Radiofrequency ablation for early esophageal squamous cell neoplasia
|
|
|
- Jessica Ryan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Radiofrequency ablation for early esophageal squamous cell neoplasia Authors Y. M. Zhang 1, J. J. G. H. M. Bergman 2, B. Weusten 2, 3, S. M. Dawsey 4, D. E. Fleischer 5,N.Lu 6,S.He 1,G.Q.Wang 1 Institutions Institutions are listed at the end of article. submitted 2 February 2010 accepted 2 February 2010 Bibliography DOI /s Published ahead of print Endoscopy Georg Thieme Verlag KG Stuttgart New York ISSN X Corresponding author G. Q. Wang, MD, PhD Cancer Institute and Hospital Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Department of Endoscopy 17 Panjiayuan Chaoyang District Beijing P.R. China Fax: wangguiq@126.com Introduction Esophageal cancer is the sixth most common cause of cancer death in the world [1]. Over 80 % of esophageal cancers occur in developing countries [1], and in these areas, 90 % of these cancers are esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) [2]. The precursor lesion of ESCC is squamous intraepithelial neoplasia (squamous dysplasia), defined histologically as nuclear atypia (enlargement, pleomorphism, and hyperchromasia), loss of normal cellular polarity, and abnormal tissue maturation [3, 4]. The World Health Organization (WHO) subclassifies squamous intraepithelial neoplasia into low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia (LGIN) and high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia (HGIN), depending on the extent of the nuclear atypia and the involvement of the epithelium [4]. In China, where ESCC and its precursors are very common in some areas, a three-tier system is used, including LGIN (mild dysplasia, involving the lower third of the epithelium), medium-grade intraepithelial neoplasia (MGIN, moderate dysplasia, involving the lower two-thirds of the epithelium), and HGIN (severe dysplasia, involving the full thickness of the epithelium) [3]. Followup studies in China have shown that the rate of progression to ESCC differs significantly between LGIN (5.3 % over 3.5 years), MGIN (26.7 %), and HGIN (65.2 %), and because of their significant risk of progression, MGIN and HGIN are targets for screening and therapy [5,6]. Current treatment of esophageal squamous cell neoplasia (ESCN, including squamous intraepithelial neoplasia and invasive squamous cell carcinoma) involves surgery for lesions invading into the deep submucosa or beyond and endoscopic treatment for lesions restricted to the epithelial layer (intraepithelial neoplasia; m1) or the lamina propria (m2). Lesions invading into the muscularis mucosae (m3) or superficial submucosa (sm1) are considered the grey zone between endoscopic and surgical treatment. One option for endoscopic treatment of early ESCN involves endoscopic resection of unstained lesions (USLs) after Lugol s chromoscopy, as USLs are predictive for the presence of neoplasia. Endoscopic resection allows for histologic staging of infiltration depth, tumor differentiation, and lymph-vascular invasion, while completely removing the visible lesion. USLs larger than 15 mm require either piecemeal resection with the standard cap-based endoscopic resection techniques or endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for complete resection. Widespread endoscopic resection/esd, however, is technically demanding, with procedure times of many hours; it is also associated with severe esophageal stenosis for lesions that encompass > 75 % of the circumference and a significant risk for esophageal perforation and bleeding. Complete endoscopic resection is also not necessarily the best approach for all patients with early ESCN. Large flat-type lesions (i. e. type 0-IIb), which carry a very low risk for deeper invasion, can be effectively treated by an endoscopic ablation technique that is much easier to apply and is associated with a very low rate of complications, such as esophageal stenosis. A safe, effective, and technically easy-to-administer ablation method is especially attractive for geographic areas where ESCN is endemic and most endoscopists have a lower level of expertise in endoscopic resection/esd. In China, there are many high-risk areas for ESCN, such as the Taihang mountain range in North- Central China and areas in Sichuan, Shandong, Jiangsu, and Fujian Provinces and the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region [7]. These high-risk areas in China are estimated to include a total of over 100 million people, and invasive ESCN occurs here at rates approaching or surpassing 100 / people per year [2], an incidence approximately 30-fold that of Barrett s-related
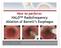
2 Fig. 1 Primary circumferential radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of a 4-cmlong flat type early esophageal squamous cell neoplasia with high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia. a Pretreatment white light endoscopy image showing minimal reddish discoloration; b, c Corresponding views with narrowband imaging and after Lugol s chromoscopy; d, e The distal and proximal margins of the treatment zone have been marked by tattoos; e The deflated RFA balloon is positioned at the level of the proximal tattoo (visible at the 6o clock position); f Appearance of the mucosa after the initial ablation; g Appearance of the ablation zone after cleaning off the coagulum; h, i Appearance of the proximal (h) and distal (i) part of the ablation zone after the second ablation pass. esophageal adenocarcinoma in the Western world [8]. The Chinese government is supporting widespread endoscopic screening using Lugol s chromoscopy in these high-risk areas, and in 2010 it is estimated that individuals will undergo such a screening endoscopy. From this screening process, it is estimated that 5% of patients will have MGIN, HGIN, or early cancer limited to the epithelium and will be eligible for endoscopic therapy. Radiofrequency ablation: technical background and application in Barrett s esophagus Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) using the HALO system is a relatively new ablation technique that has been extensively studied in Barrett s esophagus [9 12]. RFA in Barrett s esophagus generally involves primary circumferential RFA using a balloon-based bipolar electrode (HALO 360+, " Fig. 1), followed after 2 3 months by focal RFA of residual Barrett s esophagus using the endoscope-mounted HALO 90 catheter ( " Fig. 2). For both catheters, an energy generator delivers radiofrequency energy in an automated and controlled manner to the electrode upon activation via a foot switch. Ablative therapy is delivered twice to each area of targeted tissue in the esophagus using a fixed energy and power density. An intervening step of cleaning off any coagulum may be used to improve the ablation effect during the second delivery, although current studies are evaluating double treatment without interval cleaning resulting in shorter total procedure times (< 10 minutes). Uniformity of ablation effect and control of depth of ablation to the muscularis mucosae or superficial submucosa (maximum 1000 microns) is achieved by flattening the mucosa prior to ablation, using a standardized energy density dose, delivering the energy rapidly with highpower density, and using a tightly spaced bipolar electrode array
3 Fig. 2 Secondary focal radiofrequency ablation of small residual unstained lesions. a White light view 3 months after primary circumferential ablation; b Corresponding image with narrow-band imaging; c Residual small unstained lesions after Lugol s chromoscopy; d Ablation effect immediately after ablation with the HALO 90 system; the distal end of the catheter is visible at the 12 o clock position in the endoscopic field. Reproduced with permission of to create the electrical field. In this manner, the treatment effect is less operator-dependent. After initial dosimetry studies in the porcine esophagus and human esophagus prior to esophagectomy, a number of prospective clinical studies have evaluated the safety and efficacy of RFA in nondysplastic intestinal metaplasia, LGIN, HGIN, and intramucosal adenocarcinoma developing in Barrett s esophagus [9 12]. These studies have yielded success rates for eradication of neoplasia and Barrett s esophagus mucosa of 90 % 95 %, with remarkably few complications. Further, in a randomized, sham-controlled trial, Shaheen et al. reported that in patients with dysplastic Barrett s esophagus, RFA was associated with a high rate of complete eradication of both dysplasia and intestinal metaplasia and a reduced risk for disease progression [11]. In addition, RFA in Barrett s esophagus has been associated with a low rate (< 5%) of ablation-related stenosis