of Plasmin in Arteriosclerosis
|
|
|
- Dale Nicholson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Significance of Plasmin in Arteriosclerosis Yuichiro GOTO Department of Medicine, School of Medicine, Keio University Introduction Arteriosclerosis is not only based on single pathological change, but also on fibrosis, atheroma and hyalinosis etc. The pathogensis of arteriosclerosis, therefore, also included various factors. Since the measurement of fibrinolysin (plasmin) has recently been performed, plasmin also has called attention as to one of pathogenic factor of arteriosclerosis. Astrupn and Mole2) considered that fibrin deposit was main cause of arteriosclerosis in relation to change of plasmin activity and Ohneda3) insisted that plasmin inhibition in plasmic state caused angionecrosis. Sarkar4) also reported that plasmin inhibitory effect in blood of arteriosclerotic patients was twenty to thirty percent higher than normal subjects. In their reports, while one stated decrease of plasmin activity accelerated degree of arteriosclerosis, and the other, elevation of plasmin activity accelerated angionecrosis. In order to analyse the correlation between plasmin activity and pathogenesis of arteriosclerosis, clinical and experimental studies were performed and reported in this paper. Method of Study 1. Materials Clinical materials were selected from patients with cerebral vascular disease and/or hypertension complicated with arteriosclerosis. Experimental studies were performed in rabbits and dogs. 2. Method of observation a. In the clinical cases, changes of fibrinolytic activity and lipid concentration in blood were followed up (periodically). In
2 Vol. 2, No. 4 SIGNIFICANCE OF PLASMIN IN ARTERIOSCLEROSIS 535 some cases, high-fat meals were given to see the correlation between them. For the determination of plasmic activity, measurements of fibrinogen concentration, Ratnoff's whole clotlysis test, S. K. activated whole plasmin value, and of Lewis' euglobulin-lysis time were performed. In the lipid determination, cholesterol was measured by modified Zak-Henly, phospholipid by Allen, and mucoprotein by Weimer-Moshin's method. b. Rabbits were grouped from Ato G according to the method of feeding or medication as shown in Table 1. In all animals, plasmin activity and lipid concentration in blood were determined Table 1. Experimental Methods in Rabbits periodically during the course of feeding. At the end of the feeding, animals were sacrificed, and the tissue plasmic activity in aorta was determined as a plasmin index. The method of determination is to calculate plasmic and anti-plasmic activities from the lysis time of the standard fibrin clot to which the aortic tissue extract and known amount of plasmin are added. Results 1. Clinical results Values of plasmic activities in cases with retinal bleeding, cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral infarction, hypertension and arteriosclerosis were as shown in Figs. 1-3.
3 536 Goto Jap. J. Med Fig. 1. Fibrinogen. Fig. 2. Whole clotlysis. Fig. 3. Whole plasmin. The higher plasmic activities are plotted in the upper part of the figures. As to fibrinogen, it was decreased in cases with retinal bleeding and cerebral hemorrhage, indicating the possible elevation of plasmic activity. Contrary to this, in cases with cerebral infarction, fibrinogen was rather increased than decreased, indicating the reduction of plasmic activity. Though in the majority of hypertensive or arteriosclerotic cases, it was ranged within normal limit, in some instances, an elevation or reduction of plasmic activity was noted. As for whole clotlysis, it was accelerated in some cases of retinal bleeding and cerebral hemorrhage, indicating the elevation of plasmic activity. But, in a few cases, reduction of plasmic activity was also noted. No cases of cerebral infarction revealed the acceleration of whole clotlysis, but in most of them, it was rather prolonged, indicating the reduction of plasmic activity. In hypertensive and arteriosclerotic cases, whole clotlysis times were variable, indicating elevation or reduction of plasmic activity. In whole plasmin value by S. K. activation, similar directions of changes were noted. Namely, plasmic activity calculated by this method was elevated in the cases with retinal bleeding or cerebral hemorrhage, whereas it was reduced in those with cerebral infarction, and, in hypertensive or arteriosclerotic cases, it was rather reduced with some exception.
