Relationship between betel quid chewing and radiographic alveolar bone loss among Taiwanese aboriginals: a retrospective study
|
|
|
- Charlene Fleming
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hsiao et al. BMC Oral Health 2014, 14:133 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Relationship between betel quid chewing and radiographic alveolar bone loss among Taiwanese aboriginals: a retrospective study Chun-Nan Hsiao 1, Chun-Chan Ting 1,2,3, Tien-Yu Shieh 4 and Edward Chengchuan Ko 1,2,5,6* Abstract Background: Betel quid chewing is associated with the periodontal status; however, results of epidemiological studies are inconsistent. To the best of our knowledge, no study has reported radiographic alveolar bone loss (RABL) associated with betel quid chewing. Methods: This survey was conducted in an aboriginal community in Taiwan because almost all betel quid chewers were city-dwelling cigarette smokers. In total, 114 subjects, aged years, were included. Full-mouth intraoral RABL was retrospectively measured and adjusted for age, gender, and plaque index (PI). Multiple regression analysis was used to assess the relationship between RABL and potential risk factors. Results: Age-, gender-, and PI-adjusted mean RABL was significantly higher in chewers with or without cigarette smoking than in controls. Multiple regression analysis showed that the RABL for consumption of 100,000 pieces betel quid for the chewer group was 0.40 mm. Full-mouth plotted curves for adjusted mean RABL in the maxilla were similar between the chewer and control groups, suggesting that chemical effects were not the main factors affecting the association between betel quid chewing and the periodontal status. Conclusion: Betel quid chewing significantly increases RABL. The main contributory factors are age and oral hygiene; however, the major mechanism underlying this process may not be a chemical mechanism. Regular dental visits, maintenance of good oral hygiene, and reduction in the consumption of betel quid, additives, and cigarettes are highly recommended to improve the periodontal status. Keywords: Areca, Betel, Alveolar bone loss, Periodontitis Background Betel quid is the fourth most psychoactive substance worldwide [1]. It is usually added to the flower and/or leaf of Piper betle along with several other chemical additives; the mixture is known as betel quid. Betel quid chewing has been associated with oral submucous fibrosis, oral cancer [2,3] as well as cancer of the esophagus, liver, pancreas, larynx, and lungs; type 2 diabetes mellitus; cardiovascular disease; and adverse pregnancy outcomes [3-7]. * Correspondence: ko.edward.kaseizen@gmail.com 1 School of Dentistry, College of Dental Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan 2 Lab of Tissue Engineering, College of Dental Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan Full list of author information is available at the end of the article The chemical composition of betel quid varies [1,8], and the effect of factors related to betel quid chewing on the periodontal status are complex [9]. Several in vitro studies have suggested that areca nut extracts inhibit immune reactions [10-12], indirectly increase gingival inflammation [13,14], affect osteoblast viability [15], and may be cytotoxic to periodontal fibroblasts [16]; however, the results of epidemiological studies are not convergent. Hospital-based studies have reported that betel quid chewing is associated with a high prevalence of bleeding on sulcus probing [17] and that betel quid additives may significantly aggravate periodontitis [18]. In contrast, another study reported that betel quid additives have no significant association with chronic periodontitis after adjustment for smoking habits [19]. The results from community-based studies are also inconsistent Hsiao et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly credited.
2 Hsiao et al. BMC Oral Health 2014, 14:133 Page 2 of 7 Betel quid chewing showed no significant effect on clinical attachment loss after adjusting for oral hygiene in a cross-sectional study [20] and a longitudinal study [21], while it was reportedly a contributing factor to tooth loss in certain cross-sectional studies [22,23]; in contrast, it was found to be a protecting factor in another longitudinal study [24]. Many factors could have caused the discrespancies in the results of the above investigations. First, tobacco use or cigarette smoking is a confounding factor [25,26]. Betel quid chewing is almost all coexistent with tobacco usage among men in India [1]. In Taiwan, only 2% male betel quid chewers are nonsmokers [3]. Second, betel quid additives are many and varied. Third, periodontitis is associated with a group of risk factors [9]. To our knowledge, no study has reported the association between betel quid chewing and radiographic alveolar bone loss (RABL). Aboriginal communities in Taiwan comprise a relatively high percentage of nonsmoking betel quid chewers, thereby constituting a suitable population to examine the relationship between betel quid chewing and RABL. The level of consumption and betel quid additives, sociodemographic, lifestyle, and oral hygiene behavioral variables were also investigated. Methods Ethics and informed consent The present study was part of a project approved by the Human Experiment and Ethics Committee of Kaohsiung Medical University. Informed written consent was given by all subjects prior to the study. Subjects were informed about any diagnosed pathological findings and were given treatment immediately or were scheduled for further treatment in the public health station. Study samples The subjects were recruited form the aboriginal community, Mutan. Between 2010 and 2011, all subjects belonging to the Paiwan tribe near the Mutan public health station were invited to the station for removal of tooth stains and ultrasonic scaling. Eligibility criteria included no known systemic medical condition such as diabetes mellitus or pregnancy, no dental visits within the preceding 6 months, no consumption of drugs known to affect the periodontium, age between 30 and 60 years, a body mass index of , and right-handedness (for evaluation of differences between the right and left sides). Retrospective radiographs (Kodak DF-58, Ultra-speed periapical film; Eastman, Kodak Co., Ltd., Rochester, NY, USA) from 2000 to 2009 were used to detect proximal caries. The paralleling technique was mainly used for the anterior teeth, while the vertical bitewing technique was mainly used for the posterior teeth using XCP film holders (Rinn, Elgin, IL, USA) Radiographs were automatically processed at room temperature (Perio- Pro automatic processors, Pearson Dental Supply Co.) in a freshly mixed developer and fixer (Kodak RP X-Omat developer and replenisher; Kodak RP X-Omat Lo, fixer and replenisher). Questionnaire-based interviews The subjects were interviewed and data were collected on sociodemographic variables, i.e., age, gender, occupation, education, and ethnicity; lifestyle; i.e., a history of betel quid chewing and smoking (including the number of units consumed per day), the duration of the habit (years), and the additives consumed and oral hygiene practices, i.e., frequency and methods of tooth brushing. Clinical examination Visible bacterial plaque and gingival inflammation were assessed according to the plaque index (PI) [27] and gingival index (GI) [28], respectively, on the facial and palatal/ lingual aspects of all existing teeth, except the third molars. Radiographic examination Radiographic examination was performed using the digital scanning radiographic image analysis method (DSRIA) [29], and RABL was defined as the distance between the highest alveolar bone ridge adjacent to the tooth surface and the cementoenamel junction. Reliability was confirmed over a 4-week period by double-reading of 30 molars, 30 canines, and 30 incisors selected randomly, and the reliability coefficients [30] were 0.92, 0.83, and 0.90, respectively. Interexaminer reliability was assessed through replicate readings of 60 sites, and the reliability coefficient was 0.88 for assessing RABL. Statistical analysis Least-square means were used to adjust the measurements by variables and were compared among different subgroups. Descriptive statistics were calculated for relative means, and the differences were tested between groups. The radiographic measurements of tilted, missing, or elongated teeth as well as those of teeth with a large restoration, prosthesis, or apparent root fractures were recorded as missing data. Data were recorded as missing if the chewing and smoking habits were irregular or the question was not answered, particularly in the multiple regression model. Multiple regression analysis was used to assess the relationship between potential risk factors and RABL. Finally, the participants were divided into three groups as follows: betel quid chewers with a smoking habit (smoker and chewer group), betel quid chewers with no smoking habit (chewer group), and subjects with no chewing or smoking habits (control group). All statistical analyses were performed using SAS v9.13 software (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
3 Hsiao et al. BMC Oral Health 2014, 14:133 Page 3 of 7 Results In total, 114 subjects (mean age, 43.3 ± 6.1 years; range, years) were included in this study. The chewer group as well as the smoker and chewer group included 41 males and 37 females, while the control group included 11 males and 25 females (Table 1). The adjusted mean RABL in the chewer group as well as the smoker and chewer group showed significant differences with regard to age. Age- and gender-adjusted mean RABL also showed significant differences between the chewer group as well as the smoker and chewer group and the control group with regard to the chewing pattern, chewing quantity, and betel quid additives (Table 2). Compared with the nonchewers, the adjusted mean RABL was significantly higher if there was a daily chewing habit, if >10 pieces were chewed per day, if the chewing habit persisted for >10 years, if >33,000 pieces were chewed till the present date, or if betel fruit, betel leaves, or lime was used with betel quid. The frequency of chewing, duration, and cumulative amount exhibited dose response characteristics. Oralhygienewasacontributoryfactorassociatedwith the periodontal status. After adjustment for age, gender, and PI, the full-mouth mean RABL was significantly higher in the smoker and chewer group as well as the chewer group than in the control group; furthermore, it was comparable with the mean RABL obtained on the basis of the Ramfjord tooth index in all three groups (Table 3). Only 47 regular chewers and 36 nonchewers were included in regression analysis. In the multiple regression for RABL, age, PI, and cumulative amount of betel quid intake were significant contributing factors (Table 4). The gender variable was excluded because most smokers and chewers were males and most chewers were females. Mean RABL increased by 0.40 mm (p = 0.03) for every 100,000 pieces chewed in the chewer group and 0.34 mm (p < 0.01) in the smoker and chewer group. The data for full-mouth mean RABL are shown in Figure 1. In the maxilla, the mean RABL in the chewer group was lower than that in the smoker and chewer group but higher than that in the control group. After adjustment for age, gender, and mean PI, the mean RABL in the chewer group was similar to that in the control group in the maxilla and similar to that in the smoker and chewer group in the mandible, with the exception of RABL around the mandibular right first molar (Figure 2). The mean RABL in all chewers was significantly higher than that in the control group in the mandibular anterior region. Discussion Intraoral radiography provides information on the height and configuration of the interproximal alveolar bone; however, it is not sufficient to identify the outline of the buccal and lingual alveolar bony crest [26]. Although intraoral radiography plays only a supplementary role in the evaluation of the periodontal status in conjunction with periodontal probing, it has high sensitivity, yields few false-negative results, and has high reproducibility compared with the periodontal chart-based RABL evaluation used in previous clinical studies [26,31]. Although the effects of betel quid chewing on periodontal disease are clinically obvious, research results are controversial. The present study is the first to investigate the association between betel quid chewing and RABL. The present study showed that after adjustment for age, gender, and PI, the mean RABL in the smoker and chewer group as well as the chewer group was significantly higher than that in the control group, showing an upward trend in RABL with older age, cigarette smoking, poor oral hygiene, higher consumption of betel quid, and consumption of extra additives with betel quid. Furthermore, areca nut chewing without additives may not be the major risk factor of oral submucous Table 1 Comparison of the adjusted mean RABL of all chewer and control group adjusted by age and gender according to different education level, dental visiting habit and frequency of dental cleaning All chewer Control group N (%) Adjusted means (CI) N (%) Adjusted means (CI) Age 51 to 60 years old 13 (16.7) 4.25 ( )* 3 (8.3) 2.68 ( ) 41 to 50 years old 43 (55.1) 3.73 ( ) 16 (44.4) 2.77 ( ) 30 to 40 years old 22 (28.2) 2.98 ( ) 17 (47.2) 2.64 ( ) Gender Male 41 (53.6) 3.82 ( ) 11 (30.6) 2.95 ( ) Female 37 (46.4) 3.34 ( ) 25 (69.4) 2.59 ( ) CI, confidence interval. *Testing equivalence among groups, p < Gender-adjusted alone without age adjustment. Age-adjusted alone without gender adjustment.
4 Hsiao et al. BMC Oral Health 2014, 14:133 Page 4 of 7 Table 2 The means RABL of different betel quid chewing habit with or without adjusting by age and gender N (%) Means ± SD Adjusted means (CI) Control group ± ( ) Frequency of chewing/week 7 days/week 47 (75.8) 3.79 ± 1.19* 3.65 ( )* 4-6 days/week 7 (11.3) 3.12 ± ( ) 1-3 days/week 8 (12.9) 2.93 ± ( ) Daily chewing habit > = 20 pieces/day 16 (32.7) 3.96 ± 1.41* 3.82 ( )* pieces/day 20 (40.8) 3.39 ± ( )* 1-9 pieces/day 13 (26.5) 3.37 ± ( ) Duration of intake >20 years 30 (44.6) 4.07 ± 1.33* 3.85 ( )* years 18 (27.7) 3.50 ± 0.71* 3.56 ( )* <10 years 18 (27.7) 2.91 ± ( ) Cumulative amount >100 k pieces 19 (39.6) 4.07 ± 1.33* 3.84 ( )* 33 k-100 k pieces 14 (29.1) 3.71 ± 1.10* 3.69 ( )* 0-33 k pieces 15 (31.2) 2.77 ± ( ) Areca nut additives (multiple choices) White lime, leaf of betel pepper 43 (55.1) 3.86 ± 1.24* 3.75 ( )* Red lime, fruit of betel pepper 10 (12.8) 3.86 ± 1.62* 3.67 ( )* Stem of betel pepper 14 (17.9) 3.34 ± 0.86* 3.35 ( )* No additives 4 (5.1) 3.16 ± ( ) Other 2 (2.6) 3.77 ± ( ) SD, standard deviation; CI, confidence interval. *Significant compare with control group. Significant compare with <10 years. Significant compare with 0-33 k pieces. Table 3 The means and adjusted means of RABL adjusted by age, gender and plaque index according to different teeth group Means ± SD Adjusted means (CI) Full mouth Smoker and chewer 3.73 (1.09)* 3.62 ( )* Chewer 3.46 (1.10) 3.47 ( ) Control group 2.70 (0.68) 2.87 ( ) Ramfjord Teeth Smoker and chewer 3.81 (1.16)* 3.68 ( )* Chewer 3.53 (1.17) 3.56 ( ) Control group 2.75 (0.63) 2.92 ( ) SD, standard deviation; CI, confidence interval. *Testing equivalence among groups, p < Significant pair between smoker/chewer and control group. Significant pair between chewer and control group. fibrosis [32]. Plotted curves for adjusted mean RABL in the maxilla were similar between the chewer and control groups, with the exception of RABL around the mesial root of the right maxillary molar (Figure 2). These findings may indicate that chemical effects were not the main contributory factors affecting the association between betel quid chewing and the periodontal status, Table 4 Multiple regression for RABL Estimate (mm) Standard error T for H 0 : Parameter = 0 P-value Age <0.01 Means of PI <.001 Cumulative amount of areca nut intake (100,000 pieces) Smoker and chewer <0.01 Chewer R 2 = 0.51, F =
5 Hsiao et al. BMC Oral Health 2014, 14:133 Page 5 of 7 Figure 1 The means of radiographic alveolar bone loss. Significant pairs: smoker and chewer with control group, chewer with control group and smoker and chewer with control group, p < suggesting that the influence of chemical or mechanical factors should be identical for both the maxilla and mandible. This finding also implied that specific details of the results may have been submerged after averaging the measurements; therefore, the true result could be observed first after full-mouth analysis. Extensive and heavy calculus deposition is usually observed in the cervical area of the mandibular teeth of chewers [33]. In the present study, this greatly exceeded the existing measurement index and could not be recorded accurately. Excessive calculus deposition can result in an altered microflora [17] and mechanical interference with soft tissues. Further research is required to modify PI or develop a new oral hygiene index that can adequately describe the oral hygiene status of chewers. After grouping the cumulative amounts in three levels, we found a significant dose response of betel quid chewing with RABL. To our knowledge, this is the first investigation to demonstrate the cumulative effect of chewing quantity. Chewing more than 33,000 pieces will lead to significant RABL and dose response confirmed by multiple regression analysis; however, mean PI and age were stronger contributing factors. Multiple regression analysis showed that the chewer group only had 0.40 mm (p = 0.03) mean RABL after chewing 100,000 pieces of betel quid. It appears as a clinically insignificant value but also means that the chewer group had 22.4 mm more RABL than the control group in total. For decades, studies have shown that smoking (both tobacco and cigarette usage) is a major risk factor for periodontitis [25,34,35]. For the maxilla, the plotted curves for adjusted mean RABL in the smoker and chewer group were steeper than those in the chewer group and similar to those in the control group, whereas for the mandible, the curves were similar between the chewer group and the chewer and smoker group. It was observed that cigarette smoking primarily affected RABL in the maxilla, whereas betel quid chewing primarily affected RABL in the mandible. Therefore, a combination of chewing and cigarette smoking is associated with a risk of significant clinical periodontal problems. Women chew betel quid during social events and traditional activities, whereas men chew them for refreshment while working. This behavioral difference may affect the mean duration of chewing the same quantity. We also noted several apparent vertical root fractures
6 Hsiao et al. BMC Oral Health 2014, 14:133 Page 6 of 7 Figure 2 The adjusted means of radiographic alveolar bone loss adjusted by age, gender and plaque index. Significant pairs: smoker and chewer with control group, chewer with control group and smoker and chewer with control group, p < with intact crowns in the radiographs of chewers, which were not noted in the control group. In the present study, most participants in the chewer group were female, and the high level of RABL around the right first molars of these subjects may have resulted from the longer duration of chewing force compared with that in men. This study had several limitations. First, although all residents were invited, individuals who either did not pay attention to oral hygiene or were almost edentulous may not have responded to our invitation. Second, retrospective radiographs cannot provide conclusive evidence of any significant correlation between betel quid chewing and alveolar bone loss; however, dose response effects support the possibility of a causal relation. Furthermore, several other factors that may be correlated with alveolar bone height were not examined in this study, such as microorganism profiles and blood chemistry factors. Conclusions The present study indicated that betel quid chewing is a contributory factor associated with RABL. RABL was significantly higher in the chewer group as well as the smoker and chewer group than in the control group. Additives and cumulative consumption had dose response effects on RABL. The main contributory factor associated with alveolar bone loss caused by betel quid chewing may be uncontrolled heavy deposition rather than any chemical or mechanical factors. Regular dental visits, maintenance of good oral hygiene, and reduction in the consumption of betel quid, additives, and cigarettes are highly recommended to improve the periodontal status. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions TYS conceptualized and designed the study. CNH carried out the study, data collection and performed the statistical analysis. CNH, ECK and CCT drafted manuscript, critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Acknowledgments The authors wish to thank Prof. Yang Yi-hsin, Dr. Chun Zengtai, Director of Mutan public station, Dr. Dong Sen, Former Director of Mutan Public Station, all staff, and all participants for their invaluable contribution to the study; Enago, Crimson Interactive Pvt. Ltd for editing the English language.
7 Hsiao et al. BMC Oral Health 2014, 14:133 Page 7 of 7 Author details 1 School of Dentistry, College of Dental Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan. 2 Lab of Tissue Engineering, College of Dental Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan. 3 Department of Periodontology, College of Dentistry, Aichi-Gakuin University, Nagoya, Japan. 4 Department of Oral Hygiene, College of Dental Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan. 5 Division of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan. 6 Department of Cartilage and Bone Regeneration (Fujisoft), Graduate School of Medicine, The University of Tokyo, Hongo, Bunkyo, Tokyo , Japan. Received: 9 August 2013 Accepted: 17 October 2014 Published: 4 November 2014 References 1. Gupta PC, Ray CS: Epidemiology of betel quid usage. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2004, 33(4 Suppl): Yang YH, Lien YC, Ho PS, Chen CH, Chang JSF, Cheng TC, Shieh TY: The effects of chewing areca/betel quid with and without cigarette smoking on oral submucous fibrosis and oral mucosal lesions. Oral Dis 2005, 11(2): Wen CP, Tsai MK, Chung WS, Hsu HL, Chang YC, Chan HT, Chiang PH, Cheng TY, Tsai SP: Cancer risks from betel quid chewing beyond oral cancer: a multiple-site carcinogen when acting with smoking. Cancer Causes Control 2010, 21(9): Tseng CH: Betel nut chewing and incidence of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus in Taiwan. BMC Res Notes 2010, 3(1): Lin WY, Chiu TY, Lee LT, Lin CC, Huang CY, Huang KC: Betel nut chewing is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality in Taiwanese men. Am J Clin Nutr 2008, 87(5): Yang MJ, Chung TC, Hsu TY, Ko YC: Betel quid chewing and risk of adverse birth outcomes among aborigines in eastern Taiwan. J Toxicol Environ Health A 2001, 64(6): Yang MS, Chang FT, Chen SS, Lee CH, Ko YC: Betel quid chewing and risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes among aborigines in southern Taiwan. Public Health 1999, 113(4): Gupta PC, Warnakulasuriya S: Global epidemiology of areca nut usage. Addict Biol 2002, 7(1): Bouchard P, Boutouyrie P, Mattout C, Bourgeois D: Risk assessment for severe clinical attachment loss in an adult population. J Periodontol 2006, 77(3): Hung SL, Lee YY, Liu TY, Peng JL, Cheng YY, Chen YT: Modulation of phagocytosis, chemotaxis, and adhesion of neutrophils by areca nut extracts. J Periodontol 2006, 77(4): Lai YL, Lin JC, Yang SF, Liu TY, Hung SL: Areca nut extracts reduce the intracellular reactive oxygen species and release of myeloperoxidase by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Periodontal Res 2007, 42(1): Hung SL, Cheng YY, Peng JL, Chang LY, Liu TY, Chen YT: Inhibitory effects of areca nut extracts on phagocytosis of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans ATCC by neutrophils. J Periodontol 2005, 76(3): Chang LY, Wan HC, Lai YL, Kuo YF, Liu TY, Chen YT, Hung SL: Areca nut extracts increased expression of inflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6 and interleukin-8, in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Periodontal Res 2009, 44(2): Tseng YH, Chang KW, Liu CJ, Lin CY, Yang SC, Lin SC: Areca nut extract represses migration and differentiation while activating matrix metalloproteinase-9 of normal gingival epithelial cells. J Periodontal Res 2008, 43(5): Ling LJ, Ho FC, Chen YT, Holborow DW, Liu TY, Hung SL: Areca nut extracts modulated expression of alkaline phosphatase and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappab ligand in osteoblasts. J Clin Periodontol 2005, 32(4): Chang YC, Tai KW, Lii CK, Chou LS, Chou MY: Cytopathologic effects of arecoline on human gingival fibroblasts in vitro. Clin Oral Investig 1999, 3(1): Ling LJ, Hung SL, Tseng SC, Chen YT, Chi LY, Wu KM, Lai YL: Association between betel quid chewing, periodontal status and periodontal pathogens. Oral Microbiol Immunol 2001, 16(6): Akhter R, Hassan NM, Aida J, Takinami S, Morita M: Relationship between betel quid additives and established periodontitis among Bangladeshi subjects. J Clin Periodontol 2008, 35(1): Teng HC, Lee CH, Hung HC, Tsai CC, Chang YY, Yang YC, Lu CT, Yen YY, Wu YM: Lifestyle and psychosocial factors associated with chronic periodontitis in Taiwanese adults. JPeriodontol2003, 74(8): Amarasena N, Ekanayaka AN, Herath L, Miyazaki H: Tobacco use and oral hygiene as risk indicators for periodontitis. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2002, 30(2): Neely AL, Holford TR, Loe H, Anerud A, Boysen H: The natural history of periodontal disease in man. Risk factors for progression of attachment loss in individuals receiving no oral health care. J Periodontol 2001, 72(8): Pearson N, Croucher R, Marcenes W, O Farrell M: Dental health and treatment needs among a sample of Bangladeshi medical users aged 40 years and over living in Tower Hamlets. UK Int Dent J 2001, 51(1): Chatrchaiwiwatana S: Factors affecting tooth loss among rural Khon Kaen adults: analysis of two data sets. Public Health 2007, 121(2): Neely: The natural history of periodontal disease in humans: risk factors for tooth loss in caries-free subjects receiving no oral health care. J Clin Periodontol 2005, 32(9): Bergstrom J, Preber H: Tobacco use as a risk factor. J Periodontol 1994, 65(5 Suppl): Salvi GE, Lindhe J, Lang NP: Examination of Patients with Periodontal Disease. In Clinical Periodontology and Implant Dentistry. 5th edition. Edited by Lindhe J, Lang NP, Karring T. United Kindom: Blackwell Publishing Ltd; 2008: Silness J, Loe H: Periodontal disease in pregnancy. Ii. Correlation between oral hygiene and periodontal condtion. Acta Odontol Scand 1964, 22: Loe H, Silness J: Periodontal disease in pregnancy. I. Prevalence and severity. Acta Odontol Scand 1963, 21: Hou GL, Hung CC, Yang YS, Shieh TY, Tsai CC: Radiographic alveolar bone loss in untreated Taiwan Chinese subjects with adult periodontitis measured by the digital scanning radiographic image analysis method. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2003, 32(2): FJ L: Reliability of Measurment. In The Design and Analysis of Clinical Experiments. Canada: John wiley & sons, Inc; 1999: Lang NP, Hill RW: Radiographs in periodontics. J Clin Periodontol 1977, 4(1): Sarode SC, Mahuli A, Sarode GS, Mahuli S: Why only areca nut chewing cannot cause oral submucous fibrosis? Med Hypotheses 2013, 81(1): Mehta FS, Sanjana MK, Barretto MA: Relation of betel leaf chewing to periodontal disease. J Am Dent Assoc 1955, 50(5): Machtei EE, Dunford R, Hausmann E, Grossi SG, Powell J, Cummins D, Zambon JJ, Genco RJ: Longitudinal study of prognostic factors in established periodontitis patients. J Clin Periodontol 1997, 24(2): Grossi SG, Genco RJ, Machtei EE, Ho AW, Koch G, Dunford R, Zambon JJ, Hausmann E: Assessment of risk for periodontal disease. II. Risk indicators for alveolar bone loss. J Periodontol 1995, 66(1): doi: / Cite this article as: Hsiao et al.: Relationship between betel quid chewing and radiographic alveolar bone loss among Taiwanese aboriginals: a retrospective study. BMC Oral Health :133. Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Malignant transformation of oral submucous fibrosis in Taiwan: A nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study
 Accepted: 9 March 2017 DOI: 10.1111/jop.12570 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Malignant transformation of oral submucous fibrosis in Taiwan: A nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study Po-Yu Yang 1,2 Yi-Tzu
Accepted: 9 March 2017 DOI: 10.1111/jop.12570 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Malignant transformation of oral submucous fibrosis in Taiwan: A nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study Po-Yu Yang 1,2 Yi-Tzu
The Effect of X Ray Vertical Angulation on Radiographic Assessment of Alveolar Bone Loss
 1 The Effect of X Ray Vertical Angulation on Radiographic Assessment of Alveolar Bone Loss ABSTRACT M. Mehdizadeh MD*, M. Amintavakoli MD**, M. Allahverdi MD*** Introduction: Radiographs provide unique
1 The Effect of X Ray Vertical Angulation on Radiographic Assessment of Alveolar Bone Loss ABSTRACT M. Mehdizadeh MD*, M. Amintavakoli MD**, M. Allahverdi MD*** Introduction: Radiographs provide unique
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Radiographic Evaluation of Bone Formation and Density Changes after Mandibular Third Molar Extraction: A 6 Month Follow up
 Original Article Radiographic Evaluation of Bone Formation and Density Changes after Mandibular Third Molar Extraction: A Follow up Abbas Haghighat, Ehsan Hekmatian, Mehrdad Abdinian, Ezzeddin Sadeghkhani
Original Article Radiographic Evaluation of Bone Formation and Density Changes after Mandibular Third Molar Extraction: A Follow up Abbas Haghighat, Ehsan Hekmatian, Mehrdad Abdinian, Ezzeddin Sadeghkhani
Proposed score for occlusal-supporting ability
 Open Journal of Stomatology, 2013, 3, 230-234 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojst.2013.33040 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojst/) OJST Proposed score for occlusal-supporting ability
Open Journal of Stomatology, 2013, 3, 230-234 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojst.2013.33040 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojst/) OJST Proposed score for occlusal-supporting ability
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
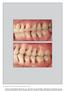 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
14/09/15. Assessment of Periodontal Disease. Outline. Why is Periodontal assessment needed? The Basics of Periodontal assessment
 Assessment of Periodontal Disease Dr Wendy Turner Outline Why is Periodontal assessment needed? The Basics of Periodontal assessment Probing: Basic Periodontal Examination for adults and children. Detailed
Assessment of Periodontal Disease Dr Wendy Turner Outline Why is Periodontal assessment needed? The Basics of Periodontal assessment Probing: Basic Periodontal Examination for adults and children. Detailed
A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran
 Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
An Overview of Gingival and Periodontal Diseases in 12 to 15 years using Gingivitis and Periodontitis Site Prevalence Index (WHO, 1978)
 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1079 ORIGINL RESERCH WJD n Overview of Gingival and Periodontal Diseases in 12 to 15 years n Overview of Gingival and Periodontal Diseases in 12 to 15 years using Gingivitis and
10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1079 ORIGINL RESERCH WJD n Overview of Gingival and Periodontal Diseases in 12 to 15 years n Overview of Gingival and Periodontal Diseases in 12 to 15 years using Gingivitis and
Periodontal disease is characterized by progressive periodontal pathogens. It is known that coronary heart disease is
 ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com PREVALENCE OF PERIODONTAL DISEASES IN PATIENTS WITH CORONARY HEART DISEASE Niha Naveed* BDS student, Saveetha
ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com PREVALENCE OF PERIODONTAL DISEASES IN PATIENTS WITH CORONARY HEART DISEASE Niha Naveed* BDS student, Saveetha
In the United States, about $1.5 billion
 J Periodontol July 2005 Periodontal Disease and the Incidence of Tooth Loss in Postmenopausal Women Mine Tezal,* Jean Wactawski-Wende, Sara G. Grossi,* Jacek Dmochowski, and Robert J. Genco* Background:
J Periodontol July 2005 Periodontal Disease and the Incidence of Tooth Loss in Postmenopausal Women Mine Tezal,* Jean Wactawski-Wende, Sara G. Grossi,* Jacek Dmochowski, and Robert J. Genco* Background:
A qualitative study on tobacco smoking and betel quid use among Burmese refugees in Australia
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2013 A qualitative study on tobacco smoking and betel quid use among Burmese
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2013 A qualitative study on tobacco smoking and betel quid use among Burmese
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Abstract Purpose: Materials and methods Results:
 Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Relationship Between Gingivitis and Anterior Teeth Irregularities Among 18 to 26 Years Age Group: A Hospital Based Study in Belgaum, Karnataka
 Relationship Between Gingivitis and Anterior Teeth Irregularities Among 18 to 26 Years Age Group: A Hospital Based Study in Belgaum, Karnataka V Chandrasekhara Reddy, BR Ashok Kumar, Anil Ankola ABSTRACT
Relationship Between Gingivitis and Anterior Teeth Irregularities Among 18 to 26 Years Age Group: A Hospital Based Study in Belgaum, Karnataka V Chandrasekhara Reddy, BR Ashok Kumar, Anil Ankola ABSTRACT
CURRICULUM VITAE China Medical College, College of Medicine, Taichung, Taiwan, R.O.C.
 CURRICULUM VITAE NAME: Huang, Chung-Ming OFFICE ADDRESS: China Medical University Hospital, No. 2, Yuh-Der Road, Taichung, Taiwan, R.O.C., 北 路 2 EDUCATION: 1978-1985 China Medical College, College of Medicine,
CURRICULUM VITAE NAME: Huang, Chung-Ming OFFICE ADDRESS: China Medical University Hospital, No. 2, Yuh-Der Road, Taichung, Taiwan, R.O.C., 北 路 2 EDUCATION: 1978-1985 China Medical College, College of Medicine,
ISSN % 47
 ISSN 1560-1587 7 30 60% 7 The Taiwan J Oral Med Sci 007; 3:7-68 Printed in Taiwan, All rights reserved Tonzetich 1 volatile sulfide compounds,vcsc VSCs 90% amines skatole indole VSCs Yaegaki -ketobutyrate
ISSN 1560-1587 7 30 60% 7 The Taiwan J Oral Med Sci 007; 3:7-68 Printed in Taiwan, All rights reserved Tonzetich 1 volatile sulfide compounds,vcsc VSCs 90% amines skatole indole VSCs Yaegaki -ketobutyrate
Professor, Department of Craniofacial Orthodontics, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital,
 Dr. Ellen Wen-Ching Ko, DDS, MS Professor, Department of Craniofacial Orthodontics, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan Professor, Graduate Institute of Craniofacial and Dental Science, Chang
Dr. Ellen Wen-Ching Ko, DDS, MS Professor, Department of Craniofacial Orthodontics, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan Professor, Graduate Institute of Craniofacial and Dental Science, Chang
Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig
 Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
CURRICULUM VITAE Name : Gender : Birth Place : address : Contact Tel : Education: Training and Working Experiences: Awards:
 Name : Szu-Hua Pan Gender : Female Birth Place : Taipei, Taiwan E-mail address : shpan@ntu.edu.tw Contact Tel : 02-23123456 ext. 88661 CURRICULUM VITAE Education: 1991~1994 B.S., Department of Nutrition
Name : Szu-Hua Pan Gender : Female Birth Place : Taipei, Taiwan E-mail address : shpan@ntu.edu.tw Contact Tel : 02-23123456 ext. 88661 CURRICULUM VITAE Education: 1991~1994 B.S., Department of Nutrition
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
A study of the consequences of smoking on periodontal health
 A study of the consequences of smoking on periodontal health Cristina Gabriela Puscasu1, Irina Totolici 2, Anca Silvia Dumitriu 3, Dragos Totolici 4, Doru Petrovici 5 Constanta, Romania Abstract Background:
A study of the consequences of smoking on periodontal health Cristina Gabriela Puscasu1, Irina Totolici 2, Anca Silvia Dumitriu 3, Dragos Totolici 4, Doru Petrovici 5 Constanta, Romania Abstract Background:
Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports
 0 Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports R.G. Caffesse, B.A. Smith/ B. Duff, E.C. Morrison, D. Merrill/ and W. Becker In the cases reported here, the response
0 Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports R.G. Caffesse, B.A. Smith/ B. Duff, E.C. Morrison, D. Merrill/ and W. Becker In the cases reported here, the response
Diagnosis. overt Examination. Definitive Examination. History. atient interview. Personal History. Clinical Examination.
 Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
Introduction. Clinical Periodontal Examination 11/1/16
 Is Radiologic Assessment of Alveolar Crest Height Useful to Monitor Periodontal Disease Activity? Based on DCNA chapter: Hattan A.M. Zaki, Kenneth R. Hoffmann, Ernest Hausmann, Frank A. Scannapieco Periodontitis,
Is Radiologic Assessment of Alveolar Crest Height Useful to Monitor Periodontal Disease Activity? Based on DCNA chapter: Hattan A.M. Zaki, Kenneth R. Hoffmann, Ernest Hausmann, Frank A. Scannapieco Periodontitis,
Delta Dental of Virginia Clinical Policy # 402
 Delta Dental of Virginia Clinical Policy # 402 Subject Mucogingival Surgery and Soft Tissue Grafting Originating Department Clinical Professional Services Signature Authority Dental Director Type: New
Delta Dental of Virginia Clinical Policy # 402 Subject Mucogingival Surgery and Soft Tissue Grafting Originating Department Clinical Professional Services Signature Authority Dental Director Type: New
Attachment G. Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080. ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA for Permanent Dentition YES NO
 First Review IL HFS Dental Program Models Second Review Ortho cad Attachment G Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080 Ceph Film X-Rays Photos Narrative Patient Name: DOB: ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA
First Review IL HFS Dental Program Models Second Review Ortho cad Attachment G Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080 Ceph Film X-Rays Photos Narrative Patient Name: DOB: ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA
Areca Nut Chewing Complicated with Non-Obstructive and Obstructive ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction
 Case Report Acta Cardiol Sin 2016;32:103 107 doi: 10.6515/ACS20141225A Areca Nut Chewing Complicated with Non-Obstructive and Obstructive ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction Ying-Chih Chen, 1 Hsiang-Chun
Case Report Acta Cardiol Sin 2016;32:103 107 doi: 10.6515/ACS20141225A Areca Nut Chewing Complicated with Non-Obstructive and Obstructive ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction Ying-Chih Chen, 1 Hsiang-Chun
Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar
 www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar Toshiko Inoue, Makoto Saito, Fumio Nishimura, Takashi Miyazaki ABSTRACT Abstract
www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar Toshiko Inoue, Makoto Saito, Fumio Nishimura, Takashi Miyazaki ABSTRACT Abstract
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION. By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur
 COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement
 Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement Abstract Aim: The purpose of this article is to report a case of conditioned gingival enlargement managed by nonsurgical periodontal therapy.
Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement Abstract Aim: The purpose of this article is to report a case of conditioned gingival enlargement managed by nonsurgical periodontal therapy.
Tobacco as risk factor for periodontal disease in green marble mine laborers of Rajasthan, India
 Braz J Oral Sci. October/December 2008 - Vol. 7 - Number 27 Tobacco as risk factor for periodontal disease in green marble mine laborers of Rajasthan, India Santhosh Kumar 1 ; Prabu D 2 ; Suhas Kulkarni
Braz J Oral Sci. October/December 2008 - Vol. 7 - Number 27 Tobacco as risk factor for periodontal disease in green marble mine laborers of Rajasthan, India Santhosh Kumar 1 ; Prabu D 2 ; Suhas Kulkarni
Dental Radiography Series
 Dental Radiography Series Guidelines for prescribing dental radiographs. Background Radiological s are used to discover and define the type and extent of disease in many clinical situations. However, public
Dental Radiography Series Guidelines for prescribing dental radiographs. Background Radiological s are used to discover and define the type and extent of disease in many clinical situations. However, public
Appendix 4. Case Summary Template. Social history. Patient (Name and Date of birth): Presenting complaints. History Medical history
 Appendix 4 Case Summary Template Patient (Name and Date of birth): Presenting complaints Chief complaint Subsidiary complaints History of complaints Patient s expectations History Medical history Medical
Appendix 4 Case Summary Template Patient (Name and Date of birth): Presenting complaints Chief complaint Subsidiary complaints History of complaints Patient s expectations History Medical history Medical
The Epidemiologic Transition of Diabetes Mellitus in Taiwan: Implications for Reversal of Female Preponderance from a National Cohort
 18 The Open Diabetes Journal, 29, 2, 18-23 Open Access The Epidemiologic Transition of Diabetes Mellitus in Taiwan: Implications for Reversal of Female Preponderance from a National Cohort Chin-Hsiao Tseng
18 The Open Diabetes Journal, 29, 2, 18-23 Open Access The Epidemiologic Transition of Diabetes Mellitus in Taiwan: Implications for Reversal of Female Preponderance from a National Cohort Chin-Hsiao Tseng
Root Proximity Characteristics and Type of Alveolar Bone Loss: A Case-control Study
 Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 011 13/3: 73-79 Root Proximity Characteristics and Type of Alveolar Bone Loss: A Case-control Study 1 1 1 Maria-Anna Loukideli, Alexandra Tsami, Eudoxie
Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 011 13/3: 73-79 Root Proximity Characteristics and Type of Alveolar Bone Loss: A Case-control Study 1 1 1 Maria-Anna Loukideli, Alexandra Tsami, Eudoxie
Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(4): 217 224 Case Report Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report Takashi
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(4): 217 224 Case Report Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report Takashi
Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Patient had no significant findings in medical history. Her vital signs were 130/99, pulse 93.
 Julia Collins Den 1200 Journal #4 1. Demographics Patient is J.S. age 29, Heavy/II 2. Assessment Patient had no significant findings in medical history. Her vital signs were 130/99, pulse 93. Patient does
Julia Collins Den 1200 Journal #4 1. Demographics Patient is J.S. age 29, Heavy/II 2. Assessment Patient had no significant findings in medical history. Her vital signs were 130/99, pulse 93. Patient does
Periodontal Screening and Scoring Of Patients Attended Periodontal Clinic of School Of Dentistry at University Of Sulaimani
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 8 Ver. I (Aug. 2015), PP 71-75 www.iosrjournals.org Periodontal Screening and Scoring Of Patients
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 8 Ver. I (Aug. 2015), PP 71-75 www.iosrjournals.org Periodontal Screening and Scoring Of Patients
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences PERIODONTAL DISEASE-SYSTEMIC DISEASE INTER RELATIONSHIP QUESTIONNAIRE STUDY ABSTRACT
 Research Article Periodontology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 PERIODONTAL DISEASE-SYSTEMIC DISEASE INTER RELATIONSHIP QUESTIONNAIRE STUDY MEENAKSHI PRIYANKA V 1* AND DR.
Research Article Periodontology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 PERIODONTAL DISEASE-SYSTEMIC DISEASE INTER RELATIONSHIP QUESTIONNAIRE STUDY MEENAKSHI PRIYANKA V 1* AND DR.
Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (JDMS) ISSN: 2279-0853, ISBN: 2279-0861. Volume 1, Issue 4 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 36-41 Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool 1 Ashu Bhardwaj,
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (JDMS) ISSN: 2279-0853, ISBN: 2279-0861. Volume 1, Issue 4 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 36-41 Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool 1 Ashu Bhardwaj,
Comparison between different papillary recession classification systems
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 373e378 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison between different papillary recession classification systems
Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 373e378 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison between different papillary recession classification systems
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Risk Factors in Implant Therapy
 Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Risk Factors in Implant Therapy David L. Cochran, DDS, MS, PhD, MMSci 1 /Søren Schou, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont 2 / Lisa J. A. Heitz-Mayfield,
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Risk Factors in Implant Therapy David L. Cochran, DDS, MS, PhD, MMSci 1 /Søren Schou, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont 2 / Lisa J. A. Heitz-Mayfield,
Betel quid chewing in Dagon (East) township
 Introduction Betel quid chewing in Dagon (East) township An estimated 600 million people worldwide, 10% of the world s population, chew betel quid. 1 Betel quid chewing has been common in South and Southeast
Introduction Betel quid chewing in Dagon (East) township An estimated 600 million people worldwide, 10% of the world s population, chew betel quid. 1 Betel quid chewing has been common in South and Southeast
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This
 1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
Journal of Oral & Dental Health
 Research Article Effect of Tobacco and Betel Nut on Periodontal Health in Diabetics Jebun Nessa 1 *, Md Obaidur R Chowdhury 2 and Atiquzzaman Khan 3 Journal of Oral & Dental Health ISSN: 2573-8224 1 Chairman
Research Article Effect of Tobacco and Betel Nut on Periodontal Health in Diabetics Jebun Nessa 1 *, Md Obaidur R Chowdhury 2 and Atiquzzaman Khan 3 Journal of Oral & Dental Health ISSN: 2573-8224 1 Chairman
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
RESUME Sep National Medical License, Taiwan Oct Board of Interal Medicine, Taiwan Aug Board of Cardiology, Internal Medicine, Taiwan
 RESUME Ye-Hsu Lu, M.D. Office Address: No.100, Ziyou 1st Rd., Sanmin Dist., Kaohsiung City 80708, Taiwan TEL: +886-7-3121101 ext. 7741 (Office), +886-918867017 (Cell) FAX: +886-7-3234845 E-mail: yehslu@gmail.com
RESUME Ye-Hsu Lu, M.D. Office Address: No.100, Ziyou 1st Rd., Sanmin Dist., Kaohsiung City 80708, Taiwan TEL: +886-7-3121101 ext. 7741 (Office), +886-918867017 (Cell) FAX: +886-7-3234845 E-mail: yehslu@gmail.com
Electronic Dental Records
 Electronic Dental Records Dr. Douglas K Benn, Professor of Maxillofacial Radiology & Director of Oral Diagnostic Systems, University of Florida and Health Conundrums LLC 8/2/2008 Dr Benn, University of
Electronic Dental Records Dr. Douglas K Benn, Professor of Maxillofacial Radiology & Director of Oral Diagnostic Systems, University of Florida and Health Conundrums LLC 8/2/2008 Dr Benn, University of
Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors
 Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors Faiza M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc. (1) Zainab M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc (2) ABSTRACT Background: Gingival recession
Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors Faiza M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc. (1) Zainab M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc (2) ABSTRACT Background: Gingival recession
Subject: Periodontal Maintenance Guideline #: Publish Date: 03/15/2018 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/05/2018
 Dental Policy Subject: Periodontal Maintenance Guideline #: 04-901 Publish Date: 03/15/2018 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/05/2018 Description This document addresses periodontal maintenance. Note:
Dental Policy Subject: Periodontal Maintenance Guideline #: 04-901 Publish Date: 03/15/2018 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/05/2018 Description This document addresses periodontal maintenance. Note:
Intrusion of Incisors to Facilitate Restoration: The Impact on the Periodontium
 Note: This is a sample Eoster. Your EPoster does not need to use the same format style. For example your title slide does not need to have the title of your EPoster in a box surrounded with a pink border.
Note: This is a sample Eoster. Your EPoster does not need to use the same format style. For example your title slide does not need to have the title of your EPoster in a box surrounded with a pink border.
Assessment of periodontal status and oral hygiene habits in a group of adults with type I diabetes mellitus
 Assessment of periodontal status and oral hygiene habits in a group of adults with type I diabetes mellitus Doina Lucia Ghergic, Claudia Florina Andreescu, Catalina Grigore Constanta, Romania Summary Diabetes
Assessment of periodontal status and oral hygiene habits in a group of adults with type I diabetes mellitus Doina Lucia Ghergic, Claudia Florina Andreescu, Catalina Grigore Constanta, Romania Summary Diabetes
Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(1): 9 18 Original Article doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0500 Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago Hiroki Imai 1), Tetsuhide Makiguchi
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(1): 9 18 Original Article doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0500 Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago Hiroki Imai 1), Tetsuhide Makiguchi
An International Journal for the Study of Veterinary Dentistry
 An International Journal for the Study of Veterinary Dentistry JOURNAL OF VeterinaryDentistry Official Journal of the American Veterinary Dental Society Academy of Veterinary Dentistry American Veterinary
An International Journal for the Study of Veterinary Dentistry JOURNAL OF VeterinaryDentistry Official Journal of the American Veterinary Dental Society Academy of Veterinary Dentistry American Veterinary
Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis
 Martin Saaby Eva Karring Søren Schou Flemming Isidor Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis Authors affiliations: Martin Saaby, Søren Schou, Section for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral
Martin Saaby Eva Karring Søren Schou Flemming Isidor Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis Authors affiliations: Martin Saaby, Søren Schou, Section for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral
The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography
 Clinical The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography Tony Druttman 1 The periapical view is one of the standard intra-oral radiographs by which diagnostic
Clinical The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography Tony Druttman 1 The periapical view is one of the standard intra-oral radiographs by which diagnostic
Toothbrushing Frequency as It Relates to Plaque Development and Gingival Health*
 Toothbrushing Frequency as It Relates to Plaque Development and Gingival Health* by NIKLAUS P. LANG* BOYD R. CUMMING*** HARALD LÖE** EPIDEMIOLOGICAL and experimental studies have demonstrated that gingival
Toothbrushing Frequency as It Relates to Plaque Development and Gingival Health* by NIKLAUS P. LANG* BOYD R. CUMMING*** HARALD LÖE** EPIDEMIOLOGICAL and experimental studies have demonstrated that gingival
It has been proposed that partially edentulous maxillectomy
 CLASSICAL ARTICLE Basic principles of obturator design for partially edentulous patients. Part II: Design principles Mohamed A. Aramany, DMD, MS* Eye and Ear Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh,
CLASSICAL ARTICLE Basic principles of obturator design for partially edentulous patients. Part II: Design principles Mohamed A. Aramany, DMD, MS* Eye and Ear Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh,
Regenerative treatment of periodontitis using diode laser: Case study.
 Case Report http://www.alliedacademies.org/oral-medicine-and-toxicology/ Regenerative treatment of periodontitis using diode laser: Case study. Balsam Mirdan 1*, Asseel Rashid 2 1 Ministry of Higher Education,
Case Report http://www.alliedacademies.org/oral-medicine-and-toxicology/ Regenerative treatment of periodontitis using diode laser: Case study. Balsam Mirdan 1*, Asseel Rashid 2 1 Ministry of Higher Education,
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES. 86 Stomatologija, Baltic Dental and Maxillofacial Journal, 2007, Vol. 9, No. 3 SUMMARY
 Stomatologija, Baltic Dental and Maxillofacial Journal, 9:86-9, 7 The relationship between the severity of malposition of the frontal teeth and periodontal health in age 5- and 5-44 Jolanta Pugaca, Ilga
Stomatologija, Baltic Dental and Maxillofacial Journal, 9:86-9, 7 The relationship between the severity of malposition of the frontal teeth and periodontal health in age 5- and 5-44 Jolanta Pugaca, Ilga
Keratinized Gingiva Width Alteration during Orthodontic Alignment and Leveling Phase; a Preliminary Investigation
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 7 Number 2 Keratinized Gingiva Width Alteration during Orthodontic Alignment and Leveling Phase; a Preliminary A Dannan, M Darwish, M Sawan Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 7 Number 2 Keratinized Gingiva Width Alteration during Orthodontic Alignment and Leveling Phase; a Preliminary A Dannan, M Darwish, M Sawan Citation
Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research. DOI: /sjodr ISSN (Print)
 DOI:10.21276/sjodr.2017.2.1.9 Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-1300 (Print) ISSN 2518-1297
DOI:10.21276/sjodr.2017.2.1.9 Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-1300 (Print) ISSN 2518-1297
 ISSN 1560-1587 81 7.18 11.51 9.21 72.84 4.94 22.22 4 Exploring the distance between upper central incisor edge and incisive papilla in Taiwanese population Sheau-Jiuan Huang 1, Tsau-Mau Chou 1, Huey-Er
ISSN 1560-1587 81 7.18 11.51 9.21 72.84 4.94 22.22 4 Exploring the distance between upper central incisor edge and incisive papilla in Taiwanese population Sheau-Jiuan Huang 1, Tsau-Mau Chou 1, Huey-Er
Tooth Retained Implant: No More an Oxymoron
 بنام خدا بنام خدا OPEN ACCESS Freely Available Online Original Hypothesis Tooth Retained Implant: No More an Oxymoron Divya Bhat a Abstract a Department of Periodontics, D.A.P.M.R.V. Dental College, Karnataka,
بنام خدا بنام خدا OPEN ACCESS Freely Available Online Original Hypothesis Tooth Retained Implant: No More an Oxymoron Divya Bhat a Abstract a Department of Periodontics, D.A.P.M.R.V. Dental College, Karnataka,
Oral Health Matters from Head to Toe
 Oral Health Matters from Head to Toe Your Guide to Preventing and Treating Gum Disease for Overall Health Gums and Overall Health We all know that prevention is one of the keys to maintaining overall health.
Oral Health Matters from Head to Toe Your Guide to Preventing and Treating Gum Disease for Overall Health Gums and Overall Health We all know that prevention is one of the keys to maintaining overall health.
Periodic exacerbation of gingival inflammation during the menstrual cycle
 159 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 3, 159-164, 2005 Case report Periodic exacerbation of gingival inflammation during the menstrual cycle Nobuko Koreeda 1), Yoshihiro Iwano 1), Mamoru Kishida 1),
159 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 3, 159-164, 2005 Case report Periodic exacerbation of gingival inflammation during the menstrual cycle Nobuko Koreeda 1), Yoshihiro Iwano 1), Mamoru Kishida 1),
Mesial Step Class I or Class III Dependent upon extent of step seen clinically and patient s growth pattern Refer for early evaluation (by 8 years)
 Orthodontics and Dentofacial Development Overview Development of Dentition Treatment Retention and Relapse Growth of Naso-Maxillary Complex Develops postnatally entirely by intramenbranous ossification
Orthodontics and Dentofacial Development Overview Development of Dentition Treatment Retention and Relapse Growth of Naso-Maxillary Complex Develops postnatally entirely by intramenbranous ossification
Evaluation of Guided Tissue Regeneration Following Third Molar Extraction by Bone Scintigraphy Using Tc99m-MDP
 CASE REPORT Evaluation of Guided Tissue Regeneration Following Third Molar Extraction by Bone Scintigraphy Using Tc99m-MDP Orit Oettinger-Barak, Eli E. Machtei, Zohar Keidar, Dan Mahler, Imad Abu EL-Naaj,
CASE REPORT Evaluation of Guided Tissue Regeneration Following Third Molar Extraction by Bone Scintigraphy Using Tc99m-MDP Orit Oettinger-Barak, Eli E. Machtei, Zohar Keidar, Dan Mahler, Imad Abu EL-Naaj,
The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea
 Review Article Endocrinol Metab 2016;31:349-33 http://dx.doi.org/.3803/enm.2016.31.3.349 pissn 2093-96X eissn 2093-978 The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea Junghyun Noh Department of Internal Medicine, Inje
Review Article Endocrinol Metab 2016;31:349-33 http://dx.doi.org/.3803/enm.2016.31.3.349 pissn 2093-96X eissn 2093-978 The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea Junghyun Noh Department of Internal Medicine, Inje
Dentistry at Willow Mill Veterinary Hospital. Importance of Good Oral Hygiene. Steps for a Healthy Mouth
 Willow Mill Veterinary Hospital 11 Willow Mill Park Road Mechanicsburg, PA 17050 www.willowmillvet.com Phone: (717)766-7981 Fax: (717) 766-6727 Email:willowmillvethosp@gmail.com Mon-Fri: 8AM-7PM, Sat:
Willow Mill Veterinary Hospital 11 Willow Mill Park Road Mechanicsburg, PA 17050 www.willowmillvet.com Phone: (717)766-7981 Fax: (717) 766-6727 Email:willowmillvethosp@gmail.com Mon-Fri: 8AM-7PM, Sat:
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
AETIOLOGY AND SEVERITY OF GINGIVAL RECESSION AMONG YOUNG INDIVIDUALS IN BELGAUM DISTRICT IN INDIA
 AETIOLOGY AND SEVERITY OF GINGIVAL RECESSION AMONG YOUNG INDIVIDUALS IN BELGAUM DISTRICT IN INDIA V. Dodwad. Aetiology and severity of gingival recession among young individuals in Belgaum district in
AETIOLOGY AND SEVERITY OF GINGIVAL RECESSION AMONG YOUNG INDIVIDUALS IN BELGAUM DISTRICT IN INDIA V. Dodwad. Aetiology and severity of gingival recession among young individuals in Belgaum district in
Gingival and labial vestibular in young individuals
 Journal of Dentistry, 3, No. 4, 985, pp. 323-330 Printed in Great Britain Gingival and labial vestibular in young individuals temperature A. Volchansky, BDS, PhD (Dent.) P. Cleaton-Jones, BDS, MBBCh, PhD
Journal of Dentistry, 3, No. 4, 985, pp. 323-330 Printed in Great Britain Gingival and labial vestibular in young individuals temperature A. Volchansky, BDS, PhD (Dent.) P. Cleaton-Jones, BDS, MBBCh, PhD
Authors: Archita Kikani*, Mihir Shah**, Hiral Parikh***, Sandip Ladani****, Pratik Shah*****
 Original Research Kikani et al Socio-economic Position, Tobacco Habit, and Plaque: A Pathway To Severe Chronic Periodontitis Authors: Archita Kikani*, Mihir Shah**, Hiral Parikh***, Sandip Ladani****,
Original Research Kikani et al Socio-economic Position, Tobacco Habit, and Plaque: A Pathway To Severe Chronic Periodontitis Authors: Archita Kikani*, Mihir Shah**, Hiral Parikh***, Sandip Ladani****,
Gingival enlargement originating from medication and tooth migration
 CLINICAL REPORT 109 Publication Frédéric Duffau Gingival enlargement originating from medication and tooth migration Frédéric Duffau 26 Avenue Kléber, 75116 Paris France KEY WORDS drug-induced gingival
CLINICAL REPORT 109 Publication Frédéric Duffau Gingival enlargement originating from medication and tooth migration Frédéric Duffau 26 Avenue Kléber, 75116 Paris France KEY WORDS drug-induced gingival
1B Getting Ready for Instrumentation: Mathematical Principles and Anatomic Descriptors
 MODULE 1B Getting Ready for Instrumentation: Mathematical Principles and Anatomic Descriptors Module Overview This module contains a review of the mathematical principles and anatomic descriptors used
MODULE 1B Getting Ready for Instrumentation: Mathematical Principles and Anatomic Descriptors Module Overview This module contains a review of the mathematical principles and anatomic descriptors used
The Study in Change of Nutrition Knowledge, Attitude, and Behavior of College Students as Affected by Different Method of Nutrition Education
 The Study in Change of Nutrition Knowledge, Attitude, and Behavior of College Students as Affected by Different Method of Nutrition Education Dr. Huang, C.Y., Dept. of Hotel Mgt., National Kaohsiung University
The Study in Change of Nutrition Knowledge, Attitude, and Behavior of College Students as Affected by Different Method of Nutrition Education Dr. Huang, C.Y., Dept. of Hotel Mgt., National Kaohsiung University
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Periodontal Treatment Protocol Department of Orthodontics and Restorative Dentistry, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester
 Periodontal Treatment Protocol Department of Orthodontics and Restorative Dentistry, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester 1. Periodontal Assessment Signs of perio disease: - Gingivae become red/purple - Gingivae
Periodontal Treatment Protocol Department of Orthodontics and Restorative Dentistry, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester 1. Periodontal Assessment Signs of perio disease: - Gingivae become red/purple - Gingivae
Clinical observations concerning the role of dental crowding among the local etiopathogenical factors of periodontal disease-case report
 Clinical observations concerning the role of dental crowding among the local etiopathogenical factors of periodontal disease-case report Cristina Puºcaºu 1, Dragoº Totolici 1, Anca Dumitriu 2, Horia Traian
Clinical observations concerning the role of dental crowding among the local etiopathogenical factors of periodontal disease-case report Cristina Puºcaºu 1, Dragoº Totolici 1, Anca Dumitriu 2, Horia Traian
"Designing a fixed partial denture without a pontic"- Case report
 Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 "Designing a fixed partial denture without a pontic"- Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Khurshid Mattoo, Assistant Professor, Prosthodontics, College of Dental
Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 "Designing a fixed partial denture without a pontic"- Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Khurshid Mattoo, Assistant Professor, Prosthodontics, College of Dental
Orthodontic-prosthetic implant anchorage in a partially edentulous patient
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2011) 6, 176e180 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com Clinical Report Orthodontic-prosthetic implant anchorage in a partially edentulous patient
Journal of Dental Sciences (2011) 6, 176e180 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com Clinical Report Orthodontic-prosthetic implant anchorage in a partially edentulous patient
Surveying. 3rd year / College of Dentistry/University of Baghdad ( ) Page 1
 د. فائزة Lec.3 Prosthodontics Surveying The ideal requirements for successful removable partial denture are: 1. Be easily inserted and removed by the patient. 2. Resist dislodging forces. 3. It should
د. فائزة Lec.3 Prosthodontics Surveying The ideal requirements for successful removable partial denture are: 1. Be easily inserted and removed by the patient. 2. Resist dislodging forces. 3. It should
Chief complaints. General information. Medical history. Dental history. Findings in masticatory system. Personal habits
 0 General information Chief complaints Name: Birthday:53.12.19 Age:50 y/o Gender:Female Personality:philosophic Occupation: Medical history NPC s/p RT 20 years ago follow up every 6 months at Gastroesophageal
0 General information Chief complaints Name: Birthday:53.12.19 Age:50 y/o Gender:Female Personality:philosophic Occupation: Medical history NPC s/p RT 20 years ago follow up every 6 months at Gastroesophageal
Periodontal Maintenance
 Periodontal Maintenance Friday, February 20, 2015 1:06 PM Periodontal disease control always begins with patient education - Plaque control, diet, smoking cessation, impact that systemic health has on
Periodontal Maintenance Friday, February 20, 2015 1:06 PM Periodontal disease control always begins with patient education - Plaque control, diet, smoking cessation, impact that systemic health has on
Journal of Chinese Medicine. Vol.20, No.1, Vol.20, No.3,
 163 Journal of Chinese Medicine Vol.20, No.1,2 1-96 Vol.20, No.3,4 97-162 ~ - 145 45-135 21 117 79-19 137-135 ~ - 137 65 87-65 - 145-65 - 153-79 - 153-87 47-137 - 65-87 - 47-145 - 145-47 - 19 164 153 HT7
163 Journal of Chinese Medicine Vol.20, No.1,2 1-96 Vol.20, No.3,4 97-162 ~ - 145 45-135 21 117 79-19 137-135 ~ - 137 65 87-65 - 145-65 - 153-79 - 153-87 47-137 - 65-87 - 47-145 - 145-47 - 19 164 153 HT7
HDS PROCEDURE CODE GUIDELINES
 D0100 - D0999 Clinical Oral Evaluations D0120 - D0180 The codes in this section have been revised to recognize the cognitive skills necessary for patient evaluation. The collection and recording of some
D0100 - D0999 Clinical Oral Evaluations D0120 - D0180 The codes in this section have been revised to recognize the cognitive skills necessary for patient evaluation. The collection and recording of some
Oral Health Status of Pregnant Women
 Oral Health Status of Pregnant Women Ingrida Vasiliauskiene Stomatologija, Baltic Dental and Maxillofacial Journal, 5:57-61, 2003 SUMMARY The aim of the study was to determine the prevalence and severity
Oral Health Status of Pregnant Women Ingrida Vasiliauskiene Stomatologija, Baltic Dental and Maxillofacial Journal, 5:57-61, 2003 SUMMARY The aim of the study was to determine the prevalence and severity
The dentogingival junction to the
 Volume 79 Number 10 RedefiningtheBiologicWidthinSevere, Generalized, Chronic Periodontitis: Implications for Therapy M. John Novak,* Huda M. Albather, and John M. Close Background: Previous studies demonstrated
Volume 79 Number 10 RedefiningtheBiologicWidthinSevere, Generalized, Chronic Periodontitis: Implications for Therapy M. John Novak,* Huda M. Albather, and John M. Close Background: Previous studies demonstrated
The Clarion International Multidisciplinary Journal
 The Clarion Volume 3 Number 1 (2014) PP 8-12 The Clarion International Multidisciplinary Journal ISSN : 2277-1697 Periodontal treatment needs of a rural population of North East India Dilip Goswami Department
The Clarion Volume 3 Number 1 (2014) PP 8-12 The Clarion International Multidisciplinary Journal ISSN : 2277-1697 Periodontal treatment needs of a rural population of North East India Dilip Goswami Department
Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery
 CASE SERIES 1 OPEN ACCESS Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery Sangeeta ABSTRACT Introduction:
CASE SERIES 1 OPEN ACCESS Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery Sangeeta ABSTRACT Introduction:
