Clinical and histopathological spectrum of lichen planus
|
|
|
- Arnold Nash
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Clinical and histopathological spectrum of lichen planus Rohit Rampal, Sunil K. Gupta, Neena Sood*, Anupama Rampal**, Shweta Karkara, Jaspreet Kaur Department of Dermatology, Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. * Department of Pathology, Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. ** Department of Dermatology, Deepak Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Abstract Objective To determine histopathological correlation with clinical presentation of lichen planus (LP). Methods From the patients attending the outpatient department of Dermatology of Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, those who were clinically diagnosed as LP constituted the study material. Results Oral LP was the most common clinical variant with 24 (40%) cases, out of which 18 (30%) were of reticular oral LP, 6 (10%) were of erosive oral lichen planus. 19 (31.7%) cases were of classical LP, 6 (10%) were of hypertrophic LP, 5 (8.3%) were of LP pigmentosus, 3 (5%) were of eruptive LP, 1 (1.7%) was of genital LP, 1 (1.7%) was of lichen planopilaris, 1 (1.7%) was of actinic LP with DLE overlap. Both oral LP and classical LP were the most common histopathological variants with both having 21 (35%) cases. Second most common histopathological variant was that of hypertrophic LP with 6 (10%) cases. Majority of patients were in the age group of years. Our study had a female preponderance. Most of the cases sought medical help within 6-10 months of development of symptoms. Lower limbs were the most common site involved in cutaneous LP. Burning sensation was the main presenting complaint in the patients of oral LP. In cutaneous LP moderate to severe itching was the most common symptom. The commonest recognized histopathological features were saw-toothed rete ridges/ irregular acanthosis, vacuolar degeneration of basal layer and band like infiltrate in our study. Conclusion Oral LP is the most common clinical variant followed by classical LP with histopathological findings adequately consistent with the clinical diagnosis. Key words Clinical features, histopathology, lichen planus. Introduction Lichen planus (LP) is an idiopathic inflammatory skin disease affecting the skin and mucous membranes, often with a chronic course with relapses and periods of remission. Its prevalence is approximately 0.5% of the Address for correspondence Dr. Sunil K. Gupta, Skin OPD, Dayananad Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India vsunilgupta@rediffmail.com population. 1 The incidence varies between 0.22% and 1% of the adult population worldwide. 2 In contrast, oral LP seems to be more frequent with a reported incidence between 1% and 4% of the population. 1 LP is rare in children and commonly affects adults during their fourth to sixth decade. According to one study, LP represents 0.38% of all dermatology outpatients in India
2 Several hypotheses have been made regarding its etiology including genetic, infective, psychogenic and autoimmune factors. 4 Several studies have suggested a role for hepatitis C virus (HCV) in LP. 5 Both antigen-specific and nonspecific mechanisms are involved in initiation of the immune reaction. 6 The classic clinical presentation of LP includes primary lesions consisting of firm, shiny, polygonal, 1-3 mm diameter papules with a red to violet colour. Pruritic, Purple, Polygonal, Planar, Papules and Plaques are the traditional 6 P s of LP. 7 Annular lesions are especially common on the penis and rarely may be the predominant type of lesion present, later leading to atrophy. 8 When the palms and soles are affected, the lesions tend to be firm and rough with a yellowish hue. 9 Linear LP occurring in Blaschko s lines can also be observed. 10 Mucous membrane lesions are very common, occurring in 30-70% of cases. The buccal mucosa and tongue are most often involved. White streaks, often forming a lacework, on the buccal mucosa are highly characteristic. Oral LP carries a significant risk of malignant transformation. Many studies have reported malignant transformation rate between 0.4 and 1.5%. 11 Nail involvement occurs in up to 10% of cases. 12 On standard histopathology, LP is characterized by the presence of a band-like lymphohistiocytic infiltrate at the dermal-epidermal junction with hydropic degeneration of the epidermis. Resultant dyskeratosis is represented by the presence of necrotic keratinocytes (Civatte bodies or cytoid bodies), which are extruded into the papillary dermis. Subepidermal clefts (Max- Joseph spaces) may form as a consequence of interface inflammation. Irregular acanthosis may assume a saw-toothed appearance. Hyperkeratosis is also seen. 13 Methods Sixty clinically diagnosed patients of LP attending the outpatient department of Dermatology of Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, constituted the study material. An informed consent was taken from the patients regarding the biopsy and participation in the study. The patients were subjected to detailed clinical examination and skin/mucosal biopsy was done which was subjected to detailed histopathological examination. Results Out of 60 patients of LP enrolled in the study, 24 (40%) were of oral LP, 19 (31.7%) were of classical LP (Table1). Oral LP and classical LP constituted the most common histopathological variants (35%). Biopsy was inconclusive in 10 (16%) cases (Table 2). Majority of patients i.e. 24 (40%) were in age group of years. LP in our study showed a female preponderance with 38 (63.3%) patients enrolled in the study being females. Majority of the cases (36.7%) sought medical help within 6-10 months of development of symptoms. Only 5% cases waited for more than 15 months before seeking medical help. Maximum number of cases (45%) showed only cutaneous involvement while 43.3% cases showed only mucosal involvement (Table 3). Oral cavity was the most common site involved with 28 (46.7%) cases showing oral involvement. Lower limbs were the second most common site involved in 27 (45%) cases. Burning sensation was reported in 48.3% cases. It was closely followed by pruritus in 45% cases. 345
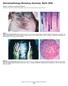
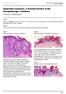
3 Table 1 Various clinical variants of lichen planus (n=60). Clinical diagnosis N (%) Classical lichen planus 19 (31.7) Reticular oral lichen planus 18 (30.0) Erosive oral lichen planus 6 (10.0) Hypertrophic lichen planus 6 (10.0) Lichen planus pigmentosus 5 (8.3) Eruptive lichen planus 3 (5.0) Genital lichen planus 1 (1.7) Lichen planopilaris 1 (1.7) Actinic lichen planus with discoid lupus erythematosus overlap 1 (1.7) Table 2 Histopathological variants of lichen planus (n=60). Histopathological diagnosis N (%) Classical lichen planus 21 (35) Reticular oral lichen planus 19 (31.7) Hypertrophic lichen planus 6 (10.0) Erosive oral lichen planus 2 (3.3) Lichen Planopilaris 1 (1.7) Lichen planus pigmentosus 1 (1.7) Inconsistent 10 (16.7) Table 3 Sites of involvement (n=60). Sites involved N (%) Cutaneous 27 (45.0) Mucosal 26 (43.3) Cutaneous + nail 4 (6.7) Cutaneous + oral 2 (3.3) Cutaneous + nail+ oral 1 (1.7) Table 4 Spectrum of signs and symptoms of lichen planus (n=60). Signs and symptoms N (%) Burning sensation 29 (48.3) Pruritus 27 (45.0) Pain 14 (23.3) Ulcers/erosions 7 (11.7) Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation 5 (8.3) Cicatricial alopecia 1 (1.7) Longitudinal ridging 6 (10.0) Nail plate thinning 2 (3.3) Onycholysis 1 (1.7) Koebner's phenomenon 10 (16.7) Wickham striae 21 (35) 23.3% of patients complained of pain. Wickham s striae were observed in 35% of cases while Koebner s phenomenon (Figure 1) was seen in 16.7% of cases. Table 5 Various histopathological features (n=60). Clinical diagnosis N (%) Hyperkeratosis/ orthokeratosis 38 (63.3) Wedge shaped hypergranulosis 37 (61.7) Irregular acanthosis/sawtooth rete ridges 51 (85.0) Vacuolar degeneration of basal layer 49 (81.7) Band-like infiltrate 43 (71.7) Melanophages in upper dermis 26 (43.3) Civatte bodies 27 (45.0) Max-Joseph spaces 10 (16.7) Pigment incontinence 25 (41.7) Follicular plugging 5 (8.3) Perivascular infiltrate 17 (28.3) Papillomatosis 1 (1.7) Chronic inflammatory infiltrate 6 (10.0) Atrophy 5 (8.3) Erosion 2 (3.3) In nail changes, longitudinal ridging was the most common finding observed in 10% cases (Table 4). Of all the cases, 16.7% patients complained of intense pruritus, 15% complained of moderate pruritus and only 13.3% experienced mild pruritus. 5 (8.3%) cases presented with only hyperpigmented violaceous papules and plaques without any associated symptoms. The commonest histopathological features recognized in our study were sawtooth rete ridges/ irregular acanthosis in 85%, vacuolar degeneration of basal layer in 81.7%, band-like infiltrate in 71.7%, hyperkeratosis/ orthokeratosis in 63.3% and wedge-shaped hypergranulosis in 61.7% of cases (Figure 2). Classical LP was the most common histopathological diagnosis, followed by oral reticular LP. LP pigmentosus showed sawtoothed rete ridges/ irregular acanthosis, vacuolar degeneration of the basal layer, bandlike infiltrate, melanophages in upper dermis, Civatte bodies, pigment incontinence, chronic inflammatory infiltrate and perivascular infiltrate. Single case of lichen planopilaris enrolled in our study showed vacuolar 346