and the neosquamous mucosa that regenerates after RFA is free of genetic abnormalities, suggesting that it holds no residual malignant potential [9 14]. Radiofrequency ablation may also have significant utility for treatment of early ESCN, for several reasons. First, RFA is technically easy to apply, carries a low risk of complications, and is generally performed as an outpatient procedure. This compares favorably with piecemeal endoscopic resection and ESD which require a higher level of endoscopic expertise, long procedure times, and clinical observation for several days, issues that are especially important for the screening programs in the endemic areas mentioned above. Second, circumferential RFA with the HALO 360+ has been associated with a low rate of post-rfa stenosis in Barrett s esophagus, and if this is also true in ESCN then this would enable treatment of widespread or mosaic-like early ESCN for which endoscopic resection or ESD would surely result in severe esophageal stricturing. Third, RFA in Barrett s esophagus is associated with a complete reset of genetic abnormalities, and if this is also true in ESCN it may reduce the rate of late recurrences compared with resection techniques where the resection margin is generally less than 2 mm. Current experience with RFA of early esophageal squamous cell neoplasia The clinical experience related to RFA for early ESCN is limited but promising. After a first case report in 2008, a heterogeneous group of 13 patients (with and without prior endoscopic resection, different energy settings) was treated in Amsterdam [15]. Based on these results and a pilot study in Beijing in October 2008, our group initiated a prospective cohort study in Beijing and Feicheng (P. R. China). In this study 60 patients with flattype ESCN (MGIN, HGIN, T1m2) have been enrolled and the first results will be available later this year. Representative images from this study are shown in " Figs RFA for early esophageal squamous cell neoplasia How to apply RFA in early esophageal squamous cell neoplasia Consent Although the HALO systems are FDA cleared and CE marked for esophageal ablation we feel that patients should be informed that limited clinical trial outcomes are available related to the use of this technology for early ESCN. For the same reason, the following guidelines should be regarded as preliminary. Patient selection We currently feel that RFA as a single-modality treatment should be restricted to patients with completely flat-type ESCN (type 0- IIb) without nodularity or ulceration, and with a pretreatment biopsy diagnosis of MGIN, HGIN or well-to-moderately differentiated invasive cancer limited to the lamina propria (m2). Type 0- IIa and/or 0-IIc lesions require endoscopic resection/esd for focal
4 Fig. 3 Three cases of early esophageal squamous cell neoplasia before and after radiofrequency ablation treatment, as seen with white light endoscopy, narrow-band imaging, and Lugol s chromoscopy. 1a c Endoscopic view of a semi-circumferential flat type early squamous cell neoplasia containing high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia (HGIN). 1d f After primary circumferential ablation there are no signs of residual neoplasia. 2a c Mosaic-like flattype squamous cell neoplasia containing HGIN. 2d f After primary circumferential ablation and one focal ablation session, only a small unstained area is observed upon Lugol s chromoscopy showing no dysplasia upon biopsy. 3a c A 4-cm-long early squamous cell neoplasia stretching from the 5 11 o clock position and containing HGIN. 3d f Primary circumferential ablation and one focal ablation session have resulted in complete removal of the neoplastic lesion. Reproduced with permission of www. endosurgery.eu. Continuation see following page.
5 Fig. 3 Continuation. removal and histologic staging; type 0-I and 0-III lesions generally invade into the submucosa and are not eligible for endoscopic treatment. Imaging Lugol s chromoscopy (1 % 2%) is required in all cases of ESCN. Given the caustic effect of this solution, RFA should not be performed within 2 weeks after Lugol s chromoscopy, as the Lugol s solution has been shown to make the epithelium vulnerable to superficial bleeding, which hampers visibility and the proper application of RFA. During the pretreatment chromoendoscopy exam, we place two 0.25 ml tattoos at opposite sites of the esophagus, 1 cm proximal to the most proximal USL and 1 cm distal to the most distal USL. These tattoos serve as permanent markers, allowing easy identification of the treatment area at the actual RFA session ( " Fig. 1 d, e) and subsequent follow-up sessions. Sizing Given the mosaic nature of USLs and uncertainties regarding the oncogenetic alterations present in normal staining epithelium, we prefer to perform primary ablation with the circumferential HALO 360+ catheter. This enables treatment of the entire field with minimal overlap. Prior to circumferential ablation, sizing of the esophageal inner diameter is required. A sizing catheter is connected to the HALO 360 generator, calibrated, and introduced over a guide wire. The sizing procedure is a blind procedure using the 1-cm scale on the catheter shaft for reference. For the first measurement the catheter is placed about 4 cm above the most proximal set of tattoos. The measurement cycle is started by pressing the foot switch, which inflates the sizing balloon, and the esophageal inner diameter is automatically calculated for the entire length of the 4-cm-long balloon. This action is repeated for every 1 2 cm of the targeted portion of the esophagus. If any blood is seen on the sizing balloon after removal, endoscopic inspection should be performed to rule out esophageal injury prior to introducing the ablation balloon. If esophageal injury is noted, ablation should be delayed to allow healing. Choosing the appropriate ablation catheter The HALO 360+ ablation balloon is available in five separate outer diameter sizes (18, 22, 25, 28, and 31 mm). The appropriate size is selected based on the smallest single measurement obtained during sizing. If any measurement is less than 18 mm, balloonbased circumferential ablation should not be performed, as the smallest available ablation balloon is 18 mm in outer diameter. Focal ablation using the smaller HALO 90 ablation catheter may be considered in these cases, but circumferential treatment with the HALO 90 catheter may carry a higher theoretical risk of stenosis due to overlap of adjacent ablation zones Energy setting and cleaning of the ablation zone The HALO 360+ catheter is introduced over a guide wire and the endoscope is introduced alongside the ablation catheter. Under endoscopic visualization the proximal margin of the electrode is positioned at the level of the most proximal set of tattoos ( " Fig. 1 e). The balloon is inflated, the esophagus is deflated using endoscope suction to optimize tissue contact, and the electrode is then activated via a foot switch. Energy delivery typically lasts less than 1.5 seconds, after which the balloon is automatically deflated. Moving proximally to distally, the balloon is repositioned, allowing a 5 10-mm overlap with the previous ablation zone. In our initial studies we have used an energy setting of 12 J/ cm 2 with cleaning of the ablation zone after the first ablation pass ( " Fig. 1 g). These settings were, however, mainly derived from experience with RFA of Barrett s mucosa. We are currently evaluating delivery of 10 or 12 J/cm 2 twice to each location, without in-
