Evaluation of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Combination with Anorganic Bovine Bone in the Rabbit Cranium: A Pilot Study
|
|
|
- Scarlett Gregory
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Evaluation of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Combination with Anorganic Bovine Bone in the Rabbit Cranium: A Pilot Study Tara L. Aghaloo, DDS, MD 1 /Peter K. Moy, DMD 2 /Earl G. Freymiller, DMD, MD 3 Purpose: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is potentially useful as an adjunct to allograft and xenograft materials in oral and maxillofacial bone and implant reconstructive surgery. This study compares bone healing and formation in 4 cranial defects in rabbits grafted with autogenous bone, xenograft, and xenograft with PRP (with a no-graft group as a control). Materials and Methods: Fifteen New Zealand white rabbits were included in this randomized, blind, prospective pilot study. Four identical 8-mmdiameter defects were created in each rabbit cranium and immediately grafted with the above materials. Five rabbits were evaluated at 1 month, 5 at 2 months, and 5 at 4 months. Radiographs were used to evaluate bone density. Results: Radiographically, sites at which Bio-Oss, autogenous bone, and Bio-Oss + PRP were grafted showed a significant increase in bone density at 1 month (P =.05 for Bio-Oss, P =.02 for autogenous bone, P =.008 for Bio-Oss + PRP) and at 4 months (P =.02 for Bio-Oss, P =.04 for autogenous bone, P =.05 for Bio-Oss + PRP). Autogenous bone sites (P.001) and Bio-Oss + PRP sites (P.001) also showed significant increases at 2 months. Histomorphometrically, autogenous bone sites showed a significantly greater increase than control sites (P =.08 at 1 month, P =.03 at 2 months, P =.01 at 4 months), Bio-Oss sites (P.001 at all 3 evaluation points), or Bio-Oss + PRP sites (P =.009 at 1 month, P =.02 at 2 months, P =.01 at 4 months). Furthermore, Bio-Oss + PRP sites showed a significantly greater increase in bone area at 1, 2, and 4 months than Bio-Oss alone (P =.003 at 1 month, P =.02 at 2 months, P =.006 at 4 months). Discussion: Radiographs showed significantly greater bone density at the Bio-Oss, autogenous bone, and Bio-Oss + PRP sites than at control sites at nearly every point in time evaluated; however, clinical significance is difficult to determine, since all materials appeared dense on the radiograph. Histomorphometry showed that the increase in bone area at autogenous sites was significantly greater than that seen with other grafting materials or at the control sites. Conclusion: This study showed a histomorphometric increase in bone formation with the addition of PRP to Bio-Oss in non critical-sized defects in the rabbit cranium. INT J ORAL MAX- ILLOFAC IMPLANTS 2004;19:59 65 Key words: bone grafting, bone substitutes, bovine bone, cranial defects, platelet-rich plasma Alveolar bone resorption is a major problem in oral and maxillofacial rehabilitation with dental implants. Bone resorption around teeth results in tooth loss and creates a compromised situation for restoration with osseointegrated implants. Bone grafting is a common surgical procedure performed 1 Assistant Professor, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, University of California, Los Angeles, California. 2 Adjunct Associate Professor, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, University of California, Los Angeles, California. 3 Chairman, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, University of California, Los Angeles, California. Correspondence to: Dr Tara L. Aghaloo, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, UCLA, School of Dentistry, Le Conte Ave. Rm. A0-156, Los Angeles, CA Fax: taghaloo@ucla.edu to regenerate resorbed alveolar bone. Autogenous bone is considered the gold standard for grafting oral bony defects. 1,2 However, the required amount of autogenous bone may not always be available, and bone graft harvesting is not without complications and disadvantages, such as the need for a secondary surgical donor site, increased postoperative morbidity, and increased surgical time. Surgeons are always searching for nonautogenous materials to substitute for autogenous bone. An ideal bone grafting material must be able to produce bone by means of viable transplanted osteoblasts, by osteoinduction of mesenchymal cells, or by osteoconduction along the cell surface. It must maintain mature bone over time without loss of function and provide a low risk for infection and antigenicity. It must have the capability to The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 59
2 incorporate into the host bone and be available in unlimited quantities. 3,4 Furthermore, its structure must stabilize implants. Numerous studies have shown the success of anorganic bovine bone grafting materials, but the parameters of success often differ Clinicians are constantly attempting to improve the results obtained with anorganic bovine bone alone by adding barrier membranes, 12,13 fibrin glue, 7,14,15 platelet concentrates, 16 autogenous bone, osteogenic protein (BMP-7/OP-1), 20 and other nonautogenous grafting materials. 21 Bio-Oss is natural bovine bone that is completely deproteinized to prevent a potential immune response. 22,23 Electron microscopic evaluation shows that this material has a structural configuration similar to human bone. Its compressive strength and modulus of elasticity are also similar to the values for human bone. 15,24 It has been shown in numerous studies to have osteoconductive properties; ie, it provides a scaffold on which bone may form. 5,19,25 28 (Osteoconduction, which permits bone apposition from existing bone, requires the presence of bone or differentiated mesenchymal cells. 29,30 ) There is no evidence that Bio-Oss is osteoinductive, but it does tend to enable bone healing. 5,27 Nonintegrated bovine material is resorbed by osteoclastic cells. 5 Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is potentially useful as an adjunct to allograft and xenograft materials in oral and maxillofacial bone and implant reconstructive surgery. Kim and coworkers suggest that the addition of PRP to osteoconductive grafting materials can potentiate osteoinduction. 3 Platelets are very important in the wound healing process. They quickly arrive at the wound site and begin the coagulation process. They release multiple wound healing growth factors and cytokines, including platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), transforming growth factors -1 and -2 (TGF- 1 and TGF- 2 ), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor, interleukin-1, basic fibroblast growth factor, and platelet activating factor These growth factors are thought to contribute to bone regeneration and increased vascularity, vital features of a healing bone graft. We do not know whether PRP can be used with alloplasts, xenografts, or other nonautogenous materials without the addition of autogenous donor bone to create a bone graft comparable to or superior to autogenous bone. There are very few studies in refereed journals in which PRP was added to allograft or alloplast bone. 3,36 38 These articles describe the PRP techniques used and reported the formation of some osteoid material or bone. However, the results are conflicting or equivocal. 36,37,39,40 In many of these studies, few cases were evaluated and no statistical testing was performed to confirm the validity of the results Scientific conclusions cannot be reached based on these limited studies. Further scientific testing of PRP in combination with xenograft materials such as anorganic bovine bone is obviously necessary. The present study was designed to test the effectiveness of PRP when added to a xenograft. MATERIALS AND METHODS Animal Surgical Procedure Fifteen New Zealand white male rabbits weighing between 2.8 and 4 kg were included in this randomized, blind, prospective pilot study. The University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) Animal Research Committee, in accordance with staff in the UCLA Department of Laboratory and Animal Medicine, approved all animal protocols. Each rabbit was anesthetized with ketamine hydrochloride (10 mg/kg) and acepromazine (1 to 1.5 mg/kg) and given enrofloxacin as a preoperative antibiotic (Baytril, 5 mg/kg, Bayer, Shawnee Mission, KS). To prepare the PRP, 10 ml of autologous blood was drawn from each rabbit. The rabbits underwent general anesthesia with 1% to 2% isoflurane with standard monitoring. The fur was shaved over the cranium and prepped and draped in a sterile fashion. An incision was made to the bony cranium, and the periosteum was reflected. Four 8-mm-diameter defects were created with a trephine bur using copious irrigation. Three of the defects were randomly grafted with autogenous bone alone (obtained by particulating the trephinated bone), Bio-Oss mixed with PRP, or Bio-Oss alone. As a control, the fourth defect was not grafted. The wound was closed with 3-0 Dexon (Owens and Minor, Irvine, CA) and the rabbits were recovered. They were given postoperative narcotic pain medication and antibiotics. PRP Preparation The 10 ml of autologous blood drawn from each rabbit was combined with 1.1 ml of anticoagulant citrate dextrose phosphate (ACD-A) to prevent coagulation. The blood was spun in a centrifuge (Sorvall, Kendro Laboratory Products, Newtown, CT) at 1,500 rpm (215 g) for 10 minutes to separate the plasma containing the platelets from the red blood cells. The plasma was drawn off the top of the test tube, mixed with 0.4 ml of ACD-A, and centrifuged for an additional 10 minutes at 3,000 rpm (863 g) to separate the platelets. The platelet-poor plasma 60 Volume 19, Number 1, 2004
3 Fig 1 (Left) Radiograph of a rabbit cranium harvested after 2 months of healing: (a) Bio-Oss, (b) control, (c) autogenous bone, (d) Bio-Oss + PRP. a b Fig 2 (Below) Average platelet counts in peripheral blood, PPP, and PRP. Platelet counts confirmed that PRP preparation produced highly concentrated platelets. c d Platelet count ( 10 5 ) Blood PPP PRP (PPP) was separated from the PRP and the buffy coat. The buffy coat and the PRP, approximately 1 to 1.5 ml, were resuspended and added to the grafting materials within minutes. Five thousand units of topical bovine thrombin powder (King, St Louis, MO) was reconstituted with 5 ml of 10% calcium chloride (American Regent, Shirley, NY). The ratio of PRP to calcium chloride activator was 10:1. This protocol is similar to that utilized in clinical practice with some of the commercially available machines and described in an article by Jones and coworkers. 34 Platelet counts were performed on each sample, including a peripheral blood count, a PPP count, and a PRP count. A Unopette microcollection system (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lanes, NJ) was used to lyse the leukocytes and erythrocytes, as well as provide a standard dilution of 1:100 for platelet counts. The platelets were hand counted with a standard hemocytometer, and the total was calculated for each sample. Sample Evaluation The rabbits were divided into 3 groups of 5. One group was sacrificed at 1 month, one at 2 months, and one at 4 months. Pentobarbital (100 mg/kg intravenously) was used for this purpose. The entire cranium was removed with a reciprocating saw without encroaching upon the grafted areas. Radiographs were taken of the rabbit cranium in its entirety before histologic sectioning was performed (Fig 1). A calcium carbonate step-wedge was used in each radiograph for comparison. Quantification was performed with digital subtraction radiography. Computer software (UCLA Image, Los Angeles, CA) compared the pixels and grams per square inch of all 4 sites for each rabbit. Specimens were treated with hydrochloric acid decalcifying solution (Fisher Scientific, Tustin, CA) and sectioned by bisecting the 8-mm-diameter defects. Specimens were then dehydrated with graded alcohols and embedded in paraffin. They were subsequently sectioned at 6 µm with a steel knife. These 6-µm sections were prepared in the usual fashion with hematoxylin and eosin staining. Histologic evaluation was performed at 10, 25, and 40 magnification. The 40 magnification was used for histomorphometric analysis. The bone area was calculated using ImagePro software (Media Cybernetics, Silver Springs, MD). Evaluators were blind to the grafting material and time period for each sample. The data were analyzed by a Student t test with a significance level at P.05. RESULTS Platelet counts confirmed that the PRP preparation technique used in this study produced a highly concentrated source of platelets (Fig 2). The average peripheral blood platelet count was 118,000/mm 3, with a range of 100,000 to 135,000/mm 3. The average platelet count in PPP was 22,330/mm 3, with a range of 15,000 to 30,000/mm 3. The average platelet count in PRP was 960,000/mm 3, with a range from 660,000 to 1,265,000/mm 3. Radiographic Evaluation Figure 3 demonstrates the bone density as determined radiographically. Autogenous bone (P =.02 at 1 month, P =.001 at 2 months, P =.04 at 4 months) and Bio-Oss + PRP (P =.08 at 1 month, P =.001 at 2 months, P =.05 at 4 months) showed a significant The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 61
4 Grams/square inch Bio-Oss + PRP Bone Bio-Oss Control Months Fig 3 Amount of bone fill, determined radiographically over the 4-month study period. increase in radiographic bone density when compared to the control at all 3 time points. Bio-Oss alone was significantly better than the control at 1 month (P =.05) and 4 months (P =.02) but not at 2 months. However, at no time was there a statistically significant difference in radiographic density when Bio-Oss alone was compared to Bio-Oss + PRP. All statistical analyses were performed utilizing the mean and standard errors to determine significance. Histologic Evaluation Figure 4 shows the histologic evaluation of all grafting materials at 1 and 4 months at 10 magnification. Fibrous tissue, which filled the defect gradually over the 4 months, was minimal at 1 month. Bio-Oss sites showed Bio-Oss particles surrounded by fibrous connective tissue, which underwent remodeling at 1 month, with minimal bony ingrowth by 4 months. Autogenous bone graft material mixed with fibrous connective tissue was seen at 1 month. The graft material underwent remodeling and became significantly more dense by 4 months. Bio-Oss + PRP at 1 month showed fibrous connective tissue with Bio-Oss particles surrounded by bony ingrowth. This bone consolidated, and few Bio-Oss particles were seen by 4 months. Histomorphometric Evaluation Figure 5 shows the histomorphometric percent bone area as a function of time for each grafting material. Autogenous bone graft showed a significantly greater bone area when compared with each of the other grafting materials at each time point. Only autogenous bone graft showed a statistically significant increase in bone area histomorphometrically compared to all 3 other sites at all 3 evaluation points (for control sites, P =.08, P =.03, P =.01, at 1, 2, and 4 months, respectively; for Bio-Oss, P.001 at all 3 evaluation points; for Bio-Oss + PRP, P =.009, P =.02, P =.01, at 1, 2, and 4 months, respectively). When Bio-Oss + PRP was evaluated histomorphometrically, there was a statistically significant increase in bone area at 1, 2, and 4 months compared to Bio-Oss alone (P =.003, P =.02, P =.006, respectively). Bio-Oss alone actually showed a histomorphometric tendency toward decreased bone area at 1, 2, and 4 months when compared to the control, but this was not statistically significant (P.05). DISCUSSION Oral and maxillofacial surgery researchers strive continuously to improve upon current bone-grafting techniques and provide faster and denser bony regeneration. Growth factors are a realistic way to improve and expedite both soft tissue and bony wound healing. Platelets contain angiogenic, mitogenic, and vascular growth factors in their granules, 41,42 such as VEGF, a powerful angiogenic growth factor with an important role in wound healing 43 ; TGF- 1 and TGF- 2, which have been shown to inhibit bone resorption, osteoclast formation, and osteoclast activity, as well as trigger rapid maturation of collagen in early wounds 44,45 ; and PDGF, which increases the population of wound-healing cells and recruits other angiogenic growth factors to the wound site. 45 It is therefore a reasonable hypothesis that increasing the concentration of platelets in a bone defect may lead to improved and faster healing. However, little evidence exists evaluating the ability of these growth factors to improve bone healing when added to osteoconductive materials. 3,16 Quantitative platelet counts verified that PRP, consisting of 660,000 to 1,265,000 platelets in 1 to 1.5 ml of concentrate, 46 was used in this study. Digital subtraction radiography with step-wedge calibration showed a significant increase in bone density when Bio-Oss, autogenous bone, and Bio-Oss + PRP were grafted, compared to ungrafted controls, at nearly every evaluation point. The clinical significance of these data is difficult to determine because any radiopaque bone grafting material will look more dense on a radiograph. No significant difference could be seen between the 3 grafting materials radiographically. These results conflict with those of Kim and associates, who showed significantly greater bone density at 1 and 2 months when evaluating digitized radiographs and computed tomography scans when PRP was added to Bio-Oss in rabbit cranial defects. 16 When histologic sections were evaluated with histomorphometry, autogenous bone graft demonstrated a statistically significant increase in bone 62 Volume 19, Number 1, 2004
5 a b c d e f g h i j k l Fig 4 Histologic evaluation of all grafted materials at 1, 2, and 4 months. Magnification 40 : (a) control, 1 month; (b) control, 2 months; (c) control, 4 months; (d) Bio-Oss, 1 month; (e) Bio-Oss, 2 months; (f) Bio-Oss, 4 months; (g) autogenous bone, 1 month; (h) autogenous bone, 2 months; (i) autogenous bone, 4 months; (j) Bio-Oss + PRP, 1 month; (k) Bio-Oss + PRP, 2 months; (l) Bio-Oss + PRP, 4 months. area over the control, Bio-Oss alone, and Bio-Oss + PRP at 1, 2, and 4 months. No other animal or human studies that have compared Bio-Oss + PRP to autogenous bone grafting are currently available. Adding PRP to Bio-Oss resulted in a significant increase in bone area at all time periods compared with Bio-Oss alone. These data are not in agreement with the results of Froum and associates. 38 In that study, human sinus-grafted core samples were evaluated histomorphometrically after grafting with Bio-Oss alone or Bio-Oss + PRP. The authors found no histologic benefit by the addition of PRP. They did not use radiographic comparison in their study. Other preliminary reports have shown that freeze-dried demineralized bone combined with PRP forms numerous areas of osteoid and bone without inflammatory infiltrate or soft tissue epithelialization, with osseous trabeculae surrounding the connective tissue. 36,37 However, quantitative analysis was not performed in these studies, and the grafted sites were not standardized or randomized. When the Bio-Oss alone sites were analyzed, a histomorphometric tendency toward decreased bone area was observed at 1, 2, and 4 months compared to control, but this was not statistically significant. As stated in the introduction, this product has been shown in numerous other studies to have osteoconductive properties, where it provides a scaffold onto which bone may form. 5,19,25 28 The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 63
6 % bone area In this study, the addition of PRP to Bio-Oss in the rabbit cranial defect model was shown to be potentially beneficial. However, autogenous bone alone still showed the greatest histomorphometric bone area at all evaluation points. Furthermore, the sample was small, consisting of only 15 rabbits. Further studies are needed to evaluate the potential benefits of PRP in combination with various autogenous, allograft, and alloplast grafting materials. Four critical-sized defects (critical size being 15 mm wide 47 ) cannot be created in the rabbit cranium because it is too small. Therefore, this study was designed to evaluated non critical-sized cranial defects. However, future studies need to evaluate the potential benefits of PRP in healing critical-sized defects. CONCLUSION This study evaluated grafting materials in rabbit cranial defects, and showed significant histomorphometric improvement at 1, 2, and 4 months with the addition of PRP to Bio-Oss. However, when autogenous bone was used in the same model, the results were still superior to the ungrafted control, Bio-Oss alone, and Bio-Oss + PRP at all evaluation points. REFERENCES Bio-Oss + PRP Bone Bio-Oss Control Months Fig 5 Histomorphometric evaluation of bone area over the 4- month study period. 1. Moy PK, Lundgren S, Holmes RE. Maxillary sinus augmentation: Histomorphometric analysis of graft materials for maxillary sinus floor augmentation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1993;51: Gross JS. Bone grafting materials for dental applications: A practical guide. Compend Contin Educ Dent 1997;18: , , Kim SG, Chung CH, Kim YK, Park JC, Lim SC. Use of particulate dentin-plaster of Paris combination with/without platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of bone defects around implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2002;17: Block MS, Kent JN. Sinus augmentation for dental implants: The use of autogenous bone. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1997; 55: Merkx MAW, Maltha JC, Freihofer HPM, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM. Incorporation of three types of bone block implants in the facial skeleton. Biomaterials 1999;20: Carmagnola D, Berglundh T, Araujo M, Albrektsson T, Lindhe J. Bone healing around implants placed in a jaw defect augmented with Bio-Oss: An experimental study in dogs. J Clin Periodontol 2000;27: Carmagnola D, Berglundh T, Lindhe J. The effect of fibrin glue on the integration of Bio-Oss with bone tissue: An experimental study in labrador dogs. J Clin Periodontol2002;29: Mayfield LA, Skoglund A, Hising P, Lang NP, Attstrom R. Evaluation following functional loading of titanium fixtures placed in ridges augmented by deproteinized bone mineral: A human case study. Clin Oral Implants Res 2001;12: Zitzmann NU, Scharer P, Marinello CP, Schupbach P, Berglundh T. Alveolar ridge augmentation with Bio-Oss: A histologic study in humans. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2001;21: van Steenberghe D, Callens A, Geers L, Jacobs R. The clinical use of deproteinized bovine bone mineral on bone regeneration in conjunction with immediate implant installation. Clin Oral Implants Res 2000;11: Tal H. Autogenous masticatory mucosal grafts in extraction socket seal procedures: A comparison between sockets grafted with demineralized freeze-dried bone and deproteinized bovine bone material. Clin Oral Implants Res 1999;10: Houser BE, Mellonig JT, Brunsvold MA, Cochran DL, Meffert RM, Alder ME. Clinical evaluation of anorganic bovine bone xenograft with a bioabsorbable collagen barrier in the treatment of molar furcation defects. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2001;21: Hämmerle CH, Chiantella GC, Karring T, Lang NP. The effect of a deproteinized bovine bone mineral on bone regeneration around titanium dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res 1998;9: Hallman M, Cederlund A, Lindskog S, Lundgren S, Sennerby L. A clinical histologic study of bovine hydroxyapatite in combination with autogenous bone and fibrin glue for maxillary sinus floor augmentation. Results after 6 to 8 months of healing. Clin Oral Implants Res 2001;12: Yildirim M, Spiekermann H, Biesterfeld S, Edelhoff D. Maxillary sinus augmentation using xenogenic bone substitute material Bio-Oss in combination with venous blood: A histologic and histomorphometric study in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res 2000;11: Kim ES, Park EJ, Choung PH. Platelet concentration and its effect on bone formation in calvarial defects: An experimental study in rabbits. J Prosthet Dent 2001;86: Maiorana C, Santoro F, Rabagliati M, Salina S. Evaluation of the use of iliac cancellous bone and anorganic bovine bone in the reconstruction of the atrophic maxilla with titanium mesh: A clinical and histologic investigation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2001;16: Maiorana C, Redemagni M, Rabagliati M, Salina S. Treatment of maxillary ridge resorption by sinus augmentation with iliac cancellous bone, anorganic bovine bone, and endosseous implants: A clinical and histologic report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2000;15: Yildirim M, Spiekermann H, Handt S, Edelhoff D. Maxillary sinus augmentation with the xenograft Bio-Oss and autogenous intraoral bone for qualitative improvement of the implant site: A histologic and histomorphometric clinical study in humans. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2001;16: Volume 19, Number 1, 2004
7 20. McAllister BS, Margolin MD, Cogan AG, Taylor M, Wollins J. Residual lateral wall defects following sinus grafting with recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 or Bio-Oss in the chimpanzee. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 1998;18: Su-Gwan K, Hak-Kyun K, Sung-Chul L. Combined implantation of particulate dentine, plaster of Paris, and a bone xenograft (Bio-Oss) for bone regeneration in rats. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2001;29: Hislop WS, Finlay PM, Moos KF. A preliminary study into the uses of anorganic bone in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1993;31: Indovina A, Block MS. Comparison of 3 bone substitutes in canine extraction sites. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2002;60: Thaller SR, Hoyt J, Borieson K, Dart A, Tesluk H. Reconstruction of calvarial defects with anorganic bovine bone mineral (Bio-Oss) in a rabbit model. J Craniofac Surg 1993; 4: Wetzel AC, Stich H, Caffesse RG. Bone apposition onto oral implants in the sinus area filled with different grafting materials: A histological study in beagle dogs. Clin Oral Implants Res 1995;6: Valentini P, Abensur D. Maxillary sinus floor elevation for implant placement with demineralized freeze-dried bone and bovine bone (Bio-Oss): A clinical study of 20 patients. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 1997;17: Klinge B, Alberius P, Isaksson S, Jonsson J. Osseous response to implanted natural bone mineral and synthetic hydroxylapatite ceramics in repair of experimental skull bone defects. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1992;50: Hämmerle CH, Olah AJ, Schmid J, et al. The biological effect of natural bone mineral on bone neoformation on the rabbit skull. Clin Oral Implants Res 1997;8: Masters DH. Implants: Bone and bone substitutes. J Calif Dent Assoc 1988;16: Misch CE, Dietsh F. Bone-grafting materials in implant dentistry. Implant Dent 1993;2: Linder BL, Chernoff A, Kaplan KL, Goodman DS. Release of PDGF from human platelets by arachidonic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1979;76: Miyadera K, Sumizawa T, Haraguchi M, et al. Role of thymidine phosphorylase activity in the angiogenic effect of PDEGF/ thymidine phosphorylase. Cancer Res 1995;55: Mohle R, Green D, Moore MA, Nachman RL, Rafii S. Constitutive production and thrombin-induced release of VEGF by human megakaryoctes and platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997;94: Jones CL, Witte DP, Feller MJ, Fugman DA, Dorn GW II, Lieberman MA. Response of human megakaryocytic cell line to thrombin: Increase in intracellular free calcium and mitogen release. Biochim Biophys Acta 1992;1136: Harrison P, Cramer EM. Platelet alpha granules. Blood Rev 1993;7: Kassolis JD, Rosen PS, Reynolds MA. Alveolar ridge and sinus augmentation utilizing platelet-rich plasma in combination with freeze-dried bone allograft: Case series. J Periodontol 2000;71: Shanaman R, Filstein MR, Danesh-Meyer MJ. Localized ridge augmentation using GBR and platelet-rich plasma: Case reports. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2001;21: Froum S, Cho SC, Rosenberg E, Rohrer M, Tarnow D. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on bone growth and osseointegration in human maxillary sinus grafts: Three bilateral case reports. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2002;22: Rosenberg ES, Torosian J. Sinus grafting using platelet-rich plasma Initial case presentation. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent 2000;12: Anitua E. Plasma rich in growth factors: Preliminary results of use in the preparation of future sites for implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1999;14: Banks RE, Forbes MA, Kinsey SE, et al. Release of the angiogenic cytokine VEGF from platelets: Significance for VEGF measurements and cancer biology. Br J Cancer 1998;77: Maloney JP, Silliman CC, Ambruso DR, Wang J, Tuder RM, Voelkel NF. In vitro release of vascular endothelial growth factor during platelet aggregation. Am J Physiol 1998;275(3 Pt 2):H1054 H Thomas KA. Vascular endothelial growth factor, a potent and selective angiogenic agent. J Biol Chem 1996;271: Bonewald LF, Mundy GF. Role of TGF- in bone remodeling. Clin Orthop 1990;250: Steenfos HH. Growth factors and wound healing. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 1994;28: Marx RE, Carlson ER, Eichstaedt RM, Schimmele SR, Strauss JE, Georgeff KR. Platelet-rich plasma: Growth factor enhancement for bone grafts. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1998;85: Vikjaer D, Blom S, Hjorting-Hansen E, Pinholt EM. Effect of platelet-derived growth factor-bb on bone formation in calvarial defects: An experimental study in rabbits. Eur J Oral Sci 1997;105: The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 65
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
More than bone regeneration. A total solution.
 More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up
 643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
PRP Usage in Today's Implantology
 Volume 1, December 2004 www.implant.co.il PRP Usage in Today's Implantology by Dr. R. Shapira Introduction: Treating patients suffering from hematological disorders or using anticoagulant medications always
Volume 1, December 2004 www.implant.co.il PRP Usage in Today's Implantology by Dr. R. Shapira Introduction: Treating patients suffering from hematological disorders or using anticoagulant medications always
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft
 Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical presentation of a horse-derived biomaterial and its Biocompatibility: A Clinical Case Report
 Case report J Korean Acad Periodontol 2009;39:287-291 Clinical presentation of a horse-derived biomaterial and its Biocompatibility: A Clinical Case Report Ki-Tae Koo, Jang-Yeol Park, Jun-Seok Park, Tae-Il
Case report J Korean Acad Periodontol 2009;39:287-291 Clinical presentation of a horse-derived biomaterial and its Biocompatibility: A Clinical Case Report Ki-Tae Koo, Jang-Yeol Park, Jun-Seok Park, Tae-Il
A WIDE RANGE OF REGENERATIVE SOLUTIONS
 A WIDE RANGE OF REGENERATIVE SOLUTIONS INDICATIONS: 1/ SOCKET AND RIDGE PRESERVATION 2/ FILLING OF EXTRACTION SOCKETS Biomaterials offers portfolio of regenerative materials for implantology, aimed at
A WIDE RANGE OF REGENERATIVE SOLUTIONS INDICATIONS: 1/ SOCKET AND RIDGE PRESERVATION 2/ FILLING OF EXTRACTION SOCKETS Biomaterials offers portfolio of regenerative materials for implantology, aimed at
Socket preservation using deproteinized horsederived
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2010;40:227-231 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.5.227 Socket preservation using deproteinized horsederived bone mineral Jang-Yeol Park, Ki-Tae Koo, Tae-Il Kim, Yang-Jo
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2010;40:227-231 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.5.227 Socket preservation using deproteinized horsederived bone mineral Jang-Yeol Park, Ki-Tae Koo, Tae-Il Kim, Yang-Jo
Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material- A case Report
 A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
Platelets are cells originating from megakariocytes
 RESEARCH AVOIDING LEUKOCYTE CONTAMINATION AND EARLY PLATELET ACTIVATION IN PLATELET-RICH PLASMA Ivy K. Trindade-Suedam, DDS, MS; Fábio R. M. Leite, DDS, MS; Juliana A. N. D. de Morais, DDS, MS; Elza R.
RESEARCH AVOIDING LEUKOCYTE CONTAMINATION AND EARLY PLATELET ACTIVATION IN PLATELET-RICH PLASMA Ivy K. Trindade-Suedam, DDS, MS; Fábio R. M. Leite, DDS, MS; Juliana A. N. D. de Morais, DDS, MS; Elza R.
Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs
 Current Applied Physics 5 (2005) 507 511 www.elsevier.com/locate/cap Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs Ui-Won Jung a, Hee-Il
Current Applied Physics 5 (2005) 507 511 www.elsevier.com/locate/cap Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs Ui-Won Jung a, Hee-Il
Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Sinus Augmentation Studies Methods and Definition
 FDA approved indications for Infuse Bone Graft in the Maxillofacial Skeleton Alveolar Ridge Augmentation (Buccal Wall Defects) in the Maxilla Maxillary Sinus Floor augmentation Sinus Augmentation Studies
FDA approved indications for Infuse Bone Graft in the Maxillofacial Skeleton Alveolar Ridge Augmentation (Buccal Wall Defects) in the Maxilla Maxillary Sinus Floor augmentation Sinus Augmentation Studies
The Original remains unique.
 The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
REASONS TO USE R.T.R.
 3 REASONS TO USE R.T.R. AFTER EACH EXTRACTION Fully resorbable ß-TCP material RTR 3raisons 120x280.indd 1 16/06/15 10:52 1AVOID SPONTANEOUS RIDGE RESORPTION After tooth extraction, spontaneous healing
3 REASONS TO USE R.T.R. AFTER EACH EXTRACTION Fully resorbable ß-TCP material RTR 3raisons 120x280.indd 1 16/06/15 10:52 1AVOID SPONTANEOUS RIDGE RESORPTION After tooth extraction, spontaneous healing
ALVEOLAR RIDGE AUGMENTATION UTILIZING PLATELET RICH FIBRIN IN COMBINATION WITH DEMINERALIZED FREEZE-DRIED BONE ALLOGRAFT A CASE REPORT
 ALVEOLAR RIDGE AUGMENTATION UTILIZING PLATELET RICH FIBRIN IN COMBINATION WITH DEMINERALIZED FREEZE-DRIED BONE ALLOGRAFT A CASE REPORT * Mishal Piyush Shah 1 and Sheela Kumar Gujjari 2 1 Department of
ALVEOLAR RIDGE AUGMENTATION UTILIZING PLATELET RICH FIBRIN IN COMBINATION WITH DEMINERALIZED FREEZE-DRIED BONE ALLOGRAFT A CASE REPORT * Mishal Piyush Shah 1 and Sheela Kumar Gujjari 2 1 Department of
Immediate Implant Placement in Deficient Bone Sites
 clinical Raj Chopra BSc, DDS Immediate Implant Placement in Deficient Bone Sites THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN PEER-REVIEWED. Introduction The presence of a low-lying sinus floor and inadequate bone volume often
clinical Raj Chopra BSc, DDS Immediate Implant Placement in Deficient Bone Sites THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN PEER-REVIEWED. Introduction The presence of a low-lying sinus floor and inadequate bone volume often
Socket Treatment. Procedure Guide
 Socket Treatment Procedure Guide www.implantdirect.com 888.649.6425 Extraction Healing and Ridge Resorption The Why Working with patients to educate them on the benefits of bone maintenance post extraction
Socket Treatment Procedure Guide www.implantdirect.com 888.649.6425 Extraction Healing and Ridge Resorption The Why Working with patients to educate them on the benefits of bone maintenance post extraction
Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Survival of Maxillary Intrasinus and Extrasinus Implants After 2 Years
 Original Article Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Survival of Maxillary Intrasinus and Extrasinus Implants After 2 Years AR. Rokn 1,2, AAR. Rasouli Ghahroudi 3,4, S. Hemati 5, A. Soolari 6 1 Associate
Original Article Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Survival of Maxillary Intrasinus and Extrasinus Implants After 2 Years AR. Rokn 1,2, AAR. Rasouli Ghahroudi 3,4, S. Hemati 5, A. Soolari 6 1 Associate
Symbios Xenograft Granules Porcine Bone Graft Material
 Symbios Xenograft Granules Porcine Bone Graft Material 32671122-USX-1607_Symbios Highlight Brochure.indd 1 2016-09-27 12:12 Symbios Xenograft Granules Porcine bone graft material Symbios Xenograft Granules
Symbios Xenograft Granules Porcine Bone Graft Material 32671122-USX-1607_Symbios Highlight Brochure.indd 1 2016-09-27 12:12 Symbios Xenograft Granules Porcine bone graft material Symbios Xenograft Granules
PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH
 PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH Headline Contents Headline Appendix 4 5 7 8 13 14 Clinical Benefits Self-Forming Porous Scaffold
PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH Headline Contents Headline Appendix 4 5 7 8 13 14 Clinical Benefits Self-Forming Porous Scaffold
SOCKET WHETHER TO PRESERVE IT NOW OR TO CREATE LATER? - A CASE REPORT
 MAVEN CASE REPORT SOCKET WHETHER TO PRESERVE IT NOW OR TO CREATE LATER? - A CASE REPORT Dr. Parthasarathi Biswas 1, Dr. Debajyoti Mondal 1, Dr. B Praveena Devi 1, Dr. Indrasri Das 2, Dr. Somen Bagchi 3,
MAVEN CASE REPORT SOCKET WHETHER TO PRESERVE IT NOW OR TO CREATE LATER? - A CASE REPORT Dr. Parthasarathi Biswas 1, Dr. Debajyoti Mondal 1, Dr. B Praveena Devi 1, Dr. Indrasri Das 2, Dr. Somen Bagchi 3,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
Clinical Usage Experience and Evaluation of Application of Platelet Rich Plasma Gel in Impacted Tooth Extraction: A Preliminary Study
 Fukui et al., Platelet-rich Plasma in Tooth Extraction ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Usage Experience and Evaluation of Application of Platelet Rich Plasma Gel in Impacted Tooth Extraction: A Preliminary Study
Fukui et al., Platelet-rich Plasma in Tooth Extraction ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Usage Experience and Evaluation of Application of Platelet Rich Plasma Gel in Impacted Tooth Extraction: A Preliminary Study
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report
 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft
 Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Effect of GBR in Combination with Deproteinized Bovine Bone Mineral on the Healing of Calvarial Defects in Rabbits
 Original Article Effect of GBR in Combination with Deproteinized Bovine Bone Mineral on the Healing of Calvarial Defects in Rabbits AA. Khoshkhoonejad 1, A. Miremadi 2, AR. Rokn 2,3, B. Eslami 4, M. Dehghan
Original Article Effect of GBR in Combination with Deproteinized Bovine Bone Mineral on the Healing of Calvarial Defects in Rabbits AA. Khoshkhoonejad 1, A. Miremadi 2, AR. Rokn 2,3, B. Eslami 4, M. Dehghan
regeneration 6 (GBR), and sinus augmentation
 551 Sinus Augmentation Utilizing Anorganic Bovine Bone (Bio-Oss) with Absorbable and Nonabsorbable Membranes Placed over the Lateral Window: Histomorphometric and Clinical Analyses Stephen 5. Wallace,
551 Sinus Augmentation Utilizing Anorganic Bovine Bone (Bio-Oss) with Absorbable and Nonabsorbable Membranes Placed over the Lateral Window: Histomorphometric and Clinical Analyses Stephen 5. Wallace,
Long-term results of new deproteinized bovine bone material in a maxillary sinus graft procedure
 Long-term results of new deproteinized bovine bone material in a maxillary sinus graft procedure pissn 2093-2278 eissn 2093-2286 Seung-Yun Shin 1, You-Jeong Hwang 2, Jung-Hoon Kim 3,4, Yang-Jo Seol 3,
Long-term results of new deproteinized bovine bone material in a maxillary sinus graft procedure pissn 2093-2278 eissn 2093-2286 Seung-Yun Shin 1, You-Jeong Hwang 2, Jung-Hoon Kim 3,4, Yang-Jo Seol 3,
Years of research and advancement in
 Immediate Implants with Guided Bone Regeneration Using Titanium Mesh and Alloplast in an Infected Site: A Case Report Mahesh et al Dr. Lanka Mahesh 1 Dr. Ajay Bibra 2 Dr. Vishal Gupta 3 Abstract Years
Immediate Implants with Guided Bone Regeneration Using Titanium Mesh and Alloplast in an Infected Site: A Case Report Mahesh et al Dr. Lanka Mahesh 1 Dr. Ajay Bibra 2 Dr. Vishal Gupta 3 Abstract Years
The Essential Choice. With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability
 The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration. Ph.D. Thesis. Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban
 Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Using autologous thrombin in making PRP gel - case reports-
 60 Using autologous thrombin in making PRP gel - case reports- LivingWell Dental Hospital LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Seung-gul So, Jang-yeol Lee, Jae-bong Park, Hyoun-chull Kim, Il-hae Park,
60 Using autologous thrombin in making PRP gel - case reports- LivingWell Dental Hospital LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Seung-gul So, Jang-yeol Lee, Jae-bong Park, Hyoun-chull Kim, Il-hae Park,
chronos Bone Void Filler. Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate ( β-tcp) bone graft substitute.
 chronos Bone Void Filler. Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate ( β-tcp) bone graft substitute. Osteoconductive Resorbable Synthetic chronos Bone Void Filler chronos granules and preforms are synthetic, porous, osteoconductive,
chronos Bone Void Filler. Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate ( β-tcp) bone graft substitute. Osteoconductive Resorbable Synthetic chronos Bone Void Filler chronos granules and preforms are synthetic, porous, osteoconductive,
There is considerable interest in developing substitute
 A Comparative Study of Anorganic Xenogenic Bone and Autogenous Bone Implants for Bone Regeneration in Rabbits Cecilia Young, DDS, PhD*/Peter Sandstedt, DDS**/Annika Skoglund*** The aim of this study was
A Comparative Study of Anorganic Xenogenic Bone and Autogenous Bone Implants for Bone Regeneration in Rabbits Cecilia Young, DDS, PhD*/Peter Sandstedt, DDS**/Annika Skoglund*** The aim of this study was
A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material
 74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94
 ( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS. Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel GTO I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E
 GTO THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel R E G E N E R A T I O N S C I E N C E I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E A unique biotechnology
GTO THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel R E G E N E R A T I O N S C I E N C E I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E A unique biotechnology
Augmentation of Peri-implant Bone Defects with Different Bone Grafts and Guided Bone Regeneration: A Pilot Experimental Study in the Dog
 Original J.Hard Tissue Biology.15(3): 82-88,2006 Journal of Hard Tissue Biology 15[3] (2006) p82-88 2006The Society for Regenerative Hard Tissue Biology Printed in Japan, All rights reserved. CODEN-JHTBFF,
Original J.Hard Tissue Biology.15(3): 82-88,2006 Journal of Hard Tissue Biology 15[3] (2006) p82-88 2006The Society for Regenerative Hard Tissue Biology Printed in Japan, All rights reserved. CODEN-JHTBFF,
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
Biomaterials Line. MIS Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
 7. Biomaterials Line MIS Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 6. MIS s Quality System complies with international quality standards: ISO 13485: 2003 - Quality Management System for Medical Devices, ISO 9001:
7. Biomaterials Line MIS Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 6. MIS s Quality System complies with international quality standards: ISO 13485: 2003 - Quality Management System for Medical Devices, ISO 9001:
Space maintenance in autogenous fresh demineralized tooth blocks with platelet rich plasma for maxillary sinus bone formation: a prospective study
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1886-1 RESEARCH Open Access Space maintenance in autogenous fresh demineralized tooth blocks with platelet rich plasma for maxillary sinus bone formation: a prospective study Eun
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1886-1 RESEARCH Open Access Space maintenance in autogenous fresh demineralized tooth blocks with platelet rich plasma for maxillary sinus bone formation: a prospective study Eun
Continuing Education 2
 Posterior Tooth Replacement with Dental Implants in Sites Augmented with rhbmp-2 at Time of Extraction A Case Series Barry P. Levin, DMD; and Peter Tawil, DDS Learning Objectives discuss the augmentation
Posterior Tooth Replacement with Dental Implants in Sites Augmented with rhbmp-2 at Time of Extraction A Case Series Barry P. Levin, DMD; and Peter Tawil, DDS Learning Objectives discuss the augmentation
The long-term fate of some biomaterials is. Eight-Year Results of Site Retention of Anorganic Bovine Bone and Anorganic Bovine Matrix CASE REPORT
 CASE REPORT Eight-Year Results of Site Retention of Anorganic Bovine Bone and Anorganic Bovine Matrix Marco Degidi, MD, DDS 1 Vittoria Perrotti, DDS, PhD 2 * Adriano Piattelli, MD, DDS 2 Giovanna Iezzi,
CASE REPORT Eight-Year Results of Site Retention of Anorganic Bovine Bone and Anorganic Bovine Matrix Marco Degidi, MD, DDS 1 Vittoria Perrotti, DDS, PhD 2 * Adriano Piattelli, MD, DDS 2 Giovanna Iezzi,
SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary
 SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary Summary of In Vivo Use Of Bioresorbable Xenograft Bone Graft Materials In The Treatment Of One-Walled Intrabony Defects In A Canine Model
SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary Summary of In Vivo Use Of Bioresorbable Xenograft Bone Graft Materials In The Treatment Of One-Walled Intrabony Defects In A Canine Model
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
The Essential Choice. With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability
 The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging
 Bone Grafting: Essential Indications and Techniques in Implant Dentistry Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging and sometimes unpredictable. Candidates for implant therapy must have
Bone Grafting: Essential Indications and Techniques in Implant Dentistry Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging and sometimes unpredictable. Candidates for implant therapy must have
Posterior mandible and vertical augmentation
 CASE REPORT Bilateral Vertical Ridge Augmentation With Block Grafts and Guided Bone Regeneration in the Posterior Mandible: A Case Report Maria A. Peñarrocha* Jose A. Vina Laura Maestre David Peñarrocha-Oltra
CASE REPORT Bilateral Vertical Ridge Augmentation With Block Grafts and Guided Bone Regeneration in the Posterior Mandible: A Case Report Maria A. Peñarrocha* Jose A. Vina Laura Maestre David Peñarrocha-Oltra
An aging world population and a progressive
 Evaluation of the Use of Iliac Cancellous Bone and Anorganic Bovine Bone in the Reconstruction of the Atrophic Maxilla with Titanium Mesh: A Clinical and Histologic Investigation Carlo Maiorana, MD, DDS
Evaluation of the Use of Iliac Cancellous Bone and Anorganic Bovine Bone in the Reconstruction of the Atrophic Maxilla with Titanium Mesh: A Clinical and Histologic Investigation Carlo Maiorana, MD, DDS
Alloplastic Grafts - Beta-tricalcium phosphate
 Alloplastic Grafts - Beta-tricalcium phosphate Presentation of clinical cases Mario Ernesto García-Briseño DDS and Professor in Periodontics - Autonomous University of Guadalajara (UAG), Mexico This case
Alloplastic Grafts - Beta-tricalcium phosphate Presentation of clinical cases Mario Ernesto García-Briseño DDS and Professor in Periodontics - Autonomous University of Guadalajara (UAG), Mexico This case
Pattern of bone resorption after extraction
 Teeth loss Pattern of bone resorption after extraction 50% in 1st year 2/ 3 in first 3 months Reich KM, Huber CD, Lippnig WR, Um C, Watzek G, Tangl S. (2011, 17). Atrophy of Residual Alveolar Ridge following
Teeth loss Pattern of bone resorption after extraction 50% in 1st year 2/ 3 in first 3 months Reich KM, Huber CD, Lippnig WR, Um C, Watzek G, Tangl S. (2011, 17). Atrophy of Residual Alveolar Ridge following
Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP)
 REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP) Daif ET. Autologous blood injection as a new treatment modality for chronic recurrent temporomandibular joint dislocation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP) Daif ET. Autologous blood injection as a new treatment modality for chronic recurrent temporomandibular joint dislocation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
Clinical UM Guideline
 Clinical UM Guideline Subject: Bone Grafts for Dental and Oral Surgical Services Guideline #: 04-201 Current Effective Date: 03/24/2017 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/08/2017 Description This document
Clinical UM Guideline Subject: Bone Grafts for Dental and Oral Surgical Services Guideline #: 04-201 Current Effective Date: 03/24/2017 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/08/2017 Description This document
Chemicals in Surgical Periodontal Therapy
 Chemicals in Surgical Periodontal Therapy von Alexandrina L. Dumitrescu 1. Auflage Chemicals in Surgical Periodontal Therapy Dumitrescu schnell und portofrei erhältlich bei beck-shop.de DIE FACHBUCHHANDLUNG
Chemicals in Surgical Periodontal Therapy von Alexandrina L. Dumitrescu 1. Auflage Chemicals in Surgical Periodontal Therapy Dumitrescu schnell und portofrei erhältlich bei beck-shop.de DIE FACHBUCHHANDLUNG
Vertical and horizontal alveolar ridge augmentation
 CLINICAL SIMULTANEOUS VERTICAL GUIDED BONE REGENERATION AND GUIDED TISSUE REGENERATION IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA USING RECOMBINANT HUMAN PLATELET-DERIVED GROWTH FACTOR: A CASE REPORT Istvan Urban, DMD,
CLINICAL SIMULTANEOUS VERTICAL GUIDED BONE REGENERATION AND GUIDED TISSUE REGENERATION IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA USING RECOMBINANT HUMAN PLATELET-DERIVED GROWTH FACTOR: A CASE REPORT Istvan Urban, DMD,
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Horizontal bone augmentation by means of guided bone regeneration
 Periodontology 2000, Vol. 66, 2014, 13 40 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Horizontal bone augmentation by means
Periodontology 2000, Vol. 66, 2014, 13 40 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Horizontal bone augmentation by means
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation. Sanju P. Jose
 Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation by Sanju P. Jose B.S., University of Maryland Baltimore County, 2008 D.D.S., University of Maryland School
Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation by Sanju P. Jose B.S., University of Maryland Baltimore County, 2008 D.D.S., University of Maryland School
Bone Grafting for Socket Preservation
 Bone Grafting for Socket Preservation Dr. Karl R. Koerner Normal extraction facial bone loss. Excessive force. Commonly the thickness of facial bone. Hussain, A. et al. Ridge preservation comparing a nonresorbable
Bone Grafting for Socket Preservation Dr. Karl R. Koerner Normal extraction facial bone loss. Excessive force. Commonly the thickness of facial bone. Hussain, A. et al. Ridge preservation comparing a nonresorbable
Versatile grafting Solutions
 Versatile grafting Solutions A Canadian company serving Canadian dentists since 1997 Here s why your colleagues are calling us for their bone regeneration needs Founded in 1997 Citagenix has been providing
Versatile grafting Solutions A Canadian company serving Canadian dentists since 1997 Here s why your colleagues are calling us for their bone regeneration needs Founded in 1997 Citagenix has been providing
Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation
 Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation Historical Background Guided tissue regeneration is a well established concept in the repair of oral bone defects. The exclusion of soft tissue epithelial
Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation Historical Background Guided tissue regeneration is a well established concept in the repair of oral bone defects. The exclusion of soft tissue epithelial
Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla
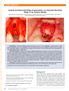 CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
Vertical Augmentation
 Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
P105 Predictable Bone Grafting for Site Preparation for Implants and Prosthetics Workshop JAMES GRISDALE, DDS THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 26
 P105 Predictable Bone Grafting for Site Preparation for Implants and Prosthetics Workshop JAMES GRISDALE, DDS THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 26 Please complete the speaker evaluation form in the Midwinter Meeting
P105 Predictable Bone Grafting for Site Preparation for Implants and Prosthetics Workshop JAMES GRISDALE, DDS THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 26 Please complete the speaker evaluation form in the Midwinter Meeting
Platelet Rich Fibrin- A New Hope for Regeneration of Osseous Defects in Aggressive Periodontitis Patients: A Case Report
 American Journal of Advanced Drug Delivery www.ajadd.co.uk Original Article Platelet Rich Fibrin- A New Hope for Regeneration of Osseous Defects in Aggressive Periodontitis Patients: A Case Report Jayant
American Journal of Advanced Drug Delivery www.ajadd.co.uk Original Article Platelet Rich Fibrin- A New Hope for Regeneration of Osseous Defects in Aggressive Periodontitis Patients: A Case Report Jayant
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
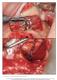 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 413 Schneiderian Membrane Perforation Rate During Sinus Elevation Using Piezosurgery: Clinical Results of 100 Consecutive Cases Stephen
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 413 Schneiderian Membrane Perforation Rate During Sinus Elevation Using Piezosurgery: Clinical Results of 100 Consecutive Cases Stephen
Innovative Range of Regenerative Solutions
 TM Innovative Range of Regenerative Solutions MIS Implant Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved. Optimal volumes and quality of hard and soft tissue are required to satisfy the goals of oral rehabilitation
TM Innovative Range of Regenerative Solutions MIS Implant Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved. Optimal volumes and quality of hard and soft tissue are required to satisfy the goals of oral rehabilitation
botiss dental bone & tissue regeneration biomaterials collacone max Innovative composite matrix socket preservation form-fitting resorbable composite
 dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials socket preservation Innovative composite matrix form-fitting resorbable composite 1 botiss regeneration system maxresorb flexbone* collacone.. max
dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials socket preservation Innovative composite matrix form-fitting resorbable composite 1 botiss regeneration system maxresorb flexbone* collacone.. max
The search for an ideal intraoperative
 CLINICAL PLATELET-RICH PLASMA APPLICATION IN SINUS GRAFT SURGERY: PART I BACKGROUND AND PROCESSING TECHNIQUES Jaime L. Lozada, DDS Nicholas Caplanis, DMD, MS Periklis Proussaefs, DDS, MS John Willardsen,
CLINICAL PLATELET-RICH PLASMA APPLICATION IN SINUS GRAFT SURGERY: PART I BACKGROUND AND PROCESSING TECHNIQUES Jaime L. Lozada, DDS Nicholas Caplanis, DMD, MS Periklis Proussaefs, DDS, MS John Willardsen,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
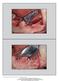 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 355 Vertical Ridge Augmentation Around Implants Using e-ptfe Titanium- Reinforced Membrane and Deproteinized Bovine Bone Mineral (Bio-Oss):
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 355 Vertical Ridge Augmentation Around Implants Using e-ptfe Titanium- Reinforced Membrane and Deproteinized Bovine Bone Mineral (Bio-Oss):
Scientific & Clinical Evidence Jason membrane
 Scientific & Clinical Evidence Jason membrane Pericardium GBR/GTR Membrane Facts - CE since 2009 - so far no serious clinical complication or objection - approx. 250.000 successful clinical treatments
Scientific & Clinical Evidence Jason membrane Pericardium GBR/GTR Membrane Facts - CE since 2009 - so far no serious clinical complication or objection - approx. 250.000 successful clinical treatments
Long-term success for osteointegrated
 CASE REPORT Symphyseal Bone Cylinders Tapping With the Dental Implant Into Insufficiency Bone Situated Esthetic Area at One-Stage Surgery: A Case Report and the Description of the New Technique Umut Tekin,
CASE REPORT Symphyseal Bone Cylinders Tapping With the Dental Implant Into Insufficiency Bone Situated Esthetic Area at One-Stage Surgery: A Case Report and the Description of the New Technique Umut Tekin,
We Want to Keep You Smiling. Bone Regeneration with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide
 We Want to Keep You Smiling Bone Regeneration with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Strong Bone for a Healthier Smile Strong and healthy teeth provide a feeling of well-being, self-confidence and
We Want to Keep You Smiling Bone Regeneration with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Strong Bone for a Healthier Smile Strong and healthy teeth provide a feeling of well-being, self-confidence and
Guided Tissue and Bone Regeneration
 Guided Tissue and Bone Regeneration One toolbox for your needs! Tefguide 9000 742 401 12x24 mm pc 1 Osgide 9000 701 520 15 x 20 mm pc 1 Osbone 9000 800 255 250-1000 μm 0.25 cc 5 Product Specifications
Guided Tissue and Bone Regeneration One toolbox for your needs! Tefguide 9000 742 401 12x24 mm pc 1 Osgide 9000 701 520 15 x 20 mm pc 1 Osbone 9000 800 255 250-1000 μm 0.25 cc 5 Product Specifications
Familial tooth bone graft for ridge and sinus augmentation: a report of two cases
 CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.1.37 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Familial tooth bone graft for ridge and sinus augmentation: a report of two cases Young-Kyun Kim 1, Su-Gwan Kim
CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.1.37 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Familial tooth bone graft for ridge and sinus augmentation: a report of two cases Young-Kyun Kim 1, Su-Gwan Kim
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
News No. 24 July BONDBONE a Biphasic Calcium Sulfate: A Preliminary Study in Socket Therapy
 24 News No. 24 July 2010 BONDBONE a Biphasic Calcium Sulfate: A Preliminary Study in Socket Therapy 2 News 24, July 2010 BONDBONE a Biphasic Calcium Sulfate: A preliminary study in socket therapy Ziv Mazor,
24 News No. 24 July 2010 BONDBONE a Biphasic Calcium Sulfate: A Preliminary Study in Socket Therapy 2 News 24, July 2010 BONDBONE a Biphasic Calcium Sulfate: A preliminary study in socket therapy Ziv Mazor,
Maxillary Sinus Augmentation:
 Earn 4 CE credits This course was written for dentists, dental hygienists, and assistants. Maxillary Sinus Augmentation: Fixed Restorations in the Compromised Posterior Maxilla A Peer-Reviewed Publication
Earn 4 CE credits This course was written for dentists, dental hygienists, and assistants. Maxillary Sinus Augmentation: Fixed Restorations in the Compromised Posterior Maxilla A Peer-Reviewed Publication
botiss biomaterials bone & tissue regeneration collacone max Innovative composite matrix socket preservation form-fitting resorbable composite
 bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials socket preservation Innovative composite matrix form-fitting resorbable composite 1 Socket preservation safeguarding your sockets collacone.. max flexbone*
bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials socket preservation Innovative composite matrix form-fitting resorbable composite 1 Socket preservation safeguarding your sockets collacone.. max flexbone*
Endosseous cylindric implants are well accepted
 Soft Tissue Exposure of Endosseous Implants Between Stage I and Stage II Surgery as a Potential Indicator of Early Crestal Bone Loss Joseph A. Toljanic, DDS*/Mark L. Banakis, DDS**/Leslee A. K. Willes,
Soft Tissue Exposure of Endosseous Implants Between Stage I and Stage II Surgery as a Potential Indicator of Early Crestal Bone Loss Joseph A. Toljanic, DDS*/Mark L. Banakis, DDS**/Leslee A. K. Willes,
Growth Factor-Mediated Sinus Augmentation Grafting With Recombinant Human Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB (rhpdgf-bb): Two Case Reports
 CASE REPORT Growth Factor-Mediated Sinus Augmentation Grafting With Recombinant Human Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB (rhpdgf-bb): Two Case Reports E. Todd Scheyer* and Michael K. McGuire* Introduction:
CASE REPORT Growth Factor-Mediated Sinus Augmentation Grafting With Recombinant Human Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB (rhpdgf-bb): Two Case Reports E. Todd Scheyer* and Michael K. McGuire* Introduction:
Clinical UM Guideline
 Clinical UM Guideline Subject: Biological Materials to Aid in Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting Guideline #: 03-401 Current Effective Date: 03/24/2017 Status: New Last Review Date: 02/08/2017 Description This
Clinical UM Guideline Subject: Biological Materials to Aid in Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting Guideline #: 03-401 Current Effective Date: 03/24/2017 Status: New Last Review Date: 02/08/2017 Description This
Inion BioRestore. Bone Graft Substitute. Product Overview
 Inion BioRestore Bone Graft Substitute Product Overview Inion BioRestore Introduction Inion BioRestore is a synthetic bone graft substitute, which remodels into bone and is easy to use. Inion BioRestore
Inion BioRestore Bone Graft Substitute Product Overview Inion BioRestore Introduction Inion BioRestore is a synthetic bone graft substitute, which remodels into bone and is easy to use. Inion BioRestore
Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic. Review
 Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic Review A dissertation submitted to the University of Manchester for the degree of Master of Science in Dentistry (Oral and
Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic Review A dissertation submitted to the University of Manchester for the degree of Master of Science in Dentistry (Oral and
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
Product Information. MIS Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
 Product Information MIS Corporation. All Rights Reserved. MIS Warranty: MIS exercises great care and effort in maintaining the superior quality of its products. All MIS products are guaranteed to be free
Product Information MIS Corporation. All Rights Reserved. MIS Warranty: MIS exercises great care and effort in maintaining the superior quality of its products. All MIS products are guaranteed to be free
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla
 IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
The effect of concentrated growth factors on ridge augmentation
 USERREPORT The effect of concentrated growth factors on ridge augmentation 34 Introduction The bony defects can be developed by periodontal disease, tooth loss, trauma and infection. Guided bone generation(gbr)
USERREPORT The effect of concentrated growth factors on ridge augmentation 34 Introduction The bony defects can be developed by periodontal disease, tooth loss, trauma and infection. Guided bone generation(gbr)
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Using Various Bone Substitutes -A Web Form of Titanium Fibers Promotes Rapid Bone Development-
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 53, No. 5, pp. 257-263 2007 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Using Various Bone Substitutes -A Web Form of Titanium Fibers Promotes Rapid Bone Development- HIROSHI MASAGO 1, YASUYUKI
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 53, No. 5, pp. 257-263 2007 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Using Various Bone Substitutes -A Web Form of Titanium Fibers Promotes Rapid Bone Development- HIROSHI MASAGO 1, YASUYUKI
A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation. Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics
 A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics Boyne, 1980 Maxillary Sinus Augmentations Maxillary sinus augmentation,
A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics Boyne, 1980 Maxillary Sinus Augmentations Maxillary sinus augmentation,
Histologic and histomorphometric evaluation of anorganic bovine bone (ABB) retrieved 7 years after a sinus augmentation procedure
 MARCO DEGIDI 1, ADRIANO PIATTELLI 2, VITTORIA PERROTTI 2, GIOVANNA IEZZI 2 1 Private Practice, Bologna, Italy 2 Dental School, University of Chieti-Pescara, Chieti, Italy Histologic and histomorphometric
MARCO DEGIDI 1, ADRIANO PIATTELLI 2, VITTORIA PERROTTI 2, GIOVANNA IEZZI 2 1 Private Practice, Bologna, Italy 2 Dental School, University of Chieti-Pescara, Chieti, Italy Histologic and histomorphometric
Management of peri-implant recession associated with bone fenestration and dehiscence in the anterior region
 CLINICAL REPORT 269 George Nikou, Dimitris Nikolidakis, Peter Thoolen, Anton Sculean Management of peri-implant recession associated with bone fenestration and dehiscence in the anterior region KEY WORDS
CLINICAL REPORT 269 George Nikou, Dimitris Nikolidakis, Peter Thoolen, Anton Sculean Management of peri-implant recession associated with bone fenestration and dehiscence in the anterior region KEY WORDS
