffuse nerve enlargement Solid tumoral enhancement 10
11 MR Case Based Review of LS Plexus Pathology Intrinsic neuropathy Acute vs chronic Focal vs Diffuse Tumor /Tumor like lesions NF/Neurofibromatosis Perineuroma Lymphoma Inflammatory Radiation plexitis/ plexopathy CIDP Trauma Inflammatory: Radiation induced plexopathy LS plexus often included in the therapeutic FOV for XRT of prostate cancer, colorectal cancer and gynecological tumors Inflammatory: Radiation induced plexopathy LS plexus often included in therapeutic FOV for XRT of prostate cancer, colorectal cancer and gynecological tumors Neuropathy related to radiation therapy tends to occur between 5 and 30 months after treatment, with a peak incidence between 10 and 20 month Inflammatory: Radiation induced plexopathy LS plexus often included in therapeutic FOV for XRT of prostate cancer, colorectal cancer and gynecological tumors Neuropathy related to radiation therapy tends to occur between 5 and 30 months after treatment, with a peak incidence between 10 and 20 month Clinically evident damage is most likely to occur when at least 6000 cgy is administered Inflammatory: Radiation induced plexopathy 59 yo M with progrssive RLE pain and weakness s/p XRT for PCa nodal mets Inflammatory: CIDP AX T1 FS Post contrast Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy Acquired immune-mediated inflammatory disorder of the PNS Progressive symmetrical weakness in both proximal and distal muscles, with sensory deficits and areflexia Patients present with radicular pain, which can be progressive and intermittent Rare; chronic counterpart of GBS Mild to moderate diffuse nerve enlargement within XRT field Variable T2 signal intensity, hypointensity on T1, + perineural edema Mild diffuse enhancement and / or thin tram track pattern of enhancement +/- peripheral soft-tissue scarring in the chronic phase + Downstream denervation changes Crush et al, Radiographics
12 Inflammation: CIDP 26 YO F with progressive neck and back pain progressed over a 2 month period Inflammation: CIDP vs Charcot Marie Tooth (CMT) 26 YO F with CIDP 30 yo F known hx of CMT Bilateral, symmetrical mild diffuse nerve enlargement with abnormal T2/STIR hyperintensity in the classic symmetric form of CIDP DDx: Charcot Marie Tooth and Neurofibromatosis Wadhwa V et al.skeletal Radiology, 2012, V 41, I7, Charcot Marie Tooth: Inherited demyelinating polyneuropathy characterized by distal muscle weakness and atrophy, impaired sensation, and diminished deep tendon reflexes Affected nerves are hyperintense on T2/STIR, diffusely enlarged Thawait et al. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32: Sep Top 3 take home points Clinical history is key to diagnosis Be cautious when interpreting the LS plexus post treatment setting as radiation plexitis and recurrent tumor can look the same! Symmetry is your friend Ensure your FOV covers both sides MR Case Based Review of LS Plexus Pathology Intrinsic neuropathy Acute vs chronic Focal vs Diffuse Tumor /Tumor like lesions NF/Neurofibromatosis Perineuroma Lymphoma Inflammatory Radiation plexitis/ plexopathy CIDP Trauma Traumatic Injuries to LS Plexus Traumatic Injuries to LS Plexus Commonly occur in conjunction with bony injuries Acetabulum and pelvic ring Sacral plexus most frequently injured Commonly occur in conjunction with bony injuries Acetabulum and pelvic ring Sacral plexus most frequently injured Post-operative plexus injuries can occur due to XS compressive / traction during the procedure and / or development of a psoas hematoma 12
13 Cranial Caudal 4/14/2017 Traumatic Injuries: Sacral plexus stretch injury 70 yo F with Sacral insufficiency fracture Asymmetric left sided S1 and S2 nerve edema with focal kinking Lateral L3 spinal root L2 spinal root 70 yo M s/p lateral spine surgery w/ acute lumbar plexopathy Femoral nerve Dr. Chhabra L4-5 interspace L3-4 interspace Medial Dr. Mark Mahan Summary Understanding the complex anatomy of the LS plexus is key to interpretation on MRI Recognizing direct and indirect imaging findings of LS plexus pathology aids in early diagnosis and early intervention Don t forget about the soft tissues! Clinical history is key Thank you! Sarah Stilwill MD Sarah.stilwill@hsc.utah.edu References Kim, Y. H., Lee, P. B., Lee, C. J., Lee, S. C., Kim, Y. C., & Huh, J. (2008). Dermatome variation of lumbosacral nerve roots in patients with transitional lumbosacral vertebrae. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 106(4), table of contents. Seyfert, S. (1997). Dermatome variations in patients with transitional vertebrae. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 63(6), Kim, Su-Fin et al.