Thermal Injury to Reconstructed Breasts from Commonly Used Warming Devices: A Risk for Reconstructive Failure
|
|
|
- Andrew Basil Hensley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thermal Injury to Reconstructed Breasts from Commonly Used Warming Devices: A Risk for Reconstructive Failure The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed Citable Link Terms of Use Faulkner, Heather R., Amy S. Colwell, Eric C. Liao, Jonathan M. Winograd, and William G. Austen Thermal Injury to Reconstructed Breasts from Commonly Used Warming Devices: A Risk for Reconstructive Failure. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Global Open 4 (10): e1033. doi: /gox doi: /gox August 16, :46:51 PM EDT This article was downloaded from Harvard University's DASH repository, and is made available under the terms and conditions applicable to Other Posted Material, as set forth at (Article begins on next page)
2 Original Article Breast Thermal Injury to Reconstructed Breasts from Commonly Used Warming Devices: A Risk for Reconstructive Failure Heather R. Faulkner, MD, MPH Amy S. Colwell, MD Eric C. Liao, MD, PhD Jonathan M. Winograd, MD William G. Austen Jr, MD Background: Sensation is decreased or absent after breast reconstruction. This leaves reconstructed breasts vulnerable to injury from common household thermal sources such as heating pads and hot water bottles. We sought to categorize these injuries, provide a treatment plan, and prevent these injuries in the future. Methods: A retrospective review of patients who had sustained burns to reconstructed breasts with household devices was performed at a single institution. A PubMed search was performed to identify and summarize articles cataloguing patients who had suffered burns to breast reconstructions. Results: Five patients in our practice were affected. Fifteen articles were identified in the literature search. A total of 40 patients had sustained thermal injury to reconstructed breasts, with the majority being full thickness burns (67.5%). Patients who sustained full thickness burns to reconstructed breasts were more likely to require an operative procedure compared with patients who sustained partial thickness burns (P = ). Conclusions: Reconstructed breasts are at risk for injury from commonly used household warming devices and ambient heat from the sun. As a result, patients should be counseled about these risks accordingly, to avoid injury or loss of reconstruction. These injuries require immediate vigilant treatment. (Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2016;4:e1033; doi: /GOX ; Published online 27 October 2016.) Sensibility of the skin to touch and temperature (cold and warmth) after immediate breast reconstruction with implants is decreased or absent postoperatively. 1 This finding has also been noted in patients who have undergone autologous breast reconstruction. 2 Decreased sensation after breast reconstruction has been shown to be relatively permanent. 3 As a result, reconstructed breasts are vulnerable to thermal injury. In addition, patients with implants may experience a cold sensation in their reconstructed breasts in cooler ambient temperatures, which may prompt patients to use warming devices on their breasts. 4 From the Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Mass. Received for publication March 11, 2016; accepted July 22, Copyright 2016 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons. All rights reserved. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial- No Derivatives License 4.0 (CCBY-NC-ND), where it is permissible to download and share the work provided it is properly cited. The work cannot be changed in any way or used commercially without permission from the journal. DOI: /GOX During the previous winter season in New England, multiple plastic surgeons in our division treated patients that had sustained injury to their reconstructed breasts as a result of the use of common household warming devices. The goals of this study are to characterize thermal injuries to reconstructed breasts, review the various methods of treatment, and prevent this type of injury in the future. METHODS A retrospective review was performed of patients in our division that underwent breast reconstruction of any modality in addition to having sustained a burn from a commonly used warming device or household device within the past year. We collected demographic information, method of reconstruction, degree of thermal injury, and outcome for each patient. Additionally, a PubMed search was performed to identify peer-reviewed studies, case reports, or letters to the editor cataloguing thermal injuries to reconstructed breasts. Articles were culled for information about each patient, including method of reconstruction, degree of thermal Disclosure: The authors have no financial interest to declare in relation to the content of this article. The Article Processing Charge was paid for by the authors. 1
3 PRS Global Open 2016 Table 1. Massachusetts General Hospital Patients Age at No. of Days from Mechanism of Patient Surgery (y) Surgery to Injury Burn Burn Thickness Reconstructive Method Electric heating Superficial Implant with acellular pad partial dermal matrix Microwaveable Full Expander (total muscle heating pad coverage) Hot water bottle Full Implant with acellular dermal matrix ,201 Hand warmer Full Expander (total muscle coverage) implant Electric blanket Full Implant with acellular dermal matrix Received Radiation Therapy? Yes No No Yes Yes Outcome Spontaneous resolution Excised and closed Excised, implant removed Excised, latissimus flap performed, implant exchanged Excised, implant removed Fig. 1. Superficial burn to left breast reconstructed with implant. injury, and outcome. Stata/IC version 13.1 was used for statistical analysis. RESULTS A summary of the affected patients (n = 5) from our practice is shown in Table 1. The mean age at surgery was 46 years (range, years). One patient had diabetes mellitus. All patients had bilateral mastectomies (1 skin-sparing, 4 nipple-sparing). Three patients received radiation (2 preoperatively, 1 postoperatively). All patients had chemotherapy preoperatively, or postoperatively, or both. All patients had an implant or expander in place. One patient sustained a superficial partial thickness burn, which resolved completely (Fig. 1). The remaining 4 patients (80%) sustained full thickness burns (Fig. 2). Two patients had the implant/expander removed without further reconstruction. One patient required a latissimus dorsi flap with implant exchange (Fig. 3). Patient 1 was 51 years old, and had prior left breast lumpectomy and radiation therapy. She developed a recurrent cancer in the left breast, and underwent bilateral nipple-sparing mastectomies and immediate reconstruction with implants and acellular dermal matrix. She developed a focal hematoma on the left after drain removal, and the patient used a heating pad for discomfort. She developed a superficial partial thickness burn of the left breast which resolved spontaneously, as did the hematoma. Patient 2 was 45 years old and was diagnosed with left breast cancer, which was node positive. She underwent neoadjuvant chemotherapy. She underwent bilateral nipple-sparing mastectomies and immediate reconstruction with tissue expanders using total muscle coverage. About 1 week after surgery, she had used a heating pad on the left breast for discomfort, and sustained a full thickness burn. This was treated with Silvadene for 1 week, and then without significant improvement, she was taken to the op- Fig. 2. Full-thickness burns to breasts reconstructed with implants, one with implant exposure (A). 2
4 Faulkner et al. Thermal Injury to Reconstructed Breasts Fig. 3. Full thickness burn, salvaged with latissimus flap and implant exchange. A, 1 week postburn. B, 4 weeks postburn. C, 6 weeks after latissimus dorsi flap. Table 2. Summary of Peer-reviewed Literature Reference Year Burn Mechanism Burn Type Reconstructive Method Radiation Therapy Outcome Maxwell et al Electric curlers Full Pedicled TRAM n/a Healed by secondary intention after Hot beverage Partial Pedicled TRAM debridement of necrotic tissue Hyperthermia device Full Pedicled TRAM (2 patients required excisional scar Heating pad Partial Expander revision) Sunlamp Partial Pedicled TRAM Sunlamp Partial Pedicled TRAM Hot beverage Full Pedicled TRAM Heating pad Partial Pedicled TRAM Heating pad Partial Pedicled latissimus dorsi Heating pad Partial Pedicled latissimus dorsi Lejour Sunburn Full Implant Yes Latissimus dorsi, implant exchange Alexandrides et al 7 * Beckenstein et al 8 * 1997 Sunburn Full Pedicled TRAM n/a Healed by secondary intention Sunburn Full Pedicled TRAM Healed by secondary intention Prolonged contact with Full Pedicled TRAM Excision and full thickness skin graft vessel of hot beverage Sunburn Partial Pedicled TRAM Healed by secondary intention 1997 Sunburn Partial Pedicled TRAM n/a Excision and split thickness skin graft Sunburn Partial Pedicled TRAM Healed by secondary intention Hair dryer Full Pedicled TRAM Healed by secondary intention Heating pad Full Pedicled TRAM Healed by secondary intention Kay and 1997 Hair dryer Full Free TRAM n/a Healed by secondary intention McGeorge 9 Restifo Heating pad Full Pedicled TRAM n/a Split thickness skin graft Davison and Mercer Hot water bottle Full Implant Yes Excised and covered with local transposition flap Davison Sunburn Partial Pedicled TRAM n/a Healed by secondary intention Hot water bottle Full Implant Yes Excised and covered with local transposition flap Prolonged contact with Full Pedicled TRAM n/a Split thickness skin graft vessel of hot beverage Price et al Hot water bottle Full Implant Yes Implant removal, primary closure Agarwal and 2002 Hot water bottle Full Pedicled latissimus Yes Healed by secondary intention Williams 14 dorsi-expander Hot water bottle Full Pedicled latissimus No dorsi expander Seth et al Microwaved heating pad Full Implant No Implant removal, excision, split thickness skin graft Delfino et al Sunburn Full Pedicled TRAM Yes Healed by secondary intention Sunburn Partial full Expander n/a Sunburn Partial full Expander implant Yes Mahajan et al Sunlight through reading Full Pedicled latissimus dorsi n/a n/a glasses Jabir et al Hot water bottle Full DIEP n/a Split thickness skin graft Gandolfi et al Cigarette Full Expander implant Yes Implant removal *One patient in each report sustained a burn to the abdomen, but not the breast. These 2 patients are not included in the table. Likely same patient, 2 separate reports. TRAM, transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap; DIEP, Deep inferior epigastric perforator flap; n/a, not available. 3
5 PRS Global Open 2016 Fig. 4. Sources of thermal injuries to reconstructed breasts. *Hyperthermia device includes electric blanket and personal warming device. **Other: 1 patient each with burns from electric curlers, cigarette, and sunlight through reading glasses. Fig. 5. Method of reconstruction in patients sustaining thermal injury to reconstructed breasts. erating room and the burn was excised and closed primarily. The expander was not exposed. Two months later, the patient successfully underwent exchange of tissue expanders for implants. Patient 3 was 41 years old, and had right breast cancer, which was node positive. She underwent neoadjuvant chemotherapy, followed by bilateral nipple-sparing mastectomies and immediate reconstruction directly with implants and acellular dermal matrix. One and a half months later, she had used a hot water bottle on the right breast for discomfort, and sustained a full thickness burn. She was taken to the operating room for removal of the right breast implant and primary closure. This sequence of events relating to the burn delayed the patient s receipt of chemotherapy postoperatively. Patient 4 was 51 years old, and had diabetes (type 2). She had prior left breast cancer and lumpectomy with radiation. She developed a recurrent cancer on the left, and underwent bilateral skin-sparing mastectomies and immediate reconstruction with tissue expanders with total muscle coverage. She subsequently had exchange of the tissue expanders for implants. Four years afterward, the patient placed hand warmers into her bra for a cold sensation in the implants, and she sustained a full thickness burn to the left breast. She was taken to the operating room for a latissimus flap and implant exchange. Patient 5 was 41 years old, and was diagnosed with right breast cancer, node positive. She underwent neoadjuvant chemotherapy, followed by bilateral nipple-sparing mastectomies and immediate reconstruction with implants and acellular dermal matrix. She was diagnosed with metastatic cancer and underwent postoperative chemotherapy and radiation therapy to the right breast and multiple other sites. One year later, she used a heating blanket, and sustained a full thickness burn to the right breast with implant exposure. The implant was removed and the wound was closed primarily. One month later, the patient died of metastatic breast cancer. A summary of the 15 articles of the PubMed search is shown in Table 2. Combining our patients with the patients from the review, a total of 40 patients sustained thermal injury to reconstructed breasts. The top 3 most common causes of thermal injury to reconstructed breasts were sunburn (26%), heating pad (21%), and hot water bottle (19%). The frequency of burn sources responsible for injury in the 39 patients is represented in Figure 4. Most patients sustained full thickness burn injury (n = 27; 67.5%). The top 3 methods of reconstruction overall were pedicled TRAM (47%), implant or expander (35%), and pedicled latissimus dorsi flap (7%; Fig. 5). Fifteen patients (5 in our group and 10 in the peer-reviewed papers) had information regarding the receipt of radiation; of those, 11 patients had received radiation. Most burns healed by secondary intention (n = 24, 60%), 11 of whom had sustained partial thickness burns (45.8%). The proportion of patients requiring treatment with a surgical procedure was significantly higher in the group that sustained full thickness burns in comparison with partial thickness burns [n = 14, 51.9% (full) versus n = 1, 8.3% (partial); P = ). Five patients had full or split thickness skin grafts, 6 had removal of the implant or expander (one required a split thickness skin graft in addition), 2 patients required salvage with latissimus dorsi flaps, and 2 had local flaps (local tissue rearrangement). CONCLUSIONS After breast reconstruction using any available method, patients are vulnerable to thermal injury to their recon- 4
6 Faulkner et al. Thermal Injury to Reconstructed Breasts structed breasts, because of loss of sensation. 1, 20 Although a subset of patients may have partial return of sensation after breast reconstruction, there is still insufficient sensation to provide protection from exposure to commonly utilized household thermal devices such as heating pads and hot water bottles. In addition, patients are not routinely made aware of the perils of these devices on their reconstructed breasts, and it may be helpful to furnish patients with a list of such devices to avoid. Once a patient has sustained a thermal injury to a reconstructed breast, immediate evaluation and treatment is necessary. Partial thickness burns can often be treated with local wound care and close observation. Full thickness burns are likely to require surgery (either immediately or in a delayed fashion) to remove an exposed implant or expander, and excise a full thickness burn. These patients may require split or full thickness skin grafts or a myocutaneous flap for salvage. Burn injuries to reconstructed breasts may occur more frequently in colder climates. As such, we have added an item to our postoperative instructions for patients explicitly stating to avoid the use of warming or cooling devices on reconstructed breasts. We counsel patients to avoid direct sun exposure to reconstructed breasts in addition. We have extended these instructions to patients that have undergone free tissue transfer, as these types of injuries have been shown to also occur in patients who have undergone free tissue transfer for reconstruction of other body regions, such as the scalp or extremities. 21 Patients should be notified that these risks are not just in the immediate postoperative period, and in fact do last for their lifetime. Heather R. Faulkner, MD, MPH Department of Surgery/Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Massachusetts General Hospital/Harvard Medical School 104 Endicott Street, Suite 200 Danvers, MA hrfaulkner@partners.org REFERENCES 1. Lagergren J, Wickman M, Hansson P. Sensation following immediate breast reconstruction with implants. Breast J. 2010;16: Shridharani SM, Magarakis M, Stapleton SM, et al. Breast sensation after breast reconstruction: a systematic review. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2010;26: Unukovych D, Johansson H, Johansson E, et al. Physical therapy after prophylactic mastectomy with breast reconstruction: a prospective randomized study. Breast 2014;23: Snell L, McCarthy C, Klassen A, et al. Clarifying the expectations of patients undergoing implant breast reconstruction: a qualitative study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126: Maxwell GP, Tornambe R. Second- and third-degree burns as a complication in breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 1989;22: Lejour M. Burn of a reconstructed breast. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996;97: Alexandrides IJ, Shestak KC, Noone RB. Thermal injuries following TRAM flap breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 1997;38: Beckenstein MS, Beegle PH, Hartrampf CR Jr. Thermal injury to TRAM flaps: a report of five cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;99: Kay AR, McGeorge D. Susceptibility of the insensate reconstructed breast to burn injury. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;99: Restifo RJ. Heating pad burn of a reconstructed breast. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;100: Davison JA, Mercer DM. Accidental burns following subcutaneous mastectomy and reconstruction with a prosthesis. Br J Plast Surg. 1998;51: Davison JA. Burns to reconstructed breasts. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1999;81: Price RK, Mokbel K, Carpenter R. Hot-water bottle induced thermal injury of the skin overlying Becker s mammary prosthesis. Breast 1999;8: Agarwal SK, Williams MR. Burn injuries after latissimus dorsi breast reconstruction in a cold climate. Breast 2002;11: Seth R, Lamyman MJ, Athanassopoulos A, et al. Too close for comfort: accidental burn following subcutaneous mastectomy and immediate implant reconstruction. J R Soc Med. 2008;101: Delfino S, Brunetti B, Toto V, et al. Burn after breast reconstruction. Burns 2008;34: Mahajan AL, Chapman TW, Mandalia MR, et al. Sun burn as a consequence of resting reading glasses on a reconstructed breast. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010;63:e Jabir S, Frew Q, Griffiths M, et al. Burn injury to a reconstructed breast via a hot water bottle. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013;66:e334 e Gandolfi S, Vaysse C, Garrido I, et al. Burn injury to a reconstructed breast via a cigarette causing implant exposure. The importance of the patient s education. Breast J. 2014;20: Lagergren J, Edsander-Nord A, Wickman M, et al. Long-term sensibility following nonautologous, immediate breast reconstruction. Breast J. 2007;13: Butler CE, Davidson CJ, Breuing K, et al. Thermal injuries to free flaps: better prevented than treated. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;107:
Thermal injury in TAPIA breast reconstruction Børsen-Koch, Mikkel; Gunnarsson, Gudjon L.; Sørensen, Jens Ahm; Thomsen, Jørn Bo
 Syddansk Universitet Thermal injury in TAPIA breast reconstruction Børsen-Koch, Mikkel; Gunnarsson, Gudjon L.; Sørensen, Jens Ahm; Thomsen, Jørn Bo Published in: Gland Surgery DOI: 10.21037/gs.2017.01.01
Syddansk Universitet Thermal injury in TAPIA breast reconstruction Børsen-Koch, Mikkel; Gunnarsson, Gudjon L.; Sørensen, Jens Ahm; Thomsen, Jørn Bo Published in: Gland Surgery DOI: 10.21037/gs.2017.01.01
Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities
 Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction
 Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 12 th Annual School of
Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 12 th Annual School of
Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC
 Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
Case Study. TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication. Repair using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis.
 Case Study TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication. Repair using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis. TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication Challenge Insulin-dependent diabetes
Case Study TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication. Repair using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis. TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication Challenge Insulin-dependent diabetes
Advances in Breast Surgery. Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015
 Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts. Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA
 The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA Changing issues in breast cancer management Early detection
The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA Changing issues in breast cancer management Early detection
Breast Reconstruction Options
 Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate surgical options
 A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
Breast Reconstruction. Westmead Breast Cancer Institute
 Breast Reconstruction Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast reconstruction? Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that creates a shape on the chest wall following a mastectomy. Occasionally,
Breast Reconstruction Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast reconstruction? Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that creates a shape on the chest wall following a mastectomy. Occasionally,
Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps
 Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
Breast Reconstruction
 Steven E. Copit, M.D. Chief- Division of Plastic Surgery Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA analysis of The Defect Skin Breast Volume Nipple Areola Complex analysis of The Defect the
Steven E. Copit, M.D. Chief- Division of Plastic Surgery Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA analysis of The Defect Skin Breast Volume Nipple Areola Complex analysis of The Defect the
Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps
 Original Article Breast Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps James L. Mayo, MD Robert J. Allen, MD, FACS Alireza Sadeghi, MD, FACS Background: In cases of bilateral breast
Original Article Breast Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps James L. Mayo, MD Robert J. Allen, MD, FACS Alireza Sadeghi, MD, FACS Background: In cases of bilateral breast
Interesting Case Series. Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle
 Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer. Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Plastic-reconstructive aspects after mastectomy Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Bauerfeind
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Plastic-reconstructive aspects after mastectomy Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Bauerfeind
Breast Cancer Reconstruction
 Breast Cancer Jerome H. Liu, MD Tom S. Liu, MD Jerome H. Liu, MD Undergraduate: Brown University Medical School: University of California, Los Angeles Residency: UCLA Medical Center Fellowship:UCLA Medical
Breast Cancer Jerome H. Liu, MD Tom S. Liu, MD Jerome H. Liu, MD Undergraduate: Brown University Medical School: University of California, Los Angeles Residency: UCLA Medical Center Fellowship:UCLA Medical
Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications
 Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications Minas T Chrysopoulo, MD PRMA Center For Advanced Breast Reconstruction Prophylactic Mastectomy Surgical removal of one or both breasts to reduce the
Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications Minas T Chrysopoulo, MD PRMA Center For Advanced Breast Reconstruction Prophylactic Mastectomy Surgical removal of one or both breasts to reduce the
Use of Intraoperative Computed Tomography for Revisional Procedures in Patients with Complex Maxillofacial Trauma
 Use of Intraoperative Computed Tomography for Revisional Procedures in Patients with Complex Maxillofacial Trauma The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
Use of Intraoperative Computed Tomography for Revisional Procedures in Patients with Complex Maxillofacial Trauma The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy This handout explains the most common procedures that are used at University of Washington Medical Center (UWMC) to restore a
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy This handout explains the most common procedures that are used at University of Washington Medical Center (UWMC) to restore a
Breast Reconstruction Surgery
 Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni
 SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni Icro Meattini, MD Radiation Oncology Department - University of Florence Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Careggi Firenze Breast
SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni Icro Meattini, MD Radiation Oncology Department - University of Florence Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Careggi Firenze Breast
Breast reconstruction has an important role BREAST. A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions
 BREAST A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions Amy K. Alderman, M.D. William M. Kuzon, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. Edwin G. Wilkins, M.D. Ann Arbor, Mich. Background: Functional
BREAST A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions Amy K. Alderman, M.D. William M. Kuzon, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. Edwin G. Wilkins, M.D. Ann Arbor, Mich. Background: Functional
How many procedures to make a breast?
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (00 ), 5, 7-3 9 00 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 0.05/bjps.000.3538 BRITISH JOURNAL OF PLASTIC SURGERY How many procedures to make a breast? A. D.
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (00 ), 5, 7-3 9 00 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 0.05/bjps.000.3538 BRITISH JOURNAL OF PLASTIC SURGERY How many procedures to make a breast? A. D.
Updates in Breast Care. Truth or Hype. History of Breast Cancer Surgery. Dr Karen Barbosa 5/3/2017 4/20/2017
 Updates in Breast Care Dr Karen Barbosa 4/20/2017 Truth or Hype Princess Bust Developer Sears, Roebuck and Co. 1897 Promised to make the breast round, firm and beautiful History of Breast Cancer Surgery
Updates in Breast Care Dr Karen Barbosa 4/20/2017 Truth or Hype Princess Bust Developer Sears, Roebuck and Co. 1897 Promised to make the breast round, firm and beautiful History of Breast Cancer Surgery
Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014). Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health?
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health? Benditte-Klepetko, H.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health? Benditte-Klepetko, H.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014).
Infectious Complications Leading to Explantation in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction With AlloDerm
 Infectious Complications Leading to Explantation in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction With AlloDerm Minh-Doan Nguyen, MD, PhD, a Chen Chen, MS, b Salih Colakoğlu, MD, b Donald J. Morris, MD, b Adam M.
Infectious Complications Leading to Explantation in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction With AlloDerm Minh-Doan Nguyen, MD, PhD, a Chen Chen, MS, b Salih Colakoğlu, MD, b Donald J. Morris, MD, b Adam M.
High-dose-rate Interstitial Brachytherapy Boost with a Pedicled Latissimus. Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Myxofibrosarcoma of the Arm.
 High-dose-rate Interstitial Brachytherapy Boost with a Pedicled Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Myxofibrosarcoma of the Arm The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
High-dose-rate Interstitial Brachytherapy Boost with a Pedicled Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Myxofibrosarcoma of the Arm The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
Goals of Care. Restore shape and function after cancer
 Goals of Care Restore shape and function after cancer Aid in physiological and psychological benefit Relationship with significant other Self esteem and positive body image Feeling of a whole body Avoid
Goals of Care Restore shape and function after cancer Aid in physiological and psychological benefit Relationship with significant other Self esteem and positive body image Feeling of a whole body Avoid
The decision to repair a partial mastectomy CME. State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction.
 CME State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, M.D. Houston, Texas Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should be able to: 1.
CME State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, M.D. Houston, Texas Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should be able to: 1.
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap
 Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap Joshua T. Henderson, BA, a ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Andrew M. Swiergosz, BS, a Andrea R.
Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap Joshua T. Henderson, BA, a ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Andrew M. Swiergosz, BS, a Andrea R.
Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction
 Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D., and Charles E. Butler, M.D. Houston, Texas Skin-sparing
Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D., and Charles E. Butler, M.D. Houston, Texas Skin-sparing
Neil J. Zemmel, MD, FACS Steven J. Montante, MD Megan J. Russell, PA-C. Your Guide To BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
 Neil J. Zemmel, MD, FACS Steven J. Montante, MD Megan J. Russell, PA-C Your Guide To BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Introduction The diagnosis of breast cancer begins a journey of making many informed decisions
Neil J. Zemmel, MD, FACS Steven J. Montante, MD Megan J. Russell, PA-C Your Guide To BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Introduction The diagnosis of breast cancer begins a journey of making many informed decisions
NIPPLE SPARING PRE-PECTORAL BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
 NIPPLE SPARING PRE-PECTORAL BREAST RECONSTRUCTION 42 yo female healthy athlete Right breast mass. Past medical history: none Family history: aunt with Breast cancer Candidates for nipple-sparing mastectomy
NIPPLE SPARING PRE-PECTORAL BREAST RECONSTRUCTION 42 yo female healthy athlete Right breast mass. Past medical history: none Family history: aunt with Breast cancer Candidates for nipple-sparing mastectomy
A multiple logistic regression analysis of complications following microsurgical breast reconstruction
 Original Article A multiple logistic regression analysis of complications following microsurgical breast reconstruction Samir Rao 1, Ellen C. Stolle 1, Sarah Sher 1, Chun-Wang Lin 1, Bahram Momen 2, Maurice
Original Article A multiple logistic regression analysis of complications following microsurgical breast reconstruction Samir Rao 1, Ellen C. Stolle 1, Sarah Sher 1, Chun-Wang Lin 1, Bahram Momen 2, Maurice
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION FOLLOWING PROPHYLACTIC OR THERAPEUTIC MASTECTOMY FOR BREAST CANCER
 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION FOLLOWING PROPHYLACTIC OR THERAPEUTIC MASTECTOMY FOR BREAST CANCER Effective Date: September 2013 The recommendations contained in this guideline are a consensus of the Alberta Provincial
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION FOLLOWING PROPHYLACTIC OR THERAPEUTIC MASTECTOMY FOR BREAST CANCER Effective Date: September 2013 The recommendations contained in this guideline are a consensus of the Alberta Provincial
INFORMED-CONSENT-SKIN GRAFT SURGERY
 INFORMED-CONSENT-SKIN GRAFT SURGERY 2000 American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Purchasers of the Patient Consultation Resource Book are given a limited license to modify documents contained herein and
INFORMED-CONSENT-SKIN GRAFT SURGERY 2000 American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Purchasers of the Patient Consultation Resource Book are given a limited license to modify documents contained herein and
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty
 CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: Revised Date: Page 1 of 8
 Page 1 of 8 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans, or the plan
Page 1 of 8 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans, or the plan
Procedure Information Guide
 Procedure Information Guide Breast reconstruction with abdominal tissue flap Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every
Procedure Information Guide Breast reconstruction with abdominal tissue flap Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every
Few would deny that lower abdominal tissue BREAST. An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction.
 BREAST An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D. Farah N. Khan, M.D. Houston, Texas Background: The deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP)
BREAST An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D. Farah N. Khan, M.D. Houston, Texas Background: The deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP)
In a second stage or a second operation that tissue expander is removed through the same incision and the implant is placed within the chest pocket.
 Hello, I m Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor in the Department of Plastics & Reconstructive Surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and today I m going to talk about the role
Hello, I m Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor in the Department of Plastics & Reconstructive Surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and today I m going to talk about the role
Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction: Added Benefits, Added Risks
 Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction: Added Benefits, Added Risks Grant W. Carlson Wadley R. Glenn Professor of Surgery Divisions of Plastic Surgery & Surgical Oncology Emory
Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction: Added Benefits, Added Risks Grant W. Carlson Wadley R. Glenn Professor of Surgery Divisions of Plastic Surgery & Surgical Oncology Emory
Methods of autologous tissue breast reconstruction BREAST
 BREAST Comparison of Donor-Site Morbidity of SIEA, DIEP, and Muscle-Sparing TRAM Flaps for Breast Reconstruction Liza C. Wu, M.D. Anureet Bajaj, M.D. David W. Chang, M.D. Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D.
BREAST Comparison of Donor-Site Morbidity of SIEA, DIEP, and Muscle-Sparing TRAM Flaps for Breast Reconstruction Liza C. Wu, M.D. Anureet Bajaj, M.D. David W. Chang, M.D. Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D.
Is Unilateral Implant or Autologous Breast Reconstruction Better in Obtaining Breast Symmetry?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Unilateral Implant or Autologous Breast Reconstruction Better in Obtaining Breast Symmetry? Oriana Cohen, MD, Kevin Small, MD, Christina Lee, BA, Oriana Petruolo, MD, Nolan Karp, MD,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Unilateral Implant or Autologous Breast Reconstruction Better in Obtaining Breast Symmetry? Oriana Cohen, MD, Kevin Small, MD, Christina Lee, BA, Oriana Petruolo, MD, Nolan Karp, MD,
PROS AND CONS OF IMMEDIATE PROSTHETIC IMPLANTS VS USE OF EXPANDER FOR POST MASTECTOMY BREAST RECONSTRUCTIONS
 PROS AND CONS OF IMMEDIATE PROSTHETIC IMPLANTS VS USE OF EXPANDER FOR POST MASTECTOMY BREAST Dr Tienie van Rooyen Mediclinic Kloof Hospital Pretoria IMMEDIATE Since 1990 s Skin sparing mastectomies proven
PROS AND CONS OF IMMEDIATE PROSTHETIC IMPLANTS VS USE OF EXPANDER FOR POST MASTECTOMY BREAST Dr Tienie van Rooyen Mediclinic Kloof Hospital Pretoria IMMEDIATE Since 1990 s Skin sparing mastectomies proven
Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience Warren A. Ellsworth, MD,* Barbara L. Bass, MD, FACS, Roman J. Skoracki, MD, à and Lior Heller, MD* *Division of Plastic Surgery,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience Warren A. Ellsworth, MD,* Barbara L. Bass, MD, FACS, Roman J. Skoracki, MD, à and Lior Heller, MD* *Division of Plastic Surgery,
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: February 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: February 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy. Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD
 How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
Flaps vs Grafts. Ronen Avram, MD MSc FRCSC
 Flaps vs Grafts Ronen Avram, MD MSc FRCSC POS Keratoacanthoma is not a malignant tumor! Methods of Reconstruction Reconstructive Ladder Primary closure Primary Delayed Secondary Intention Skin Graft Pedicled
Flaps vs Grafts Ronen Avram, MD MSc FRCSC POS Keratoacanthoma is not a malignant tumor! Methods of Reconstruction Reconstructive Ladder Primary closure Primary Delayed Secondary Intention Skin Graft Pedicled
B11 Breast Reconstruction with Abdominal Tissue Flap
 B11 Breast Reconstruction with Abdominal Tissue Flap Issued March 2011 You can get more information about this procedure from www.aboutmyhealth.org Tell us how useful you found this document at www.patientfeedback.org
B11 Breast Reconstruction with Abdominal Tissue Flap Issued March 2011 You can get more information about this procedure from www.aboutmyhealth.org Tell us how useful you found this document at www.patientfeedback.org
The use of postmastectomy radiation therapy (PMRT) to prevent
 NORTHEASTERN SOCIETY OF PLASTIC SURGEONS Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy and Breast An Analysis of Complications and Patient Satisfaction Bernard T. Lee, MD,* Tolulope A. Adesiyun, BS,* Salih Colakoglu,
NORTHEASTERN SOCIETY OF PLASTIC SURGEONS Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy and Breast An Analysis of Complications and Patient Satisfaction Bernard T. Lee, MD,* Tolulope A. Adesiyun, BS,* Salih Colakoglu,
Advances in Localized Breast Cancer
 Advances in Localized Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD, MPH and Fariba Asrari, MD June 18, 2018 Moderated by Elissa Bantug 1 Advances in Surgery for Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD June 18, 2018 2 Historical
Advances in Localized Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD, MPH and Fariba Asrari, MD June 18, 2018 Moderated by Elissa Bantug 1 Advances in Surgery for Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD June 18, 2018 2 Historical
Immediate versus delayed free TRAM breast reconstruction: an analysis of perioperative factors and complications
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (22), 55, l-6 9 22 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi:.54/bjps.22.3747 BRITISH JOURNAL OF / ~ ] PLASTIC SURGERY Immediate versus delayed free TRAM breast
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (22), 55, l-6 9 22 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi:.54/bjps.22.3747 BRITISH JOURNAL OF / ~ ] PLASTIC SURGERY Immediate versus delayed free TRAM breast
Reduction Mammaplasty and Mastopexy in Previously Irradiated Breasts
 Breast Surgery Reduction Mammaplasty and Mastopexy in Previously Irradiated Breasts Scott L. Spear, MD; Samir S. Rao, MD; Ketan M. Patel, MD; and Maurice Y. Nahabedian, MD The combination of lumpectomy
Breast Surgery Reduction Mammaplasty and Mastopexy in Previously Irradiated Breasts Scott L. Spear, MD; Samir S. Rao, MD; Ketan M. Patel, MD; and Maurice Y. Nahabedian, MD The combination of lumpectomy
Medical Journal of the Volume 20 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 1385 November Original Articles
 Medical Journal of the Volume 0 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 38 November 00 Original Articles ANATOMY OF THE SUPERFICIAL INFERIOR EPIGASTRIC ARTERY FLAP MAHDI FATHI, M.D., EBRAHIM HATAMIPOUR,
Medical Journal of the Volume 0 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 38 November 00 Original Articles ANATOMY OF THE SUPERFICIAL INFERIOR EPIGASTRIC ARTERY FLAP MAHDI FATHI, M.D., EBRAHIM HATAMIPOUR,
A Combined Practice. Why Its Worked. Barriers to Breast Reconstruction. As a breast oncologist the patient gets seemless care
 A Combined Practice A Combined Breast Oncology and Plastic Surgery Practice Why It Works Anne M. Wallace, MD, FACS Director, Comprehensive Breast Health Center Professor of Clinical Surgery, Surgical Oncology
A Combined Practice A Combined Breast Oncology and Plastic Surgery Practice Why It Works Anne M. Wallace, MD, FACS Director, Comprehensive Breast Health Center Professor of Clinical Surgery, Surgical Oncology
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title: Classifying breast cancer surgery: a novel, complexity-based system for oncological, oncoplastic and reconstructive procedures, and proof of principle by analysis of
Author's response to reviews Title: Classifying breast cancer surgery: a novel, complexity-based system for oncological, oncoplastic and reconstructive procedures, and proof of principle by analysis of
The Use of the Latissimus dorsi Flap in Breast Reconstruction of Post-Mastectomy Patients: Is Superior to the Use of Expander / Prosthesis?
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Aesthetic & Reconstructive Surgery DOI: 10.4172/2472-1905.100014 The Use of the Latissimus dorsi Flap in Breast Reconstruction of Post-Mastectomy
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Aesthetic & Reconstructive Surgery DOI: 10.4172/2472-1905.100014 The Use of the Latissimus dorsi Flap in Breast Reconstruction of Post-Mastectomy
RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2
 RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Sathyanarayana B. C, Somashekar Srinivas. Reconstruction of Scalp Defects:
RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Sathyanarayana B. C, Somashekar Srinivas. Reconstruction of Scalp Defects:
Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Breast Reconstruction: Bad Rap or Good Flap?
 Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Breast Reconstruction: Bad Rap or Good Flap? Galen Perdikis, MD, Stephanie Koonce, MD, George Collis, MD, and Dustin Eck, MD Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL Correspondence:
Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Breast Reconstruction: Bad Rap or Good Flap? Galen Perdikis, MD, Stephanie Koonce, MD, George Collis, MD, and Dustin Eck, MD Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL Correspondence:
Reconstructive Breast Surgery and Management of Breast Implants
 Reconstructive Breast Surgery and Management of Breast Implants Policy Number: 7.01.22 Last Review: 1/2018 Origination: 3/1993 Next Review: 1/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Reconstructive Breast Surgery and Management of Breast Implants Policy Number: 7.01.22 Last Review: 1/2018 Origination: 3/1993 Next Review: 1/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
 Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION BREAST RECONSTRUCTION: A WOMAN S DECISION Options and Information Our approach to breast reconstruction entails a very
Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION BREAST RECONSTRUCTION: A WOMAN S DECISION Options and Information Our approach to breast reconstruction entails a very
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION/REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT OF IMPLANTS
 Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon
Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon
Diagnostic Accuracy of Lymphoscintigraphy for Lymphedema and Analysis of False-Negative Tests
 Diagnostic Accuracy of Lymphoscintigraphy for Lymphedema and Analysis of False-Negative Tests The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Diagnostic Accuracy of Lymphoscintigraphy for Lymphedema and Analysis of False-Negative Tests The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Extending breast conservation and other new oncoplastic techniques
 Extending breast conservation and other new oncoplastic techniques Dick Rainsbury BSBR 11-12 November 2013 Liverpool What s the maximum volume of the breast which can be resected during lumpectomy without
Extending breast conservation and other new oncoplastic techniques Dick Rainsbury BSBR 11-12 November 2013 Liverpool What s the maximum volume of the breast which can be resected during lumpectomy without
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. JPRAS Open. journal homepage:
 JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
INFORMED CONSENT-BREAST RECONSTRUCTION WITH TRAM ABDOMINAL MUSCLE FLAP
 INFORMED CONSENT-BREAST RECONSTRUCTION WITH TRAM ABDOMINAL MUSCLE FLAP 2000 American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Purchasers of the Patient Consultation Resource Book are given a limited license to modify
INFORMED CONSENT-BREAST RECONSTRUCTION WITH TRAM ABDOMINAL MUSCLE FLAP 2000 American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Purchasers of the Patient Consultation Resource Book are given a limited license to modify
National Mastectomy & Breast Reconstruction Audit Datasheet - Mastectomy +/- Immediate Reconstruction
 Patient Registration data Surname Forename NHS/Private Hospital Number Date of birth Postcode Ethnicity Patient-reported outcomes consent Has this patient consented to being sent outcome questionnaires?
Patient Registration data Surname Forename NHS/Private Hospital Number Date of birth Postcode Ethnicity Patient-reported outcomes consent Has this patient consented to being sent outcome questionnaires?
Plastic Reconstructive Aspects after Mastectomy
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Plastic Reconstructive Aspects after Mastectomy Plastic Reconstructive Aspects after Mastectomy Version 2002: Brunnert Version
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Plastic Reconstructive Aspects after Mastectomy Plastic Reconstructive Aspects after Mastectomy Version 2002: Brunnert Version
Challenging a Traditional Paradigm: 12-Year Experience with Autologous Free Flap Breast Reconstruction for Inflammatory Breast Cancer
 BREAST Challenging a Traditional Paradigm: 12-Year Experience with Autologous Free Flap Breast Reconstruction for Inflammatory Breast Cancer Edward I. Chang, M.D. Eric I. Chang, M.D. Ran Ito, M.D., Ph.D.
BREAST Challenging a Traditional Paradigm: 12-Year Experience with Autologous Free Flap Breast Reconstruction for Inflammatory Breast Cancer Edward I. Chang, M.D. Eric I. Chang, M.D. Ran Ito, M.D., Ph.D.
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Abt NB, Flores JM, Baltodano PA, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy and short-term in patients undergoing mastectomy with and without breast reconstruction. JAMA Surg. Published
Supplementary Online Content Abt NB, Flores JM, Baltodano PA, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy and short-term in patients undergoing mastectomy with and without breast reconstruction. JAMA Surg. Published
Despite breast reduction being one of the BREAST. Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction?
 BREAST Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction? Jamil Ahmad, M.D. Sarah M. McIsaac, M.D. Frank Lista, M.D. Mississauga and Ottawa, Ontario, Canada Background:
BREAST Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction? Jamil Ahmad, M.D. Sarah M. McIsaac, M.D. Frank Lista, M.D. Mississauga and Ottawa, Ontario, Canada Background:
The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 395 400 The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q D. Erni*, Y.D. Harder
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 395 400 The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q D. Erni*, Y.D. Harder
Plastic surgery of the breast includes; augmentation, reduction, Plastic Surgery of the Breast. Abstract. Continuing Education Column
 Plastic Surgery of the Breast Keuk Shun Shin, M.D. Keuk SHUN SHIN s Asthetic Plastic Surgery E mail: drsks@drsks.co.kr Abstract Plastic surgery of the breast includes; augmentation, reduction, reconstruction
Plastic Surgery of the Breast Keuk Shun Shin, M.D. Keuk SHUN SHIN s Asthetic Plastic Surgery E mail: drsks@drsks.co.kr Abstract Plastic surgery of the breast includes; augmentation, reduction, reconstruction
The success of breast conservation protocols BREAST. Implant Reconstruction in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Radiation Therapy
 BREAST Implant Reconstruction in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Radiation Therapy Jeffrey A. Ascherman, M.D. Matthew M. Hanasono, M.D. Martin I. Newman, M.D. Duncan B. Hughes, M.D. New York, N.Y.
BREAST Implant Reconstruction in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Radiation Therapy Jeffrey A. Ascherman, M.D. Matthew M. Hanasono, M.D. Martin I. Newman, M.D. Duncan B. Hughes, M.D. New York, N.Y.
PAPER. Impact of Chemotherapy on Postoperative Complications After Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction
 PAPER Impact of Chemotherapy on Postoperative Complications After Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction Anne Warren Peled, MD; Kaoru Itakura, BA; Robert D. Foster, MD; Debby Hamolsky, RN, MS;
PAPER Impact of Chemotherapy on Postoperative Complications After Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction Anne Warren Peled, MD; Kaoru Itakura, BA; Robert D. Foster, MD; Debby Hamolsky, RN, MS;
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION FOLLOWING PROPHYLACTIC OR THERAPEUTIC MASTECTOMY FOR BREAST CANCER
 Page 1 of 44 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION FOLLOWING PROPHYLACTIC OR THERAPEUTIC MASTECTOMY FOR BREAST CANCER Effective Date: February, 2017 The recommendations contained in this guideline are a consensus of the
Page 1 of 44 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION FOLLOWING PROPHYLACTIC OR THERAPEUTIC MASTECTOMY FOR BREAST CANCER Effective Date: February, 2017 The recommendations contained in this guideline are a consensus of the
Acellular Dermal Matrix in Reconstructive Breast Surgery: Survey of Current Practice among Plastic Surgeons
 Acellular Dermal Matrix in Reconstructive Breast Surgery: Survey of Current Practice among Plastic Surgeons The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Acellular Dermal Matrix in Reconstructive Breast Surgery: Survey of Current Practice among Plastic Surgeons The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Reconstruction with autologous tissue remains a
 Original Article Increased Flap Weight and Decreased Perforator Number Predict Fat Necrosis in DIEP Breast Reconstruction Carolyn L. Mulvey, BS* Carisa M. Cooney, MPH* Francis F. Daily, BS* Elizabeth Colantuoni,
Original Article Increased Flap Weight and Decreased Perforator Number Predict Fat Necrosis in DIEP Breast Reconstruction Carolyn L. Mulvey, BS* Carisa M. Cooney, MPH* Francis F. Daily, BS* Elizabeth Colantuoni,
Medical Review Criteria Breast Surgeries
 Medical Review Criteria Breast Surgeries Effective Date: November 8, 2016 Subject: Breast Surgeries Policy: HPHC covers medically necessary breast surgeries including mastectomy, breast reconstruction,
Medical Review Criteria Breast Surgeries Effective Date: November 8, 2016 Subject: Breast Surgeries Policy: HPHC covers medically necessary breast surgeries including mastectomy, breast reconstruction,
Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction
 Follow the link from the online version of this article to obtain certified continuing medical education credits Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction Paul T R Thiruchelvam, 1 Fiona McNeill, 2 Navid Jallali,
Follow the link from the online version of this article to obtain certified continuing medical education credits Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction Paul T R Thiruchelvam, 1 Fiona McNeill, 2 Navid Jallali,
The cosmetic result of immediate mastectomy
 Esther February 14, 20147:45 PM 19:45 4 Color Fig(s): F1-3 Art: GOX-D-14-00014 Ideas and Innovations Breast Immediate Single-stage Endoscopic Latissimus Dorsi Breast and Nipple Reconstruction AQ2 Joaquim
Esther February 14, 20147:45 PM 19:45 4 Color Fig(s): F1-3 Art: GOX-D-14-00014 Ideas and Innovations Breast Immediate Single-stage Endoscopic Latissimus Dorsi Breast and Nipple Reconstruction AQ2 Joaquim
Plastic Surgery: An International Journal
 Plastic Surgery: An International Journal Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 874416, 29 minipages. DOI:10.5171/2013.874416 www.ibimapublishing.com Copyright 2013 Akira Saito, Noriko Saito, Emi Funayama and Hidehiko
Plastic Surgery: An International Journal Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 874416, 29 minipages. DOI:10.5171/2013.874416 www.ibimapublishing.com Copyright 2013 Akira Saito, Noriko Saito, Emi Funayama and Hidehiko
Breast Surgery. for Reconstructive. Center of Excellence. city center of Düsseldorf. You will find us in the
 You will find us in the city center of Düsseldorf Rathaus Rhein Steinstraße Berger Allee Poststraße Bastionstraße Kasernenstraße Breite Straße Königsallee Grünstraße Berliner Allee Königsallee 88 Graf-Adolf-Platz
You will find us in the city center of Düsseldorf Rathaus Rhein Steinstraße Berger Allee Poststraße Bastionstraße Kasernenstraße Breite Straße Königsallee Grünstraße Berliner Allee Königsallee 88 Graf-Adolf-Platz
Radiation Therapy And Expander-Implant Breast Reconstruction: Analysis Of Timing And Complications
 Yale University EliScholar A Digital Platform for Scholarly Publishing at Yale Yale Medicine Thesis Digital Library School of Medicine January 2013 Radiation Therapy And Expander-Implant Breast Reconstruction:
Yale University EliScholar A Digital Platform for Scholarly Publishing at Yale Yale Medicine Thesis Digital Library School of Medicine January 2013 Radiation Therapy And Expander-Implant Breast Reconstruction:
INNOVATIVE RECONSTRUCTIVE STRATEGIES IN BREAST CANCER SURGERY
 INNOVATIVE RECONSTRUCTIVE STRATEGIES IN BREAST CANCER SURGERY Jane L. Kakkis, MD, MPH Breast Surgeon, Director Orange Coast Memorial Medical Center, Fountain Valley, CA USA WHEN RADIATION IS NECESSARY
INNOVATIVE RECONSTRUCTIVE STRATEGIES IN BREAST CANCER SURGERY Jane L. Kakkis, MD, MPH Breast Surgeon, Director Orange Coast Memorial Medical Center, Fountain Valley, CA USA WHEN RADIATION IS NECESSARY
Allograft Based Breast Reconstruction: Opportunity for a Second Look
 Allograft Based Breast Reconstruction: Opportunity for a Second Look Martin I. Newman, MD, FACS Director of Resident Education and Associate Program Director Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Allograft Based Breast Reconstruction: Opportunity for a Second Look Martin I. Newman, MD, FACS Director of Resident Education and Associate Program Director Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Breast Reconstruction: Bad Rap or Good Flap?
 eplasty: Vol. 11 Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Breast Reconstruction: Bad Rap o Galen Perdikis, MD, Stephanie Koonce, MD, Geor Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL Correspondence: perdikis.galen@mayo.edu
eplasty: Vol. 11 Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Breast Reconstruction: Bad Rap o Galen Perdikis, MD, Stephanie Koonce, MD, Geor Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL Correspondence: perdikis.galen@mayo.edu
Reconstruction of axillary scar contractures retrospective study of 124 cases over 25 years
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2003), 56, 100 105 q 2003 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(03)00035-3 Reconstruction
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2003), 56, 100 105 q 2003 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(03)00035-3 Reconstruction
Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty?
 Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty? Michele A. Shermak, MD, Jessie Mallalieu, PA-C, and David Chang, PhD, MPH, MBA The Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Division
Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty? Michele A. Shermak, MD, Jessie Mallalieu, PA-C, and David Chang, PhD, MPH, MBA The Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Division
Assessment of Breast Volume Change after Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous Flap
 Assessment of Breast Volume Change after Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous Flap Sang Uk Park, Jeong Su Shim Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Catholic University of Daegu School
Assessment of Breast Volume Change after Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous Flap Sang Uk Park, Jeong Su Shim Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Catholic University of Daegu School
Samer Saour, Guido Libondi, Venkat Ramakrishnan. Introduction
 Original Article Microsurgical refinements with the use of internal mammary (IM) perforators as recipient vessels in transverse upper gracilis (TUG) autologous breast reconstruction Samer Saour, Guido
Original Article Microsurgical refinements with the use of internal mammary (IM) perforators as recipient vessels in transverse upper gracilis (TUG) autologous breast reconstruction Samer Saour, Guido
Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects
 Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects Joshua L. Levine, M.D., Nassif E. Soueid, M.D., and Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La. Background: The use of lateral thoracic
Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects Joshua L. Levine, M.D., Nassif E. Soueid, M.D., and Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La. Background: The use of lateral thoracic
Original Article. Keywords Mastectomy / Nipples / Necrosis / Surgical flaps
 Immediate breast reconstruction following nipplesparing mastectomy in an Asian population: Aesthetic outcomes and mitigating nipple-areolar complex necrosis Wan-Sze Pek 1, Bien-Keem Tan 1, Yvonne Ying
Immediate breast reconstruction following nipplesparing mastectomy in an Asian population: Aesthetic outcomes and mitigating nipple-areolar complex necrosis Wan-Sze Pek 1, Bien-Keem Tan 1, Yvonne Ying
Reconstructive surgery following mastectomy
 Reconstructive surgery following mastectomy Kseniya Roudakova, MD A CASE FROM SUNY DOWNSTATE 60F who presented for right mastectomy with immediate TRAM flap reconstruction for recurrent breast cancer Oncologic
Reconstructive surgery following mastectomy Kseniya Roudakova, MD A CASE FROM SUNY DOWNSTATE 60F who presented for right mastectomy with immediate TRAM flap reconstruction for recurrent breast cancer Oncologic
Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps
 BREAST SURGERY Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps Joshua L. Levine, MD,* Quintessa Miller, MD, Julie Vasile, MD,* Kamran Khoobehi,
BREAST SURGERY Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps Joshua L. Levine, MD,* Quintessa Miller, MD, Julie Vasile, MD,* Kamran Khoobehi,
Medical Review Criteria Breast Surgeries
 Medical Review Criteria Breast Surgeries Subject: Breast Surgeries Authorization: Prior authorization is required for the following procedures requested for members enrolled in HPHC commercial (HMO, POS,
Medical Review Criteria Breast Surgeries Subject: Breast Surgeries Authorization: Prior authorization is required for the following procedures requested for members enrolled in HPHC commercial (HMO, POS,
Figure 1. Anatomy of the breast
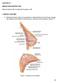 CHAPTER 12 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Mihaela Rapolti, MD and Michelle Roughton, MD I. BREAST ANATOMY A. Mastering breast anatomy is essential for understanding how the breast changes with aging and principles
CHAPTER 12 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Mihaela Rapolti, MD and Michelle Roughton, MD I. BREAST ANATOMY A. Mastering breast anatomy is essential for understanding how the breast changes with aging and principles
