Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma and Pruritus: The Expression of IL-31 and its Receptors in the Skin
|
|
|
- Oswin Bridges
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Derm Venereol 1; 9: 9 9 INVESTIGATIVE REPORT Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma and Pruritus: The Expression of IL-31 and its Receptors in the Skin Leigh A. NATTKEMPER 1, Maria-Estela MARTINEZ-ESCALA, Ari B. GELMAN 1, Elisha M. SINGER 3, Alain H. ROOK 3, Joan GUITART and Gil YOSIPOVITCH 1 1 Department of Dermatology and Temple Itch Center, Temple University School of Medicine, Philadelphia, Department of Dermatology, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, and 3 Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA, USA Approximately % of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma () patients are affected by pruritus that responds poorly to current anti therapies. Interleukin (IL)-31, a Th cytokine, has been found to be increased in the serum of patients and to correlate with itch severity. This study investigated the role of IL-31 and its receptors (IL-31 receptor-alpha [IL-31RA] and OSMRβ) in the skin of patients with mild versus moderate/severe pruritus. Expression levels of IL- 31, IL-31RA, and OSMRβ in the skin were measured using immunohistochemistry and correlated to pruritus severity and disease stage. In patients with moderate/severe pruritus, IL-31 was significantly elevated in the epidermis and dermal infiltrate, while IL-31RA and OSMRβ were significantly elevated only in the epidermis. Furthermore, epidermal IL-31 levels correlated to itch severity. These results show that IL-31 may play a role in pruritus by exerting indirect effects on sensory nerves through epidermal neoplastic T cells and keratinocytes to transmit itch. Key words: ; skin; pruritus; IL-31; IL-31RA; OSMRβ. Accepted Mar 17, 1; Epub ahead of print Mar, 1 Acta Derm Venereol 1; 9: 9 9. Gil Yosipovitch, MD, Department of Dermatology and Temple Itch Center, Temple University School of Medicine, 33 North Broad Street, Medical Office Building, suite 1, Philadelphia, PA 191, USA. Gil. Yosipovitch@tuhs.temple.edu Acta Derm Venereol 9 Pruritus significantly impacts the lives of patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (), the most common forms of which are mycosis fungoides (MF) and Sézary syndrome (SS) (1 ). Surveys of patients with have found a prevalence of pruritus between % and % (1 3). Because pruritus of is nonhistaminergic, it is difficult to treat and responds poorly to antihistamines (, ). The need for a more complete understanding of the pathophysiology of pruritus has led to an investigation into potential mediators. Cytokines may play an important role in the pruritus of. skin lesions typically express Th cytokines, such as interleukins (IL)-, 5,, 9, 1, and 13. Th expression increases as the disease progresses, which may explain why pruritus can be more severe at later stages of the disease (, 7). Studies in other disorders have found elevated levels of IL-31, a member of the IL- family of cytokines, in atopic dermatitis, prurigo nodularis, and allergic contact dermatitis ( 11). IL-31 acts through a heterodimeric receptor composed of IL- 31 receptor alpha (IL-31RA) and oncostatin M receptor beta (OSMRβ) (1). IL-31 is produced by a variety of sources, including Th T-cells, dendritic cells, mast cells, and keratinocytes. IL-31RA and OSMRβ are expressed on keratinocytes and dorsal root ganglia, which conduct the afferent sensation of pruritus (1). Recently, Singer et al. (13) found that the malignant T-cell population produced IL-31 and that the increased levels of this cytokine in serum and peripheral blood mononuclear cells correlated with pruritus severity. In another study, IL-31 serum levels were elevated in patients but did not correlate with pruritus severity (1). However, these observed differences could be due to differences in the patients stages of. Given the potential association between IL-31 and pruritus, we investigated the expression of IL-31 and its receptors in patients with and correlated our findings with both the clinical stage of each patient and the severity of their pruritus. We discovered that expression levels of IL-31, IL- 31RA, and OSMRβ were elevated in the epidermis of affected skin and that IL-31 expression was significantly correlated with itch severity. These results offer insight into the pathophysiology of pruritus in. METHODS Subjects Skin biopsies were obtained from patients and healthy subjects at the dermatology clinics of Temple University, Northwestern University, and the University of Pennsylvania in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and with approval by each institution s Institutional Review Board. Patients were diagnosed based on clinical, histopathological, and immunohistological criteria and staged using the Tumor- Node-Metastasis-Blood (TNMB) 7 International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas (ISCL) and European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) revised classifica- 1 The Authors. doi: 1.3/ Journal Compilation 1 Acta Dermato-Venereologica. ISSN
2 IL-31 and receptors in the skin of 95 tion system (15, 1). Patient characteristics are described in Table I. Patients with MF had patch lesions biopsied for stage IB and plaque lesions biopsied for stage IIB. Tumor lesions were biopsied for patients with stage IIB folliculotropic MF. SS patients had patch lesion biopsies performed and the patient with primary cutaneous γδ T-cell lymphoma was biopsied in a plaque lesion. Pruritus severity was measured at the time of the biopsy using a visual analog scale (VAS). Subjects were grouped into the following categories: mildly (VAS 1 5; n = ), moderately/ (VAS 1; n = 15), and healthy controls (VAS ; n = ). We did not recruit patients without pruritus. Histology and immunohistochemistry Researchers were blinded to the identity of the biopsies and the results were only decoded after the analysis was fully performed. For histology to confirm disease stage, 5-μm thick sections of paraffin-embedded skin tissue were processed for standard hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. For immunohistochemistry, a total of 1 -μm thick sections of paraffin-embedded skin tissue were double stained from each biopsy. Sections were deparaffinized and then underwent antigen retrieval using Target Retrieval Solutions (DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark) heated in a humidified oven overnight at C, then washed in PBS. Sections were blocked with 5% normal donkey serum and.% Triton X-1 in PBS for h and then incubated with primary antibodies overnight at C. Primary antibody combinations were: anti-pgp9.5 (1:5; Abcam, Cambridge, MA) and anti-il-31 (1:1; Abcam); anti-il-31ra (1:, Abcam) and anti-osmrβ (1:1; Santa Cruz, Dallas, Texas). Alexa Fluor ( & 59, 1:3; Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR) secondary antibodies were used for detection. The slides were mounted with Vectashield with DAPI (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA) and imaged under a fluorescence microscope. Sections treated without any primary antibodies were used as negative controls. Furthermore, specificity of the IL-31 and IL- 31RA antibody was confirmed by pre-absorbing the full length IL-31 and IL-31RA peptides ( μg/ml; Abcam) in blocking solutions with their respective antibodies overnight at C with gentle agitation. Solutions were centrifuged, and the supernatant was used for IHC as described above, which resulted in blocking the IL-31 and IL-31RA immunoreactivity. Quantification Three fields (X objective magnification) were measured for every section. The total field and selected field (epidermis) Table I. Sample demographic data fluorescence area (in μm ) were measured and normalized to background staining using ImageJ Software. Data is presented as the mean epidermal fluorescence and mean dermal infiltrate fluorescence, which was calculated as the total field selected field fluorescence. Inter-epidermal nerve fibers were counted and normalized to tissue length as previously described (17). The immunofluorescence staining was further compared to the H&E staining to examine localization of positive staining to lymphocytes. Statistical analysis was carried out using one-way ANOVAs with Bonferroni post hoc tests and non-paramentric two-tailed Spearman correlations with linear regression; significance was set at p <.5 (GraphPad Prism; La Jolla, CA). RESULTS n = 15 n = controls n = Age, years, mean ± SD 5 ± ± 1..9 ± 9.7 Sex (M:F), n 7: : : VAS rating, mean ± SD 7.5 ± 1..5 ± 1.5 Diagnosis, n Mycosis fungoides (MF) 3 (IB) a, 1 (IIB) 1 (IB) Folliculotropic MF 3 (IIB) (IIB) Sézary syndrome 7 (IVA) 5 (IVA) PCGDTCL 1 (T3NM) a Stage (Tumor-Node-Metastasis-Blood). PCGDTCL: primary cutaneous gamma delta T-cell lymphoma. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma characteristics and pruritus The mean ages of the 3 groups (Table I) did not significantly differ from one another. There was a statistically significant difference (p <.1) in pruritus VAS ratings among healthy (VAS ), mildly (VAS.5 ± 1.5), and moderately/ (VAS 7.5 ± 1.) subjects (Fig. 1A). No correlation was found between age and VAS ratings (Fig. 1B). The stage of correlated to VAS ratings (r =.5, p =.) in mildly subjects only (Fig. 1C) Non Age IA IB IIB III IVA IVB Stage Fig. 1. Pruritic VAS rating and its correlation to cutaneous T-cell lymphoma () stage. (A) The VAS rating was significantly higher in patients when compared to healthy controls (p <.1, p <.1). (B) The pruritus rating did not correlate to subject age. (C) The pruritus ratings correlated to disease stage in the mildly group only. Acta Derm Venereol 9
3 L. A. Nattkemper et al. 9 IL-31 and epidermal innervation (PGP 9.5) IL-31 was significantly (p <.1) increased in the epidermis and lymphocytic infiltrate of subjects, with the moderately/ subjects having the highest levels of IL-31 in the skin (Fig. A). The mean ± SD IL-31 fluorescence levels in the epidermis of moderately/ subjects were 1,59 ± 71, while the infiltrate levels were 1,9 ± 1. In mildly subjects, the IL-31 levels were 1,9 ± 13 in the epidermis and 5 ± 13 in the infiltrate. controls did present with some constitutive IL-31 in the epidermis, with levels of 39 ± 7, but little to none in the dermis (5 ± 15). Interestingly, in all subjects, IL-31 expression was limited to the lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis and in the epidermis (representative image: Fig. B). No significant difference among groups was found in the number of epidermal nerve fibers, and IL-31 did not appear to co-localize to any afferent fibers (data not shown). Epidermal IL-31 levels significantly correlated (r =.9; p <.1) with VAS ratings (Fig. C), but not with stage (r =.; p =.; Fig. D). IL-31RA and OSMRβ IL-31RA was significantly (p <.1) elevated in only the epidermis of subjects (Fig. 3A; representative image: Fig. 3C). The mean ± SD IL-31RA fluorescence levels were highest in moderately/ subjects, with levels of 1,39 ± 13 in the epidermis and 5 ± 1 in the lymphocytic infiltrate. subjects had expression levels of ± in the IL-31 flourescence (µm ) C 5 DISCUSSION Although several recent studies have found increased levels of IL-31 in, these studies largely focus on serum analysis and do not address the crucial question of IL-31 s role in the skin (13, 1, 1). This is the first study to show the expression levels and patterns of IL-31 and both of its receptors within the skin of subjects with pruritus. Similar to most of the previous serum studies, this study shows that elevated IL-31 is positively correlated to itch intensity (13, 1). We also report that IL-31 was not correlated to disease stage, suggesting that IL-31 does not play an essential B 15 1 ns 5 Non D 5 IL-31 flourescence (µm ) IL-31 flourescence (µm ) A epidermis and 1 ± 9 in the infiltrate, while healthy controls had levels of only 377 ± 5 in the epidermis and 1 ± 3 in the dermis. Epidermal IL-31RA levels significantly correlated (r =.; p <.1) with VAS ratings (Fig. 3B), but not with stage (r =.1; p =.9). Furthermore, OSMRβ was also significantly (p <.1) higher in the epidermis of subjects (Fig. 3D); representative image: Fig. 3F). In moderately/ subjects, the mean ± SD OSMRβ fluorescence levels were 93 ± 1 in the epidermis and 1 ± 93 in the lymphatic infiltrate. subjects had levels of 1 ± 3 in epidermis and 17 ± 13 in the lymphocytic infiltrate. The lowest levels of OSMRβ were observed in healthy controls (epidermis 13 ± ; dermis 7 ± 15). Epidermal OSMRβ levels significantly correlated (r =.5; p <.1) with VAS ratings (Fig. 3E), but not with stage (r =.1; p =.7) Non- Acta Derm Venereol IA IB IIB III IVA IVB Stage Fig.. IL-31 is increased in patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (). (A) IL-31 was elevated in the epidermis and lymphocytic infiltrate of patients (p <.1, p <.1), with the highest expression in the epidermis of the moderately/ group (B). Scale bar = 1 µm. (C) Epidermal IL-31 expression correlated to VAS ratings, but not with stage (D). DAPI: Blue staining of nuclei.
4 IL-31 and receptors in the skin of OSMRβ flourescence (µm ) D B IL-31RA flourescence (µm ) 5 15 ** Non E 15 * 1 5 OSMRβ flourescence (µm ) IL-31RA flourescence (µm ) A 97 C F 5 5 Non 1 Non- Fig. 3. IL-31RA and ncostatin M receptor beta (OSMRβ) are increased in patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (). IL-31 receptors (A) IL-31RA and (D) OSMRβ are elevated in the epidermis of patients (*p <.5, **p <.1, p <.1, p <.1), with the highest levels found in moderately/ group (C and F). Scale bar = 1 µm. Epidermal IL-31RA (B) and OSMRβ (E) expression correlated to VAS ratings. DAPI: Blue staining. role in the pathogenesis of. However, our study was limited by the low number of early stage patients and by the lack of patients without itch. This study also found increased expression of the IL-31 receptors, IL-31RA and OSMRβ. The previous findings for these receptors in is limited to one serum and cancer cell line study, which did not find evidence of significant elevation of these receptors, possibly due to their focus on the blood compartment of cells (1). The IL-31RA and OSMRβ receptors are known to be located on keratinocytes, rather than serum, making this study better suited to assess the role of IL-31 signaling in. Interestingly, a recent study in mice showed that repeated IL-31 exposure caused elevated expression of IL-31RA and OSMRβ in the dorsal root ganglia (19). This mechanism could explain the increase in receptor density we found in the epidermis. In another study, a single intradermal exposure of IL-31 did not cause pruritus in healthy subjects (). Therefore, the increase in IL-31RA and OSMRβ expression after chronic exposure to IL-31 may be necessary in order for a subsequent exposure to IL-31 to induce pruritus. Our study showed elevated expression of IL-31 in the epidermis. This result is similar to studies performed in atopic dermatitis subjects, which localized IL-31 to lymphocytes infiltrating the skin (11), and in lichen planus, which found overexpression of IL-31 in the epidermis. However, IL-31 expression in lichen planus did not correlate to pruritus ratings (1). It is thought that IL-31 can induce keratinocytes and infiltrating cells to release additional mediators involved in pruritus. Furthermore, IL-31 has also been shown to cause the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines from eosinophils, monocytes, and macrophages (, 3). It would be of great interest to investigate the role of other mediators and cell types involved in pruritus. The finding of elevated IL-31 and its receptors in the skin of subjects adds the missing link to previous studies investigating the role of IL-31 in pruritus. As pruritus treatments begin to focus on reducing IL-31 in patients, it will be interesting to correlate the therapeutic response with epidermal IL-31, as well as possible changes in the expression of IL-31 receptors (13,, 5). ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors thank Kristen Sanders for helpful comments and edits to the manuscript. Acta Derm Venereol 9
5 9 L. A. Nattkemper et al. The authors declare no conflict of interest. REFERENCES 1. Wright A, Wijeratne A, Hung T, Gao W, Whittaker S, Morris S, et al. Prevalence and severity of pruritus and quality of life in patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Pain Sym Manag 13; 5: Vij A, Duvic M. Prevalence and severity of pruritus in cutaneous T cell lymphoma. Int J Dermatol 1; 51: Demierre MF, Gan S, Jones J, Miller DR. Significant impact of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma on patients quality of life: Results of a 5 national cutaneous lymphoma foundation survey. Cancer ; 17: Ahern K, Gilmore ES, Poligone B. Pruritus in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: A review. J Am Acad Dermatol 1; 7: Sampogna F, Frontani M, Baliva G, Lombardo GA, Alvetreti G, Di Pietro C, et al. Quality of life and psychological distress in patients with cutaneous lymphoma. Br J Dermatol ; 1: 15.. Meyer N, Paul C, Misery L. Pruritus in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas: Frequent, often severe and difficult to treat. Acta Derm Venereol 1; 9: Kim EJ, Hess S, Richardson SK, Newton S, Showe LC, Benoit BM, et al. Immunopathogenesis and therapy of cutaneous T cell lymphoma. J Clin Invest 5; 115: Sonkoly E, Muller A, Lauerma AI, Pivarcsi A, Soto H, Kemeny L, et al. IL-31: a new link between T cells and pruritus in atopic skin inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol ; 117: Neis MM, Peters B, Dreuw A, Wenzel J, Bieber T, Mauch C, et al. Enhanced expression level of IL-31 correlate with IL- and IL-13 in atopic and allergic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol ; 11: Nobbe S, Dziunycz P, Mühleisen B, Bilsborough J, Dillon SR, French LE, Hofbauer GF. IL-31 expression by inflammatory cells is preferentially elevated in atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol 1; 9:. 11. Kato A, Fujii E, Watanabe T, Takashima Y, Matsushita H, Furuhashi T, Morita A. Distribution of IL-31 and its receptor expressing cells in skin of atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol Sci 1 7: Cornelissen C, Luscher-Firzlaff J, Baron JM, Luscher B. Signaling by IL-31 and functional consequences. Eur J of Cell Bio 11; 91: Singer EM, Shin DB, Nattkemper LA, Benoit BM, Klein RS, Didigu CA, et al. Il-31 is produced by malignant T-cell population in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and correlates with pruritus. J Invest Dermatol 13; 133: Malek M, Gleń J, Rębała K, Kowalczyk A, Sobjanek M, Nowicki R, et al. IL-31 does not correlate to pruritus related to early stage cutaneous T-cell lymphomas but is involved in pathogenesis of the disease. Acta Derm Venereol 15; 95: Murphy GF. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Adv Pathol 19; 1: Olsen E, Vonderheid E, Pimpinelli N, Willemze R, Kim Y, Knobler R, et al. Revisions to the staging and classification of mycosis fungoides and Sezary syndrome: a proposal of the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas (ISCL) and the cutaneous lymphoma task force of the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Blood 7; 11: McArthur JC, Stocks EA, Hauer P, Cornblath DR, Griffin JW. Epidermal nerve fiber density: normative reference range and diagnostic efficiency. Arch Neurol 199; 55: Möbs M, Gryzik S, Haidar A, Humme D, Beyer M, Vandersee S. Analysis of IL-31 pathway in mycosis fungoides and sezary syndrome. Arch Dermatol Res 15; 37: Arai I, Tsuji M, Miyagawa K, Takeda H, Akiyama N, Saito S. Repeated administration of IL 31 upregulates IL-31 receptor A (IL-31RA) in dorsal root ganglia and causes sever itch associated scratching behavior in mice. Exp Dermatol 15; : Hawro T, Saluja R, Weller K, Altrichter S, Metz M, Maurer M. Interleukin-31 does not induced immediate itch in atopic dermatitis patients and healthy controls after skin challenge. Allergy 1; 9: Welz-Kubiak K, Kobuszewska A, Reich A. IL-31 is overexpressed in lichen planus but its level does not correlate with pruritus severity. J Immunol Res 15; 15: Cheung PF, Wong CK, Ho AW, Hu S, Chen DP, Lam CW. Activation of human eosinophils and epidermal keratinocytes by Th cytokine IL-31: implication for the immunopathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Int Immunol 1; : Kasraie S, Niebuhr M, Werfel T. Interleukin (IL)-31 induces pro-inflammatory cytokines in human monocytes and macrophages following stimulation with staphylococcal exotoxins. Allergy 1; 5: Kasutani K, Fujii E, Ohyama S, Adachi H, Hasegawa M, Kitamura H, Yamashita N. Anti-IL-31 receptor antibody is shown to be a potential therapeutic option for treating itch and dermatitis in mice. Br J Pharmacol 1; 171: Cedeno-Laurent F, Singer EM, Wysocka M, Benoit BM, Vittorio CC, Kim EJ, et al. Improved pruritus correlates with lower levers of IL-31 in patients under different therapeutic modalities. Clin Immunol 15; 15: 1 7. Acta Derm Venereol 9
Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma
 Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma Laura B. Pincus, MD Co-Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic Associate Professor Dermatology and Pathology University of California, San Francisco I HAVE NO RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma Laura B. Pincus, MD Co-Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic Associate Professor Dermatology and Pathology University of California, San Francisco I HAVE NO RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology
 Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology Agenda Overview of cutaneous T and B- cell lymphomas Diagnosis, Staging, Prognosis
Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology Agenda Overview of cutaneous T and B- cell lymphomas Diagnosis, Staging, Prognosis
Microscopic study of the normal skin in cases of mycosis fungoides
 Microscopic study of the normal skin in cases of mycosis fungoides M. El Darouti, S. Marzook, M. Bosseila, O. Abu Zeid, O. El- Safouri, A. Zayed, A. El-Ramly Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 2 (1):
Microscopic study of the normal skin in cases of mycosis fungoides M. El Darouti, S. Marzook, M. Bosseila, O. Abu Zeid, O. El- Safouri, A. Zayed, A. El-Ramly Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 2 (1):
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2010 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Benner, Marchina Frederika Title: Cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferations
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2010 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Benner, Marchina Frederika Title: Cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferations
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: Updated results from a single center
 Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: Updated results from a single center Madeleine Duvic, MD Professor and Deputy Chairman Blanche Bender Professor in Cancer Research Departments
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: Updated results from a single center Madeleine Duvic, MD Professor and Deputy Chairman Blanche Bender Professor in Cancer Research Departments
Increase of DC-LAMP+ mature dendritic cell subsets in dermatopathic lymphadenitis of mycosis fungoides
 Increase of DC-LAMP+ mature dendritic cell subsets in dermatopathic lymphadenitis of mycosis fungoides Kotaro TADA 1,2, Toshihisa HAMADA 1, Kenji ASAGOE 3, Hiroshi UMEMURA 1, Kazuko MIZUNO-IKEDA 1, Yumi
Increase of DC-LAMP+ mature dendritic cell subsets in dermatopathic lymphadenitis of mycosis fungoides Kotaro TADA 1,2, Toshihisa HAMADA 1, Kenji ASAGOE 3, Hiroshi UMEMURA 1, Kazuko MIZUNO-IKEDA 1, Yumi
ISPUB.COM. M Duvic, E Olsen PURPOSE OF REVISION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 International Society of Cutaneous Lymphoma (ISCL) and the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) revisions to
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 International Society of Cutaneous Lymphoma (ISCL) and the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) revisions to
Classification of Cutaneous T cell Lymphomas (CTCLs) Hernani Cualing, MD
 Classification of Cutaneous T cell Lymphomas (CTCLs) Hernani Cualing, MD Pathology and Cell Biology, USF IFLOW, Inc. CTCL, MF, and Sézary syndrome In 1806, mycosis fungoides (MF) was first described 1
Classification of Cutaneous T cell Lymphomas (CTCLs) Hernani Cualing, MD Pathology and Cell Biology, USF IFLOW, Inc. CTCL, MF, and Sézary syndrome In 1806, mycosis fungoides (MF) was first described 1
Summary. lymphoma/myeloma, regulatory T cells (T reg) Introduction. Clinical and Experimental Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi: /cei.
 bs_bs_banner Clinical and Experimental Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi:1.1111/cei.1273 Increased frequency of skin-infiltrating FoxP3 + regulatory T cells as a diagnostic indicator of severe atopic dermatitis
bs_bs_banner Clinical and Experimental Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi:1.1111/cei.1273 Increased frequency of skin-infiltrating FoxP3 + regulatory T cells as a diagnostic indicator of severe atopic dermatitis
Therapeutic Management of Early Cutaneous Mycosis Fungoides
 Therapeutic Management of Early Cutaneous Mycosis Fungoides L Frank Glass, MD Cutaneous Lymphoma Programs H Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute George Washington University Dermatology and
Therapeutic Management of Early Cutaneous Mycosis Fungoides L Frank Glass, MD Cutaneous Lymphoma Programs H Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute George Washington University Dermatology and
Nodular Prurigo Associated with Mycosis Fungoides Case Report
 2015;23(3):203-207 CASE REPORT Nodular Prurigo Associated with Mycosis Fungoides Case Report Sandra Jerković Gulin 1, Romana Čeović 2, Davorin Lončarić 2, Ivana Ilić 3, Ivo Radman 4 1 Department of Dermatology
2015;23(3):203-207 CASE REPORT Nodular Prurigo Associated with Mycosis Fungoides Case Report Sandra Jerković Gulin 1, Romana Čeović 2, Davorin Lončarić 2, Ivana Ilić 3, Ivo Radman 4 1 Department of Dermatology
Clusterin Expression Correlates With Stage and Presence of Large Cells in Mycosis Fungoides
 Anatomic Pathology / Clusterin Expression in Mycosis Fungoides Clusterin Expression Correlates With Stage and Presence of Large Cells in Mycosis Fungoides Pranil Chandra, DO, 1 Jose A. Plaza, MD, 2,4 Zhuang
Anatomic Pathology / Clusterin Expression in Mycosis Fungoides Clusterin Expression Correlates With Stage and Presence of Large Cells in Mycosis Fungoides Pranil Chandra, DO, 1 Jose A. Plaza, MD, 2,4 Zhuang
Cluster of differentiation (CD) markers in erythrodermic patients: A case series study
 Original Article Cluster of differentiation (CD) markers in erythrodermic patients: A case series study Fariba Ghalamkarpour, MD Faranak Niknafs, MD Shima Younespour, PhD Skin Research Center, Shahid Beheshti
Original Article Cluster of differentiation (CD) markers in erythrodermic patients: A case series study Fariba Ghalamkarpour, MD Faranak Niknafs, MD Shima Younespour, PhD Skin Research Center, Shahid Beheshti
Everant.in/index.php/jmpr. Journal of Medical Practice and Review
 Everant.in/index.php/jmpr Journal of Medical Practice and Review Real world Efficacy and Tolerance of Bepotastine, a new 2 nd generation antihistamine, in Pruritis and other symptoms associated with cutaneous
Everant.in/index.php/jmpr Journal of Medical Practice and Review Real world Efficacy and Tolerance of Bepotastine, a new 2 nd generation antihistamine, in Pruritis and other symptoms associated with cutaneous
Brian S. Kim, MD, MTR, FAAD
 What s New In the Pathophysiology of Itch? Brian S. Kim, MD, MTR, FAAD Assistant Professor of Dermatology, Anesthesiology, and Pathology and Immunology Co-Director, Center for the Study of Itch Itch is
What s New In the Pathophysiology of Itch? Brian S. Kim, MD, MTR, FAAD Assistant Professor of Dermatology, Anesthesiology, and Pathology and Immunology Co-Director, Center for the Study of Itch Itch is
Grass pollen immunotherapy induces Foxp3 expressing CD4 + CD25 + cells. in the nasal mucosa. Suzana Radulovic MD, Mikila R Jacobson PhD,
 Radulovic 1 1 2 3 Grass pollen immunotherapy induces Foxp3 expressing CD4 + CD25 + cells in the nasal mucosa 4 5 6 7 Suzana Radulovic MD, Mikila R Jacobson PhD, Stephen R Durham MD, Kayhan T Nouri-Aria
Radulovic 1 1 2 3 Grass pollen immunotherapy induces Foxp3 expressing CD4 + CD25 + cells in the nasal mucosa 4 5 6 7 Suzana Radulovic MD, Mikila R Jacobson PhD, Stephen R Durham MD, Kayhan T Nouri-Aria
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration
 Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
The Utility Of Congo Red Stain And Cytokeratin Immunostain In The Detection Of Primary Cutaneous Amyloidosis
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 17 Number 1 The Utility Of Congo Red Stain And Cytokeratin Immunostain In The Detection Of Primary Cutaneous A,A Citation A, A.. The Internet Journal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 17 Number 1 The Utility Of Congo Red Stain And Cytokeratin Immunostain In The Detection Of Primary Cutaneous A,A Citation A, A.. The Internet Journal
Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal Vol. 6 No 1: 14, June 2010
 Wells Syndrome H. Gammaz, H. Amer, A. Adly and S. Mahmoud Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 6 (1): 14 Al-Haud Al-Marsoud Hospital, Cairo, Egypt e-mail: hananderma@hotmail.com Submitted: April 15, 2010
Wells Syndrome H. Gammaz, H. Amer, A. Adly and S. Mahmoud Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 6 (1): 14 Al-Haud Al-Marsoud Hospital, Cairo, Egypt e-mail: hananderma@hotmail.com Submitted: April 15, 2010
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE
 Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies?
 Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Recalcitrant Warty Erythroderma With Severe Pruritus. Gil Yosipovitch Professor & Chair Department of Dermatology & Itch Center Temple University
 Recalcitrant Warty Erythroderma With Severe Pruritus Gil Yosipovitch Professor & Chair Department of Dermatology & Itch Center Temple University DISCLOSURE OF RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Gil Yosipovitch,
Recalcitrant Warty Erythroderma With Severe Pruritus Gil Yosipovitch Professor & Chair Department of Dermatology & Itch Center Temple University DISCLOSURE OF RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Gil Yosipovitch,
ISPUB.COM. Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Long-term Management with Low Dose Methotrexate. S Parker INTRODUCTION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Long-term Management with Low Dose S Parker Citation S Parker.. The Internet Journal of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Long-term Management with Low Dose S Parker Citation S Parker.. The Internet Journal of
EPIDERMAL NERVE FIBER DENSITY ANALYSIS OF PATIENT EE
 Pathology report by BAKO PATHOLOGY SERVICES EPIDERMAL NERVE FIBER DENSITY ANALYSIS OF PATIENT EE Patient Information: 83-year-old female 68% increase in nerve fiber density Physician: Kevin F Sunshein,
Pathology report by BAKO PATHOLOGY SERVICES EPIDERMAL NERVE FIBER DENSITY ANALYSIS OF PATIENT EE Patient Information: 83-year-old female 68% increase in nerve fiber density Physician: Kevin F Sunshein,
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in
 Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
A correlation between acute phase proteins and cytokines in patients suffering from mycosis fungoides
 C l i n i c a l s t u d y Acute phase proteins and cytokines in mycosis fungoides A correlation between acute phase proteins and cytokines in patients suffering from mycosis fungoides M. Pawlaczyk and
C l i n i c a l s t u d y Acute phase proteins and cytokines in mycosis fungoides A correlation between acute phase proteins and cytokines in patients suffering from mycosis fungoides M. Pawlaczyk and
Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, University of Florida College of Medicine-Jacksonville, Jacksonville, FL 32209, USA
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Dermatology Volume 2012, Article ID 759630, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/759630 Research Article A Comparative Analysis of Mast Cell Quantification in Five Common
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Dermatology Volume 2012, Article ID 759630, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/759630 Research Article A Comparative Analysis of Mast Cell Quantification in Five Common
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging. Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology
 Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(4): /ISSN: /IJCEP Tadashi Terada
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(4):749-756 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1301060 Case Report Mycosis fungoides in plaque stage with pronounced eosinophilic infiltration, folliculotropism, and concomitant
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(4):749-756 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1301060 Case Report Mycosis fungoides in plaque stage with pronounced eosinophilic infiltration, folliculotropism, and concomitant
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation. Dermatopathology Specialists Needed. Changing Trends
 Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
The Natural History of Psoriasis and Treatment Goals
 The Natural History of Psoriasis and Treatment Goals Psoriasis Epidemiology Prevalence Affects 2 3% of adult population (>7 million in US) Caucasians: 25% 2.5% African Americans: 1.3% (more likely to have
The Natural History of Psoriasis and Treatment Goals Psoriasis Epidemiology Prevalence Affects 2 3% of adult population (>7 million in US) Caucasians: 25% 2.5% African Americans: 1.3% (more likely to have
a b c Esophageal eosinophilia
 TSLP-elicited basophil responses can mediate the pathogenesis of eosinophilic esophagitis. Mario Noti, Elia D. Tait Wojno, Brian S. Kim, Mark C. Siracusa, Paul R. Giacomin, Meera G. Nair, Alain J. Benitez,
TSLP-elicited basophil responses can mediate the pathogenesis of eosinophilic esophagitis. Mario Noti, Elia D. Tait Wojno, Brian S. Kim, Mark C. Siracusa, Paul R. Giacomin, Meera G. Nair, Alain J. Benitez,
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), available at
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
Immunohistochemical Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 in Psoriasis Vulgaris
 Immunohistochemical Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 in Psoriasis Vulgaris Amina Gamal el Din 1 *, Hanan M Saleh 2, Nermeen Abdel Fattah 2 and Abdel Maksoud A 3 1.Pathology Department, Medical Research
Immunohistochemical Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 in Psoriasis Vulgaris Amina Gamal el Din 1 *, Hanan M Saleh 2, Nermeen Abdel Fattah 2 and Abdel Maksoud A 3 1.Pathology Department, Medical Research
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
OBSERVATION. Psoralen Plus Long-Wave UV-A (PUVA) and Bexarotene Therapy
 OBSERVATION Psoralen Plus Long-Wave UV-A (PUVA) and Bexarotene Therapy An Effective and Synergistic Combined Adjunct to Therapy for Patients With Advanced Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma Karen S. McGinnis, MD;
OBSERVATION Psoralen Plus Long-Wave UV-A (PUVA) and Bexarotene Therapy An Effective and Synergistic Combined Adjunct to Therapy for Patients With Advanced Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma Karen S. McGinnis, MD;
Narrow band UVB (311 nm), psoralen UVB (311 nm) and PUVA therapy in the treatment of early-stage mycosis fungoides: a right left comparative study
 Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 2005; 21: 281 286 Blackwell Munksgaard Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Narrow band UVB (311 nm), psoralen UVB (311 nm) and therapy in the treatment of early-stage
Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 2005; 21: 281 286 Blackwell Munksgaard Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Narrow band UVB (311 nm), psoralen UVB (311 nm) and therapy in the treatment of early-stage
Title proteinase-activated receptor 2 ago. Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Olopatadine hydrochloride inhibits proteinase-activated receptor 2 ago Yoshizaki, Ayumi; Sato, Shinichi Citation Journal of dermatological science, Issue
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Olopatadine hydrochloride inhibits proteinase-activated receptor 2 ago Yoshizaki, Ayumi; Sato, Shinichi Citation Journal of dermatological science, Issue
Morbidity and Causes of Death in Patients with Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma in Finland
 https://helda.helsinki.fi Morbidity and Causes of Death in Patients with Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma in Finland Vakeva, Liisa 2017-06 Vakeva, L, Lipsanen, T, Sintonen, H & Ranki, A 2017, ' Morbidity and
https://helda.helsinki.fi Morbidity and Causes of Death in Patients with Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma in Finland Vakeva, Liisa 2017-06 Vakeva, L, Lipsanen, T, Sintonen, H & Ranki, A 2017, ' Morbidity and
Prevalence of pruritus in psoriatic skin lesions and its relations to different variables
 Original Article Prevalence of pruritus in psoriatic skin lesions and its relations to different variables Satyendra Kumar Singh Department of Dermatology & Venereology, Institute of Medical Sciences,
Original Article Prevalence of pruritus in psoriatic skin lesions and its relations to different variables Satyendra Kumar Singh Department of Dermatology & Venereology, Institute of Medical Sciences,
Phase 1 Trial Evaluating MRG-106, a Synthetic Inhibitor of microrna- 155, in Patients with CTCL
 EORTC CLTF 2017 meeting on Cutaneous Lymphomas: Insights & Therapeutic Progress Phase 1 Trial Evaluating MRG-106, a Synthetic Inhibitor of microrna- 155, in Patients with CTCL Christiane Querfeld, Francine
EORTC CLTF 2017 meeting on Cutaneous Lymphomas: Insights & Therapeutic Progress Phase 1 Trial Evaluating MRG-106, a Synthetic Inhibitor of microrna- 155, in Patients with CTCL Christiane Querfeld, Francine
Grover s disease: A case report.
 320 Case report Thai J Dermatol, October-December 2011 ABSTRACT: Grover s disease: A case report. Supicha Chavanich MD, Praneet Sajjachareonpong MD. CHAVANICH C, SAJJACHAREONPONG P. GROVER S DISEASE: A
320 Case report Thai J Dermatol, October-December 2011 ABSTRACT: Grover s disease: A case report. Supicha Chavanich MD, Praneet Sajjachareonpong MD. CHAVANICH C, SAJJACHAREONPONG P. GROVER S DISEASE: A
Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Invest Dermatol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 April 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Invest Dermatol. 2013 October ; 133(10): 2311 2314. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.239. Mechanisms of contact sensitization offer insights
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Invest Dermatol. 2013 October ; 133(10): 2311 2314. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.239. Mechanisms of contact sensitization offer insights
Tetsuji WAKUDA, Masanao SHIBASAKI,Tadashi TANITSU* National University Corporation, Tsukuba University of Technology *Cooperation with research
 NTUT Education of Disabilities, 2009 Vol. 7 Effects of Acupuncture on Control of Pruritus Associated with Atopic Dermatitis Course in Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Department of Health, Tsukuba University
NTUT Education of Disabilities, 2009 Vol. 7 Effects of Acupuncture on Control of Pruritus Associated with Atopic Dermatitis Course in Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Department of Health, Tsukuba University
EPIDERMAL NERVE FIBER DENSITY ANALYSIS OF PATIENT EE
 Pathology report by BAKO PATHOLOGY SERVICES EPIDERMAL NERVE FIBER DENSITY ANALYSIS OF PATIENT EE Patient Information: 83-year-old female 68% increase in nerve fiber density Physician: Kevin F Sunshein,
Pathology report by BAKO PATHOLOGY SERVICES EPIDERMAL NERVE FIBER DENSITY ANALYSIS OF PATIENT EE Patient Information: 83-year-old female 68% increase in nerve fiber density Physician: Kevin F Sunshein,
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Nitric Oxide-Releasing Topical Therapeutic for Atopic Dermatitis
 Nitric Oxide-Releasing Topical Therapeutic for Atopic Dermatitis K. McHale 1, J. Gil 2, S. Davis 2, S. Hollenbach 1, and N. Stasko 1 1 Novan, Inc., Morrisville, NC; 2 Department of Dermatology and Cutaneous
Nitric Oxide-Releasing Topical Therapeutic for Atopic Dermatitis K. McHale 1, J. Gil 2, S. Davis 2, S. Hollenbach 1, and N. Stasko 1 1 Novan, Inc., Morrisville, NC; 2 Department of Dermatology and Cutaneous
The Skinny of the Immune System
 The Skinny of the Immune System Robert Hostoffer, DO, FACOP, FAAP Associate Professor of Pediatrics Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio Overview 1. Immune system of the skin 2. Immune Players
The Skinny of the Immune System Robert Hostoffer, DO, FACOP, FAAP Associate Professor of Pediatrics Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio Overview 1. Immune system of the skin 2. Immune Players
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide
 Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Diffuse Pigmentation of Back and Arms: Macular Amyloidosis or Other?
 ORIGINAL REPORT Diffuse Pigmentation of Back and Arms: Macular Amyloidosis or Other? Seyed Zahra Ghodsi 1, Pari Rahimi 1, Amir Ehsani 1, Pedram Noormohammadpour 1, Masood Asgrai 2, and Fatemeh Gholamali
ORIGINAL REPORT Diffuse Pigmentation of Back and Arms: Macular Amyloidosis or Other? Seyed Zahra Ghodsi 1, Pari Rahimi 1, Amir Ehsani 1, Pedram Noormohammadpour 1, Masood Asgrai 2, and Fatemeh Gholamali
Rare paraneoplastic erythroderma associated with ectopic neuron-specific enolase deposition in basal cells
 Case Report Page 1 of 12 Rare paraneoplastic erythroderma associated with ectopic neuron-specific enolase deposition in basal cells Lei Wang 1#, Ting Guo 1,2#, Hao Zhang 1#, Weimiao Li 3, Yifang Zhu 1,
Case Report Page 1 of 12 Rare paraneoplastic erythroderma associated with ectopic neuron-specific enolase deposition in basal cells Lei Wang 1#, Ting Guo 1,2#, Hao Zhang 1#, Weimiao Li 3, Yifang Zhu 1,
Mapping Basal Cell and Squamous Carcinoma By 10 Min CK5 Direct Immunohistochemistry on Frozen Section Skin Tissues during Mohs Micrographic Surgery
 Mapping Basal Cell and Squamous Carcinoma By 10 Min CK5 Direct Immunohistochemistry on Frozen Section Skin Tissues during Mohs Micrographic Surgery Robert Glinert, MD and Song Q. Zhao, MD, Ph.D., MPH Department
Mapping Basal Cell and Squamous Carcinoma By 10 Min CK5 Direct Immunohistochemistry on Frozen Section Skin Tissues during Mohs Micrographic Surgery Robert Glinert, MD and Song Q. Zhao, MD, Ph.D., MPH Department
Sezary Syndrome(SS) and other malignancies. Hernani Cualing MD Hematopathologist IHCFLOW Lab
 Sezary Syndrome(SS) and other malignancies Hernani Cualing MD Hematopathologist IHCFLOW Lab Disclosures IHCFLOW Laboratory:consultant and director NEOGENOMICS: contract consultant USF: contract reviewer
Sezary Syndrome(SS) and other malignancies Hernani Cualing MD Hematopathologist IHCFLOW Lab Disclosures IHCFLOW Laboratory:consultant and director NEOGENOMICS: contract consultant USF: contract reviewer
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung
 IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive
 Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Interhospital Dermatology Conference 2013
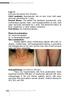 Case 21 A 50-year-old woman from Chonburi. Chief complaint: Asymptomatic rash on neck, trunk, both upper and lower extremities for 2 years. Present illness: The patient has developed asymptomatic scaly
Case 21 A 50-year-old woman from Chonburi. Chief complaint: Asymptomatic rash on neck, trunk, both upper and lower extremities for 2 years. Present illness: The patient has developed asymptomatic scaly
Product Datasheet. DC-LAMP Antibody (104G4) DDX0190P-100. Unit Size: 0.1 mg. Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
 Product Datasheet DC-LAMP Antibody (104G4) DDX0190P-100 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 18 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and
Product Datasheet DC-LAMP Antibody (104G4) DDX0190P-100 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 18 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH
 FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
Downregulation of angiotensin type 1 receptor and nuclear factor-κb. by sirtuin 1 contributes to renoprotection in unilateral ureteral
 Supplementary Information Downregulation of angiotensin type 1 receptor and nuclear factor-κb by sirtuin 1 contributes to renoprotection in unilateral ureteral obstruction Shao-Yu Yang 1,2, Shuei-Liong
Supplementary Information Downregulation of angiotensin type 1 receptor and nuclear factor-κb by sirtuin 1 contributes to renoprotection in unilateral ureteral obstruction Shao-Yu Yang 1,2, Shuei-Liong
Clinical Study The Influence of the Coexpression of CD4 and CD8 in Cutaneous Lesions on Prognosis of Mycosis Fungoides: A Preliminary Study
 Skin Cancer, Article ID 624143, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/624143 Clinical Study The Influence of the Coexpression of CD4 and CD8 in Cutaneous Lesions on Prognosis of Mycosis Fungoides: A Preliminary
Skin Cancer, Article ID 624143, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/624143 Clinical Study The Influence of the Coexpression of CD4 and CD8 in Cutaneous Lesions on Prognosis of Mycosis Fungoides: A Preliminary
Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA)
 Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) Ahmed Abdullah Alhumidi King saud university, Riyadh, kingdom of Saudi Arabia Abstract Background: This
Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) Ahmed Abdullah Alhumidi King saud university, Riyadh, kingdom of Saudi Arabia Abstract Background: This
Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India.
 Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Anti-IL-31 receptor antibody is shown to be a potential therapeutic option for treating itch and dermatitis in mice
 British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:10.1111/bph.12823 www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Anti-IL-31 receptor antibody is shown to be a potential therapeutic option for treating itch and dermatitis in
British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:10.1111/bph.12823 www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Anti-IL-31 receptor antibody is shown to be a potential therapeutic option for treating itch and dermatitis in
Melanoma Update: 8th Edition of AJCC Staging System
 Melanoma Update: 8th Edition of AJCC Staging System Rosalie Elenitsas, M.D. Professor of Dermatology Director, Dermatopathology University of Pennsylvania DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY None
Melanoma Update: 8th Edition of AJCC Staging System Rosalie Elenitsas, M.D. Professor of Dermatology Director, Dermatopathology University of Pennsylvania DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY None
Pruritus Reduction with Systemic Anti-lymphoma Treatments in Patients with Cutaneous T Cell Lymphoma: A Narrative Review
 Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) (2016) 6:579 595 DOI 10.1007/s13555-016-0143-4 REVIEW Pruritus Reduction with Systemic Anti-lymphoma Treatments in Patients with Cutaneous T Cell Lymphoma: A Narrative Review Halle
Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) (2016) 6:579 595 DOI 10.1007/s13555-016-0143-4 REVIEW Pruritus Reduction with Systemic Anti-lymphoma Treatments in Patients with Cutaneous T Cell Lymphoma: A Narrative Review Halle
Dermatologica Sinica
 DERMATOLOGICA SINICA 31 (2013) 3e Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Dermatologica Sinica journal homepage: http://www.derm-sinica.com CASE REPORT Early stage mycosis fungoides with focal
DERMATOLOGICA SINICA 31 (2013) 3e Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Dermatologica Sinica journal homepage: http://www.derm-sinica.com CASE REPORT Early stage mycosis fungoides with focal
Sézary syndrome. Diagnosis and staging
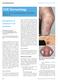 CME DERMATOLOGY Clinical Medicine 2012, Vol 12, No 2: 160 4 Edited by Clive B Archer, consultant dermatologist and lead for Medical Education, St John s Institute of Dermatology, Guy s and St Thomas NHS
CME DERMATOLOGY Clinical Medicine 2012, Vol 12, No 2: 160 4 Edited by Clive B Archer, consultant dermatologist and lead for Medical Education, St John s Institute of Dermatology, Guy s and St Thomas NHS
Assessing and Treating the Patient with Chronic Itch
 Assessing and Treating the Patient with Chronic Itch Sonja Ständer, MD sonja.stander@uni-muenster.de Center for Chronic Pruritus Department of Dermatology University Hospital of Muenster Germany Acute
Assessing and Treating the Patient with Chronic Itch Sonja Ständer, MD sonja.stander@uni-muenster.de Center for Chronic Pruritus Department of Dermatology University Hospital of Muenster Germany Acute
Evaluation of the Protective Effect of Plant Extracts Against Pheophorbide a-induced Photosensitive Damage
 Trace Nutrients Research 26 : 88 92 (2009) Evaluation of the Protective Effect of Plant Extracts Against Pheophorbide a-induced Photosensitive Damage Amy TOMITA, Tomoyo KAJIURA and Shuichi KIMURA Showa
Trace Nutrients Research 26 : 88 92 (2009) Evaluation of the Protective Effect of Plant Extracts Against Pheophorbide a-induced Photosensitive Damage Amy TOMITA, Tomoyo KAJIURA and Shuichi KIMURA Showa
Phase 1 Study of the Safety and Efficacy of MRG-106, a Synthetic Inhibitor of microrna-155, in CTCL Patients
 ASH Annual Meeting, December 11, 2017 Atlanta, Georgia, U.S.A. Phase 1 Study of the Safety and Efficacy of MRG-106, a Synthetic Inhibitor of microrna-155, in CTCL Patients Christiane Querfeld, Francine
ASH Annual Meeting, December 11, 2017 Atlanta, Georgia, U.S.A. Phase 1 Study of the Safety and Efficacy of MRG-106, a Synthetic Inhibitor of microrna-155, in CTCL Patients Christiane Querfeld, Francine
COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate. bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic
 COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic mucus SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES AND FIGURES Tables S1 S8, page 1 and separate
COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic mucus SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES AND FIGURES Tables S1 S8, page 1 and separate
Rameshwar Gutte and Uday Khopkar
 Extragenital unilateral lichen sclerosus et atrophicus in a child: a case report Rameshwar Gutte and Uday Khopkar Department of Dermatolgy, Seth GSMC and KEM Hospital, Parel, Mumbai-400012, India Egyptian
Extragenital unilateral lichen sclerosus et atrophicus in a child: a case report Rameshwar Gutte and Uday Khopkar Department of Dermatolgy, Seth GSMC and KEM Hospital, Parel, Mumbai-400012, India Egyptian
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Skin Disease in the Elderly
 Special Issue Skin Disease in the Elderly DoWon Kim, M.D. Department of Dermatology Kyungpook National University School of Medicine & Hospital Email : kimdw@knu.ac.kr Abstract With the advance of socioeconomy
Special Issue Skin Disease in the Elderly DoWon Kim, M.D. Department of Dermatology Kyungpook National University School of Medicine & Hospital Email : kimdw@knu.ac.kr Abstract With the advance of socioeconomy
Comment on Association of bullous pemphigoid with malignancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis
 Accepted Manuscript Comment on Association of bullous pemphigoid with malignancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis Maglie Roberto, MD, Antiga Emiliano, MD, PhD, Caproni Marzia, MD, PhD PII: S0190-9622(17)32812-8
Accepted Manuscript Comment on Association of bullous pemphigoid with malignancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis Maglie Roberto, MD, Antiga Emiliano, MD, PhD, Caproni Marzia, MD, PhD PII: S0190-9622(17)32812-8
Clinical and Histopathological Spectrum of Mycosis Fungoides
 Awad Hasan Al-Tarawneh, MD, Jordan Board* Background: Early diagnosis of mycosis fungoides is essential but difficult and can be easily missed because it mimics many inflammatory skin diseases both clinically
Awad Hasan Al-Tarawneh, MD, Jordan Board* Background: Early diagnosis of mycosis fungoides is essential but difficult and can be easily missed because it mimics many inflammatory skin diseases both clinically
ISPUB.COM. Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides and Lymphomatoid Papulosis. E Kim PHYSICAL FINDINGS INTRODUCTION INITIAL PRESENTATION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides and Lymphomatoid Papulosis E Kim Citation E Kim. Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides and Lymphomatoid Papulosis E Kim Citation E Kim. Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Invest Dermatol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2015 February 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Invest Dermatol. 2014 August ; 134(8): 2071 2074. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.141. A possible role for IL-17A in establishing Th2 inflammation
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Invest Dermatol. 2014 August ; 134(8): 2071 2074. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.141. A possible role for IL-17A in establishing Th2 inflammation
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Mycosis Fungoides: A Retrospective Study of 44 Swedish Cases
 Acta Derm Venereol 2016; 96: 669 673 CLINICAL REPORT Mycosis Fungoides: A Retrospective Study of 44 Swedish Cases Yvonne EKLUND 1, Annika ARONSSON 1, Artur SCHMIDTCHEN 1 and Thomas RELANDER 2 1 Section
Acta Derm Venereol 2016; 96: 669 673 CLINICAL REPORT Mycosis Fungoides: A Retrospective Study of 44 Swedish Cases Yvonne EKLUND 1, Annika ARONSSON 1, Artur SCHMIDTCHEN 1 and Thomas RELANDER 2 1 Section
Sézary syndrome presenting with leonine facies ajd_560
 285..288 Australasian Journal of Dermatology (2009) 50, 285 288 doi: 10.1111/j.1440-0960.2009.00560.x CASE REPORT Sézary syndrome presenting with leonine facies ajd_560 Shano Nassem, 1 Rajesh Kashyap,
285..288 Australasian Journal of Dermatology (2009) 50, 285 288 doi: 10.1111/j.1440-0960.2009.00560.x CASE REPORT Sézary syndrome presenting with leonine facies ajd_560 Shano Nassem, 1 Rajesh Kashyap,
ITO, Yasuhiro ; FUJII, Mizue ; SHIBUYA, Takashi ; UEHARA, Jiro ; SATO, Katsuhiko ; IIZUKA, Hajime
 Journal of Dermatology (2011) 38(5):515-517. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor-producing squamous cell carcinoma of the skin ITO, Yasuhiro ; FUJII, Mizue ; SHIBUYA, Takashi ; UEHARA, Jiro ; SATO, Katsuhiko
Journal of Dermatology (2011) 38(5):515-517. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor-producing squamous cell carcinoma of the skin ITO, Yasuhiro ; FUJII, Mizue ; SHIBUYA, Takashi ; UEHARA, Jiro ; SATO, Katsuhiko
Mycosis Fungoides and Variants
 Mycosis Fungoides and Variants Jennifer Madison McNiff, M.D. Associate Professor, Dermatology and Pathology Yale University School of Medicine Classic mycosis fungoides The most common cutaneous lymphoma
Mycosis Fungoides and Variants Jennifer Madison McNiff, M.D. Associate Professor, Dermatology and Pathology Yale University School of Medicine Classic mycosis fungoides The most common cutaneous lymphoma
Granulomatous Slack Skin with an unusually aggressive course due to the subsequent development of a CD30-positive Large Cell Lymphoma
 Granulomatous Slack Skin with an unusually aggressive course due to the subsequent development of a CD30-positive Large Cell Lymphoma Alexandra Papoudou-Bai 1, Eleni Kapsali 2, Ioannis Kostas-Agnantis
Granulomatous Slack Skin with an unusually aggressive course due to the subsequent development of a CD30-positive Large Cell Lymphoma Alexandra Papoudou-Bai 1, Eleni Kapsali 2, Ioannis Kostas-Agnantis
Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL)
 Original Research Article Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) Sridhar Reddy Erugula 1, P. Sujatha 2, Ayesha Sameera 3, B. Suresh Reddy 4, Jesudass Govada 5, G. Sudhakar 6, Kandukuri
Original Research Article Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) Sridhar Reddy Erugula 1, P. Sujatha 2, Ayesha Sameera 3, B. Suresh Reddy 4, Jesudass Govada 5, G. Sudhakar 6, Kandukuri
A middle-aged man with self-healing papulonecrotic lesions over the trunk and proximal limbs
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2011) 19, 30-34 Case Report A middle-aged man with self-healing papulonecrotic lesions over the trunk and proximal limbs JC Chan, N Trendell-Smith, CK Yeung Lymphomatoid
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2011) 19, 30-34 Case Report A middle-aged man with self-healing papulonecrotic lesions over the trunk and proximal limbs JC Chan, N Trendell-Smith, CK Yeung Lymphomatoid
Urticarial Dermatitis: Clinical Characteristics of Itch and Therapeutic Response to Cyclosporine
 Itch and Cyclosporine in Urticarial Dermatitis pissn 1013-9087ㆍeISSN 2005-3894 Ann Dermatol Vol. 29, No. 2, 2017 https://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.2.143 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Urticarial Dermatitis: Clinical
Itch and Cyclosporine in Urticarial Dermatitis pissn 1013-9087ㆍeISSN 2005-3894 Ann Dermatol Vol. 29, No. 2, 2017 https://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.2.143 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Urticarial Dermatitis: Clinical
A Comparison of the Efficacy of Ablative Fractional Laser-assisted Photodynamic Therapy according to the Density of Ablative Laser Channel
 A Comparison of the Efficacy of Ablative Fractional Laser-assisted Photodynamic Therapy according to the Density of Ablative Laser Channel in the Treatment of Actinic Keratosis Yeo-Rye Cho, Jeong-Hwan
A Comparison of the Efficacy of Ablative Fractional Laser-assisted Photodynamic Therapy according to the Density of Ablative Laser Channel in the Treatment of Actinic Keratosis Yeo-Rye Cho, Jeong-Hwan
IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1, TNF- ELISA. 1 Candida albicans ,,,, C. albicans., Clonetics BioWhittaker 5% CO 2. TLD-0142, TLD-0143, 37 C, 3,
 Jpn. J. Med. Mycol. Vol. 45, 131 136, 2004 ISSN 0916 4804,,.,,.,,,, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1, TNF- ELISA., IL-8, IL-8, TNF-, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-.,,,,,.,. key word: cytokine, keratinocyte, ELISA enzyme-linked
Jpn. J. Med. Mycol. Vol. 45, 131 136, 2004 ISSN 0916 4804,,.,,.,,,, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1, TNF- ELISA., IL-8, IL-8, TNF-, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-.,,,,,.,. key word: cytokine, keratinocyte, ELISA enzyme-linked
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
Dermatopathology. Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia
 Dermatopathology Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia DERMATOPATHOLOGY CASE CHALLENGE: RECOGNIZING MIMIS AND MASQUERADERS Rosalie Elenitsas. University of Pennsylvania Spectrum Lupus
Dermatopathology Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia DERMATOPATHOLOGY CASE CHALLENGE: RECOGNIZING MIMIS AND MASQUERADERS Rosalie Elenitsas. University of Pennsylvania Spectrum Lupus
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 10 Page October 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i10.125 Histomorphological Study of Lichen Planus
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i10.125 Histomorphological Study of Lichen Planus
DISTRIBUTION OF HUMAN Β-DEFENSIN 2, TNF-ALPHA, IL-1 ALPHA, IL-6 AND IL-8 IN PSORIATIC SKIN
 Papers on Anthropology XX, 2011, pp. 289 302 DISTRIBUTION OF HUMAN Β-DEFENSIN 2, TNF-ALPHA, IL-1 ALPHA, IL-6 AND IL-8 IN PSORIATIC SKIN E. Mozeika 1,2, M. Pilmane 1, J. Kisis 2 1 Institute of Anatomy and
Papers on Anthropology XX, 2011, pp. 289 302 DISTRIBUTION OF HUMAN Β-DEFENSIN 2, TNF-ALPHA, IL-1 ALPHA, IL-6 AND IL-8 IN PSORIATIC SKIN E. Mozeika 1,2, M. Pilmane 1, J. Kisis 2 1 Institute of Anatomy and
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Ultraviolet Light Therapy in the Home Setting(UVB) File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: ultraviolet_light_therapy_in_the_home 3/1996 11/2017 11/2018
Corporate Medical Policy Ultraviolet Light Therapy in the Home Setting(UVB) File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: ultraviolet_light_therapy_in_the_home 3/1996 11/2017 11/2018
Étude de la coopération entre les cellules dendritiques et les lymphocytes T dans les allergies aux produits chimiques FPH42
 Étude de la coopération entre les cellules dendritiques et les lymphocytes T dans les allergies aux produits chimiques FPH42 Dr Diane Antonios-Gholam PharmD, PhD Laboratoire de Toxicologie Clinique et
Étude de la coopération entre les cellules dendritiques et les lymphocytes T dans les allergies aux produits chimiques FPH42 Dr Diane Antonios-Gholam PharmD, PhD Laboratoire de Toxicologie Clinique et
