Ahmad O. Olimat. Abdallah Al-Qawasmeh. Dr.Mamoun
|
|
|
- Roderick Scott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 10 Ahmad O. Olimat Abdallah Al-Qawasmeh Mohammed Yousef Dr.Mamoun
2 A QUICK RECAP Eicosanoids They are derived from Arachidonic acid, a fatty acid that contains 20 carbon atoms and four double bonds. They regulate a wide variety of physiological responses and pathological processes, and control important cellular processes. Lipids Classified under the term of Eicosanoids: Prostaglandins Leukotrienes Thromboxane Prostacyclins They were discussed previously. For more information, see sheet 9. Arachidonic Acid can be converted into other compounds (such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes) by metabolism by an enzyme known as cyclooxygenases (COX). Cyclooxygenase is present in three forms in different tissues, COX1, COX2, and COX3. There are two major pathways arachidonic can take depending on which enzyme is used; 1 st pathway: arachidonic acid is converted into thromboxane by COX1, which in turn induces platelet aggregation. 2 nd pathway: arachidonic acid is converted into prostaglandins by COX2, they can cause pain, fever and inflammation making the environment unhospitable for any pathogen invading the body, prostaglandins also inhibit platelet aggregation. Cyclooxygenases Inhibitors 1) ASPIRIN: a drug that is widely used for reducing body temperature and preventing inflammation process. As a side result it also inhibits platelet aggregation as well as blood clotting, so it reduces heart disease. Mechanism: it was discovered that prostaglandins seem to be responsible for causing fever, inflammation and pain. ASPIRIN treats these symptoms by preventing the production of prostaglandins. BUT what ASPIRIN really does is that it prevents COX from working, which in turn blocks prostaglandins production. Aspirin targets both, but COX2 should only be targeted. 1 P a g e
3 One of the prostaglandins that aspirin prevents from synthesizing is thromboxane, which is involved in activation of platelets to initiate aggregation and blood clotting. That means if you take aspirin daily it becomes harder for blood to clot. This is extremely useful in preventing diseases caused by blood clots such as heart attacks and stroke, that s why its recommended for older aged people who have a higher risk of suffering from those diseases. As mentioned earlier, prostaglandins aren t just involved in inflammation and pain, using aspirin also stops other body functions as well as it decreases production of protective mucous in the stomach which means that stomach acid can burn through the stomach lining leading to gastric ulcers and internal bleeding since there is also less clotting occurring, this side effect becomes even more dangerous (because a clot is what stops the bleeding when you have a wound) therefore it s not recommended for people who have a tendency of developing gastric ulcers or have genetic problems with clotting and it is also not recommended for people who are treated with blood thinners or are prone to bleed easily. 2) CELEBREX: A new generation drug, but is prescribed with a strong warning of side effects on the label. what is special about it is that CELBREX is a selective-inhibitor of COX 2 so that it doesn t affect aggregation and clotting of blood. Celebrex isn t recommended for people who have heart problems as it increases heart rate leading to fatal results. OMEGA FATTY ACID Omega-3 fatty acids: α-linolenic acid eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) Functions: They reduce inflammatory reactions by: Reducing conversion of arachidonic acid into eicosanoids, Promoting synthesis of anti-inflammatory molecules. 2 P a g e
4 *omega-3 is good for your memory, so TAKE IT DAILY!!!!(You can get omega 3 from fish and walnuts, or simply buy supplements) Omega-6 fatty acids: The precursor is Linoleic acid, ω-6 has many functions such as: stimulates platelet and leukocyte activation, signals pain Induces bronchoconstriction, regulates gastric secretion. NOTE Linoleic and linolenic acids are both ESSETNTIAL FATTY ACIDS, our body can t synthesize them we take them from diet. Omega-9 fatty acids: They are derived from Oleic acid, they reduce cholesterol in the circulation. Mediterranean food is a great source of omega-9 due to the amount of olive oil used; Olive oil is a great source of Oleic acid. WAXES Solid simple lipids containing a monohydric alcohol (C16 ~ C30, higher molecular weight than glycerol) esterified to long-chain fatty acids (C14 ~ C36). Ex: Palmitoyl alcohol A long chain fatty acid + A long hydrocarbon chain alcohol GIVES an ESTER, characterized by being quite hydrophobic (Insoluble in water) FEATURES: Coatings that prevent loss of water by leaves of plants, Are of no nutritional value, because it s indigestible. Are not easily hydrolyzed (fats) & are indigestible by lipases, Are very resistant to rancidity (unpleasant odors ). 3 P a g e
5 COMPLEX LIPIDS Complex lipids have in common two main parts Backbone and attached functional groups. the backbone can be either glycerol or sphingosine. attached groups can be phosphate, nitrogen base, carbohydrate etc. Another classification for complex lipids: Triacylglycerols Glycerophospholipids Sphingolipids; that could either be Sphingophospholipids or Glycolipids. 1) Triacylglycerol (Triglyceride) In glycerol there are 3 hydroxyl groups each can be substituted/replaced with a fatty acid chain. So, we can get monoacylglycerol, diacylglycerol and triacylglycerol. In our bodies, we store fat in the form of triacylglycerol. the fatty acid chains substituted for hydroxyl groups can be similar or different, they also can be saturated or not. simple triacylglycerol 3 similar fatty acids mixed triacylglycerol 3 different fatty acids 4 P a g e
6 Solid vs liquid fats: depends mainly on the saturation of the fatty acid chains from which triacylglycerol is formed, since double bonds cause kinks in the structure of fatty acids. This is the primary reason for the different melting points of fats and oils. So you can say that the fluidity of fat is inversely proportional to the saturation at the same temperature *It is worth mentioning that vegetable oils consist almost entirely of unsaturated fatty acids, whereas animal fats contain a much larger percentage of saturated fatty acids. Saponification (hydrolysis): since lipids have ester linkages, they can be cleaved back into a salt of fatty acid and an alcohol (glycerol) by reacting with water and a base (such as an aqueous solution of NaOH). It can be also cleaved in our bodies by certain enzymes (lipase of pancreas). how does soap work? When mixed with water, the hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails cluster together and orient inward to create a nonpolar microenvironment and the hydrophilic ionic heads interact with water. The resulting spherical clusters are called Micelles. Grease and dirt are trapped inside micelles and the complex can be rinsed away. *Basically, soap causes emulsification of oily material. Hydrogenation: In a hydrogenation reaction, two hydrogen atoms are added across C-C double bond, resulting in a hydrogen-saturated bond. So, chemists invented a method of converting unsaturated fat into a more solid form by partially hydrogenating it, but it was found that Partial hydrogenation converts some, but not all, double bonds into single bonds generating (trans fats). So, we will still have double bonds but in the trans form. 5 P a g e
7 * The primary health risk identified for trans-fat consumption is an elevated risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) and heart attacks as it accumulates in our circulation without being digested because the double bonds aren t recognized by our body enzymes. *The main reason behind using trans-fat is that it gives a longer shelf life and it tastes way better. * In margarine, only about two-thirds of the double bonds present in the starting vegetable oil is hydrogenated, so that the margarine remains soft in the refrigerator and will melt on warm toast. Note that Margarine has no trans-fat. Membrane Lipids The most prevalent class of lipids in membranes is the glycerophospholipids, the least is glycolipids. *The only sphingophospholipids present in plasma membrane is sphingomyelin. *Membrane lipids are amphipathic. *The existence of the lipid bilayer depends On hydrophobic interactions. 1) glycerophospholipids: The common structure in glycerophospholipids is glycerol, two fatty acid and a phosphate group to which a head group is attached. *head group can be either choline, serine or ethanolamine. *the simplest form is phosphatidic acid in which the head group is just a hydrogen. 6 P a g e
8 * Classification of Glycerophospholipids phosphatidylcholine: * most abundant membrane lipid * it was found that phosphatidylcholine is the target of snake venom. This venom contains lecithinase, which hydrolyzes polyunsaturated fatty acids and converting lecithin into lysolecithin. [causing hemolysis of RBCs] phosphatidic acid: The simplest glycerophospholipid, has 2 fatty acids and a phosphate group. Cephalins: Phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylserine (abundant in brain) Phosphatidylinositol: *Sends messages across cell membranes *The head group is a sugar molecule. *Nitrogenous base: cyclic sugar alcohol (inositol). *Structure: glycerol, saturated FA, unsaturated FA, phosphoric acid, & inositol. *Source: Brain tissues *Note that it is not in the membrane but it is attached to it and works as a Signaling molecule Functions: Major component of cell membrane Second messenger during signal transduction On hydrolysis by phospholipase C, phosphatidyl-inositol-4,5diphosphate produces diacyl-glycerol (DAG) & inositol triphosphate (IP3); which liberates calcium Cardiolipins: * From the name is related to the heart; abundant in the heart muscle. * Diphosphatidyl-glycerol * Found in the inner membrane of mitochondria * Initially isolated (when it was first discovered in early 1940s ) from heart muscle (cardio) * Structure: 3 molecules of glycerol, 4 fatty acids & 2 phosphate groups 7 P a g e
9 * The following picture shows the structure of cardiolipin which you must know and you must also have enough knowledge to be able to distinguish different glycerophospholipids from each other Plasmalogens * they are found in the cell membrane phospholipids fraction of brain & muscle, liver, and semen. * they have a protective role against reactive oxygen species * Structure: Precursor: Dihydroxyacetone phosphate. (simplest ketose) Unsaturated fatty alcohol at C1 connected by ether bond. In mammals: at C3; phosphate + ethanolamine or choline. The picture below, shows a Choline plasmalogens, notice the double bond on C1 Major classes of Plasmalogens: 1-Ethanolamine plasmalogen (myelin-nervous tissues) 2- Choline plasmalogen (cardiac tissue) *Platelet activating factor 3- Serine plasmalogens (serine is an amino acid 8 P a g e
10 *The following picture shows the difference between plasmalogens and other phospholipids, the main difference is the presence of a double bond adjacent to the oxygen of C1 of the glycerol molecule. Emulsification: a process by which we can dissolve hydrophobic material (such a fat) in an aqueous environment or when being mixed with water using an emulsifying (agent) such as lecithin Because of their amphipathic nature. *Emulsifying agent: A substance that can surround nonpolar molecules (fat) and keep them in suspension in water, therefore fat and water molecules can mix together more easily. * So, what really happens is that when fat is mixed with water, as mentioned earlier, it s broken up into smaller droplets and then fat become surrounded by hydrophobic fatty acid chains of lecithin, with its phosphate hydrophilic heads exposed to the watery or aqueous environment. * The same thing happens in our bodies but it s the BILE acid which emulsifies the fat we consume instead of lecithin. So basically, Bile is the emulsifying agent in our body. 9 P a g e
11 finally, the different structures of phospholipids. The difference between a liposome and a micelle is the interior, the liposome has a hydrophilic interior, while the micelle has a hydrophobic one. Phospholipids role in therapeutics sometimes it could be extremely hard to get a specific drug to enter the cell, or we want to apply gene therapy ( get DNA(which is very hydrophilic and charged) in the cell ) because of the hydrophobic lipid bilayer which makes up most of the plasma membrane, so the molecule that is destined to enter the cell ( which is polar or charged ) will be packed in a liposome( lipid balls which you can insert a molecule inside of it, then integration between the liposome and the plasma membrane occurs so the molecule enters the cell (endocytosis)). Best of luck يتبع P a g e
Nebal Al - Gallab. Shatha Al - Jabri. Mamoon Ahram
 10 Nebal Al - Gallab Shatha Al - Jabri Mamoon Ahram Note: the doctor showed extra examples, they were in the slides, you can refer to them... Naming of Fatty Acids - 1 st Method ( IUPAC system ) We start
10 Nebal Al - Gallab Shatha Al - Jabri Mamoon Ahram Note: the doctor showed extra examples, they were in the slides, you can refer to them... Naming of Fatty Acids - 1 st Method ( IUPAC system ) We start
Dr. Mamoun. Loai Azar
 13 Dr. Mamoun Loai Azar Lipids (2) - To get the best of this sheet PLEASE study it side by side with the doctor s slides. - In this lecture the doctor continued talking about Eicosanoids. Derived Fatty
13 Dr. Mamoun Loai Azar Lipids (2) - To get the best of this sheet PLEASE study it side by side with the doctor s slides. - In this lecture the doctor continued talking about Eicosanoids. Derived Fatty
Lipids. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8
 Lipids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8 Lipids Lipids are a heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds
Lipids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8 Lipids Lipids are a heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups)
 Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1
 Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of compounds, the common and defining feature of which is their insolubility in water. By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Fats and oils are the principal stored forms
Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of compounds, the common and defining feature of which is their insolubility in water. By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Fats and oils are the principal stored forms
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush A heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds Formed mainly from alcohol & fatty acids combined together
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush A heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds Formed mainly from alcohol & fatty acids combined together
Lipids Definition. Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups)
 Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 6 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 26 th 2013 Noor Salem 1 Not corrected Review Lipids are composed of two main connected parts : o Alcohol Sphingosine Glycerol o Fatty Acids (3 in number) Saturated Long Chain
6 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 26 th 2013 Noor Salem 1 Not corrected Review Lipids are composed of two main connected parts : o Alcohol Sphingosine Glycerol o Fatty Acids (3 in number) Saturated Long Chain
Functions of Lipids. - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g).
 Chapter 8: Lipids Functions of Lipids - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g). - Membrane Components Lipid barriers keep water out. - Messengers Hormones
Chapter 8: Lipids Functions of Lipids - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g). - Membrane Components Lipid barriers keep water out. - Messengers Hormones
TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
 Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/testbank-for-lehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-6th-edition-bynelson TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/testbank-for-lehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-6th-edition-bynelson TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
Chapter 20 Lipids. Organic and Biochem
 Chapter 20 Lipids rganic and Biochem 20.1 Introduction Found in living organisms Insoluble in water but Soluble in non-polar substances Example of Lipid Solvent: diethyl ether Polar groups in lipids are
Chapter 20 Lipids rganic and Biochem 20.1 Introduction Found in living organisms Insoluble in water but Soluble in non-polar substances Example of Lipid Solvent: diethyl ether Polar groups in lipids are
Lipids. Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids.
 Chapter 28 Lipids Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison, and Susan Arena Course 28.1 Lipids:
Chapter 28 Lipids Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison, and Susan Arena Course 28.1 Lipids:
Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules
 Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General structure and functional groups
Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General structure and functional groups
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 4 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 24 th 2013 Ahmad Moayd 1 Definition and general properties refer to slide no. 2 Lipids: macromolecules made from Alcohol and Fatty acid bonded by ester linkage. Amphipathic
4 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 24 th 2013 Ahmad Moayd 1 Definition and general properties refer to slide no. 2 Lipids: macromolecules made from Alcohol and Fatty acid bonded by ester linkage. Amphipathic
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson
 Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 5 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 25 th 2013 Mohammad Abu Dosh Sheet 5.. Lipids ( Dr. Nafith ) : Classification of fatty acids : - they are classified depending on the existence of double bonds to : 1) Saturated
5 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 25 th 2013 Mohammad Abu Dosh Sheet 5.. Lipids ( Dr. Nafith ) : Classification of fatty acids : - they are classified depending on the existence of double bonds to : 1) Saturated
Classification, functions and structure
 Classification, functions and structure Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" Lipids
Classification, functions and structure Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" Lipids
OBJECTIVE. Lipids are largely hydrocarbon derivatives and thus represent
 Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 20: Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, Nomenclature of fatty acids and Essential and non-essential fatty acids OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module
Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 20: Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, Nomenclature of fatty acids and Essential and non-essential fatty acids OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module
Introduction to the Study of Lipids
 Introduction to the Study of Lipids Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General
Introduction to the Study of Lipids Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General
Lecture 3 6/28/10. Membrane Lipids. Importance of Membranes. Categories of Lipids. Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7. ! Membranes are important in
 Lecture 3 Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7! The most polar lipids are found in the membranes of cells and organelles! Why?! These lipids are amphipathic! Membranes are complex and have many components Membrane
Lecture 3 Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7! The most polar lipids are found in the membranes of cells and organelles! Why?! These lipids are amphipathic! Membranes are complex and have many components Membrane
King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry. General Biochemistry-II (BCH 302) Chapter 4. Lipids
 King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry General Biochemistry-II (BCH 302) Chapter 4 Lipids Prepared by Dr. Farid Ataya http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/fataya http://faculty.ksu.edu.sa/75112
King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry General Biochemistry-II (BCH 302) Chapter 4 Lipids Prepared by Dr. Farid Ataya http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/fataya http://faculty.ksu.edu.sa/75112
Biological role of lipids
 Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
Chapter 11: Lipids. Voet & Voet: Pages
