Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 50, No. 24, by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN /07/$32.
|
|
|
- Howard Dalton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 50, No. 24, by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN /07/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi: /j.jacc Recombinant Antibodies to an Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Epitope Induce Rapid Regression of Atherosclerosis in Apobec-1 / / Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor / Mice Alexandru Schiopu, MD, PHD,* Björn Frendéus, PHD, Bo Jansson, PHD, Ingrid Söderberg, BSI,* Irena Ljungcrantz, BSI,* Zufan Araya, PHD, Prediman K. Shah, MD, FACC, Roland Carlsson, PHD, Jan Nilsson, MD, PHD,* Gunilla Nordin Fredrikson, PHD* Malmö and Lund, Sweden; and Los Angeles, California Objectives Background Methods Results Conclusions The present study tested the hypothesis that treatment with human recombinant immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) antibodies against a specific oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxldl) epitope will induce regression of existing atherosclerotic lesions in LDL receptor-deficient mice expressing apolipoprotein B-100 (apob-100) (Apobec-1 / / LDLR / ). Oxidized LDL plays an essential role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. We previously showed that an antibody against oxldl reduces progression of atherosclerosis in mice. Apobec-1 / /LDLR / mice were fed a high-fat diet until they were 24 weeks and were subsequently transferred to chow. Starting at 25 weeks, mice were given 3 weekly injections of either of 2 recombinant human IgG1 antibodies (IEI-E3 or 2D03) against a malondialdehyde-modified apob-100 peptide sequence. At 25 weeks, atherosclerotic lesions covered % of the descending aorta. Transfer to chow diet resulted in a modest regression of atherosclerosis over a 5-week period ( %; p NS). Antibody treatment induced additional regression of atherosclerosis by 50% (2D03; p 0.001) and 36% (IEI-E3; p 0.004) compared with control IgG1. The 2D03 treatment also reduced plaque inflammation, enhanced plaque expression of the adenosine triphosphate binding cassette transporter A1, and inhibited expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in cultured monocytes. Human IgG1 against a specific oxldl epitope can induce rapid and substantial regression of atherosclerotic lesions, possibly by stimulating lipid efflux and inhibiting macrophage recruitment. These recombinant human antibodies could represent a novel strategy for rapid regression/stabilization of atherosclerotic lesions. (J Am Coll Cardiol 2007;50:2313 8) 2007 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation From the *Department of Clinical Sciences, Malmö University Hospital, Lund University, Malmö, Sweden; BioInvent International AB, Lund, Sweden; Atherosclerosis Research Center and Division of Cardiology, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, California; and the Department of Biomedical Laboratory Science, Malmö University, Malmö, Sweden. Supported by grants from the Swedish Medical Research Council; Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation; Crafoord Foundation; Royal Physiographic Society; Albert Påhlsson Foundation, Malmö University Hospital Foundation; Lundström Foundation; Heart Foundation; and the United Hostesses at Cedars-Sinai. Manuscript received May 4, 2007; revised manuscript received July 5, 2007, accepted July 24, Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxldl) is one of the most important targets for the immune system in atherosclerosis (1,2). Oxidation of LDL results in formation of neoepitopes such as oxidized phospholipids and aldehydemodified breakdown fragments of apolipoprotein B-100 (apob-100), leading to escape from self-tolerance (3). Immunization of hypercholesterolemic rabbits with oxldl inhibits the development of atherosclerosis, suggesting that immune responses against oxldl may have an atheroprotective effect (4,5). We have characterized the apob-100 See page 2319 peptide sequences in oxldl that give rise to autoantibody formation in humans (6) and demonstrated that immunization with some of these peptide sequences significantly reduces the development of atherosclerosis in ApoE / mice (7,8). Peptide 45, corresponding to the sequence between amino acids 661 and 680 of apob-100, was
2 2314 Schiopu et al. JACC Vol. 50, No. 24, 2007 IgG1 Against OxLDL Induces Plaque Regression December 11, 2007: Abbreviations and Acronyms ABCA1 adenosine triphosphate binding cassette transporter A1 apob-100 apolipoprotein B-100 IgG1 immunoglobulin G1 LDL low-density lipoprotein LDLR low-density lipoprotein receptor MCP-1 monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 MDA malondialdehyde oxldl oxidized lowdensity lipoprotein found to be one of the most effective peptides in these studies. The presence of autoantibodies against this peptide sequence was recently shown to be associated with reduced risk for development of acute myocardial infarction in humans (9). We have developed human recombinant immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) antibodies specific for this aldehyde-modified peptide (10). Antibody treatment was found to reduce early lesion development by up to 50% in ApoE / mice. The aim of the present study was to test the hypothesis that human recombinant IgG1 against the peptide 45 sequence in apob-100 induces regression of existing atherosclerotic plaques in Apobec-1 / /low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) / mice and to explore the mechanisms through which this regression is achieved. Methods Antibody treatment and tissue preparation. Antibodies were produced against the malondialdehyde (MDA)- modified human apob-100 p45 sequence as previously described (10). Antibodies were produced against the human sequence rather than the mouse sequence because the long-term aim of these studies is to develop an antibodybased therapy that can be used in humans. Both the IEI-E3 and 2D03 antibodies raised against the MDA-modified apob-100 p45 specifically recognized MDA-modified LDL but not native LDL. Fluorescein isothiocyanate-8 (FITC- 8), the control IgG1 directed to FITC did not bind to MDA LDL or native LDL (data not shown). The binding of 2D03 to MDA apob-100 was 10 times higher than that of IEI-E3, as determined by the Biacore technique ( vs , respectively). We used male Apobec-1 / /LDLR / mice with C57BL/6 background from Jackson Laboratories (Bar Harbor, Maine). These mice express full-length apob-100 in their LDL particles and have 3-fold higher plasma levels of apob-100 Figure 1 Antibody-Induced Regression of Plaque Area in the Descending Aorta Assessed by Oil Red O Staining The values are expressed as the percentages of total plaque area per total area of the descending aorta. p values were calculated versus fluorescein isothiocyanate-8 (FITC-8). p 0.01 and p versus FITC-8. than LDLR / mice (11). From 4 weeks of age, the mice were fed a high-cholesterol diet (0.15% cholesterol, 21% fat; Lactamin AB, Kimstad, Sweden) provided ad libitum. One week before the first immunization, the diet was changed to normal chow. At 25 weeks of age, the mice were injected intraperitoneally with 1 mg (0.5 ml) of 2D03, IEI-E3, or FITC-8 antibodies. The injections were repeated 2 times at 1-week intervals, and the mice were sacrificed 2 weeks after the last injection (Table 1). For a detailed description of tissue preparation and staining for lipids, macrophages, and ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA-1), please see the Online Appendix. Quantitation of monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 and ABCA-1 expression. The effect of antibodies on MCP-1 gene expression, MCP-1 secretion, and ABCA-1 protein expression in cultured human monocytes/ macrophages was measured by real-time reverse transcrip- Experimental Design and Treatment Groups Table 1 Experimental Design and Treatment Groups Group No. of Mice Beginning of Diet, Weeks* End of Diet, Weeks* Antibody Treatment, Weeks* Sacrificed, Weeks* 25-week control (baseline) No week control No 29 FITC-8 (isotype control) , 26, IEI-E , 26, D , 26, *Weeks of age. FITC-8 fluorescein isothiocyanate-8.
