Cellular and Tissue Effects. Pathophysiology of the Burn Wound. Special Topics: Thermal Burns & Smoke Inhalation
|
|
|
- Aron Garrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Special Topics: Thermal Burns & Smoke Inhalation MEDICAL RESPONDER AND RECEIVER SEMINAR; EXPLOSION AND BLAST INJURIES Pathophysiology of the Burn Wound The burn wound is the source of virtually all ill effects seen in the burn patient. Removal of the burn wound results in much improved patient outcome. Cellular and Tissue Effects Damage to the cells and tissue is a function of temperature and time. Sustained temperatures between 40C and 44C cause various enzymes to malfunction. Higher temperatures cause protein breakdown. 1
2 Cellular and Tissue Effects Zone of coagulation - Protein coagulation and cell necrosis * Zone of stasis - Cell initially viable, but blood flow compromised Zone of hyperemia - Minimal cellular injury, but increased blood flow and vasodilatation Zones of Injury DERMIS \ \ Zonao,Sta*l& i Zono of Hyparwnta _ j j Source Fellcune DV. Matte* Kt, Moo*«tt Trauma, 6th edition I*to//wymy.acmcsu'gery com Copy 'UJtit c The McGraw-Hill CompameC, Inc All HgtiU revcrvrd Systemic Effects Consumption of clotting factors and platelets Suppression of cellular immunity Myocardial depression * Pulmonary dysfunction * Hypermetabolism Fat and skeletal muscle catabolism Renal dysfunction 2
3 Primary Survey Airway: - Can deteriorate abruptly and rapidly - Airway obstruction due to progressive edema Breathing - Circumferential full thickness burns Lunginjury can affect oxygenation - Circulation - BP, Pulse, circumferential burns and third-spacing * Disability - Neurologic status may be affected due tomultiplecauses Exposure - Pay attention to hypothermia-induced stress Inhalation Injury - Upper airway burns $ Tracheobronchial injury - Lower airway burns Lungs -Toxic compounds Carbon monoxide Cyanide Ziad Kazzi 2012 Smoke Inhalation Smoke particles - Clinical manifestations: S3 Stridor, cough, shortness of breath Carbonaceous sputum, soot in airway, singed nasal vibrissae, facial burns - Can lead to rapid airway compromise - Surgical airway may be needed if oral intubation is not successful 3
4 Carbon Monoxide-Mechanism Binds hemoglobin to form carboxyhemoglobin that is unable to carry oxygen May inhibit to a certain degree cytochrone oxidase Carbon Monoxide-Clinical Most common presentation: - Flu-like illness CNS CV Carbon Monoxide-Labs Carboxyhemoglobin level (Arterial or Venous) Creatine kinase EKG, CXR 4
5 1Q0% Oxygen therapy Carbon Monoxide Hyperbaric oxygen therapy Long-term Effects Hydrogen Cyanide-Mechanism * Inhibits cytrochrome oxidase Cells are unable to use oxygen Anerobic metabolism prevails Lactate accumulates 5
6 CYTOlOi H3C =N / 5/ Im**" PPKpMt!P T- _ d,..*h--. 2H/3 Hyrdrogen Cyanide-Clinical Clinical: CNS -CV - Bitter almond: only 60% of population can detect it. - Cherry red skin, fundoscopic exami Hydrogen Cyanide-Labs -Lactic acidosis with a lactate > 7 mmol/l -Elevated venous 02 saturation >90% -Low 02 extraction when comparing a Venous P02 with and Arterial P02 6
7 Cyanide Antidote Kit AKA the Lilly kit Contains: -Amyl nitrite pearls -Sodium nitrite -Sodium thiosulfate I Tÿl! " : it J! V ' Hydroxocobalamin 5 g IV over 15 minutes May repeat dose if no response and patient is critically ill Adverse Effects of Hydroxocobalamin? * r ' * 2 7
8 History Secondary Survey Circumstances Cause mziad Kazzi 2012 <0 Secondary Survey * Duration of contact with flame Method used to extinguish the fire * Substances placed on the burns during pre hospital/bystander wound care Secondary Survey Setting - Indoors versus outdoors Associated trauma - Blast injuries Associated smoke inhalation 8
9 Past Medical History Comorbid conditions - Diabetes, renal failure, cardiovascular disease - Immunocompromised state - Previous disabilities and special needs AMPLE Allergies Medications Last meal Tetanus status Depth of Burn First degree Second degree or partial thickness - Superficial and deep Third degree or full thickness Fourth degree 9m tplder L l Hypcdermu'US 9
10 Burn Depth Estimation First degree: painful erythematous like a sunburn Partial thickness or second degree: painful, blisters, erythematous Full thickness or third degree: insensate, pale, without viable hair follicles, cadaveric/leathery consistency to palpation First Degree Burn *j 3 r " j / / fc j / /) Safes 10
11 Second Degree Burn &L _ Egg Explosion from Microwave Ls. Ziad Kazri 2012 (0 r: \ M Ziad Kaui
12 fr- ' ; Ziad Kazzi 2012 % r2012 t> mthird Degree Burn 12
13 , 10/2/2015 f VT. : *1 13
14 Burn Surface Area mestimation The patient's hand including fingers is approximately 1% of Total BSA Rule of 9 4.S >.9 9 &.. / tf v * W CJLL-) A r EH ; [ÿleg LEG TOTAL BURN RELATIVE PERCENTAGEOF BODY SURFACE AREA AFFECTED BY GROWTH ARE t TAGEO 1 TS 10 ~1S ADULT HIS fg-g-?- j 14
15 The Berkow Chart Tabic 30 3 Btrfcow chart Tor Estimation el Bum Size in children 3-* Y*4 Jppw arrr 4 Foot Assessment for Perfusion/Ventilation Circumferential full thickness burns -Extremity perfusion may be compromised -Ventilation may be compromised V, 1 ', 15
16 Special Consideration-Pediatrics Larger surface area of head More susceptible to hypothermia Moral support to patient and parents Fluid Resuscitation Fluid is determined by the severity of injury Amount of 2"a and 3ra degree burn Lactated ringers Initial fluid determined by parkland formula - 2-4cc/kg/%TBSA - 'A over the first 8 hours DO NOT BOLUS Titrate fluid to urine output cc/hour Fluid Resuscitation FORMULA CRYSTALLOID Parkland 4 ml/kg/%tbsa None burn Brooke Galveston (Pediatric) 1.5 ml/kg/%tbsa 0,5 ml/kg/% TBSA 2L burn burn 5000 ml/m2 None burned ml/m2 total NONE None Adapted from Feliciano 16
17 Maintenance Fluids Note that maintenance fluids need to be added in children to the Parkland formula. When using the Galveston formula, maintenance fluids are already included. Wound Care If the patient is to be transferred, cover the burns with sterile, dry, towels or sheets * Do not soak the burns or wrap with wet towels, this may induce hypothermia and worsen outcome. \ / Ziad Kazzi 2012 Q 17
18 Debridement -2S, Ziad Ka2Zi 2012 P Ziad Kazzi 2012 O 18
19 Job Well Done! 7tad Kÿy7i?017 (0 Antispectic scrub - Chlorhexidine versus Povidone-Iodine Cleansing Solution Ointments Silver preparations (e.g., silver sulfadiazine) - 5 mm layer every 24 hours * Sulfa allergy Staining of skin Silver nitrate (0.5%) - Can be used in sulfa allergy - less burn eschar penetration 19
20 Ointments Acticoat silver based dressing - No need for dressing change - Need for frequent application of silver nitrate Mafenide Acetate (Sulfamylon ) - Sulfonamide. Excellent antibiotic coverage - Cartilage Ointments Neosporin, Polysporin and Bacitracin are the most commonly used. Neosporin activity is due to the combination of three different types of antibiotics with different spectra: Bacitracin (gram-positive activity) Neomycin (gram-negative activity) Polymyxin B (gram-negative activity) Escharotomy- Indications Used to treat full thickness (third-degree) circumferential burns. Underlying tissues become constricted due to the eschar's loss of elasticity, leading to impaired circulation distal to the wound. The ability to ventilate a patient may be impaired by a circumferential chest burn. 20
21 10/2/2015 Escharotomy- Description H shaped incision ( hi r 21
22 \ V A Transfer to Burn Center Partial thickness burns >10% TBSA. * Burns involving the face, hands, feet, genitalia, perineum, or major joints. Third degree burns in any age group. Electrical burns, including lightning. Chemical burns. Inhalation injury. Burns in patients with pre-existing medical problems. Combination of burns and trauma. 22
23 *rr r, r T.r m P.. \ =% :: Questions or Comments? 23
EmergencyKT: Management of Thermal Injury in Adult Patients
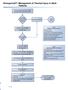 EmergencyKT: Management of Thermal Injury in Adult Patients Remove patient from source of injury, including burned clothing and jewelry Does patient appear to have minor burns? (See Box A) No Notify Burn
EmergencyKT: Management of Thermal Injury in Adult Patients Remove patient from source of injury, including burned clothing and jewelry Does patient appear to have minor burns? (See Box A) No Notify Burn
BURNS MODULE. In the paediatric population consider non-accidental injury as a mechanism for burn injuries.
 BURNS MODULE INTRODUCTION Burns are a common cause of trauma. Most burn injuries are a result of flame burns, with scalds also occurring commonly. Electrical and chemical burns are less common. 1 Concurrent
BURNS MODULE INTRODUCTION Burns are a common cause of trauma. Most burn injuries are a result of flame burns, with scalds also occurring commonly. Electrical and chemical burns are less common. 1 Concurrent
PEDIATRIC TRAUMA I: ABDOMINAL TRAUMA BURNS. December 19, 2012
 PEDIATRIC TRAUMA I: ABDOMINAL TRAUMA BURNS Niel F. Miele,, M.D. December 19, 2012 EPIDEMIOLOGY Major Trauma responsible for
PEDIATRIC TRAUMA I: ABDOMINAL TRAUMA BURNS Niel F. Miele,, M.D. December 19, 2012 EPIDEMIOLOGY Major Trauma responsible for
Burn Priorities of Care: Triage/Treatment/Transfer. Via Christi Regional Burn Center Sarah Fischer, MSN, RN
 Burn Priorities of Care: Triage/Treatment/Transfer Via Christi Regional Burn Center Sarah Fischer, MSN, RN Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Identify American Burn Association referral criteria
Burn Priorities of Care: Triage/Treatment/Transfer Via Christi Regional Burn Center Sarah Fischer, MSN, RN Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Identify American Burn Association referral criteria
Children's National Medical Center The Division of Trauma and Burn Burn Education Module Post-test
 Children's National Medical Center The Division of Trauma and Burn Burn Education Module Post-test Purpose: To provide nurses with on overview of burn injuries in pediatric patients. Learning Objectives:
Children's National Medical Center The Division of Trauma and Burn Burn Education Module Post-test Purpose: To provide nurses with on overview of burn injuries in pediatric patients. Learning Objectives:
Wisecracks 1. What are the indications for an escharotomy 2. What are the primary considerations in mechanical ventilation of burn patients
 Chapter 63 Thermal Burns Episode Overview Questions 1. List zones of burns 2. List 6 indications for intubation in the burn patient 3. List and describe 2 formulas for fluid resuscitation 4. Describe depth
Chapter 63 Thermal Burns Episode Overview Questions 1. List zones of burns 2. List 6 indications for intubation in the burn patient 3. List and describe 2 formulas for fluid resuscitation 4. Describe depth
Pediatric Burn Management Justin D. Klein, MD Associate Burn Director Lisa C. Vitale, RN Burn Program Coordinator
 Pediatric Burn Management Justin D. Klein, MD Associate Burn Director Lisa C. Vitale, RN Burn Program Coordinator Lecture Overview Burn statistics and etiologies Pre-hospital evaluation Anatomy of a burn
Pediatric Burn Management Justin D. Klein, MD Associate Burn Director Lisa C. Vitale, RN Burn Program Coordinator Lecture Overview Burn statistics and etiologies Pre-hospital evaluation Anatomy of a burn
Approved By: Airway and Breathing A. Initially give humidified high flow oxygen at 15 L (100%) using a nonrebreather
 Subject: BURN CARE CLINICAL GUIDELINE Originator: Approval Date: 2015 Approved By: Policy: All burn patients presenting to XXXXXX Hospital will have appropriate assessment, stabilization and evaluation
Subject: BURN CARE CLINICAL GUIDELINE Originator: Approval Date: 2015 Approved By: Policy: All burn patients presenting to XXXXXX Hospital will have appropriate assessment, stabilization and evaluation
IMMEDIATE EMERGENCY BURN CARE » THERMAL BURNS » ELECTRICAL BURNS » CHEMICAL BURNS FIRST AID FOR THE THREE MAJOR CATEGORIES
 IMMEDIATE EMERGENCY BURN CARE 1. Treat according to BLS or ACLS Protocol 2. Use airway and C-Spine precautions. 3. Stop the burning process. FIRST AID FOR THE THREE MAJOR CATEGORIES» THERMAL BURNS + Stop
IMMEDIATE EMERGENCY BURN CARE 1. Treat according to BLS or ACLS Protocol 2. Use airway and C-Spine precautions. 3. Stop the burning process. FIRST AID FOR THE THREE MAJOR CATEGORIES» THERMAL BURNS + Stop
Burn injury. A : patent airway with smoking inhalation, stridor. D: E4V5M6,pupil 2mm RTLBE
 Burn injury Pinyong Uthaitas Emergency Department Faculty of Medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital A Thai man 52 year old came to the hospital due to flam burn ½ hr ago at his house. He gain conscious but hoarseness
Burn injury Pinyong Uthaitas Emergency Department Faculty of Medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital A Thai man 52 year old came to the hospital due to flam burn ½ hr ago at his house. He gain conscious but hoarseness
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 46 Caring for Clients with Burns Types of Burns Thermal Dry heat flame Moist heat steam or hot liquid
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 46 Caring for Clients with Burns Types of Burns Thermal Dry heat flame Moist heat steam or hot liquid
Management of Acute Burn Injuries: The First 24 Hours
 Speaker Disclosure I, Debbie Harrell, MSN, RN, NE BC, have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss off label uses of any pharmaceutical products or medical devices. Management of Acute
Speaker Disclosure I, Debbie Harrell, MSN, RN, NE BC, have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss off label uses of any pharmaceutical products or medical devices. Management of Acute
Burns. A Comprehensive Review Assessment & Management
 Burns A Comprehensive Review Assessment & Management 1 Objectives Understand types of Burns Understand the pathophysiology of the Burns Understand Rule of Nine Understand Classification of Burns Identify
Burns A Comprehensive Review Assessment & Management 1 Objectives Understand types of Burns Understand the pathophysiology of the Burns Understand Rule of Nine Understand Classification of Burns Identify
Dóra Ujvárosy MD. Medical University of Debrecen Oxyology and Emergency Department
 Dóra Ujvárosy MD. Medical University of Debrecen Oxyology and Emergency Department Functions Definition A burn is a type of injury to the skin caused by heat, electricity, chemicals, light, radiation or
Dóra Ujvárosy MD. Medical University of Debrecen Oxyology and Emergency Department Functions Definition A burn is a type of injury to the skin caused by heat, electricity, chemicals, light, radiation or
Burn Injuries & Its Management M JARI.MD
 Burn Injuries & Its Management M JARI.MD 1 BURNS Wounds caused by exposure to: 1. excessive heat 2. Chemicals 3. fire/steam 4. radiation 5. electricity 2 BURNS Results in 10-20 thousand deaths annually
Burn Injuries & Its Management M JARI.MD 1 BURNS Wounds caused by exposure to: 1. excessive heat 2. Chemicals 3. fire/steam 4. radiation 5. electricity 2 BURNS Results in 10-20 thousand deaths annually
The immediate management of burns patients should be similar to management of trauma.
 CATS Clinical Guideline Burns The National Burn Care Review recommends that children with burns should be treated in a Burn Centre. Chelsea and Westminster may take non-ventilated children, Broomfield
CATS Clinical Guideline Burns The National Burn Care Review recommends that children with burns should be treated in a Burn Centre. Chelsea and Westminster may take non-ventilated children, Broomfield
At the conclusion of this course the learner will be able to
 Objectives At the conclusion of this course the learner will be able to 1. Discuss basic anatomy and pathophysiology of burns 2. Describe burn injuries in terms of size, depth, coloration and characteristics
Objectives At the conclusion of this course the learner will be able to 1. Discuss basic anatomy and pathophysiology of burns 2. Describe burn injuries in terms of size, depth, coloration and characteristics
Pediatrics Grand Rounds 1 June University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio. Management of Burn Wounds. Management of Burn Wounds
 Management of Burn Wounds Management of Burn Wounds History of Burn Care Pathophysiology of Burn Lillian F. Liao, MD, MPH Division of Trauma and Emergency Surgery Department of Surgery UTHSCSA Acute burn
Management of Burn Wounds Management of Burn Wounds History of Burn Care Pathophysiology of Burn Lillian F. Liao, MD, MPH Division of Trauma and Emergency Surgery Department of Surgery UTHSCSA Acute burn
Thermal Burns PFN: SOMEML07. Terminal Learning Objective. References. Hours: 3.0 Instructor: Action: Communicate knowledge of thermal burns
 Thermal Burns PFN: SOMEML07 Hours: 3.0 Instructor: Slide 1 Terminal Learning Objective Action: Communicate knowledge of thermal burns Condition: Given a lecture in a classroom environment Standard: Received
Thermal Burns PFN: SOMEML07 Hours: 3.0 Instructor: Slide 1 Terminal Learning Objective Action: Communicate knowledge of thermal burns Condition: Given a lecture in a classroom environment Standard: Received
Burn wounds - Determining the size and type degree
 1 Burn wounds - Determining the size and type degree Determining surface area of burn (Open hand only for small burns) 1 2 Burn depth Most burns are a combination of superficial and deeper burns and the
1 Burn wounds - Determining the size and type degree Determining surface area of burn (Open hand only for small burns) 1 2 Burn depth Most burns are a combination of superficial and deeper burns and the
Lecture Notes. Chapter 9: Smoke Inhalation Injury and Burns
 Lecture Notes Chapter 9: Smoke Inhalation Injury and Burns Objectives List the factors that influence mortality rate Describe the nature of smoke inhalation and the fire environment Recognize the pulmonary
Lecture Notes Chapter 9: Smoke Inhalation Injury and Burns Objectives List the factors that influence mortality rate Describe the nature of smoke inhalation and the fire environment Recognize the pulmonary
EMERGENCYROOM BURN MANAGEMENT
 EMERGENCYROOM INITIAL ASSESSMENT PRIMARY SURVEY A = Airway and C-spine immobilization B = Breathing and Ventilation C = Circulation D = Disability, Neurologic Deficit E = Expose (remove all clothing and
EMERGENCYROOM INITIAL ASSESSMENT PRIMARY SURVEY A = Airway and C-spine immobilization B = Breathing and Ventilation C = Circulation D = Disability, Neurologic Deficit E = Expose (remove all clothing and
Current Trends in Burn Care
 Objectives Current Trends in Burn Care Jordan Murphy, BSN, CFRN Clinical Educator-KY/FL PHI Air Medical Describes normal skin anatomy. Differentiates pathophysiology related to etiology of injury. Identify
Objectives Current Trends in Burn Care Jordan Murphy, BSN, CFRN Clinical Educator-KY/FL PHI Air Medical Describes normal skin anatomy. Differentiates pathophysiology related to etiology of injury. Identify
Burns Management in the Emergency Department
 Management in the Emergency Department (Referral Proforma) Time/Date of injury (24hr) Patient demographic data sticker Airway Please remember to protect C-spine until clinically cleared as stable Administer
Management in the Emergency Department (Referral Proforma) Time/Date of injury (24hr) Patient demographic data sticker Airway Please remember to protect C-spine until clinically cleared as stable Administer
Chapter 23 Caring for Clients with Burns
 Chapter 23 Caring for Clients with Burns Burn Injuries 4500 people die from burns each year High risk group ~ children and the elderly The most common cause of burns Smoking material Scalding Lighting
Chapter 23 Caring for Clients with Burns Burn Injuries 4500 people die from burns each year High risk group ~ children and the elderly The most common cause of burns Smoking material Scalding Lighting
BLS, ILS, ALS OTEP BURNS BURN INTRODUCTION TYPES OF BURNS
 BURNS BLS, ILS, ALS OTEP While we do understand this presentation is an instructional tool for all levels of certification, taking this into consideration everyone taking this class must remember that
BURNS BLS, ILS, ALS OTEP While we do understand this presentation is an instructional tool for all levels of certification, taking this into consideration everyone taking this class must remember that
Thermal Injuries. Manika Bhandari, Malika Bhola, Rucha Desai, Dhruvika Joshi, Abir Shamim Life Science 4M03
 Thermal Injuries Manika Bhandari, Malika Bhola, Rucha Desai, Dhruvika Joshi, Abir Shamim Life Science 4M03 INTRODUCTION Anatomy of the skin The skin has three anatomical layers Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous
Thermal Injuries Manika Bhandari, Malika Bhola, Rucha Desai, Dhruvika Joshi, Abir Shamim Life Science 4M03 INTRODUCTION Anatomy of the skin The skin has three anatomical layers Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous
INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES. When the student has finished this module, he/she will be able to:
 Burn Care and Management WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September 2017, Expires September 2019 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2017 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG,
Burn Care and Management WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September 2017, Expires September 2019 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2017 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG,
Advanced Paediatric Nursing. Burn Trauma. 26 April Wong Tze Wing NC (Burns), Burns Centre, Surgery, PWH
 Advanced Paediatric Nursing Burn Trauma 26 April 2016 Wong Tze Wing NC (Burns), Burns Centre, Surgery, PWH Objective: Understand burn trauma in children Understand Important nursing interventions in burn
Advanced Paediatric Nursing Burn Trauma 26 April 2016 Wong Tze Wing NC (Burns), Burns Centre, Surgery, PWH Objective: Understand burn trauma in children Understand Important nursing interventions in burn
INITIAL CARE AND TREATMENT OF BURN INJURIES. November 10,
 INITIAL CARE AND TREATMENT OF BURN INJURIES 2 11/10/2012 November 10, 2012 2 Oregon Burn Center Only burn center in Oregon and SW Washington New unit 16 beds, 20,000 square feet Opened in February 2002
INITIAL CARE AND TREATMENT OF BURN INJURIES 2 11/10/2012 November 10, 2012 2 Oregon Burn Center Only burn center in Oregon and SW Washington New unit 16 beds, 20,000 square feet Opened in February 2002
Speaker Disclosure Emergent Burn Care I, Debbie Harrell, MSN, RN, NE BC, have no financial relationships to disclose.
 Speaker Disclosure Emergent Burn Care I, Debbie Harrell, MSN, RN, NE BC, have no financial relationships to disclose. Debbie Harrell RN, MSN, Shriners Hospitals for Children Cincinnati Cincinnati, Ohio
Speaker Disclosure Emergent Burn Care I, Debbie Harrell, MSN, RN, NE BC, have no financial relationships to disclose. Debbie Harrell RN, MSN, Shriners Hospitals for Children Cincinnati Cincinnati, Ohio
Chapter 29. Objectives. Objectives 01/09/2013. Burns
 Chapter 29 Burns Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 1. Define key terms introduced in
Chapter 29 Burns Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 1. Define key terms introduced in
Outpatient Burn Care for Primary Care: Who needs a referral?
 Outpatient Burn Care for Primary Care: Who needs a referral? J. Kevin Bailey, MD Associate Professor Department of Surgery Division of Trauma, Critical Care and Burn The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Outpatient Burn Care for Primary Care: Who needs a referral? J. Kevin Bailey, MD Associate Professor Department of Surgery Division of Trauma, Critical Care and Burn The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Pediatric Burns: Epidemiology, Etiology and Treatment. Susan Ziegfeld, MSN, PNP-BC Manager, Pediatric Trauma and Burn Program
 Pediatric Burns: Epidemiology, Etiology and Treatment Susan Ziegfeld, MSN, PNP-BC Manager, Pediatric Trauma and Burn Program No Disclosers The Problem: Statistics 486,000 - Burn Injuries Receiving Medical
Pediatric Burns: Epidemiology, Etiology and Treatment Susan Ziegfeld, MSN, PNP-BC Manager, Pediatric Trauma and Burn Program No Disclosers The Problem: Statistics 486,000 - Burn Injuries Receiving Medical
Case Report: Burns Reid Sadoway PGY1 Emergency Medicine, Dalhousie
 Case Report: Burns Reid Sadoway PGY1 Emergency Medicine, Dalhousie History 3 yo boy, presents to pediatric ED with mother Child can be heard crying inside waiting/patient room, has both hands bandaged
Case Report: Burns Reid Sadoway PGY1 Emergency Medicine, Dalhousie History 3 yo boy, presents to pediatric ED with mother Child can be heard crying inside waiting/patient room, has both hands bandaged
Initial assessment. ATLS/ABLS protocol and assess for other injuries/fractures based on mechanism. Inhalational injury. Vascular compromise:
 Complex Hand Burns Brent Egeland, MD Assistant Professor Dell Medical School Department of Surgery and Perioperative Care Institute of Reconstructive Plastic Surgery Plastic, Hand, and Reconstructive Microsurgery
Complex Hand Burns Brent Egeland, MD Assistant Professor Dell Medical School Department of Surgery and Perioperative Care Institute of Reconstructive Plastic Surgery Plastic, Hand, and Reconstructive Microsurgery
Purpose To outline the pre-hospital and inter-hospital assessment and management of patients with major burns.
 Major Burns HELI.CLI.08 Purpose To outline the pre-hospital and inter-hospital assessment and management of patients with major burns. Procedure Management of Severe Burns For Review Aug 2015 1. Introduction
Major Burns HELI.CLI.08 Purpose To outline the pre-hospital and inter-hospital assessment and management of patients with major burns. Procedure Management of Severe Burns For Review Aug 2015 1. Introduction
Burns. Chapter 9. Burns
 Burns Chapter 9 Burns Introduction Natural childhood curiosity and lack of supervision frequently combine to make thermal injuries a major cause of morbidity and mortality in the pediatric patient. Whether
Burns Chapter 9 Burns Introduction Natural childhood curiosity and lack of supervision frequently combine to make thermal injuries a major cause of morbidity and mortality in the pediatric patient. Whether
Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of WSAVA http://www.ivis.org 14(Fri)
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of WSAVA http://www.ivis.org 14(Fri)
Objectives. Initial Burn Care and Fluid Resuscitation 6/5/2015 INITIAL MANAGEMENT
 Initial Burn Care and Fluid Resuscitation Sarah Taylor MSN, RN, ACNS-BC Clinical Nurse Specialist Trauma Burn Center University of Michigan Health System Ann Arbor, MI Objectives Discuss the initial assessment
Initial Burn Care and Fluid Resuscitation Sarah Taylor MSN, RN, ACNS-BC Clinical Nurse Specialist Trauma Burn Center University of Michigan Health System Ann Arbor, MI Objectives Discuss the initial assessment
Responsibility This guideline applies to teams of health professions caring for burn patients.
 Page 1 of 9 Guideline: Initial Assessment & Management of Burn Injuries Purpose This document provides a guideline for the initial assessment and management of burn patients. It is not intended as a full
Page 1 of 9 Guideline: Initial Assessment & Management of Burn Injuries Purpose This document provides a guideline for the initial assessment and management of burn patients. It is not intended as a full
Mr Zachary Moaveni Plastic Surgeon, Middlemore Hospital. Mr Adam Bialostocki Plastic Surgeon, Tauranga
 Mr Zachary Moaveni Plastic Surgeon, Middlemore Hospital Mr Adam Bialostocki Plastic Surgeon, Tauranga Mr. Adam Bialostocki Plastic Surgeon Minor Burns First Aid Remove the burning agent / wet clothes
Mr Zachary Moaveni Plastic Surgeon, Middlemore Hospital Mr Adam Bialostocki Plastic Surgeon, Tauranga Mr. Adam Bialostocki Plastic Surgeon Minor Burns First Aid Remove the burning agent / wet clothes
Each year in the United States, approximately 1.2
 Assessment, Triage, and Early Management of Burns in Children Brian J. Duffy, MD,* Patrick M. McLaughlin, MS, BS,y Martin R. Eichelberger, MD* This comprehensive overview provides the reader with an understanding
Assessment, Triage, and Early Management of Burns in Children Brian J. Duffy, MD,* Patrick M. McLaughlin, MS, BS,y Martin R. Eichelberger, MD* This comprehensive overview provides the reader with an understanding
Burn Management. Praz Patcha, MD 13 March 2014
 Burn Management Praz Patcha, MD 13 March 2014 Epidemiology 500,000 / yr 40,000 to 60,000 requiring admission < 1% total injuries in US but $10.4 billion Risk Factors Age Location Demographics Socioeconomics
Burn Management Praz Patcha, MD 13 March 2014 Epidemiology 500,000 / yr 40,000 to 60,000 requiring admission < 1% total injuries in US but $10.4 billion Risk Factors Age Location Demographics Socioeconomics
Applicable to. Team Members Performing MD House Staff APRN/PA RN LPN
 Protocol: Adult Burn Fluid Resuscitation Category Clinical Practice Protocol Number Approval Date vember 1, 2016 Due for review vember 1, 2018 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations VMG
Protocol: Adult Burn Fluid Resuscitation Category Clinical Practice Protocol Number Approval Date vember 1, 2016 Due for review vember 1, 2018 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations VMG
Applicable to. Team Members Performing
 Protocol: Pediatric Burn Inhalation Injury Category Clinical Practice Protocol Number Approval Date November 1, 2016 Due for review November 1, 2018 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations
Protocol: Pediatric Burn Inhalation Injury Category Clinical Practice Protocol Number Approval Date November 1, 2016 Due for review November 1, 2018 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations
Printed copies of this document may not be up to date, obtain the most recent version from Author Position
 Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Burns Management Document Control Information Author E Borrows E Randle Author Position PICU/BURNS Consultant CATS Consultant Document Owner E. Polke
Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Burns Management Document Control Information Author E Borrows E Randle Author Position PICU/BURNS Consultant CATS Consultant Document Owner E. Polke
STS Care of Thermal Burns 20% Total Body Surface Area
 Temp Regulation Transfer Pain Fluids Airway Initial Assessment STS Care of Thermal Burns 20% Total Body Surface Area Remove burned clothing, rings, watches, and jewelry Cervical spine precautions (if history
Temp Regulation Transfer Pain Fluids Airway Initial Assessment STS Care of Thermal Burns 20% Total Body Surface Area Remove burned clothing, rings, watches, and jewelry Cervical spine precautions (if history
Urgent Care Burn Management. Neil Uspal Division of Emergency Medicine Seattle Children s Hospital October 6 th, 2017
 Urgent Care Burn Management Neil Uspal Division of Emergency Medicine Seattle Children s Hospital October 6 th, 2017 Objectives Epidemiology of Burn Injuries Classification of Burns Initial Burn Management
Urgent Care Burn Management Neil Uspal Division of Emergency Medicine Seattle Children s Hospital October 6 th, 2017 Objectives Epidemiology of Burn Injuries Classification of Burns Initial Burn Management
LRI Emergency Department. Burn injuries management in adults
 LRI Emergency Department Clinical guideline for: Burn injuries management in adults Authors: Approved by: Martin Wiese Reena Agarwal Claire Porter EF guidelines committee Approval date: 21 Sep 16 Approval
LRI Emergency Department Clinical guideline for: Burn injuries management in adults Authors: Approved by: Martin Wiese Reena Agarwal Claire Porter EF guidelines committee Approval date: 21 Sep 16 Approval
Student Guide Module 4: Pediatric Trauma
 Student Guide Module 4: Pediatric Trauma Problem based learning exercise objectives Understand how to manage traumatic injuries in mass casualty events. Discuss the features and the approach to pediatric
Student Guide Module 4: Pediatric Trauma Problem based learning exercise objectives Understand how to manage traumatic injuries in mass casualty events. Discuss the features and the approach to pediatric
Review. A. abrasion B. contusion C. hematoma D. avulsion
 Chapter 24 Review Review 1. A young male was struck in the forearm with a baseball and complains of pain to the area. Slight swelling and ecchymosis are present, but no external bleeding. What type of
Chapter 24 Review Review 1. A young male was struck in the forearm with a baseball and complains of pain to the area. Slight swelling and ecchymosis are present, but no external bleeding. What type of
Management of severe burns
 Management of severe burns Who gets admitted to the ICU? Large % surface area burns >25% adults >15% children/elderly Inhalational or airway burns Multi-trauma Co-morbidities Burns centres Regional referral
Management of severe burns Who gets admitted to the ICU? Large % surface area burns >25% adults >15% children/elderly Inhalational or airway burns Multi-trauma Co-morbidities Burns centres Regional referral
Printed copies of this document may not be up to date, obtain the most recent version from Author Position
 Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Burns Management Document Control Information Author E Borrows E Randle, L Chigaru Author Position PICU/BURNS Consultant CATS Consultants Document
Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Burns Management Document Control Information Author E Borrows E Randle, L Chigaru Author Position PICU/BURNS Consultant CATS Consultants Document
Dr. Muhammad Shamim. FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA), MHPE (Nl & Eg)
 Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA), MHPE (Nl & Eg) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Salman bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com Web: surgeonshamim.com
Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA), MHPE (Nl & Eg) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Salman bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com Web: surgeonshamim.com
Management of Burns under Prolonged Field Care
 This Role 1, prolonged field care (PFC) guideline is intended to be used after TCCC Guidelines when evacuation to higher level of care is not immediately possible. A provider of PFC must first and foremost
This Role 1, prolonged field care (PFC) guideline is intended to be used after TCCC Guidelines when evacuation to higher level of care is not immediately possible. A provider of PFC must first and foremost
COBIS Management of airway burns and inhalation injury PAEDIATRIC
 COBIS Management of airway burns and inhalation injury PAEDIATRIC 1 A multidisciplinary team should provide the management of the child with inhalation injury. Childhood inhalation injury mandates transfer
COBIS Management of airway burns and inhalation injury PAEDIATRIC 1 A multidisciplinary team should provide the management of the child with inhalation injury. Childhood inhalation injury mandates transfer
General Burn Care. Introduction. Overview of burn injury
 By: Kate Pape PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Assistant Professor (Clinical), University of Iowa College of Pharmacy Kate Pape is currently a Clinical
By: Kate Pape PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Assistant Professor (Clinical), University of Iowa College of Pharmacy Kate Pape is currently a Clinical
C H A P T E R 8 T H E R M A L I N J U R I E S
 CHAPTER 8 THERMAL INJURIES Thermal destruction of the skin results in severe local and systemic alterations. This destruction can occur from thermal energy, chemical reactions, electricity, or the response
CHAPTER 8 THERMAL INJURIES Thermal destruction of the skin results in severe local and systemic alterations. This destruction can occur from thermal energy, chemical reactions, electricity, or the response
TBSA Burn Estimation Chart Adult Major Burn Clinical Practice Guideline
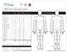 TBSA Burn Estimation Chart Adult Major Burn Clinical Practice Guideline Patient Label Anatomical Subunit Percent Total Percent One Side Anterior Posterior Injury Subtotal 3.5% 2nd and 3rd degree burns
TBSA Burn Estimation Chart Adult Major Burn Clinical Practice Guideline Patient Label Anatomical Subunit Percent Total Percent One Side Anterior Posterior Injury Subtotal 3.5% 2nd and 3rd degree burns
HEAVY METALS : Review
 HEAVY METALS : Review INHALED TOXINS Dr. Tawfiq Almezeiny MBBS FRCPC (CCM) Introduction Airborne toxins typically produce local noxious effects on the airways and lungs. Examples of Inhalational exposure:
HEAVY METALS : Review INHALED TOXINS Dr. Tawfiq Almezeiny MBBS FRCPC (CCM) Introduction Airborne toxins typically produce local noxious effects on the airways and lungs. Examples of Inhalational exposure:
Applicable to. Team Members Performing
 Protocol: Category Clinical Practice Approval Date March 13, 2019 Due for review March 13, 2021 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations VMG VPH Other All faculty & staff Other: Faculty
Protocol: Category Clinical Practice Approval Date March 13, 2019 Due for review March 13, 2021 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations VMG VPH Other All faculty & staff Other: Faculty
Wound Care in the Community. Lisa Sutherland MSc Tissue Viability Senior Lead Ipswich Hospital & Community NHS Trusts
 Wound Care in the Community Lisa Sutherland MSc Tissue Viability Senior Lead Ipswich Hospital & Community NHS Trusts What are the key elements? What is the patient s goal or aim for the wound? What are
Wound Care in the Community Lisa Sutherland MSc Tissue Viability Senior Lead Ipswich Hospital & Community NHS Trusts What are the key elements? What is the patient s goal or aim for the wound? What are
SAEMS BURN STANDING ORDER Self-Learning Module
 SAEMS BURN STANDING ORDER Self-Learning Module Mary Ann Matter University Medical Center November, 2009 Page 1 of 22 PURPOSE This SAEMS Standing Order Training Module has been developed to serve as a template
SAEMS BURN STANDING ORDER Self-Learning Module Mary Ann Matter University Medical Center November, 2009 Page 1 of 22 PURPOSE This SAEMS Standing Order Training Module has been developed to serve as a template
INSTRUCTOR GUIDE FOR TACTICAL FIELD CARE 3B BURNS AND FRACTURES
 INSTRUCTOR GUIDE FOR TACTICAL FIELD CARE 3B BURNS AND FRACTURES 180801 1 Tactical Combat Casualty Care for Medical Personnel 1. August 2017 (Based on TCCC-MP Guidelines 180801 In this presentation, we
INSTRUCTOR GUIDE FOR TACTICAL FIELD CARE 3B BURNS AND FRACTURES 180801 1 Tactical Combat Casualty Care for Medical Personnel 1. August 2017 (Based on TCCC-MP Guidelines 180801 In this presentation, we
A. Pathophysiology: Amount of tissue destruction is based on temperature (> 40 C) and time of exposure (Figure 1).
 CHAPTER 24 THERMAL, ELECTRICAL AND CHEMICAL INJURIES Maureen Beederman, MD and Eamon O Reilly, MD, LCDR, USN Thermal injuries can result from exposure to heat, chemicals, electricity, or cold, and can
CHAPTER 24 THERMAL, ELECTRICAL AND CHEMICAL INJURIES Maureen Beederman, MD and Eamon O Reilly, MD, LCDR, USN Thermal injuries can result from exposure to heat, chemicals, electricity, or cold, and can
Update on Burn Care and Resuscitation
 Niknam Eshraghi, M.D., F.A.C.S General and Burn Surgery; The Oregon Clinic Director; Oregon Burn Center, Legacy Emanuel Medical Center Affiliate Professor of Surgery, Oregon Health Sciences University
Niknam Eshraghi, M.D., F.A.C.S General and Burn Surgery; The Oregon Clinic Director; Oregon Burn Center, Legacy Emanuel Medical Center Affiliate Professor of Surgery, Oregon Health Sciences University
Fire Deaths. Dr Julie McAdam Consultant Forensic Pathologist Glasgow University
 Fire Deaths Dr Julie McAdam Consultant Forensic Pathologist Glasgow University Forensic investigation multidisciplinary fire officers, police officers, scientists, photographers, pathologist, procurator
Fire Deaths Dr Julie McAdam Consultant Forensic Pathologist Glasgow University Forensic investigation multidisciplinary fire officers, police officers, scientists, photographers, pathologist, procurator
Evaluation and Management of Thermal Burns
 Emergency Medicine Board Review Manual Statement of Editorial Purpose The Hospital Physician Emergency Medicine Board Review Manual is a peer-reviewed study guide for residents and practicing physicians
Emergency Medicine Board Review Manual Statement of Editorial Purpose The Hospital Physician Emergency Medicine Board Review Manual is a peer-reviewed study guide for residents and practicing physicians
MANAGING THE BURN WOUND
 MANAGING THE BURN WOUND Robert H. Demling, M.D. Leslie DeSanti R.N., Brigham and Women s Hospital Burn Center Harvard Medical School Boston, MA TABLE OF CONTENTS Section I: Section II: Section III: Section
MANAGING THE BURN WOUND Robert H. Demling, M.D. Leslie DeSanti R.N., Brigham and Women s Hospital Burn Center Harvard Medical School Boston, MA TABLE OF CONTENTS Section I: Section II: Section III: Section
Burn Injury: Thermal and Electrical
 CHAPTER 63 Burn Injury: Thermal and Electrical Winston T. Richards, David J. Hall, Martin D. Rosenthal, and David W. Mozingo Introduction Burn injury accounts for 40,000 hospital admissions/year, including
CHAPTER 63 Burn Injury: Thermal and Electrical Winston T. Richards, David J. Hall, Martin D. Rosenthal, and David W. Mozingo Introduction Burn injury accounts for 40,000 hospital admissions/year, including
Applicable to. Team Members Performing MD House Staff APRN/PA RN LPN
 Protocol: Adult Burn Inhalation Injury Category Clinical Practice Approval Date: March 26, 2019 Review Date: March 26, 2020 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations VMG VPH Other All faculty
Protocol: Adult Burn Inhalation Injury Category Clinical Practice Approval Date: March 26, 2019 Review Date: March 26, 2020 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations VMG VPH Other All faculty
ULCERS 1/12/ million diabetics in the US (2012) Reamputation Rate 26.7% at 1 year 48.3% at 3 years 60.7% at 5 years
 Jay Christensen D.P.M Advanced Foot and Ankle of Wisconsin 2-4% of the population at any given time will have ulcers 0.06-0.20% of the total population Average age of patients 70 years increased as more
Jay Christensen D.P.M Advanced Foot and Ankle of Wisconsin 2-4% of the population at any given time will have ulcers 0.06-0.20% of the total population Average age of patients 70 years increased as more
Pediatric emergencies (SHOCK & COMA) Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University
 Pediatric emergencies (SHOCK & COMA) Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University SHOCK Definition: Shock is a syndrome = inability to provide sufficient oxygenated blood to tissues. Oxygen
Pediatric emergencies (SHOCK & COMA) Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University SHOCK Definition: Shock is a syndrome = inability to provide sufficient oxygenated blood to tissues. Oxygen
10/13/2014. Pediatric Burn Trauma Timothy Jeter, BSN, RN, CCEMT-P, NREMT-P, Objectives. Objectives
 Pediatric Burn Trauma Timothy Jeter, BSN, RN, CCEMT-P, NREMT-P, With assistance from Christina Blottner, MSN, RN, FNP, CWOCN Evans-Haynes Burn Center Division of Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery VCU Health
Pediatric Burn Trauma Timothy Jeter, BSN, RN, CCEMT-P, NREMT-P, With assistance from Christina Blottner, MSN, RN, FNP, CWOCN Evans-Haynes Burn Center Division of Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery VCU Health
Modern management of paediatric burns
 Modern management of paediatric burns Burn injuries pose a major threat to children in South Africa and remain a devastating injury, because of the resulting severe emotional and physical scarring and
Modern management of paediatric burns Burn injuries pose a major threat to children in South Africa and remain a devastating injury, because of the resulting severe emotional and physical scarring and
TITLE OF CASE: Burn Injuries and Management
 TITLE OF CASE: Burn Injuries and Management AUTHOR OF CASE: Magdalena Malinowska SUMMARY: Patient is a 23 year old female who was brought in by EMS to the Emergency Room post a motor vehicle accident in
TITLE OF CASE: Burn Injuries and Management AUTHOR OF CASE: Magdalena Malinowska SUMMARY: Patient is a 23 year old female who was brought in by EMS to the Emergency Room post a motor vehicle accident in
Jihan Safwan, Pharm.D. Clinical Assistant Professor School of Pharmacy LIU
 1 Jihan Safwan, Pharm.D. Clinical Assistant Professor School of Pharmacy LIU LEARNING OBJECTIVES Define and classify the different types of burns Select optimal treatment for burn cases presenting to a
1 Jihan Safwan, Pharm.D. Clinical Assistant Professor School of Pharmacy LIU LEARNING OBJECTIVES Define and classify the different types of burns Select optimal treatment for burn cases presenting to a
Knowledge Objectives (2 of 2) Skills Objectives. Death Scene Considerations. Introduction 12/20/2013
 Fire and Explosion Deaths and Injuries Knowledge Objectives (1 of 2) Identify the effects of fire and explosion on the human body. Discuss the various issues involved in fire or explosion death investigation.
Fire and Explosion Deaths and Injuries Knowledge Objectives (1 of 2) Identify the effects of fire and explosion on the human body. Discuss the various issues involved in fire or explosion death investigation.
TOTW Burns in children October 2007
 TOTW Burns in children October 2007 A J Pittaway FRCA Andrew.pittaway@seattlechildrens.org Before reading the tutorial, consider this case scenario and answer the following questions (answers & discussion
TOTW Burns in children October 2007 A J Pittaway FRCA Andrew.pittaway@seattlechildrens.org Before reading the tutorial, consider this case scenario and answer the following questions (answers & discussion
Hemostasis Inflammatory Phase Proliferative/rebuilding Phase Maturation Phase
 The presenters are staff members of the CHI Health St. Elizabeth Burn and Wound Center. Many of the products discussed are used in our current practice but we have no conflict of interest to disclose.
The presenters are staff members of the CHI Health St. Elizabeth Burn and Wound Center. Many of the products discussed are used in our current practice but we have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Principle Management of Wound and Fracture in Emergency Department
 Principle Management of Wound and Fracture in Emergency Department Presented in Clinical Update Seminar January 15 th 2011 dr. Tedjo Rukmoyo, SpOT (K) Spine Initial Management ATLS Procedure A : airway
Principle Management of Wound and Fracture in Emergency Department Presented in Clinical Update Seminar January 15 th 2011 dr. Tedjo Rukmoyo, SpOT (K) Spine Initial Management ATLS Procedure A : airway
Trauma in children. Paediatric burns and associated injuries
 Paediatric burns and associated injuries Reprinted with revisions from Pittaway AJ. Managing Paediatric Burns. Anaesthesia Tutorial of the Week 78 (2007) A J Pittaway* and N Hardcastle *Correspondence
Paediatric burns and associated injuries Reprinted with revisions from Pittaway AJ. Managing Paediatric Burns. Anaesthesia Tutorial of the Week 78 (2007) A J Pittaway* and N Hardcastle *Correspondence
 55-year-old male with 2nd and 3rd degree burns to face, chest, and arms on 25% of the body Respirations: 34 Pulse: 120 Mental Status: moans to painful stimulus Mucous membranes charred Stridor 10 cm scalp
55-year-old male with 2nd and 3rd degree burns to face, chest, and arms on 25% of the body Respirations: 34 Pulse: 120 Mental Status: moans to painful stimulus Mucous membranes charred Stridor 10 cm scalp
Pediatric Code Blue. Goals of Resuscitation. Focus Conference November Ensure organ perfusion
 Pediatric Code Blue Focus Conference November 2015 Duane C. Williams, MD Pediatric Critical Care Department of Pediatrics Children s Hospital of Richmond at VCU Goals of Resuscitation Ensure organ perfusion
Pediatric Code Blue Focus Conference November 2015 Duane C. Williams, MD Pediatric Critical Care Department of Pediatrics Children s Hospital of Richmond at VCU Goals of Resuscitation Ensure organ perfusion
January Adult Burn Injured patients
 Guideline Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience, state if Trust wide): Review date (when this version goes out of date): Explicit definition
Guideline Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience, state if Trust wide): Review date (when this version goes out of date): Explicit definition
EMERGENCY MEDICINE PRACTICE
 EMERGENCY MEDICINE PRACTICE AN EVIDENCE-BASED APPROACH TO EMERGENCY MEDICINE Thermal Burns: Rapid Assessment And Treatment WHILE the incidence of burns has steadily declined over the last few decades,
EMERGENCY MEDICINE PRACTICE AN EVIDENCE-BASED APPROACH TO EMERGENCY MEDICINE Thermal Burns: Rapid Assessment And Treatment WHILE the incidence of burns has steadily declined over the last few decades,
warning properties) Early symptoms are often mistaken for the flu asleep CO often strikes in cold weather when heating are closed
 CO is odorless, tasteless and colorless (no warning properties) Early symptoms are often mistaken for the flu High levels can kill while family members are asleep CO often strikes in cold weather when
CO is odorless, tasteless and colorless (no warning properties) Early symptoms are often mistaken for the flu High levels can kill while family members are asleep CO often strikes in cold weather when
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders
 Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders Blood Pressure Normal blood pressure is 120/80 mmhg (millimeters of mercury) Hypertension is when the resting blood pressure is too high Systolic BP is 140 mmhg
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders Blood Pressure Normal blood pressure is 120/80 mmhg (millimeters of mercury) Hypertension is when the resting blood pressure is too high Systolic BP is 140 mmhg
CARE OF PATIENTS WITH BURNS. NUR 240 Donna Ricketts, MSN, RN, OCN
 CARE OF PATIENTS WITH BURNS NUR 240 Donna Ricketts, MSN, RN, OCN INCIDENCE/PREVALENCE OF BURN INJURY 5 th most common unintentional injury deaths 3 rd leading cause of fatal home injuries 4,000 burn deaths
CARE OF PATIENTS WITH BURNS NUR 240 Donna Ricketts, MSN, RN, OCN INCIDENCE/PREVALENCE OF BURN INJURY 5 th most common unintentional injury deaths 3 rd leading cause of fatal home injuries 4,000 burn deaths
Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials
 Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials 1 1. A high-risk bodily fluid for spreading infection is blood. 2. Items that can reduce the spread of infection include masks, gloves, and
Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials 1 1. A high-risk bodily fluid for spreading infection is blood. 2. Items that can reduce the spread of infection include masks, gloves, and
Burn Resuscitation Formulas. John P. Sabra, MD Seton Surgical Group Department of Surgery Dell Medical School Austin, TX
 Burn Resuscitation Formulas John P. Sabra, MD Seton Surgical Group Department of Surgery Dell Medical School Austin, TX BURN INJURY % Physiologic Change % TBSA burn Stasis BURN VASCULAR PERMEABILITY
Burn Resuscitation Formulas John P. Sabra, MD Seton Surgical Group Department of Surgery Dell Medical School Austin, TX BURN INJURY % Physiologic Change % TBSA burn Stasis BURN VASCULAR PERMEABILITY
Epidemiology. Burn Rehabilitation. Epidemiology. Epidemiology. United States. United States Cause of injury. Incidence has declined
 Burn Rehabilitation Peter Esselman, MD Professor and Chair Department of Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington Epidemiology United States 450,000 burn injuries/year in USA that receive medical
Burn Rehabilitation Peter Esselman, MD Professor and Chair Department of Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington Epidemiology United States 450,000 burn injuries/year in USA that receive medical
Appendix. Sedatives and Pain Medications. Gabapentin ( mg po q8h) or Pregabalin ( mg po q8h)
 Appendix Sedatives and Pain Medications Non-intubated patients Non-opioid analgesics Acetaminophen (500 1,000 mg po q6h) NSAID (Ibuprofen, Naprosyn, Celebrex) Gabapentin (100 300 mg po q8h) or Pregabalin
Appendix Sedatives and Pain Medications Non-intubated patients Non-opioid analgesics Acetaminophen (500 1,000 mg po q6h) NSAID (Ibuprofen, Naprosyn, Celebrex) Gabapentin (100 300 mg po q8h) or Pregabalin
-Cardiogenic: shock state resulting from impairment or failure of myocardium
 Shock chapter Shock -Condition in which tissue perfusion is inadequate to deliver oxygen, nutrients to support vital organs, cellular function -Affects all body systems -Classic signs of early shock: Tachycardia,tachypnea,restlessness,anxiety,
Shock chapter Shock -Condition in which tissue perfusion is inadequate to deliver oxygen, nutrients to support vital organs, cellular function -Affects all body systems -Classic signs of early shock: Tachycardia,tachypnea,restlessness,anxiety,
Chapter 21: Burns Introduction to Burn Injuries (1 of 2) Introduction to Burn Injuries (2 of 2) Reduction in Burn Injuries Pathophysiology of Burns
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Chapter 21: Burns Introduction to Burn Injuries (1 of 2) 1.25-2 million Americans treated for burns annually 50,000 require 3-5% considered life threatening leading cause of death for children
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Chapter 21: Burns Introduction to Burn Injuries (1 of 2) 1.25-2 million Americans treated for burns annually 50,000 require 3-5% considered life threatening leading cause of death for children
Smoke inhalation damages the body by simple asphyxiation (lack of oxygen), chemical irritation, chemical asphyxiation, or a combination of these.
 Print Close 2011 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved. Smoke Inhalation Recommend 13 Medical Author: Christopher P Holstege, MD Medical Editor: Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD Smoke Inhalation Overview Smoke Inhalation
Print Close 2011 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved. Smoke Inhalation Recommend 13 Medical Author: Christopher P Holstege, MD Medical Editor: Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD Smoke Inhalation Overview Smoke Inhalation
Getting Strarted using the Nursing Care Plans Templates
 Getting Strarted using the Nursing Care Plans Templates Using available Nursing Care Plan Templates. These templates are delivered as is and there is nothing which prevents you to use and modify these
Getting Strarted using the Nursing Care Plans Templates Using available Nursing Care Plan Templates. These templates are delivered as is and there is nothing which prevents you to use and modify these
Care of Burns. Serious burns require inpatient care, ideally in a verified burn center.
 感謝長庚吳吉妮醫師整理製作 Care of Burns Serious burns require inpatient care, ideally in a verified burn center. The majority of burns can be successfully managed in the outpatient setting. However, poorly provided
感謝長庚吳吉妮醫師整理製作 Care of Burns Serious burns require inpatient care, ideally in a verified burn center. The majority of burns can be successfully managed in the outpatient setting. However, poorly provided
Clinical Connections April 16, 2014
 Management of Burns Eric McCoy PA-C Kathy Johnston RN, BSN Trauma/Burn Service UPMC Mercy A Long Tradition of Caring Comprehensive burn care from initial treatment through rehabilitation Region s only
Management of Burns Eric McCoy PA-C Kathy Johnston RN, BSN Trauma/Burn Service UPMC Mercy A Long Tradition of Caring Comprehensive burn care from initial treatment through rehabilitation Region s only
