they found no foam cells or cellular proliferation and concluded that
|
|
|
- Avis Wiggins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EXPERIMENTAL ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN THE RAT * JoM H. B u.mo, MID, and OwFMxN, Ph.D. From the Laboratory of Metabolm, Naional Heart Istiute (Dr. Bragdon), axd Laboratory of Nutrion, National lstitute of Arthritis and Metabolic Disease (Dr. Mickelsen), Bethesda z4, Yd. The rat has proved refractory to the development of experimental atherosclerosis. Page and Brown' were able to maintain very high serum-cholesterol levels for prolonged periods by feeding high. cholesterol, high-cholic-acid diets to hypothyroid rats. Although the aortas and coronary arteries of their animals showed lipid deposition, they found no foam cells or cellular proliferation and concluded that the vessels of the rat did not respond to the presence of lipid. Several other groups, however, have caimed success in producng lesions simulating atherosclerosis in this species. In X952, Wissler et al.2 reported moderate hypercholesterolemia and coronary atheromas in old rats fed a high-fat diet for many months. Increasing the choline content of the diet increased the incidence of lesions. In the same year Hartroft et al.3 reported the production of lipid deposits in the coronary arteries of rats on choline-deficient diets. More recently Malinow et al.4 have reported atheromatous lesions following the forced feeding of vegetable oil in the presence of unilateral cellophane perinephritis. Also in I952 one of us5 reported the production of early lesions in rats by the repeated intravenous injection of lipoproteins from the serum of cholesterol-fed rabbits. Lesions are readily produced in rabbits by this method,' but the occurrence of spontaneous lesions7 is a complicating factor in acute experiments. The purpose of the present paper is to report in more detail the effects of injecting serum lipoproteins into rats and to illustrate the tissue response of rats to hypercholesterolemia. METHODS Young rabbits were rendered hypercholesterolemic by feeding a i per cent cholesterol diet. The cholesterol was dissolved in ether and the solution distributed over commercial rabbit pellets. After 6 to io weeks the animals were exsangliinated. Ten gm, of sodium chloride were added to each ioo ml. of serum This increased the saline density to about i.o65. The serum was then centrifuged for i8 hours in the 30 rotor of the Spinco model L ultracentrifuge at 78,ooo G. Under these * Presented at the Forty-ninth Annual Meeing of the Amerian Aiation of Pathologists and Bacteriologists, New York City, April IO, Received for pubication, JanUary 24, I
2 966 BRAGDON AND RICKELSEN conditions all the low-density lipoproteins (Gofman's Sf classes8) rose to the surface, where they appeared as a butter-like mass. This material re-emulsified readily in physiologic saline solution, against which it was then dialyzed to remove any excess salt. No attempt was made to keep the emulsions sterile. In the chronic experiments fresh emulsions were prepared weekly. The experimental animals were male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing about 200 gin. Injections were made into a tail vein. The volume injected varied from i to 4 ml. At the termination of an experiment the animals were exsanguinated from the aorta under sodium pentobarbital anesthesia. The heart and thoracic aorta were removed en bloc and irrigated with physiologic saline solution. They were then fixed in formalin, embedded in gelatin, sectioned with the freezing microtome, and stained with oil red 0 and hematoxylin. The following lipid analyses were made both of the emulsions and of the recipients' serum: free and total cholesterol,9 phospholipid,10 and total fat." From these, neutral fat was determined by difference. Other rats were offered the following diet: vitamin-test casein, I9 per cent; dextrin, 31 per cent; lard, 30 per cent; wheat bran, 6 per cent; salt mixture, 6 per cent; complete vitamin powder, 5 per cent; cholic acd, 2 per cent; oleic acid, i per cent; cholesterol, 0.3 per cent, and 6-propyl-2-thiouracil, o.o65 per cent. Fat-soluble vitamins were supplied as Natola,* io drops per kg. of diet. The animals were housed in individual cages and offered the diet and water ad libitum. RESULTS Because the lipoprotein emulsions represented pools of several donor rabbits, they were relatively constant in chemical composition. The following analysis, expressed as mg. per ioo ml., is typical: total cholesterol, 6,86o; free cholesterol, I,740; phospholipid, 2,440, and neutral fat, 980. The average cholesterol-phospholipid ratio was 2.8. Some preparations were more concentrated. The greater the injected dose, expressed as mg. of total cholesterol per kg. of body weight, the higher was the serum cholesterol level 24 hours later. Thus, rats receiving a dose of 2,650 mg. had serum levels of about 2,650 mg. per ioo ml.; animals receiving 2,000 mg. had serum levels of about I,250, and those receiving 650 mg. had levels of i8o. The serum of normal rats contains about 50 mg. of cholesterol and IOO mg. of phospholipid per IOO ml. After subtracting these values, the cholesterol-phospholipid ratio in several rats receiving the same * Parke, Davis & Co, Detroit, chigan.
3 EXPERIMENTAL ATHEROSCLEROSIS 967 emulsion dropped from the immediate post-injection value of 2.9 to about 2.5 at 7 hours and i.6 at 24 hours. Control rats have never shown stainable lipid wthin the intima or media of the aorta or coronary arteries, or in the endocardium. Animals receiving lipoproteins in doses of ii,ooo mg. total cholesterol per kg. uniformly show focal deposits of sudanophilic material at 24 hours. These areas are characterized by small, discrete granules of lipid within the cytoplasm of endothelial cells and, in the endocardium, in cells immediately beneath the endothelium. In the aorta there may also be very fine sudanophilic partides, apparently extracellular, along the inner surface of the innermost elastic lamella. In the aorta these deposits appear to have no sites of predilection, such as about the mouths of the great vessels. In the heart they appear on the aortic cusps and mitral leaflets. The endothelium of the coronary arteries is only rarely involved. With larger doses these changes have been observed as early as 4 hours after injection. More advanced lesions may be produced either by continuous intravenous infusion or by repeated daily injections. Two rats received a constant infusion at a rate slightly in excess of i ml. per hour for 24 hours, at which time their serum cholesterol levels were II,700 and 10,700 mg. per IOO ml., respectively. Endothelial and subendothelial cells of the endocardium had assumed the appearance of foam cells and there was evidence of their focal proliferation. Figure i shows a section of aorta of a rat which had received five daily injections. At one end of the photomicrograph the endothelial cells contain lipid granules; at the other end there is a collection of sudanophilic material which appears to have accumulated along the inner surface of the most internal elastic lamella. There is no evidence of tissue reaction. Sixteen animals received daily intravenous injections for periods varying from 22 to 30 days. All animals gained weight during that time. Figures 2 and 4 illustrate lesions in a rat killed 24 hours after receiving 28 daily injections. Figure 2 shows a lesion on the endocardial surface of the left ventricle. The endocardium is thickened by masses of foam cells. Figure 4 shows a coronary artery at its origin from the aorta. Two focal accumulations of foam cells are protruding into the lumen of the vessel. Schultz stains revealed cholesterol in these lesions. Neither necrosis nor inflammatory response was seen. The sections originally showed no anisotropism, but doubly refractile crystals became abundant with the passage of time. Other coronary lesions have been limited to infiltration of the intima and media with-
4 968 BRAGDON AND MICKELSEN out cellular reaction. In the aorta this infiltration has been limited to the ntima. Some of the rats receiving repeated injections were permitted to survive for periods up to 3 months following the last injection. The amount of sudanophilic material in the endocardium gradually diminished although even at 3 months some was present both intracellularly and extracellularly. Anisotropic crystals became a prominent feature of the lesions. Eventually they were embedded in fibrous tissue, although at no time was there evidence of necrosis or active inflammation. Emination of other organs of rats killed 24 hours after 28 daily injections showed slight enlargement of the adrenal glands, and microscopic, but not gross, fatty infiltration of the liver. Sudanophilic material was present within a few cells of the splenic corpuscles and within the renal glomeruli The tubules, however, were practically free of fat. The pulmonary arteries occasionally showed some sudanophilla. Other vessels were not examined. No quantitative or qualitative differences were observed in the tissue response of 2 female and 2 male rats receiving repeated injections of the same material Old males were compared with young males, the dose being constant on a weight basis. The older animals appeared to have more extensive lesions than the younger. Old animals were not used routinely in this study because greater difficulty was encountered in injeting their tail veins. Twenty-four hours following intraperitoneal injection the serum cholesterol level was higher than following an intravenous injection of the same dose. Foam-cellular lesions were produced following repeated intraperitoneal injections, but peritonitis was a complicating factor. Three rats received 28 daily intravenous injections of a synthetic cholesterol emulsion in a dose of 200 mg. per kg. per day. Twenty-four hours after the last injection serum cholesterol levels were in the normal range and no sudanophilic material could be found in the endocardium or arterial intima. In this respect the rat differs from the rabbit, which converts injected cholesterol into lipoproteins. The emulsions could not be concentrated to permit larger doses. In order to compare these lesions with those observed in hypothyroid rats fed cholesterol and cholic acid, 5 rats were placed on the diet described. All animals slowly lost weight over a period of 22 weeks, at the end of which time they were killed. Serum cholesterol levels at that time averaged 944 mg. (776 to 1,370) per i0o ml. The cholesterolphospholipid ratio averaged 2.0 (I.7 to 2.2). All animals showed
5 EXPERMENTAL ATHEROSCLEROSIS 965 vascular sudanophilic deposits. In 2 cases there were foci of foam cel proliferation in the endocardium. They appeared identical to thos( produced by injecting lipoproteins. Figure 3 illustrates such a lesior on a mitral leaflet. Lesions in the coronary arteries were characterizec by foci of massive infiltration of the media with sudanophilic, anisotropic material but without tissue reaction. The infiltration occasionall) was sufficient to reduce the lumen of the vessel substantially. Lesion. in the aorta were, like those following lipoprotein injections, withoul cellular reaction. DIscussIoN The evidence presented here demonstrates that parts of the vasculai system of the rat are capable of responding to hypercholesterolemia ir an atheromatous manner. Figures 2 and 3 from injected and dietary rats, respectively, show masses of foam cells thickening the endo. cardium. This has been a frequent finding. Figure 4 shows the same process in a coronary artery near its ostium. This remai s a unquc example in our material. Usually, in the smaller branches, there arc seen only foci of massive infiltration of the wall with sudanophilic. anisotropic material, but without cellular reaction. An illustration in a recent paper by Wissler et al.1 apparently shows foam-ellular pro. liferation in a coronary artery. In our experience, with the one exception illustrated, tissue reaction to the presence of lipid has occurred only in the endocardium. These proliferating lesions may be lost when frozen sections are cut from unembedded hearts. This may explain the failure of Page and Brown' to observe them. To date, apparently no one has succeeded in producng atheromatous lesions in the aorta of the rat. The lesions illustrated in the paper by Hartroft et al.3 from choline-deficient rats represent primarily media] degeneration. It is possible that this immunity of the aorta of the rat has an anatomical basis. The inti consits of little more than endothelium. We have seen masses of lipid granules between the innermost elastic lamella and the endothelium, so that the latter protrudes into the lumen, and yet there has been no evidence of cellular reaction. The data further suggest that the development of atheromatous lesions in the endocardium of the rat depends primarily on maintaining a sufficient concentration in the blood of cholesterol-bearing lipoproteins for a sufficient period. This does not deny that factors such as hypertension and local vascular injury may accentuate the atherosclerotic process.
6 970 BRLAGDON AND MICELSMEN Focal atheroma-like lesions have been produced in the rat by intravenous or intraperitoneal injection of lipoproteins from the serum of cholesterol-fed rabbits. The lesions are characterized by groups of foam cells in the endocardium and intima and later by masses of anisotropic crystals embedded in fibrous tissue. Similar lesions have appeared in hypothyroid rats fed a diet relatively high in cholesterol and cholic acid. The lesions occur most frequently on the aortic and mitral valves and in the endocardium of the left ventricle. One such lesion has been found in a coronary artery near its ostium. Coronary arteries usually show only massive infiltration of the wall without tissue reaction. The aortic intima may also show heavy deposits of lipid without tissue reaction. It is conduded that the arteries of the rat are relatively immune to those lipoproteins which in the rabbit are highly atherogenic. REFERENCES i. Page, L H., and Brown, H. B. Induced hypercholesterolemia and atherogenesis. Circulatio, 1952, 6, 68I Wissler, R. W.; Eilert, M. L.; Schroeder, M. A., and Cohen, L. omatous lesions in rat. Federation Proc., I952, II, 434. Arterial ather- 3. Hartroft, W. S.; Ridout, J. H.; Sellers, E. A-, and Best, C. H. Atheromatous changes in aorta, carotid and coronary arteries of choline-deficient rats. Proc. Soc. Exper. Biol. & Med., 1952, 8I, Malinow, M. R_; Hojman, D., and Pellegrino, A. Different methods for the experimental production of generalized atherosclerosis in the ral Acta cardiol., I954, 9, Bragdon, J. H-, and Boyle, E. Experimental atherosclerosis in the rat. (Abstract.) Am. J. Path., I952, 28, Bragdon, J. H Transfusion transfer of expemental atherosclerosis. tion Proc., I95I, 10, 350. Federa- 7. Bragdon, J. EH Spontaneous atherosclerosis in the rabbil Circulation, I952, 5, 64I Gofman, J. W.; Lindgren, F.; Elliott, H.; Mantz, W.; Hewitt, J.; Strisower, B.; Herring, V., and Lyons, T. P. The role of lipids and lipoproteins in atherosclerosis. Science, ig50, III, i66.-17i, i Sperry, W. M., and Webb, M. A revision of the Schoenheimer-Sperry method for cholesterol determination. J. Biol. Chem., i950, I87, 97-I&6. io. Fiske, C. H, and Subbarow, Y. The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J. Biol. Chem., 1925, 66, ii. Bragdon, J. H. Colorimetric determination of blood lipides. J. Biol. Chem., I951, 190, 513-5I7- I2. WLssler, R. W.; Eilert, M. L.; Schroeder, M. A., and Cohen, L. Production of lipomatous and atheromatous arterial lesions in the albino rat. A. M. A. Arch. Path., I954, 57,
7 EXPERITENTAL ATIERCLOSS 971 [I lustration fouow ]
8 972 9BAGDON AND MI EN LEGENDS FOR FIGURES Fm. 3. Aorta of a rat which received five daily tveous injections of lipoproteins from the serm of cholesterol-fed rabbits. Sudan c maerial is apparent both within endohelil cells and extracelularly betwee ndothelium and innermost eastic lamela X 210. Fm 2. Endoardlum of left ventricle of a rat which received twenty-eight daily injections of lipoprotein. The endocardium is thickened by masses of foam cells X 140. Fm. 3. Section of base of mitral leaflet from a rat with dietary hypercholesterolemia. The endocardium is greatly thickened by foam cells. Under polaized light this lesion coained doubly refractile crystals. X 170. Flm 4. Secion thrugh ostium of a coronary artey of the same rat from which Fiure 2 was secured Two masses of foam cells e into the lumen of the vessel S_danophilicm atl is see also within the aortic intima and within the media of a small coronary branch, but without celular raction X 140.
9 N EXPERIMENTAL ATHEROSCLEROSIS 973 It. I-
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Effect of Glomerulonephritis on -A Special Reference to the Glomeru Aortic Intima- Ohi, Junji Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32 Issue Date
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Effect of Glomerulonephritis on -A Special Reference to the Glomeru Aortic Intima- Ohi, Junji Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32 Issue Date
THE EFFECTS OF CHOLESTEROL DOSAGE, CORTISONE, AND DCA ON TOTAL SERUM CHOLESTEROL, LIPOPROTEINS, AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN THE RABBIT
 THE EFFECTS OF CHOLESTEROL DOSAGE, CORTISONE, AND DCA ON TOTAL SERUM CHOLESTEROL, LIPOPROTEINS, AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN THE RABBIT BY DONALD L. COOK, PH.D., ROGER RAY, PH.D., EDWIN DAVISSON, LOIS M. FELDSTEIN,
THE EFFECTS OF CHOLESTEROL DOSAGE, CORTISONE, AND DCA ON TOTAL SERUM CHOLESTEROL, LIPOPROTEINS, AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN THE RABBIT BY DONALD L. COOK, PH.D., ROGER RAY, PH.D., EDWIN DAVISSON, LOIS M. FELDSTEIN,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
Consequently, lipoprotein fractions have been analyzed
 THE PHOSPHOLIPID COMPOSITION OF HUMAN SERUM LIPOPROTEIN FRACTIONS SEPARATED BY ULTRACENTRIFUGATION * BY GERALD B. PHILLIPS (From the Departments of Biochemistry and Medicine, College of Physicians and
THE PHOSPHOLIPID COMPOSITION OF HUMAN SERUM LIPOPROTEIN FRACTIONS SEPARATED BY ULTRACENTRIFUGATION * BY GERALD B. PHILLIPS (From the Departments of Biochemistry and Medicine, College of Physicians and
STUDIES ON EXPERIMENTAL HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 STUDIES ON EXPERIMENTAL HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS C. SITARAMAYYA AND TAHER ALl From the Department of Physiology, Osmania Medical College, Hyderabad (Received on March 11th, 1962) Separate
STUDIES ON EXPERIMENTAL HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS C. SITARAMAYYA AND TAHER ALl From the Department of Physiology, Osmania Medical College, Hyderabad (Received on March 11th, 1962) Separate
Independence of arterial phospholipid synthesis
 ndependence of arterial phospholipid synthesis from alterations in blood lipids* J. Lipid Research Oct.ober. 1951) D. B. ZLVERsMTt and E. L. MCCANDLESS Department of Physiology, University of Tennessee,
ndependence of arterial phospholipid synthesis from alterations in blood lipids* J. Lipid Research Oct.ober. 1951) D. B. ZLVERsMTt and E. L. MCCANDLESS Department of Physiology, University of Tennessee,
(Received for publication, September 4, 1953)
 THE MECHANISM OF ALLOXAN PROTECTION IN EXPERIMENTAL ATHEROSCLEROSIS BY D. L. COOK, P~r.D., LOIS M. MILLS, AND D. M. GREEN,* M.D. (From the Division of Biological Research, G. D. Searle and Co., Chicago)
THE MECHANISM OF ALLOXAN PROTECTION IN EXPERIMENTAL ATHEROSCLEROSIS BY D. L. COOK, P~r.D., LOIS M. MILLS, AND D. M. GREEN,* M.D. (From the Division of Biological Research, G. D. Searle and Co., Chicago)