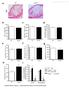
3 JACC Vol. 50, No. 24, 2007 December 11, 2007: Schiopu et al. IgG1 Against OxLDL Induces Plaque Regression 2315 Figure 2 Recombinant Human Antibodies to MDA apob-100 Peptides Upregulate ABCA-1 Expression In Vivo and In Vitro (A) ABCA-1 staining of aortic arch plaques from FITC-8, IEI-E3, and 2D03-treated mice. (B) The values represent the percentages of ABCA-1 stained area per total plaque area. (C) Flow cytometry histogram showing ABCA-1 expression of untreated (gray shaded peak), FITC-8 treated (black line overlay), and 2D03-treated (red line overlay) cells. (D) Mean ABCA-1 expression of untreated and FITC-8 and 2D03-treated cells. The values are expressed as percentages of mean fluorescent intensity of the untreated control. Scale bar 100 m. p 0.02 and p 0.01 versus FITC-8. ABCA-1 adenosine triphosphate binding cassette transporter A1; apob-100 apolipoprotein B-100; FITC-8 fluorescein isothiocyanate-8; MDA malondialdehyde. tion, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and flow cytometry, respectively. Please see the Online Appendix for a detailed method description. Statistical analysis. Analysis of all the in vivo data was performed using the 2-tailed Mann-Whitney test and is presented as box plots demonstrating median and 25th and Figure 3 Macrophage and ABCA-1 Immunoreactivity Colocalize in Aortic Arch Plaques (A and C) ABCA-1 and (B and D) macrophage staining of aortic arch plaques from 2 different mice treated with the 2D03 antibody and sacrificed at 29 weeks of age. Abbreviations as in Figure 2.
4 2316 Schiopu et al. JACC Vol. 50, No. 24, 2007 IgG1 Against OxLDL Induces Plaque Regression December 11, 2007: th percentiles, with whiskers showing the highest and lowest values. Analysis of the in vitro data was performed using parametric analysis of variance with Tukey post test and is presented as mean SD. Results were considered statistically significant at p Results Effect of antibody treatment on the extent of atherosclerosis. The design of the experiments and the different treatment groups are outlined in Table 1. A modest decrease in plaque area was observed in animals transferred to chow diet alone and sacrificed at 29 weeks of age ( % vs %) (Fig. 1). The remaining groups received intraperitoneal injections of 1 mg of 2D03, IEI-E3, or control FITC-8 antibodies at 25, 26, and 27 weeks. There were no significant differences among the treatment groups and the chow-fed control group with respect to weight and the plasma levels of cholesterol and triglycerides (data not shown). Treatment with the FITC-8 control antibody had no effect on atherosclerosis compared with transfer to chow diet alone, whereas treatment with the 2D03 antibody resulted in a more than 50% regression of atherosclerosis ( %) compared with treatment with control IgG1 (p 0.001) (Fig. 1). A less pronounced regression was observed in mice treated with the IEI-E3 antibody ( %; p 0.004). Effect on ABCA-1 expression. The reduction in oil red O staining of neutral lipids in the aorta of 2D03- and IEI-E3 treated mice compared with that in the FITC-8 group suggested a stimulation of lipid efflux from the plaques. To study the effect of the antibodies on pathways mediating reverse cholesterol transport, we analyzed the expression of ABCA-1 in aortic plaques of antibody-treated mice and in cultured human monocytes. The fraction of total plaque area demonstrating positive ABCA-1 immunoreactivity was found to be increased by 30% (p 0.02) in the atherosclerotic plaques of 2D03-treated mice compared with that in the FITC-8 control group (Figs. 2A and 2B). There was a close colocalization between ABCA-1 and macrophage immunoreactivity in the lesions, suggesting that ABCA-1 was primarily expressed by macrophages (Fig. 3). Monocytes cultured in oxldl-containing human serum in the presence of 2D03 for 48 h showed increased ABCA-1 expression Figure 4 Decreased Macrophage Content in Plaques From the Innominate Artery in the Antibody-Treated Groups The values in the graph represent percentages of stained area per total plaque area. Scale bar 100 m. p 0.05 versus FITC-8. Abbreviations as in Figure 2.
5 JACC Vol. 50, No. 24, 2007 December 11, 2007: Schiopu et al. IgG1 Against OxLDL Induces Plaque Regression 2317 compared with FITC-8 treated or untreated cells as measured by flow-cytometry (Figs. 2C and 2D). Effect on inflammatory activity. Treatment with the 2D03 antibody resulted in a 38% reduction of macrophage immunoreactivity compared with the FITC-8 control group (Fig. 4). A similar trend was also observed in mice treated with the IEI-E3 antibody. To study the possible mechanisms involved in the antiinflammatory effect of antibody treatment, we examined the effect of 2D03 and IEI-E3 on macrophage expression of MCP-1. Freshly isolated CD14-positive human monocytes were cultured in oxldl-containing human serum in the presence or absence of the antibodies for 48 h. Both 2D03 and IEI-E3 inhibited monocyte MCP-1 release and mrna expression in a dose-dependent manner, whereas the FITC-8 control antibody had no effect (Fig. 5). Figure 5 Antibodies to MDA apob-100 Peptides Block oxldl-induced Monocyte MCP-1 Production In Vitro (A) MCP-1 levels in conditioned medium from monocytes incubated with titrated concentrations of IEI-E3 (shaded squares), 2D03 (solid squares), or FITC-8 control IgG1 (open squares) in the presence of oxldl-containing human serum. The graph shows mean SD of triplicate values from a representative experiment. (B) MCP-1 messenger ribonucleic acid (mrna) relative to 18S mrna levels in human monocytes incubated with 60 g/ml 2D03, IEI-E3, or FITC-8 in the presence of oxldl-containing human serum. Graphs show mean SD of triplicate values using cells obtained from 3 different donors (n 9). p versus FITC-8. IgG immunoglobulin G; MCP monocyte chemoattractant protein; oxldl oxidized low-density lipoprotein; other abbreviations as in Figure 2. Discussion This study demonstrated for the first time that treatment with recombinant human IgG1 antibodies against an oxldl-specific antigen induces regression of advanced pre-existing atherosclerotic plaques in the aorta of Apobec- 1 / /LDLR / mice by more than 50% over a 4-week period. The present observation that 2D03 antibodies stimulated the expression of ABCA-1, a key protein in reverse cholesterol transport, identifies an important mechanism likely to be involved in plaque regression. Moreover, our results showed that 2D03 treatment inhibits macrophage release of the chemoattractant chemokine MCP-1, leading to a less inflammatory plaque phenotype in vivo. Antibody-induced plaque regression and the role of ABCA-1. Transfer of cholesterol-fed Apobec-1 / /LDLR / mice to a low-fat diet halted further progression of atherosclerosis but was alone not sufficient to induce a significant regression of aortic lesions. In contrast, a marked reduction in aortic lipid-rich plaques was found in 2D03 and IEI-E3 antibody-treated mice, suggesting that the antibodies facilitated net removal of lipids from the aorta by activation of reverse cholesterol transport. Our findings that 2D03 stimulated the expression of ABCA-1 in cultured monocytes and that 2D03 treatment in mice resulted in increased expression of ABCA-1 in atherosclerotic plaques point to a possible mechanism responsible for this effect. ABCA-1 has an important role in reverse cholesterol transport by controlling the efflux rate of cholesterol and phospholipids to apoa-i (12), and overexpression of ABCA-1 has been shown to inhibit atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic mice (13). The macrophage expression of ABCA-1 is strongly induced by lipid loading (14) and IgG1 against MDA-modified apob-100 promotes uptake of oxldl in macrophages (10). These observations suggested that 2D03 antibodies increase lipid efflux from plaques by enhancing macrophage uptake of oxldl from the surrounding extracellular matrix. This subsequently resulted in increased macrophage expression of ABCA-1 and stimulation of apoa-i mediated reverse cholesterol transport. Possible mechanisms of antibody-induced plaque macrophage depletion. Our in vitro results demonstrated the ability of MDA apob-100 antibodies to inhibit macrophage expression of the chemokine MCP-1. Expression of the potent chemokine MCP-1 is enhanced by oxidized lipids, and MCP-1 deficiency reduces development of atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic mice (15). Accordingly, blocking of monocyte MCP-1 release by anti-oxldl IgG1 would provide an attractive means of selectively neutralizing MCP-1 in atherosclerotic plaques where ox- LDL and macrophages colocalize. Study limitations. The mouse homology for the human p45 sequence is 85%, suggesting that the affinity of the antibodies may be lower for mouse than for human oxldl. Because the present results suggested that antibodies with higher binding affinities are more effective, it is likely that
