Multiple Choice Review- Membranes & Enzymes
|
|
|
- Melinda Glenn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Multiple Choice Review- Membranes & Enzymes 1. Cell membranes are and regulate the materials moving into and out of the cell, in order to maintain equilibrium. a. completely permeable b. ionically permeable c. selectively permeable d. protein permeable 2. When we determine the direction and rate of solute movement we must consider the both outside and inside of the cell, as well as the magnitude of the concentration gradient. a. The concentration of all solutes added together b. The concentration of water c. The concentration of each solute independently d. The concentration of ions only Use the illustration below to answer questions 3 and 4. 20gNaCl 300ml water 2g NaCl, 20ml water 3. Using the information found within the illustration above, determine the concentration of NaCl outside of the cell and the concentration of NaCl inside of the cell. a. Outside =.67g/ml; inside = 0.1g/ml b. Outside =.067g/ml; inside = 0.1g/ml c. Outside = 66g/ml; inside =1g/ml d. Outside = 132g/ml; inside 10g/ml 4. Based upon the concentrations of NaCl inside and outside of the cell, the outside environment is considered to be relative to the inside of the cell. a. hypertonic b. isotonic c. hypotonic d. equatonic
2 5. Solutes and water will diffuse into and out of a cell in order to maintain. a. equanimity b. a concentration gradient c. equilibrium d. a concentration difference 6. Using the illustration, which of the statements below correctly identifies the movement of the O2 molecules as well as the CO2 molecules? a. O2 will diffuse into the cell while the CO2 will diffuse out of the cell. b. Both the O2 and the CO2 will diffuse out of the cell c. Both the O2 and the CO2 will diffuse out of the cell d. O2 will diffuse out the cell while the CO2 will diffuse into of the cell. 7. A cell will likely shrink or shrivel up when placed into a environment. a. Hypotonic b. Hypertonic c. Isotonic d. Neutral tonic 8. During osmosis, diffusion of water molecules will move from a. areas of low solute concentration to areas of high solute concentration b. areas of high solute concentration to areas of low solute concentration c. areas of equal solute concentration to areas of unequal solute concentration d. areas of low water concentration to areas of high water concentration
3 9. Which of the following best describes the characteristics of the fluid mosaic model of cell membranes? a. Fluid because the phospholipids can move and mosaic because the phospholipids form different shapes.. b. Fluid because the membrane has water between the phospholipids and mosaic because the phospholipids differ from each other. c. Fluid because water can diffuse through the membrane and mosaic because different molecule types can also diffuse through. d. Fluid because of the movement of phospholipids and mosaic because of the proteins. 10. What do simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion have in common? a. They both involved the movement of molecules from low concentration to high concentration. b. They both involve the movement of molecules but facilitated diffusion requires energy. c. They both involve the movement of large molecules that require special channels to diffuse. d. They both involve the movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration. 11. How do carrier proteins and channel proteins differ in their roles within the cell membrane? a. Carrier proteins are integral proteins while channel proteins are peripheral proteins b. Carrier proteins are utilized for both facilitated and active transport while channel proteins function only in passive transport. c. Carrier proteins function in passive transport while channel proteins function in active transport. d. Carrier proteins function in osmosis while channel proteins function in active transport. 12. What is the purpose of active transport if molecules can already move into and out of the cell by diffusion or facilitated transport? a. Some molecules must move down the concentration gradient and energy is required to accomplish this. b. Water molecules need to move even when solutions are isotonic and energy is needed for this. c. Some molecules must move up the concentration gradient and energy is needed to accomplish this. d. Molecules that are too large to pass directly through the phospholipid membrane must use energy to pass through.
4 13. Some molecules are required by the cell for metabolism, however they are larger molecules and have a charge. What is the process most likely used to transport these molecules across the phospholipid bilayer, from higher to lower concentration? a. Passive diffusion b. Osmosis c. Active transport d. Facilitated diffusion Cells are placed in a liquid environment. The concentration of glucose outside of the cells is 30mg/ml. The concentration of glucose inside of the cells is 3g/l. Use this information to answer questions 14 and 15 below: 14. After comparing the concentrations, using like units, which way will the glucose diffuse? a. Out of the cells b. Into the cells c. Net diffusion is equal d. Cannot determine by the information provided 15. Assuming the glucose is the only solute, in which direction will osmosis occur? a. Water will diffuse into the cell. b. Water will diffuse out of the cell. c. Water is already in equilibrium d. The solute will move out of the cell. 16. The illustration below shows a lab set-up to simulate diffusion and osmosis across a semi-permeable membrane. Based upon the information provided, we hypothesize that the sucrose and glucose will diffuse out of the cell. Assuming the bag is equally permeable to sucrose and glucose, what can we predict regarding the rates of diffusion? a. Glucose will diffuse at a higher rate than the sucrose. b. Sucrose will diffuse at a higher rate than the glucose. c. The sucrose and glucose will diffuse at the same rate. d. We cannot compare the rates given the information provided.
5 17. The formation of a membrane has allowed cells to regulate materials coming into and out of the cell. This allows the cell to maintain. a. an isotonic state b. homeostasis c. ph conditions d. temperature conditions 18. While early cell membranes were primarily composed of phospholipid bilayers alone, cells have evolved to include proteins in their membranes structures. What is the primary function of these proteins? a. They act as doorways to allow larger molecules to pass through the cell membrane. b. They act as enzymes to break larger molecules into smaller molecules, to pass through the cell membrane. c. They act only in active transport, to move molecules across the cell membrane. d. They act only in facilitated diffusion as channels to allow molecules to move across the cell membrane. 19. Molarity is one way to measure the concentration of a solution. For a diffusion experiment we are preparing a solution into which we will place a semi-permeable bag. We dissolve 2.00 moles of solute into 1.00 liter of solution. What is the molarity of the solution? a. 0.5M b. 1.0M c. 1.5M d. 2.0M 20. Which of the following characteristics are not associated with catalysts? a. Speed up or slow down reactions b. Speed up reactions c. Remain unchanged d. Less energy need to start a chemical reaction 21. Which of the following best describes the relationship between an enzyme and a substrate? a. Enzymes are specific to many different types of substrates. b. Enzymes are specific to certain substrates. c. Enzymes can be denatured to bind with different substrates. d. Enzymes can only bind with specific proteins.
6 22. The graph below represents the decomposition of a molecule both with and without an enzyme catalyst. The enzyme decreases the energy required for the reaction. How much more energy is required for this reaction to occur, in the absence of the enzyme? a. 80 kj b. 60 kj c. 20 kj d. not enough information 23. Enzymes function optimally in a range of temperature and ph. How might a significant variation from the optimal temperature or ph affect a reaction? a. Changes in ph will increase the rate of reaction; changes in temperature will decrease the rate of reaction b. If the activation site is physically altered, the reaction will not be catalyzed by the enzyme c. The reaction cannot occur at all without the enzyme. d. The reaction will proceed at the same rate because other enzymes can change shape to fit the substrate. 24. The average human body temperature is 37 o Celsius. Our immune system may react to a bacterial infection by raising our body temperature, typically referred to as a fever. However, if our temperature increases to 40 o C or above for an extended period time, this may cause its own concern. What is the most likely reason for such a concern? a. The optimal temperature for bacterial enzymes are 40 o C and above. b. At 40 o C and above, human enzymes will be denatured. c. At 40 o C and above, bacterial enzymes will be denatured. d. The optimal temperature for viral enzymes are 40 o C and above.
7 25. Most biological enzymes have a ph of between. a. 2 and 4 b. 4 and 6 c. 6 and 8 d. 8 and Use the data provided in the table below to answer this question: Normal values for human blood test for five indicators: Partial pressure of oxygen mmhg Partial pressure of carbon dioxide mmhg Arterial blood ph Oxygen saturation % Bicarbonate meq/l Based upon the data provided, enzymes found in our blood most likely have an optimal ph range, which is. a. acidic b. basic c. neutral d. acidic or basic Two graphs are seen below. Use the data from these graphs to answer questions 27, 28 and 29 Enzymes #2 #1 #3 Enzymes #1 #2 #3 oc 4fv/page/enz_act.htm Describe the environmental conditions under which enzyme #1 functions optimally a. 4 o C and ph of approximately 3.8 b. 37 o C and ph of approximately 3.8 c. 95 o C and ph of approximately 6 d. 95 o C and ph of approximately 9
8 28. Describe the environmental conditions under which enzyme #2 is most likely to denature. a. Temperatures between 30 and 100; ph of 9 b. Temperatures between 0 and 30; ph of 5 c. Temperatures between 30 and 100; ph of 6 d. Temperatures between 0 and 30; ph of Which of the three enzymes, (1, 2 or 3 above) is most likely to be found within the human stomach? a. Not enough information b. Enzyme #1 c. Enzyme #2 d. Enzyme #3 30. Coenzymes are: a. Organic molecules that replace enzymes b. Organic or inorganic molecules that are a substitute substrate c. Inorganic molecules that replace enzyme d. Organic molecules that bind at the active site 31. Increasing temperature and the presence of a catalyst may produce similar results in reactions. Why is this? a. The both may produce collisions of greater frequency and energy. b. The both may increase the concentration of an enzyme. c. They both may produce collisions of lesser frequency and energy. d. They both may increase the concentration of a reactant. 32. Which of the following is not true regarding the active site of an enzyme? a. It is specific to a substrate b. It may require a cofactor c. It can be denatured d. It can be utilized only once 33. Which of the following best describes how a competitive inhibitor may affect the enzyme substrate complex? a. A competitive inhibitor binds to the active site of an enzyme. b. A competitive inhibitor binds to an area away from the active site on an enzyme. c. A competitive inhibitor is a substrate that binds to the active site preventing the true substrate from binding. d. A competitive inhibitor is an enzyme that binds to a substrate but does not cause the intended reaction to occur.
9 34. The image below represents a type of inhibition. Which type of inhibition is seen in this illustration? mike/spring2003/ a. Noncompetitive inhibition b. Competitive inhibition c. Accidental inhibition d. Irreversible inhibition 35. Increasing the concentration of the substrate will most likely a. Inhibit the reaction b. Inhibit the enzyme s function c. Increase the enzyme concentration d. Increase the rate of the reaction 36. What is one way in which vitamins may play a role in enzyme functions? a. Vitamins may play a role as coenzymes b. Vitamins may play a role as an enzyme c. Vitamins typically decrease enzyme activity d. Vitamins prevent infections allowing for enzyme reactions. 37. In allosteric regulation, which of the following may occur? a. Reactions can be either inhibited or activated with this type of regulation. b. Reactions can be inhibited only. c. Reactions can be activated only d. Reactions are not altered, only the enzyme.
10 38. The illustration below represents a process where a product is regulated. In this way, it prevents an overabundance of a product from being produced. What is this process shown in the illustration below? a. Allosteric activation b. Feedback activation c. Allosteric denaturation d. Feedback inhibition 39. If you have a solution containing of 10 grams of NaCl in 200 ml of water, what is the molarity of your solution? a. 0.43M NaCl b. 0.05M NaCl c. 20M NaCl d NaCl 40. Epinephrine (a human hormone) has the formula C9H13O3N. Suppose a molarity of 10M C9H13O3N was considered a normal concentration. Upon measurement, the molarity is currently 5M C9H13O3N. How much more epinephrine must be produced to reach normal levels? a. Half as much b. Twice as much c. Three times as much d. Cannot answer with information provided.
11 Answer Key Question # Correct response Question # correct response 1 C 21 B 2 C 22 C 3 B 23 B 4 A 24 B 5 C 25 C 6 A 26 B 7 B 27 B 8 A 28 D 9 D 29 B 10 D 30 D 11 B 31 A 12 C 32 D 13 D 33 A 14 C 34 B 15 C 35 D 16 A 36 A 17 B 37 A 18 A 38 D 19 D 39 D 20 A 40 B
Membranes & Enzymes. Practice Questions. Slide 1 / 91. Slide 2 / 91. Slide 3 / 91
 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 91 Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 91 Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
Biology. Membranes.
 1 Biology Membranes 2015 10 28 www.njctl.org 2 Vocabulary active transport carrier protein channel protein concentration gradient diffusion enzymatic activity facilitated diffusion fluid mosaic hypertonic
1 Biology Membranes 2015 10 28 www.njctl.org 2 Vocabulary active transport carrier protein channel protein concentration gradient diffusion enzymatic activity facilitated diffusion fluid mosaic hypertonic
Passive Cellular Transport. Unit 2 Lesson 4
 Unit 2 Lesson 4 Students will be able to: Define passive transport Enumerate the three types of passive transport Described each type of passive transport: osmosis, diffusion, and facilitated diffusion
Unit 2 Lesson 4 Students will be able to: Define passive transport Enumerate the three types of passive transport Described each type of passive transport: osmosis, diffusion, and facilitated diffusion
Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes
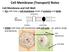 Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes Cell Membrane and Cell Wall: ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump SOME cells
Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes Cell Membrane and Cell Wall: ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump SOME cells
Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane: Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment Function: 1) Isolate cell s contents from outside environment
Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane: Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment Function: 1) Isolate cell s contents from outside environment
Chapter 5. The Working Cell. Lecture by Richard L. Myers
 Chapter 5 The Working Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
Chapter 5 The Working Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
How Cells Work. Chapter 4
 How Cells Work Chapter 4 Energy Laws Energy is the capacity to do work The total amount of energy in the universe is constant-energy can t be created or destroyed..only transferred! Energy is flowing from
How Cells Work Chapter 4 Energy Laws Energy is the capacity to do work The total amount of energy in the universe is constant-energy can t be created or destroyed..only transferred! Energy is flowing from
CELL BOUNDARIES. Cells create boundaries through: Cell Membranes made of the phospholipid bilayer Cell Walls made of cellulose in plants
 CELL BOUNDARIES CELL BOUNDARIES Cells create boundaries through: Cell Membranes made of the phospholipid bilayer Cell Walls made of cellulose in plants TYPES OF MEMBRANES Some substances = too large or
CELL BOUNDARIES CELL BOUNDARIES Cells create boundaries through: Cell Membranes made of the phospholipid bilayer Cell Walls made of cellulose in plants TYPES OF MEMBRANES Some substances = too large or
David Huang! AP Biology! Oct. 4,2013! AP Biology Osmosis Laboratory Analysis! Introduction:!! There are several different methods for the
 David Huang AP Biology Oct. 4,2013 AP Biology Osmosis Laboratory Analysis Introduction: There are several different methods for the transportation of molecules across the phospholipid bilayer. These transportation
David Huang AP Biology Oct. 4,2013 AP Biology Osmosis Laboratory Analysis Introduction: There are several different methods for the transportation of molecules across the phospholipid bilayer. These transportation
Biology. Slide 1 / 74. Slide 2 / 74. Slide 3 / 74. Membranes. Vocabulary
 Slide 1 / 74 Slide 2 / 74 iology Membranes 2015-10-28 www.njctl.org Vocabulary Slide 3 / 74 active transport carrier protein channel protein concentration gradient diffusion enzymatic activity facilitated
Slide 1 / 74 Slide 2 / 74 iology Membranes 2015-10-28 www.njctl.org Vocabulary Slide 3 / 74 active transport carrier protein channel protein concentration gradient diffusion enzymatic activity facilitated
The Cell Membrane. Why cells must control materials. Living cells must maintain homeostasis for survival.
 The Cell Membrane Why cells must control materials Living cells must maintain homeostasis for survival. The cell membrane is the boundary between the cell and its environment. It is the cell membrane s
The Cell Membrane Why cells must control materials Living cells must maintain homeostasis for survival. The cell membrane is the boundary between the cell and its environment. It is the cell membrane s
Cellular Transport Notes
 Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes All cells have a cell membrane Functions: a. Controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b. Provides protection
Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes All cells have a cell membrane Functions: a. Controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b. Provides protection
Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life 2.2 Cell Membrane Structure Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different conditions
Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life 2.2 Cell Membrane Structure Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different conditions
Plasma Membrane Function
 Plasma Membrane Function Cells have to maintain homeostasis, they do this by controlling what moves across their membranes Structure Double Layer of phospholipids Head (polar) hydrophiliclikes water -
Plasma Membrane Function Cells have to maintain homeostasis, they do this by controlling what moves across their membranes Structure Double Layer of phospholipids Head (polar) hydrophiliclikes water -
3.2.3 Transport across cell membranes
 alevelbiology.co.uk 3.2.3 Transport across cell membranes SPECIFICATION The basic structure of all cell membranes, including cell-surface membranes and the membranes around the cell organelles of eukaryotes,
alevelbiology.co.uk 3.2.3 Transport across cell membranes SPECIFICATION The basic structure of all cell membranes, including cell-surface membranes and the membranes around the cell organelles of eukaryotes,
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
Transport. Slide 1 of 47. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 & Transport 1 of 47 Learning Targets TN Standard CLE 3216.1.3 Explain how materials move into and out of cells. CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through
& Transport 1 of 47 Learning Targets TN Standard CLE 3216.1.3 Explain how materials move into and out of cells. CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through
Multiple Choice Review Membranes and Proteins
 Multiple Choice Review Membranes and Proteins 1. What is the difference between carrier proteins and channel proteins? a. Carrier proteins change shape when a specific molecule binds to move it across
Multiple Choice Review Membranes and Proteins 1. What is the difference between carrier proteins and channel proteins? a. Carrier proteins change shape when a specific molecule binds to move it across
Key Concepts - All Cells Use Energy Energy Conversions - Reactions Absorb or Release Energy Endergonic, Exergonic - ATP is Cellular Energy
 Key Concepts - All Cells Use Energy Energy Conversions - Reactions Absorb or Release Energy Endergonic, Exergonic - ATP is Cellular Energy ATP Cycle - Enzymes Speed Up Reactions Enzyme Function, Factors
Key Concepts - All Cells Use Energy Energy Conversions - Reactions Absorb or Release Energy Endergonic, Exergonic - ATP is Cellular Energy ATP Cycle - Enzymes Speed Up Reactions Enzyme Function, Factors
9/20/2016 CHAPTER 7 LECTURE NOTES. Section Objectives. Explain how a cell s plasma membrane functions.
 CHAPTER 7 LECTURE NOTES Kennedy biol. 1ab Section Objectives Explain how a cell s plasma membrane functions. Relate the function of the plasma membrane to the fluid mosaic model. All living cells must
CHAPTER 7 LECTURE NOTES Kennedy biol. 1ab Section Objectives Explain how a cell s plasma membrane functions. Relate the function of the plasma membrane to the fluid mosaic model. All living cells must
Membrane structure & function
 Membrane structure & function Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The phospholipid bilayer describes a structure with. a. polar layers on the
Membrane structure & function Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The phospholipid bilayer describes a structure with. a. polar layers on the
Cells and Their Environment Chapter 8. Cell Membrane Section 1
 Cells and Their Environment Chapter 8 Cell Membrane Section 1 Homeostasis Key Idea: One way that a cell maintains homeostasis is by controlling the movement of substances across the cell membrane. Homeostasis
Cells and Their Environment Chapter 8 Cell Membrane Section 1 Homeostasis Key Idea: One way that a cell maintains homeostasis is by controlling the movement of substances across the cell membrane. Homeostasis
1. I can explain the structure of ATP and how it is used to store energy.
 1. I can explain the structure of ATP and how it is used to store energy. ATP is the primary energy molecule for the cell. It is produced in the mitochondria during cellular respiration, which breaks down
1. I can explain the structure of ATP and how it is used to store energy. ATP is the primary energy molecule for the cell. It is produced in the mitochondria during cellular respiration, which breaks down
Biology Unit 3 Review. Objective 1. Describe the important functions of organic molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids
 Biology Unit 3 Review Name Objective 1. Describe the important functions of organic molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids 1. What is the difference between organic and inorganic molecules?
Biology Unit 3 Review Name Objective 1. Describe the important functions of organic molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids 1. What is the difference between organic and inorganic molecules?
Biology Unit 3 Review. Objective 1. Describe the important functions of organic molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids
 Biology Unit 3 Review Name Objective 1. Describe the important functions of organic molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids 1. What is the difference between organic and inorganic molecules?
Biology Unit 3 Review Name Objective 1. Describe the important functions of organic molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids 1. What is the difference between organic and inorganic molecules?
Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment. Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane
 Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane Transport? Cells need things water, oxygen, balance of ions, nutrients (amino acids, sugars..building
Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane Transport? Cells need things water, oxygen, balance of ions, nutrients (amino acids, sugars..building
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology
 CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
FIGURE A. The phosphate end of the molecule is polar (charged) and hydrophilic (attracted to water).
 PLASMA MEMBRANE 1. The plasma membrane is the outermost part of a cell. 2. The main component of the plasma membrane is phospholipids. FIGURE 2.18 A. The phosphate end of the molecule is polar (charged)
PLASMA MEMBRANE 1. The plasma membrane is the outermost part of a cell. 2. The main component of the plasma membrane is phospholipids. FIGURE 2.18 A. The phosphate end of the molecule is polar (charged)
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
Gateway to the Cell 11/1/2012. The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move FLUID MOSAIC MODEL
 Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
1.14. Passive Transport
 Passive Transport 1.14 Simple Diffusion Cell s are selectively permeable only certain substances are able to pass through them. As mentioned in section 1.2, cell s are largely composed of a phospholipid
Passive Transport 1.14 Simple Diffusion Cell s are selectively permeable only certain substances are able to pass through them. As mentioned in section 1.2, cell s are largely composed of a phospholipid
Review: Cellular Transport
 Review: Cellular Transport OSMOSIS 1. Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic). The dots represent solutes. A. B. C. 2. means there is a GREATER concentration of solute molecules
Review: Cellular Transport OSMOSIS 1. Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic). The dots represent solutes. A. B. C. 2. means there is a GREATER concentration of solute molecules
Constant Motion of Molecules. Kinetic Theory of Matter Molecules move randomly and bump into each other and other barriers
 CELL TRANSPORT Constant Motion of Molecules Kinetic Theory of Matter Molecules move randomly and bump into each other and other barriers Solution homogenous liquid throughout which two or more substances
CELL TRANSPORT Constant Motion of Molecules Kinetic Theory of Matter Molecules move randomly and bump into each other and other barriers Solution homogenous liquid throughout which two or more substances
Unit 2 Warm Ups. Equilibrium
 Unit 2 Warm Ups Equilibrium 1. Cell wall 2. Mitochondria 3. Chloroplast 4. Vesicle 5. Vacuole 6. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 8. Cytoskeleton 9. Lysosomes 10.Cell Membrane
Unit 2 Warm Ups Equilibrium 1. Cell wall 2. Mitochondria 3. Chloroplast 4. Vesicle 5. Vacuole 6. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 8. Cytoskeleton 9. Lysosomes 10.Cell Membrane
Passive Transport. Does not expend cellular energy for the movement to take place. Ex-rolling down a hill
 Passive Transport Fluid Mosaic Model Passive Transport Does not expend cellular energy for the movement to take place Ex-rolling down a hill Parts of a Solution Solute: what gets dissolved Solvent: What
Passive Transport Fluid Mosaic Model Passive Transport Does not expend cellular energy for the movement to take place Ex-rolling down a hill Parts of a Solution Solute: what gets dissolved Solvent: What
Chapter 5 Ground Rules Of Metabolism
 Chapter 5 Ground Rules Of Metabolism Energy and the World of Life Energy Capacity to do work Two Forms Of energy Kinetic Energy is the energy an object has because it is moving Potential Energy is the
Chapter 5 Ground Rules Of Metabolism Energy and the World of Life Energy Capacity to do work Two Forms Of energy Kinetic Energy is the energy an object has because it is moving Potential Energy is the
Example - Paramecium contain contractile vacuoles that collect and remove excess water, thereby helping to achieve homeostasis
 Homeostasis Process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment; All organisms have ranges that are tolerated (i.e. ph and temperature) Example - Paramecium contain contractile
Homeostasis Process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment; All organisms have ranges that are tolerated (i.e. ph and temperature) Example - Paramecium contain contractile
CELL TRANSPORT and THE PLASMA MEMBRANE. SB1d. Explain the impact of water on life processes (i.e., osmosis, diffusion).
 CELL TRANSPORT and THE PLASMA MEMBRANE SB1d. Explain the impact of water on life processes (i.e., osmosis, diffusion). What if What would happen if an organism could not get energy or get rid of wastes?
CELL TRANSPORT and THE PLASMA MEMBRANE SB1d. Explain the impact of water on life processes (i.e., osmosis, diffusion). What if What would happen if an organism could not get energy or get rid of wastes?
The Working Cell: G: Membrane Transport & H: Enzymes. Chapter 5
 The Working Cell: G: Membrane Transport & H: Enzymes Chapter 5 Standards Unit G: Membrane Transport I can recognize the fluid mosaic model and accurately identify and describe the function of the components.
The Working Cell: G: Membrane Transport & H: Enzymes Chapter 5 Standards Unit G: Membrane Transport I can recognize the fluid mosaic model and accurately identify and describe the function of the components.
The Cell Membrane. Also known as the Plasma Membrane
 Student Objectives Know the different parts of the cell membrane Understand the role of the cell membrane in cellular transport Understand diffusion and osmosis Determine what will happen to plant and
Student Objectives Know the different parts of the cell membrane Understand the role of the cell membrane in cellular transport Understand diffusion and osmosis Determine what will happen to plant and
Equilibrium when two areas have the same concentration or are filled evenly
 Aim: How does the cell membrane function to maintain homeostasis? Do Now: Describe what homeostasis is. Homework: Vocab: Homeostasis, equilibrium, concentration gradient, diffusion, carrier protein, osmosis,
Aim: How does the cell membrane function to maintain homeostasis? Do Now: Describe what homeostasis is. Homework: Vocab: Homeostasis, equilibrium, concentration gradient, diffusion, carrier protein, osmosis,
Chapter 3. Section 3.3 Transport Across Membranes Pages 63-66
 Chapter 3 Section 3.3 Transport Across Membranes Pages 63-66 Membrane Transport The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer. The inside of the bilayer is hydrophobic and the outside of the bilayer is
Chapter 3 Section 3.3 Transport Across Membranes Pages 63-66 Membrane Transport The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer. The inside of the bilayer is hydrophobic and the outside of the bilayer is
Unit 3 : Homeostasis and Cell Transport
 Unit 3 : Homeostasis and Cell Transport A. Maintaining Homeostasis 1. Homeostasis process of regulating and maintaining a constant internal env. 2. Need to maintain homeostasis of water levels, glucose
Unit 3 : Homeostasis and Cell Transport A. Maintaining Homeostasis 1. Homeostasis process of regulating and maintaining a constant internal env. 2. Need to maintain homeostasis of water levels, glucose
WEDNESDAY 10/18/17. Why is the cell/plasma membrane important? What is the cell/plasma membrane made of? Label the cell membrane on your notes.
 WEDNESDAY 10/18/17 Why is the cell/plasma membrane important? What is the cell/plasma membrane made of? Label the cell membrane on your notes. THE PLASMA MEMBRANE - 2 Gateway to Cell HOMEOSTASIS Balanced
WEDNESDAY 10/18/17 Why is the cell/plasma membrane important? What is the cell/plasma membrane made of? Label the cell membrane on your notes. THE PLASMA MEMBRANE - 2 Gateway to Cell HOMEOSTASIS Balanced
Lab 4: Osmosis and Diffusion
 Page 4.1 Lab 4: Osmosis and Diffusion Cells need to obtain water and other particles from the fluids that surround them. Water and other particles also move out of cells. Osmosis (for water) and diffusion
Page 4.1 Lab 4: Osmosis and Diffusion Cells need to obtain water and other particles from the fluids that surround them. Water and other particles also move out of cells. Osmosis (for water) and diffusion
Consider the structure of the plasma membrane (fig. 8.6)- phospholipid bilayer with peripheral and integral proteins.
 Topic 8: MEMBRANE TRANSPORT (lectures 11-12) OBJECTIVES: 1. Have a basic appreciation of the chemical characteristics of substances that impact their ability to travel across plasma membranes. 2. Know
Topic 8: MEMBRANE TRANSPORT (lectures 11-12) OBJECTIVES: 1. Have a basic appreciation of the chemical characteristics of substances that impact their ability to travel across plasma membranes. 2. Know
Ch3: Cellular Transport Review KEY
 Ch3: Cellular Transport Review KEY OSMOSIS Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic environments) hypotonic hypertonic isotonic hypertonic means there is a GREATER concentration of
Ch3: Cellular Transport Review KEY OSMOSIS Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic environments) hypotonic hypertonic isotonic hypertonic means there is a GREATER concentration of
Cell Structure and Function. Cell Membrane and Osmosis
 Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane and Osmosis Cell Membrane All living things must maintain homeostasis. The cell membrane is the boundary between the cell and the environment that surrounds the
Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane and Osmosis Cell Membrane All living things must maintain homeostasis. The cell membrane is the boundary between the cell and the environment that surrounds the
Chapter 5. The Working Cell. Lecture by Richard L. Myers
 Chapter 5 The Working Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Richard L.
Chapter 5 The Working Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Richard L.
Ch 3 Membrane Transports
 Ch 3 Membrane Transports what's so dynamic about cell membranes? living things get nutrients and energy from the envrionment this is true of the entire organism and each cell this requires transport in/out
Ch 3 Membrane Transports what's so dynamic about cell membranes? living things get nutrients and energy from the envrionment this is true of the entire organism and each cell this requires transport in/out
Chapter 5. The Working Cell. PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey
 Chapter 5 The Working Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Lesson Plans Flipped Classroom
Chapter 5 The Working Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Lesson Plans Flipped Classroom
Equilibrium is a condition of balance. Changes in temperature, pressure or concentration can cause a shift in the equilibrium.
 Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Passive Transport Objectives Relate concentration gradients, diffusion, and equilibrium. Predict the direction of water
Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Passive Transport Objectives Relate concentration gradients, diffusion, and equilibrium. Predict the direction of water
The Cell Membrane and Homeostasis What is the cell membrane? A quick review A. Cell Membrane and Cell Transport. Unit 2: Cells and Cell Transport
 Unit 2: Cells and Cell Transport Cell Membrane and Cell Transport Name: Directions: Go to https://shimkoscience.weebly.com/ and on the Biology page, find the document labelled Cell Membrane and Cell Transport
Unit 2: Cells and Cell Transport Cell Membrane and Cell Transport Name: Directions: Go to https://shimkoscience.weebly.com/ and on the Biology page, find the document labelled Cell Membrane and Cell Transport
Ch. 5 Homeostasis & Cell Transport
 Ch. 5 Homeostasis & Cell Transport 5.1 Homeostasis & Permeability Homeostasis ability of cell to maintain balance needed for life To maintain balance: cells must transport needed materials into cells &
Ch. 5 Homeostasis & Cell Transport 5.1 Homeostasis & Permeability Homeostasis ability of cell to maintain balance needed for life To maintain balance: cells must transport needed materials into cells &
Plasma Membranes. Plasma Membranes WJEC GCE BIOLOGY 4.6
 4.6 Repeat Fig 3.20A here Fluid Mosaic Model of the Plasma Membrane Carbohydrate chain Glycoprotein Intrinsic Protein Non-polar hydrophobic fatty acid Phospholipids Appearance of the Cell Membrane Seen
4.6 Repeat Fig 3.20A here Fluid Mosaic Model of the Plasma Membrane Carbohydrate chain Glycoprotein Intrinsic Protein Non-polar hydrophobic fatty acid Phospholipids Appearance of the Cell Membrane Seen
CHAPTER. Movement Across Plasma Membrane. Chapter 6 Outline. Diffusion Osmosis. Membrane Potential Cell Signaling
 CHAPTER 6 Interaction Between Cells and the Extracellular Environment Chapter 6 Outline Extracellular Environment Diffusion Osmosis Carrier-Mediated Carrier Mediated Transport Membrane Potential Cell Signaling
CHAPTER 6 Interaction Between Cells and the Extracellular Environment Chapter 6 Outline Extracellular Environment Diffusion Osmosis Carrier-Mediated Carrier Mediated Transport Membrane Potential Cell Signaling
TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANES
 Unit 2: Cells, Membranes and Signaling TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANES Chapter 5 Hillis Textbook TYPES OF TRANSPORT ACROSS THE CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE: What do you remember? Complete the chart with what you
Unit 2: Cells, Membranes and Signaling TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANES Chapter 5 Hillis Textbook TYPES OF TRANSPORT ACROSS THE CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE: What do you remember? Complete the chart with what you
HOMEOSTASIS and CELL TRANSPORT. Chapter 5
 HOMEOSTASIS and CELL TRANSPORT Chapter 5 Cells get things in and out using two methods PASSIVE TRANSPORT does NOT use energy ACTIVE TRANSPORT does use energy (ATP) Passive Transport & Cell Membrane Cell
HOMEOSTASIS and CELL TRANSPORT Chapter 5 Cells get things in and out using two methods PASSIVE TRANSPORT does NOT use energy ACTIVE TRANSPORT does use energy (ATP) Passive Transport & Cell Membrane Cell
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different
Cell Membrane and Transport Cell Membrane and Cell Wall: ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids
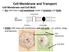 Cell Membrane and Transport Cell Membrane and Cell Wall: ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump SOME cells have
Cell Membrane and Transport Cell Membrane and Cell Wall: ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump SOME cells have
Unit 3: Cellular Processes. 1. SEPARTION & PROTECTION: the contents of the cell from the. 2. TRANSPORT: the transport of in and out of the cell
 Unit 3: Cellular Processes Name: Aim #14 Cell Membrane: How does the cell membrane function to maintain homeostasis? Date: _ I. The Cell Membrane: What is it? Also known as A thin structure that acts as
Unit 3: Cellular Processes Name: Aim #14 Cell Membrane: How does the cell membrane function to maintain homeostasis? Date: _ I. The Cell Membrane: What is it? Also known as A thin structure that acts as
Cell Biology. The Plasma Membrane
 Cell Biology The Plasma Membrane recall Fluid Mosiac Model S.J. Singer Semipermeable membrane fluid portion is double layer of phospholipids (=phospholipid bilayer) mosaic portion is the proteins and carbohydrates
Cell Biology The Plasma Membrane recall Fluid Mosiac Model S.J. Singer Semipermeable membrane fluid portion is double layer of phospholipids (=phospholipid bilayer) mosaic portion is the proteins and carbohydrates
Unit 7: Topic 7.4 Cellular Transport
 Unit 7: Topic 7.4 Cellular Transport Name: Class key Period: Page 1 of 39 Topic 7.4 assignments Pages/Sections Date Assigned Date Due Page 2 of 39 Topic: Membrane Channels Objective: Why do molecules move
Unit 7: Topic 7.4 Cellular Transport Name: Class key Period: Page 1 of 39 Topic 7.4 assignments Pages/Sections Date Assigned Date Due Page 2 of 39 Topic: Membrane Channels Objective: Why do molecules move
Chapter 7-3 Cell Boundaries
 Chapter 7-3 Cell Boundaries The Plasma Membrane: Cell Membrane Regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Provides protection and support. Highly selective barrier!!!! What the plasma membrane is made
Chapter 7-3 Cell Boundaries The Plasma Membrane: Cell Membrane Regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Provides protection and support. Highly selective barrier!!!! What the plasma membrane is made
Section 4: Cellular Transport. Cellular transport moves substances within the cell and moves substances into and out of the cell.
 Section 4: Cellular transport moves substances within the cell and moves substances into and out of the cell. Essential Questions What are the processes of diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active
Section 4: Cellular transport moves substances within the cell and moves substances into and out of the cell. Essential Questions What are the processes of diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active
Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment
 Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Cell Membrane KEY IDEAS > How does the cell membrane help a cell maintain homeostasis? > How does the cell membrane restrict the exchange
Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Cell Membrane KEY IDEAS > How does the cell membrane help a cell maintain homeostasis? > How does the cell membrane restrict the exchange
LAB 4: OSMOSIS AND DIFFUSION
 Page 4.1 LAB 4: OSMOSIS AND DIFFUSION Cells need to obtain water and other particles from the fluids that surround them. Water and other particles also move out of cells. Osmosis (for water) and diffusion
Page 4.1 LAB 4: OSMOSIS AND DIFFUSION Cells need to obtain water and other particles from the fluids that surround them. Water and other particles also move out of cells. Osmosis (for water) and diffusion
Cell Transport. Movement of molecules
 Cell Transport Movement of molecules TEKS Students will investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis and transport of molecules Homeostasis The maintaining of a stable body system
Cell Transport Movement of molecules TEKS Students will investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis and transport of molecules Homeostasis The maintaining of a stable body system
Slide 2 of 47. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall. End Show
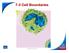 2 of 47 7-3 Cell Boundaries All cells are surrounded by a thin, flexible barrier known as the cell membrane. Many cells also produce a strong supporting layer around the membrane known as a cell wall.
2 of 47 7-3 Cell Boundaries All cells are surrounded by a thin, flexible barrier known as the cell membrane. Many cells also produce a strong supporting layer around the membrane known as a cell wall.
CHAPTER 2- ENZYMES PROTEINS B. AMINO ACID- 10/4/2016
 CHAPTER 2- ENZYMES BIOL. 1 AB KENNEDY PROTEINS A. DEFINITION- LARGE MACROMOLECULES MADE OF CARBON, HYDROGEN, NITROGEN, OXYGEN, AND SULFUR THEIR PRIMARY BUILDING BLOCK IS THE AMINO ACID THEY FUNCTION AS
CHAPTER 2- ENZYMES BIOL. 1 AB KENNEDY PROTEINS A. DEFINITION- LARGE MACROMOLECULES MADE OF CARBON, HYDROGEN, NITROGEN, OXYGEN, AND SULFUR THEIR PRIMARY BUILDING BLOCK IS THE AMINO ACID THEY FUNCTION AS
LAB 04 Diffusion and Osmosis
 LAB 04 Diffusion and Osmosis Objectives: Describe the physical mechanisms of diffusion and osmosis. Understand the relationship between surface area and rate of diffusion. Describe how molar concentration
LAB 04 Diffusion and Osmosis Objectives: Describe the physical mechanisms of diffusion and osmosis. Understand the relationship between surface area and rate of diffusion. Describe how molar concentration
Homeostasis and The Plasma Membrane
 Mosaic Homeostasis and The Plasma Membrane phospholipid cholesterol PLASMA MEMBRANE (FLUID MOSAIC MODEL) membrane protein filaments of cytoskeleton phospholipid cytoplasm (inside of cell) PHOSPHOLIPID
Mosaic Homeostasis and The Plasma Membrane phospholipid cholesterol PLASMA MEMBRANE (FLUID MOSAIC MODEL) membrane protein filaments of cytoskeleton phospholipid cytoplasm (inside of cell) PHOSPHOLIPID
7.3 Cell Boundaries. Regents Biology. Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham
 7.3 Cell Boundaries Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham Don t look at your reading guide/textbook or talk with each other yet! Write down one thing you know/remember
7.3 Cell Boundaries Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham Don t look at your reading guide/textbook or talk with each other yet! Write down one thing you know/remember
The Cell and Cellular transport
 Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membranes. Chapter 5
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Ch. 7 Diffusion, Osmosis, and Movement across a Membrane
 Ch. 7 Diffusion, Osmosis, and Movement across a Membrane Diffusion Spontaneous movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Does not require energy (exergonic)
Ch. 7 Diffusion, Osmosis, and Movement across a Membrane Diffusion Spontaneous movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Does not require energy (exergonic)
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
 Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane 1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Directions: Questions 2 and 3 refer to
Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane 1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Directions: Questions 2 and 3 refer to
POLAR COVALENT BOND 1 P
 POLAR COVALENT BOND 1 P HP OXYGEN HIGHER ELECTRO- O WATER MOLECULE HYDROGEN LOWER ELECTRO- H BOND BOND H ELECTRO- = 3.5 ELECTRO- = 2.1 ELECTRO- = 2.1 = E- POLAR COVALENT BOND +/- - 1 P? CHARGE OXYGEN HIGHER
POLAR COVALENT BOND 1 P HP OXYGEN HIGHER ELECTRO- O WATER MOLECULE HYDROGEN LOWER ELECTRO- H BOND BOND H ELECTRO- = 3.5 ELECTRO- = 2.1 ELECTRO- = 2.1 = E- POLAR COVALENT BOND +/- - 1 P? CHARGE OXYGEN HIGHER
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structures Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structures Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many
STATION 4: TONICITY due to OSMOSIS / Turgor Pressure in Plants
 STATION 4: TONICITY due to OSMOSIS / Turgor Pressure in Plants Tonicity is the concentration of solutions that determines the direction water will move across a semi-permeable membrane. A solution is a
STATION 4: TONICITY due to OSMOSIS / Turgor Pressure in Plants Tonicity is the concentration of solutions that determines the direction water will move across a semi-permeable membrane. A solution is a
Movement of Substances in the Cell
 Movement of Substances in the Cell The Marble Memories Biology All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane (also called cell membrane). This membrane regulates the entry and exit of substances into and
Movement of Substances in the Cell The Marble Memories Biology All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane (also called cell membrane). This membrane regulates the entry and exit of substances into and
[S] [S] Hypertonic [H O] [H 2 O] g. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through membranes! 15. Osmosis. Concentrated sugar solution
![[S] [S] Hypertonic [H O] [H 2 O] g. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through membranes! 15. Osmosis. Concentrated sugar solution [S] [S] Hypertonic [H O] [H 2 O] g. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through membranes! 15. Osmosis. Concentrated sugar solution](/thumbs/88/115710711.jpg) Concentrated sugar solution Sugar molecules (Water molecules not shown) 100ml 100ml Hypertonic [S] g [H2 Hypotonic [H O] 2 O] [H 2 O] g Semipermeable Dilute sugar solution (100ml) Time 125ml Osmosis 75ml
Concentrated sugar solution Sugar molecules (Water molecules not shown) 100ml 100ml Hypertonic [S] g [H2 Hypotonic [H O] 2 O] [H 2 O] g Semipermeable Dilute sugar solution (100ml) Time 125ml Osmosis 75ml
Cell Membrane-Structure and Function
 Cell Membrane-Structure and Function BIO 250 Living things are composed of cells and cell products (extracellular) Cells are the basic unit of structure They are the basic unit of function They vary in
Cell Membrane-Structure and Function BIO 250 Living things are composed of cells and cell products (extracellular) Cells are the basic unit of structure They are the basic unit of function They vary in
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes
 BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes
 BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY
 Biology 12 Name: Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY Cell parts and Function 1. Identify each part of the cell indicated and give one role for each structure in the secretion and/or synthesis
Biology 12 Name: Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY Cell parts and Function 1. Identify each part of the cell indicated and give one role for each structure in the secretion and/or synthesis
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function
 Plasma Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane separates the internal environment of the cell from its surroundings. The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane separates the internal environment of the cell from its surroundings. The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The
Cellular Transport Notes
 Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes 1.All cells have a cell membrane a.controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b.provides protection and support
Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes 1.All cells have a cell membrane a.controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b.provides protection and support
Cellular Transport. Biology Honors
 Cellular Transport Biology Honors Review of Concepts and Introduction to the Current Concepts https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ptmlvtei 8hw Passive Active No energy Requires / needs energy Passive Transport-
Cellular Transport Biology Honors Review of Concepts and Introduction to the Current Concepts https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ptmlvtei 8hw Passive Active No energy Requires / needs energy Passive Transport-
COMMON ASSESSMENT
 1. The diagram above is a model of a cellular process called transcription. What class of biological molecules is represented in the diagram? A. Carbohydrates B. Nucleic acids C. Proteins D. Lipids B.9.A.R
1. The diagram above is a model of a cellular process called transcription. What class of biological molecules is represented in the diagram? A. Carbohydrates B. Nucleic acids C. Proteins D. Lipids B.9.A.R
Cell Membrane Structure and Function. What is the importance of having a cell membrane?
 Cell Membrane Structure and Function What is the importance of having a cell membrane? I. Membrane Structure a. Membranes contain proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates (which are all types of macromolecules)
Cell Membrane Structure and Function What is the importance of having a cell membrane? I. Membrane Structure a. Membranes contain proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates (which are all types of macromolecules)
Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function
 Section 1: Cell Discovery and Theory Section 2: The Plasma Membrane Section 3: Structures and Organelles Section 4: Cellular Transport Click on a lesson name to select. 7.2 The Plasma/Cell Membrane Thin,
Section 1: Cell Discovery and Theory Section 2: The Plasma Membrane Section 3: Structures and Organelles Section 4: Cellular Transport Click on a lesson name to select. 7.2 The Plasma/Cell Membrane Thin,
Movement Through the Cell Membrane
 Movement Through the Cell Membrane Cellular Movement All living organisms rely on diffusion Get oxygen for respiration Removing waste products Transpiration in plants Cellular Movement The cell membrane
Movement Through the Cell Membrane Cellular Movement All living organisms rely on diffusion Get oxygen for respiration Removing waste products Transpiration in plants Cellular Movement The cell membrane
I. Membrane Structure Figure 1: Phospholipid. Figure 1.1: Plasma Membrane. Plasma Membrane:
 I. Membrane Structure Figure 1: Phospholipid Figure 1.1: Plasma Membrane Plasma Membrane: 1 II. Early Plasma Membrane Models Figure 2: Davson-Danielli Sandwich Model In the 1960 s new evidence suggested
I. Membrane Structure Figure 1: Phospholipid Figure 1.1: Plasma Membrane Plasma Membrane: 1 II. Early Plasma Membrane Models Figure 2: Davson-Danielli Sandwich Model In the 1960 s new evidence suggested
Ch 4 Cells & Their Environment
 Ch 4 Cells & Their Environment Biology Mrs. Stolipher MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells Membranes are selectively permeable They control the flow of substances
Ch 4 Cells & Their Environment Biology Mrs. Stolipher MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells Membranes are selectively permeable They control the flow of substances
5.6 Diffusion, Membranes, and Metabolism
 5.6 Diffusion, Membranes, and Metabolism Concentration of a substance Number of atoms or molecules in a given volume Concentration gradient of a substance A difference in concentration between two regions
5.6 Diffusion, Membranes, and Metabolism Concentration of a substance Number of atoms or molecules in a given volume Concentration gradient of a substance A difference in concentration between two regions
Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer. Membrane Structure and Function. Fluid Mosaic Model. Chapter 5
 Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer Phospholipid Hydrophilic Head Hydrophobic Tail Lipid Bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model Mixture of saturated and unsaturated fatty
Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer Phospholipid Hydrophilic Head Hydrophobic Tail Lipid Bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model Mixture of saturated and unsaturated fatty
DIFFUSON AND OSMOSIS INTRODUCTION diffusion concentration gradient. net osmosis water potential active transport
 DIFFUSON AND OSMOSIS NAME DATE INTRODUCTION The life of a cell is dependent on efficiently moving material into and out of the cell across the cell membrane. Raw materials such as oxygen and sugars needed
DIFFUSON AND OSMOSIS NAME DATE INTRODUCTION The life of a cell is dependent on efficiently moving material into and out of the cell across the cell membrane. Raw materials such as oxygen and sugars needed
The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation
 The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation Oct 20 7:07 PM Cell Membrane Forms a barrier between the cell and the external environment. Has three main functions: 1) helps the cell retain the molecules
The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation Oct 20 7:07 PM Cell Membrane Forms a barrier between the cell and the external environment. Has three main functions: 1) helps the cell retain the molecules
