Decreasing of Deuterium Concentration of Water: A Possible Tool in Diabetes Therapy
|
|
|
- Donna Stanley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Decreasing of Deuterium Concentration of Water: A Possible Tool in Diabetes Therapy Kamal Yavari 1, *, Mehrdad Gholamali 2, Fatemeh Yazdian 3 1 Nuclear Biochemistry Lab, Nuclear Science and Technology Research Institute (NSTRI), North Kargar Street, Tehran, Iran; 2 Faculty of New Sciences and Technologies (FNST), University of Tehran, Iran. *Corresponding author. Tel: ; kyavari@aeoi.org.ir Citation: Yavari K, Gholamali M, Yazdian F. The Biological Effects of Deuterium Depleted Water: A Possible Tool in Diabetes Therapy. Electronic J Biol, 13:4 Received: May 31, 2017; Accepted: August 29, 2017; Published: September 05, 2017 Research Article Abstract Background: Developing new diabetes care agent is of great importance and incites increasing demand for new products to improve the diabetes care. Several compounds have been made and investigated for this purpose. DDW is a type of water that has several health benefits and has been used for medicinal purposes in recent years. The aim of this study is to test the effect of removal of D 2 O on the glucose metabolism in sreptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rat model and to explore the possible mechanism. Methods: Diabetes was induced by a single i.p., injection of 60 mg/kg body weight of STZ. After 2 weeks, animals were randomly distributed into several groups to test the effect of D 2 O ( ppm) on glucose metabolism in diabetic animals with or without insulin treatment. The serum glucose and HbA1C parameters were tested and at the end of 8 weeks of intervention, the expression of membrane associated GLUT-4 mrna detected by semi-quantitative RT-PCR. Results: Our results indicate that STZ treatment significantly increased serum glucose and HbA 1 C. Depletion of D 2 O has minor influence on the measured parameters in animals not received insulin. However the measured parameters were significantly lower in those animals received lower D 2 O containing drinking water and insulin treatment. The membrane associated GLUT-4 was significantly higher in these animals also. Conclusions: These data suggest that D 2 O depletion enhance insulin effect on GLUT-4 translocation and potentiate glucose uptake in diabetic animals, provided good evidence for its potential use in diabetes care. Keywords: Diabetes; Deuterium-depleted water; Glucose; HbA 1 C; GLUT Introduction Diabetes describes a group of metabolic diseases in which the person has high blood glucose. Diabetes develops when the body doesn't make enough insulin or is not able to use insulin effectively (insulin resistance, relative lack of insulin) or both. Due to the absolute or relative lack of insulin the cells are unable to take up glucose, that is why the blood glucose level increases (hyperglycemia) leading to the symptoms of the disease. In these instances the patient blood glucose level is higher than the normal range of mmol/l. It is common for persons in this diseases group that, in spite of different pathogenesis, they cannot secret the amount of insulin required by their metabolic processes or insulin, although present, has no effect. Several factors that have effect on the insulin action/synthesis [1-8]. Several lines of evidences suggest that D2O inhibits action/synthesis from pancreatic islets [9-11]. Deuterium, a stable isotope of hydrogen, binds to oxygen to from D2O. D2O exist in the environment at 1/6700 of H2O (150 ppm) and is expected to have some biological effects [11,12]. Recently, papers were published anti-tumor effect of deuterium-depleted water (DDW). Over the past few years, nearly 10 thousand patients consumed 2000 tons of DDW and 1500 cancer patients were followed-up for long time. These cases confirmed that the cancer cells are sensitive to D depletion and in the majority of cases (70-80%) cannot adapt to the altered environment, resulting in shrinkage or even total elimination of the tumor. There were a number of diabetic persons among the tumor patients who consumed DDW in the last years. The patients began to drink DDW because of their cancer but, surprisingly, it was beneficial also for their diabetes [13-22]. We could draw the unexpected consequence that lowering D concentration has advantageous influence also on the blood glucose level in a diabetic organism. Very little or no data is available on the complex actions of lowering D2O content of the cellular environment. Some experimental and clinical observations suggest that depletion of D2O interferes with glucose metabolism in diabetic patients. In this study we wanted to test the effect of removal of D2O on glucose metabolism in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rat model and reveal the molecular mechanism of the processes induced by lowered D concentration. 2. Materials and Methods 2.1 Chemicals and reagents STZ were purchased from Sigma, RNA extraction kit ISSN
2 were obtained from QiaGene (Tehran, Iran); DNase I, RNase free kit were purchased from Fermentas (Ontario, Canada), RT kit and primers from Bioneer (Daejon, Korea), dntps from BioFlux (Tokyo, Japan). All other chemicals and solvent were of the highest commercial grade from Merck (KGaA, Germany) or from Sigma (St Louis, Mo, USA). Deuterium-depleted water: DDW was produced by Mesbah Company in concentration of ppm of deuterium content. 2.3 Animals Male Wistar rats, weighing g (Pasteur Institute, Tehran, Iran) were used in this study. Animals were housed three per standard rat cage, in a 12:12 h light-dark cycle nd controlled temperature (22 ± 1 C). Commercial rodent pellets and tap water were available and libitum. They were allowed to adapt to the laboratory conditions for one week before beginning of the study. There were eight rats per group in each experiment. The procedures were performed in accordance with institutional guidelines for animal care and use. 2.4 Preparation of STZ-induced diabetic rats Diabetes was induced by a single i.p., injection of STZ (60 mg/kg body weight). 2.5 Experimental design Rats were randomly divided into the following two groups, each group consisting of eight subgroup with three animals in anyone. Group 1: In this group, rats, dependent on step of examinations, were including: Subgroup 1-1: In this step, all of the rats were healthy (prediabetic step; two week before of diabetes induction) and consisted of these species; DDW30, DDW50, DDW75, DDW100, DDW125, DDW150, DDW control (C1H) and control 2(C2D). Subgroup 1-2: in this step, all of the rats except control1 were diabetic and named as; DDW30, DDW50, DDW75, DDW100, DDW125, DDW150, DDW control 1 and DDWD control 2. Subgroup 1-3: Diabetic rats treated with DDW alone and named as: DDWT30, DDWT50, DDWT75, DDWT100, DDWT125, DDWT150, DDWT control 1(C2H) and DDWD (control 2). Group 2: In this group, rats, dependent on step of examinations, were including: Subgroup 2-1: in this step all of the rats are healthy (prediabetic; two week of before of diabetes induction) and are; DDWi30, DDWi50, DDWi75, DDWi100, DDWi125, DDWi150, DDWi control 1 and control 2. Subgroup 2-2: In this step all of the rats except control1 were diabetic and named as; DDWi30, DDWi50, DDWi75, DDWi100, DDWi125, DDWi150, DDWi control 1 and DDWDi control 2. Subgroup 2-3: Diabetic rats treated with DDW along insulin and including: DDWTi30, DDWTi50, DDWTi75, DDWTi100, DDWTi125, DDWTi150, DDWTi (control 1i) 1 and DDWDTi (control 2). In the 1-1, 1-2, 2-1, 2-2 all of rats and also rats of control 1, control 1(i), DDWD control 2 and DDWDi control2 were fed with commercial rodent pellets and tap water in all time of study. The rats of treatment step, except control subgroups, treated with various concentration of DDW. All of examination in two groups was done with parallel. Administration of the DDW; DDW was administered orally to rats in treatment step for 8 weeks. 2.6 Measurement of glucose and HbA1C The serum glucose and HbA1C parameters were tested in prediabetic (2 weeks before of diabetes induction), diabetic (two week after of diabetes induction) and treated rats (for 8 weeks) in all of the rats. Blood samples were obtained from the tail vein and glucose and HbA1C levels were measured with glucosoxidase and immunoturbidometry technique, respectively. 2.7 Gene expression To investigate the mechanism of DDW anti -hyperglycemic action, at the end of 8 weeks of treatment, all of the animal s two groups were analyzed for soleus membrane Glut-4 mrnas expression by RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction) technique. 2.8 Statistical analysis All data are presented as mean ± SD. For 8 animals in each group. Comparisons between time points were by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Duncan s test to analyze the difference. Differences were considered significant when P-values were less than All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS Results and Discussion The aim of research was to reveal anti-hyperglycaemic effects of DDW and also the molecular mechanism of the processes induced by lowered D concentration. In this study administration of STZ significantly increased the blood glucose and HbA1C levels in rats. The stimulation of experimental diabetes in rat, using chemicals that selectively destroy pancreatic β-cell is very convenient and simple to use. The most usual substance to induce diabetes in rats is streptozotocin. Diabetic rats treated with DDW alone ISSN
3 and with insulin. In the results of Figure 1 in group 1 of rats, it can be seen that blood glucose levels in diabetic rats have increased in all rats. By analyzing the results of the post-treatment analysis, we find that blood glucose levels in rats of group 1 are different. Blood glucose levels have increased in rats fed with deuterium-depleted water at concentrations of 30, 50, 150 ppm and also diabetic control. In rats that fed with deuterium water at concentrations of 100, 75 and 125 ppm, glucose levels have decreased slightly, especially in rats that faded with depleted water in 125 ppm concentration of DDW. We find that inhibited blood glucose levels are seen in comparison with other rats. As predicted, there was no change in blood glucose levels in healthy control rats. Also, rats drinking 150 ppm of water had significantly increased their blood glucose levels. It is observed that the rate of reduction in blood glucose in rats drinking 100 ppm water was higher than ones treated with 75 ppm of DDW. The results of Figure 2 show the variation in HbA1C in group 1 of rats. Its blood levels have increased in all rats during diabetic induction. After the treatment with DDW alone, the blood level of HbA1C increased in all rats in group1, but this increase in rats that consumed deuterium water with a concentration of 125 ppm, was lower than other rats. No change was in the blood HbA1C levels in the healthy control rats. Also, in rats drinking 150 ppm of DDW, blood HbA1C levels increased compared to other rats. It was observed that the rate of increase in HbA1C in Figure 1. Serum glucose level in the group 1 of rats. Figure 2. HbA1C level in the group 1 of rats. ISSN
4 rats drinking 100 ppm water was less than ones with fed 75 ppm of DDW. Figure 3 shows the changes in glucose levels in group 2 of rats. The results indicated that blood glucose levels in diabetic rats have increased in all rats. In the DDWi treatment rats, it can be seen that blood glucose levels are different. Blood glucose increased in rats that drinking deuterium water with 150 ppm concentrations and diabetic control. It is observed that in the rats that received both DDW and insulin, blood glucose levels have decreased. The rats that fed with deuterium water at a concentration of 125 and 100 ppm had greater amount of glucose lowering. Particularly, in the rat s drinking deuterium water at a concentration of 125 ppm, the amount of glucose significantly decreased. No changes in blood glucose levels have been observed in healthy control rats. As predicted, there was no change in blood glucose levels in healthy control rats. In group 2 rats, also, in rats receiving 30 and 50 ppm of DDW, glucose level was reduced. By observing the results of Figure 4, in the rats of group 2, it can be seen that blood levels of HbA1C have increased in all rats during diabetic step. After Figure 3. Serum glucose level in the group 2 of rats. Figure 4. HbA1C level in the group 2 of rats. ISSN
5 Figure 5. Expression of GLUT-4 in three groups of rats shown in A and B (lane 1: Health control 1; 2: DDWT125; 3: DDWT100; 4: DDWi75; 5: DDWT50; 6: DDWT25; 7: DDWT150; 8: Health control 2; 9: DDWTi125; 10: DDWTi100; 11: DDWTi75; 12: DDWTi50; 13: DDWTi25; 14: DDWTi150). treatment rats of group 2 with both insulin and DDW, it can be seen that HbA1C is changes in different rats. In the rat receiving insulin and DDW with concentrations of 30, 50 and 150 ppm and also in diabetic control rats, the HbA1C is increased. HbA1C level reduced in the rat receiving insulin and DDW at concentrations of 75, 100 and 125 ppm and the highest reduction was observed in the rats drinking deuterium water with a concentration of 125 ppm. There was no change in blood HbA1C levels in healthy control rats. It is observed that the reduction in HbA1C in the rats drinking 100 ppm of water is higher than it in rats fed with 75 ppm and 50 ppm. Also, the HbA1C blood levels increased in rats drinking 150ppm water more than of rats dirking DDWi with 30 and 50 ppm of deuterium. Results of this study indicated that depletion of D2O alone has minor influence on the measured parameters in animals not received insulin. Figures 1-4 depicts glucose and HbA1C amounts in group 1 of rats. As shown in these figures, the effects of DDW alone in various concentrations on the glucose and HbA1C amounts are not significant with compromised with diabetic control (P>0.05) and are very high relative to amount of them in health control subgroups (P<0.001). However lowering of the D2O content of waster caused a significant reduction of the blood glucose and HbA1C in insulin treated rats (group 2 of rats) in a dose dependent manner. The highest effect was shown in 125 ppm of D2O. The statistical analysis showed compared to the diabetic rats, the amounts of glucose (p<0.001) and HbA1C (p<0.01) in the DDWTi 125 ppm treated rats were reduced significantly. To reveal the molecular of the processes induced by lowered D concentration, the effect of D depletion on GLUT4 was investigated in streptozotocin (STZ) treated rats lacking insulin production (Figures 4 and 5). The results indicated that the lowering of D2O promoted the expression of GLUT4 in soleus muscle of DDW treated animals. In STZ-treated rats consuming normal water and DDW alone the amount of GLUT4 was less than 45% of the health control (p<0.001). However In STZ-treated rats consuming DDW (30, 75, 105, 125 ppm) with insulin injection, GLUT4 amount was higher than in the STZ-control (150 ppm) group (p<0.001). Taken tougher, our results suggest that the molecular mechanism of D2O depletion in the glucose and HA1C reduction is the enhancement of GLUT4 expression and potentiate glucose uptake in the peripheral tissue of diabetic animal. 4. Conclusion DDW provide a method for treating and preventing ISSN
6 the diseases such as diabetes mellitus, are usually coped with surgery, radiation treatments, medicinal treatments, and the like, and in these cases, patients visit directly to hospitals or clinics and receive treatments. These problems can be solved by using deuterium depleted water as the raw material can be used for the treatment and prevention of the diabetes mellitus. References [1] Gregory P, Forlenza A, Marian R. (2011). Current opinion in endocrinology, diabetes and obesity. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 248: [2] Kahn R. (2013). Type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents. World J Diabetes. 154: [3] Gunasekaran U, Gannon M. (2011). Type2 diabetes and the aging pancreatic beta cell. Aging. 3: [4] Virally M, Laloi MM. (2010). Methods for the screening and diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. Diabetes Metabol. 36: [5] National Diabetes Data Group. (1995). Diabetes in America, 2nd Edn. Bethesda National Institutes of Health. 95: [6] Mohammad NA. (2013). Effects of treatment of overt hypothyroidism on insulin resistance. World J Diabetes [7] Buschard K. (2011). What causes type 1 diabetes? Lessons from animal models. APMIS. 119: 1-19 [8] Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. (1997). Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 20: [9] Ignat I, Oleg M, Borislav V, et al. (2017). Influence of isotopic composition of water with varying deuterium content in composition with mountain water of Bulgaria on human longevity. J Med Physiol Biophys. 7: [10] Atkison MA, Malaren NK. (1994). The pathogenesis of non-insulin dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med. 331: [11] Obberghen G, Somers, Devism G, et al. (1974). Dynamics of insulin release and microtubularmicrofilamentous system VI Effect of D2O. Endocrinl. 95: [12] Somlyai G, Jancsó G, Jákli G, et al. (1993). Naturally occurring deuterium is essential for the normal growth rate of cells. FEBS Lett. 317: 1-4. [13] Oxana, Ekaterina B, Denis S, et al. (2014). Changes of oxidation during use the food diet with deuterium depleted water in laboratory animals with purulent inflammation. Russian Open Med J. 3:1-6. [14] Olariu L, Petcu M, Tulcan C, et al. (2007).Deuterium depleted water Antioxidant or pro-oxidant. Lucrari st Med Vet [15] Avila DS, Somlyai G, Somlyai I, et al. Anti-aging effects of deuterium depletion on Mn-induced toxicity in C. elegans model. Toxicol Lett. 211: [16] Krempels K, Somlyai I, Somlyai G. (2008). A retrospective evaluation of the effects of deuterium depleted water consumption on 4 patients with brain metastases from lung cancer. Integr Cancer Ther. 7: [17] Cong FS, Zhang YR, Sheng HC, et al. (2010). Deuteriumdepleted water inhibits human lung carcinoma cell growth by apoptosis. Exp Ther Med. 1: [18] Kovács A, Guller I, Krempels K, et al. (2011). Deuterium depletion may delay the progression of prostate cancer. J Cancer Ther. 2: [19] Gyongyi Z, Somlyai G. (2000). Deuterium depletion can decrease the expression of c-myc, Ha-ras and p53 gene in carcinogen-treated mice. In Vivo. 14: [20] Gyongyi Z, Budan F, Szabo I, et al. (2013) Deuterium depleted water effects on survival of lung cancer patients and expression of Kras, Bcl2 and Myc genes in mouse lung. Nutr Cancer. 65: [21] 2nd International Congress on Deuterium Depletion. (2012). Eur Chem Bull. 1: [22] ISSN
Pharmacologyonline 3: (2009) I VESTIGATIO OF A TIHYPERGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF MORUS IGRA O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I STREPTOZOTOCI DIABETIC RATS
 I VESTIGATIO OF A TIHYPERGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF MORUS IGRA O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I STREPTOZOTOCI DIABETIC RATS Hassan Fallah Hoseini 1, Soodabeh Saeidnia 2, Ahmad R. Gohari 2*, Mojgan Yazdanpanah 2, Abbass
I VESTIGATIO OF A TIHYPERGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF MORUS IGRA O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I STREPTOZOTOCI DIABETIC RATS Hassan Fallah Hoseini 1, Soodabeh Saeidnia 2, Ahmad R. Gohari 2*, Mojgan Yazdanpanah 2, Abbass
A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets
 Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Discussion & Conclusion
 Discussion & Conclusion 7. Discussion DPP-4 inhibitors augment the effects of incretin hormones by prolonging their half-life and represent a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Discussion & Conclusion 7. Discussion DPP-4 inhibitors augment the effects of incretin hormones by prolonging their half-life and represent a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Diabetes: Definition Pathophysiology Treatment Goals. By Scott Magee, MD, FACE
 Diabetes: Definition Pathophysiology Treatment Goals By Scott Magee, MD, FACE Disclosures No disclosures to report Definition of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus comprises a group of disorders characterized
Diabetes: Definition Pathophysiology Treatment Goals By Scott Magee, MD, FACE Disclosures No disclosures to report Definition of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus comprises a group of disorders characterized
Ebrahim Abbasi Oshaghi 1,2
 1 2 Flaxseed normalized antioxidant status and also changed ABCG5 and ABCG8 genes expression in diabetic rat Fatemeh Mirzaei 1,Mona Pourjafarr 1, Seyyed Alireza Vafaei 1, Rezvan Mostoli 1, Ebrahim Abbasi
1 2 Flaxseed normalized antioxidant status and also changed ABCG5 and ABCG8 genes expression in diabetic rat Fatemeh Mirzaei 1,Mona Pourjafarr 1, Seyyed Alireza Vafaei 1, Rezvan Mostoli 1, Ebrahim Abbasi
Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes Prof. Marc Y. Donath
 Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes 1, MD Chief Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism University Hospital Basel Petersgraben 4 CH-431 Basel, Switzerland MDonath@uhbs.ch Innate immunity as a sensor of metabolic
Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes 1, MD Chief Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism University Hospital Basel Petersgraben 4 CH-431 Basel, Switzerland MDonath@uhbs.ch Innate immunity as a sensor of metabolic
Week 3, Lecture 5a. Pathophysiology of Diabetes. Simin Liu, MD, ScD
 Week 3, Lecture 5a Pathophysiology of Diabetes Simin Liu, MD, ScD General Model of Peptide Hormone Action Hormone Plasma Membrane Activated Nucleus Cellular Trafficking Enzymes Inhibited Receptor Effector
Week 3, Lecture 5a Pathophysiology of Diabetes Simin Liu, MD, ScD General Model of Peptide Hormone Action Hormone Plasma Membrane Activated Nucleus Cellular Trafficking Enzymes Inhibited Receptor Effector
Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle.
 Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle. (a) mrna levels of Dj1 measured by quantitative RT-PCR in soleus, gastrocnemius (Gastroc.) and extensor digitorum longus
Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle. (a) mrna levels of Dj1 measured by quantitative RT-PCR in soleus, gastrocnemius (Gastroc.) and extensor digitorum longus
Analysis of Blood Glucose and Plasma Insulin Levels of Tea and Cinnamon Tea Drink against People with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
 IOSR Journal of Biotechnology and Biochemistry (IOSR-JBB) ISSN: 2455-264X, Volume 3, Issue 2 (Mar. Apr. 2017), PP 48-52 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis of Blood Glucose and Plasma Insulin Levels of Tea and
IOSR Journal of Biotechnology and Biochemistry (IOSR-JBB) ISSN: 2455-264X, Volume 3, Issue 2 (Mar. Apr. 2017), PP 48-52 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis of Blood Glucose and Plasma Insulin Levels of Tea and
DEVELOPMENT OF NEW ANIMAL MODELS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS AND PHARMACOLOGICAL SCREENING
 2) LITERATURE REVIEW 1. Srinivasan et al., (2005) developed a new rat model that replicates the natural history and metabolic characteristics of human type 2 diabetes and is also suitable for pharmacological
2) LITERATURE REVIEW 1. Srinivasan et al., (2005) developed a new rat model that replicates the natural history and metabolic characteristics of human type 2 diabetes and is also suitable for pharmacological
Control of Glucose Metabolism
 Glucose Metabolism Control of Glucose Metabolism The pancreas is both an exocrine and endocrine gland. It secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum (exocrine) and 3 specific hormones into the bloodstream
Glucose Metabolism Control of Glucose Metabolism The pancreas is both an exocrine and endocrine gland. It secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum (exocrine) and 3 specific hormones into the bloodstream
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Female Pro-ins2 -/- mice at 5-6 weeks of age were either inoculated i.p. with a single dose of CVB4 (1x10 5 PFU/mouse) or PBS and treated with αgalcer or control vehicle. On day
Supplementary Figure 1. Female Pro-ins2 -/- mice at 5-6 weeks of age were either inoculated i.p. with a single dose of CVB4 (1x10 5 PFU/mouse) or PBS and treated with αgalcer or control vehicle. On day
Effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and inflammatory factors of rats with diabetic nephropathy
 Effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and inflammatory factors of rats with diabetic nephropathy J. Guan 1,2, L. Long 1, Y.-Q. Chen 1, Y. Yin 1, L. Li 1, C.-X. Zhang 1, L. Deng 1 and L.-H. Tian
Effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and inflammatory factors of rats with diabetic nephropathy J. Guan 1,2, L. Long 1, Y.-Q. Chen 1, Y. Yin 1, L. Li 1, C.-X. Zhang 1, L. Deng 1 and L.-H. Tian
Pre-Clinical and Clinical Data Confirm the Anticancer Effect of Deuterium Depletion
 Biomacromol. J. Vol. 2, No. 1, 1-7, June 2016. Biomacromolecular Journal www.bmmj.org Pre-Clinical and Clinical Data Confirm the Anticancer Effect of Deuterium Depletion G. Somlyai a, *, B. Javaheri b,
Biomacromol. J. Vol. 2, No. 1, 1-7, June 2016. Biomacromolecular Journal www.bmmj.org Pre-Clinical and Clinical Data Confirm the Anticancer Effect of Deuterium Depletion G. Somlyai a, *, B. Javaheri b,
STUDY ON ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF DEUTERIUM-DEPLETED WATER (DDW) IN EXPERIMENTAL ONCOLOGY
 Scientific Works. Series C. Veterinary Medicine. Vol. LX (2) ISSN 2065-1295, ISSN Online 2067-3663, ISSN CD-ROM 2343-9394, ISSN-L 2065-1295 STUDY ON ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF DEUTERIUM-DEPLETED WATER (DDW)
Scientific Works. Series C. Veterinary Medicine. Vol. LX (2) ISSN 2065-1295, ISSN Online 2067-3663, ISSN CD-ROM 2343-9394, ISSN-L 2065-1295 STUDY ON ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF DEUTERIUM-DEPLETED WATER (DDW)
What is Diabetes Mellitus?
 Normal Glucose Metabolism What is Diabetes Mellitus? When the amount of glucose in the blood increases, After a meal, it triggers the release of the hormone insulin from the pancreas. Insulin stimulates
Normal Glucose Metabolism What is Diabetes Mellitus? When the amount of glucose in the blood increases, After a meal, it triggers the release of the hormone insulin from the pancreas. Insulin stimulates
Pharmacologyonline 3: (2009)
 THE EFFECT OF ASTURTIUM OFFICIALE O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I DIABETIC RATS Hassan Fallah Hoseini 1, Ahmad R. Gohari 2, Soodabeh Saeidnia 2 *, aghi Shahabi Majd 3, Abbass Hadjiakhoondi 2 1- Department of Pharmacology,
THE EFFECT OF ASTURTIUM OFFICIALE O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I DIABETIC RATS Hassan Fallah Hoseini 1, Ahmad R. Gohari 2, Soodabeh Saeidnia 2 *, aghi Shahabi Majd 3, Abbass Hadjiakhoondi 2 1- Department of Pharmacology,
Pharmacologyonline 2: (2009) Pharmacodynamic Drug Interaction of Gliclazide and Mexiletine in Rats
 Pharmacodynamic Drug Interaction of Gliclazide and Mexiletine in Rats K. Abedulla Khan 1, S. Satyanarayana 2, K. Eswar Kumar 2, K. Pavan Kumar 1, K. Anupama 1 1 Sultan-ul-uloom College of pharmacy, Banjarahills,
Pharmacodynamic Drug Interaction of Gliclazide and Mexiletine in Rats K. Abedulla Khan 1, S. Satyanarayana 2, K. Eswar Kumar 2, K. Pavan Kumar 1, K. Anupama 1 1 Sultan-ul-uloom College of pharmacy, Banjarahills,
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus
 Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Gene therapy: State of the art. Ramon Gomis MD, PhD, MAE. Hospital Clínic. IDIBAPS. University of Barcelona.
 Gene therapy: State of the art Ramon Gomis MD, PhD, MAE. Hospital Clínic. IDIBAPS. University of Barcelona. Gene Therapy: First Steps Type 1 diabetes: An islet disease Alpha cell Beta cell Pancreatic
Gene therapy: State of the art Ramon Gomis MD, PhD, MAE. Hospital Clínic. IDIBAPS. University of Barcelona. Gene Therapy: First Steps Type 1 diabetes: An islet disease Alpha cell Beta cell Pancreatic
Dr. Hayam Gad Associate Professor of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University
 Dr. Hayam Gad Associate Professor of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University INTRODUCTION Diabetic nephropathy (DN) DN is defined as the appearance of persistent clinical albuminuria in an
Dr. Hayam Gad Associate Professor of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University INTRODUCTION Diabetic nephropathy (DN) DN is defined as the appearance of persistent clinical albuminuria in an
IMPACT OF NATUAL ANTIOXIDANT ON REDUCTION OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN HYPERGLYCEMIC RAT FED GERMINATED PIGEON PEA DIET
 IMPACT OF NATUAL ANTIOXIDANT ON REDUCTION OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN HYPERGLYCEMIC RAT FED GERMINATED PIGEON PEA DIET UCHEGBU NNEKA NKECHI DEPARTMENT OF FOOD TECHNOLOGY INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY,
IMPACT OF NATUAL ANTIOXIDANT ON REDUCTION OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN HYPERGLYCEMIC RAT FED GERMINATED PIGEON PEA DIET UCHEGBU NNEKA NKECHI DEPARTMENT OF FOOD TECHNOLOGY INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY,
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Figure S1. Body composition, energy homeostasis and substrate utilization in LRH-1 hep+/+ (white bars) and LRH-1 hep-/- (black bars) mice.
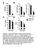 Figure S1. Body composition, energy homeostasis and substrate utilization in LRH-1 hep+/+ (white bars) and LRH-1 hep-/- (black bars) mice. (A) Lean and fat masses, determined by EchoMRI. (B) Food and water
Figure S1. Body composition, energy homeostasis and substrate utilization in LRH-1 hep+/+ (white bars) and LRH-1 hep-/- (black bars) mice. (A) Lean and fat masses, determined by EchoMRI. (B) Food and water
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence IL-1α Forward primer 5 -CAAGATGGCCAAAGTTCGTGAC-3' Reverse primer 5 -GTCTCATGAAGTGAGCCATAGC-3 IL-1β
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence IL-1α Forward primer 5 -CAAGATGGCCAAAGTTCGTGAC-3' Reverse primer 5 -GTCTCATGAAGTGAGCCATAGC-3 IL-1β
Helpful Hints for Taking Care of Your Diabetes. Farahnaz Joarder, MD and Don Kain, MA, RD,CDE Harold Schnitzer Diabetes Health Center
 Helpful Hints for Taking Care of Your Diabetes Farahnaz Joarder, MD and Don Kain, MA, RD,CDE Harold Schnitzer Diabetes Health Center Objectives How big of a problem is diabetes? What is diabetes? How is
Helpful Hints for Taking Care of Your Diabetes Farahnaz Joarder, MD and Don Kain, MA, RD,CDE Harold Schnitzer Diabetes Health Center Objectives How big of a problem is diabetes? What is diabetes? How is
Exercise Prescription in Type 1 Diabetes
 Exercise Prescription in Type 1 Diabetes Michael Riddell, PhD Professor, Muscle Health Research Centre and School of Kinesiology & Health Science, York University Senior Scientist, LMC Diabetes & Endocrinology,
Exercise Prescription in Type 1 Diabetes Michael Riddell, PhD Professor, Muscle Health Research Centre and School of Kinesiology & Health Science, York University Senior Scientist, LMC Diabetes & Endocrinology,
Obesity and Insulin Resistance According to Age in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Patients in Korea
 https://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2016.31.2.157 KMJ Original Article Obesity and Insulin Resistance According to Age in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Patients in Korea Ju Won Lee, Nam Kyu Kim, Hyun Joon Park,
https://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2016.31.2.157 KMJ Original Article Obesity and Insulin Resistance According to Age in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Patients in Korea Ju Won Lee, Nam Kyu Kim, Hyun Joon Park,
Strain Differences in the Diabetogenic Activity of Streptozotocin in Mice
 1110 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 29(6) 1110 1119 (2006) Vol. 29, No. 6 Strain Differences in the Diabetogenic Activity of Streptozotocin in Mice Koji HAYASHI, Rhyoji KOJIMA, and Mikio ITO* Laboratory of Analytical
1110 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 29(6) 1110 1119 (2006) Vol. 29, No. 6 Strain Differences in the Diabetogenic Activity of Streptozotocin in Mice Koji HAYASHI, Rhyoji KOJIMA, and Mikio ITO* Laboratory of Analytical
Fructose Upregulates FGF23 Expression In MC3T3 Pre-osteoblasts
 Fructose Upregulates FGF23 Expression In MC3T3 Pre-osteoblasts Edek A. Williams, B.S.E., Veronique Douard, Ph.D., Joseph M. Lomuti, B.S., Ronaldo Ferraris, Ph.D., J. C. Fritton, Ph.D.. Rutgers University,
Fructose Upregulates FGF23 Expression In MC3T3 Pre-osteoblasts Edek A. Williams, B.S.E., Veronique Douard, Ph.D., Joseph M. Lomuti, B.S., Ronaldo Ferraris, Ph.D., J. C. Fritton, Ph.D.. Rutgers University,
Department of Statistics, Qom University, Qom, Iran 4. School of medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran 5
 ISSN 1738-6055 (Print) ISSN 2233-7660 (Online) Lab Anim Res 2016: 32(3), 160-165 http://dx.doi.org/10.5625/lar.2016.32.3.160 The effects of dosage and the routes of administrations of streptozotocin and
ISSN 1738-6055 (Print) ISSN 2233-7660 (Online) Lab Anim Res 2016: 32(3), 160-165 http://dx.doi.org/10.5625/lar.2016.32.3.160 The effects of dosage and the routes of administrations of streptozotocin and
Does It Work for Weight Loss or Cancer Prevention? Intermittent Fasting, Alkaline Diet and Functional Food
 Does It Work for Weight Loss or Cancer Prevention? Intermittent Fasting, Alkaline Diet and Functional Food Sarah Gunnell Bellini, PhD, RDN, CD Intermountain Nutrition Update 2016 Objectives Evaluate quality
Does It Work for Weight Loss or Cancer Prevention? Intermittent Fasting, Alkaline Diet and Functional Food Sarah Gunnell Bellini, PhD, RDN, CD Intermountain Nutrition Update 2016 Objectives Evaluate quality
Supplementary Information. Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase
 Journal: Nature Medicine Supplementary Information Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase 1,2 Peng Wang PhD, 1,2 Juan-Carlos Alvarez-Perez
Journal: Nature Medicine Supplementary Information Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase 1,2 Peng Wang PhD, 1,2 Juan-Carlos Alvarez-Perez
Associations among Body Mass Index, Insulin Resistance, and Pancreatic ß-Cell Function in Korean Patients with New- Onset Type 2 Diabetes
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE korean j intern med 2012;27:66-71 pissn 1226-3303 eissn 2005-6648 Associations among Body Mass Index, Insulin Resistance, and Pancreatic ß-Cell Function in Korean Patients with New- Onset
ORIGINAL ARTICLE korean j intern med 2012;27:66-71 pissn 1226-3303 eissn 2005-6648 Associations among Body Mass Index, Insulin Resistance, and Pancreatic ß-Cell Function in Korean Patients with New- Onset
Glucose Homeostasis. Liver. Glucose. Muscle, Fat. Pancreatic Islet. Glucose utilization. Glucose production, storage Insulin Glucagon
 Glucose Homeostasis Liver Glucose Glucose utilization Glucose production, storage Insulin Glucagon Muscle, Fat Pancreatic Islet Classification of Diabetes Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes Other types of
Glucose Homeostasis Liver Glucose Glucose utilization Glucose production, storage Insulin Glucagon Muscle, Fat Pancreatic Islet Classification of Diabetes Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes Other types of
For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin
 Materials and Methods Pair Feeding Experiment For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin (0.005%), which is average daily food intake of mice fed control HFD ad libitum at week
Materials and Methods Pair Feeding Experiment For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin (0.005%), which is average daily food intake of mice fed control HFD ad libitum at week
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research. International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research
 U. Venkatesh et al, IJMPR, 2017, 5(2): 38-42 CODEN (USA): IJMPMW ISSN: 2321-2624 International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research
U. Venkatesh et al, IJMPR, 2017, 5(2): 38-42 CODEN (USA): IJMPMW ISSN: 2321-2624 International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research
28/04/51. Introduction. Insulin signaling effects on memory and mood. Is accelerated brain aging a consequence of diabetes? chronic hyperglycemia
 Introduction Insulin signaling effects on memory and mood (Review) Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both Long-term diabetes Lawrence
Introduction Insulin signaling effects on memory and mood (Review) Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both Long-term diabetes Lawrence
Report on Pathology. Study: The effect of Compound X on pancreatic islets in rhesus macaques
 Report on Pathology Study: The effect of Compound X on pancreatic islets in rhesus macaques Prepared for: Client Name Client Address January 1, 2013 Prepared by: Charter Preclinical Services 21 Main St.,
Report on Pathology Study: The effect of Compound X on pancreatic islets in rhesus macaques Prepared for: Client Name Client Address January 1, 2013 Prepared by: Charter Preclinical Services 21 Main St.,
298 Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(4):
 298 Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(4): 298-302 Letter to the Editor Effects of Maternal Linseed Oil Supplementation on Metabolic Parameters in Cafeteria Diet-induced Obese Rats * BENAISSA Nawel 1, MERZOUK
298 Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(4): 298-302 Letter to the Editor Effects of Maternal Linseed Oil Supplementation on Metabolic Parameters in Cafeteria Diet-induced Obese Rats * BENAISSA Nawel 1, MERZOUK
The liver in poisoning: what can we learn from animal models?
 The liver in poisoning: what can we learn from animal models? Stephan Krähenbühl Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology University Hospital 4031 Basel/Switzerland Kraehenbuehl@uhbs.ch Outcome and causes of
The liver in poisoning: what can we learn from animal models? Stephan Krähenbühl Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology University Hospital 4031 Basel/Switzerland Kraehenbuehl@uhbs.ch Outcome and causes of
ΦΛΕΓΜΟΝΗ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΒΗΤΗΣ
 ΦΛΕΓΜΟΝΗ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΒΗΤΗΣ ΘΩΜΑΣ ΠΑΠΑΔΟΠΟΥΛΟΣ, MD, PHD ΕΠΕΜΒΑΤΙΚΟΣ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΟ ΔΙΑΒΑΛΚΑΝΙΚΟ ΚΕΝΤΡΟ Inflammation as a cause of disease has entered the popular imagination. Diet ( macronutrients )
ΦΛΕΓΜΟΝΗ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΒΗΤΗΣ ΘΩΜΑΣ ΠΑΠΑΔΟΠΟΥΛΟΣ, MD, PHD ΕΠΕΜΒΑΤΙΚΟΣ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΟ ΔΙΑΒΑΛΚΑΝΙΚΟ ΚΕΝΤΡΟ Inflammation as a cause of disease has entered the popular imagination. Diet ( macronutrients )
Cellecta Overview. Started Operations in 2007 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA
 Cellecta Overview Started Operations in 2007 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA Focus: Development of flexible, scalable, and broadly parallel genetic screening assays to expedite the discovery and characterization
Cellecta Overview Started Operations in 2007 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA Focus: Development of flexible, scalable, and broadly parallel genetic screening assays to expedite the discovery and characterization
Comparison between intraperitoneal and subcutaneous insulin infusion: link between routes of administration and hepatic oxidative stress
 omparison between intraperitoneal and subcutaneous insulin infusion: link between routes of administration and hepatic oxidative stress S DAL, S Sigrist, W Bietiger, Peronet, M Pinget and N Jeandidier
omparison between intraperitoneal and subcutaneous insulin infusion: link between routes of administration and hepatic oxidative stress S DAL, S Sigrist, W Bietiger, Peronet, M Pinget and N Jeandidier
Metabolic syndrome, obesity, diabetes, and theier implications
 Metabolic syndrome, obesity, diabetes, and theier implications jan.krtil@lf1.cuni.cz Institute of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Diagnostics &1 st Department of Medicine Diabetes mellitus type 2 (T2DM)
Metabolic syndrome, obesity, diabetes, and theier implications jan.krtil@lf1.cuni.cz Institute of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Diagnostics &1 st Department of Medicine Diabetes mellitus type 2 (T2DM)
Oxidative Stress Unify the Pathophysiological Mechanism of Experimental Hypertension and Diabetes of Spontaneously Hypertensive Stroke-Prone Rats
 Oxidative Stress Unify the Pathophysiological Mechanism of Experimental Hypertension and Diabetes of Spontaneously Hypertensive Stroke-Prone Rats Stenio Fiorelli¹, Camille F França¹, Carlos Alberto Basílio
Oxidative Stress Unify the Pathophysiological Mechanism of Experimental Hypertension and Diabetes of Spontaneously Hypertensive Stroke-Prone Rats Stenio Fiorelli¹, Camille F França¹, Carlos Alberto Basílio
THE ANALYZATION OF TIME-BLOOD GLUCOSE CURVE DURING ORAL GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST IN PREGNANT WOMEN
 Acta Transitional Medicine An International Scientific Journal ISSN: 2521-8662 Volume 1 Issue 2 pp.10-14 June 2018 THE ANALYZATION OF TIME-BLOOD GLUCOSE CURVE DURING ORAL GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST IN PREGNANT
Acta Transitional Medicine An International Scientific Journal ISSN: 2521-8662 Volume 1 Issue 2 pp.10-14 June 2018 THE ANALYZATION OF TIME-BLOOD GLUCOSE CURVE DURING ORAL GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST IN PREGNANT
MPB333:Molecular Endocrinology of Obesity and Diabetes
 MPB333:Molecular Endocrinology of Obesity and Diabetes The Use of Stem Cells as a Cure for Type 1 Diabetes January 15, 2010 Trish Labosky 9415C MRBIV trish.labosky@vanderbilt.edu In theory. 2. ~Easy and
MPB333:Molecular Endocrinology of Obesity and Diabetes The Use of Stem Cells as a Cure for Type 1 Diabetes January 15, 2010 Trish Labosky 9415C MRBIV trish.labosky@vanderbilt.edu In theory. 2. ~Easy and
The enteroinsular axis in the pathogenesis of prediabetes and diabetes in humans
 The enteroinsular axis in the pathogenesis of prediabetes and diabetes in humans Young Min Cho, MD, PhD Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism Seoul National University College of Medicine Plasma glucose
The enteroinsular axis in the pathogenesis of prediabetes and diabetes in humans Young Min Cho, MD, PhD Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism Seoul National University College of Medicine Plasma glucose
Ct=28.4 WAT 92.6% Hepatic CE (mg/g) P=3.6x10-08 Plasma Cholesterol (mg/dl)
 a Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna8 Ct=4.3 Ct=8.4 Ct=8.8 Ct=8.9 Ct=.8 Ct=.5 Relative TM6SF mrna Level P=.5 X -5 b.5 Liver WAT Small intestine Relative TM6SF mrna Level..5 9.6% Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna mtm6sf-shrna6
a Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna8 Ct=4.3 Ct=8.4 Ct=8.8 Ct=8.9 Ct=.8 Ct=.5 Relative TM6SF mrna Level P=.5 X -5 b.5 Liver WAT Small intestine Relative TM6SF mrna Level..5 9.6% Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna mtm6sf-shrna6
The Endocrine Pancreas (Chapter 10) *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m62118 1 The Endocrine Pancreas (Chapter 10) * Ildar Yakhin Based on The Endocrine Pancreas by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m62118 1 The Endocrine Pancreas (Chapter 10) * Ildar Yakhin Based on The Endocrine Pancreas by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(1):452-456 Evaluation of anti hyperglycaemic activity
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(1):452-456 Evaluation of anti hyperglycaemic activity
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Diabetologia. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 February 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Diabetologia. 2013 February ; 56(2): 231 233. doi:10.1007/s00125-012-2788-6. Lipotoxicity impairs incretin signalling V. Poitout 1,2
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Diabetologia. 2013 February ; 56(2): 231 233. doi:10.1007/s00125-012-2788-6. Lipotoxicity impairs incretin signalling V. Poitout 1,2
Supplemental methods. Total RNA was extracted from the stomach, liver, pancreas, pituitary, and
 Supplemental methods Real-time quantitative RT-PCR and Semi-quantitative PCR Total RNA was extracted from the stomach, liver, pancreas, pituitary, and hypothalamus as previously described (). Primers and
Supplemental methods Real-time quantitative RT-PCR and Semi-quantitative PCR Total RNA was extracted from the stomach, liver, pancreas, pituitary, and hypothalamus as previously described (). Primers and
Effect of 6-Aminonicotinamide on the activity of hexokinase and lactate dehydrogenase isoenzymes in regions of the rat brain
 J. Biosci., Vol. 6, Number 3, September 1984, pp. 331-336. Printed in India. Effect of 6-Aminonicotinamide on the activity of hexokinase and lactate dehydrogenase isoenzymes in regions of the rat brain
J. Biosci., Vol. 6, Number 3, September 1984, pp. 331-336. Printed in India. Effect of 6-Aminonicotinamide on the activity of hexokinase and lactate dehydrogenase isoenzymes in regions of the rat brain
Potentiation of Glucose-stimulated Insulin Secretion by the GPR40 PLC TRPC
 Supplementary information Potentiation of Glucose-stimulated Insulin Secretion by the GPR40 PLC TRPC Pathway in Pancreatic -Cells Authors: Hodaka Yamada 1,*, Masashi Yoshida 1,*, Kiyonori Ito 1, Katsuya
Supplementary information Potentiation of Glucose-stimulated Insulin Secretion by the GPR40 PLC TRPC Pathway in Pancreatic -Cells Authors: Hodaka Yamada 1,*, Masashi Yoshida 1,*, Kiyonori Ito 1, Katsuya
The efficacy of a Chinese herbal formula GQD on type 2 diabetes and its mechanism
 The efficacy of a Chinese herbal formula GQD on type 2 diabetes and its mechanism Dr. Linhua Zhao Guang anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Science Beijing, China Melonzhao (Dr. Linhua Zhao)
The efficacy of a Chinese herbal formula GQD on type 2 diabetes and its mechanism Dr. Linhua Zhao Guang anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Science Beijing, China Melonzhao (Dr. Linhua Zhao)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Effect of High-fat or High-glucose Diet on Obesity and Visceral Adipose Tissue in Mice
 ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
BIOL212- Biochemistry of Disease. Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes
 BIOL212- Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes Diabetes mellitus is, after heart disease and cancer, the third leading cause of death in the west. Insulin is either not secreted in sufficient
BIOL212- Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes Diabetes mellitus is, after heart disease and cancer, the third leading cause of death in the west. Insulin is either not secreted in sufficient
Know what s ahead the earlier, the better
 Cardio IQ Insulin Resistance Panel with Score Know what s ahead the earlier, the better Detecting insulin resistance now can help you and your patients take action to change its course Put your patients
Cardio IQ Insulin Resistance Panel with Score Know what s ahead the earlier, the better Detecting insulin resistance now can help you and your patients take action to change its course Put your patients
THE EFFECT OF EIGHT WEEKS ENDURANCE TRAINING ON APELIN RECEPTOR GENE EXPRESSION IN ADIPOSE TISSUE OF OLD MALE RATS
 THE EFFECT OF EIGHT WEEKS ENDURANCE TRAINING ON APELIN RECEPTOR GENE EXPRESSION IN ADIPOSE TISSUE OF OLD MALE RATS Zahra Rostami Angasi and Asieh Abbassi Daloii Department of Sport Physiology, Ayatollah
THE EFFECT OF EIGHT WEEKS ENDURANCE TRAINING ON APELIN RECEPTOR GENE EXPRESSION IN ADIPOSE TISSUE OF OLD MALE RATS Zahra Rostami Angasi and Asieh Abbassi Daloii Department of Sport Physiology, Ayatollah
A Comparitive Study of Biochemical Profile of Type I and II Diabetes Mellitus
 IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn: 2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 9, Issue 1 Ver. III (Jan. 2014), PP 30-35 A Comparitive Study of Biochemical Profile of Type I and
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn: 2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 9, Issue 1 Ver. III (Jan. 2014), PP 30-35 A Comparitive Study of Biochemical Profile of Type I and
Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl
 Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells First isolation from bone marrow 30 ys ago Isolation from: spleen, heart, skeletal muscle, synovium, amniotic fluid, dental pulp,
Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells First isolation from bone marrow 30 ys ago Isolation from: spleen, heart, skeletal muscle, synovium, amniotic fluid, dental pulp,
METABOLISMO E VITAMINA D
 CONVEGNO NAZIONALE GIBIS ROMA 14-15 MAGGIO 2015 METABOLISMO E VITAMINA D Alfredo Scillitani UO Endocrinologia Ospedale Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza Holick MF, NEJM 2007 Sindrome Metabolica E un cluster
CONVEGNO NAZIONALE GIBIS ROMA 14-15 MAGGIO 2015 METABOLISMO E VITAMINA D Alfredo Scillitani UO Endocrinologia Ospedale Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza Holick MF, NEJM 2007 Sindrome Metabolica E un cluster
Abstract. Introduction
 International Journal of PharmTech Research ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1,No.1,pp 43-49, Jan March 2009 Comparative evaluation of antidiabetic activity of some marketed polyherbal formulations in alloxan induced
International Journal of PharmTech Research ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1,No.1,pp 43-49, Jan March 2009 Comparative evaluation of antidiabetic activity of some marketed polyherbal formulations in alloxan induced
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO Mice. WT mice and KHK-A/C KO mice were provided drinking water containing 10% glucose or tap water with normal chow ad
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO Mice. WT mice and KHK-A/C KO mice were provided drinking water containing 10% glucose or tap water with normal chow ad
Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring Methods for Diabetes Mellitus: Comparative Effectiveness
 Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring Methods for Diabetes Mellitus: Comparative Effectiveness Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) www.ahrq.gov Outline of Material Introduction
Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring Methods for Diabetes Mellitus: Comparative Effectiveness Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) www.ahrq.gov Outline of Material Introduction
Diagnosis of Diabetes National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse
 Diagnosis of Diabetes National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
Diagnosis of Diabetes National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Effects of deuterium oxide on folate metabolism in Lactobacillus casei
 Indian Journal of Biochemistry & Biophysics Vol. 40, June 2003, pp. 175-179 Effects of deuterium oxide on folate metabolism in Lactobacillus casei M S Pote, G Viswanathan and V Kesavan* Radiation Biology
Indian Journal of Biochemistry & Biophysics Vol. 40, June 2003, pp. 175-179 Effects of deuterium oxide on folate metabolism in Lactobacillus casei M S Pote, G Viswanathan and V Kesavan* Radiation Biology
Prognostic Impact of Hyperglycemia in Patients with Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix Receiving Definite Radiotherapy
 Prognostic Impact of Hyperglycemia in Patients with Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix Receiving Definite Radiotherapy 2016.04.08 KCCH 김문홍 DM and prediabetes in cancer Negative impact on
Prognostic Impact of Hyperglycemia in Patients with Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix Receiving Definite Radiotherapy 2016.04.08 KCCH 김문홍 DM and prediabetes in cancer Negative impact on
EFFECT OF DYKURE A POLYHERBAL FORMULATION ON TYPE-I AND TYPE-II DIABETES
 EFFECT OF DYKURE A POLYHERBAL FORMULATION ON TYPE-I AND TYPE-II DIABETES Address for Correspondence: Harshul Parikh a, R. Balaraman b Prof. R. Balaraman Pharmacy Department Faculty of Tech. & Engg., The
EFFECT OF DYKURE A POLYHERBAL FORMULATION ON TYPE-I AND TYPE-II DIABETES Address for Correspondence: Harshul Parikh a, R. Balaraman b Prof. R. Balaraman Pharmacy Department Faculty of Tech. & Engg., The
Effects of Starvation on Glycogen Contents of Heart, Skeletal Muscle and Liver in Several Mammals
 Effects of Starvation on Glycogen Contents of Heart, Skeletal Muscle and Liver in Several Mammals Mitsuto MATSUMOTO and Tatsuo HAMADA National Institute of Animal Industry, Tsukuba Norindanchi P. O. Box
Effects of Starvation on Glycogen Contents of Heart, Skeletal Muscle and Liver in Several Mammals Mitsuto MATSUMOTO and Tatsuo HAMADA National Institute of Animal Industry, Tsukuba Norindanchi P. O. Box
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3461 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 (associated to Figure 1). Cpeb4 gene-targeted mice develop liver steatosis. a, Immunoblot displaying CPEB4
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3461 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 (associated to Figure 1). Cpeb4 gene-targeted mice develop liver steatosis. a, Immunoblot displaying CPEB4
Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
R. Leibel Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center 19 March 2010
 Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus R. Leibel Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center 19 March 2010 Body Mass Index Chart 25-29.9 29.9 = overweight; 30-39.9= 39.9 obese; >40= extreme obesity 5'0" 5'2" 52
Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus R. Leibel Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center 19 March 2010 Body Mass Index Chart 25-29.9 29.9 = overweight; 30-39.9= 39.9 obese; >40= extreme obesity 5'0" 5'2" 52
The Use of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) and Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) in Alloxan Induced Diabetes Mellitus in Rats
 The Use of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) and Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) in Alloxan Induced Diabetes Mellitus in Rats Florin Muselin*, Diana Brezovan, Jelena Savici, Romeo T. Cristna, Eugenia
The Use of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) and Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) in Alloxan Induced Diabetes Mellitus in Rats Florin Muselin*, Diana Brezovan, Jelena Savici, Romeo T. Cristna, Eugenia
Designing An)gen- specific Immunotherapy for Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes.
 Designing An)gen- specific Immunotherapy for Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. Kristin V. Tarbell Immune Tolerance Unit, Diabetes Endocrinology and Obesity Branch, NIDDK Outline Background on type 1 diabetes
Designing An)gen- specific Immunotherapy for Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. Kristin V. Tarbell Immune Tolerance Unit, Diabetes Endocrinology and Obesity Branch, NIDDK Outline Background on type 1 diabetes
Convergent and Divergent Mechanisms in Aging and Cancer
 Convergent and Divergent Mechanisms in Aging and Cancer Mariana S. De Lorenzo, PhD Department of Cell Biology & Molecular Medicine delorems@umdnj.edu LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. To identify convergent and divergent
Convergent and Divergent Mechanisms in Aging and Cancer Mariana S. De Lorenzo, PhD Department of Cell Biology & Molecular Medicine delorems@umdnj.edu LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. To identify convergent and divergent
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
Antidiabetic Action of Low Molecular Weight Chitosan in Genetically Obese Diabetic KK-A y Mice
 188 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 25(2) 188 192 (2002) Vol. 25, No. 2 Antidiabetic Action of Low Molecular Weight Chitosan in Genetically Obese Diabetic KK-A y Mice Koji HAYASHI and Mikio ITO* Laboratory of Analytical
188 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 25(2) 188 192 (2002) Vol. 25, No. 2 Antidiabetic Action of Low Molecular Weight Chitosan in Genetically Obese Diabetic KK-A y Mice Koji HAYASHI and Mikio ITO* Laboratory of Analytical
ROLE OF TASTE IN METABOLIC CONTROL OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS
 Progress report ROLE OF TASTE IN METABOLIC CONTROL OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS Dr Gianluca Tornese, MD, PhD Background The sense of taste is one of the main factors that determine the choice of food and
Progress report ROLE OF TASTE IN METABOLIC CONTROL OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS Dr Gianluca Tornese, MD, PhD Background The sense of taste is one of the main factors that determine the choice of food and
Does metformin modify the effect on glycaemic control of aerobic exercise, resistance exercise or both?
 Diabetologia (2013) 56:2378 2382 DOI 10.1007/s00125-013-3026-6 SHORT COMMUNICATION Does metformin modify the effect on glycaemic control of aerobic exercise, resistance exercise or both? Normand G. Boulé
Diabetologia (2013) 56:2378 2382 DOI 10.1007/s00125-013-3026-6 SHORT COMMUNICATION Does metformin modify the effect on glycaemic control of aerobic exercise, resistance exercise or both? Normand G. Boulé
Received: 10 March 2014, Accepted: 30 May 2014, Published Online: 19 June 2014 Abstract
 Research Article www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ajmps ISSN: 2348-0165 Asian Journal of Medical and Pharmaceutical Sciences Pharmacodynamic Drug Interaction of Anti-Hypertensive Drug Combination Metoprolol
Research Article www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ajmps ISSN: 2348-0165 Asian Journal of Medical and Pharmaceutical Sciences Pharmacodynamic Drug Interaction of Anti-Hypertensive Drug Combination Metoprolol
Activation of Chemical Biological Defense Mechanisms and Remission of Vital Oxidative Injury by Low Dose Radiation
 Activation of Chemical Biological Defense Mechanisms and Remission of Vital Oxidative Injury by Low Dose Radiation K.Yamaoka 1, T.Nomura 2 and S.Kojima 3 1 Okayama University Medical School, Okayama 700-8558,
Activation of Chemical Biological Defense Mechanisms and Remission of Vital Oxidative Injury by Low Dose Radiation K.Yamaoka 1, T.Nomura 2 and S.Kojima 3 1 Okayama University Medical School, Okayama 700-8558,
Inflammasome-mediated caspase-1 activity Gatekeeper of inflammation in the adipose tissue. Rinke Stienstra
 Inflammasome-mediated caspase-1 activity Gatekeeper of inflammation in the adipose tissue Rinke Stienstra Obesity promotes the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes County-level Estimates
Inflammasome-mediated caspase-1 activity Gatekeeper of inflammation in the adipose tissue Rinke Stienstra Obesity promotes the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes County-level Estimates
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
Antidiabetic effect of Teucrium polium aqueous extract in multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced model of type 1 diabetes in rat
 Antidiabetic effect of Teucrium polium aqueous extract in multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced model of type 1 diabetes in rat Zari Sabet 1, Mehrdad Roghani 2*, Maryam Najafi 3, Zahra Maghsoudi 3 1.
Antidiabetic effect of Teucrium polium aqueous extract in multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced model of type 1 diabetes in rat Zari Sabet 1, Mehrdad Roghani 2*, Maryam Najafi 3, Zahra Maghsoudi 3 1.
PHARMACODYNAMIC EFFECTS OF CIMETIDINE AND METRONIDAZOLE ON THE BLOOD GLUCOSE LOWERING EFFECT OF GLYBURIDE IN RATS.
 Journal of Pharmaceutical and Allied Sciences 3 (1) (2006) 283-288 Journal of Pharmaceutical and Allied Sciences PHARMACODYNAMIC EFFECTS OF CIMETIDINE AND METRONIDAZOLE ON THE BLOOD GLUCOSE LOWERING EFFECT
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Allied Sciences 3 (1) (2006) 283-288 Journal of Pharmaceutical and Allied Sciences PHARMACODYNAMIC EFFECTS OF CIMETIDINE AND METRONIDAZOLE ON THE BLOOD GLUCOSE LOWERING EFFECT
A1c conversion to average blood sugar
 A1c conversion to average blood sugar The Borg System is 100 % A1c conversion to average blood sugar Convert HbA1c (%) to estimated Average Glucose (mg/dl). eag for plasma calibrated meters. HbA1c, 4.0,
A1c conversion to average blood sugar The Borg System is 100 % A1c conversion to average blood sugar Convert HbA1c (%) to estimated Average Glucose (mg/dl). eag for plasma calibrated meters. HbA1c, 4.0,
PUBLICATIONS. cells. J. Physiol. (London) 517P:91P (Manchester, England, UK).
 277 PUBLICATIONS Abstracts Haddad JJ, Land SC (1999). Differential activation of oxygen-responsive transcription factors over fetal-to-neonatal alveolar oxygen tensions in rat fetal distal lung epithelial
277 PUBLICATIONS Abstracts Haddad JJ, Land SC (1999). Differential activation of oxygen-responsive transcription factors over fetal-to-neonatal alveolar oxygen tensions in rat fetal distal lung epithelial
Effects of Rosiglitazone and Metformin as monotherapy and in combination on high fructose diet induced hyperglycemia and dyslipidaemia in rats
 Original Research Article Effects of Rosiglitazone and Metformin as monotherapy and in combination on high fructose diet induced hyperglycemia and dyslipidaemia in rats Sushil Sharma*, Amol Khanapure 1Department
Original Research Article Effects of Rosiglitazone and Metformin as monotherapy and in combination on high fructose diet induced hyperglycemia and dyslipidaemia in rats Sushil Sharma*, Amol Khanapure 1Department
902 Biomed Environ Sci, 2014; 27(11):
 902 Biomed Environ Sci, 2014; 27(11): 902-906 Letter to the Editor Curcuminoids Target Decreasing Serum Adipocyte-fatty Acid Binding Protein Levels in Their Glucose-lowering Effect in Patients with Type
902 Biomed Environ Sci, 2014; 27(11): 902-906 Letter to the Editor Curcuminoids Target Decreasing Serum Adipocyte-fatty Acid Binding Protein Levels in Their Glucose-lowering Effect in Patients with Type
Supplementary Figure 1. Blood glucose and insulin levels in mice during 4-day infusion.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Blood glucose and insulin levels in mice during 4-day infusion. (A-B) WT and HT mice infused with saline or glucose had overlapping achieved blood glucose and insulin levels, necessitating
Supplementary Figure 1. Blood glucose and insulin levels in mice during 4-day infusion. (A-B) WT and HT mice infused with saline or glucose had overlapping achieved blood glucose and insulin levels, necessitating
Adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity. Gijs Goossens, PhD
 Adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity -The role of adipose tissue oxygenation - Gijs Goossens, PhD NUTRIM School of Nutrition and Translational Research in Metabolism Maastricht University Medical Centre
Adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity -The role of adipose tissue oxygenation - Gijs Goossens, PhD NUTRIM School of Nutrition and Translational Research in Metabolism Maastricht University Medical Centre
What systems are involved in homeostatic regulation (give an example)?
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Larsen JR, Vedtofte L, Jakobsen MSL, et al. Effect of liraglutide treatment on prediabetes and overweight or obesity in clozapine- or olanzapine-treated patients with schizophrenia
Supplementary Online Content Larsen JR, Vedtofte L, Jakobsen MSL, et al. Effect of liraglutide treatment on prediabetes and overweight or obesity in clozapine- or olanzapine-treated patients with schizophrenia
Improving Diabetes Research: Moving Beyond Animal Models. Charu Chandrasekera, Ph.D. Anne Bunner, Ph.D.
 Improving Diabetes Research: Moving Beyond Animal Models Charu Chandrasekera, Ph.D. Anne Bunner, Ph.D. July 19, 2014 From Bench-to-Bedside Sulfonylurea Biguanide Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor Glucagon-like
Improving Diabetes Research: Moving Beyond Animal Models Charu Chandrasekera, Ph.D. Anne Bunner, Ph.D. July 19, 2014 From Bench-to-Bedside Sulfonylurea Biguanide Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor Glucagon-like