4 Vol. 2, No. 4 SIGNIFICANCE OF PLASMIN IN ARTERIOSCLEROSIS 537 Regarding the relationship between plasmic activity and serum lipid level, no correlation was observed between serum cholesterol level and the above mentioned three values. In arteriosclerotic patients who were given gm. of fat daily, cholesterol, phospholipid and mucoprotein were all increased, and at the same time, fibrinogen level was also increased, indicating the possible reduction of plasmic activity (Figs. 4, 5). However, those plasmic activities calculated by Lewis' method or whole clotlysis were variable, Fig. 4. Influence of high fat diet on serum lipids Fig. 5. Influence of high fat diet on plasmin activity some being elevated, others reduced. Thus, if one attaches more importance to the fibrinogen level, which might indicate an integrated plasmic activity during a period of time, it could be concluded that plasmic activities were definitely reduced in these cases except one case. Animal Experiment In an attempt to clarify the implication of plasmin in the development of arteriosclerosis, animal experiments were performed by dividing rabbits into several groups as shown in Table 1. As to the changes of serum lipid, marked lipemia was noticed after one month of the feeding in Lanolin-adrenalin, and Lanolin-antiplasmin (Ipsilon) groups. Blood plasmic activities in each group
5 538 Goto Jap. J. Med Fig. 6. Fibrinogen. Fig. 7. Whole clotlysis. Fig. 9. Lewis* unit Fig. 8. Whole plasmin. are as shown in Figs There was no significant difference of fibrinogen among each group. Plasmic activity was not so markedly elevated even in the group in which plasmin preparation was administered. However, the activity in the group changed as time went by, revealing the highest value immediately after the injection. Whole clotlysis was accelerated only in some cases of plasmin group. Although the rabbit has a low plasmic activity in general, one rabbit in control group exhibited a strong plasmic activity. Whole plasmin value tended to increase in adrenalin and adrenalin-lanolin groups. Also, it was found that there was some difference between whole plasmin values in serum and those in euglobulin fraction. While euglobulin-lysis time was normal in almost all animals in control group and Lanolin group, it was accelerated in some animals in adrenalin, adrenalin-lanolin, Plasmin, and Plasmin-Lanolin groups. In Ipsilon-Lanolin group, it was markedly prolonged. The correlation between /2-lipoprotein containing abundant serum cholesterol
6 Vol. 2, No. 4 SIGNIFICANCE OF PLASMIN IN ARTERIOSCLEROSIS 539 which is said to be related closely with plasmic activity, and whole plasmin value or fibrinogen level was not clearly demonstrated in these groups. The results of aortic tissue plasmin level in these groups of rabbits are as follows (Fig. 10). Plasmin index in the control group ranged from 0.89 to 2.44, and its mean was 1.64, whereas, in Ipsilon-Lanolin group, the mean was 2.ll, indicating a marked reduction of the activity. The mean for adrenalin group was 1.23, indicating a relatively Mgher activity than control. In plasmin group, enzymatic activity in the aorta was not always elevated. This is probably due to the fact that these Fig. 10. Plasmin index of aorta-extract. animals were sacrificed several days after the injection of tjie plasmin preparation. Therefore, in some cases sacrificed shortly.after the injection, marked elevation of the activity was noticed. Thus, tissue plasmic activity of the aorta tended to be reduced in Lanolin-Ipsilon group and to be increased in adrenalin group. There was no correlation between the tissue plasmic activity and serum cholesterol level. As to the histopathological findings, arteriosclerotic changes were hardly observed in control group except very mild one in a few cases. In Lanolin group, atherosclerosis with fat deposition was formed after 3 months of feeding. In adrenalin group, coarsening or edematous swelling of the aortic intima was noticed in some cases despite the relatively short period of administration. In Lanolin-adrenalin group, marked arteriosclerotic changes, including intimal thickening, vacuolation, and fat deposition were observed. It is interesting to note that edematous swelling and coarsening of the intima were also noticed in this group. The more severe the arteriosclerotic changes were, the longer the feeding periods were. The coarsening of the intima was, however, noticed within one month of feeding. In Dlasmin groud. the
7 540 Goto Jap. J. Med coarsening of the intima was severe and the edematous swelling of the media was also noticed in some cases. Not only in rabbits but also in dogs, the coarsening of subendothelial tissue was noticed. In plasmin-lanolin group, the effects of both plasmin and Lanolin were exhibited histopathologically. In Lanolin-Ipsilon group, although serum cholesterol was markedly elevated, there were several cases in which atherosclerotic changes were not observed. On the other hand, in these cases, intimal thickening and severe medial changes were paradoxically observed. Furthermore, while vascular changes in other groups were relatively diffuse and generalized, some of vascular changes in this group were fairly localized, being felt as a hard nodule of the vascular wall on palpation. Discussion In the clinical data, while plasmin activity elevated in cases of retinal bleeding and cerebral hemorrhage, it decreased in cerebral infarction. In hypertensive and arteriosclerotic patients it ranged within normal limit, but in some instances, an elevation or reduction of plasmic activity was observed.5) In the group with high fat meals, cholesterol, phospholipid and mucoprotein increased after administration, and at the same time, it caused an increase of fibrinogen indicating reduced plasmin activity. In the animal experiment, adrenalin and plasmin group demonstrated high value of plasmic activity in blood and tissue. Administration of lipid and antiplasmic preparation was found to cause a antiplasmic state. In the group with fat meal, atherosclerosis developed as well as elevation of lipid, and adrenalin and plasmin group showed arteriosclerotic changes which were characterized by edematous swelling of intima and media as an initiating pathological change. In the group with antiplasmic preparation (Ipsilon), it produced marked increase of hardening of arterial wall and arteriosclerotic change which consisted of various histopathological changes within different adjacent location. These findings suggested occurrence of plasma inhibition due to increased permeability of intima in case with elevated plasmic activity, and possible process to
8 Vol. 2, No. 4 SIGNIFICANCE OF PLASMIN IN ARTERIOSCLEROSIS 541 arteriosclerosis through plasma inhibition was assumed. On the other hand, in antiplasmic case, metabolism between blood and blood vessel has not smoothly carried out as a result of reduced permeability of blood vessel, causing disordered metabolism in the blood vessels. It resulted in arteriosclerosis via retention of metabolic end-product. Therefore, in order to maintain normal construction of blood vessel, it is necessary to make a balance of plasmin and antiplasmin in both blood and tissue. The disturbance of this equilibrium suggested that both plasmic and antiplasmic states seemed to accelerate the process toward arteriosclerosis, although each one resulted in different histopathological change. However,, in antiplasmic case the increase of fibrin in blood could be considered of possibility of thrombus formation6^ Summary With clinical and animal experiments, the significance of fibrinolytic enzyme, plasmin, in arteriosclerosis was investigated. The elevation of plasmic activity in blood related to pathogenesis of arteriosclerosis with increase of permeability of blood vessel and the reduction of plasmic activity could be one of factor of thrombus through the increase of plasma fibrinogen. Furthermore, the change of blood and tissue plasmic activity was assumed to disturb the metabolism of blood vessel and the unbalance of plasmin enzymatic system with antiplasmic substance was considered to influence directly and indirectly on pathogenesis and development of arteriosclerosis. 1) Astrup, T.: Lancet 2: 565, References 2) Mole, B.: J. Path. Bacteriol. 60: 413, ) Ohneda, G.: Nihon-Rinsho 17: 711, ) Sarkar, N.: Proc. VIII Internat. Congr. Hematology, Tokyo, ) Goto,Y. et al.: Keio J.Med. 8: 293, ) Duguid, J.B.: Brit. Med. Bull. ll: 36, ) Greig, H.B.W.: Lancet 2: 16, ) Greig, H.B.W. and Rund, LA.: Lancet 2: 461, ) Ungar, G.: Acta Inc. Montreal 151, ) Matsuoka, M. et al.: Geriatrics 9: 711, 1960.
