Journal of Ethnopharmacology
|
|
|
- Frank Stokes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Ethnopharmacology 122 (2009) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Ethnopharmacology journal homepage: Anti-hyperglycemic effects and mechanism of Bidens pilosa water extract Yi-Jou Hsu a,c,1, Tsung-Han Lee a,1, Cicero Lee-Tian Chang b, Yuh-Ting Huang c, Wen-Chin Yang a,c, a Department of Life Sciences, National Chung Hsing University, Taiwan, ROC b Department of Veterinary Medicine, National Chung Hsing University, Taiwan, ROC c Agricultural Biotechnology Research Center, Academia Sinica, Taiwan, ROC article info abstract Article history: Received 18 May 2008 Received in revised form 1 July 2008 Accepted 9 December 2008 Available online 30 December 2008 Keywords: Bidens pilosa Blood glucose Insulin cells Insulin releaser Type 2 diabetes Aim of study: Bidens pilosa has traditionally been used as an anti-diabetic phytomedicine. However, its alleged benefits and mechanism remain elusive. This study aimed to evaluate the effect and action of Bidens pilosa water extract on type 2 diabetes. Materials and methods: A daily dose of Bidens pilosa water extract or glimepiride, a positive control, was given orally to C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice once or for 28 days. Levels of blood glucose, serum insulin, and glycosylated hemoglobulin A1C, glucose tolerance, and islet structure were used to evaluate its antidiabetic effects in db/db mice. Rat pancreatic islets and streptozocin-treated mice were tested for insulinreleasing mechanism of Bidens pilosa water extract. Results: A daily dose of Bidens pilosa water extract given once or for 28 days significantly decreased blood glucose levels and increased serum insulin levels in db/db mice. Besides, 28-day treatment with Bidens pilosa water extract significantly improved glucose tolerance, decreased HbA1C levels and protected islet structure in db/db mice. Mechanism study showed that Bidens pilosa water extract stimulated insulin secretion via pancreatic islets. Conclusions: Our results suggest that Bidens pilosa water extract ameliorates type 2 diabetes in db/db mice via regulation of insulin secretion and islet protection Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved. 1. Introduction Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disease which now afflicts 3% of the world population. Diabetes mellitus is classified into two types (type 1 and type 2) based on individual etiologies. Around 95% of diabetic patients are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes (Attele et al., 2002). A major feature of type 2 diabetes is insulin resistance and/or insulin deficiency which can cause hyperglycemia (Laakso, 2001). Therefore, a key strategy in treating patients with type 2 diabetes is maintenance of blood glucose level. Current oral anti-diabetic agents, which include insulin releasers, insulin Abbreviations: BPWE, Bidens pilosa water extract; BW, body weight; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; FBS, fetal bovine serum; GLM, glimepiride; HbA1C, glycosylated hemoglobin A1C; OGTT, oral glucose tolerance test; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; STZ, streptozocin; KRB buffer, Krebs Ringer bicarbonate buffer. Corresponding author at: Agricultural Biotechnology Research Center, 128 Sec. 2, Academia Road, Nankang, Taipei 115, Taiwan, ROC. Tel.: ; fax: address: wcyang@gate.sinica.edu.tw (W.-C. Yang). 1 These authors contributed equally to this work. sensitizers and -glucosidase inhibitors, have modest efficacy and limited of modes of action. In addition, current anti-diabetic drugs usually have adverse side effects, decreased efficacy over time, ineffectiveness against some long-term diabetic complications and low cost-effectiveness (Grover et al., 2002). Therefore, discovery and development of novel drugs for diabetes is still needed. Plants are recognized as a wonderful source for medicines. It is estimated that 1200 species of plants are used as folk medicines for diabetes (Marles and Farnsworth, 1995). Most of them lack of scientific evidence for their alleged benefits. Among them, Bidens pilosa belongs to the Asteraceae family has been used to treat diabetes in different regions of the world (Marles and Farnsworth, 1995; Brandao et al., 1997; Pereira et al., 1999; Ubillas et al., 2000). One report showed that an aqueous ethanol fraction of Bidens pilosa had an anti-hyperglycemic effect in db/db mice (Ubillas et al., 2000). Moreover, a mixture of two acetylenic compounds showed a higher anti-hyperglycemic effect than of its component alone (Ubillas et al., 2000). However, the mechanism by which Bidens pilosa can treat type 2 diabetes is not yet clear. In this study, we investigated the anti-hyperglycemic effects of Bidens pilosa water extract (BPWE) in db/db mice, a leptin receptordeficient mouse model for type 2 diabetes study (Cefalu, 2006). We /$ see front matter 2009 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved. doi: /j.jep
2 380 Y.-J. Hsu et al. / Journal of Ethnopharmacology 122 (2009) also studied the mode(s) of action of BPWE using pancreatic islet cells and streptozocin (STZ)-treated mice. 2. Materials and methods 2.1. Chemicals Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), STZ, glimepiride (GLM), hematoxylin, eosin Y diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride, and Hank s buffer were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). GLM was dissolved in DMSO to make a stock solution of 25 mg/ml. Insulin and anti-insulin antibody (H-86) were purchased from Novo Nordisk (Princeton, NJ, USA) and Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). RPMI 1640, Fetal bovine serum (FBS), collagenase XI, penicillin/streptomycin/glutamine, 2-mercaptoethanol and sodium pyruvate were purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA). The water extract of Bidens pilosa L. var. radiata was prepared by shade-drying whole Bidens pilosa plants. The dried plants were then ground into homogenized powder. 100 g of powder was boiled in water (1:10, w/v) for 2 h twice. The water extract was filtered by the Advantec No. 2 filter paper (diameter 125 mm), concentrated with rotary evaporators, dried by lyophilization and then dissolved in water to make stock solutions. The yield of water extract was 19.4 g of BPWE out of 100 g of dried plants. Different batches of BPWE were chemically characterized by HPLC analysis. The Bidens pilosa plants were collected from the campus of Academia Sinica, Taiwan, on 18 and 31 August, and 3 September 2005 and authenticated by Dr. Ching-I Pen (Biodiversity Center, Academia Sinica, Taiwan). A voucher specimen (No ) was deposited at the herbarium of Academia Sinica Cells and animals Both single-dose experiments and long-term dose experiments were performed on female C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice purchased from Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME, USA). Female C57BL mice and Wistar rats from National Laboratory Animal Center (Taipei, Taiwan) were used to study the anti-diabetic action of BPWE. All animals were maintained in the institutional animal facility and handled according to the guidelines of the Academia Sinica Institutional Animal Care and Utilization Committee. Light cycle (12 h light and 12 h dark), temperature (23 ± 3 C) and humidity (70 ± 10%) were controlled in the animal facility. Proper care and use of the animals were monitored. Hank s buffer containing collagenase XI (1.5 mg/ml) was injected into the pancreatic ducts of fasting 8-week-old Wistar rats. Pancreatic islets were collected after 30 min digestion and grown in a glucose-free RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% FBS, penicillin (100 U/ml), streptomycin (100 g/ml), 2-mercaptoethanol (50 M), sodium pyruvate (1 mm), and glutamate (292 g/ml) and subsequently used for insulin release assays Drug administration in db/db or C57BL mice In the single-dose experiments, 6 8-week-old diabetic db/db mice were fasted for 16 h. After 2 h food intake, the mice were grouped and mice were tube-fed with vehicle (0.2 ml PBS), BPWE (10, 50 and 250 mg/kg body weight (BW)) or GLM (2.5 mg/kg BW). Postprandial blood glucose and insulin levels were monitored for 4 h. In the long-term dose experiments, 6 8-week-old db/db mice were grouped and tube-fed with PBS, BPWE (50 mg/kg) or GLM (2.5 mg/kg), once a day, for 4 weeks. Body weight, daily food intake and oral glucose tolerance were measured at the beginning of the experiment and at the end of the fourth week. Levels of postprandial blood glucose and serum insulin were