( 2011). MR imaging mapping of skeletal muscle denervation in entrapment and compressive neuropathies. Radiographics, 31: Filler, A. (2009) Diagnosis and treatment of pudendal nerve entrapment syndrome subtypes: imaging, injections, and minimal access surgery. Neurosurgery Focus, 26(2),1-14 Nerve imaging- Neurofibromatosis- Ferner, R. et al.(2004). Neurofibromatous neuropathy in neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1). J. Med. Genet. 41: Sperfeld, A. et al. (2002). Occurrence and characterization of peripheral nerve involvement in neurofibromatosis type 2. Brain, 125: Staser, K. et al. (2012). Pathogenesis of plexiform neurofibroma: tumor-stromal/hematopoetic interactions in tumor progression. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis., 7: Bouchard,C. et al. (1999). Clinicopathologic findings and prognosis of chronic inflammatory demyelinating ployneuropathy. Neurology, 52(3), Plexopathy mimics- Torriani, M. et al. (2009). Isciofemoral impingement syndrome: an entity with hip pain and abnormalities of the quadratus femoris muscle. AJR, 193: Koulouris, G., Connell, D. (2005). Hamstring muscle complex: an imaging review. Radiographics, 25: O Briem, S., Bui-Mansfield, L. (2007). MRI of quadratus femuris muscle tear: another cause of hip pain. AJR, 189: De Smet, A, Best, T. (2000). MR imaging of the distribution and location of acute hamstring injuries in atheletes. AJR, 174:
Carlos Torres MD, FRCPC, Associate Professor of Radiology Department of Radiology, University of Ottawa
 Carlos Torres MD, FRCPC, Associate Professor of Radiology Department of Radiology, University of Ottawa catorres@toh.on.ca None 1. Simplify the complex imaging anatomy of the BP using clear anatomical
Carlos Torres MD, FRCPC, Associate Professor of Radiology Department of Radiology, University of Ottawa catorres@toh.on.ca None 1. Simplify the complex imaging anatomy of the BP using clear anatomical
Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Structure of Spinal Nerves: Somatic Pathways dorsal root CNS interneuron spinal nerve dorsal ramus somatic sensory
Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Structure of Spinal Nerves: Somatic Pathways dorsal root CNS interneuron spinal nerve dorsal ramus somatic sensory
Lower Limb Nerves. Clinical Anatomy
 Lower Limb Nerves Clinical Anatomy Lumbar Plexus Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh Major nerves.. Lumbar Plexus Nerves relation to psoas m. : Obturator n.
Lower Limb Nerves Clinical Anatomy Lumbar Plexus Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh Major nerves.. Lumbar Plexus Nerves relation to psoas m. : Obturator n.
Lumbar Plexus. Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Major nerves.. Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh
 Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
The Value of MR Neurography for Evaluating Extraspinal Neuropathic Leg Pain: A Pictorial Essay
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:786 794, April 2001 The Value of MR Neurography for Evaluating Extraspinal Neuropathic Leg Pain: A Pictorial Essay Kevin R. Moore, Jay S. Tsuruda, and Andrew T. Dailey Summary:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:786 794, April 2001 The Value of MR Neurography for Evaluating Extraspinal Neuropathic Leg Pain: A Pictorial Essay Kevin R. Moore, Jay S. Tsuruda, and Andrew T. Dailey Summary:
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB. Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Gluteal Region Cutaneous nerve supply of (Gluteal region) 1. Lateral cutaneous
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Gluteal Region Cutaneous nerve supply of (Gluteal region) 1. Lateral cutaneous
Musculoskeletal Imaging Review
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Kassarjian et al. MRI of the Quadratus Femoris Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Ara Kassarjian 1 Xavier Tomas 2 Luis Cerezal 3 Ana Canga 4,5 Eva Llopis 6 Kassarjian A, Tomas
Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Kassarjian et al. MRI of the Quadratus Femoris Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Ara Kassarjian 1 Xavier Tomas 2 Luis Cerezal 3 Ana Canga 4,5 Eva Llopis 6 Kassarjian A, Tomas
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 1 done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 1 done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer What is the importance of plexuses? plexuses provides us the advantage of a phenomenon called convergence
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 1 done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer What is the importance of plexuses? plexuses provides us the advantage of a phenomenon called convergence
LAB Notes#1. Ahmad Ar'ar. Eslam
 LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
CNS & PNS Entrapment. Disclosure - Nothing
 Peripheral Nerve Entrapments That Mimic Spinal Pathology: Evaluation And Treatment Both Medical And Surgical Michel Kliot MD Clinical Professor UCSF Department of NeuroSurgery Director Center For Evaluation