4 Figure 1 Wickham s striae and Koebner s phenomenon. Figure 2 Hyperkeratosis, irregular acanthosis and vacuolar degeneration of basal layer along with pigment incontinence. Table 6 Clinico-histopathological correlation of lichen planus (n=60). Histopathological diagnosis Clinical Consistent Subtype Consistent with lichen diagnosis with Inconsistent planus but not subtype subtype Sensitivity to dig lichen planus Classical lichen planus inconsistent 17-lichen planus 89.50% Reticular oral lichen planus inconsistent 17- oral lichen planus 94.40% Erosive oral lichen planus inconsistent 2-oral lichen planus 33.30% Eruptive lichen planus lichen planus % Genital lichen planus lichen planus % Hypertrophic lichen planus % Lichen planopilaris % Actinic lichen planus with DLE overlap inconsistent % Lichen planus pigmentosus inconsistent 1-lichen planus 20.00% degeneration of basal layer, melanophages in upper dermis and perivascular infiltrate on histopathological examination. Ten cases did not show any features of lichen planus and were labelled as inconsistent (Table 5). In the present study, 50 out of 60 clinically diagnosed cases were confirmed on histopathology and only 10 cases were found inconsistent hence giving a sensitivity of 83.3%. Histopathological examination showed a sensitivity of 71.6% in identifying the various subtypes of lichen planus (Table 6). Regarding various associated comorbidities, hypertension was present in 18.3% cases, diabetes mellitus was seen in 6.7% cases, hepatitis C infection was present in 6.7% cases. Discussion Lichen planus (LP) is an idiopathic inflammatory skin disease affecting the skin and mucous membranes, often with a chronic course with relapses and periods of remission. In our study, majority of patients i.e. 24 (40%) were in age group of years, close second i.e. 20 (33.4%) patients were in the age group of
5 years. These findings are similar with other studies of the western population 14,15 ; however, in the studies of Indian population by Bhattacharya et al., 3 Singh and Kanwar, 16 a younger age group has been reported. However, in one Indian study by Arora et al. 17 an older age group of years has been reported. Furthermore, in the western literature LP is considered to be rare in children. 18 Even in those studies, which are published from the European countries, a proportion of patients were Indians. 19 In our study, we found that female gender is more commonly affected with lichen planus than males. Even though in the literature there has been no consensus regarding any sex preference of LP, but most of the studies have shown that females are more commonly affected than males 20,21,22 ; however, study by Kachhawa et al. 23 have shown male preponderance. In our study, the most common variant was oral LP seen in 40% of all enrolled cases. Reticular oral LP was the most common variant seen in 75% of total cases of oral LP followed by erosive oral LP seen in 25%. These findings are consistent with the study done by Munde et al. 24 Classical LP (31.7%) was the second most common subtype overall and the most common subtype (52.7%) in cutaneous LP followed by hypertrophic LP (16.6%). These findings are consistent with another study by Abdallat et al. 25 Oral cavity was the most common site involved in 46.7% of cases. In cutaneous LP lower limbs was the most commonly involved site seen in 75% of cases, which is in concordance with other studies done by Kachhawa et al. 23 and Kanwar et al. 26 Lichen planus pigmentosus showed a predilection for back involving 60% of cases. In another study by Parihar et al. 27 it was observed that face and neck were the most frequent initial sites of involvement followed by the trunk. Similar findings have been reported in previous studies by Bhutani et al. 28 and Kanwar et al. 29 Only one case of lichen planopilaris was enrolled in our study and it had lesions on the scalp. In the study by Parihar et al. 27 also, the most common site involved was scalp, seen in 82% patients. In the present study, burning sensation was the most common symptom in oral LP, although pruritus was the most common symptom in cutaneous LP as observed in the studies done by Parihar et al. 27 and Arora et al. 17 In the present study, Wickham s striae were observed in 35% of cases while Koebner s phenomenon was seen in 16.7% of cases. However, Koebner s phenomenon was observed in only 6% patients in the study done by Kanwar and De. 19 In our study, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation was seen in 8.3% of cases, while it was seen in 15.9% of patients in a study done by Abdallat et al. 25 In our study, nail involvement in the form of longitudinal ridging was seen in 10% of cases similar to a study by Garg et al. 30 On the contrary, Kanwar and De 26 have observed nail involvement in 19% of their patients In our study, the commonest histopathological features recognized were saw-toothed rete ridges/ irregular acanthosis seen in 85%, vacuolar degeneration of basal layer in 81.7%, band-like infiltrate in 71.7%, hyperkeratosis/ orthokeratosis in 63.3% and wedge-shaped hypergranulosis in 61.7% of cases followed by Civatte bodies in 45%, melanophages in upper dermis in 43.3%, pigment incontinence in 41.7%, perivascular infiltrate in 28.3% and Max- Joseph spaces in 16.7% of cases. In a study done by Arora et al. 17 and Garg et al., 30 epidermal changes included hypergranulosis (82%), hyperkeratosis (92%) and basal cell vacuolization (100%). The dermis showed band-like lymphocytic inflammatory cell infiltrate, predominantly perivascular in location. 17,30 348
6 In another study done by Parihar et al. 27 all the cases showed orthokeratosis. Irregular acanthosis was seen in 94% cases. Pointed rete ridges and dome-shaped papillae were identified in 76% cases, wedge-shaped hypergranulosis in 96.5%. The infiltrate in the upper dermis was band-like in 94% of cases, Civatte bodies or necrotic keratinocytes were present in 82% of cases in the lower epidermis and especially in the papillary dermis. Pigment incontinence was seen in 99% of cases. Max-Joseph spaces were apparent in 29.5% of cases. In our study, single case of lichen planopilaris enrolled showed vacuolar degeneration of basal layer, melanophages in upper dermis and perivascular infiltrate on histopathological examination. In the study done by Garg et al. 30 lichen planopilaris showed more marked keratotic plugging than classical LP and inflammatory infiltrate was predominantly perifollicular in nature. LP pigmentosus showed saw-toothed rete ridges/ irregular acanthosis, vacuolar degeneration of basal layer, band-like infiltrate, melanophages in upper dermis, Civatte bodies, erosion, pigment incontinence, chronic inflammatory infiltrate and perivascular infiltrate. In study by Parihar et al. 30 all the cases showed epidermal thinning and pigment incontinence, and 85% cases showed basal layer vacuolation. In our study hypertension was present in 18.3% of cases and diabetes mellitus in 6.7% of cases. While in a study done by Kachhawa et al., 23 hypertension was seen in 2.3% of cases and association with diabetes was also noted. Association with hypertension and diabetes was also noted by Bajaj et al. 31 Hepatitis C infection was present in 6.7% of cases enrolled in our study, while study done by Das et al. 32 showed associated HCV infection in 3.07% of cases while no association was found in the study done by Prabhu et al. 33 Conclusion Lichen planus is a common entity encountered in our day-to-day practice. In the majority of cases diagnosis can be made clinically. However, in difficult cases diagnosis can be clinched by histopathological examination as it shows a high sensitivity. Histopathological examination also shows a high sensitivity to effectively identify the various subtypes of lichen planus. It is important to identify the various subtypes of lichen planus as the prognosis, duration of treatment and advice to the patient varies for different subtypes. References 1. Darier J. Précis de Dermatologie. Paris: Masson, p Boyd AS, Neldner KH. Lichen planus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;25: Bhattacharya M, Kaur I, Kumar B. Lichen planus: a clinical and epidemiological study. J Dermatol. 2000;27: Sugerman PB, Satterwhite K, Bigby M. Autocytotoxic T-cell clones in lichen planus. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142: Deguchi M, Aiba S, Ohtani H, Nagura H, Tagami H. Comparison of the distribution and numbers of antigen-presenting cells among T lymphocyte-mediated dermatoses: CD1a+, factor XIIIa+, and CD68+ cells in eczematous dermatitis, psoriasis, lichen planus and graft-versus-host disease. Arch Dermatol Res. 2002;294: Sugerman PB, Savage NW, Walsh LJ, Zhao ZZ, Zhou XJ, Khan A et al. The pathogenesis of oral lichen planus. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2002;13: Lazar AJF, Murphy GF. The Skin. In: Kumar V, Abbas A, Fausto N, Aster JC. Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 8 th edn. Philadelphia: Saunders; P
7 8. Weedon D. The lichenoid tissue reaction. Int J Dermatol. 1982;21: Gorouhi F, Davari P, Fazel N. Cutaneous and mucosal lichen planus: a comprehensive review of clinical subtypes, risk factors, diagnosis, and prognosis. Sci World J. 2014;2014: Schmidt H. Frequency, duration and localization of lichen planus. A study based on 181 patients. Acta Derm Venereol. 1961;41: Shen ZY, Liu W, Zhu LK, Feng JQ, Tang GY, Zhou ZT. A retrospective clinicopathological study on oral lichen planus and malignant transformation: analysis of 518 cases. Med Oral Pathol Oral Cir Bucal. 2012;17:e Daramola OO, Ogunbiyi AO, George AO. Evaluation of clinical types of cutaneous lichen planus in anti-hepatitis C virus seronegative and seropositive Nigerian patients. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42: Lehman JS, Tolleffson MM, Gibson LE. Lichen Planus. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48: Andreason J. Oral lichen planus. A clinical evaluation of 115 cases. Oral Surg. 1968;25: Scully C, EI-Kom M. Lichen planus-review and update of pathogenesis. J Oral Pathol. 1985;14: Singh OP, Kanwar AI. Lichen planus in India - an appraisal of 441 cases. Int J Dermatol. 1976;15: Arora KS, Chhabra S, Saikia UN, Dogra S, Minz RW. Lichen planus: A clinical and immuno-histological analysis. Indian J Dermatol. 2014;59: Mellgren L, Hersle K. Lichen planus a clinical study with statistical methods. Indian J Dermatol. 1965;11: Kanwar AJ, De D. Lichen planus in childhood: report of 100 cases. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35: White CJ. Lichen Planus: a critical analysis of 64 cases. J Cutan Dis. 1919;37: Altman J, Perry HO. The variations and course of lichen planus. Arch Dermatol. 1961;84: Little EG. Lichen Planus. J Cutan Dis. 1919;37: Kachhawa D, Kachhawa V, Kalla G, Gupta L. A clinico-aetiological profile of 375 cases of lichen planus. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 1995;61: Munde AD, Karle RR, Wankhade PK, Shaik SS, Kulkumi M. Demographic and clinical profile of oral lichen planus: A retrospective study. Contemp Clin Dent. 2013;4: Abdallat SA, Maaita TJ. Epidemiological and clinical features of lichen planus in Jordanian patients. Pak J Med Sci. 2007;23: Kanwar AJ, De D. Lichen planus in children. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2010;76: Parihar A, Sharma S, Bhattacharya SN, Singh UR. A clinicopathological study of cutaneous lichen planus. J Dermatol Surg. 2015;19(1): Bhutani LK, Bedi TR. Lichen planus pigmentosus. Dermatologica. 1974;149: Kanwar AJ, Dogra S, Handa S, Parsad D, Radotra BD. A study of 124 Indian patients with lichen planus pigmentosus. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003;28: Garg VK, Nangia A, Logani K, Sharma RC. Lichen Planus-a Clinico-histopathological. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2000;66: Bajaj DR, Khoso NA, Devrajani BR, Matlani BL, Lohana P. Oral lichen planus: A clinical study. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2010;20: Das A, Das J, Majumdar G, Bhattacharya N, Neogi DK, Saha B. No association between seropositivity for hepatitis C virus and lichen planus: A case control study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2006;72: Prabhu S, Pavithran K, Sobhanadevi G. Lichen planus and hepatitis c virus (HCV) - Is there an association? A serological study of 65 cases. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2002;68:
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 10 Page October 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i10.125 Histomorphological Study of Lichen Planus
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i10.125 Histomorphological Study of Lichen Planus
Epidemiological study of Lichen Planus
 Year: 2014; Volume: 1; Issue: 1 Article ID: MD14 20; Pages: 1-9 BioMed Research The Open Access Publisher BMR Medicine Research Article Epidemiological study of Lichen Planus Shankar Gouda Ireddy 1 and
Year: 2014; Volume: 1; Issue: 1 Article ID: MD14 20; Pages: 1-9 BioMed Research The Open Access Publisher BMR Medicine Research Article Epidemiological study of Lichen Planus Shankar Gouda Ireddy 1 and
Title: Dermographic, clinical and histopathological pro le of cutaneous lichen planus
 Original Research Paper Dermatology Title: Dermographic, clinical and histopathological pro le of cutaneous lichen planus Dr. Rikeeta S. Deshmukh Dr. Raju G. Chaudhary ABSTRACT KEYWORDS Introduction: Unique,
Original Research Paper Dermatology Title: Dermographic, clinical and histopathological pro le of cutaneous lichen planus Dr. Rikeeta S. Deshmukh Dr. Raju G. Chaudhary ABSTRACT KEYWORDS Introduction: Unique,
Clinico - Histopathological features of Lichen Planus-an Appraisal
 Original Article Clinico - Histopathological features of Lichen Planus-an Appraisal Raghavendra B N 1, Jaffer Basha S K 1 Associate Professor, Department of Dermatology, M V J Medical College and Research
Original Article Clinico - Histopathological features of Lichen Planus-an Appraisal Raghavendra B N 1, Jaffer Basha S K 1 Associate Professor, Department of Dermatology, M V J Medical College and Research
Histopathological spectrum of non-infectious erythematous, papulo-squamous lesions
 Histopathological spectrum of non-infectious erythematous, papulo-squamous lesions B. Rajasekhar Reddy 1*, Nalini Krishna.M 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Mediciti Institute of Medical
Histopathological spectrum of non-infectious erythematous, papulo-squamous lesions B. Rajasekhar Reddy 1*, Nalini Krishna.M 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Mediciti Institute of Medical
Lichen planus along with Blaschko lines "Blaschkoian lichen planus"
 Original Article Lichen planus along with Blaschko lines "Blaschkoian lichen planus" Hossein Kavoussi, Mazaher Ramazani, Elias Salimi Dermatology Department, Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences,
Original Article Lichen planus along with Blaschko lines "Blaschkoian lichen planus" Hossein Kavoussi, Mazaher Ramazani, Elias Salimi Dermatology Department, Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences,
Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), available at
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
A Descriptive Study on Patients of Papulosquamous Lesion at Tertiary Care Institute
 MVP Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol 1(1), 30 35, January 2014 A Descriptive Study on Patients of Papulosquamous Lesion at Tertiary Care Institute S. D. Chavhan 1*, S. V. Mahajan 2 and A. J. Vankudre 3
MVP Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol 1(1), 30 35, January 2014 A Descriptive Study on Patients of Papulosquamous Lesion at Tertiary Care Institute S. D. Chavhan 1*, S. V. Mahajan 2 and A. J. Vankudre 3
A CLINICAL AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF LICHEN PLANUS
 A CLINICAL AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF LICHEN PLANUS Ch. Madhu Babu 1, P. Padmaja 2, M. Roopa Shree 3 1Professor, Department of Dermatology, Venereology, and Leprology, Osmania Medical College and General
A CLINICAL AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF LICHEN PLANUS Ch. Madhu Babu 1, P. Padmaja 2, M. Roopa Shree 3 1Professor, Department of Dermatology, Venereology, and Leprology, Osmania Medical College and General
ISPUB.COM. A Case of Actinic Lichen Planus. K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 8 Number K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park Citation K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park.. The Internet Journal of Dermatology. 2009 Volume 8 Number. Abstract The