Effect of infusions of phosphatides upon the atherosclerotic aorta in situ and as an ocular aortic implant*
 Volume 1 Number 4 Effect of infusions of phosphatides upon the atherosclerotic aorta in situ and as an ocular aortic implant* SANFORD. BYERS and MEYER FRIEDMAK Harold Brunn Institute, Mount Zion Hospital
Volume 1 Number 4 Effect of infusions of phosphatides upon the atherosclerotic aorta in situ and as an ocular aortic implant* SANFORD. BYERS and MEYER FRIEDMAK Harold Brunn Institute, Mount Zion Hospital
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
WITH THE TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE OF P. CONNORS, A. GOTSIS, AND T. FAHERT
 Published Online: 1 November, 1957 Supp Info: http://doi.org/1084/jem.106.5.757 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on October 2, 2018 INTERRELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN EXPERIMENTAL HYPERCHOLESTEREMIA, MAGNESIUM
Published Online: 1 November, 1957 Supp Info: http://doi.org/1084/jem.106.5.757 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on October 2, 2018 INTERRELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN EXPERIMENTAL HYPERCHOLESTEREMIA, MAGNESIUM
Calcified Aortic Sinotubular Ridge: A Source of Coronary Ostial Stenosis or Embolism
 1510 JACC Vol. 12, No, 6 December 1988:1510--4 Calcified Aortic Sinotubular Ridge: A Source of Coronary Ostial Stenosis or Embolism KEVIN J. TVETER, MD, JESSE E. EDWARDS, MD, FACC St, Paul, Minnesota This
1510 JACC Vol. 12, No, 6 December 1988:1510--4 Calcified Aortic Sinotubular Ridge: A Source of Coronary Ostial Stenosis or Embolism KEVIN J. TVETER, MD, JESSE E. EDWARDS, MD, FACC St, Paul, Minnesota This
THE INTIMA of the arterial system, a
 Lipids of the Serum and Connective Tissue of the and By NANCY L. NOBLE, PH.D. AND ROBERT J. BOUCEK, M.S., M.D. The lipicl profile of connective tissue, isolated from the rat and the rabbit, by the sponge-implantation
Lipids of the Serum and Connective Tissue of the and By NANCY L. NOBLE, PH.D. AND ROBERT J. BOUCEK, M.S., M.D. The lipicl profile of connective tissue, isolated from the rat and the rabbit, by the sponge-implantation
For unclear reasons, only about 40% of patients with calcific aortic stenosis also have coronary
 Αθηροσκλήρωση και ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας. Οµοιότητες και διαφορές Ν. Μεζίλης Κλινική «Άγιος Λουκάς» Ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας: Μία ακόµα µορφή αθηρωµάτωσης; Some observations
Αθηροσκλήρωση και ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας. Οµοιότητες και διαφορές Ν. Μεζίλης Κλινική «Άγιος Λουκάς» Ασβεστοποιός στένωση της αορτικής βαλβίδας: Μία ακόµα µορφή αθηρωµάτωσης; Some observations
Fourth Practical Pathology. Circulatory disturbances
 Fourth Practical Pathology Circulatory disturbances 12.12.2018 1 Organ: Lung (40X, low power) 1) The blood capillaries within the alveolar septa are engorged with blood 2) Pinkish proteinaceous fluid,
Fourth Practical Pathology Circulatory disturbances 12.12.2018 1 Organ: Lung (40X, low power) 1) The blood capillaries within the alveolar septa are engorged with blood 2) Pinkish proteinaceous fluid,
diets with EDTA supplements exhibited moderate loss of weight. This could not be ascribed to diminished induced progressive chronic hypercholesteremia
 THE EFFECT OF CERTAIN CHELATING SUBSTANCES (EDTA) UPON CHOLESTEROL METABOLISM IN THE RAT" By RAY H. ROSENMAN AND MALCOLM K. SMITH (From the Harold Brunn Institute, Mount Zion Hospital, San Francisco, Calif.)
THE EFFECT OF CERTAIN CHELATING SUBSTANCES (EDTA) UPON CHOLESTEROL METABOLISM IN THE RAT" By RAY H. ROSENMAN AND MALCOLM K. SMITH (From the Harold Brunn Institute, Mount Zion Hospital, San Francisco, Calif.)
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System. Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD
 Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
ULAR LESIONS CAUSED BY CROTALUS VENOM.*
 AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE LATE GLOMER- ULAR LESIONS CAUSED BY CROTALUS VENOM.* BY RICHARD M. PEARCE, M.D. (From the John Herr Musser Department of Research Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania,
AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE LATE GLOMER- ULAR LESIONS CAUSED BY CROTALUS VENOM.* BY RICHARD M. PEARCE, M.D. (From the John Herr Musser Department of Research Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania,
Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system
 1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر. Zaid. Th. Jaber
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide
 FUNctions: Name: 3-27-14 Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide Heart: Pumps and delivers through the body Blood: Vessels: Delivers and to the body Carries waste and Maintains homeostasis - Carries blood
FUNctions: Name: 3-27-14 Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide Heart: Pumps and delivers through the body Blood: Vessels: Delivers and to the body Carries waste and Maintains homeostasis - Carries blood
"dosed" and "open" nephrons.' Because of this unanticipated finding,
 THE PERMEABILITY OF THE RENAL GLOMERULI OF SEVERAL MAMMAIJAN SPECIES TO LABEILED PROTEINS * HANS SMN, M.D. (From the Department of Pathology, Collge of Physics axd Surgeons, Columbia University, New York
THE PERMEABILITY OF THE RENAL GLOMERULI OF SEVERAL MAMMAIJAN SPECIES TO LABEILED PROTEINS * HANS SMN, M.D. (From the Department of Pathology, Collge of Physics axd Surgeons, Columbia University, New York
Elsevier Publishing Company, Amsterdam- Printed in The Netherlands EXPERIMENTAL ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN RABBITS FED CHOLESTEROL-FREE DIETS
 Journal of A therosclerosis Research Elsevier Publishing Company, Amsterdam- Printed in The Netherlands EXPERIMENTAL ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN RABBITS FED CHOLESTEROL-FREE DIETS PART 2. INFLUENCE OF VARIOUS CARBOHYDRATES
Journal of A therosclerosis Research Elsevier Publishing Company, Amsterdam- Printed in The Netherlands EXPERIMENTAL ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN RABBITS FED CHOLESTEROL-FREE DIETS PART 2. INFLUENCE OF VARIOUS CARBOHYDRATES
Atherosclerosis II. 1. Anatomical Distribution of Atherosclerosis
 Ch02.qxd 08/12/06 7:03 PM Page 20 2 Atherosclerosis II 1. Anatomical Distribution of Atherosclerosis....................... 20 1.1. Atherosclerosis and Functions of the Artery.................. 22 1.2.
Ch02.qxd 08/12/06 7:03 PM Page 20 2 Atherosclerosis II 1. Anatomical Distribution of Atherosclerosis....................... 20 1.1. Atherosclerosis and Functions of the Artery.................. 22 1.2.