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Effect of Glomerulonephritis on -A Special Reference to the Glomeru Aortic Intima- Ohi, Junji Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32 Issue Date
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Effect of Glomerulonephritis on -A Special Reference to the Glomeru Aortic Intima- Ohi, Junji Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32 Issue Date
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein
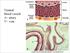 Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Arterial Diseases Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis
Arterial Diseases Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis
HEART HEALTH WEEK 2 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Fatty deposits can narrow and harden the artery
 WEEK 2 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease ATHEROSCLEROSIS FIGURE 1 Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory process where cholesterol is deposited in the wall of arteries and
WEEK 2 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease ATHEROSCLEROSIS FIGURE 1 Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory process where cholesterol is deposited in the wall of arteries and
-21- ANIMAL FAT IN THE DIET. by A. J. Siedlerll
 -21- ANIMAL FAT IN THE DIET by A. J. Siedlerll One of the problems confronting the meat industry is the implication that saturated fats in the human diet may cause hardening of the arteries or arteriosclerosis.
-21- ANIMAL FAT IN THE DIET by A. J. Siedlerll One of the problems confronting the meat industry is the implication that saturated fats in the human diet may cause hardening of the arteries or arteriosclerosis.
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر. Zaid. Th. Jaber
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System. Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD
 Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
THE BLOOD VESSELS. Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department.
 THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Apolipoprotein B (APOB or ApoB) are the primary apolipoproteins of chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins (LDL - known commonly by the misnomer "bad cholesterol"
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Apolipoprotein B (APOB or ApoB) are the primary apolipoproteins of chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins (LDL - known commonly by the misnomer "bad cholesterol"
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock. Richard A. McPherson, M.D.
 Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Incorporating HDL interaction in an ODE model of Atherosclerosis
 Incorporating HDL interaction in an ODE model of Atherosclerosis Diego Lopez Texas A&M University July 29, 2015 Diego Lopez (TAMU) July 29, 2015 1 / 10 Introduction Atherosclerosis A disease of the arteries
Incorporating HDL interaction in an ODE model of Atherosclerosis Diego Lopez Texas A&M University July 29, 2015 Diego Lopez (TAMU) July 29, 2015 1 / 10 Introduction Atherosclerosis A disease of the arteries
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
HISTOPATHOLOGY OF THE HEART. I. practical training 3 rd year General Medicine
 HISTOPATHOLOGY OF THE HEART I. practical training 3 rd year General Medicine Acute myocardial infarction coagulative necrosis subendocardialy 2 hyperemic layer 3 normal myocard 4 epicard Acute myocardial
HISTOPATHOLOGY OF THE HEART I. practical training 3 rd year General Medicine Acute myocardial infarction coagulative necrosis subendocardialy 2 hyperemic layer 3 normal myocard 4 epicard Acute myocardial
The Impact of Smoking on Acute Ischemic Stroke
 Smoking The Impact of Smoking on Acute Ischemic Stroke Wei-Chieh Weng, M.D. Department of Neurology, Chang-Gung Memorial Hospital, Kee-Lung, Taiwan Smoking related mortality Atherosclerotic vascular disease
Smoking The Impact of Smoking on Acute Ischemic Stroke Wei-Chieh Weng, M.D. Department of Neurology, Chang-Gung Memorial Hospital, Kee-Lung, Taiwan Smoking related mortality Atherosclerotic vascular disease
Lipids Testing
 Previously Listed as Edit 12 190.23 - Lipids Testing Lipoproteins are a class of heterogeneous particles of varying sizes and densities containing lipid and protein. These lipoproteins include cholesterol
Previously Listed as Edit 12 190.23 - Lipids Testing Lipoproteins are a class of heterogeneous particles of varying sizes and densities containing lipid and protein. These lipoproteins include cholesterol
Introduction. Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level.
