Stromal PD-L1 Expression Is Associated With Better Disease-Free Survival in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
|
|
|
- Gavin Conley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stromal PD-L1 Expression Is Associated With Better Disease-Free Survival in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Xiaoxian Li, MD, PhD, 1 Ceyda Sonmez Wetherilt, MD, 5 Uma Krishnamurti, MD, PhD, 1 Jing Yang, MS, 2 Yamin Ma, MD, PhD, 6 Toncred M. Styblo, MD, 3 Jane L. Meisel, MD, 4 Limin Peng, PhD, 2 Momin T. Siddiqui, MD, 1 Cynthia Cohen, MD, 1 and Ritu Aneja, PhD 5 From the Departments of 1 Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, 2 Biostatistics, 3 Surgery, and 4 Hematology and Medical Oncology, Emory University, Atlanta, GA; 5 Department of Biology, Georgia State University, Atlanta; and 6 Morehouse College, Atlanta, GA. CME/SAM Key Words: Breast cancer; TNBC; PD-1; PD-L1; Disease-free survival; Overall survival; Full-face section; Stromal PD-L1 expression Am J Clin Pathol October 2016;146: DOI: /AJCP/AQW134 ABSTRACT Objectives: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive subtype of breast cancer, and there is no approved targeted therapy. We studied the expression of programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1) in TNBC. Methods: Full-face sections from 136 TNBC cases without neoadjuvant therapy between 2004 and 2013 were stained and evaluated for immune cell PD-1 staining and stromal or tumoral PD-L1 staining using the H-score (staining percentage intensity). Nottingham histologic grade, lymphovascular invasion (LVI), mitotic count, and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) were evaluated. Tumor size, lymph node status, Ki-67 score, metastasis, overall survival (OS), and disease-free survival (DFS) were retrieved from medical records. Results: Of the 136 TNBC cases, 69 (51%) had any PD-L1 staining and 35 (26%) had PD-L1 staining with an H-score of 5 or more; 117 (86%) had any PD-1 staining and 68 (50%) had PD-1 staining with an H-score of 5 or more. Tumor size and LVI were significantly associated with worse OS and DFS, and TILs and LVI were significantly associated with metastasis in univariate analysis. Stromal PD-L1 expression was significantly associated with better DFS in multivariate analysis. PD-1 expression was not associated with DFS, OS, or metastasis. Conclusions: PD-L1 expression is seen in a high proportion of TNBCs and associated with better DFS. Upon completion of this activity you will be able to: predict the proportion of triple-negative breast cancers that express PD-L1. outline basic mechanisms underlying the effect of PD-L1 expression on cancer progression. The ASCP is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians. The ASCP designates this journal-based CME activity for a maximum of 1 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit TM per article. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity. This activity qualifies as an American Board of Pathology Maintenance of Certification Part II Self-Assessment Module. The authors of this article and the planning committee members and staff have no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose. Exam is located at The programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and its ligand PD-L1 have critical roles in tumor surveillance. PD-1 is an immune checkpoint protein expressed in mononuclear immune cells. It can bind its ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2. PD-L1 is expressed on antigen-presenting cells such as B cells or macrophages. Tumor cells can also express PD-L1. 1 PD-L2 expression is seen on macrophages and dendritic cells. When PD-1 binds to PD-L1, PD-1 suppresses the T-cell immune functions by inhibiting expression of transcription factors of T cells such as GATA-3 and T-bet, 2 which leads to apoptosis of T cells and potentiates tumor progression. Immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as PD-L1 antibody, block the interaction of PD-1 and PD-L1. Several PD-L1 blocking antibodies have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat melanoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, and lung and bladder carcinomas. 3 PD-L1 expression has been identified in cancers of other organs such as kidney, pancreas, esophagus, ovary, and glioblastoma. 4-8 Few studies have 496 Am J Clin Pathol 2016;146: American Society for Clinical Pathology, All rights reserved. For permissions, please journals.permissions@oup.com
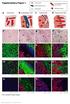
2 investigated PD-L1 expression in breast cancers, especially triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Clinically, breast carcinomas are classified as estrogen receptor positive (ERþ), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive (HER2þ), and TNBC. Different subtypes have different molecular and immunohistochemical profiles, prognosis, and response to treatments TNBC refers to breast cancers with negative expression of ER, progesterone receptor, and HER2. 13,14 TNBCs account for approximately 15% of breast cancers, with a high prevalence in African American and Hispanic women. Compared with ERþ or HER2þ breast carcinoma, TNBC has the worst prognosis, and there is no approved targeted therapy. 15,16 In this study, we analyzed PD-1 and PD-L1 expression in full-face sections of 136 TNBC cases and correlated them with prognosis. Materials and Methods Patient Information In total, 136 TNBC cases diagnosed from 2004 to 2013 were retrieved from the pathology archives after the protocol was approved by the institutional review board. All were from segmental mastectomies without exposure to neoadjuvant systemic therapies. All 136 cases were reviewed by a breast pathologist (X.L.) to evaluate Nottingham histologic grade, lymphovascular invasion (LVI), mitosis, and tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). TILs were evaluated as the percentage of intratumoral stroma covered by mononuclear lymphocytes. One tumor block of each case was selected for immunohistochemical studies. Tumor size, lymph node status, Ki-67 score, and survival information were retrieved from pathology reports and patient medical records. Overall survival (OS) was defined as the length of time from the date of initial diagnosis to the date of last contact. Diseasefree survival (DFS) was defined as the length of time from the date of initial diagnosis to the date of diagnosis of local and/or distant recurrence. DFS included distant recurrences (metastasis to other organs not including regional lymph nodes) and local recurrences. Immunohistochemical Studies and Evaluation Consecutive full-face 5-lm formalin-fixed, paraffinembedded sections were stained using PD-1 mouse monoclonal antibody (clone NAT105, 1:100 dilution; Abcam, Cambridge, MA) and PD-L1 rabbit monoclonal antibody (clone E1L3N, 1:200 dilution; Cell Signaling, Beverly, CA). Citrate low ph antigen retrieval was used for 20 minutes with the Bond III (Leica, Bannockburn, IL). Positive controls for PD-1 and PD-L1 were tonsil and placenta, respectively. Negative controls had the antibody replaced by buffer only. All stained slides were reviewed and scored by one breast pathologist (X.L.). Membranous staining of PD-1 Image 1B and Image 1C and PD-L1 Image 1E and Image 1F was regarded as positive. PD-L1 staining was evaluated in tumor and stromal cells. PD-1 staining was evaluated in mononuclear immune cells only. PD-1 and PD-L1 staining was evaluated only within the boundary of invasive carcinoma. Overall percentage of positive cells and their staining intensity (1-3) were evaluated. An H-score (PD-1 or PD-L1 staining intensity percentage of positive cells with a range between 0 and 300) was used to correlate with OS, DFS, and metastasis. Statistical Analysis Tumor size, Ki-67 score, TILs, mitosis, lymph node status (positive or negative), Nottingham histologic grade (1 and 2 vs 3), and LVI (positive or negative) were evaluated for potential association with OS, DFS, and metastasis. Log-rank test and Cox regression model were used in univariate analysis of their relationships with OS and DFS. The relationships between the clinical parameters with metastasis were assessed using a two-sample t test and Pearson v 2 test. The associations between PD-L1 expression and OS and DFS were evaluated using a log-rank test with hazard ratio (HR), and the 95% confidence interval (CI) was calculated using a univariate Cox regression model. Considering the confounding effects of the potential parameters, all variables were considered for inclusion in a multivariate Cox model through the use of backward selection (a-to-stay was set as 0.1 to adjust for confounding). Univariate and multivariate logistic regression with similar backward selection was used to evaluate the association between PD-L1 expression and metastasis. Odds ratio (OR) and 95% CI were reported. Results PD-L1 Expression in TNBC Of the 136 TNBCs evaluated for PD-L1 expression, the number of cases with any tumoral cell staining was 28 (21%). Of the 136 cases, 14 (10%) showed an H-score of 5 or more. The number of cases with any stromal cell staining was 55 (40%), and 32 (24%) cases showed an H-score of 5 or more. Some cases had PD-L1 expression in both tumoral and stromal cells Image 1D (Images 1E and 1F). In total, the number of cases with any PD-L1 staining in either the tumoral or the stromal cells was 69 (51%), and 35 (26%) cases showed an H-score of 5 or more. Any PD-L1 expression was noted at the periphery of tumor (tumor front at the interface between tumor and surrounding normal breast American Society for Clinical Pathology Am J Clin Pathol 2016;146: Downloaded 497 from