6 2318 Schiopu et al. JACC Vol. 50, No. 24, 2007 IgG1 Against OxLDL Induces Plaque Regression December 11, 2007: this will limit the effectiveness of the antibodies when used in mice. A second limitation is that the functional studies of possible mechanisms mediating the protective effects of the IEI-E3 and 2D03 antibodies were performed on human macrophages. Accordingly, these observations cannot be directly extrapolated to the animal experiments. On the other hand, they add support to the possibility that the antiinflammatory effects of the antibodies can also be achieved in humans. A third limitation of the present study is the generation of mouse anti-human IgG1 antibodies (10). These antibodies may reduce the effectiveness of human IgG1 treatment in mice by blocking their binding sites or by inducing their clearance from the circulation. Conclusions The present findings showed that treatment with human IgG1 against a specific oxldl antigenic epitope can induce a rapid and substantial regression of atherosclerotic lesions, possibly mediated by the macrophage reverse cholesterol transport, as indicated by increased ABCA-1 expression. Our studies also indicated that 2D03 treatment reduces macrophage MCP-1 release, leading to a less inflammatory plaque phenotype. These recombinant human IgG1 represent a potentially novel approach for treatment of atherosclerosis in humans. However, in this respect, the present study needs to be interpreted with due caution because the atherosclerotic disease process of Apobec-1 / /LDLR / mice is not likely to be identical to that of human atherosclerosis. Reprint requests and correspondence: Dr. Alexandru Schiopu, Transplantation Immunology Unit, Nuffield Department of Surgery, Level 6, John Radcliffe Hospital, Headington, Oxford, OX3 9DU, United Kingdom. alexandru.schiopu@med.lu.se. REFERENCES 1. Glass CK, Witztum JL. Atherosclerosis: the road ahead. Cell 2001; 104: Hansson GK. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 2005;352: Palinski W, Witztum JL. Immune responses to oxidative neoepitopes on LDL and phospholipids modulate the development of atherosclerosis. J Intern Med 2000;247: Palinski W, Miller E, Witztum JL. Immunization of low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor-deficient rabbits with homologous malondialdehyde-modified LDL reduces atherogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA1995;92: Ameli S, Hultgårdh-Nilsson A, Regnström J, et al. Effect of immunization with homologous LDL and oxidized LDL on early atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1996;16: Fredrikson GN, Hedblad B, Berglund G, et al. Identification of immune responses against aldehyde-modified peptide sequences in Apo B-100 associated with cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2003;23: Fredrikson GN, Söderberg I, Lindholm M, et al. Inhibition of atherosclerosis in ApoE-null mice by immunization with ApoB- 100 peptide sequences. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2003;23: Chyu KY, Zhao X, Reyes OS, et al. Immunization using an Apo B-100 related epitope reduces atherosclerosis and plaque inflammation in hypercholesterolemic Apo E / mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005;338: Fredrikson GN, Schiopu A, Berglund G, Alm R, Shah PK, Nilsson J. Autoantibody against the amino acid sequence in Apo B-100 is associated with decreased carotid stenosis and cardiovascular events. Atherosclerosis 2007;194:e Schiopu A, Bengtsson J, Söderberg I, et al. Recombinant human antibodies against aldehyde-modified apolipoprotein B-100 peptide sequences inhibit atherosclerosis. Circulation 2004;110: Nakamuta M, Taniguchi S, Ishida BY, Kobayashi K, Chan L. Phenotype interaction of Apobec-1 and CETP, LDLR, and ApoE gene expression in mice: role of ApoB mrna editing in lipoprotein phenotype expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1998;18: Schmitz G, Langmann T. Structure, function and regulation of the ABC1 gene product. Curr Opin Lipidol 2001;12: Van Eck M, Singaraja RR, Ye D, et al. Macrophage ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 overexpression inhibits atherosclerotic lesion progression in low-density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2006;26: Langmann T, Klucken J, Reil M, et al. Molecular cloning of the human ATP-binding cassette transporter 1 (habc1): evidence for sterol-dependent regulation in macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1999;257: Gu L, Okada Y, Clinton SK, et al. Absence of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 reduces atherosclerosis in low density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice. Mol Cell 1998;2: APPENDIX For a detailed description of tissue preparation and staining for lipids, macrophages, and ABCA-1, please see the online version of this article.
Atherosclerosis develops as a result of chronic arterial
 Recombinant Human Antibodies Against Aldehyde-Modified Apolipoprotein B-100 Peptide Sequences Inhibit Atherosclerosis Alexandru Schiopu, MD; Jenny Bengtsson, PhD; Ingrid Söderberg, BSI; Sabina Janciauskiene,
Recombinant Human Antibodies Against Aldehyde-Modified Apolipoprotein B-100 Peptide Sequences Inhibit Atherosclerosis Alexandru Schiopu, MD; Jenny Bengtsson, PhD; Ingrid Söderberg, BSI; Sabina Janciauskiene,
LU:research Institutional Repository of Lund University
 LU:research Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in Atherosclerosis. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher
LU:research Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in Atherosclerosis. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher
LUP. Lund University Publications. Institutional Repository of Lund University
 LUP Lund University Publications Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. This paper has been peer-reviewed
LUP Lund University Publications Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. This paper has been peer-reviewed
Original Research. Low Levels of Apolipoprotein B-100 Autoantibodies Are Associated With Increased Risk of Coronary Events
 Original Research Low Levels of Apolipoprotein B-100 Autoantibodies Are Associated With Increased Risk of Coronary Events Harry Björkbacka, Ragnar Alm, Margaretha Persson, Bo Hedblad, Jan Nilsson, Gunilla
Original Research Low Levels of Apolipoprotein B-100 Autoantibodies Are Associated With Increased Risk of Coronary Events Harry Björkbacka, Ragnar Alm, Margaretha Persson, Bo Hedblad, Jan Nilsson, Gunilla
Identification of autoantibodies in human plasma recognizing an apob-100 LDL receptor binding site peptide
 Identification of autoantibodies in human plasma recognizing an apob-100 LDL receptor binding site peptide Gunilla Nordin Fredrikson, 1, *, Göran Berglund,* Ragnar Alm,* Jan-Åke Nilsson,* Prediman K. Shah,
Identification of autoantibodies in human plasma recognizing an apob-100 LDL receptor binding site peptide Gunilla Nordin Fredrikson, 1, *, Göran Berglund,* Ragnar Alm,* Jan-Åke Nilsson,* Prediman K. Shah,
LUP. Lund University Publications Institutional Repository of Lund University
 LUP Lund University Publications Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in Diabetologia. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include
LUP Lund University Publications Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in Diabetologia. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include
Antigen Presenting Cell. T cell proliferation Disclosures
 Dynamic T-cell and APC Interaction Perpetuates Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis!"#$%&'()*+*,-.,'/1#.%-13'4-"1-3''5*6'789:' ' ;"
Dynamic T-cell and APC Interaction Perpetuates Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis!"#$%&'()*+*,-.,'/1#.%-13'4-"1-3''5*6'789:' ' ;"
Low levels of IgG autoantibodies against the apolipoprotein B antigen p210 increases the risk of cardiovascular death after carotid endarterectomy.
