The Open Access Institutional Repository at Robert Gordon University
|
|
|
- Priscilla Pitts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Open Access Institutional Repository at Robert Gordon University This is an author produced version of a paper published in Oncology Letters (ISSN , eissn ) This version may not include final proof corrections and does not include published layout or pagination. Citation Details Citation for the version of the work held in OpenAIR@RGU : WEICHHAUS, M., BROOM, J., WAHLE, K. and BERMANO, G., Leptin inhibits proliferation of breast cancer cells at supraphysiological concentrations by inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. Available from OpenAIR@RGU. [online]. Available from: Citation for the publisher s version: WEICHHAUS, M., BROOM, J., WAHLE, K. and BERMANO, G., Leptin inhibits proliferation of breast cancer cells at supraphysiological concentrations by inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. Oncology Letters, 8 (1), pp Copyright Items in OpenAIR@RGU, Robert Gordon University Open Access Institutional Repository, are protected by copyright and intellectual property law. If you believe that any material held in OpenAIR@RGU infringes copyright, please contact openair-help@rgu.ac.uk with details. The item will be removed from the repository while the claim is investigated.
2 374 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 8: , 2014 Leptin inhibits proliferation of breast cancer cells at supraphysiological concentrations by inhibiting mitogen activated protein kinase signaling MICHAEL WEICHHAUS 1, JOHN BROOM 1, KLAUS WAHLE 2 and GIOVANNA BERMANO 1 1 Centre for Obesity Research and Epidemiology (CORE), Institute for Health and Welfare Research, Robert Gordon University, Aberdeen AB10 7GJ; 2 Cancer Medicine Research Group, School of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Aberdeen, Medical School, Aberdeen AB25 2ZD, UK Received August 23, 2013; Accepted February 18, 2014 DOI: /ol Abstract. Leptin is a hormone secreted by white fat tissue and signals the amount of overall body fat to the hypothalamus. The circulating concentration of leptin correlates with the level of obesity. Breast cancer risk is higher in obese postmenopausal women compared with postmenopausal women of a normal weight, and high leptin concentrations may contribute to this risk. In the present study, SK BR 3 and MDA MB 231 breast cancer cell lines were treated with various concentrations (6.25 1,600 ng ml) of recombinant leptin and changes in cell proliferation were assessed. The SK BR 3 breast cancer cells exhibited a concentration dependent increase in proliferation with physiological leptin concentrations (<100 ng ml), but no further increase in proliferation at high leptin concentrations (>100 ng ml) was observed. Cell proliferation was not affected at supraphysiological leptin concentrations (>800 ng ml) in SK BR 3 cells, whereas it decreased in MDA MB 231 cells. Therefore, cell signaling and cell cycle changes were assessed at supraphysiological concentrations (1,600 ng ml). In the two cell lines, leptin treatment decreased the mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) cell signaling pathway activation. Leptin treatment did not increase Akt phosphorylation or significantly alter the cell population distribution across cell cycle stages. To the best of our knowledge, leptin induced growth inhibition of breast cancer cells at supraphysiological concentrations has not been reported in the literature to date, and the findings of this study suggest that reduced MAPK activity may be the underlying cause. Thus, the effect of leptin on breast cancer growth warrants further investigation since Correspondence to: Dr Giovanna Bermano, Centre for Obesity Research and Epidemiology (CORE), Institute for Health and Welfare Research, Robert Gordon University, Riverside East, Garthdee Road, Aberdeen AB10 7GJ, UK E mail: g.bermano@rgu.ac.uk Key words: leptin, breast cancer, obesity, cell proliferation, mitogen activated protein kinase cell signaling pathway leptin is considered to be one of the main mediators in the obesity breast cancer connection. Introduction Obesity, the accumulation of excess fat tissue, is a risk factor for the development of postmenopausal breast cancer (1). The molecular changes in metabolism associated with obesity are thought to contribute to this phenomenon (2). One of these molecular changes is increased circulating leptin levels in obese individuals (3). Leptin is a 16 kda peptide hormone predominantly produced by white fat tissue (4). Its main function is to signal to the hypothalamus, which in response regulates satiety and energy expenditure (5). Notably, leptin is also responsible for the normal formation of the mammary gland in humans (6), suggesting an involvement in mammary tissue growth and differentiation, and potentially malignant transformation. Epidemiologically, leptin concentrations are higher in patients with breast cancer compared with healthy individuals, independent of body weight (7). Additionally, leptin receptor (Ob R) expression is increased in breast tumor tissue compared with surrounding tissue (8). Breast cancer cell lines have also been found to express leptin and Ob R (9). Previous in vitro experiments investigating the effects of leptin treatment on cell proliferation and tumor growth have revealed conflicting results. In MDA MB 231 breast cancer cells, leptin induced a robust concentration dependent increase in proliferation in two independent studies (10,11). Conversely, in MCF 7 breast cancer cells, leptin treatment increased (12) and decreased (11) proliferation. Similarly, in human epidermal growth factor (HER) 2 overexpressing SK BR 3 breast cancer cells, leptin treatment increased proliferation between 5 and 50 ng ml, but not at 100 ng ml (11). These controversial findings warrant the need for further investigation into the effects of leptin on proliferation in a human breast cancer in vitro cell system. Notably, a number of studies investigating the effect of cytokines on proliferation changes in cell culture models used concentrations which are several fold greater than the highest known physiological concentration, such as insulin treatment (13,14) or tumor necrosis factor α treatment (15,16).