determined once a week. Glycosylated hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) level was determined at the end of the experiment. C57BL mice aged 6 8 weeks were treated with an intraperitoneal injection of STZ (200 mg/kg). Mice with postprandial blood glucose level over 500 mg/dl and serum insulin level below 0.18 ng/ml were grouped and tube-fed with PBS, BPWE (10, 50 and 250 mg/kg) or injected with insulin at 5 IU/kg BW. Blood glucose levels were measured for 4 h Measurement of glucose, insulin and HbA1C Blood glucose concentration was measured using an Elite glucometer (Bayer, Pittsburgh, PA, USA). Insulin levels in serum samples and rat islet cell supernatants were determined using ELISA assays (Mercodia, Uppsala, Sweden). The percentage of HbA1C in blood samples was measured using a DCA 2000 analyzer (Bayer, Pittsburgh, PA, USA) Insulin release Pancreatic islets (10 islets/ml) from fasting Wistar rats were incubated with glucose-free KRB buffer (Miwa et al., 2000) containing PBS, GLM (10 M) or BPWE (0.15, 0.75 and 1.5 mg/ml) for 30 min. The KRB buffer was then collected for ELISA assays Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) On week 0, db/db mice were fasted for 12 h. An oral dose of vehicle (PBS) was given to all the mice at 0 h (half an hour before oral glucose administration). Afterward, a daily dose of vehicle (PBS), GLM, or BPWE was administered to the mice of each group for 4 weeks. On week 4, the mice were fasted for 12 h. An oral dose of vehicle (PBS), GLM (2.5 mg/kg) or BPWE (50 mg/kg) was given half an hour before oral glucose administration (1 g/kg BW) at 0 h. The blood glucose levels were monitored from 0.5 h before glucose administration to 3 h after glucose administration Immunohistochemical staining Multiple parallel sections of the pancreata from db/db mice that had been administered BPWE for 4 weeks were flash-frozen. The sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin or anti-insulin antibody, with development of diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride, followed by image analysis (Chang et al., 2007) Statistical analysis The results from three or more independent experiments were presented as mean ± S.E. Differences between group averages were analyzed by ANOVA, followed by Fischer-LSD test. Differences of p-value less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. 3. Results 3.1. Single-dose effects of BPWE on blood glucose levels and insulin levels in db/db mice The aqueous ethanol layer and two acetylenic compounds of Bidens pilosa were previously reported to have low antihyperglycemic effects in db/db mice (Ubillas et al., 2000). However, this result contradicts the fact that this plant is widely used as an anti-diabetic remedy across Africa, America and Asia. Therefore, we decided to reevaluate the potential of this plant to treat type 2 diabetes. We first evaluated the anti-hyperglycemic effect of BPWE in db/db mice. The water extract, rather than the aqueous ethanol fraction of this plant was chosen because of the use
3 Y.-J. Hsu et al. / Journal of Ethnopharmacology 122 (2009) in db/db mice compared to vehicle alone (Fig. 1B). The increase in serum insulin levels by BPWE seemed to be dose-dependent (0.5 h, Fig. 1B) and BPWE and GLM seemed to have different kinetics in insulin secretion (Fig. 1B). Overall the data in Fig. 1 showed that BPWE was able to lower blood glucose levels and increase serum insulin levels in db/db mice Long-term effects of BPWE on diabetes in db/db mice Fig. 1. Single-dose effects of BPWE on the levels of postprandial blood glucose and serum insulin in db/db mice. Levels of blood glucose (A) and serum insulin (B) from db/db mice which have received a dose of PBS, GLM and BPWE were measured from 0 to 4 h after tube-feeding. The mouse number (n) is indicated. Values are expressed as mean ± S.E. *p < of the water extract as a folk medicine in Taiwan. Diabetic db/db mice aged 6 8 weeks that were fed normally, had hyperglycemia, with postprandial blood glucose levels somewhere between 350 and 400 mg/dl (Fig. 1A). The levels of blood glucose in mice receiving a dose of vehicle decreased from 355 to 238 mg/dl in 4 h (Fig. 1A). In contrast, an oral dose of 2.5 mg/kg GLM effectively decreased blood glucose levels from 374 to 144 mg/dl in db/db mice (Fig. 1A). Similarly, single-dose of BPWE significantly lowered blood glucose levels in a dose-dependent fashion (1 h, Fig. 1A). We also compared serum insulin levels in db/db mice that received vehicle, GLM and BPWE. Consistent with their glucose-lowering effects, both GLM and BPWE significantly elevated the serum insulin levels To further evaluate the therapeutic effects of BPWE on diabetes, we examined the long-term anti-diabetic effects of BPWE in db/db mice. We found that BPWE at 50 mg/kg decreased blood glucose levels in fed db/db mice as effectively as GLM at 2.5 mg/kg (left panel, Fig. 2A). The blood glucose-lowering effects of BPWE might not be due to food uptake (Table 1). Consistently, BPWE at 50 mg/kg has similar serum insulin-increasing effects as GLM (right panel, Fig. 2A). Next, we assessed the effect of BPWE on glucose tolerance. Six-week-old diabetic db/db females showed similar glucose tolerance before treatment (left column, Fig. 2B). After 4-week administration, GLM improved glucose tolerance in db/db mice compared to control vehicle (right panel, Fig. 2B). The db/db mice treated with BPWE at 50 mg/kg also showed an improvement in glucose tolerance. Our data showed that BPWE was slightly more effective than GLM at improving glucose tolerance (right panel, Fig. 2B). Next, we examined the effects of BPWE on the percentage of HbA1C, a well-known indicator of long-term glycemic control in db/db mice following different treatments. In the blood from diabetic db/db mice aged weeks, the percentage of HbA1C was 7.4% (Fig. 2C). In contrast, the percentage of HbA1C was 7.0% and 6.5% in the blood of age-matched mice following treatment with 2.5 mg/kg GLM and 50 mg/kg BPWE, respectively (Fig. 2C). These data suggest that BPWE (0.9% decrease of HbA1C is relatively better at controlling glycemia than GLM (0.4% decrease of HbA1C in db/db mice (Fig. 2C). Diabetic db/db mice usually develop severe atrophy of pancreatic islets. Therefore, we assessed the protective effect of BPWE on islet destruction in db/db mice. Pancreatic islets of GLM-treated or untreated control mice were destroyed (Fig. 2D). In contrast, the treatment of pancreatic islets of mice with BPWE increased islet preservation (Fig. 2D) Mechanism of anti-diabetic action of BPWE To better understand the mechanism of BPWE as an insulin releaser, we tested its effect in rat pancreatic islets. We treated these islets with PBS, GLM or BPWE at different concentrations in KRB buffer. As expected, GLM stimulated insulin release from rat pancreatic islets (Fig. 3A). Similarly, BPWE enhanced insulin secretion in a dose-dependent fashion (Fig. 3A). To further examine thein vivo response where BPWE reduced hyperglycemia via insulin production from pancreatic islets, we evaluated the anti-hyperglycemic effects of BPWE in STZ-treated C57BL mice whose pancreatic islets were already depleted. As expected, glimepride, an insulin releaser, could not reduce hyperglycemia in these mice (Fig. 3B). BPWE was Table 1 Effect of BPWE on body weight and food intake in db/db mice. 6 8-Week-old db/db mice were given free access to food. The mice were daily tube-fed with PBS, glimepiride (GLM, 2.5 mg/kg) and BPWE (50 mg/kg) for 4 weeks. Body weight and food intake were measured. Treatment Pre-treatment (week 0) Post-treatment (week 4) PBS GLM 2.5 BPWE 50 PBS GLM 2.5 BPWE 50 Mouse number Body weight (g/mouse) 27.2 ± ± ± ± ± ± 0.3 * Food intake (g/(day mouse)) 3.0 ± ± ± ± ± ± 0.5 The data are expressed as mean ±S.E. * p < 0.05 is considered to be statistically significant when compared with control group.
4 382 Y.-J. Hsu et al. / Journal of Ethnopharmacology 122 (2009) Fig. 2. Anti-diabetic effects of BPWE in db/db mice during a 4-week treatment. (A) Blood glucose and serum insulin levels from db/db mice, which were daily tube-fed with PBS, GLM and BPWE, were monitored 0, 2 and 4 weeks after tube-feeding. (B) Oral glucose tolerance tests were conducted on the same mice at week 0 and week 4 (A). (C) After 4 weeks of treatment, the percentage of HbA1C was measured in blood samples from the db/db mice (A). (D) The pancreata of the mice were then stained with hematoxylin plus eosin Y (H&E) or hematoxylin plus anti-insulin antibody (H&I). The scale bars are 100 m. All the data are expressed as mean ± S.E. The mouse number (n) is indicated. *p < 0.05.