Peripheral Nerve Entrapments That Mimic Spinal Pathology: Evaluation And Treatment Both Medical And Surgical Michel Kliot MD Clinical Professor UCSF Department of NeuroSurgery Director Center For Evaluation
Muscles of the lower extremities. Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
The Lower Limb. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
MR Neurography Technique & Brachial Plexus Evaluation. Avneesh Chhabra, MD
 MR Neurography Technique & Brachial Plexus Evaluation Avneesh Chhabra, MD Introduction The ventral rami of the C5-8 and T1 nerve root unite to form the brachial plexus. It is a network of nerve convergences
MR Neurography Technique & Brachial Plexus Evaluation Avneesh Chhabra, MD Introduction The ventral rami of the C5-8 and T1 nerve root unite to form the brachial plexus. It is a network of nerve convergences
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The thigh. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
The Role of IDEAL and DTI in Peripheral Nerve MR Imaging
 In Practice The Role of IDEAL and DTI in Peripheral Nerve MR Imaging y Darryl. Sneag, MD, Assistant Attending Radiologist, and Hollis G. Potter, MD, Chairman and The Coleman Chair, MRI Research, Department
In Practice The Role of IDEAL and DTI in Peripheral Nerve MR Imaging y Darryl. Sneag, MD, Assistant Attending Radiologist, and Hollis G. Potter, MD, Chairman and The Coleman Chair, MRI Research, Department
Neurologic complications - whom to blame? Benno Rehberg Médecin adjoint agrégé Unité d anesthésiologie gynéco-obstétricale, HUG
 Neurologic complications - whom to blame? Benno Rehberg Médecin adjoint agrégé Unité d anesthésiologie gynéco-obstétricale, HUG SAOA spring meeting 2015 The simple surgical answer: outline Epidemiology
Neurologic complications - whom to blame? Benno Rehberg Médecin adjoint agrégé Unité d anesthésiologie gynéco-obstétricale, HUG SAOA spring meeting 2015 The simple surgical answer: outline Epidemiology
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH
 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH Peter G Gerbino, MD, FACSM Orthopedic Surgeon Monterey Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Monterey, CA TPC, San Diego, 2017 The lecturer has no
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH Peter G Gerbino, MD, FACSM Orthopedic Surgeon Monterey Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Monterey, CA TPC, San Diego, 2017 The lecturer has no
Imaging lumbosacral plexus using CT and MR: Anatomic and clinical correlations
 Imaging lumbosacral plexus using CT and MR: Anatomic and clinical correlations Poster No.: C-737 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: S. Belião, Á. Almeida; Lisbon/PT Keywords:
Imaging lumbosacral plexus using CT and MR: Anatomic and clinical correlations Poster No.: C-737 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: S. Belião, Á. Almeida; Lisbon/PT Keywords:
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint. Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa
 The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
Field Strength. California clinic scrutinizes peripheral nerves role in symptomology
 Field Strength Publication for the Philips MRI Community California clinic scrutinizes peripheral s role in symptomology Oak Tree Medical Center, builds expertise in brachial/sacral plexus MRI This article
Field Strength Publication for the Philips MRI Community California clinic scrutinizes peripheral s role in symptomology Oak Tree Medical Center, builds expertise in brachial/sacral plexus MRI This article
Electrodiagnostics for Back & Neck Pain. Steven Andersen, MD Providence Physiatry Clinic
 Electrodiagnostics for Back & Neck Pain Steven Andersen, MD Providence Physiatry Clinic Electrodiagnostics Electromyography (EMG) Needle EMG exam (NEE) Nerve conduction studies (NCS) Motor Sensory Late
Electrodiagnostics for Back & Neck Pain Steven Andersen, MD Providence Physiatry Clinic Electrodiagnostics Electromyography (EMG) Needle EMG exam (NEE) Nerve conduction studies (NCS) Motor Sensory Late
From Targeted Fascicular Biopsy of Major Nerve to Targeted Cutaneous Nerve Biopsy: Implementing Clinical Anatomy Can Catalyze a Paradigm Shift
 Clinical Anatomy 31:616 621 (2018) EDITORIAL From Targeted Fascicular Biopsy of Major Nerve to Targeted Cutaneous Nerve Biopsy: Implementing Clinical Anatomy Can Catalyze a Paradigm Shift TOMAS MAREK,
Clinical Anatomy 31:616 621 (2018) EDITORIAL From Targeted Fascicular Biopsy of Major Nerve to Targeted Cutaneous Nerve Biopsy: Implementing Clinical Anatomy Can Catalyze a Paradigm Shift TOMAS MAREK,
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
Where should you palpate the pulse of different arteries in the lower limb?
