Recruitment of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Blood Vessels by Orthotopic Liver Tumors Imaged in Red Fluorescent Protein (RFP) Transgenic Nude Mice
|
|
|
- Maximillian Goodman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Recruitment of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Blood Vessels by Orthotopic Liver Tumors Imaged in Red Fluorescent Protein (RFP) Transgenic Nude Mice ATSUSHI SUETSUGU 1,2,3, YUKIHIKO HIROSHIMA 2,3, TAKURO MATSUMOTO 1, KOSUKE HASAGAWA 1, MIKI NAKAMURA 1, MASAHITO SHIMIZU 1, SHIGETOYO SAJI 1, HISATAKA MORIWAKI 1, MICHAEL BOUVET 3 and ROBERT M. HOFFMAN 2,3 1 Gifu University Graduate School of Medicine, Gifu, Japan; 2 AntiCancer, Inc. San Diego, CA, U.S.A; 3 Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego, CA, U.S.A. Abstract. Background/Aim: The tumor microenvironment (TME) is critical for tumor growth and progression. We report here an imageable model of the TME of orthotopic liver cancer. Materials and Methods: The transgenic red fluorescent protein (RFP)-expressing nude mouse was used as the host. The RFP nude mouse expresses RFP in all organs. Non-colored Huh-7 human hepatoma cells were injected in the spleen of RFP nude mice to establish an orthotopic liver cancer model. TME formation resulting from the orthotopic liver tumor was observed using the Olympus OV100 small animal fluorescence imaging system. Results: Non-colored liver cancer cells formed tumor colonies in the liver 28 days after cell transplantation to the spleen. RFP-expressing host cells and blood vessels were recruited by the liver tumors as visualized by fluorescence imaging. A desmin- and sirus-red-positive area increased around and within the liver tumor over time. Conclusion: These results indicate cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) were recruited by the liver tumors suggesting that CAFs, along with the angiogenic tumor blood vessels, were necessary for livertumor growth and could serve as visible therapeutic targets. Our laboratory previously developed a color-coded model of the tumor microenvironment (TME) using red fluorescent protein (RFP), cyan fluorescent protein (CFP), and green fluorescent protein (GFP) transgenic nude mice as hosts for cancer cells expressing a different color fluorescent protein (1-11). Correspondence to: Robert M. Hoffman, Ph.D., AntiCancer, Inc., 7917 Ostrow Street, San Diego, CA 92111, U.S.A. Tel: , Fax: , all@anticancer.com Key Words: Tumor microenvironment, cancer-associated fibroblasts, blood vessels, liver metastasis, RFP, fluorescence; color-coded imaging. Our color-coded TME imaging technology was used by Egeblad et al. (12) to show that stromal cells had higher motility in the periphery of the tumor. Our color-coded model was also used by Egeblad to demonstrate macrophages, fibroblasts, dendritic cells, and lymphocytes in the TME (12). We have also demonstrated, using color-coded imaging, that tumors acquired fluorescent protein-expressing stroma over time, during growth in fluorescent protein-expressing nude mice, including during passage. The acquired stroma grew along with the tumor. The bright stroma enabled non-invasive imaging of a pancreatic-cancer patient-derived orthotopic xenograft (PDOX) mouse model (7-9). We previously showed that CAFs are recruited by metastasis, which stimulate their growth (6, 8, 11). We also discovered that stromal cells are necessary for metastasis (13). We previously used a GFP-expressing transgenic nude mouse as the host which expresses GFP in all organs, but only dimly in the parenchymal cells of the liver, to study the role of the TME in liver metastasis of colon cancer. Noncolored HCT-116 human colon cancer cells were injected in the spleen of GFP nude mice, which led to the formation of experimental liver metastasis. TME formation resulting from the liver metastasis was observed using the Olympus OV100 small animal fluorescence imaging system. HCT-116 cells formed tumor colonies in the liver by 28 days after cell transplantation to the spleen. GFP-expressing host cells were recruited by the metastatic tumors as visualized by fluorescence imaging. A desmin-positive area increased around and within the liver metastasis over time, suggesting cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) were recruited by the liver metastasis (6). The present study images the recruitment of blood vessels and cancer-associated fibroblasts by orthotopic liver tumors growing in transgenic RFP nude mice /2015 $
2 Figure 1. A: Schematic representation of experimental protocol. Non-colored Huh-7 human hepatoma cells ( /50 μl) were injected in the spleen of RFP nude mice to establish an orthotopic liver tumor model. B: Imaging of an orthotopic liver tumor on day 28 after cancer-cell injection. RFP fluorescence was observed in the orthotopic liver tumor. The liver tumor was observed using the Olympus OV100 small animal fluorescence imaging system. Upper panels are low magnification (left panel: bright-field; central panel: fluorescence; right panel: merge). Yellow arrows indicate non-colored tumor (Bar=10 mm). Lower panels are high magnification (left panel: bright-field; central panel: fluorescence; right panel: merge). Green arrows indicate non-color tumor (Bar=1 mm). Materials and Methods Cell culture. Huh-7 human liver cancer cells were maintained in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% FCS (14) as well as with penicillin and streptomycin (Gibco BRL, Grand Island, NY, USA). The Huh-7 cell line was cultured at 37 C in a 5% incubator. Transgenic red fluorescent protein-expressing nude mice. Transgenic red fluorescent protein (RFP) nude mice (AntiCancer, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA), expressing RFP (DsRed.T3) under the control of a chicken β-actin promoter and cytomegalovirus enhancer, were used in this study. All tissues from this transgenic line, with the exception of erythrocytes, were red under blue excitation light. Orthotopic liver-cancer model. Non-colored Huh-7 cells were first harvested by trypsinization and washed three times with cold serumfree medium and then resuspended with serum-free RPMI 1640 medium. RFP nude mice were anesthetized with a ketamine mixture (0.02 ml solution of 20 mg/kg ketamine, 15.2 mg/kg xylazine, and 5822
3 Suetsugu et al: Imaging Recruitment of Stroma by Liver Cancer Figure 2. Fluorescence imaging of liver sections. A: High magnification image of the orthotopic Huh-7 liver tumors. The orthotopic liver tumor was observed using the Olympus OV100 small animal fluorescence imaging system. Yellow arrows indicate tumor vessels. Green arrows indicate RFP stroma. (Bar=500 μm). B: Image of Huh-7 liver tumor section. Blue arrows indicate Huh-7 tumor. Green arrows indicate RFP stroma recruited by the liver tumor. (left panel: Bar=2 mm); (right panel: Bar=200 μm). Figure 3. Hematoxylin and eosin, sirus-red and desmin staining. Liver sections from RFP nude mice with orthotopic Huh-7 liver tumors were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), sirus-red and desmin. There were significantly more sirus-red and desmin positive areas in the tumor than in the non-tumor part of the liver. The liver tumor contained RFP-, and desmin-expressing cells, sirus-red-stained cells as well as suggesting that cancerassociated fibroblast (CAFs) have a role in liver tumor development. Left panel: H&E stain; central panel: sirus-red stain; right panel: desmin stain. Non-colored Huh-7 liver tumor sections (original magnification, 200). Red arrows indicate sirus red- positive area. Blue arrows indicate desminpositive area. (Bar=100 μm) mg/kg acepromazine maleate) injected into the peritoneal cavity. Non-colored Huh-7 cancer cells ( ) were injected in the spleen of RFP nude mice during open laparotomy in order for tumors in the liver to form (Figure 1). In vivo imaging. For in vivo imaging based on fluorescent proteins (16-19), the Olympus OV100 Small Animal Imaging System (Olympus Corp., Tokyo, Japan) was used. The Olympus OV100, which contains an MT-20 light source (Olympus Biosystems, Planegg, Germany) and DP70 CCD camera (Olympus), were used for cellular imaging in live mice. The optics of the OV100 fluorescence imaging system have been specially developed for macro-imaging as well as micro-imaging with high light-gathering capacity. High-resolution images were captured directly on a PC (Fujitsu Siemens, Munich, Germany). Images were processed for contrast and brightness and analyzed with the use of Paint Shop Pro 8 and CellR (Olympus Biosystems) (20). 5823
4 Histological and immunohistochemical analysis. The host livers were fixed with 10% buffered formalin, sectioned at a thickness of 4 μm, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Desmin was stained with anti-desmin antibody (Lab Vision, Fremont, CA, USA) using an avidin biotin peroxidase complex technique (Vector, Burlingame, CA). Collagen deposition was assessed by Sirius-red staining. Results and Discussion Imaging recruitment of blood vessels and cancerassociated fibroblasts by a non-colored orthotopic liver tumor. Huh-7 human liver cancer cells were injected in the spleen of RFP nude mice. Low-magnification imaging showed the contrast between the non-colored liver tumor and RFP-expressing liver (Figure 1). High-magnification fluorescence imaging showed extensive RFP fluorescence in the tumor due to recruitment of RFP-expressing blood vessels and fibroblast-like cells (Figure 2). Thus, host RFP cells were imaged extensively accumulating in the liver tumor. Immunohistochemical experiments showed that expression of desmin was prominent in the liver tumor, but not in the host liver, suggesting that cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) were recruited and grew in the tumor (Figure 3). The tumor also was stained with sirus-red, which marks collagen, possibly produced by the CAFs. CAFs have an important role in tumor progression (21). CAFs have a high rate of proliferation and differential expression of extracellular matrix (ECM) components, such as collagen, and growth factors compared to normal fibroblasts (21-23). CAFs promote tumor growth by inducing angiogenesis, recruiting bone marrow-derived endothelial-progenitor cells, and remodeling the ECM (24-28). CAFs can confer resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy (21, 29). CAFs also mediate tumorenhancing inflammation mediated by NF-kB (21). However, the formation of the TME is still largely unknown. The present report demonstrates a color-coded imaging model in which the development of the TME can be visualized in an orthotopic liver cancer model. RFP transgenic nude mice are useful to image stromal development in the tumor, since bright RFP-expressing stromal cells are recruited by the liver tumors. A desmin- and sirus-red-positive area increased around the liver tumors over time, suggesting CAFs were recruited by the liver tumors and have an important role in tumor progression. Stromal cells essential for the liver tumors to develop can be imaged as visual therapeutic targets. RFP-expressing blood vessels are also recruited by the liver tumor, enabling visual therapeutic targeting of angiogenesis as well. Dedication This paper is dedicated to the memory of A.R. Moossa, M.D. Acknowledgements This study was supported in part by National Cancer Institute grant CA References 1 Yang M, Li L, Jiang P, Moossa AR, Penman S and Hoffman RM: Dual-color fluorescence imaging distinguishes tumor cells from induced host angiogenic vessels and stromal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: , Yang M, Reynoso J, Jiang P, Li L, Moossa AR and Hoffman RM: Transgenic nude mouse with ubiquitous green fluorescent protein expression as a host for human tumors. Cancer Res 64: , Yang M, Reynoso J, Bouvet M and Hoffman RM: A transgenic red fluorescent protein-expressing nude mouse for color-coded imaging of the tumor microenvironment. J Cell Biochem 106: , Amoh Y, Li L, Yang M, Jiang P, Moossa AR, Katsuoka K and Hoffman RM: Hair follicle-derived blood vessels vascularize tumors in skin and are inhibited by doxorubicin. Cancer Res 65: , Amoh Y, Yang M, Li L, Reynoso J, Bouvet M, Moossa AR, Katsuoka K and Hoffman RM: Nestin-linked green fluorescent protein transgenic nude mouse for imaging human tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res 65: , Suetsugu A, Osawa Y, Nagaki M, Saji S, Moriwaki H, Bouvet M and Hoffman RM: Imaging the recruitment of cancerassociated fibroblasts by liver-metastatic colon cancer. J Cell Biochem 112: , Suetsugu A, Katz M, Fleming J, Moriwaki H, Bouvet M, Saji S and Hoffman RM: Multi-color palette of fluorescent proteins for imaging the tumor microenvironment of orthotopic tumorgraft mouse models of clinical pancreatic cancer specimens. J Cell Biochem 113: , Suetsugu A, Katz M, Fleming J, Truty M, Thomas R, Saji S, Moriwaki H, Bouvet M and Hoffman RM: Imageable fluorescent metastasis resulting in transgenic GFP mice orthotopically implanted with human-patient primary pancreatic cancer specimens. Anticancer Res 32: , Suetsugu A, Katz M, Fleming J, Truty M, Thomas R, Saji S, Moriwaki H, Bouvet M and Hoffman RM: Non-invasive fluorescent-protein imaging of orthotopic pancreatic-cancerpatient tumorgraft progression in nude mice. Anticancer Res 32: , Suetsugu A, Hassanein MK, Reynoso J, Osawa Y, Nagaki M, Moriwaki H, Saji S, Bouvet M and Hoffman RM: The cyan fluorescent protein nude mouse as a host for multicolor-coded imaging models of primary and metastatic tumor microenvironments. Anticancer Res 32: 31-38, Suetsugu A, Snyder CS, Moriwaki H, Saji S, Bouvet M and Hoffman RM: Imaging the interaction of pancreatic cancer and stellate cells in the tumor microenvironment during metastasis. Anticancer Res 35: , Egeblad M, Ewald AJ, Askautrud HA, Truitt ML, Welm BE, Bainbridge E, Peeters G, Krummel MF and Werb Z: Visualizing stromal cell dynamics in different tumor microenvironments by spinning disk confocal microscopy. Dis Model Mech 1: ,
5 Suetsugu et al: Imaging Recruitment of Stroma by Liver Cancer 13 Bouvet M, Tsuji K, Yang M, Jiang P, Moossa AR and Hoffman RM: In vivo color-coded imaging of the interaction of colon cancer cells and splenocytes in the formation of liver metastases. Cancer Res 66: , Suetsugu A, Osawa Y, Nagaki M, Moriwaki H, Saji S, Bouvet M, Hoffman RM: Simultaneous color-coded imaging to distinguish cancer stem-like and non-stem cells in the same tumor. J Cell Biochem 111: , Hoffman RM: The multiple uses of fluorescent proteins to visualize cancer in vivo. Nat Rev Cancer 5: , Hoffman RM, Yang M: Subcellular imaging in the live mouse. Nat Protoc 1: , Hoffman RM and Yang M: Color-coded fluorescence imaging of tumor host interactions. Nat Protoc 1: , Hoffman RM and Yang M: Whole-body imaging with fluorescent proteins. Nat Protoc 1: , Hoffman RM: Application of GFP imaging in cancer. Laboratory Investigation 95: , Yamauchi K, Yang M, Jiang P, Xu M, Yamamoto N, Tsuchiya H, Tomita K, Moossa AR, Bouvet M and Hoffman RM: Development of real-time subcellular dynamic multicolor imaging of cancer-cell trafficking in live mice with a variablemagnification whole-mouse imaging system. Cancer Res 66: , Erez N, Truitt M, Olson P, Arron ST and Hanahan D: Cancerassociated fibroblasts are activated in incipient neoplasia to orchestrate tumor- promoting inflammation in an NF-kappaBdependent manner. Cancer Cell 17: , Bhowmick NA, Neilson EG and Moses HL: Stromal fibroblasts in cancer initiation and progression. Nature 432: , Kalluri R, Zeisberg M: Fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6: , Egeblad M, Nakasone ES and Werb Z: Tumors as organs: Complex tissues that interface with the entire organism. Dev Cell 18: , Olumi AF, Grossfeld GD, Hayward SW, Carroll PR, Tlsty TD and Cunha GR: Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts direct tumor progression of initiated human prostatic epithelium. Cancer Res 59: , Allinen M, Beroukhim R, Cai L, Brennan C, Lahti-Domenici J, Huang H, Porter D, Hu M, Chin L, Richardson A, Schnitt S, Sellers WR and Polyak K: Molecular characterization of the tumor microenvironment in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 6: 17-32, Orimo A, Gupta PB, Sgroi DC, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Delaunay T, Naeem R, Carey VJ, Richardson AL and Weinberg RA: Stromal fibroblasts present in invasive human breast carcinomas promote tumor growth and angiogenesis through elevated SDF- 1/CXCL12 secretion. Cell 121: , Pietras K, Pahler J, Bergers G and Hanahan D: Functions of paracrine PDGF signaling in the proangiogenic tumor stroma revealed by pharmacological targeting. PLoS Med 5: e19, Crawford Y, Kasman I, Yu L, Zhong C, Wu X, Modrusan Z, Kaminker J and Ferrara N: PDGF-C mediates the angiogenic and tumorigenic properties of fibroblasts associated with tumors refractory to anti-vegf treatment. Cancer Cell 15: 21-34, Received July 17, 2015 Revised September 1, 2015 Accepted September 3,
Imaging Nuclear Cytoplasmic Dynamics in Primary and Metastatic Colon Cancer in Nude Mice
 Imaging Nuclear Cytoplasmic Dynamics in Primary and Metastatic Colon Cancer in Nude Mice KOSUKE HASEGAWA 1, ATSUSHI SUETSUGU 1,2,3, MIKI NAKAMURA 1, TAKURO MATSUMOTO 1, HITOMI AOKI 1, TAKAHIRO KUNISADA
Imaging Nuclear Cytoplasmic Dynamics in Primary and Metastatic Colon Cancer in Nude Mice KOSUKE HASEGAWA 1, ATSUSHI SUETSUGU 1,2,3, MIKI NAKAMURA 1, TAKURO MATSUMOTO 1, HITOMI AOKI 1, TAKAHIRO KUNISADA
The Cyan Fluorescent Protein Nude Mouse as a Host for Multicolor-coded Imaging Models of Primary and Metastatic Tumor Microenvironments
 The Cyan Fluorescent Protein Nude Mouse as a Host for Multicolor-coded Imaging Models of Primary and Metastatic Tumor Microenvironments ATSUSHI SUETSUGU 1,2,3, MOHAMED K. HASSANEIN 1,2, JOSE REYNOSO 1,
The Cyan Fluorescent Protein Nude Mouse as a Host for Multicolor-coded Imaging Models of Primary and Metastatic Tumor Microenvironments ATSUSHI SUETSUGU 1,2,3, MOHAMED K. HASSANEIN 1,2, JOSE REYNOSO 1,
ANTICANCER RESEARCH 36: (2016) Abstract. Background/Aim: Fluorescence-guided surgery /2016 $
 doi:10.21873/anticanres.10988 Color-coded Imaging Enables Fluorescence-guided Surgery to Resect the Tumor Along with the Tumor Microenvironment in a Syngeneic Mouse Model of EL-4 Lymphoma KOSUKE HASEGAWA
doi:10.21873/anticanres.10988 Color-coded Imaging Enables Fluorescence-guided Surgery to Resect the Tumor Along with the Tumor Microenvironment in a Syngeneic Mouse Model of EL-4 Lymphoma KOSUKE HASEGAWA
Imaging the Interaction of Pancreatic Cancer and Stellate Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment during Metastasis
 Imaging the Interaction of Pancreatic Cancer and Stellate Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment during Metastasis ATSUSHI SUETSUGU 1,2,3, CYNTHIA S. SNYDER 2, HISATAKA MORIWAKI 3, SHIGETOYO SAJI 3, MICHAEL
Imaging the Interaction of Pancreatic Cancer and Stellate Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment during Metastasis ATSUSHI SUETSUGU 1,2,3, CYNTHIA S. SNYDER 2, HISATAKA MORIWAKI 3, SHIGETOYO SAJI 3, MICHAEL
In vivo Color-Coded Imaging of the Interaction of Colon Cancer Cells and Splenocytes in the Formation of Liver Metastases
 In vivo Color-Coded Imaging of the Interaction of Colon Cancer Cells and Splenocytes in the Formation of Liver Metastases Michael Bouvet, 1 Kazuhiko Tsuji, 1,2 Meng Yang, 2 Ping Jiang, 2 Abdool R. Moossa,
In vivo Color-Coded Imaging of the Interaction of Colon Cancer Cells and Splenocytes in the Formation of Liver Metastases Michael Bouvet, 1 Kazuhiko Tsuji, 1,2 Meng Yang, 2 Ping Jiang, 2 Abdool R. Moossa,
ANTICANCER RESEARCH 35: (2015)
 Complementarity of Variable-magnification and Spectralseparation Fluorescence Imaging Systems for Noninvasive Detection of Metastasis and Intravital Detection of Single Cancer Cells in Mouse Models YONG
Complementarity of Variable-magnification and Spectralseparation Fluorescence Imaging Systems for Noninvasive Detection of Metastasis and Intravital Detection of Single Cancer Cells in Mouse Models YONG
Tumor-educated Macrophages Promote Tumor Growth and Peritoneal Metastasis in an Orthotopic Nude Mouse Model of Human Pancreatic Cancer
 Tumor-educated Macrophages Promote Tumor Growth and Peritoneal Metastasis in an Orthotopic Nude Mouse Model of Human Pancreatic Cancer RHIANA S. MENEN 1,2,3*, MOHAMED K. HASSANEIN 1,2*, MASASHI MOMIYAMA
Tumor-educated Macrophages Promote Tumor Growth and Peritoneal Metastasis in an Orthotopic Nude Mouse Model of Human Pancreatic Cancer RHIANA S. MENEN 1,2,3*, MOHAMED K. HASSANEIN 1,2*, MASASHI MOMIYAMA
Inflammatory Cells and Metastasis
 Inflammatory Cells and Metastasis Experimentelle Krebsforschung SS 07 Gerhard Christofori Institute of Biochemistry and Genetics Department of Clinical-Biological Sciences Center of Biomedicine University
Inflammatory Cells and Metastasis Experimentelle Krebsforschung SS 07 Gerhard Christofori Institute of Biochemistry and Genetics Department of Clinical-Biological Sciences Center of Biomedicine University
COVER STORIES. Hoffman, R.M. Visualization of GFP-expressing tumors and metastasis in vivo. BioTechniques 30, , 2001.