 Low levels of IgG autoantibodies against the apolipoprotein B antigen p210 increases the risk of cardiovascular death after carotid endarterectomy. Asciutto, Giuseppe; Dias, Nuno; Edsfeldt, Andreas; Alm,
Low levels of IgG autoantibodies against the apolipoprotein B antigen p210 increases the risk of cardiovascular death after carotid endarterectomy. Asciutto, Giuseppe; Dias, Nuno; Edsfeldt, Andreas; Alm,
Associations between autoantibodies against apolipoprotein B-100 peptides and vascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes
 Diabetologia (2009) 52:1426 1433 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1377-9 ARTICLE Associations between autoantibodies against apolipoprotein B-100 peptides and vascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes
Diabetologia (2009) 52:1426 1433 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1377-9 ARTICLE Associations between autoantibodies against apolipoprotein B-100 peptides and vascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes
Summary and concluding remarks
 Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 338 (2005)
 Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 338 (2005) 1982 1989 BBRC www.elsevier.com/locate/ybbrc Immunization using an Apo B-100 related epitope reduces atherosclerosis and plaque inflammation
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 338 (2005) 1982 1989 BBRC www.elsevier.com/locate/ybbrc Immunization using an Apo B-100 related epitope reduces atherosclerosis and plaque inflammation
The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema
 The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema Dept Cardiology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden,
The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema Dept Cardiology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden,
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3561
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation and APOB p.gly1829glufs8 mutation (a,b) Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation. (c) Pedigree of family with APOB p.gly1829glufs8
Supplementary Figure 1 Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation and APOB p.gly1829glufs8 mutation (a,b) Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation. (c) Pedigree of family with APOB p.gly1829glufs8
Current Cholesterol Guidelines and Treatment of Residual Risk COPYRIGHT. J. Peter Oettgen, MD
 Current Cholesterol Guidelines and Treatment of Residual Risk J. Peter Oettgen, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, Preventive Cardiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Current Cholesterol Guidelines and Treatment of Residual Risk J. Peter Oettgen, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, Preventive Cardiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Recent studies suggest that the immune system modulates
 Identification of Immune Responses Against Aldehyde-Modified Peptide Sequences in ApoB Associated With Cardiovascular Disease Gunilla Nordin Fredrikson, Bo Hedblad, Göran Berglund, Ragnar Alm, Mikko Ares,
Identification of Immune Responses Against Aldehyde-Modified Peptide Sequences in ApoB Associated With Cardiovascular Disease Gunilla Nordin Fredrikson, Bo Hedblad, Göran Berglund, Ragnar Alm, Mikko Ares,
Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice.
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Supplemental Material. Results
 Supplemental Material Results Fractionation of mouse plasma by high-resolution SEC. APOA1 eluted as a single major peak in fractions 16 of plasma (the apparent size of mature, lipidated HDL) when it was
Supplemental Material Results Fractionation of mouse plasma by high-resolution SEC. APOA1 eluted as a single major peak in fractions 16 of plasma (the apparent size of mature, lipidated HDL) when it was
Accumulation, aggregation, and modification of LDL
 Inhibition of Atherosclerosis in ApoE-Null Mice by Immunization with ApoB-100 Peptide Sequences Gunilla Nordin Fredrikson, Ingrid Söderberg, Marie Lindholm, Paul Dimayuga, Kuang-Yuh Chyu, Prediman K. Shah,
Inhibition of Atherosclerosis in ApoE-Null Mice by Immunization with ApoB-100 Peptide Sequences Gunilla Nordin Fredrikson, Ingrid Söderberg, Marie Lindholm, Paul Dimayuga, Kuang-Yuh Chyu, Prediman K. Shah,
Immune Cells in Atherosclerosis Regulatory vs Inflammatory T cells Göran K Hansson
 Immune Cells in Atherosclerosis Regulatory vs Inflammatory T cells Göran K Hansson Center for Molecular Medicine Karolinska Institute Stockholm, Sweden DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Goran Hansson
Immune Cells in Atherosclerosis Regulatory vs Inflammatory T cells Göran K Hansson Center for Molecular Medicine Karolinska Institute Stockholm, Sweden DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Goran Hansson
Metabolism and Atherogenic Properties of LDL
 Metabolism and Atherogenic Properties of LDL Manfredi Rizzo, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine, University of Palermo, Italy & Affiliate Associate Professor of Internal
Metabolism and Atherogenic Properties of LDL Manfredi Rizzo, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine, University of Palermo, Italy & Affiliate Associate Professor of Internal
Novel Reduction of PCSK9 Expression: Mechanistic Insights into the Anti-Atherosclerotic & Hypolipidemic Effects of Heat Shock Protein 27
 Novel Reduction of PCSK9 Expression: Mechanistic Insights into the Anti-Atherosclerotic & Hypolipidemic Effects of Heat Shock Protein 27 Ed O Brien, Jean-Claude Bakala-N Goma, Chunhua Shi Cumming School
Novel Reduction of PCSK9 Expression: Mechanistic Insights into the Anti-Atherosclerotic & Hypolipidemic Effects of Heat Shock Protein 27 Ed O Brien, Jean-Claude Bakala-N Goma, Chunhua Shi Cumming School
Hypertriglyceridemia, Inflammation, & Pregnancy
 Hypertriglyceridemia, Inflammation, & Pregnancy Richard L. Nemiroff, MD, FACOG, NLA Professor, Clinical Gynecology Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA Disclosure of
Hypertriglyceridemia, Inflammation, & Pregnancy Richard L. Nemiroff, MD, FACOG, NLA Professor, Clinical Gynecology Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA Disclosure of
Prediction of epileptic seizures: are nonlinear methods relevant?