6 terval cleaning, which reduces treatment time and minimizes unintended overlap between zones. Post-RFA patient care After RFA of Barrett s esophagus, proper acid-suppressant therapy is very important, not only to minimize patient discomfort, but also to allow the esophagus to heal optimally and regenerate with squamous epithelium. Although the importance of acidsuppressant therapy may be less in ESCN, we prescribe all patients esomeprazole 40 mg twice daily for 1 month to optimize the conditions for healing. In addition, patients are advised to adhere to a liquid diet for 24 hours, gradually progressing to a soft and normal diet at their own discretion. Patients may experience symptoms of chest discomfort, sore throat, difficulty or pain with swallowing and/or nausea, which usually improve each day. Proposed medications consist of an oral antacid/lidocaine mixture for the first 24 hours (e.g. 15 ml every 4 hours), liquid acetaminophen with or without oral codeine on demand, and anti-emetic medication. Subsequent RFA sessions Follow-up sessions are scheduled at 2 3-month intervals. The initial treatment area is easily identified by the tattoos and is inspected with standard endoscopy for healing and stenosis followed by Lugol s chromoscopy to identify USLs. As USLs may represent reactive changes after RFA or residual ESCN, we obtain biopsies of each USL for histologic analysis followed by immediate ablation using the HALO 90 catheter ( " Fig. 2). HALO 90 ablation is guided by the biopsy sites, with repeated Lugol s chromoscopy in case of doubt. The target area is positioned at the 12 o clock position in the endoscopic video image. The electrode is brought into close contact with the mucosa, deflected upward, and activated via a foot switch. While keeping the electrode in place, three sequential ablations at 12 J/cm 2 are performed without cleaning of the ablation zone. Combining endoscopic resection and RFA Many patients with early ESCN have lesions that consist of a large type 0-IIb component as well as one or more focal type 0-IIa/IIc components. As mentioned, RFA is only a suitable treatment strategy for flat-type lesions as it lacks the histologic correlation of endoscopic resection and is not designed to penetrate a thickened raised lesion. Therefore, a combination therapy of endoscopic resection and RFA may combine the best features of these two techniques. Endoscopic resection allows for focal removal of the type 0-IIa/IIc component and enables optimal histologic staging. It also renders the remaining mucosa flat, and thus eligible for subsequent RFA. Our group is currently investigating the optimal timing and combination of these treatments in both animal and human trials. In Barrett s esophagus the combination of endoscopic resection for staging, followed 8 weeks later by RFA, has been shown to be safe and effective, with a low rate of RFArelated stenosis [10, 12]. It is advised, however, to limit the extent of endoscopic resection to < 50 % of the circumference and < 2 cm in length, as focal narrowing after endoscopic resection may make subsequent circumferential RFA more difficult [12]. This issue may be even more relevant for patients with early ESCN, who often have an esophagus with a much smaller inner diameter and reduced compliance compared with Barrett s patients. Also, it may be more difficult to limit the extent of endoscopic resection of ESCN when using cap-based resection techniques, as the squamous mucosa is more easily sucked into the cap than Barrett s epithelium, resulting in relatively larger resection areas. Finally, after a prior endoscopic resection, care should be taken not to overestimate the inner esophageal diameter when performing circumferential RFA. The sizing balloon calculates a mean inner diameter based on esophageal wall compliance over a length of 4 cm, which may result in an overestimation of the esophageal inner diameter at the site of the endoscopic resection scar. It is therefore advisable to be conservative when choosing the appropriate diameter of the HALO 360+ catheter, with a low threshold to perform a careful test-dilation to avoid overstretching or even lacerating the treatment area with the ablation balloon. Unresolved issues and future prospects More studies are underway on the use of RFA for early ESCN. The HALO ablation devices have only recently become available for study in Asia, where early ESCN is more prevalent and more homogeneous cohorts can be studied. Future studies should aim to determine the optimal energy setting and technique for circumferential RFA, the relative roles of HALO 360+ and HALO 90 as primary treatment tools, the optimal strategy for combined endoscopic resection and RFA treatments, the genetic and other properties of the squamous mucosa that regenerates at the site of the original lesion, and the long-term durability of the treatment outcome. Acknowledgments We thank Roos Pouw, MD, PhD for her support with the manuscript and illustrations. This work was supported in part by intramural funds from the Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics of the National Cancer Institute. Competing interests: None Institutions 1 Department of Endoscopy, Cancer Institute and Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, P. R. China 2 Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Academic Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands 3 Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, St Antonius Hospital, Nieuwegein, The Netherlands 4 Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics, National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Maryland, USA 5 Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Arizona, USA 6 Department of Pathology, Cancer Institute and Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, P.R. China References 1 Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J et al. Global cancer statistics, CA Cancer J Clin 2005; 55: Blot WJ, McLaughlin JK, Fraumeni JF Jr.. Esophageal cancer. In: Schottenfeld D, Fraumeni JF Jr., eds Cancer epidemiology and prevention. 3rd edn. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2006: Dawsey SM, Lewin KJ, Liu FS et al. Esophageal morphology from Linxian, China. Squamous histologic findings in 754 patients. Cancer 1994; 73: Hamilton SR, Aaltonen LA. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. Pathology and genetics of tumours of the digestive system. Lyon: IARC Press, 2000
7 5 Dawsey SM, Lewin KJ, Wang GQ et al. Squamous esophageal histology and subsequent risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. A prospective follow-up study from Linxian, China. Cancer 1994; 74: Wang GQ, Abnet CC, Shen Q et al. Histological precursors of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma: results from a 13 year prospective follow up study in a high risk population. Gut 2005; 54: Li JY, Liu BQ, Li GY et al. Atlas of cancer mortality in the People s Republic of China. Shanghai: China Map Press, Horner MJ, Ries LAG, Krapcho M et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, , National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD. seer.cancer.gov/ csr/1975_2006/; Publication date: based on November 2008 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, Fleischer DE, Overholt BF, Sharma VK et al. Endoscopic ablation of Barrett s esophagus: a multicenter study with 2.5-year follow-up. Gastrointest Endosc 2008; 68: Gondrie JJ, Pouw RE, Sondermeijer CM et al. Stepwise circumferential and focal ablation of Barrett s esophagus with high-grade dysplasia: results of the first prospective series of 11 patients. Endoscopy 2008; 40: Shaheen NJ, Sharma P, Overholt BF et al. Radiofrequency ablation in Barrett s esophagus with dysplasia. N Engl J Med 2009; 360: Pouw RE, Wirths K, Eisendrath P et al. Efficacy of radiofrequency ablation combined with endoscopic resection for Barrett s esophagus with early neoplasia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010; 8: Beaumont H, Gondrie JJ, McMahon BP et al. Stepwise radiofrequency ablation of Barrett s esophagus preserves esophageal inner diameter, compliance, and motility. Endoscopy 2009; 41: Pouw RE, Gondrie JJ, Rygiel AM et al. Properties of the neosquamous epithelium after radiofrequency ablation of Barrett s esophagus containing neoplasia. Am J Gastroenterol 2009; 104: Pouw RE, Gondrie JJ, Curvers WL et al. Successful balloon-based radiofrequency ablation of a widespread early squamous cell carcinoma and high-grade dysplasia of the esophagus: a case report. Gastrointest Endosc 2008; 68:
Barrett s Esophagus. Radiofrequency Ablation with the HALO Technology A Reference Book
 Radiofrequency Ablation with the HALO Technology A Reference Book 540 Oakmead Parkway, Sunnyvale, CA 94085 What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a change that occurs within the cellular lining
Radiofrequency Ablation with the HALO Technology A Reference Book 540 Oakmead Parkway, Sunnyvale, CA 94085 What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a change that occurs within the cellular lining
How to perform: HALO 360 Radiofrequency Ablation of Barrett s s Esophagus
 How to perform: HALO 360 Radiofrequency Ablation of Barrett s s Esophagus Used abbreviations BE: EID: ER: RFA: Barrett s esophagus Esophageal inner diameter Endoscopic resection Radiofrequency ablation
How to perform: HALO 360 Radiofrequency Ablation of Barrett s s Esophagus Used abbreviations BE: EID: ER: RFA: Barrett s esophagus Esophageal inner diameter Endoscopic resection Radiofrequency ablation
Ablation for Barrett s Esophagus: Burn or Freeze
 Ablation for Barrett s Esophagus: Burn or Freeze John R. Saltzman MD Director of Endoscopy Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Disclosures No relevant disclosures
Ablation for Barrett s Esophagus: Burn or Freeze John R. Saltzman MD Director of Endoscopy Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Disclosures No relevant disclosures
Gregory G. Ginsberg, M.D.
 Radiofrequency Ablation for Barrett s Esophagus with HGD Gregory G. Ginsberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine Abramson Cancer Center Gastroenterology Division Executive
Radiofrequency Ablation for Barrett s Esophagus with HGD Gregory G. Ginsberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine Abramson Cancer Center Gastroenterology Division Executive
Radiofrequency Ablation: Stepwise circumferential and focal RFA of Barrett s s esophagus using the HALO System
 Radiofrequency Ablation: Stepwise circumferential and focal RFA of Barrett s s esophagus using the HALO System Used abbreviations BE: Barrett s esophagus EC: Early cancer ER: Endoscopic resection HGD:
Radiofrequency Ablation: Stepwise circumferential and focal RFA of Barrett s s esophagus using the HALO System Used abbreviations BE: Barrett s esophagus EC: Early cancer ER: Endoscopic resection HGD:
Citation for published version (APA): Phoa, K. Y. N. (2014). Endoscopic management of Barrett s esophagus with dysplasia
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Endoscopic management of Barrett s esophagus with dysplasia Phoa, Nadine Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Phoa, K. Y. N. (2014). Endoscopic
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Endoscopic management of Barrett s esophagus with dysplasia Phoa, Nadine Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Phoa, K. Y. N. (2014). Endoscopic
Current Management: Role of Radiofrequency Ablation
 Esophageal Adenocarcinoma And Barrett s Esophagus: Current Management: Role of Radiofrequency Ablation Ketan Kulkarni, MD Regional Gastroenterology Associates of Lancaster INTRODUCTION The prognosis of
Esophageal Adenocarcinoma And Barrett s Esophagus: Current Management: Role of Radiofrequency Ablation Ketan Kulkarni, MD Regional Gastroenterology Associates of Lancaster INTRODUCTION The prognosis of
Treat Barrett s, Remove the Risk. HALO System
 Treat Barrett s, Remove the Risk HALO System The HALO 360 System Advanced Ablation Technology for Barrett s Esophagus The HALO 360 System is designed to remove the Barrett s epithelium in a short, well-tolerated
Treat Barrett s, Remove the Risk HALO System The HALO 360 System Advanced Ablation Technology for Barrett s Esophagus The HALO 360 System is designed to remove the Barrett s epithelium in a short, well-tolerated
Barrett Esophagus - RadioFrequency Ablation (BE-RFA) - Project manual + FAQ
 Barrett Esophagus - RadioFrequency Ablation (BE-RFA) - Project manual + FAQ Table of contents 1 General project information...3 1.1 Inclusion criteria...3 1.2 Registration time points...3 1.3 Project variable
Barrett Esophagus - RadioFrequency Ablation (BE-RFA) - Project manual + FAQ Table of contents 1 General project information...3 1.1 Inclusion criteria...3 1.2 Registration time points...3 1.3 Project variable
Barrett s esophagus. Barrett s neoplasia treatment trends
 Options for endoscopic treatment of Barrett s esophagus Patrick S. Yachimski, MD MPH Director of Pancreatobiliary Endoscopy Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition
Options for endoscopic treatment of Barrett s esophagus Patrick S. Yachimski, MD MPH Director of Pancreatobiliary Endoscopy Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition
How to remove BE cancer: EMR or ESD? Expected outcome
 How to remove BE cancer: EMR or ESD? Expected outcome Presented by Horst Neuhaus Institution Dpt. of Gastroenterology Evangelisches Krankenhaus Düsseldorf, Germany Indications for endoscopic resection
How to remove BE cancer: EMR or ESD? Expected outcome Presented by Horst Neuhaus Institution Dpt. of Gastroenterology Evangelisches Krankenhaus Düsseldorf, Germany Indications for endoscopic resection
Advances in endoscopic resection and radiofrequency ablation of early esophageal neoplasia van Vilsteren, F.G.I.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Advances in endoscopic resection and radiofrequency ablation of early esophageal neoplasia van Vilsteren, F.G.I. Link to publication Citation for published version
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Advances in endoscopic resection and radiofrequency ablation of early esophageal neoplasia van Vilsteren, F.G.I. Link to publication Citation for published version
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks
 Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Barrett s Esophagus: What to Do for No Dysplasia, LGD, and HGD?
 Barrett s Esophagus: What to Do for No Dysplasia, LGD, and HGD? Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina 1 Outline What are the risks of progression
Barrett s Esophagus: What to Do for No Dysplasia, LGD, and HGD? Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina 1 Outline What are the risks of progression
Barrett s Esophagus. Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI
 Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Efficacy of Radiofrequency Ablation Combined With Endoscopic Resection for Barrett s Esophagus With Early Neoplasia
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:23 29 ENDOSCOPY CORNER Efficacy of Radiofrequency Ablation Combined With Endoscopic Resection for Barrett s Esophagus With Early Neoplasia ROOS E. POUW,*
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:23 29 ENDOSCOPY CORNER Efficacy of Radiofrequency Ablation Combined With Endoscopic Resection for Barrett s Esophagus With Early Neoplasia ROOS E. POUW,*
Endoscopic Management of Barrett s Esophagus
 Endoscopic Management of Barrett s Esophagus Sammy Ho, MD Director of Pancreaticobiliary Services and Endoscopic Ultrasound Montefiore Medical Center Barrett s Esophagus Consequence of chronic GERD Mean
Endoscopic Management of Barrett s Esophagus Sammy Ho, MD Director of Pancreaticobiliary Services and Endoscopic Ultrasound Montefiore Medical Center Barrett s Esophagus Consequence of chronic GERD Mean
Present Day Management of Barrett s Esophagus
 Slide 1 Present Day Management of Barrett s Esophagus Kinnari R. Kher, M.D. Slide 2 Goals Risk factors for development of Barrett s esophagus Risks for progression to Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Current
Slide 1 Present Day Management of Barrett s Esophagus Kinnari R. Kher, M.D. Slide 2 Goals Risk factors for development of Barrett s esophagus Risks for progression to Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Current
RFA and Cyrotherapy for Esophageal Disease
 RFA and Cyrotherapy for Esophageal Disease Daniel L. Miller MD Chief, General Thoracic Surgery WellStar Healthcare System/ Mayo Clinic Care Network Clinical Professor of Surgery Medical College of Georgia/
RFA and Cyrotherapy for Esophageal Disease Daniel L. Miller MD Chief, General Thoracic Surgery WellStar Healthcare System/ Mayo Clinic Care Network Clinical Professor of Surgery Medical College of Georgia/
New Developments in the Endoscopic Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus
 New Developments in the Endoscopic Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus Prateek Sharma, MD Key Clinical Management Points: Endoscopic recognition of a columnar lined distal esophagus is crucial
New Developments in the Endoscopic Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus Prateek Sharma, MD Key Clinical Management Points: Endoscopic recognition of a columnar lined distal esophagus is crucial
Management of Barrett s: From Imaging to Resection
 Management of Barrett s: From Imaging to Resection Michael Wallace, MD, MPH, FACG Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida Goals of Endoscopic Evaluation in Barrett s Detect Barrett s and dysplasia Reduce/eliminate
Management of Barrett s: From Imaging to Resection Michael Wallace, MD, MPH, FACG Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida Goals of Endoscopic Evaluation in Barrett s Detect Barrett s and dysplasia Reduce/eliminate
Is Radiofrequency Ablation Effective In Treating Barrett s Esophagus Patients with High-Grade Dysplasia?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 12-2016 Is Radiofrequency Ablation Effective
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 12-2016 Is Radiofrequency Ablation Effective
American Journal of Gastroenterology. Volumetric Laser Endomicroscopy Detects Subsquamous Barrett s Adenocarcinoma
 Volumetric Laser Endomicroscopy Detects Subsquamous Barrett s Adenocarcinoma Journal: Manuscript ID: AJG-13-1412.R1 Manuscript Type: Letter to the Editor Keywords: Barrett-s esophagus, Esophagus, Endoscopy
Volumetric Laser Endomicroscopy Detects Subsquamous Barrett s Adenocarcinoma Journal: Manuscript ID: AJG-13-1412.R1 Manuscript Type: Letter to the Editor Keywords: Barrett-s esophagus, Esophagus, Endoscopy
Barrett s Esophagus: Ablate Everyone?
 Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, FACG Barrett s Esophagus: Ablate Everyone? Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, FACG Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina Greetings from UNC,
Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, FACG Barrett s Esophagus: Ablate Everyone? Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, FACG Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina Greetings from UNC,
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus
 Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Endoscopic therapy of Barrett s esophagus Oliver Pech and Christian Ell
 Endoscopic therapy of Barrett s esophagus Oliver Pech and Christian Ell Department of Internal Medicine 2, HSK Wiesbaden, Wiesbaden, Germany Correspondence to Oliver Pech, MD, PhD, Department of Gastroenterology,
Endoscopic therapy of Barrett s esophagus Oliver Pech and Christian Ell Department of Internal Medicine 2, HSK Wiesbaden, Wiesbaden, Germany Correspondence to Oliver Pech, MD, PhD, Department of Gastroenterology,
Citation for published version (APA): Phoa, K. Y. N. (2014). Endoscopic management of Barrett s esophagus with dysplasia
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Endoscopic management of Barrett s esophagus with dysplasia Phoa, Nadine Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Phoa, K. Y. N. (2014). Endoscopic
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Endoscopic management of Barrett s esophagus with dysplasia Phoa, Nadine Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Phoa, K. Y. N. (2014). Endoscopic
Opinion Statement. Esophagus (E Dellon, Section Editor)
 Curr Treat Options Gastro (2016) 14:1 18 DOI 10.1007/s11938-016-0080-4 Esophagus (E Dellon, Section Editor) Current Controversies in Radiofrequency Ablation Therapy for Barrett s Esophagus Kamar Belghazi,
Curr Treat Options Gastro (2016) 14:1 18 DOI 10.1007/s11938-016-0080-4 Esophagus (E Dellon, Section Editor) Current Controversies in Radiofrequency Ablation Therapy for Barrett s Esophagus Kamar Belghazi,
Cryospray ablation using pressurized CO 2 for ablation of Barrett s esophagus with early neoplasia: early termination of a prospective series
 E17 Cryospray ablation using pressurized CO 2 for ablation of Barrett s esophagus with early neoplasia: early termination of a prospective series Authors Romy E. Verbeek 1, Frank P. Vleggaar 1, Fiebo J.
E17 Cryospray ablation using pressurized CO 2 for ablation of Barrett s esophagus with early neoplasia: early termination of a prospective series Authors Romy E. Verbeek 1, Frank P. Vleggaar 1, Fiebo J.
Evaluating Treatments of Barrett s Esophagus That Shows High-Grade Dysplasia
 ...PRESENTATIONS... Evaluating Treatments of Barrett s Esophagus That Shows High-Grade Dysplasia Based on a presentation by Bergein F. Overholt, MD Presentation Summary Thermal ablation and surgery are
...PRESENTATIONS... Evaluating Treatments of Barrett s Esophagus That Shows High-Grade Dysplasia Based on a presentation by Bergein F. Overholt, MD Presentation Summary Thermal ablation and surgery are
The Pathologist s Role in the Diagnosis and Management of Neoplasia in Barrett s Oesophagus Cian Muldoon, St. James s Hospital, Dublin
 The Pathologist s Role in the Diagnosis and Management of Neoplasia in Barrett s Oesophagus Cian Muldoon, St. James s Hospital, Dublin 24.06.15 Norman Barrett Smiles [A brief digression - Chair becoming
The Pathologist s Role in the Diagnosis and Management of Neoplasia in Barrett s Oesophagus Cian Muldoon, St. James s Hospital, Dublin 24.06.15 Norman Barrett Smiles [A brief digression - Chair becoming
Medicare Advantage Medical Policy
 Medicare Advantage Medical Policy Current Policy Effective Date: 1/1/18 Title: Endoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation or Cryoablation for Barrett Esophagus Description/Background Barrett Esophagus and the
Medicare Advantage Medical Policy Current Policy Effective Date: 1/1/18 Title: Endoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation or Cryoablation for Barrett Esophagus Description/Background Barrett Esophagus and the
Philip Chiu Associate Professor Department of Surgery, Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong
 Application of Chromoendoscopy, NBI and AFI in Esophagus why, who, and how? Philip Chiu Associate Professor Department of Surgery, Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong Cancer of
Application of Chromoendoscopy, NBI and AFI in Esophagus why, who, and how? Philip Chiu Associate Professor Department of Surgery, Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong Cancer of
Endoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation or Cryoablation for Barrett s Esophagus
 Endoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation or Cryoablation for Barrett s Esophagus Policy Number: 2.01.80 Last Review: 6/2018 Origination: 6/2012 Next Review: 6/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
Endoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation or Cryoablation for Barrett s Esophagus Policy Number: 2.01.80 Last Review: 6/2018 Origination: 6/2012 Next Review: 6/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
Changes to the diagnosis and management of Barrett s Oesophagus
 Changes to the diagnosis and management of Barrett s Oesophagus A review of the new BSG and NICE guidelines and best practice Anjan Dhar DM, MD, FRCPE, AGAF, MBBS (Hons.), Cert. Med. Ed Senior Lecturer
Changes to the diagnosis and management of Barrett s Oesophagus A review of the new BSG and NICE guidelines and best practice Anjan Dhar DM, MD, FRCPE, AGAF, MBBS (Hons.), Cert. Med. Ed Senior Lecturer
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD
 Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
Definition of GERD American College of Gastroenterology
 Definition of GERD American College of Gastroenterology GERD is defined as chronic symptoms or mucosal damage produced by the abnormal reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus DeVault et al. Am J
Definition of GERD American College of Gastroenterology GERD is defined as chronic symptoms or mucosal damage produced by the abnormal reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus DeVault et al. Am J
Endoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation or Cryoablation for Barrett Esophagus
 Endoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation or Cryoablation for Barrett Esophagus Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.005 09/01/2010 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: PPO; HMO; QUEST Integration
Endoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation or Cryoablation for Barrett Esophagus Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.005 09/01/2010 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: PPO; HMO; QUEST Integration
Editorial: Advanced endoscopic therapeutics in Barrett s neoplasia; where are we now and where are we heading?
 Editorial: Advanced endoscopic therapeutics in Barrett s neoplasia; where are we now and where are we heading? Dr. Gaius Longcroft-Wheaton MB,BS, MD, MRCP(UK), MRCP(Gastro) Consultant gastroenterologist
Editorial: Advanced endoscopic therapeutics in Barrett s neoplasia; where are we now and where are we heading? Dr. Gaius Longcroft-Wheaton MB,BS, MD, MRCP(UK), MRCP(Gastro) Consultant gastroenterologist
EMR, ESD and Beyond. Peter Draganov MD. Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida
 EMR, ESD and Beyond Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated by Endoscopy
EMR, ESD and Beyond Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated by Endoscopy
Volumetric laser endomicroscopy can target neoplasia not detected by conventional endoscopic measures in long segment Barrett s esophagus
 E318 Volumetric laser endomicroscopy can target neoplasia not detected by conventional endoscopic measures in long segment esophagus Authors Institution Arvind J. Trindade, Benley J. George, Joshua Berkowitz,
E318 Volumetric laser endomicroscopy can target neoplasia not detected by conventional endoscopic measures in long segment esophagus Authors Institution Arvind J. Trindade, Benley J. George, Joshua Berkowitz,
Early detection and treatment for Esophageal Cancer in Africa
 Early detection and treatment for Esophageal Cancer in Africa Dr Michael Mwachiro Tenwek Hospital NCI-IARC ESCC Tumor Workshop Where is Tenwek Hospital? Tenwek Nairobi Tenwek Hospital Identification of
Early detection and treatment for Esophageal Cancer in Africa Dr Michael Mwachiro Tenwek Hospital NCI-IARC ESCC Tumor Workshop Where is Tenwek Hospital? Tenwek Nairobi Tenwek Hospital Identification of
Faculty Disclosure. Objectives. State of the Art #3: Referrals for Gastroscopy (focus on common esophagus problems) 24/11/2014
 State of the Art #3: Referrals for Gastroscopy (focus on common esophagus problems) Dr. Amy Morse November 2014 Faculty: Amy Morse Faculty Disclosure Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research
State of the Art #3: Referrals for Gastroscopy (focus on common esophagus problems) Dr. Amy Morse November 2014 Faculty: Amy Morse Faculty Disclosure Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research
Advances in endoscopic resection and radiofrequency ablation of early esophageal neoplasia van Vilsteren, F.G.I.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Advances in endoscopic resection and radiofrequency ablation of early esophageal neoplasia van Vilsteren, F.G.I. Link to publication Citation for published version
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Advances in endoscopic resection and radiofrequency ablation of early esophageal neoplasia van Vilsteren, F.G.I. Link to publication Citation for published version
Section: Medicine Effective Date: July 15, 2015 Subsection: Original Policy Date: December 7, 2011 Subject:
 Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 Page: 1 of 16 Cryoablation for Barrett s Esophagus Description Barrett s esophagus (BE) is a condition in which the normal squamous epithelium is replaced by specialized
Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 Page: 1 of 16 Cryoablation for Barrett s Esophagus Description Barrett s esophagus (BE) is a condition in which the normal squamous epithelium is replaced by specialized
Endoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation or Cryoablation for Barrett`s Esophagus. Original Policy Date
 MP 2.01.52 Endoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation or Cryoablation for Barrett`s Esophagus Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature
MP 2.01.52 Endoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation or Cryoablation for Barrett`s Esophagus Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature
Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행
 Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행 JGCA classification - Japanese Gastric Cancer Association - Type 0 superficial polypoid, flat/depressed, or excavated tumors Type 1 polypoid carcinomas, usually attached
Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행 JGCA classification - Japanese Gastric Cancer Association - Type 0 superficial polypoid, flat/depressed, or excavated tumors Type 1 polypoid carcinomas, usually attached
Diagnosis and staging of superficial esophageal precursor based on pre-endoscopic resection system comparable to endoscopic resection
 Qin et al. BMC Cancer 2014, 14:774 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Diagnosis and staging of superficial esophageal precursor based on pre-endoscopic resection system comparable to endoscopic resection Xiumin
Qin et al. BMC Cancer 2014, 14:774 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Diagnosis and staging of superficial esophageal precursor based on pre-endoscopic resection system comparable to endoscopic resection Xiumin
The Paris classification of colonic lesions
 The Paris classification of colonic lesions Training to improve the interobserver agreement among international experts Sascha van Doorn, MD, PhD-student in CRC-reserach group of Evelien Dekker Introduction
The Paris classification of colonic lesions Training to improve the interobserver agreement among international experts Sascha van Doorn, MD, PhD-student in CRC-reserach group of Evelien Dekker Introduction
University Mainz. Early Gastric Cancer. Ralf Kiesslich. Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany. Early Gastric Cancer 15.6.
