Colo-Rectal Cancer. Surgery. Adrian P. Ireland. Academic RCSI Department of Surgery, Beaumont Hospital.
|
|
|
- Violet Reeves
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Surgery Colo-Rectal Cancer Adrian P. Ireland Academic RCSI Department of Surgery, Beaumont Hospital Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.1/59
2 Today we will be talking about Colorectal Cancer Review of Anatomy Colo-rectal cancer genetics How colo-rectal cancer spreads Staging Dukes and TNM History, Examination and Investigations Neo-adjuvant and Adjuvant therapy Operations for colon and rectal cancer Followup CEA, scope, liver Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.2/59
3 Epidemiology 2nd commonest cancer in the Western World 10% of all Irish Cancers 1800 new cases in Ireland per year Surgery offers potential for cure in 50 % Burkitt s observation on fibre Role of consumption of broccoli Heriditary cacers and the adenoma-carcinoma sequence Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.3/59
4 Anatomy The most important anatomy is the blood supply. Because the lymphatics follow the vessels. Surgical definition of the rectum Surgical definition of the anal canal Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.4/59
5 Arterial supply of the colon Superior mesenteric artery (Red) Inferior mesenteric artery (Green) Middle rectal arteries (Pink) Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.5/59
6 Anatomy of the rectum Starts; where the taenia coli fuse to form the a fully circimferential longitudinal muscle Parts; Upper, Middle and Lower Outside the rectum posteriorly is the mesorectum where most of the rectal lymphatics drain Valves of Houston; Two on one side and one on the other Ends at the anal canal Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.6/59
7 Anatomy of the anal canal Starts; at the end of the rectum Haemmoroidal Cushions; Terminal branches of the rectal arteries Sphincters; Two internal (circular smooth muscle, involuntary), external (skeletal muscle, three parts, voluntary) Dentate line; where the columnar lining changes to squamous, the squamous lining is very, very sensitive (don t inject haemmoroids here) Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.7/59
8 Polyps Mass of tissue protruding into the bowel lumen. If it has a stalk it is pedunculted otherwise it is sessile. Adenomatous (Villous, Tubular, Tubulo-Villous) Hyperplastic Hamartomatous Pseudopolyps (false polyps) Others, Juvenile polyp, Serrated Adenoma Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.8/59
9 Polyps - Facts Controversy about adenoma carcinoma sequence (Vogelgram) Less than 1% of polyps smaller than 1.2 cm are malignant You have to remove about 36 adenomatous polyps to prevent one cancer Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.9/59
10 Colorectal cancer - Predispositions Heridatary cancer syndromes Polyps (Adenomatous) Chronic inflammation, in particular chronic ulcerative colitis (more than 10 years of pan-colitis) Previous uretero-sigmoidostomy Previous gastrectomy, vagotomy (about 2 fold increase) Previous cholecystectomy, controversial (probably not) Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.10/59
11 Genetics of colo-rectal cancer Heriditary non polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) Familial adenomatous polyposis coli (FAP) Jeuvenile Polyposis Peutz-Jegher s Cowden Mixed Polyposis Syndromes Hyperplastic Polyposis Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.11/59
12 HNPCC Lynch syndrome I and II Mutator Phenotype, mismatch repair genes 6 different genes hmlh1, hmsh(2,3,6), hpms(1,2) Mucinous, right, metachranous, synchronous Endometrial, ureteric, renal pelvis, small bowel Amsterdam I (1990) and II (1999) criteria Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.12/59
13 HNPCC - Amsterdam II At least 3 relatives with an HNPCC associated cancer (colorectal, endometrial, small bowel, ureter, renal pelvis), one of these should be a first degree relative of the other two At least two successive generations should be affected At least one should be diagnosed before the age of 50 FAP excluded in the colo-rectal cancer cases The tumors should be verified pathologically Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.13/59
14 FAP APC gene, on 5q? cell adhesion Dense and Attenuated varities, depending on APC mutation Hundreds of polyps in the colon by age % will develop colon cancer if they survive Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.14/59
15 FAP - Surgical options for the colon Total abdominal colectomy with ileo-rectal anastamosis Pan proctocolectomy with end ileostomy Restorative proctocolectomy with ileal pouch-anal anastamosis Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.15/59
16 FAP - Extra colonic manifestations Adenomas Gastric (10%), lower but not absent malignant potential Duodenal (100%, severe in 10%), around the ampulla,? need for pancreatico-duodenectomy? Hepatobiliary system, Small bowel, Pancreas, Adrenal cortex and Thyroid Epidermoid cysts, Pilomatrixoma, Osteoma, Exostosis, Desmoid tumors Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.16/59
17 FAP - NSAID Sulindac shown to reduce rectal and pouch polyps Celoxicab reduces large bowel polyps Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.17/59
18 FAP - Desmoids Troublesome in about 10% of patients with FAP 10% mortality in those affected Associated with specific APC mutations Associated with two hits (ie both alleles) Aggrevated by trauma and oestrogen May be in the abdominal wall or intra-abdominal NSAID and anti-oestrogens Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.18/59
19 Distribution of Colo-Rectal tumors 33% may be palpable 70% within reach of the 60 cm flexible scope Flexures favoured sites are Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.19/59
20 Presentation of Colon cancer Left sided tumours present with altered bowel habit, a mass and rectal bleeding Right sided tumours present later Liquid stool Greater diameter Right sided tumours present with anaemia Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.20/59
21 How colo-rectal cancer spreads Direct invasion Haematogenous Lymphatic Trans coelomic Trans luminal Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.21/59
22 Staging - Dukes Dukes depended on pathology rather than what the surgeon saw Initially for rectal, he did not describe Duke s D Stage Description 5 year survival A Not breaching muscularis propria 80-85% B Through the muscularis propria 60-67% C Involving the lymph nodes 30-37% Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.22/59
23 Staging - T (tumour) N (nodes) M (metastases) T 1 T 2 T 3 T 4 Involves the submucosa Involves muscularis propria Into subserosa or non peritonealised peri-colic or peri rectal tissues Through the visceral peritoneum or invading adjacent organs Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.23/59
24 History - Presenting Complaint Change in bowel habit Rectal bleeding - don t ascribe to haemmoroids Loss in appetite Weight loss -? metastatic with cachexia Abdominal pain -? locally advanced Symptoms of obstruction Tenesemus Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.24/59
25 History Had this before? Previous surgery Other illness (drugs)/ Co-morbidities Famial cancer? Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.25/59
26 Important other points in History Problems with anaesthetics Family history of problems with surgery Drug allergies (document; when, what happened) Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.26/59
27 Examination Anaemia, Jaundice, Stigmata weight loss Pleural effusions, Hepatomegaly Mass on abdominal examination Mass on rectal examination (differentiate prostate, cervix etc) FOB test positive Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.27/59
28 Investigation FOB test Blood; U & E, FBC, Liver, CEA Endoscopy; Proctoscopy, Rigid Sigmoid, Flex sigmoid, Colonoscopy Radiological; PFA, Erect CXR, CT scan, MRI, PET, Enemas Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.28/59
29 Investigations; Faecal Occult Blood (FOB) Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.29/59
30 FOB test Blotting paper impregnanted with GUAIC Rub a small amount of stool on the paper Drop a few drops of dilute Blood in stool will act a peroxidase and catalyse the breakdown of the The released substance will cause a change in colour of the GUAIC to blue Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.30/59
31 Colonoscopy; Polyps Two polyps in the sigmoid Bx Snare exicsion Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.31/59
32 Colonoscopy; Local recurrance Tumour at site of colo-rectal anastamosis? implantation? hematogenous and healing milieu? ingrowth Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.32/59
33 Work up Clinical indication Examination Scope and biopsy? Need for contrast study (? Virtual colonoscopy)? Proceed if biopsy negative If rectal local staging? neoadjuvant therapy Liver work up Baseline CEA Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.33/59
34 Neo adjuvant and adjuvant therapy Neo-adjuvant For T3 rectal cancer Before surgery Chemotherapy Radiotherapy Followed by surgery Followed by further treatment Adjuvant Colon and Rectal Ca Dukes C Post operative 5-FU based Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.34/59
35 Adjuvant 5FU and Levamisole Intergroup study % of patients could not complete course This study initially showed a benefit in Dukes B(2) but this has not been substanciated by other trials. Stage Without Adjuvant With Adjuvant C 55% 71% Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.35/59
36 Adjuvant 5FU and Folinic Acid Intergroup study 1993 Addition of Folinic Acid doubled response to 5FU This study initially showed a benefit in Dukes B(2) but this has not been substanciated by other trials. Stage Without Adjuvant With Adjuvant B2 and C 71% 77% Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.36/59
37 QUASAR: QUick And Simple And Reliable Study UK study Four regimes compared, Levamisole contributes little Stage B2 and C Regimen 5FU + High dose Folinic Acid + Levamisole 5FU + High dose Folinic Acid + Placebo 5FU + Low dose Folinic Acid + Levamisole 5FU + Low dose Folinic Acid + Placebo Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.37/59
38 Other Folinic Acid + Bolus + Infusion of 5FU, + Oxaliplatin (FOLFOX), adds 5% Loco-regional chemotherapy, AXIS trial Portal Vein Infusion for 1 week post op Survival benefit of 5% Anti growth factor, anit EGFR, ( Cetuximab ) Anti angiogeneis, anti VEGF, ( Bevacizimab ) Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.38/59
39 Preparation for surgery Informed consent, risks, benefits and alternatives Major co-morbidities? Group and Cross Match, ECG, CXR, U&E, FBC,? COAG Thrombo-embolism prophylaxis, sc heparin, TEDS Mechanical Bowel Preparation Antibiotic prohylaxis; Single dose, Metronidazole, Cefuroxime Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.39/59
40 Right Hemicolectomy Nodes follow arteries Ureter Gonadal Vessels Duodenum Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.40/59
41 Caecal tumor Encroachment on ileum Adjacent polyp Characteristic rolled edge everted Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.41/59
42 Hepatic Flexure tumour - Extent of Resection Need to take Middle Colic Preserve ileum more Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.42/59
43 Hepatic Flexure tumour - Operative Specimen Hugely dilated ascending colon Huge caecum Little ileum resected Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.43/59
44 Splenic flexure tumors Somewhat poorer prognosis? related to difficulty in surgery? related to inadequate surgery May invade, stomach, pancreas, Gerota s fascia Most prefer the extended right hemicolectomy Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.44/59
45 Extended Right Hemicolectomy Nodes follow arteries Ureter (Both) Gonadal Vessels (Both) Duodenum Spleen Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.45/59
46 Left Hemicolectomy Nodes follow arteries Ureter Gonadal Vessels Spleen Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.46/59
47 Inferior Mesenteric Artery - High or Low ligation The inferior mesenteric artery may be divided flush with the aorta or below the origin of the left colic artery. This seems to make no difference to outcome in patients with rectal cancer, exact role in sigmoid cancer is not totally definite but probably makes no difference. Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.47/59
48 Laparoscopic Assited? It appears that the greater the surgical insult the worse the oncological outcome from the patient. Initial sceptisism regarding oncological principle Initial sceptisism regarding port site mets Barcelona Spain Lancet Improved outcome in Dukes C compared to open surgery Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.48/59
49 Emergency Surgery 16-20% of presentations Mortality much higher than in elective Higher rate of advanced disease Outcome stage for stage with elective cases worse Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.49/59
50 Perforated caecum due to obstruction in recto-sigmoid Total abdominal colectomy with end ileostomy Total abdominal colectomy with ileo-rectal anastamosis Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.50/59
51 Large bowel obstruction - tumor in recto-sigmoid One, two and three stage operations Three stage; stoma, then resect and join, then close stoma Two stage (Hartman s); resect and stoma, then restore continuity One stage; On table lavage and then resect and anastamose Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.51/59
52 Emergency Surgery; Hartmann s Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.52/59
53 Rectal cancer Local staging important in tumors in the middle and lower third EUA Stage liver MRI Endoluminal Ultrasound? need Neo-adjuvant therapy T3 Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.53/59
54 Rectal cancer - Upper Some treat as recto-sigmoid tumor Left hemicolectemy extended to include upper half of the rectum Role of TME unproven Clear mesorectum to 5 cm below tumour Better function with preservation of distal rectal pouch Hand sewn or stapled anastamosis Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.54/59
55 Rectal cancer - Middle Local staging +/- Neoadjuvant therapy Anterior Resection (Left hemicolectemy extended to include upper 2/3 of the rectum) Total mesorectal incision important Most prefer stapled anastamosis Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.55/59
56 Rectal cancer - Lower Local staging +/- Neoadjuvant therapy Local trans anal surgery in selected cases (early tumors) Abdomino-Perineal Resection of the rectum and anal canal Total mesorectal incision important End colostomy Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.56/59
57 Radiology; What is this? Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.57/59
58 Colorectal cancer - By the Numbers 5% mortaility for elective 20% for emergency surgery 10% wound infection rate 20% present with disseminated disease 30% palpable on rectal exam 30% 5 year survival following hepatic resection of metastases 70% within reach of the flexible sigmoidiscope 80% survival for Dukes A Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.58/59
59 Thanks Look for the pdf download (1275 K, 1.24 M) at Questions please Surgery, Final Med, Colo-Rectal Cancer p.59/59
COLORECTAL CANCER FAISALGHANISIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOETHICS; MCPS-HPE
 COLORECTAL CANCER FAISALGHANISIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY & DIRECTOR, PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT CENTRE J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y faisal.siddiqui@jsmu.edu.pk
COLORECTAL CANCER FAISALGHANISIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY & DIRECTOR, PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT CENTRE J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y faisal.siddiqui@jsmu.edu.pk
IMAGING GUIDELINES - COLORECTAL CANCER
 IMAGING GUIDELINES - COLORECTAL CANCER DIAGNOSIS The majority of colorectal cancers are diagnosed on colonoscopy, with some being diagnosed on Ba enema, ultrasound or CT. STAGING CT chest, abdomen and
IMAGING GUIDELINES - COLORECTAL CANCER DIAGNOSIS The majority of colorectal cancers are diagnosed on colonoscopy, with some being diagnosed on Ba enema, ultrasound or CT. STAGING CT chest, abdomen and
colorectal cancer Colorectal cancer hereditary sporadic Familial 1/12/2018
 colorectal cancer Adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum is the third most common site of new cancer cases and deaths in men (following prostate and lung or bronchus cancer) and women (following breast
colorectal cancer Adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum is the third most common site of new cancer cases and deaths in men (following prostate and lung or bronchus cancer) and women (following breast
This is the portion of the intestine which lies between the small intestine and the outlet (Anus).
 THE COLON This is the portion of the intestine which lies between the small intestine and the outlet (Anus). 3 4 5 This part is responsible for formation of stool. The large intestine (colon- coloured
THE COLON This is the portion of the intestine which lies between the small intestine and the outlet (Anus). 3 4 5 This part is responsible for formation of stool. The large intestine (colon- coloured
COLORECTAL CARCINOMA
 QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS MANAGEMENT OF COLORECTAL CARCINOMA Ministry of Health Malaysia Malaysian Society of Colorectal Surgeons Malaysian Society of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Malaysian
QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS MANAGEMENT OF COLORECTAL CARCINOMA Ministry of Health Malaysia Malaysian Society of Colorectal Surgeons Malaysian Society of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Malaysian
Colorectal Cancer. Mark Chapman. MA MS FRCS EBSQ(coloproct) 21 st March 2018 Consultant Coloproctologist
 Colorectal Cancer Mark Chapman MA MS FRCS EBSQ(coloproct) 21 st March 2018 Consultant Coloproctologist Overview Epidemiology of colorectal cancer Adenoma carcinoma sequence Tumour diagnosis & staging Treatment
Colorectal Cancer Mark Chapman MA MS FRCS EBSQ(coloproct) 21 st March 2018 Consultant Coloproctologist Overview Epidemiology of colorectal cancer Adenoma carcinoma sequence Tumour diagnosis & staging Treatment
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM SURGICAL PROCEDURES May 1, 2015 INTESTINES (EXCEPT RECTUM) Asst Surg Anae
 ENDOSCOPY Z50 Duodenoscopy (not to be claimed if Z399 and/or Z00 performed on same patient within 3 months)... 92.10 Z9 Subsequent procedure (within three months following previous endoscopic procedure)...
ENDOSCOPY Z50 Duodenoscopy (not to be claimed if Z399 and/or Z00 performed on same patient within 3 months)... 92.10 Z9 Subsequent procedure (within three months following previous endoscopic procedure)...
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal surgery prior as factor in laparoscopic colorectal surgery, 554 555 Abscess(es) CRC presenting as, 539 540 Adenocarcinoma of
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal surgery prior as factor in laparoscopic colorectal surgery, 554 555 Abscess(es) CRC presenting as, 539 540 Adenocarcinoma of
11/21/13 CEA: 1.7 WNL
 Case Scenario 1 A 70 year-old white male presented to his primary care physician with a recent history of rectal bleeding. He was referred for imaging and a colonoscopy and was found to have adenocarcinoma.
Case Scenario 1 A 70 year-old white male presented to his primary care physician with a recent history of rectal bleeding. He was referred for imaging and a colonoscopy and was found to have adenocarcinoma.
LOINC. Clinical information. RCPA code. Record if different to report header Operating surgeon name and contact details. Absent.
 Complete as narrative or use the structured format below 55752-0 17.02.28593 Clinical information 22027-7 17.02.30001 Record if different to report header Operating surgeon name and contact details 52101004
Complete as narrative or use the structured format below 55752-0 17.02.28593 Clinical information 22027-7 17.02.30001 Record if different to report header Operating surgeon name and contact details 52101004
8. The polyp in the illustration can be described as (circle all that apply) a. Exophytic b. Pedunculated c. Sessile d. Frank
 Quiz 1 Overview 1. Beginning with the cecum, which is the correct sequence of colon subsites? a. Cecum, ascending, splenic flexure, transverse, hepatic flexure, descending, sigmoid. b. Cecum, ascending,
Quiz 1 Overview 1. Beginning with the cecum, which is the correct sequence of colon subsites? a. Cecum, ascending, splenic flexure, transverse, hepatic flexure, descending, sigmoid. b. Cecum, ascending,
Colorectal Pathway Board (Clinical Subgroup): Imaging Guidelines September 2015
 Colorectal Pathway Board (Clinical Subgroup): Imaging Guidelines September 2015 1 Contents Page No. 1. Objective 3 2. Imaging Techniques 3 3. Staging of Colorectal Cancer 5 4. Radiological Reporting 6
Colorectal Pathway Board (Clinical Subgroup): Imaging Guidelines September 2015 1 Contents Page No. 1. Objective 3 2. Imaging Techniques 3 3. Staging of Colorectal Cancer 5 4. Radiological Reporting 6
Navigators Lead the Way
 RN Navigators Their Role in patients with Cancers of the GI tract Navigators Lead the Way Nurse Navigator Defined Nurse Navigator A clinically trained individual responsible for the identification and
RN Navigators Their Role in patients with Cancers of the GI tract Navigators Lead the Way Nurse Navigator Defined Nurse Navigator A clinically trained individual responsible for the identification and
Preoperative Data Colorectal Cancer Database
 Preoperative Data Please place patient label here Patient Information Patient s Last Name First Middle Initial UR MH MP Birth Date Sex Post Code / / M F ECOG (see codes below) Date of Diagnosis Consultant
Preoperative Data Please place patient label here Patient Information Patient s Last Name First Middle Initial UR MH MP Birth Date Sex Post Code / / M F ECOG (see codes below) Date of Diagnosis Consultant
Colorectal Neoplasia. Dr. Smita Devani MBChB, MRCP. Consultant Physician and Gastroenterologist Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi
 Colorectal Neoplasia Dr. Smita Devani MBChB, MRCP Consultant Physician and Gastroenterologist Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Case History BT, 69yr male Caucasian History of rectal bleeding No change
Colorectal Neoplasia Dr. Smita Devani MBChB, MRCP Consultant Physician and Gastroenterologist Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Case History BT, 69yr male Caucasian History of rectal bleeding No change
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GASTROINTESTINAL RECTAL CANCER GI Site Group Rectal Cancer Authors: Dr. Jennifer Knox, Dr. Mairead McNamara 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. SCREENING AND
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GASTROINTESTINAL RECTAL CANCER GI Site Group Rectal Cancer Authors: Dr. Jennifer Knox, Dr. Mairead McNamara 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. SCREENING AND
OPEN ACCESS TEXTBOOK OF GENERAL SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS TEXTBOOK OF GENERAL SURGERY COLORECTAL POLYPS P Goldberg POLYP A polyp is a localised elevated lesion arising from a epithelial surface. If it has a stalk it is called a pedunculated polyp
OPEN ACCESS TEXTBOOK OF GENERAL SURGERY COLORECTAL POLYPS P Goldberg POLYP A polyp is a localised elevated lesion arising from a epithelial surface. If it has a stalk it is called a pedunculated polyp
Clinical Colon Cancer Abby Siegel MD COLON CANCER. 1. Epidemiology 2. Risk factors 3. Manifestations 4. Treatment
 Clinical Colon Cancer 2008 Abby Siegel MD COLON CANCER 1. Epidemiology 2. Risk factors 3. Manifestations 4. Treatment 1 1. EPIDEMIOLOGY - Colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer in the United
Clinical Colon Cancer 2008 Abby Siegel MD COLON CANCER 1. Epidemiology 2. Risk factors 3. Manifestations 4. Treatment 1 1. EPIDEMIOLOGY - Colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer in the United
Colorectal Cancer Structured Pathology Reporting Proforma DD MM YYYY
 Colorectal Cancer Structured Pathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.03). Family name Given name(s) Date of birth DD MM YYYY S1.02 Clinical details
Colorectal Cancer Structured Pathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.03). Family name Given name(s) Date of birth DD MM YYYY S1.02 Clinical details
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM SURGICAL PROCEDURES December 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 2016) INTESTINES (EXCEPT RECTUM) Asst Surg Anae
 December 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 201) INTESTINES (EXCEPT RECTUM) Z513 Hydrostatic - Pneumatic dilatation of colon stricture(s) through colonoscope... 10.50 Z50 Fulguration of first polyp through colonoscope...
December 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 201) INTESTINES (EXCEPT RECTUM) Z513 Hydrostatic - Pneumatic dilatation of colon stricture(s) through colonoscope... 10.50 Z50 Fulguration of first polyp through colonoscope...
David P. Ryan, M.D. Clinical Director, MGH Cancer Center Chief, Hematology-Oncology, MGH
 Colon Cancer 2015 David P. Ryan, M.D. Clinical Director, MGH Cancer Center Chief, Hematology-Oncology, MGH Colon Cancer Case presentation 72yo woman presented 1/03 abd discomfort and nausea Found to have
Colon Cancer 2015 David P. Ryan, M.D. Clinical Director, MGH Cancer Center Chief, Hematology-Oncology, MGH Colon Cancer Case presentation 72yo woman presented 1/03 abd discomfort and nausea Found to have
Colorectal adenocarcinoma leading cancer in developed countries In US, annual deaths due to colorectal adenocarcinoma 57,000.
 Colonic Neoplasia Remotti Colorectal adenocarcinoma leading cancer in developed countries In US, annual incidence of colorectal adenocarcinoma 150,000. In US, annual deaths due to colorectal adenocarcinoma
Colonic Neoplasia Remotti Colorectal adenocarcinoma leading cancer in developed countries In US, annual incidence of colorectal adenocarcinoma 150,000. In US, annual deaths due to colorectal adenocarcinoma
COLORECTAL CANCER STAGING in 2010
 COLORECTAL CANCER STAGING in 2010 Robert A. Halvorsen, MD, FACR MCV Hospitals / VCU Medical Center Richmond, Virginia I do not have any relevant financial relationships with any commercial interests COLON
COLORECTAL CANCER STAGING in 2010 Robert A. Halvorsen, MD, FACR MCV Hospitals / VCU Medical Center Richmond, Virginia I do not have any relevant financial relationships with any commercial interests COLON
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
 Familial Adenomatous Polyposis 1 in 10,000 incidence 100 s to 1000 s of colonic adenomas by teens Cancer risk: colon, gastric, duodenum (periampulla), small bowel, pancreas, papillary thyroid, childhood
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis 1 in 10,000 incidence 100 s to 1000 s of colonic adenomas by teens Cancer risk: colon, gastric, duodenum (periampulla), small bowel, pancreas, papillary thyroid, childhood
Alison Douglass Gillian Lieberman, MD. November. Colon Cancer. Alison Douglass, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD
 November Colon Cancer Alison Douglass, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient Mr. K. is a 67 year old man with no prior medical problems other than hemorrhoids which have caused occasional rectal
November Colon Cancer Alison Douglass, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient Mr. K. is a 67 year old man with no prior medical problems other than hemorrhoids which have caused occasional rectal
SMALL BOWEL ADENOCARCINOMA. Dr. C. Jeske
 SMALL BOWEL ADENOCARCINOMA Dr. C. Jeske Case presentation 54 year old female. Presents with OJ and weight loss. Abdominal examination only reveals a palpable gallbladder. ERCP reveals a circumferential
SMALL BOWEL ADENOCARCINOMA Dr. C. Jeske Case presentation 54 year old female. Presents with OJ and weight loss. Abdominal examination only reveals a palpable gallbladder. ERCP reveals a circumferential
Bowel obstruction and tumors
 Bowel obstruction and tumors Intestinal Obstruction Obstruction of the GI tract may occur at any level, but the small intestine is most often involved because of its relatively narrow lumen. Causes: Hernias
Bowel obstruction and tumors Intestinal Obstruction Obstruction of the GI tract may occur at any level, but the small intestine is most often involved because of its relatively narrow lumen. Causes: Hernias
ADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY...
 Colorectal Pathway Board: Non-Surgical Oncology Guidelines October 2015 Organization» Table of Contents ADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY... 2 DUKES C/ TNM STAGE 3... 2 DUKES B/ TNM STAGE 2... 3 LOCALLY ADVANCED
Colorectal Pathway Board: Non-Surgical Oncology Guidelines October 2015 Organization» Table of Contents ADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY... 2 DUKES C/ TNM STAGE 3... 2 DUKES B/ TNM STAGE 2... 3 LOCALLY ADVANCED
Pathology reports, related operative reports and consult letters must be provided with a request for assessment.
 Page 1 of 6 Polyposis Syndromes Inherited risk for colorectal cancer is associated with a number of polyposis syndromes (genes), some of which are well-defined and others are less common. Identification
Page 1 of 6 Polyposis Syndromes Inherited risk for colorectal cancer is associated with a number of polyposis syndromes (genes), some of which are well-defined and others are less common. Identification
Handling & Grossing of Colo-rectal Specimens for Tumours. for Medical Officers in Pathology
 Handling & Grossing of Colo-rectal Specimens for Tumours for Medical Officers in Pathology Dr Gayana Mahendra Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya Your Role in handling colorectal
Handling & Grossing of Colo-rectal Specimens for Tumours for Medical Officers in Pathology Dr Gayana Mahendra Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya Your Role in handling colorectal
Colonic Polyp. Najmeh Aletaha. MD
 Colonic Polyp Najmeh Aletaha. MD 1 Polyps & classification 2 Colorectal cancer risk factors 3 Pathogenesis 4 Surveillance polyp of the colon refers to a protuberance into the lumen above the surrounding
Colonic Polyp Najmeh Aletaha. MD 1 Polyps & classification 2 Colorectal cancer risk factors 3 Pathogenesis 4 Surveillance polyp of the colon refers to a protuberance into the lumen above the surrounding
Neoplastic Colon Polyps. Joyce Au SUNY Downstate Grand Rounds, October 18, 2012
 Neoplastic Colon Polyps Joyce Au SUNY Downstate Grand Rounds, October 18, 2012 CASE 55M with Hepatitis C, COPD (FEV1=45%), s/p vasectomy, knee surgery Meds: albuterol, flunisolide, mometasone, tiotropium
Neoplastic Colon Polyps Joyce Au SUNY Downstate Grand Rounds, October 18, 2012 CASE 55M with Hepatitis C, COPD (FEV1=45%), s/p vasectomy, knee surgery Meds: albuterol, flunisolide, mometasone, tiotropium
B Base excision repair, in MUTYH-associated polyposis and colorectal cancer, BRAF testing, for hereditary colorectal cancer, 696
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatous polyposis, familial. See Familial adenomatous polyposis. Anal anastomosis, ileal-pouch, proctocolectomy with, in FAP, 591
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatous polyposis, familial. See Familial adenomatous polyposis. Anal anastomosis, ileal-pouch, proctocolectomy with, in FAP, 591
Gastric and Colon Cancer. Dr. Andres Wiernik 2017
 Gastric and Colon Cancer Dr. Andres Wiernik 2017 GASTRIC CANCER Gastric Cancer Classification Epidemiology General principles of Management 25% GE Junction Gastric Cancer 75% Gastric Cancer Epidemiology
Gastric and Colon Cancer Dr. Andres Wiernik 2017 GASTRIC CANCER Gastric Cancer Classification Epidemiology General principles of Management 25% GE Junction Gastric Cancer 75% Gastric Cancer Epidemiology
Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy
 Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy Educational Objectives Identify classifications of polyps Describe several types of polyps Verbalize rationale for polypectomy Identify risk factors
Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy Educational Objectives Identify classifications of polyps Describe several types of polyps Verbalize rationale for polypectomy Identify risk factors
Colorectal polyps. Colorectal polyps may be classified as
 Colorectal polyps Polyp is a clinical term that describes any projection from the surface of the intestinal mucosa regardless of its histologic nature. Colorectal polyps may be classified as A) Neoplastic
Colorectal polyps Polyp is a clinical term that describes any projection from the surface of the intestinal mucosa regardless of its histologic nature. Colorectal polyps may be classified as A) Neoplastic
Locally Advanced Colon Cancer. Feiran Lou MD. MS. Richmond University Medical Center Department of Surgery
 Locally Advanced Colon Cancer Feiran Lou MD. MS. Richmond University Medical Center Department of Surgery Case 34 yo man presented with severe RLQ abdominal pain X 24 hrs. No nausea/vomiting/fever. + flatus.
Locally Advanced Colon Cancer Feiran Lou MD. MS. Richmond University Medical Center Department of Surgery Case 34 yo man presented with severe RLQ abdominal pain X 24 hrs. No nausea/vomiting/fever. + flatus.
A916: rectum: adenocarcinoma
 General facts of colorectal cancer The colon has cecum, ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid colon sections. Cancer can start in any of the r sections or in the rectum. The wall of each of these
General facts of colorectal cancer The colon has cecum, ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid colon sections. Cancer can start in any of the r sections or in the rectum. The wall of each of these
UPDATE IN THE MANAGEMENT AND TREATMENT OF COLORECTAL CANCER. Edwin A. Empaynado, MD Advocare Colon and Rectal Surgical Specialists
 UPDATE IN THE MANAGEMENT AND TREATMENT OF COLORECTAL CANCER Edwin A. Empaynado, MD Advocare Colon and Rectal Surgical Specialists WHAT IS COLON CANCER? WHAT CAUSES COLORECTAL CANCER? WHAT ARE THE RISK
UPDATE IN THE MANAGEMENT AND TREATMENT OF COLORECTAL CANCER Edwin A. Empaynado, MD Advocare Colon and Rectal Surgical Specialists WHAT IS COLON CANCER? WHAT CAUSES COLORECTAL CANCER? WHAT ARE THE RISK
Resident Seminar Aug 19 th, 2015 Colon: Neoplastic. Scott Rieder Dr. Colquhoun
 Resident Seminar Aug 19 th, 2015 Colon: Neoplastic Scott Rieder Dr. Colquhoun Objectives Medical Expert: 1. The biologic basis of colon neoplasia 2. Colon cancer screening (guidelines and evidence) 3.
Resident Seminar Aug 19 th, 2015 Colon: Neoplastic Scott Rieder Dr. Colquhoun Objectives Medical Expert: 1. The biologic basis of colon neoplasia 2. Colon cancer screening (guidelines and evidence) 3.
Familial and Hereditary Colon Cancer
 Familial and Hereditary Colon Cancer Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, FACG, FASGE, FACP GI Section Chief, Minneapolis VAMC Associate Professor, Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, University of
Familial and Hereditary Colon Cancer Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, FACG, FASGE, FACP GI Section Chief, Minneapolis VAMC Associate Professor, Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, University of
Disclosures. Colorectal Cancer Update GAFP November Risk Assessment. Colon and Rectal Cancer The Challenge. Issues in Colon and Rectal Cancer
 Disclosures Colorectal Cancer Update GAFP November 2006 Robert C. Hermann, MD Georgia Center for Oncology Research and Education Northwest Georgia Oncology Centers, PC WellStar Health System Marietta,
Disclosures Colorectal Cancer Update GAFP November 2006 Robert C. Hermann, MD Georgia Center for Oncology Research and Education Northwest Georgia Oncology Centers, PC WellStar Health System Marietta,
Razvan I. Arsenescu, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Digestive Diseases EARLY DETECTION OF COLORECTAL CANCER
 Razvan I. Arsenescu, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Digestive Diseases EARLY DETECTION OF COLORECTAL CANCER Epidemiology of CRC Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a common and lethal disease Environmental
Razvan I. Arsenescu, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Digestive Diseases EARLY DETECTION OF COLORECTAL CANCER Epidemiology of CRC Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a common and lethal disease Environmental
ADVANCES IN COLORECTAL CANCERS IS THERE HOPE? Dr Lim Hwee Yong Medical Oncologist
 ADVANCES IN COLORECTAL CANCERS IS THERE HOPE? Dr Lim Hwee Yong Medical Oncologist limhweeyong@live.com CRC: Epidemiology in 2012 Third most common cancer diagnosis in US [1] Estimated 143,460 new cases
ADVANCES IN COLORECTAL CANCERS IS THERE HOPE? Dr Lim Hwee Yong Medical Oncologist limhweeyong@live.com CRC: Epidemiology in 2012 Third most common cancer diagnosis in US [1] Estimated 143,460 new cases
EARLY DETECTION OF COLORECTAL CANCER. Epidemiology of CRC
 Razvan I. Arsenescu, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Digestive Diseases EARLY DETECTION OF COLORECTAL CANCER Epidemiology of CRC Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a common and lethal disease Environmental
Razvan I. Arsenescu, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Digestive Diseases EARLY DETECTION OF COLORECTAL CANCER Epidemiology of CRC Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a common and lethal disease Environmental
Colon Cancer Screening & Surveillance. Amit Patel, MD PGY-4 GI Fellow
 Colon Cancer Screening & Surveillance Amit Patel, MD PGY-4 GI Fellow Epidemiology CRC incidence and mortality rates vary markedly around the world. Globally, CRC is the third most commonly diagnosed cancer
Colon Cancer Screening & Surveillance Amit Patel, MD PGY-4 GI Fellow Epidemiology CRC incidence and mortality rates vary markedly around the world. Globally, CRC is the third most commonly diagnosed cancer
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominoperineal excision, of rectal cancer, 93 111 current controversies in, 106 109 extent of perineal dissection and removal of pelvic floor,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominoperineal excision, of rectal cancer, 93 111 current controversies in, 106 109 extent of perineal dissection and removal of pelvic floor,
Colon and Rectum. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6th edition
 Colon and Rectum Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the colon and rectum. Carcinoid tumors, lymphomas, sarcomas, and tumors of the vermiform appendix are excluded. Protocol revision date: January
Colon and Rectum Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the colon and rectum. Carcinoid tumors, lymphomas, sarcomas, and tumors of the vermiform appendix are excluded. Protocol revision date: January
Term: FIMS Week: CBL SESSION Surgery
 Term: FIMS Week: CBL SESSION Surgery CBL Title: Colo-Rectal Cancer CBL Session Coordinators: Coordinators email/phone: Key issues that may be addressed in CBL sessions: SUGGESTED LIKELY CASES FOR DISCUSSION
Term: FIMS Week: CBL SESSION Surgery CBL Title: Colo-Rectal Cancer CBL Session Coordinators: Coordinators email/phone: Key issues that may be addressed in CBL sessions: SUGGESTED LIKELY CASES FOR DISCUSSION
Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels.
 Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels. Abscess A localised collection of pus in a cavity that is formed by the decay of diseased
Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels. Abscess A localised collection of pus in a cavity that is formed by the decay of diseased
Colorectal or bowel cancer
 Colorectal or bowel cancer What is colorectal or bowel cancer? Colorectal cancer is a malignant (spreading) tumour that affects the large bowel. It is the second most common cause of death from cancer
Colorectal or bowel cancer What is colorectal or bowel cancer? Colorectal cancer is a malignant (spreading) tumour that affects the large bowel. It is the second most common cause of death from cancer
A superficial radiotherapy B single pass curettage C excision with 2 mm margins D excision with 5 mm margins E Mohs micrographic surgery.
 1- A 63-year-old woman presents with a non-healing lesion on her right temple that has been present for over two years. On examination there is a 6 mm well defined lesion with central ulceration, telangiectasia
1- A 63-year-old woman presents with a non-healing lesion on her right temple that has been present for over two years. On examination there is a 6 mm well defined lesion with central ulceration, telangiectasia
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System
 Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
BOWEL CANCER. Causes of bowel cancer
 A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
RECTAL CANCER CLINICAL CASE PRESENTATION
 RECTAL CANCER CLINICAL CASE PRESENTATION Francesco Sclafani Medical Oncologist, Clinical Research Fellow The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK esmo.org Disclosure I have nothing to declare
RECTAL CANCER CLINICAL CASE PRESENTATION Francesco Sclafani Medical Oncologist, Clinical Research Fellow The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK esmo.org Disclosure I have nothing to declare
Locally aggressive colonic and rectal cancer clinical trial
 Journal of Medicine and Life Vol. 3, No.3, July September 2010, pp.314 319 Locally aggressive colonic and rectal cancer clinical trial Victor Radu, Daniel Ion, Mihai Bogdan Şerban, Mircea Ciurea General
Journal of Medicine and Life Vol. 3, No.3, July September 2010, pp.314 319 Locally aggressive colonic and rectal cancer clinical trial Victor Radu, Daniel Ion, Mihai Bogdan Şerban, Mircea Ciurea General
COLON CANCER CARE GUIDELINES NON-METASTATIC DISEASE
 COLON CANCER CARE GUIDELINES NON-METASTATIC DISEASE Guideline Authors: Todd S. Crocenzi, M.D.; Mark Whiteford, M.D.; Matthew Solhjem, M.D.; Carlo Bifulco, M.D.; Melissa Li, M.D.; Christopher Cai, M.D.;
COLON CANCER CARE GUIDELINES NON-METASTATIC DISEASE Guideline Authors: Todd S. Crocenzi, M.D.; Mark Whiteford, M.D.; Matthew Solhjem, M.D.; Carlo Bifulco, M.D.; Melissa Li, M.D.; Christopher Cai, M.D.;
[A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
![[A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE] [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]](/thumbs/88/117127924.jpg) 2013 COLORECTAL SURGERY GROUP Dr. Carl J. Brown Dr. Ahmer A. Karimuddin Dr. P. Terry Phang Dr. Manoj J. Raval Authored by Jennifer Lee A cartoon about colonoscopies. 1 [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
2013 COLORECTAL SURGERY GROUP Dr. Carl J. Brown Dr. Ahmer A. Karimuddin Dr. P. Terry Phang Dr. Manoj J. Raval Authored by Jennifer Lee A cartoon about colonoscopies. 1 [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
Disclosure. Acknowledgement. What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Rectal cancer imaging. None
 What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
Bowel obstruction and tumors
 Bowel obstruction and tumors Intestinal Obstruction Obstruction of the GI tract may occur at any level, but the small intestine is most often involved because of its relatively narrow lumen. Causes: Hernias
Bowel obstruction and tumors Intestinal Obstruction Obstruction of the GI tract may occur at any level, but the small intestine is most often involved because of its relatively narrow lumen. Causes: Hernias
COLORECTAL CANCER CASES
 COLORECTAL CANCER CASES Case #1 Case #2 Colorectal Cancer Case 1 A 52 year-old female attends her family physician for her yearly complete physical examination. Her past medical history is significant
COLORECTAL CANCER CASES Case #1 Case #2 Colorectal Cancer Case 1 A 52 year-old female attends her family physician for her yearly complete physical examination. Her past medical history is significant
Mr Chris Wakeman. General Surgeon University of Otago, Christchurch. 12:15-12:40 Management of Colorectal Cancer
 Mr Chris Wakeman General Surgeon University of Otago, Christchurch 12:15-12:40 Management of Colorectal Cancer Bowel cancer Chris Wakeman Colorectal Surgeon Christchurch Sam Simon (Simpsons) Elizabeth
Mr Chris Wakeman General Surgeon University of Otago, Christchurch 12:15-12:40 Management of Colorectal Cancer Bowel cancer Chris Wakeman Colorectal Surgeon Christchurch Sam Simon (Simpsons) Elizabeth
Structured Follow-Up after Colorectal Cancer Resection: Overrated. R. Taylor Ripley University of Colorado Grand Rounds April 23, 2007
 Structured Follow-Up after Colorectal Cancer Resection: Overrated R. Taylor Ripley University of Colorado Grand Rounds April 23, 2007 Guidelines for Colonoscopy Production: Surveillance US Multi-Society
Structured Follow-Up after Colorectal Cancer Resection: Overrated R. Taylor Ripley University of Colorado Grand Rounds April 23, 2007 Guidelines for Colonoscopy Production: Surveillance US Multi-Society
COLON AND RECTAL CANCER
 COLON AND RECTAL CANCER Mark Sun, MD Clinical Associate Professor of Surgery University of Minnesota No disclosures Objectives 1) Understand the epidemiology, management, and prognosis of colon and rectal
COLON AND RECTAL CANCER Mark Sun, MD Clinical Associate Professor of Surgery University of Minnesota No disclosures Objectives 1) Understand the epidemiology, management, and prognosis of colon and rectal
For identification, support and follow up related to Familial Gastrointestinal Cancer conditions. South Island Cancer Nurses Network September 2013
 For identification, support and follow up related to Familial Gastrointestinal Cancer conditions South Island Cancer Nurses Network September 2013 Who are we? Specialist multidisciplinary team: Nurse coordinators,
For identification, support and follow up related to Familial Gastrointestinal Cancer conditions South Island Cancer Nurses Network September 2013 Who are we? Specialist multidisciplinary team: Nurse coordinators,
Familial and Hereditary Colon Cancer
 Familial and Hereditary Colon Cancer Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, FACG, FASGE, FACP GI Section Chief, Minneapolis VAMC Associate Professor, Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, University of
Familial and Hereditary Colon Cancer Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, FACG, FASGE, FACP GI Section Chief, Minneapolis VAMC Associate Professor, Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, University of
Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci. Colon polyps. Colorectal cancer
 Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Colon polyps Colorectal cancer Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine 18 Ed. 2012 Colorectal cancer 70% Colorectal cancer CRC and colon
Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Colon polyps Colorectal cancer Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine 18 Ed. 2012 Colorectal cancer 70% Colorectal cancer CRC and colon
Rectal Cancer. GI Practice Guideline
 Rectal Cancer GI Practice Guideline Dr. Brian Dingle MSc, MD, FRCPC Dr. Francisco Perera MD, FRCPC (Radiation Oncologist) Dr. Jay Engel MD, FRCPC (Surgical Oncologist) Approval Date: 2006 This guideline
Rectal Cancer GI Practice Guideline Dr. Brian Dingle MSc, MD, FRCPC Dr. Francisco Perera MD, FRCPC (Radiation Oncologist) Dr. Jay Engel MD, FRCPC (Surgical Oncologist) Approval Date: 2006 This guideline
Rectal Cancer. About the Colon and Rectum. Symptoms. Colorectal Cancer Screening
 Patient information regarding care and surgery associated with RECTAL CANCER by Robert K. Cleary, M.D., John C. Eggenberger, M.D., Amalia J. Stefanou., M.D. location: Michigan Heart and Vascular Institute,
Patient information regarding care and surgery associated with RECTAL CANCER by Robert K. Cleary, M.D., John C. Eggenberger, M.D., Amalia J. Stefanou., M.D. location: Michigan Heart and Vascular Institute,
COLON CANCER GENETICS (FOR SURGEONS) Mark W. Arnold MD Chief, Division of Colon and Rectal Surgery Professor of Surgery The Ohio State University
 COLON CANCER GENETICS (FOR SURGEONS) Mark W. Arnold MD Chief, Division of Colon and Rectal Surgery Professor of Surgery The Ohio State University 1. I am a surgeon; of course I have nothing to disclose.
COLON CANCER GENETICS (FOR SURGEONS) Mark W. Arnold MD Chief, Division of Colon and Rectal Surgery Professor of Surgery The Ohio State University 1. I am a surgeon; of course I have nothing to disclose.
Appendix 1 (as supplied by the authors): Supplementary tables. Supplementary Table A1. Description of OHIP codes used in the current study.
 Appendix 1 (as supplied by the authors): Supplementary tables Supplementary Table A1. Description of OHIP codes used in the current study. OHIP Billing Code OHIP Billing Code Description Colonoscopy and
Appendix 1 (as supplied by the authors): Supplementary tables Supplementary Table A1. Description of OHIP codes used in the current study. OHIP Billing Code OHIP Billing Code Description Colonoscopy and
References. GI Biopsies. What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD
 What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD jcrawford1@nshs.edu Executive Director and Senior Vice President for Laboratory Services North
What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD jcrawford1@nshs.edu Executive Director and Senior Vice President for Laboratory Services North
Colon Cancer , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. oc Last reviewed: 05/17/2017 1
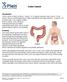 Colon Cancer Introduction Colon cancer is fairly common. About 1 in 15 people develop colon cancer. Colon cancer can be a life threatening condition that affects the large intestine. However, if it is
Colon Cancer Introduction Colon cancer is fairly common. About 1 in 15 people develop colon cancer. Colon cancer can be a life threatening condition that affects the large intestine. However, if it is
Guidelines for Laparoscopic Resection of Curable Colon and Rectal Cancer
 SAGES Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons http://www.sages.org Guidelines for Laparoscopic Resection of Curable Colon and Rectal Cancer Author : SAGES Webmaster PREAMBLE The following
SAGES Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons http://www.sages.org Guidelines for Laparoscopic Resection of Curable Colon and Rectal Cancer Author : SAGES Webmaster PREAMBLE The following
Screening & Surveillance Guidelines
 Chapter 2 Screening & Surveillance Guidelines I. Eligibility Coloradans ages 50 and older (average risk) or under 50 at elevated risk for colon cancer (personal or family history) that meet the following
Chapter 2 Screening & Surveillance Guidelines I. Eligibility Coloradans ages 50 and older (average risk) or under 50 at elevated risk for colon cancer (personal or family history) that meet the following
Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Surgery: What You Should Know
 Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Surgery: What You Should Know Ask the Experts March 9, 2019 Kristen Blaker, MD Colon and Rectal Surgery MetroHealth Medical Center Disclosures None Outline Who undergoes
Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Surgery: What You Should Know Ask the Experts March 9, 2019 Kristen Blaker, MD Colon and Rectal Surgery MetroHealth Medical Center Disclosures None Outline Who undergoes
COLON AND RECTAL CANCER
 No disclosures COLON AND RECTAL CANCER Mark Sun, MD Clinical Assistant Professor of Surgery University of Minnesota Colon and Rectal Cancer Statistics Overall Incidence 2016 134,490 new cases 8.0% of all
No disclosures COLON AND RECTAL CANCER Mark Sun, MD Clinical Assistant Professor of Surgery University of Minnesota Colon and Rectal Cancer Statistics Overall Incidence 2016 134,490 new cases 8.0% of all
Classification of polyposis syndromes two major groups. Adenomatous polyposis syndromes. Hamartomatous polyposis syndromes
 Hereditary polyposis syndromes Classification of polyposis syndromes two major groups adenomatous and non-adenomatous polyposis syndromes Adenomatous polyposis syndromes Familial adenomatous polyposis(fap)
Hereditary polyposis syndromes Classification of polyposis syndromes two major groups adenomatous and non-adenomatous polyposis syndromes Adenomatous polyposis syndromes Familial adenomatous polyposis(fap)
Clinical Practice Guidelines
 Clinical Practice Guidelines FOR THE PREVENTION, EARLY DETECTION AND MANAGEMENT OF COLORECTAL CANCER APPROVED BY Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention, Early Detection and Management of Colorectal
Clinical Practice Guidelines FOR THE PREVENTION, EARLY DETECTION AND MANAGEMENT OF COLORECTAL CANCER APPROVED BY Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention, Early Detection and Management of Colorectal
Gastroenterology Tutorial
 Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Colon, or Colorectal, Cancer Information
 Colon, or Colorectal, Cancer Information Definition Colon, or colorectal, cancer is cancer that starts in the large intestine (colon) or the rectum (end of the colon). Other types of cancer can affect
Colon, or Colorectal, Cancer Information Definition Colon, or colorectal, cancer is cancer that starts in the large intestine (colon) or the rectum (end of the colon). Other types of cancer can affect
GUIDANCE ON THE INDICATIONS FOR DIAGNOSTIC UPPER GI ENDOSCOPY, FLEXIBLE SIGMOIDOSCOPY AND COLONOSCOPY
 Position Statement produced by BSG, AUGIS and ACPGBI GUIDANCE ON THE INDICATIONS FOR DIAGNOSTIC UPPER GI ENDOSCOPY, FLEXIBLE SIGMOIDOSCOPY AND COLONOSCOPY Introduction In 2011 the Independent Practice
Position Statement produced by BSG, AUGIS and ACPGBI GUIDANCE ON THE INDICATIONS FOR DIAGNOSTIC UPPER GI ENDOSCOPY, FLEXIBLE SIGMOIDOSCOPY AND COLONOSCOPY Introduction In 2011 the Independent Practice
Small Plicae Circularis. Short Closely packed together. Sparse, completely absent at distal part Lymphoid Nodule
 Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Surgery for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 Surgery for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Emily Steinhagen, MD Assistant Professor Department of Surgery, Division of Colorectal Surgery University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center Common Questions Why
Surgery for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Emily Steinhagen, MD Assistant Professor Department of Surgery, Division of Colorectal Surgery University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center Common Questions Why
Rectal cancer with synchroneous liver mets: A challenging clinical case
 ESMO Preceptorship Programme Rectal cancer Singapur November 2017 Rectal cancer with synchroneous liver mets: A challenging clinical case Andrés Cervantes Disclosures Consulting and advisory services,
ESMO Preceptorship Programme Rectal cancer Singapur November 2017 Rectal cancer with synchroneous liver mets: A challenging clinical case Andrés Cervantes Disclosures Consulting and advisory services,
Cancer Genomics 101. BCCCP 2015 Annual Meeting
 Cancer Genomics 101 BCCCP 2015 Annual Meeting Objectives Identify red flags in a person s personal and family medical history that indicate a potential inherited susceptibility to cancer Develop a systematic
Cancer Genomics 101 BCCCP 2015 Annual Meeting Objectives Identify red flags in a person s personal and family medical history that indicate a potential inherited susceptibility to cancer Develop a systematic
Colonic polyps and colon cancer. Andrew Macpherson Director of Gastroentology University of Bern
 Colonic polyps and colon cancer Andrew Macpherson Director of Gastroentology University of Bern Improtance of the problem of colon cancers - Epidemiology Lifetime risk 5% Incidence/10 5 /annum (US Detroit
Colonic polyps and colon cancer Andrew Macpherson Director of Gastroentology University of Bern Improtance of the problem of colon cancers - Epidemiology Lifetime risk 5% Incidence/10 5 /annum (US Detroit
By: Tania Cortas, MD Arizona Oncology 03/10/2015
 By: Tania Cortas, MD Arizona Oncology 03/10/2015 Epidemiology In the United States, CRC incidence rates have declined about 2 to 3 percent per year over the last 15 years Death rates from CRC have declined
By: Tania Cortas, MD Arizona Oncology 03/10/2015 Epidemiology In the United States, CRC incidence rates have declined about 2 to 3 percent per year over the last 15 years Death rates from CRC have declined
OFCCR CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT FORM
 OFCCR CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT FORM Name: _, OFCCR # _ OCGN # _ OCR Group # _ HIN# Sex: MALE FEMALE UNKNOWN Date of Birth: DD MMM YYYY BASELINE DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT 1. Place of Diagnosis: Name
OFCCR CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT FORM Name: _, OFCCR # _ OCGN # _ OCR Group # _ HIN# Sex: MALE FEMALE UNKNOWN Date of Birth: DD MMM YYYY BASELINE DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT 1. Place of Diagnosis: Name
Case Conference. Craig Morgenthal Department of Surgery Long Island College Hospital
 Case Conference Craig Morgenthal Department of Surgery Long Island College Hospital Neoadjuvant versus Adjuvant Radiation Therapy in Rectal Carcinoma Epidemiology American Cancer Society statistics for
Case Conference Craig Morgenthal Department of Surgery Long Island College Hospital Neoadjuvant versus Adjuvant Radiation Therapy in Rectal Carcinoma Epidemiology American Cancer Society statistics for
Department of Surgery, Aizu Central Hospital, Fukushima
 Case Reports Resection of Asynchronous Quadruple Advanced Colonic Carcinomas Followed by Reconstruction with Ileal Interposition between the Transverse Colon and Rectum Sho Mineta 1, Kimiyoshi Shimanuki
Case Reports Resection of Asynchronous Quadruple Advanced Colonic Carcinomas Followed by Reconstruction with Ileal Interposition between the Transverse Colon and Rectum Sho Mineta 1, Kimiyoshi Shimanuki
PANCREAS DUCTAL ADENOCARCINOMA PDAC
 CONTENTS PANCREAS DUCTAL ADENOCARCINOMA PDAC I. What is the pancreas? II. III. IV. What is pancreas cancer? What is the epidemiology of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC)? What are the risk factors
CONTENTS PANCREAS DUCTAL ADENOCARCINOMA PDAC I. What is the pancreas? II. III. IV. What is pancreas cancer? What is the epidemiology of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC)? What are the risk factors
GENETIC MANAGEMENT OF A FAMILY HISTORY OF FAP or MUTYH ASSOCIATED POLYPOSIS. Family Health Clinical Genetics. Clinical Genetics department
 GENETIC MANAGEMENT OF A FAMILY HISTORY OF FAP or MUTYH ASSOCIATED POLYPOSIS Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: GUIDELINES FOR THE GENETIC MANAGEMENT OF A FAMILY
GENETIC MANAGEMENT OF A FAMILY HISTORY OF FAP or MUTYH ASSOCIATED POLYPOSIS Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: GUIDELINES FOR THE GENETIC MANAGEMENT OF A FAMILY
PATHOLOGY GROUP GUIDELINES FOR THE EXAMINATION AND REPORTING OF COLORECTAL CANCER SPECIMENS
 PATHOLOGY GROUP GUIDELINES FOR THE EXAMINATION AND REPORTING OF COLORECTAL CANCER SPECIMENS Produced by: Address: Yorkshire Cancer Network Pathology Group Arthington House, Cookridge Hospital, Hospital
PATHOLOGY GROUP GUIDELINES FOR THE EXAMINATION AND REPORTING OF COLORECTAL CANCER SPECIMENS Produced by: Address: Yorkshire Cancer Network Pathology Group Arthington House, Cookridge Hospital, Hospital
Nasogastric tube. Stomach. Pylorus. Duodenum 1. Duodenum 2. Duodenum 3. Duodenum 4
 Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Seventh Edition Staging 2017 Colorectum. Overview. This webinar is sponsored by. the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
 Seventh Edition Staging 2017 Colorectum Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Validating science. Improving patient care. No materials in this presentation may be repurposed in print or online without the express
Seventh Edition Staging 2017 Colorectum Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Validating science. Improving patient care. No materials in this presentation may be repurposed in print or online without the express
Bowel Cancer Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
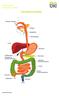 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about bowel cancer Throughout our lives, the lining of the bowel constantly renews itself. This lining contains many millions of tiny cells, which grow, serve their
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about bowel cancer Throughout our lives, the lining of the bowel constantly renews itself. This lining contains many millions of tiny cells, which grow, serve their
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN
 UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
