Title oral squamous cell carcinoma. Alternative. Takano, N. Journal Oral oncology, 43(3):
|
|
|
- Magdalen Georgiana Riley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Establishment of a murine model of Title oral squamous cell carcinoma Author(s) Nomura, T; Shibahara, T; Katakura, Alternative Takano, N Journal Oral oncology, 43(3): URL Right Posted at the Institutional Resources for Unique Colle Available from
2 Establishment of a murine model of bone invasion by oral squamous cell carcinoma Takeshi Nomura, DDS, PhD,* Takahiko Shibahara, DDS, PhD Akira katakura, DDS, PhD,* Shizuka Matsubara, DDS,? and Nobuo Takano, DDS, PhD, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Tokyo Dental College, Chiba, Japan. * Assistant Professor. Professor and Chairman.? Research Fellow. Professor. Address correspondence and reprint requests to Dr Takeshi Nomura: Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Tokyo Dental College, Masago, Mihamaku, Chiba , JAPAN. Tel / Fax: / , tanomura@tdc.ac.jp Manuscript: 2 tables, 6 figures and 15 pages Key words: animal model, bone invasion, cytokine, SCC cell line, C3H mice, squamous cell carcinoma Running title: murine model of bone invasion 1
3 Abstruct: Purpose: This study examines the establishment an animal model of bone invasion by oral squamous cell carcinoma to clarify the mechanisms of osteoclast-mediated bone invasion. Materials and Methods: C3H/HeN mice were inoculated with SCCVII cells into the masseter region. At the end of week 3, all surviving mice were sacrificed and analyzed by three-dimensional imaging using micro-computed tomography, histopathological observation using Hematoxylin-Eosin staining and Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase staining, and confirmation of mrna expression of the osteoclast-related cytokines IL-6, TNF-α, and PTHrP. Results: SCCVII cells rapidly multiplied in the masseter muscle of the mice. Bone invasion was evident only in the SCCVII transplanted group on micro-computed tomography. The histopathologic findings obtained with H-E and TRAP staining indicated that the tumor cells in the mandible of all animals of the SCCVII transplanted group exhibited funicular invasion and presented a serrated pattern of bone resorption. The mrna expression of IL-6, PTHrP, and TNF-α increased as the control decreased. Conclusion: SCCVII cells were highly invasive into mandibular bone in C3H/HeN mice. This model was similar to the invasion of human oral cancer into maxillary and mandibular bone. Our mandibular invasion 2
4 model may provide a powerful new modality for the diagnosis and treatment of oral cancer with bone invasion. 3
5 Introduction Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is known to have a potent activity of local invasion. Its invasion into the adjoining maxilla and mandible, in particular, is a major clinical problem. 1,2 While gingival and oral floor carcinoma are frequently associated with mandibulectomy the extent of bone invasion can only be assessed by diagnostic imaging. It has been pointed out that resection of the maxilla and mandible occasionally amounts to oversurgery. In recent years, it has been reported that osteoclast associated with bone invasion and metastasis to the bone by cancer cells is mediated by osteoclasts rather than being directly caused by cancer cells (i.e., osteoclastic bone resorption). 3 We have carried out immunohistological analysis using specimens obtained from oral squamous cell carcinoma patients following mandibulectomy. 4 The results of these analytical studies have demonstrated in particular, that the presence of the osteoclast activation factors interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) have a strong involvement in this process. 5 In this study, we have prepared a murine model of mandibular invasion by cancer cells and investigated the presence of the osteoclast activation factors IL-6, TNF-α, and PTHrP in order to shed light on the mechanism of bone invasion by OSCC. 4
6 Materials and Methods Cell culture. The SCCVII used in this study is an established cell strain derived from OSCC on the oral floor in mice. 6 It has been reported both as a model for distant metastasis and as a model for salivary gland tumor transplanted to the submandibular gland. 7 The basal medium was Dulbecco Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) with a 10% addition of fetal bovine serum (FBS). This SCCVII cell strain was cultured in DMEM+10%FBS and used for experiments. This was allowed to stand in a 100mm dish for incubation at 37 C in the presence of 5%CO 2. The cell concentration was approximately 1.3 x 10 5 /ml. The cells were collected by centrifugation, and the cell concentration was adjusted to 1.0 x 10 5 /ml with DMEM. Animal model. The experimental animals consisted of twelve male C3H/HeN mice weighing approximately 20g (Sankyo Laboratories, Tokyo, Japan). They were divided into two groups: the control group and the SCCVII transplanted group, consisting of three and nine animals, respectively. All of the mice were maintained in the ordinary manner and treated in accordance with the Guidelines for Animal Experiments of the Tokyo Dental College. The animals in the SCCVII transplant group were maintained normally for three weeks after injection, into the left masseter region, of 50µL SCCVII cells adjusted to 2 x 10 7 /ml in a serum-free 5
7 medium in such a manner that no lesions were caused to the periosteum. The mice of the control group received 50µL of physiological saline solution alone, likewise injected into the left masseter region. Both groups were maintained under normal conditions in the same manner for three weeks. Treatment was given for 3 weeks. On days 1, 7, and 14, the mice were weighed and the longest diameter of the mass in the buccal region was measured in three directions. At the end of week 3, all surviving mice were sacrificed. The tumors were resected and preserved at -70 C, and the heads of the mice were fixed in 10% formalin (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., Osaka, Japan). The specimens were analyzed by (1) three-dimensional imaging using micro-computed tomography (micro-ct), (2) histopathological observation using Hematoxylin-Eosin (H-E) staining and Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase (TRAP) staining, and (3) confirmation of mrna expression of the osteoclast-related cytokines IL-6, TNF-α, and PTHrP. Micro-computed tomography (CT) and 3-dimensional reconstruction. The head and neck of the mice was imaged with a micro-ct (ultra-micro focus X ray CT unit KMS-755, Kashimura, Osaka, Japan), at a minimum tomographic width of 20-30µm. The imaging conditions were: lamp 6
8 voltage 45.0kV, lamp current 100.0µA, multiplying factor 2.0. After preparing two-dimensional slice data from the resulting images by the back projection method, a steric image was constructed with 3-dimensional reconstruction software (TRI/3D Bon; R S Ratoc, Tokyo, Japan). Hematoxylin-eosin (H-E) staining and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining. After subsequent decalcification with 10% formalin formate, the frontal sections of the occipital region were embedded in paraffin by the routine method to prepare thin slices for microscopy using a H-E double-stain. After decalcification with a 10% aqueous solution of EDTA, paraffin-embedded specimens were prepared and TRAP staining was performed using a TRAP Kit (Hokudo Co., Sapporo, Japan) and Mayer s hematoxylin (Mutoo Pure Chemicals Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Preparation of mrna and semiquantative RT-PCR. Specimens were taken from the SCCVII cultured cells as well as from the injected portions of the mice in the control group and the SCCVII transplanted group for RNA isolation using the AGPC method. After heating for five minutes, 1µg of the RNA sample was mixed with the reverse transcriptase solution to synthesize cdna. The reaction took place at 30 C for 60 minutes. IL-6, TNF-α, and PTHrP were then amplified by the PCR method and the 7
