Anthrax. Nina Marano DVM, MPH, Dipl. ACVPM Meningitis and Special Pathogens Branch National Center for Infectious Diseases
|
|
|
- Ashley McCoy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anthrax Nina Marano DVM, MPH, Dipl. ACVPM Meningitis and Special Pathogens Branch National Center for Infectious Diseases
2 Overview History, etiology, pathogenesis Burden of natural disease Disease forms Recognition and diagnosis Differential diagnosis Treatment Prevention
3 History Malignant Pustule, Malignant Edema, Siberian plague, Black Baine, Ragpicker's disease, Woolsorter's disease Described since ancient times Medieval Period - multiple pandemics The first microbial etiology (Koch) The first live bacterial vaccine (Pasteur)
4 Bacillus anthracis Etiology Gram positive, spore forming, non-motile bacillus
5 Bacillus anthracis: Microbiology Tacky (egg white) Non-hemolytic Penicillin susceptible (97%) Tails (medusa head) colony morphology Phage susceptible
6 Anthrax Binary Toxins Lethal Factor (LF, 90kDa) Endopeptidase Protective Antigen (PA, 83kDa) Receptor binding & toxin internalisation Edema Factor (EF, 89kDa) Adenylyl cyclase Lethal Toxin Edema Toxin MAPKK cleavage MØ lysis Cytokine modulation Fatal toxic shock ATP -->camp Cytokine modulation Edema
7 Anthrax Toxin - Mode of Action (from Leppla, 1999) Furin PA 20 PA63 PA83 CaM ATP EF H + EF or LF camp MEK-1 Translocation Target Cell LF Endocytosis
8 Pathogenesis of Anthrax Spores NEJM 1999; 341:
9 Anthrax in Animals Rapid progression from febrile illness to death with hemorrhage Dogs and pigs get a pharyngeal form more resistant
10 Epidemiology and Transmission in Humans Spores live in the soil for many yrs: at least 60 yrs Animals ingest spores Humans become infected from animal products - Cutaneous: direct contact - Gastrointestinal: ingestion of infected meat - Inhalation: inhalation of aerosolized spores Generally, not transmissible person-to-person
11 Why is Anthrax a Threat Agent? Persistence of endospore in environment Pathogenicity Delayed onset of recognizable symptoms renders treatment ineffective Can be manufactured using standard laboratory equipment No recognizable color, taste, or odor
12 2001 Anthrax Threat Letters
13 Examples of Sources Animals with anthrax - veterinarians Contaminated hair, hides - mill workers, hobbyists Contaminated meat (not in milk) - Africa Biological warfare-related Sverdlosk, Russia Bioterrorism-related US anthrax letters, 2001
14 Burden of Natural Disease Disease absent/sporadic in Northern Europe More common in Greece, Italy, Spain, Turkey, Yugoslavia U.S. - South Dakota, Nebraska, Oklahoma, Texas Enzootic in Central America, Peru, Bolivia, Venezuela Hyperendemic in Middle Eastern and adjoining countries of former USSR republics Largest recent epidemic: Zimbabwe, ,000 human cases Reporting deficiencies due to decreasing veterinary experience in case recognition and civil unrest
15 Cases of Anthrax in the United States Animal (Sterne strain) vaccine started in 1957, after Oklahoma enzootic; recommended in endemic areas thereafter Cases Formalin treatment of imported hides Vaccine for humans approved in BT Year
16 Cutaneous Anthrax 95% of human cases 1-2 days post exposure, papule develops (2-19 days) 2-4 days, ulcer surrounded by vesicles Black eschar forms - painless with edema Most common site is head, forearm, hands Untreated: 5-20% case-fatality rate
17 Anthrax: Cutaneous Vesicle development Day 2 Day 4 Day 6 Day 10 Eschar formation
18 Anthrax: Cutaneous
19 Cutaneous Anthrax Resulting from Bioterrorism, NYC, October, 2001
20 Diagnosis of Cutaneous Anthrax Eschar formation Culture of vesicular fluid or exudate Blood culture Biopsy Polymerase chain reaction Immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry
21 Differential Diagnosis of Cutaneous Anthrax Spider bite Rickettsialpox Varicella zoster Herpes simplex Staphylococcal or streptococcal cellulitis Ecthyma gangrenosum Ulceroglandular tularemia Plague
22 Gastrointestinal Anthrax Ingestion Rare natural incidence Undercooked, ground beef Most simple, high-consequence application method Possible route of choice for criminals and non-state sponsored terrorists Symptoms Nausea 2-5 days after ingestion Mortality Up to 50% without treatment Intestinal lesion of GI anthrax
23 Inhalation Anthrax Inhalation of spores Incubation, 2-3 days (range up to 60 days) Spores engulfed by macrophages and transported to mediastinal and peribronchial lymph nodes Insidious onset: malaise, low grade fever, nonproductive cough Abrupt development of respiratory distress Hemorrhagic mediastinitis Hematogenous spread Meningitis in 50% Case fatality rate before %
24 Inhalation Anthrax
25 Inhalation Anthrax: Diagnosis Chest radiographs - widened mediastinum, pleural effusions Blood or cerebrospinal fluid culture and Gram stain Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) Immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry
26 Differential Diagnosis of Inhalation Anthrax Mycoplasmal pneumonia Legionnaires disease Psittacosis Tularemia Q fever Viral pneumonia Histoplasmosis (fibrous mediastinitis) Coccidioidomycosis
27 Distinguishing Anthrax from Influenza-like Illness (ILI) ILI: Nasal congestion and rhinorrhea ILI not usually associated with radiographic findings of pneumonia Person-to-person spread Rapid influenza testing and viral culture useful to indicate whether viruses are circulating among specific populations Anthrax: Abnormal chest radiographs No person-to-person spread