Published Online: 1 April, 1951 Supp Info: on December 15, 2018 jem.rupress.org Downloaded from
 Published Online: 1 April, 1951 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.93.4.385 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on December 15, 2018 THE INFLUENCE OF INTRAVENOUSLY ADMINISTERED SUR- FACE-ACTIVE AGENTS ON
Published Online: 1 April, 1951 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.93.4.385 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on December 15, 2018 THE INFLUENCE OF INTRAVENOUSLY ADMINISTERED SUR- FACE-ACTIVE AGENTS ON
CHRONIC RENAL DISEASE IN RATS FOLLOWING A TEMPORARY
 40 CHRONIC RENAL DISEASE IN RATS FOLLOWING A TEMPORARY DEFICIENCY OF POTASSIUM P. FOURMAN, R. A. McCANCE AND R. A. PARKER From the Departments of Experimental Medicine and Pathology, University of Cambridge
40 CHRONIC RENAL DISEASE IN RATS FOLLOWING A TEMPORARY DEFICIENCY OF POTASSIUM P. FOURMAN, R. A. McCANCE AND R. A. PARKER From the Departments of Experimental Medicine and Pathology, University of Cambridge
clearing activity is produced and destroyed in the rat. Both the
 THE SITES AT WHICH PLASMA CLEARING ACTIVITY IS PRODUCED AND DESTROYED IN THE RAT. By G. H. JEFFRIES. From the Sir William Dunn School of Pathology, Oxford. (Received for publication 25th June 1954.) CLEARING
THE SITES AT WHICH PLASMA CLEARING ACTIVITY IS PRODUCED AND DESTROYED IN THE RAT. By G. H. JEFFRIES. From the Sir William Dunn School of Pathology, Oxford. (Received for publication 25th June 1954.) CLEARING
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
A CRITICAL STUDY OF VITAMIN A AND CARCINOGENESIS
 A CRITICAL STUDY OF VITAMIN A AND CARCINOGENESIS KANEMATSU SUGIURA AND STANLEY R. BENEDICT (From tha Huntington Fund for Cancer hearch, Memorial Hoepitcrl and the Hamman Raearch Fund, New York) In recent
A CRITICAL STUDY OF VITAMIN A AND CARCINOGENESIS KANEMATSU SUGIURA AND STANLEY R. BENEDICT (From tha Huntington Fund for Cancer hearch, Memorial Hoepitcrl and the Hamman Raearch Fund, New York) In recent
OF FATTY LIVERS. XLII. PROTEIN AND THE DIETARY PRODUCTION. On a number of occasions however use of this diet has failed to produce in our
 XLII. PROTEIN AND THE DIETARY PRODUCTION OF FATTY LIVERS. BY HAROLD JOHN CHANNON AND HARRY WILKINSON. From the Department of Biochemistry, The University, Liverpool. (Received December 20th, 1934.) THE
XLII. PROTEIN AND THE DIETARY PRODUCTION OF FATTY LIVERS. BY HAROLD JOHN CHANNON AND HARRY WILKINSON. From the Department of Biochemistry, The University, Liverpool. (Received December 20th, 1934.) THE
Elastic Skeleton of Intracranial Cerebral Aneurysms in Rats
 1722 Elastic Skeleton of Intracranial Cerebral Aneurysms in Rats Naohiro Yamazoe, MD, Nobuo Hashimoto, MD, Haruhiko Kikuchi, MD, and Fumitada Hazama, MD In an attempt to clarify the developmental mechanism
1722 Elastic Skeleton of Intracranial Cerebral Aneurysms in Rats Naohiro Yamazoe, MD, Nobuo Hashimoto, MD, Haruhiko Kikuchi, MD, and Fumitada Hazama, MD In an attempt to clarify the developmental mechanism
Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases
 Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases Trends in egg consumption in U.S. and the reason A. Egg Consumption: - 403 in 1945-234 in 1993 (176 Table eggs, 58 Processed eggs) - 256 in
Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases Trends in egg consumption in U.S. and the reason A. Egg Consumption: - 403 in 1945-234 in 1993 (176 Table eggs, 58 Processed eggs) - 256 in
Prevalence of Coronary Artery Disease: A Tertiary Care Hospital Based Autopsy Study
 Article History Received: 03 Feb 2016 Revised: 05 Feb 2016 Accepted: 08 Feb 2016 *Correspondence to: Dr. Alpana Jain Senior demonstrator SMS Medical College, Jaipur, Rajasthan, INDIA. dr.alpana.jain@gmail.com
Article History Received: 03 Feb 2016 Revised: 05 Feb 2016 Accepted: 08 Feb 2016 *Correspondence to: Dr. Alpana Jain Senior demonstrator SMS Medical College, Jaipur, Rajasthan, INDIA. dr.alpana.jain@gmail.com
The Role of Fats. Fat provides flavour and texture to foods. Fat contributes to making us feel satiated because
 The Role of Fats Fat provides flavour and texture to foods. Fat contributes to making us feel satiated because Fats are more energy dense than carbohydrates or protein Fats take longer to digest Emulsion
The Role of Fats Fat provides flavour and texture to foods. Fat contributes to making us feel satiated because Fats are more energy dense than carbohydrates or protein Fats take longer to digest Emulsion
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein
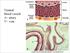 Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Hydrophobic Surfactant Treatment Prevents Atherosclerosis in the Rabbit
 Hydrophobic Surfactant Treatment Prevents Atherosclerosis in the Rabbit RAPID PUBLICATIONS J. B. RODGERS, E. C. KYRIAKIDES, B. KAPUSCINSKA, S. K. PENG, and W. J. BOCHENEK, Department of Medicine, Albany
Hydrophobic Surfactant Treatment Prevents Atherosclerosis in the Rabbit RAPID PUBLICATIONS J. B. RODGERS, E. C. KYRIAKIDES, B. KAPUSCINSKA, S. K. PENG, and W. J. BOCHENEK, Department of Medicine, Albany
Invloeden op de hypercholesterolemie bij proefdieren en bij de mens Valkema, Albert Jan
 University of Groningen Invloeden op de hypercholesterolemie bij proefdieren en bij de mens Valkema, Albert Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
University of Groningen Invloeden op de hypercholesterolemie bij proefdieren en bij de mens Valkema, Albert Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Nutrition & Wellness for Life 2012 Chapter 6: Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source
 Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Tissue in which the body
Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Tissue in which the body
Prevention of Plasma Cholesterol Elevation
 Prevention of Plasma Cholesterol Elevation and Atheromatosis in the Cholesterol-Fed Bird by the Administration of Dihydrocholesterol By M. D. SIPERSTEIN, M.D., C. W. NICHOLS, JR., M.A., AND I. L. CHAIKOFF,
Prevention of Plasma Cholesterol Elevation and Atheromatosis in the Cholesterol-Fed Bird by the Administration of Dihydrocholesterol By M. D. SIPERSTEIN, M.D., C. W. NICHOLS, JR., M.A., AND I. L. CHAIKOFF,
Invited Review. Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases
 Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
THE PLASMA LIPIDS IN CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
 THE PLASMA LIPIDS IN CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE BY M. F. OLIVER* AND G. S. BOYDt From the Dept. of Cardiology, Royal Infirmary, Edinburgh, and the Dept. of Biochemistry, Received June 8, 1953 University of
THE PLASMA LIPIDS IN CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE BY M. F. OLIVER* AND G. S. BOYDt From the Dept. of Cardiology, Royal Infirmary, Edinburgh, and the Dept. of Biochemistry, Received June 8, 1953 University of
Figure 10.1A Transparency Master 79
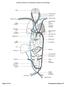 Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
of Plasmin in Arteriosclerosis
 Significance of Plasmin in Arteriosclerosis Yuichiro GOTO Department of Medicine, School of Medicine, Keio University Introduction Arteriosclerosis is not only based on single pathological change, but
Significance of Plasmin in Arteriosclerosis Yuichiro GOTO Department of Medicine, School of Medicine, Keio University Introduction Arteriosclerosis is not only based on single pathological change, but
RADIOACTIVE PHOSPHORUS AS AN INDICATOR OF PHOSPHOLIPID METABOLISM
 RADIOACTIVE PHOSPHORUS AS AN INDICATOR OF PHOSPHOLIPID METABOLISM XI. THE INFLUENCE OF METHIONINE, CYSTINE, AND CYSTEINE UPON THE PHOSPHOLIPID TURNOVER IN THE LIVER* BY I. PERLMAN, N. STILLMAN, AND I.
RADIOACTIVE PHOSPHORUS AS AN INDICATOR OF PHOSPHOLIPID METABOLISM XI. THE INFLUENCE OF METHIONINE, CYSTINE, AND CYSTEINE UPON THE PHOSPHOLIPID TURNOVER IN THE LIVER* BY I. PERLMAN, N. STILLMAN, AND I.
According to the etiology, edema may be:
 What is edema? Edema : It refers to the accumulation of excess liquid in the interstitial (extracellular) spaces of a tissue or in pre-existing cavities. It may affect any organ, but most often it appears
What is edema? Edema : It refers to the accumulation of excess liquid in the interstitial (extracellular) spaces of a tissue or in pre-existing cavities. It may affect any organ, but most often it appears
7 ANIMALS Blood Vessels.notebook. January 11, Human Blood Vessels
 Human Blood Vessels 1 Arteries All arteries take blood AWAY from the heart, and most arteries carry oxygenated blood. The one exception is the PULMONARY ARTERY which carries de oxygenated blood to the
Human Blood Vessels 1 Arteries All arteries take blood AWAY from the heart, and most arteries carry oxygenated blood. The one exception is the PULMONARY ARTERY which carries de oxygenated blood to the
Experiments were carried out then with the object of producing complete disappearance of the A
 Relation of Glucagon to A Cells of the Pancreas*. (22339) SERGIO A. BENCOSME AND J. FREI. (Introduced by J.S.L. Browne Departament of pathology, Queen`s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada. In spite
Relation of Glucagon to A Cells of the Pancreas*. (22339) SERGIO A. BENCOSME AND J. FREI. (Introduced by J.S.L. Browne Departament of pathology, Queen`s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada. In spite
Mechanism of hypercholesterolemia produced by biotin deficiency
 J. Biosci., Vol. 13, Number 4, December 1988, pp. 393 399. Printed in India. Mechanism of hypercholesterolemia produced by biotin deficiency ANNIE ABRAHAM and P. A. KURUP* Department of Biochemistry, University
J. Biosci., Vol. 13, Number 4, December 1988, pp. 393 399. Printed in India. Mechanism of hypercholesterolemia produced by biotin deficiency ANNIE ABRAHAM and P. A. KURUP* Department of Biochemistry, University
THE BLOOD VESSELS. Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department.
 THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
Effects of Sitosterol on the Cholesterol Concentration in Serum and Liver in Hypothyroidism
 Effects of Sitosterol on the Cholesterol Concentration in Serum and Liver in thyroidism By MAURICE MI. BEST, M.D., AND CHARLES H. DUNCAN, M.D. With the Technical Assistance of Joan D. Wathen, B.S. and
Effects of Sitosterol on the Cholesterol Concentration in Serum and Liver in thyroidism By MAURICE MI. BEST, M.D., AND CHARLES H. DUNCAN, M.D. With the Technical Assistance of Joan D. Wathen, B.S. and
ANEMIA CAUSED BY FEEDING CHOLESTEROL TO GUINEA PIGS
 ANEMIA CAUSED BY FEEDING CHOLESTEROL TO GUINEA PIGS BY RUTH OKEY AND VERA D. GREAVES (From the Division of Home Economics, College of Agriculture, University of California, Berkeley) (Received for publication,
ANEMIA CAUSED BY FEEDING CHOLESTEROL TO GUINEA PIGS BY RUTH OKEY AND VERA D. GREAVES (From the Division of Home Economics, College of Agriculture, University of California, Berkeley) (Received for publication,
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones?
 1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
EFFECT OF VOLUNTARY EXERCISE ON PHYSIO LOGICAL FUNCTION AND FEEDING BEHAVIOR OF MICE ON A 20% CASEIN DIET OR A 10% CASEIN DIET
 J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol., 25, 23-32, 1979 EFFECT OF VOLUNTARY EXERCISE ON PHYSIO LOGICAL FUNCTION AND FEEDING BEHAVIOR OF MICE ON A 20% CASEIN DIET OR A 10% CASEIN DIET Masanori YASHIRO and Shuichi KIMURA1
J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol., 25, 23-32, 1979 EFFECT OF VOLUNTARY EXERCISE ON PHYSIO LOGICAL FUNCTION AND FEEDING BEHAVIOR OF MICE ON A 20% CASEIN DIET OR A 10% CASEIN DIET Masanori YASHIRO and Shuichi KIMURA1
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease
 Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Reducing the risk of CVD
 1 The risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) can be reduced in several ways. Lowering blood cholesterol levels and lowering blood pressure are two ways of reducing CVD. (a) (i) Complete the diagram
1 The risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) can be reduced in several ways. Lowering blood cholesterol levels and lowering blood pressure are two ways of reducing CVD. (a) (i) Complete the diagram
PLATES 24 TO 26. (Received for publication, December 4, 1935)
 Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
The Antiatherogenic Effect of Iridium192 upon the Cholesterolfed
 Journal of Clinical Investigation Vol. 43, No. 2, 1964 The Antiatherogenic Effect of Iridium192 upon the Cholesterolfed Rabbit * MEYER FRIEDMAN, LELAND FELTON, AND SANFORD BYERS WITH THE TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE
Journal of Clinical Investigation Vol. 43, No. 2, 1964 The Antiatherogenic Effect of Iridium192 upon the Cholesterolfed Rabbit * MEYER FRIEDMAN, LELAND FELTON, AND SANFORD BYERS WITH THE TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System
 Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System Piryaei May 2011 Circulatory System Heart Blood Vessels Macrovasculature (More than 0.1mm) Elastic Artery Muscular (Distributing) Artery Large Arteriol Small Vein Muscular
Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System Piryaei May 2011 Circulatory System Heart Blood Vessels Macrovasculature (More than 0.1mm) Elastic Artery Muscular (Distributing) Artery Large Arteriol Small Vein Muscular
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Arterial Diseases Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis
Arterial Diseases Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis
Effects of Regression of Atherosclerotic Lesions on the Content and Ester if ication of Cholesterol by Cell-Free Preparations of Pigeon Aorta
 Effects of Regression of Atherosclerotic Lesions on the Content and Ester if ication of Cholesterol by Cell-Free Preparations of Pigeon Aorta By Richard W. St. Clair, Thomas B. Clarkson, and Hugh B. Lofland
Effects of Regression of Atherosclerotic Lesions on the Content and Ester if ication of Cholesterol by Cell-Free Preparations of Pigeon Aorta By Richard W. St. Clair, Thomas B. Clarkson, and Hugh B. Lofland
Part 1 Risk Factors and Atherosclerosis. LO1. Define the Different Forms of CVD
 Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
Nutrition, Food, and Fitness. Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source
 Nutrition, Food, and Fitness Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source Tools: Printer (color optional) 4 sheets of 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut
Nutrition, Food, and Fitness Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source Tools: Printer (color optional) 4 sheets of 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut
IS CHOLINE THE FACTOR IN THE PANCREAS THAT PREVENTS FATTY LIVERS IN DEPANCREATIZED DOGS MAINTAINED WITH INSULIN?
 IS CHOLINE THE FACTOR IN THE PANCREAS THAT PREVENTS FATTY LIVERS IN DEPANCREATIZED DOGS MAINTAINED WITH INSULIN? BY C. ENTENMAN AND I. L. CHAIKOFF (From the Division of Physiology, University of California
IS CHOLINE THE FACTOR IN THE PANCREAS THAT PREVENTS FATTY LIVERS IN DEPANCREATIZED DOGS MAINTAINED WITH INSULIN? BY C. ENTENMAN AND I. L. CHAIKOFF (From the Division of Physiology, University of California
value as a medium for the in vivo cultivation of different
 THE BEHAVIOR OF THE VIRUS OF EQUINE ENCEPH- ALOMYELITIS ON THE CHORIOALLANTOIC MEMBRANE OF THE DEVELOPING CHICK' ELIZABETH HIGBIE AND BEATRICE HOWITT George Williams Hooper Foundation, University of California,
THE BEHAVIOR OF THE VIRUS OF EQUINE ENCEPH- ALOMYELITIS ON THE CHORIOALLANTOIC MEMBRANE OF THE DEVELOPING CHICK' ELIZABETH HIGBIE AND BEATRICE HOWITT George Williams Hooper Foundation, University of California,
Benefit from Testosterone and Hydrocortisone on Coronary Atherogenesis in Cockerels on a Low Protein Atherogenic Diet
 Benefit from and on Coronary Atherogenesis in Cockerels on a Low Protein Atherogenic Diet By Savitri Jain, M.D., Ruth Pick, M.D., and Louis N. Kat, M.D. During the course of our studies on the role of
Benefit from and on Coronary Atherogenesis in Cockerels on a Low Protein Atherogenic Diet By Savitri Jain, M.D., Ruth Pick, M.D., and Louis N. Kat, M.D. During the course of our studies on the role of
Summary and concluding remarks
 Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
Case Presentation VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Vasculitis
 Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
G. MARQUIE. Effect of insulin in the induction and regression of experimental cholesterol atherosclerosis in the rabbit
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (February 1978) 54, 80-85. Effect of insulin in the induction and regression of experimental cholesterol atherosclerosis in the rabbit G. MARQUIE Departement de Physiologie
Postgraduate Medical Journal (February 1978) 54, 80-85. Effect of insulin in the induction and regression of experimental cholesterol atherosclerosis in the rabbit G. MARQUIE Departement de Physiologie
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
(Received 22 July 1957) It is now generally accepted that the unequal distribution of ions between cells
 190 J. Physiol. (I958) I40, I90-200 THE EFFECT OF ALTERATIONS OF PLASMA SODIUM ON THE SODIUM AND POTASSIUM CONTENT OF MUSCLE IN THE RAT By F. 0. DOSEKUN AND D. MENDEL From the Department of Physiology,
190 J. Physiol. (I958) I40, I90-200 THE EFFECT OF ALTERATIONS OF PLASMA SODIUM ON THE SODIUM AND POTASSIUM CONTENT OF MUSCLE IN THE RAT By F. 0. DOSEKUN AND D. MENDEL From the Department of Physiology,
IN a previous publication (Hewitt, 1954) a description was given of the
 i 9 9 Further Observations on the Histochemistry of Fat Absorption in the Small Intestine of the Rat By W. HEWITT, M.B., B.S. (From the Department of Anatomy, St. Thomas' Hospital Medical School, London,
i 9 9 Further Observations on the Histochemistry of Fat Absorption in the Small Intestine of the Rat By W. HEWITT, M.B., B.S. (From the Department of Anatomy, St. Thomas' Hospital Medical School, London,
The cardiovascular system
 The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
Incidence and significance of coronary artery calcification
 British Heart journal, I974, 36, 499-506. Incidence and significance of coronary artery calcification J. H. McCarthy and F. J. Palmer From the Departments of Pathology and Radiology, Prince Henry Hospital,
British Heart journal, I974, 36, 499-506. Incidence and significance of coronary artery calcification J. H. McCarthy and F. J. Palmer From the Departments of Pathology and Radiology, Prince Henry Hospital,
Exam 3 Study Guide. 4) The process whereby the binding of antibodies to antigens causes RBCs to clump is called:
 Exam 3 Study Guide 1) Where does hematopoiesis produce new red blood cells: 2) Which of the following is a blood clotting disorder: 3) Treatment of hemophilia often involves: 4) The process whereby the
Exam 3 Study Guide 1) Where does hematopoiesis produce new red blood cells: 2) Which of the following is a blood clotting disorder: 3) Treatment of hemophilia often involves: 4) The process whereby the
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1
 PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation
 VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
LYMPHOBLASTOMA OF THE SPLEEN
 LYMPHOBLASTOMA OF THE SPLEEN By ELLIS KELLERT, M.D. (From the Ellis Hospital Laboratory, Schenectady, N. Y.) Several recently reported cases have stimulated interest in a newly described form of the ever
LYMPHOBLASTOMA OF THE SPLEEN By ELLIS KELLERT, M.D. (From the Ellis Hospital Laboratory, Schenectady, N. Y.) Several recently reported cases have stimulated interest in a newly described form of the ever
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Intermediate Methods in Epidemiology Exercise No. 4 - Passive smoking and atherosclerosis
 Intermediate Methods in Epidemiology 2008 Exercise No. 4 - Passive smoking and atherosclerosis The purpose of this exercise is to allow students to recapitulate issues discussed throughout the course which
Intermediate Methods in Epidemiology 2008 Exercise No. 4 - Passive smoking and atherosclerosis The purpose of this exercise is to allow students to recapitulate issues discussed throughout the course which
Unusual Causes of Aortic Regurgitation. Case 1
 Unusual Causes of Aortic Regurgitation Judy Hung, MD Cardiology Division Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA No Disclosures Case 1 54 year old female with h/o cerebral aneurysm and vascular malformation
Unusual Causes of Aortic Regurgitation Judy Hung, MD Cardiology Division Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA No Disclosures Case 1 54 year old female with h/o cerebral aneurysm and vascular malformation
Heart Facts. The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime.
 Circulatory System Heart Facts The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime. Heart Facts Weighs 11 oz A healthy heart pumps
Circulatory System Heart Facts The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime. Heart Facts Weighs 11 oz A healthy heart pumps
Unclog Your Life. pursuit because statistic has show that Heart failure is now increasing in the UK. QUESTION: Why?
 Unclog Your Life INTRO: heart disease is the number one killer of all people in every population throughout the world. Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death of both men and women in the
Unclog Your Life INTRO: heart disease is the number one killer of all people in every population throughout the world. Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death of both men and women in the
EFFECT OF ETHIONINE ON PROTEIN CONTENT OF LIVER IN GROWING RATS*
 EFFECT OF ETHIONINE ON PROTEIN CONTENT OF LIVER IN GROWING RATS* BY MELVIN LEVINE AND JOHN V. FOPEANO, JR. (From the Department of Biological Chemistry, Medical School, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor,
EFFECT OF ETHIONINE ON PROTEIN CONTENT OF LIVER IN GROWING RATS* BY MELVIN LEVINE AND JOHN V. FOPEANO, JR. (From the Department of Biological Chemistry, Medical School, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor,
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders
 Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Intimal Thickening in Normocholesterolemic Rhesus Monkeys Fed Low Supplements of Dietary Cholesterol
 Intimal Thickening in Normocholesterolemic Rhesus Monkeys Fed Low Supplements of Dietary Cholesterol By Mark L. Armstrong, Marjorie B. Megan, and Emory D. Warner ABSTRACT Rhesus monkeys were fed a high-fat
Intimal Thickening in Normocholesterolemic Rhesus Monkeys Fed Low Supplements of Dietary Cholesterol By Mark L. Armstrong, Marjorie B. Megan, and Emory D. Warner ABSTRACT Rhesus monkeys were fed a high-fat
Topic 1: Lifestyle, Health and Risk
 alevelbiology.co.uk Topic 1: Lifestyle, Health and Risk SPECIFICATION Many animals have a heart and circulation (mass transport to overcome limitations of diffusion in meeting the requirements of organisms).
alevelbiology.co.uk Topic 1: Lifestyle, Health and Risk SPECIFICATION Many animals have a heart and circulation (mass transport to overcome limitations of diffusion in meeting the requirements of organisms).
AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart
 AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart Project 1 - Formed Elements Identification & Recognition See fig. 17.10 and Table 17.2. Instructor may also provide other images. Note: See Fig. 17.11 All formed elements are
AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart Project 1 - Formed Elements Identification & Recognition See fig. 17.10 and Table 17.2. Instructor may also provide other images. Note: See Fig. 17.11 All formed elements are
Effects of Dietary Proteins, Methionine and Vitamins on Plasma Lipids and Atherogenesis in Cholesterol-Fed Cockerels
 Effects of Dietary Proteins, Methionine Vitamins on Plasma Lipids Atherogenesis in Cholesterol-Fed Cockerels By JEREMIAH STAMLER, M.D., RUTH PICK, M.D. AND LOUIS N. KATZ, M.D. With the assistance of Mrs.
Effects of Dietary Proteins, Methionine Vitamins on Plasma Lipids Atherogenesis in Cholesterol-Fed Cockerels By JEREMIAH STAMLER, M.D., RUTH PICK, M.D. AND LOUIS N. KATZ, M.D. With the assistance of Mrs.
reached, and then rotated with moderate pressure until the tip entered the PULMONARY FAT EMBOLISM FOLLOWING INFUSIONS VIA THE BONE MARROW1
 PULMONARY FAT EMBOLISM FOLLOWING INFUSIONS VIA THE BONE MARROW1 IJDO J. WILE, M.D., AND IRA LEO SCHAMBERG, M.D. (Received for publication April 4, 1942) Following the demonstration by Tocantins and his
PULMONARY FAT EMBOLISM FOLLOWING INFUSIONS VIA THE BONE MARROW1 IJDO J. WILE, M.D., AND IRA LEO SCHAMBERG, M.D. (Received for publication April 4, 1942) Following the demonstration by Tocantins and his
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012
 LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012 The Lipid Family Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols All types of lipids are: soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and ether, but not in water. Differ
LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012 The Lipid Family Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols All types of lipids are: soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and ether, but not in water. Differ
The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the
 The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the limbs and major organs. A range of important pathologies
The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the limbs and major organs. A range of important pathologies
Lipid Histochemistry of Surgically Resected Adrenal. Glands in Hyperadrenocorticism
 Lipid Histochemistry of Surgically Resected Adrenal Glands in Hyperadrenocorticism Hideo TSUCHIYAMA Department of Pathology, Nagasaki University School of Medicine, Nagasaki Recently, fresh adrenal tissue
Lipid Histochemistry of Surgically Resected Adrenal Glands in Hyperadrenocorticism Hideo TSUCHIYAMA Department of Pathology, Nagasaki University School of Medicine, Nagasaki Recently, fresh adrenal tissue