 Where should you palpate the pulse of different arteries in the lower limb? The femoral artery In the femoral triangle, its pulse is easily felt just inferior to the inguinal ligament midway between the
Where should you palpate the pulse of different arteries in the lower limb? The femoral artery In the femoral triangle, its pulse is easily felt just inferior to the inguinal ligament midway between the
Regional Anaesthesia
 Regional Anaesthesia Lower limb anatomy and blocks Hip and Knee Joint Hip Joint: Nerve supply Lumbar plexus Femoral nerve through the nerve to the Rectus Femoris Ant division of the Obturator nerve The
Regional Anaesthesia Lower limb anatomy and blocks Hip and Knee Joint Hip Joint: Nerve supply Lumbar plexus Femoral nerve through the nerve to the Rectus Femoris Ant division of the Obturator nerve The
MR Imaging in Athlete s Hip/Pelvis
 MR Imaging in Athlete s Hip/Pelvis Tara Lawrimore, MD FRCPC Department of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School No disclosures MR and Hip Pain in the
MR Imaging in Athlete s Hip/Pelvis Tara Lawrimore, MD FRCPC Department of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School No disclosures MR and Hip Pain in the
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL
 Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
MSK Imaging Conference. 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology
 MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT ***
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Hip pain in children may refer to the knee from Legg-Calve-Perthes
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Hip pain in children may refer to the knee from Legg-Calve-Perthes
Lower Limb Dr. Robin Paudel
 Lower Limb n What is a limb? n Skeleton n Joints n Pelvis or limb girdle n Hip/Hip Muscles n Lumber and sacral plexus getting spinal nerves out onto limb n Muscles anterior and posterior compartments n
Lower Limb n What is a limb? n Skeleton n Joints n Pelvis or limb girdle n Hip/Hip Muscles n Lumber and sacral plexus getting spinal nerves out onto limb n Muscles anterior and posterior compartments n
Mohammad Ashraf. Abdulrahman Al-Hanbali. Ahmad Salman. 1 P a g e
 - 7 Mohammad Ashraf Abdulrahman Al-Hanbali Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Structures under the cover of Gluteus Maximus: 1-Bones: Ileum, Femur (Head, greater trochanter and gluteal tuberosity), Ischium (ischial
- 7 Mohammad Ashraf Abdulrahman Al-Hanbali Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Structures under the cover of Gluteus Maximus: 1-Bones: Ileum, Femur (Head, greater trochanter and gluteal tuberosity), Ischium (ischial
Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for
 Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
Synapse Homework. Back page last question not counted. 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts. 26/34 students answered correctly!
 Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
MR imaging of the quadratus femoris: Anatomic considerations and pathologic lesions
 MR imaging of the quadratus femoris: Anatomic considerations and pathologic lesions Poster No.: C-2355 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: A. Kassarjian, X. Tomás,
MR imaging of the quadratus femoris: Anatomic considerations and pathologic lesions Poster No.: C-2355 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: A. Kassarjian, X. Tomás,
Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis
 Hip Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis The terms hip and pelvis are frequently used interchangeably, but strictly speaking, the pelvis is a girdle of bones and the hip is a joint. The pelvis consists of The sacrum
Hip Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis The terms hip and pelvis are frequently used interchangeably, but strictly speaking, the pelvis is a girdle of bones and the hip is a joint. The pelvis consists of The sacrum
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
Evaluation of Posterior Hip Pain
 Evaluation of Posterior Hip Pain Anthony J. Ferretti, D.O., MHSA Hip Pain in the Adult Various etiologies: Traumatic Infectious Neurovascular Degenerative Congenital Pathologic 1 Hip Pain Complex interaction
Evaluation of Posterior Hip Pain Anthony J. Ferretti, D.O., MHSA Hip Pain in the Adult Various etiologies: Traumatic Infectious Neurovascular Degenerative Congenital Pathologic 1 Hip Pain Complex interaction
ANATOMY TEAM GLUTEAL REGION & BACK OF THIGH
 ANATOMY TEAM GLUTEAL REGION & BACK OF THIGH OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to identify and discuss: Contents of gluteal region: Groups of Glutei muscles and small muscles
ANATOMY TEAM GLUTEAL REGION & BACK OF THIGH OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to identify and discuss: Contents of gluteal region: Groups of Glutei muscles and small muscles
Organization of the Lower Limb Audrone Biknevicius, Ph.D. Dept. Biomedical Sciences, OU HCOM at Dublin Clinical Anatomy Immersion 2014
 Organization of the Lower Limb Audrone Biknevicius, Ph.D. Dept. Biomedical Sciences, OU HCOM at Dublin Clinical Anatomy Immersion 2014 www.thestudio1.co.za LIMB FUNCTION choco-locate.com blog.coolibar.com
Organization of the Lower Limb Audrone Biknevicius, Ph.D. Dept. Biomedical Sciences, OU HCOM at Dublin Clinical Anatomy Immersion 2014 www.thestudio1.co.za LIMB FUNCTION choco-locate.com blog.coolibar.com
lower limb Anterior Compartment: lecture 3 The deep fascia ( fascia lata) divides the thigh into 3 compartments:
 lower limb lecture 3 The deep fascia ( fascia lata) divides the thigh into 3 compartments: 1. Anterior Extensor compartment 2. Medial Adductor compartment 3. Posterior Flexor compartment Anterior Compartment:
lower limb lecture 3 The deep fascia ( fascia lata) divides the thigh into 3 compartments: 1. Anterior Extensor compartment 2. Medial Adductor compartment 3. Posterior Flexor compartment Anterior Compartment:
Sciatica due to pelvic hematoma: case report
 Romanian Neurosurgery (2016) XXX 4: 507 511 507 DOI: 10.1515/romneu-2016-0080 Sciatica due to pelvic hematoma: case report Umit Kocaman 1, Muhammet Bahadir Yilmaz 1, Hakan Yilmaz 2 1 University of Izmir
Romanian Neurosurgery (2016) XXX 4: 507 511 507 DOI: 10.1515/romneu-2016-0080 Sciatica due to pelvic hematoma: case report Umit Kocaman 1, Muhammet Bahadir Yilmaz 1, Hakan Yilmaz 2 1 University of Izmir
Muscles of Gluteal Region
 1 The Gluteal Region In the gluteal region the skin is tough with many layers underneath. Directly under it is the superficial fascia followed by the deep fascia then the muscles and the bones of the thigh.
1 The Gluteal Region In the gluteal region the skin is tough with many layers underneath. Directly under it is the superficial fascia followed by the deep fascia then the muscles and the bones of the thigh.
MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB
 MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB Spinal Cord Lumbar and Sacral Regions Spinal cord Dorsal root ganglion Conus medullaris Cauda equina Dorsal root ganglion of the fifth lumbar nerve End of subarachnoid space
MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB Spinal Cord Lumbar and Sacral Regions Spinal cord Dorsal root ganglion Conus medullaris Cauda equina Dorsal root ganglion of the fifth lumbar nerve End of subarachnoid space
lesser trochanter of femur lesser trochanter of femur iliotibial tract (connective tissue) medial surface of proximal tibia
 LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
rotation of the hip Flexion of the knee Iliac fossa of iliac Lesser trochanter Femoral nerve Flexion of the thigh at the hip shaft of tibia
 Anatomy of the lower limb Anterior & medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Hayder The fascia lata encloses the entire thigh like a sleeve/stocking. Three intramuscular fascial septa (lateral, medial, and
Anatomy of the lower limb Anterior & medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Hayder The fascia lata encloses the entire thigh like a sleeve/stocking. Three intramuscular fascial septa (lateral, medial, and
Non-arthritic anterior hip pain in the younger patient: examination and intervention strategies
 Non-arthritic anterior hip pain in the younger patient: examination and intervention strategies Melodie Kondratek, PT, DScPT, OMPT Bryan Kuhlman, PT, DPT, OMPT Oakland University Orthopedic Spine and Sports
Non-arthritic anterior hip pain in the younger patient: examination and intervention strategies Melodie Kondratek, PT, DScPT, OMPT Bryan Kuhlman, PT, DPT, OMPT Oakland University Orthopedic Spine and Sports
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
Organization of the Lower Limb
 Organization of the Lower Limb Limb Development Lower limb develops in an aterolateral position at the level of the L2 to S3 trunk segments Great toe positioned cephalic direction with the soles of the
Organization of the Lower Limb Limb Development Lower limb develops in an aterolateral position at the level of the L2 to S3 trunk segments Great toe positioned cephalic direction with the soles of the
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis
 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
Lower Extremity Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia. Stephanie Duffy, CRNA Regional Anesthesia Faculty Acute Pain Service NMCSD
 Lower Extremity Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia Stephanie Duffy, CRNA Regional Anesthesia Faculty Acute Pain Service NMCSD Objectives Review anatomy of lumbosacral plexus Lumbar plexus blocks Psoas
Lower Extremity Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia Stephanie Duffy, CRNA Regional Anesthesia Faculty Acute Pain Service NMCSD Objectives Review anatomy of lumbosacral plexus Lumbar plexus blocks Psoas
Variation in Bifurcation of Sciatic Nerve Found in Gluteal Region in Dissection Deepa 1 * and Bhanu Pratap Singh 2
 CASE STUDY www.ijapc.com e-issn 2350-0204 Variation in Bifurcation of Sciatic Nerve Found in Gluteal Region in Dissection Deepa 1 * and Bhanu Pratap Singh 2 1 Dept. of Sharira Rachana, National Institute
CASE STUDY www.ijapc.com e-issn 2350-0204 Variation in Bifurcation of Sciatic Nerve Found in Gluteal Region in Dissection Deepa 1 * and Bhanu Pratap Singh 2 1 Dept. of Sharira Rachana, National Institute
Evaluation of the Hip
 Evaluation of the Hip Adam Lewno, DO PCSM Fellow, University of Michigan Primary Care Sports Update 2017 Disclosures Financial: None Images: I would like to acknowledge the work of the original owners
Evaluation of the Hip Adam Lewno, DO PCSM Fellow, University of Michigan Primary Care Sports Update 2017 Disclosures Financial: None Images: I would like to acknowledge the work of the original owners
Imaging findings of Lower Extremity Peripheral Nerves in Charcot-Marie Tooth
 Original Research Imaging findings of Lower Extremity Peripheral Nerves in Charcot-Marie Tooth Jonelle M Petscavage-Thomas*, Sangeeta Chaudhary, Stephanie A Bernard, Eric A Walker and Gary A. Thomas Department
Original Research Imaging findings of Lower Extremity Peripheral Nerves in Charcot-Marie Tooth Jonelle M Petscavage-Thomas*, Sangeeta Chaudhary, Stephanie A Bernard, Eric A Walker and Gary A. Thomas Department
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves mediate reactions to environmental changes. B. The spinal cord has several functions. 1. It processes reflexes. 2. It is
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves mediate reactions to environmental changes. B. The spinal cord has several functions. 1. It processes reflexes. 2. It is
Lower limb summary. Anterior compartment of the thigh. Done By: Laith Qashou. Doctor_2016
 Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
MR Neurography: Cervical Plexus and Shoulder Girdle
 MR Neurography: Cervical Plexus and Shoulder Girdle Gustav Andreisek, MD, MBA 3rd MSK MRI Meeting 2016 Date: April 23th, 2016 Time: 11:10-11:30 AM Head MSK and MR Imaging Department of Radiology University
MR Neurography: Cervical Plexus and Shoulder Girdle Gustav Andreisek, MD, MBA 3rd MSK MRI Meeting 2016 Date: April 23th, 2016 Time: 11:10-11:30 AM Head MSK and MR Imaging Department of Radiology University
Human Anatomy. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities
 Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities Prostate Cancer Leiomyoma Retroverted Anteverted Ovarian Cyst Gone Wrong Fibroid (Leiomyoma) IUD Ovary Hysterectomy? What are we to see when imaging a female pelvis
Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities Prostate Cancer Leiomyoma Retroverted Anteverted Ovarian Cyst Gone Wrong Fibroid (Leiomyoma) IUD Ovary Hysterectomy? What are we to see when imaging a female pelvis
Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy: MR Imaging
 Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy 85 Chapter 5 Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy: MR Imaging Neurological symptoms and signs of brachial plexopathy may develop in patients who have had radiation
Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy 85 Chapter 5 Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy: MR Imaging Neurological symptoms and signs of brachial plexopathy may develop in patients who have had radiation
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
Anatomy and principles of the fascia iliaca block
 Anatomy and principles of the fascia iliaca block Dr Ganesh Kumar 23 rd November 2016 Courtesy Dr Fred Sage Objectives Why do peripheral nerves blocks work? Why choose FIB over FNB? How does it work? How
Anatomy and principles of the fascia iliaca block Dr Ganesh Kumar 23 rd November 2016 Courtesy Dr Fred Sage Objectives Why do peripheral nerves blocks work? Why choose FIB over FNB? How does it work? How
Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord
 Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord M/O Chapters 16 69. Describe the relationship(s) between the following structures: root, nerve, ramus, plexus, tract, nucleus, and ganglion. 70. Trace the path of information
Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord M/O Chapters 16 69. Describe the relationship(s) between the following structures: root, nerve, ramus, plexus, tract, nucleus, and ganglion. 70. Trace the path of information
DISSECTION SCHEDULE. Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial)
 DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
Organization of the Lower Limb
 Organization of the Lower Limb Most illustrations from: Thieme Atlas of Anatomy: Musculoskeletal System. M Schuenke, et al, 2006. Anatomy: A Regional Atlas of the Human Body. Carmine Clemente, 4th edition.
Organization of the Lower Limb Most illustrations from: Thieme Atlas of Anatomy: Musculoskeletal System. M Schuenke, et al, 2006. Anatomy: A Regional Atlas of the Human Body. Carmine Clemente, 4th edition.
Surgery Under Regional Anesthesia
 Surgery Under Regional Anesthesia Jean Daniel Eloy, MD Assistant Professor Residency Program Director Rutgers-New Jersey Medical School Rutgers The State University of New Jersey Peripheral Nerve Block
Surgery Under Regional Anesthesia Jean Daniel Eloy, MD Assistant Professor Residency Program Director Rutgers-New Jersey Medical School Rutgers The State University of New Jersey Peripheral Nerve Block
Electrophysiology of Brachial and Lumbosacral Plexopathies
 18 Electrophysiology of Brachial and Lumbosacral Plexopathies Juan A. Acosta and Elizabeth M. Raynor Summary Brachial and lumbosacral plexopathies represent a heterogeneous group of disorders including
18 Electrophysiology of Brachial and Lumbosacral Plexopathies Juan A. Acosta and Elizabeth M. Raynor Summary Brachial and lumbosacral plexopathies represent a heterogeneous group of disorders including
Snapping Hip and Impingement
 Snapping Hip and Impingement Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board: GE,
Snapping Hip and Impingement Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board: GE,
MRI of the Hips and Pelvis
 MRI of the Hips and Pelvis Hips and Pelvis Protocols Vascular abnormalities Fractures Soft tissues Labrum and FAI Hips and Pelvis Protocols Vascular abnormalities Fractures Soft tissues Labrum and FAI
MRI of the Hips and Pelvis Hips and Pelvis Protocols Vascular abnormalities Fractures Soft tissues Labrum and FAI Hips and Pelvis Protocols Vascular abnormalities Fractures Soft tissues Labrum and FAI
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
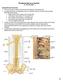 Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
66 yr old female with groin and hip pain. Paul Jabour, MD
 66 yr old female with groin and hip pain Paul Jabour, MD 2 months later 12 months later 14 months after initial presentation Acetabular Insufficiency Fracture Pelvic stress fracture Fatigue
66 yr old female with groin and hip pain Paul Jabour, MD 2 months later 12 months later 14 months after initial presentation Acetabular Insufficiency Fracture Pelvic stress fracture Fatigue
A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies
 Objectives A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies Tahseen Mozaffar, MD FAAN Professor and Vice Chair of Neurology Director, UC Irvine-MDA ALS and Neuromuscular Center Director, Neurology Residency Training
Objectives A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies Tahseen Mozaffar, MD FAAN Professor and Vice Chair of Neurology Director, UC Irvine-MDA ALS and Neuromuscular Center Director, Neurology Residency Training
Bony Anatomy. Femur. Femoral Head Femoral Neck Greater Trochanter Lesser Trochanter Intertrochanteric Crest Intertrochanteric Line Gluteal Tuberosity
 Hip Anatomy Bony Anatomy Femur Femoral Head Femoral Neck Greater Trochanter Lesser Trochanter Intertrochanteric Crest Intertrochanteric Line Gluteal Tuberosity Bony Anatomy Pelvic Girdle Acetabulum 3 bones
Hip Anatomy Bony Anatomy Femur Femoral Head Femoral Neck Greater Trochanter Lesser Trochanter Intertrochanteric Crest Intertrochanteric Line Gluteal Tuberosity Bony Anatomy Pelvic Girdle Acetabulum 3 bones
Objectives. Non-Traumatic Muscle Pathologies. Abnormal Muscle Signal Intensity. Inflammatory Myositis. Polymyostis / Dermatomyositis.
 Non-Traumatic Muscle Pathologies Ali Naraghi Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology Joint Department of Medical Imaging University of Toronto Objectives Define the range of non-traumatic pathologies affecting
Non-Traumatic Muscle Pathologies Ali Naraghi Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology Joint Department of Medical Imaging University of Toronto Objectives Define the range of non-traumatic pathologies affecting
Lesson 24. A & P Hip
 Lesson 24 A & P Hip 1 Aims of the Session This session will allow candidates to have an understanding of the bony prominences and soft tissues of the hip 2 Learning Outcomes By the end of the lesson the
Lesson 24 A & P Hip 1 Aims of the Session This session will allow candidates to have an understanding of the bony prominences and soft tissues of the hip 2 Learning Outcomes By the end of the lesson the
Main Menu. Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
Direct visualization of nerves can influence surgery decisions
 Direct visualization of nerves can influence surgery decisions FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - April 2018 www.philips.com/fieldstrength Northern Fukushima MRI team adds 3D NerveVIEW sequence
Direct visualization of nerves can influence surgery decisions FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - April 2018 www.philips.com/fieldstrength Northern Fukushima MRI team adds 3D NerveVIEW sequence
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Chapter 12
 Chapter 12 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 Spinal Cord Extends from foramen magnum to second lumbar vertebra Segmented: Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar & Sacral Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves Not uniform
Chapter 12 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 Spinal Cord Extends from foramen magnum to second lumbar vertebra Segmented: Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar & Sacral Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves Not uniform
Lecture 08 THIGH MUSCLES ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT. Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai. Dated:
 Lecture 08 THIGH MUSCLES ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 11.02.2017 INTRODUCTION to the thigh Muscles. The musculature of the thigh can be split into three sections by intermuscular
Lecture 08 THIGH MUSCLES ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 11.02.2017 INTRODUCTION to the thigh Muscles. The musculature of the thigh can be split into three sections by intermuscular
Hailee Gibson, CCPA Neurosurgery Physician Assistant. Windsor Neurosurgery & Spine Associates. Windsor Regional Hospital Ouellette Campus
 Hailee Gibson, CCPA Neurosurgery Physician Assistant Windsor Neurosurgery & Spine Associates Windsor Regional Hospital Ouellette Campus Disclosures I have no disclosures Learning Objectives Provide information
Hailee Gibson, CCPA Neurosurgery Physician Assistant Windsor Neurosurgery & Spine Associates Windsor Regional Hospital Ouellette Campus Disclosures I have no disclosures Learning Objectives Provide information
Case Studies, Impairment of the Spine in Washington State
 Case Studies, Impairment of the Spine in Washington State NAOEM at Skamania, 2015 25 Sep, 2015 Tim Gilmore, MD Several Slides from this Presentation Borrowed with permission from the Washington State Department
Case Studies, Impairment of the Spine in Washington State NAOEM at Skamania, 2015 25 Sep, 2015 Tim Gilmore, MD Several Slides from this Presentation Borrowed with permission from the Washington State Department
Lumbar Plexopathy Caused by Metastatic Tumor, Which Was Mistaken for Postoperative Femoral Neuropathy
 Case Report Korean J Pain 2011 December; Vol. 24, No. 4: 226-230 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.4.226 Lumbar Plexopathy Caused by Metastatic Tumor, Which Was Mistaken
Case Report Korean J Pain 2011 December; Vol. 24, No. 4: 226-230 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.4.226 Lumbar Plexopathy Caused by Metastatic Tumor, Which Was Mistaken
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Back Pain. John W. Engstrom, MD December 16, Disclosures. A Clinical Approach to the Evaluation of Back Pain and Lumbar Radiculopathy
 Disclosures Nothing to declare --- or --- Significant ownership interests Speaker bureaus, honorarium, grants A Clinical Approach to the Evaluation of and Lumbar Radiculopathy John Engstrom, MD Acute Low
Disclosures Nothing to declare --- or --- Significant ownership interests Speaker bureaus, honorarium, grants A Clinical Approach to the Evaluation of and Lumbar Radiculopathy John Engstrom, MD Acute Low
Hip joint and pelvic girdle. Lower Extremity. Pelvic Girdle 6/5/2017
 Hip joint and pelvic girdle Lower Extremity The relationship between the pelvic girdle and hip is similar to that between the shoulder girdle and shoulder joint. The lower limbs are attached to the axial
Hip joint and pelvic girdle Lower Extremity The relationship between the pelvic girdle and hip is similar to that between the shoulder girdle and shoulder joint. The lower limbs are attached to the axial
Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles.