5 Y.-J. Hsu et al. / Journal of Ethnopharmacology 122 (2009) diabetic patients with delayed diagnosis and in type 1 diabetic patients. There is a discrepancy in the anti-hyperglycemic efficacy of Bidens pilosa in our study and other studies (Ubillas et al., 2000). This may be due to differences in the methods of preparing the extract of this plant. The boiling water extraction method used here and the aqueous ethanol extraction method used in Ubillas and colleagues study, may result in different compositions or contents of active phytochemicals. This discrepancy may also be that the Bidens pilosa used in our study and the Bidens pilosa used in other studies have different compositions or contents of active constituents due to different environmental factors and therefore, have loss in antihyperglycemic efficacy. For instance, cytopiloyne, the most potent Bidens pilosa polyacetylene for type 1 diabetes, was isolated by Chiang et al. (2007) but was not detected in the same species of plant used by Ubillas et al. This study provides scientific evidence for the ethnobotanical use and action of Bidens pilosa, which helps research and development of Bidens pilosa for type 2 diabetes. Further studies need to be conducted to elucidate the bioactive compounds and molecular mechanisms. Acknowledgements Fig. 3. Insulin-releasing effects of BPWE on pancreatic islet cells in vitro and STZtreated mice in vivo. (A) Insulin secretion of rat pancreatic islet cells by PBS, GLM and BPWE were measured. (B) The reduction of blood glucose by PBS, GLM and BPWE in STZ-treated C57BL mice (n indicates the mouse number). Values are expressed as mean ± S.E. *p < The authors would like to thank their laboratory members for valuable suggestions and technical assistance. They would also like to thank Miranda Loney for revision of this manuscript and Dr. Ching-I Peng for his plant authentication. This research was supported by the National Science Council (NSC B and NSC B ) and Academia Sinica (94F002-2). also unable to reduce hyperglycemia (Fig. 3B). In contrast, insulin injected improved hyperglycemia. These data suggest that BPWE controls blood glucose via its regulation of insulin release from pancreatic islets. 4. Discussion and conclusion Our results show that BPWE can effectively treat diabetes in db/db mice. We demonstrate for the first time that BPWE ameliorates type 2 diabetes through enhancement of insulin secretion and possibly islet protection. BPWE can augment serum insulin levels and, in turn, reduce blood glucose levels (Figs. 1, 2A and 3B). These data are consistent with our observation that serum insulin levels reached the plateau 0.5 h after oral uptake in db/db mice, proceeding the peak of the decrease in blood glucose levels (Fig. 1). Type 2 diabetes always accompanies pancreatic islet destruction. However, most of the anti-diabetic drugs currently available can not prevent pancreatic atrophy in patients and animal models with type 2 diabetes. In contrast, BPWE but not GLM could protect pancreatic islets in db/db mice (Fig. 2D). This mechanism needs to be further investigated. Protection of cells will be useful for prevention of type 2 diabetes in obese patients and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients. However, it might not be effective for chronic type 2 References Attele, A.S., Zhou, Y.P., Xie, J.T., Wu, J.A., Zhang, L., Dey, L., Pugh, W., Rue, P.A., Polonsky, K.S., Yuan, C.S., Antidiabetic effects of Panax ginseng berry extract and the identification of an effective component. Diabetes 51, Brandao, M.G., Krettli, A.U., Soares, L.S., Nery, C.G., Marinuzzi, H.C., Antimalarial activity of extracts and fractions from Bidens pilosa and other Bidens species (Asteraceae) correlated with the presence of acetylene and flavonoid compounds. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 57, Cefalu, W.T., Animal models of type 2 diabetes: clinical presentation and pathophysiological relevance to the human condition. ILAR Journal 47, Chang, C.L., Chang, S.L., Lee, Y.M., Chiang, Y.M., Chuang, D.Y., Kuo, H.K., Yang, W.C., Cytopiloyne, a polyacetylenic glucoside, prevents type 1 diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. Journal of Immunology 178, Chiang, Y.M., Chang, C.L., Chang, S.L., Yang, W.C., Shyur, L.F., Cytopiloyne, a novel polyacetylenic glucoside from Bidens pilosa, functions as a T helper cell modulator. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 110, Grover, J.K., Yadav, S., Vats, V., Medicinal plants of India with anti-diabetic potential. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 81, Laakso, M., Insulin resistance and its impact on the approach to therapy of type 2 diabetes. International Journal of Clinical Practice Supplement, Marles, R.J., Farnsworth, N.R., Antidiabetic plants and their active constituents. Phytomedicine 2, Miwa, I., Ichimura, N., Sugiura, M., Hamada, Y., Taniguchi, S., Inhibition of glucose-induced insulin secretion by 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal and other lipid peroxidation products. Endocrinology 141, Pereira, R.L., Ibrahim, T., Lucchetti, L., da Silva, A.J., Goncalves de Moraes, V.L., Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory effects of methanolic extract and the polyacetylene isolated frombidens pilosal. Immunopharmacology 43, Ubillas, R.P., Mendez, C.D., Jolad, S.D., Luo, J., King, S.R., Carlson, T.J., Fort, D.M., Antihyperglycemic acetylenic glucosides from Bidens pilosa. Planta Medica 66,
Research Article Antidiabetic Effect and Mode of Action of Cytopiloyne
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 213, Article ID 685642, 13 pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/213/685642 Research Article Antidiabetic Effect and
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 213, Article ID 685642, 13 pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/213/685642 Research Article Antidiabetic Effect and
Phytochemistry 70 (2009) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Phytochemistry. journal homepage:
 Phytochemistry 70 (2009) 1246 1254 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Phytochemistry journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/phytochem Anti-diabetic properties of three common Bidens pilosa variants
Phytochemistry 70 (2009) 1246 1254 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Phytochemistry journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/phytochem Anti-diabetic properties of three common Bidens pilosa variants
Pharmacologyonline 3: (2009) I VESTIGATIO OF A TIHYPERGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF MORUS IGRA O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I STREPTOZOTOCI DIABETIC RATS
 I VESTIGATIO OF A TIHYPERGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF MORUS IGRA O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I STREPTOZOTOCI DIABETIC RATS Hassan Fallah Hoseini 1, Soodabeh Saeidnia 2, Ahmad R. Gohari 2*, Mojgan Yazdanpanah 2, Abbass
I VESTIGATIO OF A TIHYPERGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF MORUS IGRA O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I STREPTOZOTOCI DIABETIC RATS Hassan Fallah Hoseini 1, Soodabeh Saeidnia 2, Ahmad R. Gohari 2*, Mojgan Yazdanpanah 2, Abbass
Research Article Anti-Hyperglycemic Properties of Crude Extract and Triterpenes from Poria cocos
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 211, Article ID 12842, 8 pages doi:1.1155/211/12842 Research Article Anti-Hyperglycemic Properties of Crude Extract
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 211, Article ID 12842, 8 pages doi:1.1155/211/12842 Research Article Anti-Hyperglycemic Properties of Crude Extract
SCIFED. Publishers. SciFed Journal of Public Health. Comparing Modified and Relationship Study of Gymnema Sylvestre Against Diabetes
 Research Article SCIFED Publishers Rahul Hajare,, 2018, 2:2 SciFed Journal of Public Health Open Access Comparing Modified and Relationship Study of Gymnema Sylvestre Against Diabetes * Rahul Hajare *
Research Article SCIFED Publishers Rahul Hajare,, 2018, 2:2 SciFed Journal of Public Health Open Access Comparing Modified and Relationship Study of Gymnema Sylvestre Against Diabetes * Rahul Hajare *
Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic Agent that May Act through IRS-1, Akt and GSK-3β Pathways
![Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic Agent that May Act through IRS-1, Akt and GSK-3β Pathways Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic Agent that May Act through IRS-1, Akt and GSK-3β Pathways](/thumbs/96/128474991.jpg) Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for MedChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary Data Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for MedChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary Data Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator. of the Interaction with Macrophages
 Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Antidiabetic effect of Teucrium polium aqueous extract in multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced model of type 1 diabetes in rat
 Antidiabetic effect of Teucrium polium aqueous extract in multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced model of type 1 diabetes in rat Zari Sabet 1, Mehrdad Roghani 2*, Maryam Najafi 3, Zahra Maghsoudi 3 1.
Antidiabetic effect of Teucrium polium aqueous extract in multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced model of type 1 diabetes in rat Zari Sabet 1, Mehrdad Roghani 2*, Maryam Najafi 3, Zahra Maghsoudi 3 1.
