Sickle Cell Disease- Case studies
|
|
|
- Alice Nelson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sickle Cell Disease- Case studies Subarna Chakravorty King s College Hospital 2017 Conditions requiring immediate admission Agonising pain (i.e. requiring opiate analgesia) Increased pallor, breathlessness, exhaustion Marked pyrexia (> 38 o C), tachycardia or tachypnoea, hypotension Chest pain; signs of lung consolidation Abdominal pain or distension, diarrhoea, vomiting Severe thoracic/back pain Headache, drowsiness, CVA, TIA or any abnormal CNS signs Priapism (> 4 hours) 1
2 Haemoglobinopathy- global perspective 5% of the world s population carry a haemoglobinopathy mutation, either sickle cell or thalassaemia 300,000 children are born annually worldwide with a major haemoglobinopathy, including 200,00 in Africa with sickle cell anaemia Distribution of sickle carrier status varies according to geographical region Sickle cell disease is now the most common genetic disorder in the UK, affecting over 1 in 2000 live births and up to 1 in 300 births in some urban areas WHO Provisional agenda item 11.4 Main types of Sickle Cell Disease Name Sickle cell anaemia SC disease Sickleb 0 thalassaemia Sickleb + thalassaemia Other names HbSS (homozygous) HbSC S-β 0 thal S-β + thal 2
3 Rees et al Lancet 2010; 376: Complications of SCD- acute Painful crisis Susceptibility to infection due to functional asplenia Dactylitis Sequestration crisis- hepatic/splenic Chest crisis Priapism Stroke 3
4 UK standards of treatment New born screening Penicillin prophylaxis Regular hospital clinic review Additional vaccination (Pneumovax, influenza) Transcranial doppler from age 2-16 Parent and patient education Transition to adult Support of emergency admissions including analgesia within 30 minutes of presentation Case 1 7 y/o girl, HbSS arrived at A&E department with severe left leg and left arm pain. Pain score 8.5/10 Hb 80g/L MCV 68fl, Neutrophils 11 x10*9/l, Platelets 505 x10*9/l, Reticulocytes 276 x10*9/l, LDH 650IU/L Treated with oral morphine with some initial response. IV fluids started as mildly dehydrated, continued with usual penicillin prophylaxis as not febrile 4
5 Case 1a Needed 2 doses of morphine in A&E- admitted to the ward on regular morphine (300mcg/kg every 4 hours). IV fluids continue. Adjunct therapy with regular paracetamol and ibuprofen Morphine continued regularly for 48 hours, and then changed to PRN IV fluids discontinued on day 1 as patient drinking well Laxatives started with morphine, good response after 48 hours Discharged home on Day 3 (Repeat FBC on day 3- no change) Case 1b No response to 2 doses of oramorph in A&E Intravenous morphine started on a PCA pump, along with optimum doses of paracetamol and ibuprofen IV morphine infusion complicated by nausea and itch- treated with naloxone and ondansetron Repeat FBC in 24 hours : Hb 65g/L MCV 68fl, Neutrophils 18 x10*9/l, Platelets 525 x10*9/l, Reticulocytes 450 x10*9/l CRP 118 mg/l 5
6 Case 1b IV fluids continued as reluctant to drink IV antibiotics (due to low grade fever and high CRP) 72 hours of IV morphine Changed to regular oral morphine and subsequently stopped Home on oral antibiotics and a supply of dihydrocodeine. Hb on discharge 72g/l Case 1c No response to 2 doses of oramorph in A&E Intravenous morphine started on a PCA pump, along with optimum doses of paracetamol and ibuprofen. Low grade fever, CXR done Febrile, and noted to have increased work of breathing on Day 2. Started IV broad spectrum antibiotics and macrolide. Nasopharyngeal aspirate sent for respiratory viral screen Repeat FBC in 24 hours : Hb 65g/L MCV 68fl, Neutrophils 18 x10*9/l, Platelets 525 x10*9/l, Reticulocytes 450 x10*9/l CRP 118 mg/l 6
7 Case 1c Day 1 Day 3 Case 1c continued Top up transfusion Optiflow Transfer to HDU for observation Good response to above measures Back on ward after 2 days in HDU Incentive spirometry Home on day 7 following morphine wean and completion of IV antibiotics 7
8 Case 2 9 year old girl with HbSS PMH- Splenectomy age 7 for recurrent sequestration crisis, frequent vaso occlusive crises leading to school absenteeism Mum community nurse, had previously declined hydroxycarbamide Case 2-presentation Presented to local hospital with chest and arm pain following 7 days of fever and cough at home, CXR showed bilateral infiltrates Rapid deterioration in 72 hours with worsening respiratory symptoms and anaemia. R elbow swollen Day 4 of admission to local hospital- respiratory failure, intubated and ventilated locally by specialist transfer team 8
9 PICU Case 1- progress High ventilatory requirement High frequency oscillation and NO Triple inotropes, broad spectrum antibiotics Full volume red cell exchange transfusion R brachial vein thrombosis- LMWH for 12 weeks Day 1 PICU Day 2 PICU 9
10 Case 1- outcome Prolonged ventilation (10 days) Successful ventilatory wean No renal failure Discussions with local hospital regarding early warning scores in chest crisis and early referral for respiratory support and exchange transfusion ACS High index of suspicion Oxygen saturation in air: if <95% and no past history of hypoxia: CXR If Oxygen saturation in air: <95%-, increased respiratory effort, new infiltrates on CXR, chest pain- may need ventilatory support and red cell exchange transfusion Severe respiratory failure in about 2-5% (? Delayed diagnosis)- invasive ventilation 10
11 Treatment of recurrent chest crisis Hydroxycarbamide Chemotherapy agent licensed for many cancershas been used in SCD for 15 years, even in very young children Usually started at a lower dose, and then increased to maximum of 25mg/kg/d Among other beneficial effects, it increases Fetal haemoglobin levels, which is protective Reduced incidence of painful crises, chest crises, duration of admission with painful crises, Sepsis Universal prophylaxis with Penicillin V, Pneumovax/HiB/MenC/Prevenar, Double up PenV when unwell at home Seek medical help if high fever, cough, pallor, lethargy Prompt assessment for sepsis : Vital signs Septic screen: Clinical and laboratory including blood and urine cultures, Xray Prompt institution of antibiotics as indicated 11
12 Sepsis Osteomyelitis/septic arthritis: may present with localised pain and fever- relatively rare in UK, often mimics VOE X ray of bone usually unhelpful- MRI is investigation of choice, but can still be nondiagnostic Gold standard- positive blood cultures. Septic joints need evacuation Prolonged course of antibiotics upto 8 weeks IV or oral, depending on pathogen Most cases of presumed OM are likely VOE Sepsis- malaria High index of suspicion in febrile children returning from holiday from endemic areas Blood film for malaria parasite Beware of G6PD deficiency 12
13 Case 3 3 year old girl (Hb SS) PMH 2 vaso-occlusive crises requiring hospital admission Recurrent splenic sequestration Anti-S allo antibody Needlephobia Day 1 (local hosp) Febrile, Splenic sequestration Hb 34g/L Day 2 Transfused. Taz + Gent 7days Day 7 Discharged Day 8-9 Respiratory distress, metabolic acidosis. Hb 20 (post tx) Flying squad blood Day 8 Transfused Hb Day 8 (readmission) dark urine, LUQ abdo pain, leg pain, jaundiced, pale, febrile Day 9 Transferred to PICU Day 10 IVIG 2g/kg Methypred 3mg/kg RBC tx Day 17 Hb 39, transfused. Methylpred 13
14 Tx 25/09/2017 Complexity of Case 2 Manifestations of an acute or delayed haemolytic transfusion reaction. Antibodies Anti S (known for 1 year; Emergency O neg blood was S positive) Anti C developed subsequent to recent admission Marked reticulocytopenia Development of a more severe anaemia after transfusion Subsequent transfusions may further exacerbate the anaemia and therefore required significant immunosuppression 14