 Chapter 11: Lipids Voet & Voet: Pages 380-394 Slide 1 Lipids Lipids are distinguished by their high solubility in non polar solvents and low solubility in H2O Diverse group of compounds including Fats,
Chapter 11: Lipids Voet & Voet: Pages 380-394 Slide 1 Lipids Lipids are distinguished by their high solubility in non polar solvents and low solubility in H2O Diverse group of compounds including Fats,
LIPIDS II: TRIACYLGLYCEROLS:
 LIPIDS II: TRIACYLGLYCEROLS: How are they broken down? o Hydrolyzed into 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol o Physiologically in body: Enzyme called a LIPASE present in adipocytes and intestines o Saponification
LIPIDS II: TRIACYLGLYCEROLS: How are they broken down? o Hydrolyzed into 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol o Physiologically in body: Enzyme called a LIPASE present in adipocytes and intestines o Saponification
BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12
 BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12 General topic for week 6 Session 12 Lipids Useful Links: 1. Animations on Cholesterol (its synthesis, lifestyle factors, LDL) http://www.wiley.com/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cholesterol/cholesterol.htm
BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12 General topic for week 6 Session 12 Lipids Useful Links: 1. Animations on Cholesterol (its synthesis, lifestyle factors, LDL) http://www.wiley.com/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cholesterol/cholesterol.htm
GUTS Lecture Syllabus for Lipid Structure and Nomenclature
 GUTS Lecture Syllabus for Lipid Structure and Nomenclature For Questions or Assistance contact: Dr. Gwen Sancar, gsancar@ad.unc.edu Learning bjectives After completing the GUTS lecture and associated self-
GUTS Lecture Syllabus for Lipid Structure and Nomenclature For Questions or Assistance contact: Dr. Gwen Sancar, gsancar@ad.unc.edu Learning bjectives After completing the GUTS lecture and associated self-
Organic molecules highly hydrophobic and water insoluble.
 UNIT 5. LIPIDS OUTLINE 5.1. Introduction. 5.2. Fatty acids. 5.3. Eicosanoids. 5.4. Triacylglycerols = Triglycerides. 5.5. Waxes. 5.6. Membrane lipids: glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids. 5.7. Isoprenoids
UNIT 5. LIPIDS OUTLINE 5.1. Introduction. 5.2. Fatty acids. 5.3. Eicosanoids. 5.4. Triacylglycerols = Triglycerides. 5.5. Waxes. 5.6. Membrane lipids: glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids. 5.7. Isoprenoids
II- Compound Lipids. 1- Phospholipids
 II- ompound Lipids ompound (conjugated) lipids are lipids conjugated with other substances. They include: 1- Phospholipids formed of lipid, phosphoric acid and nitrogenous base. 2- Glycolipids, formed
II- ompound Lipids ompound (conjugated) lipids are lipids conjugated with other substances. They include: 1- Phospholipids formed of lipid, phosphoric acid and nitrogenous base. 2- Glycolipids, formed
Lipids are used to store and excess energy from extra carbohydrates in animals
 Lipids Lipids are a major source of energy used by cells, however lipids are more difficult for your body to break down. They produce nearly twice the amount of energy than proteins or carbohydrates. Lipids
Lipids Lipids are a major source of energy used by cells, however lipids are more difficult for your body to break down. They produce nearly twice the amount of energy than proteins or carbohydrates. Lipids
Phospholipids Metabolism
 Chapter VI: Phospholipids Metabolism Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Phospholipids Features: Amphipatic: - Hydrophobic head: fatty acids - Hydropholic head: P group+ alcohol Composed of alcohol attached by a phosphodiester
Chapter VI: Phospholipids Metabolism Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Phospholipids Features: Amphipatic: - Hydrophobic head: fatty acids - Hydropholic head: P group+ alcohol Composed of alcohol attached by a phosphodiester
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 10 Lipids
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids CHAPTER 10 Lipids Key topics: Biological roles of lipids Structure and properties of storage lipids Structure and properties of membrane lipids Structure and properties
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids CHAPTER 10 Lipids Key topics: Biological roles of lipids Structure and properties of storage lipids Structure and properties of membrane lipids Structure and properties
Lipids. OpenStax College
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44401 1 Lipids OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
OpenStax-CNX module: m44401 1 Lipids OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids
 I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
MCQS ON LIPIDS. Dr. RUCHIKA YADU
 MCQS ON LIPIDS Dr. RUCHIKA YADU Q1. THE FATS AND OILS ARE RESPECTIVELY RICH IN a) Unsaturated fatty acids b) Saturated fatty acids c) Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids d) None of these Q2. ESSENTIAL
MCQS ON LIPIDS Dr. RUCHIKA YADU Q1. THE FATS AND OILS ARE RESPECTIVELY RICH IN a) Unsaturated fatty acids b) Saturated fatty acids c) Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids d) None of these Q2. ESSENTIAL
Lipid Chemistry. Presented By. Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair
 Lipid Chemistry Presented By Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair 4 Objectives: 1. By the end of this chapter the student should be able to: define lipids. describe the biological importance of lipids.
Lipid Chemistry Presented By Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair 4 Objectives: 1. By the end of this chapter the student should be able to: define lipids. describe the biological importance of lipids.
Lipids and Classification:
 Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids. Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 15 Lipids 15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but
Chapter 15 Lipids 15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush A heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds formed mainly from alcohol & fatty acids combined together
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush A heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds formed mainly from alcohol & fatty acids combined together
MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS
 December 6, 2011 Lecturer: Eileen M. Lafer MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS Reading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapter 26 Images: All images in these notes were taken from Lehninger,
December 6, 2011 Lecturer: Eileen M. Lafer MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS Reading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapter 26 Images: All images in these notes were taken from Lehninger,
Chapter 8. Functions of Lipids. Structural Nature of Lipids. BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes. Slide 1. Slide 2.
 BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
Chapter 19 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 19 Lecture utline Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette Lipids! Introduction to Lipids! Lipids are biomolecules that are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in
Chapter 19 Lecture utline Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette Lipids! Introduction to Lipids! Lipids are biomolecules that are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in
3.1.3 Lipids. Source: AQA Spec
 alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Triglycerides and phospholipids are two groups of lipid. Triglycerides are formed by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid. A
alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Triglycerides and phospholipids are two groups of lipid. Triglycerides are formed by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid. A
PHOSPHOLIPIDS METABOLISM. BY Dr. Walid Said Zaki Dr. Marwa Ali LECTURER OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 PHOSPHOLIPIDS METABOLISM BY Dr. Walid Said Zaki Dr. Marwa Ali LECTURER OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1. State the definition and classification of Phospholipids. 2. Describe the general structure
PHOSPHOLIPIDS METABOLISM BY Dr. Walid Said Zaki Dr. Marwa Ali LECTURER OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1. State the definition and classification of Phospholipids. 2. Describe the general structure
Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition. phospholipids. Sphingolipids. Cholesterol. db=books&itool=toolbar
 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez? db=books&itool=toolbar 1 The surface of a soap bubble is a bilayer formed by detergent molecules 2 Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition phospholipids Sphingolipids
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez? db=books&itool=toolbar 1 The surface of a soap bubble is a bilayer formed by detergent molecules 2 Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition phospholipids Sphingolipids
Biochemistry sheet #19. Biosynthesis of Triacylglycerol and Phosphoacylglycerol
 Biochemistry sheet #19 Biosynthesis of Triacylglycerol and Phosphoacylglycerol Slide 1 This slide shows the components of triacylglycerol (TAG) and phosphoacylglycerol. TAG (Glycerol) Esterified to 3(
Biochemistry sheet #19 Biosynthesis of Triacylglycerol and Phosphoacylglycerol Slide 1 This slide shows the components of triacylglycerol (TAG) and phosphoacylglycerol. TAG (Glycerol) Esterified to 3(
Experiment 12 Lipids. Structures of Common Fatty Acids Name Number of carbons
 Experiment 12 Lipids Lipids are a class of biological molecules that are insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar solvents. There are many different categories of lipids and each category has different
Experiment 12 Lipids Lipids are a class of biological molecules that are insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar solvents. There are many different categories of lipids and each category has different
Classification of Lipids
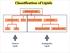 Classification of Lipids Neutral Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Most cell-membrane lipids are one of two main classes of amphipathic hydrolyzable lipids. Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides):
Classification of Lipids Neutral Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Most cell-membrane lipids are one of two main classes of amphipathic hydrolyzable lipids. Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides):
The main biological functions of the many varied types of lipids include: energy storage protection insulation regulation of physiological processes
 Big Idea In the biological sciences, a dehydration synthesis (condensation reaction) is typically defined as a chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecules. This reaction
Big Idea In the biological sciences, a dehydration synthesis (condensation reaction) is typically defined as a chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecules. This reaction
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids Lipids are hydrophobic or amphiphilic insoluble in water soluble in organic solvents soluble in lipids Lipids are used as energy storage molecules structural components of membranes protective molecules
Lipids Lipids are hydrophobic or amphiphilic insoluble in water soluble in organic solvents soluble in lipids Lipids are used as energy storage molecules structural components of membranes protective molecules
Saba Al Fayoumi. Nour Hamdan. Bann Khraisat. Dr. Mamoun Ahram
 9 Saba Al Fayoumi Nour Hamdan Bann Khraisat Dr. Mamoun Ahram Proteoglycans and glycoproteins have been previously discussed and the differences between them have been noted. Protein glycosylation (protein-linked
9 Saba Al Fayoumi Nour Hamdan Bann Khraisat Dr. Mamoun Ahram Proteoglycans and glycoproteins have been previously discussed and the differences between them have been noted. Protein glycosylation (protein-linked
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 7 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 27 th 2013 Lozan Al-Ashi Lipids The last lecture about lipids Just to refresh your memory:- What are lipids? Alcohol+fatty acid, estrefication between them gives me lipids.
7 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 27 th 2013 Lozan Al-Ashi Lipids The last lecture about lipids Just to refresh your memory:- What are lipids? Alcohol+fatty acid, estrefication between them gives me lipids.