3 Li et al /STROMAL PD-L1 EXPRESSION IN TNBC A B C D Image 1 Representative staining patterns of programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1) in two representative cases. In case 1 (A-C), PD-1 expression was seen at the periphery of the tumor. Case 2 (D-F) had PD-L1 expression in both stromal and tumoral cells. A, Routine H&E staining of case 1 (80). B, PD-1 expression in peripheral lymphocytes of case 1 (80). C, PD-1 expression in peripheral lymphocytes of case 1 at a higher power (800). D, Routine H&E staining of case 2 (80). tissue) Image 1A in seven (10%) of 69 cases. Among the 35 cases with a PD-L1 staining H-score of 5 or more, three (9%) had peripheral staining. PD-1 expression was noted in the mononuclear immune cells in the tumoral stroma. The number of cases with any PD-1 staining was 117 (86%), and 68 (50%) cases showed an H-score of 5 or more. Tumor Size and LVI Were Significantly Associated With Worse OS and DFS Tumor size and LVI were significantly associated with worse OS (HR, 1.36; 95% CI, ; P <.0001 and HR, 2.62; 95% CI, ; P ¼.0214, respectively) and DFS (HR, 1.33; 95% CI, ; P <.0001 and HR, 3.07; 95% CI, ; P ¼.0027, respectively) in univariate analysis. Ki-67 score was significantly associated with worse DFS (HR, 1.02; 95% CI, ; P ¼.0144) but not with OS. The results are summarized in Table 1 and Table 2. TILs and LVI Were Significantly Associated With Metastasis The association between different parameters and metastasis was analyzed. Among all the parameters summarized in Table 3, TILs and LVI were significantly associated with a higher metastatic rate (P ¼.0077 and P ¼.0029, 498 Am J Clin Pathol 2016;146: American Society for Clinical Pathology 498
4 E F Image 1 (cont) E, PD-L1 expression in stromal cells in case 2 (800). F, PD-L1 expression in tumor cells in case 2 (800). Table 1 Univariate Analysis of Association Between Confounders and Overall Survival Characteristic No. HR (95% CI) P Value P Value for Log-Rank Test Tumor size ( ) <.0001 Ki ( ).1357 TIL ( ).1351 Mitosis ( ).2423 Lymph node ( ) (positive vs negative) Nottingham grade (1 and 2 vs 3) ( ) LVI (positive vs negative) ( ) CI, confidence interval; HR, hazard ratio; LVI, lymphovascular invasion; TIL, tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte. Table 2 Univariate Analysis of Association Between Confounders and Disease-Free Survival Characteristic No. HR (95% CI) P Value P Value for Log-Rank Test Tumor size ( ) <.0001 Ki ( ).0144 TIL ( ).0746 Mitosis ( ).1437 Lymph node ( ) (positive vs negative) Nottingham grade (1 and 2 vs 3) ( ) LVI (positive vs negative) ( ) CI, confidence interval; HR, hazard ratio; LVI, lymphovascular invasion; TIL, tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte. respectively) in univariate analysis. The results are summarized in Table 3. Stromal PD-L1 Expression but Not PD-1 Expression Was Significantly Associated With Better DFS Both tumoral and stromal PD-L1 expressions were found to correlate with OS, DFS, and metastasis. Any stromal PD-L1 expression (>0 vs 0) was associated with better DFS in multivariate analysis (P ¼.0458) but not in univariate analysis Table 4. This was also true when comparing tumors with an H-score of 5 or more vs less than 5 for stromal PD-L1 expression (Table 4). However, positive stromal PD-L1 expression was not associated with OS Table 5. Positive tumoral PD-L1 expression was not associated with either OS or DFS (Tables 4 and 5). Table 3 Association Between Confounders and Metastasis a Metastasis Characteristic No Yes P Value Tumor size, cm Ki-67, % TIL, % Mitosis, 10 hpf Lymph node Negative 95 (91.4) 9 (8.6).23 Positive 17 (81.0) 4 (19.0) Nottingham grade 1 and 2 24 (96.0) 1 (4.0) (85.3) 16 (14.7) LVI Negative 89 (92.7) 7 (7.3).0029 Positive 28 (73.7) 10 (26.3) hpf, high-power field; LVI, lymphovascular invasion; TIL, tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte. a Values are expressed as mean 6 SD or number (%). American Society for Clinical Pathology Am J Clin Pathol 2016;146: Downloaded 499 from
5 Li et al /STROMAL PD-L1 EXPRESSION IN TNBC Table 4 Association Between PD-L1 Expression and Disease-Free Survival a Multivariate Analysis Univariate Analysis PD-L1 HR (95% CI) P Value HR (95% CI) P Value for Log-Rank Test Tumoral (>0 vs 0) 0.21 ( ) ( ).7909 Tumoral (5vs< 5) 0.59 ( ) ( ).685 Stromal (>0 vs 0) 0.28 ( ) ( ).096 Stromal (5vs< 5) 0.11 ( ) ( ).0904 CI, confidence interval; HR, hazard ratio; PD-L1, programmed cell death protein 1 ligand. a Multivariate analysis for tumoral (>0 vs 0): adjusting for tumor size, Ki-67, and lymph node. Multivariate analysis for tumoral (5 vs<5): adjusting for tumor size, Ki-67, and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Multivariate analysis for stromal (>0 vs 0): adjusting for tumor size and Ki-67. Multivariate analysis for stromal (5 vs<5): adjusting for tumor size and Ki-67. Table 5 Association Between PD-L1 Expression and Overall Survival a Multivariate Analysis Univariate Analysis PD-L1 HR (95% CI) P Value HR (95% CI) P Value for Log-Rank Test Tumoral (>0 vs 0) 0.45 ( ) ( ).8631 Tumoral (5vs< 5) 0.69 ( ) ( ).9345 Stromal (>0 vs 0) 0.53 ( ) ( ).1598 Stromal (5vs< 5) 0.23 ( ) ( ).1014 CI, confidence interval; HR, hazard ratio; PD-L1, programmed cell death protein 1 ligand. a Multivariate analysis adjusting for tumor size. Table 6 Association Between PD-L1 Expression and Metastasis a Multivariate Analysis Univariate Analysis PD-L1 OR (95% CI) P Value OR (95% CI) P Value Tumoral (>0 vs 0) 3.26 ( ) ( ).3456 Tumoral (5vs< 5) 0.70 ( ) ( ).5745 Stromal (>0 vs 0) 0.18 ( ) ( ).0435 Stromal (5vs< 5) 0.32 ( ) ( ).1046 CI, confidence interval; OR, odds ratio; PD-L1, programmed cell death protein 1 ligand. a Multivariate analysis adjusting for tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and lymphovascular invasion. Model selection would remove all confounders. Neither tumoral nor stromal PD-L1 expression was associated with metastasis Table 6. When PD-1 expression was analyzed, it was not associated with metastasis, DFS, or OS using H-scores of 0, 5, or 10 as cutoffs (data not shown). Discussion The PD-1 pathway plays a critical role in tumor surveillance. PD-L1 antibodies have been approved to treat several malignancies. However, few studies examined its role in breast cancer, especially in TNBC. TNBC is an aggressive breast cancer subtype with high metastatic rate and poor prognosis. 13,17 In the studies of melanomas, Massi et al 18 reported increased aggressiveness and invasiveness in PD-L1 positive melanomas, and Madore et al 19 also showed that PD-L1 expression was associated with locoregional recurrence and melanoma-specific survival. Wang et al 20 found that positive PD-L1 expression was associated with poor OS in a meta-analysis. Bertucci et al 21 reported that in gastrointestinal stromal tumors, low expression of PD-L1 messenger RNA (mrna) was associated with a higher risk of metastatic relapse. These studies showed the different relationship between PD-L1 expression and prognosis in various tumors. Baptista et al 22 reported that PD-L1 expression was seen in 50.8% of breast cancers and associated with better OS, but the role of PD-L1 expression in TNBC was not further analyzed. Sabatier et al 23 reported that PD-L1 mrna expression was associated with basal and HER2-enriched breast cancers. They also reported that increased PD-L1 500 Am J Clin Pathol 2016;146: American Society for Clinical Pathology 500
6 expression was associated with better metastasis-free survival and OS in basal cancers and higher pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Beckers et al 24 also reported that PD-L1 expression was seen in up to 93% of TNBCs. They reported that tumoral PD-L1 expression was associated with a lower risk of breast cancer specific death, and stromal PD-L1 expression was associated with a lower risk of death from all causes. In contrast to this high expression rate of PD-L1 in TNBC, Ali et al 25 reported a much lower expression rate of PD-L1 in basal-like breast cancer (19%). This is consistent with the study from Mittendorf et al. 26 We found that 51% of TNBCs have either tumoral or stromal PD-L1 expression. The different staining rate of PD-L1 may at least partially stem from different methods. Most of the aforementioned studies have used tissue microarray (TMA) for the immunohistochemical studies. One drawback of using TMA is the limited tissue sampling. PD-L1 expression can be focal and only seen at the periphery of the tumor. As shown in our study, 9% of tumors had peripheral PD-L1 expression. If only central tissue were used to construct a TMA, these 9% of tumors would be PD-L1 negative. Therefore, we recommend using full-face sections for PD-L1 expression studies. Consistent with other studies, we found stromal PD-L1 expression was associated with better DFS in TNBC in multivariate analysis. TILs have been shown to be associated with better prognosis and response to neoadjuvant therapies in TNBC. 27 Both TILs and PD-L1 expression are immune responses in breast cancers. Few studies have investigated the relationship between TILs and PD-L1. Ali et al 25 reported a positive correlation between TILs and PD- L1 in breast cancer. Such positive correlation was not seen in ovarian cancers, 7 indicating possible different immune responses in different tumors. We observed a significant positive correlation between TILs and metastasis and a positive but not significant correlation between TILs and DFS. The correlation between TILs and DFS may reach a significant number if the sample size were increased. Large tumor size and LVI are associated with poor prognosis. 