 Ralf Kiesslich Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany DIAGNOSIS Unmask lesions - Chromoendoscopy -NBI Red flag technology - Autofluorescence Surface and detail analysis - Magnifying endoscopy - High
Ralf Kiesslich Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany DIAGNOSIS Unmask lesions - Chromoendoscopy -NBI Red flag technology - Autofluorescence Surface and detail analysis - Magnifying endoscopy - High
Review Article Outcomes of Radiofrequency Ablation for Dysplastic Barrett s Esophagus: A Comprehensive Review
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2016, Article ID 4249510, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4249510 Review Article Outcomes of Radiofrequency Ablation for Dysplastic Barrett s Esophagus:
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2016, Article ID 4249510, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4249510 Review Article Outcomes of Radiofrequency Ablation for Dysplastic Barrett s Esophagus:
How to stage early BE cancer - EUS or endoscopic removal?
 How to stage early BE cancer - EUS or endoscopic removal? Presented by Bas Weusten Institution St. Antonius Hospital, Nieuwegein Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam case 56 y old female patient Lung transplant
How to stage early BE cancer - EUS or endoscopic removal? Presented by Bas Weusten Institution St. Antonius Hospital, Nieuwegein Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam case 56 y old female patient Lung transplant
Oesophagus and Stomach update dysplasia and early cancer
 Oesophagus and Stomach update dysplasia and early cancer Dr Tim Bracey STR teaching 13/4/16 Please check pathkids.com for previous talks One of the biggest units in the country (100 major resections per
Oesophagus and Stomach update dysplasia and early cancer Dr Tim Bracey STR teaching 13/4/16 Please check pathkids.com for previous talks One of the biggest units in the country (100 major resections per
Current Management of Low-Grade Dysplasia in Barrett Esophagus
 Current Management of Low-Grade Dysplasia in Barrett Esophagus Gary W. Falk, MD, MS Dr Falk is a professor of medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School
Current Management of Low-Grade Dysplasia in Barrett Esophagus Gary W. Falk, MD, MS Dr Falk is a professor of medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School
Sixteen-year follow-up of Barrett s esophagus, endoscopically treated with argon plasma coagulation
 Original Article Sixteen-year of Barrett s esophagus, endoscopically treated with argon plasma coagulation United European Gastroenterology Journal 2014, Vol. 2(5) 367 373! Author(s) 2014 Reprints and
Original Article Sixteen-year of Barrett s esophagus, endoscopically treated with argon plasma coagulation United European Gastroenterology Journal 2014, Vol. 2(5) 367 373! Author(s) 2014 Reprints and
Case Scenario 1. The patient has now completed his neoadjuvant chemoradiation and has been cleared for surgery.
 Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Are You Living with Barrett s Esophagus?
 Are You Living with Barrett s Esophagus? Wouldn t you rather live without it? If you re living with Barrett s esophagus you are not alone. Barrett s esophagus is caused by the long-term exposure of your
Are You Living with Barrett s Esophagus? Wouldn t you rather live without it? If you re living with Barrett s esophagus you are not alone. Barrett s esophagus is caused by the long-term exposure of your
Long-term recurrence of neoplasia and Barrett s epithelium after complete endoscopic resection
 Editor s choice Scan to access more free content For numbered affiliations see end of article. Correspondence to Professor Thomas Rösch, Department of Interdisciplinary Endoscopy, University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf,
Editor s choice Scan to access more free content For numbered affiliations see end of article. Correspondence to Professor Thomas Rösch, Department of Interdisciplinary Endoscopy, University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf,
Long-term recurrence of neoplasia and Barrett s epithelium after complete endoscopic resection
 Editor s choice Scan to access more free content ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-term recurrence of neoplasia and Barrett s epithelium after complete endoscopic resection Mario Anders, 1 Christina Bähr, 1 Muhammad
Editor s choice Scan to access more free content ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-term recurrence of neoplasia and Barrett s epithelium after complete endoscopic resection Mario Anders, 1 Christina Bähr, 1 Muhammad
MANAGEMENT OF BARRETT S RELATED NEOPLASIA IN 2018
 MANAGEMENT OF BARRETT S RELATED NEOPLASIA IN 2018 Sachin Wani Medical Director Esophageal and Gastric Center Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus DISCLOSURES
MANAGEMENT OF BARRETT S RELATED NEOPLASIA IN 2018 Sachin Wani Medical Director Esophageal and Gastric Center Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus DISCLOSURES
Barrett s Oesophagus Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Barrett s Oesophagus Barrett s Oesophagus is the term used for a pre-cancerous condition where the normal
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Barrett s Oesophagus Barrett s Oesophagus is the term used for a pre-cancerous condition where the normal
Recurrent intestinal metaplasia at the gastroesophageal junction following endoscopic eradication of dysplastic Barrett s esophagus may not be benign
 THIEME E849 Recurrent intestinal metaplasia at the gastroesophageal junction following endoscopic eradication of dysplastic Barrett s esophagus may not be benign Authors Georgina R. Cameron 1, 3, Paul
THIEME E849 Recurrent intestinal metaplasia at the gastroesophageal junction following endoscopic eradication of dysplastic Barrett s esophagus may not be benign Authors Georgina R. Cameron 1, 3, Paul
Colon Polyps: Detection, Inspection and Characteristics
 Colon Polyps: Detection, Inspection and Characteristics Stephen Kim, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Interventional Endoscopy Services UCLA Division of Digestive Diseases September 29, 2018 1 Disclosures
Colon Polyps: Detection, Inspection and Characteristics Stephen Kim, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Interventional Endoscopy Services UCLA Division of Digestive Diseases September 29, 2018 1 Disclosures
Yanfang Chen, 1,2 Ye Zhao, 1,2 Xiaojing Zhao, 2 and Ruihua Shi Introduction
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2016, Article ID 3741456, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3741456 Research Article Clinical Outcomes of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Early Esophageal