 COVER STORIES Hoffman, R.M. Three-dimensional histoculture: origins and applications in cancer research. Cancer Cells 3, 86-92, 1991. Hoffman, R.M. Visualization of GFP-expressing tumors and metastasis
COVER STORIES Hoffman, R.M. Three-dimensional histoculture: origins and applications in cancer research. Cancer Cells 3, 86-92, 1991. Hoffman, R.M. Visualization of GFP-expressing tumors and metastasis
this mutation. However, VEM was not effective. The PDOX model thus helped identify
 /, Vol. 7, No. 44 Vemurafenib-resistant BRAF-V600E-mutated melanoma is regressed by MEK-targeting drug trametinib, but not cobimetinib in a patient-derived orthotopic xenograft (PDOX) mouse model Kei Kawaguchi
/, Vol. 7, No. 44 Vemurafenib-resistant BRAF-V600E-mutated melanoma is regressed by MEK-targeting drug trametinib, but not cobimetinib in a patient-derived orthotopic xenograft (PDOX) mouse model Kei Kawaguchi
ANTICANCER RESEARCH 36: (2016)
 Orthotopic Implantation of Intact Tumor Tissue Leads to Metastasis of OCUM-2MD3 Human Gastric Cancer in Nude Mice Visualized in Real Time by Intravital Fluorescence Imaging TAKASHI MURAKAMI 1,2,3, YONG
Orthotopic Implantation of Intact Tumor Tissue Leads to Metastasis of OCUM-2MD3 Human Gastric Cancer in Nude Mice Visualized in Real Time by Intravital Fluorescence Imaging TAKASHI MURAKAMI 1,2,3, YONG
Dual-color Imaging of Nascent Angiogenesis and its Inhibition in Liver Metastases of Pancreatic Cancer
 Dual-color Imaging of Nascent Angiogenesis and its Inhibition in Liver Metastases of Pancreatic Cancer YASUYUKI AMOH 1,2,3, CHISA NAGAKURA 1, ANIRBAN MAITRA 4, A. R. MOOSSA 2, KENSEI KATSUOKA 3, ROBERT
Dual-color Imaging of Nascent Angiogenesis and its Inhibition in Liver Metastases of Pancreatic Cancer YASUYUKI AMOH 1,2,3, CHISA NAGAKURA 1, ANIRBAN MAITRA 4, A. R. MOOSSA 2, KENSEI KATSUOKA 3, ROBERT
Development of the Transgenic Cyan Fluorescent Protein (CFP)-Expressing Nude Mouse for Technicolor Cancer Imaging
 ARTICLE Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 107:328 334 (2009) Journal of Cellular Biochemistry Development of the Transgenic Cyan Fluorescent Protein (CFP)-Expressing Nude Mouse for Technicolor Cancer Imaging
ARTICLE Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 107:328 334 (2009) Journal of Cellular Biochemistry Development of the Transgenic Cyan Fluorescent Protein (CFP)-Expressing Nude Mouse for Technicolor Cancer Imaging
INTRODUCTION. Journal of Surgical Research 132, (2006) doi: /j.jss
 Journal of Surgical Research 132, 164 169 (2006) doi:10.1016/j.jss.2005.12.028 Dual-Color Imaging of Nascent Blood Vessels Vascularizing Pancreatic Cancer in an Orthotopic Model Demonstrates Antiangiogenesis
Journal of Surgical Research 132, 164 169 (2006) doi:10.1016/j.jss.2005.12.028 Dual-Color Imaging of Nascent Blood Vessels Vascularizing Pancreatic Cancer in an Orthotopic Model Demonstrates Antiangiogenesis
2007 AACR Annual Meeting April 14-18, 2007 Los Angeles, CA PRESENTATION SCHEDULE
 2007 AACR Annual Meeting April 14-18, 2007 Los Angeles, CA PRESENTATION SCHEDULE Abstract 501 Presentation Title: An imageable bone and multi-organ metastatic model of human neuroblastoma Presentation
2007 AACR Annual Meeting April 14-18, 2007 Los Angeles, CA PRESENTATION SCHEDULE Abstract 501 Presentation Title: An imageable bone and multi-organ metastatic model of human neuroblastoma Presentation
Whole-Body Subcellular Multicolor Imaging of Tumor-Host Interaction and Drug Response in Real Time
 Research Article Whole-Body Subcellular Multicolor Imaging of Tumor-Host Interaction and Drug Response in Real Time Meng Yang, 1 Ping Jiang, 1 and Robert M. Hoffman 1,2 1 AntiCancer, Inc. and 2 Department
Research Article Whole-Body Subcellular Multicolor Imaging of Tumor-Host Interaction and Drug Response in Real Time Meng Yang, 1 Ping Jiang, 1 and Robert M. Hoffman 1,2 1 AntiCancer, Inc. and 2 Department
ANTICANCER RESEARCH 32: (2012)
 Inhibition of Metastasis of Circulating Human Prostate Cancer Cells in the Chick Embryo by an Extracellular Matrix Produced by Foreskin Fibroblasts in Culture RHIANA MENEN 1,4,5, EMMETT PINNEY 2, MOHAMED
Inhibition of Metastasis of Circulating Human Prostate Cancer Cells in the Chick Embryo by an Extracellular Matrix Produced by Foreskin Fibroblasts in Culture RHIANA MENEN 1,4,5, EMMETT PINNEY 2, MOHAMED
sensors ISSN by MDPI
 Sensors 2008, 8, 1157-1173 Review sensors ISSN 1424-8220 2008 by MDPI www.mdpi.org/sensors Imaging In Mice With Fluorescent Proteins: From Macro To Subcellular Robert M. Hoffman AntiCancer, Inc., 7917
Sensors 2008, 8, 1157-1173 Review sensors ISSN 1424-8220 2008 by MDPI www.mdpi.org/sensors Imaging In Mice With Fluorescent Proteins: From Macro To Subcellular Robert M. Hoffman AntiCancer, Inc., 7917
MELANOMA CANCER TEST
 MELANOMA CANCER TEST Efficacy Evaluation of Antitumor Activity of Alka Vita - Alkahydroxy in the LOX-GFP Human Melanoma Model Final Report by: Anti-Cancer Lab San Diego California March 4, 2005 Efficacy
MELANOMA CANCER TEST Efficacy Evaluation of Antitumor Activity of Alka Vita - Alkahydroxy in the LOX-GFP Human Melanoma Model Final Report by: Anti-Cancer Lab San Diego California March 4, 2005 Efficacy
Supplementary Materials. for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis
 Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Hair Follicle Derived Blood Vessels Vascularize Tumors in Skin and Are Inhibited by Doxorubicin
 Research Article Hair Follicle Derived Blood Vessels Vascularize Tumors in Skin and Are Inhibited by Doxorubicin Yasuyuki Amoh, 1,2,3 Lingna Li, 1 Meng Yang, 1 Ping Jiang, 1 Abdool R. Moossa, 2 Kensei
Research Article Hair Follicle Derived Blood Vessels Vascularize Tumors in Skin and Are Inhibited by Doxorubicin Yasuyuki Amoh, 1,2,3 Lingna Li, 1 Meng Yang, 1 Ping Jiang, 1 Abdool R. Moossa, 2 Kensei
BMC Cancer. Open Access. Abstract. BioMed Central
 BMC Cancer BioMed Central Research article Complementarity of ultrasound and fluorescence imaging in an orthotopic mouse model of pancreatic cancer Cynthia S Snyder 1, Sharmeela Kaushal 1, Yuko Kono 2,
BMC Cancer BioMed Central Research article Complementarity of ultrasound and fluorescence imaging in an orthotopic mouse model of pancreatic cancer Cynthia S Snyder 1, Sharmeela Kaushal 1, Yuko Kono 2,
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material Supplementary Fig. 1. EETs stimulate primary tumor growth. a) Schematic presentation of genetic and pharmacological tools used to manipulate endogenous EET levels. b) Endothelial
Supplemental Material Supplementary Fig. 1. EETs stimulate primary tumor growth. a) Schematic presentation of genetic and pharmacological tools used to manipulate endogenous EET levels. b) Endothelial
Antimetastatic efficacy of adjuvant gemcitabine in a pancreatic cancer orthotopic model
 Clinical & Experimental Metastasis 18: 379 384, 2001. 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 379 Antimetastatic efficacy of adjuvant gemcitabine in a pancreatic cancer orthotopic
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis 18: 379 384, 2001. 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 379 Antimetastatic efficacy of adjuvant gemcitabine in a pancreatic cancer orthotopic
Molecular and genetic analysis of stromal fibroblasts in prostate cancer
 Final report ESMO Translational Research Fellowship 2010-2011 Molecular and genetic analysis of stromal fibroblasts in prostate cancer Michalis Karamouzis Host Institute Department of Biological Chemistry,
Final report ESMO Translational Research Fellowship 2010-2011 Molecular and genetic analysis of stromal fibroblasts in prostate cancer Michalis Karamouzis Host Institute Department of Biological Chemistry,
Tumor-targeting Salmonella typhimurium A1-R regresses an osteosarcoma in a patient-derived xenograft model resistant to a molecular-targeting drug
 /, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 5), pp: 8035-8042 Tumor-targeting Salmonella typhimurium A1-R regresses an osteosarcoma in a patient-derived xenograft model resistant to a molecular-targeting drug Takashi Murakami
/, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 5), pp: 8035-8042 Tumor-targeting Salmonella typhimurium A1-R regresses an osteosarcoma in a patient-derived xenograft model resistant to a molecular-targeting drug Takashi Murakami
Nestin-Linked Green Fluorescent Protein Transgenic Nude Mouse for Imaging Human Tumor Angiogenesis
 Research Article Nestin-Linked Green Fluorescent Protein Transgenic Nude Mouse for Imaging Human Tumor Angiogenesis Yasuyuki Amoh, 1,2,3 Meng Yang, 1 Lingna Li, 1 Jose Reynoso, 1 Michael Bouvet, 2 Abdool
Research Article Nestin-Linked Green Fluorescent Protein Transgenic Nude Mouse for Imaging Human Tumor Angiogenesis Yasuyuki Amoh, 1,2,3 Meng Yang, 1 Lingna Li, 1 Jose Reynoso, 1 Michael Bouvet, 2 Abdool
Determination of Clonality of Metastasis by Cell-Specific Color-Coded Fluorescent-Protein Imaging
 [CANCER RESEARCH 63, 7785 7790, November 15, 2003] Determination of Clonality of Metastasis by Cell-Specific Color-Coded Fluorescent-Protein Imaging Norio Yamamoto, 1,2,3 Meng Yang, 1 Ping Jiang, 1 Mingxu
[CANCER RESEARCH 63, 7785 7790, November 15, 2003] Determination of Clonality of Metastasis by Cell-Specific Color-Coded Fluorescent-Protein Imaging Norio Yamamoto, 1,2,3 Meng Yang, 1 Ping Jiang, 1 Mingxu
Lab Med Breast Cancer: From Basics to Beyond. Basic Cancer Biology and Model Systems ZENA WERB. 4:30-6 pm November 1, 2010
 Lab Med 180.04 Breast Cancer: From Basics to Beyond Basic Cancer Biology and Model Systems ZENA WERB 4:30-6 pm November 1, 2010 Advantages of mice as breast cancer models hlp://mammary.nih.gov/atlas/histology/
Lab Med 180.04 Breast Cancer: From Basics to Beyond Basic Cancer Biology and Model Systems ZENA WERB 4:30-6 pm November 1, 2010 Advantages of mice as breast cancer models hlp://mammary.nih.gov/atlas/histology/
Cancer Biology Course. Invasion and Metastasis
 Cancer Biology Course Invasion and Metastasis 2016 Lu-Hai Wang NHRI Cancer metastasis Major problem: main reason for killing cancer patients, without it cancer can be cured or controlled. Challenging questions:
Cancer Biology Course Invasion and Metastasis 2016 Lu-Hai Wang NHRI Cancer metastasis Major problem: main reason for killing cancer patients, without it cancer can be cured or controlled. Challenging questions:
The Ufm1-activating enzyme Uba5 is indispensable for erythroid differentiation in mice
 Supplementary information The Ufm1-activating enzyme Uba5 is indispensable for erythroid differentiation in mice Kanako Tatsumi 1, 2, Harumi Yamamoto-Mukai 2, Ritsuko Shimizu 3, Satoshi Waguri 4, Yu-Shin
Supplementary information The Ufm1-activating enzyme Uba5 is indispensable for erythroid differentiation in mice Kanako Tatsumi 1, 2, Harumi Yamamoto-Mukai 2, Ritsuko Shimizu 3, Satoshi Waguri 4, Yu-Shin
Chronologically-specific metastatic targeting of human pancreatic tumors in orthotopic models
 Clinical & Experimental Metastasis 18: 213 218, 2000. 2000 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 213 Chronologically-specific metastatic targeting of human pancreatic tumors in orthotopic
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis 18: 213 218, 2000. 2000 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 213 Chronologically-specific metastatic targeting of human pancreatic tumors in orthotopic
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis
 Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression
 Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression Jarad J Wilson, Ph.D. Technical Support & Marketing Specialist Ruo-Pan Huang, MD, Ph.D. Founder and CEO What are Antibody Arrays?
Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression Jarad J Wilson, Ph.D. Technical Support & Marketing Specialist Ruo-Pan Huang, MD, Ph.D. Founder and CEO What are Antibody Arrays?
Advantages of multi-color fluorescent proteins for whole-body and in vivo cellular imaging
 Journal of Biomedical Optics 104, 041202 July/August 2005 Advantages of multi-color fluorescent proteins for whole-body and in vivo cellular imaging Robert M. Hoffman AntiCancer, Inc. 7917 Ostrow Street
Journal of Biomedical Optics 104, 041202 July/August 2005 Advantages of multi-color fluorescent proteins for whole-body and in vivo cellular imaging Robert M. Hoffman AntiCancer, Inc. 7917 Ostrow Street
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung
 IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
Clinical Findings on Fibroblast Activation Protein in Patients with Gastric Cancer
 Yonago Acta medica 2009;52:21 25 Clinical Findings on Fibroblast Activation Protein in Patients with Gastric Cancer Youji Fukumoto, Yoshinori Yamada, Kenji Fukuda, Hiroaki Saito, Shigeru Tatebe, Shunichi
Yonago Acta medica 2009;52:21 25 Clinical Findings on Fibroblast Activation Protein in Patients with Gastric Cancer Youji Fukumoto, Yoshinori Yamada, Kenji Fukuda, Hiroaki Saito, Shigeru Tatebe, Shunichi
SHREE ET AL, SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS. (A) Workflow for tumor cell line derivation and orthotopic implantation.
 SHREE ET AL, SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Derivation and characterization of TS1-TGL and TS2-TGL PyMT cell lines and development of an orthotopic
SHREE ET AL, SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Derivation and characterization of TS1-TGL and TS2-TGL PyMT cell lines and development of an orthotopic
Cancer-cell Killing by Engineered Salmonella Imaged by Multiphoton Tomography in Live Mice
 Cancer-cell Killing by Engineered Salmonella Imaged by Multiphoton Tomography in Live Mice AISADA UCHUGONOVA 1-3, MING ZHAO 1, YONG ZHANG 1, MARTIN WEINIGEL 4, KARSTEN KÖNIG 3,4 and ROBERT M. HOFFMAN 1,2
Cancer-cell Killing by Engineered Salmonella Imaged by Multiphoton Tomography in Live Mice AISADA UCHUGONOVA 1-3, MING ZHAO 1, YONG ZHANG 1, MARTIN WEINIGEL 4, KARSTEN KÖNIG 3,4 and ROBERT M. HOFFMAN 1,2
Research Article. Abstract. Introduction. Materialsand Methods
 Research Article Development of Real-time Subcellular Dynamic Multicolor Imaging of Cancer-Cell Trafficking in Live Mice with a Variable-Magnification Whole-Mouse Imaging System Kensuke Yamauchi, 1,2,3
Research Article Development of Real-time Subcellular Dynamic Multicolor Imaging of Cancer-Cell Trafficking in Live Mice with a Variable-Magnification Whole-Mouse Imaging System Kensuke Yamauchi, 1,2,3
Molecular Imaging for Cancer Visualization
 Molecular Imaging for Cancer Visualization American College of Surgeons Surgical Simulation Summit Chicago, IL March 16-17, 2018 Michael Bouvet, MD Professor of Surgery University of California San Diego
Molecular Imaging for Cancer Visualization American College of Surgeons Surgical Simulation Summit Chicago, IL March 16-17, 2018 Michael Bouvet, MD Professor of Surgery University of California San Diego
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
In vivo imaging with fluorescent proteins: the new cell biology $
 Acta histochemica 106 (2004) 77 87 www.elsevier.de/acthis In vivo imaging with fluorescent proteins: the new cell biology $ Robert M. Hoffman* AntiCancer, Inc., 7917 Ostrow Street, San Diego, CA 92111,
Acta histochemica 106 (2004) 77 87 www.elsevier.de/acthis In vivo imaging with fluorescent proteins: the new cell biology $ Robert M. Hoffman* AntiCancer, Inc., 7917 Ostrow Street, San Diego, CA 92111,
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
ASSOCIATION FOR ACADEMIC SURGERY, Characterization of HCT116 Human Colon Cancer Cells in an Orthotopic Model 1
 Journal of Surgical Research 147, 276 281 (2008) doi:10.1016/j.jss.2007.04.021 ASSOCIATION FOR ACADEMIC SURGERY, 2004 Characterization of HCT116 Human Colon Cancer Cells in an Orthotopic Model 1 Ashwani
Journal of Surgical Research 147, 276 281 (2008) doi:10.1016/j.jss.2007.04.021 ASSOCIATION FOR ACADEMIC SURGERY, 2004 Characterization of HCT116 Human Colon Cancer Cells in an Orthotopic Model 1 Ashwani
CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma.
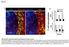 Fig S1 CD4 Fibronectin EpCM CD8 CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma. Fluorescently-labeled CD4 (CMFD, green) and CD8 (Hoechst, yellow) T cells were added to a human lung
Fig S1 CD4 Fibronectin EpCM CD8 CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma. Fluorescently-labeled CD4 (CMFD, green) and CD8 (Hoechst, yellow) T cells were added to a human lung
Supplementary Figure 1: Imaging T-ALL progression and growth in transplanted
 Supplementary Figure 1: Imaging T-ALL progression and growth in transplanted rag2e450fs fish. Monoclonal T-ALLs were serially passaged in strain fish and then used as donors (left panel). Cells were transplanted
Supplementary Figure 1: Imaging T-ALL progression and growth in transplanted rag2e450fs fish. Monoclonal T-ALLs were serially passaged in strain fish and then used as donors (left panel). Cells were transplanted
The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer
 Ang2 Ang1 The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer Tie2 An Overview: The Angiopoietin Axis Plays an Essential Role in the Regulation of Tumor Angiogenesis Growth of a tumor beyond a limiting size is dependent upon
Ang2 Ang1 The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer Tie2 An Overview: The Angiopoietin Axis Plays an Essential Role in the Regulation of Tumor Angiogenesis Growth of a tumor beyond a limiting size is dependent upon
Trevigen s Extracellular Matrix Proteins for Triculture of Breast Cancer Spheroids, Endothelial Tubules, and Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells
 Trevigen s Extracellular Matrix Proteins for Triculture of Breast Cancer Spheroids, Endothelial Tubules, and Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Gabriel Benton, Ph.D. and Jay George, Ph.D., Trevigen, Inc. Gaithersburg,
Trevigen s Extracellular Matrix Proteins for Triculture of Breast Cancer Spheroids, Endothelial Tubules, and Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Gabriel Benton, Ph.D. and Jay George, Ph.D., Trevigen, Inc. Gaithersburg,
Color-Coded Fluorescent Protein Imaging of Angiogenesis: The AngioMouse Models
 3810 Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2008, 14, 3810-3819 Color-Coded Fluorescent Protein Imaging of Angiogenesis: The AngioMouse Models Yasuyuki Amoh 1,*, Kensei Katsuoka 1 and Robert M. Hoffman 2,3 1 Department
3810 Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2008, 14, 3810-3819 Color-Coded Fluorescent Protein Imaging of Angiogenesis: The AngioMouse Models Yasuyuki Amoh 1,*, Kensei Katsuoka 1 and Robert M. Hoffman 2,3 1 Department
Supplemental Data. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Mesenchymal Progenitors. Controls Osteoblast and Chondrocyte
 Supplemental Data Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Mesenchymal Progenitors Controls Osteoblast and Chondrocyte Differentiation during Vertebrate Skeletogenesis Timothy F. Day, Xizhi Guo, Lisa Garrett-Beal, and
Supplemental Data Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Mesenchymal Progenitors Controls Osteoblast and Chondrocyte Differentiation during Vertebrate Skeletogenesis Timothy F. Day, Xizhi Guo, Lisa Garrett-Beal, and
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Heterotypy and Angiogenesis
 Heterotypy and Angiogenesis Tumors are perpetual wounds 1. Normally stroma and epithelia converse at a distance. 2. Juxtaposition of stroma and epithelia is indicative of tissue damage. 4. Activate strategies
Heterotypy and Angiogenesis Tumors are perpetual wounds 1. Normally stroma and epithelia converse at a distance. 2. Juxtaposition of stroma and epithelia is indicative of tissue damage. 4. Activate strategies
Modelling Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion Using Novel Technology for Three Dimensional Cell Culture. Introduction
 Modelling Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion Using Novel Technology for Three Dimensional Cell Culture Application Note 3 Introduction Cancer is characterised by unregulated and abnormal cell growth in
Modelling Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion Using Novel Technology for Three Dimensional Cell Culture Application Note 3 Introduction Cancer is characterised by unregulated and abnormal cell growth in
Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target
 Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target Lecture Experimentelle Krebsforschung SS 07 Prof. Gerhard Christofori Institute of Biochemistry and Genetics Department of Clinical-Biological Sciences University of
Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target Lecture Experimentelle Krebsforschung SS 07 Prof. Gerhard Christofori Institute of Biochemistry and Genetics Department of Clinical-Biological Sciences University of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3021 Supplementary figure 1 Characterisation of TIMPless fibroblasts. a) Relative gene expression of TIMPs1-4 by real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) in WT or ΔTimp fibroblasts (mean ±
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3021 Supplementary figure 1 Characterisation of TIMPless fibroblasts. a) Relative gene expression of TIMPs1-4 by real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) in WT or ΔTimp fibroblasts (mean ±
Comparison of primary tumor sections from MMTV-PyMT or MTLn3-ErbB3-
 Supplemental Data Comparison of primary tumor sections from MMTV-PyMT or MTLn3-ErbB3- GFP tumors in mice either injected with control or clodronate-containing liposomes and stained for macrophages using
Supplemental Data Comparison of primary tumor sections from MMTV-PyMT or MTLn3-ErbB3- GFP tumors in mice either injected with control or clodronate-containing liposomes and stained for macrophages using
Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis fo mation r
 Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis fo mation r Yvonne Kienast, Louisa von Baumgarten, Martin Fuhrmann, Wolfgang E.F. Klinkert, Roland Goldbrunner, Jochen Herms and Frank Winkler
Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis fo mation r Yvonne Kienast, Louisa von Baumgarten, Martin Fuhrmann, Wolfgang E.F. Klinkert, Roland Goldbrunner, Jochen Herms and Frank Winkler
200 W. Arbor Dr., San Diego, CA , USA. Key words: angiogenesis, metastasis, orthotopic fragment transplant, renal cancer
 Clinical & Experimental Metastasis 17: 265 270, 1999. 1999 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 265 Development of a high metastatic orthotopic model of human renal cell carcinoma in
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis 17: 265 270, 1999. 1999 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 265 Development of a high metastatic orthotopic model of human renal cell carcinoma in
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0212 TITLE: Wnt/Beta-Catenin, Foxa2, and CXCR4 Axis Controls Prostate Cancer Progression PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Xiuping Yu CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Vanderbilt University
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0212 TITLE: Wnt/Beta-Catenin, Foxa2, and CXCR4 Axis Controls Prostate Cancer Progression PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Xiuping Yu CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Vanderbilt University
The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis
 The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. Pusan National University Contents Part 1. The process of angiogenesis Part 2. The role of angiopoietins
The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. Pusan National University Contents Part 1. The process of angiogenesis Part 2. The role of angiopoietins
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in
 Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Figure S2: The pro-inflammatory gene signature is expressed in human tumors. Related to main Figure 2.
 Cancer Cell, Volume 17 Supplemental Information Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Are Activated in Incipient Neoplasia to Orchestrate Tumor-Promoting Inflammation in an NF-κB-Dependent Manner Neta Erez, Morgan
Cancer Cell, Volume 17 Supplemental Information Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Are Activated in Incipient Neoplasia to Orchestrate Tumor-Promoting Inflammation in an NF-κB-Dependent Manner Neta Erez, Morgan
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 /, 2016, Vol. 7, (No. 52), pp: 85929-85936 Tumor-targeting Salmonella typhimurium A1-R combined with temozolomide regresses malignant melanoma with a BRAF-V600E mutation in a patient-derived orthotopic
/, 2016, Vol. 7, (No. 52), pp: 85929-85936 Tumor-targeting Salmonella typhimurium A1-R combined with temozolomide regresses malignant melanoma with a BRAF-V600E mutation in a patient-derived orthotopic
Cancer cell movement study using 2D and 3D In Vitro models
 Cancer cell movement study using 2D and 3D In Vitro models by Ehsanul HOQUE APU Cancer and Translational Medicine Research Unit, Medical Research Center Oulu (MRC Oulu) Squamous cell carcinoma (SqCC) Squamous
Cancer cell movement study using 2D and 3D In Vitro models by Ehsanul HOQUE APU Cancer and Translational Medicine Research Unit, Medical Research Center Oulu (MRC Oulu) Squamous cell carcinoma (SqCC) Squamous
Supplementary Information. Detection and delineation of oral cancer with a PARP1 targeted optical imaging agent
 Supplementary Information Detection and delineation of oral cancer with a PARP1 targeted optical imaging agent Authors: Susanne Kossatz a, Christian Brand a, Stanley Gutiontov b, Jonathan T.C. Liu c, Nancy
Supplementary Information Detection and delineation of oral cancer with a PARP1 targeted optical imaging agent Authors: Susanne Kossatz a, Christian Brand a, Stanley Gutiontov b, Jonathan T.C. Liu c, Nancy
HIF-1-mediated metabolic reprogramming reduces ROS levels and facilitates
 HIF-1-mediated metabolic reprogramming reduces ROS levels and facilitates the metastatic colonization of cancers in lungs Authors: Tao ZHAO 1,2,3, Yuxi ZHU 1,2,4, Akiyo MORINIBU 1,2, Minoru KOBAYASHI 1,2,
HIF-1-mediated metabolic reprogramming reduces ROS levels and facilitates the metastatic colonization of cancers in lungs Authors: Tao ZHAO 1,2,3, Yuxi ZHU 1,2,4, Akiyo MORINIBU 1,2, Minoru KOBAYASHI 1,2,
A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified
 Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Cancer model Liver metastasis I
 Cancer model Liver metastasis I H. Suemizu, M. Monnai, Y. Ohnishi, M. Ito, N. Tamaoki, and M. Nakamura. 2007. Identification of a key molecular regulator of liver metastasis in human pancreatic carcinoma
Cancer model Liver metastasis I H. Suemizu, M. Monnai, Y. Ohnishi, M. Ito, N. Tamaoki, and M. Nakamura. 2007. Identification of a key molecular regulator of liver metastasis in human pancreatic carcinoma
Evaluation of STAT3 Signaling in Macrophages Using a Lentiviral Reporter System
 Evaluation of STAT3 Signaling in Macrophages Using a Lentiviral Reporter System Schwertfeger Laboratory Emily Hartsough Breast Cancer Prevalence Adapted from Siegel et. al Cancer Statistics. 2016 Tumor
Evaluation of STAT3 Signaling in Macrophages Using a Lentiviral Reporter System Schwertfeger Laboratory Emily Hartsough Breast Cancer Prevalence Adapted from Siegel et. al Cancer Statistics. 2016 Tumor
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Effects of treatments with angiogenesis inhibitors on tumor stroma in animal experimental models of child cancer Neuroblastoma
 Effects of treatments with angiogenesis inhibitors on tumor stroma in animal experimental models of child cancer Neuroblastoma Mahamed Shiikh Dahir Degree Project in Toxicology, 30 hp, Spring semester
Effects of treatments with angiogenesis inhibitors on tumor stroma in animal experimental models of child cancer Neuroblastoma Mahamed Shiikh Dahir Degree Project in Toxicology, 30 hp, Spring semester
TITLE: The Role of Cyclin D1 in Altering Stromal-Epithelial Interactions in Prostate Carcinogenesis
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0139 TITLE: The Role of Cyclin D1 in Altering Stromal-Epithelial Interactions in Prostate Carcinogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yue He CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Vanderbilt
AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0139 TITLE: The Role of Cyclin D1 in Altering Stromal-Epithelial Interactions in Prostate Carcinogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yue He CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Vanderbilt
HepaRG LX2. HepaRG HepaRG LX2 LX2
 C Supporting Figure 1. Experimental design of s between and cells. (A) -hepatocytes were isolated from a 30 days of -progenitors. Differentiation into mature hepatocytes was achieved following a 2-weeks
C Supporting Figure 1. Experimental design of s between and cells. (A) -hepatocytes were isolated from a 30 days of -progenitors. Differentiation into mature hepatocytes was achieved following a 2-weeks
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration
 Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Cancer Metastasis Directly Eradicated by Targeted Therapy With a Modified Salmonella typhimurium
 ARTICLE Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 106:992 998 (2009) Journal of Cellular Biochemistry Cancer Metastasis Directly Eradicated by Targeted Therapy With a Modified Salmonella typhimurium Katsuhiro Hayashi,
ARTICLE Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 106:992 998 (2009) Journal of Cellular Biochemistry Cancer Metastasis Directly Eradicated by Targeted Therapy With a Modified Salmonella typhimurium Katsuhiro Hayashi,
Pathologic Stage. Lymph node Stage
 ASC ASC a c Patient ID BMI Age Gleason score Non-obese PBMC 1 22.1 81 6 (3+3) PBMC 2 21.9 6 6 (3+3) PBMC 3 22 84 8 (4+4) PBMC 4 24.6 68 7 (3+4) PBMC 24. 6 (3+3) PBMC 6 24.7 73 7 (3+4) PBMC 7 23. 67 7 (3+4)
ASC ASC a c Patient ID BMI Age Gleason score Non-obese PBMC 1 22.1 81 6 (3+3) PBMC 2 21.9 6 6 (3+3) PBMC 3 22 84 8 (4+4) PBMC 4 24.6 68 7 (3+4) PBMC 24. 6 (3+3) PBMC 6 24.7 73 7 (3+4) PBMC 7 23. 67 7 (3+4)
Selective metastatic tumor labeling with green fluorescent protein and killing by systemic administration of telomerase-dependent adenoviruses
 3001 Selective metastatic tumor labeling with green fluorescent protein and killing by systemic administration of telomerase-dependent adenoviruses Hiroyuki Kishimoto, 1,2,3 Yasuo Urata, 5 Noriaki Tanaka,
3001 Selective metastatic tumor labeling with green fluorescent protein and killing by systemic administration of telomerase-dependent adenoviruses Hiroyuki Kishimoto, 1,2,3 Yasuo Urata, 5 Noriaki Tanaka,
Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies. Traditional Hypothesis Stress
 3/1/212 Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies K.R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, CO 845 Prominent Fibroproliferative
3/1/212 Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies K.R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, CO 845 Prominent Fibroproliferative
Supplementary Figure 1. Chimeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) Chimeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears.
 Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)
 In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
Supplemental Figures:
 Supplemental Figures: Figure 1: Intracellular distribution of VWF by electron microscopy in human endothelial cells. a) Immunogold labeling of LC3 demonstrating an LC3-positive autophagosome (white arrow)
Supplemental Figures: Figure 1: Intracellular distribution of VWF by electron microscopy in human endothelial cells. a) Immunogold labeling of LC3 demonstrating an LC3-positive autophagosome (white arrow)
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 Page 1 09/10/2013 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0453 TITLE: The cytoplasm translocation of the androgen receptor cofactor p44 as a target for prostate cancer treatment PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Zhengxin Wang
Page 1 09/10/2013 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0453 TITLE: The cytoplasm translocation of the androgen receptor cofactor p44 as a target for prostate cancer treatment PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Zhengxin Wang
Monoclonal antibody targeting of N-cadherin inhibits prostate cancer growth, metastasis and castration resistance
 Monoclonal antibody targeting of N-cadherin inhibits prostate cancer growth, metastasis and castration resistance Tanaka H, Kono E, Tran CP, Miyazaki H, Yamashiro J, Shimomura T, Ladan F, Wada R, Huang
Monoclonal antibody targeting of N-cadherin inhibits prostate cancer growth, metastasis and castration resistance Tanaka H, Kono E, Tran CP, Miyazaki H, Yamashiro J, Shimomura T, Ladan F, Wada R, Huang
Endothelial Tube Formation Assay (In Vitro Angiogenesis)
 Product Manual Endothelial Tube Formation Assay (In Vitro Angiogenesis) Catalog Number CBA-200 50 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Angiogenesis, or neovascularization,
Product Manual Endothelial Tube Formation Assay (In Vitro Angiogenesis) Catalog Number CBA-200 50 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Angiogenesis, or neovascularization,
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and
 Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Targeting the cgmp Pathway to Treat Colorectal Cancer
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Faculty Papers Department of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 29 Targeting the cgmp
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Faculty Papers Department of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 29 Targeting the cgmp
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast
 Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
Interactions between cancer stem cells and their niche govern metastatic colonization
 Correction Interactions between cancer stem cells and their niche govern metastatic colonization Ilaria Malanchi, Albert Santamaria-Martínez, Evelyn Susanto, Hong Peng, Hans-Anton Lehr, Jean-Francois Delaloye
Correction Interactions between cancer stem cells and their niche govern metastatic colonization Ilaria Malanchi, Albert Santamaria-Martínez, Evelyn Susanto, Hong Peng, Hans-Anton Lehr, Jean-Francois Delaloye
Integrin v 3 targeted therapy for Kaposi s sarcoma with an in vitro evolved antibody 1
 Integrin v 3 targeted therapy for Kaposi s sarcoma with an in vitro evolved antibody 1 CHRISTOPH RADER, 2 MIKHAIL POPKOV, JOHN A. NEVES, AND CARLOS F. BARBAS III 2 Department of Molecular Biology and The
Integrin v 3 targeted therapy for Kaposi s sarcoma with an in vitro evolved antibody 1 CHRISTOPH RADER, 2 MIKHAIL POPKOV, JOHN A. NEVES, AND CARLOS F. BARBAS III 2 Department of Molecular Biology and The
Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury
 Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury Bastian OW, Koenderman L, Alblas J, Leenen LPH, Blokhuis TJ. Neutrophils contribute to
Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury Bastian OW, Koenderman L, Alblas J, Leenen LPH, Blokhuis TJ. Neutrophils contribute to
Stem cells and Cancer. John Glod. December 2, 2009
 Stem cells and Cancer John Glod Lehigh University Lehigh University December 2, 2009 The Tumor Microenvironment Littlepage et al Cancer Cell 2005 Cancer Stem Cells A small group of cells within the larger
Stem cells and Cancer John Glod Lehigh University Lehigh University December 2, 2009 The Tumor Microenvironment Littlepage et al Cancer Cell 2005 Cancer Stem Cells A small group of cells within the larger
Fig 1 CD163. CD11b S100A9. Sirius Red. 100μm ** ** CD163. CD11b S100A9 ** Sirius Red (PL) Sirius Red SUM Mo.
 T47D T47D + o SU-59 Fig SU-59 + o IHC score (-3) IHC score (-2) CD63 3 2 IHC score (-3) CD63 3 ** 2 CDb CDb * * SA9 SA9 ** * 2 IHC score (-4) αsa αsa 4 ** ** 2 Sirius Red μm IHC score (%) Sirius Red 8
T47D T47D + o SU-59 Fig SU-59 + o IHC score (-3) IHC score (-2) CD63 3 2 IHC score (-3) CD63 3 ** 2 CDb CDb * * SA9 SA9 ** * 2 IHC score (-4) αsa αsa 4 ** ** 2 Sirius Red μm IHC score (%) Sirius Red 8
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chan et al. 1.173/pnas.9654916 A Patient B Xenograft C * remaining feature of normal lymph node * * * D lymphocytes Infiltrating transitional carcinoma cells E Enlarged axillary
Supporting Information Chan et al. 1.173/pnas.9654916 A Patient B Xenograft C * remaining feature of normal lymph node * * * D lymphocytes Infiltrating transitional carcinoma cells E Enlarged axillary
TITLE: Investigation of the Akt/Pkb Kinase in the Development of Hormone- Independent Prostate Cancer
 AD Award Number: TITLE: Investigation of the Akt/Pkb Kinase in the Development of Hormone- Independent Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Linda A. degraffenried, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University
AD Award Number: TITLE: Investigation of the Akt/Pkb Kinase in the Development of Hormone- Independent Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Linda A. degraffenried, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University
1.The metastatic cascade. 2.Pathologic features of metastasis. 3.Therapeutic ramifications
 Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
Beverly A. Teicher, PhD DCTD/NCI. The content reflects my professional opinions, not an NCI policy statement.
 Beverly A. Teicher, PhD DCTD/NCI The content reflects my professional opinions, not an NCI policy statement. Outline 1. Transplantable Syngeneic Tumors 2. Human Tumor Xenografts 3. Disseminated Disease
Beverly A. Teicher, PhD DCTD/NCI The content reflects my professional opinions, not an NCI policy statement. Outline 1. Transplantable Syngeneic Tumors 2. Human Tumor Xenografts 3. Disseminated Disease
Using Histoindex Genesis 200 imaging technology to analyse the Pattern of ECM Deposition in Human Breast Cancer Tissue
 Using Histoindex Genesis 200 imaging technology to analyse the Pattern of ECM Deposition in Human Breast Cancer Tissue Introduction to technology High Resolution Detects fine collagen fibers up to 0.1µm
Using Histoindex Genesis 200 imaging technology to analyse the Pattern of ECM Deposition in Human Breast Cancer Tissue Introduction to technology High Resolution Detects fine collagen fibers up to 0.1µm