28 Ki-67 is a nuclear protein associated with cellular proliferation. 29 Our results showed that tumor size and LVI were significantly associated with worse OS and DFS and that Ki-67 score was significantly associated with worse DFS in univariate analysis. In conclusion, our study examined the expression of PD-L1 and PD-1 in full-face sections of a large TNBC cohort. We showed a 51% positive staining rate for PD-L1 expression, and stromal PD-L1 expression was associated with better DFS. The high expression rate of PD-L1 in TNBC indicates a promising role for PD-L1 antibody in treatment of TNBC. Corresponding author: Xiaoxian Li, MD, PhD; xli40@emory.edu. References 1. Gatalica Z, Snyder C, Maney T, et al. Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1) in common cancers and their correlation with molecular cancer type. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014;23: Nurieva R, Thomas S, Nguyen T, et al. T-cell tolerance or function is determined by combinatorial costimulatory signals. Embo J. 2006;25: Mahoney KM, Rennert PD, Freeman GJ. Combination cancer immunotherapy and new immunomodulatory targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015;14: Thompson RH, Dong H, Lohse CM, et al. PD-1 is expressed by tumor-infiltrating immune cells and is associated with poor outcome for patients with renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13: Nomi T, Sho M, Akahori T, et al. Clinical significance and therapeutic potential of the programmed death-1 ligand/programmed death-1 pathway in human pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13: Ohigashi Y, Sho M, Yamada Y, et al. Clinical significance of programmed death-1 ligand-1 and programmed death-1 ligand-2 expression in human esophageal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11: Hamanishi J, Mandai M, Iwasaki M, et al. Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 and tumor-infiltrating CD8þ T lymphocytes are prognostic factors of human ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104: Berghoff AS, Kiesel B, Widhalm G, et al. Programmed death ligand 1 expression and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2015;17: Davis DG, Siddiqui MT, Oprea-Ilies G, et al. GATA-3 and FOXA1 expression is useful to differentiate breast carcinoma from other carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 2016;47: Li X, Lewis MT, Huang J, et al. Intrinsic resistance of tumorigenic breast cancer cells to chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100: Zelnak AB, Nikolinakos P, Srinivasiah J, et al. High pathologic complete response in Her2-positive, early-stage breast cancer to a novel nonanthracycline neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Clin Breast Cancer. 2015;15: Creighton CJ, Li X, Landis M, et al. Residual breast cancers after conventional therapy display mesenchymal as well as tumor-initiating features. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106: Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, et al. Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13: Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Chen X, et al. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Invest. 2011;121: Millar EK, Graham PH, O Toole SA, et al. Prediction of local recurrence, distant metastases, and death after breast-conserving therapy in early-stage invasive breast cancer using a five-biomarker panel. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27: American Society for Clinical Pathology Am J Clin Pathol 2016;146: Downloaded 501 from
7 Li et al /STROMAL PD-L1 EXPRESSION IN TNBC 16. Voduc KD, Cheang MC, Tyldesley S, et al. Breast cancer subtypes and the risk of local and regional relapse. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28: Haffty BG, Yang Q, Reiss M, et al. Locoregional relapse and distant metastasis in conservatively managed triple negative early-stage breast cancer. JClinOncol. 2006;24: Massi D, Brusa D, Merelli B, et al. PD-L1 marks a subset of melanomas with a shorter overall survival and distinct genetic and morphological characteristics. Ann Oncol. 2014;25: Madore J, Vilain RE, Menzies AM, et al. PD-L1 expression in melanoma shows marked heterogeneity within and between patients: implications for anti-pd-1/pd-l1 clinical trials. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2015;28: Wang A, Wang HY, Liu Y, et al. The prognostic value of PD-L1 expression for non small cell lung cancer patients: a meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2015;41: Bertucci F, Finetti P, Colpaert C, et al. PDL1 expression in inflammatory breast cancer is frequent and predicts for the pathological response to chemotherapy. Oncotarget. 2015;6: Baptista MZ, Sarian LO, Derchain SF, et al. Prognostic significance of PD-L1 and PD-L2 in breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 2016;47: Sabatier R, Finetti P, Mamessier E, et al. Prognostic and predictive value of PDL1 expression in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6: Beckers RK, Selinger CI, Vilain R, et al. Programmed death ligand 1 expression in triple-negative breast cancer is associated with tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and improved outcome. Histopathology. 2016;69: Ali HR, Glont SE, Blows FM, et al. PD-L1 protein expression in breast cancer is rare, enriched in basal-like tumours and associated with infiltrating lymphocytes. Ann Oncol. 2015;26: Mittendorf EA, Philips AV, Meric-Bernstam F, et al. PD-L1 expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 2014;2: Pruneri G, Vingiani A, Bagnardi V, et al. Clinical validity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes analysis in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2016;27: Acs G, Khakpour N, Kiluk J, et al. The presence of extensive retraction clefts in invasive breast carcinomas correlates with lymphatic invasion and nodal metastasis and predicts poor outcome: a prospective validation study of 2742 consecutive cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015;39: Gerdes J, Schwab U, Lemke H, et al. Production of a mouse monoclonal antibody reactive with a human nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation. Int J Cancer. 1983;31: Am J Clin Pathol 2016;146: American Society for Clinical Pathology 502
Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer. Cheol Min Kang 2018/04/05
 Abstract No.: ABS-0075 Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer 2018/04/05 Cheol Min Kang Department of surgery, University of Ulsan
Abstract No.: ABS-0075 Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer 2018/04/05 Cheol Min Kang Department of surgery, University of Ulsan
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/55957 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Dekker T.J.A. Title: Optimizing breast cancer survival models based on conventional
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/55957 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Dekker T.J.A. Title: Optimizing breast cancer survival models based on conventional
Prognostic significance of stroma tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes according to molecular subtypes of breast cancer
 Prognostic significance of stroma tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes according to molecular subtypes of breast cancer Hee Jung Kwon, Nuri Jang, Min Hui Park, Young Kyung Bae Department of Pathology, Yeungnam
Prognostic significance of stroma tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes according to molecular subtypes of breast cancer Hee Jung Kwon, Nuri Jang, Min Hui Park, Young Kyung Bae Department of Pathology, Yeungnam
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression
 Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers
 日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Time to Slice and Dice? Carsten Denkert, MD Charité University Hospital Berlin, Germany
 Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Time to Slice and Dice? Carsten Denkert, MD Charité University Hospital Berlin, Germany Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) 2018 Presentation Outline The molecular heterogeneity
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Time to Slice and Dice? Carsten Denkert, MD Charité University Hospital Berlin, Germany Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) 2018 Presentation Outline The molecular heterogeneity
Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer
 Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
RNA preparation from extracted paraffin cores:
 Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Androgen Receptor Expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A New Actionable Target?
 Androgen Receptor Expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A New Actionable Target? New Frontiers in Urologic Oncology Juan Chipollini, MD Clinical Fellow Department of Genitourinary Oncology Moffitt Cancer
Androgen Receptor Expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A New Actionable Target? New Frontiers in Urologic Oncology Juan Chipollini, MD Clinical Fellow Department of Genitourinary Oncology Moffitt Cancer
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences
 SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences RESEARCH PAPER April 2013 Vol.56 No.4: 335 340 doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4435-y Risk factors of recurrence in small-sized, node negative breast cancer in young women: a retrospective
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences RESEARCH PAPER April 2013 Vol.56 No.4: 335 340 doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4435-y Risk factors of recurrence in small-sized, node negative breast cancer in young women: a retrospective
SFSPM Novembre Valeur prédictive et pronostique de l infiltrat immunitaire dans les cancers du sein traités par chimiothérapie néoadjuvante
 SFSPM Novembre 217 Valeur prédictive et pronostique de l infiltrat immunitaire dans les cancers du sein traités par chimiothérapie néoadjuvante Dr Fabien REYAL Service de Chirurgie INSERM U932 Immunity
SFSPM Novembre 217 Valeur prédictive et pronostique de l infiltrat immunitaire dans les cancers du sein traités par chimiothérapie néoadjuvante Dr Fabien REYAL Service de Chirurgie INSERM U932 Immunity
WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER?
 CANCER STAGING TNM and prognosis in CRC WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER? Alessandro Lugli, MD Institute of Pathology University of Bern Switzerland Maastricht, June 19
CANCER STAGING TNM and prognosis in CRC WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER? Alessandro Lugli, MD Institute of Pathology University of Bern Switzerland Maastricht, June 19
The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative
 Original Article The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative breast cancer Shuang Li 1#, Ding Ma 2#, Hao-Hong Shi 3#, Ke-Da Yu 2, Qiang Zhang 1 1 Department of Breast Surgery,
Original Article The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative breast cancer Shuang Li 1#, Ding Ma 2#, Hao-Hong Shi 3#, Ke-Da Yu 2, Qiang Zhang 1 1 Department of Breast Surgery,
Editorial Process: Submission:11/30/2017 Acceptance:01/04/2019
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:11/30/2017 Acceptance:01/04/2019 in Non-Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer O Al jarroudi*, A Zaimi, S A Brahmi, S Afqir Abstract Introduction: Triple-negative
RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:11/30/2017 Acceptance:01/04/2019 in Non-Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer O Al jarroudi*, A Zaimi, S A Brahmi, S Afqir Abstract Introduction: Triple-negative
Patient age and cutaneous malignant melanoma: Elderly patients are likely to have more aggressive histological features and poorer survival
 MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 7: 1083-1088, 2017 Patient age and cutaneous malignant melanoma: Elderly patients are likely to have more aggressive histological features and poorer survival FARUK TAS
MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 7: 1083-1088, 2017 Patient age and cutaneous malignant melanoma: Elderly patients are likely to have more aggressive histological features and poorer survival FARUK TAS
Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer
 Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Vice Chair of Anatomic Pathology Professor of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Outline
Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Vice Chair of Anatomic Pathology Professor of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Outline
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Controversies in Breast Pathology ELENA PROVENZANO ADDENBROOKES HOSPITAL, CAMBRIDGE
 Controversies in Breast Pathology ELENA PROVENZANO ADDENBROOKES HOSPITAL, CAMBRIDGE Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Indications: Management of locally advanced invasive breast cancers including inflammatory breast
Controversies in Breast Pathology ELENA PROVENZANO ADDENBROOKES HOSPITAL, CAMBRIDGE Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Indications: Management of locally advanced invasive breast cancers including inflammatory breast
Breast cancer: Molecular STAGING classification and testing. Korourian A : AP,CP ; MD,PHD(Molecular medicine)
 Breast cancer: Molecular STAGING classification and testing Korourian A : AP,CP ; MD,PHD(Molecular medicine) Breast Cancer Theory: Halsted Operative breast cancer is a local-regional disease The positive
Breast cancer: Molecular STAGING classification and testing Korourian A : AP,CP ; MD,PHD(Molecular medicine) Breast Cancer Theory: Halsted Operative breast cancer is a local-regional disease The positive
International Society of Breast Pathology. Immune Targeting in Breast Cancer. USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting
 International Society of Breast Pathology USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting Immune Targeting in Breast Cancer Ashley Cimino-Mathews, MD Assistant Professor of Pathology and Oncology The Johns Hopkins Hospital
International Society of Breast Pathology USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting Immune Targeting in Breast Cancer Ashley Cimino-Mathews, MD Assistant Professor of Pathology and Oncology The Johns Hopkins Hospital
Disclosures. Outline. What IS tumor budding?? Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How. I have nothing to disclose
 Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
Properties of Synchronous Versus Metachronous Bilateral Breast Carcinoma with Long Time Follow Up
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.12.4921 Properties of Synchronous Versus Metachronous Bilateral Breast Carcinoma with Long Time Follow Up RESEARCH ARTICLE Properties of Synchronous Versus Metachronous
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.12.4921 Properties of Synchronous Versus Metachronous Bilateral Breast Carcinoma with Long Time Follow Up RESEARCH ARTICLE Properties of Synchronous Versus Metachronous
Clinical pathological and epidemiological study of triple negative breast cancer
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Ajay A et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 217 Jun;5(6):2657-2661 www.msjonline.org pissn 232-71 eissn 232-12 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.1823/232-12.ijrms2172465
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Ajay A et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 217 Jun;5(6):2657-2661 www.msjonline.org pissn 232-71 eissn 232-12 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.1823/232-12.ijrms2172465
Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva
 Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva Background Post-operative radiotherapy (PORT) improves disease free and overall suvivallin selected patients with breast cancer
Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva Background Post-operative radiotherapy (PORT) improves disease free and overall suvivallin selected patients with breast cancer
Circulating Tumor Cells in non- Metastatic Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 Circulating Tumor Cells in non- Metastatic Triple Negative Breast Cancer Carolyn Hall, Ph.D. Department of Surgical Oncology The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Circulating Tumor Cells in non- Metastatic Triple Negative Breast Cancer Carolyn Hall, Ph.D. Department of Surgical Oncology The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Triple Negative Breast Cancer
What to do after pcr in different subtypes?
 What to do after pcr in different subtypes? Luca Moscetti Breast Unit Università degli Studi di Modena e Reggio Emilia Policlinico di Modena, Italy Aims of neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer Primary
What to do after pcr in different subtypes? Luca Moscetti Breast Unit Università degli Studi di Modena e Reggio Emilia Policlinico di Modena, Italy Aims of neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer Primary
Impact of Prognostic Factors
 Melanoma Prognostic Factors: where we started, where are we going? Impact of Prognostic Factors Staging Management Surgical intervention Adjuvant treatment Suraj Venna, MD Assistant Clinical Professor,
Melanoma Prognostic Factors: where we started, where are we going? Impact of Prognostic Factors Staging Management Surgical intervention Adjuvant treatment Suraj Venna, MD Assistant Clinical Professor,
Are there the specific prognostic factors for triplenegative subtype of early breast cancers (pt1-2n0m0)?
 Are there the specific prognostic factors for triplenegative subtype of early breast cancers (pt1-2n0m0)? Department of General Surgery, Anam Hospital, Korea University, College of Medicine, 126-, Anam-dong
Are there the specific prognostic factors for triplenegative subtype of early breast cancers (pt1-2n0m0)? Department of General Surgery, Anam Hospital, Korea University, College of Medicine, 126-, Anam-dong
Evaluation the Correlation between Ki67 and 5 Years Disease Free Survival of Breast Cancer Patients
 BIOSCIENCES BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH ASIA, December 2015. Vol. 12(3), 2221-2225 Evaluation the Correlation between Ki67 and 5 Years Disease Free Survival of Breast Cancer Patients S.M. Hosseini¹, H. Shahbaziyan
BIOSCIENCES BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH ASIA, December 2015. Vol. 12(3), 2221-2225 Evaluation the Correlation between Ki67 and 5 Years Disease Free Survival of Breast Cancer Patients S.M. Hosseini¹, H. Shahbaziyan
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Breast Pathology Evening Specialty Conference Case #4. Clinical Case: Pathologic Features
 Breast Pathology Evening Specialty Conference Case #4 K.P. Siziopikou, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology Director of Breast Pathology and Breast Pathology Fellowship Program Northwestern University Feinberg
Breast Pathology Evening Specialty Conference Case #4 K.P. Siziopikou, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology Director of Breast Pathology and Breast Pathology Fellowship Program Northwestern University Feinberg
Modified primary tumour/vessel tumour/nodal tumour classification for patients with invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast
 British Journal of Cancer (2011) 105, 698 708 All rights reserved 0007 0920/11 www.bjcancer.com Modified primary tumour/vessel tumour/nodal tumour classification for patients with invasive ductal carcinoma
British Journal of Cancer (2011) 105, 698 708 All rights reserved 0007 0920/11 www.bjcancer.com Modified primary tumour/vessel tumour/nodal tumour classification for patients with invasive ductal carcinoma
10/15/2012. Biologic Subtypes of TNBC. Topics. Topics. Histopathology Molecular pathology Clinical relevance
 Biologic Subtypes of TNBC Andrea L. Richardson M.D. Ph.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Topics Histopathology Molecular pathology Clinical
Biologic Subtypes of TNBC Andrea L. Richardson M.D. Ph.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Topics Histopathology Molecular pathology Clinical
Post Neoadjuvant therapy: issues in interpretation
 Post Neoadjuvant therapy: issues in interpretation Disclosure: Overview D Prognostic features in assessment of post treatment specimens: Tumor size Cellularity Grade Receptors LN Neoadjuvant chemotherapy:
Post Neoadjuvant therapy: issues in interpretation Disclosure: Overview D Prognostic features in assessment of post treatment specimens: Tumor size Cellularity Grade Receptors LN Neoadjuvant chemotherapy:
SYSTEMIC TREATMENT OF TRIPLE NEGATIVE BREAST CANCER
 SYSTEMIC TREATMENT OF TRIPLE NEGATIVE BREAST CANCER Sunil Shrestha 1*, Ji Yuan Yang, Li Shuang and Deepika Dhakal Clinical School of Medicine, Yangtze University, Jingzhou, Hubei Province, PR. China Department
SYSTEMIC TREATMENT OF TRIPLE NEGATIVE BREAST CANCER Sunil Shrestha 1*, Ji Yuan Yang, Li Shuang and Deepika Dhakal Clinical School of Medicine, Yangtze University, Jingzhou, Hubei Province, PR. China Department
Letter to Editor Tissue micro arrays for immunohistochemical detection of inflammatory infiltrates in renal cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(4):1175-1179 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0000102 Letter to Editor Tissue micro arrays for immunohistochemical detection of inflammatory infiltrates in renal cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(4):1175-1179 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0000102 Letter to Editor Tissue micro arrays for immunohistochemical detection of inflammatory infiltrates in renal cell carcinoma
Clinical Features and Survival Analysis of T1mic, a, bn0m0 Breast Cancer
 Original Articles Jpn J Clin Oncol 2012;42(6)471 476 doi:10.1093/jjco/hys046 Advance Access Publication 3 April 2012 Clinical Features and Survival Analysis of T1mic, a, bn0m0 Breast Cancer Junnan Li,
Original Articles Jpn J Clin Oncol 2012;42(6)471 476 doi:10.1093/jjco/hys046 Advance Access Publication 3 April 2012 Clinical Features and Survival Analysis of T1mic, a, bn0m0 Breast Cancer Junnan Li,
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Lymphocyte density determined by computational pathology validated as a predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: secondary analysis of the ARTemis
Edinburgh Research Explorer Lymphocyte density determined by computational pathology validated as a predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: secondary analysis of the ARTemis
Association between tumour infiltrating lymphocytes, histotype and clinical outcome in epithelial ovarian cancer
 James et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:657 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3585-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Association between tumour infiltrating lymphocytes, histotype and clinical outcome in epithelial ovarian
James et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:657 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3585-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Association between tumour infiltrating lymphocytes, histotype and clinical outcome in epithelial ovarian
The Neoadjuvant Model as a Translational Tool for Drug and Biomarker Development in Breast Cancer
 The Neoadjuvant Model as a Translational Tool for Drug and Biomarker Development in Breast Cancer Laura Spring, MD Breast Medical Oncology Massachusetts General Hospital Primary Mentor: Dr. Aditya Bardia
The Neoadjuvant Model as a Translational Tool for Drug and Biomarker Development in Breast Cancer Laura Spring, MD Breast Medical Oncology Massachusetts General Hospital Primary Mentor: Dr. Aditya Bardia
Breast-Conserving Therapy for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
 Research Original Investigation PACIFIC COAST SURGICAL ASSOCIATION Breast-Conserving Therapy for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Alexandra Gangi, MD; Alice Chung, MD; James Mirocha, MS; Douglas Z. Liou,
Research Original Investigation PACIFIC COAST SURGICAL ASSOCIATION Breast-Conserving Therapy for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Alexandra Gangi, MD; Alice Chung, MD; James Mirocha, MS; Douglas Z. Liou,
TNBC: What s new Déjà vu All Over Again? Lucy R. Langer, MD MSHS Compass Oncology - SABCS 2016 Review February 21, 2017
 TNBC: What s new Déjà vu All Over Again? Lucy R. Langer, MD MSHS Compass Oncology - SABCS 2016 Review February 21, 2017 The problem with TNBC 1. Generally more aggressive 2. ONLY chemotherapy 3. No other
TNBC: What s new Déjà vu All Over Again? Lucy R. Langer, MD MSHS Compass Oncology - SABCS 2016 Review February 21, 2017 The problem with TNBC 1. Generally more aggressive 2. ONLY chemotherapy 3. No other
Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours
 Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours Workshop in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry September 19 th - 21 th 2018 Anne-Vibeke Lænkholm Department of Surgical Pathology, Zealand University Hospital,
Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours Workshop in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry September 19 th - 21 th 2018 Anne-Vibeke Lænkholm Department of Surgical Pathology, Zealand University Hospital,
Clinico- Pathological Features And Out Come Of Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 Clinico- Pathological Features And Out Come Of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Dr. HassanAli Al-Khirsani, MBChB, CABM, F.I.C.M.S AL-Sadder teaching hospital, oncology unit Dr. Nasser Ghaly Yousif, MBChB,G.P.
Clinico- Pathological Features And Out Come Of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Dr. HassanAli Al-Khirsani, MBChB, CABM, F.I.C.M.S AL-Sadder teaching hospital, oncology unit Dr. Nasser Ghaly Yousif, MBChB,G.P.
PMRT for N1 breast cancer :CONS. Won Park, M.D., Ph.D Department of Radiation Oncology Samsung Medical Center
 PMRT for N1 breast cancer :CONS Won Park, M.D., Ph.D Department of Radiation Oncology Samsung Medical Center DBCG 82 b & c Overgaard et al Radiot Oncol 2007 1152 pln(+), 8 or more nodes removed Systemic
PMRT for N1 breast cancer :CONS Won Park, M.D., Ph.D Department of Radiation Oncology Samsung Medical Center DBCG 82 b & c Overgaard et al Radiot Oncol 2007 1152 pln(+), 8 or more nodes removed Systemic
ACCME/Disclosures. Case History 4/13/2016. USCAP GU Specialty Conference Case 3. Ann Arbor, MI
 USCAP GU Specialty Conference Case 3 March 2016 L. Priya Kunju, M.D. University of Michigan Health System Ann Arbor, MI University of Michigan Health System ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone
USCAP GU Specialty Conference Case 3 March 2016 L. Priya Kunju, M.D. University of Michigan Health System Ann Arbor, MI University of Michigan Health System ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone
The Depth of Tumor Invasion is Superior to 8 th AJCC/UICC Staging System to Predict Patients Outcome in Radical Cystectomy.
 30 th Congress of the European Society of Pathology Tuesday, September 11, 2018 The Depth of Tumor Invasion is Superior to 8 th AJCC/UICC Staging System to Predict Patients Outcome in Radical Cystectomy.
30 th Congress of the European Society of Pathology Tuesday, September 11, 2018 The Depth of Tumor Invasion is Superior to 8 th AJCC/UICC Staging System to Predict Patients Outcome in Radical Cystectomy.
Podocalyxin-like protein as a prognostic marker in colorectal cancer: Functional studies and clinical implication
 Podocalyxin-like protein as a prognostic marker in colorectal cancer: Functional studies and clinical implication Karin Jirström Professor, Pathology Lund University, Regional Laboratories Region Skåne
Podocalyxin-like protein as a prognostic marker in colorectal cancer: Functional studies and clinical implication Karin Jirström Professor, Pathology Lund University, Regional Laboratories Region Skåne
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS
PD-1 and PD-L1 Expression in Male Breast Cancer in Comparison with Female Breast Cancer
 Targeted Oncology (218) 13:769 777 https://doi.org/1.7/s11523-18-61-1 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE PD-1 and PD-L1 Expression in Male Breast Cancer in Comparison with Female Breast Cancer Quirine F. Manson
Targeted Oncology (218) 13:769 777 https://doi.org/1.7/s11523-18-61-1 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE PD-1 and PD-L1 Expression in Male Breast Cancer in Comparison with Female Breast Cancer Quirine F. Manson
UK Interdisciplinary Breast Cancer Symposium. Should lobular phenotype be considered when deciding treatment? Michael J Kerin
 UK Interdisciplinary Breast Cancer Symposium Should lobular phenotype be considered when deciding treatment? Michael J Kerin Professor of Surgery National University of Ireland, Galway and Galway University
UK Interdisciplinary Breast Cancer Symposium Should lobular phenotype be considered when deciding treatment? Michael J Kerin Professor of Surgery National University of Ireland, Galway and Galway University
Immunotherapy versus targeted treatments in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: The return game?
 Immunotherapy versus targeted treatments in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: The return game? Sylvie NEGRIER MD, PhD Centre Léon Bérard, Lyon Université Lyon I IMMUNOTHERAPY: A LONG AND WIDING ROAD! WHERE
Immunotherapy versus targeted treatments in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: The return game? Sylvie NEGRIER MD, PhD Centre Léon Bérard, Lyon Université Lyon I IMMUNOTHERAPY: A LONG AND WIDING ROAD! WHERE
EGFR as paradoxical predictor of chemosensitivity and outcome among triple-negative breast cancer
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 21: 413-417, 2009 413 EGFR as paradoxical predictor of chemosensitivity and outcome among triple-negative breast cancer HIROKO NOGI 1, TADASHI KOBAYASHI 2, MASAFUMI SUZUKI 3, ISAO TABEI
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 21: 413-417, 2009 413 EGFR as paradoxical predictor of chemosensitivity and outcome among triple-negative breast cancer HIROKO NOGI 1, TADASHI KOBAYASHI 2, MASAFUMI SUZUKI 3, ISAO TABEI
Reporting of Breast Cancer Do s and Don ts
 Reporting of Breast Cancer Do s and Don ts 7 th SGH Annual Breast Pathology Course Professor Michael Bilous Conjoint Professor Western Sydney University Consultant Pathologist, Australian Clinical Labs,
Reporting of Breast Cancer Do s and Don ts 7 th SGH Annual Breast Pathology Course Professor Michael Bilous Conjoint Professor Western Sydney University Consultant Pathologist, Australian Clinical Labs,
A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Utility of AJCC 8th Edition Cancer Staging System for Breast Cancer
 Elmer ress Original Article World J Oncol. 2017;8(3):71-75 A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Utility of AJCC 8th Edition Cancer Staging System for Breast Cancer Hui Hu a, Wei Wei a, Xin Yi a, Ling Xin
Elmer ress Original Article World J Oncol. 2017;8(3):71-75 A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Utility of AJCC 8th Edition Cancer Staging System for Breast Cancer Hui Hu a, Wei Wei a, Xin Yi a, Ling Xin
Ki67 Index, HER2 Status, and Prognosis of Patients With Luminal B Breast Cancer
 ARTICLE Ki67 Index, HER2 Status, and Prognosis of Patients With Breast Cancer Maggie C. U. Cheang, Stephen K. Chia, David Voduc, Dongxia Gao, Samuel Leung, Jacqueline Snider, Mark Watson, Sherri Davies,
ARTICLE Ki67 Index, HER2 Status, and Prognosis of Patients With Breast Cancer Maggie C. U. Cheang, Stephen K. Chia, David Voduc, Dongxia Gao, Samuel Leung, Jacqueline Snider, Mark Watson, Sherri Davies,
Pregnancy and Breast Cancer. Elena Provenzano Addenbrookes Hospital Cambridge
 Pregnancy and Breast Cancer Elena Provenzano Addenbrookes Hospital Cambridge Pregnancy and Breast Cancer Pregnancy and Breast Cancer 1. Pregnancy associated breast cancer: Histology, management, clinical
Pregnancy and Breast Cancer Elena Provenzano Addenbrookes Hospital Cambridge Pregnancy and Breast Cancer Pregnancy and Breast Cancer 1. Pregnancy associated breast cancer: Histology, management, clinical
Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples
 Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples (All data were obtained from cancer microarray database Oncomine.) Analysis type* Analysis Class(number sampels) 1 2 3 4 Correlation (up/down)#
Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples (All data were obtained from cancer microarray database Oncomine.) Analysis type* Analysis Class(number sampels) 1 2 3 4 Correlation (up/down)#
Neoadjuvant Treatment of. of Radiotherapy
 Neoadjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer: Role of Radiotherapy Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Many new questions for radiation oncology? lack of path stage to guide indications should treatment response affect
Neoadjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer: Role of Radiotherapy Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Many new questions for radiation oncology? lack of path stage to guide indications should treatment response affect
Invasive breast cancer: stratification of histological grade by gene-based assays: a still relevant example from an older data set
 Histopathology 14, 65, 429 433. DOI: 1.1111/his.12423 SHORT REPORT Invasive breast cancer: stratification of histological grade by gene-based assays: a still relevant example from an older data set Leslie
Histopathology 14, 65, 429 433. DOI: 1.1111/his.12423 SHORT REPORT Invasive breast cancer: stratification of histological grade by gene-based assays: a still relevant example from an older data set Leslie
Long term survival study of de-novo metastatic breast cancers with or without primary tumor resection
 Long term survival study of de-novo metastatic breast cancers with or without primary tumor resection Dr. Michael Co Division of Breast Surgery Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Conflicts
Long term survival study of de-novo metastatic breast cancers with or without primary tumor resection Dr. Michael Co Division of Breast Surgery Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Conflicts
Intro to Cancer Therapeutics
 An Intro to Cancer Therapeutics Christopher R. Chitambar, MD Professor of Medicine Division of Hematology & Oncology Froedtert and Medical College of Wisconsin Clinical Cancer Center cchitamb@mcw.edu Intro
An Intro to Cancer Therapeutics Christopher R. Chitambar, MD Professor of Medicine Division of Hematology & Oncology Froedtert and Medical College of Wisconsin Clinical Cancer Center cchitamb@mcw.edu Intro
VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) Assay Guiding immunotherapy in NSCLC
 VENTANA (SP142) Assay Guiding immunotherapy in NSCLC Hiker s path: VENTANA (SP142) Assay on non-small cell lung cancer tissue Location: Point Conception, CA VENTANA (SP142) Assay Assess NSCLC patient benefit
VENTANA (SP142) Assay Guiding immunotherapy in NSCLC Hiker s path: VENTANA (SP142) Assay on non-small cell lung cancer tissue Location: Point Conception, CA VENTANA (SP142) Assay Assess NSCLC patient benefit
Proteomic Biomarker Discovery in Breast Cancer
 Proteomic Biomarker Discovery in Breast Cancer Rob Baxter Laboratory for Cellular and Diagnostic Proteomics Kolling Institute, University of Sydney, Royal North Shore Hospital robert.baxter@sydney.edu.au
Proteomic Biomarker Discovery in Breast Cancer Rob Baxter Laboratory for Cellular and Diagnostic Proteomics Kolling Institute, University of Sydney, Royal North Shore Hospital robert.baxter@sydney.edu.au
Low ER+ Breast Cancer. Is This a Distinct Group? Nika C. Gloyeske, MD, David J. Dabbs, MD, and Rohit Bhargava, MD ABSTRACT
 Low ER+ Breast Cancer Is This a Distinct Group? Nika C. Gloyeske, MD, David J. Dabbs, MD, and Rohit Bhargava, MD From the Magee-Womens Hospital of University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA.
Low ER+ Breast Cancer Is This a Distinct Group? Nika C. Gloyeske, MD, David J. Dabbs, MD, and Rohit Bhargava, MD From the Magee-Womens Hospital of University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA.
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine
 Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
Evaluación de la respuesta patológica completa tras tratamiento neoadyuvante en cáncer de mama. José Palacios Calvo Servicio de Anatomía Patológica
 Evaluación de la respuesta patológica completa tras tratamiento neoadyuvante en cáncer de mama José Palacios Calvo Servicio de Anatomía Patológica E-Cadherin HER2 HER2 p63 Pathological Response Pathological
Evaluación de la respuesta patológica completa tras tratamiento neoadyuvante en cáncer de mama José Palacios Calvo Servicio de Anatomía Patológica E-Cadherin HER2 HER2 p63 Pathological Response Pathological
Good Old clinical markers have similar power in breast cancer prognosis as microarray gene expression profilers q
 European Journal of Cancer 40 (2004) 1837 1841 European Journal of Cancer www.ejconline.com Good Old clinical markers have similar power in breast cancer prognosis as microarray gene expression profilers
European Journal of Cancer 40 (2004) 1837 1841 European Journal of Cancer www.ejconline.com Good Old clinical markers have similar power in breast cancer prognosis as microarray gene expression profilers
Evaluation of Pathologic Response in Breast Cancer Treated with Primary Systemic Therapy
 Evaluation of Pathologic Response in Breast Cancer Treated with Primary Systemic Therapy Eun Yoon Cho, MD, PhD Department of Pathology and Translational Genomics Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University
Evaluation of Pathologic Response in Breast Cancer Treated with Primary Systemic Therapy Eun Yoon Cho, MD, PhD Department of Pathology and Translational Genomics Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University
Understanding and Optimizing Treatment of Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 Understanding and Optimizing Treatment of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Edith Peterson Mitchell, MD, FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine and Medical Oncology Program Leader, Gastrointestinal Oncology Department
Understanding and Optimizing Treatment of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Edith Peterson Mitchell, MD, FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine and Medical Oncology Program Leader, Gastrointestinal Oncology Department
FAQs for UK Pathology Departments
 FAQs for UK Pathology Departments This is an educational piece written for Healthcare Professionals FAQs for UK Pathology Departments If you would like to discuss any of the listed FAQs further, or have
FAQs for UK Pathology Departments This is an educational piece written for Healthcare Professionals FAQs for UK Pathology Departments If you would like to discuss any of the listed FAQs further, or have
METRIC Study Key Eligibility Criteria
 The METRIC Study METRIC Study Key Eligibility Criteria The pivotal METRIC Study is evaluating glembatumumab vedotin in patients with gpnmb overexpressing metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
The METRIC Study METRIC Study Key Eligibility Criteria The pivotal METRIC Study is evaluating glembatumumab vedotin in patients with gpnmb overexpressing metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Role of the Pathologist in Guiding Immuno-oncological Therapies. Scott Rodig MD, PhD
 Role of the Pathologist in Guiding Immuno-oncological Therapies Scott Rodig MD, PhD Department of Pathology, Brigham & Women s Hospital Center for Immuno-Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Associate
Role of the Pathologist in Guiding Immuno-oncological Therapies Scott Rodig MD, PhD Department of Pathology, Brigham & Women s Hospital Center for Immuno-Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Associate
Novel RCC Targets from Immuno-Oncology and Antibody-Drug Conjugates
 Novel RCC Targets from Immuno-Oncology and Antibody-Drug Conjugates Christopher Turner, MD Vice President, Clinical Science 04 November 2016 Uveal Melanoma Celldex Pipeline CANDIDATE INDICATION Preclinical
Novel RCC Targets from Immuno-Oncology and Antibody-Drug Conjugates Christopher Turner, MD Vice President, Clinical Science 04 November 2016 Uveal Melanoma Celldex Pipeline CANDIDATE INDICATION Preclinical
Please Silence Your Cell Phones. Thank You
 Please Silence Your Cell Phones Thank You TUMOR BUDDING IN PRE OPERATIVE BIOPSIES AND RESECTIONS Alessandro Lugli, MD Institute of Pathology and Translational Research Unit (TRU) University of Bern Bern,
Please Silence Your Cell Phones Thank You TUMOR BUDDING IN PRE OPERATIVE BIOPSIES AND RESECTIONS Alessandro Lugli, MD Institute of Pathology and Translational Research Unit (TRU) University of Bern Bern,
Correlation Between GATA-3, Ki67 and p53 Expressions to Histopathology Grading of Breast Cancer in Makassar, Indonesia
 Cancer Research Journal 2016; 4(3): 43-47 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/crj doi: 10.11648/j.crj.20160403.11 ISSN: 2330-8192 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8214 (Online) Correlation Between GATA-3, Ki67
Cancer Research Journal 2016; 4(3): 43-47 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/crj doi: 10.11648/j.crj.20160403.11 ISSN: 2330-8192 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8214 (Online) Correlation Between GATA-3, Ki67
In Honour of Dr. Neera Patel
 In Honour of Dr. Neera Patel Residual Cancer Burden (RCB) vs Pathologic Complete Response (pcr) as an End-point W. Fraser Symmans, M.D. Professor of Pathology UT M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Pathologic
In Honour of Dr. Neera Patel Residual Cancer Burden (RCB) vs Pathologic Complete Response (pcr) as an End-point W. Fraser Symmans, M.D. Professor of Pathology UT M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Pathologic
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown. Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC
 Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Prognostic Impact of Signet Ring Cell Type in Node Negative Gastric Cancer Pengfei Kong1,4,Ruiyan Wu1,Chenlu Yang1,3,Jianjun Liu1,2,Shangxiang Chen1,2, Xuechao Liu1,2, Minting
Supplementary Information Prognostic Impact of Signet Ring Cell Type in Node Negative Gastric Cancer Pengfei Kong1,4,Ruiyan Wu1,Chenlu Yang1,3,Jianjun Liu1,2,Shangxiang Chen1,2, Xuechao Liu1,2, Minting
CLINICOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES AND MOLECULAR SUBTYPES OF BREAST CANCER IN FEZ-MEKNES REGION (MOROCCO): A STUDY OF 390 PATIENTS
 CLINICOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES AND MOLECULAR SUBTYPES OF BREAST CANCER IN FEZ-MEKNES REGION (MOROCCO): A STUDY OF 390 PATIENTS S. Chahbouni¹, A. Amarti 2, N. Hammas 3, L. Chbani 3, H. El fatemi 3 1 Department
CLINICOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES AND MOLECULAR SUBTYPES OF BREAST CANCER IN FEZ-MEKNES REGION (MOROCCO): A STUDY OF 390 PATIENTS S. Chahbouni¹, A. Amarti 2, N. Hammas 3, L. Chbani 3, H. El fatemi 3 1 Department
Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience
 Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience Curzon M, Curzon C, Heidel RE, Desai P, McLoughlin J, Panella T, Bell
Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience Curzon M, Curzon C, Heidel RE, Desai P, McLoughlin J, Panella T, Bell
José Palacios Calvo Servicio de Anatomía Patológica
 Criterios de respuesta patológica con los distintos subtipos de cáncer de mama. Qué cambios se dan en el tejido postquimioterapia y qué dificultades se plantean para evaluar la respuesta? José Palacios