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2016, Article ID 3741456, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3741456 Research Article Clinical Outcomes of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Early Esophageal
Learning Objectives:
 Crescent City GI Update 2018 Ochsner Clinic, NOLA Optimizing Endoscopic Evaluation of Barrett s Esophagus What Should I Do in My Practice? Gregory G. Ginsberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine University of
Crescent City GI Update 2018 Ochsner Clinic, NOLA Optimizing Endoscopic Evaluation of Barrett s Esophagus What Should I Do in My Practice? Gregory G. Ginsberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine University of
위 ESD 후내시경소견 성균관대학교의과대학내과이준행
 위 ESD 후내시경소견 성균관대학교의과대학내과이준행 문제의식 위궤양, 조기위암, 진행위암의내시경소견은배운다. 위암수술후소견은가끔배운다. 위암내시경시술후소견은배운적이없다. 관찰과조직검사에대한가이드라인이없다. ESD 후정상내시경소견 성균관대학교의과대학내과이준행 처음의뢰되었을때의사진 ESD M/D, 18mm, LP, RM (-), L/V (-) 추적내시경소견 2
위 ESD 후내시경소견 성균관대학교의과대학내과이준행 문제의식 위궤양, 조기위암, 진행위암의내시경소견은배운다. 위암수술후소견은가끔배운다. 위암내시경시술후소견은배운적이없다. 관찰과조직검사에대한가이드라인이없다. ESD 후정상내시경소견 성균관대학교의과대학내과이준행 처음의뢰되었을때의사진 ESD M/D, 18mm, LP, RM (-), L/V (-) 추적내시경소견 2
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration
 Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Frozen Section Analysis of Esophageal Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Specimens in the Real-Time Management of Barrett s Esophagus
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:173 178 Frozen Section Analysis of Esophageal Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Specimens in the Real-Time Management of Barrett s Esophagus GANAPATHY A. PRASAD,*
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:173 178 Frozen Section Analysis of Esophageal Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Specimens in the Real-Time Management of Barrett s Esophagus GANAPATHY A. PRASAD,*
SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT
 THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PATHOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Program SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT Developing Self-Assessment Modules (SAMs) www.abpath.org The American Board of Pathology (ABP) approves educational
THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PATHOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Program SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT Developing Self-Assessment Modules (SAMs) www.abpath.org The American Board of Pathology (ABP) approves educational
Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens C Rose, H Wu Citation C Rose, H Wu.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens C Rose, H Wu Citation C Rose, H Wu.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes Individuals: With Barrett esophagus with high-grade dysplasia
 Endoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation or Cryoablation for Barrett (20180) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/16 Next Review Date: 09/19 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 05/09, 03/10, 03/11, 03/12, 07/12,
Endoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation or Cryoablation for Barrett (20180) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/16 Next Review Date: 09/19 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 05/09, 03/10, 03/11, 03/12, 07/12,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, FACG 1, Gary W. Falk, MD, MS, FACG 2, Prasad G. Iyer, MD, MSc, FACG 3 and Lauren Gerson, MD, MSc, FACG
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, FACG 1, Gary W. Falk, MD, MS, FACG 2, Prasad G. Iyer, MD, MSc, FACG 3 and Lauren Gerson, MD, MSc, FACG
Barrett s esophagus (BE) is a precancerous state
 CLINICAL ALIMENTARY TRACT Gastroenterology 2017;153:681 688 Late Recurrence of Barrett s Esophagus After Complete Eradication of Intestinal Metaplasia is Rare: Final Report From Ablation in Intestinal
CLINICAL ALIMENTARY TRACT Gastroenterology 2017;153:681 688 Late Recurrence of Barrett s Esophagus After Complete Eradication of Intestinal Metaplasia is Rare: Final Report From Ablation in Intestinal
CLINICAL TRIAL OUTCOMES: RADIOFREQUENCY ABLATION (RFA) FOR BARRETT S ESOPHAGUS
 CLINICAL TRIAL OUTCOMES: RADIOFREQUENCY ABLATION (RFA) FOR BARRETT S ESOPHAGUS CLIN-0115 (Rev. D) Clinical Trial Outcomes of RFA for BE (Ref. ECO#12339) Page 1 of 82 T ABLE OF C O N T E N T S 1. INTRODUCTION...
CLINICAL TRIAL OUTCOMES: RADIOFREQUENCY ABLATION (RFA) FOR BARRETT S ESOPHAGUS CLIN-0115 (Rev. D) Clinical Trial Outcomes of RFA for BE (Ref. ECO#12339) Page 1 of 82 T ABLE OF C O N T E N T S 1. INTRODUCTION...
Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 Final Pathology:
 Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 A 74 year old male with a history of GERD presents complaining of dysphagia. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 A 74 year old male with a history of GERD presents complaining of dysphagia. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia
 Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia Ralf Kiesslich I. Medical Department Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany Cumulative cancer risk in ulcerative colitis 0.5-1.0%
Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia Ralf Kiesslich I. Medical Department Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany Cumulative cancer risk in ulcerative colitis 0.5-1.0%
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath
 Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Eosinophilic esophagitis Incidence of eosinophilic gastritis is increasing. Symptoms: food impaction and dysphagia. Histology: infiltration
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Eosinophilic esophagitis Incidence of eosinophilic gastritis is increasing. Symptoms: food impaction and dysphagia. Histology: infiltration
Barrett s esophagus, reflux esophagitis, and eosinophilic esophagitis F. P. Vleggaar, P. D. Siersema Utrecht, the Netherlands
 DDW HIGHLIGHTS F. P. Vleggaar, P. D. Siersema Utrecht, the Netherlands Many new and exciting endoscopy-related studies on Barrett s esophagus, reflux esophagitis, and eosinophilic esophagitis were presented
DDW HIGHLIGHTS F. P. Vleggaar, P. D. Siersema Utrecht, the Netherlands Many new and exciting endoscopy-related studies on Barrett s esophagus, reflux esophagitis, and eosinophilic esophagitis were presented
AGA SECTION. Gastroenterology 2016;150:
 Gastroenterology 2016;150:1026 1030 April 2016 AGA Section 1027 Procedural intervention (3) Upper endoscopy indications 3 6 Non-response of symptoms to a 4 8 week empiric trial of twice-daily PPI Troublesome
Gastroenterology 2016;150:1026 1030 April 2016 AGA Section 1027 Procedural intervention (3) Upper endoscopy indications 3 6 Non-response of symptoms to a 4 8 week empiric trial of twice-daily PPI Troublesome
What Is Barrett s Esophagus?