 Introduction Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level. Cells live in aqueous environments. The resources that they
Introduction Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level. Cells live in aqueous environments. The resources that they
Invited Review. Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases
 Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Blood Vessels. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Blood Vessels Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the structure and function of blood vessels. Discuss the different mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Compare and contrast the following types
Blood Vessels Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the structure and function of blood vessels. Discuss the different mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Compare and contrast the following types
Blood clotting. Subsequent covalent cross-linking of fibrin by a transglutaminase (factor XIII) further stabilizes the thrombus.
 Blood clotting It is the conversion, catalyzed by thrombin, of the soluble plasma protein fibrinogen (factor I) into polymeric fibrin, which is deposited as a fibrous network in the primary thrombus. Thrombin
Blood clotting It is the conversion, catalyzed by thrombin, of the soluble plasma protein fibrinogen (factor I) into polymeric fibrin, which is deposited as a fibrous network in the primary thrombus. Thrombin
Fourth Practical Pathology. Circulatory disturbances
 Fourth Practical Pathology Circulatory disturbances 12.12.2018 1 Organ: Lung (40X, low power) 1) The blood capillaries within the alveolar septa are engorged with blood 2) Pinkish proteinaceous fluid,
Fourth Practical Pathology Circulatory disturbances 12.12.2018 1 Organ: Lung (40X, low power) 1) The blood capillaries within the alveolar septa are engorged with blood 2) Pinkish proteinaceous fluid,
Arterial Diseases & Grafts What Can Go Wrong and How to Fix It
 Arterial Diseases & Grafts What Can Go Wrong and How to Fix It Lecture #9 Ref: Harloff, Jan, Are Biomaterials the Limiting Factor in the Progress of Arterial Prosthesis? Termpaper, BE 512, introduction
Arterial Diseases & Grafts What Can Go Wrong and How to Fix It Lecture #9 Ref: Harloff, Jan, Are Biomaterials the Limiting Factor in the Progress of Arterial Prosthesis? Termpaper, BE 512, introduction
Pathology of Hypertension
 2016-03-07 Pathology of Hypertension Honghe Zhang honghezhang@zju.edu.cn Tel:88208199 Department of Pathology ❶ Genetic predisposition ❷ Dietary factors ❸ Environmental factors ❹ Others Definition and
2016-03-07 Pathology of Hypertension Honghe Zhang honghezhang@zju.edu.cn Tel:88208199 Department of Pathology ❶ Genetic predisposition ❷ Dietary factors ❸ Environmental factors ❹ Others Definition and
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial
 An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
Part IV Antithrombotics, Anticoagulants and Fibrinolytics
 Part IV Antithrombotics, Anticoagulants and Fibrinolytics "The meaning of good and bad, of better and worse, is simply helping or hurting" Emerson Chapter 16: Blood Coagulation and Fibrinolytic System
Part IV Antithrombotics, Anticoagulants and Fibrinolytics "The meaning of good and bad, of better and worse, is simply helping or hurting" Emerson Chapter 16: Blood Coagulation and Fibrinolytic System
THROMBOSIS. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan
 THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
What are blood clots?
 What are blood clots? Dr Matthew Fay GP Principal The Willows Medical Practice- Queensbury GPwSI and Co-Founder Westcliffe Cardiology Service GP Partner Westcliffe Medical Group Created 5/31/18 Dr. Matthew
What are blood clots? Dr Matthew Fay GP Principal The Willows Medical Practice- Queensbury GPwSI and Co-Founder Westcliffe Cardiology Service GP Partner Westcliffe Medical Group Created 5/31/18 Dr. Matthew
12 Lead EKG Chapter 4 Worksheet
 Match the following using the word bank. 1. A form of arteriosclerosis in which the thickening and hardening of the vessels walls are caused by an accumulation of fatty deposits in the innermost lining
Match the following using the word bank. 1. A form of arteriosclerosis in which the thickening and hardening of the vessels walls are caused by an accumulation of fatty deposits in the innermost lining
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
Banff-SCT 2017 Towards Uniformity of Terminology for the Pathology of CAV. Gerald J. Berry, MD Dept. of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA
 Banff-SCT 2017 Towards Uniformity of Terminology for the Pathology of CAV Gerald J. Berry, MD Dept. of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA Objectives Review current terminology Identify key histopathologic
Banff-SCT 2017 Towards Uniformity of Terminology for the Pathology of CAV Gerald J. Berry, MD Dept. of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA Objectives Review current terminology Identify key histopathologic
Topic 1: Lifestyle, Health and Risk
 alevelbiology.co.uk Topic 1: Lifestyle, Health and Risk SPECIFICATION Many animals have a heart and circulation (mass transport to overcome limitations of diffusion in meeting the requirements of organisms).
alevelbiology.co.uk Topic 1: Lifestyle, Health and Risk SPECIFICATION Many animals have a heart and circulation (mass transport to overcome limitations of diffusion in meeting the requirements of organisms).