28 Treatment of Inhalation or Complicated Cutaneous Anthrax Assumptions: Rapid progression / systemic Beta-lactamases were present in isolates from FL, NY, DC (2001) Toxin mediated High fatality Strategy: Early treatment Combination therapy Avoid penicillins, at least early? Antitoxin (not available)? Steroids Treat for 60 days total
29 Recommended Initial* Anthrax Treatment Therapy Duration Cutaneous Ciprofloxacin 14 days 500mg BID PO OR Doxycycline 100 mg BID PO Inhalation Ciprofloxacin 400 mg IV BID 14 days, OR may switch Doxycycline 100 mg BID IV to PO when clinically appropriate Ciprofloxacin or doxycycline also recommended as initial therapy for children in appropriate doses *Until antibiotic susceptibility test results available
30 Recommended Postexposure Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Prevention of Inhalation Anthrax Initial Therapy Duration Adults Ciprofloxacin 60 days (including pregnant 500 mg PO BID women and OR immunocompromised) Doxycycline 100 mg PO BID Children Ciprofloxacin 60 days mg/kg PO Q 12 hrs OR Doxycycline: >8 yrs and >45 kg: 100 mg PO BID >8 yrs and <45 kg: 2.2 mg/kg PO BID <8 yrs: 2.2 mg/kg PO BID
31 Control / Prevention Human disease is controlled by: - Reducing infection in livestock - Supervised slaughter and meat inspection - Reducing exposure through import restriction, biosafety precautions, education - Vaccination of high-risk human populations - Treatment and post-exposure prophylaxis
32 Anthrax Vaccine US Vaccine: BioThrax or Anthrax Vaccine Adsorbed Cell-free filtrate of a nonencapsulated, toxigenic strain of B. anthracis Produces humoral response against protective antigen Preexposure vaccination schedule: 6 doses SQ at 0,2,4 weeks, 6.12,18 months will yearly booster Postexposure vaccination schedule: 3 doses SQ at 0,2,4 weeks + 60 days of antibiotics Precautionary use in immunosuppressed individuals Contraindicated for pregnant women
33 Human Anthrax Vaccine Trial Brachman PS et al. Field Evaluation of a Human Anthrax Vaccine Am J Pub Health 52: Randomized adjuvant control trial using alum vaccine 4 mills processing goat hair 379 vaccinated and 870 controls - 3 cases (cutaneous) in vaccinated group: 2 had not completed series - 23 cases in unvaccinated group, 5 inhalation - 93% efficacy (95%CI = 65% to 95%)
34 Animal Studies of Post-exposure Prophylaxis - Henderson, et al (1956): Alum precipitate PA filtrate vaccine Methods: 5 days of penicillin compared to penicillin with postexposure vaccination Results: 9 of the 10 receiving only penicillin died, while all of the macaques receiving penicillin and vaccine survived - Friedlander et al (1993): Aluminum hydroxide PA filtrate vaccine Methods: 30 days of various antibiotics compared to 30 days of doxycycline with postexposure vaccination Results: 9 of the 10 animals in the doxycycline-alone arm survived, while all receiving doxycycline and vaccine survived
35 Anthrax Vaccine Safety Mild local reactions (tenderness, swelling, nodule formation) occur in 30% - 60% of recipients Large local reactions occur in < 1% of vaccinees Systemic reactions: 5%-35% experience muscle ache, joint ache, headache, malaise, fever Serious side effect profile similar to other vaccines given to adults (influenza and hepatitis)
36 No Program Deaths with and without post-exposure prophylaxis following an anthrax release Deaths (1000,s/100,000) Without With chemoprophylaxis 83% 15% Start of post-attack treatment (days) Source: Kaufmann AF, Meltzer MI, Schmid GP. Emerging Infect Dis 1997; 3:83-94.
37 Case Study 1 It is 5pm on a Friday afternoon in December and you are getting ready to go a Christmas party with your family. Your last appointment of the day is a 53 year old male office worker with the following complaints: Headache, malaise, muscle ache, feels feverish and having some difficulty breathing Your exam findings: absence of breath sounds on the right side of the thorax, crackles on the left side, body temperature 37.5 C
38 Chest X-Ray Results What is on your list of differential diagnoses?
39 You hospitalize the patient; his condition worsens rapidly with dyspnea, cyanosis, and hemoptysis What samples should you consider collecting?
40 Specimen Selection is Important Anthrax Blood or cerebrospinal fluid gram stain Pleural fluid request immunohistochemical staining Tularemia Serum for antibody titer Pharyngeal wash or sputum specimen for culture, direct flourescent antibody, organism gram stains poorly Pneumonic Plague Sputum/throat or bronchial washings- request Wayson stain to see bipolar organism, or direct flourescent antibody of smear
41 Case Study 2: A US tourist comes to see you with this lesion on her arm. What questions would you ask this patient?
42 Seven days after her first visit, she comes to see you again. The lesion now looks like this what is on your list of differential diagnoses?
43 DO NOT PANIC! Individuals must be exposed to B. Anthracis spores To cause disease, B. anthracis spores must enter the skin, be swallowed, or inhaled Disease can be prevented after exposure to anthrax spores by early treatment with appropriate antibiotics Anthrax is NOT spread from person to person
44 Anthrax Information
45 Acknowledgements Marc Fischer MD MPH David Ashford DVM MPH DSci Conrad Quinn PhD Tanya Popovic PhD Nancy Rosenstein MD Bradley Perkins MD David Stephens MD Richard Besser MD
Anthrax and Anthrax Vaccine
 Anthrax and Anthrax Vaccine Under Supervision of : Prof. Dr\ Ekram M. El-Shabrawy Team Work : Mostafa Emad Ahmed Mohammed Bahaa El-Din Mostafa Abd-Elsamee Ahmed Mohamed Taha Contents Causative Organism.
Anthrax and Anthrax Vaccine Under Supervision of : Prof. Dr\ Ekram M. El-Shabrawy Team Work : Mostafa Emad Ahmed Mohammed Bahaa El-Din Mostafa Abd-Elsamee Ahmed Mohamed Taha Contents Causative Organism.
Anthrax: An Epidemiologic Perspective. Denise Dietz Public Health Epidemiologist
 Anthrax: An Epidemiologic Perspective Denise Dietz Public Health Epidemiologist Outline Overview of anthrax Explain different types of anthrax Clinical Why a good weapon Epidemiology Bacillus anthracis
Anthrax: An Epidemiologic Perspective Denise Dietz Public Health Epidemiologist Outline Overview of anthrax Explain different types of anthrax Clinical Why a good weapon Epidemiology Bacillus anthracis
Anthrax. Department of Child Health Medical Faculty University of Sumatera Utara
 Anthrax Malignant pustule, malignant edema, Woolsorters Disease, Ragpickers Disease, Maladi Charbon, Splenic Fever Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health Medical Faculty
Anthrax Malignant pustule, malignant edema, Woolsorters Disease, Ragpickers Disease, Maladi Charbon, Splenic Fever Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health Medical Faculty
ANTHRAX (Malignant Edema, Malignant Pustule, Woolsorter's Disease, Charbon, Ragpicker's Disease)
 ANTHRAX (Malignant Edema, Malignant Pustule, Woolsorter's Disease, Charbon, Ragpicker's Disease) REPORTING INFORMATION Class A: Report immediately via telephone the case or suspected case and/or a positive
ANTHRAX (Malignant Edema, Malignant Pustule, Woolsorter's Disease, Charbon, Ragpicker's Disease) REPORTING INFORMATION Class A: Report immediately via telephone the case or suspected case and/or a positive
Lecture (14) Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology
 AEROBIC BACILLUS Lecture (14) Dr. Baha,H,AL-Amiedi Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology General Characteristics of Bacillus 60 species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um) Most
AEROBIC BACILLUS Lecture (14) Dr. Baha,H,AL-Amiedi Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology General Characteristics of Bacillus 60 species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um) Most
Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7. Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods. Bacillus
 Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7 Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods Bacillus 1 Bacillus Characteristics - Gram positive - Large rod. - Arranged in long chain - Spore forming - Aerobic or facultative anaerobic
Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7 Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods Bacillus 1 Bacillus Characteristics - Gram positive - Large rod. - Arranged in long chain - Spore forming - Aerobic or facultative anaerobic
Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli: Bacillus & Clostridium Species: Introduction
 Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli: Bacillus & Clostridium Species: Introduction The gram-positive spore-forming bacilli are the bacillus and clostridium species. These bacilli are ubiquitous, and because
Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli: Bacillus & Clostridium Species: Introduction The gram-positive spore-forming bacilli are the bacillus and clostridium species. These bacilli are ubiquitous, and because
species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli 60 (Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um Most are saprophytic contaminants or normal flora
 AEROBIC BACILLUS (Lecture (15 Dr. Baha,H,AL-Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology General Characteristics of Bacillus species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli 60 (Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um Most are saprophytic
AEROBIC BACILLUS (Lecture (15 Dr. Baha,H,AL-Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology General Characteristics of Bacillus species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli 60 (Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um Most are saprophytic
Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology
 BACILLUS ANTHRAX Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology BACILLUS ANTHRACIS BACILLUS ANTHRAX Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Bacillus:General characters Anthrax is a zoonotic disease (could
BACILLUS ANTHRAX Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology BACILLUS ANTHRACIS BACILLUS ANTHRAX Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Bacillus:General characters Anthrax is a zoonotic disease (could
An Overview of Bioterrorism. SAEMS January 30, Charles A. Schable, M.S. Institutional Biosafety Committee University of Arizona
 An Overview of Bioterrorism SAEMS January 30, 2008 Charles A. Schable, M.S. Institutional Biosafety Committee University of Arizona Bioterrorism Intentional or threatened use of viruses, bacteria, fungi,
An Overview of Bioterrorism SAEMS January 30, 2008 Charles A. Schable, M.S. Institutional Biosafety Committee University of Arizona Bioterrorism Intentional or threatened use of viruses, bacteria, fungi,
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC
 UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC 28542-0042 FMST 304 Manage Biological Agent Casualties TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1. Given a casualty and the absence of a
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC 28542-0042 FMST 304 Manage Biological Agent Casualties TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1. Given a casualty and the absence of a
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat
 How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives Define - What is anthrax and what do I need to know. - The three forms of anthrax and treatment. Identify - What to look for
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives Define - What is anthrax and what do I need to know. - The three forms of anthrax and treatment. Identify - What to look for
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat
 How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives U.S.GENERAL SERVICES ADMINISTRATION Define What is anthrax and what do I need to know. The three forms of anthrax and treatment.
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives U.S.GENERAL SERVICES ADMINISTRATION Define What is anthrax and what do I need to know. The three forms of anthrax and treatment.
Infection Control Protocol for the Management of Anthrax Cases in Health Care settings
 State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate Infection Control Protocol for the Management of Anthrax Cases in Health Care settings 2002 Introduction: Anthrax is a bacterial infectious
State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate Infection Control Protocol for the Management of Anthrax Cases in Health Care settings 2002 Introduction: Anthrax is a bacterial infectious
Biological Warfare Agents
 Biological Warfare Agents Chapter 29 Biological Warfare Agents The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of
Biological Warfare Agents Chapter 29 Biological Warfare Agents The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of
Anthrax. Dr.T.V.Rao MD. Dr.T.V.Rao MD 1
 Anthrax Dr.T.V.Rao MD Dr.T.V.Rao MD 1 General Characteristics of Bacillus ~ 60 species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um) Most are saprophytic contaminants or normal
Anthrax Dr.T.V.Rao MD Dr.T.V.Rao MD 1 General Characteristics of Bacillus ~ 60 species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um) Most are saprophytic contaminants or normal
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani
 RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani Lower Respiratory Tract Upper Respiratory Tract Anatomy of the Respiratory System Nasopharynx Oropharynx Respiratory Tract Infections
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani Lower Respiratory Tract Upper Respiratory Tract Anatomy of the Respiratory System Nasopharynx Oropharynx Respiratory Tract Infections
Anthrax. Surveillance Protocol. Provider Responsibilities. Laboratory Responsibilities. Infectious Disease Epidemiology Program
 January 2007 may result from a naturally occurring, unintentional exposure such as from infected animals or from an intentional exposure such as from a bioterrorism (BT) event. When necessary this protocol
January 2007 may result from a naturally occurring, unintentional exposure such as from infected animals or from an intentional exposure such as from a bioterrorism (BT) event. When necessary this protocol
Biological Warfare Agents
 Chapter 29 The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID). Medical Management of
Chapter 29 The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID). Medical Management of
Mike Rossman, MD; Daniel J. Schissel, MD
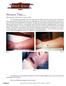 Picture This. Mike Rossman, MD; Daniel J. Schissel, MD You are building relationships with a tribe that primarily inhabits the border region between Iraq and Syria when you are asked to examine a skin
Picture This. Mike Rossman, MD; Daniel J. Schissel, MD You are building relationships with a tribe that primarily inhabits the border region between Iraq and Syria when you are asked to examine a skin
Fundamental Principles about Bioterrorism
 Fundamental Principles about Bioterrorism The following discussion provides a useful framework for putting into perspective the enormous volume of information being disseminated regarding health and Bioterrorism.
Fundamental Principles about Bioterrorism The following discussion provides a useful framework for putting into perspective the enormous volume of information being disseminated regarding health and Bioterrorism.
ANTHRAX VACCINE ADSORBED (BIOTHRAX )
 ANTHRAX VACCINE ADSORBED (BIOTHRAX ) DESCRIPTION Anthrax Vaccine Adsorbed, (BioThrax ) is a sterile, milky-white suspension (when mixed) made from cell-free filtrates of microaerophilic cultures of an
ANTHRAX VACCINE ADSORBED (BIOTHRAX ) DESCRIPTION Anthrax Vaccine Adsorbed, (BioThrax ) is a sterile, milky-white suspension (when mixed) made from cell-free filtrates of microaerophilic cultures of an
Yersinia pestis. Yersinia and plague. Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Anthrax is ancient. It's been around since biblical times, and is mentioned by Homer, Virgil & Hippocrates.
 Anthrax I. Introduction & history: Anthrax is ancient. It's been around since biblical times, and is mentioned by Homer, Virgil & Hippocrates. - Some people attribute the sixth plague (in Exodus) to Anthrax.
Anthrax I. Introduction & history: Anthrax is ancient. It's been around since biblical times, and is mentioned by Homer, Virgil & Hippocrates. - Some people attribute the sixth plague (in Exodus) to Anthrax.
Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? 19 October 2017
 19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
MMG 301 Lec. 35 Epidemiology and Bioterrorism
 MMG 301 Lec. 35 Epidemiology and Bioterrorism Questions for Today: (consider Med Micro course) 1. What is epidemiology? 2. How is epidemiology important to public health? 3. What pathogens are important
MMG 301 Lec. 35 Epidemiology and Bioterrorism Questions for Today: (consider Med Micro course) 1. What is epidemiology? 2. How is epidemiology important to public health? 3. What pathogens are important
Effect of Host Species on the Dose Response of Inhaled Bacillus anthracis Spores
 Effect of Host Species on the Dose Response of Inhaled Bacillus anthracis Spores Mark H. Weir E.I.T. Dr. Charles N. Haas Drexel University Department of Civil Architectural and Environmental Engineering
Effect of Host Species on the Dose Response of Inhaled Bacillus anthracis Spores Mark H. Weir E.I.T. Dr. Charles N. Haas Drexel University Department of Civil Architectural and Environmental Engineering
Bioterrorism: Medical and Public Health Perspectives
 Bioterrorism: Medical and Public Health Perspectives Overview and Historical Perspective Marcelle Layton As weapons, biological agents have a number of advantages. There is the potential for wide dissemination
Bioterrorism: Medical and Public Health Perspectives Overview and Historical Perspective Marcelle Layton As weapons, biological agents have a number of advantages. There is the potential for wide dissemination
Fourth Quarter / 2001 Volume 20 No. 4 Division of Surveillance West Virginia & Disease Control Statewide Disease Facts & Comparisons
 Bob Wise, Governor Paul L. Nusbaum, Secretary (DHHR) Fourth Quarter / 2001 Volume 20 No. 4 West Virginia EPI-LOG Division of Surveillance & Disease Control AIDS Surveillance (304) 558-2987 AIDS Prevention
Bob Wise, Governor Paul L. Nusbaum, Secretary (DHHR) Fourth Quarter / 2001 Volume 20 No. 4 West Virginia EPI-LOG Division of Surveillance & Disease Control AIDS Surveillance (304) 558-2987 AIDS Prevention
2. According to the information provided by the WHO, there is no justification at this stage for restrictions on travel or trade.
 Outbreak of Plague in Madagascar The following information is being disseminated by both the International Chamber of Shipping and The International Transport Workers Federation to draw attention to the
Outbreak of Plague in Madagascar The following information is being disseminated by both the International Chamber of Shipping and The International Transport Workers Federation to draw attention to the
B-NICE Overview. Types of WMD Agents. Types of WMD Agents. Types of WMD Agents. Job Aid Version 1.0 and 2.0. CDC & Prevention
 B-NICE Overview Types of WMD Agents Biological Nuclear Incendiary Chemical Explosive Types of WMD Agents Job Aid Version 1.0 and 2.0 Chemical Biological Radiological Nuclear Explosive Types of WMD Agents
B-NICE Overview Types of WMD Agents Biological Nuclear Incendiary Chemical Explosive Types of WMD Agents Job Aid Version 1.0 and 2.0 Chemical Biological Radiological Nuclear Explosive Types of WMD Agents
AVIAN FLU BACKGROUND ABOUT THE CAUSE. 2. Is this a form of SARS? No. SARS is caused by a Coronavirus, not an influenza virus.
 AVIAN FLU BACKGROUND 1. What is Avian Influenza? Is there only one type of avian flu? Avian influenza, or "bird flu", is a contagious disease of animals caused by Type A flu viruses that normally infect
AVIAN FLU BACKGROUND 1. What is Avian Influenza? Is there only one type of avian flu? Avian influenza, or "bird flu", is a contagious disease of animals caused by Type A flu viruses that normally infect
(Splenic fever, Siberian ulcer, Charbon, Milzbrand)
 MSD MANUAL Veterinary / Generalized Conditions / Anthrax Veterinary Manual Overview of Anthrax (Splenic fever, Siberian ulcer, Charbon, Milzbrand) By Martin E. Hugh Jones, VetMB, MPH, PhD, MRCVS, Professor
MSD MANUAL Veterinary / Generalized Conditions / Anthrax Veterinary Manual Overview of Anthrax (Splenic fever, Siberian ulcer, Charbon, Milzbrand) By Martin E. Hugh Jones, VetMB, MPH, PhD, MRCVS, Professor
Characteristics and Management of Selected Bioterrorism Agents 1, 4
 Anthrax Bacillus anthracis 1-5 days possibly up to 60 days). Data from 21 patients infected in October 2001 indicate a 5-11 day (mean of 7 days) incubation period for inhalational anthrax and 1-10 day
Anthrax Bacillus anthracis 1-5 days possibly up to 60 days). Data from 21 patients infected in October 2001 indicate a 5-11 day (mean of 7 days) incubation period for inhalational anthrax and 1-10 day
Should Anthrax Vaccine Be Tested in Children?
 21 November 2011 voaspecialenglish.com Should Anthrax Vaccine Be Tested in Children? Investigators outside the Dirksen Senate Office Building in Washington in October 2001 (You can download an MP3 of this
21 November 2011 voaspecialenglish.com Should Anthrax Vaccine Be Tested in Children? Investigators outside the Dirksen Senate Office Building in Washington in October 2001 (You can download an MP3 of this
THIS ACTIVITY HAS EXPIRED. CME CREDIT IS NO LONGER AVAILABLE
 THIS ACTIVITY HAS EXPIRED. CME CREDIT IS NO LONGER AVAILABLE The following content is provided for informational purposes only. PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF INFLUENZA Lisa McHugh, MPH Influenza can be a serious
THIS ACTIVITY HAS EXPIRED. CME CREDIT IS NO LONGER AVAILABLE The following content is provided for informational purposes only. PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF INFLUENZA Lisa McHugh, MPH Influenza can be a serious
Anthrax. Information for Health Care Providers. Physicians D Nurses D Laboratory Personnel D Infection Control Practitioners
 Anthrax Information for Health Care Providers Physicians D Nurses D Laboratory Personnel D Infection Control Practitioners Anthrax Caused by Bacillus anthracis, a large, encapsulated, gram-positive, aerobic,
Anthrax Information for Health Care Providers Physicians D Nurses D Laboratory Personnel D Infection Control Practitioners Anthrax Caused by Bacillus anthracis, a large, encapsulated, gram-positive, aerobic,
July 1, 2005 Page 1 of 5
 Abstract: Consensus Statement: Tularemia as a Biological Weapon: Medical and Public Health Abstracted from Dennis DT, Inglesby TV, Henderson DA, et al. Journal of the American Medical Association, June
Abstract: Consensus Statement: Tularemia as a Biological Weapon: Medical and Public Health Abstracted from Dennis DT, Inglesby TV, Henderson DA, et al. Journal of the American Medical Association, June
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
 Corynebacterium diphtheriae Aerobic gram-positive bacillus Toxin production occurs only when C. diphtheriae infected by virus (phage) carrying tox gene If isolated, must be distinguished from normal diphtheroid
Corynebacterium diphtheriae Aerobic gram-positive bacillus Toxin production occurs only when C. diphtheriae infected by virus (phage) carrying tox gene If isolated, must be distinguished from normal diphtheroid
Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C: Occupational Considerations 357 for the Anesthesiologist Stephen H. Jackson and Eddie C. Cheung
 INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND BIOTERRORISM Foreword Lee A. Fleisher xi Preface Samuel C. Hughes and James D. Marks xiii Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C: Occupational Considerations 357 for the Anesthesiologist Stephen
INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND BIOTERRORISM Foreword Lee A. Fleisher xi Preface Samuel C. Hughes and James D. Marks xiii Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C: Occupational Considerations 357 for the Anesthesiologist Stephen
Use of Anthrax Vaccine in the United States Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2009
 Vol. 59 / RR-6 Recommendations and Reports 1 Use of Anthrax Vaccine in the United States Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2009 Prepared by Jennifer Gordon Wright,
Vol. 59 / RR-6 Recommendations and Reports 1 Use of Anthrax Vaccine in the United States Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2009 Prepared by Jennifer Gordon Wright,
Microbiology of Atypical Pneumonia. Dr. Mohamed Medhat Ali
 Microbiology of Atypical Pneumonia Dr. Mohamed Medhat Ali Pneumonia P n e u m o n i a i s a n infection of the lungs that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Atypical! Pneumonia Symptoms. X-ray
Microbiology of Atypical Pneumonia Dr. Mohamed Medhat Ali Pneumonia P n e u m o n i a i s a n infection of the lungs that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Atypical! Pneumonia Symptoms. X-ray
Scientific and Medical Differences of Category A Pathogens
 Scientific and Medical Differences of Category A Pathogens Richard Gorman, M.D. Chair, Pediatric and Obstetrics Integrated Program Team HHS Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response
Scientific and Medical Differences of Category A Pathogens Richard Gorman, M.D. Chair, Pediatric and Obstetrics Integrated Program Team HHS Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response
Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia
 Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia Medicine Review Course 2018 Dr Lee Tau Hong Consultant Department of Infectious Diseases National Centre for Infectious Diseases Scope 1. Diagnosis
Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia Medicine Review Course 2018 Dr Lee Tau Hong Consultant Department of Infectious Diseases National Centre for Infectious Diseases Scope 1. Diagnosis
Conference Proceedings
 Conference Proceedings Severe Febrile Respiratory Illnesses As a Cause of Mass Critical Care Christian E Sandrock MD MPH Introduction Importance of Febrile Respiratory Illnesses Febrile Respiratory Illnesses
Conference Proceedings Severe Febrile Respiratory Illnesses As a Cause of Mass Critical Care Christian E Sandrock MD MPH Introduction Importance of Febrile Respiratory Illnesses Febrile Respiratory Illnesses
Influenza Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison
 Influenza Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals about
Influenza Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals about
Health Department MEMORANDUM Office of the Commissioner
 Health Department MEMORANDUM Office of the Commissioner TO: FROM: Halton Robert Physicians M. Nosal, Medical Medical Officer Chiefs of Health of Staff: Joseph Brant Memorial Hospital DATE: October 11,
Health Department MEMORANDUM Office of the Commissioner TO: FROM: Halton Robert Physicians M. Nosal, Medical Medical Officer Chiefs of Health of Staff: Joseph Brant Memorial Hospital DATE: October 11,
and Fosfomycin Acta Medica et Biologica followed by massive bacteremia, and results in severe
 Acta Medica et Biologica Vol. 49, No.3, 4, 95-99, 2001 In Vitro Susceptibility of Bacillus anthracis to Antimicrobial Agents Including Carbapenems and Fosfomycin Tatsuo YAMAMOTO, Ikue TANEIKE, Yukiko TAMURA
Acta Medica et Biologica Vol. 49, No.3, 4, 95-99, 2001 In Vitro Susceptibility of Bacillus anthracis to Antimicrobial Agents Including Carbapenems and Fosfomycin Tatsuo YAMAMOTO, Ikue TANEIKE, Yukiko TAMURA
Viruses: Select Agents and Emerging Pathogens. Patricia Bolívar MS., CLS, PHM
 Viruses: Select Agents and Emerging Pathogens Patricia Bolívar MS., CLS, PHM Objectives Review Select Agent Viruses. Key features to recognize Smallpox virus Update on emerging Viruses of possible pandemic
Viruses: Select Agents and Emerging Pathogens Patricia Bolívar MS., CLS, PHM Objectives Review Select Agent Viruses. Key features to recognize Smallpox virus Update on emerging Viruses of possible pandemic
Infectious Rashes of Interest to Infection Control and Occupational Health Dr. Justin Graham A Webber Training Teleclass
 Spot That Spot! Infectious Rashes of Interest to Infection Control and Occupational Health Justin Graham, MD MS Webber Training Teleclass 2005 Hosted by Paul Webber paul@webbbertraining.com It s Friday
Spot That Spot! Infectious Rashes of Interest to Infection Control and Occupational Health Justin Graham, MD MS Webber Training Teleclass 2005 Hosted by Paul Webber paul@webbbertraining.com It s Friday
UNION COUNTY 2017 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT
 UNION COUNTY 7 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT The communicable disease summary of reportable infectious disease for January 7 December 7. TABLE OF CONTENTS Annual Communicable Diseases... 3 Communicable
UNION COUNTY 7 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT The communicable disease summary of reportable infectious disease for January 7 December 7. TABLE OF CONTENTS Annual Communicable Diseases... 3 Communicable
Updated Recommendations for Management
 JAMA Vol. 287 No. 17, May 1, 2002 JAMA. 2002;287:2236-2252 Anthrax as a Biological Weapon, 2002 Updated Recommendations for Management Consensus Statement ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION CONSENSUS METHODS HISTORY
JAMA Vol. 287 No. 17, May 1, 2002 JAMA. 2002;287:2236-2252 Anthrax as a Biological Weapon, 2002 Updated Recommendations for Management Consensus Statement ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION CONSENSUS METHODS HISTORY
Lecture Notes. Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia
 Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
Chapters 21-26: Selected Viral Pathogens
 Chapters 21-26: Selected Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens 2. RNA Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens Smallpox (pp. 623-4) Caused by variola virus (dsdna, enveloped): portal of entry is the respiratory
Chapters 21-26: Selected Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens 2. RNA Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens Smallpox (pp. 623-4) Caused by variola virus (dsdna, enveloped): portal of entry is the respiratory
Bacillus anthracis. Summary Data
 Bacillus anthracis Overview: Bacillus anthracis and Anthrax Bacillus anthracis is a rod shaped gram negative bacterium which is the causative of a multi-symptom disease anthrax. There are three main types
Bacillus anthracis Overview: Bacillus anthracis and Anthrax Bacillus anthracis is a rod shaped gram negative bacterium which is the causative of a multi-symptom disease anthrax. There are three main types
WYANDOT COUNTY 2016 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT
 WYANDOT COUNTY 216 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT February 217 Wyandot County saw a.87% increase in communicable disease cases from 21 to 216 (11 cases and 116 cases respectively). Numerous infectious diseases
WYANDOT COUNTY 216 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT February 217 Wyandot County saw a.87% increase in communicable disease cases from 21 to 216 (11 cases and 116 cases respectively). Numerous infectious diseases
BIOLOGICAL WARFARE AND TERRORISM
 BIOLOGICAL WARFARE AND TERRORISM Pierrette Melin Medical microbiology, University hospital of Liege, Belgium The dark side of microbiology 1 Definition Historical perspective How real is the threat Biological
BIOLOGICAL WARFARE AND TERRORISM Pierrette Melin Medical microbiology, University hospital of Liege, Belgium The dark side of microbiology 1 Definition Historical perspective How real is the threat Biological
Q Fever What men and women on the land need to know
 Q Fever What men and women on the land need to know Dr. Stephen Graves Director, Australian Rickettsial Reference Laboratory Director, Division of Microbiology, Pathology North (Hunter) NSW Health Pathology,
Q Fever What men and women on the land need to know Dr. Stephen Graves Director, Australian Rickettsial Reference Laboratory Director, Division of Microbiology, Pathology North (Hunter) NSW Health Pathology,
SUBJECT: ISOLATION PRECAUTIONS REFERENCE #6003 PAGE: 1 DEPARTMENT: REHABILITATION SERVICES OF: 6 EFFECTIVE:
 PAGE: 1 STANDARD PRECAUTIONS: Precautions which are designed for care of all patients, regardless of diagnosis or presumed infection status to reduce the risk of transmission from both recognized and unrecognized
PAGE: 1 STANDARD PRECAUTIONS: Precautions which are designed for care of all patients, regardless of diagnosis or presumed infection status to reduce the risk of transmission from both recognized and unrecognized
Cases in employees. Cases. Day of onset (July)
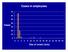 Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
Answers to these questions are available on LF is a zinc-dependent protease EF is a calmodulin-dependent adenylate cyclase
 21 Bacillus Two hours after a dinner, a family of four developed acute abdominal cramps with nausea and vomiting. The illness lasted for less than a day. 1. Bacillus cereus is associated with two forms
21 Bacillus Two hours after a dinner, a family of four developed acute abdominal cramps with nausea and vomiting. The illness lasted for less than a day. 1. Bacillus cereus is associated with two forms
Welcome to Pathogen Group 4
 Welcome to Pathogen Group 4 Chlamydia trachomatis Trachoma Genital chlamydia Chlamydophila (Chlamydia) psittaci Bacillus anthracis Neisseria meningitidis Haemophilus influenzae, type B Helicobacter pylori
Welcome to Pathogen Group 4 Chlamydia trachomatis Trachoma Genital chlamydia Chlamydophila (Chlamydia) psittaci Bacillus anthracis Neisseria meningitidis Haemophilus influenzae, type B Helicobacter pylori
Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Terminology Pathology study of disease Etiology cause of disease Pathogenesis disease process Infection colonization by microbes Disease illness
Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Terminology Pathology study of disease Etiology cause of disease Pathogenesis disease process Infection colonization by microbes Disease illness
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
PUBLIC HEALTH SIGNIFICANCE SEASONAL INFLUENZA AVIAN INFLUENZA SWINE INFLUENZA
 INFLUENZA DEFINITION Influenza is an acute highly infectious viral disease characterized by fever, general and respiratory tract catarrhal manifestations. Influenza has 3 Types Seasonal Influenza Avian
INFLUENZA DEFINITION Influenza is an acute highly infectious viral disease characterized by fever, general and respiratory tract catarrhal manifestations. Influenza has 3 Types Seasonal Influenza Avian
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum
 The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Community Acquired Pneumonia Based on CPS Practice Point Pneumonia in healthy Canadian children and youth and the British Thoracic Society Guidelines on CAP Objectives
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Community Acquired Pneumonia Based on CPS Practice Point Pneumonia in healthy Canadian children and youth and the British Thoracic Society Guidelines on CAP Objectives
WYANDOT COUNTY 2016 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT
 WYANDOT COUNTY 216 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT February 217 Wyandot County saw a.87% increase in communicable disease cases from 21 to 216 (11 cases and 116 cases respectively). Numerous infectious diseases
WYANDOT COUNTY 216 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT February 217 Wyandot County saw a.87% increase in communicable disease cases from 21 to 216 (11 cases and 116 cases respectively). Numerous infectious diseases
1918 Influenza; Influenza A, H1N1. Basic agent information. Section I- Infectious Agent. Section II- Dissemination
 1918 Influenza; Influenza A, H1N1 Basic agent information Section I- Infectious Agent Risk Group: - RG3 Synonym or Cross reference: - Spanish Flu - 1918 Flu - El Grippe Characteristics: - SELECT AGENT
1918 Influenza; Influenza A, H1N1 Basic agent information Section I- Infectious Agent Risk Group: - RG3 Synonym or Cross reference: - Spanish Flu - 1918 Flu - El Grippe Characteristics: - SELECT AGENT
Endemic: rhinovirus, Epidemic: pertussis several years ago Pandemic: H1N1 in was a pandemic just not as severe as originally feared
 1 2 3 Endemic: rhinovirus, Epidemic: pertussis several years ago Pandemic: H1N1 in 2009 10 was a pandemic just not as severe as originally feared 4 5 Endemic, Epidemic 6 Endemic, Epidemic 7 H5N1 H7N9 8
1 2 3 Endemic: rhinovirus, Epidemic: pertussis several years ago Pandemic: H1N1 in 2009 10 was a pandemic just not as severe as originally feared 4 5 Endemic, Epidemic 6 Endemic, Epidemic 7 H5N1 H7N9 8
NFECTIONS THROUGH THE RESPIRATORY TRACT
 NFECTIONS THROUGH THE RESPIRATORY TRACT **Infective agent s **Transmission **Host * viral infections * Bacterial infections *Fungal infections **Control of air-borne infections **INFECTIVE AGENTS The infective
NFECTIONS THROUGH THE RESPIRATORY TRACT **Infective agent s **Transmission **Host * viral infections * Bacterial infections *Fungal infections **Control of air-borne infections **INFECTIVE AGENTS The infective
Bio Agents of Concern/Interest
 Bio Agents of Concern/Interest Potential Biological Threats 1. Ricin 2. Botulism toxin (Clostridium botulinum) 3. Anthrax (Bacillus( anthracis) 4. Plague (Yersinia( pestis) 5. Tularemia (Francisella( tularensis)
Bio Agents of Concern/Interest Potential Biological Threats 1. Ricin 2. Botulism toxin (Clostridium botulinum) 3. Anthrax (Bacillus( anthracis) 4. Plague (Yersinia( pestis) 5. Tularemia (Francisella( tularensis)
Weapons of Mass Destruction. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012
 Weapons of Mass Destruction Lesson Goal To become familiarize with the concept of weapons of mass destruction (WMD), how these weapons might be used, and the type of treatment that would be appropriate
Weapons of Mass Destruction Lesson Goal To become familiarize with the concept of weapons of mass destruction (WMD), how these weapons might be used, and the type of treatment that would be appropriate
Below you will find information about diseases, the risk of contagion, and preventive vaccinations.
 Vaccinations Below you will find information about diseases, the risk of contagion, and preventive vaccinations. DTP - Diphtheria Tetanus Polio Yellow fever Hepatitis A Typhoid fever Cerebrospinal meningitis
Vaccinations Below you will find information about diseases, the risk of contagion, and preventive vaccinations. DTP - Diphtheria Tetanus Polio Yellow fever Hepatitis A Typhoid fever Cerebrospinal meningitis
INFLUENZA-2 Avian Influenza
 INFLUENZA-2 Avian Influenza VL 7 Dec. 9 th 2013 Mohammed El-Khateeb Overview 1. Background Information 2. Origin/History 3. Brief overview of genome structure 4. Geographical Distribution 5. Pandemic Nature
INFLUENZA-2 Avian Influenza VL 7 Dec. 9 th 2013 Mohammed El-Khateeb Overview 1. Background Information 2. Origin/History 3. Brief overview of genome structure 4. Geographical Distribution 5. Pandemic Nature
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13. Mycobacterium Actinomycetes
 Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
TB & HIV CO-INFECTION IN CHILDREN. Reené Naidoo Paediatric Infectious Diseases Broadreach Healthcare 19 April 2012
 TB & HIV CO-INFECTION IN CHILDREN Reené Naidoo Paediatric Infectious Diseases Broadreach Healthcare 19 April 2012 Introduction TB & HIV are two of the leading causes of morbidity & mortality in children
TB & HIV CO-INFECTION IN CHILDREN Reené Naidoo Paediatric Infectious Diseases Broadreach Healthcare 19 April 2012 Introduction TB & HIV are two of the leading causes of morbidity & mortality in children
WYANDOT COUNTY 2018 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT. The communicable disease summary of reportable infectious diseases for January 2018 December 2018.
 WYANDOT COUNTY 2018 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT The communicable disease summary of reportable infectious diseases for January 2018 December 2018. TABLE OF CONTENTS Annual Communicable Diseases... 3 Communicable
WYANDOT COUNTY 2018 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT The communicable disease summary of reportable infectious diseases for January 2018 December 2018. TABLE OF CONTENTS Annual Communicable Diseases... 3 Communicable
Health care workers and infectious diseases
 Introduction Health care workers and infectious diseases Objectives 1. What is an infectious disease?? 2. What is an infection and disease?? 3. Causes of re-emerging of the problem of the infectious diseases
Introduction Health care workers and infectious diseases Objectives 1. What is an infectious disease?? 2. What is an infection and disease?? 3. Causes of re-emerging of the problem of the infectious diseases
Western Veterinary Conference 2013
 Western Veterinary Conference 2013 SA283 EMERGING CANINE INFECTIOUS RESPIRATORY DISEASES Stephanie D Janeczko, DVM, MS, Dipl. ABVP (Canine/Feline) ASPCA New York, NY, USA Management of infectious respiratory
Western Veterinary Conference 2013 SA283 EMERGING CANINE INFECTIOUS RESPIRATORY DISEASES Stephanie D Janeczko, DVM, MS, Dipl. ABVP (Canine/Feline) ASPCA New York, NY, USA Management of infectious respiratory
PEDIATRIC INFLUENZA CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PEDIATRIC INFLUENZA CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DEFINITIONS AND BACKGROUND Uncomplicated influenza illness is characterized by the abrupt onset of constitutional and respiratory signs and symptoms. Signs
PEDIATRIC INFLUENZA CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DEFINITIONS AND BACKGROUND Uncomplicated influenza illness is characterized by the abrupt onset of constitutional and respiratory signs and symptoms. Signs
INFLUENZA (Outbreaks; hospitalized or fatal pediatric cases)
 INFLUENZA (Outbreaks; hospitalized or fatal pediatric cases) 1. Agent: Influenza viruses A, B, and C. Only influenza A and B are of public health concern since they are responsible for epidemics. 2. Identification:
INFLUENZA (Outbreaks; hospitalized or fatal pediatric cases) 1. Agent: Influenza viruses A, B, and C. Only influenza A and B are of public health concern since they are responsible for epidemics. 2. Identification:
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10. Mycobacterium. Actinomycetes. Nocardia
 Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Bioterrorism. Eric S. Toner, MD. National Governors Association July 22, 2009
 Bioterrorism Eric S. Toner, MD National Governors Association July 22, 2009 Biological Weapons Have a Long History 14th century: Tartars catapulted bodies of plague victims over siege walls in Crimea 1750
Bioterrorism Eric S. Toner, MD National Governors Association July 22, 2009 Biological Weapons Have a Long History 14th century: Tartars catapulted bodies of plague victims over siege walls in Crimea 1750
The Current Status of Influenza Testing
 The Current Status of Influenza Testing Norman Moore, PhD Director of Scientific Affairs, Infectious Diseases 0 Objectives Discuss the health impacts of influenza in the US Discuss the diagnostic options
The Current Status of Influenza Testing Norman Moore, PhD Director of Scientific Affairs, Infectious Diseases 0 Objectives Discuss the health impacts of influenza in the US Discuss the diagnostic options
Communicable diseases. Gastrointestinal track infection. Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology
 Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
Anthrax as a Biological Weapon, Updated Recommendations for Management JAMA. 2002;287:
 CONSENSUS STATEMENT Anthrax as a Biological Weapon, 2002 Updated Recommendations for Management Thomas V. Inglesby, MD Tara O Toole, MD, MPH Donald A. Henderson, MD, MPH John G. Bartlett, MD Michael S.
CONSENSUS STATEMENT Anthrax as a Biological Weapon, 2002 Updated Recommendations for Management Thomas V. Inglesby, MD Tara O Toole, MD, MPH Donald A. Henderson, MD, MPH John G. Bartlett, MD Michael S.
Peterborough County-City Health Unit Pandemic Influenza Plan Section 1: Background
 1. Background Every expert on influenza agrees that the ability of the influenza virus to re-assort genes means that another influenza pandemic not only can happen, it almost certainly will happen Influenza
1. Background Every expert on influenza agrees that the ability of the influenza virus to re-assort genes means that another influenza pandemic not only can happen, it almost certainly will happen Influenza
Meningococcal Invasive Disease
 Meningococcal Invasive Disease Communicable Disease Control Unit NOTE: The main difference between this and previous protocols is reporting and management of meningococcal conjunctivitis. Criteria for
Meningococcal Invasive Disease Communicable Disease Control Unit NOTE: The main difference between this and previous protocols is reporting and management of meningococcal conjunctivitis. Criteria for
Avian Influenza: Armageddon or Hype? Bryan E. Bledsoe, DO, FACEP The George Washington University Medical Center
 Avian Influenza: Armageddon or Hype? Bryan E. Bledsoe, DO, FACEP The George Washington University Medical Center Definitions: Epidemic The occurrence of cases of an illness in a community or region which
Avian Influenza: Armageddon or Hype? Bryan E. Bledsoe, DO, FACEP The George Washington University Medical Center Definitions: Epidemic The occurrence of cases of an illness in a community or region which
INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY FOR HEART AND LUNG TRANSPLANTATION a Society that includes Basic Science, the Failing Heart, and Advanced Lung Disease
 International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation Advisory Statement on the Implications of Pandemic Influenza for Thoracic Organ Transplantation This advisory statement has been produced by the
International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation Advisory Statement on the Implications of Pandemic Influenza for Thoracic Organ Transplantation This advisory statement has been produced by the
Critical Care Nursing Theory. Pneumonia. - Pneumonia is an acute infection of the pulmonary parenchyma
 - is an acute infection of the pulmonary parenchyma - is a common infection encountered by critical care nurses when it complicates the course of a serious illness or leads to acute respiratory distress.
- is an acute infection of the pulmonary parenchyma - is a common infection encountered by critical care nurses when it complicates the course of a serious illness or leads to acute respiratory distress.
Bioterrorism. Environmental Encyclopedia, 2011 Updated: August 30, 2017 From Opposing Viewpoints in Context
 Bioterrorism Environmental Encyclopedia, 2011 Updated: August 30, 2017 From Opposing Viewpoints in Context Bioterrorism refers to the use of lethal biological agents to wage terror against a civilian population.
Bioterrorism Environmental Encyclopedia, 2011 Updated: August 30, 2017 From Opposing Viewpoints in Context Bioterrorism refers to the use of lethal biological agents to wage terror against a civilian population.
Alberta Health and Wellness Public Health Disease Under Surveillance Management Guidelines March 2011
 March 2011 Histoplasmosis Case Definition Confirmed Case Clinical illness [1] with laboratory confirmation of infection: Isolation of Histoplasma capsulatum from an appropriate clinical specimen (tissue
March 2011 Histoplasmosis Case Definition Confirmed Case Clinical illness [1] with laboratory confirmation of infection: Isolation of Histoplasma capsulatum from an appropriate clinical specimen (tissue
MYCOBACTERIA. Pulmonary T.B. (infect bird)
 MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
Haemophilus influenzae, Invasive Disease rev Jan 2018
 Haemophilus influenzae, Invasive Disease rev Jan 2018 BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent Haemophilus influenzae (H. influenzae) is a small, Gram-negative bacillus, a bacterium capable of causing a range
Haemophilus influenzae, Invasive Disease rev Jan 2018 BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent Haemophilus influenzae (H. influenzae) is a small, Gram-negative bacillus, a bacterium capable of causing a range
YERSINIA MODULE 26.1 INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 26.2 YERSINIA PESTIS. Notes
 MODULE Yersinia 26 YERSINIA 26.1 INTRODUCTION Genus Yersinia belongs to tribe Yersinieae of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Yersinia are Gram-negative rod shaped bacteria and are facultative anaerobes.
MODULE Yersinia 26 YERSINIA 26.1 INTRODUCTION Genus Yersinia belongs to tribe Yersinieae of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Yersinia are Gram-negative rod shaped bacteria and are facultative anaerobes.
Haemophilus influenzae
 Haemophilus influenzae type b Severe bacterial infection, particularly among infants During late 19th century believed to cause influenza Immunology and microbiology clarified in 1930s Haemophilus influenzae
Haemophilus influenzae type b Severe bacterial infection, particularly among infants During late 19th century believed to cause influenza Immunology and microbiology clarified in 1930s Haemophilus influenzae
Anthrax: A Review For The Medical Officer
 J R Army Med Corps 2003; 149: 101-105 FOCUS ON Maj Guy Vautier BM BSc MRCP RAMC Consultant Physician Royal Hospital Haslar, Gosport, PO12 2AA. E-mail: guy.vaut@dsca.mod.uk Anthrax: A Review For The Medical
J R Army Med Corps 2003; 149: 101-105 FOCUS ON Maj Guy Vautier BM BSc MRCP RAMC Consultant Physician Royal Hospital Haslar, Gosport, PO12 2AA. E-mail: guy.vaut@dsca.mod.uk Anthrax: A Review For The Medical
INFECTIOUS DISEASES IN THE LONG TERM CARE FACILITY
 INFECTIOUS DISEASES IN THE LONG TERM CARE FACILITY The following is a list of the most common infectious diseases that are to be found in the long term care facility. Precautions are recommended and the
INFECTIOUS DISEASES IN THE LONG TERM CARE FACILITY The following is a list of the most common infectious diseases that are to be found in the long term care facility. Precautions are recommended and the
ANTHRAX. [Back to NBC Information Server]
![ANTHRAX. [Back to NBC Information Server] ANTHRAX. [Back to NBC Information Server]](/thumbs/85/92717428.jpg) [Back to NBC Information Server] Index Anthrax Botulism Brucellosis Cholera Plague Q Fever Ricin Intoxication Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B Disease Tricothecene Mycotoxicosis Tularemia Variola (Smallpox)
[Back to NBC Information Server] Index Anthrax Botulism Brucellosis Cholera Plague Q Fever Ricin Intoxication Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B Disease Tricothecene Mycotoxicosis Tularemia Variola (Smallpox)