15 Case 3: Outcome Recovered well despite needing further transfusion and immunosuppression on day 17 Needs splenectomy to prevent recurrent sequestration crisis- life threatening in an untransfusable child Baseline Hb 6 g/dl- but untransfusable Therefore erythropoietin and hydroxycarbamide given to increase pre op Hb-surgery 6 year old girl (HbSS) Case 4 Recurrent infections previous UTI, pneumonia, and recurrent vaso- occlusive episodes Persistent raised transcranial doppler velocity for 12 months, parents not agreed to start transfusion Adenotonsillectomy Hydroxycarbamide started 2 months earlier 15
16 Case 4- clinical progress Fever + cough for 4 days at home Unresponsiveness + hypertonic episode at homeadmitted to local hospital Hb 45g/l- top up transfusion, transfer to PICU. MRI : New watershed infarcts (normal MRI/MRA 12 months ago). No neurological deficit- hence defined as silent cerebral infarction (SCI) MRA : MCA stenosis and collateral vessel formation Parvovirus IgM positive- Aplastic crisis and silent cerebral infarct MRI scan of brain showing new infarct 16
17 MRA Case 4- outcome No neurological deficit Neuropsychometry shows significant abnormalities in processing, memory and FSIQ Chronic transfusion therapy for SCI and primary stroke prevention Brother HLA match- underwent successful bone marrow transplant with normalisation of TCD velocities and SCI. 17
18 Cerebral vasculopathy in sickle cell disease 11% of patients with sickle cell anaemia have a stroke by age 20 yrs (Ohene- Frempong, 1998)- 75% ischaemic, 25% haemorrhagic Most frequent cause of ischaemic stroke is blockage of intracranial ICA or MCA 24% of patients by age 45 yrs (Ohene-Frempong) Highest risk in first decade of life: 1% per year 2-5 years 1.02 per 100 patient years 6-9 years Strokes recur in 2/3 of patients, mostly within 2-3 years of the initial event (Powars, 1978) Children with SCD are at 300 times higher risk of developing strokes compared to their normal counterparts Risk factors for stroke in SCD High blood flow velocity on transcranial Doppler (TCD), low hemoglobin high white cell count Hypertension silent brain infarction history of chest crisis Familial predisposition Nocturnal hypoxaemia Exchange transfusion 18
19 Transfusion therapy to prevent recurrent strokes If left untreated, about 90% of children with a stroke will have a recurrence Transfusion therapy to keep S% to <30% causes reduction of this recurrence to <10% Russell et al, Blood, This study also demonstrated for the first time that pathophysiology of stokes was due to arterial stenosis in the Circle of Willis rather than distal capillary or venular occlusion Emergency management of stroke in sickle cell disease High index of suspicion Thorough physical examination Often coexists with chest syndrome May known to be at risk Urgent imaging Involve neurologists early Exchange transfusion 19
20 Role of transfusion Raised cerebral blood-flow velocities related to severe anemia, vessel stenosis, cerebral vasodilatation caused by tissue hypoxia. Transfusion reduces cerebral blood flow velocities by correcting these abnormalities to some degree, and may explain the reduction in stroke risk Detection of at-risk children Transcranial doppler Adams et al NEJM TCD can identify the children with sickle cell disease who are at highest risk for cerebral infarction. 190 children with SCD (3-18) were followed up for average of 29 months- children with abnormal TCDs were at a significantly higher risk of developing strokes (p< ) Longer term follow up ( up to 4 years of 315 children ) showed similar rates of pick up 20
21 Transcranial doppler screening Risk of overt stroke in 3 years TAMMV Abnormal Conditional Normal Annual screening SS/Sβ y 2% 40% 7% >200 cm/s cm/s Adams NEJM 1992 Annals neurol Source: Nat Clin Pract neurol 2007 Stroke-free survival vs TCD velocities Adams NEJM
22 Case 5 8 y/o boy HbSS Severe abdo pain and distension BNO for 4 days Admitted with IV fluids and 22
23 Other complications of SCD Aplastic (severe anaemia, reticulocytopaenia), Parvovirus IgM/ PCR positive Priapism-past h/o stuttering priapism Sequestration syndrome-hepatosplenomegaly Girdle Syndrome-ileus Hyperahaemolysis-severe pallor, jaundice, reticlocytosis Delayed transfusion reaction, jaundice and pallor 23
24 Avascular necrosis Nocturnal enuresis Chronic pain School absenteeism for health reasons Socially deprived backgrounds- problems with housing, cross infection, learning difficulty Lack of self esteem, bullying, poverty, unemployment, lack of understanding of own disease Hydroxycarbamide Only agent to have shown significant efficacy in RCT Reduction in number and duration of painful crises Reduction in chest crises Increase in well being, Hb, HbF Prolongation of life expectancy Reduction of long term organ damage 24
25 Blood transfusion in SCD Children may present with severe haemolysis and anaemia during a painful crisis and may require a top-up transfusion Sequestration and aplastic crises need to be urgently treated with blood transfusion and can be life saving Acute chest crisis, stroke and sever painful crises also need transfusion- usually exchange transfusion- aim is to reduce HbS% to<20% Blood transfusion in Sickle Acute exchange transfusions are critical procedures and can precipitate stroke Best done in ITU in children Routine exchanges are performed in children with strokes or increased risk of stroke- this is to reduce HbS% as well as minimise the risk of transfusional iron overload- this can be done as OPD Automated red cell exchanges can reduce further the risk of iron overload 25
26 SCD in adolescents Chronic disease Quality of life issues Chronic pain Substance abuse Relationships Moving from paediatric to adult services Exams, university, jobs 26
Sickle cell disease. Fareed Omar 10 March 2018
 Sickle cell disease Fareed Omar 10 March 2018 Physiology Haemoglobin structure HbA2: 2α and 2δ chains (2-3%) HbF: 2α and 2γ chains (
Sickle cell disease Fareed Omar 10 March 2018 Physiology Haemoglobin structure HbA2: 2α and 2δ chains (2-3%) HbF: 2α and 2γ chains (
Guideline for the Management of Acute Chest Syndrome in Children with Sickle Cell Disease
 Guideline for the Management of Acute Chest Syndrome in Children with Sickle Cell Disease Definition Acute chest syndrome (ACS) is defined as an acute illness characterized by fever and/or respiratory
Guideline for the Management of Acute Chest Syndrome in Children with Sickle Cell Disease Definition Acute chest syndrome (ACS) is defined as an acute illness characterized by fever and/or respiratory
Guidelines on the Management of a Child with Sickle Cell Disease and low Haemoglobin
 Guidelines on the Management of a Child with Sickle Cell Disease and low Haemoglobin Document Information Version: 2 Date: 28 th December 2013 Authors (incl. job title): Professor David Rees (Consultant
Guidelines on the Management of a Child with Sickle Cell Disease and low Haemoglobin Document Information Version: 2 Date: 28 th December 2013 Authors (incl. job title): Professor David Rees (Consultant
Guidelines on the Management of a Child with Sickle Cell Disease and low Haemoglobin
 Guidelines on the Management of a Child with Sickle Cell Disease and low Haemoglobin Version: 6 Date: 2 nd March 2010 Authors: Responsible committee or Director: Review date: Target audience: Stakeholders/