 L 8 A B O R A T O R Y Thigh MEDIAL THIGH Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles. Identify the actions of these
L 8 A B O R A T O R Y Thigh MEDIAL THIGH Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles. Identify the actions of these
Chapter 13. The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Cord Protection. Meninges. Together with brain forms the CNS Functions
 Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Surgery. Conus medullaris and Cauda Equina Syndromes. Anatomy. See online here
 Surgery Conus medullaris and Cauda Equina Syndromes See online here Conus medullaris and cauda equina syndromes are spinal cord injuries that involve injury to the lumbosacral segment of the spinal cord.
Surgery Conus medullaris and Cauda Equina Syndromes See online here Conus medullaris and cauda equina syndromes are spinal cord injuries that involve injury to the lumbosacral segment of the spinal cord.
Case Example. Nerve Entrapments in the Lower limb
 Nerve Entrapments in the Lower limb February, 2013 William S. Pease, M.D. Ernest W. Johnson Professor of PM&R Case Example CC: Right ankle dorsiflexion weakness with minimal paresthesias HPI: 87 year-old
Nerve Entrapments in the Lower limb February, 2013 William S. Pease, M.D. Ernest W. Johnson Professor of PM&R Case Example CC: Right ankle dorsiflexion weakness with minimal paresthesias HPI: 87 year-old
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Dana Alrafaiah. - Amani Nofal. - Ahmad Alsalman. 1 P a g e
 - 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
- 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
Anatomy of Peripheral Nerve 가톨릭대학교 재활의학과 김재민
 Anatomy of Peripheral Nerve 가톨릭대학교 재활의학과 김재민 Contents US appearance of nerves Scanning technique Peripheral nerve pathology Nerves of arm Nerves of leg US Appearance of Nerve Multiple longitudinal hypoechoic
Anatomy of Peripheral Nerve 가톨릭대학교 재활의학과 김재민 Contents US appearance of nerves Scanning technique Peripheral nerve pathology Nerves of arm Nerves of leg US Appearance of Nerve Multiple longitudinal hypoechoic
Outline. Introduction / Epidemiology. Anatomy / Pain generators. Diagnosis. Treatment. Most Important lecture!!
 Acute Low Back Pain Outline Introduction / Epidemiology. Most Important lecture!! Anatomy / Pain generators Diagnosis Treatment Course Objectives Know the RED FLAGS in history taking. Know the Pain Generators
Acute Low Back Pain Outline Introduction / Epidemiology. Most Important lecture!! Anatomy / Pain generators Diagnosis Treatment Course Objectives Know the RED FLAGS in history taking. Know the Pain Generators
How to Think like a Neurologist Review of Exam Process and Assessment Findings
 Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
61 year-old woman with right thigh lump
 61 year-old woman with right thigh lump Skin marker was placed about here TFL is enlarged TFL is enlarged Hypertrophy of the TFL muscle, presenting as palpable proximal anterior thigh mass Unilateral hypertrophy
61 year-old woman with right thigh lump Skin marker was placed about here TFL is enlarged TFL is enlarged Hypertrophy of the TFL muscle, presenting as palpable proximal anterior thigh mass Unilateral hypertrophy
MR Imaging of the Cauda Equina in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
 MR Imaging of the Cauda Equina in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease Poster No.: C-0741 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: Y. Tatewaki, S. Nishiyama, Y. Kato, T. Murata, S. Mugikura, L. Li,
MR Imaging of the Cauda Equina in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease Poster No.: C-0741 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: Y. Tatewaki, S. Nishiyama, Y. Kato, T. Murata, S. Mugikura, L. Li,
