The influence of vegetable-oil based polyols on physico-mechanical and thermal properties of polyurethane foams
|
|
|
- Whitney Quinn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Short communication The influence of vegetable-oil based polyols on physico-mechanical and thermal properties of polyurethane foams Aleksandra Badan 1, *, Tomasz M. Majka 1 1 Aleksandra Badan Cracow University of Technology, Department of chemistry and technology of polymers, Warszawska 24, Cracow Poland; aleksandrabadan@gmail.com 1 Tomasz M. Majka Cracow University of Technology, Department of chemistry and technology of polymers, Warszawska 24, Cracow Poland; tomasz.majka@pk.edu.pl * Correspondence: aleksandrabadan@gmail.com; Tel.: Received: 24/10/2017 Abstract: Polyurethanes during the last 50 years have become one of the most developing polymers and it is almost impossible to find an industry field, where they are not used. This term concerns a wide range of materials, both expanded and non-expanded products. PUs are widely used in many applications as foams (flexible, semi-flexible and rigid foams), elastomers, adhesives, fibers and obtained by the exothermic reaction of an oligomeric polyol (the substance which contains at least two hydroxyl groups) and polyfunctional isocyanates. PU foams are considered to be one of the most efficient materials for insulation with many desirable properties (very low conductivity, low density and water absorption, dimensional stability and high eco-efficiency index to save energy). Nowadays, rigid polyurethane foams are synthesized using vegetable-oil based polyols, which is connected to their abundance and economy. What is more, materials synthesized from renewable resources can almost fully replace their petrochemical analogs. Several types of vegetable oils have been already used, such as soy bean oil, palm oil, linseed oil and sunflower oil. Such oils are characterized by low amount of functional groups, however present in the structure unsaturated bonds can be successfully converted into hydroxyl groups. The great possibility is using waste cooking oil to synthesize polyol, but the biggest problem is low number of hydroxyl value and contaminations from food. It is necessary to check the influence of various polyol systems on physical, mechanical and thermal insulation properties, as well as on the cellular structure. Keywords: polyurethanes, vegetable oils, biobased polyols 1. Introduction Polyurethanes (PUs) have actually very short history, but very fast became one of the most developing group of polymers. Polyurethane is a material widely used in many different applications, such as foams, elastomers, adhesives or fibers and so on. Additionally, they are used in some specialty applications (biomedical surgery). They are clearly a great research subject due to their mechanical, physical and chemical properties. Polyurethanes are obtained by the reaction of an oligomeric polyol and diisocyanate. The structure and properties of polyol have a great influence on the properties of the resulting polymer [1]. In addition, to control reactions and properties of PU foams, many additives such as catalysts, surfactants, fillers, chain extenders and flame retardants are added [2]. Nowadays, mostly petrochemical raw materials are used to produce polyurethanes. It has changed due to the uncertainty in terms of price and availability of petroleum. What is more, there are tendencies to develop a sustainable chemistry and use of renewable resources. This is the reason Proceedings 2017, 1, x; doi: FOR PEER REVIEW
2 Proceedings 2017, 1, x FOR PEER REVIEW 2 of 7 why chemical industry has paid their attention to the production of biobased polyols, mainly synthesized from vegetable oils [3]. It is important to realize that biobased product is not necessarily a biodegradable material, but only a material made from renewable resources [1-3]. Most of the polyols used for polyurethane synthesis are polyether polyols (75%), which are obtained by the reaction between a starter polyol and an alkylene oxide. Typical industrial starters are ethylene glycol, glycerol, sorbitol, sucrose, water, ethylenediamine and diaminotoluene. The most important for synthesis of polyether polyols is glycerol which is produced by the hydrolysis of natural triglycerides, from vegetable or animal resources [3]. Long-chain polyether polyols usually have on OH number below 100 mg KOH/g and around 2-3 hydroxyl groups/mol, and molecular weights of daltons. They are mainly used for flexible foams. On the contrary, short-chain polyether polyols usually have an OH number of 200 mg KOH/g, high functionality (3-8 hydroxyl groups/mol) and molecular weight about daltons. Using short-chain polyether polyols leads to a rigid crosslinked polyurethane. Polyester polyols are also used (25%), resulting from step growth polycondensation between dicarboxylic acid and polyol in excess [3-4]. Unfortunately, a 100% biobased polyurethane is not available yet because of the unsatisfactory properties. So far researchers have developed materials that contains about 50% biobased components with no worse properties than petrobased polyurethanes [5]. Depending on the application the renewable content of commercially available bio-based polyols varies between %. As a consequence the renewable content of bio-based substract in PU also varies around 8-70% (Table 1) [6]. Table 1. Renewable content of commercial available bio-based polyols and PURs Renewable source for polyols Bio-content in polyols Bio-content in PUR sucrose 30% <8%(rigid foam) soybean % 5-60% (rigid&flexible foam) castor oil % 22-70% (flexible&rigid foam) sunflower oil n/a 25% (flexible foam) corn sugar 100% n/a 2. Synthesis of bio-polyols Vegetable oils come from many various plants, such as soybean, palm, rapeseed and so on and contain mainly triglycerides molecules, where the three hydroxyl functions of glycerin are esterified with fatty acids, which could be saturated or unsaturated [3]. The most important are unsaturated oils, which double bonds can be transformed into hydroxyl groups [3,7]. There are four methods that could be used to prepare polyols from vegetable oils (Table 2) [8]: oxidation and epoxidation; esterification; hydroformylation; ozonolysis. Table 2. Methods of preparing polyols from vegetable oils Name of reaction Scheme
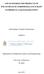
3 Proceedings 2017, 1, x FOR PEER REVIEW 3 of 7 epoxidation ring-opening reaction hydrogenation of epoxides ozonolysis and hydrogenation hydroformylation transesterification By the direct action of hydrogen peroxide on double bonds and then ring opening by using alcohols or inorganic acids a high degree of hydroxylation may be incorporated into polyols [3-4]. Vegetable oils that are characterized by a higher degree of unsaturation always produce polyols with much higher hydroxyl functionalities, which results in higher crosslinked density PUs[ 4]. Castor oil, derived from the bean contains 87-90% ricinoleic acid (fatty acid triglyceride) and it can be transesterified with a polyhydroxylated compound such as glycerine in order to obtain higher hydroxyl functionality. Hydroformylation route consists of two steps. In the first one, vegetable oils react with syngas- CO and H2 in the presence of rhodium, which is a better catalyst (almost 100% efficiency) or cobalt carbonyls (about 60% efficiency). This reaction introduces aldehyde groups, which are then converted to hydroxyls in the second step (hydrogenation). Polyols obtained in this route have longer network chains than the polyols prepared by epoxidation due to an extra carbon at every double bond. Ozonolysis of vegetable oil typically involves two main steps: formation of ozonide at the unsaturation sites of vegetable oils and its decomposition into aldehyde and carboxylic acid. The second step is reduction of aldehyde into alcohol (with a catalyst). Ozonolysis of soybean oils results in triols, triglyceride diols and some mono-ols [1,7-8]. A special vegetable oil is castor oil, extracted from the seeds of the plant Ricinus communis, which is a triglyceride of ricinoleic acid and contains naturally occurring hydroxyl groups ( Figure 1).
4 Proceedings 2017, 1, x FOR PEER REVIEW 4 of 7 Figure 1. Chemical structure of major fatty acid in castor oil Natural castor oil has a functionality of around 2.7 OH groups/mol and an hydroxyl number of around 160 mg KOH/g and is used in many various applications, such as: coatings, rigid foams, adhesives, thermoplastic elastomers, flexible foams and so on. On the other side, castor oil has some major disadvantages: low functionality and low reactivity due to the secondary hydroxyl groups. It is possible to use two major modification to improve the properties and applicability of castor oil-based polyols for producing PUs. The first one is the transesterification/amidation and the other one is the alkoxylation using its hydroxyl groups and both lead to new polyols which can be used to obtain rigid polyurethane foams with good physico-mechanical properties. Castor oil used solo leads to semi-flexible to semi-rigid PU foams, but by mixing it with polyols such as glycerol a higher hydroxyl number of polyol is obtained [4,7]. 3. Properties of PU foams obtained by using bio-based polyols It is known that most of the conducted researches concerned soybean oil, which has become one of the most popular and used oils of the recent years. A.A. Beltran et all have conducted interesting researches which concern using soy-based polyols to obtain rigid polyurethane foams. As an isocyanate they used polymeric MDI (A side) and as a B ingredient they mixed polyols that constitutes 100 parts for the formulation of the rest of compounds (catalyst, surfactant, foaming agent). The polyol mix included Voranol 446, Voranol 640 and soy-based polyols with hydroxyl numbers of 120 from ethanol and 331 mg KOH/g from ethylene glycol. Both used polyols were prepared through an in situ epoxidation of the soybean oil. The soybean oil polyol percentage in the mix varied between 20 and 30% for a total of 4 blocks of rigid foam, two for each type of oleochemical polyol. Rigid PU foams are mainly used for thermal insulation and the most optimal density value between kg/m 3. When it comes to best possible compressive strength, for densities of 30 kg/m 3 it is in kpa. Obtained values (Table 3) indicate that these results validate the use of the produced foams in the polymeric industry. The author marks that produced foams can be especially used for insulation in refrigeration and cooling appliances [5]. Table 3. Properties for obtained PU foams Soybean based polyol from ethanol from ethylene glycol Block % Compressive strength [kpa] Conductivity [W/mK] Table 2 also presents conductivity of different PU foams. The characteristics of the obtained materials are comparable with the commercial ones [5]. Yusuf A.K. et all have also checked an influence of castor oil polyols on mechanical properties of rigid PU foams. They used two formulations: isocyanate/polyol (NCO/OH) ratios of ½ and 1/1 and one shot method. The glycerolized castor oil contained varying concentrations (10-60%) of the modifier and other ingredients were mixture of 2,4- and 2,6- toluene diisocyanate at room temperature, catalyst, physical blowing agent (methylene chloride) and surfactant (silicone oil). Hydroxyl number range for the modified castor oil polyols was mgkoh/g. Compressive
5 Proceedings 2017, 1, x FOR PEER REVIEW 5 of 7 strength of obtained PU foams increased steadily up to about 30 wt% of modifier concentration, followed by a sharp steep rise up to 60% (foams prepared using formulation II). The highest showed compressive strength value up to 450 KN/m 2. Higher hydroxyl functionality in polyol results in increased crosslinking reactions and therefore in formation of inter-chain network. This structure can results in increased density and rigidity in foam structure, which makes foam harder to compress [9]. Researches from Cracow University of Technology used bio-polyol based on rapeseed oil to produce flexible PU foams. One of the aims was to check the influence of bio-polyols production scale on selected mechanical and physical properties. However, it was observed that it has no significant impact on flexible PU foams properties (density, hardness, hysteresis, support factor and resilience), but it turned out that different values of bio-polyol has a great influence on the foams properties compared to the references foams which were not modified with the bio-polyols. PU formulations for the periodical synthesis are shown in Table 4 [10]. polyol symbol Table 4. The characteristics of applied bio-polyols and PUR formulation LOH [mgkoh/g] foam symbol content of petrochemical polyol [g] content of rapeseed oil-based polyol [g] content of catalysts [g] F REF1P RziP52 52 RziP52P RziP58 58 RziP58P RziP72 72 RziP72P RziP75 75 RziP75P RziP84 84 RziP84P Figure 2 shows the effect of polyol type on apparent density and hardness at 40% deformation of foams which were obtained with periodical method. It was observed that bio-polyol addition reduces the density of the obtained materials. It is connected to the increase of a catalyst amount [10]. Figure 2. Apparent density and hardness at 40% deformation of foams obtained using different bio-polyols The addition of a bio-polyol to PUR formulation increases the hardness at 40% deformation in a majority of foams, in comparison to the reference foam despite the apparent density reduction, what can be caused by the higher content of hard segments and difference in crosslinking density. The results of the conducted researches confirmed that the modification of polyurethane systems with rapeseed oil-based polyols can give beneficial effects [10]. Syuhada Mohd Tahir et all carried out studies to determine the potential of waste cooking oil in preparation of rigid PU foam. First, the raw waste cooking oil was filtered and adsorbed by using
6 Proceedings 2017, 1, x FOR PEER REVIEW 6 of 7 sugarcane bagasse activated carbon to purify the oil. Next, the transesterification reaction was used to synthesize polyol and then the obtained polyol was mixed with other chemicals to form PU rigid foam. The density and compressive strength of 60:54:90:40 of glycerol:water:polyol:amine polyurethane foam are kg/m 3 and 0.10 MPa. The study shows that waste cooking oils can be used in production of rigid PU foams with obtaining a satisfactory properties. The similarities in organic structure of waste cooking oil to vegetables oil make it a perfect starting material [11]. 4. Future perspectives Vegetable oils are becoming more and more popular in polyols synthesis due to their properties which let change them into the valuable polyols that can be used to produce not only PU foams but also elastomers, coatings and rigid plastics. Every material is characterized by the same or even better properties as products from the petroleum-based substracts. It is possible to obtain polyols with different reactivities, functionalities, molecular weights and other important properties. It is a great potential to change totally the world of PU foams, but vegetable oils and their derivatives still face challenges which are hard to solve, including costs of obtaining. However, advanced technologies are promising and the future of bio-based polyols looks very bright [1,12]. Author Contributions: Aleksandra Badan performed the experiments and analyzed the data; Aleksandra Badan and Tomasz M. Majka wrote the paper. Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results. References 1. Eaves David, Handbook of Polymer Foams, Rapra Technology Limited, Shawbury, UK, 2004, pp Chuayjuljit S., Maungchareon A., Saravari O., Preparation and Properties of Palm Oil-Based Rigid Polyurethane Nanocomposite Foams, Sage, 2008, , / Ionescu Michail, Chemistry and Technology of Polyols for Polyurethanes, Rapra Technology Limited, Shawbury, UK, 2005, pp Li Yebo, Luo Xiolan, Hu Shengjun, Bio-based Polyols and Polyurethanes, Springer, New York, 2015, pp A.A.Beltrán, L.A. Boyacá, Production of Rigid Polyurethane Foams from Soy-based Polyols, Latin American Applied Research, 2009, pp Li Shen, Juliane Haufe, Martin K. Patel, Product overview and market projection of emerging bio-based plastics, Group Science, Technology and Society, Copernicus Institute for Sustainable Development and Innovation Utrecht University, 2009, Guo A., Demydov D., Zhang W., Petrovic Z.S., Polyols and polyurethanes from hydroformylation of soybean oil, Journal of Polymers and the Environment, United States, 2002, Volume 10, 49-52, /A: Desroches M., Escouvois M., Auvergne R., Caillol S., Boutevin B., From Vegetable Oils to Polyurethanes: Synthetic Routes to Polyols and Moin Industrial Products, Polymer Reviews, Taylor&Francis, 2012, 52(1), pp.38., / A.K. Yusuf, P.A.P. Mamza, A.S. Ahmed, U. Agunwa, Physico-Mechanical Properties of Rigid Polyurethane Foams Synthesized From Modified Castor Oil Polyols, International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 7, , Malewska E., Bąk Sz., Kurańska M., Prociak A., The effect of various rapeseed oil-based polyols on selected properties of flexible polyurethane foams, Polimery, 2016, 61, , dx.doi.org/ /polimery Syuhada Mohd Tahir, Wan Norfir daus Wan Salleh, Nur Syahamatun Nor Hadid, Nor Fatihah Enderus, Nurul Aina Ismail, Synthesis of Waste Cooking Oil-Based Polyol Using Sugarcane Bagasse Activated Carbon and Tranesterification Reaction for Rigid Polyurethane Foam, Materials Science Forum, Vol.846, pp , 2015, / 12. Guo A., Zhang W., Petrovic Z.S., Structure-property relationships in polyurethanes derived from soybean oil, Springer, 2005, /s