3 WEICHHAUS et al: LEPTIN AND BREAST CANCER 375 However, previous studies investigating the effect of leptin treatment on proliferation in breast cancer cells (10,11,17) did not or only marginally exceeded maximal physiological leptin concentrations of 100 ng ml (3). The highest leptin concentration used in vitro to examine changes in T47D breast cancer cell proliferation was 1,000 ng ml. However, increased cell proliferation was only observed with up to 100 ng ml leptin (18). Thus, while previous data appear to indicate a growth inhibitory effect of leptin at above physiological concentrations, it has not yet been fully investigated. Therefore, the present study aimed to explore the effects of supraphysiological leptin concentrations on proliferation in two breast cancer cell lines. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of physiological and supraphysiological levels of leptin ( 1,600 ng ml) on proliferation in SK BR 3 and MDA MB 231 breast cancer cells, two cell lines representative of HER 2 positive and basal type breast cancer subtypes, respectively. The activation of phosphatidylinositide 3 kinase (PI3K) and mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) cell signaling pathways and distribution across cell cycle stages were assessed in the two cell lines following treatment with 1,600 ng ml leptin. Materials and methods Cell lines. SK BR 3 and MDA MB 231 breast cancer cell lines were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). The two cell lines were routinely cultured in RPMI 1640 medium (including 25 mm HEPES, 1X Glutamax ; Gibco, Paisley, UK) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (FCS; Pierce Biosciences, Cramlington, UK), 100 U ml penicillin and 100 µg ml streptomycin (Gibco). Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) proliferation assay. Cell proliferation was detected using the Proliferation ELISA kit (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Penzberg, Germany). The two cell lines were plated at a density of 5x10 3 cells well in 96 well plates with 100 µl well growth medium and incubated for 24 h at 37 C. Cells were starved for 24 h in RPMI 1640 medium without FCS supplementation, and then treated for 24 or 48 h with ,600 ng ml leptin in replicates of six in starvation medium. During treatment, the medium was supplemented with 10 µm BrdU. Cell proliferation was assessed as previously described (16). The experiment was repeated for a total of three independent times. Each experiment had six replicates for each leptin concentration. PI3K and MAPK phosphorylation ELISA. Cell based ELISA Phospho Akt (S473) Immunoassay and Phospho extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK)1 ERK2 (T202 Y204) Immunoassay were purchased from R&D Systems (Abingdon, UK). The cells were plated in a supplied clear bottom, black-walled, 96 well plate at a density of 5x10 3 cells well with 100 µl well growth medium, and incubated for 24 h at 37 C. The cells were starved for 24 h as mentioned above and then treated with 1,600 ng ml leptin for 5 20 min in duplicates. Phosphorylation of protein kinase B (Akt) or ERK1 2 was then assessed as previously described (16). The experiment was repeated for a total of three independent experiments with two replicates for each time point in each experiment. Cell cycle analysis. Changes in the cell distribution across cell cycle stages were assessed by measuring the DNA content in cells using flow cytometry following leptin treatment. The DNA specific dye was propidium iodide (PI; Sigma Aldrich, Gillingham, UK). The cells were plated at a density of 5x10 5 cells well in six well plates with 3 ml growth medium, and incubated for 24 h at 37 C. The cells were starved for 24 h, treated with 1,600 ng ml leptin for 24 h and then harvested, treated and analyzed as described previously (16). Statistical analysis. The findings were analyzed for statistical significance using univariate analysis of variance between the control and each treatment concentration for cell proliferation analysis and between the control and each time point in the cell signaling pathway analysis, followed by Dunnett's post hoc t tests. Differences in the distribution across cell cycle stages between the control and leptin treated cells were assessed for each cell cycle stage using Student's t test. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. Results Changes in cell proliferation following leptin treatment. In the SK BR 3 cells, proliferation increased by 61, 96, 104, 115, 115, 110 and 51% following treatment with 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200 and 400 ng ml leptin, respectively, for 24 h compared with the untreated control (all P<0.001) (Fig. 1A). There was no significant difference in cell proliferation between the untreated cells and cells treated with 800 or 1,600 ng ml leptin for 24 h (Fig. 1A). After 48 h of treatment, cell proliferation increased significantly by 44, 53, 53, 69, 75, 69, 52 and 33% following treatment with 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200, 400 ng ml (all P<0.001) and 800 ng ml (P=0.009) leptin, respectively compared with the untreated control (Fig. 1B). There was no change in proliferation after 48 h of treatment with 1,600 ng ml leptin (Fig. 1B). In MDA MB 231 breast cancer cells, proliferation did not change significantly after 24 h of treatment with leptin (Fig. 1C) and decreased significantly by 11% (P=0.023) and 26% (P<0.001) after 48 h of treatment with 400 and 800 ng ml (P<0.001) of leptin, respectively, compared with the untreated control (Fig. 1D). Based on the findings obtained on growth inhibition following treatment with 1,600 ng ml leptin, cell signaling and cell cycle changes were assessed to determine the underlying mechanisms responsible for growth inhibition in the two breast cancer cell lines. Changes in PI3K and MAPK cell signaling pathway activity following leptin treatment. In the SK BR 3 cells, Akt phosphorylation did not change significantly following treatment with 1,600 ng ml leptin for up to 20 min compared with the control (Fig. 2A). ERK1 2 phosphorylation decreased by 32 and 34% after 10 (P<0.001) and 15 min (P<0.001) of treatment with 1,600 ng ml leptin, respectively, compared with the control (Fig. 2B). In the MDA MB 231 cells, Akt phosphorylation did not change significantly following treatment with 1,600 ng ml leptin (Fig. 2C), whereas ERK1 2 phosphorylation decreased significantly by 17 and 20% after 15 (P=0.026) and 20 min (P=0.011) of treatment with 1,600 ng ml leptin, respectively, compared with the control (Fig. 2D).
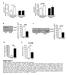
4 376 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 8: , 2014 Table I. Changes of cell population distribution across cell cycle stages after 24 h of treatment with 1,600 ng/ml leptin. SK BR 3 cells MDA MB 231 cells Cell cycle stage (%) Control Leptin treated P value Control Leptin treated P value SubG ± ± ± ± G 0 /G ± ± ± ± S 6.30± ± ± ± G ± ± ± ± Values represent the mean ± standard error of three independent experiments. P values were determined by Student's t test. Each experiment had two replicates, i.e., six data points for control and treatment. A B C D Figure 1. Changes in cell proliferation following treatment of (A and B) SK BR 3 and (C and D) MDA MB 231 breast cancer cells for (A and C) 24 h and (B and D) 48 h, with a range of leptin concentrations. Bars represent BrdU incorporation in relation to the respective control within each graph, and are expressed as a percentage of the control. Error bars represent standard error of the mean of two experiments, each consisting of six replicates, i.e., 12 data points for each bar. Significance was determined using Dunnett's post hoc t test following one way analysis of variance ( * P<0.05, ** 0.01<P<0.001 and *** P<0.001, vs. the control). BrdU, bromodeoxyuridine A B C D Figure 2. Changes in (A and C) Akt phosphorylation and (B and D) ERK1/2 phosphorylation as indicators of changes in the PI3K or MAPK cell signaling pathway, respectively, following 1,600 ng/ml leptin treatment of (A and B) SK BR 3 and (C and D) MDA MB 231 breast cancer cells for the indicated time periods. Bars represent Akt or ERK1/2 phosphorylation in relation to their respective control within each graph, and are expressed as a percentage of the control. Error bars represent standard error of the mean of three experiments, each consisting of two replicates, i.e., six data points for each bar. Significance was obtained using Dunnett's post hoc t test following univariate analysis of variance ( * P<0.05, vs. the control). ERK, extracellular signal regulated kinase; PI3K, phosphatidylinositide 3 kinase; MAPK, mitogen activated protein kinase.