 Prediction of epileptic seizures: are nonlinear methods relevant? a b c d EEG Variance C(r ) C(r ) 2 2 3 2.6.4.2.6.5.4.3.2. To the editor Epilepsy is one of the most common serious neurological disorders,
Prediction of epileptic seizures: are nonlinear methods relevant? a b c d EEG Variance C(r ) C(r ) 2 2 3 2.6.4.2.6.5.4.3.2. To the editor Epilepsy is one of the most common serious neurological disorders,
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 53, No. 23, by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN /09/$36.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 53, No. 23, 2009 2009 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/09/$36.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.02.041
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 53, No. 23, 2009 2009 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/09/$36.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.02.041
CIC Edizioni Internazionali. Cardio-metabolic comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis and SLE. Review. 120 Clinical Dermatology 2013; 1 (2):
 Review Cardio-metabolic comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis and SLE Andrea Doria Division of Rheumatology University of Padua, Italy Address for correspondence: Division of Rheumatology University of
Review Cardio-metabolic comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis and SLE Andrea Doria Division of Rheumatology University of Padua, Italy Address for correspondence: Division of Rheumatology University of
Decreased levels of autoantibodies against apolipoprotein B-100 antigens are associated with cardiovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus
 Clinical and Experimental Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi:10.1111/cei.12651 Decreased levels of autoantibodies against apolipoprotein B-100 antigens are associated with cardiovascular disease in systemic
Clinical and Experimental Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi:10.1111/cei.12651 Decreased levels of autoantibodies against apolipoprotein B-100 antigens are associated with cardiovascular disease in systemic
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview)
 Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis. Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk
 The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
Humoral Immune Response Against Defined Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Antigens Reflects Structure and Disease Activity of Carotid Plaques
 Humoral Immune Response Against Defined Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Antigens Reflects Structure and Disease Activity of Carotid Plaques Isabel Gonçalves, Marie-Louise M. Gronholdt, Ingrid Söderberg,
Humoral Immune Response Against Defined Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Antigens Reflects Structure and Disease Activity of Carotid Plaques Isabel Gonçalves, Marie-Louise M. Gronholdt, Ingrid Söderberg,
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
High density lipoprotein metabolism
 High density lipoprotein metabolism Lipoprotein classes and atherosclerosis Chylomicrons, VLDL, and their catabolic remnants Pro-atherogenic LDL HDL Anti-atherogenic Plasma lipid transport Liver VLDL FC
High density lipoprotein metabolism Lipoprotein classes and atherosclerosis Chylomicrons, VLDL, and their catabolic remnants Pro-atherogenic LDL HDL Anti-atherogenic Plasma lipid transport Liver VLDL FC
There are many ways to lower triglycerides in humans: Which are the most relevant for pancreatitis and for CV risk?
 There are many ways to lower triglycerides in humans: Which are the most relevant for pancreatitis and for CV risk? Michael Davidson M.D. FACC, Diplomate of the American Board of Lipidology Professor,
There are many ways to lower triglycerides in humans: Which are the most relevant for pancreatitis and for CV risk? Michael Davidson M.D. FACC, Diplomate of the American Board of Lipidology Professor,
Potential Atheroprotective Effects of Ixmyelocel-T Cellular Therapy. Kelly J. Ledford, Nikki Murphy, Frank Zeigler, Ronnda L.
 Potential Atheroprotective Effects of Ixmyelocel-T Cellular Therapy Kelly J. Ledford, Nikki Murphy, Frank Zeigler, Ronnda L. Bartel 1 Ixmyelocel-T, an expanded, autologous multicellular therapy cultured
Potential Atheroprotective Effects of Ixmyelocel-T Cellular Therapy Kelly J. Ledford, Nikki Murphy, Frank Zeigler, Ronnda L. Bartel 1 Ixmyelocel-T, an expanded, autologous multicellular therapy cultured
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD
 Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Medial Expression of TNF-α and TNF Receptors Precedes the Development of Atherosclerotic Lesions in Apolipoprotein E/LDL Receptor Double Knockout Mice
 International journal of Biomedical science Medial Expression of TNF-α and TNF Receptors Precedes the Development of Atherosclerotic Lesions in Apolipoprotein E/LDL Receptor Double Knockout Mice Audrey
International journal of Biomedical science Medial Expression of TNF-α and TNF Receptors Precedes the Development of Atherosclerotic Lesions in Apolipoprotein E/LDL Receptor Double Knockout Mice Audrey
Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both
 Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both Lluís Masana Vascular Medicine and Metabolism Unit. Sant Joan University Hospital. IISPV. CIBERDEM Rovira i Virgili
Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both Lluís Masana Vascular Medicine and Metabolism Unit. Sant Joan University Hospital. IISPV. CIBERDEM Rovira i Virgili
Lp(a) Ready for prime time? E Stroes AMC
 Lp(a) Ready for prime time? E Stroes AMC Case Male, 45 years old Hypertension: DM: Smoking: Dyslipidemia: Fam history: brother MI (55yr) Lipoprotein(a): 1240 mg/l!!! Lipoprotein(a) = LDL + apo(a) tail
Lp(a) Ready for prime time? E Stroes AMC Case Male, 45 years old Hypertension: DM: Smoking: Dyslipidemia: Fam history: brother MI (55yr) Lipoprotein(a): 1240 mg/l!!! Lipoprotein(a) = LDL + apo(a) tail
Cardiovascular Division, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School
 Low Endothelial Shear Stress Upregulates Atherogenic and Inflammatory Genes Extremely Early in the Natural History of Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic Hyperlipidemic Juvenile Swine Michail I. Papafaklis,
Low Endothelial Shear Stress Upregulates Atherogenic and Inflammatory Genes Extremely Early in the Natural History of Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic Hyperlipidemic Juvenile Swine Michail I. Papafaklis,
Lipid metabolism in familial hypercholesterolemia
 Lipid metabolism in familial hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
Lipid metabolism in familial hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
Differential inhibition of macrophage foam-cell formation and atherosclerosis in mice by PPARα, β/δ, and γ
 Research article Related Commentary, page 1538 Differential inhibition of macrophage foam-cell formation and atherosclerosis in mice by PPARα, β/δ, and γ Andrew C. Li, 1 Christoph J. Binder, 2 Alejandra
Research article Related Commentary, page 1538 Differential inhibition of macrophage foam-cell formation and atherosclerosis in mice by PPARα, β/δ, and γ Andrew C. Li, 1 Christoph J. Binder, 2 Alejandra
Immune Responses Aginst Aldehyde Modified Extracellular Matrix in Atherosclerosis
 Immune Responses Aginst Aldehyde Modified Extracellular Matrix in Atherosclerosis Dunér, Pontus 2009 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Dunér, P. (2009). Immune Responses Aginst
Immune Responses Aginst Aldehyde Modified Extracellular Matrix in Atherosclerosis Dunér, Pontus 2009 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Dunér, P. (2009). Immune Responses Aginst
Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL
 Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL Sung-Joon Lee, PhD Division of Food Science Institute of Biomedical Science and Safety Korea University Composition of Lipoproteins:
Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL Sung-Joon Lee, PhD Division of Food Science Institute of Biomedical Science and Safety Korea University Composition of Lipoproteins:
Disclosures. Background 1 What is Known MENOPAUSE, ESTROGENS, AND LIPOPROTEIN PARTICLES. Background 2 What is Not Known 10/2/2017
 Disclosures MENOPAUSE, ESTROGENS, AND LIPOPROTEIN PARTICLES Grants: NIH, Quest Diagnostics Consultant: Quest Diagnostics Merck Global Atherosclerosis Advisory Board Ronald M. Krauss, Children s Hospital
Disclosures MENOPAUSE, ESTROGENS, AND LIPOPROTEIN PARTICLES Grants: NIH, Quest Diagnostics Consultant: Quest Diagnostics Merck Global Atherosclerosis Advisory Board Ronald M. Krauss, Children s Hospital
LIPOPROTEIN-ASSOCIATED PHOSPHOLIPASE A 2 : EFFECTS OF LOW DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN APHERESIS
 LIPOPROTEIN-ASSOCIATED PHOSPHOLIPASE A 2 : EFFECTS OF LOW DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN APHERESIS Patrick M. Moriarty, M.D., FACP, Director, Atherosclerosis and LDL-Apheresis Center, University of Kansas Medical