Guidelines on the Management of a Child with Sickle Cell Disease and low Haemoglobin Version: 6 Date: 2 nd March 2010 Authors: Responsible committee or Director: Review date: Target audience: Stakeholders/
The Management of Acute Chest Syndrome in Children with Sickle Cell Disease
 The Management of Acute Chest Syndrome in Children with Sickle Cell Disease Document Information Version: 4 Date: Dec 2013 Authors (incl. job title): Professor David Rees and Dr Sue Height, consultant
The Management of Acute Chest Syndrome in Children with Sickle Cell Disease Document Information Version: 4 Date: Dec 2013 Authors (incl. job title): Professor David Rees and Dr Sue Height, consultant
Sickle Cell Disease. Edward Malters, MD
 Sickle Cell Disease Edward Malters, MD Introduction Vaso-occlusive phenomena and hemolysis are the clinical hallmarks of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) Inherited disorder due to homozygosity for the abnormal
Sickle Cell Disease Edward Malters, MD Introduction Vaso-occlusive phenomena and hemolysis are the clinical hallmarks of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) Inherited disorder due to homozygosity for the abnormal
Health Maintenance and Education for Children and Adults
 Health Maintenance and Education for Children and Adults Richard Ward, MSc, MRCP, FRCPath Director, Red Blood Cell Disorders Program, UHN Assistant Professor, Hematology, University of Toronto Chair, Canadian
Health Maintenance and Education for Children and Adults Richard Ward, MSc, MRCP, FRCPath Director, Red Blood Cell Disorders Program, UHN Assistant Professor, Hematology, University of Toronto Chair, Canadian
Drug and Therapeutics committee, Clinical Haematology Directorate. Department of Haematology, Nottingham City Hospital
 Version: 5 Date: 03/08/2005 Date Ratified: 03/08/2005 Date Reviewed 3/08/2017 Date due for Review: August 2018 Approval: Author: Drug and Therapeutics committee, Clinical Haematology Directorate Dr Jennifer
Version: 5 Date: 03/08/2005 Date Ratified: 03/08/2005 Date Reviewed 3/08/2017 Date due for Review: August 2018 Approval: Author: Drug and Therapeutics committee, Clinical Haematology Directorate Dr Jennifer
Congenital Haemoglobinopathies
 Congenital Haemoglobinopathies L. DEDEKEN, MD H O P I T A L U N I V E R S I T A I R E D E S E N F A N T S R E I N E F A B I O L A U N I V E R S I T E L I B R E DE B R U X E L L E S Red Blood Cell Disorders
Congenital Haemoglobinopathies L. DEDEKEN, MD H O P I T A L U N I V E R S I T A I R E D E S E N F A N T S R E I N E F A B I O L A U N I V E R S I T E L I B R E DE B R U X E L L E S Red Blood Cell Disorders
Managing Emergencies
 Managing Emergencies Richard Ward, MSc, MRCP, FRCPath Director, Red Blood Cell Disorders Program, UHN Assistant Professor, Hematology, University of Toronto Chair, Canadian Hemoglobinopathy Association
Managing Emergencies Richard Ward, MSc, MRCP, FRCPath Director, Red Blood Cell Disorders Program, UHN Assistant Professor, Hematology, University of Toronto Chair, Canadian Hemoglobinopathy Association
Guideline for the Acute Management of Stroke in Paediatric Patients with Sickle Cell Disease
 Guideline for the Acute Management of Stroke in Paediatric Patients with Sickle Cell Disease Summary Outline of the presentation of stroke in paediatric patients with sickle cell disease, urgent investigations,
Guideline for the Acute Management of Stroke in Paediatric Patients with Sickle Cell Disease Summary Outline of the presentation of stroke in paediatric patients with sickle cell disease, urgent investigations,
Guidelines for Shared Care Centres and Community Staff
 Reference: CG1411 Written by: Dr Jenny Welch Peer reviewer Dr Jeanette Payne Approved: September 2015 Approved by D&TC: 10 th July 2015 Review Due: September 2018 Intended Audience This document contains
Reference: CG1411 Written by: Dr Jenny Welch Peer reviewer Dr Jeanette Payne Approved: September 2015 Approved by D&TC: 10 th July 2015 Review Due: September 2018 Intended Audience This document contains
Emergency Presentations of Sickle cell disease. Dr S Pancham Sickle Cell & Thalassaemia Centre City Hospital
 Emergency Presentations of Sickle cell disease Dr S Pancham Sickle Cell & Thalassaemia Centre City Hospital Aims Key features to elicit at presentation What complications to look for When to phone for
Emergency Presentations of Sickle cell disease Dr S Pancham Sickle Cell & Thalassaemia Centre City Hospital Aims Key features to elicit at presentation What complications to look for When to phone for
Guidelines for the Immediate Management of Paediatric Patients with Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) and Acute Neurological Symptoms
 Guidelines for the Immediate Management of Paediatric Patients with Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) and Acute Neurological Symptoms Document Information Version: 2 Date: Sept 2014 Authors (incl. job title):
Guidelines for the Immediate Management of Paediatric Patients with Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) and Acute Neurological Symptoms Document Information Version: 2 Date: Sept 2014 Authors (incl. job title):
Dr Banu Kaya Consultant Haematologist Barts Health NHS Trust Royal London Hospital, London, UK SICKLE CELL AND THALASSAEMIA OVERVIEW
 Dr Banu Kaya Consultant Haematologist Barts Health NHS Trust Royal London Hospital, London, UK SICKLE CELL AND THALASSAEMIA OVERVIEW Objectives Gain awareness of haemoglobinopathy inheritance, pathophysiology
Dr Banu Kaya Consultant Haematologist Barts Health NHS Trust Royal London Hospital, London, UK SICKLE CELL AND THALASSAEMIA OVERVIEW Objectives Gain awareness of haemoglobinopathy inheritance, pathophysiology
Hydroxyurea (Hydroxycarbamide) - Guidelines for treating children with Sickle Cell Disease
 Hydroxyurea (Hydroxycarbamide) - Guidelines for treating children with Sickle Cell Disease Patient selection The benefits of hydroxycarbamide should be discussed with all parents/carers of children with
Hydroxyurea (Hydroxycarbamide) - Guidelines for treating children with Sickle Cell Disease Patient selection The benefits of hydroxycarbamide should be discussed with all parents/carers of children with
HbSC disease is it different and how should we manage it? David Rees Department of Paediatric Haematology, King s College Hospital, London
 HbSC disease is it different and how should we manage it? David Rees Department of Paediatric Haematology, King s College Hospital, London Different types of sickle cell disesease Severe sickle cell disease
HbSC disease is it different and how should we manage it? David Rees Department of Paediatric Haematology, King s College Hospital, London Different types of sickle cell disesease Severe sickle cell disease
Sickle Cell Disease and impact on the society
 Sickle Cell Disease and impact on the society Professor Z.A.Jeremiah Ph.D, FRCPath (London) Professor of Haematology and Blood Transfusion Science Niger Delta University, Wilberforce Island Outline What
Sickle Cell Disease and impact on the society Professor Z.A.Jeremiah Ph.D, FRCPath (London) Professor of Haematology and Blood Transfusion Science Niger Delta University, Wilberforce Island Outline What
How to Write a Life Care Plan for a Child with Hemoglobinopathy
 How to Write a Life Care Plan for a Child with Hemoglobinopathy Tamar Fleischer, BSN, MSN, CNLCP & Mona Yudkoff, RN, MPH, CRRN, CNLCP BalaCare Solutions March 2018 St. Peterburg, Florida What is Hemoglobinopathy?
How to Write a Life Care Plan for a Child with Hemoglobinopathy Tamar Fleischer, BSN, MSN, CNLCP & Mona Yudkoff, RN, MPH, CRRN, CNLCP BalaCare Solutions March 2018 St. Peterburg, Florida What is Hemoglobinopathy?