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 8 Number K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park Citation K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park.. The Internet Journal of Dermatology. 2009 Volume 8 Number. Abstract The
Rameshwar Gutte and Uday Khopkar
 Extragenital unilateral lichen sclerosus et atrophicus in a child: a case report Rameshwar Gutte and Uday Khopkar Department of Dermatolgy, Seth GSMC and KEM Hospital, Parel, Mumbai-400012, India Egyptian
Extragenital unilateral lichen sclerosus et atrophicus in a child: a case report Rameshwar Gutte and Uday Khopkar Department of Dermatolgy, Seth GSMC and KEM Hospital, Parel, Mumbai-400012, India Egyptian
Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions. Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX
 1 Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX Susan Müller, DMD, MS Professor Department of Pathology
1 Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX Susan Müller, DMD, MS Professor Department of Pathology
Papulosquamous: clinicopathological
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Narayankar SL et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2018 Jan;6(1):309-316 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20175740
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Narayankar SL et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2018 Jan;6(1):309-316 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20175740
A Histopathologic Study of Papulosquamous Lesions of Skin
 Original 404 Article Indian Journal of Pathology: Research and Practice Volume 6 Number 2, April - June 2017 (Part 2) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21088/ijprp.2278.148x.6217.11 A Histopathologic Study of
Original 404 Article Indian Journal of Pathology: Research and Practice Volume 6 Number 2, April - June 2017 (Part 2) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21088/ijprp.2278.148x.6217.11 A Histopathologic Study of
Dermoscopic patterns in active and regressive lichen planus and lichen planus variants: a morphological study
 DERMTOLOGY PRCTICL & CONCEPTUL www.derm101.com Dermoscopic patterns in active and regressive lichen planus and lichen planus variants: a morphological study Şule Güngör 1, Ilteriş O. Topal 1, Emek K. Göncü
DERMTOLOGY PRCTICL & CONCEPTUL www.derm101.com Dermoscopic patterns in active and regressive lichen planus and lichen planus variants: a morphological study Şule Güngör 1, Ilteriş O. Topal 1, Emek K. Göncü
4. Pityriasis lichenoides
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details usually more than 5 cm in diameter and accompanied by poikiloderma. Some but not all patients may develop mycosis fungoides (Fig. 22.35).
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details usually more than 5 cm in diameter and accompanied by poikiloderma. Some but not all patients may develop mycosis fungoides (Fig. 22.35).
Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA)
 Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) Ahmed Abdullah Alhumidi King saud university, Riyadh, kingdom of Saudi Arabia Abstract Background: This
Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) Ahmed Abdullah Alhumidi King saud university, Riyadh, kingdom of Saudi Arabia Abstract Background: This
Dermoscopic findings in different clinical variants of lichen planus. Is dermoscopy useful?
 DERMATOLOGY PRACTICAL & CONCEPTUAL www.derm101.com Dermoscopic findings in different clinical variants of lichen planus. Is dermoscopy useful? Paula Friedman 1, Emilia Cohen Sabban 2, Carolina Marcucci
DERMATOLOGY PRACTICAL & CONCEPTUAL www.derm101.com Dermoscopic findings in different clinical variants of lichen planus. Is dermoscopy useful? Paula Friedman 1, Emilia Cohen Sabban 2, Carolina Marcucci
Original Research Article
 CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF PAPULOSQUAMOUS SKIN LESIONS Chowdari Balaji 1, Metta Parvathi 2, Seeram Satish Kumar 3, Gunta Divya Lekha 4, Latchupatula Lavanya 5, Mantripragada Vidya Soundarya Lahari 6,
CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF PAPULOSQUAMOUS SKIN LESIONS Chowdari Balaji 1, Metta Parvathi 2, Seeram Satish Kumar 3, Gunta Divya Lekha 4, Latchupatula Lavanya 5, Mantripragada Vidya Soundarya Lahari 6,
Scientific Dental Journal
 Scientific Dental Journal Pigmented Oral Lichen Planus: A Case Report Firstine Kelsi Hartanto 1, Thomas George Kallarakal 2 1 Department of Oral Medicine, Faculty of Dentistry, Trisakti University Indonesia
Scientific Dental Journal Pigmented Oral Lichen Planus: A Case Report Firstine Kelsi Hartanto 1, Thomas George Kallarakal 2 1 Department of Oral Medicine, Faculty of Dentistry, Trisakti University Indonesia
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide
 Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
ISSN X (Print)
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(9A):3211-3215 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(9A):3211-3215 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
A Histopathologic Study of Connective Tissue Diseases of Skin
 Original Article Indian Journal of Pathology: Research and Practice 393 Volume 6 Number 2, April - June 2017 (Part 2) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21088/ijprp.2278.148x.6217.9 A Histopathologic Study of Connective
Original Article Indian Journal of Pathology: Research and Practice 393 Volume 6 Number 2, April - June 2017 (Part 2) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21088/ijprp.2278.148x.6217.9 A Histopathologic Study of Connective
Blaschkoian Lichen Planus in an Amazghi; A Rare Case Report
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net The Open Dermatology Journal, 2014, 8, 45-50 45 Blaschkoian Lichen Planus in an Amazghi; A Rare Case Report Ebtisam Elghblawi * Open Access Dermatology
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net The Open Dermatology Journal, 2014, 8, 45-50 45 Blaschkoian Lichen Planus in an Amazghi; A Rare Case Report Ebtisam Elghblawi * Open Access Dermatology
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
 S023 Hair and Scalp Dermoscopy Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Bruna Duque Estrada, M.D. Instituto de Dermatologia Prof. Rubem David Azulay Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Disclosure of Relationship with Industry
S023 Hair and Scalp Dermoscopy Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Bruna Duque Estrada, M.D. Instituto de Dermatologia Prof. Rubem David Azulay Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Disclosure of Relationship with Industry
Immunoflourescent assessment of Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) type 1 in oral lichen planus
 Immunoflourescent assessment of Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) type 1 in oral lichen planus Muthanna K. Ali, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) ABSTRACT Background: Oral lichen planus is one of the most common dermatological
Immunoflourescent assessment of Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) type 1 in oral lichen planus Muthanna K. Ali, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) ABSTRACT Background: Oral lichen planus is one of the most common dermatological
A RARE CASE OF LICHEN PLANUS PEMPHIGOIDES Ashok Jain 1, Anjali Dalal 2
 A RARE CASE OF LICHEN PLANUS PEMPHIGOIDES Ashok Jain 1, Anjali Dalal 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ashok Jain, Anjali Dalal. A Rare Case of Lichen Planus Pemphigoides. Journal of Evolution of Medical and
A RARE CASE OF LICHEN PLANUS PEMPHIGOIDES Ashok Jain 1, Anjali Dalal 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ashok Jain, Anjali Dalal. A Rare Case of Lichen Planus Pemphigoides. Journal of Evolution of Medical and
Benign Lichenoid Keratosis
 Benign Lichenoid Keratosis ALAN F. FRIGY, M.D. AND PHILIP H. COOPER, M.D. The microscopic spectrum of benign lichenoid keratosis (BLK) was studied by examination of 30 examples. BLK consists of a segment
Benign Lichenoid Keratosis ALAN F. FRIGY, M.D. AND PHILIP H. COOPER, M.D. The microscopic spectrum of benign lichenoid keratosis (BLK) was studied by examination of 30 examples. BLK consists of a segment
Original Article. Palmoplantar Psoriasis versus Eczema: Major Histopathologic Clues for Diagnosis
 Iranian Journal of Pathology (2014) 9 (4), 251-256 251 Original Article Palmoplantar Psoriasis versus Eczema: Major Histopathologic Clues for Diagnosis Kambiz Kamyab Hesari, Zahra Safaei Naraghi, Azita
Iranian Journal of Pathology (2014) 9 (4), 251-256 251 Original Article Palmoplantar Psoriasis versus Eczema: Major Histopathologic Clues for Diagnosis Kambiz Kamyab Hesari, Zahra Safaei Naraghi, Azita
Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India.
 Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Antonella Tosti Fredric Brandt Endowed Professor of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery
 Dermoscopy in the evaluation and treatment of hair loss Antonella Tosti Fredric Brandt Endowed Professor of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Antonella Tosti, MD
Dermoscopy in the evaluation and treatment of hair loss Antonella Tosti Fredric Brandt Endowed Professor of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Antonella Tosti, MD
Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2
 Interface diseases Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2 Histological findings Severe hydropic vacuolation of epidermal and follicular basal cells/ interface dermatitis Multifocally apoptotic keratinocytes
Interface diseases Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2 Histological findings Severe hydropic vacuolation of epidermal and follicular basal cells/ interface dermatitis Multifocally apoptotic keratinocytes
Darier's Disease: Report Of A New Case With A Rare Clinical Appearance
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 1 Number 2 Darier's Disease: Report Of A New Case With A Rare Clinical Appearance A Darjani, A Ramezanpour Citation A Darjani, A Ramezanpour.. The Internet
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 1 Number 2 Darier's Disease: Report Of A New Case With A Rare Clinical Appearance A Darjani, A Ramezanpour Citation A Darjani, A Ramezanpour.. The Internet
A QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION OF EPITHELIUM AND INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE OF LICHEN PLANUS AND LICHENOID REACTIONS
 A QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION OF EPITHELIUM AND INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE OF LICHEN PLANUS AND LICHENOID REACTIONS 1 2 Usha Balan Nitin Gonsalves Maji Jose 1 Departments of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology, KMCT
A QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION OF EPITHELIUM AND INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE OF LICHEN PLANUS AND LICHENOID REACTIONS 1 2 Usha Balan Nitin Gonsalves Maji Jose 1 Departments of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology, KMCT
Epidemiology of Oral Lichen Planus in a Cohort of South Indian Population: A Retrospective Study
 JOURNAL OF CANCER PREVENTION Vol. 21, No. 1, March 2016 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.15430/jcp.2016.21.1.55&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-3-30 http://dx.doi.org/10.15430/jcp.2016.21.1.55 pissn
JOURNAL OF CANCER PREVENTION Vol. 21, No. 1, March 2016 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.15430/jcp.2016.21.1.55&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-3-30 http://dx.doi.org/10.15430/jcp.2016.21.1.55 pissn
Study Design. Patients
 Our Dermatology Online Lichen planus pigmentosus and association with autoimmune diseases: A case control study Monia Youssef 1, Ines Lahouel 1, Mouna Korbi 1, Yosra Soua 1, Hela Marmouch 2, Hayet Akkari
Our Dermatology Online Lichen planus pigmentosus and association with autoimmune diseases: A case control study Monia Youssef 1, Ines Lahouel 1, Mouna Korbi 1, Yosra Soua 1, Hela Marmouch 2, Hayet Akkari
Lichen planopilaris and its variants. Antonella Tosti. Fredric Brandt Endowed Professor of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery
 Lichen planopilaris and its variants Antonella Tosti Fredric Brandt Endowed Professor of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Antonella Tosti, MD S023 Lichen planopilaris
Lichen planopilaris and its variants Antonella Tosti Fredric Brandt Endowed Professor of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Antonella Tosti, MD S023 Lichen planopilaris
Grover s disease: A case report.
 320 Case report Thai J Dermatol, October-December 2011 ABSTRACT: Grover s disease: A case report. Supicha Chavanich MD, Praneet Sajjachareonpong MD. CHAVANICH C, SAJJACHAREONPONG P. GROVER S DISEASE: A
320 Case report Thai J Dermatol, October-December 2011 ABSTRACT: Grover s disease: A case report. Supicha Chavanich MD, Praneet Sajjachareonpong MD. CHAVANICH C, SAJJACHAREONPONG P. GROVER S DISEASE: A
Evaluation of Epidermal Reaction Pattern and Assessment of Histopathological Findings of Various Skin Disorders
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH www.ijcmr.com Evaluation of Epidermal Reaction Pattern and Assessment of Histopathological Findings of Various Skin Disorders Shweta Sharma 1, Dhara P Trivedi 2, Ronak Vyas 3 ABSTRACT
ORIGINAL RESEARCH www.ijcmr.com Evaluation of Epidermal Reaction Pattern and Assessment of Histopathological Findings of Various Skin Disorders Shweta Sharma 1, Dhara P Trivedi 2, Ronak Vyas 3 ABSTRACT
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation. Dermatopathology Specialists Needed. Changing Trends
 Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
Clinicoepidemiological and histopathological study of cutaneous amyloidosis with histopathological correlation
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Kilaparty K et al. Int J Adv Med. 2016 Aug;3(3):731-736 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20162526
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Kilaparty K et al. Int J Adv Med. 2016 Aug;3(3):731-736 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20162526
Pathology of the skin. Dr Fónyad László, 1sz. Patológiai és Kísérleti Rákkutató Intézet, SE
 Pathology of the skin Dr Fónyad László, 1sz. Patológiai és Kísérleti Rákkutató Intézet, SE The skin Biggest organ Kb. 1.8 nm Kb. 10 kg Most frequent site for tumor development (BCC) Pathology of the skin
Pathology of the skin Dr Fónyad László, 1sz. Patológiai és Kísérleti Rákkutató Intézet, SE The skin Biggest organ Kb. 1.8 nm Kb. 10 kg Most frequent site for tumor development (BCC) Pathology of the skin
Inflammatory skin disease I Jade Wititsuwannakul, MD Chulalongkorn University, Thailand
 Inflammatory skin disease I Jade Wititsuwannakul, MD Chulalongkorn University, Thailand Superficial Perivascular Dermatitis Interface Dermatitis Vacuolar Dermatitis Lichenoid Dermatitis Barnhill Textbook
Inflammatory skin disease I Jade Wititsuwannakul, MD Chulalongkorn University, Thailand Superficial Perivascular Dermatitis Interface Dermatitis Vacuolar Dermatitis Lichenoid Dermatitis Barnhill Textbook
Lichenoid Tissue Reaction in Malignant Melanoma A Potential Diagnostic Pitfall
 natomic Pathology / LICHENOID TISSUE RECTION IN MLIGNNT MELNOM Lichenoid Tissue Reaction in Malignant Melanoma Potential Diagnostic Pitfall CPT Scott R. Dalton, MC, US, 1,3 Capt Matt. aptista, USF, MC,
natomic Pathology / LICHENOID TISSUE RECTION IN MLIGNNT MELNOM Lichenoid Tissue Reaction in Malignant Melanoma Potential Diagnostic Pitfall CPT Scott R. Dalton, MC, US, 1,3 Capt Matt. aptista, USF, MC,
International Journal of Allied Medical Sciences and Clinical Research (IJAMSCR)
 International Journal of Allied Medical Sciences and Clinical Research (IJAMSCR) IJAMSCR Volume 4 Issue 3 July - Sep - 2016 www.ijamscr.com ISSN:2347-6567 Case report Medical research Reticulate acropigmentation
International Journal of Allied Medical Sciences and Clinical Research (IJAMSCR) IJAMSCR Volume 4 Issue 3 July - Sep - 2016 www.ijamscr.com ISSN:2347-6567 Case report Medical research Reticulate acropigmentation
Oral Lichen Planus A Case Report with Current Trends Review of Literature
 ISSN 2455-4499; Vol.05, Issue 01 (2016) Institute of Research Advances Pg. no. 6-17 http://research-advances.org/index.php/irajas Oral Lichen Planus A Case Report with Current Trends Review of Literature
ISSN 2455-4499; Vol.05, Issue 01 (2016) Institute of Research Advances Pg. no. 6-17 http://research-advances.org/index.php/irajas Oral Lichen Planus A Case Report with Current Trends Review of Literature
Porokeratosis: Introduction
 Porokeratosis: Introduction Benign epidermal proliferation Distinct clinical & histologic features 5 clinical subtypes Erroneously named porokeratosis CLINICAL SUBTYPES 1. Porokeratosis of Mibelli 2. Disseminated
Porokeratosis: Introduction Benign epidermal proliferation Distinct clinical & histologic features 5 clinical subtypes Erroneously named porokeratosis CLINICAL SUBTYPES 1. Porokeratosis of Mibelli 2. Disseminated
A New Diagnostic Approach for Idiopathic Circumscribed Acquired Hypermelanosis; A Clinicopathological Study
 American Journal of Dermatology and Venereology 214, 3(2): 35-42 DOI: 1.5923/j.ajdv.21432.3 A New Diagnostic Approach for Idiopathic Circumscribed Maytham M. Al-Hilo 1,2, Shakir J. Al-Saedy 1,2, Ali F.
American Journal of Dermatology and Venereology 214, 3(2): 35-42 DOI: 1.5923/j.ajdv.21432.3 A New Diagnostic Approach for Idiopathic Circumscribed Maytham M. Al-Hilo 1,2, Shakir J. Al-Saedy 1,2, Ali F.
Childhood Oral Lichen Planus: Report of Two Cases
 Case Report Sageena George 1, Sheen Ann John 2, Anandaraj S 3, Jyoti Sumi Issac 4, Anoop Harris 5, Reshmi J 6 1 Professor, Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry, PMS College of Dental Science
Case Report Sageena George 1, Sheen Ann John 2, Anandaraj S 3, Jyoti Sumi Issac 4, Anoop Harris 5, Reshmi J 6 1 Professor, Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry, PMS College of Dental Science
A prospective case control study on metabolic syndrome in lichen planus in a tertiary care centre
 International Journal of Research in Dermatology Kurian G et al. Int J Res Dermatol. 2017 Sep;3(3):427-432 http://www.ijord.com Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20173925
International Journal of Research in Dermatology Kurian G et al. Int J Res Dermatol. 2017 Sep;3(3):427-432 http://www.ijord.com Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20173925
Scenario of Histoid Hansen at a Tertiary Care Hospital in South India
 Indian J Lepr 2018, 90 : 235-240 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Case Series Scenario of Histoid Hansen at a Tertiary Care Hospital in South India 1 2 3 R Subha, M Ananthi, V
Indian J Lepr 2018, 90 : 235-240 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Case Series Scenario of Histoid Hansen at a Tertiary Care Hospital in South India 1 2 3 R Subha, M Ananthi, V
A DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA: ORAL LICHEN PLANUS OR LICHENOID REACTION - A SERIES OF CASE REPORTS
 CASE REPORT A DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA: ORAL LICHEN PLANUS OR LICHENOID REACTION - A SERIES OF CASE REPORTS Chanchal Sareen 1, Aparna Pathak 2, Puneet Ahuja 3, Moulshree Kohli 4 1 Senior Lecturer, 3 Prof & Head,
CASE REPORT A DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA: ORAL LICHEN PLANUS OR LICHENOID REACTION - A SERIES OF CASE REPORTS Chanchal Sareen 1, Aparna Pathak 2, Puneet Ahuja 3, Moulshree Kohli 4 1 Senior Lecturer, 3 Prof & Head,
Clinical profile of 108 cases of oral lichen planus
 43 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 58, No. 1, 43-47, 2016 Original Clinical profile of 108 cases of oral lichen planus Pritam K. Mankapure, Jayanti G. Humbe, Mandakini S. Mandale, and Jyoti D. Bhavthankar
43 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 58, No. 1, 43-47, 2016 Original Clinical profile of 108 cases of oral lichen planus Pritam K. Mankapure, Jayanti G. Humbe, Mandakini S. Mandale, and Jyoti D. Bhavthankar
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Acute generalized lichen planus with diffuse palmoplantar involvement in a 4-year old child: A case report and review
 CASE REPORT Acute generalized lichen planus with diffuse palmoplantar involvement in a 4-year old child: A case report and review Arun Joshi, MD, Manish Rijhwani, MD, Mohammed Alajmi, MD Department of
CASE REPORT Acute generalized lichen planus with diffuse palmoplantar involvement in a 4-year old child: A case report and review Arun Joshi, MD, Manish Rijhwani, MD, Mohammed Alajmi, MD Department of
Histoid Hansens The Current Perspective
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 36-41 www.iosrjournals.org Histoid Hansens The Current Perspective
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 36-41 www.iosrjournals.org Histoid Hansens The Current Perspective
Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 31-35 www.iosrjournals.org Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 31-35 www.iosrjournals.org Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Epidemiological study, clinical spectrum and associations of childhood vitiligo in a tertiary care centre
 International Journal of Research in Dermatology Murugaiyan R. Int J Res Dermatol. 2016 Dec;2(4):86-90 http://www.ijord.com Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20163976
International Journal of Research in Dermatology Murugaiyan R. Int J Res Dermatol. 2016 Dec;2(4):86-90 http://www.ijord.com Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20163976
Lichen sclerosus. Lichen planus
 Lichen sclerosus Lichen planus Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist, Heatherwood and Wexham Park NHS Foundation Trust & St John s Institute of Dermatology, GSTT Outline Typical features of lichen sclerosus
Lichen sclerosus Lichen planus Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist, Heatherwood and Wexham Park NHS Foundation Trust & St John s Institute of Dermatology, GSTT Outline Typical features of lichen sclerosus
CD30 + cells in benign inflammatory infiltrate of some dermatological diseases. Abstract. Latef M. El Balshy. Benha University-Benha, Egypt.
 CD30 + cells in benign inflammatory infiltrate of some dermatological diseases 1 Asmaa M. El Refaeie, 1 Osama H. Abdel Salam, 1 Sherine H.Abd EL-Rahman and 2 Abdel Latef M. El Balshy. 1 Dermatology & Andrology
CD30 + cells in benign inflammatory infiltrate of some dermatological diseases 1 Asmaa M. El Refaeie, 1 Osama H. Abdel Salam, 1 Sherine H.Abd EL-Rahman and 2 Abdel Latef M. El Balshy. 1 Dermatology & Andrology
PSORIASIS PSORIASIS. Anatomic sites FACTS ABOUT PROSIASIS PSORIASIS 11/16/2017 STIGMATA OF PSORIASIS
 PSORIASIS Dr. Sami Alsuwaidan President, Saudi Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery Associate Professor and Consultant Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine King Saud University PSORIASIS
PSORIASIS Dr. Sami Alsuwaidan President, Saudi Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery Associate Professor and Consultant Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine King Saud University PSORIASIS
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology Dermatologic Diseases Chapter 16 ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA o Two or more ectodermally derived anatomic structures fail to develop o
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology Dermatologic Diseases Chapter 16 ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA o Two or more ectodermally derived anatomic structures fail to develop o
INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I. Immunopathology Part I
 INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I Immunopathology Part I Nonspecific & T Cell Mediated Mucosal Inflammatory Lesions Nonspecific and Idiopathic Mucositis Hypersensitivity and Autoimmune T cell mediated Immunoglobulin
INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I Immunopathology Part I Nonspecific & T Cell Mediated Mucosal Inflammatory Lesions Nonspecific and Idiopathic Mucositis Hypersensitivity and Autoimmune T cell mediated Immunoglobulin
Vaginal involvement in genital erosive lichen planus
 Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica. 2010; 89: 966 970 SHORT REPORT Vaginal involvement in genital erosive lichen planus ANNE LISE ORDING HELGESEN 1,2,3, PETTER GJERSVIK 3,4, PETER JEBSEN 5, ROLF KIRSCHNER
Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica. 2010; 89: 966 970 SHORT REPORT Vaginal involvement in genital erosive lichen planus ANNE LISE ORDING HELGESEN 1,2,3, PETTER GJERSVIK 3,4, PETER JEBSEN 5, ROLF KIRSCHNER
The Utility Of Congo Red Stain And Cytokeratin Immunostain In The Detection Of Primary Cutaneous Amyloidosis
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 17 Number 1 The Utility Of Congo Red Stain And Cytokeratin Immunostain In The Detection Of Primary Cutaneous A,A Citation A, A.. The Internet Journal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 17 Number 1 The Utility Of Congo Red Stain And Cytokeratin Immunostain In The Detection Of Primary Cutaneous A,A Citation A, A.. The Internet Journal
04/09/2018. Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions. Agenda. Squamous Dysplasia. Squamo-proliferative lesions. Architectural features
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Skin Deep: Cutaneous Lupus. Dr Sarah Sasson Immunology Registrar, Liverpool Hospital 2016
 Skin Deep: Cutaneous Lupus Dr Sarah Sasson Immunology Registrar, Liverpool Hospital 2016 Introduction: Cutaneous lupus erythematosus LE is an autoimmune disease with a range of clinical manifestations
Skin Deep: Cutaneous Lupus Dr Sarah Sasson Immunology Registrar, Liverpool Hospital 2016 Introduction: Cutaneous lupus erythematosus LE is an autoimmune disease with a range of clinical manifestations
Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus. Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university
 Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university A 50-year old lady, who is otherwise healthy, presented to the dermatology clinic with
Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university A 50-year old lady, who is otherwise healthy, presented to the dermatology clinic with
Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations
 Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations Martin S. Greenberg DDS, FDS RCSEd Professor Emeritus Department of Oral Medicine University of Pennsylvania Disclosure Statement I have no actual or potential
Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations Martin S. Greenberg DDS, FDS RCSEd Professor Emeritus Department of Oral Medicine University of Pennsylvania Disclosure Statement I have no actual or potential
A. Erythema multiforme and related diseases
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Erythema, Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis) Erythema is caused by telangiectasia or hyperemia in the papillary and reticular
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Erythema, Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis) Erythema is caused by telangiectasia or hyperemia in the papillary and reticular
Histopathological evaluation of oral lichen planus
 Histopathological evaluation of oral lichen planus Layla S. Yas, B.D.S. M.Sc. (1) ABSTRACT Background: Oral lichen planus( OLP) is a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting mucosal surfaces, which can
Histopathological evaluation of oral lichen planus Layla S. Yas, B.D.S. M.Sc. (1) ABSTRACT Background: Oral lichen planus( OLP) is a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting mucosal surfaces, which can
R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology
 Rom J Morphol Embryol 2011, 52(4):1355 1360 CASE REPORT R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Atypical variant of lichen planus mimicking normal skin histology FLAVIA
Rom J Morphol Embryol 2011, 52(4):1355 1360 CASE REPORT R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Atypical variant of lichen planus mimicking normal skin histology FLAVIA
Interesting Case Series. Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis
 Interesting Case Series Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis Sean Chen, BA, a Peter Mattei, MD, a Max Fischer, MD, MPH, a Joshua D. Gay, PA-C, b Stephen M. Milner, MBBS, BDS, FRCS (Ed), FACS, b and Leigh Ann
Interesting Case Series Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis Sean Chen, BA, a Peter Mattei, MD, a Max Fischer, MD, MPH, a Joshua D. Gay, PA-C, b Stephen M. Milner, MBBS, BDS, FRCS (Ed), FACS, b and Leigh Ann
Clinical and Histopathological Spectrum of Mycosis Fungoides
 Awad Hasan Al-Tarawneh, MD, Jordan Board* Background: Early diagnosis of mycosis fungoides is essential but difficult and can be easily missed because it mimics many inflammatory skin diseases both clinically
Awad Hasan Al-Tarawneh, MD, Jordan Board* Background: Early diagnosis of mycosis fungoides is essential but difficult and can be easily missed because it mimics many inflammatory skin diseases both clinically
Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses
 Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses Vu A. Ngo, DO Department of Family Medicine and Dermatology Choctaw Nation Health Services Authority Learning Objectives Introduction to dermoscopy
Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses Vu A. Ngo, DO Department of Family Medicine and Dermatology Choctaw Nation Health Services Authority Learning Objectives Introduction to dermoscopy
Inflammatory Dermatoses of the Vulva for the General/Gyn Pathologist with emphasis in the lichenoid pattern
 Inflammatory Dermatoses of the Vulva for the General/Gyn Pathologist with emphasis in the lichenoid pattern By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor
Inflammatory Dermatoses of the Vulva for the General/Gyn Pathologist with emphasis in the lichenoid pattern By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor
CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE
 CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE Generalized vesiculo-bullous and pustular eruption in an adult man Hassab El-Naby H, MD, El-Khalawany M, MD Department of Dermatology, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt CLINICAL
CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE Generalized vesiculo-bullous and pustular eruption in an adult man Hassab El-Naby H, MD, El-Khalawany M, MD Department of Dermatology, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt CLINICAL
Degos Disease: A Case Report and Review of Literature
 Degos Disease: A Case Report and Review of Literature Monira waked Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 4 (1): 5, June 2008 Al Houd Al Marsod Hospital Submitted for publication: May 25 th, 2008 Accepted
Degos Disease: A Case Report and Review of Literature Monira waked Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 4 (1): 5, June 2008 Al Houd Al Marsod Hospital Submitted for publication: May 25 th, 2008 Accepted
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS A CASE REPORT *Prathima
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS A CASE REPORT *Prathima
Pyrex Journals
 Pyrex Journals 235-212 Pyrex Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences Vol 2 (2) pp 31-36 May, 215 http:///pjmms Copyright 215 Pyrex Journals Full Length Research Paper Lichen Planus Not Associated With
Pyrex Journals 235-212 Pyrex Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences Vol 2 (2) pp 31-36 May, 215 http:///pjmms Copyright 215 Pyrex Journals Full Length Research Paper Lichen Planus Not Associated With
IJCMR 1. Jay Ashokkumar Pandya, 1 Srikant Natarajan, 2 Karen Boaz, 3 Nidhi Manaktala, 4 Amitha J Lewis, 5 Supriya Nikita Kapila 1 ABSTRACT
 IJCMR 1 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Assessment And Comparison of Keratin, Epithelial And Inflammatory Thickness In Oral Lichen Planus And Oral Reaction Using Picrosirius Red Stain Jay Ashokkumar Pandya, 1 Srikant
IJCMR 1 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Assessment And Comparison of Keratin, Epithelial And Inflammatory Thickness In Oral Lichen Planus And Oral Reaction Using Picrosirius Red Stain Jay Ashokkumar Pandya, 1 Srikant
Case Report Giant Verrucous Haemangioma with Linear Features A Rare Entity and Successful Treatment with Complete Excision and Grafting
 IBIMA Publishing JMED Research http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/jmed/jmed.html Vol. 2016 (2016), Article ID 952849, 5 pages DOI: 10.5171/2016.952849 Case Report Giant Verrucous Haemangioma with
IBIMA Publishing JMED Research http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/jmed/jmed.html Vol. 2016 (2016), Article ID 952849, 5 pages DOI: 10.5171/2016.952849 Case Report Giant Verrucous Haemangioma with
Verrucous porokeratosis: A case report
 Case Report Verrucous porokeratosis: case report Hojat Eftekhari, MD 1 Rana Rafiei, MD 1 Fatemeh Shamsa, MD 1 ehnam Rafiee, MD 2 1. Skin Research Center, Dermatology Department, Guilan University of Medical
Case Report Verrucous porokeratosis: case report Hojat Eftekhari, MD 1 Rana Rafiei, MD 1 Fatemeh Shamsa, MD 1 ehnam Rafiee, MD 2 1. Skin Research Center, Dermatology Department, Guilan University of Medical
Pigmented skin lesions: are they all of melanocytic origin? A histopathological perspective
 Original Article Pigmented skin lesions: are they all of melanocytic origin? A histopathological perspective Rajesh Singh Laishram, Barida Ginia Myrthong, Sharmila Laishram, Rachel Shimray, Arun Kumar
Original Article Pigmented skin lesions: are they all of melanocytic origin? A histopathological perspective Rajesh Singh Laishram, Barida Ginia Myrthong, Sharmila Laishram, Rachel Shimray, Arun Kumar
CHAPTER 22 Brocq s alopecia (pseudopelade of Brocq) and burnt out scarring alopecia
 CHAPTER 22 Brocq s alopecia (pseudopelade of Brocq) and burnt out scarring alopecia BROCQ S ALOPECIA The term pseudopelade of Brocq is a source of much confusion and fruitless debate, and should be abandoned.
CHAPTER 22 Brocq s alopecia (pseudopelade of Brocq) and burnt out scarring alopecia BROCQ S ALOPECIA The term pseudopelade of Brocq is a source of much confusion and fruitless debate, and should be abandoned.
=ﻰﻤاﻤﺤﻠا ﺔﻴﻘﻠﺤﻠا ﺔذﺒاﻨﻠا
 1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
Dermatopathology Workshop Summary, Berlin 2004
 Dermatopathology Workshop Summary, Berlin 2004 David A. Whiting and Rolf Hoffmannw Baylor Hair Research and Treatment Center, Dallas, Texas, USA; wdermatology Practice, Freiburg, Germany Figure 1 Case
Dermatopathology Workshop Summary, Berlin 2004 David A. Whiting and Rolf Hoffmannw Baylor Hair Research and Treatment Center, Dallas, Texas, USA; wdermatology Practice, Freiburg, Germany Figure 1 Case
Imatinib mesylate is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor
 Induced Lichenoid Drug Eruption Erin H. Penn, MD; Hye Jin Chung, MD; Matthew Keller, MD PRACTICE POINTS mesylate can cause cutaneous adverse reactions including dry skin, alopecia, facial edema, photosensitivity
Induced Lichenoid Drug Eruption Erin H. Penn, MD; Hye Jin Chung, MD; Matthew Keller, MD PRACTICE POINTS mesylate can cause cutaneous adverse reactions including dry skin, alopecia, facial edema, photosensitivity
Mucinoses Diverse group of disorders which have in common deposition of basophilic, finely granular and stringy material in the connective tissues of
 Cutaneous Mucinoses Nathan C. Walk, M.D. Mucinoses Diverse group of disorders which have in common deposition of basophilic, finely granular and stringy material in the connective tissues of the dermis.
Cutaneous Mucinoses Nathan C. Walk, M.D. Mucinoses Diverse group of disorders which have in common deposition of basophilic, finely granular and stringy material in the connective tissues of the dermis.
Dilated Lymphatics in Gottron s Papules
 2010;18(2):99-103 CASE REPORT Dilated Lymphatics in Gottron s Papules Angel Fernandez-Flores Service of Cellular Pathology, Clinica Ponferrada, Ponferrada, Spain Corresponding author: Angel Fernandez-Flores,
2010;18(2):99-103 CASE REPORT Dilated Lymphatics in Gottron s Papules Angel Fernandez-Flores Service of Cellular Pathology, Clinica Ponferrada, Ponferrada, Spain Corresponding author: Angel Fernandez-Flores,
المركب النموذج--- سبيتز وحمة = Type Spitz's Nevus, Compound SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7
 SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
Correlation of clinical and histopathological classification of Leprosy in post elimination era
 Indian J Lepr 2012, 84 : 271-275 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article Correlation of clinical and histopathological classification of Leprosy in post elimination era
Indian J Lepr 2012, 84 : 271-275 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article Correlation of clinical and histopathological classification of Leprosy in post elimination era
Lichen planopilaris in a Latin American (Chilean) population: demographics, clinical profile and treatment experience
 Original article CED Clinical and Experimental Dermatology Lichen planopilaris in a Latin American (Chilean) population: demographics, clinical profile and treatment experience F. Mardones 1 and J. Shapiro
Original article CED Clinical and Experimental Dermatology Lichen planopilaris in a Latin American (Chilean) population: demographics, clinical profile and treatment experience F. Mardones 1 and J. Shapiro
ISPUB.COM. Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations. D Sarma, S Repertinger
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
Bullous Darier s Disease Mimicking Hailey-Hailey Disease
 Dermatol Ther (2011) 1(2):31-35. DOI 10.1007/s13555-011-0007-x CASE REPORT Bullous Darier s Disease Mimicking Hailey-Hailey Disease Aida Khaled Myriam Ben Hamida Samia Goucha Rachida Zermani Soumaya Rameh
Dermatol Ther (2011) 1(2):31-35. DOI 10.1007/s13555-011-0007-x CASE REPORT Bullous Darier s Disease Mimicking Hailey-Hailey Disease Aida Khaled Myriam Ben Hamida Samia Goucha Rachida Zermani Soumaya Rameh
CLINICAL, LABORATORY AND THERAPEUTIC PROFILE OF LICHEN PLANUS
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2017 vol. 121, no. 1 INTERNAL MEDICINE - PEDIATRICS ORIGINAL PAPERS CLINICAL, LABORATORY AND THERAPEUTIC PROFILE OF LICHEN PLANUS Daciana Elena Brănișteanu 1, A. Pintilie
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2017 vol. 121, no. 1 INTERNAL MEDICINE - PEDIATRICS ORIGINAL PAPERS CLINICAL, LABORATORY AND THERAPEUTIC PROFILE OF LICHEN PLANUS Daciana Elena Brănișteanu 1, A. Pintilie
A study of treatment modalities in psoriasis in dermatology outpatient department of a tertiary care teaching hospital
 Original article A study of treatment modalities in psoriasis in dermatology outpatient department of a tertiary care teaching hospital 1Y Roja Ramani, 2 Benu Panigrahy, 3 Sailenkumar Mishra, 4 BTPS Singh
Original article A study of treatment modalities in psoriasis in dermatology outpatient department of a tertiary care teaching hospital 1Y Roja Ramani, 2 Benu Panigrahy, 3 Sailenkumar Mishra, 4 BTPS Singh
International Journal of Scientific Research and Innovative Technology ISSN: Vol. 4 No. 12; December 2017
 THE FREQUENCY OF ORAL LICHEN PLANUS IN SAMPLES SENT TO PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF TABRIZ DENTAL SCHOOL (2006-2016) AND ITS RELATION WITH AGE, SEX, LESION TYPE AND LOCATION Farzaneh Pakdel 1, Parya Emamverdizadeh
THE FREQUENCY OF ORAL LICHEN PLANUS IN SAMPLES SENT TO PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF TABRIZ DENTAL SCHOOL (2006-2016) AND ITS RELATION WITH AGE, SEX, LESION TYPE AND LOCATION Farzaneh Pakdel 1, Parya Emamverdizadeh
Tejinder Kaur; Rajesh Rani Gupta; BB Mahajan; Rajiv Sachdeva
 Pachyonychia congenita type 1- Jadassohn Lewandowsky syndrome Tejinder Kaur; Rajesh Rani Gupta; BB Mahajan; Rajiv Sachdeva Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Institute- Guru Gobind Singh medical
Pachyonychia congenita type 1- Jadassohn Lewandowsky syndrome Tejinder Kaur; Rajesh Rani Gupta; BB Mahajan; Rajiv Sachdeva Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Institute- Guru Gobind Singh medical