9 DNA product was confirmed by electrophoresis with 1.5% agarose gel, stained with ethidium-bromide, and photographed. Statistical analysis. To assess the statistical significance of body weights and tumor size, student s t test was performed. Differences of means among the percentage of mrna of 3 cytokines in the two groups were compared by 2 test. A value of 0.05 was considered statistically significant (SPSS 11.0 for windows 2001 software, USA). Results During the 3 weeks of treatment, 12 mice survived. In our bone invasion models, tumors usually grew for about 3-4 weeks and died after that (Fig 1). Body weights changed in each group during the initial three weeks. Compared with the control, the body weights of SCCVII transplanted group tended to decrease (Fig 2). The differences in tumor size were significant between the two groups. The tumors transplanted into the SCCVII transplanted group of mice grew rapidly. Mean tumor diameter was mm 3 in the SCCVII transplanted group after 3 weeks (Fig 1,2). Three-dimensional image analysis using micro-ct. Micro-CT showed bone invasion only in the SCCVII transplanted group. Anatomical observation of the maxilla and mandible using the micro-ct revealed an inclination of the teeth and bone resorption in the mandibular angle, on the 8
10 surface of the mandible and in the zygomatic arch, being different from the ordinary facial bones. The mandibles were obviously asymmetric, and the zygomas were bowed (Fig 3). Appearance of resorption in the mandibular bone. The histopathologic findings obtained with H-E staining indicated that the tumor cells in the mandible of all animals of the SCCVII transplanted group exhibited funicular invasion and presented a serrated pattern of bone resorption (Fig 4). The TRAP stain findings showed evidence of accumulated osteoclasts in considerable numbers around the mandible (Fig 5). Expression of the osteoclast-related cytokine mrna. It has been confirmed that SCCVII cells express IL-6, TNF-α, and PTHrP at the mrna level. Similarly, tumors of the SCCVII transplanted mice showed mrna expression of IL-6, TNF-α, and PTHrP. In contrast, the control group showed no evidence of expression (Fig 6). This makes it clear that the newly established murine model of invasive OSCC closely reflects the clinical features of human invasive OSCC and is thus useful in shedding light on the mechanism of bone invasion. Given that IL-6, TNF-α, and PTHrP are involved in the same manner as in humans it can be surmised that bone resorption is mediated by the cytokines produced by the tumor cells. 9
11 Discussion Animal models are essential for studies of the mechanism of bone invasion by OSCC. SCCVII is a malignant tumor cell line derived from the mouse and grows without being affected by the immune system. 6,7 This cell line was first used to develop an animal model of oral cancer of the oral floor. 6 Tumor growth, cervical lymph node metastasis, and pulmonary metastasis have been confirmed. In the present study, SCCVII cells were injected into the masseter region of mice. It has been confirmed that the transplantation of SCCVII cells into the masseter region of C3H/HeN mice resulted in significant tumor proliferation after three weeks. 3 This tumor is characterized by its bone invasion potential, and marked bone resorption was detected in the mandible and the facial bones. The histopathologic findings showed evidence of funicular invasion of the tumor cells into the mandible with a serrated bone resorption pattern in all specimens of the SCCVII transplanted group. Moreover, it was possible to extract osteoclasts not only in the H-E but also in the TRAP stained specimens. This was clear evidence of the fact that bone resorption was osteoclast-mediated. The present experimental setup can thus be evaluated as being extremely useful as a bone invasion model that closely reflects the clinical features. 10
12 In human invasive OSCC the tumor cells are known to show a strong expression of IL-6, TNF-α, and PTHrP. 2,3,8 In our animal models, it was possible to confirm the expression of these cytokines from the SCCVII cultured cells at the mrna level. Roughly the same results (i.e., enhanced expression of all cytokines at the mrna level) were also obtained with neoplastic tumor tissues that had been transplanted. This substantiates the fact that the SCCVII cell strains are also subject to the influence of the osteoclast-related cytokines. Much of the significant progress made in the determination of the bone invasion mechanism is due to the recent spectacular advances in the basic study of bone metabolism. 8,9 The isolation and identification of the PTHrP, the causal factor of hypercalcemia associated with cancer, in particular, was a milestone in the development of research on bone metastasis and bone invasion by cancer cells. 9 Okamoto et al. produced evidence in their in-vitro study that IL-6 is involved in the bone invasion of OSCC. 2 Recently, it has been clarified that the differentiation and functions of osteoclasts are strictly controlled by the RANKL expressed on the cell membranes of the osteoblasts or marrow interstitial cells. 10 We, for our part, have carried out immunohistochemical analyses on various osteoclast related cytokines, and have been able to demonstrate the possibility that IL-6, TNF-α, and PTHrP may be involved at least in bone 11
13 invasion by human gingival cancer. 3,5 In much the same manner it has also been possible, in our present study with the SCCVII cell strain, to substantiate the production of these cytokines and their involvement in bone invasion and in causing the formation of osteoclasts in large numbers. The use of the animal model may provide a means of shedding light on the mechanism by which OSCC with the potential for cytokine production causes bone invasion. There is no doubting the fact that the clarification of the cytokine network is strategically most important in establishing a method for the diagnosis and treatment of bone invasion by gingival cancer. The preoperative testing of biopsy samples to determine the extent to which cytokines are present is likely to become, in the foreseeable future, a therapy planning approach that is consistent with the principles of evidence-based medicine. In any event, however, these studies make use of animal models related to bone invasion, but the bone invasion model involving the cell transplantation of OSCC has been established only at our Department. It is our understanding that this model reflects the clinical features most closely and is thus most effective and useful in elucidating the invasion mechanism and in clarifying the treatment method. In this context we would like to emphasize that the determination of the mechanism of bone 12
14 invasion in the oral cancer domain in fuller detail is bound to substantially benefit the further progress of dental medicine. 11,12 In the future, it will be necessary to investigate the expression of cytokines and calcium in the serum in fuller detail at the protein level. It is also felt essential for progress studying research and in the interest of developing new methods for cancer therapy targeting the osteoclast activating factors to introduce antisense oligonucleotides of the respective cytokines in this cell strain to inhibit the expression of these cytokines and investigate their involvement in bone invasion and suppress bone invasion through the administration of their antibodies and bone resorption inhibitors. 13
15 References 1. Senba I, Matsuuchi H, Miura, Y. Histomorphometric analysis of osteoclastic resorption in bone directly invaded by gingival squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med 1996; 25(8): Okamoto M, Hiura K, Ohe G, Ohba Y, Terai K, Oshikawa T, et al. Mechanism for bone invasion of oral cancer cells mediated by interleukin-6 in vitro and in vivo. Cancer 2000; 89(9): Cui N, Nomura T, Noma H, Yokoo K, Takagi R, Hashimoto S, et al. Effect of YM529 on mandibular invasion model by oral squmous cell carcinoma in mice. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11(7): Nomura T, Shibahara T, Cui N, Noma H. Patterns of mandibular invasion by gingival squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2005; 63(10): Nomura T, Shibahara T, Cui N, Noma H. A study of osteoclast-related cytokines in mandibular invasion by squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2005; 34(7): O'Malley BW, Cope KA, Chen SH, Li D, Schwarta MR, Woo SL. Combination gene therapy for oral cancer in a murine model. Cancer Res 1996; 56(8):
16 7. O'Malley BW Jr, Cope KA, Johnson CS, Schwartz MR. A new immunocompetent murine model for oral cancer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1997; 123(1): Roux S, Orcel P. Bone loss. Factors that regulate osteoclast differentiation: an update. Arthritis Res 2000; 2(6): Rodan GA: Bisphosphonates and primary hyperparathyroidism. J Bone Miner Res 2002; 17 Suppl 2: Palmqvist P, Persson E, Conaway HH, Lerner UH. IL-6, leukemia inhibitory factor, and oncostatin M stimulate bone resorption and regulate the expression of receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand, osteoprotegerin, and receptor activator of NF-kappa B in mouse calvariae. J immunol 2002; 169(6): Rani CS, Macdougall M. Dental cells express factors that regulate bone resorption. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun 2000; 3(3): Morony S, Capparelli C, Sarosi I, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Kostenuik PJ. Osteoprotegerin inhibits osteolysis and decreases skeletal tumor burden in syngeneic and nude mouse models of experimental bone metastasis. Cancer Res 2001; 61(11):
17 16
18 17
19 18
20 19
21 20
22 21
23 22
24 23
Immunohistochemical expression of RANKL, RANK, and OPG in human oral squamous cell carcinoma
 Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2009.00793.x J Oral Pathol Med (2009) 38: 753 758 ª John Wiley & Sons A/S Æ All rights reserved interscience.wiley.com/journal/jop Immunohistochemical
Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2009.00793.x J Oral Pathol Med (2009) 38: 753 758 ª John Wiley & Sons A/S Æ All rights reserved interscience.wiley.com/journal/jop Immunohistochemical
Siglec-15 Is A Potential Therapeutic Target For Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
 Siglec-15 Is A Potential Therapeutic Target For Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Yusuke Kameda, Masahiko Takahata, Tomohiro Shimizu, Hiroki Hamano, Norimasa Iwasaki. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hokkaido
Siglec-15 Is A Potential Therapeutic Target For Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Yusuke Kameda, Masahiko Takahata, Tomohiro Shimizu, Hiroki Hamano, Norimasa Iwasaki. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hokkaido
The inhibition of RANKL/RANK signaling by osteoprotegerin suppresses bone invasion by oral squamous cell carcinoma cells
 Carcinogenesis vol.32 no.11 pp.1634 1640, 2011 doi:10.1093/carcin/bgr198 Advance Access publication September 1, 2011 The inhibition of RANKL/RANK signaling by osteoprotegerin suppresses bone invasion
Carcinogenesis vol.32 no.11 pp.1634 1640, 2011 doi:10.1093/carcin/bgr198 Advance Access publication September 1, 2011 The inhibition of RANKL/RANK signaling by osteoprotegerin suppresses bone invasion
Maxillary Verrucous Carcinoma Coincident With Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Colon Adenocarcinoma
 Int Surg 2012;97:270 274 Case Report Maxillary Verrucous Carcinoma Coincident With Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Colon Adenocarcinoma Hatsumi Yano Kato 1, Hiroaki Ishibashi 1, Yoshiki Nariai 1, Katsumi
Int Surg 2012;97:270 274 Case Report Maxillary Verrucous Carcinoma Coincident With Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Colon Adenocarcinoma Hatsumi Yano Kato 1, Hiroaki Ishibashi 1, Yoshiki Nariai 1, Katsumi
Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 2, pp. 45-49, 2003 Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case MASAHIRO UMEDA 1), SATOSHI YOKOO 1), YASUYUKI SHIBUYA 1), TAKAHIDE KOMORI
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 2, pp. 45-49, 2003 Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case MASAHIRO UMEDA 1), SATOSHI YOKOO 1), YASUYUKI SHIBUYA 1), TAKAHIDE KOMORI
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Osteoclast Culture Kit
 K-ASSAY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Osteoclast Culture Kit For the culture of Osteoclasts from precursor cells. Cat. No.: CC-107 Rat Osteoclast Precursor Cells, V-1 CC-109 Mouse Osteoclast Precursor Cells,
K-ASSAY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Osteoclast Culture Kit For the culture of Osteoclasts from precursor cells. Cat. No.: CC-107 Rat Osteoclast Precursor Cells, V-1 CC-109 Mouse Osteoclast Precursor Cells,
ITO, Yasuhiro ; FUJII, Mizue ; SHIBUYA, Takashi ; UEHARA, Jiro ; SATO, Katsuhiko ; IIZUKA, Hajime
 Journal of Dermatology (2011) 38(5):515-517. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor-producing squamous cell carcinoma of the skin ITO, Yasuhiro ; FUJII, Mizue ; SHIBUYA, Takashi ; UEHARA, Jiro ; SATO, Katsuhiko
Journal of Dermatology (2011) 38(5):515-517. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor-producing squamous cell carcinoma of the skin ITO, Yasuhiro ; FUJII, Mizue ; SHIBUYA, Takashi ; UEHARA, Jiro ; SATO, Katsuhiko
Osteoclast Culture Kit
 K-ASSAY Osteoclast Culture Kit For the culture of Osteoclasts from precursor cells. Cat. No.: CC-107 Rat Osteoclast Precursor Cells, V-1 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 091708 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION
K-ASSAY Osteoclast Culture Kit For the culture of Osteoclasts from precursor cells. Cat. No.: CC-107 Rat Osteoclast Precursor Cells, V-1 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 091708 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION
hypercalcemia of malignancy hyperparathyroidism PHPT the most common cause of hypercalcemia in the outpatient setting the second most common cause
 hyperparathyroidism A 68-year-old woman with documented osteoporosis has blood tests showing elevated serum calcium and parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels: 11.2 mg/dl (8.8 10.1 mg/dl) and 88 pg/ml (10-60),
hyperparathyroidism A 68-year-old woman with documented osteoporosis has blood tests showing elevated serum calcium and parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels: 11.2 mg/dl (8.8 10.1 mg/dl) and 88 pg/ml (10-60),
The morphological studies of root r maxillary primary canines and their Title the position of successive permanen Micro-CT
 The morphological studies of root r maxillary primary canines and their Title the position of successive permanen Micro-CT Author(s) Saka, H; Koyama, T; Tamatsu, Y; Usa Alternative Journal Pediatric dental
The morphological studies of root r maxillary primary canines and their Title the position of successive permanen Micro-CT Author(s) Saka, H; Koyama, T; Tamatsu, Y; Usa Alternative Journal Pediatric dental
Comparison of salivary cytokine lev Title cancer patients and healthy subject
 Comparison of salivary cytokine lev Title cancer patients and healthy subject Katakura, A; Kamiyama, I; Takano, N Author(s) Muramatsu, T; Ishihara, K; Takagi, Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College,
Comparison of salivary cytokine lev Title cancer patients and healthy subject Katakura, A; Kamiyama, I; Takano, N Author(s) Muramatsu, T; Ishihara, K; Takagi, Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College,
THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S.
 THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S. Skeletal anchorage, the concept of using the facial skeleton to control tooth
THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S. Skeletal anchorage, the concept of using the facial skeleton to control tooth
TitleTemporomandibular joint ankylosis: Mitarashi, S; Abe, S; Watanabe, H; Author(s) Hashimoto, M; Ide, Y
 TitleTemporomandibular joint ankylosis: Mitarashi, S; Abe, S; Watanabe, H; Author(s) Hashimoto, M; Ide, Y Cranio : the journal of craniomandi Journal 20(1): 67-71 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/1098 Right
TitleTemporomandibular joint ankylosis: Mitarashi, S; Abe, S; Watanabe, H; Author(s) Hashimoto, M; Ide, Y Cranio : the journal of craniomandi Journal 20(1): 67-71 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/1098 Right
Delayed diagnosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma following dental treatment
 ORAL doi 10.1308/003588413X13629960045599 T Singh 1, M Schenberg 2 1 Maxillofacial Surgery Unit, Dandenong Hospital, Melbourne, Australia 2 Honorary Senior Lecturer, Department of Surgery, Monash University,
ORAL doi 10.1308/003588413X13629960045599 T Singh 1, M Schenberg 2 1 Maxillofacial Surgery Unit, Dandenong Hospital, Melbourne, Australia 2 Honorary Senior Lecturer, Department of Surgery, Monash University,
Case Scenario. 7/13/12 Anterior floor of mouth biopsy: Infiltrating squamous cell carcinoma, not completely excised.
 Case Scenario 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of alcohol.
Case Scenario 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of alcohol.
(formalin fixed) 6 non-neoplastic spots (6 spots) Corresponding normal tissues with cancers: Yes Diameter: 1. 0 mm
 CBA729-Test slide, Head and neck cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 6 Tissue type: Test slide, Head and neck cancer tissues No. of spots: 6 spots from each
CBA729-Test slide, Head and neck cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 6 Tissue type: Test slide, Head and neck cancer tissues No. of spots: 6 spots from each
RD-100i OSNA the new generation of sentinel lymph node analysis in breast cancer
 RD-1i OSNA the new generation of sentinel lymph node analysis in breast cancer RD-1i OSNA the new generation of sentinel lymph node analysis in breast cancer Sentinel node biopsy has rapidly emerged as
RD-1i OSNA the new generation of sentinel lymph node analysis in breast cancer RD-1i OSNA the new generation of sentinel lymph node analysis in breast cancer Sentinel node biopsy has rapidly emerged as
Repair of the mandibular nerve by a Title grafting after ablative surgery of. Shibahara, T; Noma, H; Takasaki, Y; Author(s) Fujikawa, M
 Repair of the mandibular nerve by a Title grafting after ablative surgery of Shibahara, T; Noma, H; Takasaki, Y; Author(s) Fujikawa, M Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/1019
Repair of the mandibular nerve by a Title grafting after ablative surgery of Shibahara, T; Noma, H; Takasaki, Y; Author(s) Fujikawa, M Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/1019
Case Scenario 1. 7/13/12 Anterior floor of mouth biopsy: Infiltrating squamous cell carcinoma, not completely excised.
 Case Scenario 1 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of
Case Scenario 1 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of
Supplementary methods:
 Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS
 MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin
 Materials and Methods Pair Feeding Experiment For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin (0.005%), which is average daily food intake of mice fed control HFD ad libitum at week
Materials and Methods Pair Feeding Experiment For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin (0.005%), which is average daily food intake of mice fed control HFD ad libitum at week
RD-100i OSNA the new generation of sentinel lymph node analysis in breast cancer
 RD-1i OSNA the new generation of sentinel lymph node analysis in breast cancer www.sysmex-europe.com RD-1i OSNA the new generation of sentinel lymph node analysis in breast cancer Sentinel node biopsy
RD-1i OSNA the new generation of sentinel lymph node analysis in breast cancer www.sysmex-europe.com RD-1i OSNA the new generation of sentinel lymph node analysis in breast cancer Sentinel node biopsy
Establishment of in Vivo Metastasis Model of Human Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma: Detection of Metastasis by PCR with Human β -Globin Gene
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 48, No. 5, pp. 145-152, 2002 Establishment of in Vivo Metastasis Model of Human Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma: Detection of Metastasis by PCR with Human β -Globin Gene HIDEKI KOMATSUBARA,
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 48, No. 5, pp. 145-152, 2002 Establishment of in Vivo Metastasis Model of Human Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma: Detection of Metastasis by PCR with Human β -Globin Gene HIDEKI KOMATSUBARA,
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 OMPJ Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia 10.5005/jp-journals-10037-1003 and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma ORIGINAL RESEARCH Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression
OMPJ Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia 10.5005/jp-journals-10037-1003 and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma ORIGINAL RESEARCH Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
(loco-regional disease)
 (loco-regional disease) (oral cavity) (circumvillae papillae) (subsite) A (upper & lower lips) B (buccal membrane) C (mouth floor) D (upper & lower gingiva) E (hard palate) F (tongue -- anterior 2/3 rds
(loco-regional disease) (oral cavity) (circumvillae papillae) (subsite) A (upper & lower lips) B (buccal membrane) C (mouth floor) D (upper & lower gingiva) E (hard palate) F (tongue -- anterior 2/3 rds
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Stromal Fat Content of the Parathyroid Gland
 Stromal Fat Content of the Parathyroid Gland TAKAO OBARA,* YOSHIHIDE FUJIMOTO* AND MOTOHIKO AIBA** *Department of Endocrine Surgery and **Department of Surgical Pathology, Tokyo Women's Medical College,
Stromal Fat Content of the Parathyroid Gland TAKAO OBARA,* YOSHIHIDE FUJIMOTO* AND MOTOHIKO AIBA** *Department of Endocrine Surgery and **Department of Surgical Pathology, Tokyo Women's Medical College,
Cancer of the Oral Cavity
 The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies Current Concepts in Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology Cancer of the Oral Cavity Ashok Shaha Principals of Management of Oral Cancer A)
The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies Current Concepts in Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology Cancer of the Oral Cavity Ashok Shaha Principals of Management of Oral Cancer A)
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
The influence of radiotherapy on osseointegration
 Experience with Osseointegrated Implants Placed in Irradiated Tissues in Japan and the United States Atsushi Niimi, DDS, DMSc*/Minoru Ueda, DDS, PhD**/ Eugene E. Keller, DDS, PhD***/Philip Worthington,
Experience with Osseointegrated Implants Placed in Irradiated Tissues in Japan and the United States Atsushi Niimi, DDS, DMSc*/Minoru Ueda, DDS, PhD**/ Eugene E. Keller, DDS, PhD***/Philip Worthington,
Case Report A Case of Primary Submandibular Gland Oncocytic Carcinoma
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 384238, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/384238 Case Report A Case of Primary Submandibular Gland Oncocytic Carcinoma Kunihiko Tokashiki, Kiyoaki
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 384238, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/384238 Case Report A Case of Primary Submandibular Gland Oncocytic Carcinoma Kunihiko Tokashiki, Kiyoaki
Osteoclast Activity Assay Substrate
 Osteoclast Activity Assay Substrate For Research Use Only OSCOTECT INC. #3201 Trade Tower Samsung-dong 159, Kangnam-ku Seoul 135-729, Korea Tel: +82-2-6000-7666 / Fax: +82-2-6000-7667 customer@oscotec.com
Osteoclast Activity Assay Substrate For Research Use Only OSCOTECT INC. #3201 Trade Tower Samsung-dong 159, Kangnam-ku Seoul 135-729, Korea Tel: +82-2-6000-7666 / Fax: +82-2-6000-7667 customer@oscotec.com
Skeletal. Parathyroid hormone-related protein Analyte Information
 Skeletal Parathyroid hormone-related protein Analyte Information 1 2012-04-04 Parathyroid hormone related protein (PTHrP) Introduction Parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) is actually a family of
Skeletal Parathyroid hormone-related protein Analyte Information 1 2012-04-04 Parathyroid hormone related protein (PTHrP) Introduction Parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) is actually a family of
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
II. RELATION TO BONE DISEASE INTRODUCTION. M.M. POPOVTZER, W.E. HUFFER, W.P. GElS, W.S. HAMMOND, T.E. STARZL
 II. RELATION TO BONE DISEASE M.M. POPOVTZER, W.E. HUFFER, W.P. GElS, W.S. HAMMOND, T.E. STARZL INTRODUCTION It has been generally assumed that azotemic osteodystrophy resolves after kidney transplantation
II. RELATION TO BONE DISEASE M.M. POPOVTZER, W.E. HUFFER, W.P. GElS, W.S. HAMMOND, T.E. STARZL INTRODUCTION It has been generally assumed that azotemic osteodystrophy resolves after kidney transplantation
Supplementary Materials. for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis
 Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Iatrogenic seeding of osteosarcoma in a tracheotomy tract a case report
 CASE REPORT Iatrogenic seeding of osteosarcoma in a tracheotomy tract a case report Irit Duek 1, Richard Lopchinsky 1, Sharon Akrish 2 & Ziv Gil 1 1 Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery,
CASE REPORT Iatrogenic seeding of osteosarcoma in a tracheotomy tract a case report Irit Duek 1, Richard Lopchinsky 1, Sharon Akrish 2 & Ziv Gil 1 1 Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery,
Three-dimensional characterization of osteoclast bone-resorbing activity in the resorption lacunae
 J Med Dent Sci 2009; 56: 107-112 Original Article Three-dimensional characterization of osteoclast bone-resorbing activity in the resorption lacunae Niroshani Surangika Soysa 1, Neil Alles 1,2, Kazuhiro
J Med Dent Sci 2009; 56: 107-112 Original Article Three-dimensional characterization of osteoclast bone-resorbing activity in the resorption lacunae Niroshani Surangika Soysa 1, Neil Alles 1,2, Kazuhiro
A Novel Murine Model Of Adynamic Bone Disease (ABD)
 A Novel Murine Model Of Adynamic Bone Disease (ABD) Adeline H. Ng 1,2, Thomas L. Willett, PhD 2,1, Benjamin A. Alman 3,1, Marc D. Grynpas 1,2. 1 University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2 Samuel Lunenfeld
A Novel Murine Model Of Adynamic Bone Disease (ABD) Adeline H. Ng 1,2, Thomas L. Willett, PhD 2,1, Benjamin A. Alman 3,1, Marc D. Grynpas 1,2. 1 University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2 Samuel Lunenfeld
Survival impact of cervical metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of hard palate
 Vol. 116 No. 1 July 2013 Survival impact of cervical metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of hard palate Quan Li, MD, a Di Wu, MD, b,c Wei-Wei Liu, MD, PhD, b,c Hao Li, MD, PhD, b,c Wei-Guo Liao, MD,
Vol. 116 No. 1 July 2013 Survival impact of cervical metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of hard palate Quan Li, MD, a Di Wu, MD, b,c Wei-Wei Liu, MD, PhD, b,c Hao Li, MD, PhD, b,c Wei-Guo Liao, MD,
Osteoma of Mandibular Condyle as Ca Title Pain and Limited-mouth-opening: Cas. Yonezu, H; Wakoh, M; Otonari, T; Sa Author(s) Hashimoto, S; Uchiyama, T
 Osteoma of Mandibular Condyle as Ca Title Pain and Limited-mouth-opening: Cas Yonezu, H; Wakoh, M; Otonari, T; Sa Author(s) Hashimoto, S; Uchiyama, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/417
Osteoma of Mandibular Condyle as Ca Title Pain and Limited-mouth-opening: Cas Yonezu, H; Wakoh, M; Otonari, T; Sa Author(s) Hashimoto, S; Uchiyama, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/417
ORAL MELANOMA Definition Epidemiology Clinical Presentation
 ORAL MELANOMA Definition Melanoma is a highly malignant neoplasia, arising from melanocytes, the cells that produce the brownish pigment melanin. Melanin is the determinant in skin colour and protects
ORAL MELANOMA Definition Melanoma is a highly malignant neoplasia, arising from melanocytes, the cells that produce the brownish pigment melanin. Melanin is the determinant in skin colour and protects
Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts
 77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
Reconstruction of a Mandibular Osteoradionecrotic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap.
 Case Report Reconstruction of a Mandibular Osteoradionecrotic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap. Using Synthes ProPlan CMF, Patient Specific Plate Contouring (PSPC) and the MatrixMANDIBLE Plating
Case Report Reconstruction of a Mandibular Osteoradionecrotic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap. Using Synthes ProPlan CMF, Patient Specific Plate Contouring (PSPC) and the MatrixMANDIBLE Plating
Spontaneous Regeneration of the Mandible after Hemimandibulectomy:
 Case Report Spontaneous Regeneration of the Mandible after Hemimandibulectomy: Report of a Case A. Khodayari 1, A. Khojasteh 2, MT. Kiani 3, A. Nayebi 4, L. Mehrdad 5, M. Vahdatinia 6 1 DMD, MS. Associate
Case Report Spontaneous Regeneration of the Mandible after Hemimandibulectomy: Report of a Case A. Khodayari 1, A. Khojasteh 2, MT. Kiani 3, A. Nayebi 4, L. Mehrdad 5, M. Vahdatinia 6 1 DMD, MS. Associate
Lung cancer pleural invasion was recognized as a poor prognostic
 Visceral pleural invasion classification in non small cell lung cancer: A proposal on the basis of outcome assessment Kimihiro Shimizu, MD a Junji Yoshida, MD a Kanji Nagai, MD a Mitsuyo Nishimura, MD
Visceral pleural invasion classification in non small cell lung cancer: A proposal on the basis of outcome assessment Kimihiro Shimizu, MD a Junji Yoshida, MD a Kanji Nagai, MD a Mitsuyo Nishimura, MD
Survey of Laryngeal Cancer at SBUH comparing 108 cases seen here from to the NCDB of 9,256 cases diagnosed nationwide in 2000
 Survey of Laryngeal Cancer at comparing 108 cases seen here from 1998 2002 to the of 9,256 cases diagnosed nationwide in 2000 Stony Brook University Hospital Cancer Program Annual Report 2002-2003 Gender
Survey of Laryngeal Cancer at comparing 108 cases seen here from 1998 2002 to the of 9,256 cases diagnosed nationwide in 2000 Stony Brook University Hospital Cancer Program Annual Report 2002-2003 Gender
EXPANSION RESEARCH FOR DEVELOPMENT OF LOCAL ANESTHETIC HAVING ANTI INFLAMMATORY ACTION
 No. 137 EXPANSION RESEARCH FOR DEVELOPMENT OF LOCAL ANESTHETIC HAVING ANTI INFLAMMATORY ACTION Takuya MIYAWAKI Professor Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences Okayama University
No. 137 EXPANSION RESEARCH FOR DEVELOPMENT OF LOCAL ANESTHETIC HAVING ANTI INFLAMMATORY ACTION Takuya MIYAWAKI Professor Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences Okayama University
Prognostic Significance of Extranodal Cancer Invasion of Mediastinal Lymph Nodes in Lung Cancer
 Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 198, 1 (), 7-1 Prognostic Significance of Extranodal Cancer Invasion of Mediastinal Lymph Nodes in Lung Cancer KEIICHI SUEMASU, M.D. AND TSUGUO NARUKE, M.D. Department of Surgery,
Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 198, 1 (), 7-1 Prognostic Significance of Extranodal Cancer Invasion of Mediastinal Lymph Nodes in Lung Cancer KEIICHI SUEMASU, M.D. AND TSUGUO NARUKE, M.D. Department of Surgery,
An Analysis of Distant Metastases in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 Original Araki Yasui et al. : Distant Metastases in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Journal of Hard Tissue Biology 19[1] (2010) p27-32 2010 The Hard Tissue Biology Network Association Printed in Japan, All
Original Araki Yasui et al. : Distant Metastases in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Journal of Hard Tissue Biology 19[1] (2010) p27-32 2010 The Hard Tissue Biology Network Association Printed in Japan, All
Supplemental Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
IRA-International Journal of Applied Sciences ISSN Vol. 03 Issue 02 (May, 2016) Paper DOI:
 IRA-International Journal of Applied Sciences ISSN 2455-4499 Vol. 03 Issue 02 (May, 2016) Paper DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.21013/jas.v3.n2.p8 Pathophysiology of Giant Cell Formation in Giant Cell Tumor
IRA-International Journal of Applied Sciences ISSN 2455-4499 Vol. 03 Issue 02 (May, 2016) Paper DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.21013/jas.v3.n2.p8 Pathophysiology of Giant Cell Formation in Giant Cell Tumor
Screw hole-positioning guide and plate-positioning guide: A novel method to assist mandibular reconstruction
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 301e305 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com CASE REPORT Screw hole-positioning guide and plate-positioning guide: A novel method
Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 301e305 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com CASE REPORT Screw hole-positioning guide and plate-positioning guide: A novel method
Award Number: W81XWH TITLE: Regenerative Stem Cell Therapy for Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-593 TITLE: Regenerative Stem Cell Therapy for Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Selvarangan Ponnazhagan, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Alabama
AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-593 TITLE: Regenerative Stem Cell Therapy for Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Selvarangan Ponnazhagan, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Alabama
Catholic University of Louvain, St - Luc University Hospital Head and Neck Oncology Programme. Anatomopathology. Pathology 1 Sept.
 Anatomopathology Pathology 1 Anatomopathology Biopsies Frozen section Surgical specimen Peculiarities for various tumor site References Pathology 2 Biopsies Minimum data, which should be given by the pathologist
Anatomopathology Pathology 1 Anatomopathology Biopsies Frozen section Surgical specimen Peculiarities for various tumor site References Pathology 2 Biopsies Minimum data, which should be given by the pathologist
Ameloblastic Carcinoma-Secondary Type,A Rare Case Report and Distinction from Malignant Ameloblastoma
 Ameloblastic Carcinoma-Secondary Type,A Rare Case Report and Distinction from Malignant Ameloblastoma Rajesh B Dhirawani, Sumit Asrani, Anshalika Agrawal, Sauvik Singha* and Kshitij Aggarwal Department
Ameloblastic Carcinoma-Secondary Type,A Rare Case Report and Distinction from Malignant Ameloblastoma Rajesh B Dhirawani, Sumit Asrani, Anshalika Agrawal, Sauvik Singha* and Kshitij Aggarwal Department
CRIPTO-1 A POSSIBLE NEW BIOMARKER IN GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME PIA OLESEN, MD, PHD STUDENT
 CRIPTO-1 A POSSIBLE NEW BIOMARKER IN GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME PIA OLESEN, MD, PHD STUDENT Glioblastoma WHO Grade IV Glioma Heterogenic Undiffenrentiated phenotype 50% of all Gliomas Around 600 patients
CRIPTO-1 A POSSIBLE NEW BIOMARKER IN GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME PIA OLESEN, MD, PHD STUDENT Glioblastoma WHO Grade IV Glioma Heterogenic Undiffenrentiated phenotype 50% of all Gliomas Around 600 patients
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(1): 9 18 Original Article doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0500 Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago Hiroki Imai 1), Tetsuhide Makiguchi
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(1): 9 18 Original Article doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0500 Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago Hiroki Imai 1), Tetsuhide Makiguchi
Expression analysis of histidine decarboxylase in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Annals of Biological Research, 2013, 4 (6):36-40 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0976-1233 CODEN (USA): ABRNBW Expression analysis