Hydroxyurea (Hydroxycarbamide) - Guidelines for treating children with Sickle Cell Disease
 Hydroxyurea (Hydroxycarbamide) - Guidelines for treating children with Sickle Cell Disease Document Information Version: 2 Date: July 2014 Authors (incl. job title): Dr Moira Dick Consultant Paediatrician
Hydroxyurea (Hydroxycarbamide) - Guidelines for treating children with Sickle Cell Disease Document Information Version: 2 Date: July 2014 Authors (incl. job title): Dr Moira Dick Consultant Paediatrician
Blood Transfusions in Children with Haemoglobinopathies
 Blood Transfusions in Children with Haemoglobinopathies Version: 2 Date: 22 nd April 2010 Authors: Responsible committee or Director: Review date: Target audience: Stakeholders/ committees involved in
Blood Transfusions in Children with Haemoglobinopathies Version: 2 Date: 22 nd April 2010 Authors: Responsible committee or Director: Review date: Target audience: Stakeholders/ committees involved in
Acute painful crisis in patients with sickle cell disease: Clinical Guidelines (HN-506a)
 Acute painful crisis in patients with sickle cell disease: Clinical Guidelines (HN-506a) Introduction The majority of acute painful crises in patients with sickle cell disease will be managed independently
Acute painful crisis in patients with sickle cell disease: Clinical Guidelines (HN-506a) Introduction The majority of acute painful crises in patients with sickle cell disease will be managed independently
Acute Complications of Sickle Cell Disease Case Study 5 year old girl with Hemoglobin SS, weakness and slurred speech
 Acute Complications of Sickle Cell Disease Case Study 5 year old girl with Hemoglobin SS, weakness and slurred speech Beatrice E. Gee, MD Medical Director, Sickle Cell and Hematology Program Children s
Acute Complications of Sickle Cell Disease Case Study 5 year old girl with Hemoglobin SS, weakness and slurred speech Beatrice E. Gee, MD Medical Director, Sickle Cell and Hematology Program Children s
Hydroxyurea and Transfusion Therapy for the Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease
 Hydroxyurea and Transfusion Therapy for the Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease A Pocket Guide for the Clinician Susan E. Creary, MD, MSc 1 John J. Strouse, MD, PhD 2 1 The Ohio State University School of
Hydroxyurea and Transfusion Therapy for the Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease A Pocket Guide for the Clinician Susan E. Creary, MD, MSc 1 John J. Strouse, MD, PhD 2 1 The Ohio State University School of
Sickle cell anaemia. GP Education Update 19 th July 2018 Croydon University Hospital. Arne de Kreuk Consultant Haematologist
 Sickle cell anaemia GP Education Update 19 th July 201 Croydon University Hospital Arne de Kreuk Consultant Haematologist Outline: Prevention of sickle cell related complications; annual review Identification
Sickle cell anaemia GP Education Update 19 th July 201 Croydon University Hospital Arne de Kreuk Consultant Haematologist Outline: Prevention of sickle cell related complications; annual review Identification
Family Centered Pediatric Emergency Department Sickle Cell Assessment of Needs and Strengths (FC-Peds-ED-SCANS) Overall Algorithm
 Family Centered Pediatric Emergency Department Sickle Cell Assessment of Needs and Strengths (FC-Peds-ED-SCANS) Overall Algorithm Decision 1: Triage Decision 2: Analgesic Management Decision 3: Diagnostic
Family Centered Pediatric Emergency Department Sickle Cell Assessment of Needs and Strengths (FC-Peds-ED-SCANS) Overall Algorithm Decision 1: Triage Decision 2: Analgesic Management Decision 3: Diagnostic
Aneurin Bevan University Health Board Sickle Cell Anaemia and Haemoglobinopathy Screening and Management in Pregnancy Guidelines
 Sickle Cell Anaemia and Haemoglobinopathy Screening and Management in Pregnancy Guidelines N.B. Staff should be discouraged from printing this document. This is to avoid the risk of out of date printed
Sickle Cell Anaemia and Haemoglobinopathy Screening and Management in Pregnancy Guidelines N.B. Staff should be discouraged from printing this document. This is to avoid the risk of out of date printed
Anemia s. Troy Lund MSMS PhD MD
 Anemia s Troy Lund MSMS PhD MD lundx072@umn.edu Hemoglobinopathy/Anemia IOM take home points. 1. How do we identify the condtion? Smear, CBC Solubility Test (SCD) 2. How does it present clincally? 3. How
Anemia s Troy Lund MSMS PhD MD lundx072@umn.edu Hemoglobinopathy/Anemia IOM take home points. 1. How do we identify the condtion? Smear, CBC Solubility Test (SCD) 2. How does it present clincally? 3. How
Stroke in adults with Sickle Cell Disease
 Stroke in adults with Sickle Cell Disease Dr Paul Holmes Consultant Neurologist Guy s and St Thomas Hospitals Stroke and SCD Children and adults with SCA (haemoglobin SS) have a high prevalence (4.01%)
Stroke in adults with Sickle Cell Disease Dr Paul Holmes Consultant Neurologist Guy s and St Thomas Hospitals Stroke and SCD Children and adults with SCA (haemoglobin SS) have a high prevalence (4.01%)
Atlantic Provinces Pediatric Hematology Oncology Network Réseau d Oncologie et Hématologie Pédiatrique des Provinces Atlantiques
 Atlantic Provinces Pediatric Hematology Oncology Network Réseau d Oncologie et Hématologie Pédiatrique des Provinces Atlantiques 5850/5980 University Avenue, PO Box 9700 Halifax, NS, B3K 6R8 1.902.470.7429
Atlantic Provinces Pediatric Hematology Oncology Network Réseau d Oncologie et Hématologie Pédiatrique des Provinces Atlantiques 5850/5980 University Avenue, PO Box 9700 Halifax, NS, B3K 6R8 1.902.470.7429
Rationale for RBC Transfusion in SCD
 Rationale for RBC Transfusion in SCD Dilution of HgbS-containing RBCs via the addition of HgbA-containing cells from the blood of normal donors Suppression of erythropoietin release caused by the rise
Rationale for RBC Transfusion in SCD Dilution of HgbS-containing RBCs via the addition of HgbA-containing cells from the blood of normal donors Suppression of erythropoietin release caused by the rise
High Hemoglobin F in a Saudi Child Presenting with Pancytopenia
 Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Pediatric Care ISSN 2471-805X DOI: 10.21767/2471-805X.100002 High Hemoglobin F in a Saudi Child Presenting with Pancytopenia Abstract Saudi
Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Pediatric Care ISSN 2471-805X DOI: 10.21767/2471-805X.100002 High Hemoglobin F in a Saudi Child Presenting with Pancytopenia Abstract Saudi
SICKLE CELL DISEASE. Dr. MUBARAK ABDELRAHMAN MD PEDIATRICS AND CHILD HEALTH. Assistant Professor FACULTY OF MEDICINE -JAZAN
 SICKLE CELL DISEASE Dr. MUBARAK ABDELRAHMAN MD PEDIATRICS AND CHILD HEALTH Assistant Professor FACULTY OF MEDICINE -JAZAN Objective: The student should be able: To identify the presentation, diagnosis,
SICKLE CELL DISEASE Dr. MUBARAK ABDELRAHMAN MD PEDIATRICS AND CHILD HEALTH Assistant Professor FACULTY OF MEDICINE -JAZAN Objective: The student should be able: To identify the presentation, diagnosis,
Putting some hematology into Pediatric Hematology/Oncology: a review of Hemophilia and Sickle Cell Disease in the Pediatric Patient
 Putting some hematology into Pediatric Hematology/Oncology: a review of Hemophilia and Sickle Cell Disease in the Pediatric Patient Kristina Haley, DO March 10, 2012 Jovita Reyes Memorial Pediatric Hematology/Oncology
Putting some hematology into Pediatric Hematology/Oncology: a review of Hemophilia and Sickle Cell Disease in the Pediatric Patient Kristina Haley, DO March 10, 2012 Jovita Reyes Memorial Pediatric Hematology/Oncology
TACO CASE STUDIES RTC JUNE Kerry Dowling Blood Transfusion Laboratory Manager Jonathan Ricks Blood Transfusion Nurse Practitioner
 TACO CASE STUDIES RTC JUNE 2017 Kerry Dowling Blood Transfusion Laboratory Manager Jonathan Ricks Blood Transfusion Nurse Practitioner RISK FACTORS - TACO Age over 70 years although also seen in younger
TACO CASE STUDIES RTC JUNE 2017 Kerry Dowling Blood Transfusion Laboratory Manager Jonathan Ricks Blood Transfusion Nurse Practitioner RISK FACTORS - TACO Age over 70 years although also seen in younger
Sickle cell disease (SCD) and other hemoglobinopathies
 Sickle cell disease (SCD) and other hemoglobinopathies You have received this leaflet, because your child has been diagnosed with sickle cell disease. We can imagine how overwhelming such a diagnosis must
Sickle cell disease (SCD) and other hemoglobinopathies You have received this leaflet, because your child has been diagnosed with sickle cell disease. We can imagine how overwhelming such a diagnosis must
Introduction reduction in output alter the amino acid sequence combination
 Sickle cell anemia. Introduction Mutations in the globin genes can cause a quantitative reduction in output from that gene or alter the amino acid sequence of the protein produced or a combination of the
Sickle cell anemia. Introduction Mutations in the globin genes can cause a quantitative reduction in output from that gene or alter the amino acid sequence of the protein produced or a combination of the
Hydroxycarbamide. Sickle and Thalassaemia Training days. September Dr Sara Stuart-Smith. Why do sickle cells cause pain and organ damage?
 Sickle and Thalassaemia Training days September 2017 Hydroxycarbamide Dr Sara Stuart-Smith Why do sickle cells cause pain and organ damage? Under certain conditions, haemoglobin S forms long rigid strands
Sickle and Thalassaemia Training days September 2017 Hydroxycarbamide Dr Sara Stuart-Smith Why do sickle cells cause pain and organ damage? Under certain conditions, haemoglobin S forms long rigid strands
Clinical Guidelines on the Use of Iron Chelation in Children Receiving Regular Blood Transfusions
 Clinical Guidelines on the Use of Iron Chelation in Children Receiving Regular Blood Transfusions Version: 1 Date: 4 th May 2010 Authors: Responsible committee or Director: Review date: Target audience:
Clinical Guidelines on the Use of Iron Chelation in Children Receiving Regular Blood Transfusions Version: 1 Date: 4 th May 2010 Authors: Responsible committee or Director: Review date: Target audience:
Pediatric Red Cell Exchange Indications, Benefits, Barriers. View from California Saturday May 9 th ASFA 2015
 Pediatric Red Cell Exchange Indications, Benefits, Barriers View from California Saturday May 9 th ASFA 2015 Red Cell Exchange: Not SCD Recommendations for Red Cell Exchange Indication Procedure Recommendation
Pediatric Red Cell Exchange Indications, Benefits, Barriers View from California Saturday May 9 th ASFA 2015 Red Cell Exchange: Not SCD Recommendations for Red Cell Exchange Indication Procedure Recommendation
ADULT (>16) ACUTE SICKLE PAIN GUIDELINE
 ADULT (>16) ACUTE SICKLE PAIN GUIDELINE ID 2013 065 Author s Name Dr Anna Wood Author s Job Title Consultant Haematologist Division Consultant Haematologist Department Haematology Version number 3 Ratifying
ADULT (>16) ACUTE SICKLE PAIN GUIDELINE ID 2013 065 Author s Name Dr Anna Wood Author s Job Title Consultant Haematologist Division Consultant Haematologist Department Haematology Version number 3 Ratifying
Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI) and Strategies for Prevention. Khalid Abdulla Sharif, MD, MRCP (UK)*
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 29, No.4, December 2007 Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI) and Strategies for Prevention Khalid Abdulla Sharif, MD, MRCP (UK)* Background: Transfusion-Related
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 29, No.4, December 2007 Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI) and Strategies for Prevention Khalid Abdulla Sharif, MD, MRCP (UK)* Background: Transfusion-Related
Anaemia in Pregnancy
 Anaemia in Pregnancy Definition :anaemia is a pathological condition in which the oxygen-carrying capacity of red blood cells is insufficient to meet the body needs. The WHO : haemoglobin concentration
Anaemia in Pregnancy Definition :anaemia is a pathological condition in which the oxygen-carrying capacity of red blood cells is insufficient to meet the body needs. The WHO : haemoglobin concentration
Predictors of Cerebral Blood Flow Velocity in Children with Sickle Cell Anaemia in Lagos State, Nigeria
 Predictors of Cerebral Blood Flow Velocity in Children with Sickle Cell Anaemia in Lagos State, Nigeria Motunrayo Oluwabukola Adekunle 1*, Ijeoma Nnenna Diaku-Akinwumi 1, Adeola Barakat Animasahun 1, Olisamedua
Predictors of Cerebral Blood Flow Velocity in Children with Sickle Cell Anaemia in Lagos State, Nigeria Motunrayo Oluwabukola Adekunle 1*, Ijeoma Nnenna Diaku-Akinwumi 1, Adeola Barakat Animasahun 1, Olisamedua
Sickle cell disease: Complications in adult patients
 Sickle cell disease: Complications in adult patients Dr Sara Stuart-Smith Haematology Consultant Sickle cell and thalassaemia Nurses, AHP and Junior Doctor Training Days September 2017 SCD is caused by
Sickle cell disease: Complications in adult patients Dr Sara Stuart-Smith Haematology Consultant Sickle cell and thalassaemia Nurses, AHP and Junior Doctor Training Days September 2017 SCD is caused by
Biance Rowe Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital Paediatric Haematology Oncology University of the Witwatersrand
 Biance Rowe Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital Paediatric Haematology Oncology University of the Witwatersrand SCD affects 20-25 million people globally 12-15 million in Africa 300 000 children with SCD
Biance Rowe Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital Paediatric Haematology Oncology University of the Witwatersrand SCD affects 20-25 million people globally 12-15 million in Africa 300 000 children with SCD
Tenth Visit posttest
 Test Code 10C Patient s name: Tenth Visit posttest Patient s birth date: Your name and relationship to patient: Today s date: 1. Which one of the medications listed below should every child with a sickle
Test Code 10C Patient s name: Tenth Visit posttest Patient s birth date: Your name and relationship to patient: Today s date: 1. Which one of the medications listed below should every child with a sickle
Title: Improving the patient experience for children with Sickle Cell Disease Author/Responsible Director: Carole Ribbins Director of Nursing
 Trust Board Paper S To: Trust Board From: Kate Wilkins Divisional Head of Nursing Hilliary Killer Children s CBU Nurse Lead and General Manager Liz James Matron, Children s CBU Date: 28 March 2013 All
Trust Board Paper S To: Trust Board From: Kate Wilkins Divisional Head of Nursing Hilliary Killer Children s CBU Nurse Lead and General Manager Liz James Matron, Children s CBU Date: 28 March 2013 All
Transfusion in Sickle Cell Disease What the guidelines [are likely to] say. Dr Bernard Davis Whittington Hospital, London
![Transfusion in Sickle Cell Disease What the guidelines [are likely to] say. Dr Bernard Davis Whittington Hospital, London Transfusion in Sickle Cell Disease What the guidelines [are likely to] say. Dr Bernard Davis Whittington Hospital, London](/thumbs/85/91702350.jpg) Transfusion in Sickle Cell Disease What the guidelines [are likely to] say Dr Bernard Davis Whittington Hospital, London Background to BCSH Guideline Rationale Current guidance in disparate publications
Transfusion in Sickle Cell Disease What the guidelines [are likely to] say Dr Bernard Davis Whittington Hospital, London Background to BCSH Guideline Rationale Current guidance in disparate publications
Anaemia / SCD/ Bleeding disorders in Children
 Anaemia / SCD/ Bleeding disorders in Children Dr Neil Kennedy Handouts by Steve Graham Learning Outcomes Describe mechanisms of anaemia in Malawian children Discuss important causes of anaemia Describe
Anaemia / SCD/ Bleeding disorders in Children Dr Neil Kennedy Handouts by Steve Graham Learning Outcomes Describe mechanisms of anaemia in Malawian children Discuss important causes of anaemia Describe
Abnormal blood counts in children Dr Tina Biss Consultant Paediatric Haematologist Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
 Abnormal blood counts in children Dr Tina Biss Consultant Paediatric Haematologist Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Regional Paediatric Specialty Trainees teaching 4 th July 2017 Scope
Abnormal blood counts in children Dr Tina Biss Consultant Paediatric Haematologist Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Regional Paediatric Specialty Trainees teaching 4 th July 2017 Scope
Sickle Cell Disease 101. Objectives. What is SCD? 4/20/2016. Discuss the pathophysiology & genetics of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD).
 Sickle Cell Disease 101 Jennifer Young, RN, MS, CPNP-AC Sickle Cell & Thalassemia Nurse Practitioner Nationwide Children s Hospital Objectives Discuss the pathophysiology & genetics of Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle Cell Disease 101 Jennifer Young, RN, MS, CPNP-AC Sickle Cell & Thalassemia Nurse Practitioner Nationwide Children s Hospital Objectives Discuss the pathophysiology & genetics of Sickle Cell Disease
Acute vaso-occlusive Pain in children
 Acute vaso-occlusive Pain in children Dr François Angoulvant 1 Dr Sebastien Redant 2 Dr Malika Benkerrou 1 Pr Alina Ferster 2 Hôpital Robert Debré - Paris Hôpital des Enfants Reine Fabiola Bruxelles Réseau
Acute vaso-occlusive Pain in children Dr François Angoulvant 1 Dr Sebastien Redant 2 Dr Malika Benkerrou 1 Pr Alina Ferster 2 Hôpital Robert Debré - Paris Hôpital des Enfants Reine Fabiola Bruxelles Réseau
The Child with a Hematologic Alteration
 47 The Child with a Hematologic Alteration HELPFUL HINT Review the anatomy and physiology of the hematologic system in an anatomy and physiology textbook. MATCHING KEY TERMS Match the term with the correct
47 The Child with a Hematologic Alteration HELPFUL HINT Review the anatomy and physiology of the hematologic system in an anatomy and physiology textbook. MATCHING KEY TERMS Match the term with the correct
Boot Camp Transfusion Reactions
 Boot Camp Transfusion Reactions Dr. Kristine Roland Regional Medical Lead for Transfusion Medicine, VCH Objectives By the end of this session, you should be able to: Describe in common language the potential
Boot Camp Transfusion Reactions Dr. Kristine Roland Regional Medical Lead for Transfusion Medicine, VCH Objectives By the end of this session, you should be able to: Describe in common language the potential
CURRENT RESEARCH STUDIES
 CURRENT RESEARCH STUDIES SCAGO SICKLE CELL RESEARCH DAY MAY 12, 2018 REBECCA LEROUX RN, BSCN, CCRP RED BLOOD CELL DISORDERS PROGRAM, UNIVERSITY HEALTH NETWORK MANUELA MERELLES-PULCINI RN, BSCN, MSN, CCRP
CURRENT RESEARCH STUDIES SCAGO SICKLE CELL RESEARCH DAY MAY 12, 2018 REBECCA LEROUX RN, BSCN, CCRP RED BLOOD CELL DISORDERS PROGRAM, UNIVERSITY HEALTH NETWORK MANUELA MERELLES-PULCINI RN, BSCN, MSN, CCRP
SICKLE CELL DISEASE TO TREAT OR
 SICKLE CELL DISEASE TO TREAT OR NOT TO TREAT COHEM Barcelona September 8, 2012 Sujit Sheth, M.D. Pediatric Hematology Oncology Disclosures None Outline Morbidity and mortality Definitive therapies Risk
SICKLE CELL DISEASE TO TREAT OR NOT TO TREAT COHEM Barcelona September 8, 2012 Sujit Sheth, M.D. Pediatric Hematology Oncology Disclosures None Outline Morbidity and mortality Definitive therapies Risk
Cell Disease. Dr SM Donohue. Consultant Haematologist. Clinical Haematology
 Full Title of Guideline: Guideline for Management of Acute Sickle Cell Disease. Author (include email and role): Dr Consultant Haematologist Division & Speciality: Clinical Haematology Version: 2 Ratified
Full Title of Guideline: Guideline for Management of Acute Sickle Cell Disease. Author (include email and role): Dr Consultant Haematologist Division & Speciality: Clinical Haematology Version: 2 Ratified
Disclosure. Presented analysis part of larger study funded by Terumo BCT
 1 Comparison of Transfusion Adverse Events in Children with Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) Receiving or Automated Red Blood Cell Exchange (arbx) Transfusions for Stroke Prevention Shannon Kelly, M.D. 2 Disclosure
1 Comparison of Transfusion Adverse Events in Children with Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) Receiving or Automated Red Blood Cell Exchange (arbx) Transfusions for Stroke Prevention Shannon Kelly, M.D. 2 Disclosure
PAEDIATRIC FEBRILE NEUTROPENIA CARE PATHWAY
 PAEDIATRIC FEBRILE NEUTROPENIA CARE PATHWAY Purpose: This document is intended as a guide to the investigation and management of children presenting in Salisbury District Hospital with suspected neutropenic
PAEDIATRIC FEBRILE NEUTROPENIA CARE PATHWAY Purpose: This document is intended as a guide to the investigation and management of children presenting in Salisbury District Hospital with suspected neutropenic
Division of General Internal Medicine and Geriatrics Hospital Medicine 2014
 Division of General Internal Medicine and Geriatrics Hospital Medicine 2014 Objectives Understand workup of acute pain crisis Identify key aspects of management of acute pain crisis in sickle cell patients
Division of General Internal Medicine and Geriatrics Hospital Medicine 2014 Objectives Understand workup of acute pain crisis Identify key aspects of management of acute pain crisis in sickle cell patients
Protocol for stroke management in Sickle Cell Disease. Baba Inusa. Paediatric Haematology Evelina London Children s Hospital
 Protocol for stroke management in Sickle Cell Disease Baba Inusa Paediatric Haematology Evelina London Children s Hospital Honorary Reader, King s College London 29 th November, 2017; STSTN STSTN Guidelines
Protocol for stroke management in Sickle Cell Disease Baba Inusa Paediatric Haematology Evelina London Children s Hospital Honorary Reader, King s College London 29 th November, 2017; STSTN STSTN Guidelines
Transfusion reactions. Jim Taylor Haematology SpR Sheffield
 Transfusion reactions Jim Taylor Haematology SpR Sheffield Pre questions 1. Platelet transfusions are more prone to bacterial contamination compared to red cells. T/F 2. Common causes of an acute transfusion
Transfusion reactions Jim Taylor Haematology SpR Sheffield Pre questions 1. Platelet transfusions are more prone to bacterial contamination compared to red cells. T/F 2. Common causes of an acute transfusion
Pulmonary complications in the Elderly. Paula Bolton-Maggs Medical Director
 Pulmonary complications in the Elderly Paula Bolton-Maggs Medical Director What does SHOT do? Serious Hazards of Transfusion Collect data on serious adverse reactions and events related to transfusion
Pulmonary complications in the Elderly Paula Bolton-Maggs Medical Director What does SHOT do? Serious Hazards of Transfusion Collect data on serious adverse reactions and events related to transfusion
Apheresis red cell exchange and transfusion therapy for management of sickle cell disease. Dr Paul Telfer
 Apheresis red cell exchange and transfusion therapy for management of sickle cell disease Dr Paul Telfer OVERVIEW Pathophysiology and epidemiology Physiological and clinical considerations prior to transfusion
Apheresis red cell exchange and transfusion therapy for management of sickle cell disease Dr Paul Telfer OVERVIEW Pathophysiology and epidemiology Physiological and clinical considerations prior to transfusion
Lessons in Management of Sickle Cell Disease. CME Conference, Lloyd Erskine Sandiford Centre, November 15, 2015
 Lessons in Management of Sickle Cell Disease CME Conference, Lloyd Erskine Sandiford Centre, November 15, 2015 Age at Death in African SS Disease The greatest chance of death is in the first is in the
Lessons in Management of Sickle Cell Disease CME Conference, Lloyd Erskine Sandiford Centre, November 15, 2015 Age at Death in African SS Disease The greatest chance of death is in the first is in the
Children who are neutropenic and unwell, even if normothermic, should be assumed to have infection and be treated appropriately.
 PAEDIATRIC FEBRILE NEUTROPENIA CARE PATHWAY Purpose: This document is intended as a guide to the investigation and management of children presenting in Salisbury District Hospital with suspected neutropenic
PAEDIATRIC FEBRILE NEUTROPENIA CARE PATHWAY Purpose: This document is intended as a guide to the investigation and management of children presenting in Salisbury District Hospital with suspected neutropenic
DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER: This Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) generally describes a recommended course of treatment for patients with the identified health
DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER: This Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) generally describes a recommended course of treatment for patients with the identified health
1.3 What is the mechanism of action of adrenaline in anaphylactic shock? (20 marks)
 DCH Examination -Short Answer Questions Time - Two and half hours Model paper 1.1 A 10 month old child presented with urticaria within one hour following ingestion of an egg. Mother claims that a week
DCH Examination -Short Answer Questions Time - Two and half hours Model paper 1.1 A 10 month old child presented with urticaria within one hour following ingestion of an egg. Mother claims that a week
Hydroxurea: A Novel Approach to Optimizing the Health of Pediatric Patients with Sickle Cell Disease. Maa Ohui Quarmyne September 9 th, 2017
 Hydroxurea: A Novel Approach to Optimizing the Health of Pediatric Patients with Sickle Cell Disease Maa Ohui Quarmyne September 9 th, 2017 Outline Sickle Cell Disease Pathophysiology and Clinical Manifestations
Hydroxurea: A Novel Approach to Optimizing the Health of Pediatric Patients with Sickle Cell Disease Maa Ohui Quarmyne September 9 th, 2017 Outline Sickle Cell Disease Pathophysiology and Clinical Manifestations
Clinical guideline Published: 27 June 2012 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg143
 Sickle cell disease: managing acute painful episodes in hospital Clinical guideline Published: 27 June 2012 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg143 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Sickle cell disease: managing acute painful episodes in hospital Clinical guideline Published: 27 June 2012 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg143 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Is there a rationale for treatment of sickle cell anemia, except for acute complications?
 Is there a rationale for treatment of sickle cell anemia, NO, but JL Vives Corrons Red Cell Pathology Unit Hospital Clnic. University of Barcelona Head of ENERCA Project EUROPEAN NETWORK FOR RARE AND CONGENITAL
Is there a rationale for treatment of sickle cell anemia, NO, but JL Vives Corrons Red Cell Pathology Unit Hospital Clnic. University of Barcelona Head of ENERCA Project EUROPEAN NETWORK FOR RARE AND CONGENITAL
Voxelotor for sickle cell disease
 NIHR Innovation Observatory Evidence Briefing: November 2017 Voxelotor for sickle cell disease NIHRIO (HSRIC) ID: 10748 NICE ID: 9700 LAY SUMMARY Sickle cell disease (SCD) describes a group of inherited
NIHR Innovation Observatory Evidence Briefing: November 2017 Voxelotor for sickle cell disease NIHRIO (HSRIC) ID: 10748 NICE ID: 9700 LAY SUMMARY Sickle cell disease (SCD) describes a group of inherited
PART II: PREVENTING AND MANAGING COMPLICATIONS OF SICKLE CELL DISEASE
 PART II: PREVENTING AND MANAGING COMPLICATIONS OF SICKLE CELL DISEASE 1. PAIN Principles To educate patients, family and other caregivers about prevention, rapid identification and management of vaso-occlusive
PART II: PREVENTING AND MANAGING COMPLICATIONS OF SICKLE CELL DISEASE 1. PAIN Principles To educate patients, family and other caregivers about prevention, rapid identification and management of vaso-occlusive
Approach to Hemolysis
 Objectives: Approach to Hemolysis To know the function of platelets and the relationship between the platelet count in peripheral blood and the extent of abnormal bleeding. To know about the diseases associated
Objectives: Approach to Hemolysis To know the function of platelets and the relationship between the platelet count in peripheral blood and the extent of abnormal bleeding. To know about the diseases associated
Education Visit #1 *** All Sickle Cell Patients*** from A Parent s Handbook for Sickle Cell Disease Booklet.
 Education Visit #1 *** All Sickle Cell Patients*** Step 1: Administer Pretest A. Step 2: Education Watch DVD: Education Visit #1 For All Patients Handout So You Have Sickle Cell Disorder Handout Infection
Education Visit #1 *** All Sickle Cell Patients*** Step 1: Administer Pretest A. Step 2: Education Watch DVD: Education Visit #1 For All Patients Handout So You Have Sickle Cell Disorder Handout Infection
Dependance on chronic transfusion
 Dependance on chronic transfusion Pr Saliou Diop Hematology Blood transfusion Dakar- Sénégal diop@cnts-dakar.sn Introduction Chronic transfusion: Regular use of blood transfusion in patients with chronic
Dependance on chronic transfusion Pr Saliou Diop Hematology Blood transfusion Dakar- Sénégal diop@cnts-dakar.sn Introduction Chronic transfusion: Regular use of blood transfusion in patients with chronic
Acute Complications of Sickle Cell Disease
 Management of Acute Complications of Sickle Cell Disease A Pocket Guide for the Clinician Timothy McCavit, MD, MSCS 1 Payal Desai, MD 1 University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center The Ohio State University,
Management of Acute Complications of Sickle Cell Disease A Pocket Guide for the Clinician Timothy McCavit, MD, MSCS 1 Payal Desai, MD 1 University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center The Ohio State University,
Alister Jones Patient Blood Management Practitioner NHS Blood and Transplant
 Alister Jones Patient Blood Management Practitioner NHS Blood and Transplant All medical RCC transfusions (but only 1 in 3 haematology or oncology cases) in 3 x one week periods Medical specialties include:
Alister Jones Patient Blood Management Practitioner NHS Blood and Transplant All medical RCC transfusions (but only 1 in 3 haematology or oncology cases) in 3 x one week periods Medical specialties include:
ED-SCANS: OVERALL DECISION SUPPORT ALGORITHM. Is This Strictly a Pain Episode? Decision 7: Referrals
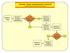 ED-SCANS: OVERALL DECISION SUPPORT ALGORITHM Decision 1: Triage Decision 2: Analgesic Management Is This Strictly a Pain Episode? Decision 3: Diagnostic Evaluation Decision 4: High Risk / High User Decision
ED-SCANS: OVERALL DECISION SUPPORT ALGORITHM Decision 1: Triage Decision 2: Analgesic Management Is This Strictly a Pain Episode? Decision 3: Diagnostic Evaluation Decision 4: High Risk / High User Decision
Sickle Cell Disease Patient Handbook
 Sickle Cell Disease Patient Handbook , Important Contact Information Office/Unit Phone Number: Outpatient Clinic: 708.684.3898 Make an appointment: 708.684.3113 Please leave a message and a receptionist
Sickle Cell Disease Patient Handbook , Important Contact Information Office/Unit Phone Number: Outpatient Clinic: 708.684.3898 Make an appointment: 708.684.3113 Please leave a message and a receptionist
CARE PATHWAY FOR CHILDREN AND YOUNG PERSONS WITH FEBRILE NEUTROPENIA, NEUTROPENIC SEPSIS OR SUSPECTED CENTRAL VENOUS LINE INFECTIONS
 CARE PATHWAY FOR CHILDREN AND YOUNG PERSONS WITH FEBRILE NEUTROPENIA, NEUTROPENIC SEPSIS OR SUSPECTED CENTRAL VENOUS LINE INFECTIONS This Care Pathway has been developed by a multidisciplinary team. It
CARE PATHWAY FOR CHILDREN AND YOUNG PERSONS WITH FEBRILE NEUTROPENIA, NEUTROPENIC SEPSIS OR SUSPECTED CENTRAL VENOUS LINE INFECTIONS This Care Pathway has been developed by a multidisciplinary team. It
Management of sickle cell disease in the community
 Follow the link from the online version of this article to obtain certified continuing medical education credits Management of sickle cell disease in the community Valentine Brousse, 1 Julie Makani, 2
Follow the link from the online version of this article to obtain certified continuing medical education credits Management of sickle cell disease in the community Valentine Brousse, 1 Julie Makani, 2
Full Case: Questions: What is sickle cell crisis?
 Full Case: 30 y/o with avascular necrosis of her right hip was admitted for a total hip arthroplasty. Her hematocrit was 22%, blood pressure was 130/90 mm Hg, and pulse was 107 beats per minute. She had
Full Case: 30 y/o with avascular necrosis of her right hip was admitted for a total hip arthroplasty. Her hematocrit was 22%, blood pressure was 130/90 mm Hg, and pulse was 107 beats per minute. She had
Hemolytic anemias (2 of 2)
 Hemolytic anemias (2 of 2) Sickle Cell Anemia The most common familial hemolytic anemia in the world Sickle cell anemia is the prototypical (and most prevalent) hemoglobinopathy Mutation in the β-globin
Hemolytic anemias (2 of 2) Sickle Cell Anemia The most common familial hemolytic anemia in the world Sickle cell anemia is the prototypical (and most prevalent) hemoglobinopathy Mutation in the β-globin
An overview of Thalassaemias and Complications
 An overview of Thalassaemias and Complications Haemoglobin Haemoglobin is the most abundant protein in blood, and exists as three main types in normal adults: HbA ( ) - 97% HbA 2 ( ) - 2.5% HbF ( ) - 0.5%
An overview of Thalassaemias and Complications Haemoglobin Haemoglobin is the most abundant protein in blood, and exists as three main types in normal adults: HbA ( ) - 97% HbA 2 ( ) - 2.5% HbF ( ) - 0.5%
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Sickle cell acute episode: management of an acute painful sickle cell episode in hospital 1.1 Short title Sickle cell acute
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Sickle cell acute episode: management of an acute painful sickle cell episode in hospital 1.1 Short title Sickle cell acute
Guidelines for management of stroke in childhood
 Guidelines for management of stroke in childhood A clinical syndrome typified by rapidly developing signs of focal or global disturbance of cerebral functions, lasting more than 24 hrs or leading to death,
Guidelines for management of stroke in childhood A clinical syndrome typified by rapidly developing signs of focal or global disturbance of cerebral functions, lasting more than 24 hrs or leading to death,
TRANSFUSION PRACTICES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF SICKLE CELL DISEASE AMONG FLORIDA PHYSICIANS
 TRANSFUSION PRACTICES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF SICKLE CELL DISEASE AMONG FLORIDA PHYSICIANS By LEVETTE NICOLE DUNBAR A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
TRANSFUSION PRACTICES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF SICKLE CELL DISEASE AMONG FLORIDA PHYSICIANS By LEVETTE NICOLE DUNBAR A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
Symptoms and Signs in Hematology (2)/ 2013
 Symptoms and Signs in Hematology (2)/ 2013 Abdallah Abbadi.MD.FRCP Professor of Medicine,Hematology & Oncology University of Jordan & JUH Email: abdalla.awidi@gmail.com Case one: A 24 yr old female complains
Symptoms and Signs in Hematology (2)/ 2013 Abdallah Abbadi.MD.FRCP Professor of Medicine,Hematology & Oncology University of Jordan & JUH Email: abdalla.awidi@gmail.com Case one: A 24 yr old female complains
Dr Ben Edwards Consultant Anaesthetist Sheffield Teaching Hospitals
 Dr Ben Edwards Consultant Anaesthetist Sheffield Teaching Hospitals 70-75,000 #NOF per annum (costs 2 billion) 10% die within 1 month 33% die within 1 year Operative delays >48hs more than doubles risk
Dr Ben Edwards Consultant Anaesthetist Sheffield Teaching Hospitals 70-75,000 #NOF per annum (costs 2 billion) 10% die within 1 month 33% die within 1 year Operative delays >48hs more than doubles risk
Comprehensive Care for Children and Adolescents with Sickle Cell Diseases
 Comprehensive Care for Children and Adolescents with Sickle Cell Diseases Objectives To review the system for newborn screening of infants for sickling diseases To provide the framework for a comprehensive
Comprehensive Care for Children and Adolescents with Sickle Cell Diseases Objectives To review the system for newborn screening of infants for sickling diseases To provide the framework for a comprehensive
Moving from child to adult sickle cell disease services
 What will happen when I move from child to adult? When you move over from child to adult sickle cell services you will be under the care of the Sickle Cell and Thalassaemia (SCaT) team at City Hospital.
What will happen when I move from child to adult? When you move over from child to adult sickle cell services you will be under the care of the Sickle Cell and Thalassaemia (SCaT) team at City Hospital.
Stroke Case Histories
 Stroke Case Histories STSTN Education and Peer Support Meeting Wednesday 29th November 2017 Dr Sara Stuart-Smith Haematology Consultant Sickle cell disease, HbSS 36 year old female Previously well controlled
Stroke Case Histories STSTN Education and Peer Support Meeting Wednesday 29th November 2017 Dr Sara Stuart-Smith Haematology Consultant Sickle cell disease, HbSS 36 year old female Previously well controlled
Year 2004 Paper two: Questions supplied by Megan 1
 Year 2004 Paper two: Questions supplied by Megan 1 QUESTION 93 A 16yo adolescent male presents with lethargy and lower respiratory tract infection. Physical examination shows him to be febrile, icteric
Year 2004 Paper two: Questions supplied by Megan 1 QUESTION 93 A 16yo adolescent male presents with lethargy and lower respiratory tract infection. Physical examination shows him to be febrile, icteric
Stroke: Guidelines for In-patient Management in Children with Sickle Cell Disease
 Version 02 Approved by Inter-professional Patient Care Committee: December 2, 2016 1.0 Introduction Target Users: Clinicians managing patients with Sickle Cell Disease who present acutely with a change
Version 02 Approved by Inter-professional Patient Care Committee: December 2, 2016 1.0 Introduction Target Users: Clinicians managing patients with Sickle Cell Disease who present acutely with a change
Extra Notes 3. Warm. In the core (center) of the body, where the temperature is 37 C.
 Extra Notes 3 *The numbers of the slides are according to the last year slides. Slide 33 Autoimmune hemolytic anemia : Abnormal circulating antibodies that target normal antigen on the RBC and cause lysis.
Extra Notes 3 *The numbers of the slides are according to the last year slides. Slide 33 Autoimmune hemolytic anemia : Abnormal circulating antibodies that target normal antigen on the RBC and cause lysis.
Supplementary Appendix
 Outcomes of adult patients with sickle cell disease admitted to the intensive care unit: a case series. Jérôme Cecchini, MD 1, François Lionnet, MD 2, Michel Djibré, MD 1, Antoine Parrot, MD 1, Katia Stankovic
Outcomes of adult patients with sickle cell disease admitted to the intensive care unit: a case series. Jérôme Cecchini, MD 1, François Lionnet, MD 2, Michel Djibré, MD 1, Antoine Parrot, MD 1, Katia Stankovic
SICKLE CELL BROCHURE
 SICKLE CELL BROCHURE SICKLE CELL DIESEASE According to CDC, Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of inherited red blood cell disorders. Healthy red blood cells are round and SCD C -shaped farm tool called
SICKLE CELL BROCHURE SICKLE CELL DIESEASE According to CDC, Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of inherited red blood cell disorders. Healthy red blood cells are round and SCD C -shaped farm tool called
