CT Safety: Realities and Myths of Radiation and Contrast Medium Adverse Events
|
|
|
- Ezra Lambert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CT Safety: Realities and Myths of Radiation and Contrast Medium Adverse Events Dushyant Sahani MD Director of CT Associate Professor of Radiology MGH Disclosure Research Grant Support GE Healthcare BD Consultant, Bracco Diagnostics HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL Effective Dose Per Individual E (US) 6.2 msv Ubiquitous Background and other non-medical 3.2 msv Medical 3.0 msv Calculations based on data from NCRP Report 160 >72 million scans in USA in 2008 Dose with Various Exams Chest x-ray 0.01 msv CT of the chest 7 msv Abdomen-pelvis CT msv Dental x-ray msv Panoramic x-ray msv Dental CT 0.2 msv Head CT 2.0 msv Crew on an airline flight (annual) 2 msv Passenger on an airline flight 0.07 msv Emergency workers in Chernobyl >100mSv Background radiation in US (annual) 3.7 msv Berrington de González et al Arch Intern Med Smith-Bindman et al Arch Intern Med Do CT scans cause cancer? No study with definite link between a CT scan and later cancer development (Why) Definite link very difficult to prove Radiation induced cancer is identical to nonradiation induced cancer Cancer risk from radiation is higher < 30 yo Lifetime risk of death by cancer per million people exposed to 10 mgy Based on atomic bomb survivor data. Colon cancer Lung cancer Too many confounding factors: age, genetic/family history, diet, weight, smoking BEIR VII 2005 report AGE (yrs) 1
2 Lancet Study-June 2012 (Pearce M et al) 180,000 children in UK who get several CT scans ( ) have a slightly higher chance of brain cancer and leukemia in later life Very small (0.023%) increase in lifetime risk, once the overall rarity of brain tumors was taken into account Limitations of the Lancet study CT dose were significantly higher than currently used (70-85% lower at MGH) Lack of control group for cancer risk in children of same age who did not have CT scan Average Effective Doses (msv) msv Phoenix 1 Avg background radiation 3 3 Denver CXR Mammo Head CT CTC Chest CT Abd CT AP CT Liver CT Smith-Bindman R. Arch Intern Med 2009;169(22): Max/yr nuclear worker Lifetime risk of dying from Risk of dying Activity per 1000 people Cancer (non-radiation induced) 228 Motor vehicle accident 12 Married to a smoker 10 US average radon level in home 3 Drowning 0.9 Dental x-rays/panoramic 0 Abdomen CT 0.05 Two Pillars of Radiation Dose Reduction Appropriate Utilization + Optimization of CT Protocols Splitting scan volumes increases dose Faster gantry rotation reduces radiation dose. However, noise is increased if the other factors are constant Scanning Parameters Off-centering increases dose 1. Localizer radiograph 2. Helical/axial 3. Tube current 4. Tube voltage 5. AEC 6. Rotation time Collimation, beam pitch, Automatic exposure control 7. Table feed/speed table speed 8. Pitch 9. Scan length 10. Detector configuration 11. Slice Thickness 12. Recon alg / kernel Extra images = 13. Phases (arterial/venous) Extra dose increases Decreasing 14. tissue kvp reduces dose and recon tech FBP/IRT contrast; increasing mas could reduce noise Strategies Commonsense Steps Leveraging Technology Innovative Solutions 2
3 MINIMIZE COVERAGE: Less is More Limit Scanning Area MINIMIZE COVERAGE Routine AP: hemidiaphragms to pubic symph Dose Reduction by 20% Top of diaphragm to lower border of ischium Top of L 1 to upper border of symphysis CTC (colon only) CTA (stent only) Renal/Adrenal (limited to anatomy) CTU: (kidneys to bladder only) Post-cystogram (bladder) Overlap Scanning: Extra Radiation Dose MINIMIZE COVERAGE 25% EXTRA DOSE Χ Renal/Adrenal Delayed phase Limiting Phases in CT Urography Triple phase CTU vs Split Bolus Unenhanced CT ml IV CM (370 mgi/ml) 250 ml saline drip infusion Wait minutes (Prone) ml IV 3 ml/s Scan at 100 sec delay Limiting the Phases: Renal Donor CT Dose Reduction by 60 70% Base scan only in patients less than 40 yrs of age if a stone is seen Split Bolus: 25 % Dose Reduction compared to Triple phase CTU kvp: 80 Scout image at 8 minutes for excretory phase 80 kvp 3
4 WL=0 WW=100 WL=0 WW=100 Patient Off centering Increases Dose and Noise Parameters and Dose 0 mm 30 mm dose kvp 2 Tube potential Gantry center WL=0 WW=100 Phantom scanned at different centering positions in CT gantry 60 mm Patient CT Scanner dose mas Exposure time Tube Current Beam Quality Collimation 6% Noise 22% 21% Surface dose 49% 18% Peripheral dose 41% Li et al, ARRS 2006 Effect of CT Adaptations on Dose Steps for Lowering Dose 50% decrease in ma = 50% dose reduction kv = 40% dose reduction Increase in pitch = dose decrease Thicker slices = dose decrease DECREASE IN Tube current Tube potential Gantry rotation time * Scan length Overlap scanning Number of scan phases INCREASE IN Pitch (Table speed) * Beam collimation *Provided other scanning factors are kept constant Indication Appropriate Image Quality 151 lbs 162 lbs Radiation Dose from MDCT Exams A B C D CT dose 6.8 msv CT dose 2.2 msv 430 lbs 156 lbs CT dose 1.6mSv CT dose 18 msv 140 kvp NI-15 5 mm 0.8 sec 100 kvp NI mm 0.5 sec 120kVp NI-25 5 mm 0.5 sec 80kVp NI mm 0.5 sec CT dose 1.06 msv 14.3 msv 7.3 msv 5.5 msv 1.7 msv Obtained by EUR EN using an abdomen factor of 0.015*DLP and a pelvis factor of 0.019*DLP 4
5 Options for ma Reduction? Manual selection of a fixed ma Automated technology Automated Exposure Control (AEC) AEC changes ma to follow changing patient anatomy in order to maintain a constant image noise/quality & optimize dose Adjusts tube current Based on patient size From slice-to-slice (z modulation) Within each slice (xy angular modulation) Constant ma Reduced dose level based on scout Real time angular dose modulation A D B Graser AJR 2006; 659 Herzog et al. AJR 2008, 1232 Mulkens Radiology 2005; 213 C AEC on Different Scanner Types SCANNER TYPE GE-64 Toshiba-64 ACE TRADE NAME Auto ma Smart ma Sure Exposure OPERATOR CHOSEN PARAMETER PATIENT SIZE ACE Z-AXIS ACE ANGULA R ACE GOAL (Regardless of attenuation level) Noise Index Yes Yes Yes Constant image noise, within user prescribed minimum and maximum ma Standard Deviation Yes Yes Yes Noise Index and dose Noise index: to choose the desired image quality (image noise) NI is inversely related to radiation dose NI-15 Higher the NI, lower is the CT dose NI-35 Siemens-64 Philips-64 CARE Dose 4D Dose Right Reference Effective mas Reference Image Yes Yes Yes Constant image quality, with reference to a mas level for an average sized patient Yes Yes Yes Same image quality as reference image. 12 msv 4 msv Dose increases by 10% for a decrease in NI of 5% Dose decreases by 9% for a increase in NI of 5% Noise Index, Slice Thickness, and Relative Dose Reconstruction Slice Thickness (mm) Relative Dose NI NI NI NI NI Weight Based CT Protocol: Routine Abdomen Weight < 135 lbs lbs lbs Siemens (Care Dose 4D) kv Ref ma Pitch kv GE 16/64 (Auto ma 3D) Auto ma (minmax) Pitch Noise index Phillips 64 (Z-DOM) kv mas Pitch > 300 lbs Kanal K et al. AJR July 2007 vol. 189 no
6 When do want to use manually selected fixed ma? Lung cancer screening chest CT CT colonography Ultra-low dose exams Benefits of low-kv selection Increased iodine contrast CTA studies 140 kv 100 kv Stiller et al, Eur J Radiol Perisinakis et al, Br J Radiol Utsunomiya et al, Eur Radiol Marin et al, Radiology Kim et al, AJR Hunsaker AR. AJR Godoy MC. Eur J Radiol Feuchtner GM. Eur J Radiol Benefits / Challenges of low-kv selection Reduction in radiation dose dose kv 2 Small and medium size patients NOISE Strategies for low kv (80-100) selection Body weight Body mass index (BMI) Workflow kv / 440 ma 120 kv / 350 ma Siegel MJ Radiology 2004; 233:515 Huda, et al., Med Phys 2004 Nakayama, et al. AJR 2006 Abdominal width 34 Huda et al, Radiology 2000 Nakayama et al, AJR 2006 Schindera et al, Radiology 2008 Szucs-Farkas et al, Invest Rad 2008 Guimarães et al, Radiology 2010 dose kvp 2 kvp Selection Based on Body Weight & Indication: CTA Tube potential lbs > lbs < 150 lbs kvp ma= THE OTHER OPTION Automated kv Selection Technology A tool which automatically adjusts kv for body size determined from topogram and the exam type Up to 60% dose reduction 120kvp 100kvp 80kvp > 300 lbs= 140 kvp 6
7 MDCT protocols into 3-4 groups MGH CT Dose Fact Sheet Low-Contrast I+ phase CECT (portal/nephro) Hi-Contrast CTA/CTU/CTC Arterial phase Screening Stone/CTC Post Procedure Low ma options kvp+/- (fixed) Low kvp options ma optimized Low kvp Low ma Ultra-low dose approaches Radiation Dose-ULD Stone CT Renal stone Post catheter drainage Crohn s disease/pancreatitis % 90% 85% msv Initial scan Standard dose CT view KUB Follow up scan ultra-low dose CT Wt Category Std dose CT ULD CT CTDI msv CTDI msv Over all < 200 lbs > 200 lbs Weight & Indication Adapted Protocols Cancer Follow-up Weight Noise Index kvp ma Ref mas mas/ Pitch < 200 lbs > 200 lbs
8 Low Dose Imaging Dose -30% -50 % -70% Dose -90% CT Image Reconstruction Standard Filtered back projection (FBP) Makes several assumptions Time efficient NOT dose efficent Excessive image noise at low dose Artifacts in large patients and dense structures Reduced CNR Standard FBP Raw data recon Fast Image Data Space Slow Raw Data Space Iterative Reconstruction GE: ASiR (Adaptive Statistical Iterative Reconstruction) MBIR (Model Based Iterative Reconstruction) Siemens: IRIS (Iterative Reconstruction in Image Space) SAFIRE (Sinogram Affirmed IR) Philips: idose/idose4 (Fourth Generation) Toshiba: AIDR (Adaptive Iterative Dose Reduction) IRIS/ASIR/iDOSE/ADIR/SAFIRE (30-50%) MBIR/Veo (>50%) FBP VS. Partial IR VS. Full IR MBIR/VEO: ULD Abdomen Pelvis 0.8mSv* Simple Comprehensive Advanced Blend FBP+IR Ideal System Few Iterations Advanced model Renal tumor in a horse-sh shaped kidney Dose report CPU CPU CPU Simple Better IQ Fast Low dose High noise Low noise Optimal IQ Low noise Better resolution FBP ASIR Veo/MBIR 120 kv, 10 ma, 0.5 rot 0.625mm slice thickness Courtesy: De Ann Haas GE *Obtained by EUR EN, using an abdomen factor of 0.015*DLP and a pelvis factor of 0.019*DLP 8
9 * The information about this product is being provided for planning purposes. The product is pending 510(k) review, and is not yet commercially available in the U.S. In clinical practice the use of SAFIRE may reduce CT patient dose depending on the clinical task, patient size, anatomical location, and clinical practice. A consultation with a radiologist and a physicist schould be made to determine the appropriate dose to obtain diagnostic image quality for the particular clinical task. SAFIRE FBP = 26.8 HU 35% less noise WFBP = 17.6 HU up to 55% less noise 30% less up noise to 70% less noise IRIS = 12.3 HU = 7.8 HU SAFIRE What should we tell patients? (Take home points) Radiation does indeed have the potential to cause cancer at larger doses Cancer risk data at low radiation doses is controversial In adults: Minimal to no increased cancer risk from a single CT exam Courtesy: Mitya Barreto, Siemens Minimize CT (use MR or US) Patients < 30 yo Pregnant patients More efficient detectors $$ Technical innovations Blended FBP and iterative reconstruction More efficient filters $ $$ Other design innovations $-$$$ Protocol optimization: Tube current modulation Full iterative reconstruction $$$$$ $ Protocol optimization: Clinical indication $ Protocol optimization: kvp $ Protocol optimization: Pitch $ End user Initiatives Contrast Media: An Overview Utilization One of the highest volume medical drugs used compared with any other pharmaceutical Over 80 million doses administered with iodinated intravascular contrast media in 2003 corresponding to approximately 8 million liters Persson, PB. Nephrol Dial Transplant CM Safety CT CM AE s at 6 Partners Hospital Safety profile of non-ionic CM is well established AE s %, majority minor Severe AE s uncommon but still encountered Severe CM extravasation uncommon influenced by the quality of IV access and injection rate 54 9
10 AE s with Iodinated CM: ACR Classification Systemic (0.2%) Local Mild Moderate Sever Delayed CM Extrav Rash Itchy Sneeze Vasovagal Tachycardia Reassure Vitals Benadryl Atropine Wheeze Hypotensive Pulm edema CHF Severe Tachy ACLS Fluids/Lasix Epinephrine Code Anaphylaxis Collapse Laryngeal angioedema Code ACLS Rash CIN Fragile veins Power inj Rapid bolus Flush Patch Warm/cold compress Contrast Media Induced Nephropathy (CIN) CIN can be defined as either of the following: Relative increase of serum creatinine (SCr) from baseline values from 25%- 50% OR Absolute increase of SCr from 0.5 to 1.0 mg/dl Risk Factors for CIN Risk Factors for CIN There is general consensus that renal insufficiency and diabetes are major risk factors for CIN, particularly when coexisting. Secondary Diabetes mellitus, alone Cardiovascular disease and diuretics Advanced age (>75 years) Multiple myeloma (in dehydrated patient) Hypertension Uricosuria The NEPHRIC Study, 2003: IOCM & LOCM Briguori et al., 2005: IOCM & LOCM 129 patients with renal impairment and diabetes mellitus undergoing cardiac or peripheral angiography Baseline SCr: > 1.5 mg/dl CIN endpoint: 0.5 mg/dl SCr from baseline Overall incidence of CIN: Visipaque-320: 2/64 (3.1%) Omnipaque-350: 17/65 (26.2%) Difference: p<0.002 IOCM Iodixanol (Visipaque-320, 300mOsm/kg) LOCM iobitridol (Xenetix -350, 915 mosm/kg) Renally-impaired (SCr > 1.5 mg/dl) undergoing cardiac catheterization All patients were well hydrated (standard protocol) and received NAC Overall incidence of CIN: Visipaque: 3/110 (2.7%) Xenetix: 4/115 (3.5%) NEJM. 2003; 348: Kidney Int. 2005; 68:
11 CIN and Intravenous Contrast Administration CIN with Head-to-Head Comparisons Risk Patients Receiving I.V. Contrast Material Study LOCM (monomers) Carraro et al (1998) 0/32 (iopromide) IOCM Criteria (Iodixanol) 1/32 50% SCr Kolehmainen et al (2003) IMPACT Barrett et al ACTIVE Catalano /25 (Xenetix) 0/77 (iopamidol) TOTAL 4/210 (3%) 0/76 5/72 4/25 44 m/l SCr 2/ mg/dl SCr 12/205 (6%) Prevention of CIN Identify at risk group Estimate egfr from S.Cr: Use MDRD or other equations (egfr> 60mL/min) Discontinue nephrotoxic drugs Prevention of CIN Keep the dose as low as possible-but still get a diagnostic study 70-80% of the calculated dose usually reasonable Space studies > 72 hours if possible With IV LOCM, risk of CIN is low For current CM (LOCM & IOCM), osmolality is not a significant factor for reducing the incidence of CIN Preventing Contrast Nephropathy: Screening and risk stratification Pharmacologic prophylaxis and CIN prevention Pharmacologic agent Study design Results Atrial natriuretic peptide Prospective, randomized No benefit Dopamine Prospective, randomized Worsened or no benefit Endothelin antagonist Prospective, randomized Worsened CIN Adenosine antagonist Prospective randomized No benefit Estimated GFR <30 ml/min/1.73 m2 Estimated GFR ml/min/1.73 m2 Estimated GFR >45 ml/min/1.73 m2 Ca channel blocker Prospective Not studied adequately Fenoldopam Mesylate Prospective, randomized No benefit NO CONTRAST* Prophylactic Measures + CONTRAST Prostaglandin E1 Prospective randomized Further studies required. N-acetyl Cysteine Prospective randomized Mixed benefit 11
12 Summary Incidence of CIN with CT in high risk group is 2-7% Majority are self limiting IV saline hydration or nephroprotective drug use is encouraged to reduce CIN but their benefits in CT are unclear Choice of non-ionic CM has no substantial benefit in reducing the CIN risk Summary CT dose is the biggest threat to radiology dept Critical to invest efforts in lowering CT dose and Education Optimize CT protocols based on body size, age and clinical indications Weight adapted ma and kvp reductions Limit scan acquisition phases and scan length Use thicker slices (5 mm) and include Multiplanar reconstructions Summary Low dose CT scans with IR technique allows substantial radiation dose reduction while providing diagnostic image More drastic dose reduction with low kvp easier to apply Large Body Habitus scans are of optimal quality with modest dose reduction Moving towards the goal of sub msv to minimize risk and improve CT utilization Thank you 12
How do the Parameters affect Image Quality and Dose for Abdominal CT? Image Review
 How do the Parameters affect Image Quality and Dose for Abdominal CT? Image Review Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD, DNB Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Financial Disclosure This presentation
How do the Parameters affect Image Quality and Dose for Abdominal CT? Image Review Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD, DNB Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Financial Disclosure This presentation
Translating Protocols Across Patient Size: Babies to Bariatric
 Translating Protocols Across Patient Size: Babies to Bariatric Cynthia H. McCollough, PhD, FACR, FAAPM Professor of Radiologic Physics Director, CT Clinical Innovation Center Department of Radiology Mayo
Translating Protocols Across Patient Size: Babies to Bariatric Cynthia H. McCollough, PhD, FACR, FAAPM Professor of Radiologic Physics Director, CT Clinical Innovation Center Department of Radiology Mayo
SPECIFIC PRINCIPLES FOR DOSE REDUCTION IN HEAD CT IMAGING. Rajiv Gupta, MD, PhD Neuroradiology, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 SPECIFIC PRINCIPLES FOR DOSE REDUCTION IN HEAD CT IMAGING Rajiv Gupta, MD, PhD Neuroradiology, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School OUTLINE 1 st Presentation: Dose optimization strategies
SPECIFIC PRINCIPLES FOR DOSE REDUCTION IN HEAD CT IMAGING Rajiv Gupta, MD, PhD Neuroradiology, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School OUTLINE 1 st Presentation: Dose optimization strategies
Ultralow Dose Chest CT with MBIR
 Ultralow Dose Chest CT with MBIR Ella A. Kazerooni, M.D. Professor & Director Cardiothoracic Radiology Associate Chair for Clinical Affairs University of Michigan Disclosures Consultant: GE Healthcare
Ultralow Dose Chest CT with MBIR Ella A. Kazerooni, M.D. Professor & Director Cardiothoracic Radiology Associate Chair for Clinical Affairs University of Michigan Disclosures Consultant: GE Healthcare
Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach
 Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. University of Alabama at Birmingham Before Contrast Prep and Hydration Hydration single most important
Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. University of Alabama at Birmingham Before Contrast Prep and Hydration Hydration single most important
Low-Dose CT: Clinical Studies & the Radiologist Perspective
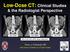 Low-Dose CT: Clinical Studies & the Radiologist Perspective RD-ASiR RD-MBIR SD-FBP RD=0.35 msv (80% dose reduction) Perry J. Pickhardt, MD UW School of Medicine & Public Health Low-Dose CT: Clinical Overview
Low-Dose CT: Clinical Studies & the Radiologist Perspective RD-ASiR RD-MBIR SD-FBP RD=0.35 msv (80% dose reduction) Perry J. Pickhardt, MD UW School of Medicine & Public Health Low-Dose CT: Clinical Overview
Dual-Energy CT: The Technological Approaches
 Dual-Energy CT: The Technological Approaches Dushyant Sahani, M.D Director of CT Associate Professor of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Email-dsahani@partners.org Disclosure
Dual-Energy CT: The Technological Approaches Dushyant Sahani, M.D Director of CT Associate Professor of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Email-dsahani@partners.org Disclosure
Managing Radiation Risk in Pediatric CT Imaging
 Managing Radiation Risk in Pediatric CT Imaging Mahadevappa Mahesh, MS, PhD, FAAPM, FACR, FACMP, FSCCT. Professor of Radiology and Cardiology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Chief Physicist
Managing Radiation Risk in Pediatric CT Imaging Mahadevappa Mahesh, MS, PhD, FAAPM, FACR, FACMP, FSCCT. Professor of Radiology and Cardiology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Chief Physicist
Low Dose Era in Cardiac CT
 Low Dose Era in Cardiac CT DIANA E. LITMANOVICH, MD Department of Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Disclosures Neither I nor my immediate family members have a financial
Low Dose Era in Cardiac CT DIANA E. LITMANOVICH, MD Department of Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Disclosures Neither I nor my immediate family members have a financial
(Non-EKG Gated) CTA Thoracic Aorta = CTA Chest
 (Non-EKG Gated) CTA Thoracic Aorta = CTA Chest Reviewed By: Dan Verdini, MD, Rachael Edwards, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA
(Non-EKG Gated) CTA Thoracic Aorta = CTA Chest Reviewed By: Dan Verdini, MD, Rachael Edwards, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA
Why is CT Dose of Interest?
 Why is CT Dose of Interest? CT usage has increased rapidly in the past decade Compared to other medical imaging CT produces a larger radiation dose. There is direct epidemiological evidence for a an increase
Why is CT Dose of Interest? CT usage has increased rapidly in the past decade Compared to other medical imaging CT produces a larger radiation dose. There is direct epidemiological evidence for a an increase
Doses from Cervical Spine Computed Tomography (CT) examinations in the UK. John Holroyd and Sue Edyvean
 Doses from Cervical Spine Computed Tomography (CT) examinations in the UK John Holroyd and Sue Edyvean Why a new dose survey? Number of enquires received concerning the current NDRL Concern that could
Doses from Cervical Spine Computed Tomography (CT) examinations in the UK John Holroyd and Sue Edyvean Why a new dose survey? Number of enquires received concerning the current NDRL Concern that could
ESTABLISHING DRLs in PEDIATRIC CT. Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
 ESTABLISHING DRLs in PEDIATRIC CT Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine CT Dose Indices CTDI INTRODUCTION CTDI 100, CTDI w, CTDI vol
ESTABLISHING DRLs in PEDIATRIC CT Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine CT Dose Indices CTDI INTRODUCTION CTDI 100, CTDI w, CTDI vol
CTA Pulmonary Embolism CTA Chest W (arterial)
 CTA Pulmonary Embolism CTA Chest W (arterial) Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
CTA Pulmonary Embolism CTA Chest W (arterial) Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
CT Pancreas 3 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V
 CT Pancreas 3 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
CT Pancreas 3 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
Liver 4 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V.D
 Liver 4 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V.D Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA
Liver 4 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V.D Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA
CTA Chest Pulmonary Embolism & Routine CT Abdomen + Pelvis W CTA Chest W (arterial) & CT Abdomen + Pelvis W (venous)
 CTA Chest Pulmonary Embolism & Routine CT Abdomen + Pelvis W CTA Chest W (arterial) & CT Abdomen + Pelvis W (venous) Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact:
CTA Chest Pulmonary Embolism & Routine CT Abdomen + Pelvis W CTA Chest W (arterial) & CT Abdomen + Pelvis W (venous) Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact:
CT Radiation Risks and Dose Reduction
 CT Radiation Risks and Dose Reduction Walter L. Robinson, M.S. D.A.B.S.N.M., D.A.B.M.P., D.A.B.R. Consultant Certified Medical Radiation Health & Diagnostic Imaging Physicist Medical Radiation and Children
CT Radiation Risks and Dose Reduction Walter L. Robinson, M.S. D.A.B.S.N.M., D.A.B.M.P., D.A.B.R. Consultant Certified Medical Radiation Health & Diagnostic Imaging Physicist Medical Radiation and Children
Cardiac CT Lowering the Dose Dramatically
 Cardiac CT Lowering the Dose Dramatically U. Joseph Schoepf, MD, FAHA, FSCBT MR, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director of Cardiovascular Imaging Disclosures Consultant for / research
Cardiac CT Lowering the Dose Dramatically U. Joseph Schoepf, MD, FAHA, FSCBT MR, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director of Cardiovascular Imaging Disclosures Consultant for / research
Radiation Dose Reduction Strategies in Coronary CT Angiography
 Radiation Dose Reduction Strategies in Coronary CT Angiography Noor Diyana Osman, PhD noordiyana@usm.my Contents: Introduction Radiation dosimetry in CT Radiation risk associated with coronary CT angiography
Radiation Dose Reduction Strategies in Coronary CT Angiography Noor Diyana Osman, PhD noordiyana@usm.my Contents: Introduction Radiation dosimetry in CT Radiation risk associated with coronary CT angiography
Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT
 GE Healthcare Case studies Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT Jean-Louis Sablayrolles, M.D. Centre Cardiologique du Nord, Saint-Denis, France Case 1 Whole Brain Perfusion and
GE Healthcare Case studies Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT Jean-Louis Sablayrolles, M.D. Centre Cardiologique du Nord, Saint-Denis, France Case 1 Whole Brain Perfusion and
Dual Energy CT Aortography: Can We Reduce Iodine Dose??
 Dual Energy CT Aortography: Can We Reduce Iodine Dose?? William P. Shuman MD, FACR FSCBTMR Department of Radiology University of Washington SCBTMR Annual Course Boston, October 10, 2012 Conflict of Interest
Dual Energy CT Aortography: Can We Reduce Iodine Dose?? William P. Shuman MD, FACR FSCBTMR Department of Radiology University of Washington SCBTMR Annual Course Boston, October 10, 2012 Conflict of Interest
BrightSpeed Elite CT with ASiR: Comparing Dose & Image Quality Rule Out Pulmonary Embolism on Initial & Follow-Up Exam
 GE Healthcare BrightSpeed Elite CT with ASiR: Comparing Dose & Image Quality Rule Out Pulmonary Embolism on Initial & Follow-Up Exam Michael Swack, MD Diagnostic Radiologist Irvington Radiologists, PC
GE Healthcare BrightSpeed Elite CT with ASiR: Comparing Dose & Image Quality Rule Out Pulmonary Embolism on Initial & Follow-Up Exam Michael Swack, MD Diagnostic Radiologist Irvington Radiologists, PC
A more accurate method to estimate patient dose during body CT examinations with tube current modulation
 A more accurate method to estimate patient dose during body CT examinations with tube current modulation Poster No.: C-0738 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Kawaguchi 1, Y. Matsunaga
A more accurate method to estimate patient dose during body CT examinations with tube current modulation Poster No.: C-0738 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Kawaguchi 1, Y. Matsunaga
Radiology Rounds A Newsletter for Referring Physicians Massachusetts General Hospital Department of Radiology
 Radiology Rounds A Newsletter for Referring Physicians Massachusetts General Hospital Department of Radiology Minimizing CT Radiation Dose CT examinations improve health care and are an essential part
Radiology Rounds A Newsletter for Referring Physicians Massachusetts General Hospital Department of Radiology Minimizing CT Radiation Dose CT examinations improve health care and are an essential part
Cardiac CT Techniques in Neonates (and infants)
 Cardiac CT Techniques in Neonates (and infants) Siddharth P. Jadhav, MD Director, Body CT and MRI Edward B. Singleton Department of Pediatric Radiology Texas Children s Hospital Disclosures None Objectives
Cardiac CT Techniques in Neonates (and infants) Siddharth P. Jadhav, MD Director, Body CT and MRI Edward B. Singleton Department of Pediatric Radiology Texas Children s Hospital Disclosures None Objectives
Cardiac CT - Coronary Calcium Basics Workshop II (Basic)
 Cardiac CT - Coronary Calcium Basics Workshop II (Basic) J. Jeffrey Carr, MD, MSCE Dept. of Radiology & Public Health Sciences Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, NC USA No significant
Cardiac CT - Coronary Calcium Basics Workshop II (Basic) J. Jeffrey Carr, MD, MSCE Dept. of Radiology & Public Health Sciences Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, NC USA No significant
HI-Res Extremity Sensation 16
 Page 1 Routine Extremity - (2/14/2013) CTDI: ~20 mgy per acquisition Used for evaluation of: Humerus Forearm Femur Knee Tib/Fib Billing: 1. CT Upper/Lower Extremity of concern without contrast, with contrast,
Page 1 Routine Extremity - (2/14/2013) CTDI: ~20 mgy per acquisition Used for evaluation of: Humerus Forearm Femur Knee Tib/Fib Billing: 1. CT Upper/Lower Extremity of concern without contrast, with contrast,
CT Chest HRCT CT Chest WO
 CT Chest HRCT CT Chest WO Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA policies and protocols
CT Chest HRCT CT Chest WO Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA policies and protocols
Optimal Use of Iodinated Contrast Media In Oncology Patients. Focus on CI-AKI & cancer patient management
 Optimal Use of Iodinated Contrast Media In Oncology Patients Focus on CI-AKI & cancer patient management Dr. Saritha Nair Manager-Medical Affairs-India & South Asia GE Healthcare Context Cancer patients
Optimal Use of Iodinated Contrast Media In Oncology Patients Focus on CI-AKI & cancer patient management Dr. Saritha Nair Manager-Medical Affairs-India & South Asia GE Healthcare Context Cancer patients
CT Renal 3 Phase + Pelvis CT Abdomen Pelvis WO W - NC.A.V, Pelvis during V
 CT Renal 3 Phase + Pelvis CT Abdomen Pelvis WO W - NC.A.V, Pelvis during V Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance
CT Renal 3 Phase + Pelvis CT Abdomen Pelvis WO W - NC.A.V, Pelvis during V Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance
Toshiba Aquillion 64 CT Scanner. Phantom Center Periphery Center Periphery Center Periphery
 Comparison of radiation dose and imaging performance for the standard Varian x-ray tube and the Richardson Healthcare ALTA750 replacement tube for the Toshiba Aquillion CT scanners. by Robert L. Dixon,
Comparison of radiation dose and imaging performance for the standard Varian x-ray tube and the Richardson Healthcare ALTA750 replacement tube for the Toshiba Aquillion CT scanners. by Robert L. Dixon,
Optimizing radiation dose by varying age at pediatric temporal bone CT
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 1, 2015 Optimizing radiation dose by varying age at pediatric temporal bone CT Daichi Noto, 1 Yoshinori Funama, 2a Mika Kitajima, 3 Daisuke
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 1, 2015 Optimizing radiation dose by varying age at pediatric temporal bone CT Daichi Noto, 1 Yoshinori Funama, 2a Mika Kitajima, 3 Daisuke
Radiography/Radiology
 Radiography/Radiology Activity for 2017 Activity No: A1(17) Topic CT radiation Article CT radiation: key concepts for gentle and wise use Approved for (3) Clinical Continuing Educational Units (CEU s)
Radiography/Radiology Activity for 2017 Activity No: A1(17) Topic CT radiation Article CT radiation: key concepts for gentle and wise use Approved for (3) Clinical Continuing Educational Units (CEU s)
CT Optimisation for Paediatric SPECT/CT Examinations. Sarah Bell
 CT Optimisation for Paediatric SPECT/CT Examinations Sarah Bell Sarah.bell14@nhs.net Outline 1. Introduction 2. Aims and Objectives 3. Methods 4. Results 5. Discussion 6. Conclusions 7. References Introduction
CT Optimisation for Paediatric SPECT/CT Examinations Sarah Bell Sarah.bell14@nhs.net Outline 1. Introduction 2. Aims and Objectives 3. Methods 4. Results 5. Discussion 6. Conclusions 7. References Introduction
8/18/2011. Acknowledgements. Managing Pediatric CT Patient Doses INTRODUCTION
 Managing Pediatric CT Patient Doses Keith J. Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR President X-Ray Computations, Inc. Boston, Massachusetts Acknowledgements Marilyn Goske, MD John Boone, PhD Cynthia McCollough, PhD
Managing Pediatric CT Patient Doses Keith J. Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR President X-Ray Computations, Inc. Boston, Massachusetts Acknowledgements Marilyn Goske, MD John Boone, PhD Cynthia McCollough, PhD
Introduction and Background
 CT Lung Cancer Screening and the Medical Physicist: Background, Findings and Participant Dosimetry Summary of the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST) Randell Kruger, PhD, DABR Medical Physics Section
CT Lung Cancer Screening and the Medical Physicist: Background, Findings and Participant Dosimetry Summary of the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST) Randell Kruger, PhD, DABR Medical Physics Section
CATH LAB SYMPOSIUM 2010
 CATH LAB SYMPOSIUM 2010 Low resistance system High Pressure in Capillaries to filter plasma RBF: 1.2-1.3 L/min (25% of C.O.) Low AV difference ( shunt ) Kidney: 14 ml O2/L blood Brain: 62 ml O2/L blood
CATH LAB SYMPOSIUM 2010 Low resistance system High Pressure in Capillaries to filter plasma RBF: 1.2-1.3 L/min (25% of C.O.) Low AV difference ( shunt ) Kidney: 14 ml O2/L blood Brain: 62 ml O2/L blood
Accounting for Imaging Dose
 Accounting for Imaging Dose High Profile Over-exposures Lead to Growing Concern FDA issues warning in October 2009-209 patients exposed to 8 times typical dose for CT brain perfusion scan (3-4 Gy) - Some
Accounting for Imaging Dose High Profile Over-exposures Lead to Growing Concern FDA issues warning in October 2009-209 patients exposed to 8 times typical dose for CT brain perfusion scan (3-4 Gy) - Some
Simon Nepveu 1, Irina Boldeanu 1, Yves Provost 1, Jean Chalaoui 1, Louis-Mathieu Stevens 2,3, Nicolas Noiseux 2,3, Carl Chartrand-Lefebvre 1,3
 Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Imaging with CT Angiography and Iterative Reconstruction: Quantitave Evaluation of Radiation Dose Reduction and Image Quality Simon Nepveu 1, Irina Boldeanu 1, Yves Provost
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Imaging with CT Angiography and Iterative Reconstruction: Quantitave Evaluation of Radiation Dose Reduction and Image Quality Simon Nepveu 1, Irina Boldeanu 1, Yves Provost
Doses from pediatric CT examinations in Norway Are pediatric scan protocols developed and in daily use?
 Doses from pediatric CT examinations in Norway Are pediatric scan protocols developed and in daily use? Eva Godske Friberg * Norwegian Radiation Protection Authority, P.O. Box, Østerås, Norway Abstract.
Doses from pediatric CT examinations in Norway Are pediatric scan protocols developed and in daily use? Eva Godske Friberg * Norwegian Radiation Protection Authority, P.O. Box, Østerås, Norway Abstract.
Hi RES Extremity - (04/18/2011) CTDI: ~13 mgy per acquisition Used for evaluation of: Ankle Elbow Hand Wrist Foot /Calcaneous Toes Fingers
 P a g e 1 Hi RES Extremity - (04/18/2011) CTDI: ~13 mgy per acquisition Used for evaluation of: Ankle Elbow Hand Wrist Foot /Calcaneous Toes Fingers Billing: 1. CT Upper/Lower Extremity of concern without
P a g e 1 Hi RES Extremity - (04/18/2011) CTDI: ~13 mgy per acquisition Used for evaluation of: Ankle Elbow Hand Wrist Foot /Calcaneous Toes Fingers Billing: 1. CT Upper/Lower Extremity of concern without
CT Low Dose Lung Cancer Screening. Part I. Journey to LDCT LCS Program
 CT Low Dose Lung Cancer Screening Part I Journey to LDCT LCS Program Paul Johnson, M.S., DABHP, DABR Cleveland Clinic September 26, 2015 Lung Caner is No. 1 In Cancer Related Death In The United States
CT Low Dose Lung Cancer Screening Part I Journey to LDCT LCS Program Paul Johnson, M.S., DABHP, DABR Cleveland Clinic September 26, 2015 Lung Caner is No. 1 In Cancer Related Death In The United States
Cancer Risks from CT Scans: Now We Have Data What Next?
 Cancer Risks from CT Scans: Now We Have Data What Next? David J. Brenner, PhD, DSc Center for Radiological Research Columbia University Medical Center djb3@columbia.edu There is no question that CT has
Cancer Risks from CT Scans: Now We Have Data What Next? David J. Brenner, PhD, DSc Center for Radiological Research Columbia University Medical Center djb3@columbia.edu There is no question that CT has
Reducing Radiation Dose in Body CT: A Primer on Dose Metrics and Key CT Technical Parameters
 Medical Physics and Informatics Review Maldjian and Goldman Reducing Radiation Dose in Body CT Medical Physics and Informatics Review FOCUS ON: Pierre D. Maldjian 1 Alice R. Goldman Maldjian PD, Goldman
Medical Physics and Informatics Review Maldjian and Goldman Reducing Radiation Dose in Body CT Medical Physics and Informatics Review FOCUS ON: Pierre D. Maldjian 1 Alice R. Goldman Maldjian PD, Goldman
Acknowledgments. A Specific Diagnostic Task: Lung Nodule Detection. A Specific Diagnostic Task: Chest CT Protocols. Chest CT Protocols
 Personalization of Pediatric Imaging in Terms of Needed Indication-Based Quality Per Dose Acknowledgments Duke University Medical Center Ehsan Samei, PhD Donald Frush, MD Xiang Li PhD DABR Cleveland Clinic
Personalization of Pediatric Imaging in Terms of Needed Indication-Based Quality Per Dose Acknowledgments Duke University Medical Center Ehsan Samei, PhD Donald Frush, MD Xiang Li PhD DABR Cleveland Clinic
CT angiography techniques. Boot camp
 CT angiography techniques Boot camp Overview Basic concepts Contrast administration arterial opacification Time scan acquisition during the arterial phase Protocol examples Helical non-gated CTA Pulmonary
CT angiography techniques Boot camp Overview Basic concepts Contrast administration arterial opacification Time scan acquisition during the arterial phase Protocol examples Helical non-gated CTA Pulmonary
Radiation Exposure 1980 to 2006
 Radiation Exposure 1980 to 2006 Background 3-6 msv/yr Natural (85% 45%) Radon Cosmic Rays Air travel Living at Altitude Man-made (15% 55%) Medical Imaging** mgy Radiation Therapy cgy Radiation Whole Body
Radiation Exposure 1980 to 2006 Background 3-6 msv/yr Natural (85% 45%) Radon Cosmic Rays Air travel Living at Altitude Man-made (15% 55%) Medical Imaging** mgy Radiation Therapy cgy Radiation Whole Body
Low Dose CT Lung Screening: What is Technically Required?
 Low Dose CT Lung Screening: What is Technically Required? COMP/CCPM Annual Scientific Meeting Ottawa, Ontario July 15 th, 2017 Yogesh Thakur, PhD, MCCPM Medical Physicist Lead and Regional RSO (X-Ray)
Low Dose CT Lung Screening: What is Technically Required? COMP/CCPM Annual Scientific Meeting Ottawa, Ontario July 15 th, 2017 Yogesh Thakur, PhD, MCCPM Medical Physicist Lead and Regional RSO (X-Ray)
Routine CT Chest + Abdomen WO
 Routine CT Chest + Abdomen WO Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA policies and protocols
Routine CT Chest + Abdomen WO Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA policies and protocols
Implementation of the 2012 ACR CT QC Manual in a Community Hospital Setting BRUCE E. HASSELQUIST, PH.D., DABR, DABSNM ASPIRUS WAUSAU HOSPITAL
 Implementation of the 2012 ACR CT QC Manual in a Community Hospital Setting BRUCE E. HASSELQUIST, PH.D., DABR, DABSNM ASPIRUS WAUSAU HOSPITAL Conflict of Interest Disclaimer Employee of Aspirus Wausau
Implementation of the 2012 ACR CT QC Manual in a Community Hospital Setting BRUCE E. HASSELQUIST, PH.D., DABR, DABSNM ASPIRUS WAUSAU HOSPITAL Conflict of Interest Disclaimer Employee of Aspirus Wausau
Chief Radiographer TEI Clinical Associate 2016
 MDCT Principles i and Applications Ε ΑGADAKOS MSc Ε. ΑGADAKOS MSc Chief Radiographer TEI Clinical Associate 2016 Aim To understand d recent technological advances in MSCT and how they can be effectively
MDCT Principles i and Applications Ε ΑGADAKOS MSc Ε. ΑGADAKOS MSc Chief Radiographer TEI Clinical Associate 2016 Aim To understand d recent technological advances in MSCT and how they can be effectively
Patient preparation and coronary CTA techniques. Gregory Kicska, M.D. Ph.D. University of Washington, Thoracic Imaging
 Patient preparation and coronary CTA techniques Gregory Kicska, M.D. Ph.D. University of Washington, Thoracic Imaging Overview 1. Patient preparation 2. Scanning techniques Patient preparation Preparation
Patient preparation and coronary CTA techniques Gregory Kicska, M.D. Ph.D. University of Washington, Thoracic Imaging Overview 1. Patient preparation 2. Scanning techniques Patient preparation Preparation
Outcomes in the NLST. Health system infrastructure needs to implement screening
 Outcomes in the NLST Health system infrastructure needs to implement screening Denise R. Aberle, MD Professor of Radiology and Bioengineering David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA 1 Disclosures I have
Outcomes in the NLST Health system infrastructure needs to implement screening Denise R. Aberle, MD Professor of Radiology and Bioengineering David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA 1 Disclosures I have
Tracking Doses in the Pediatric Population
 Tracking Doses in the Pediatric Population Frederic H. Fahey DSc Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School frederic.fahey@childrens.harvard.edu Disclosures Sadly, none that pay me any money! SNMMI
Tracking Doses in the Pediatric Population Frederic H. Fahey DSc Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School frederic.fahey@childrens.harvard.edu Disclosures Sadly, none that pay me any money! SNMMI
Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography procedures: Contrast media dilution from the venous to the systemic circulation
 Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography procedures: Contrast media dilution from the venous to the systemic circulation Petter Bugge Askeland Project thesis at the Faculty of Medicine UNIVERSITETET
Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography procedures: Contrast media dilution from the venous to the systemic circulation Petter Bugge Askeland Project thesis at the Faculty of Medicine UNIVERSITETET
CT dose survey data acquisition form
 CT dose survey data acquisition form CT Protocol page CT Head (acute stroke) C-spine (fracture) Chest (lung cancer) Chest High-Res. (interstitial lung disease) CTA (blood vessels) CTPA (PE) Abdomen (liver
CT dose survey data acquisition form CT Protocol page CT Head (acute stroke) C-spine (fracture) Chest (lung cancer) Chest High-Res. (interstitial lung disease) CTA (blood vessels) CTPA (PE) Abdomen (liver
The radiation dose in retrospective
 The radiation dose in retrospective gated tdcoronary computed td tomography (CCT) Saeed AL Ahmari, Ghormallah AL Zahrani, Sumiah AL Helali, Samir AL Dulikan, Abdullah Bafagih, HibaKhashojji Prince Sultan
The radiation dose in retrospective gated tdcoronary computed td tomography (CCT) Saeed AL Ahmari, Ghormallah AL Zahrani, Sumiah AL Helali, Samir AL Dulikan, Abdullah Bafagih, HibaKhashojji Prince Sultan
Neuro CT What s a Good Head Exam?
 Neuro CT What s a Good Head Exam? Rajiv Gupta, PhD, MD Neuroradiology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Outline What we need to see? Routine Head CT protocols Dose optimization strategies
Neuro CT What s a Good Head Exam? Rajiv Gupta, PhD, MD Neuroradiology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Outline What we need to see? Routine Head CT protocols Dose optimization strategies
Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose?
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose? To cite this article: M Smarda et
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose? To cite this article: M Smarda et
Debra Pennington, MD Director of Imaging Dell Children s Medical Center
 Debra Pennington, MD Director of Imaging Dell Children s Medical Center 1 Gray (Gy) is 1 J of radiation energy/ 1 kg matter (physical quantity absorbed dose) Diagnostic imaging doses in mgy (.001 Gy)
Debra Pennington, MD Director of Imaging Dell Children s Medical Center 1 Gray (Gy) is 1 J of radiation energy/ 1 kg matter (physical quantity absorbed dose) Diagnostic imaging doses in mgy (.001 Gy)
CURRENT CT DOSE METRICS: MAKING CTDI SIZE-SPECIFIC
 CURRENT CT DOSE METRICS: MAKING CTDI SIZE-SPECIFIC Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Acknowledgments John Boone, PhD Michael McNitt-Grey,
CURRENT CT DOSE METRICS: MAKING CTDI SIZE-SPECIFIC Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Acknowledgments John Boone, PhD Michael McNitt-Grey,
Application of CARE kv and SAFIRE in Contrast-Enhanced CT Examination on Thorax
 Application of CARE kv and SAFIRE in Contrast-Enhanced CT Examination on Thorax Poster No.: C-0013 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit Z. Dejian 1, X. Zhuodong 2, J. Hui 2, L. Xiao 3 ;
Application of CARE kv and SAFIRE in Contrast-Enhanced CT Examination on Thorax Poster No.: C-0013 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit Z. Dejian 1, X. Zhuodong 2, J. Hui 2, L. Xiao 3 ;
Prevention of Contrast induced Nephropathy
 55 th Annual Scientific Meeting of The Korean Society of Cardiology 11:50 12:10 Message from Nephrologists Dec 03, 2011 Prevention of Contrast induced Nephropathy Soo Wan Kim, MD, PhD Department of Internal
55 th Annual Scientific Meeting of The Korean Society of Cardiology 11:50 12:10 Message from Nephrologists Dec 03, 2011 Prevention of Contrast induced Nephropathy Soo Wan Kim, MD, PhD Department of Internal
Technology Assessment Institute: Summit on CT Dose Cardiac CT - Optimal Use of Evolving Scanner Technologies
 Cardiac CT - Optimal Use of Evolving Scanner Technologies P. Rogalla, M.D. Dept. of Medical Imaging University of Toronto Special thanks to Dr. Lembcke, Dr. Hein Charité, Berlin Disclosures No salaries
Cardiac CT - Optimal Use of Evolving Scanner Technologies P. Rogalla, M.D. Dept. of Medical Imaging University of Toronto Special thanks to Dr. Lembcke, Dr. Hein Charité, Berlin Disclosures No salaries
Ask EuroSafe Imaging. Tips & Tricks. CT Working Group. Optimization of scan length to reduce CT radiation dose
 Ask EuroSafe Imaging Tips & Tricks CT Working Group Optimization of scan length to reduce CT radiation dose Alban Gervaise (Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Nancy, FR) Mika Kortesniemi (HUS Medical Imaging
Ask EuroSafe Imaging Tips & Tricks CT Working Group Optimization of scan length to reduce CT radiation dose Alban Gervaise (Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Nancy, FR) Mika Kortesniemi (HUS Medical Imaging
8/1/2017. Financial Disclosures. Dose Tracking at MGH. How Dose Tracking Affected Protocol Optimization in a Tertiary Quaternary Healthcare Center
 How Dose Tracking Affected Protocol Optimization in a Tertiary Quaternary Healthcare Center Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD Webster Center for Quality and Safety Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
How Dose Tracking Affected Protocol Optimization in a Tertiary Quaternary Healthcare Center Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD Webster Center for Quality and Safety Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
Estimating Risks from CT Scans - in the Context of CT Scan Benefits
 Estimating Risks from CT Scans - in the Context of CT Scan Benefits David J. Brenner Center for Radiological Research Columbia University Medical Center djb3@cumc.columbia.edu There is no question that
Estimating Risks from CT Scans - in the Context of CT Scan Benefits David J. Brenner Center for Radiological Research Columbia University Medical Center djb3@cumc.columbia.edu There is no question that
Radiation Dose Optimization in Cardiac CT: A Technical Review. CHENG Wai Kwong. 17 May Contents
 Radiation Dose Optimization in Cardiac CT: A Technical Review CHENG Wai Kwong 17 May 2014 Contents 1. Introduction and background 2. Cardiac CT synchronization techniques 3. 4. Conclusion 1 Introduction
Radiation Dose Optimization in Cardiac CT: A Technical Review CHENG Wai Kwong 17 May 2014 Contents 1. Introduction and background 2. Cardiac CT synchronization techniques 3. 4. Conclusion 1 Introduction
Automatic Patient Centering for MDCT: Effect on Radiation Dose
 Patient Centering for MDCT CT Imaging Original Research Jianhai Li 1 Unni K. Udayasankar 1 Thomas L. Toth 2 John Seamans 2 William C. Small 1 Mannudeep K. Kalra 1,3 Li J, Udayasankar UK, Toth TL, Seamans
Patient Centering for MDCT CT Imaging Original Research Jianhai Li 1 Unni K. Udayasankar 1 Thomas L. Toth 2 John Seamans 2 William C. Small 1 Mannudeep K. Kalra 1,3 Li J, Udayasankar UK, Toth TL, Seamans
SOMATOM Drive System Owner Manual Dosimetry and imaging performance report
 www.siemens.com/healthcare SOMATOM Drive System Owner Manual Dosimetry and imaging performance report Table of contents 1 Dosimetry and imaging performance report 5 1.1 Dose information 5 1.1.1 General
www.siemens.com/healthcare SOMATOM Drive System Owner Manual Dosimetry and imaging performance report Table of contents 1 Dosimetry and imaging performance report 5 1.1 Dose information 5 1.1.1 General
Computed tomography Acceptance testing and dose measurements
 Computed tomography Acceptance testing and dose measurements Jonas Andersson Medical Physicist, Ph.D. Department of Radiation Sciences University Hospital of Norrland, Umeå Sweden Contents The Computed
Computed tomography Acceptance testing and dose measurements Jonas Andersson Medical Physicist, Ph.D. Department of Radiation Sciences University Hospital of Norrland, Umeå Sweden Contents The Computed
Bone Densitometry Radiation dose: what you need to know
 Bone Densitometry Radiation dose: what you need to know John Damilakis, PhD Associate Professor and Chairman University of Crete, Iraklion, Crete, GREECE Estimation of bone status using X-rays Assessment
Bone Densitometry Radiation dose: what you need to know John Damilakis, PhD Associate Professor and Chairman University of Crete, Iraklion, Crete, GREECE Estimation of bone status using X-rays Assessment
X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT
 Computed Tomography-Basic Principles and Good Practice X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT INSTRUCTORS: Dane Franklin, MBA, RT (R) (CT) Office hours will be Tuesdays from 5pm to 6pm CLASSROOM: TIME: REQUIRED
Computed Tomography-Basic Principles and Good Practice X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT INSTRUCTORS: Dane Franklin, MBA, RT (R) (CT) Office hours will be Tuesdays from 5pm to 6pm CLASSROOM: TIME: REQUIRED
Automated CT Protocol Design Advantages and Pitfalls of Algorithm-Based Technique Selection in Pediatrics. Disclosures 7/22/2014. Learning Objectives
 Automated CT Protocol Design Advantages and Pitfalls of Algorithm-Based Technique Selection in Pediatrics Robert MacDougall, M.Sc. Department of Radiology Boston Children s Hospital Disclosures 2 Learning
Automated CT Protocol Design Advantages and Pitfalls of Algorithm-Based Technique Selection in Pediatrics Robert MacDougall, M.Sc. Department of Radiology Boston Children s Hospital Disclosures 2 Learning
Whole Body CT Protocol Update 2018
 Whole Body CT Protocol Update 2018 10 th Nordic Course in Trauma Radiology Gothenburg, Sweden K.SHANMUGANATHAN M.D. Disclosure of Commercial Interest Neither I nor my immediate family members have a financial
Whole Body CT Protocol Update 2018 10 th Nordic Course in Trauma Radiology Gothenburg, Sweden K.SHANMUGANATHAN M.D. Disclosure of Commercial Interest Neither I nor my immediate family members have a financial
THE TUFFEST STUFF CT REGISTRY REVIEW Live Lecture Seminar SUNDAY CURRICULUM
 A. INJECTION TECHNIQUES a. Drug administration routes i. Oral ii. Buccal iii. Topical iv. Rectal v. Parenteral b. Injection techniques i. Hand ii. Mechanical injector c. Injection parameters i. Catheters
A. INJECTION TECHNIQUES a. Drug administration routes i. Oral ii. Buccal iii. Topical iv. Rectal v. Parenteral b. Injection techniques i. Hand ii. Mechanical injector c. Injection parameters i. Catheters
To Shield or Not to Shield? Lincoln L. Berland, M.D.
 To Shield or Not to Shield? Lincoln L. Berland, M.D. Disclosures Consultant to: Nuance, Inc. Page 2 Breast Radiation on CT Use of chest CT has increased in women vulnerable to cancer induction by radiation.
To Shield or Not to Shield? Lincoln L. Berland, M.D. Disclosures Consultant to: Nuance, Inc. Page 2 Breast Radiation on CT Use of chest CT has increased in women vulnerable to cancer induction by radiation.
Aquilion ONE: Pediatric Imaging. Richard Mather, PhD. Senior Manager, CT Clinical Science Toshiba America Medical Systems, Inc.
 Aquilion ONE: Pediatric Imaging Richard Mather, PhD Senior Manager, CT Clinical Science Toshiba America Medical Systems, Inc. The use of CT in pediatric diagnostic procedures has increased significantly
Aquilion ONE: Pediatric Imaging Richard Mather, PhD Senior Manager, CT Clinical Science Toshiba America Medical Systems, Inc. The use of CT in pediatric diagnostic procedures has increased significantly
With increased use of contrast media (CM), interest in
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Langner S. Stumpe M. Kirsch M. Petrik N. Hosten No Increased Risk for Contrast-Induced Nephropathy after Multiple CT Perfusion Studies of the Brain with a Nonionic, Dimeric, Iso-Osmolal
ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Langner S. Stumpe M. Kirsch M. Petrik N. Hosten No Increased Risk for Contrast-Induced Nephropathy after Multiple CT Perfusion Studies of the Brain with a Nonionic, Dimeric, Iso-Osmolal
Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement
 Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement 3 rd Annual Imaging & Physiology Summit November 20-21, 21, 2009 Seoul, Korea Wm. Guy Weigold, MD, FACC Cardiovascular
Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement 3 rd Annual Imaging & Physiology Summit November 20-21, 21, 2009 Seoul, Korea Wm. Guy Weigold, MD, FACC Cardiovascular
Patient / Organ Dose in CT
 Patient / Organ Dose in CT Patient specific and organ dose estimation H.D. Nagel Dr. HD Nagel, Science & Technology for Radiology Buchholz / Germany www.sascrad.com 1 Topics CTDI & patient dose SSDE Organ
Patient / Organ Dose in CT Patient specific and organ dose estimation H.D. Nagel Dr. HD Nagel, Science & Technology for Radiology Buchholz / Germany www.sascrad.com 1 Topics CTDI & patient dose SSDE Organ
Calculation of Effective Doses for Radiotherapy Cone-Beam CT and Nuclear Medicine Hawkeye CT Laura Sawyer
 Calculation of Effective Doses for Radiotherapy Cone-Beam CT and Nuclear Medicine Hawkeye CT Laura Sawyer Department of Medical Physics and Bioengineering, Royal United Hospital, Bath Overview Varian Acuity
Calculation of Effective Doses for Radiotherapy Cone-Beam CT and Nuclear Medicine Hawkeye CT Laura Sawyer Department of Medical Physics and Bioengineering, Royal United Hospital, Bath Overview Varian Acuity
Triple Rule-out using 320-row-detector volume MDCT: A comparison of the wide volume and helical modes
 Triple Rule-out using 320-row-detector volume MDCT: A comparison of the wide volume and helical modes Poster No.: C-0488 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E.-J. Kang,
Triple Rule-out using 320-row-detector volume MDCT: A comparison of the wide volume and helical modes Poster No.: C-0488 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E.-J. Kang,
Outline. Lifetime Attributable Risk 10 mgy in 100,000 exposed persons (BEIR VII 2006) SPECT/CT and PET/CT Dosimetry
 SPECT/CT and PET/CT Dosimetry Lifetime Attributable Risk 10 mgy in 100,000 exposed persons (BEIR VII 2006) All Solid Tumors Leukemia Frederic H. Fahey DSc Male Female Male Female Children s Hospital Boston
SPECT/CT and PET/CT Dosimetry Lifetime Attributable Risk 10 mgy in 100,000 exposed persons (BEIR VII 2006) All Solid Tumors Leukemia Frederic H. Fahey DSc Male Female Male Female Children s Hospital Boston
Low-dose and High-resolution Cardiac Imaging with Revolution CT
 GE Healthcare Case study Low-dose and High-resolution Cardiac Imaging with Revolution CT Prof. Philipp A. Kaufmann, M.D. Ronny R. Buechel, M.D. Fran Mikulicic, M.D. Dominik C. Benz, M.D. University of
GE Healthcare Case study Low-dose and High-resolution Cardiac Imaging with Revolution CT Prof. Philipp A. Kaufmann, M.D. Ronny R. Buechel, M.D. Fran Mikulicic, M.D. Dominik C. Benz, M.D. University of
WHAT WE CAN LEARN FROM CURRENT CARDIAC CT TECHNOLOGY AND WHAT S NEXT FOR CARDIAC?
 WHAT WE CAN LEARN FROM CURRENT CARDIAC CT TECHNOLOGY AND WHAT S NEXT FOR CARDIAC? Gilbert Raff, MD Director of Advanced Cardiovascular Imaging Oakland University William Beaumont Medical School DISCLOSURES
WHAT WE CAN LEARN FROM CURRENT CARDIAC CT TECHNOLOGY AND WHAT S NEXT FOR CARDIAC? Gilbert Raff, MD Director of Advanced Cardiovascular Imaging Oakland University William Beaumont Medical School DISCLOSURES
Ultrasound. Computed tomography. Case studies. Utility of IQon Spectral CT in. cardiac imaging
 Ultrasound Computed tomography Case studies Utility of IQon Spectral CT in cardiac imaging Cardiac imaging is a challenging procedure where it is necessary to image a motion-free heart. This requires a
Ultrasound Computed tomography Case studies Utility of IQon Spectral CT in cardiac imaging Cardiac imaging is a challenging procedure where it is necessary to image a motion-free heart. This requires a
N-acetylcysteine in the prevention of contrast agent-induced nephrotoxicity in patients undergoing computed tomography studies
 RESEARCH REPORT N-acetylcysteine in the prevention of contrast agent-induced nephrotoxicity in patients undergoing computed tomography studies Hossein Khalili, Simin Dashti-Khavidaki, Hamed Tabifar, Nasrin
RESEARCH REPORT N-acetylcysteine in the prevention of contrast agent-induced nephrotoxicity in patients undergoing computed tomography studies Hossein Khalili, Simin Dashti-Khavidaki, Hamed Tabifar, Nasrin
CT Urography. Ureter. Stuart G. Silverman, M.D.
 CT Urography Stuart G. Silverman, M.D. Professor of Radiology Harvard Medical School Director, Abdominal Imaging and Intervention Brigham and Women s Hospital Ureter Boston, MA CT Urography Stuart G. Silverman,
CT Urography Stuart G. Silverman, M.D. Professor of Radiology Harvard Medical School Director, Abdominal Imaging and Intervention Brigham and Women s Hospital Ureter Boston, MA CT Urography Stuart G. Silverman,
Evaluating the Efficacy of Single Daily Dose of 1200mg of N-Acetyl-Cysteine in Preventing Contrast Agent-Associated Nephrotoxicity
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 6 Number 1 Evaluating the Efficacy of Single Daily Dose of 1200mg of N-Acetyl-Cysteine in Preventing Contrast Agent-Associated Nephrotoxicity
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 6 Number 1 Evaluating the Efficacy of Single Daily Dose of 1200mg of N-Acetyl-Cysteine in Preventing Contrast Agent-Associated Nephrotoxicity
A study on CT pulmonary angiography at low kv and low-concentration contrast medium using iterative reconstruction.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (17): 7683-7687 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on CT pulmonary angiography at low kv and low-concentration contrast medium using iterative reconstruction. Yanhe
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (17): 7683-7687 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on CT pulmonary angiography at low kv and low-concentration contrast medium using iterative reconstruction. Yanhe
Contrast Induced Nephropathy
 Contrast Induced Nephropathy O CIAKI refers to an abrupt deterioration in renal function associated with the administration of iodinated contrast media O CIAKI is characterized by an acute (within 48 hours)
Contrast Induced Nephropathy O CIAKI refers to an abrupt deterioration in renal function associated with the administration of iodinated contrast media O CIAKI is characterized by an acute (within 48 hours)
Radiation related cancer risk & benefit/risk assessment for screening procedures
 WHO Workshop on Justification of CT for IHA 15-17 Oct 2014 Radiation related cancer risk & benefit/risk assessment for screening procedures Elke A. Nekolla BfS Federal Office for Radiation Protection Radiation
WHO Workshop on Justification of CT for IHA 15-17 Oct 2014 Radiation related cancer risk & benefit/risk assessment for screening procedures Elke A. Nekolla BfS Federal Office for Radiation Protection Radiation
ASDIN 10th Annual Scientific Meeting Final. COI Disclosure Statement. Intravenous Contrast Media: Basics
 COI Disclosure Statement There are no financial relationships or conflicts of interest to disclose with this presentation Melissa Hicks, BA, RT(R)(VI) Vascular Interventional Technologist University of
COI Disclosure Statement There are no financial relationships or conflicts of interest to disclose with this presentation Melissa Hicks, BA, RT(R)(VI) Vascular Interventional Technologist University of
Benefits and Risks of Cancer Imaging
 Benefits and Risks of Cancer Imaging Jeffrey T. Yap, PhD http://catalyst.harvard.edu/ services/imagingconsulting.html Senior Diagnostic Physicist, Department of Imaging, DFCI Assistant Professor of Radiology,
Benefits and Risks of Cancer Imaging Jeffrey T. Yap, PhD http://catalyst.harvard.edu/ services/imagingconsulting.html Senior Diagnostic Physicist, Department of Imaging, DFCI Assistant Professor of Radiology,
 Page 1 of 5 Patient Safety: Radiation Dose in X-Ray and CT Exams What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate the
Page 1 of 5 Patient Safety: Radiation Dose in X-Ray and CT Exams What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate the
Contrast media Purpose of using contrast Contrast reaction Nephrotoxicity from contrast Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis When should contrast be used
 Contrast vs Non-Contrast When to Order Stephen McManus, M.D. Contrast media Purpose of using contrast Contrast reaction Nephrotoxicity from contrast Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis When should contrast be
Contrast vs Non-Contrast When to Order Stephen McManus, M.D. Contrast media Purpose of using contrast Contrast reaction Nephrotoxicity from contrast Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis When should contrast be