5 WEICHHAUS et al: LEPTIN AND BREAST CANCER 377 Changes in distribution of cell population across cell cycle stages. In the SK BR 3 cells, 1,600 ng ml leptin treatment may increase the G 1 phase population and decrease the G 2 phase population (Table I). Cells in the G 1 phase increased by 4.5 percentage points (11% increase) and cells in the G 2 phase decreased by 2.0 percentage points (12% decrease). In MDA MB 231 cells, the subg 1 phase population increased by 1.2 percentage points (7% increase) and the G 1 -phase population decreased by 1.0 percentage point (2% decrease) following treatment with 1,600 ng ml leptin (Table I). None of the observed changes were significantly different. Discussion Previous in vitro studies have demonstrated that leptin induces cell proliferation in a variety of breast cancer cell types, within physiological concentrations ( ng ml) (6,9 12,18). Conversely, the same studies did not observe increased cell proliferation with leptin concentrations exceeding 100 ng ml. The findings of the present study confirmed the increased cell proliferation in SK BR 3 breast cancer cells, but not in MDA MB 231 cells at physiological concentrations. Furthermore, leptin treatment at supraphysiological concentrations did not increase cell proliferation in the SK BR 3 cells, but inhibited proliferation of the MDA MB 231 cells. To the best of our knowledge, this study was the first to indicate the potential of leptin treatment to inhibit cell proliferation in breast cancer cells. The mechanism by which supraphysiological leptin concentrations induce growth inhibition may involve decreased activation of the Ras mediated MAPK pathway. As a potential explanation, leptin may interact with the HER 2 neu receptor in SK BR 3 breast cancer cells, which is overexpressed in these cells, resulting in decreased MAPK activity. Soma et al reported that SK BR 3 cells treated with leptin (500 ng ml) resulted in increased phosphorylation of the HER 2 neu receptor (20). This cross talk was identified as being responsible for an increase in ERK1 2 phosphorylation, which was also observed following leptin treatment. The findings of the present study suggest that at higher leptin concentrations, this effect is inhibited. This may either be by high leptin levels inhibiting the potential of HER 2/neu to activate ERK1 2 or by inhibiting ERK1 2 phosphorylation directly. HER 2 neu and Ob R transduct their proliferative signal through the PI3K and or MAPK pathways (21), suggesting there may be an interaction on the targets downstream of the two receptors. Thus, leptin may have at least two modes of action, which appear to be antagonistic. First, leptin increases phosphorylation of HER 2 neu, which results in increased proliferation of SK BR 3 breast cancer cells; second, leptin inhibits ERK1 2 phosphorylation, which is predominant at high leptin concentrations, thereby reducing the effect of increased HER 2 neu signaling. In MDA MB 231 breast cancer cells, which are HER 2 negative, interplay with HER 2 neu cannot account for the observed reduction in proliferation, indicating that growth inhibition at supraphysiological leptin concentrations is HER-2/neu independent. In a study aiming to potentiate the antitumor effects of camp agonists, leptin induced apoptosis in MDA MB 231 breast cancer cells when camp levels were increased (22), which resulted in ERK1 2 inactivation and the subsequent inhibition of protein kinase A (PKA) expression (23). Thus, at supraphysiological concentrations, leptin may not require elevated camp levels to decrease PKA, and this may provide a mechanism for the effects observed in our study. These findings suggest that leptin exerts a biphasic effect on cell proliferation in SK BR 3 breast cancer cells and that leptin signaling may play a role in breast cancer development and progression. Therefore, the inhibition of leptin signaling may be relevant for breast cancer prevention, particularly for obese individuals showing high levels of leptin and occurrence of breast cancer. Nutritional interventions (24) or anti leptin treatment (25) may be considered as a potential preventative strategy and treatment for HER 2 neu overexpressing breast tumors, respectively. Further investigations into the inhibitory effects of leptin at high concentrations may reveal the unknown mechanisms in the connection between obesity and postmenopausal breast cancer. References 1. Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker Thurmond K and Thun MJ: Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med 348: , Lorincz AM and Sukumar S: Molecular links between obesity and breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 13: , Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, et al: Serum immunoreactive leptin concentrations in normal weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med 334: , Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, et al: Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 372: , Stephens TW, Basinski M, Bristow PK, et al: The role of neuropeptide Y in the antiobesity action of the obese gene product. Nature 377: , Hu X, Juneja SC, Maihle NJ and Cleary MP: Leptin a growth factor in normal and malignant breast cells and for normal mammary gland development. J Natl Cancer Inst 94: , Tessitore L, Vizio B, Pesola D, et al: Adipocyte expression and circulating levels of leptin increase in both gynaecological and breast cancer patients. Int J Oncol 24: , Révillion F, Charlier M, Lhotellier V, et al: Messenger RNA expression of leptin and leptin receptors and their prognostic value in 322 human primary breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res 12: , Ishikawa M, Kitayama J and Nagawa H: Enhanced expression of leptin and leptin receptor (OB R) in human breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10: , Frankenberry KA, Skinner H, Somasundar P, McFadden DW and Vona Davis LC: Leptin receptor expression and cell signaling in breast cancer. Int J Oncol 28: , Ray A, Nkhata KJ and Cleary MP: Effects of leptin on human breast cancer cell lines in relationship to estrogen receptor and HER2 status. Int J Oncol 30: , Dieudonne MN, Machinal Quelin F, Serazin Leroy V, Leneveu MC, Pecquery R and Giudicelli Y: Leptin mediates a proliferative response in human MCF7 breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 293: , Costantino A, Milazzo G, Giorgino F, et al: Insulin resistant MDA MB231 human breast cancer cells contain a tyrosine kinase inhibiting activity. Mol Endocrinol 7: , Weichhaus M, Broom J, Wahle K and Bermano G: A novel role for insulin resistance in the connection between obesity and postmenopausal breast cancer. Int J Oncol 41: , Rivas MA, Carnevale RP, Proietti CJ, et al: TNF alpha acting on TNFR1 promotes breast cancer growth via p42 P44 MAPK, JNK, Akt and NF kappa B dependent pathways. Exp Cell Res 314: , Weichhaus M, Broom I and Bermano G: The molecular contribution of TNF alpha in the link between obesity and breast cancer. Oncol Rep 25: , 2011.
