STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE
|
|
|
- Ira Franklin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is a total of 25 points in this exam. Fill in your answers on the separate answer sheet. The format for this exam is: Fill in A if A is the only correct answer. Fill in B if B is the only correct answer. Fill in C if C is the only correct answer. Fill in D if both A and B are correct (and C is NOT correct). Fill in E if both A and C are correct (and B is NOT correct). Fill in F if both B and C are correct (and A is NOT correct). Fill in G if A and B and C are all correct. Fill in H if none of the above is correct (A is NOT correct, B is NOT correct, and C is NOT correct). ONLY MARK ONE LETTER PER QUESTION. You may keep the question sheets. Use a dark (black or blue) pencil or dark (black or blue) pen to fill in the answers. DO NOT USE A RED PEN; DO NOT USE A RED PENCIL. 1. A complete motor neuron is removed from a frog and placed in a large volume of modified extracellular saline. The neuron is healthy; it has a stable resting voltage of -90 millivolts. It is not producing any action potentials; its threshold for an action potential is -50 millivolts. The only ligand-gated Receptors in the neuron's plasma membrane are AMPA Receptors, GABAB Receptors, and Glycine Receptors. The equilibrium potential for chloride ions is -70 millivolts, the equilibrium potential for potassium ions is -90 millivolts, and the equilibrium potential for sodium ions is +60 millivolts. A. The addition of GABA to the physiological saline will lead to no change in the amount of intracellular potassium. B. The addition of glycine to the physiological saline will lead to an increase in the amount of intracellular chloride. C. The addition of glutamate to the physiological saline will lead to an increase in the amount of intracellular sodium and a decrease in the amount of intracellular potassium. 2. Which of the following is a ligand that binds to a receptor site that is part of a ligand-gated metabotropic receptor? A. ACh (acetylcholine). B. Muscarine. C. GABA. STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 1 of 9
2 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 2 of 9 3. Consider a single cycle in a healthy heart. Define the start of the cycle as the beginning of the action potential in a SA node cell, which occurs at t 1, and the end of the cycle as the beginning of the following action potential in that same SA node cell, which occurs at t 2. The beginning of the SA node cell action potential is the time when the voltage of the SA node cell crosses the threshold for an action potential, that is, the time when SA node cell voltage goes from below threshold to above threshold. During the interval between t 1 and t 2, there are 2 heart sounds. The first heart sound is lub; the second heart sound is dub. Which of the following is true? A. In the electrocardiogram, the peak value of the T wave occurs during the time interval between t 1 and the end of the lub sound in that single cycle. B. In that single cycle, the volume of blood in the left ventricle at t 1 is greater than the volume of blood in the left ventricle at the start of the lub sound. C. In that single cycle during the time interval between t 1 and the time immediately prior to the start of the QRS wave in the electrocardiogram, the pressure in the left atrium is greater than the pressure in the left ventricle and the left AV valve is in the open position. 4. Which of the following serves as an effector, or as part of an effector, in a negative feedback system? A. GLUT2 spanning proteins in plasma membranes of rib-cage inspiratory muscles. B. Insulin Receptors in the diaphragm muscle. C. Action potentials in the diaphragm muscle. 5. Which of the following is true? A. The partial pressure of oxygen in the blood plasma in the pulmonary artery is higher than the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood plasma in the pulmonary vein. B. The percent Hemoglobin saturation (percent of oxygen-binding sites in Hemoglobin that have oxygen bound to them) in the red blood cells in the pulmonary artery is lower than the percent Hemoglobin saturation in the red blood cells in the pulmonary vein. C. The blood plasma levels of bicarbonate in the pulmonary artery are lower than the blood plasma levels of bicarbonate in the pulmonary vein. STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 2 of 9
3 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 3 of 9 6. Which of the following processes in capillaries in the leg assist in the removal of carbon dioxide from the body? A. Breakdown of carbonic acid into carbon dioxide and water by carbonic anhydrase in red blood cells. B. Net flux of bicarbonate from blood plasma into red blood cells. C. Net flux of carbon dioxide from blood plasma into red blood cells. 7. Which of the following processes in capillaries in the lung assist in the removal of carbon dioxide from the body? A. Breakdown of carbonic acid into carbon dioxide and water by carbonic anhydrase in red blood cells. B. Net flux of bicarbonate from blood plasma into red blood cells. C. Net flux of carbon dioxide from blood plasma into red blood cells. 8. Which of the following processes help bring oxygen to the body cells that are in a leg? A. An increase in hydrogen ion concentration in the cytosol of red blood cells in the body capillaries in the leg. B. Removal of oxygen from hemoglobin in response to a high partial pressure (concentration) of oxygen in the body capillaries in the leg. C. Net flux of oxygen from blood plasma into red blood cells in the capillaries in the leg. 9. Which of the following are involved in the long-term regulation of the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood? A. Secretion of the hormone erythropoietin (EPO) from bone marrow cells in response to low partial pressure levels of oxygen in the interstitial spaces surrounding these bone marrow cells. B. Changes in the amount of red blood cells produced by peritubular interstitial cells (PIC) of the renal cortex in response to EPO binding to EPO Receptors in the plasma membranes of these peritubular interstitial cells (PIC) of the renal cortex. C. Changes in the total amount of hemoglobin in the blood. STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 3 of 9
4 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 4 of Which of the following is true for ventilation? A. When the pressure within the alveoli is less than atmospheric pressure, there will be expiration of air from the lungs into the atmosphere. B. The problems with ventilation induced by injection of curare occur because of the drug's binding to Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptors (machrs) in the plasma membranes of respiratory muscles (the diaphragm and the rib-cage muscles). C. An increase in the hydrogen ion concentration in the interstitial spaces of the brainstem leads to an increase in the duration of the respiratory cycle (duration of respiratory cycle equals duration of inspiration plus duration of expiration). 11. Which of the following is an actuating signal in a negative feedback system? A. Levels of vasopressin in the blood plasma. B. Levels of erythropoietin (EPO) in the blood plasma. C. Action potentials in motor neurons that synapse upon skeletal muscles in the lung. 12. In epithelial cells of the small intestine, which of the following are involved in processes that contribute to the absorption of glucose from the lumen of the small intestine into the blood plasma? A. Net flux of sodium across the basolateral membranes of the epithelial cells from interstitial spaces to intracellular spaces via sodium-potassium ATPase pumps. B. Net flux of glucose across the luminal membranes of the epithelial cells from intracellular spaces to luminal spaces via SGLT1 transporters (sodium-glucose transporters 1). C. Net flux of glucose across basolateral membranes of the epithelial cells from interstitial spaces to intracellular spaces via GLUT2 transporters. STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 4 of 9
5 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 5 of Which of the following is true? A. Trypsinogen is produced in the pancreas and is secreted into the lumen of the small intestine. It is converted into trypsin by enterokinase. Enterokinase is located in the membranes of cells in the walls of the small intestine. In the lumen of the small intestine, trypsin breaks down carbohydrates into double sugars. B. Pancreatic amylase is produced in the pancreas and is secreted into the lumen of the small intestine. In the small intestine, it breaks proteins down into small chains of amino acids. C. Pepsinogen is produced by cells in the walls of the stomach and is secreted into the lumen of the stomach. It is converted into pepsin by HCl in the lumen of the stomach. In the stomach, it converts triglycerides into monoglycerides and fatty acids. 14. Healthy Person P takes a drug that produces a condition with a strong effect on the epithelial cells of the kidney medullary collecting duct within one hour and lasts for one week after taking the drug. There is no direct effect of the drug on other cells in the body. One day after taking the drug, which of the following drugs will produce a condition with the symptoms of diabetes insipidus in Healthy Person P? A. Drug X that is an antagonist at V2 receptors and remains bound to V2 receptors in the basolateral membranes of the epithelial cells of the kidney medullary collecting duct for one week. B. Drug Y that produces a condition in which the amounts of cytosolic camp in the epithelial cells of the kidney medullary collecting duct are very high for one week. C. Drug Z that stimulates exocytosis of AQP2 and blocks endocytosis of AQP2 for one week in the epithelial cells of the kidney medullary collecting duct. 15. From March 1 to March 31, Healthy Person W ate a normal diet with normal amounts of food and water. From April 1 to April 30, Healthy Person W was on a diet that consisted of normal amounts of food and very large amounts of water. A. April 15 values of W's blood plasma levels of vasopressin were lower than March 15 values of W's blood plasma levels of vasopressin. B. April 15 values of the concentration of dissolved solutes in W's urine were lower than March 15 values of the concentration of dissolved solutes in W's urine. C. April 15 values of W's water permeability across the luminal membranes of the medullary collecting duct epithelial cells were lower than March 15 values of W's water permeability across the luminal membranes of the medullary collecting duct epithelial cells. STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 5 of 9
6 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 6 of Consider the case of a rare mutant in which the concentration of solutes in the kidney medulla interstitial spaces is equal to the concentration of solutes in the liquid in the lumen of the medullary collecting duct in the kidney. The defective molecules associated with this rare mutation are NOT located in the epithelial cells of the kidney medullary collecting duct; the defective molecules are located in other cells of the kidney. The epithelial cells of the kidney medullary collecting duct are all normal. In this rare mutant, an increase in the amount of vasopressin that binds to V2 Receptors in the kidney will lead to A. an increase in the water permeability of the luminal membranes of the medullary collecting duct epithelial cells. B. an increase in the amount of water that is reabsorbed into the blood plasma from the lumen of the medullary collecting duct. C. no change in the net flux of water from the luminal spaces of the medullary collecting duct to the interstitial spaces of the kidney medulla. 17. Which of the following processes assist in the maintenance of high levels of dissolved solutes in the interstitial spaces of the kidney medulla? A. Net flux of sodium ions from luminal spaces to intracellular spaces via the sodium-glucose co-transporters (SGLT1 and SGLT2) located in the luminal membranes of the epithelial cells in the ascending limb of the Loop of Henle. B. Net flux of sodium ions from intracellular spaces to interstitial spaces via sodium-potassium-atpase pumps located in the basolateral membranes of the epithelial cells in the ascending limb of the Loop of Henle. C. Net flux of sodium from luminal spaces to intracellular spaces via the sodium-potassium-2chloride co-transporters (NKCC2) located in the luminal membranes of the epithelial cells in the ascending limb of the Loop of Henle. 18. SGLT1 (sodium-glucose co-transporter 1) is A. located in luminal membranes of epithelial cells in the late proximal tubule of the kidney. B. located in luminal membranes of epithelial cells of the small intestine. C. responsible for the net flux of glucose from luminal spaces to intracellular spaces in the late proximal tubule of the kidney. STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 6 of 9
7 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 7 of Healthy Person W is a human who has volunteered to take experimental drug Z. Person W has a normal dinner at 6 PM on May 1 and then does not eat for 12 hours. At 5 PM on May 2, W takes a dose of Z that completely blocks the net flux of glucose via all sodium-glucose cotransporters (both SGLT1 and SGLT2) in the kidney for the next 12 hours. Drug Z has no direct effect on cells located outside of the kidney. Person W has a normal dinner at 6 PM on May 2 and then does not eat for 12 hours. A. At 8 PM on May 2, the net flux of glucose from intracellular spaces of early proximal tubule epithelial cells in W's kidney to interstitial spaces surrounding these cells will be lower than the net flux of glucose from intracellular spaces of early proximal tubule epithelial cells in W's kidney to interstitial spaces surrounding these cells at 8 PM on May 1. B. At 8 PM on May 2, the amount of glucose in W's urine will be lower than the amount of glucose in W's urine at 8 PM on May 1. C. At 8 PM on May 2, the amount of glucose in the cytosol of early proximal tubule epithelial cells in W's kidney will be lower than the amount of glucose in the cytosol of early proximal tubule epithelial cells of W's kidney at 8 PM on May Healthy Person P takes a new drug that is a member of a drug family that results in a condition in which there are constant very high levels of cytosolic cyclic AMP (camp) in one and only one cell type in the body. A single dose of each member of the new drug family works within one hour to produce this condition and the condition lasts for one week. Which of the following is true for P two days after taking a specific member of the new drug family? Compare the situation two days after taking the drug with the situation prior to taking the drug. A. Consider the situation that P takes Drug X that results in a condition in which the levels of cytosolic camp in the cells of the liver are constant at a very high level. For this situation, ignore any effects related to insulin binding to insulin receptors in the liver. The amount of glycogen in P's liver cells two days after taking Drug X will be higher than the amount of glycogen in P's liver cells prior to taking Drug X. B. Consider the situation that P takes Drug Y that results in a condition in which the levels of cytosolic camp in the SA node cells of the heart are constant at a very high level. The firing rate of action potentials in P's SA node cells two days after taking Drug Y will be higher than the firing rate of action potentials in P's SA node cells prior to taking Drug Y. C. Consider the situation that P takes Drug Z that results in a condition in which the levels of cytosolic camp in the epithelial cells of the medullary collecting duct of the kidney are constant at a very high level. The amount of net flux of water from luminal spaces to intracellular spaces across the luminal membranes of these cells in P two days after taking Drug Z will be lower than the amount of net flux of water from luminal spaces to intracellular spaces across the luminal membranes of these cells in P prior to taking Drug Z. STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 7 of 9
8 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 8 of Person X is a healthy human who has volunteered to take experimental drug Y. Person X has a normal dinner at 6 PM on April 1 and then does not eat for 12 hours. At 2 AM on April 2, X takes a dose of Y that closes all the ATP-sensitive potassium channels in X's beta-islet cells of the pancreas for 6 hours. For this question, ignore any effects due to alpha-islet cells of the pancreas. A. At 3 AM on April 2, X's blood plasma levels of insulin will be higher than X's blood plasma levels of insulin at 1 AM. B. At 3 AM on April 2, the glucose permeability of X's skeletal muscle cells will be higher than the glucose permeability of X's skeletal muscle cells at 1 AM. C. At 3 AM on April 2, the glucose permeability of X's liver cells will be higher than the glucose permeability of X's liver cells at 1 AM. 22. In a healthy person, which of the following is true? A. GLUT2 transporter molecules are responsible for the net flux of glucose from the interstitial spaces surrounding beta-islet cells of the pancreas into the intracellular spaces of beta-islet cells of the pancreas. B. GLUT2 transporter molecules are responsible for the net flux of glucose from the interstitial spaces of the kidney cortex into the intracellular spaces of early proximal tubule epithelial cells. C. When blood plasma levels of glucagon are high and blood plasma levels of insulin are low, GLUT2 transporter molecules are responsible for the net flux of glucose from the interstitial spaces surrounding liver cells into the intracellular spaces of liver cells. 23. Which of the following is an effect of the following drugs? A. Drug X is an agonist of the Insulin Receptor. High levels of Drug X in the interstitial spaces surrounding fat cells will lead to high levels of endocytosis of GLUT4 molecules in these cells. B. Drug Y is an agonist of the Vasopressin2 Receptor (V2R). High levels of Drug Y in the interstitial spaces surrounding cells of the kidney medullary collecting ducts will lead to high levels of exocytosis of AQP2 molecules in these cells. C. Drug Z is an agonist of the Insulin Receptor. High levels of Drug Z in the interstitial spaces surrounding liver cells will lead to high levels of exocytosis of GLUT4 molecules in these cells. STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 8 of 9
9 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 9 of Glucagon A. binding to Glucagon Receptors in the plasma membrane of a liver cell leads to an increase in the levels of camp in the cytosol of the liver cell. B. binding to Glucagon Receptors in the plasma membrane of a liver cell leads to an increase in glucose permeability of the plasma membrane of the liver cell. C. levels in the cytosol of a liver cell decrease in response to an increase in camp levels in the cytosol of the liver cell. 25. Person Y is a healthy human who has volunteered to take experimental drug Z. Person Y has a normal dinner at 6 PM on May 1 and then does not eat for 12 hours. At 6 AM on May 2, Y takes a dose of Z that completely blocks the net flux of glucose via all GLUT2 transporters in the beta-islet cells of the pancreas for 24 hours. Drug Z has no effect on any other cells. Person Y has a normal dinner at 6 PM on May 2 and then does not eat for 12 hours. For this question, ignore any effects due to alpha-islet cells of the pancreas. A. At 8 PM on May 2, the glucose permeability of Y's skeletal muscle cells will be much lower than the glucose permeability of Y's skeletal muscle cells at 8 PM on May 1. B. At 8 PM on May 2, Y's blood plasma levels of glucose will be much higher than Y's blood plasma levels of glucose at 8 PM on May 1. C. At 8 PM on May 2, the potassium conductance of the ATP-sensitive potassium channels in Y's beta-islet cells will be higher than potassium conductance of the ATP-sensitive potassium channels in Y's beta-islet cells at 8 PM on May 1. STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE 9 of 9
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 19, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- APRIL 19, 2018 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- APRIL 19, 2018 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 21, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- APRIL 21, 2016 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- APRIL 21, 2016 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is
STEIN FINAL EXAM -- BIOLOGY MAY 1, PAGE
 STEIN FINAL EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- MAY 1, 2015 -- PAGE 1 of 18 There are 50 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is a total
STEIN FINAL EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- MAY 1, 2015 -- PAGE 1 of 18 There are 50 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is a total
STEIN FINAL EXAM -- BIOLOGY MAY 2, PAGE
 STEIN FINAL EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- MAY 2, 2014 -- PAGE 1 of 18 There are 50 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is a total
STEIN FINAL EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- MAY 2, 2014 -- PAGE 1 of 18 There are 50 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is a total
STEIN FINAL EXAM -- BIOLOGY MAY 5, PAGE
 STEIN FINAL EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- MAY 5, 2017 -- PAGE 1 of 17 There are 50 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is a total
STEIN FINAL EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- MAY 5, 2017 -- PAGE 1 of 17 There are 50 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is a total
STEIN FINAL EXAM -- BIOLOGY MAY 4, PAGE
 STEIN FINAL EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- MAY 4, 2018 -- PAGE 1 of 17 There are 50 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is a total
STEIN FINAL EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- MAY 4, 2018 -- PAGE 1 of 17 There are 50 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is a total
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 18, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 18, 2016 -- PAGE 1 of 8 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 18, 2016 -- PAGE 1 of 8 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 15, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 15, 2018 -- PAGE 1 of 8 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 15, 2018 -- PAGE 1 of 8 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 16, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 16, 2017 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 16, 2017 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
1. In a normal negative feedback loop the Comparator sends a(n) signal to the.
 Quiz 1-G 1. In a normal negative feedback loop the Comparator sends a(n) signal to the. a. Actuating, Sensor b. Effector, Sensor c. Error, Effector d. Actuating, Effector 2. What organ, discussed in lecture
Quiz 1-G 1. In a normal negative feedback loop the Comparator sends a(n) signal to the. a. Actuating, Sensor b. Effector, Sensor c. Error, Effector d. Actuating, Effector 2. What organ, discussed in lecture
CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis
 CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis Notes Communication is essential for the survival of organism as all living organisms must be able to detect and respond to changes in both their internal and
CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis Notes Communication is essential for the survival of organism as all living organisms must be able to detect and respond to changes in both their internal and
5. Maintaining the internal environment. Homeostasis
 5. Maintaining the internal environment Homeostasis Blood and tissue fluid derived from blood, flow around or close to all cells in the body. Blood and tissue fluid form the internal environment of the
5. Maintaining the internal environment Homeostasis Blood and tissue fluid derived from blood, flow around or close to all cells in the body. Blood and tissue fluid form the internal environment of the
Functions of Proximal Convoluted Tubules
 1. Proximal tubule Solute reabsorption in the proximal tubule is isosmotic (water follows solute osmotically and tubular fluid osmolality remains similar to that of plasma) 60-70% of water and solute reabsorption
1. Proximal tubule Solute reabsorption in the proximal tubule is isosmotic (water follows solute osmotically and tubular fluid osmolality remains similar to that of plasma) 60-70% of water and solute reabsorption
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
 Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Biology December 2009 Exam Four FORM W KEY
 Biology 251 3 December 2009 Exam Four FORM W KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your
Biology 251 3 December 2009 Exam Four FORM W KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
The Excretory System. Biology 20
 The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
Biology 12 Final Exam Samples Digestion to Nervous System
 Biology 12 Final Exam Samples Digestion to Nervous System Digestive System 1. Secretions from which of the following would have the effect shown in the diagram? A. liver B. mouth C. stomach D. large intestine
Biology 12 Final Exam Samples Digestion to Nervous System Digestive System 1. Secretions from which of the following would have the effect shown in the diagram? A. liver B. mouth C. stomach D. large intestine
Station One: Nutrition
 Station One: Nutrition Name that thing! 1. Chemical substances, found in foods, which are used in the human body. 2. Nutrient in human diet where foods are the only possible source of the nutrient. 3.
Station One: Nutrition Name that thing! 1. Chemical substances, found in foods, which are used in the human body. 2. Nutrient in human diet where foods are the only possible source of the nutrient. 3.
Transport of Solutes and Water
 Transport of Solutes and Water Across cell membranes 1. Simple and Facilitated diffusion. 2. Active transport. 3. Osmosis. Simple diffusion Simple diffusion - the red particles are moving from an area
Transport of Solutes and Water Across cell membranes 1. Simple and Facilitated diffusion. 2. Active transport. 3. Osmosis. Simple diffusion Simple diffusion - the red particles are moving from an area
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Oxygen is transported across the cell membrane by the process of
 Oxygen is transported across the cell membrane by the process of a) Simple diffusion b) Facilitated diffusion c) Diffusion through channels d) Primary active transport e) Secondary active transport Oxygen
Oxygen is transported across the cell membrane by the process of a) Simple diffusion b) Facilitated diffusion c) Diffusion through channels d) Primary active transport e) Secondary active transport Oxygen
Homeostatic Regulation
 Homeostatic Regulation A hormone is :a Water-soluble hormones: Composed of amino acids and bind a receptor protein on the of the target cell. This starts a signal cascade inside the cell and the signal
Homeostatic Regulation A hormone is :a Water-soluble hormones: Composed of amino acids and bind a receptor protein on the of the target cell. This starts a signal cascade inside the cell and the signal
Collin College. BIOL Anatomy & Physiology. Urinary System. Summary of Glomerular Filtrate
 Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology Urinary System 1 Summary of Glomerular Filtrate Glomerular filtration produces fluid similar to plasma without proteins GFR ~ 125 ml per min If nothing else
Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology Urinary System 1 Summary of Glomerular Filtrate Glomerular filtration produces fluid similar to plasma without proteins GFR ~ 125 ml per min If nothing else
EXCRETION QUESTIONS. Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
 EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
Biology 12 June 1999 Provincial Examination
 Biology 12 June 1999 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Application 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H I,
Biology 12 June 1999 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Application 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H I,
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX
 One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure
 Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Comprehensive and Easy Course Notes for BIOL1040 Exams and Assessment
 Comprehensive and Easy Course Notes for BIOL1040 Exams and Assessment MODULE 1: PRINCIPLES OF CELL FUNCTION Membrane Structure & Function Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Phospholipids
Comprehensive and Easy Course Notes for BIOL1040 Exams and Assessment MODULE 1: PRINCIPLES OF CELL FUNCTION Membrane Structure & Function Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Phospholipids
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
Digestion of Carbohydrates. BCH 340 Lecture 2
 Digestion of Carbohydrates BCH 340 Lecture 2 Carbohydrates are called carbohydrates because they are essentially hydrates of carbon (i.e. they are composed of carbon and water and have a composition of
Digestion of Carbohydrates BCH 340 Lecture 2 Carbohydrates are called carbohydrates because they are essentially hydrates of carbon (i.e. they are composed of carbon and water and have a composition of
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES PROGRAMME
 ᄋセM@セ @ POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES PROGRAMME QUALIFICATION(S): Bachelor of Biomedical Sciences QUALIFICATION CODE: 50BBMS
ᄋセM@セ @ POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES PROGRAMME QUALIFICATION(S): Bachelor of Biomedical Sciences QUALIFICATION CODE: 50BBMS
2 Answer all the questions.... [1] (b) Fig. 1.1 is an electron micrograph of the junction between two neurones.
![2 Answer all the questions.... [1] (b) Fig. 1.1 is an electron micrograph of the junction between two neurones. 2 Answer all the questions.... [1] (b) Fig. 1.1 is an electron micrograph of the junction between two neurones.](/thumbs/93/111729479.jpg) 2 Answer all the questions. 1 (a) The cells of the body need to communicate with one another. State the name given to this process of communication.... [1] (b) Fig. 1.1 is an electron micrograph of the
2 Answer all the questions. 1 (a) The cells of the body need to communicate with one another. State the name given to this process of communication.... [1] (b) Fig. 1.1 is an electron micrograph of the
WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.44 - OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
!! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
Biology 12 August 1999 Provincial Examination
 Biology 12 August 1999 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Applications 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H
Biology 12 August 1999 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Applications 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Answer Marks Guidance ( 1 idea of maintaining (relatively) stable internal, environment / state ;
 Question Answer Marks Guidance 1 (a) ( 1 idea of maintaining (relatively) stable internal, environment / state ; 1 Need the idea of constant or steady and regulation or keeping and in the body within (narrow)
Question Answer Marks Guidance 1 (a) ( 1 idea of maintaining (relatively) stable internal, environment / state ; 1 Need the idea of constant or steady and regulation or keeping and in the body within (narrow)
Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages )
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
Chapter 15 Fluid and Acid-Base Balance
 Chapter 15 Fluid and Acid-Base Balance by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Fluid Balance Water constitutes ~60% of body weight. All cells and tissues are surrounded by an aqueous environment.
Chapter 15 Fluid and Acid-Base Balance by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Fluid Balance Water constitutes ~60% of body weight. All cells and tissues are surrounded by an aqueous environment.
SECOND MIDTERM EXAM November 15, 2011 BILD 2. Nasha 10. (10 points) Josh 2. (10 points) Josh 3. (10 points) Mary 4. (5 points) 8.
 SECOND MIDTERM EXAM November 15, 2011 BILD 2 WRITE YOUR NAME ON ALL 7 PAGES. ANSWER ALL 10 QUESTIONS (100 POINTS). CONFINE YOUR ANSWERS TO THE SPACE ALLOWED. If you would like to write on the back of the
SECOND MIDTERM EXAM November 15, 2011 BILD 2 WRITE YOUR NAME ON ALL 7 PAGES. ANSWER ALL 10 QUESTIONS (100 POINTS). CONFINE YOUR ANSWERS TO THE SPACE ALLOWED. If you would like to write on the back of the
11/05/1431. Urine Formation by the Kidneys Tubular Processing of the Glomerular Filtrate
 Urine Formation by the Kidneys Tubular Processing of the Glomerular Filtrate Chapter 27 pages 327 347 1 OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture you should be able to describe: Absorptive Characteristics
Urine Formation by the Kidneys Tubular Processing of the Glomerular Filtrate Chapter 27 pages 327 347 1 OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture you should be able to describe: Absorptive Characteristics
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Membrane Transport. Anatomy 36 Unit 1
 Membrane Transport Anatomy 36 Unit 1 Membrane Transport Cell membranes are selectively permeable Some solutes can freely diffuse across the membrane Some solutes have to be selectively moved across the
Membrane Transport Anatomy 36 Unit 1 Membrane Transport Cell membranes are selectively permeable Some solutes can freely diffuse across the membrane Some solutes have to be selectively moved across the
Physio 12 -Summer 02 - Renal Physiology - Page 1
 Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Physiology 12. Overview. The Gastrointestinal Tract. Germann Ch 19
 Physiology 12 The Gastrointestinal Tract Germann Ch 19 Overview 1 Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion Secretion Absorption Motility Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion: : Dissolving and breaking
Physiology 12 The Gastrointestinal Tract Germann Ch 19 Overview 1 Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion Secretion Absorption Motility Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion: : Dissolving and breaking
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like
 Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number. Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet.
 BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. The homeostatic value of a particular controlled variable in the body
BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. The homeostatic value of a particular controlled variable in the body
BYA6. BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 6 Physiology and the Environment. General Certificate of Education January 2005 Advanced Level Examination
 Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2005 Advanced Level Examination BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 6 Physiology and
Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2005 Advanced Level Examination BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 6 Physiology and
Urinary system. Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal. Nephrons
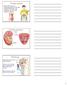 Urinary system Aids homeostasis by removing cellular wastes and foreign compounds, and maintains salt and water balance of plasma Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal pelvis Renal medulla Cortex Ureter Medulla
Urinary system Aids homeostasis by removing cellular wastes and foreign compounds, and maintains salt and water balance of plasma Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal pelvis Renal medulla Cortex Ureter Medulla
Asma Karameh Omar Sami
 5 Asma Karameh Omar Sami Mohammad khatatbeh Happy day friends! This lecture will be discussing what we have said in the previous lectures relating to different mechanisms of transport across a biological
5 Asma Karameh Omar Sami Mohammad khatatbeh Happy day friends! This lecture will be discussing what we have said in the previous lectures relating to different mechanisms of transport across a biological
TKheory Section: [Total 16 Marks]
![TKheory Section: [Total 16 Marks] TKheory Section: [Total 16 Marks]](/thumbs/96/128475268.jpg) Bloomfield Hall School Test (Unit 0-) Name :... Pa: Biolog y Date :... Class: FIV Time Allowed: 0Minutes Maximum Marks: TKheory Section: [Total 6 Marks] (a) Define the term excretion. [] (b) Fig.. shows
Bloomfield Hall School Test (Unit 0-) Name :... Pa: Biolog y Date :... Class: FIV Time Allowed: 0Minutes Maximum Marks: TKheory Section: [Total 6 Marks] (a) Define the term excretion. [] (b) Fig.. shows
Acid-Base Balance 11/18/2011. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulatory Site: Cortical Collecting Ducts.
 Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Cellular Messengers. Intracellular Communication
 Cellular Messengers Intracellular Communication Most common cellular communication is done through extracellular chemical messengers: Ligands Specific in function 1. Paracrines Local messengers (neighboring
Cellular Messengers Intracellular Communication Most common cellular communication is done through extracellular chemical messengers: Ligands Specific in function 1. Paracrines Local messengers (neighboring
Renal Physiology Part II. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 19-1c. Efferent arteriole. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
 /6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
/6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Renal Functions: Renal Functions: Renal Function: Produce Urine
 Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Physiology Unit 4
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation
 Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
Identify and describe. mechanism involved in Glucose reabsorption
 Define tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion, transcellular and paracellular transport. Identify and describe mechanism involved in Glucose reabsorption Describe tubular secretion with PAH transport
Define tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion, transcellular and paracellular transport. Identify and describe mechanism involved in Glucose reabsorption Describe tubular secretion with PAH transport
Laura - Bio 212 Exam 4 Review
 Laura - Bio 212 Exam 4 Review 1. Which of the following is not a factor that affects obesity.. a. Diet b. Leptin genes c. Economics d. Social interactions e. None of these 2. What was the difference in
Laura - Bio 212 Exam 4 Review 1. Which of the following is not a factor that affects obesity.. a. Diet b. Leptin genes c. Economics d. Social interactions e. None of these 2. What was the difference in
Hormones and Homeostasis
 Hormones and Homeostasis The endocrine system is a system of organs that releases chemical message molecules, called hormones, into the blood. Unlike the nervous system whose action helps the body react
Hormones and Homeostasis The endocrine system is a system of organs that releases chemical message molecules, called hormones, into the blood. Unlike the nervous system whose action helps the body react
Section 12.1 Principle of homeostasis
 Section 12.1 Principle of homeostasis The maintenance of a constant internal environment By maintaining a relatively constant environment (of the tissue fluid) for their cells, organisms can limit the
Section 12.1 Principle of homeostasis The maintenance of a constant internal environment By maintaining a relatively constant environment (of the tissue fluid) for their cells, organisms can limit the
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH ACID-BASE BALANCE-- CONTROLLING BLOOD PH
 !! www.clutchprep.com ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: INTRO. TO DISTURBING AND MAINTAINING BLOOD ph Physiological Sources of Acid (and Base): Acids are molecules/substances that H+ to a solution.
!! www.clutchprep.com ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: INTRO. TO DISTURBING AND MAINTAINING BLOOD ph Physiological Sources of Acid (and Base): Acids are molecules/substances that H+ to a solution.
Biology 12 November 2002 Provincial Examination
 Biology 12 November 2002 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Applications 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G,
Biology 12 November 2002 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Applications 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G,
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
BIOLOGY 12 SAMPLE QUESTIONS
 BIOLOGY 12 SAMPLE QUESTIONS The following are examples of the cognitive levels: K (), U ( and Application) and H (). It should be noted that cognitive level does not necessarily reflect level of difficulty.
BIOLOGY 12 SAMPLE QUESTIONS The following are examples of the cognitive levels: K (), U ( and Application) and H (). It should be noted that cognitive level does not necessarily reflect level of difficulty.
Overview. Physiology 1. The Gastrointestinal Tract. Guyton section XI
 Overview Physiology 1 The Gastrointestinal Tract Guyton section XI Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion Secretion Absorption Motility Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion: : Dissolving and breaking
Overview Physiology 1 The Gastrointestinal Tract Guyton section XI Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion Secretion Absorption Motility Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion: : Dissolving and breaking
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
Acids and Bases their definitions and meanings
 Acids and Bases their definitions and meanings Molecules containing hydrogen atoms that can release hydrogen ions in solutions are referred to as acids. (HCl H + Cl ) (H 2 CO 3 H + HCO 3 ) A base is an
Acids and Bases their definitions and meanings Molecules containing hydrogen atoms that can release hydrogen ions in solutions are referred to as acids. (HCl H + Cl ) (H 2 CO 3 H + HCO 3 ) A base is an
Transport through membranes
 Transport through membranes Membrane transport refers to solute and solvent transfer across both cell membranes, epithelial and capillary membranes. Biological membranes are composed of phospholipids stabilised
Transport through membranes Membrane transport refers to solute and solvent transfer across both cell membranes, epithelial and capillary membranes. Biological membranes are composed of phospholipids stabilised
Therapeutics of Diuretics
 (Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Therapeutics of Diuretics Thambi, M. (2017). The Clinical Use of Diuretics. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago.
(Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Therapeutics of Diuretics Thambi, M. (2017). The Clinical Use of Diuretics. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago.
Other Factors Affecting GFR. Chapter 25. After Filtration. Reabsorption and Secretion. 5 Functions of the PCT
 Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
I. Digestive System Salivary Amylase Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) Pepsin Pyloric Sphincter Pancreatic Amylase Pancreatic Lipase Trypsin Chymo tripsin
 Animal Systems I. Digestive System a. Process i. Mouth 1. Salivary Amylase a. Digests starch ii. Esophagus iii. Stomach 1. Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) a. Digests proteins b. Creates a low ph environment for
Animal Systems I. Digestive System a. Process i. Mouth 1. Salivary Amylase a. Digests starch ii. Esophagus iii. Stomach 1. Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) a. Digests proteins b. Creates a low ph environment for
Excretory System. Biology 2201
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System. Excretory System
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
EB Education Revision Guide. How to work with Homeostasis: Part 2 Blood Glucose Regulation
 EB Education Revision Guide How to work with Homeostasis: Part 2 Blood Glucose Regulation Blood Glucose Regulation a) Why your body regulates glucose levels What you need to know about Homeostasis: Part
EB Education Revision Guide How to work with Homeostasis: Part 2 Blood Glucose Regulation Blood Glucose Regulation a) Why your body regulates glucose levels What you need to know about Homeostasis: Part
Quick Quiz Revision Questions Cell Membranes
 Quick Quiz Revision Questions Cell Membranes 1. What is the model for cell membrane structure called? Why is it called this? 2. What is the function of plasma membrane? 3. Draw one phospholipid, label
Quick Quiz Revision Questions Cell Membranes 1. What is the model for cell membrane structure called? Why is it called this? 2. What is the function of plasma membrane? 3. Draw one phospholipid, label
Membrane Structure and Function
 BIOL1040 Page 1 Membrane Structure and Function Friday, 6 March 2015 2:58 PM Cellular Membranes Fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Phospholipids - abundant Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules (has
BIOL1040 Page 1 Membrane Structure and Function Friday, 6 March 2015 2:58 PM Cellular Membranes Fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Phospholipids - abundant Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules (has
The Endocrine System 2
 The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
DIURETICS-2. Dr. Shariq Syed. Shariq AIKC/TYB/2014
 DIURETICS-2 Dr. Syed Structure of Kidney Blood filtered by functional unit: Nephron Except for cells, proteins, other large molecules, rest gets filtered Structure of Kidney 3 major regions of nephron
DIURETICS-2 Dr. Syed Structure of Kidney Blood filtered by functional unit: Nephron Except for cells, proteins, other large molecules, rest gets filtered Structure of Kidney 3 major regions of nephron
Homeostasis involves maintaining the volume, chemical make up and other factors of blood and tissue fluid within restricted limits and set-points.
 = The maintenance of a constant internal environment Homeostasis involves maintaining the volume, chemical make up and other factors of blood and tissue fluid within restricted limits and set-points. The
= The maintenance of a constant internal environment Homeostasis involves maintaining the volume, chemical make up and other factors of blood and tissue fluid within restricted limits and set-points. The
At this second appointment, however, it was discovered that the dietary changes had not been effective, which was unexpected.
 Question: 1 (a) The control of blood glucose is a very important aspect of homeostasis. (i) Explain what is meant by the term homeostasis. (ii) Describe how negative feedback is used to control blood glucose
Question: 1 (a) The control of blood glucose is a very important aspect of homeostasis. (i) Explain what is meant by the term homeostasis. (ii) Describe how negative feedback is used to control blood glucose
9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar
 9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar Regulate Stress Response Regulate Blood Sugar Stress Response Involves hormone pathways that regulate metabolism, heart, rate and breathing The Adrenal Glands a pair
9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar Regulate Stress Response Regulate Blood Sugar Stress Response Involves hormone pathways that regulate metabolism, heart, rate and breathing The Adrenal Glands a pair
