2008 Tuberculosis Report
|
|
|
- Cecil Nelson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2008 Tuberculosis Report County of Sacramento Department of Health and Human Services Division of Public Health Page 1
2 Table of Contents Figure 1. Tuberculosis Incidence Rates, County of Sacramento Vs California, (Page 7) Figure 2. Tuberculosis Cases by Year, County of Sacramento, (Page 7) Table 1. Average Incidence Rate of TB by Age Group, County of Sacramento, (Page 8) Figure 3. Proportion of TB Cases by Age Group, County of Sacramento, (Page 8) Figure 4. Tuberculosis Cases by Age Group, County of Sacramento, (Page 8) Figure 5. Proportion of Tuberculosis Cases Among Children Less Than 15 Years of Age, County of Sacramento Vs California, (Page 9) Figure 6. Tuberculosis Cases by Gender, County of Sacramento, (Page 9) Figure 7. TB Incidence Rates by Gender, County of Sacramento, (Page 9) Figure 8. Proportion of TB Cases by Race/Ethnicity, County of Sacramento, 2006 (Page 10) Figure 9. Incidence Rates by Race/Ethnicity, County of Sacramento, (Page 10) Figure 10. Table 2. Figure 11. Table 3. Figure 12. Table 4. Proportion of U.S.-Born TB Cases by Race/Ethnicity, County of Sacramento, (Page 11) Tuberculosis Cases in U.S.-Born Persons by Race/Ethnicity, Sex, and Age Group, County of Sacramento,, (Page 11) Proportion of Foreign-Born Tuberculosis Cases by Race/Ethnicity, County of Sacramento, (Page 12) Tuberculosis Cases in Foreign-Born Persons by Race/Ethnicity, Gender, and Age Group, County of Sacramento (Page 12) Proportion of Foreign Born TB Cases by Selected Country of Origin, County of Sacramento, (Page 13) Tuberculosis Among Foreign-Born Cases by Number of Years in the U.S. and Selected Country of Origin, County of Sacramento, (Page 13) Page 2
3 Table of Contents Figure 13. Table 5. Tuberculosis Among Foreign-Born by Number of Years in the U.S., Three Year Average, County of Sacramento, (Page 13) Tuberculosis Cases Among Hmong Refugees by Sex and Age Group, County of Sacramento, (Page 14) Figure 14. Epidemic Curve of Hmong Refugee Cases, County of Sacramento, (Page 14) Table 6. TB Among Miien by Gender and Age, County of Sacramento (Page 15) Figure 15. Epidemic Curve of Mien Outbreak Cases, County of Sacramento, (Page 15) Figure 16. Figure 17. Table 7. Figure 18. TB Among Homeless, Three Year Average Number of Cases, County of Sacramento, (Page 16) Number of TB Cases Among the Homeless and Proportion of Homeless Cases Among All TB Cases, County of Sacramento, (Page 16) TB Among Homeless Persons by Gender, Race/Ethnicity and Age, County of Sacramento,, (Page 17) Epidemic Curve of Homeless TB Cases by Month of Diagnosis, County of Sacramento, (Page 17) Table 8. Drug Resistant TB by Year, V, (Page 18) Table 9. Tuberculosis Cases by Resistance to First Line Drugs, County of Sacramento, (Page 18) Page 3
4 Introduction Introduction Tuberculosis (TB) is an airborne disease caused by a group of bacteria referred to as the Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) complex. The five species in this complex are M. tuberculosis, M. bovis, M. africanum, M. canettii, and M. microti. General symptoms may include a prolonged productive cough, blood-tinged sputum, night sweats, fever, fatigue, and weight loss. TB affects several sites most commonly the lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body like the brain, kidneys, or spine. TB bacteria are aerosolized into respiratory droplet nuclei when a person who has TB of the lungs or larynx coughs, sneezes, laughs, or sings. Subsequently, another person inhales the droplet nuclei that are formed. Individuals who become infected but do not become ill are considered to have latent TB infection (LTBI) and cannot transmit the infection to others. LTBI is evidenced by a positive tuberculin skin test (TST) or a positive blood test using T-cell Inteferon-gamma Release Assay (TIGRA) testing and without evidence of disease after evaluation. Approximately 10% of infected individuals will progress to active disease at some point in their lives. During 2006, there were 97 new cases of TB reported to the County of Sacramento, Division of Public Health. Globally, anti- TB chemotherapy has made a significant impact on lowering the rate of active TB and deaths due to TB. However, many challenges still remain, including the increase in drug resistance. Report of Verified Cases of TB In 1993, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in conjunction with state and local health departments, began using the expanded Report of Verified Case of Tuberculosis (RVCT) to collect information on each case of TB. A TB case is defined as active disease, not old infections or LTBI. In addition to the demographic and clinical features of TB that were previously collected, the RVCT includes information on drug resistance, risk factors for TB, and treatment outcomes. In 1998, CDC implemented the Tuberculosis Information Management System (TIMS) for data entry and transmission of case reports. Acknowledgments The Division of Public Health acknowledges Chest Clinic staff for their efforts in tuberculosis (TB) control and patient management. We also acknowledge staff at the State Department of Public Health, Tuberculosis Control Branch (TBCB) for their assistance and guidance in outbreak management. Purpose The purpose of this report is to provide the community with an overview and enhanced understanding of TB in Sacramento County including trends, racial disparities, multi-drug resistance, TB among foreign born residents, outbreaks, and the distribution of TB cases. For comments or questions contact: County of Sacramento Epidemiology Services Division of Public Health Department of Health and Human Services 7001-A East Parkway Sacramento CA (916) Page 4
5 Executive Summary Executive Summary This report summarizes recent TB data from the Tuberculosis Information Management System for the County of Sacramento. Case Counts and Rates During 2006, there were 97 cases of tuberculosis reported in the County of Sacramento. In 2005, the incidence rate was 10.2 per 100,000 population compare to 6.8 per 100,000 in Of the 397 TB cases diagnosed from , 86.6% (344) were diagnosed with pulmonary TB. Thirty-six percent of those cases were smear positive, thus posing a greater risk of disease transmission. For the past ten years, statewide incidence rates for TB have steadily declined, whereas rates in the County of Sacramento have fluctuated due to sporadic local outbreaks among different race/ethnic groups and homeless persons. Foreign-born persons and racial/ethnic minority populations continue to be affected disproportionately by TB statewide as well as locally. The proportion of cases occurring in children less than 15 years of age continues to decline with only 1% of cases in 2006 less than 15 years compared to 4.8% statewide. Racial Disparities The TB rates among Asians, African Americans, and Hispanics, in 2006, were 16.6, 5.1, and 3.8 times higher than rates among Caucasians, respectively. Asians accounted for 56.7% of cases in Burden in Foreign-born In 2006, the number of TB cases among foreign-born persons in Sacramento County was 2.6 times higher than that of U.S.-born persons. From , 74.7% of TB cases among foreign-born persons occurred in persons from five countries: Laos/Thailand (59), Philippines (49), Vietnam (40), Mexico (39), and India (23). Drug Resistance From , 10 TB cases were multi-drug resistant. All MDR cases were foreign born. From , for those cases who had susceptibility testing done, 9.2% were resistant to isoniazid, compared to 10.4% statewide Page 5
6 Executive Summary Technical Notes TB Cases TB cases submitted to the TBCB Registry by January 15, 2007, were counted as cases in After reporting a case, the final disposition of that case may change and we may decide that a reported case did not have active TB. This case will be deleted from the TB database. Therefore, data is provisional since the total number of TB cases counted in a given year may change, although usually by a very small number of cases. This report incorporates any subsequent changes in the number of cases. In their annual report, the TBCB uses the original number of reported cases, not the revised; therefore the numbers in this report may differ slightly from those reported by TBCB. Population Population totals and data by age, sex and race/ethnic group are from the State of California, Department of Finance, Race/Ethnic Population with Age and Sex Detail, Sacramento, CA, May Small Case Numbers There are different methods for reporting the rates of rare events, we have chosen not to report rates when the total number of TB cases is less than twenty. Race/Ethnicity The RVCT has one variable for race and one for ethnicity. If a case is classified as Hispanic on the RVCT, then the case is reported as Hispanic in this report, regardless of race. Beginning in 2003, the federal Office of Management and Budget (OMB) reporting mandates required separate reporting of Asian and Pacific Islander/Native Hawaiian races, as well as the opportunity for persons to identify themselves by one or more racial groups. In tables where data on race/ethnicity are presented these persons are combined in the Asian/Pacific Islander race/ethnic group, in order to provide comparability to previous years data. No persons reported more than one race category Drug Resistance Multi-drug resistance is defined as resistance to both isoniazid and rifampin. Poly-drug resistance is defined as resistance to more than one first line drug, but not resistant to both isoniazid and rifampin. Mono-drug resistance is defined as resistance to one first line drug. Page 6
7 Tuberculosis in Sacramento TB Incidence Figure 1 compares incidence rates for the County of Sacramento with statewide incidence rates for the past ten years. While statewide incidence rates have steadily declined, rates for the County of Sacramento have fluctuated due to sporadic local outbreaks and changes in immigration patterns. National, statewide, and local incidence rates declined in Figure 2 shows the number of cases for the County of Sacramento by year. Of the 97 cases reported in 2006, 75 (77.3%) were culture confirmed, one case was smear positive only, and 21 (21.6%) were verified as clinical or provider diagnosed cases. Pulmonary tuberculosis accounted for 82 (84.5%) of cases. Sputum specimens were collect on 81 of the pulmonary tuberculosis patients, with 61 (75.3%) being culture positive, 40 (49.4%) smear positive and 38 (46.9%) both smear and culture positive. Figure 1. Tuberculosis Incidence Rates County of Sacramento Vs California, Incidence Rate per 100, Sacramento California Incidence Rate per 100, Figure 2. Tuberculosis Cases by Year County of Sacramento TB Cases Page 7
8 Tuberculosis by Age Group Age From 2002 to 2006, there were 652 TB cases in the County of Sacramento. The greatest proportion of TB cases occurred in individuals aged years (36.6%) (Figure 3). Table 1 shows the average incidence rate per 100,000 by age group from 2002 to Although the year old age group comprise the greatest proportion of TB cases (Figure 4), the highest incidence rate was among individuals 65 years and older. Table 1. Average Incidence Rate of TB by Age Group, County of Sacramento Age Group Rate per 100, Figure 3. Proportion of Tuberculosis Cases by Age Group County of Sacramento % 0-14 yrs 7.5% yrs 10.1% yrs 21.5% yrs 31.6% yrs 29.3% Number of Cases Figure 4. Tuberculosis Cases by Age Group County of Sacramento Page 8
9 TB Among Children & TB by Gender TB Among Children Since 2002, the proportion of cases occurring in children less than 15 has fluctuated, most likely due to local outbreaks and changes in immigration patters (Figure 5). However, consistent with statewide trends, since 2004 there has been a continuous downward trend in cases occurring in this age group. Figure 5. Proportion of Tuberculosis Cases Among Children Less Than 15 years of Age County of Sacramento Vs. California, Number of Cases 20.0% 15.0% 10.0% 5.0% 0.0% Sacramento 15.0% 5.2% 9.4% 6.3% 1.0% California 7.0% 7.2% 7.5% 5.2% 4.8% Gender Figure 6 shows the number of TB cases by gender from Typically, males have a higher incidence of TB than females. It appears the incidence rate among males and females in the County of Sacramento is becoming similar. (Figure 7). However, gender aspects of TB has been a neglected research area, more data is needed. TB Cases Figure 6. Tuberculosis Cases by Gender, County of Sacramento Male Female Per 100, Figure 7. TB Incidence Rates by Gender County of Sacramento Male Female Page 9
10 Tuberculosis by Race/Ethnicity Race/Ethnicity In 2006, Asian/Pacific Islanders made up the highest proportion (56.7%) of TB cases in the County of Sacramento (Figure 8), followed by Hispanics (18.6%), African Americans (13.4%) and Caucasians (11.3%). While incidence rates among all ethnic groups have declined, the rates among Asians, African Americans, and Hispanics are 16.6, 5.1, and 3.8 times higher than their Caucasian counterparts (Figure 9). Figure 8. Proportion of Tuberculosis Cases by Race/Ethnicity County of Sacramento, 2006 Hispanic 18.6% Native Amer 0.0% Unknow n 0.0% Caucasian 11.3% African Amer 13.4% Asian/PI 56.7% Figure 9. TB Incidence Rates by Race /Ethnicity County of Sacramento A sian/p I African Amer Caucasian Hispanic Note: For 2002 African Americans and Hisppanics had less than 20 cases. For 2003, African Americans had less than 20 cases. For 2006, African Americans, Caucasians, and Hispanics had less 20 cases. As a result, these rates may not be reliable. Page 10
11 Tuberculosis: US-Born Cases US-Born In 1993, 38.4% of TB cases in the County of Sacramento occurred in U.S. -born persons compared to 26.8% in The greatest proportion of cases among U.S.-born persons from occurred in individuals who were African American or Caucasian (46.2% and 35.0% respectively) (Figure 10). Table 2 shows the number of U.S.-born cases by race/ethnicity, sex, and age group in Sacramento from Figure 10. Proportion of U.S.-Born Tuberculosis Cases by Race/Ethnicity County of Sacramento, Hispanic 10.3% Asian 8.5% Caucasian 35.0% African Amer 46.2% Table 2. Tuberculosis Cases in US Born Persons by Race/Ethnicity, Sex, and Age Group, County of Sacramento Total Total n=24 n=36 n=44 n=47 n=26 n=178 Gender Male Female Race/Ethnicity Asian African American Caucasian Hispanic Age Group Page 11
12 Tuberculosis: Foreign-Born Cases Foreign-Born The proportion of TB cases that occurred in foreign-born persons increased statewide and locally. In 1993, 62.8% of cases statewide were foreign-born compared to 76.8% in In the County of Sacramento 61.6% of cases in 1993 were foreign-born compared to 72.2% in 2006, a 17.2% increase. Among foreign-born TB cases from , Asians accounted for 71.1% of cases (Figure 7). Table 3 shows foreign-born cases by race/ethnicity, sex, and age group in Sacramento from Figure 11. Proportion of Foreign-Born Tuberculosis Cases by Race/Ethnicity Sacramento County, Caucasian 8.4% Hispanic 17.2% African Amer 3.3% Asian 71.1% Table 3. Tuberculosis Cases in Foreign-Born Persons by Race/ Ethicity, Gender, and Age Group, County of Sacramento Total Total n=75 n=110 n=111 n=92 n=70 n=458 Gender Male Female Race/Ethnicity Asian African American Caucasian Hispanic Age Group Page 12
13 Tuberculosis: Foreign-Born Cases Foreign-Born From , the top five countries of origin of foreign-born persons with TB were Laos/ Thailand, Philippines, Vietnam, Mexico, and India (Figure 12). The average number of foreignborn TB cases who have been in the U.S. for less than one year increased 38.0% from when compared to the average number of foreign-born cases from (Figure 13) Table 5 shows the number of years in the U.S. at the time of diagnosis for foreign-born persons with TB. by selected countries of origin. Figure 12. Proportion of Foreign Born TB Cases by Selected Country of Origin County of Sacramento, Former Soviet Union 5.9% All Others 16.1% Philippines 17.9% India 8.4% China 3.3% Laos/Thailand 19.4% Mexico 14.3% Vietnam 14.7% Table 4. Tuberculosis Among Foreign Born Cases by Number of Years in the U.S. and Selected Country of Origin, County of Sacramento Total Total < >20 n=273 n=109 n=29 n=20 n=25 n=48 n=42 Laos/Thailand Philippines Vietnam Mexio India Former Soviet Union China All Others Figure 13. Tuberculosis Among Foreign Born by Number of Years in the U.S. Three Year Average, County of Sacramento, < >20 Aver Aver Aver Page 13
14 Tuberculosis Outbreak Outbreak of Tuberculosis in Newly Arrived Hmong Refugees From June 2004 through January 2005, the U.S. Department of State resettled over 9,000 Hmong refugees from Wat Tham Krabok (WTK), a refugee camp in central Thailand, into the United States. About one-third, or 3,106, of the refugees were resettled in California, including 938 in the County of Sacramento. By July 2005, 16 newly arrived Hmong refugees in the County of Sacramento had been diag- nosed with tuberculosis (Figure 14). All cases were diagnosed within a month of their arrival in the United States. Of the 16 cases, five were culture positive. Three of those cases were multi-drug resistant. The peak number of cases occurred from September-December, Ages for all cases ranged from 4-72 years of age (Table 5). There was no evidence of transmission in the U.S. from these cases. Table 5. Tuberculosis Cases Among Hmong Refugees by Sex and Age Group County of Sacramento, Total Total n=1 n=3 n=2 n=3 n=3 n=4 n=16 Male Female Figure 14. Epidemic Curve of Hmong Refugee Cases County of Sacramento Number of Cases Yellow boxes indicate MDR cases June-04 July-04 Aug-04 Sept-04 Oct-04 Nov-04 Dec-04 Jan-05 Feb-05 Mar-05 April-05 May-05 June-05 July-05 Page 14
15 Tuberculosis Outbreak Cluster of Tuberculosis among Mien Refugee The Mien (Iu Mien) ethnic group is native to Laos, Thailand, and Vietnam. Mien arrivals in the United States peaked in the 1980s as a large group of Mien, who had been relocated to Thai camps in the aftermath of the Indochina Wars, were assigned refugee status and resettled to the U.S. along with Hmong refugees in similar circumstances. Mien population data are not available, but an estimated 12,000 Mien currently live in the County of Sacramento. While there are some cultural similarities to the Hmong, the Mien are a distinct group, and speak a different language (Iu Mien). In March 2006, a cluster of 11 tuberculosis cases was identified in Mien communities in Sacramento, starting in Further investi- gation identified five more cases for a total of 16 cases in 15 persons (one case had two episodes of TB, with diagnosis dates between January 2001 and December 2006 (Figure 15). Of the 16 cases 12 were culture positive with seven isolates available for genotyping. All seven isolates had matching genotype data. Cases ranged in age from years (Table 6). Three cases were U.S. born; the remaining cases were born in Laos or Thailand. Of the foreign born cases, the average length of stay in the U.S. ranged from 9-26 years with an average of 17 years. The last case in this cluster was diagnosed in November of No new cases have been identified with the same genotype. Table 6. TB Among Mien by Gender and Age County of Sacramento Gender Age Total Fem ale Male Total Number of Cases Figure 15. Epidemic Curve of Mien Outbreak Cases, County of Sacramento Page 15
16 Tuberculosis Among the Homeless Tuberculosis Among the Homeless The number of TB cases that occurred among homeless persons in the County of Sacramento has fluctuated over the past 10 years. Threeyear averages from show an increase in the number of cases among the homeless (Figure 15). Without knowledge of the true number of homeless persons, we were unable to determine if the rate of TB among the homeless increased. From , 11.8% of TB cases in the County of Sacramento were homeless (Figure 16). In comparison, from , 11.0% of TB cases in the County of Sacramento were homeless, whereas, statewide 6.5% of cases were homeless for the same period. Figure 16. TB Among Homeless, Three Year Average Number of Cases, County of Sacramento Number of Cases Figure 17. Number of TB Cases Among the Homeless and Proportion of Homeless Cases Among All TB Cases County of Sacramento County, Number of Cases Number of Cases Percent of Total Cases 13.5% 7.5% 6.7% 8.3% 13.6% 6.3% 9.3% 10.4% 13.8% 12.4% Page 16
17 Tuberculosis Among the Homeless The majority of homeless TB cases in Sacramento occurred among Caucasian and African American males age years of age (Table 7). In early 2000, a cluster of TB cases was identified among the homeless community in Sacramento County, all with matching DNA fingerprints, suggesting a single source. Intensive investigative efforts were undertaken to identify new cases and contacts. From April of 1999, through June of 2000, 12 TB cases with matching DNA fingerprints were identified, 11 were homeless individuals and one was a shelter volunteer (Figure 17). As a result of this investigation, in February 2001, mandatory screening by chest x-ray and proof of TB clearance to access homeless services was initiated. From February 2001 through 2006, 34 cases of TB were identified. Table 7. TB Among Homeless Persons by Gender, Race/Ethnicity and Age, County of Sacramento Total n=47 Gender Male 34 Female 13 Race/Ethnicity Asian 0 African American 20 Caucasian 22 Hispanic 5 Age Group Figure 18. Epidemic Curve of Homeless TB Cases by Month of Diagnosis, County of Sacramento, Number of Cases Apr-99 May-99 Jun-99 Jul-99 Aug-99 Sep-99 Oct-99 Nov-99 Dec-99 Jan-00 Feb-00 Mar-00 Apr-00 May-00 Jun-00 Month of Diagnosis Page 17
18 Tuberculosis Drug Resistance Drug Resistance From , 10 cases were multi-drug resistant (MDR). All MDR cases were foreign born. During that same time period, for those cases who had susceptibility testing done, 9.2% were resistant to isoniazid (Tables 8 and 9) Table 8. Drug Resistant TB by Year County of Sacramento Year Multi Drug Resistant Poly Drug Resistant Mono Drug Resistant Total Table 9. Tuberculosis Cases by Resistance to First Line Drugs, County of Sacramento Year No. of Isoniazid Rifampin Pyrazinamide Ethambutol Tested No. % No. % No. % No. % Total Page 18
19 Introduction County of Sacramento Board of Supervisors Roger Dickinson, District 1 Jimmie R. Yee, District 2 Susan Peters, District 3 Roberta MacGlashan, District 4 Don Nottoli, District 5 Terry Schutten, County Executive Department of Health & Human Services Lynn Frank, Director County Health Officer Glennah Trochet, M.D. Epidemiology Program Manager Cassius Lockett, Ph.D., MS Prepared by Alix Gillam, MPH Page 20
TB EPIDEMIOLOGY. Outline. Estimated Global TB Burden, TB epidemiology
 TB EPIDEMIOLOGY TB Clinical Intensive Course Curry International Tuberculosis Center September 30, 2015 Varsha Nimbal, MPH Tuberculosis Control Branch California Department of Public Health 1 Outline TB
TB EPIDEMIOLOGY TB Clinical Intensive Course Curry International Tuberculosis Center September 30, 2015 Varsha Nimbal, MPH Tuberculosis Control Branch California Department of Public Health 1 Outline TB
Tuberculosis Epidemiology
 Tuberculosis Epidemiology TB CLINICAL INTENSIVE COURSE Curry International Tuberculosis Center October 18, 2017 Varsha Hampole, MPH Tuberculosis Control Branch California Department Of Public Health Outline
Tuberculosis Epidemiology TB CLINICAL INTENSIVE COURSE Curry International Tuberculosis Center October 18, 2017 Varsha Hampole, MPH Tuberculosis Control Branch California Department Of Public Health Outline
Tuberculosis in Alameda County, 2009
 Tuberculosis in Alameda County, 29 Alameda County Public Health Department Tuberculosis Overview Tuberculosis (TB) is a communicable disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. TB is spread
Tuberculosis in Alameda County, 29 Alameda County Public Health Department Tuberculosis Overview Tuberculosis (TB) is a communicable disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. TB is spread
Annual Tuberculosis Report Oregon 2007
 Annual Tuberculosis Report Oregon 7 Oregon Department of Human Services Public Health Division TB Program April 8 Page 2 Table of Contents Charts Chart 1 TB Incidence in the US and Oregon, 1985-7.. page
Annual Tuberculosis Report Oregon 7 Oregon Department of Human Services Public Health Division TB Program April 8 Page 2 Table of Contents Charts Chart 1 TB Incidence in the US and Oregon, 1985-7.. page
Scott Lindquist MD MPH Tuberculosis Medical Consultant Washington State DOH and Kitsap County Health Officer
 Tuberculosis in the 21 st Century Scott Lindquist MD MPH Tuberculosis Medical Consultant Washington State DOH and Kitsap County Health Officer Feedback Poll In my opinion, the recent media coverage of
Tuberculosis in the 21 st Century Scott Lindquist MD MPH Tuberculosis Medical Consultant Washington State DOH and Kitsap County Health Officer Feedback Poll In my opinion, the recent media coverage of
I. Demographic Information GENDER NUMBER OF CASES PERCENT OF CASES. Male % Female %
 San Joaquin County (SJC) in 03, (N=43) County Rate = 6. Cases per 00,000 Population I. Demographic Information Table I-A: TB cases by gender, SJC, 03 (N=43) GENDER NUMBER OF CASES Male 6 60.5% Female 7
San Joaquin County (SJC) in 03, (N=43) County Rate = 6. Cases per 00,000 Population I. Demographic Information Table I-A: TB cases by gender, SJC, 03 (N=43) GENDER NUMBER OF CASES Male 6 60.5% Female 7
Summary Statistics of Reported and Verified Cases of Tuberculosis in San Joaquin County in 2012, (N=44) County Rate = 6.3 Cases per 100,000 Population
 I. Demographic Information GENDER NUMBER OF CASES PERCENT OF CASES Male 29 65.9% Female 15 34.1% AGE GROUP NUMBER OF CASES PERCENT OF CASES 04 3 6.8% 514 2 4.5% 1524 3 6.8% 2544 6 13.6% 4564 15 34.1% 65+
I. Demographic Information GENDER NUMBER OF CASES PERCENT OF CASES Male 29 65.9% Female 15 34.1% AGE GROUP NUMBER OF CASES PERCENT OF CASES 04 3 6.8% 514 2 4.5% 1524 3 6.8% 2544 6 13.6% 4564 15 34.1% 65+
2014 Annual Report Tuberculosis in Fresno County. Department of Public Health
 214 Annual Report Tuberculosis in Fresno County Department of Public Health www.fcdph.org Tuberculosis (TB) is a common communicable disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis and occasionally
214 Annual Report Tuberculosis in Fresno County Department of Public Health www.fcdph.org Tuberculosis (TB) is a common communicable disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis and occasionally
Tuberculosis in Chicago 2007
 City of Chicago Communicable Disease Information Department of Public Health Richard M. Daley, Mayor May 2008 Terry Mason, MD, FACS, Commissioner www.cityofchicago.org/health/ West Side Center For Disease
City of Chicago Communicable Disease Information Department of Public Health Richard M. Daley, Mayor May 2008 Terry Mason, MD, FACS, Commissioner www.cityofchicago.org/health/ West Side Center For Disease
TB trends and TB genotyping
 Management of a TB Contact Investigation for Public Health Workers Albuquerque, NM October 1, 214 TB trends and TB genotyping Marcos Burgos MD October 1, 214 Marcos Burgos, MD has the following disclosures
Management of a TB Contact Investigation for Public Health Workers Albuquerque, NM October 1, 214 TB trends and TB genotyping Marcos Burgos MD October 1, 214 Marcos Burgos, MD has the following disclosures
2016 Annual Tuberculosis Report For Fresno County
 206 Annual Tuberculosis Report For Fresno County Cases Rate per 00,000 people 206 Tuberculosis Annual Report Fresno County Department of Public Health (FCDPH) Tuberculosis Control Program Tuberculosis
206 Annual Tuberculosis Report For Fresno County Cases Rate per 00,000 people 206 Tuberculosis Annual Report Fresno County Department of Public Health (FCDPH) Tuberculosis Control Program Tuberculosis
2015 Annual Report Tuberculosis in Fresno County. Department of Public Health
 215 Annual Report Tuberculosis in Fresno County Department of Public Health www.fcdph.org Number of Cases Rate per 1, Population 215 Tuberculosis Annual Report Fresno County Department of Public Health
215 Annual Report Tuberculosis in Fresno County Department of Public Health www.fcdph.org Number of Cases Rate per 1, Population 215 Tuberculosis Annual Report Fresno County Department of Public Health
ANNUAL TUBERCULOSIS REPORT OREGON Oregon Health Authority Public Health Division TB Program November 2012
 ANNUAL TUBERCULOSIS REPORT OREGON 211 Oregon Health Authority Public Health Division TB Program November 212 Page 2 Table of Contents Charts Chart 1 TB Incidence in the US and Oregon, 1985-211... page
ANNUAL TUBERCULOSIS REPORT OREGON 211 Oregon Health Authority Public Health Division TB Program November 212 Page 2 Table of Contents Charts Chart 1 TB Incidence in the US and Oregon, 1985-211... page
Chapter 1 Overview of Tuberculosis Epidemiology in the United States
 Chapter 1 Overview of Tuberculosis Epidemiology in the United States Table of Contents Chapter Objectives.... 1 Progress Toward TB Elimination in the United States... 3 TB Disease Trends in the United
Chapter 1 Overview of Tuberculosis Epidemiology in the United States Table of Contents Chapter Objectives.... 1 Progress Toward TB Elimination in the United States... 3 TB Disease Trends in the United
2014 TUBERCULOSIS FACT SHEET A Profile of Mecklenburg County Reported Cases
 OVERVIEW T uberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. TB is spread through the air
OVERVIEW T uberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. TB is spread through the air
Tuberculosis in Chicago 2006
 Chicago Department of Public Health May 27 Communicable Disease Information Tuberculosis in Chicago 26 City of Chicago Richard M. Daley, Mayor Department of Public Health Terry Mason, MD, FACS Commissioner
Chicago Department of Public Health May 27 Communicable Disease Information Tuberculosis in Chicago 26 City of Chicago Richard M. Daley, Mayor Department of Public Health Terry Mason, MD, FACS Commissioner
The Epidemiology of Tuberculosis in Minnesota,
 The Epidemiology of Tuberculosis in Minnesota, 2011 2015 Minnesota Department of Health Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Program (651) 201-5414 Tuberculosis surveillance data for Minnesota are available
The Epidemiology of Tuberculosis in Minnesota, 2011 2015 Minnesota Department of Health Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Program (651) 201-5414 Tuberculosis surveillance data for Minnesota are available
Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB)
 TB in the United States Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB) From 1953 to 1984, reported cases decreased by approximately 5.6% each year From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% 25,313 cases reported
TB in the United States Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB) From 1953 to 1984, reported cases decreased by approximately 5.6% each year From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% 25,313 cases reported
Yakima Health District BULLETIN
 Yakima Health District BULLETIN Summary Volume 13, Issue 1 February, 2014 Tuberculosis in Yakima County The rate of active tuberculosis (TB) in Yakima County has declined by about two-thirds over the past
Yakima Health District BULLETIN Summary Volume 13, Issue 1 February, 2014 Tuberculosis in Yakima County The rate of active tuberculosis (TB) in Yakima County has declined by about two-thirds over the past
TB in California: Costs, Transmission, and Selecting from the Latent Pool
 TB in California: Costs, Transmission, and Selecting from the Latent Pool Pennan Barry, MD, MPH Tuberculosis Control Branch California Department of Public Health California Tuberculosis Controller s Association
TB in California: Costs, Transmission, and Selecting from the Latent Pool Pennan Barry, MD, MPH Tuberculosis Control Branch California Department of Public Health California Tuberculosis Controller s Association
Tuberculosis Populations at Risk
 Tuberculosis Populations at Risk One-third of the world is infected with TB, an average of one new infection per second Two million people died from tuberculosis in 2010, 1 every 20 seconds TB is the leading
Tuberculosis Populations at Risk One-third of the world is infected with TB, an average of one new infection per second Two million people died from tuberculosis in 2010, 1 every 20 seconds TB is the leading
Tuberculosis in Alameda County, 2014 Alameda County Public Health Department
 Tuberculosis in Alameda, 214 Alameda Public Health Department Tuberculosis (TB) is a preventable and curable disease that remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide. TB is a communicable disease
Tuberculosis in Alameda, 214 Alameda Public Health Department Tuberculosis (TB) is a preventable and curable disease that remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide. TB is a communicable disease
TUBERCULOSIS. Presented By: Public Health Madison & Dane County
 TUBERCULOSIS Presented By: Public Health Madison & Dane County What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, or TB, is a disease caused by a bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria can attack any
TUBERCULOSIS Presented By: Public Health Madison & Dane County What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, or TB, is a disease caused by a bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria can attack any
Tuberculosis in Alameda County, 2011
 Tuberculosis in Alameda County, 211 Alameda County Public Health Department Tuberculosis Overview Tuberculosis (TB) is a preventable and curable disease that remains one of the leading causes of death
Tuberculosis in Alameda County, 211 Alameda County Public Health Department Tuberculosis Overview Tuberculosis (TB) is a preventable and curable disease that remains one of the leading causes of death
Haley Blake Sage Nagai, MPH. Disease Investigation and Intervention Specialists Tuberculosis Treatment and Control Clinic
 Haley Blake Sage Nagai, MPH Disease Investigation and Intervention Specialists Tuberculosis Treatment and Control Clinic Discuss the prevalence of tuberculosis in Clark County Describe factors influencing
Haley Blake Sage Nagai, MPH Disease Investigation and Intervention Specialists Tuberculosis Treatment and Control Clinic Discuss the prevalence of tuberculosis in Clark County Describe factors influencing
Substance Abuse and Tuberculosis Oklahoma City, Oklahoma November 17, 2010
 Substance Abuse and Tuberculosis Oklahoma City, Oklahoma November 17, 2010 Epidemiology of Substance Abuse and Tuberculosis: Where is the Problem? Mary Long, MPSH; Heartland Phillip Lindsey, MD; OK State
Substance Abuse and Tuberculosis Oklahoma City, Oklahoma November 17, 2010 Epidemiology of Substance Abuse and Tuberculosis: Where is the Problem? Mary Long, MPSH; Heartland Phillip Lindsey, MD; OK State
Descriptive Epidemiology Project: Tuberculosis in the. United States. MPH 510: Applied Epidemiology. Summer A 2014
 Descriptive Epidemiology Project: Tuberculosis in the United States MPH 510: Applied Epidemiology Summer A 2014 June 1, 2014 1 The white plague affected thousands upon thousands of people in the 18 th
Descriptive Epidemiology Project: Tuberculosis in the United States MPH 510: Applied Epidemiology Summer A 2014 June 1, 2014 1 The white plague affected thousands upon thousands of people in the 18 th
Etiological Agent: Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT. Definition
 Pulmonary Tuberculosis Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT Definition Tuberculosis is a contagious bacterial infection of the lungs caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (TB) Etiological Agent: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
Pulmonary Tuberculosis Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT Definition Tuberculosis is a contagious bacterial infection of the lungs caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (TB) Etiological Agent: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
Substance Abuse and Tuberculosis Springfield, IL April 27, 2011
 5/6/2011 Substance Abuse and Tuberculosis Springfield, IL April 27, 2011 Epidemiology of Substance Abuse and Tuberculosis: Where is the Problem? Debra Stephens, RN, BSN, MPH April 27, 2011 Debra Stephens,
5/6/2011 Substance Abuse and Tuberculosis Springfield, IL April 27, 2011 Epidemiology of Substance Abuse and Tuberculosis: Where is the Problem? Debra Stephens, RN, BSN, MPH April 27, 2011 Debra Stephens,
Report on Tuberculosis in California, 2012
 Golden Gate University School of Law GGU Law Digital Commons California Agencies California Documents 2012 Report on Tuberculosis in California, 2012 California Department of Public Health Follow this
Golden Gate University School of Law GGU Law Digital Commons California Agencies California Documents 2012 Report on Tuberculosis in California, 2012 California Department of Public Health Follow this
Tuberculosis in Alameda County, 2012
 Tuberculosis in Alameda County, 212 Alameda County Public Health Department Tuberculosis Overview Tuberculosis (TB) is a preventable and curable disease that remains one of the leading causes of death
Tuberculosis in Alameda County, 212 Alameda County Public Health Department Tuberculosis Overview Tuberculosis (TB) is a preventable and curable disease that remains one of the leading causes of death
TB Transmission, Pathogenesis & Infection Control
 TB Transmission, Pathogenesis & Infection Control Bradley Allen, MD, PhD, FACP, FIDSA. 2014 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures Medical Consultant, TB Control Program Indiana State Department of Health Past clinical
TB Transmission, Pathogenesis & Infection Control Bradley Allen, MD, PhD, FACP, FIDSA. 2014 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures Medical Consultant, TB Control Program Indiana State Department of Health Past clinical
ACTIVE TUBERCULOSIS IN MACOMB COUNTY, A Review of TB Program Data,
 ACTIVE TUBERCULOSIS IN MACOMB COUNTY, 1996-2010 A Review of TB Program Data, 1996-2010 Prepared by: Janice M. Chang, MBBS, MPH Division Director, Health Promotion and Disease Control Macomb County Health
ACTIVE TUBERCULOSIS IN MACOMB COUNTY, 1996-2010 A Review of TB Program Data, 1996-2010 Prepared by: Janice M. Chang, MBBS, MPH Division Director, Health Promotion and Disease Control Macomb County Health
Tuberculosis & Refugees in Philadelphia
 Tuberculosis & Refugees in Philadelphia Philadelphia TB Control Program Daniel P. Dohony, MPH Philadelphia TB Control Program Health Information Portal Website: hip.phila.gov Contains Information On» Disease
Tuberculosis & Refugees in Philadelphia Philadelphia TB Control Program Daniel P. Dohony, MPH Philadelphia TB Control Program Health Information Portal Website: hip.phila.gov Contains Information On» Disease
Tuberculosis What you need to know. James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director
 Tuberculosis What you need to know James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, (TB) is a communicable disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillus
Tuberculosis What you need to know James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, (TB) is a communicable disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillus
2013 Annual Report Tuberculosis in Fresno County. Department of Public Health
 2013 Annual Report Tuberculosis in Fresno County Department of Public Health www.fcdph.org In 2013, provisional data indicates that tuberculosis (TB) affected 3.0 / 100,000 people in the United States
2013 Annual Report Tuberculosis in Fresno County Department of Public Health www.fcdph.org In 2013, provisional data indicates that tuberculosis (TB) affected 3.0 / 100,000 people in the United States
Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know
 Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know Sixth Edition 2013 National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention Division of Tuberculosis Elimination 1 Chapters
Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know Sixth Edition 2013 National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention Division of Tuberculosis Elimination 1 Chapters
Global, National, Regional
 Epidemiology of TB: Global, National, Regional September 13, 211 Edward Zuroweste, MD Chief Medical Officer Migrant Clinicians Network Assistant Professor of Medicine Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Epidemiology
Epidemiology of TB: Global, National, Regional September 13, 211 Edward Zuroweste, MD Chief Medical Officer Migrant Clinicians Network Assistant Professor of Medicine Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Epidemiology
Global, National, Regional
 Epidemiology of TB: Global, National, Regional September 13, 211 Edward Zuroweste, MD Chief Medical Officer Migrant Clinicians Network Assistant Professor of Medicine Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Epidemiology
Epidemiology of TB: Global, National, Regional September 13, 211 Edward Zuroweste, MD Chief Medical Officer Migrant Clinicians Network Assistant Professor of Medicine Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Epidemiology
Epidemiology of Tuberculosis in the Northeast Region of the United States Surveillance Data Source. States included in the Northeast Region
 Epidemiology of Tuberculosis in the Northeast Region of the United States 993-8 Marian R. Passannante, PhD UMDNJ-New Jersey Medical School UMDNJ-School of Public Health Epidemiologist, New Jersey Medical
Epidemiology of Tuberculosis in the Northeast Region of the United States 993-8 Marian R. Passannante, PhD UMDNJ-New Jersey Medical School UMDNJ-School of Public Health Epidemiologist, New Jersey Medical
TB-Free California: How close are we? How can we get closer?
 TB-Free California: How close are we? How can we get closer? California TB Controllers Association April 21, 2015 Pennan Barry, MD, MPH Chief, Surveillance and Epidemiology Section Acknowledgments Local
TB-Free California: How close are we? How can we get closer? California TB Controllers Association April 21, 2015 Pennan Barry, MD, MPH Chief, Surveillance and Epidemiology Section Acknowledgments Local
Arizona Annual Tuberculosis Surveillance Report
 Arizona Annual Tuberculosis Surveillance Report 2014 Table of Contents I. Executive Summary 1 II. Case Rates 3 III. Cases and Case Rates by Race and Ethnicity 4 IV. Cases by Gender 4 V. Cases and Case
Arizona Annual Tuberculosis Surveillance Report 2014 Table of Contents I. Executive Summary 1 II. Case Rates 3 III. Cases and Case Rates by Race and Ethnicity 4 IV. Cases by Gender 4 V. Cases and Case
4/25/2012. The information on patterns of infection and disease can assist in: Assessing current and evolving trends in TB
 Sindy M. Paul, MD, MPH, FACPM May 1, 2012 The information on patterns of infection and disease can assist in: Assessing current and evolving trends in TB morbidity, including resistance Identifying people
Sindy M. Paul, MD, MPH, FACPM May 1, 2012 The information on patterns of infection and disease can assist in: Assessing current and evolving trends in TB morbidity, including resistance Identifying people
Global TB Burden, 2016 estimates
 TUBERCULOSIS EPIDEMIOLOGY LOCAL, STATE, NATIONAL, GLOBAL Office of Communicable Disease Epidemiology Global TB Burden, 216 estimates Total TB Estimated number of TB cases 1.4 million 14 per 1, Estimated
TUBERCULOSIS EPIDEMIOLOGY LOCAL, STATE, NATIONAL, GLOBAL Office of Communicable Disease Epidemiology Global TB Burden, 216 estimates Total TB Estimated number of TB cases 1.4 million 14 per 1, Estimated
Symptoms Latent TB Active TB
 1 Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease that can spread through the air. It is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually affect the lungs. However, it can also affect other
1 Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease that can spread through the air. It is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually affect the lungs. However, it can also affect other
Expanding Latent Tuberculosis Infection Testing and Treatment to Accelerate Tuberculosis Elimination
 IUATLD North American Region Conference February 24, 2017 Vancouver, BC Expanding Latent Tuberculosis Infection Testing and Treatment to Accelerate Tuberculosis Elimination Philip LoBue, MD National Center
IUATLD North American Region Conference February 24, 2017 Vancouver, BC Expanding Latent Tuberculosis Infection Testing and Treatment to Accelerate Tuberculosis Elimination Philip LoBue, MD National Center
The Triple Axel: Influenza, TB and MERS-CoV. Carolyn Pim, MD December 10, 2015
 The Triple Axel: Influenza, TB and MERS-CoV Carolyn Pim, MD December 10, 2015 1. Influenza 2 Influenza 10-20% of the population is infected each year (up to 30% of children) Infection rates are highest
The Triple Axel: Influenza, TB and MERS-CoV Carolyn Pim, MD December 10, 2015 1. Influenza 2 Influenza 10-20% of the population is infected each year (up to 30% of children) Infection rates are highest
TB Outbreak in a Homeless Shelter
 TB Outbreak in a Homeless Shelter Objectives Epidemiology of Outbreak Population Health Interventions Population Health Goals 2007 One active case identified Less than compliant Prolonged recovery Contact
TB Outbreak in a Homeless Shelter Objectives Epidemiology of Outbreak Population Health Interventions Population Health Goals 2007 One active case identified Less than compliant Prolonged recovery Contact
Appendix B. Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases (Revised July 1997)
 Appendix B Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases (Revised July 1997) Since publication of the Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases 1 in January 1977, numerous changes
Appendix B Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases (Revised July 1997) Since publication of the Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases 1 in January 1977, numerous changes
Outline. Tuberculosis (TB) Medical Evaluation for TB 5/5/2014. Chest Radiograph with Lower Lobe Cavity
 Jean Beinemann RN, Terri Boxrucker RN, and LT Dee Dee Downie MPH Outline The disease The outbreak The response The conclusions May 18, 2014 Wisconsin Public Health Association Annual Meeting Tuberculosis
Jean Beinemann RN, Terri Boxrucker RN, and LT Dee Dee Downie MPH Outline The disease The outbreak The response The conclusions May 18, 2014 Wisconsin Public Health Association Annual Meeting Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses
 Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses June 9, 2015 Kristin Gall, RN, MSN/Pat Infield, RN-TB Program Manager Marsha Carlson, RN, BSN Two Rivers Public Health Department Nebraska Department of
Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses June 9, 2015 Kristin Gall, RN, MSN/Pat Infield, RN-TB Program Manager Marsha Carlson, RN, BSN Two Rivers Public Health Department Nebraska Department of
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection
 Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of. Latent Tuberculosis. Infection and Tuberculosis Disease
 Self-Study Study Modules on Tuberculosis Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tuberculosis Disease 1 Module 3: Objectives At completion of this module, learners will
Self-Study Study Modules on Tuberculosis Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tuberculosis Disease 1 Module 3: Objectives At completion of this module, learners will
VERSION STUDENT. Outbreak of Tuberculosis in a Homeless Men s Shelter. Cases in Population-Oriented Prevention (C-POP)-based teaching cases
 STUDENT VERSION This project has the objective to develop preventive medicine teaching cases that will motivate medical students, residents and faculty to improve clinical preventive competencies complemented
STUDENT VERSION This project has the objective to develop preventive medicine teaching cases that will motivate medical students, residents and faculty to improve clinical preventive competencies complemented
Northwestern Polytechnic University
 Clinical Tuberculosis Assessment by Health Care Provider Clinicians should review and verify the information in the Tuberculosis (TB) Screening Questionnaire (attached). Persons answering YES to any questions
Clinical Tuberculosis Assessment by Health Care Provider Clinicians should review and verify the information in the Tuberculosis (TB) Screening Questionnaire (attached). Persons answering YES to any questions
Epidemiology of TB: A Local and National Overview
 Epidemiology of TB: A Local and National Overview Sonal S. Munsiff, MD Director, Bureau of Tuberculosis Control NYC Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Medical Officer, DTBE, CDC February 4, 24 Tuberculosis
Epidemiology of TB: A Local and National Overview Sonal S. Munsiff, MD Director, Bureau of Tuberculosis Control NYC Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Medical Officer, DTBE, CDC February 4, 24 Tuberculosis
HIV Incidence Report, Sexually Transmitted Diseases, HIV and Tuberculosis Section, Epidemiology and Surveillance Unit
 HIV Incidence Report, 2017 Sexually Transmitted Diseases, HIV and Tuberculosis Section, Epidemiology and Surveillance Unit Introduction (I) These two introduction slides provide a general context for the
HIV Incidence Report, 2017 Sexually Transmitted Diseases, HIV and Tuberculosis Section, Epidemiology and Surveillance Unit Introduction (I) These two introduction slides provide a general context for the
Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know DR.RUPNATHJI( DR.RUPAK NATH )
 Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know Introduction to the Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know i Introduction to the Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis:
Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know Introduction to the Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know i Introduction to the Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis:
TUBERCULOSIS CONTACT INVESTIGATION
 TB CASE MANAGEMENT AND CONTACT INVESTIGATION INTENSIVE TUBERCULOSIS CONTACT INVESTIGATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this session, participants will be able to: 1. Describe the criteria used
TB CASE MANAGEMENT AND CONTACT INVESTIGATION INTENSIVE TUBERCULOSIS CONTACT INVESTIGATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this session, participants will be able to: 1. Describe the criteria used
TB in Foreign Born and High Risk Populations
 TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas December 8-10, 2009 TB in Foreign Born and High Risk Populations John J. Nava, M.D. December 9, 2009 Tuberculosis in High Risk Populations and the Foreign Born
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas December 8-10, 2009 TB in Foreign Born and High Risk Populations John J. Nava, M.D. December 9, 2009 Tuberculosis in High Risk Populations and the Foreign Born
Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis
 Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Diagnosis of active TB Screening
Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Diagnosis of active TB Screening
Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016. Table of Contents
 Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016 Table of Contents Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016... 1 What is Tuberculosis?... 2 Any required definitions/explanations... 2 NHFT... 2 Tuberculosis (TB)... 3 Latent TB...
Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016 Table of Contents Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016... 1 What is Tuberculosis?... 2 Any required definitions/explanations... 2 NHFT... 2 Tuberculosis (TB)... 3 Latent TB...
2017/2018 Annual Volunteer Tuberculosis Notice
 Lewis Center for Educational Research Academy for Academic Excellence Norton Science and Language Academy Business Offices 17500 Mana Road Apple Valley, CA 92307 E-mail: hr@lcer.org 760-946-5414 Fax 760-946-9193
Lewis Center for Educational Research Academy for Academic Excellence Norton Science and Language Academy Business Offices 17500 Mana Road Apple Valley, CA 92307 E-mail: hr@lcer.org 760-946-5414 Fax 760-946-9193
11/1/2017. Disclosures. Update In Tuberculosis, Indiana Outline/Objectives. Pathogenesis of M.tb Global/U.S. TB Burden, 2016
 Disclosures Update In Tuberculosis, Indiana 2017 Bradley Allen, MD, PhD, FACP, FIDSA Indiana University School of Medicine Division of Infectious Diseases Roudebush VAMC Indianapolis Medical Consultant,
Disclosures Update In Tuberculosis, Indiana 2017 Bradley Allen, MD, PhD, FACP, FIDSA Indiana University School of Medicine Division of Infectious Diseases Roudebush VAMC Indianapolis Medical Consultant,
The American Experience with TB Elimination
 Reaching the Goal of TB Elimination by 2035 March 3, 2015 The American Experience with TB Elimination John Jereb, M.D. Medical officer Division of Tuberculosis Elimination National Center for HIV/AIDS,
Reaching the Goal of TB Elimination by 2035 March 3, 2015 The American Experience with TB Elimination John Jereb, M.D. Medical officer Division of Tuberculosis Elimination National Center for HIV/AIDS,
Tuberculosis 6/7/2018. Objectives. What is Tuberculosis?
 Tuberculosis Understanding, Investigating, Eliminating Jeff Maupin, RN Tuberculosis Control Nurse Sedgwick County Division of Health Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation, you will be able
Tuberculosis Understanding, Investigating, Eliminating Jeff Maupin, RN Tuberculosis Control Nurse Sedgwick County Division of Health Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation, you will be able
Appendix C. Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases (Revised July 1997)
 Appendix C Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases (Revised July 1997) Since publication of the Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases 1 in January 1977, numerous changes
Appendix C Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases (Revised July 1997) Since publication of the Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases 1 in January 1977, numerous changes
TB Intensive Minneapolis, Minnesota September 23-26, 2008
 TB Intensive Minneapolis, Minnesota September 23-26, 2008 TB in the Foreign-Born Population: Background and Demographic Overview Marge Higgins, LSW September 24, 2008 TB in the Foreign-Born Population
TB Intensive Minneapolis, Minnesota September 23-26, 2008 TB in the Foreign-Born Population: Background and Demographic Overview Marge Higgins, LSW September 24, 2008 TB in the Foreign-Born Population
Appendix B. Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases (Revised July 1997)
 Appendix B Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases (Revised July 1997) Since publication of the Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases 1 in January 1977, numerous changes
Appendix B Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases (Revised July 1997) Since publication of the Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases 1 in January 1977, numerous changes
Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist
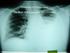 Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist Preface: What Happens when Health Care Professionals are not familiar with TB? A 15 year old student was diagnosed with highly infectious
Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist Preface: What Happens when Health Care Professionals are not familiar with TB? A 15 year old student was diagnosed with highly infectious
TB Outbreak Investigation in Fishery Workers, Maryland. Cassandra Althauser PHASE Internship Maryland Department of Health and Human Hygiene
 TB Outbreak Investigation in Fishery Workers, Maryland Cassandra Althauser PHASE Internship Maryland Department of Health and Human Hygiene Airborne Transmission Tuberculosis Small droplet nuclei (
TB Outbreak Investigation in Fishery Workers, Maryland Cassandra Althauser PHASE Internship Maryland Department of Health and Human Hygiene Airborne Transmission Tuberculosis Small droplet nuclei (
TB Contact Investigation
 Ann Raftery, RN, PHN, MS Curry International TB Center Overview Contact investigation as a core TB control and elimination activity Components of TB Contact Investigation TB Control Priority Strategies.
Ann Raftery, RN, PHN, MS Curry International TB Center Overview Contact investigation as a core TB control and elimination activity Components of TB Contact Investigation TB Control Priority Strategies.
California 2010 Pertussis Epidemic. Kathleen Winter, MPH Immunization Branch California Department of Public Health
 California 2010 Pertussis Epidemic Kathleen Winter, MPH Immunization Branch California Department of Public Health Overview Pertussis Background California Pertussis Epidemic Challenges and Success Ongoing
California 2010 Pertussis Epidemic Kathleen Winter, MPH Immunization Branch California Department of Public Health Overview Pertussis Background California Pertussis Epidemic Challenges and Success Ongoing
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS
 CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update
 Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
The Tip of the Iceberg: Addressing Latent Tuberculosis Infection to Accelerate Tuberculosis Elimination
 Four Corners TB and HIV Conference November 3, 2015 Durango, CO The Tip of the Iceberg: Addressing Latent Tuberculosis Infection to Accelerate Tuberculosis Elimination Philip LoBue, MD National Center
Four Corners TB and HIV Conference November 3, 2015 Durango, CO The Tip of the Iceberg: Addressing Latent Tuberculosis Infection to Accelerate Tuberculosis Elimination Philip LoBue, MD National Center
Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis
 Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tube rc ulos is U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for HIV/AIDS,
Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tube rc ulos is U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for HIV/AIDS,
Tuberculosis Surveillance
 Tuberculosis Surveillance Cambridge Surveillance Report on Active Tuberculosis, 26-21 Division of Epidemiology and Data Services April 211 Photo of Gram-positive Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. Source:
Tuberculosis Surveillance Cambridge Surveillance Report on Active Tuberculosis, 26-21 Division of Epidemiology and Data Services April 211 Photo of Gram-positive Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. Source:
Replaces: 02/11/16. Formulated: 7/95 EMPLOYEE TB TESTING
 Effective : 02/09/17 Page 1 of 4 PURPOSE: To describe the process where by employees may obtain routine TB skin testing by facility medical staff. POLICY: Employees of the Texas Department of Criminal
Effective : 02/09/17 Page 1 of 4 PURPOSE: To describe the process where by employees may obtain routine TB skin testing by facility medical staff. POLICY: Employees of the Texas Department of Criminal
Tuberculosis in Alaska 1999
 Department of Health and Social Services Division of Public Health Section of Epidemiology Karen Perdue, Commissioner Peter M. Nakamura, MD, MPH, Director John Middaugh, MD, Editor 361 C Street, Suite
Department of Health and Social Services Division of Public Health Section of Epidemiology Karen Perdue, Commissioner Peter M. Nakamura, MD, MPH, Director John Middaugh, MD, Editor 361 C Street, Suite
The Public Health Impact of TB in the Correctional System. Sarah Bur, RN, MPH Federal Bureau of Prisons Infection Prevention and Control Officer
 The Public Health Impact of TB in the Correctional System Sarah Bur, RN, MPH Federal Bureau of Prisons Infection Prevention and Control Officer The Public Health Impact of TB in the Correctional System
The Public Health Impact of TB in the Correctional System Sarah Bur, RN, MPH Federal Bureau of Prisons Infection Prevention and Control Officer The Public Health Impact of TB in the Correctional System
TUBERCULOSIS CONTACT INVESTIGATION
 TB CASE MANAGEMENT AND CONTACT INVESTIGATION INTENSIVE May 8-11, 2018 TUBERCULOSIS CONTACT INVESTIGATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this session, participants will be able to: 1. Describe the
TB CASE MANAGEMENT AND CONTACT INVESTIGATION INTENSIVE May 8-11, 2018 TUBERCULOSIS CONTACT INVESTIGATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this session, participants will be able to: 1. Describe the
Latent TB, TB and the Role of the Health Department
 Latent TB, TB and the Role of the Health Department Elaine Darnall, RN, BSN, CIC TB Nurse Consultant Illinois Dept of Public Health March 21, 2018 Elaine Darnall has disclosed that there is no actual or
Latent TB, TB and the Role of the Health Department Elaine Darnall, RN, BSN, CIC TB Nurse Consultant Illinois Dept of Public Health March 21, 2018 Elaine Darnall has disclosed that there is no actual or
MEMORANDUM. Re: Guidance for follow-up of newly-arrived Individual with a Class B1 Tuberculosis Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis
 MEMORANDUM To: From: Local Board of Health John Bernardo, MD, Tuberculosis Medical Officer Jennifer Cochran, MPH, Division Director Division of Global Populations and Infectious Disease Prevention Bureau
MEMORANDUM To: From: Local Board of Health John Bernardo, MD, Tuberculosis Medical Officer Jennifer Cochran, MPH, Division Director Division of Global Populations and Infectious Disease Prevention Bureau
ILI Syndromic Surveillance
 ILI Syndromic Surveillance Race/ethnicity of adult respondents with influenza-like illness (ILI) in the U.S., Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS), Sept 1- Sep 30, 2009 Race/ethnicity I
ILI Syndromic Surveillance Race/ethnicity of adult respondents with influenza-like illness (ILI) in the U.S., Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS), Sept 1- Sep 30, 2009 Race/ethnicity I
MEMORANDUM. Re: Guidance for follow-up of newly-arrived individual with Class B1 Tuberculosis Pulmonary Tuberculosis, no treatment
 MEMORANDUM To: From: Local Board of Health John Bernardo, MD, Tuberculosis Medical Officer Jennifer Cochran, MPH, Division Director Division of Global Populations and Infectious Disease Prevention Bureau
MEMORANDUM To: From: Local Board of Health John Bernardo, MD, Tuberculosis Medical Officer Jennifer Cochran, MPH, Division Director Division of Global Populations and Infectious Disease Prevention Bureau
STD, HIV and Hepatitis C 2017 Data Release. April 24,2018
 STD, HIV and Hepatitis C 2017 Data Release April 24,2018 Acronyms MDH = Minnesota Department of Health STD = Sexually transmitted disease MSM = Men who have sex with men HCV = Hepatitis C virus HBV =Hepatitis
STD, HIV and Hepatitis C 2017 Data Release April 24,2018 Acronyms MDH = Minnesota Department of Health STD = Sexually transmitted disease MSM = Men who have sex with men HCV = Hepatitis C virus HBV =Hepatitis
10/3/2017. Updates in Tuberculosis. Global Tuberculosis, WHO 2015 report. Objectives. Disclosures. I have nothing to disclose
 Disclosures Updates in Tuberculosis I have nothing to disclose Chris Keh, MD Assistant Clinical Professor, Division of Infectious Diseases, UCSF TB Controller, TB Prevention and Control Program, Population
Disclosures Updates in Tuberculosis I have nothing to disclose Chris Keh, MD Assistant Clinical Professor, Division of Infectious Diseases, UCSF TB Controller, TB Prevention and Control Program, Population
TB: Management in an era of multiple drug resistance. Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2012
 TB: Management in an era of multiple drug resistance Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2012 Objectives: 1. Explain the steps for diagnosing latent and active TB role of interferon-gamma release
TB: Management in an era of multiple drug resistance Bob Belknap M.D. Denver Public Health November 2012 Objectives: 1. Explain the steps for diagnosing latent and active TB role of interferon-gamma release
HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE INVASIVE DISEASE
 23 Annual Morbidity Report HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE INVASIVE DISEASE CRUDE DATA 35 Annual Incidence a LA County.37 California b. United States c.2 Age at Diagnosis Mean 4. years Median 36. years Range Birth
23 Annual Morbidity Report HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE INVASIVE DISEASE CRUDE DATA 35 Annual Incidence a LA County.37 California b. United States c.2 Age at Diagnosis Mean 4. years Median 36. years Range Birth
Positive Living Conference
 Positive Living Conference Ft. Walton Beach, Thomas Liberti Chief, Bureau of HIV/AIDS Department of Health March 11, 2011 Tallahassee, 1 The Epidemic in, 2010 60% White Population: 18.8 million (4 th 16%
Positive Living Conference Ft. Walton Beach, Thomas Liberti Chief, Bureau of HIV/AIDS Department of Health March 11, 2011 Tallahassee, 1 The Epidemic in, 2010 60% White Population: 18.8 million (4 th 16%
Experience with Pyrazinamide and Rifampin Regimens for Latent TB Infection
 Experience with Pyrazinamide and Rifampin Regimens for Latent TB Infection Krista Powell, MD, MPH Co-Project Officer, National Surveillance for Severe Adverse Events Associated with LTBI Treatment Lead,
Experience with Pyrazinamide and Rifampin Regimens for Latent TB Infection Krista Powell, MD, MPH Co-Project Officer, National Surveillance for Severe Adverse Events Associated with LTBI Treatment Lead,
Please distribute a copy of this information to each provider in your organization.
 HEALTH ADVISORY TO: Physicians and other Healthcare Providers Please distribute a copy of this information to each provider in your organization. Questions regarding this information may be directed to
HEALTH ADVISORY TO: Physicians and other Healthcare Providers Please distribute a copy of this information to each provider in your organization. Questions regarding this information may be directed to
The Air We Share: Principles and Practices of TB Infection Control
 The Air We Share: Principles and Practices of TB Infection Control Session Four of a Four-Part Webinar Series Presented in Partnership with the BC Lung Association January 10, 2014 Facilitators: Nash Dhalla,
The Air We Share: Principles and Practices of TB Infection Control Session Four of a Four-Part Webinar Series Presented in Partnership with the BC Lung Association January 10, 2014 Facilitators: Nash Dhalla,
The Epidemiology of Active Tuberculosis Disease in the Winnipeg Health Region,
 The Epidemiology of Active Tuberculosis Disease in the Winnipeg Health Region, 2013-2016 Mandy Whitlock, MHSc Souradet Shaw, PhD Debbie Nowicki, MSc Pierre Plourde, M.D. FRCPC For the Population Health
The Epidemiology of Active Tuberculosis Disease in the Winnipeg Health Region, 2013-2016 Mandy Whitlock, MHSc Souradet Shaw, PhD Debbie Nowicki, MSc Pierre Plourde, M.D. FRCPC For the Population Health
Disclosures. TB and CoMorbidities Challenges and Opportunities. Burden of TB. Outline of the lecture. Target testing for TB Infection TB HIV 3/25/2012
 Disclosures TB and CoMorbidities Challenges and Opportunities E. Jane Carter, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Alpert School of Medicine, Brown University Providence, Rhode Island No financial disclosures
Disclosures TB and CoMorbidities Challenges and Opportunities E. Jane Carter, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Alpert School of Medicine, Brown University Providence, Rhode Island No financial disclosures
The Workings of Outbreak Response in Refugee Communities
 The Workings of Outbreak Response in Refugee Communities ABC News Victoria Hall Epidemic Intelligence Service Officer 11 th Annual Local Public Health and Resettlement Agency Forum January 25, 2018 If
The Workings of Outbreak Response in Refugee Communities ABC News Victoria Hall Epidemic Intelligence Service Officer 11 th Annual Local Public Health and Resettlement Agency Forum January 25, 2018 If
Multidrug-resistant Tuberculosis - World, Europe, Switzerland
 Multidrug-resistant Tuberculosis - World, Europe, Switzerland Magglingen March 23, 2017 peter.helbling@bag.admin.ch Topics Definitions Epidemiology of TB and MDR-TB worldwide Treatment outcome results
Multidrug-resistant Tuberculosis - World, Europe, Switzerland Magglingen March 23, 2017 peter.helbling@bag.admin.ch Topics Definitions Epidemiology of TB and MDR-TB worldwide Treatment outcome results
The authors assessed drug susceptibility patterns
 Drug Resistance Among Tuberculosis Patients, 1991 and 1992 New York City, CYNTHIA R. DRIVER, RN, MPH THOMAS R. FRIEDEN, MD, MPH ALAN B. BLOCH, MD, MPH IDA M. ONORATO, MD All the authors are with the Division
Drug Resistance Among Tuberculosis Patients, 1991 and 1992 New York City, CYNTHIA R. DRIVER, RN, MPH THOMAS R. FRIEDEN, MD, MPH ALAN B. BLOCH, MD, MPH IDA M. ONORATO, MD All the authors are with the Division
INDEX CASE INFORMATION
 Instructions for Completing the MDH Tuberculosis Contact Investigation Report Form Please provide as much information as possible. Each field represents information that is important to the contact investigation.
Instructions for Completing the MDH Tuberculosis Contact Investigation Report Form Please provide as much information as possible. Each field represents information that is important to the contact investigation.