Seminar 6 Theoretical part
 Seminar 6 Theoretical part Lipids are a heterogeneous group of naturally occurring organic compounds, classified together on the basis of their common solubility properties. Lipids are insoluble in water,
Seminar 6 Theoretical part Lipids are a heterogeneous group of naturally occurring organic compounds, classified together on the basis of their common solubility properties. Lipids are insoluble in water,
CH 3. Lipids CHAPTER SUMMARY
 H 3 C H 3 C 15 H 3 C H Views of Cholesterol APTER SUMMARY 15.1 The Nature of can best be defined as biomolecules which are soluble to a great extent in solvents. In contrast to carbohydrates, proteins
H 3 C H 3 C 15 H 3 C H Views of Cholesterol APTER SUMMARY 15.1 The Nature of can best be defined as biomolecules which are soluble to a great extent in solvents. In contrast to carbohydrates, proteins
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE
 BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS PROPERTIES OF LIPIDS REACTIONS OF LIPIDS (CHEMICAL PROPERTIES) SOME QUANTITATIVE TESTS FOR LIPIDS CHEMISTRY AND PROPERTIES
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS PROPERTIES OF LIPIDS REACTIONS OF LIPIDS (CHEMICAL PROPERTIES) SOME QUANTITATIVE TESTS FOR LIPIDS CHEMISTRY AND PROPERTIES
Chapter 10 Homework Assignment
 hapter 10 Homework Assignment I have decided to alter the homework assignment for hapter 10. The following problems will be due once we finish the chapter: 2, 4, 5, 6, 9 Lipids are Good (and not always
hapter 10 Homework Assignment I have decided to alter the homework assignment for hapter 10. The following problems will be due once we finish the chapter: 2, 4, 5, 6, 9 Lipids are Good (and not always
Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols
 Chem 431A-L24-F'07 page 1 of 5 Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols (0) REVIEW: FA s are very reduced
Chem 431A-L24-F'07 page 1 of 5 Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols (0) REVIEW: FA s are very reduced
Lesson 2. Biological Molecules. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 2 Biological Molecules Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Carbon in Biological Molecules Organic molecules contain carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) Example: glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ) Inorganic
Lesson 2 Biological Molecules Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Carbon in Biological Molecules Organic molecules contain carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) Example: glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ) Inorganic
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Lipids (cholesterol, cholesterol esters, phospholipids & triacylglycerols) combined with proteins (apolipoprotein) in
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Lipids (cholesterol, cholesterol esters, phospholipids & triacylglycerols) combined with proteins (apolipoprotein) in
LIPIDS OF PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE
 LIPIDS OF PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE Original slides. Important. 436 Notes 438 notes Extra information رابط التعديل: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1wvdec1atp7j- ZKWOUSukSLsEcosjZ0AqV4z2VcH2TA0/edit?usp=sharing
LIPIDS OF PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE Original slides. Important. 436 Notes 438 notes Extra information رابط التعديل: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1wvdec1atp7j- ZKWOUSukSLsEcosjZ0AqV4z2VcH2TA0/edit?usp=sharing
BCH 3000 PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY
 BCH 3000 PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY (Semester 2-2012/13) 1 LIPID Learning outcome (Objectives) Function and distribution. Characteristics of fatty acids-structure and chemical properties. Saturated and
BCH 3000 PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY (Semester 2-2012/13) 1 LIPID Learning outcome (Objectives) Function and distribution. Characteristics of fatty acids-structure and chemical properties. Saturated and
General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202
 General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202 1 I would like to acknowledge Dr. Farid Ataya for his valuable input & help in this course. 2 Outline Lipids Definition, function, fatty acids, classification: simple lipids:
General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202 1 I would like to acknowledge Dr. Farid Ataya for his valuable input & help in this course. 2 Outline Lipids Definition, function, fatty acids, classification: simple lipids:
number Done by Corrected by Doctor
 number 25 Done by موسى صبح Corrected by عبد الرحمن الحنبلي Doctor فيصل الخطيب 1 P a g e Introduction The subject of this lecture is glycerophospholipids also known as phosphoglyceridesor phosphoacylglycerols,
number 25 Done by موسى صبح Corrected by عبد الرحمن الحنبلي Doctor فيصل الخطيب 1 P a g e Introduction The subject of this lecture is glycerophospholipids also known as phosphoglyceridesor phosphoacylglycerols,
Lipids and Biological Membranes
 Lipids and Biological Membranes Lipids: Found in all living organisms Especially important as components of biological membranes Defined functionally, not structurally, as compounds that are totally or
Lipids and Biological Membranes Lipids: Found in all living organisms Especially important as components of biological membranes Defined functionally, not structurally, as compounds that are totally or
Organism. Organ and organ systems. Tissue. Cells. Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids
 hemistry of Life rganism rgan and organ systems Tissue ells arbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, Thiols, Aldehydes, Ketones, arboxylic Acids, Esters, Amines,
hemistry of Life rganism rgan and organ systems Tissue ells arbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, Thiols, Aldehydes, Ketones, arboxylic Acids, Esters, Amines,
Lipids, Biological Membranes and Cellular Transport. 阮雪芬 May/9/2004
 Lipids, Biological Membranes and Cellular Transport 阮雪芬 May/9/2004 Outline Introduction Fatty Acids Triacylglycerols Polar lipids Steroids and other lipids Biological membranes Membrane transport Examples
Lipids, Biological Membranes and Cellular Transport 阮雪芬 May/9/2004 Outline Introduction Fatty Acids Triacylglycerols Polar lipids Steroids and other lipids Biological membranes Membrane transport Examples
Chemistry B11 Chapters 15 Lipids
 Chapters 15 ipids ipids: are family of biomolecules that have the common property of being soluble in organic solvents but not in water. Role of lipids: they have three important roles in nature: 1. They
Chapters 15 ipids ipids: are family of biomolecules that have the common property of being soluble in organic solvents but not in water. Role of lipids: they have three important roles in nature: 1. They
How to maximize fat energy? Swine. Poultry. Shrimp. Technical brochure about the molecular structure and mode of action of lysolecithins