Nutrition & Wellness for Life 2012 Chapter 6: Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source
 Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Tissue in which the body
Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Tissue in which the body
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders
 Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
 Glossary of Terms Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Angiogram: A diagnostic test requiring the insertion of a catheter into an artery
Glossary of Terms Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Angiogram: A diagnostic test requiring the insertion of a catheter into an artery
Ch. 45 Blood Plasma proteins, Coagulation and Fibrinolysis Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic components of plasma
 Chapt. 45 Ch. 45 Blood Plasma proteins, Coagulation and Fibrinolysis Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic components of plasma Inheritance of X-linked gene for Factor VIII hemophilia A Explain the
Chapt. 45 Ch. 45 Blood Plasma proteins, Coagulation and Fibrinolysis Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic components of plasma Inheritance of X-linked gene for Factor VIII hemophilia A Explain the
THE EFFECTS OF CHOLESTEROL DOSAGE, CORTISONE, AND DCA ON TOTAL SERUM CHOLESTEROL, LIPOPROTEINS, AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN THE RABBIT
 THE EFFECTS OF CHOLESTEROL DOSAGE, CORTISONE, AND DCA ON TOTAL SERUM CHOLESTEROL, LIPOPROTEINS, AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN THE RABBIT BY DONALD L. COOK, PH.D., ROGER RAY, PH.D., EDWIN DAVISSON, LOIS M. FELDSTEIN,
THE EFFECTS OF CHOLESTEROL DOSAGE, CORTISONE, AND DCA ON TOTAL SERUM CHOLESTEROL, LIPOPROTEINS, AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN THE RABBIT BY DONALD L. COOK, PH.D., ROGER RAY, PH.D., EDWIN DAVISSON, LOIS M. FELDSTEIN,
Nutrition, Food, and Fitness. Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source
 Nutrition, Food, and Fitness Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source Tools: Printer (color optional) 4 sheets of 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut
Nutrition, Food, and Fitness Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source Tools: Printer (color optional) 4 sheets of 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut
Students will identify factors that affect blood flow and/or describe how these factors affect blood flow through the cardiovascular system.
 Students will identify factors that affect blood flow and/or describe how these factors affect blood flow through the cardiovascular system. Content Limits Items may address factors such as blood pressure,
Students will identify factors that affect blood flow and/or describe how these factors affect blood flow through the cardiovascular system. Content Limits Items may address factors such as blood pressure,
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21)
 Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
According to the etiology, edema may be:
 What is edema? Edema : It refers to the accumulation of excess liquid in the interstitial (extracellular) spaces of a tissue or in pre-existing cavities. It may affect any organ, but most often it appears
What is edema? Edema : It refers to the accumulation of excess liquid in the interstitial (extracellular) spaces of a tissue or in pre-existing cavities. It may affect any organ, but most often it appears
Observe the effects of atherosclerosis on the coronary artery lumen
 Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
Six main classes of blood vessels (on handout) Wall structure of arteries and veins (on handout) Comparison: Arteries vs. Veins (on handout)
 Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Six main classes of blood vessels Primary Sources
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Six main classes of blood vessels Primary Sources
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease
 Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system
 1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
THE INTIMA of the arterial system, a
 Lipids of the Serum and Connective Tissue of the and By NANCY L. NOBLE, PH.D. AND ROBERT J. BOUCEK, M.S., M.D. The lipicl profile of connective tissue, isolated from the rat and the rabbit, by the sponge-implantation
Lipids of the Serum and Connective Tissue of the and By NANCY L. NOBLE, PH.D. AND ROBERT J. BOUCEK, M.S., M.D. The lipicl profile of connective tissue, isolated from the rat and the rabbit, by the sponge-implantation
Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases
 Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases Trends in egg consumption in U.S. and the reason A. Egg Consumption: - 403 in 1945-234 in 1993 (176 Table eggs, 58 Processed eggs) - 256 in
Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases Trends in egg consumption in U.S. and the reason A. Egg Consumption: - 403 in 1945-234 in 1993 (176 Table eggs, 58 Processed eggs) - 256 in
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to
 Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
Prevalence of Coronary Artery Disease: A Tertiary Care Hospital Based Autopsy Study
 Article History Received: 03 Feb 2016 Revised: 05 Feb 2016 Accepted: 08 Feb 2016 *Correspondence to: Dr. Alpana Jain Senior demonstrator SMS Medical College, Jaipur, Rajasthan, INDIA. dr.alpana.jain@gmail.com
Article History Received: 03 Feb 2016 Revised: 05 Feb 2016 Accepted: 08 Feb 2016 *Correspondence to: Dr. Alpana Jain Senior demonstrator SMS Medical College, Jaipur, Rajasthan, INDIA. dr.alpana.jain@gmail.com
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1 -
 Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT
 CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT Coronary artery disease develops because of hardening of the arteries (arteriosclerosis) that supply blood to the heart muscle. In the diagnosis of coronary artery disease,
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT Coronary artery disease develops because of hardening of the arteries (arteriosclerosis) that supply blood to the heart muscle. In the diagnosis of coronary artery disease,
SOME PATHOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF ARTERIAL DISEASE
 io8 SOME PATHOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF ARTERIAL DISEASE By T. CRAWFORD, B.Sc., M.D. Department of Pathology, St. George's Hospital Medical School, S.W.I The term arteriosclerosis was first used as long ago as
io8 SOME PATHOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF ARTERIAL DISEASE By T. CRAWFORD, B.Sc., M.D. Department of Pathology, St. George's Hospital Medical School, S.W.I The term arteriosclerosis was first used as long ago as
Thrombosis and emboli. Peter Nagy
 Thrombosis and emboli Peter Nagy A thrombus is any solid object developing from the blood in vivo within the vascular system or heart. Thrombosis is hemostasis in the wrong place. Major components, forms:
Thrombosis and emboli Peter Nagy A thrombus is any solid object developing from the blood in vivo within the vascular system or heart. Thrombosis is hemostasis in the wrong place. Major components, forms:
Understanding Cholesterol
 Understanding Cholesterol Dr Mike Laker Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT This book is intended not as a substitute for personal
Understanding Cholesterol Dr Mike Laker Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT This book is intended not as a substitute for personal
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD
 Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Pathological Studies on the Intracerebral and Retinal Arteries in Cerebrovascular and Noncerebrovascular Diseases
 Pathological Studies on the Intracerebral and Retinal Arteries in Cerebrovascular and Noncerebrovascular Diseases BY IKUO GOTO, M.D.,* KATSUHARU KIMOTO, M.D.,t SHIBANOSUKE KATSUKI, M.D.,t TAKAAKI MIMATSU,
Pathological Studies on the Intracerebral and Retinal Arteries in Cerebrovascular and Noncerebrovascular Diseases BY IKUO GOTO, M.D.,* KATSUHARU KIMOTO, M.D.,t SHIBANOSUKE KATSUKI, M.D.,t TAKAAKI MIMATSU,
Circulation.notebook March 07, Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Circulatory System p
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the
 The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the limbs and major organs. A range of important pathologies
The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the limbs and major organs. A range of important pathologies
Dyslipidemia Endothelial dysfunction Free radicals Immunologic
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism
 Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
When the learner has completed this module, she/he will be able to:
 Thrombolytics and Myocardial Infarction WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September 2017, Expires September 2019 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2017
Thrombolytics and Myocardial Infarction WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September 2017, Expires September 2019 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2017
7 ANIMALS Blood Vessels.notebook. January 11, Human Blood Vessels
 Human Blood Vessels 1 Arteries All arteries take blood AWAY from the heart, and most arteries carry oxygenated blood. The one exception is the PULMONARY ARTERY which carries de oxygenated blood to the
Human Blood Vessels 1 Arteries All arteries take blood AWAY from the heart, and most arteries carry oxygenated blood. The one exception is the PULMONARY ARTERY which carries de oxygenated blood to the
Coronary Atherosclerosis In Jammu Region - A Random Postmortem Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Coronary Atherosclerosis In Jammu Region - A Random Postmortem Study Sindhu Sharma, Jagriti Singh, P. Angmo, Chavi, K.K. Kaul Abstract Atherosclerosis is a complex and common disease contributing
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Coronary Atherosclerosis In Jammu Region - A Random Postmortem Study Sindhu Sharma, Jagriti Singh, P. Angmo, Chavi, K.K. Kaul Abstract Atherosclerosis is a complex and common disease contributing
STUDIES ON EXPERIMENTAL HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 STUDIES ON EXPERIMENTAL HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS C. SITARAMAYYA AND TAHER ALl From the Department of Physiology, Osmania Medical College, Hyderabad (Received on March 11th, 1962) Separate
STUDIES ON EXPERIMENTAL HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS C. SITARAMAYYA AND TAHER ALl From the Department of Physiology, Osmania Medical College, Hyderabad (Received on March 11th, 1962) Separate
A Case of Coronary Sclerosis in Small Arteries Associated with Diffuse Myocardial Fibrosis
 A Case of Coronary Sclerosis in Small Arteries Associated with Diffuse Myocardial Fibrosis I 'N Ryozo OKADA, M. D., Kenichi HARUMI, M. D., Masuyo NOMURA, M. D., and Satoru MURAO, M. D. recent years, diffuse
A Case of Coronary Sclerosis in Small Arteries Associated with Diffuse Myocardial Fibrosis I 'N Ryozo OKADA, M. D., Kenichi HARUMI, M. D., Masuyo NOMURA, M. D., and Satoru MURAO, M. D. recent years, diffuse
Circulation. Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications. Venous Return. Arterial flow. Regulation of Cardiac Output.
 Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Heart Disease. Signs and Symptoms
 Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Nattokinase: Powerful Enzyme Prevents Heart Attack and Stroke
 Nattokinase: Powerful Enzyme Prevents Heart Attack and Stroke Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death for men and women According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control, each year about 700,000
Nattokinase: Powerful Enzyme Prevents Heart Attack and Stroke Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death for men and women According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control, each year about 700,000
Calcified Aortic Sinotubular Ridge: A Source of Coronary Ostial Stenosis or Embolism
 1510 JACC Vol. 12, No, 6 December 1988:1510--4 Calcified Aortic Sinotubular Ridge: A Source of Coronary Ostial Stenosis or Embolism KEVIN J. TVETER, MD, JESSE E. EDWARDS, MD, FACC St, Paul, Minnesota This
1510 JACC Vol. 12, No, 6 December 1988:1510--4 Calcified Aortic Sinotubular Ridge: A Source of Coronary Ostial Stenosis or Embolism KEVIN J. TVETER, MD, JESSE E. EDWARDS, MD, FACC St, Paul, Minnesota This
Moath Darweesh. Omar Sami. Saleem Khreisha. 1 P a g e
 7 Moath Darweesh Omar Sami Saleem Khreisha 1 P a g e -First of all, I want to give a quick revision to simplify the whole hemostasis mechanism, it will be much easier here with me. Enjoy (you can skip
7 Moath Darweesh Omar Sami Saleem Khreisha 1 P a g e -First of all, I want to give a quick revision to simplify the whole hemostasis mechanism, it will be much easier here with me. Enjoy (you can skip
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis. Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk
 The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings. Cardiovascular System. Cardiovascular System 8/3/2010. Version 1/Fall 2010
 Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 5 1 Also referred to as the Circulatory system Functions Distribute blood to all areas of body Delivery of needed d substances to cells Removal
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 5 1 Also referred to as the Circulatory system Functions Distribute blood to all areas of body Delivery of needed d substances to cells Removal
Physiology of. The Blood hemostasis. By prof. Israa f. jaafar
 Physiology of The Blood hemostasis By prof. Israa f. jaafar Learning objectives Understand the Platelet structure and function Explane the Platelet production Understand the phases of hemostasis: vascular
Physiology of The Blood hemostasis By prof. Israa f. jaafar Learning objectives Understand the Platelet structure and function Explane the Platelet production Understand the phases of hemostasis: vascular
Part 1 Risk Factors and Atherosclerosis. LO1. Define the Different Forms of CVD
 Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
Cerebrovascular. Disease
 Cerebrovascular Disease People take better care of their health when they know what s going on in their bodies. For those with cerebrovascular disease, this means understanding how the arteries work and
Cerebrovascular Disease People take better care of their health when they know what s going on in their bodies. For those with cerebrovascular disease, this means understanding how the arteries work and
Hemostasis and. Blood Coagulation
 Hemostasis and Blood Coagulation Events in Hemostasis The term hemostasis means prevention of blood loss. Whenever a vessel is severed or ruptured, hemostasis is achieved by several mechanisms: (1) vascular
Hemostasis and Blood Coagulation Events in Hemostasis The term hemostasis means prevention of blood loss. Whenever a vessel is severed or ruptured, hemostasis is achieved by several mechanisms: (1) vascular
Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiovascular Disease Controlling your risk factors WE RECOMMEND THAT YOU Monitor your blood pressure on a regular basis If you have high blood pressure, reduce your intake of salt, tea and coffee Drink
Cardiovascular Disease Controlling your risk factors WE RECOMMEND THAT YOU Monitor your blood pressure on a regular basis If you have high blood pressure, reduce your intake of salt, tea and coffee Drink
Pathology of pulmonary vascular disease. Dr.Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab. Assistant Professor of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Almajma ah University
 Pathology of pulmonary vascular disease Dr.Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab Assistant Professor of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Almajma ah University Pulmonary vascular disease Type of pulmonary circulation: Types
Pathology of pulmonary vascular disease Dr.Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab Assistant Professor of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Almajma ah University Pulmonary vascular disease Type of pulmonary circulation: Types
Published Online: 1 April, 1951 Supp Info: on December 15, 2018 jem.rupress.org Downloaded from
 Published Online: 1 April, 1951 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.93.4.385 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on December 15, 2018 THE INFLUENCE OF INTRAVENOUSLY ADMINISTERED SUR- FACE-ACTIVE AGENTS ON
Published Online: 1 April, 1951 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.93.4.385 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on December 15, 2018 THE INFLUENCE OF INTRAVENOUSLY ADMINISTERED SUR- FACE-ACTIVE AGENTS ON
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors:
 Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: Risk factors are traits or habits that increase a person's chances of having cardiovascular disease. Some risk factors can be changed. These risk factors are high blood
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: Risk factors are traits or habits that increase a person's chances of having cardiovascular disease. Some risk factors can be changed. These risk factors are high blood
Interrelationship between Angiotensin Catecholamines. Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D.
 Interrelationship between Angiotensin and Catecholamines Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D. SUMMARY Urinary catecholamines were measured with an attempt
Interrelationship between Angiotensin and Catecholamines Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D. SUMMARY Urinary catecholamines were measured with an attempt
Hydrophobic Surfactant Treatment Prevents Atherosclerosis in the Rabbit
 Hydrophobic Surfactant Treatment Prevents Atherosclerosis in the Rabbit RAPID PUBLICATIONS J. B. RODGERS, E. C. KYRIAKIDES, B. KAPUSCINSKA, S. K. PENG, and W. J. BOCHENEK, Department of Medicine, Albany
Hydrophobic Surfactant Treatment Prevents Atherosclerosis in the Rabbit RAPID PUBLICATIONS J. B. RODGERS, E. C. KYRIAKIDES, B. KAPUSCINSKA, S. K. PENG, and W. J. BOCHENEK, Department of Medicine, Albany
Cardiovascular System and Health. Chapter 15
 Cardiovascular System and Health Chapter 15 Cardiovascular Disease Leading cause of death in U.S. Claims 1 life every 43 seconds Often, the first sign is a fatal heart attack Death Rates #1 CVD #2 Cancer
Cardiovascular System and Health Chapter 15 Cardiovascular Disease Leading cause of death in U.S. Claims 1 life every 43 seconds Often, the first sign is a fatal heart attack Death Rates #1 CVD #2 Cancer
G. MARQUIE. Effect of insulin in the induction and regression of experimental cholesterol atherosclerosis in the rabbit
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (February 1978) 54, 80-85. Effect of insulin in the induction and regression of experimental cholesterol atherosclerosis in the rabbit G. MARQUIE Departement de Physiologie
Postgraduate Medical Journal (February 1978) 54, 80-85. Effect of insulin in the induction and regression of experimental cholesterol atherosclerosis in the rabbit G. MARQUIE Departement de Physiologie
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
Lipids Testing
 190.23 - Lipids Testing Lipoproteins are a class of heterogeneous particles of varying sizes and densities containing lipid and protein. These lipoproteins include cholesterol esters and free cholesterol,
190.23 - Lipids Testing Lipoproteins are a class of heterogeneous particles of varying sizes and densities containing lipid and protein. These lipoproteins include cholesterol esters and free cholesterol,
Objectives. Acute Coronary Syndromes; The Nuts and Bolts. Overview. Quick quiz.. How dose the plaque start?