LIPOPROTEIN-ASSOCIATED PHOSPHOLIPASE A 2 : EFFECTS OF LOW DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN APHERESIS Patrick M. Moriarty, M.D., FACP, Director, Atherosclerosis and LDL-Apheresis Center, University of Kansas Medical
Development of a Passive Immunization Strategy Against Atherosclerosis
 Development of a Passive Immunization Strategy Against Atherosclerosis Schiopu, Alexandru 2006 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Schiopu, A. (2006). Development of a Passive Immunization
Development of a Passive Immunization Strategy Against Atherosclerosis Schiopu, Alexandru 2006 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Schiopu, A. (2006). Development of a Passive Immunization
T and B lymphocytes play a minor role in atherosclerotic plaque formation in the apolipoprotein E-deficient mouse
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 4642 4646, April 1997 Medical Sciences T and B lymphocytes play a minor role in atherosclerotic plaque formation in the apolipoprotein E-deficient mouse HAYES M.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 4642 4646, April 1997 Medical Sciences T and B lymphocytes play a minor role in atherosclerotic plaque formation in the apolipoprotein E-deficient mouse HAYES M.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Jingjin Che, Guangping Li, Weiding Wang, Qiang Li, Hongtao Liu, Kangyin Chen, Tong Liu
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiology Journal 2011, Vol. 18, No. 4, pp. 364 370 Copyright 2011 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Serum autoantibodies against human oxidized low-density lipoproteins are inversely associated
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiology Journal 2011, Vol. 18, No. 4, pp. 364 370 Copyright 2011 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Serum autoantibodies against human oxidized low-density lipoproteins are inversely associated
Tracking a Killer Molecule
 Tracking a Killer Molecule Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA www.mercodia.com Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA products Product Catalog No Kit size Oxidized LDL ELISA 10-1143-01 96 wells Oxidized LDL competitive
Tracking a Killer Molecule Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA www.mercodia.com Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA products Product Catalog No Kit size Oxidized LDL ELISA 10-1143-01 96 wells Oxidized LDL competitive
Lipid Metabolism in Familial Hypercholesterolemia
 Lipid Metabolism in Familial Hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
Lipid Metabolism in Familial Hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Bempedoic acid (ETC-1002) is an ATP-citrate lyase (ACL) inhibitor that in clinical studies has been shown to decrease plasma LDL cholesterol apparently
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Bempedoic acid (ETC-1002) is an ATP-citrate lyase (ACL) inhibitor that in clinical studies has been shown to decrease plasma LDL cholesterol apparently
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders
 Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
For unclear reasons, only about 40% of patients with calcific aortic stenosis also have coronary
 Αθηροσκλήρωση και ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας. Οµοιότητες και διαφορές Ν. Μεζίλης Κλινική «Άγιος Λουκάς» Ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας: Μία ακόµα µορφή αθηρωµάτωσης; Some observations
Αθηροσκλήρωση και ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας. Οµοιότητες και διαφορές Ν. Μεζίλης Κλινική «Άγιος Λουκάς» Ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας: Μία ακόµα µορφή αθηρωµάτωσης; Some observations
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures and Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1 A. HDL-C (mg/dl) 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Noncarriers HDL Cholesterol **** Carriers B. apoa-i (mg/dl) 325 3 275 25 225 2
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures and Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1 A. HDL-C (mg/dl) 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Noncarriers HDL Cholesterol **** Carriers B. apoa-i (mg/dl) 325 3 275 25 225 2
Review Article Immune Response to Lipoproteins in Atherosclerosis
 Cholesterol Volume 2012, Article ID 571846, 12 pages doi:10.1155/2012/571846 Review Article Immune Response to Lipoproteins in Atherosclerosis Sonia Samson, 1 Lakshmi Mundkur, 1 and Vijay V. Kakkar 1,
Cholesterol Volume 2012, Article ID 571846, 12 pages doi:10.1155/2012/571846 Review Article Immune Response to Lipoproteins in Atherosclerosis Sonia Samson, 1 Lakshmi Mundkur, 1 and Vijay V. Kakkar 1,
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of human carotid plaques. (a) Flash-frozen human plaques were separated into vulnerable (V) and stable (S),
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of human carotid plaques. (a) Flash-frozen human plaques were separated into vulnerable (V) and stable (S), regions which were then quantified for mean fluorescence
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of human carotid plaques. (a) Flash-frozen human plaques were separated into vulnerable (V) and stable (S), regions which were then quantified for mean fluorescence
Treatment of Atherosclerosis in 2007
 Treatment of Atherosclerosis in 2007 Szilard Voros, M.D. Medical Director Cardiovascular MR and CT Piedmont Hospital, Piedmont Hospital Our Paradigm Genotype Phenotype Environment Atherosclerotic Disease
Treatment of Atherosclerosis in 2007 Szilard Voros, M.D. Medical Director Cardiovascular MR and CT Piedmont Hospital, Piedmont Hospital Our Paradigm Genotype Phenotype Environment Atherosclerotic Disease
Cloning of Monoclonal Autoantibodies to Epitopes of Oxidized Lipoproteins from Apolipoprotein E-deficient Mice
 Cloning of Monoclonal Autoantibodies to Epitopes of Oxidized Lipoproteins from Apolipoprotein E-deficient Mice Demonstration of Epitopes of Oxidized Low Density Lipoprotein in Human Plasma Wulf Palinski,*
Cloning of Monoclonal Autoantibodies to Epitopes of Oxidized Lipoproteins from Apolipoprotein E-deficient Mice Demonstration of Epitopes of Oxidized Low Density Lipoprotein in Human Plasma Wulf Palinski,*
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.3150
 Nature Medicine doi:10.1038/nm.3150 Supplementary Table 1 Primer sequences used for q-pcr analysis Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Abca1 CAGCTTCCATCCTCCTTGTC CCACATCCACAACTGTCTGG Abcg1 GTACCATGACATCGCTGGTG
Nature Medicine doi:10.1038/nm.3150 Supplementary Table 1 Primer sequences used for q-pcr analysis Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Abca1 CAGCTTCCATCCTCCTTGTC CCACATCCACAACTGTCTGG Abcg1 GTACCATGACATCGCTGGTG
PPAR history of research
 PPAR Rubens, 1640 PPAR history of research number of publications 3000 2000 1000 0 till now: : 16 296 publications 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 year liver, brown adipocytes, kidney, heart, skeletal muscles,
PPAR Rubens, 1640 PPAR history of research number of publications 3000 2000 1000 0 till now: : 16 296 publications 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 year liver, brown adipocytes, kidney, heart, skeletal muscles,
Thematic review series: The Immune System and Atherogenesis
 thematic review Thematic review series: The Immune System and Atherogenesis Lipoprotein-associated inflammatory proteins: markers or mediators of cardiovascular disease? Alan Chait, 1 Chang Yeop Han, John
thematic review Thematic review series: The Immune System and Atherogenesis Lipoprotein-associated inflammatory proteins: markers or mediators of cardiovascular disease? Alan Chait, 1 Chang Yeop Han, John
Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
Original Article Regulation of macrophage cholesterol efflux and liver X receptor α activation by nicotine
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9):16374-16378 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0010359 Original Article Regulation of macrophage cholesterol efflux and liver X receptor α activation by nicotine Hongming Zhang
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9):16374-16378 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0010359 Original Article Regulation of macrophage cholesterol efflux and liver X receptor α activation by nicotine Hongming Zhang
Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers
 Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers Gene Forward Primer Reverse Primer Human ApoB gcaagcagaagccagaagta ccatttggagaagcagtttgg Human ApoA1 gaaagctgcggtgctgac agtggccaggtccttcact Human MTP acggccattcccattgtg
Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers Gene Forward Primer Reverse Primer Human ApoB gcaagcagaagccagaagta ccatttggagaagcagtttgg Human ApoA1 gaaagctgcggtgctgac agtggccaggtccttcact Human MTP acggccattcccattgtg
Decreased levels of autoantibodies against apolipoprotein B-100 antigens are associated with cardiovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus.