7 Proceedings 2017, 1, x FOR PEER REVIEW 7 of by the authors. Submitted for possible open access publication under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
Characterization of Polyol Synthesized from Epoxidized Palm Oil Using Fourier Transform Infra-Red and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
 Characterization of Polyol Synthesized from Epoxidized Palm il Using Fourier Transform Infra-Red and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance W. N. Wan Tajulruddin a, A. R. Rahmat *,b, Z. A. Mohd Yusof c, A. Fakhari
Characterization of Polyol Synthesized from Epoxidized Palm il Using Fourier Transform Infra-Red and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance W. N. Wan Tajulruddin a, A. R. Rahmat *,b, Z. A. Mohd Yusof c, A. Fakhari
Role of Silicone on Molded Flexible Polyurethane from Soy Oil
 Role of Silicone on Molded Flexible Polyurethane from Soy Oil Flora Elvistia Firdaus Dept. of Chemical Engineering, Jayabaya University Jl. Pulomas Selatan Kav 23 Jakarta Timur- 13210, Indonesia Tel: 62-21-858-3591
Role of Silicone on Molded Flexible Polyurethane from Soy Oil Flora Elvistia Firdaus Dept. of Chemical Engineering, Jayabaya University Jl. Pulomas Selatan Kav 23 Jakarta Timur- 13210, Indonesia Tel: 62-21-858-3591
PRODUCTION OF FLEXIBLE POLYURETHANE FOAM FROM COMMERCIALLY SOYBASED PRECURSOR
 MATERIALS SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY Edited by Evvy Kartini et.al. PRODUCTION OF FLEXIBLE POLYURETHANE FOAM FROM COMMERCIALLY SOYBASED PRECURSOR Flora E. Firdaus Department of Chemical Engineering, Jayabaya
MATERIALS SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY Edited by Evvy Kartini et.al. PRODUCTION OF FLEXIBLE POLYURETHANE FOAM FROM COMMERCIALLY SOYBASED PRECURSOR Flora E. Firdaus Department of Chemical Engineering, Jayabaya
Synthesis of polyols from rapeseed oil
 Synthesis of polyols from rapeseed oil Sylwia Dworakowska, Dariusz Bogdał, Aleksander Prociak Faculty of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Politechnika Krakowska, ul. Warszawska 24, 31-155 Krakow, Poland
Synthesis of polyols from rapeseed oil Sylwia Dworakowska, Dariusz Bogdał, Aleksander Prociak Faculty of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Politechnika Krakowska, ul. Warszawska 24, 31-155 Krakow, Poland
Processing and Industrial Uses of Castor beans and Oil
 Processing and Industrial Uses of Castor beans and Oil Prepared for the Castor Workshop Guelph, March 19, 2011 by Levente L. Diosady Professor of Food Engineering University of Toronto Department of Chemical
Processing and Industrial Uses of Castor beans and Oil Prepared for the Castor Workshop Guelph, March 19, 2011 by Levente L. Diosady Professor of Food Engineering University of Toronto Department of Chemical
Bio-Based and Recycled Content Polyols. Product Brochure
 Bio-Based and Recycled Content Polyols Product Brochure Pioneering natural-based innovations for 175 years Emery Oleochemicals is a leading solutions provider in renewable-based specialty chemicals with
Bio-Based and Recycled Content Polyols Product Brochure Pioneering natural-based innovations for 175 years Emery Oleochemicals is a leading solutions provider in renewable-based specialty chemicals with
PREPARATION OF OLEOCHEMICAL POLYOLS DERIVED FROM SOYBEAN OIL
 Latin American Applied Research 41:69-74 (2011) PREPARATION OF OLEOCHEMICAL POLYOLS DERIVED FROM SOYBEAN OIL A. A.BELTRÁN and L.A.BOYACÁ MSc. Ing. Química, Univ. Nac. de Colombia, Bogotá, Colombia aabeltrano@unal.edu.co
Latin American Applied Research 41:69-74 (2011) PREPARATION OF OLEOCHEMICAL POLYOLS DERIVED FROM SOYBEAN OIL A. A.BELTRÁN and L.A.BOYACÁ MSc. Ing. Química, Univ. Nac. de Colombia, Bogotá, Colombia aabeltrano@unal.edu.co
Production of Flexible Polyurethane Foam using Soya Bean Oil and Palm Kernel Oil as Surfactant and Polyol Respectively
 Production of Flexible Polyurethane Foam using Soya Bean Oil and Palm Kernel Oil as Surfactant and Polyol Respectively Aremu, M. O. *, Ojetade, J. O. Olaluwoye, O. S. Biochemical Engineering and Biotechnology
Production of Flexible Polyurethane Foam using Soya Bean Oil and Palm Kernel Oil as Surfactant and Polyol Respectively Aremu, M. O. *, Ojetade, J. O. Olaluwoye, O. S. Biochemical Engineering and Biotechnology
Synergization of silicone with developed crosslinking to soy-based polyurethane foam matrix
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Synergization of silicone with developed crosslinking to soy-based polyurethane foam matrix To cite this article: Flora Elvistia Firdaus
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Synergization of silicone with developed crosslinking to soy-based polyurethane foam matrix To cite this article: Flora Elvistia Firdaus
Polyurethane Basic Products
 Polyurethane Basic s Isocyanates and polyols for versatile polymers RZ_CMBroschuere_Iso_Poly_Update_0705015.indd Committed to the customer At BASF, our focus is on understanding and meeting our customers
Polyurethane Basic s Isocyanates and polyols for versatile polymers RZ_CMBroschuere_Iso_Poly_Update_0705015.indd Committed to the customer At BASF, our focus is on understanding and meeting our customers
Bio-based Building Blocks - Priplast. Taipei, 24 th May 2017
 Bio-based Building Blocks - Priplast Taipei, 24 th May 2017 Bio-based Building Blocks Company introduction Raw materials Technology Features & benefits Conclusion Our History Where We Operate Our Technologies
Bio-based Building Blocks - Priplast Taipei, 24 th May 2017 Bio-based Building Blocks Company introduction Raw materials Technology Features & benefits Conclusion Our History Where We Operate Our Technologies
DIGLYCEROL. Solvay Interox. Diglycerol General Overview. Product Data Sheet
 Product Data Sheet DIGLYCEROL Diglycerol General Overview Polyglycerols have been known since the beginning of the 20th century, and polyglycerol fatty acid esters have been used in Europe and America
Product Data Sheet DIGLYCEROL Diglycerol General Overview Polyglycerols have been known since the beginning of the 20th century, and polyglycerol fatty acid esters have been used in Europe and America
Synthesis and Characterization of Polyols from Refined Cooking Oil for Polyurethane Foam Formation
 Synthesis and Characterization of Polyols from Refined Cooking Oil for Polyurethane Foam Formation Synthesis and Characterization of Polyols from Refined Cooking Oil for Polyurethane Foam Formation C.S.
Synthesis and Characterization of Polyols from Refined Cooking Oil for Polyurethane Foam Formation Synthesis and Characterization of Polyols from Refined Cooking Oil for Polyurethane Foam Formation C.S.
(51) Int Cl.: C08G 18/00 ( ) C07C 29/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 76_46A_T (11) EP 2 76 146 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 13.08.14 Bulletin 14/33 (21) Application number: 12837878.3
(19) TEPZZ 76_46A_T (11) EP 2 76 146 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 13.08.14 Bulletin 14/33 (21) Application number: 12837878.3
From Vegetable Oils to Polyurethanes: Synthetic Routes to Polyols and Main Industrial Products
 From Vegetable Oils to Polyurethanes: Synthetic Routes to Polyols and Main Industrial Products Myriam Desroches, Maxime Escouvois, Rémi Auvergne, Sylvain Caillol, Bernard Boutevin To cite this version:
From Vegetable Oils to Polyurethanes: Synthetic Routes to Polyols and Main Industrial Products Myriam Desroches, Maxime Escouvois, Rémi Auvergne, Sylvain Caillol, Bernard Boutevin To cite this version:
Synthesis and Characterization of Chlorinated Oils Based on Unmodified Castor Oil Polyol
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 8, Issue 11, November 2018 36 Synthesis and Characterization of Chlorinated Oils Based on Unmodified Castor Oil Polyol A.K. Yusuf 1,
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 8, Issue 11, November 2018 36 Synthesis and Characterization of Chlorinated Oils Based on Unmodified Castor Oil Polyol A.K. Yusuf 1,
Chemicals Based on Ethylene
 Chemicals Based on Ethylene Ethylene is sometimes known as the king of petrochemicals because more commercial chemicals are produced from ethylene than from any other intermediate. This unique position
Chemicals Based on Ethylene Ethylene is sometimes known as the king of petrochemicals because more commercial chemicals are produced from ethylene than from any other intermediate. This unique position
The Synergize effect of Chain extender to Phosporic acid catalyst to the ultimate property of Soy-Polyurethane
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The Synergize effect of Chain extender to Phosporic acid catalyst to the ultimate property of Soy-Polyurethane To cite this article: Flora Elvistia
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The Synergize effect of Chain extender to Phosporic acid catalyst to the ultimate property of Soy-Polyurethane To cite this article: Flora Elvistia
4 Types of Organic Polar Reactions
 Objective 12 Apply Reactivity Principles to Electrophilic Addition Reactions 1: Alkenes Identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles Use curved arrows to predict product 4 Types of Organic
Objective 12 Apply Reactivity Principles to Electrophilic Addition Reactions 1: Alkenes Identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles Use curved arrows to predict product 4 Types of Organic
Macromolecules. The four groups of biomolecules or macromolecules found in living things which are essential to life are: 1. PROTEINS 1.
 Macromolecules The four groups of biomolecules or macromolecules found in living things which are essential to life are: 1. PROTEINS 1. CARBOHYDRATES 1. LIPIDS 1. NUCLEIC ACIDS Carbon Compounds All compounds
Macromolecules The four groups of biomolecules or macromolecules found in living things which are essential to life are: 1. PROTEINS 1. CARBOHYDRATES 1. LIPIDS 1. NUCLEIC ACIDS Carbon Compounds All compounds
RIGID POLYURETHANE FOAM FROM GRAPE SEED OIL
 Institute of Chemical and Environmental Technology Chemical Engineering Department University of Castilla La Mancha Ciudad Real, Spain RIGID POLYURETHANE FOAM FROM GRAPE SEED OIL Antonio Díaz-Medino Manuel
Institute of Chemical and Environmental Technology Chemical Engineering Department University of Castilla La Mancha Ciudad Real, Spain RIGID POLYURETHANE FOAM FROM GRAPE SEED OIL Antonio Díaz-Medino Manuel
Pierre-Marie Baudoin Vandeputte Oleochemicals
 Pierre-Marie Baudoin Vandeputte leochemicals Atelier MPR, AG de ValBiom, Gembloux, 25 avril 2012 1 Your linseed oil & vegetable oils derivatives specialist 2 1887: Foundation of the company by the Vandeputte
Pierre-Marie Baudoin Vandeputte leochemicals Atelier MPR, AG de ValBiom, Gembloux, 25 avril 2012 1 Your linseed oil & vegetable oils derivatives specialist 2 1887: Foundation of the company by the Vandeputte
The Optimization of Ozonolysis Reaction For Synthesis of Biopolyol From Used Palm Cooking Oil
 The Optimization of Ozonolysis Reaction For Synthesis of Biopolyol From Used Palm Cooking Oil Edy Purwanto *,1 Lieke Riadi 1, Nathania Tamara I. 1 Mellisha Ika K. 1 1 Chemical Engineering Department, University
The Optimization of Ozonolysis Reaction For Synthesis of Biopolyol From Used Palm Cooking Oil Edy Purwanto *,1 Lieke Riadi 1, Nathania Tamara I. 1 Mellisha Ika K. 1 1 Chemical Engineering Department, University
Abstract. Process Economics Program Report 45B POLYOLS FOR POLYURETHANES (November 1995)
 Abstract Process Economics Program Report 45B POLYOLS FOR POLYURETHANES (November 1995) This report, Supplement B to PEP Report 45, reviews the technology for producing polyether polyols (PETP), polyester
Abstract Process Economics Program Report 45B POLYOLS FOR POLYURETHANES (November 1995) This report, Supplement B to PEP Report 45, reviews the technology for producing polyether polyols (PETP), polyester
Continued Shelf-life Testing of Rigid Spray Foams with Systems Based on Methyl Formate
 ABSTRACT TITLE: Continued Shelf-life Testing of Rigid Spray Foams with Systems Based on Methyl Formate Author(s): John Murphy, Foam Supplies, Inc. ABSTRACT: Reactivity drift in polyurethane spray foams
ABSTRACT TITLE: Continued Shelf-life Testing of Rigid Spray Foams with Systems Based on Methyl Formate Author(s): John Murphy, Foam Supplies, Inc. ABSTRACT: Reactivity drift in polyurethane spray foams
The four levels of protein structure are: primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure.
 Proteins Proteins are organic complex nitrogenous compounds of high molecular weight, formed of C, H, O and N. They are formed of a number of amino acids linked together by peptide linkage [-CO-NH-]. Proteins
Proteins Proteins are organic complex nitrogenous compounds of high molecular weight, formed of C, H, O and N. They are formed of a number of amino acids linked together by peptide linkage [-CO-NH-]. Proteins
OLERIS. 2-Octanol - CAS:
 OLERIS 2-Octanol - CAS: 123-96-6 Where does the 2-Octanol come from? The 2-Octanol is produced through a cracking process of Castor oil. During this operation, the major component of Castor oil, the Ricinoleic
OLERIS 2-Octanol - CAS: 123-96-6 Where does the 2-Octanol come from? The 2-Octanol is produced through a cracking process of Castor oil. During this operation, the major component of Castor oil, the Ricinoleic
Lipids are used to store and excess energy from extra carbohydrates in animals
 Lipids Lipids are a major source of energy used by cells, however lipids are more difficult for your body to break down. They produce nearly twice the amount of energy than proteins or carbohydrates. Lipids
Lipids Lipids are a major source of energy used by cells, however lipids are more difficult for your body to break down. They produce nearly twice the amount of energy than proteins or carbohydrates. Lipids
Biodegradable Polyurethane Materials from Bark and Starch. I. Highly Resilient Foams
 Biodegradable Polyurethane Materials from Bark and Starch. I. Highly Resilient Foams JINJIE GE, 1 WEI ZHONG, 1 ZHENRONG GUO, 1 WENJUN LI, 1 KOKKI SAKAI 2 1 Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers,
Biodegradable Polyurethane Materials from Bark and Starch. I. Highly Resilient Foams JINJIE GE, 1 WEI ZHONG, 1 ZHENRONG GUO, 1 WENJUN LI, 1 KOKKI SAKAI 2 1 Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers,
Fourrier Transform Infrared and Gel Permeation Chromatography Evaluation to Prepared Polyurethane Paint from Polyol Palm Oil Based
 Proceedings of The 2 nd Annual International onference Syiah Kuala University 2012 & The 8 th IMT-GT Uninet Biosciences onference Fourrier Transform Infrared and Gel Permeation hromatography Evaluation
Proceedings of The 2 nd Annual International onference Syiah Kuala University 2012 & The 8 th IMT-GT Uninet Biosciences onference Fourrier Transform Infrared and Gel Permeation hromatography Evaluation
A study of polymer additives in mineral oil and vegetable oil-based greases
 A study of polymer additives in mineral oil and vegetable oil-based greases David A. DeVore and Shanshan Wang, Ph.D Functional Products Inc. Macedonia, hio ELGI May 2, 2011 Annual Meeting 1 The benefit
A study of polymer additives in mineral oil and vegetable oil-based greases David A. DeVore and Shanshan Wang, Ph.D Functional Products Inc. Macedonia, hio ELGI May 2, 2011 Annual Meeting 1 The benefit
Product Safety Assessment Sucrose Propoxylated Polyols
 Product Safety Assessment Sucrose Propoxylated Polyols Select a Topic: Names Product Overview Manufacture of Product Product Description Product Uses Exposure Potential ealth Information Environmental
Product Safety Assessment Sucrose Propoxylated Polyols Select a Topic: Names Product Overview Manufacture of Product Product Description Product Uses Exposure Potential ealth Information Environmental
Oleochemistry. Oleochemical derivatives
 Oleochemistry by Shamsul Bin Zakaria Faculty Industrial Science and Technology shamsulzakaria@ump.edu.my The students should be able to understand: Oleochemical reactions and their applications Five basic
Oleochemistry by Shamsul Bin Zakaria Faculty Industrial Science and Technology shamsulzakaria@ump.edu.my The students should be able to understand: Oleochemical reactions and their applications Five basic
Polymerization of Ethylene Glycol and Soy-epoxide Derived Phosphate Ester for Polyurethane Foam
 International Journal of Chemistry; Vol. 4, No. 3; 2012 ISSN 1916-9698 E-ISSN 1916-9701 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Polymerization of Ethylene Glycol and Soy-epoxide Derived Phosphate
International Journal of Chemistry; Vol. 4, No. 3; 2012 ISSN 1916-9698 E-ISSN 1916-9701 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Polymerization of Ethylene Glycol and Soy-epoxide Derived Phosphate
3.9 Carbohydrates. Provide building materials and energy storage. Are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio
 3.9 Carbohydrates Provide building materials and energy storage Are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio Are of two main types Simple carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates
3.9 Carbohydrates Provide building materials and energy storage Are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio Are of two main types Simple carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates
Bio-based Solutions for High-Performance Polyurethane Adhesives. Angela Smits Bio-based Adhesives Conference 2013
 Bio-based Solutions for High-Performance Polyurethane Adhesives Angela Smits Bio-based Adhesives Conference 213 Bio-based building blocks sustainable solutions CRODA: Naturally derived speciality chemicals
Bio-based Solutions for High-Performance Polyurethane Adhesives Angela Smits Bio-based Adhesives Conference 213 Bio-based building blocks sustainable solutions CRODA: Naturally derived speciality chemicals
Carbon. p Has four valence electrons p Can bond with many elements p Can bond to other carbon atoms
 Organic Compounds Carbon p Has four valence electrons p Can bond with many elements p Can bond to other carbon atoms n Gives carbon the ability to form chains that are almost unlimited in length. p Organic
Organic Compounds Carbon p Has four valence electrons p Can bond with many elements p Can bond to other carbon atoms n Gives carbon the ability to form chains that are almost unlimited in length. p Organic
Product Safety Assessment Propoxylated/Ethoxylated Ethylenediamine Polyol
 Product Safety Assessment Propoxylated/Ethoxylated Ethylenediamine Polyol Select a Topic: Names Product Overview Manufacture of Product Product Description Product Uses Exposure Potential Health Information
Product Safety Assessment Propoxylated/Ethoxylated Ethylenediamine Polyol Select a Topic: Names Product Overview Manufacture of Product Product Description Product Uses Exposure Potential Health Information
SYNTHESIS OF REACTIVE SOYBEAN OILS FOR USE AS BIOBASED THERMOSET RESINS IN STRUCTURAL NATURAL FIBRE COMPOSITES
 SYNTHESIS F REACTIVE SYBEAN ILS FR USE AS BIBASED THERMSET RESINS IN STRUCTURAL NATURAL FIBRE CMPSITES Kayode Adekunle, Dan Åkesson and Mikael Skrifvars School of Engineering University College of Borås
SYNTHESIS F REACTIVE SYBEAN ILS FR USE AS BIBASED THERMSET RESINS IN STRUCTURAL NATURAL FIBRE CMPSITES Kayode Adekunle, Dan Åkesson and Mikael Skrifvars School of Engineering University College of Borås
Castor Oil. Properties & Chemical. Composition. Castor Processors Workshop July 25, 2017
 Castor Processors Workshop July 25, 2017 Castor Oil Properties & Chemical Yvonne Bailey-Shaw Research Scientist Product Research& Development Division Composition Castor - Ricinus communis BACKGROUND Castor
Castor Processors Workshop July 25, 2017 Castor Oil Properties & Chemical Yvonne Bailey-Shaw Research Scientist Product Research& Development Division Composition Castor - Ricinus communis BACKGROUND Castor
Biology: Life on Earth Chapter 3 Molecules of life
 Biology: Life on Earth Chapter 3 Molecules of life Chapter 3 Outline 3.1 Why Is Carbon So Important in Biological Molecules? p. 38 3.2 How Are Organic Molecules Synthesized? p. 38 3.3 What Are Carbohydrates?
Biology: Life on Earth Chapter 3 Molecules of life Chapter 3 Outline 3.1 Why Is Carbon So Important in Biological Molecules? p. 38 3.2 How Are Organic Molecules Synthesized? p. 38 3.3 What Are Carbohydrates?
Product Safety Assessment Toluenediamine Propoxylated/Ethoxylated Polyols
 Product Safety Assessment Toluenediamine Propoxylated/Ethoxylated Polyols Product Safety Assessment documents are available at: www.dow.com/productsafety/finder/. Select a Topic: Names Product Overview
Product Safety Assessment Toluenediamine Propoxylated/Ethoxylated Polyols Product Safety Assessment documents are available at: www.dow.com/productsafety/finder/. Select a Topic: Names Product Overview
SYNTHESIS OF COMPOUND-CONTAINING SULPHONIC ACID FROM EPOXIDIZED METHYL OLEIC OF RICE BRAN OIL AND LINEAR ALKYLBENZENE SULPHONIC ACID
 Ratri Journal Ariatmi of Chemical Nugrahani Technology, Athiek Sri and Redjeki, Metallurgy, Yunita 52, Teresa, 5, 2017, Nurul 797-802 Hidayati SYNTHESIS OF COMPOUND-CONTAINING SULPHONIC ACID FROM EPOXIDIZED
Ratri Journal Ariatmi of Chemical Nugrahani Technology, Athiek Sri and Redjeki, Metallurgy, Yunita 52, Teresa, 5, 2017, Nurul 797-802 Hidayati SYNTHESIS OF COMPOUND-CONTAINING SULPHONIC ACID FROM EPOXIDIZED
FATS & OILS GLOSSARY
 FATS & OILS GLOSSARY Antioxidant A substance that slows or interferes with the reaction of a fat or oil with oxygen. The addition of antioxidants to fats or foods containing them retard rancidity and increases
FATS & OILS GLOSSARY Antioxidant A substance that slows or interferes with the reaction of a fat or oil with oxygen. The addition of antioxidants to fats or foods containing them retard rancidity and increases
Macro molecule = is all the reactions that take place in cells, the sum of all chemical reactions that occur within a living organism Anabolism:
 Macromolecule Macro molecule = molecule that is built up from smaller units The smaller single subunits that make up macromolecules are known as Joining two or more single units together form a M is all
Macromolecule Macro molecule = molecule that is built up from smaller units The smaller single subunits that make up macromolecules are known as Joining two or more single units together form a M is all
½ cup of CHEX MIX contains 13 g of carbs = 4% daily value. How much more can you have the rest of the day??? _4_ = X X= 325 g
 BIOCHEMISTRY ½ cup of CHEX MIX contains 13 g of carbs = 4% daily value. How much more can you have the rest of the day??? _4_ = 13 100 X X= 325 g These spinach imposters contain less than 2 percent of
BIOCHEMISTRY ½ cup of CHEX MIX contains 13 g of carbs = 4% daily value. How much more can you have the rest of the day??? _4_ = 13 100 X X= 325 g These spinach imposters contain less than 2 percent of
Name the ester produced when methanol and pentanoic acid react. methyl pentanoate. Name the type of reaction used to make an ester
 1 Name the ester produced when methanol and pentanoic acid react methyl pentanoate 2 Name the type of reaction used to make an ester condensation reaction 3 Name the by-product of the reaction used to
1 Name the ester produced when methanol and pentanoic acid react methyl pentanoate 2 Name the type of reaction used to make an ester condensation reaction 3 Name the by-product of the reaction used to
BIO- DEGRADABLE COMPOSITE MADE FROM STARCH AND COCONUT FIBER : MECHANICAL STRENGTH AND BIODEGRATION CHRACTERSTICS
 BIO- DEGRADABLE COMPOSITE MADE FROM STARCH AND COCONUT FIBER : MECHANICAL STRENGTH AND BIODEGRATION CHRACTERSTICS 55 Rahul Sen*, N.C.Upadhayay**, Upender Pandel*** *Research Scholar **Associate Professor
BIO- DEGRADABLE COMPOSITE MADE FROM STARCH AND COCONUT FIBER : MECHANICAL STRENGTH AND BIODEGRATION CHRACTERSTICS 55 Rahul Sen*, N.C.Upadhayay**, Upender Pandel*** *Research Scholar **Associate Professor
Carbon. Has four valence electrons Can bond with many elements. Can bond to other carbon atoms. Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Nitrogen
 Organic Compounds Carbon Has four valence electrons Can bond with many elements Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Nitrogen Can bond to other carbon atoms Gives carbon the ability to form chains
Organic Compounds Carbon Has four valence electrons Can bond with many elements Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Nitrogen Can bond to other carbon atoms Gives carbon the ability to form chains
11/5/ Oxidation of Alkenes: Cleavage to Carbonyl Compounds. Oxidation of Alkenes: Cleavage to Carbonyl Compounds
 8.8 Oxidation of Alkenes: Cleavage to Carbonyl Compounds Ozone (O 3 ) is useful double-bond cleavage reagent Ozone is generated by passing a stream of oxygen through a highvoltage electrical discharge
8.8 Oxidation of Alkenes: Cleavage to Carbonyl Compounds Ozone (O 3 ) is useful double-bond cleavage reagent Ozone is generated by passing a stream of oxygen through a highvoltage electrical discharge
PURE POLYURETHANE AND CASTOR OIL BASED POLYURETHANE: SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION. Universiti Malaysia Pahang, Kuantan Malaysia
 Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Sciences (JMES) ISSN (Print): 2289-4659; e-issn: 2231-8380; Volume 8, pp. 1507-1515, June 2015 Universiti Malaysia Pahang, Malaysia DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15282/jmes.8.2015.25.0147
Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Sciences (JMES) ISSN (Print): 2289-4659; e-issn: 2231-8380; Volume 8, pp. 1507-1515, June 2015 Universiti Malaysia Pahang, Malaysia DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15282/jmes.8.2015.25.0147
Biobased polyurethanes from microalgae. Dr Philip B. Sellars
 Biobased polyurethanes from microalgae Dr Philip B. Sellars High value-added chemicals and BIoreSIns from algae biorefineries produced from CO 2 provided by industrial emissions Project 3 Project consortium
Biobased polyurethanes from microalgae Dr Philip B. Sellars High value-added chemicals and BIoreSIns from algae biorefineries produced from CO 2 provided by industrial emissions Project 3 Project consortium
INVISTA TERRIN Polyols
 Technical Data Sheet INVISTA TERRIN Polyols Cost-Effective Alternative to Conventional Polyether and Polyester Polyols Introduction TERRIN polyols can be used in lieu of or in combination with conventional
Technical Data Sheet INVISTA TERRIN Polyols Cost-Effective Alternative to Conventional Polyether and Polyester Polyols Introduction TERRIN polyols can be used in lieu of or in combination with conventional
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids
 Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids Is it made of carbohydrates? Organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. A carbohydrate with 6 carbon atoms would have
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids Is it made of carbohydrates? Organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. A carbohydrate with 6 carbon atoms would have
Name a property of. water why is it necessary for life?
 02.09.18 Name a property of + water why is it necessary for life? n Cohesion n Adhesion n Transparency n Density n Solvent n Heat capacity + Macromolecules (2.3 & some of 2.4) + Organic Molecules All molecules
02.09.18 Name a property of + water why is it necessary for life? n Cohesion n Adhesion n Transparency n Density n Solvent n Heat capacity + Macromolecules (2.3 & some of 2.4) + Organic Molecules All molecules
3. Athawale V.D., Shetty N. J. Studies on cyclohexanone formaldehyde styrenated CNSL coatings. Surface Coatings International, 2000, 83(4),
 References 1. Chen S., Wang Q., Wang T., Pei X., Preparation, damping and thermal properties of potassium titanate whiskers filled castor oil-based polyurethane / epoxy interpenetrating polymer network
References 1. Chen S., Wang Q., Wang T., Pei X., Preparation, damping and thermal properties of potassium titanate whiskers filled castor oil-based polyurethane / epoxy interpenetrating polymer network
Reading. Learning Objectives. How are macromolecules assembled? 8. Macromolecules I. Contents
 Contents 1 Reading 2 Learning Objectives 3 How are macromolecules assembled? 4 Carbohydrates 4.1 Structural Carbohydrates 5 Lipids 5.1 Fats/Triglycerides 5.1.1 Saturated versus Unsaturated fats 5.2 Phospholipids
Contents 1 Reading 2 Learning Objectives 3 How are macromolecules assembled? 4 Carbohydrates 4.1 Structural Carbohydrates 5 Lipids 5.1 Fats/Triglycerides 5.1.1 Saturated versus Unsaturated fats 5.2 Phospholipids
Chapter 7-2 Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 7-1 Carbon C atom - atomic # is 6; it has 6 protons and therefore 6 electrons - is in group 14; it has 4 valence electrons - atomic mass is 12; it has 6 neutrons - shares electrons when forming
Chapter 7-1 Carbon C atom - atomic # is 6; it has 6 protons and therefore 6 electrons - is in group 14; it has 4 valence electrons - atomic mass is 12; it has 6 neutrons - shares electrons when forming
Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought
 Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought Do you think about the food that goes into your body and how it affects you? How can you interpret the various nutrition information found in the press? What are
Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought Do you think about the food that goes into your body and how it affects you? How can you interpret the various nutrition information found in the press? What are
POLYURETHANE FOAMS CONTAINING RENEWABLE CASTOR OIL REPLACEMENT
 POLYURETHANE FOAMS CONTAINING RENEWABLE CASTOR OIL REPLACEMENT A Thesis Presented to The Faculty of the Graduate School At the University of Missouri-Columbia In Partial Fulfillment Of the Requirements
POLYURETHANE FOAMS CONTAINING RENEWABLE CASTOR OIL REPLACEMENT A Thesis Presented to The Faculty of the Graduate School At the University of Missouri-Columbia In Partial Fulfillment Of the Requirements
Introduction to Biochemistry
 Life is Organized in Increasing Levels of Complexity Introduction to Biochemistry atom simple molecule What is the chemical makeup of living things? macromolecule organ organ system organism organelle
Life is Organized in Increasing Levels of Complexity Introduction to Biochemistry atom simple molecule What is the chemical makeup of living things? macromolecule organ organ system organism organelle
Topic 3.1 Nutrients. - Lipids are an essential part of the and are a part of cell in the body.
 Name: Topic 3.1 Nutrients Date: IB SEHS 3.1.1. List the macronutrients and micronutrients Macronutrients: - lipid (fat) - carbohydrate - protein - water (says the book) Micronutrients: - vitamins - minerals
Name: Topic 3.1 Nutrients Date: IB SEHS 3.1.1. List the macronutrients and micronutrients Macronutrients: - lipid (fat) - carbohydrate - protein - water (says the book) Micronutrients: - vitamins - minerals
Novel Approaches for Synthesis of Polyols from Soy Oils
 Novel Approaches for Synthesis of Polyols from Soy Oils by Saswati Ghosh Roy A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Forestry (M. Sc. F) Faculty of
Novel Approaches for Synthesis of Polyols from Soy Oils by Saswati Ghosh Roy A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Forestry (M. Sc. F) Faculty of
Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought
 Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought Do you think about the food that goes into your body and how it affects you? How can you interpret the various nutrition information found in the press? What are
Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought Do you think about the food that goes into your body and how it affects you? How can you interpret the various nutrition information found in the press? What are
4/7/2011. Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry. Structural Formulas. 3. Petroleum Products
 Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry 13-1. Carbon Bonds 13-2. Alkanes 13-3. Petroleum Products 13-5. Isomers 13-6. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 13-7. Benzene 13-9. 13-10. Polymers 13-11. Carbohydrates 13-12. Photosynthesis
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry 13-1. Carbon Bonds 13-2. Alkanes 13-3. Petroleum Products 13-5. Isomers 13-6. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 13-7. Benzene 13-9. 13-10. Polymers 13-11. Carbohydrates 13-12. Photosynthesis
Improving Polyurethane Performance and Energy Efficiency
 JeFFol and terol specialty Polyols Improving Polyurethane Performance and Energy Efficiency Huntsman, Delivering Solutions to the Polyurethanes Industry for Decades Dedicated to the polyurethanes business
JeFFol and terol specialty Polyols Improving Polyurethane Performance and Energy Efficiency Huntsman, Delivering Solutions to the Polyurethanes Industry for Decades Dedicated to the polyurethanes business
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins & Nucleic Acids.
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins & Nucleic Acids. Biological Compounds Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Introduction Cells join smaller organic molecules
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins & Nucleic Acids. Biological Compounds Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Introduction Cells join smaller organic molecules
Product Safety Assessment VORANOL VORACTIV Polyols
 Product Safety Assessment VORANOL VORACTIV Polyols Select a Topic: Names Product Overview Manufacture of Product Product Description Product Uses Exposure Potential Health Information Environmental Information
Product Safety Assessment VORANOL VORACTIV Polyols Select a Topic: Names Product Overview Manufacture of Product Product Description Product Uses Exposure Potential Health Information Environmental Information
slight, characteristic colour Gardner max. 4
 Castor oil CAS No. 8001-79-4 Castor oil (also known as Ricinus oil) is a vegetable oil extracted by mechanical pressing of the Castor seed. It is pale-yellowish or almost colorless with a mild characteristic
Castor oil CAS No. 8001-79-4 Castor oil (also known as Ricinus oil) is a vegetable oil extracted by mechanical pressing of the Castor seed. It is pale-yellowish or almost colorless with a mild characteristic
Linnaeus Plant Sciences. Optimizing Oil Seed Potential for Industrial Applications
 Linnaeus Optimizing Oil Seed Potential for Industrial Applications Jack Grushcow www.linnaeus.net Overview Plant Bio-technology overview Castor Case Study HFY Applications Production Issues Future Directions
Linnaeus Optimizing Oil Seed Potential for Industrial Applications Jack Grushcow www.linnaeus.net Overview Plant Bio-technology overview Castor Case Study HFY Applications Production Issues Future Directions
Biopolymers in Packaging
 Biopolymers in Packaging Section I: Introduction A. Study purpose B. Key definitions 1. Biopolymers 2. Synthetic polymers 3. Thermoplastic property 4. Biodegradability and compostability C. Study organization
Biopolymers in Packaging Section I: Introduction A. Study purpose B. Key definitions 1. Biopolymers 2. Synthetic polymers 3. Thermoplastic property 4. Biodegradability and compostability C. Study organization
Optimum Operating Conditions for Epoxidation Reaction of Jojoba and Castor Oils
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Optimum Operating Conditions for Epoxidation Reaction of Jojoba and Castor Oils El-Adly R. A. *, Shoaib A. M. **, Enas A. Ismail. *, Modather.F *** * (Process design & development
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Optimum Operating Conditions for Epoxidation Reaction of Jojoba and Castor Oils El-Adly R. A. *, Shoaib A. M. **, Enas A. Ismail. *, Modather.F *** * (Process design & development
Lesson Overview. Carbon Compounds. Lesson Overview. 2.3 Carbon Compounds
 Lesson Overview 2.3 The Chemistry of Carbon What elements does carbon bond with to make up life s molecules? Carbon can bond with many elements, including Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Nitrogen
Lesson Overview 2.3 The Chemistry of Carbon What elements does carbon bond with to make up life s molecules? Carbon can bond with many elements, including Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Nitrogen
small molecules that make up larger molecules organic compound made up of sugar molecules sugar that contains one sugar unit
 organic molecule carbon based compound inorganic molecule hydrocarbon functional group hydrophilic NON-carbon based compound organic molecule made of only carbon and hydrogen group of atoms bonded to a
organic molecule carbon based compound inorganic molecule hydrocarbon functional group hydrophilic NON-carbon based compound organic molecule made of only carbon and hydrogen group of atoms bonded to a
BIOCHEMISTRY. How Are Macromolecules Formed? Dehydration Synthesis or condensation reaction Polymers formed by combining monomers and removing water.
 BIOCHEMISTRY Organic compounds Compounds that contain carbon are called organic. Inorganic compounds do not contain carbon. Carbon has 4 electrons in outer shell. Carbon can form covalent bonds with as
BIOCHEMISTRY Organic compounds Compounds that contain carbon are called organic. Inorganic compounds do not contain carbon. Carbon has 4 electrons in outer shell. Carbon can form covalent bonds with as
Lesson Overview. Carbon Compounds. Lesson Overview. 2.3 Carbon Compounds
 Lesson Overview 2.3 THINK ABOUT IT In the early 1800s, many chemists called the compounds created by organisms organic, believing they were fundamentally different from compounds in nonliving things. We
Lesson Overview 2.3 THINK ABOUT IT In the early 1800s, many chemists called the compounds created by organisms organic, believing they were fundamentally different from compounds in nonliving things. We
2.3 Carbon Compounds 12/19/2011 BIOLOGY MRS. MICHAELSEN. Lesson Overview. Carbon Compounds The Chemistry of Carbon. Lesson Overview.
 2.3 The Chemistry of Carbon A. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons 1. Form strong covalent bonds with many other elements: H, O, P, S, N. 2. Living organisms are made up of carbon and these other
2.3 The Chemistry of Carbon A. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons 1. Form strong covalent bonds with many other elements: H, O, P, S, N. 2. Living organisms are made up of carbon and these other
Optimization of SPF with Isocyanate Compatible Silicone Surfactants. Ray Geiling September 2013
 Optimization of SPF with Isocyanate Compatible Silicone Surfactants Ray Geiling September 2013 Agenda 1. Introduction 2. pmdi Surface Tension Reduction 3. New Flow Test Method Introduction 4. High Pressure
Optimization of SPF with Isocyanate Compatible Silicone Surfactants Ray Geiling September 2013 Agenda 1. Introduction 2. pmdi Surface Tension Reduction 3. New Flow Test Method Introduction 4. High Pressure
Advantages of Palm Oil and its fractions in Food
 Advantages of Palm Oil and its fractions in Food Mr H. Slager Application Fellow at IOI Loders Croklaan Europe Malaysia-Romania Palm Oil Trade Fair/Seminar Bucharest 2012 Observations: - Food industry
Advantages of Palm Oil and its fractions in Food Mr H. Slager Application Fellow at IOI Loders Croklaan Europe Malaysia-Romania Palm Oil Trade Fair/Seminar Bucharest 2012 Observations: - Food industry
Emerging Opportunities for Natural Oil Based Chemicals
 Emerging pportunities for Natural il Based Chemicals Dr. Ray Bergstra MTN Consulting Associates Plant Bio-Industrial Workshop Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada February 27, 2007 MTN Consulting Associates
Emerging pportunities for Natural il Based Chemicals Dr. Ray Bergstra MTN Consulting Associates Plant Bio-Industrial Workshop Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada February 27, 2007 MTN Consulting Associates
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
 A23D EDIBLE OILS OR FATS, e.g. MARGARINES, SHORTENINGS, COOKING OILS (animal feeding-stuffs A23K 10/00-A23K 20/30, A23K 30/00-A23K 50/90; foods or foodstuffs containing edible oils or fats A21D, A23C,
A23D EDIBLE OILS OR FATS, e.g. MARGARINES, SHORTENINGS, COOKING OILS (animal feeding-stuffs A23K 10/00-A23K 20/30, A23K 30/00-A23K 50/90; foods or foodstuffs containing edible oils or fats A21D, A23C,
3 CHAPTER 3: RESULTS AND DISCUSSION SYNTHESIS OF PALM OLEIC ACID-BASED MACROMERS
 3 CHAPTER 3: RESULTS AND DISCUSSION SYNTHESIS OF PALM OLEIC ACID-BASED MACROMERS In view of the increasing interest in environmental protection, the use of vegetable oils in non-food applications has attracted
3 CHAPTER 3: RESULTS AND DISCUSSION SYNTHESIS OF PALM OLEIC ACID-BASED MACROMERS In view of the increasing interest in environmental protection, the use of vegetable oils in non-food applications has attracted
Chapter 8 Lecture Reactions of Alkenes
 Organic Chemistry, 9 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 8 Lecture Reactions of Alkenes 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogen (H 2 ) can be added across the double bond
Organic Chemistry, 9 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 8 Lecture Reactions of Alkenes 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogen (H 2 ) can be added across the double bond
USE OF HYDROLYSIS PRODUCTS OF POLYETHYLENE TEREPHTHALATE SCRAPS TO PRODUCE ALKYD BASED PAINT
 USE OF HYDROLYSIS PRODUCTS OF POLYETHYLENE TEREPHTHALATE SCRAPS TO PRODUCE ALKYD BASED PAINT Sudasinghage Vasantha Udayakumara (08/8053) Degree of Master of Philosophy Department of Materials Science and
USE OF HYDROLYSIS PRODUCTS OF POLYETHYLENE TEREPHTHALATE SCRAPS TO PRODUCE ALKYD BASED PAINT Sudasinghage Vasantha Udayakumara (08/8053) Degree of Master of Philosophy Department of Materials Science and
SPECIALITIES FOR TECHNICAL APPLICATIONS. Rofacer
 SPECIALITIES FOR TECHNICAL APPLICATIONS Rofacer State-of-the-Art Technology Designed for High-Standard Products Ester, Ether, Sugar Derivatives and Other Specialities By 1931, Deutsche Hydrierwerke (DHW)
SPECIALITIES FOR TECHNICAL APPLICATIONS Rofacer State-of-the-Art Technology Designed for High-Standard Products Ester, Ether, Sugar Derivatives and Other Specialities By 1931, Deutsche Hydrierwerke (DHW)
PERP/PERP ABSTRACTS Oleochemicals PERP 2011S6
 PERP/PERP ABSTRACTS 2010 Oleochemicals PERP 2011S6 Report Abstract April 2012 April 2012 Connie Lo and William Cameron CHEMSYSTEMS PERP PROGRAM The ChemSystems Process Evaluation/Research Planning (PERP)
PERP/PERP ABSTRACTS 2010 Oleochemicals PERP 2011S6 Report Abstract April 2012 April 2012 Connie Lo and William Cameron CHEMSYSTEMS PERP PROGRAM The ChemSystems Process Evaluation/Research Planning (PERP)
Oil-modified PUDs: cross-linkable, VOC compliant, cost effective
 Oil-modified PUDs: cross-linkable, VOC compliant, cost effective Waterborne Polyurethane Dispersions (PUDs) tend to show undesirably low mechnical performance and chemical resistance, which is due to their
Oil-modified PUDs: cross-linkable, VOC compliant, cost effective Waterborne Polyurethane Dispersions (PUDs) tend to show undesirably low mechnical performance and chemical resistance, which is due to their
Chemistry of Carbon. All living things rely on one particular type of molecule: carbon
 Ach Chemistry of Carbon All living things rely on one particular type of molecule: carbon Carbon atom with an outer shell of four electrons can form covalent bonds with four atoms. In organic molecules,
Ach Chemistry of Carbon All living things rely on one particular type of molecule: carbon Carbon atom with an outer shell of four electrons can form covalent bonds with four atoms. In organic molecules,
OCR A GCSE Chemistry. Topic 6: Global challenges. Organic chemistry. Notes.
 OCR A GCSE Chemistry Topic 6: Global challenges Organic chemistry Notes C6.2a recognise functional groups and identify members of the same homologous series Prefixes (beginning of the name) o remember
OCR A GCSE Chemistry Topic 6: Global challenges Organic chemistry Notes C6.2a recognise functional groups and identify members of the same homologous series Prefixes (beginning of the name) o remember
Preparation and Characterization of High-Density Polyethylene Blends and Recycled Poly(ethylene terephthalate)
 Preparation and Characterization of High-Density Polyethylene Blends and Recycled Poly(ethylene terephthalate) By: Mohd Nazry Salleh (nazrysalleh@gmail.com) Presentation outline 1. Introduction -rhdpe
Preparation and Characterization of High-Density Polyethylene Blends and Recycled Poly(ethylene terephthalate) By: Mohd Nazry Salleh (nazrysalleh@gmail.com) Presentation outline 1. Introduction -rhdpe
Synthesis and Characterization of Starch-based Aqueous Polymer Isocyanate Wood Adhesive
 Synthesis and Characterization of Starch-based Aqueous Polymer Isocyanate Wood Adhesive Shu-min Wang, a, c Jun-you Shi, b, * and Wenbiao Xu b Modified starch was prepared in this work by acid-thinning
Synthesis and Characterization of Starch-based Aqueous Polymer Isocyanate Wood Adhesive Shu-min Wang, a, c Jun-you Shi, b, * and Wenbiao Xu b Modified starch was prepared in this work by acid-thinning
Polyurethane films, foams and nanocomposites prepared from vegetable oil-based polyols
 Graduate Theses and Dissertations Iowa State University Capstones, Theses and Dissertations 2014 Polyurethane films, foams and nanocomposites prepared from vegetable oil-based polyols Chaoqun Zhang Iowa
Graduate Theses and Dissertations Iowa State University Capstones, Theses and Dissertations 2014 Polyurethane films, foams and nanocomposites prepared from vegetable oil-based polyols Chaoqun Zhang Iowa
YUAN LI A.PROF QIZHI CHEN, PROF WAYNE COOK
 Synthesis, characterization and properties of biocompatible poly(glycerol sebacate) YUAN LI A.PROF QIZHI CHEN, PROF WAYNE COOK Background Demand of biomaterials in the field of soft tissue engineering
Synthesis, characterization and properties of biocompatible poly(glycerol sebacate) YUAN LI A.PROF QIZHI CHEN, PROF WAYNE COOK Background Demand of biomaterials in the field of soft tissue engineering
Radicals. Structure and Stability of Radicals. Radicals are formed from covalent bonds by adding energy in the form of heat (Δ) or light (hν).
 Radicals Chapter 15 A small but significant group of reactions involve radical intermediates. A radical is a reactive intermediate with a single unpaired electron, formed by homolysis of a covalent bond.
Radicals Chapter 15 A small but significant group of reactions involve radical intermediates. A radical is a reactive intermediate with a single unpaired electron, formed by homolysis of a covalent bond.
Additives for waterborne coatings
 Additives for waterborne coatings Wernfried Heilen 1 Introduction 2 Wetting- and dispersing additives 2.1 Modes of action 2.1.1 Pigment wetting 2.1.2 Grinding 2.1.3 Stabilisation 2.1.3.1 Electrostatic
Additives for waterborne coatings Wernfried Heilen 1 Introduction 2 Wetting- and dispersing additives 2.1 Modes of action 2.1.1 Pigment wetting 2.1.2 Grinding 2.1.3 Stabilisation 2.1.3.1 Electrostatic
NCS. Natural Cosmetics Standard
 NCS Natural Cosmetics Standard Table of contents INTRODUCTION... 3 SCOPE OF APPLICATION... 3 ASSORTMENT REQUIREMENTS... 3 GENERAL CRITERIA... 4 1. DEFINITION OF PERMITTED RAW MATERIAL GROUPS... 4 2. RAW
NCS Natural Cosmetics Standard Table of contents INTRODUCTION... 3 SCOPE OF APPLICATION... 3 ASSORTMENT REQUIREMENTS... 3 GENERAL CRITERIA... 4 1. DEFINITION OF PERMITTED RAW MATERIAL GROUPS... 4 2. RAW
Chapter 3. Table of Contents. Section 1 Carbon Compounds. Section 2 Molecules of Life. Biochemistry
 Biochemistry Table of Contents Section 1 Carbon Compounds Section 2 Molecules of Life Section 1 Carbon Compounds Objectives Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. Explain the importance of
Biochemistry Table of Contents Section 1 Carbon Compounds Section 2 Molecules of Life Section 1 Carbon Compounds Objectives Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. Explain the importance of
Synthesis and Evaluation of Esterified Estolide
 Chapter 5 Synthesis and Evaluation of Esterified Estolide 5.1 Introduction Coconut oil has a very high congelation temperature precluding its use as base oil for industrial lubricants in temperate and
Chapter 5 Synthesis and Evaluation of Esterified Estolide 5.1 Introduction Coconut oil has a very high congelation temperature precluding its use as base oil for industrial lubricants in temperate and
Carbon Compounds. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 2.3 Carbon Compounds
 Lesson Overview Carbon Compounds Lesson Overview 2.3 THINK ABOUT IT In the early 1800s, many chemists called the compounds created by organisms organic, believing they were fundamentally different from
Lesson Overview Carbon Compounds Lesson Overview 2.3 THINK ABOUT IT In the early 1800s, many chemists called the compounds created by organisms organic, believing they were fundamentally different from