Criterios de respuesta patológica con los distintos subtipos de cáncer de mama. Qué cambios se dan en el tejido postquimioterapia y qué dificultades se plantean para evaluar la respuesta? José Palacios
Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate is associated with metastatic disease and worse survival in patients with cutaneous malignant melanoma
 1142 Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate is associated with metastatic disease and worse survival in patients with cutaneous malignant melanoma FARUK TAS and KAYHAN ERTURK Department of Medical Oncology,
1142 Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate is associated with metastatic disease and worse survival in patients with cutaneous malignant melanoma FARUK TAS and KAYHAN ERTURK Department of Medical Oncology,
* * * * Supplementary Figure 1. DS Lv CK HSA CK HSA. CK Col-3. CK Col-3. See overleaf for figure legend. Cancer cells
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Results of the ACOSOG Z0011 Trial
 DCIS and Early Breast Cancer Symposium JUNE 15-17 2012 CAPPADOCIA Results of the ACOSOG Z0011 Trial Kelly K. Hunt, M.D. Professor of Surgery Axillary Node Dissection Staging, Regional control, Survival
DCIS and Early Breast Cancer Symposium JUNE 15-17 2012 CAPPADOCIA Results of the ACOSOG Z0011 Trial Kelly K. Hunt, M.D. Professor of Surgery Axillary Node Dissection Staging, Regional control, Survival
A new way of looking at breast cancer tumour biology
 A new way of looking at breast cancer tumour biology Contents Intrinsic subtypes of breast cancer 3 Gene expression assays 3 Basis of the Prosigna test 4 Information provided by Prosigna 5 The accuracy
A new way of looking at breast cancer tumour biology Contents Intrinsic subtypes of breast cancer 3 Gene expression assays 3 Basis of the Prosigna test 4 Information provided by Prosigna 5 The accuracy
Neutrophil/Lymphocyte and Platelet/Lymphocyte Ratios are Not Different among Breast Cancer Subtypes
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Neutrophil/Lymphocyte and Platelet/Lymphocyte Ratios are Not Different among Breast Cancer Subtypes Özlem Yersal 1 *, Süleyman Çetinkünar 2, Recep Aktimur 1, Mehmet Aziret 3, Sabri Özdaş
RESEARCH ARTICLE Neutrophil/Lymphocyte and Platelet/Lymphocyte Ratios are Not Different among Breast Cancer Subtypes Özlem Yersal 1 *, Süleyman Çetinkünar 2, Recep Aktimur 1, Mehmet Aziret 3, Sabri Özdaş
J Clin Oncol 24: by American Society of Clinical Oncology INTRODUCTION
 VOLUME 24 NUMBER 36 DECEMBER 20 2006 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T Locoregional Relapse and Distant Metastasis in Conservatively Managed Triple Negative Early-Stage Breast Cancer
VOLUME 24 NUMBER 36 DECEMBER 20 2006 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T Locoregional Relapse and Distant Metastasis in Conservatively Managed Triple Negative Early-Stage Breast Cancer
The Current Status of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Arvin Yang, MD PhD Oncology Global Clinical Research Bristol-Myers Squibb
 The Current Status of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Global Overview of the Field Arvin Yang, MD PhD Oncology Global Clinical Research Bristol-Myers Squibb Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Conference, March
The Current Status of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Global Overview of the Field Arvin Yang, MD PhD Oncology Global Clinical Research Bristol-Myers Squibb Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Conference, March
Mammographic density and risk of breast cancer by tumor characteristics: a casecontrol
 Krishnan et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:859 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3871-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Mammographic density and risk of breast cancer by tumor characteristics: a casecontrol study Open Access Kavitha
Krishnan et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:859 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3871-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Mammographic density and risk of breast cancer by tumor characteristics: a casecontrol study Open Access Kavitha
Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti. Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS
 Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS Histological diversity of breast adenocarcinomas Different histological types are defined according to specific
Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS Histological diversity of breast adenocarcinomas Different histological types are defined according to specific
Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer
 Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Breast Cancer Subtypes and the Risk of Local and Regional Relapse
 VOLUME 28 NUMBER 10 APRIL 1 2010 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T Breast Cancer s and the Risk of Local and Regional Relapse K. David Voduc, Maggie C.U. Cheang, Scott Tyldesley,
VOLUME 28 NUMBER 10 APRIL 1 2010 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T Breast Cancer s and the Risk of Local and Regional Relapse K. David Voduc, Maggie C.U. Cheang, Scott Tyldesley,
Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
3/22/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Ki-67 in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms According to WHO 2017.
 Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Ki-67 in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms According to WHO 2017. USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Ki-67 in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms According to WHO 2017. USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control
RESEARCH COMMUNICATION. High Ki-67 Expression is a Poor Prognostic Indicator of 5-Year Survival in Patients with Invasive Breast Cancer
 RESEARCH COMMUNICATION High Ki-67 Expression is a Poor Prognostic Indicator of 5-Year Survival in Patients with Invasive Breast Cancer Xue-Qin Yang 1,2, Fu-Bing Wang 1, Chuang Chen 1, Chun-Wei Peng 1,
RESEARCH COMMUNICATION High Ki-67 Expression is a Poor Prognostic Indicator of 5-Year Survival in Patients with Invasive Breast Cancer Xue-Qin Yang 1,2, Fu-Bing Wang 1, Chuang Chen 1, Chun-Wei Peng 1,
Surgical Pathology Issues of Practical Importance
 Surgical Pathology Issues of Practical Importance Anne Moore, MD Medical Oncology Syed Hoda, MD Surgical Pathology The pathologist is central to the team approach needed to manage the patient with breast
Surgical Pathology Issues of Practical Importance Anne Moore, MD Medical Oncology Syed Hoda, MD Surgical Pathology The pathologist is central to the team approach needed to manage the patient with breast
Reviewing Immunotherapy for Bladder Carcinoma In Situ
 Reviewing Immunotherapy for Bladder Carcinoma In Situ Samir Bidnur Dept of Urologic Sciences, Grand Rounds March 1 st, 2017 Checkpoint Inhibition and Bladder Cancer, an evolving story with immunotherapy
Reviewing Immunotherapy for Bladder Carcinoma In Situ Samir Bidnur Dept of Urologic Sciences, Grand Rounds March 1 st, 2017 Checkpoint Inhibition and Bladder Cancer, an evolving story with immunotherapy
Clinical significance and prognostic value of receptor conversion in hormone receptor positive breast cancers after neoadjuvant chemotherapy
 Yang et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2018) 16:51 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-018-1332-7 RESEARCH Open Access Clinical significance and prognostic value of receptor conversion in hormone receptor
Yang et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2018) 16:51 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-018-1332-7 RESEARCH Open Access Clinical significance and prognostic value of receptor conversion in hormone receptor