 Introduction «Lecithin and lysolecithin «Normal fat digestion «Mode of action lysolecithins «Conclusions «Swine Poultry Fish How to maximize fat energy? Shrimp Technical brochure about the molecular structure
Introduction «Lecithin and lysolecithin «Normal fat digestion «Mode of action lysolecithins «Conclusions «Swine Poultry Fish How to maximize fat energy? Shrimp Technical brochure about the molecular structure
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 10 Lipids
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids Storage lipids: TG lipid 의기능 : 1 Energy source 3 Electrical insulator 2 Thermal insulator 4 Membrane 의구성성분, 방수, 부력, cofactor, signaling 등 지방대사이상 : obesity, atherosclerosis,
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids Storage lipids: TG lipid 의기능 : 1 Energy source 3 Electrical insulator 2 Thermal insulator 4 Membrane 의구성성분, 방수, 부력, cofactor, signaling 등 지방대사이상 : obesity, atherosclerosis,
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd
 ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules CARBON BASED MOLECULES
 CARBON BASED MOLECULES KEY CONCEPTS Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life. Lipids are one class of organic molecules. This group includes fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. Lipids are made of
CARBON BASED MOLECULES KEY CONCEPTS Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life. Lipids are one class of organic molecules. This group includes fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. Lipids are made of
Lipids do not like water! (aka: hydrophobic) Generally insoluble
 Lipids Lipids Lipids do not like water! (aka: hydrophobic) Generally insoluble Lipids They act like this because of their molecular structure (non-polar) Lipids are made mostly of C and H atoms, with O
Lipids Lipids Lipids do not like water! (aka: hydrophobic) Generally insoluble Lipids They act like this because of their molecular structure (non-polar) Lipids are made mostly of C and H atoms, with O
Lipids: Fats, Oils & Waxes: AP Biology
 Lipids: Fats, Oils & Waxes: Lipids long term energy storage concentrated energy *9 Cal/gram Lipids: Triglycerides Lipids are composed of C, H, O u long hydrocarbon chains (H-C) Family groups u fats u phospholipids
Lipids: Fats, Oils & Waxes: Lipids long term energy storage concentrated energy *9 Cal/gram Lipids: Triglycerides Lipids are composed of C, H, O u long hydrocarbon chains (H-C) Family groups u fats u phospholipids
The Chemical Building Blocks of Life. Chapter 3
 The Chemical Building Blocks of Life Chapter 3 Biological Molecules Biological molecules consist primarily of -carbon bonded to carbon, or -carbon bonded to other molecules. Carbon can form up to 4 covalent
The Chemical Building Blocks of Life Chapter 3 Biological Molecules Biological molecules consist primarily of -carbon bonded to carbon, or -carbon bonded to other molecules. Carbon can form up to 4 covalent
2. Simple lipids: Triacylglycerols and waxes are classified as simple lipids. The characteristics of each are described in the sections below.
 Paper 4: Biomolecules and their interactions Module 21: Classification of Lipids: simple and compound lipids, phospholipids, Cholesterol OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module is to introduce the students
Paper 4: Biomolecules and their interactions Module 21: Classification of Lipids: simple and compound lipids, phospholipids, Cholesterol OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module is to introduce the students
Biological Molecules
 The Chemical Building Blocks of Life Chapter 3 Biological molecules consist primarily of -carbon bonded to carbon, or -carbon bonded to other molecules. Carbon can form up to 4 covalent bonds. Carbon may
The Chemical Building Blocks of Life Chapter 3 Biological molecules consist primarily of -carbon bonded to carbon, or -carbon bonded to other molecules. Carbon can form up to 4 covalent bonds. Carbon may
Lipids. Lipids. Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague
 Lipids Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague Lipids 1. General introduction 2. Nomenclature of fatty acids 3. Degradation
Lipids Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague Lipids 1. General introduction 2. Nomenclature of fatty acids 3. Degradation
Nutrition & Wellness for Life 2012 Chapter 6: Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source
 Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Tissue in which the body
Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Tissue in which the body
2. lipophobic: Adverse to fat solvents; insoluble fat and fat solvents. 4. squalene: A cholesterol precursor found in whale liver and plants.
 Chapter 5 Lipids Key Terms 1. hydrophilic: Can mix with or dissolve in water. 2. lipophobic: Adverse to fat solvents; insoluble fat and fat solvents. 3. adipocytes: Fat cells. 4. squalene: A cholesterol
Chapter 5 Lipids Key Terms 1. hydrophilic: Can mix with or dissolve in water. 2. lipophobic: Adverse to fat solvents; insoluble fat and fat solvents. 3. adipocytes: Fat cells. 4. squalene: A cholesterol
3.9 Carbohydrates. Provide building materials and energy storage. Are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio
 3.9 Carbohydrates Provide building materials and energy storage Are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio Are of two main types Simple carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates
3.9 Carbohydrates Provide building materials and energy storage Are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio Are of two main types Simple carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates
Biomolecules. Biomolecules. Carbohydrates. Biol 219 Lec 3 Fall Polysaccharides. Function: Glucose storage Fig. 2.2
 Biomolecules Biomolecules Monomers Polymers Carbohydrates monosaccharides polysaccharides fatty acids triglycerides Proteins amino acids polypeptides Nucleic Acids nucleotides DNA, RNA Carbohydrates Carbohydrates
Biomolecules Biomolecules Monomers Polymers Carbohydrates monosaccharides polysaccharides fatty acids triglycerides Proteins amino acids polypeptides Nucleic Acids nucleotides DNA, RNA Carbohydrates Carbohydrates
Carbon. Isomers. The Chemical Building Blocks of Life
 The Chemical Building Blocks of Life Carbon Chapter 3 Framework of biological molecules consists primarily of carbon bonded to Carbon O, N, S, P or H Can form up to 4 covalent bonds Hydrocarbons molecule
The Chemical Building Blocks of Life Carbon Chapter 3 Framework of biological molecules consists primarily of carbon bonded to Carbon O, N, S, P or H Can form up to 4 covalent bonds Hydrocarbons molecule
Chapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids
 common name hapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids shorthand notations #of : # of = #of, location of = line structure comments butyric acid 4:0 in butterfat lauric
common name hapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids shorthand notations #of : # of = #of, location of = line structure comments butyric acid 4:0 in butterfat lauric
Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds.