 Decreased levels of autoantibodies against apolipoprotein B-100 antigens are associated with cardiovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Svenugnsson, Elisabet; Engelbertsen, Daniel; Wigren,
Decreased levels of autoantibodies against apolipoprotein B-100 antigens are associated with cardiovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Svenugnsson, Elisabet; Engelbertsen, Daniel; Wigren,
Stewart et al. CD36 ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer
 NFκB (fold induction) Stewart et al. ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer a. mrna (fold induction) 5 4 3 2 1 LDL oxldl Gro1a MIP-2 RANTES mrna (fold induction)
NFκB (fold induction) Stewart et al. ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer a. mrna (fold induction) 5 4 3 2 1 LDL oxldl Gro1a MIP-2 RANTES mrna (fold induction)
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Number of patients 14
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Table 1 Number of patients 14 Age, years 54.9 ± 10.0 Female gender, n (%) 6 (42.9) Diabetes, n (%) 2 (14.3) History of hypertension, n (%) 5 (35.7) Ever smoker, n (%)
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Table 1 Number of patients 14 Age, years 54.9 ± 10.0 Female gender, n (%) 6 (42.9) Diabetes, n (%) 2 (14.3) History of hypertension, n (%) 5 (35.7) Ever smoker, n (%)
The HDL hypothesis: does high-density lipoprotein protect from atherosclerosis?
 The HDL hypothesis: does high-density lipoprotein protect from atherosclerosis? review Menno Vergeer, 1 Adriaan G. Holleboom, John J. P. Kastelein, and Jan Albert Kuivenhoven Department of Vascular Medicine,
The HDL hypothesis: does high-density lipoprotein protect from atherosclerosis? review Menno Vergeer, 1 Adriaan G. Holleboom, John J. P. Kastelein, and Jan Albert Kuivenhoven Department of Vascular Medicine,
Brief Review. Godfrey S. Getz, Catherine A. Reardon
 Brief Review Animal Models of Atherosclerosis Godfrey S. Getz, Catherine A. Reardon Abstract Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that is the underlying cause of most cardiovascular disease.
Brief Review Animal Models of Atherosclerosis Godfrey S. Getz, Catherine A. Reardon Abstract Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that is the underlying cause of most cardiovascular disease.
Best Lipid Treatments
 Best Lipid Treatments Pam R. Taub MD, FACC Director of Step Family Cardiac Rehabilitation and Wellness Center Associate Professor of Medicine UC San Diego Health System Overview of Talk Review of pathogenesis
Best Lipid Treatments Pam R. Taub MD, FACC Director of Step Family Cardiac Rehabilitation and Wellness Center Associate Professor of Medicine UC San Diego Health System Overview of Talk Review of pathogenesis
Case Presentation. Rafael Bitzur The Bert W Strassburger Lipid Center Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer
 Case Presentation Rafael Bitzur The Bert W Strassburger Lipid Center Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer Case Presentation 50 YO man NSTEMI treated with PCI 1 month ago Medical History: Obesity: BMI 32,
Case Presentation Rafael Bitzur The Bert W Strassburger Lipid Center Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer Case Presentation 50 YO man NSTEMI treated with PCI 1 month ago Medical History: Obesity: BMI 32,
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease of large
 Clinical and Population Studies T-Helper 2 Immunity Is Associated With Reduced Risk of Myocardial Infarction and Stroke Daniel Engelbertsen, Linda Andersson, Irena Ljungcrantz, Maria Wigren, Bo Hedblad,
Clinical and Population Studies T-Helper 2 Immunity Is Associated With Reduced Risk of Myocardial Infarction and Stroke Daniel Engelbertsen, Linda Andersson, Irena Ljungcrantz, Maria Wigren, Bo Hedblad,
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones?
 1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 10011125 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 10011125 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
During the past few years, the liver X receptors (LXR and
 Accumulation of Foam Cells in Liver X Receptor Deficient Mice Gertrud U. Schuster, PhD*; Paolo Parini, MD, PhD*; Ling Wang, MD, PhD; Siegfried Alberti, PhD; Knut R. Steffensen, MSc; Göran K. Hansson, MD,
Accumulation of Foam Cells in Liver X Receptor Deficient Mice Gertrud U. Schuster, PhD*; Paolo Parini, MD, PhD*; Ling Wang, MD, PhD; Siegfried Alberti, PhD; Knut R. Steffensen, MSc; Göran K. Hansson, MD,
C h a p t e r 1 9 Protective HDL Cholesterol : Modalities to Elevate it
 C h a p t e r 1 9 Protective HDL Cholesterol : Modalities to Elevate it PC Manoria 1, Pankaj Manoria 2, SK Parashar 3 1 Former Professor and Head, Department of Cardiology, GMC, Bhopal, M.P. 2 Senior Resident,
C h a p t e r 1 9 Protective HDL Cholesterol : Modalities to Elevate it PC Manoria 1, Pankaj Manoria 2, SK Parashar 3 1 Former Professor and Head, Department of Cardiology, GMC, Bhopal, M.P. 2 Senior Resident,
Dyslipidemia Endothelial dysfunction Free radicals Immunologic
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the
 The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the limbs and major organs. A range of important pathologies
The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the limbs and major organs. A range of important pathologies
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
MinimallyModifiedLDLInducesActinPolymerization Macrophages viacd14signalingpathway.
 MinimallyModifiedLDLInducesActinPolymerization Macrophages viacd14signalingpathway. *Randon T. Hall I, Joseph L. Witztum2, Yury I. Miller2 From the IMSTP-SURF Program and 2Division of Endocrinology and
MinimallyModifiedLDLInducesActinPolymerization Macrophages viacd14signalingpathway. *Randon T. Hall I, Joseph L. Witztum2, Yury I. Miller2 From the IMSTP-SURF Program and 2Division of Endocrinology and
Apolipoprotein AI prevents regulatory to follicular helper T cell switching during atherosclerosis
 ARTICLE DOI: 1.138/s41467-18-3493- OPEN Apolipoprotein AI prevents regulatory to follicular helper T cell switching during atherosclerosis Dalia E. Gaddis 1, Lindsey E. Padgett 1, Runpei Wu 1, Chantel
ARTICLE DOI: 1.138/s41467-18-3493- OPEN Apolipoprotein AI prevents regulatory to follicular helper T cell switching during atherosclerosis Dalia E. Gaddis 1, Lindsey E. Padgett 1, Runpei Wu 1, Chantel
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry
 Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 51, No. 11, by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN /08/$34.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 51, No. 11, 2008 2008 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/08/$34.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.12.010
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 51, No. 11, 2008 2008 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/08/$34.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.12.010
Statin, Pleiotropic effect, Oxidized low-density lipoprotein
 Effects of Statins on Circulating Oxidized Low-density Lipoprotein in Patients With Hypercholesterolemia Shigenobu INAMI, 1 MD, Kentaro OKAMATSU, 1 MD, Masamichi TAKANO, 1 MD, Gen TAKAGI, 1 MD, Shunta
Effects of Statins on Circulating Oxidized Low-density Lipoprotein in Patients With Hypercholesterolemia Shigenobu INAMI, 1 MD, Kentaro OKAMATSU, 1 MD, Masamichi TAKANO, 1 MD, Gen TAKAGI, 1 MD, Shunta
PCSK9 Inhibition: From Genetics to Patients
 PCSK9 Inhibition: From Genetics to Patients John Chapman BSc, Ph.D., D.Sc., FESC Research Professor, University of Pierre and Marie Curie Director Emeritus, INSERM Dyslipidemia and Atherosclerosis Research
PCSK9 Inhibition: From Genetics to Patients John Chapman BSc, Ph.D., D.Sc., FESC Research Professor, University of Pierre and Marie Curie Director Emeritus, INSERM Dyslipidemia and Atherosclerosis Research
Atheromas are chronic inflammatory lesions of the vessel
 Influence of C3 Deficiency on Atherosclerosis Chiara Buono, MD*; Carolyn E. Come, BA*; Joseph L. Witztum, MD; Graham F. Maguire, BSc; Philip W. Connelly, PhD; Michael Carroll, PhD; Andrew H. Lichtman,
Influence of C3 Deficiency on Atherosclerosis Chiara Buono, MD*; Carolyn E. Come, BA*; Joseph L. Witztum, MD; Graham F. Maguire, BSc; Philip W. Connelly, PhD; Michael Carroll, PhD; Andrew H. Lichtman,
Human atherosclerotic plaques susceptible to rupture or
 Atherosclerosis and Lipoproteins Reduced In Vivo Aortic Uptake of Radiolabeled Oxidation-Specific Antibodies Reflects Changes in Plaque Composition Consistent With Plaque Stabilization Michael Torzewski,
Atherosclerosis and Lipoproteins Reduced In Vivo Aortic Uptake of Radiolabeled Oxidation-Specific Antibodies Reflects Changes in Plaque Composition Consistent With Plaque Stabilization Michael Torzewski,
CETP inhibition: pros and cons. Philip Barter The Heart Research Institute Sydney, Australia
 CETP inhibition: pros and cons Philip Barter The Heart Research Institute Sydney, Australia Philip Barter Disclosures Received honorariums for lectures, consultancies or membership of advisory boards from:
CETP inhibition: pros and cons Philip Barter The Heart Research Institute Sydney, Australia Philip Barter Disclosures Received honorariums for lectures, consultancies or membership of advisory boards from:
Cholesterol efflux pathways and other potential mechanisms involved in the athero-protective effect of high density lipoproteins
 Review Article Cholesterol efflux pathways and other potential mechanisms involved in the athero-protective effect of high density lipoproteins A. R. Tall From the Division of Molecular Medicine, Department
Review Article Cholesterol efflux pathways and other potential mechanisms involved in the athero-protective effect of high density lipoproteins A. R. Tall From the Division of Molecular Medicine, Department
Randomized trials have clearly shown that hydroxymethylglutaryl
 High-Dose Atorvastatin Reduces Total Plasma Levels of Oxidized Phospholipids and Immune Complexes Present on Apolipoprotein B-100 in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndromes in the MIRACL Trial Sotirios
High-Dose Atorvastatin Reduces Total Plasma Levels of Oxidized Phospholipids and Immune Complexes Present on Apolipoprotein B-100 in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndromes in the MIRACL Trial Sotirios
The apolipoprotein story
 Atherosclerosis Supplements 7 (2006) 23 27 The apolipoprotein story Frank M. Sacks a,b, a Department of Nutrition, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, MA, USA b Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical
Atherosclerosis Supplements 7 (2006) 23 27 The apolipoprotein story Frank M. Sacks a,b, a Department of Nutrition, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, MA, USA b Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical
Keywords Natural antibodies, lipid peroxidation, atherosclerosis, periodontitis, malondialdehyde, innate immunity
 Original Article Immunization with malondialdehydemodified low-density lipoprotein (LDL) reduces atherosclerosis in LDL receptor-deficient mice challenged with Porphyromonas gingivalis Innate Immunity
Original Article Immunization with malondialdehydemodified low-density lipoprotein (LDL) reduces atherosclerosis in LDL receptor-deficient mice challenged with Porphyromonas gingivalis Innate Immunity
Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods.
 Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
Lipid Lowering in Patients at High Risk for Cardiovascular Disease
 Lipid Lowering in Patients at High Risk for Cardiovascular Disease Prof. John J.P. Kastelein, MD PhD FESC Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medical Center / University of Amsterdam The Netherlands Novel
Lipid Lowering in Patients at High Risk for Cardiovascular Disease Prof. John J.P. Kastelein, MD PhD FESC Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medical Center / University of Amsterdam The Netherlands Novel
Mechanisms involved in the vascular response to
 UltraRapid Communication Involvement of the CD1d Natural Killer T Cell Pathway in Neointima Formation After Vascular Injury Åsa Ström, Maria Wigren, Anna Hultgårdh-Nilsson, Amit Saxena, Maria F. Gomez,
UltraRapid Communication Involvement of the CD1d Natural Killer T Cell Pathway in Neointima Formation After Vascular Injury Åsa Ström, Maria Wigren, Anna Hultgårdh-Nilsson, Amit Saxena, Maria F. Gomez,
Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer
 Supplementary Information Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer Gi-Hoon Nam, Eun-Jung Lee, Yoon Kyoung Kim, Yeonsun Hong, Yoonjeong Choi,
Supplementary Information Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer Gi-Hoon Nam, Eun-Jung Lee, Yoon Kyoung Kim, Yeonsun Hong, Yoonjeong Choi,
Update On Diabetic Dyslipidemia: Who Should Be Treated With A Fibrate After ACCORD-LIPID?
 Update On Diabetic Dyslipidemia: Who Should Be Treated With A Fibrate After ACCORD-LIPID? Karen Aspry, MD, MS, ABCL, FACC Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown
Update On Diabetic Dyslipidemia: Who Should Be Treated With A Fibrate After ACCORD-LIPID? Karen Aspry, MD, MS, ABCL, FACC Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown
Plasma cholesterol has been established as a predictor of
 Dietary Fat Induced Alterations in Atherosclerosis Are Abolished by ACAT2-Deficiency in ApoB100 Only, LDLr / Mice Thomas A. Bell III, Kathryn Kelley, Martha D. Wilson, Janet K. Sawyer, Lawrence L. Rudel
Dietary Fat Induced Alterations in Atherosclerosis Are Abolished by ACAT2-Deficiency in ApoB100 Only, LDLr / Mice Thomas A. Bell III, Kathryn Kelley, Martha D. Wilson, Janet K. Sawyer, Lawrence L. Rudel
Lipid Profiles of Non-Diabetic Healthy and Ischaemic Heart Disease Patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lipid Profiles of Non-Diabetic Healthy and Ischaemic Heart Disease Patients ABSTRACT Objective: To find any difference in the fasting lipid profile in patients with history of ischaemic
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lipid Profiles of Non-Diabetic Healthy and Ischaemic Heart Disease Patients ABSTRACT Objective: To find any difference in the fasting lipid profile in patients with history of ischaemic