Pharmacologyonline 3: (2009)
 THE EFFECT OF ASTURTIUM OFFICIALE O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I DIABETIC RATS Hassan Fallah Hoseini 1, Ahmad R. Gohari 2, Soodabeh Saeidnia 2 *, aghi Shahabi Majd 3, Abbass Hadjiakhoondi 2 1- Department of Pharmacology,
THE EFFECT OF ASTURTIUM OFFICIALE O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I DIABETIC RATS Hassan Fallah Hoseini 1, Ahmad R. Gohari 2, Soodabeh Saeidnia 2 *, aghi Shahabi Majd 3, Abbass Hadjiakhoondi 2 1- Department of Pharmacology,
IN VITRO ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF FLOWER EXTRACTS OF COUROUPITA GUIANENSIS
 CHAPTER 3 IN VITRO ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF FLOWER EXTRACTS OF COUROUPITA GUIANENSIS 3. INTRODUCTION Plants are the basic source of knowledge of modern medicine. Almost all the parts of the plant, namely
CHAPTER 3 IN VITRO ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF FLOWER EXTRACTS OF COUROUPITA GUIANENSIS 3. INTRODUCTION Plants are the basic source of knowledge of modern medicine. Almost all the parts of the plant, namely
HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTION OF THE FLAVONOID FRACTION OF ARTOCARPUS HETEROPHYLLUS LEAF
 42 Research Paper ISSN 0189-6016 2006 Afr. J. Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines www.africanethnomedicines.net HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTION OF THE FLAVONOID FRACTION OF ARTOCARPUS HETEROPHYLLUS
42 Research Paper ISSN 0189-6016 2006 Afr. J. Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines www.africanethnomedicines.net HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTION OF THE FLAVONOID FRACTION OF ARTOCARPUS HETEROPHYLLUS
ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT
 ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT Sama Venkatesh *1, G.Dayananda Reddy 1, B.Madhava Reddy 1, M.Lakshman 2. 1 Department of Pharmacognosy, G.Pulla Reddy College of Pharmacy, Mehdipatnam, Hyderabad
ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT Sama Venkatesh *1, G.Dayananda Reddy 1, B.Madhava Reddy 1, M.Lakshman 2. 1 Department of Pharmacognosy, G.Pulla Reddy College of Pharmacy, Mehdipatnam, Hyderabad
ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF RIBES NIGRUM FRUIT EXTRACT IN ALLOXAN INDUCED DIABETIC RATS
 IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 3 (Research Article) Received on 30 November, 2012; received in revised form, 05 January, 2013; accepted, 27 February, 2013 ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF RIBES NIGRUM FRUIT EXTRACT
IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 3 (Research Article) Received on 30 November, 2012; received in revised form, 05 January, 2013; accepted, 27 February, 2013 ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF RIBES NIGRUM FRUIT EXTRACT
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 9(3): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 9(3):214-218 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Extraction Optimization and Antioxidant Activity
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 9(3):214-218 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Extraction Optimization and Antioxidant Activity
IMPACT OF NATUAL ANTIOXIDANT ON REDUCTION OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN HYPERGLYCEMIC RAT FED GERMINATED PIGEON PEA DIET
 IMPACT OF NATUAL ANTIOXIDANT ON REDUCTION OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN HYPERGLYCEMIC RAT FED GERMINATED PIGEON PEA DIET UCHEGBU NNEKA NKECHI DEPARTMENT OF FOOD TECHNOLOGY INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY,
IMPACT OF NATUAL ANTIOXIDANT ON REDUCTION OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN HYPERGLYCEMIC RAT FED GERMINATED PIGEON PEA DIET UCHEGBU NNEKA NKECHI DEPARTMENT OF FOOD TECHNOLOGY INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY,
HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTIVITY OF THE LEAVES EXTRACTS OF BERSAMA ENGLERIANA IN RATS.
 215 Research Paper Afr. J. Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines www.africanethnomedicines.net ISSN 0189-6016 2005 HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTIVITY OF THE LEAVES EXTRACTS OF BERSAMA ENGLERIANA IN
215 Research Paper Afr. J. Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines www.africanethnomedicines.net ISSN 0189-6016 2005 HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTIVITY OF THE LEAVES EXTRACTS OF BERSAMA ENGLERIANA IN
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Pharmacologyonline 1: (2011) ewsletter Adolfo Andrade-Cetto
 Pharmacologyonline : -5 (0) ewsletter Adolfo Andrade-Cetto HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF Smilax moranensis ROOT O 5-STZ DIABETIC RATS. Adolfo Andrade-Cetto * Laboratorio de Etnofarmacología, Departamento de Biología
Pharmacologyonline : -5 (0) ewsletter Adolfo Andrade-Cetto HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF Smilax moranensis ROOT O 5-STZ DIABETIC RATS. Adolfo Andrade-Cetto * Laboratorio de Etnofarmacología, Departamento de Biología
BIOCHEMISTRY ondmolecular BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Poges
 Vol. 40, No. 3, October 1996 BIOCHEMISTRY ondmolecular BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Poges 515-520 ATTENUATION BY NICOTINAMIDE OF THE STREPTOZOCIN INDUCED EARLY HYPERGLYCAEMIA IN FASTING RATS Kai K. Wong Department
Vol. 40, No. 3, October 1996 BIOCHEMISTRY ondmolecular BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Poges 515-520 ATTENUATION BY NICOTINAMIDE OF THE STREPTOZOCIN INDUCED EARLY HYPERGLYCAEMIA IN FASTING RATS Kai K. Wong Department
Spermicidal activity of the hexane extract of Piper longum: An in vitro study
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Spermicidal activity of the hexane extract of Piper longum: An in vitro study Abu Hasnath Md Golam Sarwar a, b, Ranjeet Kumar Nirala a, b, Mohammed Arif a, Beena Khillare b, Sonu
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Spermicidal activity of the hexane extract of Piper longum: An in vitro study Abu Hasnath Md Golam Sarwar a, b, Ranjeet Kumar Nirala a, b, Mohammed Arif a, Beena Khillare b, Sonu
associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences with preventive measures
 Wk 9. Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus 1. Diabetes Mellitus body s inability to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, proteins hyperglycemia associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences
Wk 9. Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus 1. Diabetes Mellitus body s inability to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, proteins hyperglycemia associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences
Novel Terpenoid-Type Quinones Isolated from Pycnanthus angolensis of Potential Utility in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
 0022-3565/99/2882-0529$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 288, No. 2 Copyright 1999 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
0022-3565/99/2882-0529$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 288, No. 2 Copyright 1999 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
Arthogalin inhibits the growth of murine malignant prostate sarcoma cells in vitro.
 Journal Of Pharmacy And Pharmacological Research Vol. 3.(1) pp. 22-26 August 2013 Available online http://www.globalresearchjournals.org/journal/jppr Copyright 2013 Global Research Journals Full Length
Journal Of Pharmacy And Pharmacological Research Vol. 3.(1) pp. 22-26 August 2013 Available online http://www.globalresearchjournals.org/journal/jppr Copyright 2013 Global Research Journals Full Length
Antidiabetic and Hypoglycaemic Activity of the Crude Extracts of the Plant Leucas Aspera
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL INNOVATIONS RESEARCH ARTICLE Antidiabetic and Hypoglycaemic Activity of the Crude Extracts of the Plant Leucas Aspera Gupta N *a, Subhramanyam EVS b, Sharma R K
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL INNOVATIONS RESEARCH ARTICLE Antidiabetic and Hypoglycaemic Activity of the Crude Extracts of the Plant Leucas Aspera Gupta N *a, Subhramanyam EVS b, Sharma R K
Evaluation of Diuretic Activity of Jussiaea Suffruticosa Linn.
 Evaluation of Diuretic Activity of Jussiaea Suffruticosa Linn. R.Mythreyi 1, N.Rajkumar 1* and E.Sasikala 2 1 Maharaji College of Pharmacy, Besant Nagar, Chennai-90. 2 Central Research Institute for Siddha,
Evaluation of Diuretic Activity of Jussiaea Suffruticosa Linn. R.Mythreyi 1, N.Rajkumar 1* and E.Sasikala 2 1 Maharaji College of Pharmacy, Besant Nagar, Chennai-90. 2 Central Research Institute for Siddha,
ab Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(1):452-456 Evaluation of anti hyperglycaemic activity
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(1):452-456 Evaluation of anti hyperglycaemic activity
HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF CECROPIA PELTATA L. ON N5-STZ TYPE 2 DIABETIC RATS. México, México DF. México, México DF.
 HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF CECROPIA PELTATA L. ON N5-STZ TYPE 2 DIABETIC RATS Adolfo Andrade-Cetto a * René Cárdenas b and Brenda Ramírez-Reyes a a Lab. Etnofarmacología, Fac. de Ciencias, Universidad Nacional
HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF CECROPIA PELTATA L. ON N5-STZ TYPE 2 DIABETIC RATS Adolfo Andrade-Cetto a * René Cárdenas b and Brenda Ramírez-Reyes a a Lab. Etnofarmacología, Fac. de Ciencias, Universidad Nacional
airway inflammation, Bidens, diabetes, helper T cells (Th) Key words:
 Journal of Biomedical Science 12: 79 89, 25. DOI 1.17/s11373-4-8172-x 79 The distinct effects of a butanol fraction of Bidens pilosa plant extract on the development of Th1-mediated diabetes and Th2-mediated
Journal of Biomedical Science 12: 79 89, 25. DOI 1.17/s11373-4-8172-x 79 The distinct effects of a butanol fraction of Bidens pilosa plant extract on the development of Th1-mediated diabetes and Th2-mediated
Department of Chemistry & Nutrition and Food Technology, An-Najah National University, P.O. Box 7, Nablus, Palestine; 2
 Characterization of phenolic compounds from Globularia alypum L. (Globulariaceae) leaves by LC-QTOF-MS 2 Ibrahim M. Abu-Reidah 1,2,3 *, Nadia Amessis-Ouchemoukh 4, Rosa Quirantes-Piné 2,3, Celia Rodríguez-Pérez
Characterization of phenolic compounds from Globularia alypum L. (Globulariaceae) leaves by LC-QTOF-MS 2 Ibrahim M. Abu-Reidah 1,2,3 *, Nadia Amessis-Ouchemoukh 4, Rosa Quirantes-Piné 2,3, Celia Rodríguez-Pérez
Hypoglycemic and glucose tolerance activity of standardized extracts Ficus deltoidea varieties in normal rats
 2016; 4(5): 275-279 ISSN 2320-3862 JMPS 2016; 4(5): 275-279 2016 JMPS Received: 08-07-2016 Accepted: 09-08-2016 Halimatul Saadiah Mohammad Noor Shah Alam, Selangor,. Nor Hadiani Ismail Shah Alam, Selangor,.
2016; 4(5): 275-279 ISSN 2320-3862 JMPS 2016; 4(5): 275-279 2016 JMPS Received: 08-07-2016 Accepted: 09-08-2016 Halimatul Saadiah Mohammad Noor Shah Alam, Selangor,. Nor Hadiani Ismail Shah Alam, Selangor,.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Antiradical and antioxidant activity of flavones from Scutellariae baicalensis radix
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Antiradical and antioxidant activity of flavones from Scutellariae baicalensis radix Dorota Woźniak A, Andrzej Dryś B, and Adam Matkowski* A A Department of Pharmaceutical Biology
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Antiradical and antioxidant activity of flavones from Scutellariae baicalensis radix Dorota Woźniak A, Andrzej Dryś B, and Adam Matkowski* A A Department of Pharmaceutical Biology
Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
Cholesterol determination using protein-templated fluorescent gold nanocluster probes
 Electronic Supplementary Information for Cholesterol determination using protein-templated fluorescent gold nanocluster probes Xi Chen and Gary A. Baker* Department of Chemistry, University of Missouri-Columbia,
Electronic Supplementary Information for Cholesterol determination using protein-templated fluorescent gold nanocluster probes Xi Chen and Gary A. Baker* Department of Chemistry, University of Missouri-Columbia,
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells.
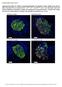 Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3*
 A STUDY ON THE ANTITUMOUR EFFECT OF TOTAL FLAVONOIDS FROM PTERIS MULTIFIDA POIR IN H22 TUMOUR-BEARING MICE 459 Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3* 1 Department of General Surgery, The Second Xiangya
A STUDY ON THE ANTITUMOUR EFFECT OF TOTAL FLAVONOIDS FROM PTERIS MULTIFIDA POIR IN H22 TUMOUR-BEARING MICE 459 Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3* 1 Department of General Surgery, The Second Xiangya
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics
 International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics ISSN Print: 2278-2648 IJRPP Vol.3 Issue 4 Oct-Dec-2014 ISSN Online: 2278-2656 Journal Home page: Research article Open Access Anti-diabetic
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics ISSN Print: 2278-2648 IJRPP Vol.3 Issue 4 Oct-Dec-2014 ISSN Online: 2278-2656 Journal Home page: Research article Open Access Anti-diabetic
Standardized biosynthesis of flavan-3-ols with effects on pancreatic beta-cell insulin secretion
 Standardized biosynthesis of flavan-3-ols with effects on pancreatic beta-cell insulin secretion Joseph A. Chemler, Lye T. Lock, Mattheos A. G. Koffas, Emmanuel S. Tzanakakis Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology
Standardized biosynthesis of flavan-3-ols with effects on pancreatic beta-cell insulin secretion Joseph A. Chemler, Lye T. Lock, Mattheos A. G. Koffas, Emmanuel S. Tzanakakis Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary experimental procedures
 Supplementary experimental procedures Glucose tolerance, insulin secretion and insulin tolerance tests Glucose tolerance test (GTT) and glucose stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) was measured in over-night
Supplementary experimental procedures Glucose tolerance, insulin secretion and insulin tolerance tests Glucose tolerance test (GTT) and glucose stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) was measured in over-night
OPTIMIZATION OF EXTRACTION PROCESS FOR TOTAL POLYPHENOLS FROM ADLAY
 OPTIMIZATION OF EXTRACTION PROCESS FOR TOTAL POLYPHENOLS FROM ADLAY Yun-Xin Liu and Qing-Ping Hu * College of Life Sciences, Shanxi Normal University, Linfen 041004, China ABSTRACT: The single-factor experiment
OPTIMIZATION OF EXTRACTION PROCESS FOR TOTAL POLYPHENOLS FROM ADLAY Yun-Xin Liu and Qing-Ping Hu * College of Life Sciences, Shanxi Normal University, Linfen 041004, China ABSTRACT: The single-factor experiment
THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY
 THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Thin layer chromatography is the best known technique of plant biochemistry. TLC is used for preliminary separation and determination of plant constituents. It is helpful for
THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Thin layer chromatography is the best known technique of plant biochemistry. TLC is used for preliminary separation and determination of plant constituents. It is helpful for
In vitro study of antibacterial activity of Carissa carandas leaf extracts
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2012, 2 (1):36-40 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY In vitro study of antibacterial activity of Carissa
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2012, 2 (1):36-40 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY In vitro study of antibacterial activity of Carissa
IN VITRO ANTICANCER SCREENING OF ASPARAGUS LARICINUS EXTRACTS. S. Mashele and N. Kolesnikova
 IN VITRO ANTICANCER SCREENING OF ASPARAGUS LARICINUS EXTRACTS S. Mashele and N. Kolesnikova Faculty of Health and Environmental Studies, Central University of Technology, Free State, Private Bag X20539,
IN VITRO ANTICANCER SCREENING OF ASPARAGUS LARICINUS EXTRACTS S. Mashele and N. Kolesnikova Faculty of Health and Environmental Studies, Central University of Technology, Free State, Private Bag X20539,
Expression of decoy receptor 3 in kidneys is associated with allograft
 Expression of decoy receptor 3 in kidneys is associated with allograft survival after kidney transplant rejection Shuo-Chun Weng 1,2,3, Kuo-Hsiung Shu 3,4, Ming-Ju Wu 1,3,4,5, Mei-Chin Wen 4,6, Shie-Liang
Expression of decoy receptor 3 in kidneys is associated with allograft survival after kidney transplant rejection Shuo-Chun Weng 1,2,3, Kuo-Hsiung Shu 3,4, Ming-Ju Wu 1,3,4,5, Mei-Chin Wen 4,6, Shie-Liang
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Acetone and methanol fruit extracts of Terminalia paniculata inhibit HIV-1 infection in vitro Ankita Durge a, Pratiksha Jadaun a, Ashish Wadhwani a, Ashish A. Chinchansure b, Madhukar
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Acetone and methanol fruit extracts of Terminalia paniculata inhibit HIV-1 infection in vitro Ankita Durge a, Pratiksha Jadaun a, Ashish Wadhwani a, Ashish A. Chinchansure b, Madhukar
Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long. Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery
 Supporting Information Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery Yongzhi Men, Shaojun Peng, Peng Yang, Qin Jiang, Yanhui Zhang, Bin Shen, Pin Dong, *, Zhiqing
Supporting Information Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery Yongzhi Men, Shaojun Peng, Peng Yang, Qin Jiang, Yanhui Zhang, Bin Shen, Pin Dong, *, Zhiqing
Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics,and Pharmacodynamics of Multiple Rising Doses of Empagliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics,and Pharmacodynamics of Multiple Rising Doses of Empagliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Journal Club (May 2013) Sara Al-Sharhan, Pharm D intern-
Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics,and Pharmacodynamics of Multiple Rising Doses of Empagliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Journal Club (May 2013) Sara Al-Sharhan, Pharm D intern-
Montri Punyatong 1, Puntipa Pongpiachan 2 *, Petai Pongpiachan 2 Dumnern Karladee 3 and Samlee Mankhetkorn 4 ABSTRACT
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 676-681 (2008) Cytotoxicity of Crude Proanthocyanidin Extract from Purple Glutinous Rice Bran (Oryza sativa L.) (Kum Doi Saket) Compared with Cyanidin 3-Glucoside on X63 Myeloma
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 676-681 (2008) Cytotoxicity of Crude Proanthocyanidin Extract from Purple Glutinous Rice Bran (Oryza sativa L.) (Kum Doi Saket) Compared with Cyanidin 3-Glucoside on X63 Myeloma
HYPOLIPIDEMIC EFFECT OF EXTRACTS FROM ABELMOSCHUS ESCULENTUS L. MALVACEAE ON TYLOXAPOL- INDUCED HYPERLIPIDEMIA IN MICE
 HYPOLIPIDEMIC EFFECT OF EXTRACTS FROM ABELMOSCHUS ESCULENTUS L. MALVACEAE ON TYLOXAPOL- INDUCED HYPERLIPIDEMIA IN MICE Huynh Ngoc Trinh 1, Nguyen Ngoc Quynh 1, Tran T Van Anh 2, Vo Phung Nguyen 1 1 Department
HYPOLIPIDEMIC EFFECT OF EXTRACTS FROM ABELMOSCHUS ESCULENTUS L. MALVACEAE ON TYLOXAPOL- INDUCED HYPERLIPIDEMIA IN MICE Huynh Ngoc Trinh 1, Nguyen Ngoc Quynh 1, Tran T Van Anh 2, Vo Phung Nguyen 1 1 Department
Optimization of Enzyme-assisted Ultrasonic Extraction of Total Ginsenosides from Ginseng Roots Guangna LIU, Yulin ZUO, Jing ZHANG
 2019 2nd International Conference on Computer Science and Advanced Materials (CSAM 2019) Optimization of Enzyme-assisted Ultrasonic Extraction of Total Ginsenosides from Ginseng Roots Guangna LIU, Yulin
2019 2nd International Conference on Computer Science and Advanced Materials (CSAM 2019) Optimization of Enzyme-assisted Ultrasonic Extraction of Total Ginsenosides from Ginseng Roots Guangna LIU, Yulin
Kazumi YAGASAKI, Masato NAGAOKA and Yutaka MIURA
 Kazumi YAGASAKI, Masato NAGAOKA and Yutaka MIURA Division of Agriscience and Bioscience, Institute of Symbiotic Science and Technology, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, Fuchu 183-8509 ABSTRACT
Kazumi YAGASAKI, Masato NAGAOKA and Yutaka MIURA Division of Agriscience and Bioscience, Institute of Symbiotic Science and Technology, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, Fuchu 183-8509 ABSTRACT
Diabetes Mellitus. Raja Nursing Instructor. Acknowledgement: Badil 09/03/2016
 Diabetes Mellitus Raja Nursing Instructor 09/03/2016 Acknowledgement: Badil Objective: Define Diabetes Mellitus (DM) & types of DM. Understand the pathophysiology of Type-I & II DM. List the clinical features
Diabetes Mellitus Raja Nursing Instructor 09/03/2016 Acknowledgement: Badil Objective: Define Diabetes Mellitus (DM) & types of DM. Understand the pathophysiology of Type-I & II DM. List the clinical features
Ph.D. Thesis Inhibition of carbonhydrate cleaving enzymes in STZ induced diabetes mellitus model
 Ph.D. Thesis Inhibition of carbonhydrate cleaving enzymes in STZ induced diabetes mellitus model István Gábor Takács Ph.D. School of Biology Supervisors Dr. Anikó Pósa Dr. András Szekeres DEPARTMENT OF
Ph.D. Thesis Inhibition of carbonhydrate cleaving enzymes in STZ induced diabetes mellitus model István Gábor Takács Ph.D. School of Biology Supervisors Dr. Anikó Pósa Dr. András Szekeres DEPARTMENT OF
A study on the effects of Moringa oleifera lam. pod extract on alloxan induced diabetic rats
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2014, 4(1):36-41 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY A study on the effects of Moringa oleifera lam. pod
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2014, 4(1):36-41 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY A study on the effects of Moringa oleifera lam. pod
Graham O Neill School of Agriculture, Food Science and Veterinary Medicine, UCD Dublin, Belfield, Dublin 4, Ireland Food For Health Ireland
 Graham O Neill School of Agriculture, Food Science and Veterinary Medicine, UCD Dublin, Belfield, Dublin 4, Ireland Food For Health Ireland Encapsulation of amino acids and peptides to target their delivery
Graham O Neill School of Agriculture, Food Science and Veterinary Medicine, UCD Dublin, Belfield, Dublin 4, Ireland Food For Health Ireland Encapsulation of amino acids and peptides to target their delivery
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
 Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Available online International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Allied Sciences, 2016, 5(2):55-59.
 Available online www.ijpras.com International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Allied Sciences, 2016, 5(2):55-59 Research Article ISSN : 2277-3657 CODEN(USA) : IJPRPM The Effects of Standardized Extract
Available online www.ijpras.com International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Allied Sciences, 2016, 5(2):55-59 Research Article ISSN : 2277-3657 CODEN(USA) : IJPRPM The Effects of Standardized Extract
cationic molecule, paracellular diffusion would be thought of as its primary mode of transport across epithelial cells.
 ABSTRACT Metformin is the most widely prescribed anti-hyperglycemic agent for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). Despite its frequent use, the intestinal absorption mechanism of this orally administered
ABSTRACT Metformin is the most widely prescribed anti-hyperglycemic agent for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). Despite its frequent use, the intestinal absorption mechanism of this orally administered
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Pharmacologyonline 1: (2009) HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF PHOEBE LA CEOLATA O ALLOXA -I DUCED DIABETIC MICE
 HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF PHOEBE LA CEOLATA O ALLOXA -I DUCED DIABETIC MICE SEMWAL DK 1 *, RAWAT U 1, SEMWAL R 2, SINGH K 3, SINGH R 3, SAINI B 3, KRISHAN P 3, SINGH M 4 1 Department of Chemistry, University
HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF PHOEBE LA CEOLATA O ALLOXA -I DUCED DIABETIC MICE SEMWAL DK 1 *, RAWAT U 1, SEMWAL R 2, SINGH K 3, SINGH R 3, SAINI B 3, KRISHAN P 3, SINGH M 4 1 Department of Chemistry, University
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Purification and biochemical properties of SDS-stable low molecular weight alkaline serine protease from Citrullus Colocynthis Muhammad Bashir Khan, 1,3 Hidayatullah khan, 2 Muhammad
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Purification and biochemical properties of SDS-stable low molecular weight alkaline serine protease from Citrullus Colocynthis Muhammad Bashir Khan, 1,3 Hidayatullah khan, 2 Muhammad
Pelagia Research Library
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Sinica, 2015, 6(1):6-10 ISSN: 0976-8688 CODEN (USA): PSHIBD Validated RP-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of metformin hydrochloride
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Sinica, 2015, 6(1):6-10 ISSN: 0976-8688 CODEN (USA): PSHIBD Validated RP-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of metformin hydrochloride
Glucagon and insulin have opposite effects on tissue chromium distribution in an obese mouse model
 Glucagon and insulin have opposite effects on tissue chromium distribution in an obese mouse model Chang Lin 1,Po-WenChen 2,Wen-YingChen 1, Chi-Ching Sun 1, Frank Chiahung Mao 1,3 * ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT
Glucagon and insulin have opposite effects on tissue chromium distribution in an obese mouse model Chang Lin 1,Po-WenChen 2,Wen-YingChen 1, Chi-Ching Sun 1, Frank Chiahung Mao 1,3 * ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT
In Vitro Antioxidant Activity and Phytochemical Screening of Pholidota articulata
 Human Journals Research Article November 2016 Vol.:5, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by Darshan Singh et al. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity and Phytochemical Screening of Pholidota articulata Keywords:
Human Journals Research Article November 2016 Vol.:5, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by Darshan Singh et al. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity and Phytochemical Screening of Pholidota articulata Keywords:
Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes Prof. Marc Y. Donath
 Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes 1, MD Chief Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism University Hospital Basel Petersgraben 4 CH-431 Basel, Switzerland MDonath@uhbs.ch Innate immunity as a sensor of metabolic
Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes 1, MD Chief Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism University Hospital Basel Petersgraben 4 CH-431 Basel, Switzerland MDonath@uhbs.ch Innate immunity as a sensor of metabolic
For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin
 Materials and Methods Pair Feeding Experiment For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin (0.005%), which is average daily food intake of mice fed control HFD ad libitum at week
Materials and Methods Pair Feeding Experiment For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin (0.005%), which is average daily food intake of mice fed control HFD ad libitum at week
Supporting Information File S2
 Pulli et al. Measuring Myeloperoxidase Activity in Biological Samples Page 1 of 6 Supporting Information File S2 Step-by-Step Protocol Reagents: Sucrose (Sigma, S3089) CaCl 2 (Sigma, C5770) Heparin Sodium
Pulli et al. Measuring Myeloperoxidase Activity in Biological Samples Page 1 of 6 Supporting Information File S2 Step-by-Step Protocol Reagents: Sucrose (Sigma, S3089) CaCl 2 (Sigma, C5770) Heparin Sodium
10.00 PBS OVA OVA+isotype antibody 8.00 OVA+anti-HMGB1. PBS Methatroline (mg/ml)
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Penh (100% of PBS) 1 PBS 8.00 +anti-hmgb1 6.00 4.00 p=0.054 Cellular & Molecular Immunology advance online publication, PBS 3.12 6.25 Methatroline (mg/ml) Neutrophil isolation and culture
RESEARCH ARTICLE Penh (100% of PBS) 1 PBS 8.00 +anti-hmgb1 6.00 4.00 p=0.054 Cellular & Molecular Immunology advance online publication, PBS 3.12 6.25 Methatroline (mg/ml) Neutrophil isolation and culture
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Received on: 08/02/2017 Published on:27/03/2017
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Received on: 08/02/2017 Published on:27/03/2017 Corresponding Author Anuradha VivekanandPhatak, Department of Pharmacology, Dr.BhanubenNanavati College of Pharmacy, Vile Parle (West),
RESEARCH ARTICLE Received on: 08/02/2017 Published on:27/03/2017 Corresponding Author Anuradha VivekanandPhatak, Department of Pharmacology, Dr.BhanubenNanavati College of Pharmacy, Vile Parle (West),
Scholars Research Library J. Nat. Prod. Plant Resour., 2017, 7(2): (
 Available online www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library J. Nat. Prod. Plant Resour., 2017, 7(2): 74-78 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory
Available online www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library J. Nat. Prod. Plant Resour., 2017, 7(2): 74-78 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory
This chapter deals with the evaluation of alpha amylase inhibitory
 This chapter deals with the evaluation of alpha amylase inhibitory activity of different extracts isolated from leaves of Aloe vera L. and leaves of Azadiracta indica A Juss. collected from Bharatpur and
This chapter deals with the evaluation of alpha amylase inhibitory activity of different extracts isolated from leaves of Aloe vera L. and leaves of Azadiracta indica A Juss. collected from Bharatpur and
Keywords: Type 2 DM, lipid profile, metformin, glimepiride ABSTRACT
 Human Journals Research Article September 2015 Vol.:4, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by K. Saravanan et al. Effects of Monotherapy and Combination Therapy Involving Metformin and Glimepiride on HbA1c
Human Journals Research Article September 2015 Vol.:4, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by K. Saravanan et al. Effects of Monotherapy and Combination Therapy Involving Metformin and Glimepiride on HbA1c
Supplementary Information. Statins Improve Long Term Patency of Arteriovenous Fistula for
 Supplementary Information Statins Improve Long Term Patency of Arteriovenous Fistula for Hemodialysis Hao-Hsiang Chang MD, MSc 1,2, Yu-Kang Chang PhD 3, Chia-Wen Lu MD 1, Chi-Ting Huang 3, Chiang-Ting
Supplementary Information Statins Improve Long Term Patency of Arteriovenous Fistula for Hemodialysis Hao-Hsiang Chang MD, MSc 1,2, Yu-Kang Chang PhD 3, Chia-Wen Lu MD 1, Chi-Ting Huang 3, Chiang-Ting
Effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and inflammatory factors of rats with diabetic nephropathy
 Effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and inflammatory factors of rats with diabetic nephropathy J. Guan 1,2, L. Long 1, Y.-Q. Chen 1, Y. Yin 1, L. Li 1, C.-X. Zhang 1, L. Deng 1 and L.-H. Tian
Effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and inflammatory factors of rats with diabetic nephropathy J. Guan 1,2, L. Long 1, Y.-Q. Chen 1, Y. Yin 1, L. Li 1, C.-X. Zhang 1, L. Deng 1 and L.-H. Tian
Program. Advanced heat stress management in dairy cows. phileo-lesaffre.com LESAFFRE ANIMAL CARE
 Advanced heat stress management in dairy cows phileo-lesaffre.com LESAFFRE ANIMAL CARE HEAT STRESS AND TEMPERATURE-HUMIDITY INDEX (THI) 1,2 Heat stress can be defined as an increase in core body temperature
Advanced heat stress management in dairy cows phileo-lesaffre.com LESAFFRE ANIMAL CARE HEAT STRESS AND TEMPERATURE-HUMIDITY INDEX (THI) 1,2 Heat stress can be defined as an increase in core body temperature
ab Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells
 ab189819 Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated
ab189819 Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated
Murugan M. et al / Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Vol. 1 (2), 2009, 69-73
 ISSN:0975-5772 Murugan M. et al / Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Vol. 1 (2), 2009, 69-73 Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activity of leaves of Mucuna pruriens in alloxan induced diabetic
ISSN:0975-5772 Murugan M. et al / Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Vol. 1 (2), 2009, 69-73 Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activity of leaves of Mucuna pruriens in alloxan induced diabetic
Pharmacologyonline 2: (2009) Pharmacodynamic Drug Interaction of Gliclazide and Mexiletine in Rats
 Pharmacodynamic Drug Interaction of Gliclazide and Mexiletine in Rats K. Abedulla Khan 1, S. Satyanarayana 2, K. Eswar Kumar 2, K. Pavan Kumar 1, K. Anupama 1 1 Sultan-ul-uloom College of pharmacy, Banjarahills,
Pharmacodynamic Drug Interaction of Gliclazide and Mexiletine in Rats K. Abedulla Khan 1, S. Satyanarayana 2, K. Eswar Kumar 2, K. Pavan Kumar 1, K. Anupama 1 1 Sultan-ul-uloom College of pharmacy, Banjarahills,
Supplemental Materials, Nishimura et al, Page1 of 22 1
 Supplemental Materials, Nishimura et al, Page of 5 Quantitative assessment of Pdx promoter activity in vivo using a secreted luciferase reporter system 6 7 8 9 Wataru Nishimura, Koki Eto, Atsushi Miki,
Supplemental Materials, Nishimura et al, Page of 5 Quantitative assessment of Pdx promoter activity in vivo using a secreted luciferase reporter system 6 7 8 9 Wataru Nishimura, Koki Eto, Atsushi Miki,
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Microwave-assisted Kochetkov amination followed by permanent charge derivatization: A facile strategy for glycomics Xin Liu a,b, Guisen Zhang* a, Kenneth Chan b and
Electronic Supplementary Information Microwave-assisted Kochetkov amination followed by permanent charge derivatization: A facile strategy for glycomics Xin Liu a,b, Guisen Zhang* a, Kenneth Chan b and
Discussion & Conclusion
 Discussion & Conclusion 7. Discussion DPP-4 inhibitors augment the effects of incretin hormones by prolonging their half-life and represent a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Discussion & Conclusion 7. Discussion DPP-4 inhibitors augment the effects of incretin hormones by prolonging their half-life and represent a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information Glycan Reductive Isotope-coded Amino Acid Labeling (GRIAL) for Mass Spectrometry-based
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information Glycan Reductive Isotope-coded Amino Acid Labeling (GRIAL) for Mass Spectrometry-based
Entrainment of the mouse circadian clock by sub-acute physical and psychological
 Supplementary Information Entrainment of the mouse circadian clock by sub-acute physical and psychological Yu Tahara 1, Takuya Shiraishi 1, Yosuke Kikuchi 1, Atsushi Haraguchi 1, Daisuke Kuriki 1, Hiroyuki
Supplementary Information Entrainment of the mouse circadian clock by sub-acute physical and psychological Yu Tahara 1, Takuya Shiraishi 1, Yosuke Kikuchi 1, Atsushi Haraguchi 1, Daisuke Kuriki 1, Hiroyuki
Toxicity, Acute and Longterm Anti-Diabetic Profile of Methanolic Extract of Leaves of Pterocarpus Marsupium on Alloxan Induced Diabetic Albino Rats
 2016; 5(7): 90-94 ISSN: 2277-7695 TPI 2016; 5(7): 90-94 2016TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 12-05-2016 Accepted: 13-06-2016 Behara Chandra Rekha PG student, Department of Pharmacology, Gandhi Medical
2016; 5(7): 90-94 ISSN: 2277-7695 TPI 2016; 5(7): 90-94 2016TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 12-05-2016 Accepted: 13-06-2016 Behara Chandra Rekha PG student, Department of Pharmacology, Gandhi Medical
The Use of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) and Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) in Alloxan Induced Diabetes Mellitus in Rats
 The Use of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) and Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) in Alloxan Induced Diabetes Mellitus in Rats Florin Muselin*, Diana Brezovan, Jelena Savici, Romeo T. Cristna, Eugenia
The Use of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) and Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) in Alloxan Induced Diabetes Mellitus in Rats Florin Muselin*, Diana Brezovan, Jelena Savici, Romeo T. Cristna, Eugenia
DEVELOPMENT OF NEW ANIMAL MODELS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS AND PHARMACOLOGICAL SCREENING
 2) LITERATURE REVIEW 1. Srinivasan et al., (2005) developed a new rat model that replicates the natural history and metabolic characteristics of human type 2 diabetes and is also suitable for pharmacological
2) LITERATURE REVIEW 1. Srinivasan et al., (2005) developed a new rat model that replicates the natural history and metabolic characteristics of human type 2 diabetes and is also suitable for pharmacological
Synopsis. Received March 2, adrenaline. Mosinger and Kujalova (1964) reported that adrenaline-induced lipolysis
 Studies on Reduction of Lipolysis in Adipose Tissue on Freezing and Thawing YASUSHI SAITO1, NoBUO MATSUOKA1, AKIRA KUMAGAI1, HIROMICHI OKUDA2, AND SETSURO FUJII3 Chiba University, Chiba 280, Japan, 2Department
Studies on Reduction of Lipolysis in Adipose Tissue on Freezing and Thawing YASUSHI SAITO1, NoBUO MATSUOKA1, AKIRA KUMAGAI1, HIROMICHI OKUDA2, AND SETSURO FUJII3 Chiba University, Chiba 280, Japan, 2Department
Supplementary Materials. Experimental Procedures. Low alpha-synuclein levels in the blood are associated with Insulin Resistance.
 Supplementary Materials Experimental Procedures. Low alpha-synuclein levels in the blood are associated with Insulin Resistance. Gerardo Rodriguez-Araujo 1, Hironori Nakagami 2,Yoichi Takami 4, Tomohiro
Supplementary Materials Experimental Procedures. Low alpha-synuclein levels in the blood are associated with Insulin Resistance. Gerardo Rodriguez-Araujo 1, Hironori Nakagami 2,Yoichi Takami 4, Tomohiro
Journal of Chinese Medicine. Vol.20, No.1, Vol.20, No.3,
 163 Journal of Chinese Medicine Vol.20, No.1,2 1-96 Vol.20, No.3,4 97-162 ~ - 145 45-135 21 117 79-19 137-135 ~ - 137 65 87-65 - 145-65 - 153-79 - 153-87 47-137 - 65-87 - 47-145 - 145-47 - 19 164 153 HT7
163 Journal of Chinese Medicine Vol.20, No.1,2 1-96 Vol.20, No.3,4 97-162 ~ - 145 45-135 21 117 79-19 137-135 ~ - 137 65 87-65 - 145-65 - 153-79 - 153-87 47-137 - 65-87 - 47-145 - 145-47 - 19 164 153 HT7
Appendix A: Preparation of Media and Chemicals. Malt Extract Agar (MEA) weighing g was dissolved in 400 ml of distilled water
 Appendix A: Preparation of Media and Chemicals Preparation of Malt Extract Agar (MEA) Malt Extract Agar (MEA) weighing 13.44 g was dissolved in 400 ml of distilled water in an Erlenmeyer flask using a
Appendix A: Preparation of Media and Chemicals Preparation of Malt Extract Agar (MEA) Malt Extract Agar (MEA) weighing 13.44 g was dissolved in 400 ml of distilled water in an Erlenmeyer flask using a
Antidiabetic Activity of Active Fractions of Leucaena Leucocephala (lmk) Dewit Seeds in Experiment Model
 European Journal of Scientific Research ISSN 1450-216X Vol.43 No.3 (2010), pp.384-391 EuroJournals Publishing, Inc. 2010 http://www.eurojournals.com/ejsr.htm Antidiabetic Activity of Active Fractions of
European Journal of Scientific Research ISSN 1450-216X Vol.43 No.3 (2010), pp.384-391 EuroJournals Publishing, Inc. 2010 http://www.eurojournals.com/ejsr.htm Antidiabetic Activity of Active Fractions of
Daily injection of insulin attenuated impairment of liver circadian clock oscillation in the streptozotocin-treated diabetic mouse
 FEBS Letters 572 (2004) 206 210 FEBS 28689 Daily injection of insulin attenuated impairment of liver circadian clock oscillation in the streptozotocin-treated diabetic mouse Koji Kuriyama, Kei Sasahara,
FEBS Letters 572 (2004) 206 210 FEBS 28689 Daily injection of insulin attenuated impairment of liver circadian clock oscillation in the streptozotocin-treated diabetic mouse Koji Kuriyama, Kei Sasahara,
ENHANCEMENT OF GLUCOSE UPTAKE IN 3T3-L1 ADIPOCYTES BY TOONA SINENSIS LEAF EXTRACT
 Effect of Toona sinensis on glucose uptake in adipocytes ENHANCEMENT OF GLUCOSE UPTAKE IN 3T3-L1 ADIPOCYTES BY TOONA SINENSIS LEAF EXTRACT Yu-Chiao Yang, Hseng-Kuang Hsu, 1 Jia-Huae Hwang, and Show-Jen
Effect of Toona sinensis on glucose uptake in adipocytes ENHANCEMENT OF GLUCOSE UPTAKE IN 3T3-L1 ADIPOCYTES BY TOONA SINENSIS LEAF EXTRACT Yu-Chiao Yang, Hseng-Kuang Hsu, 1 Jia-Huae Hwang, and Show-Jen
Anti-diabetic Effects of Compound K versus Metformin versus Compound K-Metformin Combination Therapy in Diabetic db/db Mice
 2196 Notes Biol. Pharm. Bull. 30(11) 2196 2200 (2007) Vol. 30, No. 11 Anti-diabetic Effects of Compound K versus Metformin versus Compound K-Metformin Combination Therapy in Diabetic db/db Mice Seo Hyun
2196 Notes Biol. Pharm. Bull. 30(11) 2196 2200 (2007) Vol. 30, No. 11 Anti-diabetic Effects of Compound K versus Metformin versus Compound K-Metformin Combination Therapy in Diabetic db/db Mice Seo Hyun
8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES
 8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES 8.1. Introduction Nanobiotechnology, an emerging field of nanoscience, utilizes nanobased-systems for various biomedical applications.
8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES 8.1. Introduction Nanobiotechnology, an emerging field of nanoscience, utilizes nanobased-systems for various biomedical applications.
Effect of Urtica dioica Leaf Alcoholic and Aqueous Extracts on the Number and the Diameter of the Islets in Diabetic Rats
 IJMCM Winter 2013, Vol 2, No 1 Original Article Effect of Urtica dioica Leaf Alcoholic and Aqueous Extracts on the Number and the Diameter of the Islets in Diabetic Rats Durdi Qujeq 1,2, Mohsen Tatar 2,
IJMCM Winter 2013, Vol 2, No 1 Original Article Effect of Urtica dioica Leaf Alcoholic and Aqueous Extracts on the Number and the Diameter of the Islets in Diabetic Rats Durdi Qujeq 1,2, Mohsen Tatar 2,
Evaluation of murine model of malaria using ethanolic extracts of Pride of barbados (Caesalpinia pulcherrima)
 Original Research Article Journal der Pharmazie Forschung (Formerly-Recent Advances in Pharmaceutical Science Research) Vol-2 No-1 2013 Evaluation of murine model of malaria using ethanolic extracts of
Original Research Article Journal der Pharmazie Forschung (Formerly-Recent Advances in Pharmaceutical Science Research) Vol-2 No-1 2013 Evaluation of murine model of malaria using ethanolic extracts of
The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells
 The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells Published in: Natl Med J China, February 10, 2003; Vol 83, No 3, Page 195-197. Authors: JIAO Shun-Chang,
The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells Published in: Natl Med J China, February 10, 2003; Vol 83, No 3, Page 195-197. Authors: JIAO Shun-Chang,