6 378 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 8: , Chen C, Chang YC, Liu CL, Chang KJ and Guo IC: Leptin induced growth of human ZR 75 1 breast cancer cells is associated with up regulation of cyclin D1 and c Myc and down regulation of tumor suppressor p53 and p21waf1/cip1. Breast Cancer Res Treat 98: , Laud K, Gourdou I, Pessemesse L, Peyrat JP and Djiane J: Identification of leptin receptors in human breast cancer: functional activity in the T47 D breast cancer cell line. Mol Cell Endocrinol 188: , Okumura M, Yamamoto M, Sakuma H, et al: Leptin and high glucose stimulate cell proliferation in MCF 7 human breast cancer cells: reciprocal involvement of PKC alpha and PPAR expression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1592: , Soma D, Kitayama J, Yamashita H, et al: Leptin augments proliferation of breast cancer cells via transactivation of HER2. J Surg Res 149: 9 14, Reese DM and Slamon DJ: HER 2/neu signal transduction in human breast and ovarian cancer. Stem Cells 15: 1 8, Naviglio S, Di Gesto D, Romano M, et al: Leptin enhances growth inhibition by camp elevating agents through apoptosis of MDA MB 231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther 8: , Naviglio S, Di Gesto D, Illiano F, et al: Leptin potentiates antiproliferative action of camp elevation via protein kinase A down regulation in breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol 225: , Fan C, Liu X, Shen W, Deckelbaum RJ and Qi K: The regulation of leptin, leptin receptor and pro opiomelanocortin expression by N 3 PUFAs in diet induced obese mice is not related to the methylation of their promoters. Nutr Metab (Lond) 8: 31, Guo S, Liu M, Wang G, et al: Oncogenic role and therapeutic target of leptin signaling in breast cancer and cancer stem cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1825: , 2012.
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer. Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea
 Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer
 Masur K, Thévenod F, Zänker KS (eds): Diabetes and Cancer. Epidemiological Evidence and Molecular Links. Front Diabetes. Basel, Karger, 2008, vol 19, pp 97 113 Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer Ido Wolf
Masur K, Thévenod F, Zänker KS (eds): Diabetes and Cancer. Epidemiological Evidence and Molecular Links. Front Diabetes. Basel, Karger, 2008, vol 19, pp 97 113 Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer Ido Wolf
Introduction: 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis. PI3K/Akt
 Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen
 Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen Receptor Signaling to PI3K/AKT Tiffany G. Bredfeldt, Kristen L. Greathouse, Stephen H. Safe, Mien-Chie Hung, Mark
Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen Receptor Signaling to PI3K/AKT Tiffany G. Bredfeldt, Kristen L. Greathouse, Stephen H. Safe, Mien-Chie Hung, Mark
Focus Application. Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity
 xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving Function of the xcelligence System to Optimize Endpoint Viability and
xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving Function of the xcelligence System to Optimize Endpoint Viability and
Award Number: W81XWH TITLE: Dietary Fish Oil in Reducing Bone Metastasis of Breast Cancer
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0693 TITLE: Dietary Fish Oil in Reducing Bone Metastasis of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Nandini Ghosh-Choudhury, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas
AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0693 TITLE: Dietary Fish Oil in Reducing Bone Metastasis of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Nandini Ghosh-Choudhury, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas
Part-4. Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death
 Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
TITLE: Characterization of the Mechanisms of IGF-I-Mediated Stress-Activated Protein Kinase Activation in Human Breast Cancer Cell MCF-7
 AD Award Number DAMD17-98-1-8066 TITLE: Characterization of the Mechanisms of IGF-I-Mediated Stress-Activated Protein Kinase Activation in Human Breast Cancer Cell MCF-7 PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Wei Liu,
AD Award Number DAMD17-98-1-8066 TITLE: Characterization of the Mechanisms of IGF-I-Mediated Stress-Activated Protein Kinase Activation in Human Breast Cancer Cell MCF-7 PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Wei Liu,
Enhancing the Clinical Activity of HER2/neu Specific T Cells. William Gwin, MD Internal Medicine, Resident University of Washington
 Enhancing the Clinical Activity of HER2/neu Specific T Cells William Gwin, MD Internal Medicine, Resident University of Washington Immunotherapy and Cancer Cancer vaccines were originally used in melanoma
Enhancing the Clinical Activity of HER2/neu Specific T Cells William Gwin, MD Internal Medicine, Resident University of Washington Immunotherapy and Cancer Cancer vaccines were originally used in melanoma
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
TITLE: The Role of Constitutively Active Prolactin Receptors in the Natural History of Breast Cancer
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0448 TITLE: The Role of Constitutively Active Prolactin Receptors in the Natural History of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kuang-tzu Huang CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0448 TITLE: The Role of Constitutively Active Prolactin Receptors in the Natural History of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kuang-tzu Huang CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
GPR120 *** * * Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon. UCP1 mrna ***
 a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
Yiying Zhang, PhD Research Scientist. Research Summary:
 Yiying Zhang, PhD Research Scientist Research Summary: Address: Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center at Columbia University Medical Center Russ Berrie Medical Science Pavilion 1150 St. Nicholas Avenue New York,
Yiying Zhang, PhD Research Scientist Research Summary: Address: Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center at Columbia University Medical Center Russ Berrie Medical Science Pavilion 1150 St. Nicholas Avenue New York,
Focus Application. Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity
 xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving
xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving
Effects of Antiproliferative Protein (APP) on Modulation of Cytosolic Protein Phosphorylation of Prostatic Carcinoma Cell Line LNCaP
 Effects of Antiproliferative Protein (APP) on Modulation of Cytosolic Protein Phosphorylation of Prostatic Carcinoma Cell Line LNCaP Mohsen Abolhassani Dept. of Immunology, Pasteur Institute of Iran, Tehran
Effects of Antiproliferative Protein (APP) on Modulation of Cytosolic Protein Phosphorylation of Prostatic Carcinoma Cell Line LNCaP Mohsen Abolhassani Dept. of Immunology, Pasteur Institute of Iran, Tehran
The Expression and Significance of Drainderived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Its Specific Receptor Trk B in Colon Cancer Cells
 The Expression and Significance of Drainderived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Its Specific Receptor Trk B in Colon Cancer Cells Yi Liu, Lunhui Zhang, Liang Xu * ABSTRACT This paper aims at analyzing the
The Expression and Significance of Drainderived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Its Specific Receptor Trk B in Colon Cancer Cells Yi Liu, Lunhui Zhang, Liang Xu * ABSTRACT This paper aims at analyzing the
Rat Leptin-HS ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN
 YK051 Rat Leptin-HS ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418 0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
YK051 Rat Leptin-HS ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418 0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
Leptin Intro/Signaling. ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph
 Leptin Intro/Signaling ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph Overview Intro to Leptin Definition & Sources Physiology Bound vs. Free Receptors Signaling JAK/STAT MAPK PI3K ACC Experimental findings
Leptin Intro/Signaling ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph Overview Intro to Leptin Definition & Sources Physiology Bound vs. Free Receptors Signaling JAK/STAT MAPK PI3K ACC Experimental findings
- 1 - Cell types Monocytes THP-1 cells Macrophages. LPS Treatment time (Hour) IL-6 level (pg/ml)
 Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA
 YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA-SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Ⅰ. Introduction 2 Ⅱ. Characteristics 3 Ⅲ. Composition 4 Ⅳ. Method
YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA-SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Ⅰ. Introduction 2 Ⅱ. Characteristics 3 Ⅲ. Composition 4 Ⅳ. Method
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
I. Introduction. II. Characteristics
 YK050 Rat Leptin ELISA I. Introduction Leptin, which is a product of ob gene, is a protein consisting of 167 amino acids and it is secreted from white adipose tissue. It is known that leptin acts on hypothalamus
YK050 Rat Leptin ELISA I. Introduction Leptin, which is a product of ob gene, is a protein consisting of 167 amino acids and it is secreted from white adipose tissue. It is known that leptin acts on hypothalamus
Signal Transduction Pathway Smorgasbord
 Molecular Cell Biology Lecture. Oct 28, 2014 Signal Transduction Pathway Smorgasbord Ron Bose, MD PhD Biochemistry and Molecular Cell Biology Programs Washington University School of Medicine Outline 1.
Molecular Cell Biology Lecture. Oct 28, 2014 Signal Transduction Pathway Smorgasbord Ron Bose, MD PhD Biochemistry and Molecular Cell Biology Programs Washington University School of Medicine Outline 1.
To determine the effect of over-expression and/or ligand activation of. PPAR / on cell cycle, cell lines were cultured as described above until ~80%
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Cell cycle analysis To determine the effect of over-expression and/or ligand activation of PPAR / on cell cycle, cell lines were cultured as described above until ~80%
Supplementary Materials and Methods Cell cycle analysis To determine the effect of over-expression and/or ligand activation of PPAR / on cell cycle, cell lines were cultured as described above until ~80%
Increased risk of cancer with anti-diabetes drugs? : pros
 24 th Spring Congress of Korean Diabetes Association Increased risk of cancer with anti-diabetes drugs? : pros Nan Hee Kim, MD, Ph.D. Professor Korea University Medical School Contents Diabetes and cancer
24 th Spring Congress of Korean Diabetes Association Increased risk of cancer with anti-diabetes drugs? : pros Nan Hee Kim, MD, Ph.D. Professor Korea University Medical School Contents Diabetes and cancer
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit
 Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit
 Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 1 4 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Phospho-Ser473) E011054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit
Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 1 4 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Phospho-Ser473) E011054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease. Metabolic Disorders - Obesity
 BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
Human Leptin ELISA Kit
 Product Manual Human Leptin ELISA Kit Catalog Numbers MET-5057 MET-5057-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Leptin is a polypeptide hormone
Product Manual Human Leptin ELISA Kit Catalog Numbers MET-5057 MET-5057-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Leptin is a polypeptide hormone
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells
 PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
New York, New York U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: DAMDl7-96-1-6022 TITLE: The Role of PKC in Retinoic Acid Regulation of Human Mammary Cancer Cell Proliferation PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yunhi Cho, Ph.D. David A. Talmage, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
AD Award Number: DAMDl7-96-1-6022 TITLE: The Role of PKC in Retinoic Acid Regulation of Human Mammary Cancer Cell Proliferation PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yunhi Cho, Ph.D. David A. Talmage, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
Early cell death (FGF) B No RunX transcription factor produced Yes No differentiation
 Solution Key - Practice Questions Question 1 a) A recent publication has shown that the fat stem cells (FSC) can act as bone stem cells to repair cavities in the skull, when transplanted into immuno-compromised
Solution Key - Practice Questions Question 1 a) A recent publication has shown that the fat stem cells (FSC) can act as bone stem cells to repair cavities in the skull, when transplanted into immuno-compromised
Rat Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN
 YK050 Rat Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
YK050 Rat Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
Validation & Assay Performance Summary
 Validation & Assay Performance Summary LanthaScreen IGF-1R GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1834 Modification Detected: Phosphorylation of Multiple Tyr Residues on IGF-1R LanthaScreen Cellular Assay Validation
Validation & Assay Performance Summary LanthaScreen IGF-1R GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1834 Modification Detected: Phosphorylation of Multiple Tyr Residues on IGF-1R LanthaScreen Cellular Assay Validation
A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth
 210 A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth QUCHOU LI 1, SUSU GAO 1, YONGLIN YU 1, WENHUI WANG 1, XILEI CHEN 1, RUIXUE WANG 1, TAO LI 1, CONG WANG 1, XIAOKUN LI 1,2 and XIAOPING
210 A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth QUCHOU LI 1, SUSU GAO 1, YONGLIN YU 1, WENHUI WANG 1, XILEI CHEN 1, RUIXUE WANG 1, TAO LI 1, CONG WANG 1, XIAOKUN LI 1,2 and XIAOPING
Intracellular signalling pathways activated by leptin by Gema FRUHBECK. Presentation by Amnesiacs Anonymous
 Intracellular signalling pathways activated by leptin by Gema FRUHBECK Presentation by Amnesiacs Anonymous Introduction to Leptin By Ahrial Young Why is Leptin important? Pleiotropic = it controls the
Intracellular signalling pathways activated by leptin by Gema FRUHBECK Presentation by Amnesiacs Anonymous Introduction to Leptin By Ahrial Young Why is Leptin important? Pleiotropic = it controls the
Supplemental Data. TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim.
 Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108
 Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Effect of High-fat or High-glucose Diet on Obesity and Visceral Adipose Tissue in Mice
 ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
TITLE: "Impact of Obesity on Tamoxifen Chemoprevention in a Model of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ"
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-09-1-0720 TITLE: "Impact of Obesity on Tamoxifen Chemoprevention in a Model of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ" PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Sarah Dunlap-Smith, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-09-1-0720 TITLE: "Impact of Obesity on Tamoxifen Chemoprevention in a Model of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ" PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Sarah Dunlap-Smith, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α
 Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
University of California, San Diego La Jolla CA 92093
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0131 TITLE: Role of Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Mouse Models of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jerrold Olefsky, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University
AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0131 TITLE: Role of Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Mouse Models of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jerrold Olefsky, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
The elements of G protein-coupled receptor systems
 The elements of G protein-coupled receptor systems Prostaglandines Sphingosine 1-phosphate a receptor that contains 7 membrane-spanning domains a coupled trimeric G protein which functions as a switch
The elements of G protein-coupled receptor systems Prostaglandines Sphingosine 1-phosphate a receptor that contains 7 membrane-spanning domains a coupled trimeric G protein which functions as a switch
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Neither the activation nor suppression of the MAPK pathway affects the ASK1/Vif interaction. (a, b) HEK293 cells were cotransfected with plasmids encoding
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Neither the activation nor suppression of the MAPK pathway affects the ASK1/Vif interaction. (a, b) HEK293 cells were cotransfected with plasmids encoding
RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Assay Kit
 Activity Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 March 13, 2015 RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Kit Protocol (Cat#: 68AT-Akt-S40) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll
Activity Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 March 13, 2015 RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Kit Protocol (Cat#: 68AT-Akt-S40) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll
Differential enhancement of the anti-cancer effect of doxorubicin by Akt inhibitors on human breast cancer cells with differing genetic backgrounds
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 21: 437-442, 2009 437 Differential enhancement of the anti-cancer effect of doxorubicin by Akt inhibitors on human breast cancer cells with differing genetic backgrounds YAN A. WANG, STUART
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 21: 437-442, 2009 437 Differential enhancement of the anti-cancer effect of doxorubicin by Akt inhibitors on human breast cancer cells with differing genetic backgrounds YAN A. WANG, STUART
AT1 RECEPTOR BLOCKADE ATTENUATES INSULIN RESISTANCE AND MYOCARDIAL REMODELING IN RATS WITH DIET-INDUCED OBESITY
 AT1 RECEPTOR BLOCKADE ATTENUATES INSULIN RESISTANCE AND MYOCARDIAL REMODELING IN RATS WITH DIET-INDUCED OBESITY SA Oliveira Jr, MP Okoshi, PF Martinez, DM Guizoni, BP Torres, M Dal Pai-Silva, K Okoshi,
AT1 RECEPTOR BLOCKADE ATTENUATES INSULIN RESISTANCE AND MYOCARDIAL REMODELING IN RATS WITH DIET-INDUCED OBESITY SA Oliveira Jr, MP Okoshi, PF Martinez, DM Guizoni, BP Torres, M Dal Pai-Silva, K Okoshi,
Antitumor Activity of CUDC-305, a Novel Oral HSP90 Inhibitor, in Solid and Hematological Tumor Xenograft Models
 Antitumor Activity of CUDC-5, a Novel Oral HSP Inhibitor, in Solid and Hematological Tumor Xenograft Models Rudi Bao, MD/PhD April 1, 2 AACR 1th Annual Meeting 2 Experimental and Molecular Therapeutics
Antitumor Activity of CUDC-5, a Novel Oral HSP Inhibitor, in Solid and Hematological Tumor Xenograft Models Rudi Bao, MD/PhD April 1, 2 AACR 1th Annual Meeting 2 Experimental and Molecular Therapeutics
TITLE: Adipose Estrogen and Increased Breast Cancer Risk in Obesity: Regulation by Leptin and Insulin
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0497 TITLE: Adipose Estrogen and Increased Breast Cancer Risk in Obesity: Regulation by Leptin and Insulin PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Fahumiya Samad CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0497 TITLE: Adipose Estrogen and Increased Breast Cancer Risk in Obesity: Regulation by Leptin and Insulin PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Fahumiya Samad CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
EGF receptor transactivation is crucial for cholinergic MAP kinase signaling in human keratinocytes
 1st Electronic Conference on Molecular Science EGF receptor transactivation is crucial for cholinergic MAP kinase signaling in human keratinocytes Wymke Ockenga, Sina Kühne, Antje Banning and Ritva Tikkanen
1st Electronic Conference on Molecular Science EGF receptor transactivation is crucial for cholinergic MAP kinase signaling in human keratinocytes Wymke Ockenga, Sina Kühne, Antje Banning and Ritva Tikkanen
alveolar macrophages (AMs) after 24 hours of in vitro culture in complete medium
 Online Supplement for: NF-κB ACTIVATION IN ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGES REQUIRES IκB KINASE-β, BUT NOT NF-κB INDUCING KINASE Supershift and Competition Assays for NF-κB Competition and supershift assays were performed
Online Supplement for: NF-κB ACTIVATION IN ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGES REQUIRES IκB KINASE-β, BUT NOT NF-κB INDUCING KINASE Supershift and Competition Assays for NF-κB Competition and supershift assays were performed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
Trazodone regulates neurotrophic/growth factors, mitogen-activated protein kinases and lactate release in human primary astrocytes
 Daniele et al. Journal of Neuroinflammation (2015) 12:225 DOI 10.1186/s12974-015-0446-x RESEARCH Open Access Trazodone regulates neurotrophic/growth factors, mitogen-activated protein kinases and lactate
Daniele et al. Journal of Neuroinflammation (2015) 12:225 DOI 10.1186/s12974-015-0446-x RESEARCH Open Access Trazodone regulates neurotrophic/growth factors, mitogen-activated protein kinases and lactate
A dual PI3 kinase/mtor inhibitor reveals emergent efficacy in glioma
 Supplemental data A dual PI3 kinase/mtor inhibitor reveals emergent efficacy in glioma Qi-Wen Fan, Zachary A. Knight, David D. Goldenberg, Wei Yu, Keith E. Mostov, David Stokoe, Kevan M. Shokat, and William
Supplemental data A dual PI3 kinase/mtor inhibitor reveals emergent efficacy in glioma Qi-Wen Fan, Zachary A. Knight, David D. Goldenberg, Wei Yu, Keith E. Mostov, David Stokoe, Kevan M. Shokat, and William
Kevin R. Fox, MD Rena Rowan Breast Center Abramson Cancer Center University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of MedicineR
 Kevin R. Fox, MD Rena Rowan Breast Center Abramson Cancer Center University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of MedicineR Treatment of early stage, HER2 positive breast cancer Treatment of early stage,
Kevin R. Fox, MD Rena Rowan Breast Center Abramson Cancer Center University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of MedicineR Treatment of early stage, HER2 positive breast cancer Treatment of early stage,
Signal Transduction Pathways in Human Diseases
 Molecular Cell Biology Lecture. Oct 29, 2015 Signal Transduction Pathways in Human Diseases Ron Bose, MD PhD Biochemistry and Molecular Cell Biology Programs Washington University School of Medicine Introduction
Molecular Cell Biology Lecture. Oct 29, 2015 Signal Transduction Pathways in Human Diseases Ron Bose, MD PhD Biochemistry and Molecular Cell Biology Programs Washington University School of Medicine Introduction
Phospho-PRAS40 Thr246 predicts trastuzumab response in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 785-789, 2015 Phospho-PRAS40 Thr246 predicts trastuzumab response in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer KAI YUAN, HONGYAN WU, YULONG WANG, HONGQIANG CHEN, MINGWEN
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 785-789, 2015 Phospho-PRAS40 Thr246 predicts trastuzumab response in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer KAI YUAN, HONGYAN WU, YULONG WANG, HONGQIANG CHEN, MINGWEN
Insulin Resistance. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES. Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr.
 BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr. Leah Klapper, CSO 88 BL-8040: Novel CXCR4 Antagonist For Hematological Cancers Indications:
BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr. Leah Klapper, CSO 88 BL-8040: Novel CXCR4 Antagonist For Hematological Cancers Indications:
Imaging of glycolytic metabolism in primary glioblastoma cells with
 63 Chapter 5 Imaging of glycolytic metabolism in primary glioblastoma cells with RIMChip 5.1. Introduction Glioblastoma(GBM) is one of the most common brain tumors 1. It is composed of heterogeneous subpopulations
63 Chapter 5 Imaging of glycolytic metabolism in primary glioblastoma cells with RIMChip 5.1. Introduction Glioblastoma(GBM) is one of the most common brain tumors 1. It is composed of heterogeneous subpopulations
EGFR: fundamenteel en klinisch
 EGFR: fundamenteel en klinisch Guido Lammering MAASTRO Clinic Maastricht, NL What is EGFR?? The EGFR some facts 1186 amino acids 170 kda Expressed by all cells of epithelial origin Increased activation
EGFR: fundamenteel en klinisch Guido Lammering MAASTRO Clinic Maastricht, NL What is EGFR?? The EGFR some facts 1186 amino acids 170 kda Expressed by all cells of epithelial origin Increased activation
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
Case Report Early-onset breast cancer in a woman with Graves disease
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2012;5(4):358-362 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1204004 Case Report Early-onset breast cancer in a woman with Graves disease James E Siegler 1, Xinying Li 2, Steven D Jones 3, Emad
Int J Clin Exp Med 2012;5(4):358-362 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1204004 Case Report Early-onset breast cancer in a woman with Graves disease James E Siegler 1, Xinying Li 2, Steven D Jones 3, Emad
KEY CONCEPT QUESTIONS IN SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Leptin concentrations in the follicular phase of spontaneous cycles and cycles superovulated with follicle stimulating hormone
 Human Reproduction vol.13 no.5 pp.1152 1156, 1998 Leptin concentrations in the follicular phase of spontaneous cycles and cycles superovulated with follicle stimulating hormone I.E.Messinis 1,4, S.Milingos
Human Reproduction vol.13 no.5 pp.1152 1156, 1998 Leptin concentrations in the follicular phase of spontaneous cycles and cycles superovulated with follicle stimulating hormone I.E.Messinis 1,4, S.Milingos
G-Protein Signaling. Introduction to intracellular signaling. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
PUBLICATIONS. cells. J. Physiol. (London) 517P:91P (Manchester, England, UK).
 277 PUBLICATIONS Abstracts Haddad JJ, Land SC (1999). Differential activation of oxygen-responsive transcription factors over fetal-to-neonatal alveolar oxygen tensions in rat fetal distal lung epithelial
277 PUBLICATIONS Abstracts Haddad JJ, Land SC (1999). Differential activation of oxygen-responsive transcription factors over fetal-to-neonatal alveolar oxygen tensions in rat fetal distal lung epithelial
Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3
 Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
 Many Forms of Cell-Cell Communication Regulate Tissue Function and Phenotype Physiological Functions of Gap Junctions Homeostasis buffering/sharing of ions, nutrients, and water Metabolic support nutrient
Many Forms of Cell-Cell Communication Regulate Tissue Function and Phenotype Physiological Functions of Gap Junctions Homeostasis buffering/sharing of ions, nutrients, and water Metabolic support nutrient
Biol403 MAP kinase signalling
 Biol403 MAP kinase signalling The mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is a signalling cascade activated by a diverse range of effectors. The cascade regulates many cellular activities including
Biol403 MAP kinase signalling The mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is a signalling cascade activated by a diverse range of effectors. The cascade regulates many cellular activities including
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Novel Strategies in Systemic Therapies: Overcoming Endocrine Therapy Resistance
 Novel Strategies in Systemic Therapies: Overcoming Endocrine Therapy Resistance Richard S. Finn, MD Division of Hematology/ Oncology Director, Translational Oncology Laboratory Geffen School of Medicine
Novel Strategies in Systemic Therapies: Overcoming Endocrine Therapy Resistance Richard S. Finn, MD Division of Hematology/ Oncology Director, Translational Oncology Laboratory Geffen School of Medicine
LEPTIN (Human) ELISA Kit Protocol (Catalog No. EK )
 LEPTIN (Human) ELISA Kit Protocol (Catalog No. EK-003-12) TALE OF CONTENT Introduction and Protocol Overview 4 List of Components 6 Materials Required but Not Supplied 6 Reagent Preparation 7 Human Leptin
LEPTIN (Human) ELISA Kit Protocol (Catalog No. EK-003-12) TALE OF CONTENT Introduction and Protocol Overview 4 List of Components 6 Materials Required but Not Supplied 6 Reagent Preparation 7 Human Leptin
Figure 1: The leptin/melanocortin pathway Neuronal populations propagate the signaling of various molecules (leptin, insulin, ghrelin) to control
 Leptin Deficiency Introduction The leptin/melanocortin pathway plays a key role in the hypothalamic control of food intake. It is activated following the systemic release of the adipokine leptin (LEP)
Leptin Deficiency Introduction The leptin/melanocortin pathway plays a key role in the hypothalamic control of food intake. It is activated following the systemic release of the adipokine leptin (LEP)
RNA preparation from extracted paraffin cores:
 Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
w ª wy xvwz A ª vw xvw P ª w} xvw w Æ w Æ V w,x Æ w Æ w Æ y,z Æ { Æ y,z, w w w~ w wy}æ zy Æ wyw{ xæ wz w xywæ xx Æ wv Æ } w x w x w Æ w Æ wy} zy Æ wz
 w ª wy xvwz A ª vw xvw P ª w} xvw w Æ w Æ V w,x Æ w Æ w Æ y,z Æ { Æ y,z, w w w~ w wy}æ zy Æ wyw{ xæ wz w xywæ xx Æ wv Æ } w x w x w Æ w Æ wy} zy Æ wz {w Æ Æ wyw{ x w Germ-line mutations in BRCA1 are associated
w ª wy xvwz A ª vw xvw P ª w} xvw w Æ w Æ V w,x Æ w Æ w Æ y,z Æ { Æ y,z, w w w~ w wy}æ zy Æ wyw{ xæ wz w xywæ xx Æ wv Æ } w x w x w Æ w Æ wy} zy Æ wz {w Æ Æ wyw{ x w Germ-line mutations in BRCA1 are associated
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Clin Cancer Res. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2015 December 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Clin Cancer Res. 2014 December 1; 20(23): 5866 5868. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-14-1543. p38 MAPK in Pancreatic Cancer: Finding a Protective
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Clin Cancer Res. 2014 December 1; 20(23): 5866 5868. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-14-1543. p38 MAPK in Pancreatic Cancer: Finding a Protective
MAPK Pathway
 MAPK Pathway Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) are proteins that are serine/ threonine specific kinases which are activated by a wide range of stimuli including proinflammatory cytokines, growth
MAPK Pathway Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) are proteins that are serine/ threonine specific kinases which are activated by a wide range of stimuli including proinflammatory cytokines, growth
Obesity-Associated Chemotherapy Resistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: The Role of Leptin-Induced Tumor-Initiating Cell Enrichment.
 Obesity-Associated Chemotherapy Resistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: The Role of Leptin-Induced Tumor-Initiating Cell Enrichment Joseph Gung Honors Thesis Department of Nutrition Gillings School
Obesity-Associated Chemotherapy Resistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: The Role of Leptin-Induced Tumor-Initiating Cell Enrichment Joseph Gung Honors Thesis Department of Nutrition Gillings School
Low ambient temperature lowers cholecystokinin and leptin plasma concentrations in adult men
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gastroenterology Volume 7 Number 2 Low ambient temperature lowers cholecystokinin and leptin plasma concentrations in adult men M Pizon, P Tomasic, K Sztefko, Z Szafran
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gastroenterology Volume 7 Number 2 Low ambient temperature lowers cholecystokinin and leptin plasma concentrations in adult men M Pizon, P Tomasic, K Sztefko, Z Szafran
Nitin Telang1, Guo Li2, Meena Katdare3,4 Daniel w. Sepkovic5,
 Preventive Efficacy of the Chinese Nutritional Herb Epimedium grandiflorum in a Preclinical Cell Culture Model for Luminal A Molecular Subtype of Breast Cancer Nitin Telang1, Guo Li2, Meena Katdare3,4
Preventive Efficacy of the Chinese Nutritional Herb Epimedium grandiflorum in a Preclinical Cell Culture Model for Luminal A Molecular Subtype of Breast Cancer Nitin Telang1, Guo Li2, Meena Katdare3,4
Chronic Stimulation of Leptin on Food Intake and Body Weight after Microinjection into the Ventromedial Hypothalamus of Conscious Rats
 TAJ December 2006; Volume 19 Number 2 ISSN 1019-8555 The Journal of Teachers Association RMC, Rajshahi Original Article Chronic Stimulation of Leptin on Food Intake and Body Weight after Micro into the
TAJ December 2006; Volume 19 Number 2 ISSN 1019-8555 The Journal of Teachers Association RMC, Rajshahi Original Article Chronic Stimulation of Leptin on Food Intake and Body Weight after Micro into the
Mechanisms Associated with Dietary Energy Balance Effects on Tumor Development: Alterations in Growth Factor and Energy Sensing Pathways
 Mechanisms Associated with Dietary Energy Balance Effects on Tumor Development: Alterations in Growth Factor and Energy Sensing Pathways John DiGiovanni, Ph.D. Professor and Coulter R. Sublett Endowed
Mechanisms Associated with Dietary Energy Balance Effects on Tumor Development: Alterations in Growth Factor and Energy Sensing Pathways John DiGiovanni, Ph.D. Professor and Coulter R. Sublett Endowed
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplemental material for Hernandez et al. Dicoumarol downregulates human PTTG1/Securin mrna expression. through inhibition of Hsp90
 Supplemental material for Hernandez et al. Dicoumarol downregulates human PTTG1/Securin mrna expression through inhibition of Hsp90 Dicoumarol-Sepharose co-precipitation. Hsp90 inhibitors can co-precipitate
Supplemental material for Hernandez et al. Dicoumarol downregulates human PTTG1/Securin mrna expression through inhibition of Hsp90 Dicoumarol-Sepharose co-precipitation. Hsp90 inhibitors can co-precipitate
perk/erk STAT5B
 pakt/akt relative to saline (fold).5.5.5 control perk/erk relative to saline (fold).6.4..8.6.4. p=.6 control db/+ Hsp6 VDAC Hsp6/VDAC (relative to db/+) 8 6 4 db/+ C db/+ Hsp6 Hsp6/actin (relative to db/+)
pakt/akt relative to saline (fold).5.5.5 control perk/erk relative to saline (fold).6.4..8.6.4. p=.6 control db/+ Hsp6 VDAC Hsp6/VDAC (relative to db/+) 8 6 4 db/+ C db/+ Hsp6 Hsp6/actin (relative to db/+)
TITLE: HER2/neu Antisense Therapeutics in Human Breast Cancer. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Washington University School of Medicine St.
 AD Award Number: DAMD17-99-1-9436 TITLE: HER2/neu Antisense Therapeutics in Human Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jeffrey A. Drebin, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Washington University School
AD Award Number: DAMD17-99-1-9436 TITLE: HER2/neu Antisense Therapeutics in Human Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jeffrey A. Drebin, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Washington University School
Mouse Leptin ELISA Kit (mleptin-elisa)
 Mouse Leptin ELISA Kit (mleptin-elisa) Cat. No. EK0438 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Leptin (or obese, OB) is a circulating hormone that is expressed abundantly and specifically in the
Mouse Leptin ELISA Kit (mleptin-elisa) Cat. No. EK0438 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Leptin (or obese, OB) is a circulating hormone that is expressed abundantly and specifically in the
What is survivorship? Late effects of treatment. Concerns of survivorship
 Choices to enhance vitality!!!and survival!!!!!!!!! (and how to make it work in the real world)! What is survivorship? Multiple definitions! Anyone living with cancer at any stage since diagnosis! Anyone
Choices to enhance vitality!!!and survival!!!!!!!!! (and how to make it work in the real world)! What is survivorship? Multiple definitions! Anyone living with cancer at any stage since diagnosis! Anyone
Improved Stability of the LANCE Ultra Signal in Kinase Assays
 Improved Stability of the LANCE Ultra Signal in Kinase Assays LANCE Ultra is a high throughput screening (HTS) technology platform optimized for homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy
Improved Stability of the LANCE Ultra Signal in Kinase Assays LANCE Ultra is a high throughput screening (HTS) technology platform optimized for homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy
