ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Siew Eng Choon, FRCP 1,2, Yi Shan Der 1, Nai Liang Joel Lai 1, Evelyn Sing Ee Yu 1, Xiao Ling Yap 1, Nalini Nanu Madhavan, MBBS 2
|
|
|
- Lizbeth Fisher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical characteristics, culprit drugs and outcome of patients with Acute Generalised Exanthematous Pustulosis seen in Hospital Sultanah Aminah, Johor Bahru Siew Eng Choon, FRCP 1,2, Yi Shan Der 1, Nai Liang Joel Lai 1, Evelyn Sing Ee Yu 1, Xiao Ling Yap 1, Nalini Nanu Madhavan, MBBS 2 1 Jeffrey Cheah School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Monash University Malaysia, 2 Department of Dermatology, Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru, Malaysia. ABSTRACT Background: Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a rare, cutaneous reaction characterised by sudden onset of numerous, non-follicular, sterile pustules on oedematous erythematous skin, accompanied by fever and neutrophilia. AGEP is predominantly drug-induced. Skin lesions appear rapidly within 1-3 days of drug exposure and upon drug withdrawal, resolve rapidly within 15 days. Objective: To determine the clinical characteristics, culprit drugs and outcome of patients with AGEP. Methods: A retrospective note review of all AGEP patients seen from Results: Among 21 AGEP patients, 76% were Malays, 9.5% Chinese, 9.5% Indians, and 5% Iban. Sixteen were females and 5 were males. Median age of patients was 40 years (IQR: 26). The main culprit drug was amoxicillin (10 cases), followed by cloxacillin (three cases), phenytoin (two cases) and one case each of carbamazepine, sulphasalazine, allopurinol, cephalexin, ceftriaxone, celecoxib and herbal product. The median time from drug initiation to onset of AGEP was 3 days (IQR: 5.5). Fever was documented in 52.4 %, mucosal involvement 9.5%, purpura 4.7% and blisters 4.7%. Neutrophilia was observed in 63.6% of patients and eosinophilia in 28.5%. While most patients required admission (67%), all achieved complete recovery within 15 days without any sequela. Conclusions: AGEP predominantly affects Malay females in this study. The most common culprit drug was amoxicillin. Our patients exhibited the classic clinical manifestations of AGEP and confirmed the generally benign nature of this reaction upon drug withdrawal. Although the overall prognosis is good, prompt diagnosis of AGEP is important because drug withdrawal is the mainstay therapy. KEY WORDS: AGEP, Acute generalised pustular psoriasis, SCARs, severe cutaneous adverse reactions INTRODUCTION Acute Generalised Exanthematous Pustulosis (AGEP) is a rare and severe cutaneous adverse reaction characterised by sudden onset of numerous pin-point, non-follicular sterile pustules on oedematous erythematous skin. The majority of AGEP are drug-induced Hypersensitivity to mercury and spider bites have also been reported. 2,8 Other implicated causes included infections namely with parvovirus B19, cytomegalovirus, coxsackie B4 and mycoplasma pneumoniae. 2,5,8 However, the European study of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (EuroSCAR) compared 97 cases of AGEP with 1009 normal controls and found no significant association with infection. 5 The EuroSCAR study identified seven drugs, namely pristinamycin, aminopenicillins, quinolones, hydroxychloroquine, sulphonamides, terbinafine and diltiazem which are highly associated with AGEP. AGEP can be recognised clinically by the sudden appearance of numerous pin-head sized (<5mm), sterile, non-follicular pustules overlying oedematous erythematous skin, following exposure to an offending drug. 1-7 The skin lesions typically start on intertriginous areas or face, 1 but is rapidly supervened by widespread distribution. Atypical cutaneous features including purpura, target-like lesions reminiscent of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, blisters and vesicles have been described. 1-5 Non-erosive mucous membrane involvement is seen in about 20% of cases, but this is usually mild and confined to one location (mostly oral). 1 The skin manifestations of AGEP are nearly always accompanied by some systemic symptoms, namely fever and neutrophilia. Mild eosinophilia occurs in up to 30% of patients. 8 Upon drug withdrawal, the pustules rapidly resolve with characteristic pin-point desquamation. Full recovery typically occurs within 15 days and other organs are usually not affected. 1-9 Reported mortality of 10%-20% among patients with AGEP was mainly due to secondary infections in older patients with multiple comorbidities. 10,12 In this study, we aim to determine the clinical characteristics, culprit drugs and outcome of AGEP in our population. MATERIALS AND METHODS Setting The department of dermatology in Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru keeps a registry of all patients with cutaneous adverse drug reaction (cadr) since All suspected cadr referred to our department are evaluated by This article was accepted: 1 June 2018 Corresponding Author: Siew Eng Choon choonse@yahoo.co.uk 220 Med J Malaysia Vol 73 No 4 August 2018
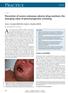
2 Clinical characteristics, culprit drugs and outcome of patients with Acute Generalised Exanthematous Pustulosis a dermatologist before they are registered and reported to our National Drug Monitoring Centre. The first author was one of the dermatologists who routinely evaluated and assessed the causality of drugs implicated in suspected cadr during the study period between January 2001 and December Of the 614 patients with cadr (mean age at onset: 41.8 years) seen during the study period, 278 (45.2%) were female. The racial composition of our cadr patients was 62.5% Malay, 28.6% Chinese, 5.8% Indian, and 2.1% others. Study design and population This study was done by analysing the ADR reporting forms of patients with dermatologist-diagnosed AGEP who were registered and reported to our National Drug Monitoring centre between January 2001 and December Patients clinical notes were traced and counterchecked for any missing or doubtful data. The information gathered included (i) patient demographics (age, gender and ethnicity), (ii) culprit drug(s), (iii) clinical features namely, type of skin eruptions, systemic manifestations, clinical course and outcome. Our National Drug monitoring centre is a member of the World Health Organization s (WHO) Programme for International Drug monitoring since All suspected ADRs in Malaysia were screened by a 12-member Malaysian Adverse Drug Reactions Advisory Committee before they were submitted to the WHO Uppsala Monitoring Centre in Sweden for inclusion into the WHO database. Hence, the WHO causality grading was and is still used to determine the causality of culprit drugs in our national ADR reporting forms. 13,14 All included patients in this study have a WHO causality grading of at least probable, defined as reasonable time relationship between drug exposure and rash, the event is unlikely to be attributable to concurrent disease or other medicines and a clinically reasonable response is observed on dechallenge. Rechallenge information is not necessary to fulfil this definition. Patients were also formally scored using the AGEP validation tool developed by the EuroSCAR group 2 and stratified as to whether their diagnosis of AGEP was possible, probable or definite. The AGEP validation score is a standardized scoring system based on clinical features and histopathology. A patient with an AGEP validation score of between 1 and 4 is defined as a possible case, 5 and 7 is defined as a probable case, whereas a score between 8 and 12 is defined as a definite case. AGEP score assigned to each included patient was based on consensus among all authors. Statistical analysis Descriptive statistics are used to analyse data and presented as counts and percentages for categorical variables. Mean with standard deviation (SD) was used for normally distributed data while median with interquartile range (IQR) was used for data which were not normally distributed. This study was approved by our Institutional Review Board (NMRR ) with exemption from a full ethical review since it was a retrospective study. RESULTS Of the 21 patients with AGEP, five (24%) had a definite, six (29%) probable, and ten (47%) possible diagnosis of AGEP based on EuroSCAR scoring system. Sixteen patients (76%) were female and five were male. Median age of patients at onset of AGEP was 40 years (IQR: 26). Among the 21 patients, 76% were Malays, 9.5% Chinese, 9.5% Indians, and 5% Iban. All patients had generalised erythema studded with characteristic numerous pin-point non-follicular pustules (Figure 1) but mucosal involvement mainly cheilitis and oral mucosa erosions were noted in only two patients. Purpura and blisters were documented in one patient. Fever ( 38ºCelsius) was documented in 11 (52.4%) patients. Leucocytosis (range X10 9 /L) with neutrophilia ( 7.5X10 9 /L) was observed in 63.6% and eosinophilia (range 6% to 19.7%) in 28.5% of patients. Three patients had transaminitis with alanine aminotransferase level of 72, 90 and 162 units/l. Skin swabs and blood culture did not reveal any infection. Only six (28%) patients underwent confirmatory skin biopsies which showed characteristic features of AGEP. (Figure 2). Three (14%) gave a previous history of drug allergies. Among them, one had a prior amoxicillin-induced AGEP. Nine (43%) had comorbidities. Two patients (9.5%) have concurrent psoriasis and one (4.8%) had pemphigus foliaceus. Other comorbid conditions included hypertension and diabetes mellitus in two patients; hypertension, diabetes mellitus, ischaemic heart disease and cerebrovascular accident (one patient); end-stage renal failure and hypertension (one patient); chronic spontaneous urticarial and asthma (one patient) and allergic rhinitis in another patient. Table I: Drugs implicated in Acute Generalised Exanthematous Pustulosis (AGEP)) Culprit drugs No. of patients (%) Days from drug initiation to onset of AGEP (mean, range) Amoxicillin 10 (47.6) 2.5 ( ) Cloxacillin 2 (9.5) 3.5 (1-6 ) Phenytoin 2 (9.5) 24.5 (21-28) Carbamazepine 1 (4.8) 2 Sulphasalazine 1 (4.8) 14 Allopurinol 1 (4.8) 4 Cephalexin 1 (4.8) 1 Ceftriaxone 1 (4.8) 2 Celecoxib 1 (4.8) 7 Herbs 1 (4.8) 1 Med J Malaysia Vol 73 No 4 August
3 Original Article Table II: Comparison of clinical characteristics of case series on drug-induced acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis Author This study Alniemi et al 3 Thienvibul et al 9 Lee et al 4 Hotz et al6 Choi et al7 Lee et al 10 Guevara- Tamir et al 12 Roujeau et al 8 (Study period) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Gutierrez et al 11 ( ) (NA) ( ) Number of ( ( ( patients, n drug-induced) (2015, drug-induced) (2013, (23 drug (2010, drug-induced) (2006, (56 drug- (year published) (2017, USA) Thailand) (2014, Taiwan) France) induced) Singapore) (2009, Mexico) Israel) induced) (2010, Korea) (1991, France) Age (years), mean (range) (7-70) (20-88) (19-84) (NA) (19-92) (4-80) (54-80) (15-56) (22-91) (6-85) Gender, n (%) 5 (23.8%) 11 (39.2%) 9 (47.4%) 10 (29.4%) 24 (42%) 12(52.1%) 3 (37.4%) 7 (58%) 3 (23%) 30 (47.7%) Male 16 (76.1%) 17 (60.7%) 10 (52.6%) 24 (70.6%) 34 (58%) 11 (47.8%) 5 (62.6%) 5 (42%) 10 (76%) 33 (52.3%) Female Top 3 culprit Amoxicillin Clindamycin Carbapenem Penicillins (6) Amoxicillin Amoxicillin (5) Ceftriaxone (3) Carbamazepine Acetami Amoxicillin drugs (number (10) (6) (3) Cephalosporin (14) Herbal Ciprofloxacin, (4) nophen (4) (18) of cases) Cloxacillin Amoxicillin Cephalosporin (3) (6) Pristinamycin medication (4) cloxacillin, Cotrimoxxazole, Penicillins (2) Mercury (8) (2) (3) Amoxicillin 2 Quinolones (4) (8) Lacquer (3) imipenem, Isoniazid, NSAIDs (2) Ampicillin (5) Phenytoin (2) Cephalexin, Omeprazole 2 Diltiazem (5) morphine, ciprofloxacin, cefepime, Hydroxychlo phenytoin cefalexin, diltiazem roquine (3) (1 each) cefotaxime, (2 cases each) Phenytoin (1 each) Days from NA NA NA NA 2.5 for drug initiation (1-28) (NA) Median (9-23) (1-6) (1-5) antibiotics to AGEP, 3 days 18 for mean (range) other drugs Fever 52% 36% 52% 82% NA NA 100% 92% 92% 92% Mucosal involvement 2 (9.5%) 3 (11%) 3 (15.8%) 3 (8.8%) 7 (12%) 0 NA 2 (17%) NA 14 (22.2%) Neutrophilia 63.6% 88% 68% 82% 73.5% 69.6% 87.5% 92% % Eosinophilia 28.5% 48% 10% 11% NA NA 12.5% 8% NA 30.1% Systemic involvement 14.2% 75% 26.3% 23.5% 17.8% % Mortality Med J Malaysia Vol 73 No 4 August 2018
4 Clinical characteristics, culprit drugs and outcome of patients with Acute Generalised Exanthematous Pustulosis Fig. 1: Amoxicillin-induced Acute Generalised Exanthematous Pustulosis showing characteristic numerous, pin-point, non-follicular pustules on erythematous skin of the abdomen. Fig. 2a: Acute Generalised Exanthematous Pustulosis showing characteristic spongiform intra-epidermal microabscesses, severe papillary oedema, neutrophil-rich perivascular and interstitial infiltrates with conspicuous eosinophils (Haematoxylin-eosin stain: original magnification X2). We, unanimously, agreed with the initial causality grading of probable or certain relationship of drugs implicated in all 21 reported AGEP during the study period. The distinctive clinical course of AGEP may explain the 100% concurrence rate in the causality assessment of implicated drugs between reporting dermatologists and authors. Table I shows drugs implicated in AGEP. The median time from drug exposure to the development of AGEP was three days (IQR: 5.5). Most of our patients required hospital admission (67%). Eleven patients (53%) were given topical steroids, one (5%) received prednisolone and six (29%) had antihistamines. Pustules settled with characteristic pin-point desquamation within 15 days after drug dechallenge in all patients. Neutrophilia and transaminitis also settled promptly with drug withdrawal. No fatality was documented. Fig. 2b: Spongiform intra-epidermal micro-abscesses containing characteristic mixed infiltrate of neutrophils and eosinophils, (Haematoxylin-eosin stain: original magnification X40). DISCUSSION Most of our patients with AGEP were female (76%), a finding consistent with the majority of studies with documented female preponderance of between 52% to 76% 3,4,8,9,12,16 (Table II). The obvious female preponderance is surprising since we have a slight male preponderance in Malaysia and in Johor population of 52.8% males. 15 Furthermore, females only accounted for 45.2% of 614 patients with cadr seen during the study period. Hence, the female preponderance observed is unlikely to be due to differences in health-seeking behaviour between the genders and being female is likely a risk factor for AGEP. Another notable finding is the high proportion of Malays with AGEP (76%) compared to other ethnic groups which comprised of Chinese (9.5%), Indians (9.5%) and Iban (5%). This ethnic distribution, which differed Med J Malaysia Vol 73 No 4 August
5 Original Article from Malaysia s general ethnic distribution of 63.1% Malays, 24.6% Chinese and 7.3% Indians suggested variation in risk for AGEP among our multi-ethnic population. 15 The most distinctive feature of AGEP is its clinical course. It has a very rapid onset and equally rapid resolution. Skin lesions appear rapidly within 1-3 days of drug exposure and resolve as rapidly by 5-7 days upon drug withdrawal, followed by pin-point desquamation. 1-9 The clinical features, course and outcome of our patients with AGEP were as expected of this distinctive cutaneous reaction. Like previous studies, our patients presented with acute onset of characteristic pin-point non-follicular sterile pustules on oedematous erythematous skin (Figure 1), a few days after ingestion of culprit drugs (median duration of 3 days) followed by rapid resolution of AGEP on drug withdrawal without any fatality (Table II). Consistent with previous studies, only a minority of our patients displayed mucosal involvement, mainly cheilitis and atypical lesions namely purpura and blisters. AGEP is often but not invariably accompanied by fever. Only about 50% of our patients had fever, a finding which is consistent with recent studies from Minnesota, USA and Thailand but contradicts observations of earlier studies from Taiwan, Singapore, Mexico, Israel and France which documented fever in between 80%-100% of patients (Table II). The neutrophilia of 63.6% and eosinophilia of 28.5% observed in our patients are not uncommon among patients with AGEP (Table II). Although only eight patients had biopsies performed, the histologic findings which included i) intra-corneal, subcorneal and/or intra-epidermal spongiform microabscesses containing both neutrophils and eosinophils (Figure 2a & b), ii) papillary dermal oedema and iii) a neutrophil-rich mid-dermal perivascular and interstitial infiltrates admixed with eosinophils are highly characteristic of AGEP and comparable to the key histologic features highlighted by Halevy et al in their analysis of 102 AGEP patients. 16 AGEP has a generally good prognosis although systemic involvement had been reported. 3,4,6,8,9 Three (14.2%) of our patients had systemic involvement, a finding that concurred with a retrospective review of 58 AGEP patients by Holtz et al., which documented systemic involvement, affecting either renal, liver, bone marrow or lungs, in 17.2% of patients. 6 Similar to our study, full recovery without mortality was achieved by all 58 patients on drug withdrawal. Outcome was also favourable with no mortality in studies from the USA, Taiwan, Thailand and France which reported systemic involvement in 23% to 75% of AGEP patients. 3,4,8,9 Although a mortality rate of 10-20% had been documented, it was mainly attributed to secondary infections in elderly patients with multiple comorbidities. 10,12 Our data is consistent with previous studies in confirming antibiotics as the most frequently implicated drug group in AGEP (Table II). Amoxicillin, the major offender, was responsible for AGEP in nearly half (47.6%) of our patients. Non-antimicrobial culprit drugs in this study, namely phenytoin, carbamazepine, sulphasalazine, allopurinol 17 and celecoxib 18 have all been previously implicated as causative drugs in AGEP (Table II). One of our patients developed AGEP after ingesting Habbatus Sauda, an herbal product from medicinal plant Nigella Sativa. Herbal medicines are widely believed to be safe although adverse reactions, including lifethreatening hepatic and renal toxicity, are not rare. 19,20 Herbal products were also implicated in studies on AGEP from Taiwan 4 and Thailand. 9 Unlike prescription drugs, the content and quality of herbal products are not tightly controlled and contamination with heavy metals including mercury and adulteration with antibiotics are well documented Both antibiotics and mercury are associated with AGEP, complicating causality assessment of medicinal herbs in resource poor setting where chemical analysis of herbal products are not readily available. However, chemical analysis of Habbatus Sauda brought by patient was negative for heavy metals and common antibiotics. Our study is limited by its retrospective nature and the missing clinical data particularly in patients diagnosed before the implementation of point-of-care electronic documentation of clinical notes in November Another limitation of this study is the small number of patients who underwent skin biopsy. The acute onset of rash and fever following exposure to culprit drugs was readily recognised by patients as drug-induced and rejection of diagnostic skin biopsy is understandable. Unfortunately, histologic features contributed up to 6 points to the EuroSCAR diagnosis of AGEP. Hence, only 53% of our patients satisfied the EuroSCAR criteria for the diagnosis of definite/probable AGEP. CONCLUSIONS AGEP predominantly affects Malay females in our study population. The most common culprit drug was amoxicillin. Our patients exhibited the classic clinical manifestations of AGEP and confirmed the generally benign nature of this reaction upon drug withdrawal. Although the overall prognosis is good, prompt recognition and diagnosis of this distinctive adverse cutaneous reaction is important because drug withdrawal is the mainstay therapy. REFERENCES 1. Sidoroff A, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, Vaillant L, Roujeau JC. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) A clinical reaction pattern. J Cutan Pathol. 2001; 28(3): Szatkowski J, Schwartz RA. Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): A review and update. J Am Acad Dermatol 2015; 73(5): Alniemi DT,Wetter DA, Bridges AG, El-Azhary RA, Davis MD, Camilleri MJ et al. Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis: clinical characteristics, etiologic associations, treatments, and outcomes in a series of 28 patients at Mayo Clinic, Int J Dermatol 2017; 56(4): Lee Y, Chung W. Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis: a retrospective study of 51 cases in Taiwan. Dermatologica Sinica 2014; 32: Sidoroff A, Dunant A, Viboud C, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, Naldi L et al. Risk factors for acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)-results of a multinational case-control study (EuroSCAR). Br J Dermatol 2007; 157(5): Hotz C, Valeyrie-Allanore L, Haddad C, Bouvresse S, Ortonne N, Duong TA et al. Systemic involvement of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: a retrospective study on 58 patients. Br J Dermatol 2013; 169(6): Choi MJ, Kim HS, Park HJ, Park CJ, Lee JD, Lee JY et al. Clinicopathologic manifestations of 36 Korean patients with acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: a case series and review of the literature. Ann Dermatol 2010; 22(2): Med J Malaysia Vol 73 No 4 August 2018
6 Clinical characteristics, culprit drugs and outcome of patients with Acute Generalised Exanthematous Pustulosis 8. Roujeau JC, Bioulac-Sage P, Bourseau C, Guillaumme JC, Bernard P, Lok C et al. Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis: Analysis of 63 cases. Arch Dermatol 1991; 127(9): Thienvibul C, Vachiramon V, Chanprapaph K. Five-Year Retrospective Review of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis. Dermatol Res Pract 2015; 2015: Lee HY, Chou D, Pang SM, Thirumoorthy T. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: analysis of cases managed in a tertiary hospital in Singapore. Int J Dermatol 2010; 49(5): Guevara-Gutierrez E, Uribe-Jimenez E, Diaz-Canchola M, Alberto Tlaciulo- Parra. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: report of 12 cases and literature review. Int J Dermatol 2009; 48(3): Tamir E, Wohl Y, Mashiah J, Brenner S. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: a retrospective analysis showing a clear predilection for Women. Skinmed 2006;5(4): Malaysian Adverse Drug Reactions Advisory Committee. Available at; Last accessed 16 March The use of the WHO-UMC system for standardised case causality assessment. Available at; Last accessed 16 March Population and housing census Available at _ Kiraan_Permulaan2010.pdf Accessed 14 Sept Halevy S, Kardaun SH, Davidovici B, Wechsler J. The spectrum of histopathological features in acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: a study of 102 cases. Br J Dermatol 2010; 163(6): Pakdeethai J, Ho SA, Aw D, Tan KB. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis-like, folliculitic drug reaction pattern caused by celecoxib. Dermatol Ther 2011; 24(5): Teo WL, Pang SM, Koh HY. Allopurinol hypersensitivity syndrome with acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis manifestations. Cutan Ocul Toxicol 2011; 30(3): Byard RW, Musgrave I, Maker G, Bunce M. What risks do herbal products pose to the Australian community? Med J Aust 2017; 206(2): Zhang J, Wider B, Shang H, Li X, Ernst E. Quality of herbal medicines: Challenges and solutions. Complementary Thera Med 2012; 20(1-2): Ernst E. Herbal medicines- they are popular, but are they also safe? Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2006; 62(1): Ernst E. Toxic heavy metals and undeclared drugs in Asian herbal medicines. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2002; 23(3): Med J Malaysia Vol 73 No 4 August
Prevalence and pattern of adverse cutaneous drug reactions presenting to a tertiary care hospital
 International Journal of Research in Dermatology Janardhan B et al. Int J Res Dermatol. 2017 Mar;3(1):74-78 http://www.ijord.com Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20164248
International Journal of Research in Dermatology Janardhan B et al. Int J Res Dermatol. 2017 Mar;3(1):74-78 http://www.ijord.com Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20164248
Vancomycin-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) masquerading septic shock an unusual presentation of a rare disease
 Mawri et al. Journal of Intensive Care (2015) 3:47 DOI 10.1186/s40560-015-0114-3 CASE REPORT Vancomycin-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) masquerading septic shock an unusual presentation
Mawri et al. Journal of Intensive Care (2015) 3:47 DOI 10.1186/s40560-015-0114-3 CASE REPORT Vancomycin-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) masquerading septic shock an unusual presentation
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis in the ambulatory care setting
 www.edoriumjournals.com CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis in the ambulatory care setting LT Mark C. Hubbard, LT John C. Walsh, LCDR Megan A. Brelsford ABSTRACT
www.edoriumjournals.com CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis in the ambulatory care setting LT Mark C. Hubbard, LT John C. Walsh, LCDR Megan A. Brelsford ABSTRACT
Herbal and homeopathic products, often considered natural and non-toxic, can also cause adverse drug reactions.
 Idiosyncratic and potentially serious cutaneous adverse drug reactions (CADRs), although relatively rare, account for significant morbidity and mortality. RANNAKOE J LEHLOENYA, BSc, MB ChB, FCDerm (SA)
Idiosyncratic and potentially serious cutaneous adverse drug reactions (CADRs), although relatively rare, account for significant morbidity and mortality. RANNAKOE J LEHLOENYA, BSc, MB ChB, FCDerm (SA)
REGISTRY OF SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE REACTIONS TO DRUGS AND COLLECTION OF BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES. R e g i S C A R PATIENT'S DATA. Age country of birth
 REGISTRY OF SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE REACTIONS TO DRUGS AND COLLECTION OF BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES R e g i S C A R PATIENT'S DATA Initials of the patient date of birth Age country of birth Gender male female
REGISTRY OF SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE REACTIONS TO DRUGS AND COLLECTION OF BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES R e g i S C A R PATIENT'S DATA Initials of the patient date of birth Age country of birth Gender male female
Drug Allergy A Guide to Diagnosis and Management
 Drug Allergy A Guide to Diagnosis and Management (Version 1 April 2015 updated April 2018) Author: Jed Hewitt Chief Pharmacist, Governance & Professional Practice Date of Preparation: April 2015 Updated:
Drug Allergy A Guide to Diagnosis and Management (Version 1 April 2015 updated April 2018) Author: Jed Hewitt Chief Pharmacist, Governance & Professional Practice Date of Preparation: April 2015 Updated:
The histopathological spectrum of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) and its differentiation from generalized pustular psoriasis
 J Cutan Pathol 2010: 37: 1220 1229 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2010.01612.x John Wiley & Sons. Printed in Singapore Copyright 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S Journal of Cutaneous Pathology The histopathological
J Cutan Pathol 2010: 37: 1220 1229 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2010.01612.x John Wiley & Sons. Printed in Singapore Copyright 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S Journal of Cutaneous Pathology The histopathological
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham
 Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham Spotlight Seminar 30 th September 2010 Why is this important? Urgent recognition and treatment of dermatologic emergencies can be life saving and prevent long term
Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham Spotlight Seminar 30 th September 2010 Why is this important? Urgent recognition and treatment of dermatologic emergencies can be life saving and prevent long term
THE SPECTRUM OF HISTOPATHOLOGICAL FEATURES IN ACUTE GENERALISED EXANTHEMATOUS PUSTULOSIS: A STUDY OF 102 CASES
 These articles have been accepted for publication in the British Journal of Dermatology and are currently being edited and typeset. Readers should note that articles published below have been fully refereed,
These articles have been accepted for publication in the British Journal of Dermatology and are currently being edited and typeset. Readers should note that articles published below have been fully refereed,
Cutaneous Drug Reactions
 Cutaneous Drug Reactions Andrei Metelitsa, MD, FRCPC, FAAD Co-Director, Institute for Skin Advancement Clinical Associate Professor, Dermatology University of Calgary, Canada Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses
Cutaneous Drug Reactions Andrei Metelitsa, MD, FRCPC, FAAD Co-Director, Institute for Skin Advancement Clinical Associate Professor, Dermatology University of Calgary, Canada Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses
New product information wording Extracts from PRAC recommendations on signals
 12 October 2017 EMA/PRAC/610988/2017 Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) New product information wording Extracts from PRAC recommendations on signals Adopted at the 25-29 September 2017
12 October 2017 EMA/PRAC/610988/2017 Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) New product information wording Extracts from PRAC recommendations on signals Adopted at the 25-29 September 2017
Cutaneous drug reactions
 Maintenance of Certification clinical management series Series editor: James T. Li, MD, PhD Cutaneous drug reactions David A. Khan, MD Dallas, Tex INSTRUCTIONS Credit can now be obtained, free for a limited
Maintenance of Certification clinical management series Series editor: James T. Li, MD, PhD Cutaneous drug reactions David A. Khan, MD Dallas, Tex INSTRUCTIONS Credit can now be obtained, free for a limited
Future of Pediatrics: Blisters, Hives and Other Tales from the Emergency Room June 14 th, 2016
 A. Yasmine Kirkorian MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology & Pediatrics Children s National Health System George Washington University School of Medicine & Health Sciences Future of Pediatrics: Blisters,
A. Yasmine Kirkorian MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology & Pediatrics Children s National Health System George Washington University School of Medicine & Health Sciences Future of Pediatrics: Blisters,
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Toxic epidermal necrolysis, DRESS, AGEP Bouvresse, Sophie; Valeyrie-Allanore, Laurence; Ortonne, Nicolas; Konstantinou, Marie Pauline; Kardaun, Sylvia H.; Bagot, Martine; Wolkenstein,
University of Groningen Toxic epidermal necrolysis, DRESS, AGEP Bouvresse, Sophie; Valeyrie-Allanore, Laurence; Ortonne, Nicolas; Konstantinou, Marie Pauline; Kardaun, Sylvia H.; Bagot, Martine; Wolkenstein,
allergy Asia Pacific Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Dr. Hasan Sadikin General Hospital Bandung, Indonesia from
 pissn -876 eissn -868 Original Article Asia Pac Allergy 6;6:-7 Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Dr. Hasan Sadikin General Hospital Bandung, Indonesia from 9 Oki Suwarsa *, Wulan
pissn -876 eissn -868 Original Article Asia Pac Allergy 6;6:-7 Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Dr. Hasan Sadikin General Hospital Bandung, Indonesia from 9 Oki Suwarsa *, Wulan
BJD. Summary. British Journal of Dermatology THERAPEUTICS
 THERAPEUTICS BJD British Journal of Dermatology Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms: is cutaneous phenotype a prognostic marker for outcome? A review of clinicopathological features of
THERAPEUTICS BJD British Journal of Dermatology Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms: is cutaneous phenotype a prognostic marker for outcome? A review of clinicopathological features of
Correspondence should be addressed to Wanjarus Roongpisuthipong; rr
 Dermatology Research and Practice, Article ID 237821, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/237821 Research Article Retrospective Analysis of Corticosteroid Treatment in Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and/or
Dermatology Research and Practice, Article ID 237821, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/237821 Research Article Retrospective Analysis of Corticosteroid Treatment in Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and/or
Hospital-based Dermatopathology. Janis M. Taube, MD Director of Dermatopathology Johns Hopkins University SOM
 Hospital-based Dermatopathology Janis M. Taube, MD Director of Dermatopathology Johns Hopkins University SOM Overview Drug-eruptions Erythroderma Manifestations of renal disease Blistering disorders Vasculitis/Vasculopathy
Hospital-based Dermatopathology Janis M. Taube, MD Director of Dermatopathology Johns Hopkins University SOM Overview Drug-eruptions Erythroderma Manifestations of renal disease Blistering disorders Vasculitis/Vasculopathy
Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India.
 Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions Related to Systemic Antibiotics
 MAJOR ARTICLE Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions Related to Systemic Antibiotics Ying-Fang Lin, 1 Chih-Hsun Yang, 2,3 Hu Sindy, 1,3 Jing-Yi Lin, 2,3 Chung-Yee Rosaline Hui, 2,3 Yun-Chen Tsai, 2 Ting-Shu
MAJOR ARTICLE Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions Related to Systemic Antibiotics Ying-Fang Lin, 1 Chih-Hsun Yang, 2,3 Hu Sindy, 1,3 Jing-Yi Lin, 2,3 Chung-Yee Rosaline Hui, 2,3 Yun-Chen Tsai, 2 Ting-Shu
An Evidenced-Based Approach to the Adult with a Morbilliform Eruption
 Relatively An Evidenced-Based Approach to the Adult with a Morbilliform Eruption Ben Kaffenberger, MD Assistant Professor, Dermatology Director, Inpatient Dermatology Consult Service Ohio State University
Relatively An Evidenced-Based Approach to the Adult with a Morbilliform Eruption Ben Kaffenberger, MD Assistant Professor, Dermatology Director, Inpatient Dermatology Consult Service Ohio State University
Clinico-epidemiological profile, including body mass index of Malaysian children with psoriasis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinico-epidemiological profile, including body mass index of Malaysian children with psoriasis Siew Eng Choon, FRCP, Chin Fang Ngim, MRCP, Premaa Supramaniam, BSc, Kwee Eng Tey, MRCP,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinico-epidemiological profile, including body mass index of Malaysian children with psoriasis Siew Eng Choon, FRCP, Chin Fang Ngim, MRCP, Premaa Supramaniam, BSc, Kwee Eng Tey, MRCP,
CUTANEOUS DRUG REACTIONS OR I WOULDN T HAVE SEEN IT, IF I HADN T BELIEVED IT Edmund J. Rosser Jr., DVM, DACVD
 CUTANEOUS DRUG REACTIONS OR I WOULDN T HAVE SEEN IT, IF I HADN T BELIEVED IT Edmund J. Rosser Jr., DVM, DACVD DERMATOLOGY Pathogenesis Immunologic: can involve Type I, II, III, IV hypersensitivity reactions.
CUTANEOUS DRUG REACTIONS OR I WOULDN T HAVE SEEN IT, IF I HADN T BELIEVED IT Edmund J. Rosser Jr., DVM, DACVD DERMATOLOGY Pathogenesis Immunologic: can involve Type I, II, III, IV hypersensitivity reactions.
A Case Report on Amoxicillin Induced Stevens- Johnson Syndrome
 Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 2 (2016) Issue 11 A Case Report on Amoxicillin Induced Stevens- Johnson Syndrome Rajendra Singh Airee*; Aastha Rawal; Binu Mathew; H. Doddayya Abstract
Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 2 (2016) Issue 11 A Case Report on Amoxicillin Induced Stevens- Johnson Syndrome Rajendra Singh Airee*; Aastha Rawal; Binu Mathew; H. Doddayya Abstract
Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA)
 Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) Ahmed Abdullah Alhumidi King saud university, Riyadh, kingdom of Saudi Arabia Abstract Background: This
Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) Ahmed Abdullah Alhumidi King saud university, Riyadh, kingdom of Saudi Arabia Abstract Background: This
Annex I. Scientific conclusions and grounds for the variation to the terms of the Marketing Authorisation(s)
 Annex I Scientific conclusions and grounds for the variation to the terms of the Marketing Authorisation(s) 1 Scientific conclusions Taking into account the PRAC Assessment Report on the PSUR(s) for ibuprofen
Annex I Scientific conclusions and grounds for the variation to the terms of the Marketing Authorisation(s) 1 Scientific conclusions Taking into account the PRAC Assessment Report on the PSUR(s) for ibuprofen
A 10-years retrospective study on Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (SCARs) in a tertiary hospital in Penang, Malaysia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A 10-years retrospective study on Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (SCARs) in a tertiary hospital in Penang, Malaysia Chai Har Loo, MRCP, Wooi Chiang Tan, AdvMDerm, Yek Huan Khor, AdvMDerm,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE A 10-years retrospective study on Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (SCARs) in a tertiary hospital in Penang, Malaysia Chai Har Loo, MRCP, Wooi Chiang Tan, AdvMDerm, Yek Huan Khor, AdvMDerm,
Skin Manifestations of Drug Reactions
 Skin Manifestations of Drug Reactions Dr Carol Hlela, Division of Dermatology Department of Medicine, University of Cape Town and Red Cross Children s Hospital What are the Skin Manifestations of Drug
Skin Manifestations of Drug Reactions Dr Carol Hlela, Division of Dermatology Department of Medicine, University of Cape Town and Red Cross Children s Hospital What are the Skin Manifestations of Drug
Dilantin (phenytoin) ROBERT A. SCHWARTZ
 Dilantin (phenytoin) ROBERT A. SCHWARTZ Bailey & Galyen Attorney in Charge, Mass Tort Litigation Managing Attorney, Houston 18333 Egret Bay Blvd., Suite 120 Houston, Texas 77058 Toll Free: (866) 715-1529
Dilantin (phenytoin) ROBERT A. SCHWARTZ Bailey & Galyen Attorney in Charge, Mass Tort Litigation Managing Attorney, Houston 18333 Egret Bay Blvd., Suite 120 Houston, Texas 77058 Toll Free: (866) 715-1529
OXCARBAZEPINE-INDUCED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME: A CASE REPORT
 OXCARBAZEPINE-INDUCED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME: A CASE REPORT Lung-Chang Lin, 1,2 Ping-Chin Lai, 3 Sheau-Fang Yang, 4 and Rei-Cheng Yang 1,5 Departments of 1 Pediatrics and 4 Pathology, Kaohsiung Medical
OXCARBAZEPINE-INDUCED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME: A CASE REPORT Lung-Chang Lin, 1,2 Ping-Chin Lai, 3 Sheau-Fang Yang, 4 and Rei-Cheng Yang 1,5 Departments of 1 Pediatrics and 4 Pathology, Kaohsiung Medical
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Drug Allergy. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The audio
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Drug Allergy. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The audio
Title: Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions in Indian population: A systematic review
 Title: Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions in Indian population: A systematic review Review question(s) To carry out a systematic review of the published evidence of the cutaneous adverse drug reactions in
Title: Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions in Indian population: A systematic review Review question(s) To carry out a systematic review of the published evidence of the cutaneous adverse drug reactions in
EFAVIRENZ ASSOCIATED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME
 EFAVIRENZ ASSOCIATED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME To the Editor: Persons with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection are highly susceptible to adverse dermatological reactions to specific medications
EFAVIRENZ ASSOCIATED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME To the Editor: Persons with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection are highly susceptible to adverse dermatological reactions to specific medications
Grover s disease: A case report.
 320 Case report Thai J Dermatol, October-December 2011 ABSTRACT: Grover s disease: A case report. Supicha Chavanich MD, Praneet Sajjachareonpong MD. CHAVANICH C, SAJJACHAREONPONG P. GROVER S DISEASE: A
320 Case report Thai J Dermatol, October-December 2011 ABSTRACT: Grover s disease: A case report. Supicha Chavanich MD, Praneet Sajjachareonpong MD. CHAVANICH C, SAJJACHAREONPONG P. GROVER S DISEASE: A
Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) Outline
 Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) Outline 1. What are Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs)? WHAT WHY HOW 2. How important are ADRs and are they preventable? 3. What are the classifications and mechanisms of ADRs?
Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) Outline 1. What are Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs)? WHAT WHY HOW 2. How important are ADRs and are they preventable? 3. What are the classifications and mechanisms of ADRs?
Warfarin-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis in combination therapy of Henoch- Schönlein purpura nephritis: a case report
 Kasahara et al. BMC Nephrology (2017) 18:237 DOI 10.1186/s12882-017-0648-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Warfarin-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis in combination therapy of Henoch- Schönlein purpura nephritis:
Kasahara et al. BMC Nephrology (2017) 18:237 DOI 10.1186/s12882-017-0648-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Warfarin-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis in combination therapy of Henoch- Schönlein purpura nephritis:
Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children
 May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE
 Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
ANTIBIOTICS ACUTE RHINOSINUSITIS IN CHILDREN
 MARCH 2016 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS This optimal usage guide is mainly intended f primary care health professionnals. It is provided f infmation purposes only and should not replace the clinician s judgement.
MARCH 2016 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS This optimal usage guide is mainly intended f primary care health professionnals. It is provided f infmation purposes only and should not replace the clinician s judgement.
CHAPTER 3 SECONDARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
 CHAPTER 3 SECONDARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS Leong Chong Men Kok Lai Sun Rosnawati Yahya 53 5th Report of the 3.1: Introduction This chapter covers the main secondary glomerulonephritis that were reported to
CHAPTER 3 SECONDARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS Leong Chong Men Kok Lai Sun Rosnawati Yahya 53 5th Report of the 3.1: Introduction This chapter covers the main secondary glomerulonephritis that were reported to
Stevens Johnson Syndrome: How Diagnosis Impacts Disease Course
 Southern Adventist Univeristy KnowledgeExchange@Southern Graduate Research Projects Nursing 12-4-2015 Stevens Johnson Syndrome: How Diagnosis Impacts Disease Course Sharon K. Hart Southern Adventist University,
Southern Adventist Univeristy KnowledgeExchange@Southern Graduate Research Projects Nursing 12-4-2015 Stevens Johnson Syndrome: How Diagnosis Impacts Disease Course Sharon K. Hart Southern Adventist University,
Emergency Dermatology. Emergency Dermatology
 Emergency Dermatology These are rapidly progressive skin conditions and some are potentially lifethreatening. Early recognition is important to implement prompt supportive care and therapy. Some are drug
Emergency Dermatology These are rapidly progressive skin conditions and some are potentially lifethreatening. Early recognition is important to implement prompt supportive care and therapy. Some are drug
Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal Vol. 6 No 1: 14, June 2010
 Wells Syndrome H. Gammaz, H. Amer, A. Adly and S. Mahmoud Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 6 (1): 14 Al-Haud Al-Marsoud Hospital, Cairo, Egypt e-mail: hananderma@hotmail.com Submitted: April 15, 2010
Wells Syndrome H. Gammaz, H. Amer, A. Adly and S. Mahmoud Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 6 (1): 14 Al-Haud Al-Marsoud Hospital, Cairo, Egypt e-mail: hananderma@hotmail.com Submitted: April 15, 2010
Pediatric Dermatology
 Pediatric Dermatology --------- Emergencies & Urgencies Nicholas V. Nguyen, M.D. Director, Pediatric Dermatology Disclosures In the past 12 months, I have had the following financial relationships with
Pediatric Dermatology --------- Emergencies & Urgencies Nicholas V. Nguyen, M.D. Director, Pediatric Dermatology Disclosures In the past 12 months, I have had the following financial relationships with
SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE DRUG REACTIONS: STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME AND TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSISA, A REPORT OF 4 CASES SEEN AT UMMC
 SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE DRUG REACTIONS: STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME AND TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSISA, A REPORT OF 4 CASES SEEN AT UMMC Shasha Khairullah, Rokiah Che Ismail Department of Medicine, Faculty
SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE DRUG REACTIONS: STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME AND TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSISA, A REPORT OF 4 CASES SEEN AT UMMC Shasha Khairullah, Rokiah Che Ismail Department of Medicine, Faculty
Department of Allergy and Immunology. Drug allergy. Dean Tey Paediatric Allergist & Immunologist FRACP LECTURE 2014
 Drug allergy Dean Tey Paediatric Allergist & Immunologist FRACP LECTURE 2014 Outline 1. Background 2. SCAR 3. Mechanism of action 4. Assessment on history 5. Investigations 6. Drug desensitisation 7. Specific
Drug allergy Dean Tey Paediatric Allergist & Immunologist FRACP LECTURE 2014 Outline 1. Background 2. SCAR 3. Mechanism of action 4. Assessment on history 5. Investigations 6. Drug desensitisation 7. Specific
Agenda* The 9th International Congress on Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions (iscar 2015)
 1 of 5 Agenda* The 9th International Congress on Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions (iscar 2015) Co-chairs: Dr. Neil H. Shear at the 23rd World Congress of Dermatology in Vancouver, Canada. Division of Dermatology,
1 of 5 Agenda* The 9th International Congress on Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions (iscar 2015) Co-chairs: Dr. Neil H. Shear at the 23rd World Congress of Dermatology in Vancouver, Canada. Division of Dermatology,
Analysis of Individual Case Safety Reports of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions in Korea
 Original Article Yonsei Med J 2019 Feb;60(2):208-215 pissn: 0513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 Analysis of Individual Case Safety Reports of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions in Korea Min-Gyu Kang 1,2,3, Kyung-Hee
Original Article Yonsei Med J 2019 Feb;60(2):208-215 pissn: 0513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 Analysis of Individual Case Safety Reports of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions in Korea Min-Gyu Kang 1,2,3, Kyung-Hee
Endocarditis. By : Mehrnoush. dianatkhah
 Endocarditis By : Mehrnoush. dianatkhah Case 5.31, 31 years old woman CC : Fever, dyspnea, 3 days postpartum PMH : Mitral prolapse Fever 38.5 WBC : 8900 ESR : 84 CRP : 10.4 Cr : 0.6 NT Pro BNP: 5469 Physical
Endocarditis By : Mehrnoush. dianatkhah Case 5.31, 31 years old woman CC : Fever, dyspnea, 3 days postpartum PMH : Mitral prolapse Fever 38.5 WBC : 8900 ESR : 84 CRP : 10.4 Cr : 0.6 NT Pro BNP: 5469 Physical
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT
 HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 31-35 www.iosrjournals.org Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 31-35 www.iosrjournals.org Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
PROFILE OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS IN SOUTH INDIAN REGION: KARAIKAL D.BADMAPRIYA*, V.SATHISH KUMAR 1
 Page47 Available Online through IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 PROFILE OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS IN SOUTH INDIAN REGION: KARAIKAL D.BADMAPRIYA*, V.SATHISH KUMAR 1 * PHARMACIST, GOVERNMENT GENERAL
Page47 Available Online through IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 PROFILE OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS IN SOUTH INDIAN REGION: KARAIKAL D.BADMAPRIYA*, V.SATHISH KUMAR 1 * PHARMACIST, GOVERNMENT GENERAL
Elizabeth J. Phillips - Professor of Medicine and Pharmacology, John A. Oates Chair in Clinical Research, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, USA
 November 10,2018 Opening OP 9:10 Eishin Morita - Shimane University, Session 1 Moderators Koji Hashimoto & Maja Mockenhaupt SCAR1-1 9:15 SCAR1-2 9:40 SCAR1-3 10:05 Maja Mockenhaupt - Medical Center and
November 10,2018 Opening OP 9:10 Eishin Morita - Shimane University, Session 1 Moderators Koji Hashimoto & Maja Mockenhaupt SCAR1-1 9:15 SCAR1-2 9:40 SCAR1-3 10:05 Maja Mockenhaupt - Medical Center and
Management of carbamazepine induced drug reaction with eosinophlia and systemic symptoms in Mediheal hospital- Nakuru, Kenya: a case report
 International Journal of Research in Dermatology http://www.ijord.com Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20184469 Management of carbamazepine induced drug reaction
International Journal of Research in Dermatology http://www.ijord.com Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20184469 Management of carbamazepine induced drug reaction
1 Introduction. Kenneth Irungu 1 David Nyamu
 Drugs - Real World Outcomes (2017) 4:79 85 DOI 10.1007/s40801-017-0105-x ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Characterization of Stevens Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Among Patients Admitted to
Drugs - Real World Outcomes (2017) 4:79 85 DOI 10.1007/s40801-017-0105-x ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Characterization of Stevens Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Among Patients Admitted to
Big rashes in little patients:
 ! Big rashes in little patients: Severe drug eruptions and cutaneous infections!! Marcia Hogeling, MD, FAAD Assistant Clinical Professor Director, Pediatric Dermatology Division of Dermatology David Geffen
! Big rashes in little patients: Severe drug eruptions and cutaneous infections!! Marcia Hogeling, MD, FAAD Assistant Clinical Professor Director, Pediatric Dermatology Division of Dermatology David Geffen
Erythema gyratumrepens-like eruption in a patient with epidermolysisbullosaacquisita associated with ulcerative colitis
 Erythema gyratumrepens-like eruption in a patient with epidermolysisbullosaacquisita associated with ulcerative colitis A. España C. Sitaru* M. Pretel L. Aguado J. Jimenez# Department of Dermatology, University
Erythema gyratumrepens-like eruption in a patient with epidermolysisbullosaacquisita associated with ulcerative colitis A. España C. Sitaru* M. Pretel L. Aguado J. Jimenez# Department of Dermatology, University
Case Rep Dermatol 2009;1:66 70 DOI: / Key Words Coma Blister Barbiturate Overdose Meningoencephalitis
 66 Coma Blisters Joana Rocha a Teresa Pereira a Filipa Ventura a Fernando Pardal b Celeste Brito a Departments of a Dermatology and b Pathology, Hospital de São Marcos, Braga, Portugal Key Words Coma Blister
66 Coma Blisters Joana Rocha a Teresa Pereira a Filipa Ventura a Fernando Pardal b Celeste Brito a Departments of a Dermatology and b Pathology, Hospital de São Marcos, Braga, Portugal Key Words Coma Blister
Clinical profile of skin diseases in accident and emergency department attenders
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2007) 15, 4-9 Original Article Clinical profile of skin diseases in accident and emergency department attenders CY Chan, KL Kam, CA Graham, TH Rainer, NM Luk Skin problems
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2007) 15, 4-9 Original Article Clinical profile of skin diseases in accident and emergency department attenders CY Chan, KL Kam, CA Graham, TH Rainer, NM Luk Skin problems
CHAPTER 2 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
 CHAPTER 2 Sunita Bavanandan Lim Soo Kun 19 5th Report of the 2.1: Introduction This chapter covers the main primary glomerulonephritis that were reported to the MRRB from the years 2005-2012. Minimal change
CHAPTER 2 Sunita Bavanandan Lim Soo Kun 19 5th Report of the 2.1: Introduction This chapter covers the main primary glomerulonephritis that were reported to the MRRB from the years 2005-2012. Minimal change
Cutaneous adverse drug reactions in a tertiary care hospital
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 202, 4 (2):408-43 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-507 USA CODEN: DPLEB4 Cutaneous
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 202, 4 (2):408-43 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-507 USA CODEN: DPLEB4 Cutaneous
An unpredictable, dose-independent adverse drug reaction which is immunologically or IgEmediated.
 R H E U M A T I S M D I S O R D E R S A N D A L L E R G I E S APPROACH TO DRUG ALLERGY Dr Bernard Thong DEFINITION OF DRUG ALLERGY An unpredictable, dose-independent adverse drug reaction which is immunologically
R H E U M A T I S M D I S O R D E R S A N D A L L E R G I E S APPROACH TO DRUG ALLERGY Dr Bernard Thong DEFINITION OF DRUG ALLERGY An unpredictable, dose-independent adverse drug reaction which is immunologically
PHM142 Autoimmune Disorders + Idiosyncratic Drug Reactions
 PHM142 Autoimmune Disorders + Idiosyncratic Drug Reactions 1 Autoimmune Disorders Auto-reactivity: low physiological levels (e.g. tolerance) vs. pathogenic levels 80+ types of autoimmune diseases affect
PHM142 Autoimmune Disorders + Idiosyncratic Drug Reactions 1 Autoimmune Disorders Auto-reactivity: low physiological levels (e.g. tolerance) vs. pathogenic levels 80+ types of autoimmune diseases affect
A case of rosacea fulminans in a pregnant woman
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2018) 26, 122-126 Views and Practice A case of rosacea fulminans in a pregnant woman JE Seol, SH Park, JU Kim, GJ Cho, SH Moon, H Kim Introduction Rosacea fulminans (RF)
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2018) 26, 122-126 Views and Practice A case of rosacea fulminans in a pregnant woman JE Seol, SH Park, JU Kim, GJ Cho, SH Moon, H Kim Introduction Rosacea fulminans (RF)
Autoimmune progesterone dermatitis presented as acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis
 Case Report Autoimmune progesterone dermatitis presented as acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis Suchibrata Das, Sangita Patra*, Saikat Banerjee, Saswati Das Department of Dermatology, Venereology
Case Report Autoimmune progesterone dermatitis presented as acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis Suchibrata Das, Sangita Patra*, Saikat Banerjee, Saswati Das Department of Dermatology, Venereology
A Retrospective Study of Spectrum of Nevirapine Induced Cutaneous Drug Reactions in HIV Positive Patients
 Journal of US-China Medical Science 12 (2015) 85-89 doi: 10.17265/1548-6648/2015.02.008 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Retrospective Study of Spectrum of Nevirapine Induced Cutaneous Drug Reactions in HIV Positive
Journal of US-China Medical Science 12 (2015) 85-89 doi: 10.17265/1548-6648/2015.02.008 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Retrospective Study of Spectrum of Nevirapine Induced Cutaneous Drug Reactions in HIV Positive
Skin testing with β-lactam antibiotics for diagnosis of β-lactam hypersensitivity in children
 Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Skin testing with β-lactam antibiotics for diagnosis of β-lactam hypersensitivity in children Wiparat Manuyakorn, 1 Prapasiri Singvijarn,
Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Skin testing with β-lactam antibiotics for diagnosis of β-lactam hypersensitivity in children Wiparat Manuyakorn, 1 Prapasiri Singvijarn,
Drug Allergy HSJ 19/09/2011
 Drug Allergy HSJ 19/09/2011 BSACI Guidelines Definitions Mechanisms Clinical Features Risk factors Diagnosis Investigations Criteria for referral/investigation Mirakian et al. Clin Exp All 2008 ; 39: 43-61
Drug Allergy HSJ 19/09/2011 BSACI Guidelines Definitions Mechanisms Clinical Features Risk factors Diagnosis Investigations Criteria for referral/investigation Mirakian et al. Clin Exp All 2008 ; 39: 43-61
=ﻰﻤاﻤﺤﻠا ﺔﻴﻘﻠﺤﻠا ﺔذﺒاﻨﻠا
 1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease:
 Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease: Hematological GIT Behcet s HIV 5. Associated with dermatological diseases:
Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease: Hematological GIT Behcet s HIV 5. Associated with dermatological diseases:
cipro loxacin; stevens-johnson syndrome; urinary tract infection; adverse drug reaction
 Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 3 (2017) Issue 7 ISSN 2379-1039 Cipro loxacin induced Stevens Johnson syndrome: A case report on Dermatology department P Mohammed Sha i*; K Narotham
Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 3 (2017) Issue 7 ISSN 2379-1039 Cipro loxacin induced Stevens Johnson syndrome: A case report on Dermatology department P Mohammed Sha i*; K Narotham
Diagnostic evaluation of suspected Drug-Induced Liver Injury
 Diagnostic evaluation of suspected Drug-Induced Liver Injury Ynto de Boer, MD Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Disclosure No disclosures Drug-induced liver injury? Outline What is DILI? What,
Diagnostic evaluation of suspected Drug-Induced Liver Injury Ynto de Boer, MD Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Disclosure No disclosures Drug-induced liver injury? Outline What is DILI? What,
A Case Report on Paracetamol Induced Generalized Fixed Drug Eruptions
 Human Journals Case report November 2016 Vol.:7, Issue:4 All rights are reserved by Dr. C Sugunakar Raju et al. A Case Report on Paracetamol Induced Generalized Fixed Drug Eruptions Keywords: Skin Eruptions,
Human Journals Case report November 2016 Vol.:7, Issue:4 All rights are reserved by Dr. C Sugunakar Raju et al. A Case Report on Paracetamol Induced Generalized Fixed Drug Eruptions Keywords: Skin Eruptions,
Clozapine Induced Skin Rash a report of two cases
 Jambulkar et al. : Clozapine induced skin rash 405 Case Report Clozapine Induced Skin Rash a report of two cases Reena Jambulkar 1, Sagar Karia 2, Akshay Chordia 3, Avinash De Sousa 4, Nilesh Shah 5 1,3
Jambulkar et al. : Clozapine induced skin rash 405 Case Report Clozapine Induced Skin Rash a report of two cases Reena Jambulkar 1, Sagar Karia 2, Akshay Chordia 3, Avinash De Sousa 4, Nilesh Shah 5 1,3
Original Article. Barvaliya M, Sanmukhani J, Patel T, Paliwal N, Shah H 1, Tripathi C
 Original Article Drug-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and SJS-TEN overlap: A multicentric retrospective study Barvaliya M, Sanmukhani J, Patel T, Paliwal N, Shah
Original Article Drug-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and SJS-TEN overlap: A multicentric retrospective study Barvaliya M, Sanmukhani J, Patel T, Paliwal N, Shah
ACUTE ANNULAR URTICARIA IN A CHILD
 The West London Medical Journal 2013 Vol 5 No 2 pp 1-5 ACUTE ANNULAR URTICARIA IN A CHILD Aaron Yon Dayse Fernandes Michelle Pike Jodi Newcombe Colin Michie 1. ABSTRACT Urticarial skin rashes have a range
The West London Medical Journal 2013 Vol 5 No 2 pp 1-5 ACUTE ANNULAR URTICARIA IN A CHILD Aaron Yon Dayse Fernandes Michelle Pike Jodi Newcombe Colin Michie 1. ABSTRACT Urticarial skin rashes have a range
Antibiotic allergy in the Intensive Care. Sanjay Swaminathan Clinical Immunologist, Westmead and Blacktown Hospitals September 28, 2017
 Antibiotic allergy in the Intensive Care Sanjay Swaminathan Clinical Immunologist, Westmead and Blacktown Hospitals September 28, 2017 Outline of talk True or false? Case example Types of drug allergy
Antibiotic allergy in the Intensive Care Sanjay Swaminathan Clinical Immunologist, Westmead and Blacktown Hospitals September 28, 2017 Outline of talk True or false? Case example Types of drug allergy
Bugs and Drugs: What s New in Hypersensitivity Reactions?
 Bugs and Drugs: What s New in Hypersensitivity Reactions? Erin Mathes, MD Associate Professor of Dermatology and Pediatrics University of California, San Francisco DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY
Bugs and Drugs: What s New in Hypersensitivity Reactions? Erin Mathes, MD Associate Professor of Dermatology and Pediatrics University of California, San Francisco DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY
New product information wording Extracts from PRAC recommendations on signals
 20 July 2017 EMA/PRAC/406976/2017 Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) New product information wording Extracts from PRAC recommendations on signals Adopted at the 3-6 July 2017 PRAC The
20 July 2017 EMA/PRAC/406976/2017 Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) New product information wording Extracts from PRAC recommendations on signals Adopted at the 3-6 July 2017 PRAC The
GOOD MORNING! AUGUST 5, 2014
 GOOD MORNING! AUGUST 5, 2014 PREP QUESTION During the health supervision visit of a term newborn boy, his mother relates that a cousins child died at age 4 months from sudden infant death syndrome. She
GOOD MORNING! AUGUST 5, 2014 PREP QUESTION During the health supervision visit of a term newborn boy, his mother relates that a cousins child died at age 4 months from sudden infant death syndrome. She
Analysis of causation of Stevens Johnson Syndrome in a patient of rheumatoid arthritis with increased dose of methotrexate
 Original Research Article Analysis of causation of Stevens Johnson Syndrome in a patient of rheumatoid arthritis with increased dose of methotrexate Manab Nandy 1, Sangeeta De 2*, Mustafa Asad 2, Nirmal
Original Research Article Analysis of causation of Stevens Johnson Syndrome in a patient of rheumatoid arthritis with increased dose of methotrexate Manab Nandy 1, Sangeeta De 2*, Mustafa Asad 2, Nirmal
Beta-Lactam Use in Penicillin Allergic Patients Clinical Guideline
 RECOMMENDATIONS: Beta-Lactam Use in Penicillin Allergic Patients Clinical Guideline 1. Penicillin Anaphylaxis (Type-1 IgE Mediated hypersensitivity) a. May use Cephalosporins and Carbapenems 2. Penicillin
RECOMMENDATIONS: Beta-Lactam Use in Penicillin Allergic Patients Clinical Guideline 1. Penicillin Anaphylaxis (Type-1 IgE Mediated hypersensitivity) a. May use Cephalosporins and Carbapenems 2. Penicillin
AOU Ospedali Riuniti - Ancona
 AOU Ospedali Riuniti - Ancona Ospedale Materno-Infantile di Alta Specializzazione G. Salesi UOC Pediatria Allergia a farmaci e infezioni: tra coesistenza e casualità fabrizio franceschini Drug Hypersensitivity
AOU Ospedali Riuniti - Ancona Ospedale Materno-Infantile di Alta Specializzazione G. Salesi UOC Pediatria Allergia a farmaci e infezioni: tra coesistenza e casualità fabrizio franceschini Drug Hypersensitivity
Preventable Adverse Drug Reaction in pharmacovigilance database
 Preventable Adverse Drug Reaction in pharmacovigilance database Vu Dinh Hoa National Drug Information and Adverse Drug Monitoring Center Hanoi University of Pharmacy Vietnam 1 Introductions Until 2017:
Preventable Adverse Drug Reaction in pharmacovigilance database Vu Dinh Hoa National Drug Information and Adverse Drug Monitoring Center Hanoi University of Pharmacy Vietnam 1 Introductions Until 2017:
CPC. Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand
 CPC Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand A 53 year-old woman with fever, facial swelling and rashes on face, trunk and upper extremities for 3
CPC Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand A 53 year-old woman with fever, facial swelling and rashes on face, trunk and upper extremities for 3
A. Erythema multiforme and related diseases
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Erythema, Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis) Erythema is caused by telangiectasia or hyperemia in the papillary and reticular
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Erythema, Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis) Erythema is caused by telangiectasia or hyperemia in the papillary and reticular
Dr. Venkateswari. R. Dr. Janani Sankar s unit Kanchi Kamakoti CHILDS Trust Hospital
 Dr. Venkateswari. R. Dr. Janani Sankar s unit Kanchi Kamakoti CHILDS Trust Hospital Acknowledgements: KKCTH Dr. Ramkumar Consultant Dermatologist Dr. Ramprakash Consultant Ophthalmologist Dr. Prasad Manne
Dr. Venkateswari. R. Dr. Janani Sankar s unit Kanchi Kamakoti CHILDS Trust Hospital Acknowledgements: KKCTH Dr. Ramkumar Consultant Dermatologist Dr. Ramprakash Consultant Ophthalmologist Dr. Prasad Manne
CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE
 CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE Generalized vesiculo-bullous and pustular eruption in an adult man Hassab El-Naby H, MD, El-Khalawany M, MD Department of Dermatology, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt CLINICAL
CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE Generalized vesiculo-bullous and pustular eruption in an adult man Hassab El-Naby H, MD, El-Khalawany M, MD Department of Dermatology, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt CLINICAL
Stevens - Johnson syndrome (SJS) and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) In Sarawak: A Four Years Review
 Stevens - Johnson syndrome (SJS) and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) In Sarawak: A Four Years Review Yap FBB, MRCP; Wahiduzzaman M, MBBS; Pubalan M, MRCP. Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 4 (1): 1,
Stevens - Johnson syndrome (SJS) and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) In Sarawak: A Four Years Review Yap FBB, MRCP; Wahiduzzaman M, MBBS; Pubalan M, MRCP. Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 4 (1): 1,
Penicillin Allergy and Use of Other Antibiotics
 Penicillin Allergy and Use of Other Antibiotics 7300-646PT Policy No.: 7310-646PT 8790-646PT Original Policy Date: 10/10/2016 Revision Date(s): Review Date(s): Approval: 11/17/16 Pharmacy & Therapeutics
Penicillin Allergy and Use of Other Antibiotics 7300-646PT Policy No.: 7310-646PT 8790-646PT Original Policy Date: 10/10/2016 Revision Date(s): Review Date(s): Approval: 11/17/16 Pharmacy & Therapeutics
Defaulter rate of follow-up of patients with gonorrhoea at the Genitourinary Medicine Clinic
 Original Article Defaulter rate of follow-up of patients with gonorrhoea at the Genitourinary Medicine Clinic CC Chang, MBBS, MRCP, K Akbal, MBBS, HB Gangaram, MBBS, FRCP and Suraiya H Hussein MBBS, FRCP
Original Article Defaulter rate of follow-up of patients with gonorrhoea at the Genitourinary Medicine Clinic CC Chang, MBBS, MRCP, K Akbal, MBBS, HB Gangaram, MBBS, FRCP and Suraiya H Hussein MBBS, FRCP
건강한성인에서의오진하기쉬운포도구균성열상피부증후군의치험례. Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome in a Healthy Adult: Easy to Misdiagnose
 Archives of Hand and Microsurgery Arch Hand Microsurg 2018;23(4):271-276. https://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.2018.23.4.271 pissn 2586-3290 eissn 2586-3533 Case Report 건강한성인에서의오진하기쉬운포도구균성열상피부증후군의치험례 김홍일ㆍ곽찬이ㆍ박언주
Archives of Hand and Microsurgery Arch Hand Microsurg 2018;23(4):271-276. https://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.2018.23.4.271 pissn 2586-3290 eissn 2586-3533 Case Report 건강한성인에서의오진하기쉬운포도구균성열상피부증후군의치험례 김홍일ㆍ곽찬이ㆍ박언주
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Clopidogrel/Acetylsalicylic acid Teva (clopidogrel / acetylsalicylic acid)
 EMA/411850/2014 London, 28 July 2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for (clopidogrel / acetylsalicylic acid) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for, which details the measures
EMA/411850/2014 London, 28 July 2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for (clopidogrel / acetylsalicylic acid) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for, which details the measures
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Max Brinsmead PhD FRANZCOG July 2011
 Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Max Brinsmead PhD FRANZCOG July 2011 This talk What is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease? Why it is important How it is spread Diagnosis Treatment Prevention What is PID? Inflammation
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Max Brinsmead PhD FRANZCOG July 2011 This talk What is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease? Why it is important How it is spread Diagnosis Treatment Prevention What is PID? Inflammation
Personalized Medical Care:Recognition, Management, and Maybe Prevention of Cutaneous Hypersensitivity Reactions
 Personalized Medical Care:Recognition, Management, and Maybe Prevention of Cutaneous Hypersensitivity Reactions Bernard A. Cohen, M.D. Johns Hopkins Children s Center Baltimore, Maryland (NO disclosures)
Personalized Medical Care:Recognition, Management, and Maybe Prevention of Cutaneous Hypersensitivity Reactions Bernard A. Cohen, M.D. Johns Hopkins Children s Center Baltimore, Maryland (NO disclosures)
Elements for a Public Summary
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Rapenin (phenoxymethylpenicillin potassium) is indicated for the treatment of infections caused by penicillin-sensitive bacteria.
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Rapenin (phenoxymethylpenicillin potassium) is indicated for the treatment of infections caused by penicillin-sensitive bacteria.
CHAPTER 2. Primary Glomerulonephritis
 2nd Report of the PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS CHAPTER 2 Primary Glomerulonephritis Sunita Bavanandan Lee Han Wei Lim Soo Kun 21 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 2nd Report of the 2.1 Introduction This chapter
2nd Report of the PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS CHAPTER 2 Primary Glomerulonephritis Sunita Bavanandan Lee Han Wei Lim Soo Kun 21 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 2nd Report of the 2.1 Introduction This chapter
Prevention of severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions: the emerging value of pharmacogenetic screening
 CMAJ Cases Prevention of severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions: the emerging value of pharmacogenetic screening Suran L. Fernando MB BS PhD, Andrew J. Broadfoot MB BS Previously published at www.cmaj.ca
CMAJ Cases Prevention of severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions: the emerging value of pharmacogenetic screening Suran L. Fernando MB BS PhD, Andrew J. Broadfoot MB BS Previously published at www.cmaj.ca
Adverse drug reactions
 Medications William Smith Adverse drug reactions Allergy? Side-effect? Intolerance? Background Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) vary from life-threatening anaphylaxis to minor common side-effects. Objective
Medications William Smith Adverse drug reactions Allergy? Side-effect? Intolerance? Background Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) vary from life-threatening anaphylaxis to minor common side-effects. Objective