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Annals of Biological Research, 2013, 4 (6):36-40 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0976-1233 CODEN (USA): ABRNBW Expression analysis
Chapter 2 Staging of Breast Cancer
 Chapter 2 Staging of Breast Cancer Zeynep Ozsaran and Senem Demirci Alanyalı 2.1 Introduction Five decades ago, Denoix et al. proposed classification system (tumor node metastasis [TNM]) based on the dissemination
Chapter 2 Staging of Breast Cancer Zeynep Ozsaran and Senem Demirci Alanyalı 2.1 Introduction Five decades ago, Denoix et al. proposed classification system (tumor node metastasis [TNM]) based on the dissemination
HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(2):155 159 HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa CRISTIANA SIMIONESCU 1), CL. MĂRGĂRITESCU 1), CLAUDIA
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(2):155 159 HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa CRISTIANA SIMIONESCU 1), CL. MĂRGĂRITESCU 1), CLAUDIA
Rat Model of Bone Metastasis Obtained by Mammary Cancer Transplantation
 Rat Model of Bone Metastasis Obtained by Mammary Cancer Transplantation ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Cancer Research and Therapy Mammary adenocarcinoma was induced by administering 7, 12-dimethylbenz (a)
Rat Model of Bone Metastasis Obtained by Mammary Cancer Transplantation ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Cancer Research and Therapy Mammary adenocarcinoma was induced by administering 7, 12-dimethylbenz (a)
Diagnosis of thoracic endometriosis with immunohistochemistry
 Original Article Diagnosis of thoracic endometriosis with immunohistochemistry Yo Kawaguchi 1,2, Jun Hanaoka 1, Yasuhiko Ohshio 1, Tomoyuki Igarashi 1, Keigo Okamoto 1, Ryosuke Kaku 1, Kazuki Hayashi 1,
Original Article Diagnosis of thoracic endometriosis with immunohistochemistry Yo Kawaguchi 1,2, Jun Hanaoka 1, Yasuhiko Ohshio 1, Tomoyuki Igarashi 1, Keigo Okamoto 1, Ryosuke Kaku 1, Kazuki Hayashi 1,
Case Report Joint Use of Skull Base Surgery in a Case of Pediatric Parotid Gland Carcinoma
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology, Article ID 158451, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/158451 Case Report Joint Use of Skull Base Surgery in a Case of Pediatric Parotid Gland Carcinoma Yuri Ueda, 1
Case Reports in Otolaryngology, Article ID 158451, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/158451 Case Report Joint Use of Skull Base Surgery in a Case of Pediatric Parotid Gland Carcinoma Yuri Ueda, 1
CASE REPORT. Abstract. Case Report. Introduction
 CASE REPORT Denosumab is Effective for Controlling Serum Calcium Levels in Patients with Humoral Hypercalcemia of Malignancy Syndrome: A Case Report on Parathyroid Hormone-related Protein-producing Cholangiocarcinoma
CASE REPORT Denosumab is Effective for Controlling Serum Calcium Levels in Patients with Humoral Hypercalcemia of Malignancy Syndrome: A Case Report on Parathyroid Hormone-related Protein-producing Cholangiocarcinoma
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE IN THE HEAD & NECK
 LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE IN THE HEAD & NECK Like other parts of the body, the head and neck contains lymph nodes (commonly called glands). Which form part of the overall Lymphatic Drainage system of the body.
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE IN THE HEAD & NECK Like other parts of the body, the head and neck contains lymph nodes (commonly called glands). Which form part of the overall Lymphatic Drainage system of the body.
THREE-DIMENSIONAL COMPUTED TOMOGRAPIDC ANALYSIS FOR PLACEMENT OF MAXILLOFACIAL IMPLANTS AFTER MAXILLECTOMY
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 56. 69-79,1993 THREE-DIMENSIONAL COMPUTED TOMOGRAPIDC ANALYSIS FOR PLACEMENT OF MAXILLOFACIAL IMPLANTS AFTER MAXILLECTOMY MINORU VEDA, YOSHIHIRO SAWAKI, and TOSHIO KANEDA Department
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 56. 69-79,1993 THREE-DIMENSIONAL COMPUTED TOMOGRAPIDC ANALYSIS FOR PLACEMENT OF MAXILLOFACIAL IMPLANTS AFTER MAXILLECTOMY MINORU VEDA, YOSHIHIRO SAWAKI, and TOSHIO KANEDA Department
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Immunohistochemical Study on Blood Antigens in Primary Breast Carcinom Tomita, Masao; Nakagoe, Toru; Kawah Tagawa, Yutaka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia.
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Immunohistochemical Study on Blood Antigens in Primary Breast Carcinom Tomita, Masao; Nakagoe, Toru; Kawah Tagawa, Yutaka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia.
Neoplasia 2018 lecture 11. Dr H Awad FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 lecture 11 Dr H Awad FRCPath Clinical aspects of neoplasia Tumors affect patients by: 1. their location 2. hormonal secretions 3. paraneoplastic syndromes 4. cachexia Tumor location Even
Neoplasia 2018 lecture 11 Dr H Awad FRCPath Clinical aspects of neoplasia Tumors affect patients by: 1. their location 2. hormonal secretions 3. paraneoplastic syndromes 4. cachexia Tumor location Even
Coexistence of parathyroid adenoma and papillary thyroid carcinoma. Yong Sang Lee, Kee-Hyun Nam, Woong Youn Chung, Hang-Seok Chang, Cheong Soo Park
 J Korean Surg Soc 2011;81:316-320 http://dx.doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2011.81.5.316 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JKSS Journal of the Korean Surgical Society pissn 2233-7903 ㆍ eissn 2093-0488 Coexistence of parathyroid
J Korean Surg Soc 2011;81:316-320 http://dx.doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2011.81.5.316 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JKSS Journal of the Korean Surgical Society pissn 2233-7903 ㆍ eissn 2093-0488 Coexistence of parathyroid
Reason for Dissection. Pleomorphic adenoma. Tongue base adenocarcinoma
 Supplementary Table S1 Human Patients Patient Sample No. Gender Age Additional Medication Treatment 1 Reason for Dissection Total Irradiation Dose Estimated Irradiation Dose to SG Gland Time of Resection
Supplementary Table S1 Human Patients Patient Sample No. Gender Age Additional Medication Treatment 1 Reason for Dissection Total Irradiation Dose Estimated Irradiation Dose to SG Gland Time of Resection
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
Bone Health in the Cancer Patient. Stavroula Otis, M.D. Primary Care and Oncology: Practical Lessons Conference Brea Community Center May 10, 2018
 Bone Health in the Cancer Patient Stavroula Otis, M.D. Primary Care and Oncology: Practical Lessons Conference Brea Community Center May 10, 2018 Overview Healthy bone is in a constant state of remodelling
Bone Health in the Cancer Patient Stavroula Otis, M.D. Primary Care and Oncology: Practical Lessons Conference Brea Community Center May 10, 2018 Overview Healthy bone is in a constant state of remodelling
Clinico-pathological Evaluation of Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma Keywords :
 29 2 14 4 Clinico-pathological Evaluation of Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma Yasuhiko Tsuyama, Takashi Nakatsuka, Yoshiyuki Mori, Tsuyoshi Takato (Department of Plastic
29 2 14 4 Clinico-pathological Evaluation of Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma Yasuhiko Tsuyama, Takashi Nakatsuka, Yoshiyuki Mori, Tsuyoshi Takato (Department of Plastic
Supplementary Material for
 Supplementary Material for Parathyroid Hormone Signaling through Low-density-lipoprotein-related Protein 6 Mei Wan, Chaozhe Yang, Jun Li, Xiangwei Wu, Hongling Yuan, Hairong Ma, Xi He, Shuyi Nie, Chenbei
Supplementary Material for Parathyroid Hormone Signaling through Low-density-lipoprotein-related Protein 6 Mei Wan, Chaozhe Yang, Jun Li, Xiangwei Wu, Hongling Yuan, Hairong Ma, Xi He, Shuyi Nie, Chenbei
The effects of computed tomography derived low doses on human peripheral blood cells
 The effects of computed tomography derived low doses on human peripheral blood cells Piroska Virág The Oncology Institute Prof. Dr. I. Chiricuta, Cluj-Napoca, Romania Low dose radiation effects on the
The effects of computed tomography derived low doses on human peripheral blood cells Piroska Virág The Oncology Institute Prof. Dr. I. Chiricuta, Cluj-Napoca, Romania Low dose radiation effects on the
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
silent epidemic,. (WHO),
 Tel: 02-740-8686; E-mail: hhbkim@snu.ac.kr silent epidemic,. (WHO),. 5 3, 1. 50 70. 50%, 25%, 20% (12~35%). 2.8% 0.7% 4. ( ). bone remodeling (osteoblast), (osteoclast),.. 3~4.. 70% (osteocyte) (bone lining
Tel: 02-740-8686; E-mail: hhbkim@snu.ac.kr silent epidemic,. (WHO),. 5 3, 1. 50 70. 50%, 25%, 20% (12~35%). 2.8% 0.7% 4. ( ). bone remodeling (osteoblast), (osteoclast),.. 3~4.. 70% (osteocyte) (bone lining
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Combined Effect of Fluoride and Arsenate on Gene Expression of Osteoclast Differentiation Factor and Osteoprotegerin
 BIOMEDICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES 19, 375-379 (2006) Combined Effect of Fluoride and Arsenate on Gene Expression of Osteoclast Differentiation Factor and Osteoprotegerin LIN JIA 1 AND TAI-YI JIN Department
BIOMEDICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES 19, 375-379 (2006) Combined Effect of Fluoride and Arsenate on Gene Expression of Osteoclast Differentiation Factor and Osteoprotegerin LIN JIA 1 AND TAI-YI JIN Department
Title. Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu. CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5. Issue Date
 Title Bilateral hypoplasia of the maxillary sinus : swelli Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5 Issue Date 2017-04 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/68826
Title Bilateral hypoplasia of the maxillary sinus : swelli Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5 Issue Date 2017-04 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/68826
DNA Methylation of Tumor Suppressor and Metastasis Suppressor Genes in Circulating Tumor Cells and corresponding Circulating Tumor DNA
 DNA Methylation of Tumor Suppressor and Metastasis Suppressor Genes in Circulating Tumor Cells and corresponding Circulating Tumor DNA Maria Chimonidou 1, Areti Strati 1, Nikos Malamos 2, Vasilis Georgoulias
DNA Methylation of Tumor Suppressor and Metastasis Suppressor Genes in Circulating Tumor Cells and corresponding Circulating Tumor DNA Maria Chimonidou 1, Areti Strati 1, Nikos Malamos 2, Vasilis Georgoulias
World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat Page 1
 World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat ---------------------Page 1 Primary Malignant Melanoma of the Tongue: A Case Report Authors: Nanayakkara PR*, Arudchelvam JD** Ariyaratne JC*, Mendis K*, Jayasekera
World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat ---------------------Page 1 Primary Malignant Melanoma of the Tongue: A Case Report Authors: Nanayakkara PR*, Arudchelvam JD** Ariyaratne JC*, Mendis K*, Jayasekera
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Mandibular Metastasis in Patients of Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma: A Rare Entity; Report of Two Cases Channabasappa
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Mandibular Metastasis in Patients of Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma: A Rare Entity; Report of Two Cases Channabasappa
Original Research THE USE OF REFORMATTED CONE BEAM CT IMAGES IN ASSESSING MID-FACE TRAUMA, WITH A FOCUS ON THE ORBITAL FLOOR FRACTURES
 DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-601 Original Research THE USE OF REFORMATTED CONE BEAM CT IMAGES IN ASSESSING MID-FACE TRAUMA, WITH A FOCUS ON THE ORBITAL FLOOR FRACTURES RALUCA ROMAN 1, MIHAELA HEDEȘIU 1, FLOAREA
DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-601 Original Research THE USE OF REFORMATTED CONE BEAM CT IMAGES IN ASSESSING MID-FACE TRAUMA, WITH A FOCUS ON THE ORBITAL FLOOR FRACTURES RALUCA ROMAN 1, MIHAELA HEDEȘIU 1, FLOAREA
CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT
 Mucocele and epidermoid cyst CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT Wen-Chen Wang, Li-Min Lin, Yee-Hsiung Shen, 1 Yu-Ju Lin, and Yuk-Kwan Chen Departments
Mucocele and epidermoid cyst CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT Wen-Chen Wang, Li-Min Lin, Yee-Hsiung Shen, 1 Yu-Ju Lin, and Yuk-Kwan Chen Departments
Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography
 Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography Eyad Fawzi AlSaeed 1 and Mutahir A. Tunio 2* 1 Consultant Radiation Oncology, Chairman
Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography Eyad Fawzi AlSaeed 1 and Mutahir A. Tunio 2* 1 Consultant Radiation Oncology, Chairman
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Ehime University Graduate School of Medicine, Ehime, Japan; 2
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(2):2085-2089 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0004342 Case Report Peripheral ameloblastoma with histologically low-grade malignant features of the buccal mucosa: a case report
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(2):2085-2089 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0004342 Case Report Peripheral ameloblastoma with histologically low-grade malignant features of the buccal mucosa: a case report
Case Presentation: Figure 1. Palatal lesion. Figure 2. Panoramic xray
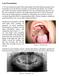 Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Case Report Metastatic Malignant Melanoma of Parotid Gland with a Regressed Primary Tumor
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 5393404, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5393404 Case Report Metastatic Malignant Melanoma of Parotid Gland with a Regressed Primary Tumor
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 5393404, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5393404 Case Report Metastatic Malignant Melanoma of Parotid Gland with a Regressed Primary Tumor
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, School of Pharmacy, Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115, USA 2
 Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
A Report of a Rare Case of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma of the Oral Cavity
 AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (2 0 1 2 )5 (1 ):9 8-1 0 2 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G CASE REPORT A Report of a Rare Case of Anaplastic
AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (2 0 1 2 )5 (1 ):9 8-1 0 2 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G CASE REPORT A Report of a Rare Case of Anaplastic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