 Objectives Acute Coronary Syndromes; The Nuts and Bolts Michael P. Gulseth, Pharm. D., BCPS Pharmacotherapy II Spring 2006 Compare and contrast pathophysiology of unstable angina (UA), non-st segment elevation
Objectives Acute Coronary Syndromes; The Nuts and Bolts Michael P. Gulseth, Pharm. D., BCPS Pharmacotherapy II Spring 2006 Compare and contrast pathophysiology of unstable angina (UA), non-st segment elevation
Differences in the Occurrence of Carotid Transient Ischemic Attacks Associated With Antiplatelet Aggregation Therapy
 Differences in the Occurrence of Carotid Transient Ischemic Attacks Associated With Antiplatelet Aggregation Therapy BY MARK L. DYKEN, M.D., OLDRICH J. KOLAR, M.D., AND F. HAVEN JONES, M.D.* Abstract:
Differences in the Occurrence of Carotid Transient Ischemic Attacks Associated With Antiplatelet Aggregation Therapy BY MARK L. DYKEN, M.D., OLDRICH J. KOLAR, M.D., AND F. HAVEN JONES, M.D.* Abstract:
AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
For each of the statements below, put a cross in the box that corresponds to the correct statement about the blood clotting process.
 1 Blood clots can form if the lining of an artery becomes damaged. (a) For each of the statements below, put a cross in the box that corresponds to the correct statement about the blood clotting process.
1 Blood clots can form if the lining of an artery becomes damaged. (a) For each of the statements below, put a cross in the box that corresponds to the correct statement about the blood clotting process.
CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE
 THE RETARDATION OF ERYTHROCYTE SEDIMENTATION IN CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE BY L. M. SANGHVI AND B. M. BOHRA From the Department of Cardiology, Sawai Man Singh Hospital and Medical College, Jaipur, India
THE RETARDATION OF ERYTHROCYTE SEDIMENTATION IN CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE BY L. M. SANGHVI AND B. M. BOHRA From the Department of Cardiology, Sawai Man Singh Hospital and Medical College, Jaipur, India
Disturbance of Circulation Hemodynamic Disorder
 Disturbance of Circulation Hemodynamic Disorder 2/17/2017 By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1 Thrombosis Definition: Thrombosis is the formation of solid or semisolid blood clot within
Disturbance of Circulation Hemodynamic Disorder 2/17/2017 By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1 Thrombosis Definition: Thrombosis is the formation of solid or semisolid blood clot within
Bacillopeptidase F Proprietary Blend (BFPB) A Natural Enzyme Extracted by a Patented Fermentation Production Process to Support Healthy Circulation
 Bacillopeptidase F Proprietary Blend (BFPB) A Natural Enzyme Extracted by a Patented Fermentation Production Process to Support Healthy Circulation What is Plasmanex1? Plasmanex1 is a dietary supplement
Bacillopeptidase F Proprietary Blend (BFPB) A Natural Enzyme Extracted by a Patented Fermentation Production Process to Support Healthy Circulation What is Plasmanex1? Plasmanex1 is a dietary supplement
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY
 MCC-006 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00269 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will be multiple
MCC-006 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00269 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will be multiple
Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both
 Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both Lluís Masana Vascular Medicine and Metabolism Unit. Sant Joan University Hospital. IISPV. CIBERDEM Rovira i Virgili
Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both Lluís Masana Vascular Medicine and Metabolism Unit. Sant Joan University Hospital. IISPV. CIBERDEM Rovira i Virgili
Report For Center Created Gender D.O.B Page 1 Sean Breen HeartSmart IMT plus 3/29/2012 Male 11/26/1973 B C D E
 Report For Center Created Gender D.O.B Page 1 Carotid Assessment A B C D E Good Satisfactory Concern Serious Highest Risk Intima-Media Thickness Additional Findings Plaque Character Percent Stenosis Comments:
Report For Center Created Gender D.O.B Page 1 Carotid Assessment A B C D E Good Satisfactory Concern Serious Highest Risk Intima-Media Thickness Additional Findings Plaque Character Percent Stenosis Comments:
