ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Role of 3T MRI in Evaluation of Bone Marrow Changes in Spine in Various Diseases
|
|
|
- Ada Lewis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 46 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 67 March 2019 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of 3T MRI in Evaluation of Bone Marrow Changes in Spine in Various Diseases Anagha Joshi 1, Sukhada Kulkarni 2*, Tilak Dedhia 2, Aakash Vaswani 2 Abstract Multiplanar MR imaging provides excellent spatial and contrast resolution necessary to differentiate the signal intensities of fatty (yellow) marrow elements from hematopoietic (red) marrow elements and hence it is useful for evaluation of various pathologies of bone marrow. Utilization of typical imaging features on conventional MR imaging techniques and other newer imaging techniques, such as diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and in- and out-of-phase MRI, for better characterisation of bone marrow pathologies has been highlighted. Aims and Objectives 1. To determine the prevalence of various bone marrow pathologies in spine. 2. To study the MRI signal changes of bone marrow in various lesions such as anaemia, leukaemia, lymphomas and various bone marrow. Materials and Methods: A total of 100 patients who were investigated between November 2012 and October 2014 were included. MRI spine studies were done on a 3.0 Tesla Philips Achieva Medical Systems. Observations and Results: In our study, out of 100 cases studied for various spinal pathologies, 48 patients were male and 52 were female indicating almost equal male to female distribution. Maximum cases were degenerative with most common site of involvement being lumbar followed by cervical region. There were only 3 cases of depletion disorder and no case with deposition disorder. The mean age group was years, with the range being 9 years to 72 years. Maximum patients (n = 67) were found in the age group of Conclusion: Various bone marrow were classified and evaluated separately. A systematic approach to its evaluation by categorization is essential with prudent use of both conventional and problem-solving techniques, such as CSI and DWI, for accurate diagnosis and appropriate patient management. Conventional radiology depicts changes of an altered bony matrix while MRI displays changes at a cellular level and is well suited for imaging the bone marrow. MRI serves as a screening method in bone marrow and the diagnosis is established in context with the clinical findings or by biopsy. Introduction Normal Bone Marrow Bone marrow is divided into two main constituents, yellow and red marrow. Yellow marrow is considered as hematopoietically inactive and is mainly composed of fat cells while Red marrow in contrast, is characterized by a rich sinusoidal system and contains approximately 60% hematopoietic cells and 40 % fat cells. During growth, conversion of red to yellow marrow occurs following a predictable and orderly pattern until a balanced distribution pattern is reached by the age of 25. The exact pattern of marrow changes depend on many factors like sex, age and the health of the individual. With age trabecular bone is also decomposed and replaced by fat cells, hence the increase in fatty marrow with age is greater than the reduction in volume of red marrow. Sometime reconversion of yellow to red marrow takes place if a sudden rise in the demand for haematopoiesis occurs. Disorders that affect bone marrow can be divided into following categories: Reconversion due to hyperplasia, Marrow infiltration or replacement, Depletion of hematopoietic marrow, Depletion of myeloid elements with fibrosis and Deposition of metabolic products. This article reviews MRI protocols, including routine and non-routine pulse sequences such as diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and in- and out-of-phase MRI and outlines a systematic approach and typical imaging features of various pathologies based on available literature. Materials and Methods A total of 100 patients who were investigated between November 2012 and October 2014 were included. MRI spine studies were done on a 3.0 Tesla Philips Achieva Medical Systems. Indications A prospective study of 100 patients who presented to the OPD or Emergency department or admitted with clinically suspected pathology involving the axial skeleton underwent MRI of spine on an elective basis. Standard tests (history taking, physical examination, relevant blood investigations) were directed to all patients, whereas, the mode of additional imaging (x-ray spine or x-ray/ct chest and abdomen in patient with primary at other known location) was also carried out. Inclusion Criteria Clinical suspected pathology involving the axial skeleton. Biochemical examination suggestive 1 Professor, 2 Resident, Lokmanya Tilak Municipal Medical College and General Hospital, Mumbai, Maharashtra; * Corresponding Author Received: ; Revised: ; Accepted:
2 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 67 March Table 1: Diagnosis and relative frequency of occurrence of various bone marrow Diagnosis No. of patient Degenerative 60 (60%) Infiltration/ replacement 16 (16%) Reconversion 11 (11%) Depletion 3 (3%) Deposition 0 (0%) Focal of bone marrow 10 (10%) of deranged haematological profile / Ineffective haematopoiesis (like in cases of thalassemia) In patients with known primary malignancy presented with backache. In patients with backache radiating to extremities without any previous significant past history. I n p a t i e n t s w i t h hyperparathyroidism. Exclusion Criteria Patients not consenting for the study Intracranial aneurysm clips (Unless the referring physician is certain that it is made of non-ferromagnetic material such as titanium) Intra-orbital metal fragments Any electrically, magnetically or mechanically activated implants 1. Including cardiac pacemakers, biostimulators, neurostimulators, 2. Cochlear implants and hearing aids. Pregnancy (Risk Vs benefit ratio to be assessed). Known h/o contrast allergy. Other implanted medical devices (eg. Swan Ganz catheter). Metal shrapnel or bullet. For use of MR contrast (gadolinium): 1. Lactating women 2. Patients with moderate to severe renal insufficiency (i.e. with GFR<30ml/min or a S. creatinine> 2mg/dl) Imaging Technique The MRI appearance of the bone marrow depends on the pulse sequence used for its evaluation as well as on the relative amount of water, fat, protein and cells within the bone marrow. Among these the major determinants of the MR appearance of bone marrow are the fat and water content. The routine spine evaluation on MRI typically includes T1-weighted, Table 2: Age distribution of the bone marrow Age group (years) No of patient (%) (1%) (6%) (7%) (15%) (33%) (34%) (3%) >71 00 (0%) T2-weighted, and Short Tau Inversion Recovery (STIR) sequences. Postcontrast (intravenous gadolinium) fat-suppressed T1W imaging should always include pre-contrast baseline fat-suppressed T1W imaging in at least one plane. Several non-routine MRI sequences include T1 FLAIR Imaging, Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), in- and out-of-phase MRI, MR spectroscopy (MRS), and dynamic contrast enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI). These aid in enhancing contrast and visualize changes in the bone marrow at a molecular level. Observation and Results Prevalence of various bone marrow Out of 100 patient studied following diagnoses were made. Diagnosis and relative frequency of occurrence of various bone marrow has been given below (Table 1). Age distribution The patients were divided on the basis of age group. Maximum patients (n = 67) were found in the age group of Otherwise an equal distribution was seen in all age groups. The mean age group was years, with the range being 9 to 68 years. Age distribution of the bone marrow has been given below (Table 2). Degenerative disorder In our study of various spinal pathologies, there were 60 cases (60%) of degenerative changes of spine on MRI - Disc degeneration, Disc bulge, Disc herniation, Modic changes, Canal stenosis/nerve root compression. Various types of degenerative changes and their frequency of distribution has been given below (Table 3). Classification of Infiltrative / Replacement diseases In our study of various spinal pathologies, there were 16 cases (16 %) of infiltrative / replacement Table 3: Various types of degenerative changes and frequency of distribution Degenerative changes Findings in patients with degenerative Disc degeneration 41 (68.3%) Disc bulge 21 (35%) Disc Herniation 28 (46.6%) Modic changes 17 (28.3%) Canal stenosis/nerve 40 (66.7%) root compression of spine, of which most common pathology was metastasis found in 11 cases (68.7%). Marrow can be replaced by either neoplastic or non-neoplastic. Various neoplastic diseases include metastatic disease, lymphoma, leukemia, and multiple myeloma. These cases were confirmed pathologically with bone biopsy. Various types of infiltrative / replacement and their frequency of distribution has been given below (Table 4). Classification of Reconversion disorder Reconversion can be classified in to the chronic anemia, hyperparathyroidism and miscellaneous conditions (Heavy smoking, increase oxygen requirements), there were total 11 (11%) cases of reconversion of spine in our study, of which most common was chronic anaemia due to thalassemia accounting for approximately 45.5% (5 cases) of all reconversion. Cases of thalassemia and sickle cell disease were proven with clinical correlation, blood parameters and Hb electrophoresis. Cases of hyperparathyroidism were proven clinically and with blood parameters viz S. PTH, calcium and phosphate levels. Various types of reconversion and their frequency of distribution has been given below (Table 5). Classification of Depletion In our study, there were 3 (3%) cases of depletion. Various depletion can be classified in to depletion secondary to radiotherapy, chemotherapy, idiopathic and depletion with fibrosis (myelofibrosis), aplastic anaemia and tabulated below. Various types of depletion and their frequency of distribution has been given below (Table 6). Bone biopsy was performed for confirmation.
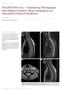
3 48 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 67 March 2019 Table 4: Various types of infiltrative / replacement and frequency of distribution. Infiltrative / replacement No of patients Metastasis 11 (68.7%) Lymphoma 2 (12.5%) Leukemia 0 (0%) Myeloma 0 (0%) Non-neoplastic 3 (18.8%) Table 5: Various types of reconversion and frequency of distribution Reconversion No of patients Chronic anaemia : Sickle cell 1 (9.09%) anaemia Chronic anaemia : Thalassemia 5 (45.4%) Hyperparathyroidism 2 (18.1%) Others (Heavy smoking, increase 3 (27.2%) Oxygen requirements) Table 6: Various types of depletion and frequency of distribution Depletion No of patients Unknown cause 1 (33.33%) Myelofibrosis 1 (33.33%) Aplastic anaemia 1 (33.33%) Secondary to chemo or 0 (0%) radiotherapy Table 7: Various types of focal and frequency of distribution Focal of bone marrow No. of patients Focal edema(infection) 6 (60%) Ischemia 0 (0%) Trauma 4 (40%) Distribution of focal of bone marrow In our study, there were 10 (10 %) cases of depletion. Various focal of bone marrow in spine are focal edema, ischemia and trauma. Various types of focal and their frequency of distribution has been given below (Table 7). Discussion The role of diagnostic imaging is to provide accurate anatomic information and to affect the management decision making. 1 This cross-sectional hospital based study used MRI to diagnose various bone marrow pathologies in spine as it has better tissue differentiation and it can show bone marrow changes at an early stage as compared to other imaging techniques (such as CT Scan and radiographs). Other advantages of MRI include a) no known side effects or morbidity, b) no radiation exposure and is c) noninvasive. 2,3 Despite its high sensitivity, few of the marrow changes are observed Fig. 1: Endplates adjacent to the L2-L3 intervertebral disc showing hyperintense signal on T1 W (A) and T2 W (B) imaging s/o Type II Modic changes. There is also decrease disc space involving L2-L3 level with posterior disc bulge on many MRI scans in asymptomatic subjects, thus questioning its specificity. Prevalence of bone marrow pathologies In our study of 100 patients of various spinal pathologies, around 60% were degenerative. Among the various bone marrow pathologies, after excluding degenerative changes, most common pathology was infiltration/replacement disorder (16%) of which most common was metastasis. Second most common pathology was reconversion disorder (11%) followed by focal of bone marrow (10%). Least common pathologies were Depletion and Deposition. Vogler et al, have grouped the bone marrow disease conditions according to common pathophysiological patterns in to reconversion disorder, infiltration, depletion, bone marrow edema and bone marrow ischemia. 4 Age Distribution In our study patients were found in all age groups with the mean age group being 45.3 years, with the range being 9 years to 68 years. The mean age group of above 45 is expected considering that a major cause of various marrow pathologies are degenerative and infiltrative / replacement disorder of which most common is metastasis, which tend to occur in elderly population. Degenerative Disorder Degenerative changes were observed in majority of patients examined i.e. in 60 patients (60%). Though degenerative changes of the disc begin early in life and are partly a consequence of aging, the actual cause is not known but many factors (autoimmune, genetic, re-absorption and biochemical) have been implicated in accelerating the process. Disc degeneration was the most frequent finding observed in 41 (68.3%) patients in our study followed by disc bulge, disc herniations and Modic changes (Figure 1 A, B). The prevalence was observed to increase with age. Proportion of degenerated discs progressively increases at lower spinal levels, and that most common part of spine involvement is lumbar region, in particular L4-L5 and L5-S1 levels. 5-7 Infiltrative / Replacement Disorders Most common neoplastic processes that involve the spine is metastatic disease which was consistent with our study. Followed in order were lymphoma, and plasma cell dyscrasia, either solitary plasmacytoma or multiple myeloma. 8 Metastasis Replacement of the bone marrow always appears hypointense relative to normal marrow on T1-weighted images. 9,10 On T2-weighted images; metastatic lesions are usually much brighter than bone marrow due to
4 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 67 March Fig. 2: In this k/c/o carcinoma prostate, multiple hyperintense lesions are seen scattered throughout the dorsal vertebral bodies and appear hyperintense in in-phase sequence (A) and do not suppress on out-phase sequence (B) s/o infiltrative disorder Fig. 3: In this k/c/o Thalassemia major patient, vertebral bodies show diffuse hypointensity on T1 W (A), T2 weighted (B) sequences compared to intervertebral disc s/o Marrow Reconversion their high water content. Metastases often (but not consistently) have a rim of bright T2 signal around them (a halo sign). 11 The halo sign and diffuse signal hyperintensity were shown to be a strong indicator of metastatic disease. In our study, all patients with metastasis had hypo to isointense signal on T1 and heterogeneously hyperintense signal on T2 with 4 out of 11 were showing halo sign and 6 out 11 were showing the post contrast enhancement. Hence, findings were almost consistent with previous data. Dual-FFE sequence was done in only 5 patients with metastasis; increased signal was noted in all the 5 patients on out phase (Figure 2 A, B). Lymphoma When lymphoma involves the spine, it is more commonly found isolated to the epidural space as a result of secondary spread. Tumour location within the epidural space can vary, but there is a proclivity for the thoracic levels. 12,13 On MRI, Spinal lymphoma is typically hypointense on T1 and in homogenously hyperintense on T2WI. 14 In our study, in patients with lymphoma, lesions were hypointense on T1 and hyperintense on T2. There was no significant post contrast enhancement in either of the patients. Reconversion Disorder 11 cases of reconversion of spine seen in our study, of which most common was chronic anaemia due to thalassemia followed in order were hyperparathyroidism and sickle cell anaemia and other causes like increase oxygen requirements and heavy smoking. Hemolytic Anaemia- Thalassemia Signal characteristics of marrow were compared with those of surrounding muscle and fat. Fatty marrow (isointense with subcutaneous fat) was compared with red marrow (hypointense to fat and slightly hyperintense to muscle). Marrow hypointense to muscle was identified as iron deposition within red marrow. There are only a few studies addressing marrow SI in transfusiondependent patients with thalassemia 15,16 and sickle cell anaemia 17,18 by using T1- and T2-w SE sequences. They report the presence of hypointense bone marrow in both T1- and T2-w images as attributed to iron deposition In our study, we found that 3 out of 5 patients (60%) with thalassemia had diffuse bone marrow hypointensity in all MR sequences (Figure 3 A, B). 2 out of 5 patients (40%) had hypointensity on the T2*-W GRE sequence alone without any significant hypointensity on T1 and T2. Hemolytic Anaemia-Sickle cell anaemia There was only one case of sickle cell anaemia found in our study and findings were diffuse hypointense signal noted on T1 involving entire
5 50 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 67 March 2019 Fig. 4: There is diffuse hypointensity noted on both T1 W (A) and T2 weighted (B) sequences involving the vertebral bodies compared to intervertebral disc resulting in a black marrow Fig. 5: Fracture line appears hypointense on T1 W (A), T2 weighted (B) sequences and hyperintense signal of marrow on T2 weighted sequence indicating marrow edema spine consistent with findings of anaemia without any complications of osteomyelitis. Depletion Disorders Only 3 cases of depletion were found in our study.various depletion can be classified into depletion secondary to radiotherapy, chemotherapy, idiopathic and depletion with fibrosis (myelofibrosis), aplastic anaemia. In study conducted by Gupta et al., Magnetic resonance imaging of the thoracolumbar spine revealed multiple focal low signal intensity lesions involving most of the thoracic and lumbar vertebral bodies 19. In our study there was diffuse T1 and T2 hypointensity noted in all patients with depletion (Figure 4 A, B). Focal Disorders of Bone Marrow Trauma In our study, out of 4 patients with trauma to spine, 3 patients had injury and associated vertebral fracture involving cervical vertebra while rest 1 had fracture involving the thoracic region. In study conducted by us, there were 4 patients of benign traumatic fractures; all had diffusely hypointense signal on T1-weighted images and hyperintense signal on FSE T2-weighted fat-suppressed images and contrast given to 1 patient showed contrast enhancement (Figure 5 A, B). Infection (Tuberculous spondylitis) Thoracolumbar spine is most common site of involvement in Tuberculous Spondylitis (50% of patients). Each of cervical spine and lumber spine are involved in 25% of patients. 20 In our study, there were 6 patients of Tuberculous Spondylitis out of which 5 had thoracolumbar spine involvement (i.e %) and 1 had multiple level diffuse involvement (16.67%). Conclusion Bone marrow lesion can be seen as a non-specific finding in a variety of conditions. A systematic approach to its evaluation by categorization is essential with prudent use of both conventional and problem-solving techniques, such as CSI and DWI, for accurate diagnosis and appropriate patient management. Conventional radiology depicts changes of an altered bony matrix while MRI displays changes at a cellular level and is well suited for imaging the bone marrow. It is very sensitive, although the specificity of MRI findings is not always without fallacies. Hence MRI serves as a screening method in bone marrow and the diagnosis is established in context with the clinical findings or by biopsy. In Hodgkin s lymphoma marrow involvement is detected more often with MR than with marrow biopsy. In low-grade NHL the involvement is diffuse and biopsy is superior. In highgrade lymphomas the involvement is more focal and MRI is more efficient. Also, the nodular nature of
6 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 67 March lymphomatous marrow deposits allow MR mapping to select the site of biopsy because blind bone marrow biopsy may give false negative results. References 1. Modic MT and Ross JS. Lumbar degenerative disc disease. Radiology 2007; 245: Modic MT, Obuchowski NA, Ross JS, et al. Acute low back pain and radiculopathy: MR imaging findings and their prognostic role and effect on outcome. Radiology 2005; 237: Shobeiri E, Khalatbari MR, Taheri MS, Tofighirad N and Moharamzad Y. Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of patients with low back pain and those with sciatica. Singapore Medical Journal 2009; 50: Vogler JB, 3rd and Murphy WA. Bone marrow imaging. Radiology 1988; 168: Cheung KM, Karppinen J, Chan D, et al. Prevalence and pattern of lumbar magnetic resonance imaging changes in a population study of one thousand forty-three individuals. Spine 2009; 34: Ong A, Anderson J and Roche J. A pilot study of the prevalence of lumbar disc degeneration in elite athletes with lower back pain at the Sydney 2000 Olympic Games. British Journal of Sports Medicine 2003; 37: Takatalo J, Karppinen J, Niinimaki J, et al. Prevalence of degenerative imaging findings in lumbar magnetic resonance imaging among young adults. Spine 2009; 34: Rodallec MH, Feydy A, Larousserie F, et al. Diagnostic imaging of solitary tumors of the spine: what to do and say. Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc 2008; 28: Daffner RH, Lupetin AR, Dash N, Deeb ZL, Sefczek RJ and Schapiro RL. MRI in the detection of malignant infiltration of bone marrow. AJR American Journal of Roentgenology 1986; 146: Baur A, Stabler A, Bruning R, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of bone marrow: differentiation of benign versus pathologic compression fractures. Radiology 1998; 207: Schweitzer ME, Levine C, Mitchell DG, Gannon FH and Gomella LG. Bull s-eyes and halos: useful MR discriminators of osseous metastases. Radiology 1993; 188: Lyons MK, O Neill BP, Marsh WR and Kurtin PJ. Primary spinal epidural non-hodgkin s lymphoma: report of eight patients and review of the literature. Neurosurgery 1992; 30: Epelbaum R, Haim N, Ben-Shahar M, Ben-Arie Y, Feinsod M and Cohen Y. Non-Hodgkin s lymphoma presenting with spinal epidural involvement. Cancer 1986; 58: BN Lakhkar MA, Jose J. Pictarial essay : MR appearances of osseous spine tumors. Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging and Imaging 2002; 12: Levin TL, Sheth SS, Ruzal-Shapiro C, Abramson S, Piomelli S and Berdon WE. MRI marrow observations in thalassemia: the effects of the primary disease, transfusional therapy, and chelation. Pediatric Radiology 1995; 25: Brasch RC, Wesbey GE, Gooding CA and Koerper MA. Magnetic resonance imaging of transfusional hemosiderosis complicating thalassemia major. Radiology 1984; 150: Levin TL, Sheth SS, Hurlet A, et al. MR marrow signs of iron overload in transfusion-dependent patients with sickle cell disease. Pediatric Radiology 1995; 25: Kaneko K, Humbert JH, Kogutt MS and Robinson AE. Iron deposition in cranial bone marrow with sickle cell disease: MR assessment using a fat suppression technique. Pediatric Radiology 1993; 23: Gupta G, Robertson P and Szer J. Focal lesions on magnetic resonance imaging in aplastic anaemia: multiple metastases or haemopoietic marrow. Australasian Radiology 2007; 51 Spec No.: B Wheeless CR. Wheeless Textbook of Orthopaedics
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
Differentiation of osteoporosis from metastasis in the vertebral fracture using chemical shift and diffusion weighted imaging
 Differentiation of osteoporosis from metastasis in the vertebral fracture using chemical shift and diffusion weighted imaging Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H.
Differentiation of osteoporosis from metastasis in the vertebral fracture using chemical shift and diffusion weighted imaging Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H.
MR Evaluation of Bone Marrow Disorders. Nisha Patel, MD
 MR Evaluation of Bone Marrow Disorders Nisha Patel, MD 1 Introduction Nearly all imaging modalities evaluate the marrow, which is a site of significant pathology Radiography Nuclear Medicine CT MR 2 Topics
MR Evaluation of Bone Marrow Disorders Nisha Patel, MD 1 Introduction Nearly all imaging modalities evaluate the marrow, which is a site of significant pathology Radiography Nuclear Medicine CT MR 2 Topics
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist. Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation
 Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation 13/12/2018 Presenter Hidayatullah Hamidi Consultant Radiologist, Radiology PGME program director, FMIC, Kabul, Afghanistan
Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation 13/12/2018 Presenter Hidayatullah Hamidi Consultant Radiologist, Radiology PGME program director, FMIC, Kabul, Afghanistan
MRI Evaluation of Disc Lesions Causing Lumbar Canal Stenosis and Backache Y Aditya 1 *, Janardhan Reddy K 2 and MV Ramanappa 3
 Indian Journal of Mednodent and Allied Sciences Vol. 2, No. 3, November, 2014, pp- 242-247 DOI : 10.5958/2347-6206.2014.00022.3 Original Research MRI Evaluation of Disc Lesions Causing Lumbar Canal Stenosis
Indian Journal of Mednodent and Allied Sciences Vol. 2, No. 3, November, 2014, pp- 242-247 DOI : 10.5958/2347-6206.2014.00022.3 Original Research MRI Evaluation of Disc Lesions Causing Lumbar Canal Stenosis
Imaging of bone metastases
 Imaging of bone metastases Antoine Feydy Service de Radiologie B Hôpital Cochin APHP Université Paris Descartes antoine.feydy@aphp.fr MEXICO 2016 INTRODUCTION Diagnostic Imaging Imaging Modalities Strengths,
Imaging of bone metastases Antoine Feydy Service de Radiologie B Hôpital Cochin APHP Université Paris Descartes antoine.feydy@aphp.fr MEXICO 2016 INTRODUCTION Diagnostic Imaging Imaging Modalities Strengths,
Role of MRI in the Evaluation of Compressive Myelopathy
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 4 Ver. XIII (Apr. 2016), PP 21-26 www.iosrjournals.org Role of MRI in the Evaluation of Compressive
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 4 Ver. XIII (Apr. 2016), PP 21-26 www.iosrjournals.org Role of MRI in the Evaluation of Compressive
MR Imaging Characteristics of Cranial Bone Marrow in Adult Patients with Underlying Systemic Disorders Compared with Healthy Control Subjects
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:248 254, February 2002 MR Imaging Characteristics of Cranial Bone Marrow in Adult Patients with Underlying Systemic Disorders Compared with Healthy Control Subjects Laurie A. Loevner,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:248 254, February 2002 MR Imaging Characteristics of Cranial Bone Marrow in Adult Patients with Underlying Systemic Disorders Compared with Healthy Control Subjects Laurie A. Loevner,
Role of Diffusion WIs and T 2 * GRE Pulse Sequences in Dubious Vertebral Marrow Pathological Lesions
 Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 19, No. 4, December: 254-262, 2007 Role of Diffusion WIs and T 2 * GRE Pulse Sequences in Dubious Vertebral Marrow Pathological Lesions OMAR M. OSMAN, M.D.*;
Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 19, No. 4, December: 254-262, 2007 Role of Diffusion WIs and T 2 * GRE Pulse Sequences in Dubious Vertebral Marrow Pathological Lesions OMAR M. OSMAN, M.D.*;
MSK Tumors and Marrow Evaluation. Bone Marrow
 MSK Tumors and Marrow Evaluation Bone Marrow Thomas M. Link, MD Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging University of California, San Francisco (i) Introduction Bone marrow consists of trabecular
MSK Tumors and Marrow Evaluation Bone Marrow Thomas M. Link, MD Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging University of California, San Francisco (i) Introduction Bone marrow consists of trabecular
Revised Dec Spine MR Protocols
 Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: September 1997 THORACIC SPINE CT Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 72128, 72129, 72130 Last Review Date: May 2013 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_043
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: September 1997 THORACIC SPINE CT Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 72128, 72129, 72130 Last Review Date: May 2013 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_043
MRI Imaging of GP Medicare Eligible Conditions
 MRI Imaging of GP Medicare Eligible Conditions By Dr. Andrew Stuart Radiologist Sydney Adventist Hospital 0562/SAH/1112/SAH Learning Objectives Indications for GP referred Medicare eligible MRI scans MRI
MRI Imaging of GP Medicare Eligible Conditions By Dr. Andrew Stuart Radiologist Sydney Adventist Hospital 0562/SAH/1112/SAH Learning Objectives Indications for GP referred Medicare eligible MRI scans MRI
Bone Marrow Changes on MRI: Self-Assessment Module
 1.5 CME 1.0 SAM AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Bone Marrow Changes on MRI: Self-Assessment Module Catherine C. Roberts 1, William B. Morrison 2, Laura W. Bancroft 3,4, Felix S.
1.5 CME 1.0 SAM AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Bone Marrow Changes on MRI: Self-Assessment Module Catherine C. Roberts 1, William B. Morrison 2, Laura W. Bancroft 3,4, Felix S.
MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect!
 MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect! Poster No.: C-2334 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, M. Paravasthu, M. Bhojak, K. Das ; Warrington/UK, 1 1 1 2 1 2 Liverpool/UK
MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect! Poster No.: C-2334 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, M. Paravasthu, M. Bhojak, K. Das ; Warrington/UK, 1 1 1 2 1 2 Liverpool/UK
Various presentations of multiple myeloma MRI review: A Case series
 Mary Hazarika Bhuyan/ International Journal of Biomedical Research 2015; 6(07): 531-536. 531 International Journal of Biomedical Research ISSN: 0976-9633 (Online); 2455-0566 (Print) Journal DOI: 10.7439/ijbr
Mary Hazarika Bhuyan/ International Journal of Biomedical Research 2015; 6(07): 531-536. 531 International Journal of Biomedical Research ISSN: 0976-9633 (Online); 2455-0566 (Print) Journal DOI: 10.7439/ijbr
Spine. Neuroradiology. Spine. Spine Pathology. Distribution of fractures. Radiological algorithm. Role of radiology 18/11/2015
 Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis
 CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
Vertebral and Paravertebral Diseases
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Vertebral and Paravertebral Diseases John R. Hesselink, M.D. Vertebral / Paravertebral Disease (Extradural) Metastatic disease Primary bone tumors
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Vertebral and Paravertebral Diseases John R. Hesselink, M.D. Vertebral / Paravertebral Disease (Extradural) Metastatic disease Primary bone tumors
Magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with low backache
 Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with low backache Narayan Bikram Thapa 1, Suraj Bajracharya 2 1 Department of Radiology, KIST Medial College Teaching Hospital, Lalitpur,
Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with low backache Narayan Bikram Thapa 1, Suraj Bajracharya 2 1 Department of Radiology, KIST Medial College Teaching Hospital, Lalitpur,
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES
 APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Neck Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Updated June, 2017 Contents
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Neck Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Updated June, 2017 Contents
Spectrum of magnetic resonance imaging findings in chronic low back pain
 Original article: Spectrum of magnetic resonance imaging findings in chronic low back pain Dr Sanjeev Sharma (1), Dr Monika Sharma (2), DR Bhardwaj (3), MD; Dr Asha Negi, (4) Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original article: Spectrum of magnetic resonance imaging findings in chronic low back pain Dr Sanjeev Sharma (1), Dr Monika Sharma (2), DR Bhardwaj (3), MD; Dr Asha Negi, (4) Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Departement of Neurosurgery A.O.R.N A. Cardarelli- Naples.
 Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
Serous Atrophy Of Bone Marrow: A Rare Disorder Worth Getting Acquainted With
 Serous Atrophy Of Bone Marrow: A Rare Disorder Worth Getting Acquainted With Poster No.: C-2535 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. K. Cheong, L. R. Chong; Singapore/SG Keywords: Metabolic
Serous Atrophy Of Bone Marrow: A Rare Disorder Worth Getting Acquainted With Poster No.: C-2535 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. K. Cheong, L. R. Chong; Singapore/SG Keywords: Metabolic
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
Epidemiology of Low back pain
 Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Case Report Solitary Osteolytic Skull Metastasis in a Case of Unknown Primary Being latter Diagnosed as Carcinoma of Gall Bladder
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS CANCER Case Report Solitary Osteolytic Skull Metastasis in a Case of Unknown Primary Being latter Diagnosed as Carcinoma of Gall Kartik Mittal 1, Rajaram Sharma 1, Amit Dey 1, Meet
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS CANCER Case Report Solitary Osteolytic Skull Metastasis in a Case of Unknown Primary Being latter Diagnosed as Carcinoma of Gall Kartik Mittal 1, Rajaram Sharma 1, Amit Dey 1, Meet
Spinal infection. Outline ANATOMY 6/2/2017. Anatomy Pathogen
 Outline Spinal infection Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology, Songklanagarind Hospital Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University Anatomy Pathogen Pyogenic spondylodiscitis Tuberculous
Outline Spinal infection Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology, Songklanagarind Hospital Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University Anatomy Pathogen Pyogenic spondylodiscitis Tuberculous
Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of patients with low back pain and those with sciatica
 87 (98) Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of patients with low back pain and those with sciatica Shobeiri E, Khalatbari M R, Taheri M S, Tofighirad N, Moharamzad Y ABSTRACT Introduction:
87 (98) Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of patients with low back pain and those with sciatica Shobeiri E, Khalatbari M R, Taheri M S, Tofighirad N, Moharamzad Y ABSTRACT Introduction:
The role of MRI in the assessment of bone marrow
 The role of MRI in the assessment of bone marrow Poster No.: C-2180 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, S. Hernandez Muñiz, B. Palomino Aguado,
The role of MRI in the assessment of bone marrow Poster No.: C-2180 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, S. Hernandez Muñiz, B. Palomino Aguado,
Case SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra
 Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients
 Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Abstract. Aim. Materials and methods. Introduction. Results
 Is anatomical distribution helpful for differentiating TB spondylitis from neoplastic causes of extradural spinal cord compression in children? A pilot study Reena George, MD, MMed Rad, FRCR (UK) Savvas
Is anatomical distribution helpful for differentiating TB spondylitis from neoplastic causes of extradural spinal cord compression in children? A pilot study Reena George, MD, MMed Rad, FRCR (UK) Savvas
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013
 Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children
 Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children Noah D. Sabin, M.D. Julie H. Harreld M.D. Kathleen J. Helton M.D. Zoltan Patay M.D., Ph.D. St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, TN Leptomeningeal
Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children Noah D. Sabin, M.D. Julie H. Harreld M.D. Kathleen J. Helton M.D. Zoltan Patay M.D., Ph.D. St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, TN Leptomeningeal
102 Results RESULTS. Age Mean=S.D Range 42= years -84 years Number % <30 years years >50 years
 102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
Ibtisam Nasir Ahmed. MBChB. DMRD. Specialist Radiological Diagnosis. Al-sadr Teaching Hospital. Basrah-Iraq.
 THE VALUE OF CORONAL IMAGE IN DETECTING EXTRA SPINAL LESION IN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF THE SPINE Ibtisam Nasir Ahmed. MBChB. DMRD. Specialist Radiological Diagnosis. Al-sadr Teaching Hospital. Basrah-Iraq.
THE VALUE OF CORONAL IMAGE IN DETECTING EXTRA SPINAL LESION IN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF THE SPINE Ibtisam Nasir Ahmed. MBChB. DMRD. Specialist Radiological Diagnosis. Al-sadr Teaching Hospital. Basrah-Iraq.
A PATIENT WITH TWO EPISODES OF THORACIC SPINAL CORD COMPRESSION CAUSED BY PRIMARY LYMPHOMA AND METASTATIC CARCINOMA OF THE PROSTATE, 11 YEARS APART
 A PATIENT WITH TWO EPISODES OF THORACIC SPINAL CORD COMPRESSION CAUSED BY PRIMARY LYMPHOMA AND METASTATIC CARCINOMA OF THE PROSTATE, 11 YEARS APART Shih-Huang Tai, 1 Yu-Chang Hung, 1 Jian-Chin Chen, 2
A PATIENT WITH TWO EPISODES OF THORACIC SPINAL CORD COMPRESSION CAUSED BY PRIMARY LYMPHOMA AND METASTATIC CARCINOMA OF THE PROSTATE, 11 YEARS APART Shih-Huang Tai, 1 Yu-Chang Hung, 1 Jian-Chin Chen, 2
Whole body MR in patients with multiple myeloma
 Whole body MR in patients with multiple myeloma Alina Piekarek, Piotr Sosnowski, Adam Nowicki, Mieczysław Komarnicki Received: 11.05.2009 Accepted: 13.07.2009 Subject: original article Clinical Radiology
Whole body MR in patients with multiple myeloma Alina Piekarek, Piotr Sosnowski, Adam Nowicki, Mieczysław Komarnicki Received: 11.05.2009 Accepted: 13.07.2009 Subject: original article Clinical Radiology
Pott disease (spinal tuberculosis): MR and CT imaging
 Pott disease (spinal tuberculosis): MR and CT imaging Poster No.: C-1422 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. Beretis, K. Giannaki, M. Fasoula, D. Kypriotis, T. Dagla, T.-P. Mantzouranis;
Pott disease (spinal tuberculosis): MR and CT imaging Poster No.: C-1422 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. Beretis, K. Giannaki, M. Fasoula, D. Kypriotis, T. Dagla, T.-P. Mantzouranis;
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE
 RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
A rare case of cervical epidural extramedullary plasmacytoma presenting with monoparesis
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 1 2017 January - March Article A rare case of cervical epidural extramedullary plasmacytoma presenting with monoparesis Okan Turk, Ibrahim Burak Atci, Hakan Yilmaz,
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 1 2017 January - March Article A rare case of cervical epidural extramedullary plasmacytoma presenting with monoparesis Okan Turk, Ibrahim Burak Atci, Hakan Yilmaz,
Brief History. Identification : Past History : HTN without regular treatment.
 Brief History Identification : Name : 陳 x - Admission : 94/10/06 Gender : male Age : 75 y/o Chief Complaint : Urinary difficulty for months. Past History : HTN without regular treatment. Brief History
Brief History Identification : Name : 陳 x - Admission : 94/10/06 Gender : male Age : 75 y/o Chief Complaint : Urinary difficulty for months. Past History : HTN without regular treatment. Brief History
MRI of Residual Red Bone Marrow in the Distal Femur of Healthy Subjects
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2015; 80: 300-304 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.894118 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2015.03.16 Accepted: 2015.04.04 Published: 2015.06.10 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2015; 80: 300-304 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.894118 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2015.03.16 Accepted: 2015.04.04 Published: 2015.06.10 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Contiguous Spinal Metastasis Mimicking Infectious Spondylodiscitis 감염성척추염과유사하게보였던연속적척추전이의증례
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.73.6.408 감염성척추염과유사하게보였던연속적척추전이의증례 Chul-Min Lee, MD 1, Seunghun Lee, MD 1 *, Jiyoon Bae, MD 2 1 Department of Radiology,
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.73.6.408 감염성척추염과유사하게보였던연속적척추전이의증례 Chul-Min Lee, MD 1, Seunghun Lee, MD 1 *, Jiyoon Bae, MD 2 1 Department of Radiology,
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Evaluation of Compressive Myelopathy in Rohilkhand Region, India
 Mohit Agarwal et al Original article 10.5005/jp-journals-10050-10091 Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Evaluation of Compressive Myelopathy in Rohilkhand Region, India 1 Mohit Agarwal, 2 Pramod
Mohit Agarwal et al Original article 10.5005/jp-journals-10050-10091 Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Evaluation of Compressive Myelopathy in Rohilkhand Region, India 1 Mohit Agarwal, 2 Pramod
The surgical treatment of metastatic disease of the spine
 The surgical treatment of metastatic disease of the spine Péter Banczerowski National Institute of Neurosurgery, Budapest Spine tumours 15% of the primary tumours of the CNS affect the spine The spine
The surgical treatment of metastatic disease of the spine Péter Banczerowski National Institute of Neurosurgery, Budapest Spine tumours 15% of the primary tumours of the CNS affect the spine The spine
Case Conference: SBRT for spinal metastases D A N I E L S I M P S O N M D 3 / 2 7 / 1 2
 Case Conference: SBRT for spinal metastases D A N I E L S I M P S O N M D 3 / 2 7 / 1 2 Case 79 yo M with hx of T3N0 colon cancer diagnosed in 2008 metastatic liver disease s/p liver segmentectomy 2009
Case Conference: SBRT for spinal metastases D A N I E L S I M P S O N M D 3 / 2 7 / 1 2 Case 79 yo M with hx of T3N0 colon cancer diagnosed in 2008 metastatic liver disease s/p liver segmentectomy 2009
T2, T2*, ute. Yeo Ju Kim. Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea
 SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis
 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
A Journey Down The Canal
 A Journey Down The Canal Radiological Assessment of Spinal Cord Masses John Berry-Candelario HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC Objectives Patient review Anatomy of the spine Imaging techniques Classification
A Journey Down The Canal Radiological Assessment of Spinal Cord Masses John Berry-Candelario HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC Objectives Patient review Anatomy of the spine Imaging techniques Classification
Bone Marrow Signal Alteration in the Spine and Sacrum
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Long et al. one Marrow Signal lteration in the Spine and Sacrum Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.204.179 on 12/22/17
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Long et al. one Marrow Signal lteration in the Spine and Sacrum Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.204.179 on 12/22/17
INDICATIONS FOR IMAGING IN DISORDERS OF THE AXIAL SKELETON
 INDICATIONS FOR IMAGING IN DISORDERS OF THE AXIAL SKELETON Geert Vanderschueren, MD, PhD Department of Musculoskeletal Radiology UZ Leuven, Leuven, Belgium 1111 DIFFERENT TOPICS 1. MRI: PATIENT S CHECKLIST
INDICATIONS FOR IMAGING IN DISORDERS OF THE AXIAL SKELETON Geert Vanderschueren, MD, PhD Department of Musculoskeletal Radiology UZ Leuven, Leuven, Belgium 1111 DIFFERENT TOPICS 1. MRI: PATIENT S CHECKLIST
Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C.
 Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
Module 1: Basic Comprehensive Course
 The Hellenic Spine Society organize 5 modules according to the following program, which is based on the Eurospine program Module 1: Basic Comprehensive Course SESSION1: SPINE THE BIGGER PICTURE Evidence
The Hellenic Spine Society organize 5 modules according to the following program, which is based on the Eurospine program Module 1: Basic Comprehensive Course SESSION1: SPINE THE BIGGER PICTURE Evidence
1/9/2013 EXTRAMEDULLARY TUMORS OF THE PEDIATRIC SPINE. Introduction. Classification for Extramedullary Tumors
 EXTRAMEDULLARY TUMORS OF THE PEDIATRIC SPINE Eugene Wang 1/20/12 Dent Neurologic Institute Introduction 2/3 of all intraspinal tumors of childhood are extramedullary 50% Extradural 10-15% Intradural Back
EXTRAMEDULLARY TUMORS OF THE PEDIATRIC SPINE Eugene Wang 1/20/12 Dent Neurologic Institute Introduction 2/3 of all intraspinal tumors of childhood are extramedullary 50% Extradural 10-15% Intradural Back
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 51. Primary Neoplasms
 51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Vertebral Compression Fractures
 Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Vertebral Compression Fractures Andrea Baur-Melnyk and Tobias Geith Contents 1 Epidemiology and Clinical Background... 145 2 Conventional Imaging Techniques in the
Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Vertebral Compression Fractures Andrea Baur-Melnyk and Tobias Geith Contents 1 Epidemiology and Clinical Background... 145 2 Conventional Imaging Techniques in the
Suspecting Tumors, or Could it be cancer?
 Suspecting Tumors, or Could it be cancer? Donna E. Reece, M.D. Princess Margaret Cancer Centre University Health Network Toronto, ON CANADA 07 February 2018 Background Low back pain is common However,
Suspecting Tumors, or Could it be cancer? Donna E. Reece, M.D. Princess Margaret Cancer Centre University Health Network Toronto, ON CANADA 07 February 2018 Background Low back pain is common However,
醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 肌肉骨骼磁振造影. 本週課程內容 General Technical Considerations 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系
 本週課程內容 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系 alvin4016@ym.edu.tw MRI of the musculoskeletal system (5th/6th edition) Editor: Thomas H. Berquist MD 2 General
本週課程內容 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系 alvin4016@ym.edu.tw MRI of the musculoskeletal system (5th/6th edition) Editor: Thomas H. Berquist MD 2 General
MRI XR, CT, NM. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # 2. Date accepted: 15 March 2013
 Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
Spinal epidural space on MRI: Abnormal findings on MRI in patients with spinal haematoma, infection and malignancy.
 Spinal epidural space on MRI: Abnormal findings on MRI in patients with spinal haematoma, infection and malignancy. Poster No.: C-1335 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Howard, E.
Spinal epidural space on MRI: Abnormal findings on MRI in patients with spinal haematoma, infection and malignancy. Poster No.: C-1335 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Howard, E.
objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University
 objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University To determine the regions of physiologic activity To understand
objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University To determine the regions of physiologic activity To understand
MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow
 Clinical Orthopedic Imaging MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow Johan Dehem, M.D. VZW Jan Yperman, Ieper, Belgium Cervical spine imaging
Clinical Orthopedic Imaging MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow Johan Dehem, M.D. VZW Jan Yperman, Ieper, Belgium Cervical spine imaging
Brain Tumors. What is a brain tumor?
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Marrow: Red, Yellow and Bad
 Marrow: Red, Yellow and Bad R. Paul Guillerman, MD Associate Professor of Radiology Baylor College of Medicine Department of Pediatric Radiology Texas Children s Hospital Houston, Texas Disclosure of Commercial
Marrow: Red, Yellow and Bad R. Paul Guillerman, MD Associate Professor of Radiology Baylor College of Medicine Department of Pediatric Radiology Texas Children s Hospital Houston, Texas Disclosure of Commercial
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PREVALENCE OF MODIC DEGENERATIVE MARROW CHANGES IN THE CERVICAL SPINE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : PREVALENCE OF MODIC DEGENERATIVE MARROW CHANGES IN THE CERVICAL SPINE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 prevalence of modic degenerative marrow changes in the cervical spine prevalence
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PREVALENCE OF MODIC DEGENERATIVE MARROW CHANGES IN THE CERVICAL SPINE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 prevalence of modic degenerative marrow changes in the cervical spine prevalence
MSCC CARE PATHWAYS & CASE STUDIES. By Michael Balloch Spine CNS
 MSCC CARE PATHWAYS & CASE STUDIES By Michael Balloch Spine CNS Aims To be familiar with the routes of MSCC prentaion How the guidelines work in practice Routes of presentation Generic intervention Managing
MSCC CARE PATHWAYS & CASE STUDIES By Michael Balloch Spine CNS Aims To be familiar with the routes of MSCC prentaion How the guidelines work in practice Routes of presentation Generic intervention Managing
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN
 ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
Imaging Choices in Occult Hip Fracture
 Introduction Imaging Choices in Occult Hip Fracture Jesse Cannon, MD; Salvatore Silvestri, MD; Mark Munro, MD J Emerg Med. 2009;32(3):144-152 Reporter PGY 宋兆家 Supervisor VS 侯勝文 990220 High dependence on
Introduction Imaging Choices in Occult Hip Fracture Jesse Cannon, MD; Salvatore Silvestri, MD; Mark Munro, MD J Emerg Med. 2009;32(3):144-152 Reporter PGY 宋兆家 Supervisor VS 侯勝文 990220 High dependence on
Imaging: When to get MRI, CT or PET-CT?
 Imaging: When to get MRI, CT or PET-CT? Alina Uzelac, D.O. Assistant Clinical Professor Neuroradiology UCSF Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging San Francisco General Hospital Overview CT MRI
Imaging: When to get MRI, CT or PET-CT? Alina Uzelac, D.O. Assistant Clinical Professor Neuroradiology UCSF Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging San Francisco General Hospital Overview CT MRI
Pictorial review of bone marrow patterns in MRI.
 Pictorial review of bone marrow patterns in MRI. Poster No.: C-1915 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. Martínez Paredes, D. Abellán Rivero, E. LOPEZ BANET, 1 2 2 2 2 M. C. Gutierrez
Pictorial review of bone marrow patterns in MRI. Poster No.: C-1915 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. Martínez Paredes, D. Abellán Rivero, E. LOPEZ BANET, 1 2 2 2 2 M. C. Gutierrez
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions
 CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
Objectives. Comprehension of the common spine disorder
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Disclosure. Acknowledgement. What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Rectal cancer imaging. None
 What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
CNS Imaging. Dr Amir Monir, MD. Lecturer of radiodiagnosis.
 CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
Granulocyte-Stimulating Factor-Induced Bone Marrow Reconversion Simulating Neuroblastoma Metastases on MRI: Case Report and Literature Review
 Radiology Case Reports Volume II, Issue 1, 2007 Granulocyte-Stimulating Factor-Induced Bone Marrow Reconversion Simulating Neuroblastoma Metastases on MRI: Case Report and Literature Review Jason C. Naples,
Radiology Case Reports Volume II, Issue 1, 2007 Granulocyte-Stimulating Factor-Induced Bone Marrow Reconversion Simulating Neuroblastoma Metastases on MRI: Case Report and Literature Review Jason C. Naples,
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 65. Benign Hepatic Masses
 65. Benign Hepatic Masses Pulse sequences acquired for abdominal MRI typically consist of fast acquisition schemes such as single-shot turbo spin echo (i.e. HASTE) and gradient echo schemes such as FLASH
65. Benign Hepatic Masses Pulse sequences acquired for abdominal MRI typically consist of fast acquisition schemes such as single-shot turbo spin echo (i.e. HASTE) and gradient echo schemes such as FLASH
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Evaluation of Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease with Clinical Correlation
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/319 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Evaluation of Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease with Clinical Correlation Avadhesh P.
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/319 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Evaluation of Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease with Clinical Correlation Avadhesh P.
Evaluation of Degenerative Lumbosacral Diseases and Common Location of Disc Herniations causing Radiculopathy
 Original Article Evaluation of Degenerative Lumbosacral Diseases and Common Location of Disc Herniations causing Radiculopathy DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/27541:2282 Radiology Section Mallikarjun MD, Chetan
Original Article Evaluation of Degenerative Lumbosacral Diseases and Common Location of Disc Herniations causing Radiculopathy DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/27541:2282 Radiology Section Mallikarjun MD, Chetan
Abdominal applications of DWI
 Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Whole body Diffusion Weighted MRI (WB-DWI) in the assessment and treatment response of multiple myeloma (MM).
 Whole body Diffusion Weighted MRI (WB-DWI) in the assessment and treatment response of multiple myeloma (MM). Poster No.: C-1467 Congress: ECR 01 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Mahatma, A. Gogbashian,
Whole body Diffusion Weighted MRI (WB-DWI) in the assessment and treatment response of multiple myeloma (MM). Poster No.: C-1467 Congress: ECR 01 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Mahatma, A. Gogbashian,
Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging as a Potential Tool in Differentiation of Vertebral Bone Marrow Lesions
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 81, No. 2, September: 249-259, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging as a Potential Tool in Differentiation of Vertebral Bone
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 81, No. 2, September: 249-259, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging as a Potential Tool in Differentiation of Vertebral Bone
Primary care referral criteria for musculoskeletal MRI scans
 Appendix 1 Primary care referral criteria for musculoskeletal MRI scans Accepted Criteria for Direct Access MRI Body Part Symptoms Imaging indicated Lumbar Spine Low Back Pain with adverse symptoms or
Appendix 1 Primary care referral criteria for musculoskeletal MRI scans Accepted Criteria for Direct Access MRI Body Part Symptoms Imaging indicated Lumbar Spine Low Back Pain with adverse symptoms or
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol.69 (2), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol.69 (2), Page 1889-1894 Role of MRI in the Diagnosis of Different Bone Marrow Lesions in Pediatric Patients with Hematological Malignancies Hanan
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol.69 (2), Page 1889-1894 Role of MRI in the Diagnosis of Different Bone Marrow Lesions in Pediatric Patients with Hematological Malignancies Hanan
Clinical Appropriateness Guidelines: Advanced Imaging
 Clinical Appropriateness Guidelines: Advanced Imaging Appropriate Use Criteria: Imaging of Bone Marrow Blood Supply Effective Date: September 5, 2017 Proprietary Date of Origin: 05/21/2007 Last revised:
Clinical Appropriateness Guidelines: Advanced Imaging Appropriate Use Criteria: Imaging of Bone Marrow Blood Supply Effective Date: September 5, 2017 Proprietary Date of Origin: 05/21/2007 Last revised:
Magnetic resonance imaging in acute spinal trauma: Pictorial essay
 Magnetic resonance imaging in acute spinal trauma: Pictorial essay Poster No.: C-1463 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Khurana 1, S. Manchanda 1, N. Rajpal 1, S. Agrawal 1, S. Gupta
Magnetic resonance imaging in acute spinal trauma: Pictorial essay Poster No.: C-1463 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Khurana 1, S. Manchanda 1, N. Rajpal 1, S. Agrawal 1, S. Gupta
Malignant Spinal cord Compression. Dr. Thiru Thirukkumaran Palliative Care Services - Northwest Tasmania
 Malignant Spinal cord Compression Dr. Thiru Thirukkumaran Palliative Care Services - Northwest Tasmania Background Statistics of SCC -1 Incidence of SCC Vertebral body metastases 85 % Para-vertebral (Lymphoma)
Malignant Spinal cord Compression Dr. Thiru Thirukkumaran Palliative Care Services - Northwest Tasmania Background Statistics of SCC -1 Incidence of SCC Vertebral body metastases 85 % Para-vertebral (Lymphoma)
Diagnostics of Spondylodiscitis and its most frequent complications
 Diagnostics of Spondylodiscitis and its most frequent complications Poster No.: C-1536 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Veselova, V. Mazaev, M. Molodtsov; Moscow/RU Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Diagnostics of Spondylodiscitis and its most frequent complications Poster No.: C-1536 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Veselova, V. Mazaev, M. Molodtsov; Moscow/RU Keywords: Musculoskeletal
MRI assessment of vertebral fractures identified by conventional radiography in osteoporotic patients: a preliminary study
 MRI assessment of vertebral fractures identified by conventional radiography in osteoporotic patients: a preliminary study Poster No.: C-1405 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Argirò,
MRI assessment of vertebral fractures identified by conventional radiography in osteoporotic patients: a preliminary study Poster No.: C-1405 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Argirò,
Disseminated Primary Non-Hodgkin s Lymphoma of Bone : A Case Re p o r t 1
 Disseminated Primary Non-Hodgkin s Lymphoma of Bone : A Case Re p o r t 1 Hee-Jin Park, M.D., Sung-Moon Lee, M.D., Hee-Jung Lee, M.D., Jung-Sik Kim, M.D., Hong Kim, M.D. Primary lymphoma of bone is uncommon
Disseminated Primary Non-Hodgkin s Lymphoma of Bone : A Case Re p o r t 1 Hee-Jin Park, M.D., Sung-Moon Lee, M.D., Hee-Jung Lee, M.D., Jung-Sik Kim, M.D., Hong Kim, M.D. Primary lymphoma of bone is uncommon
ADI Procedure Codes. August 2016 Revised April 2017 Page 1 of 7 ADI Procedure Codes
 Code Description 70450 CT Head without contrast 70460 CT Head with contrast 70470 CT Head with & without contrast 70480 CT Orbit, et al without contrast 70481 CT Orbit, et al with contrast 70482 CT Orbit,
Code Description 70450 CT Head without contrast 70460 CT Head with contrast 70470 CT Head with & without contrast 70480 CT Orbit, et al without contrast 70481 CT Orbit, et al with contrast 70482 CT Orbit,
High Field MR of the Spine
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine uses radio waves, a magnetic field and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the spine
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine uses radio waves, a magnetic field and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the spine
Multiple Myeloma: diagnosis and prognostic factors. N Meuleman May 2015
 Multiple Myeloma: diagnosis and prognostic factors N Meuleman May 2015 Diagnosis Diagnostic assessment of myeloma: what should we know? Is it really a myeloma? Is there a need for treatment? What is the
Multiple Myeloma: diagnosis and prognostic factors N Meuleman May 2015 Diagnosis Diagnostic assessment of myeloma: what should we know? Is it really a myeloma? Is there a need for treatment? What is the
Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors
 Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors Lars Stegger, Benjamin Noto Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to
Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors Lars Stegger, Benjamin Noto Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to