 Lipids Lipids Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds. u long hydrocarbon chain u composed of CHO Diverse group u fats u oils u waxes u steroids Do not form polymers u big molecules made
Lipids Lipids Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds. u long hydrocarbon chain u composed of CHO Diverse group u fats u oils u waxes u steroids Do not form polymers u big molecules made
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: Life's Components: Biological Molecules
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: Life's Components: Biological Molecules Life s Components: Biological Molecules 3.1 Carbon's Place in the Living World 3.2 Functional Groups 3.3 Carbohydrates 3.4 Lipids 3.5 Proteins
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: Life's Components: Biological Molecules Life s Components: Biological Molecules 3.1 Carbon's Place in the Living World 3.2 Functional Groups 3.3 Carbohydrates 3.4 Lipids 3.5 Proteins
History. Aron first proposed that fat may be essential for normal growth Tested on animals-vitamins A,D,E added. Fat deficiency severely affected
 Chapter 5 LIPIDS History 1918 Aron first proposed that fat may be essential for normal growth Tested on animals-vitamins A,D,E added Fat deficiency severely affected Bone growth Reproduction Called Vitamin
Chapter 5 LIPIDS History 1918 Aron first proposed that fat may be essential for normal growth Tested on animals-vitamins A,D,E added Fat deficiency severely affected Bone growth Reproduction Called Vitamin
EH1008 Biomolecules. Inorganic & Organic Chemistry. Water. Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry.
 EH1008 Biomolecules Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Inorganic & Organic Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry: generally, substances that do not contain carbon Inorganic molecules:
EH1008 Biomolecules Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Inorganic & Organic Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry: generally, substances that do not contain carbon Inorganic molecules:
Biological molecules
 Biological molecules 04-04-16 Announcements Your lab report 1 is due now Quiz 1 is on Wednesday at the beginning of class, so don t be late Review Macromolecues are large molecules necessary for life made
Biological molecules 04-04-16 Announcements Your lab report 1 is due now Quiz 1 is on Wednesday at the beginning of class, so don t be late Review Macromolecues are large molecules necessary for life made
A. Lipids: Water-Insoluble Molecules
 Biological Substances found in Living Tissues Lecture Series 3 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function A. Lipids: Water-Insoluble Lipids can form large biological molecules, but these aggregations
Biological Substances found in Living Tissues Lecture Series 3 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function A. Lipids: Water-Insoluble Lipids can form large biological molecules, but these aggregations
Lecture Series 2 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function
 Lecture Series 2 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function Reading Assignments Read Chapter 4 (Protein structure & Function) Biological Substances found in Living Tissues The big four in terms of macromolecules
Lecture Series 2 Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function Reading Assignments Read Chapter 4 (Protein structure & Function) Biological Substances found in Living Tissues The big four in terms of macromolecules
Biological Molecules
 Chemical Building Blocks of Life Chapter 3 Biological Molecules Biological molecules consist primarily of -carbon bonded to carbon, or -carbon bonded to other molecules. Carbon can form up to 4 covalent
Chemical Building Blocks of Life Chapter 3 Biological Molecules Biological molecules consist primarily of -carbon bonded to carbon, or -carbon bonded to other molecules. Carbon can form up to 4 covalent
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Part 2
 Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Part 2 Carbohydrates are Polymers of Monosaccharides Three different ways to represent a monosaccharide Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are sugars and starches and provide
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Part 2 Carbohydrates are Polymers of Monosaccharides Three different ways to represent a monosaccharide Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are sugars and starches and provide
Inorganic compounds: Usually do not contain carbon H 2 O Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 NaCl Carbon containing molecules not considered organic: CO 2
 Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties. Biochemistry: Made by living things All contain the elements carbon and hydrogen Inorganic: Inorganic compounds: All other
Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties. Biochemistry: Made by living things All contain the elements carbon and hydrogen Inorganic: Inorganic compounds: All other
METABOLISM OF ACYLGLYCEROLS AND SPHINGOLIPDS. Ben S. Ashok MSc.,FAGE.,PhD., Dept. of Biochemistry
 METABOLISM OF ACYLGLYCEROLS AND SPHINGOLIPDS Ben S. Ashok MSc.,FAGE.,PhD., Dept. of Biochemistry STORAGE AND MEMBRANE LIPIDS STORAGE LIPIDS Mainly as triacylglycerols (triglycerides) in adipose cells Constitute
METABOLISM OF ACYLGLYCEROLS AND SPHINGOLIPDS Ben S. Ashok MSc.,FAGE.,PhD., Dept. of Biochemistry STORAGE AND MEMBRANE LIPIDS STORAGE LIPIDS Mainly as triacylglycerols (triglycerides) in adipose cells Constitute
Biology. Chapter 3. Molecules of Life. Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr
 Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 3 Molecules of Life 2015 3.1 What Are the Molecules of Life? The molecules of life contain a high proportion of carbon atoms: Complex carbohydrates
Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 3 Molecules of Life 2015 3.1 What Are the Molecules of Life? The molecules of life contain a high proportion of carbon atoms: Complex carbohydrates
Chemistry Chapter 21
 Chemistry 2100 Chapter 21 Lipids Fa3y Acids CH oleic acid (mp 4 C) CH stearic acid (mp 70 C) Triacylglycerols Fatty Acids! The fatty acid components of triglycerides have certain things in common: 1.
Chemistry 2100 Chapter 21 Lipids Fa3y Acids CH oleic acid (mp 4 C) CH stearic acid (mp 70 C) Triacylglycerols Fatty Acids! The fatty acid components of triglycerides have certain things in common: 1.