 What Is Barrett s Esophagus? Having Barrett s esophagus means the cells lining the esophagus (the tube that links the mouth and the stomach) have changed into types of intestinal cells that are not normal
What Is Barrett s Esophagus? Having Barrett s esophagus means the cells lining the esophagus (the tube that links the mouth and the stomach) have changed into types of intestinal cells that are not normal
malignant polyp Daily Challenges in Digestive Endoscopy for Endoscopists and Endoscopy Nurses BSGIE Annual Meeting 18/09/2014 Mechelen
 Plan Incidental finding of a malignant polyp 1. What is a polyp malignant? 2. Role of the pathologist and the endoscopist 3. Quantitative and qualitative risk assessment 4. How to decide what to do? Hubert
Plan Incidental finding of a malignant polyp 1. What is a polyp malignant? 2. Role of the pathologist and the endoscopist 3. Quantitative and qualitative risk assessment 4. How to decide what to do? Hubert
Patterns of recurrent and persistent intestinal metaplasia after successful radiofrequency ablation of Barrett s esophagus
 Patterns of recurrent and persistent intestinal metaplasia after successful radiofrequency ablation of Barrett s esophagus Robert J. Korst, MD, a,b Sobeida Santana-Joseph, MSN, a,b John R. Rutledge, MAS,
Patterns of recurrent and persistent intestinal metaplasia after successful radiofrequency ablation of Barrett s esophagus Robert J. Korst, MD, a,b Sobeida Santana-Joseph, MSN, a,b John R. Rutledge, MAS,
History. Prevalence at Endoscopy. Prevalence and Reflux Sx. Prevalence at Endoscopy. Barrett s Esophagus: Controversy and Management
 Barrett s Esophagus: Controversy and Management History Norman Barrett (1950) Chronic Peptic Ulcer of the Oesophagus and Oesophagitis Allison and Johnstone (1953) The Oesophagus Lined with Gastric Mucous
Barrett s Esophagus: Controversy and Management History Norman Barrett (1950) Chronic Peptic Ulcer of the Oesophagus and Oesophagitis Allison and Johnstone (1953) The Oesophagus Lined with Gastric Mucous
Rings in the esophagus are not always eosinophilic esophagitis: Case series of ring forming lymphocytic esophagitis and review of the literature
 Rings in the esophagus are not always eosinophilic esophagitis: Case series of ring forming lymphocytic esophagitis and review of the literature Authors Julia L. Pleet 1,SofiaTaboada 2, Arvind Rishi 2,
Rings in the esophagus are not always eosinophilic esophagitis: Case series of ring forming lymphocytic esophagitis and review of the literature Authors Julia L. Pleet 1,SofiaTaboada 2, Arvind Rishi 2,
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA. Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital
 LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
DISCLOSURES. This program meets the requirements for GI specific Category 1 contact hours. M
 DISCLOSURES Educational Dimensions is accredited as a provider of continuing nursing education by the American Nurses Credentialing Center s Commission on Accreditation. Successful completion: Participants
DISCLOSURES Educational Dimensions is accredited as a provider of continuing nursing education by the American Nurses Credentialing Center s Commission on Accreditation. Successful completion: Participants
Prognostic analysis of gastric mucosal dysplasia after endoscopic resection: A single-center retrospective study
 JBUON 2019; 24(2): 679-685 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic analysis of gastric mucosal dysplasia after endoscopic resection:
JBUON 2019; 24(2): 679-685 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic analysis of gastric mucosal dysplasia after endoscopic resection:
Diagnostic accuracy of pit pattern and vascular pattern in colorectal lesions
 Diagnostic accuracy of pit pattern and vascular pattern in colorectal lesions Digestive Disease Center, Showa University Northern Yokohama Hospital Department of Pathology Yoshiki Wada, Shin-ei Kudo, Hiroshi
Diagnostic accuracy of pit pattern and vascular pattern in colorectal lesions Digestive Disease Center, Showa University Northern Yokohama Hospital Department of Pathology Yoshiki Wada, Shin-ei Kudo, Hiroshi
B Barrett neoplasia, early, endoscopic mucosal resection of, in Europe, 297
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achalasia, treatment of, history of, 258 259 Achalasia myotomy, 270 Adenocarcinomas, endoscopic management of, in Asia, 289 290 B Barrett neoplasia,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achalasia, treatment of, history of, 258 259 Achalasia myotomy, 270 Adenocarcinomas, endoscopic management of, in Asia, 289 290 B Barrett neoplasia,
Do any benign polyps require an operation?
 Do any benign polyps require an operation? Kevin Waschke MD.,CM., FRCPC, FASGE McGill University Health Center President Elect Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Colonoscopy Education Day - Tuesday
Do any benign polyps require an operation? Kevin Waschke MD.,CM., FRCPC, FASGE McGill University Health Center President Elect Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Colonoscopy Education Day - Tuesday
Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
 Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Alina M.Boeriu 1, Daniela E.Dobru 1, Simona Mocan 2 1) Department of Gastroenterology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy;
Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Alina M.Boeriu 1, Daniela E.Dobru 1, Simona Mocan 2 1) Department of Gastroenterology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy;
Chromoendoscopy or Narrow Band Imaging with Targeted biopsies Should be the Cancer Surveillance Endoscopy Procedure of Choice in Ulcerative Colitis
 Chromoendoscopy or Narrow Band Imaging with Targeted biopsies Should be the Cancer Surveillance Endoscopy Procedure of Choice in Ulcerative Colitis Bret A. Lashner, M.D. Professor of Medicine Director,
Chromoendoscopy or Narrow Band Imaging with Targeted biopsies Should be the Cancer Surveillance Endoscopy Procedure of Choice in Ulcerative Colitis Bret A. Lashner, M.D. Professor of Medicine Director,
Extensive (8 to 12 cm 2 ) Noncircumferential Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Early Esophageal Cancer
 SECTION V: ESOPHAGUS MALIGNANT Extensive (8 to 12 cm 2 ) Noncircumferential Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Early Esophageal Cancer Philippe Monnier, MD, Yves Jaquet, MD, Alexandre Radu, MD, Raphaelle
SECTION V: ESOPHAGUS MALIGNANT Extensive (8 to 12 cm 2 ) Noncircumferential Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Early Esophageal Cancer Philippe Monnier, MD, Yves Jaquet, MD, Alexandre Radu, MD, Raphaelle
Joel A. Ricci, MD SUNY Downstate Medical Center Department of Surgery
 Joel A. Ricci, MD SUNY Downstate Medical Center Department of Surgery Norman Barrett (1950) described the esophagus as: that part of the foregut, distal to the cricopharyngeal sphincter, which is lined
Joel A. Ricci, MD SUNY Downstate Medical Center Department of Surgery Norman Barrett (1950) described the esophagus as: that part of the foregut, distal to the cricopharyngeal sphincter, which is lined
Management of pt1 polyps. Maria Pellise
 Management of pt1 polyps Maria Pellise Early colorectal cancer Malignant polyp Screening programmes SM Invasive adenocar cinoma Advances in diagnostic & therapeutic endoscopy pt1 polyps 0.75 5.6% of large-bowel
Management of pt1 polyps Maria Pellise Early colorectal cancer Malignant polyp Screening programmes SM Invasive adenocar cinoma Advances in diagnostic & therapeutic endoscopy pt1 polyps 0.75 5.6% of large-bowel
surgery ACA Acta Chirurgica Austriaca
 Eur Surg (2009) 41/1: 19 25 DOI 10.1007/s10353-009-0447-z Springer-Verlag 2009 european surgery ACA Acta Chirurgica Austriaca Printed in Austria Radiofrequency ablation of Barrett's esophagus G. Arora
Eur Surg (2009) 41/1: 19 25 DOI 10.1007/s10353-009-0447-z Springer-Verlag 2009 european surgery ACA Acta Chirurgica Austriaca Printed in Austria Radiofrequency ablation of Barrett's esophagus G. Arora
Superficial Esophageal Neoplasms Overlying Leiomyomas Removed by Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection: Case Reports and Review of the Literature
 CASE REPORT Clin Endosc 2015;48:322-327 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.4.322 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Superficial Esophageal Neoplasms Overlying Leiomyomas Removed
CASE REPORT Clin Endosc 2015;48:322-327 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.4.322 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Superficial Esophageal Neoplasms Overlying Leiomyomas Removed
Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy
 Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy Authors: Dr Gordon Armstrong, Dr Sue Pritchard 1. General Comments 1.1 Cancer reporting: Biopsies
Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy Authors: Dr Gordon Armstrong, Dr Sue Pritchard 1. General Comments 1.1 Cancer reporting: Biopsies
Barrett s Esophagus. lining of the lower esophagus that bears his name (i.e., Barrett's esophagus). We now
 Shamika Johnson Anatomy & Physiology 206 April 20, 2010 Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s Esophagus? Norman Barrett was a pathologist. In 1950, he described an abnormality in the lining of the lower
Shamika Johnson Anatomy & Physiology 206 April 20, 2010 Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s Esophagus? Norman Barrett was a pathologist. In 1950, he described an abnormality in the lining of the lower
How to treat early gastric cancer? Endoscopy
 How to treat early gastric cancer? Endoscopy Presented by Pierre H. Deprez Institution Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc, Brussels Université catholique de Louvain 2 3 4 5 6 Background Diagnostic or therapeutic
How to treat early gastric cancer? Endoscopy Presented by Pierre H. Deprez Institution Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc, Brussels Université catholique de Louvain 2 3 4 5 6 Background Diagnostic or therapeutic
