Vancomycin-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) masquerading septic shock an unusual presentation of a rare disease
|
|
|
- Stephanie Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mawri et al. Journal of Intensive Care (2015) 3:47 DOI /s CASE REPORT Vancomycin-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) masquerading septic shock an unusual presentation of a rare disease Sagger Mawri 1*, Tarun Jain 1, Jainil Shah 1, Gina Hurst 2 and Jennifer Swiderek 3 Open Access Abstract Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a rare cutaneous adverse reaction characterized by acute sterile pustular eruptions, mostly induced by medications. Antibiotics are the most commonly implicated drugs; however, there have only been two previous reports of vancomycin-induced AGEP in the literature. In this case, we present the clinical course of a 56-year-old man who was admitted to the intensive care unit with an unusually severe form of AGEP mimicking septic shock, which developed after the recent use of vancomycin. Despite cessation of the offending agent, our patient continued to clinically decline with development of worsening skin eruptions and hemodynamic instability necessitating vasopressor support. The patient promptly responded to systemic steroid therapy with complete resolution of AGEP. In addition to highlighting the implication of vancomycin in AGEP, we herein discuss the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and management of AGEP, particularly in severe cases admitted to the intensive care unit. Keywords: Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, Vancomycin, Steroids, Septic shock, Drug eruption Background Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a rare disorder characterized by an acute-onset severe cutaneous reaction manifesting as several non-follicular pustules on a diffuse erythematous edema [1, 2]. It is usually a drug-related reaction, with antibiotics most commonly implicated [2]. It is typically a self-limited condition that resolves spontaneously with cessation of the offending agent. While it typically has systemic features such as fever and leukocytosis, it rarely causes multi-organ involvement [3]. Herein, we describe a unique case of vancomycininduced AGEP in a middle-aged male presenting with distributive shock and multi-org. Case presentation A 56-year-old man with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme underwent craniotomy and tumor resection * Correspondence: smawri1@hfhs.org 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Henry Ford Hospital, 2799 W Grand Blvd, Detroit, MI 48202, USA Full list of author information is available at the end of the article followed by external beam radiation and concurrent chemotherapy with temozolomide. His post-operative course was complicated by an epidural abscess, which was initially drained. Fluid cultures revealed methicillinresistant streptococcus epidermitis (MRSE). The patient subsequently underwent resection of the abscess followed by cranioplasty with placement of a vancomycinimpregnated titanium mesh to repair the skull defect. He was discharged home on a course of steroid therapy for vasogenic edema noted on post-operative brain MRI as well as an 8-week course of intravenous vancomycin administered via a peripherally inserted central catheter. His steroid taper was dexamethasone 4 mg po twice a day for 3 days, then 2 mg twice a day for 3 days, then 2 mg once a day for 3 days, and 1 mg once a day for 3 days. The patient tolerated the antibiotic infusion well. Two weeks later, having completed his dexamethasone taper 2 days prior, he presented to the emergency department complaining of a diffuse red, itchy rash. He also reported experiencing fevers reaching 38 C and chills over the past day. He denied any face or tongue swelling, nausea, 2015 Mawri et al. Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
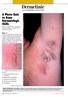
2 Mawri et al. Journal of Intensive Care (2015) 3:47 Page 2 of 5 vomiting, abdominal pain, or diarrhea. He reported no prior skin rashes or allergic reactions and no new medications or other antibiotics. He was not on any other medications except the IV antibiotic infusion. On presentation, the patient was febrile at 38.4 C, tachycardic at 130/min, tachypneic at 32/min, hypotensive at 88/55 mmhg, and saturating 96 % on room air. Physical examination revealed numerous small studded pustules on an erythematous background on the forehead, frontal scalp, cheeks, trunk, upper and lower extremities, and axilla, with numerous erythematous macules and papules coalescing into plaques noted on the back, trunk, and extremities (Fig. 1). There was no evidence of mucous membrane involvement, lymphadenopathy, or organomegaly. There was no neck stiffness, changes in speech, numbness, or weakness. Initial laboratory studies revealed a normal white blood cell count (9200/μL) with a left shift (22 % bands) and without eosinophilia, an elevated lactate level (3.2 mmol/l), normal TSH, and minimally elevated C- reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. His serum creatinine was 1.2 mg/dl with GFR of 89 ml/min. His liver function tests were mildly elevated (AST 56 IU/L; ALT 50 IU/L). The patient was aggressively resuscitated with multiple intravenous crystalloid fluid boluses. Vancomycin was stopped and intravenous linezolid was started. Chest radiograph was normal. Brain MRI did not show evidence of leptomeningeal enhancement or signs of recurrent infection. Abdominal ultrasound was unremarkable. The patient was admitted to the infectious disease ward to undergo further work-up. Dermatology was consulted and skin biopsies were obtained. He was started on topical steroids for the skin rash, which was suspected to be acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. However, the patient continued to have fevers, and he remained tachycardic, tachypneic, and hypotensive despite multiple intravenous fluid boluses. His urine output became diminished and his mental status became depressed. His antibiotic coverage was broadened to include intravenous cefepime and metronidazole in addition to linezolid. He was transferred overnight to the medical intensive care unit for escalation of care and suspected septic shock. While in the intensive care unit, the patient was continued on empiric broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage and given additional intravenous fluid boluses. He continued to have tachycardia, tachypnea, increased work of breathing, and fevers reaching 39 C. The skin examination worsened, with more diffuse skin involvement and development of edema of the face. Laboratory investigation revealed bandemia (28 %). He developed increasing somnolence, reduced urine output, signs of volume overload with elevated central venous pressure (14 mmhg), and increasing oxygen requirements. Vasopressors were started for hypotension. The infectious work-up was negative to date, including multiple sets of negative blood cultures. Histopathological examination of the skin punch biopsy revealed sub-corneal and intraepidermal pustules, widespread spongiosis, and neutrophil infiltration around the vessels in the papillary dermis findings consistent with acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (Fig. 2). In light of the patient s worsening clinical status and apparent lack of response to topical steroids, he was started on high-dose steroids with Solu-Medrol 80 mg IV daily per recommendations from the dermatology consult team. The patient s weight was 79.5 kg; thus, steroid dosing was determined using 1 mg/kg dosing calculation, which has Fig. 1 Day 3 of hospital admission, before initiation of systemic steroid therapy. Numerous small studded pustules on an erythematous background with numerous erythematous macules and papules coalescing into plaques are noted in various body parts Fig. 2 Histopathology of skin biopsy revealing spongiotic epidermis with focal parakeratosis, exocytosis, and spongiotic vesicles, along with papillary dermal edema, superficial dermal perivascular inflammatory infiltrate, and mixed dermal interstitial inflammation with eosinophils (H&E, 10). The arrow points to the "papillary dermal edema and superficial dermal perivascular inflammatory infiltrate"
3 Mawri et al. Journal of Intensive Care (2015) 3:47 Page 3 of 5 been shown to be an effective starting dose for severe AGEP and similar dermatologic conditions. The patient responded remarkably well to the systemic steroids. He had rapid clinical improvement and within hours became afebrile, was weaned off of the vasopressors, and had complete resolution of his tachycardia and tachypnea. His mental status improved, urine output increased, and respiratory status normalized. Within 24 h, the skin rash had regressed significantly (Fig. 3). The antibiotics were discontinued, except for linezolid. Intravenous Solu-Medrol was transitioned to prednisone 80 mg oral daily. The patient was discharged home in stable condition on a prednisone taper, planned to be titrated down by 10 mg weekly. He was also discharged on linezolid 600 mg oral twice a day to complete his initial antibiotic course. Six months later, the patient has completed his antibiotic and steroid treatment courses and continues to do well. The patch test for vancomycin was deemed unnecessary by the dermatology consult team because the patient was not on any home medications aside from steroids and vancomycin; thus, the only obvious culprit was vancomycin. In vitro testing such as macrophage migration inhibition factor (MIF) test or mast cell degranulation (MCD) test were not performed, as these are unavailable at our institution. Discussion AGEP is a rare disorder characterized by the acute development of sterile, non-follicular pinhead-sized pustular eruptions overlying an edematous erythema [1, 2]. Characteristically, the skin reaction arises rapidly within a few hours and tends to resolve quickly within several days after cessation of the offending agent or may resolve spontaneously. The rash mostly begins in the intertriginous areas or in the face then spreads diffusely and is often described as a burning or itching Fig. 3 Day 4 of hospital admission, after initiation of systemic steroid therapy. Significant regression of skin eruptions noted sensation. In about 20 % of cases, mucous membranes are involved but tend to be mild and usually limited to the oral cavity [1]. The incidence of AGEP has been approximated at 1 to 5 cases per million annually [4]. More than 90 % AGEP cases are related to drugs, with viruses comprising the next most common trigger. The most commonly implicated drugs are antibiotics, including pristinamycin, ampicillin, amoxicillin, macrolides, and quinolones. Other drugs include calcium channel blockers and antifungal agents [2]. Although sulfa drugs can cause many skin reactions, they are usually not implicated in AGEP [5]. AGEP commonly presents with high fevers and neutrophilia concurrently occurring with the skin eruptions, thus often misinterpreted as an acute infectious disease. It tends to occur suddenly within 1 to 2 days of exposure to the offending agent and is generally self-limited when the causative agent is eliminated. The skin pustules typically begin on the face and within hours spread to the trunk and limbs and tend to coalesce. Multi-organ involvement is rare and highly atypical of AGEP [3, 6]. Histological evaluation of the involved skin shows spongiform subcorneal and intraepidermal pustules, papillary dermal edema, and neutrophilic infiltration around papillary dermal blood vessels [1]. Important differential diagnoses for AGEP include Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). The systemic features of AGEP usually manifest early, whereas SJS/TEN tends to have a slower manifestation, usually after 3 weeks, and characteristically presents with blisters and severe mucus membrane involvement. Furthermore, the drugs implicated in SJS/ TEN are usually different, such as antiepileptic agents or allopurinol [7]. A useful algorithm for the diagnosis of AGEP was proposed by Sidoroff et al. [1]. The validation score combines clinical and histological features, such as the type and distribution of the skin rash, presence of leukocytosis, histological findings, and the timing of the skin reaction. A score of 8 to 12 is definitive for the diagnosis of AGEP. Applying the AGEP validation score resulted in a score of 11 in our patient, confirming the diagnosis. Typically self-limiting in nature, AGEP tends to resolve spontaneously with cessation of the offending agent and no further measures are usually required. The use of steroids is not routinely required and if indicated, usually topical steroids suffice in providing clinical improvement [6]. Systemic steroids have been used on rare occasions when AGEP presents atypically with severe systemic involvement [8 10]. Our case has several unique features. First, the onset of AGEP was delayed for a couple of weeks after
4 Mawri et al. Journal of Intensive Care (2015) 3:47 Page 4 of 5 initiation of the offending antibiotic, and this was most likely because the patient was on concurrent steroid therapy for his vasogenic cerebral edema. Immediately following completion of the steroid therapy, and hence loss of its anti-inflammatory effects, AGEP was abruptly unmasked. Second, in contrast to most reported cases of AGEP, our case demonstrates an atypical presentation with severe systemic involvement and multi-organ failure mimicking septic shock. The clinical presentation continued to deteriorate despite cessation of the offending antibiotic. Because the patient was only on a brief (12 days) and tapered-down course of steroid therapy, it was not felt that his hemodynamic instability was secondary to adrenal insufficiency, and thus, this was not worked up with laboratory testing. Third, the presence of antibiotic-impregnated intracranial mesh added another layer of complexity to our case, as it was not evident what role this played in our patient s clinical picture. While there is scarce data in current literature on this particular matter, it has been reported that systemic absorption and side effects in antibioticimpregnated orthopedic implants are usually minimal [11]. However, given the continued clinical decline of our patient after cessation of the systemic antibiotic, one may speculate about the potential contribution of antibiotic release from the intracranial mesh. Fourth, the role of systemic steroids in the management of AGEP is rarely indicated and topical steroids usually suffice if the disorder does not resolve with cessation of the offending agent [3]. However, as our case illustrates, despite the use of topical steroids, the patient s skin eruptions progressed rapidly coinciding with rapid clinical decline, hemodynamic instability, and multi-organ involvement necessitating vasopressors. Administration of high-dose intravenous steroids resulted in rapid clinical improvement. Finally, vancomycin as a cause of AGEP is exceptionally rare. To the best of our knowledge, there have only been three previously reported cases of vancomycininduced AGEP in the literature [8, 9, 12]. One case included another confounding antibiotic that is more commonly implicated in AGEP, and thus, the causation relationship was equivocal. The second case presented typically with resolution of AGEP following cessation of vancomycin, with no additional required interventions such as steroids. And the third case presented atypically with a severe AGEP course similar to our case and required systemic steroids. In the latter case, the patient required only several days of systemic steroids with complete clinical recovery. However, because of the presence of vancomycin-impregnated intracranial mesh in our patient with unclear clinical significance, a prolonged systemic steroid taper was chosen for our patient. Conclusion AGEP is a rare disorder characterized by acute onset of characteristic skin eruptions, often triggered by certain medications. This condition is typically self-limiting in nature and tends to resolve spontaneously with cessation of the offending agent. The use of steroids is not routinely required. However, as this case illustrates, AGEP could present atypically with aggressive multi-organ involvement and hemodynamic compromise mimicking septic shock despite cessation of the offending agent. In such cases, early systemic steroid administration appears to provide immediate hemodynamic stabilization and clinical improvement. Consent Written and verbal consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and use of accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor in Chief of this journal. Abbreviations AGEP: acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis; MRSE: methicillin-resistant streptococcus epidermitis; SJS: Stevens-Johnson syndrome; TEN: toxic epidermal necrolysis. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions SM, TJ, and JS performed the literature review, compiled the case report and discussion, and reviewed and selected the relevant images. GH and JS revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Acknowledgements None. Author details 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Henry Ford Hospital, 2799 W Grand Blvd, Detroit, MI 48202, USA. 2 Department of Internal Medicine and Emergency Medicine, Henry Ford Hospital, 2799 W Grand Blvd, Detroit, MI 48202, USA. 3 Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care, Henry Ford Hospital, 2799 W Grand Blvd, Detroit, MI 48202, USA. Received: 22 April 2015 Accepted: 5 November 2015 References 1. Sidoroff A, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, Vaillant L, Roujeau JC. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) a clinical reaction pattern. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28(3): Sidoroff A, Dunant A, Viboud C, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, Naldi L, et al. Risk factors for acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) - results of a multinational case-control study (EuroSCAR). Br J Dermatol. 2007;157(5): Hotz C, Valeyrie-Allanore L, Haddad C, Bouvresse S, Ortonne N, Duong TA, et al. Systemic involvement of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: a retrospective study on 58 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169(6): Freedberg IM EA, Wolff K, Austen KF, Goldsmith LA, SI K. Fitzpatrick s dermatology in general medicine. 6th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional Saissi EH, Beau-Salinas F, Jonville-Bera AP, Lorette G, Autret-Leca E. Drugs associated with acute generalized exanthematic pustulosis. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2003;130(6 7):612 8.
5 Mawri et al. Journal of Intensive Care (2015) 3:47 Page 5 of 5 6. Krishna S, Ortega-Loayza A, Malakouti N, Brinster N. A rapidly progressive and fatal case of atypical acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71(3):e Roujeau JC, Bioulac-Sage P, Bourseau C, Guillaume JC, Bernard P, Lok C, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Analysis of 63 cases. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127(9): Lesterhuis WJ, Tjioe M, Stumpenhausen GA, van Crevel R. Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis mimicking septic shock. Am J Med. 2004;116(8): Mohyuddin GR, Al Asad M, Scratchko L, Khaleeq G. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Am J Crit Care. 2013;22(3): Choi MJ, Kim HS, Park HJ, Park CJ, Lee JD, Lee JY, et al. Clinicopathologic manifestations of 36 Korean patients with acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: a case series and review of the literature. Ann Dermatol. 2010;22(2): Hsu VM, Tahiri Y, Wilson AJ, Grady MS, Taylor JA. A preliminary report on the use of antibiotic-impregnated methyl methacrylate in salvage cranioplasty. J Craniofac Surg. 2014;25(2): O Brien M, Shah A, Allen HB. A pentad of vancomycin reactions. Skinmed. 2011;9(4): Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Drug Allergy A Guide to Diagnosis and Management
 Drug Allergy A Guide to Diagnosis and Management (Version 1 April 2015 updated April 2018) Author: Jed Hewitt Chief Pharmacist, Governance & Professional Practice Date of Preparation: April 2015 Updated:
Drug Allergy A Guide to Diagnosis and Management (Version 1 April 2015 updated April 2018) Author: Jed Hewitt Chief Pharmacist, Governance & Professional Practice Date of Preparation: April 2015 Updated:
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis in the ambulatory care setting
 www.edoriumjournals.com CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis in the ambulatory care setting LT Mark C. Hubbard, LT John C. Walsh, LCDR Megan A. Brelsford ABSTRACT
www.edoriumjournals.com CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis in the ambulatory care setting LT Mark C. Hubbard, LT John C. Walsh, LCDR Megan A. Brelsford ABSTRACT
A case of Sweet's syndrome with marked facial swelling and fluid collection
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2017) 25, 128-132 Case Report A case of Sweet's syndrome with marked facial swelling and fluid collection JE Seol, SH Park, DH Kim, JN Kang, H Kim A 43-year-old woman
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2017) 25, 128-132 Case Report A case of Sweet's syndrome with marked facial swelling and fluid collection JE Seol, SH Park, DH Kim, JN Kang, H Kim A 43-year-old woman
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Siew Eng Choon, FRCP 1,2, Yi Shan Der 1, Nai Liang Joel Lai 1, Evelyn Sing Ee Yu 1, Xiao Ling Yap 1, Nalini Nanu Madhavan, MBBS 2
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical characteristics, culprit drugs and outcome of patients with Acute Generalised Exanthematous Pustulosis seen in Hospital Sultanah Aminah, Johor Bahru Siew Eng Choon, FRCP 1,2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical characteristics, culprit drugs and outcome of patients with Acute Generalised Exanthematous Pustulosis seen in Hospital Sultanah Aminah, Johor Bahru Siew Eng Choon, FRCP 1,2,
Skin Manifestations of Drug Reactions
 Skin Manifestations of Drug Reactions Dr Carol Hlela, Division of Dermatology Department of Medicine, University of Cape Town and Red Cross Children s Hospital What are the Skin Manifestations of Drug
Skin Manifestations of Drug Reactions Dr Carol Hlela, Division of Dermatology Department of Medicine, University of Cape Town and Red Cross Children s Hospital What are the Skin Manifestations of Drug
Example Clinician Educational Material for Providers of Immune Effector Cellular Therapy
 Example Clinician Educational Material for Providers of Immune Effector Cellular Therapy Disclaimer: This example is just one of many potential examples of clinician education material that can be provided
Example Clinician Educational Material for Providers of Immune Effector Cellular Therapy Disclaimer: This example is just one of many potential examples of clinician education material that can be provided
건강한성인에서의오진하기쉬운포도구균성열상피부증후군의치험례. Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome in a Healthy Adult: Easy to Misdiagnose
 Archives of Hand and Microsurgery Arch Hand Microsurg 2018;23(4):271-276. https://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.2018.23.4.271 pissn 2586-3290 eissn 2586-3533 Case Report 건강한성인에서의오진하기쉬운포도구균성열상피부증후군의치험례 김홍일ㆍ곽찬이ㆍ박언주
Archives of Hand and Microsurgery Arch Hand Microsurg 2018;23(4):271-276. https://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.2018.23.4.271 pissn 2586-3290 eissn 2586-3533 Case Report 건강한성인에서의오진하기쉬운포도구균성열상피부증후군의치험례 김홍일ㆍ곽찬이ㆍ박언주
Case Rep Dermatol 2009;1:66 70 DOI: / Key Words Coma Blister Barbiturate Overdose Meningoencephalitis
 66 Coma Blisters Joana Rocha a Teresa Pereira a Filipa Ventura a Fernando Pardal b Celeste Brito a Departments of a Dermatology and b Pathology, Hospital de São Marcos, Braga, Portugal Key Words Coma Blister
66 Coma Blisters Joana Rocha a Teresa Pereira a Filipa Ventura a Fernando Pardal b Celeste Brito a Departments of a Dermatology and b Pathology, Hospital de São Marcos, Braga, Portugal Key Words Coma Blister
Severe β-lactam allergy. Alternative (use for mild-moderate β-lactam allergy) therapy
 Recommended Empirical Antibiotic Regimens for MICU Patients Notes: The antibiotic regimens shown are general guidelines and should not replace clinical judgment. Always assess for antibiotic allergies.
Recommended Empirical Antibiotic Regimens for MICU Patients Notes: The antibiotic regimens shown are general guidelines and should not replace clinical judgment. Always assess for antibiotic allergies.
The histopathological spectrum of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) and its differentiation from generalized pustular psoriasis
 J Cutan Pathol 2010: 37: 1220 1229 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2010.01612.x John Wiley & Sons. Printed in Singapore Copyright 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S Journal of Cutaneous Pathology The histopathological
J Cutan Pathol 2010: 37: 1220 1229 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2010.01612.x John Wiley & Sons. Printed in Singapore Copyright 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S Journal of Cutaneous Pathology The histopathological
New product information wording Extracts from PRAC recommendations on signals
 12 October 2017 EMA/PRAC/610988/2017 Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) New product information wording Extracts from PRAC recommendations on signals Adopted at the 25-29 September 2017
12 October 2017 EMA/PRAC/610988/2017 Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) New product information wording Extracts from PRAC recommendations on signals Adopted at the 25-29 September 2017
OXCARBAZEPINE-INDUCED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME: A CASE REPORT
 OXCARBAZEPINE-INDUCED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME: A CASE REPORT Lung-Chang Lin, 1,2 Ping-Chin Lai, 3 Sheau-Fang Yang, 4 and Rei-Cheng Yang 1,5 Departments of 1 Pediatrics and 4 Pathology, Kaohsiung Medical
OXCARBAZEPINE-INDUCED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME: A CASE REPORT Lung-Chang Lin, 1,2 Ping-Chin Lai, 3 Sheau-Fang Yang, 4 and Rei-Cheng Yang 1,5 Departments of 1 Pediatrics and 4 Pathology, Kaohsiung Medical
REGISTRY OF SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE REACTIONS TO DRUGS AND COLLECTION OF BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES. R e g i S C A R PATIENT'S DATA. Age country of birth
 REGISTRY OF SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE REACTIONS TO DRUGS AND COLLECTION OF BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES R e g i S C A R PATIENT'S DATA Initials of the patient date of birth Age country of birth Gender male female
REGISTRY OF SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE REACTIONS TO DRUGS AND COLLECTION OF BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES R e g i S C A R PATIENT'S DATA Initials of the patient date of birth Age country of birth Gender male female
Warfarin-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis in combination therapy of Henoch- Schönlein purpura nephritis: a case report
 Kasahara et al. BMC Nephrology (2017) 18:237 DOI 10.1186/s12882-017-0648-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Warfarin-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis in combination therapy of Henoch- Schönlein purpura nephritis:
Kasahara et al. BMC Nephrology (2017) 18:237 DOI 10.1186/s12882-017-0648-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Warfarin-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis in combination therapy of Henoch- Schönlein purpura nephritis:
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
Prevalence and pattern of adverse cutaneous drug reactions presenting to a tertiary care hospital
 International Journal of Research in Dermatology Janardhan B et al. Int J Res Dermatol. 2017 Mar;3(1):74-78 http://www.ijord.com Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20164248
International Journal of Research in Dermatology Janardhan B et al. Int J Res Dermatol. 2017 Mar;3(1):74-78 http://www.ijord.com Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20164248
Name the condition: Canine sterile neutrophilic dermatosis (Sweet s syndrome)
 5-year-old male miniature Schnauzer dog with acute onset of severe macular erythema and multiple tender violaceus plaques all over the body. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? 1. Canine
5-year-old male miniature Schnauzer dog with acute onset of severe macular erythema and multiple tender violaceus plaques all over the body. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? 1. Canine
Early View Article: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form.
 : Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: International Journal of Case Reports and Images (IJCRI) Type of Article: Case Report Title: A Case
: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: International Journal of Case Reports and Images (IJCRI) Type of Article: Case Report Title: A Case
Osteomyelitis Samir S. Shah, MD, MSCE
 Osteomyelitis Samir S. Shah, MD, MSCE Professor, Department of Pediatrics University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Director, Division of Hospital Medicine Attending Physician in Infectious Diseases
Osteomyelitis Samir S. Shah, MD, MSCE Professor, Department of Pediatrics University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Director, Division of Hospital Medicine Attending Physician in Infectious Diseases
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT
 HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
CASE REPORT ATYPICAL BULLOUS PYODERMA GANGRENOSUM WITH EARLY LESIONS MIMICKING CHICKEN POX
 ATYPICAL BULLOUS PYODERMA GANGRENOSUM WITH EARLY LESIONS MIMICKING CHICKEN POX Ramesh M 1, Kavya Raju Nayak 2, M.G. Gopal 3, Sharath Kumar B.C 4, Nandini A.S 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ramesh M, Kavya
ATYPICAL BULLOUS PYODERMA GANGRENOSUM WITH EARLY LESIONS MIMICKING CHICKEN POX Ramesh M 1, Kavya Raju Nayak 2, M.G. Gopal 3, Sharath Kumar B.C 4, Nandini A.S 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ramesh M, Kavya
CASE 5 - Toy et al. CASE FILES: Obstetrics & Gynecology
 z CASE 5 - Toy et al. CASE FILES: Obstetrics & Gynecology A 28-year-old woman is brought into the emergency room with a blood pressure of 60/40. The patient s husband states that she had 2 days of nausea
z CASE 5 - Toy et al. CASE FILES: Obstetrics & Gynecology A 28-year-old woman is brought into the emergency room with a blood pressure of 60/40. The patient s husband states that she had 2 days of nausea
Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India.
 Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA)
 Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) Ahmed Abdullah Alhumidi King saud university, Riyadh, kingdom of Saudi Arabia Abstract Background: This
Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) Ahmed Abdullah Alhumidi King saud university, Riyadh, kingdom of Saudi Arabia Abstract Background: This
Title: Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions in Indian population: A systematic review
 Title: Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions in Indian population: A systematic review Review question(s) To carry out a systematic review of the published evidence of the cutaneous adverse drug reactions in
Title: Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions in Indian population: A systematic review Review question(s) To carry out a systematic review of the published evidence of the cutaneous adverse drug reactions in
EFAVIRENZ ASSOCIATED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME
 EFAVIRENZ ASSOCIATED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME To the Editor: Persons with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection are highly susceptible to adverse dermatological reactions to specific medications
EFAVIRENZ ASSOCIATED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME To the Editor: Persons with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection are highly susceptible to adverse dermatological reactions to specific medications
Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), available at
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Drug Allergy. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The audio
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Drug Allergy. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The audio
Staging Sepsis for the Emergency Department: Physician
 Staging Sepsis for the Emergency Department: Physician Sepsis Continuum 1 Sepsis Continuum SIRS = 2 or more clinical criteria, resulting in Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Sepsis = SIRS + proven/suspected
Staging Sepsis for the Emergency Department: Physician Sepsis Continuum 1 Sepsis Continuum SIRS = 2 or more clinical criteria, resulting in Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Sepsis = SIRS + proven/suspected
=ﻰﻤاﻤﺤﻠا ﺔﻴﻘﻠﺤﻠا ﺔذﺒاﻨﻠا
 1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
Uncommon clinical presentations of leprosy: apropos of three cases
 Lepr Rev (2016) 87, 246 251 CASE REPORT Uncommon clinical presentations of leprosy: apropos of three cases RASHMI JINDAL* & NADIA SHIRAZI** *Department of Dermatology, Venereology & Leprosy, Himalayan
Lepr Rev (2016) 87, 246 251 CASE REPORT Uncommon clinical presentations of leprosy: apropos of three cases RASHMI JINDAL* & NADIA SHIRAZI** *Department of Dermatology, Venereology & Leprosy, Himalayan
CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE
 CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE Generalized vesiculo-bullous and pustular eruption in an adult man Hassab El-Naby H, MD, El-Khalawany M, MD Department of Dermatology, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt CLINICAL
CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE Generalized vesiculo-bullous and pustular eruption in an adult man Hassab El-Naby H, MD, El-Khalawany M, MD Department of Dermatology, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt CLINICAL
SEPSIS SYNDROME
 INTRODUCTION Sepsis has been defined as a life threatening condition that arises when the body s response to an infection injures its own tissues and organs. Sepsis may lead to shock, multiple organ failure
INTRODUCTION Sepsis has been defined as a life threatening condition that arises when the body s response to an infection injures its own tissues and organs. Sepsis may lead to shock, multiple organ failure
New product information wording Extracts from PRAC recommendations on signals
 20 July 2017 EMA/PRAC/406976/2017 Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) New product information wording Extracts from PRAC recommendations on signals Adopted at the 3-6 July 2017 PRAC The
20 July 2017 EMA/PRAC/406976/2017 Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) New product information wording Extracts from PRAC recommendations on signals Adopted at the 3-6 July 2017 PRAC The
Package leaflet: Information for the patient. / / 30 mg/5 ml syrup. Ambroxol hydrochloride
 Package leaflet: Information for the patient / / 30 mg/5 ml syrup Ambroxol hydrochloride Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information
Package leaflet: Information for the patient / / 30 mg/5 ml syrup Ambroxol hydrochloride Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information
VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS
 VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS Management of Anaphylaxis IERHA Immunization Program September 2016 VACCINE-RELATED ADVERSE EVENTS Local reactions pain, edema, erythema Systemic reactions fever, lymphadenopathy
VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS Management of Anaphylaxis IERHA Immunization Program September 2016 VACCINE-RELATED ADVERSE EVENTS Local reactions pain, edema, erythema Systemic reactions fever, lymphadenopathy
Sepsis: Identification and Management in an Acute Care Setting
 Sepsis: Identification and Management in an Acute Care Setting Dr. Barbara M. Mills DNP Director Rapid Response Team/ Code Resuscitation Stony Brook University Medical Center SEPSIS LECTURE NPA 2018 OBJECTIVES
Sepsis: Identification and Management in an Acute Care Setting Dr. Barbara M. Mills DNP Director Rapid Response Team/ Code Resuscitation Stony Brook University Medical Center SEPSIS LECTURE NPA 2018 OBJECTIVES
Future of Pediatrics: Blisters, Hives and Other Tales from the Emergency Room June 14 th, 2016
 A. Yasmine Kirkorian MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology & Pediatrics Children s National Health System George Washington University School of Medicine & Health Sciences Future of Pediatrics: Blisters,
A. Yasmine Kirkorian MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology & Pediatrics Children s National Health System George Washington University School of Medicine & Health Sciences Future of Pediatrics: Blisters,
BC Cancer Protocol Summary for Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia or Prolymphocytic Leukemia with Fludarabine and rituximab
 BC Cancer Protocol Summary for Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia or Prolymphocytic Leukemia with Fludarabine and rituximab Protocol Code Tumour Group Contact Physicians LYCLLFLUDR Lymphoma Dr.
BC Cancer Protocol Summary for Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia or Prolymphocytic Leukemia with Fludarabine and rituximab Protocol Code Tumour Group Contact Physicians LYCLLFLUDR Lymphoma Dr.
DOSING GUIDE. Indications. Important Safety Information. Enable the immune system. RECOGNIZE. RESPOND.
 DOSING GUIDE For patients with unresectable Stage III NSCLC following concurrent CRT For patients with locally advanced or metastatic UC previously treated with platinum-based therapy Enable the immune
DOSING GUIDE For patients with unresectable Stage III NSCLC following concurrent CRT For patients with locally advanced or metastatic UC previously treated with platinum-based therapy Enable the immune
Disclaimer. This is a broad survey and cannot cover all differential diagnoses or each condition in thorough detail
 Objectives Pediatric Infections: Differentiating Benign from Serious Eileen Klein, MD, MPH Rashes Infectious vs non-infectious Viral vs bacterial Respiratory and GI illnesses When do you treat When do
Objectives Pediatric Infections: Differentiating Benign from Serious Eileen Klein, MD, MPH Rashes Infectious vs non-infectious Viral vs bacterial Respiratory and GI illnesses When do you treat When do
Sepsis Awareness and Education
 Sepsis Awareness and Education Meets the updated New York State Department of Health (NYSDOH) requirements for Infection Control and Barrier Precautions coursework Element VII: Sepsis Awareness and Education
Sepsis Awareness and Education Meets the updated New York State Department of Health (NYSDOH) requirements for Infection Control and Barrier Precautions coursework Element VII: Sepsis Awareness and Education
A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral
 Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
THE SPECTRUM OF HISTOPATHOLOGICAL FEATURES IN ACUTE GENERALISED EXANTHEMATOUS PUSTULOSIS: A STUDY OF 102 CASES
 These articles have been accepted for publication in the British Journal of Dermatology and are currently being edited and typeset. Readers should note that articles published below have been fully refereed,
These articles have been accepted for publication in the British Journal of Dermatology and are currently being edited and typeset. Readers should note that articles published below have been fully refereed,
Cutaneous Drug Reactions
 Cutaneous Drug Reactions Andrei Metelitsa, MD, FRCPC, FAAD Co-Director, Institute for Skin Advancement Clinical Associate Professor, Dermatology University of Calgary, Canada Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses
Cutaneous Drug Reactions Andrei Metelitsa, MD, FRCPC, FAAD Co-Director, Institute for Skin Advancement Clinical Associate Professor, Dermatology University of Calgary, Canada Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses
Conversion Dosing Guide:
 Conversion Dosing Guide: From epoetin alfa to Aranesp in patients with anemia due to CKD on dialysis Indication Aranesp (darbepoetin alfa) is indicated for the treatment of anemia due to chronic kidney
Conversion Dosing Guide: From epoetin alfa to Aranesp in patients with anemia due to CKD on dialysis Indication Aranesp (darbepoetin alfa) is indicated for the treatment of anemia due to chronic kidney
Early Klebsiella pneumoniae Liver Abscesses associated with Pylephlebitis Mimic
 Early Klebsiella pneumoniae Liver Abscesses associated with Pylephlebitis Mimic Hepatocellular Carcinoma Chih-Hao Shen, MD 3, Jung-Chung Lin, MD, PhD 2, Hsuan-Hwai Lin, MD 1, You-Chen Chao, MD 1, and Tsai-Yuan
Early Klebsiella pneumoniae Liver Abscesses associated with Pylephlebitis Mimic Hepatocellular Carcinoma Chih-Hao Shen, MD 3, Jung-Chung Lin, MD, PhD 2, Hsuan-Hwai Lin, MD 1, You-Chen Chao, MD 1, and Tsai-Yuan
Package leaflet: Information for the user. Piperacillin/Tazobactam Actavis 4 g / 0.5 g powder for solution for infusion. piperacillin / tazobactam
 Package leaflet: Information for the user Piperacillin/Tazobactam Actavis 2 g / 0.25 g powder for solution for infusion Piperacillin/Tazobactam Actavis 4 g / 0.5 g powder for solution for infusion piperacillin
Package leaflet: Information for the user Piperacillin/Tazobactam Actavis 2 g / 0.25 g powder for solution for infusion Piperacillin/Tazobactam Actavis 4 g / 0.5 g powder for solution for infusion piperacillin
CPC. Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand
 CPC Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand A 53 year-old woman with fever, facial swelling and rashes on face, trunk and upper extremities for 3
CPC Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand A 53 year-old woman with fever, facial swelling and rashes on face, trunk and upper extremities for 3
CUTANEOUS DRUG REACTIONS OR I WOULDN T HAVE SEEN IT, IF I HADN T BELIEVED IT Edmund J. Rosser Jr., DVM, DACVD
 CUTANEOUS DRUG REACTIONS OR I WOULDN T HAVE SEEN IT, IF I HADN T BELIEVED IT Edmund J. Rosser Jr., DVM, DACVD DERMATOLOGY Pathogenesis Immunologic: can involve Type I, II, III, IV hypersensitivity reactions.
CUTANEOUS DRUG REACTIONS OR I WOULDN T HAVE SEEN IT, IF I HADN T BELIEVED IT Edmund J. Rosser Jr., DVM, DACVD DERMATOLOGY Pathogenesis Immunologic: can involve Type I, II, III, IV hypersensitivity reactions.
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author. CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel
 CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May 2014 Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel An 18 years old Female, from Ukraine, diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in 2003.
CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May 2014 Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel An 18 years old Female, from Ukraine, diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in 2003.
Septic Shock. Rontgene M. Solante, MD, FPCP,FPSMID
 Septic Shock Rontgene M. Solante, MD, FPCP,FPSMID Learning Objectives Identify situations wherein high or low BP are hemodynamically significant Recognize complications arising from BP emergencies Manage
Septic Shock Rontgene M. Solante, MD, FPCP,FPSMID Learning Objectives Identify situations wherein high or low BP are hemodynamically significant Recognize complications arising from BP emergencies Manage
CRRT Fundamentals Pre-Test. AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT
 CRRT Fundamentals Pre-Test AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT Question 1 A 72-year-old man with HTN presents to the ED with slurred speech, headache and weakness after falling at home. He
CRRT Fundamentals Pre-Test AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT Question 1 A 72-year-old man with HTN presents to the ED with slurred speech, headache and weakness after falling at home. He
Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS): Cytokine release syndrome and neurological toxicities
 Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS): Cytokine release syndrome and neurological toxicities A REMS is a program required by the FDA to manage known or potential serious risks associated with
Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS): Cytokine release syndrome and neurological toxicities A REMS is a program required by the FDA to manage known or potential serious risks associated with
CT findings in patients with Cabazitaxel induced pelvic pain and haematuria: a case series
 Malalagama et al. Cancer Imaging (2017) 17:17 DOI 10.1186/s40644-017-0119-3 CASE SERIES CT findings in patients with Cabazitaxel induced pelvic pain and haematuria: a case series Geethal N. Malalagama
Malalagama et al. Cancer Imaging (2017) 17:17 DOI 10.1186/s40644-017-0119-3 CASE SERIES CT findings in patients with Cabazitaxel induced pelvic pain and haematuria: a case series Geethal N. Malalagama
PSEUDO-CELLULITIS - ALL THAT S RED IS NOT INFECTION
 JAN 18 2018 ASP ECHO CLINIC CHARLES KRASNER, M.D. PSEUDO-CELLULITIS - ALL THAT S RED IS NOT INFECTION FIRST HOSPITALIZATION: 62 YEAR OLD MALE ADMITTED WITH DIAGNOSIS OF CELLULITIS Hx of AODM, Morbid Obesity,
JAN 18 2018 ASP ECHO CLINIC CHARLES KRASNER, M.D. PSEUDO-CELLULITIS - ALL THAT S RED IS NOT INFECTION FIRST HOSPITALIZATION: 62 YEAR OLD MALE ADMITTED WITH DIAGNOSIS OF CELLULITIS Hx of AODM, Morbid Obesity,
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE
 Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Toxic epidermal necrolysis, DRESS, AGEP Bouvresse, Sophie; Valeyrie-Allanore, Laurence; Ortonne, Nicolas; Konstantinou, Marie Pauline; Kardaun, Sylvia H.; Bagot, Martine; Wolkenstein,
University of Groningen Toxic epidermal necrolysis, DRESS, AGEP Bouvresse, Sophie; Valeyrie-Allanore, Laurence; Ortonne, Nicolas; Konstantinou, Marie Pauline; Kardaun, Sylvia H.; Bagot, Martine; Wolkenstein,
Cutaneous drug reactions
 Maintenance of Certification clinical management series Series editor: James T. Li, MD, PhD Cutaneous drug reactions David A. Khan, MD Dallas, Tex INSTRUCTIONS Credit can now be obtained, free for a limited
Maintenance of Certification clinical management series Series editor: James T. Li, MD, PhD Cutaneous drug reactions David A. Khan, MD Dallas, Tex INSTRUCTIONS Credit can now be obtained, free for a limited
A case of rosacea fulminans in a pregnant woman
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2018) 26, 122-126 Views and Practice A case of rosacea fulminans in a pregnant woman JE Seol, SH Park, JU Kim, GJ Cho, SH Moon, H Kim Introduction Rosacea fulminans (RF)
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2018) 26, 122-126 Views and Practice A case of rosacea fulminans in a pregnant woman JE Seol, SH Park, JU Kim, GJ Cho, SH Moon, H Kim Introduction Rosacea fulminans (RF)
Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS): Cytokine release syndrome and neurological toxicities
 Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS): Cytokine release syndrome and neurological toxicities A REMS is a program required by the FDA to manage known or potential serious risks associated with
Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS): Cytokine release syndrome and neurological toxicities A REMS is a program required by the FDA to manage known or potential serious risks associated with
Printed copies of this document may not be up to date, obtain the most recent version from
 Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Septic Shock Document Control Information Author Claire Fraser P.Ramnarayan Author Position tanp CATS Consultant Document Owner E. Polke Document
Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Septic Shock Document Control Information Author Claire Fraser P.Ramnarayan Author Position tanp CATS Consultant Document Owner E. Polke Document
Case report. Open Access. Abstract
 Open Access Case report Acute posterior neck pain in adult: a case series Yasuhiro Homma*, Akira Itoi, Tomoya Muta, Yoshio Shimamura, Kiyohito Naito, Atsuhiko Mogami, Osamu Obayashi, Colin G Murphy and
Open Access Case report Acute posterior neck pain in adult: a case series Yasuhiro Homma*, Akira Itoi, Tomoya Muta, Yoshio Shimamura, Kiyohito Naito, Atsuhiko Mogami, Osamu Obayashi, Colin G Murphy and
DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER: This Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) generally describes a recommended course of treatment for patients with the identified health
DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER: This Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) generally describes a recommended course of treatment for patients with the identified health
Elements for a Public Summary
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Lung cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in European men and women. There are two main types of lung cancer: small
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Lung cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in European men and women. There are two main types of lung cancer: small
Case presentation. Dr Rammohan Reddy 1 st year PG, Dept of DVL, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences, Narketpally.
 Case presentation Dr Rammohan Reddy 1 st year PG, Dept of DVL, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences, Narketpally. Name : XXX Age : 33 years Sex : Female Occupation : Farmer IP no : 201608905 DOA : 15-02-2016
Case presentation Dr Rammohan Reddy 1 st year PG, Dept of DVL, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences, Narketpally. Name : XXX Age : 33 years Sex : Female Occupation : Farmer IP no : 201608905 DOA : 15-02-2016
Iatrogenic Central Diabetes Insipidus Induced by Vasopressin Withdrawal
 Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 1 (2015) Issue 7 Abstract ISSN 2379-1039 Iatrogenic Central Diabetes Insipidus Induced by Vasopressin Withdrawal * Joseph R Shiber, MD ; Donald Johnson,
Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 1 (2015) Issue 7 Abstract ISSN 2379-1039 Iatrogenic Central Diabetes Insipidus Induced by Vasopressin Withdrawal * Joseph R Shiber, MD ; Donald Johnson,
A Retrospective Study of Spectrum of Nevirapine Induced Cutaneous Drug Reactions in HIV Positive Patients
 Journal of US-China Medical Science 12 (2015) 85-89 doi: 10.17265/1548-6648/2015.02.008 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Retrospective Study of Spectrum of Nevirapine Induced Cutaneous Drug Reactions in HIV Positive
Journal of US-China Medical Science 12 (2015) 85-89 doi: 10.17265/1548-6648/2015.02.008 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Retrospective Study of Spectrum of Nevirapine Induced Cutaneous Drug Reactions in HIV Positive
Current State of Pediatric Sepsis. Jason Clayton, MD PhD Pediatric Critical Care 9/19/2018
 Current State of Pediatric Sepsis Jason Clayton, MD PhD Pediatric Critical Care 9/19/2018 Objectives Review the history of pediatric sepsis Review the current definition of pediatric sepsis Review triage
Current State of Pediatric Sepsis Jason Clayton, MD PhD Pediatric Critical Care 9/19/2018 Objectives Review the history of pediatric sepsis Review the current definition of pediatric sepsis Review triage
Update in deposition diseases
 Genoa, Italy Update in deposition diseases Prof. Franco Rongioletti, Section of Dermatology, Chair of Dermatopathology, University of Genoa,Italy Cutaneous deposition disorders Endogenous Exogenous Cutaneous
Genoa, Italy Update in deposition diseases Prof. Franco Rongioletti, Section of Dermatology, Chair of Dermatopathology, University of Genoa,Italy Cutaneous deposition disorders Endogenous Exogenous Cutaneous
Elements for a Public Summary
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Actavis is a cancer medicine used to treat two types of lung cancer, malignant pleural mesothelioma and advanced non-small-cell
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Actavis is a cancer medicine used to treat two types of lung cancer, malignant pleural mesothelioma and advanced non-small-cell
MAKING SENSE OF IT ALL AUGUST 17
 MAKING SENSE OF IT ALL AUGUST 17 @SepsisUK Dr Ron Daniels B.E.M. CEO, UK Sepsis Trust CEO, Global Sepsis Alliance Special Adviser to WHO SCALE AND BURDEN @sepsisuk Dr Ron Daniels B.E.M. CEO, UK Sepsis
MAKING SENSE OF IT ALL AUGUST 17 @SepsisUK Dr Ron Daniels B.E.M. CEO, UK Sepsis Trust CEO, Global Sepsis Alliance Special Adviser to WHO SCALE AND BURDEN @sepsisuk Dr Ron Daniels B.E.M. CEO, UK Sepsis
CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II
 MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 1 CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II Session 11 April 11, 2016 STUDENT COPY MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 2 CASE HISTORY 1 Chief complaint: Our baby
MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 1 CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II Session 11 April 11, 2016 STUDENT COPY MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 2 CASE HISTORY 1 Chief complaint: Our baby
A. Erythema multiforme and related diseases
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Erythema, Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis) Erythema is caused by telangiectasia or hyperemia in the papillary and reticular
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Erythema, Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis) Erythema is caused by telangiectasia or hyperemia in the papillary and reticular
Rochester Patient Safety C. difficile Prevention Collaborative: Long Term Care Antimicrobial Stewardship (funded by NYSDOH)
 Rochester Patient Safety C. difficile Prevention Collaborative: Long Term Care Antimicrobial Stewardship (funded by NYSDOH) Clinical Practice Guideline* for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Bacterial
Rochester Patient Safety C. difficile Prevention Collaborative: Long Term Care Antimicrobial Stewardship (funded by NYSDOH) Clinical Practice Guideline* for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Bacterial
Fever in Lupus. 21 st April 2014
 Fever in Lupus 21 st April 2014 Fever in lupus Cause of fever N= 487 % SLE fever 206 42 Infection in SLE 265 54.5 Active SLE and infection 8 1.6 Tumor fever 4 0.8 Miscellaneous 4 0.8 Crucial Question Infection
Fever in Lupus 21 st April 2014 Fever in lupus Cause of fever N= 487 % SLE fever 206 42 Infection in SLE 265 54.5 Active SLE and infection 8 1.6 Tumor fever 4 0.8 Miscellaneous 4 0.8 Crucial Question Infection
Unrestricted. Dr ppooransari fellowship of perenatalogy
 Unrestricted Dr ppooransari fellowship of perenatalogy Assessment of severity of hemorrhage Significant drops in blood pressure are generally not manifested until substantial bleeding has occurred, and
Unrestricted Dr ppooransari fellowship of perenatalogy Assessment of severity of hemorrhage Significant drops in blood pressure are generally not manifested until substantial bleeding has occurred, and
DERMATOLOGY FOR THE INTERNIST. Emilie Chow, MD 8/2017
 DERMATOLOGY FOR THE INTERNIST Emilie Chow, MD 8/2017 GOALS ALL SLIDES ARE FOCUSED ON CLINICAL CASES IN THE FORM OF QUESTIONS AND MKSAP COVERED TOPICS USING POLLEV.COM Reference for material is MKSAP 17
DERMATOLOGY FOR THE INTERNIST Emilie Chow, MD 8/2017 GOALS ALL SLIDES ARE FOCUSED ON CLINICAL CASES IN THE FORM OF QUESTIONS AND MKSAP COVERED TOPICS USING POLLEV.COM Reference for material is MKSAP 17
Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids
 Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids Joshua Malo, MD Yuval Raz, MD Linda Snyder, MD Kenneth Knox, MD University of Arizona Medical Center Department of
Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids Joshua Malo, MD Yuval Raz, MD Linda Snyder, MD Kenneth Knox, MD University of Arizona Medical Center Department of
Dermclinic
 Dermclinic /Dermclinic A Photo Quiz to Hone Dermatologic Skills DAVID L. KAPLAN, MD Series Editor University of Missouri Kansas City, University of Kansas Case 1: Upon his return from a summer visit to
Dermclinic /Dermclinic A Photo Quiz to Hone Dermatologic Skills DAVID L. KAPLAN, MD Series Editor University of Missouri Kansas City, University of Kansas Case 1: Upon his return from a summer visit to
Have you ever managed patients who have experienced an adverse reaction to transfusion?
 Have you ever managed patients who have experienced an adverse reaction to transfusion? A. Yes, often B. Yes, occasionally C. No A. 1 in 30 units? B. 1 in 100? C. 1 in 1000? D. 1 in 10,000? SHOT collects
Have you ever managed patients who have experienced an adverse reaction to transfusion? A. Yes, often B. Yes, occasionally C. No A. 1 in 30 units? B. 1 in 100? C. 1 in 1000? D. 1 in 10,000? SHOT collects
VI.2 Elements for a public summary. VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Sinus infection (Acute bacterial sinusitis) Sinus infection (upper respiratory infection) is short-lived infection of the sinuses,
VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Sinus infection (Acute bacterial sinusitis) Sinus infection (upper respiratory infection) is short-lived infection of the sinuses,
DERBY-BURTON LOCAL CANCER NETWORK FILENAME Peruse.DOC CONTROLLED DOC NO: CCPG R29
 Pertuzumab + Trastuzumab + Docetaxel (Peruse study) A Multicenter, open-label, single arm study of Pertuzumab in combination with Trastuzumab and a Taxane in first-line treatment of patients with HER2-positive
Pertuzumab + Trastuzumab + Docetaxel (Peruse study) A Multicenter, open-label, single arm study of Pertuzumab in combination with Trastuzumab and a Taxane in first-line treatment of patients with HER2-positive
Ipilimumab in Melanoma
 Ipilimumab in Melanoma Indication: Advanced (unresectable or metastatic) melanoma in adults who have received prior therapy LCNDG criteria to be met: Histologically confirmed unresectable stage III or
Ipilimumab in Melanoma Indication: Advanced (unresectable or metastatic) melanoma in adults who have received prior therapy LCNDG criteria to be met: Histologically confirmed unresectable stage III or
ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Acute Pancreatitis
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Acute Pancreatitis Scott Tenner, MD, MPH, FACG 1, John Baillie, MB, ChB, FRCP, FACG 2, John DeWitt, MD, FACG 3 and Santhi Swaroop Vege, MD, FACG 4 1 State University
ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Acute Pancreatitis Scott Tenner, MD, MPH, FACG 1, John Baillie, MB, ChB, FRCP, FACG 2, John DeWitt, MD, FACG 3 and Santhi Swaroop Vege, MD, FACG 4 1 State University
Brain abscess rupturing into the lateral ventricle causing meningitis: a case report
 Brain abscess rupturing into the lateral ventricle causing meningitis: a case report Endry Martinez, and Judith Berger SBH Health System, 4422 Third Ave, Bronx, NY 10457 Key words: brain abscess, rupture
Brain abscess rupturing into the lateral ventricle causing meningitis: a case report Endry Martinez, and Judith Berger SBH Health System, 4422 Third Ave, Bronx, NY 10457 Key words: brain abscess, rupture
Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal Vol. 6 No 1: 14, June 2010
 Wells Syndrome H. Gammaz, H. Amer, A. Adly and S. Mahmoud Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 6 (1): 14 Al-Haud Al-Marsoud Hospital, Cairo, Egypt e-mail: hananderma@hotmail.com Submitted: April 15, 2010
Wells Syndrome H. Gammaz, H. Amer, A. Adly and S. Mahmoud Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 6 (1): 14 Al-Haud Al-Marsoud Hospital, Cairo, Egypt e-mail: hananderma@hotmail.com Submitted: April 15, 2010
Annex I. Scientific conclusions and grounds for the variation to the terms of the Marketing Authorisation(s)
 Annex I Scientific conclusions and grounds for the variation to the terms of the Marketing Authorisation(s) 1 Scientific conclusions Taking into account the PRAC Assessment Report on the PSUR(s) for ibuprofen
Annex I Scientific conclusions and grounds for the variation to the terms of the Marketing Authorisation(s) 1 Scientific conclusions Taking into account the PRAC Assessment Report on the PSUR(s) for ibuprofen
Analysis of causation of Stevens Johnson Syndrome in a patient of rheumatoid arthritis with increased dose of methotrexate
 Original Research Article Analysis of causation of Stevens Johnson Syndrome in a patient of rheumatoid arthritis with increased dose of methotrexate Manab Nandy 1, Sangeeta De 2*, Mustafa Asad 2, Nirmal
Original Research Article Analysis of causation of Stevens Johnson Syndrome in a patient of rheumatoid arthritis with increased dose of methotrexate Manab Nandy 1, Sangeeta De 2*, Mustafa Asad 2, Nirmal
Herbal and homeopathic products, often considered natural and non-toxic, can also cause adverse drug reactions.
 Idiosyncratic and potentially serious cutaneous adverse drug reactions (CADRs), although relatively rare, account for significant morbidity and mortality. RANNAKOE J LEHLOENYA, BSc, MB ChB, FCDerm (SA)
Idiosyncratic and potentially serious cutaneous adverse drug reactions (CADRs), although relatively rare, account for significant morbidity and mortality. RANNAKOE J LEHLOENYA, BSc, MB ChB, FCDerm (SA)
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Pemetrexed Actavis (pemetrexed)
 EMA/58503/2016 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Pemetrexed Actavis (pemetrexed) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Pemetrexed Actavis, which details the measures to be
EMA/58503/2016 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Pemetrexed Actavis (pemetrexed) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Pemetrexed Actavis, which details the measures to be
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Suntharalingam G, Perry MR, Ward S, et al. Cytokine storm in
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Suntharalingam G, Perry MR, Ward S, et al. Cytokine storm in
Azathioprine toxicity criteria and severity descriptors for the listing of biological agents for rheumatoid arthritis on the PBS
 Azathioprine toxicity criteria and severity descriptors for the listing of biological agents for rheumatoid arthritis on the PBS Only valid for adult patients Azathioprine must be at a dose of at least
Azathioprine toxicity criteria and severity descriptors for the listing of biological agents for rheumatoid arthritis on the PBS Only valid for adult patients Azathioprine must be at a dose of at least
ACUTE ANNULAR URTICARIA IN A CHILD
 The West London Medical Journal 2013 Vol 5 No 2 pp 1-5 ACUTE ANNULAR URTICARIA IN A CHILD Aaron Yon Dayse Fernandes Michelle Pike Jodi Newcombe Colin Michie 1. ABSTRACT Urticarial skin rashes have a range
The West London Medical Journal 2013 Vol 5 No 2 pp 1-5 ACUTE ANNULAR URTICARIA IN A CHILD Aaron Yon Dayse Fernandes Michelle Pike Jodi Newcombe Colin Michie 1. ABSTRACT Urticarial skin rashes have a range
Applicable to. Team Members Performing MD House Staff APRN/PA RN LPN
 Protocol: Adult Burn Fluid Resuscitation Category Clinical Practice Protocol Number Approval Date vember 1, 2016 Due for review vember 1, 2018 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations VMG
Protocol: Adult Burn Fluid Resuscitation Category Clinical Practice Protocol Number Approval Date vember 1, 2016 Due for review vember 1, 2018 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations VMG
John Park, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine
 John Park, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Faculty photo will be placed here park.john@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Sepsis Out with the Old, In with the New Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development
John Park, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Faculty photo will be placed here park.john@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Sepsis Out with the Old, In with the New Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development
FLUID MANAGEMENT AND BLOOD COMPONENT THERAPY
 Manual: Section: Protocol #: Approval Date: Effective Date: Revision Due Date: 10/2019 LifeLine Patient Care Protocols Adult/Pediatrics AP1-011 10/2018 10/2018 FLUID MANAGEMENT AND BLOOD COMPONENT THERAPY
Manual: Section: Protocol #: Approval Date: Effective Date: Revision Due Date: 10/2019 LifeLine Patient Care Protocols Adult/Pediatrics AP1-011 10/2018 10/2018 FLUID MANAGEMENT AND BLOOD COMPONENT THERAPY
ABACAVIR HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTION
 ABACAVIR HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTION Key Risk Minimisation Points: Abacavir Hypersensitivity Reaction (HSR) Abacavir is associated with a risk for hypersensitivity reactions (HSR) characterised by fever
ABACAVIR HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTION Key Risk Minimisation Points: Abacavir Hypersensitivity Reaction (HSR) Abacavir is associated with a risk for hypersensitivity reactions (HSR) characterised by fever
Elements for a public summary. VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Epilepsy: It is the commonest neurological condition, characterized by recurrent seizures, affecting people of all ages, race
VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Epilepsy: It is the commonest neurological condition, characterized by recurrent seizures, affecting people of all ages, race
