Insulin pump therapy. Healthy Living with Diabetes
|
|
|
- Mervin Hampton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Insulin pump therapy Healthy Living with Diabetes 1
2 AGENDA Why Insulin Pump Therapy Pump Therapy Overview Benefits of Pump Therapy Getting Started on Pump Therapy 2
3 WHY INSULIN PUMP THERAPY UMPWHY INSULIN PUMP Pump therapy offers a safe, effective, convenient, flexible, and discrete, method of delivering insulin. 3
4 PUMP WEAR GALLERY UMPWHY INSULIN PUMP Insulin pump therapy provides more flexibility for patient s lifestyle while giving greater control of their diabetes 4
5 AGENDA Why Insulin Pump Therapy Pump Therapy Overview Benefits of Pump Therapy Getting Started on Pump Therapy 5
6 Benefits of Pump Therapy Insulin Reproducibility Precise & Predictable Delivery Bolus Wizard & Flexibility 6
7 7 AACE/ACE COMPREHENSIVE DIABETES MANAGEMENT ALGORITHM 2015
8 Insulin Reproducibility Clinical Article Review Scholtz- Pharmacokinetic and glucodynamic variability: assessment of insulin glargine, NPH insulin and insulin ultralente in healthy volunteers using a euglycaemic clamp. Pharmacodynamics Variability in Insulin Action* 8
9 Insulin Reproducibility The Problem with Injections Regimented lifestyle: unrealistic Long-acting insulin A large depot, with wide variations in the timing and amount actually absorbed into the blood stream Cannot match varying basal needs (e.g., dawn phenomenon) Insulin Profiles Porcellati F, et al. Diab Care. 2007;30(10):
10 Precise & Predictable Delivery Basal Insulin Delivers continuously/automatically Adjusted to match patient s hepatic glucose production - Between meals and during the night (nocturnal) Similar to a normal functioning pancreas - Maintains BG stability 10
11 Precise & Predictable Delivery Basal Rate Continuous Delivery Advantages: Very precise exact delivery Eliminates large depots Greatly reduces risk of lows Basal Rate u/hr u/hr u/hr 11
12 12-1a 2-3a 4-5a 6-7a 8-9a 10-11a 12-1p 2-3p 4-5p 6-7p 8-9p 10-11p units/hour Precise & Predictable Delivery Basal Insulin Needs Vary Throughout the Day age 3-10 age age age > hour Results indicate it is not reasonable to expect insulin needs to be met by a flat rate of insulin delivery for 24 hours. Scheiner, Gary; Boyer, Bret A. Characteristics of basal insulin requirements by age and gender in Type-1 diabetes patients using insulin pump therapy. Diab Res and Clin Prac, 69 (2005) pg
13 Bolus Wizard & Flexibility ADVANTAGES OF BOLUS WIZARD FEATURE 1. Calculates Meal and Correction Boluses: BG ICR ISF Target Range Benefit: Determines each bolus amount based on patient s individual pump settings & current needs (BG, carb intake, active insulin) 2. Keeps accurate records: Times and values of all BG readings Carbohydrate intake Type, amount, time of boluses Benefit: Provides comprehensive records for therapy evaluation 3. Tracks Active Insulin: Subtracts active insulin from insulin calculated to correct a high, before suggesting total correction amount to take. Benefit: Helps prevent insulin stacking & lows that occur from over correcting when active insulin remains from previous boluses 13
14 Insulin Efficacy of Insulin Pump vs. MDI MDI Injection Injection Injection Injection Normal Insulin Secretion Rapid-acting Insulin Lantus Insulin Pump 0 hr 12 hrs 24 hrs Normal Insulin Secretion Insulin Pump Delivery 14
15 A1C (%) Efficacy of Insulin Pump vs. MDI Pumps Achieve Significant A1C Improvement Metabolic Control (A1C) MDI 8.1% Pump 7.2% 6 Baseline Weeks Doyle, E. A. (2004). A Randomized, Prospective Trial Comparing the Efficacy of Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion with Multiple Daily Injections Using Insulin Glargine/. Diabetes Care. 27:
16 Efficacy of Insulin Pump vs. MDI CSII REDUCES INCIDENTS OF SEVERE HYPOGLYCEMIA Rudolph JW, Hirsch IB. Endocrine Practice. 2002; 8: Bode,BW, Steed RD, Davidson PC. Diabetes Care. 1996;19:324-7; Boland EA, Grey M, Oesterle A, et al. Diabetes Care. 1999; 22: ; 16
17 17 Efficacy of Insulin Pump vs. MDI
18 Getting Started on Pump Therapy 18
19 INSULIN PUMP SETTINGS Determined by using patient history & clinical judgment Calculated by using standard formulas 19
20 CALCULATE PUMP TDD Reduced Dose Based on daily injection dose Injection Dose X 0.75 Laura s Weight: 70kg 53 units x 0.75 = 40 units/day 70kg x 0.5units = 35 units/day Laura s Pump TDD:( 40 units/day + 35 units/day ) 2 = 37.5 units/day 20
21 21 INSULIN PUMP SETTINGS
22 INSULIN PUMP SETTINGS Total amount of basal insulin delivered over 24 hours Typically ~40-50% of TDD is basal Total amount of bolus insulin given for food & correction in 24 hours Typically ~ 50-60% of TDD is bolus Food Correction 22 22
23 INSULIN PUMP SETTINGS Basal Breakfas t and Bolus Lunch Dinner Snack 12am 3am 6am 9am Noon 3pm 6pm 9pm 11pm 23 23
24 24 INSULIN PUMP SETTINGS
25 BASAL RATE (BR) Basal Rate Total Daily Basal 24 hours Laura s Total Daily Basal Dose: units/day units/day 24 hrs = 0.78 units/hr (Total Daily Basal) Pump Delivers Basal in 0.05 units Starting Basal Rate = 0.75 units/hr or 0.80 units/hr 25
26 26 INSULIN PUMP SETTINGS
27 INSULIN-TO-CARBOHYDRATE RATIO (ICR) Insulin-to-Carb Ratio (Method 1) Daily Carbohydrate Intake Carb grams Total Daily Bolus Insulin-to-Carb Ratio (Method 2) 500 Rule 500 Pump TDD Laura s Total Daily Bolus units/day Laura s Total Daily Dose 37.5 units/day Estimated Daily Carbs ~ 225 grams 225 g u/day = 12 grams/unit (Carb Ratio) u/day = 13 grams/unit (Carb Ratio) 1 unit covers ~ 12 grams 1 unit covers ~ 12 grams 27
28 28 INSULIN PUMP SETTINGS
29 INSULIN SENSITIVITY FACTOR (ISF) Insulin Sensitivity Factor (Method 1) 1800 Rule 1800 Pump Total Daily Dose Laura s Total Daily Dose 37.5 units/day units/day = 48 mg/l 1 unit decreases BG ~ 48 mg/l The number of mg/l one unit of insulin lowers glucose. 29
30 INSULIN PUMP SETTINGS Bolus Wizard Settings 30
31 HOW DOES IT WORK = Insulin Pump Therapy Change reservoir and infusion set every 2 to 3 days 31
32 HOW DOES IT WORK MiniMed Paradigm Insulin Pump Technology REAL-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring Technology** The MiniMed Paradigm REAL-Time System 32
33 MEDTRONIC DIABETES UPDATES ON CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITORING & INSULIN PUMP Kulvadee A. Sales manager diabetes care
34 Medtronic Diabetes Products i-port Advance 1) Easier onboarding of insulin/ subcutaneous injections 2) Suitable for all ages ipro2 CGM 1) Diagnostic tool that reveals a patient s true glycemic pattern 2) Can be widely used Insulin Pump Therapy 1) Proven therapy when MDI is not suitable 2) Most physiological method of insulin delivery available Pag e 34
35 I-PORT ADVANCE Page 35
36 MEDTRONIC DIABETES TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITORING INSULIN PUMP THERAPY REAL TIME CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITORING CARELINK SYSTEMS 36
37 2 Categories of CGM Professional CGM Owned by clinicians Short term use on patients (6 days) Blind evaluation Retrospective data analyzed by clinician Minimal training required Personal CGM Owned by patients On-going use by patients Displays glucose values and alarms Continuously updated data viewed by patients Requires patient education ipro 2 Paradigm or Minimed 640G System 37
38 WHAT S A GLUCOSE SENSOR AND HOW DOES CGM WORK? TECHNOLOGY BEHIND CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE SENSING
39 KEY CONCEPT: BLOOD GLUCOSE VS. SENSOR GLUCOSE Blood Glucose (BG) is measured in blood Sensor Glucose (SG) is measured in interstitial fluid Sensor glucose correlates well with capillary glucose, when glucose levels are stable 39
40 THE GLUCOSE SENSOR CONSISTS OF 3 LAYERS Semi Permeable Membrane Selective to glucose and oxygen Enzyme The membrane surrounds a glucose oxidase enzyme Electrode 40
41 1 Glucose and Oxygen Enter Membrane When the glucose and oxygen come in contact with the glucose oxidase enzyme, the first chemical reaction takes place Glucose and Oxygen Membrane Enzyme Electrode 41
42 2 First Chemical Reaction Glucose and oxygen come in contact with the glucose oxidase enzyme Glucose and oxygen are converted into Hydrogen Peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) and gluconic acid Membrane Enzyme Glucose and Oxygen H Gly Acid 2 O 2 Electrode 42
43 3 Second Chemical Reaction H 2 O 2 seeps through to the Electrode layer A voltage is applied to the Electrode, causing H 2 O 2 to breakdown into: Hydrogen Oxygen 2 electrons Membrane Enzyme Electrode H 2 O 2 2e- The more glucose in your body, the more H 2 O 2 generated. The more H 2 O 2, the more current generated. 43
44 CONVERTING ISIG TO A GLUCOSE SENSOR VALUE THE GLUCOSE OXIDASE REACTION The 2 electrons generate a current called ISIG ISIG is converted to a sensor glucose value when a BG meter value is entered for calibration Membrane Enzyme Electrode 2e- ISIG The ISIG is Proportional to Glucose Concentration 44
45 Page 45 WHY CGM? RATIONALE BEHIND CGM
46 RECOMMENDATION FROM AACE Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) should be considered for patients with T1D and T2D on basal-bolus therapy to improve A1C levels and reduce hypoglycemia. Early reports suggest that even patients not taking insulin may benefit from CGM -- AACE Consensus Statement on CGM
47 CGM Provides Visual Feedback of Glucose Control Glycemic Variability CGM provides visual feedback to help patients and clinicians understand glucose variability A1C 9 A1c = 9 in both patients Profiles are very different A1C 9 47
48 A BOAT WITH NO CONTEXT 48
49 The Boat Is Moving Toward Waterfall WITH A MORE COMPLETE PICTURE SEE THE POTENTIAL RISK AND DANGER 49
50 50 WITH A MORE COMPLETE PICTURE, ONE CAN PREVENT POTENTIAL PROBLEMS AND MOVE AWAY FROM DANGER
51 3 CORE GLUCOSE TECHNOLOGIES: CGM - Complimentary and Essential Fingerstick Testing A1C CGM Advanced diabetes management requires comprehensive understanding of glucose control 51
52 CGMS IN DIAGNOSTIC CENTER Consultation in clinic Assessment of patient who requires close glucose monitoring Patients directed to Diagnostic centers for starting of CGMS study Patients goes home and resume normal activities for 6 days Reports can be ed to doctors or hardcopy printed for patient to bring to doctor for review and filed with patient records Patients returns to diagnostic center for download of CGMS data after 6 days 52
53 BENEFITS OF PROFESSIONAL CGM CGM shows the whole picture, not just snapshots of glucose levels. It provides insight into glucose trends between fingersticks, leading to improved knowledge and improved glucose control Reveals true glycaemic patterns, without patient intervention, for clinicians Identifies glucose behaviour throughout the day in response to food, exercise, medications, stress and lifestyle Reinforces daily diabetes management Three easy to read graphs 53
54 REPORTS & INTERPRETATION
55 MEDTRONIC CARELINK IPRO REPORTS: Three are generated automatically Daily Overlay (1 page) Daily Summary (2 pages) Overlay by Meal (2 pages) Page 55
56 REPORT #1: DAILY OVERLAY Summary of the study Highlights the highs and lows of a patient s glucose levels Allows for quick identification of recurring patterns 56
57 DAILY OVERLAY REPORT 57
58 DAILY OVERLAY REPORT 58
59 CASE STUDY 1: NOCTURNAL HYPOGLYCEMIA Physician reports were revealed with Professional CGM Physician Report Nocturnal Hypoglycemia > Daily 59
60 DAILY OVERLAY REPORT - HOW TO USE THE PIE CHARTS Overall, they are spending 55% above 7.8 mmol/l This means: 24 hours X 55% = 13.2 hours per day above target Is this good control? 60
61 REPORT #2: DAILY SUMMARY Shows a breakdown of daily glucose levels Provides further insights into a patient s glucose trends based on their activities 61
62 REPORT #3: MEAL OVERLAY Analyses a patient s pre and post meal glucose levels Allows for an overview of pre and post meal highs and lows. 62
63 PATIENT SELECTION FOR PROFESSIONAL CGM AACE Guidelines for Candidate Selection Patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes who: are not at their A1C target have recurrent hypoglycemia or hypo unawareness Pregnant women with: Type 1 diabetes Type 2 Gestational diabetes requiring insulin * AACE CGM Task Force. Statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists Consensus Panel on Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Endocrine Practice. 2010; 16(5):
64 PROFESSIONAL CGM TYPICAL CASES IN PRACTICE Uncontrolled DM Type 2 on oral agent with A1C 7.2-8% Patient does not check glucose regularly or bring in meter or diary I want to better identify what is the primary contributor for patient not at goal Diary has inconsistent glucose readings On basal insulin where should I add prandial insulin? Type 1 patient MDI or insulin pump (without CGM) 64
65 STARTING ON PUMP THERAPY TYPE 2
66 66
67 67
68 68
69 69
70 CARELINK PRO SOFTWARE FOR PARADIGM REAL-TIME CGM
71 CHALLENGES OF DIABETES MANAGEMENT Limited time to spend with patients Complex patient issues Difficulty obtaining precise, accurate information Ineffective time reviewing data in multiple of formats Many logbook formats Different software for every meter 71
72 MEDTRONIC CARELINK INTERFACE PATIENT S HOME PRACTICE/CLINIC Internet Device upload Reports Device upload (if needed) Reports
73 THE 5 MEDTRONIC CARELINK PRO REPORTS Adherence Sensor & Meter Overview Logbook Daily Detail Pump Settings 73
74 ADHERENCE REPORT Monitoring Information Bolus Information Reservoir + Set Information Suspend Information 74
75 Hyperglycaemia: Darker color indicates frequent occurrence Hypoglycaemia Target Range Overnight Breakfast Lunch Dinner 75
76 Plots Patient s Meter BGs Indicates Day s Average BG Target Range Target Range Overnight Breakfast Lunch Dinner Statistical Data Avg BG Number of highs Number of lows Avg carb intake Avg Total Daily Insulin Basal Bolus 76
77 Daily detail no sensor Shows BGs, Insulin delivery, Carbohydrate consumed Daily detail with sensor Shows SG trace, BGs, Insulin delivery, Carbohydrate consumed Sensor trace over consecutive days 77
78 Overnight Low Post Breakfast and Lunch High Details on each bolus Statistical information for day and reporting period 78
79 LOGBOOK REPORT Overnight Breakfast Pre-Lunch Lunch Pre-Dinner Dinner Highs Grams of Carb Lows 79
80 DEVICE SETTINGS REPORT Basal rate information Bolus information Sensor information Use as progress note to document changes in therapy and file in patient s chart Utilities information 80
81 QUESTIONS? THANK YOU Lunch Break
82 DCCT: Treating to target is important in type 1 patients DCCT showed reduction in complications in type 1 patients with 2% reduction in A1C Retinopathy risk* Microalbuminuria + Albuminuria+ Risk of any CV Event** Non-fatal MI, Stroke or CV Death** Clinical neuropathy+ 76% 39% 54% 42% 57% 60% DCCT, Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. * 76% decrease in retinopathy risk for those without retinopathy at baseline; progression slowed by 54% in those with existing retinopathy. +DCCT Research Group. N Engl J Med 1993;329(14): Slide 82 **DCCT CV Outcomes: N Engl J Med 2005;353:
83 Risk of developing hypoglycaemia/complications (%) Reasons for poor glucose control Existing insulins force a trade-off between hypoglycaemia and complications Hypoglycaemia Complications HbA1C Slide 83 DCCT Research Group. N Engl J Med 1993;329:
84 Pumps Reduce Severe Hypoglycemia Published 2008 Pump vs. MDI Severe Hypoglycemia Rate Ratio Study Inclusion Criteria Meta-analysis of 22 studies Compared severe hypoglycemia Type 1 diabetes Duration > 6 months on pump Severe hypo frequency > 10 episodes /100 pt years on MDI Results MDI has 4.19 Xs more severe hypoglycemia than pumps Greatest hypo reduction found in those with highest initial rates of severe hypo Slide 84 Adapted from Pickup JC, Sutton AJ. Diabet Med 2008;25:
85 INSULIN PUMPS LOWER A1C MORE THAN MDI Studies Published Bruttomesso D et al. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) in the Veneto region: efficacy, acceptability and quality of life. Diabet Med. 2002; 19 (8):
86 REDUCED CARDIOVASCULAR AND ALL CAUSE MORTALITY WITH CSII Presented at 50th EASD Annual Meeting, Vienna, Austria, Sept 2014 Prospective observational study of patients with T1D in the Swedish National Diabetes Registry Over 18,000 T1D patients followed for 7 years, : 2441 on pump therapy vs 15,727 on MDI Outcome Fatal CVD Events (%) Events/1000 person-years Hazard Ratio Injection P-value Pump Total mortality Injection Pump Gudbjörnsdottir S et al. Oral Presentation 196. Presented at: European Association for the Study of Diabetes Annual Meeting; Sept , 2014; Vienna, Austria. 86
87 OpT2mise Study Insulin Pump Therapy in T2D Objective Design Methodology Compare efficacy and safety of pump therapy and MDI in patients with T2D who had not responded to a basal-bolus regimen after active insulin titration. Six month randomised controlled trial adults (A1C %) entered run-in study phase. MDI control group cross over to pump therapy at the end of the 6 month treatment period. Primary endpoint: HbA1c change from baseline to 6 months Secondary endpoints: Between group change in glycaemic variability parameters assessed by blinded CGM Number of severe hypoglycaemic events and DKA events Change in Insulin dosage between baseline and 6 months Change in lipid parameters, weight and blood pressure between baseline and 6 months N=331 N=495 87
88 PRIMARY ENDPOINT: PUMP THERAPY ACHIEVES GREATER A1C REDUCTION Mean A1C and 95% C.I. (%) Change in HbA1c - 6 months 10 CSII MDI A1C Reduction: 9 CSII group : -1.1% (A1c decreases 9.0% to 7.9%) MDI group: -0.4% (HbA1c drop from 9.0% to 8.6%) 8 Run-in (8 weeks) Study Phase (6 months + 3 weeks) 0.7% difference favouring pump therapy (p<0.001) Week Insulin pump therapy significantly improves glycaemic control compared to MDI in managing type 2 diabetes Reznik Y et al. Insulin pump treatment compared with multiple daily injections for treatment of type 2 diabetes (OpT2mise): a randomised open-label controlled trial Lancet Oct 4;384(9950):
89 SIGNIFICANT AND DURABLE REDUCTION OF A1C AT 1 YEAR; OPTIMIZE STUDY (-0.7%) p< (-1.2%) p< Run-in Study Phase Continuation Phase (MDI crossover) Reznick et al and Optimize Study Group ADA Poster Presentation 2015
90 ΔA1C (MDI) - ΔA1C (CSII), % Cumulative Patientss Distribution (%) TREATMENT EFFECT ON A1C REDUCTION Difference in HbA1c according to baseline levels Distribution of HbA1c - 6 months 0 8 to 8.5% 8.6 to 9.2% 9.3 to 11.5% ±0 85% (P=0.105) % ±0 92% (P<0.02) % CSII MDI ±1 4% (P<0.001) month HbA1c (%) CSII group subjects with the highest baseline HbA1c (9.3 to 11.5%) achieved the largest improvement in glycemic control compared to MDI patients with the same baseline characteristics (-1.1±1.4%, p<0.001) Under CSII treatment, a larger proportion of the patient population achieved an HbA1c below 8% (55% versus 28%, p<0.001) Insulin pump therapy (CSII) is consistently superior to MDI therapy In the reduction of HbA1c and especially in patients with the highest baseline HbA1c
91 REDUCTION OF TOTAL DAILY INSULIN DOSE ON INSULIN PUMP THERAPY; OPTIMIZE STUDY -20% (p<0.001) -23% (p<0.0001) Run-in Study Phase Continuation Phase Reznick et al and Optimize Study Group ADA Poster Presentation 2015
92 Insulin Pumps further decrease absorption variability Pumps 3% Detemir *Percentages represent the coefficients of variation (CV) for insulin action as measured by the maximum glucose infusion rate in these euglycemic glucose clamp studies 27% Glargine Intrasubject Variability 46% NPH 59% Glucose lowering effect of intermediate and long-acting insulin can vary up to 46%, which explains drastic day-to-day variations in glucose levels despite using the same amount. Lepore et al. Diabetes 2000;49: Heise, Slide TC 92 et al, Poster Number 518
93 12-1a 2-3a 4-5a 6-7a 8-9a 10-11a 12-1p 2-3p 4-5p 6-7p 8-9p 10-11p Insulin (units/hour) AVERAGE HOURLY BASAL RATE BY AGE GROUP Published 2005 n= Age Age Age 3-10 Age > Hour of the Day Scheiner, Gary; Boyer, Bret A. Characteristics of basal insulin requirements by age and gender in Type-1 diabetes patients using insulin pump therapy. 93 Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 69 (2005) pg
94 CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITORING - MULTIPLE BASAL RATES Patient, 39 y.o on MDI (Determir BD, Aspart TD) Patient complains waking up in the morning with high blood glucose levels despite going to bed with normal BG levels. 94
95 There are limitations of insulin injection therapy MDI CSII Disease progression - High doses of insulin are required to meet glycemic goals 1 - Frequency of injections increases vs Insulin dynamics - Insulin pooling - Greater intrasubject variability 3 - Dawn phenomenon Adherence - Perceived pain with injections 2 - Missed mealtime boluses - Social limitations, patient burden, and interference with daily activities 2 1. Wainstein J, et al. Diabetic Med. 2005: Peyrot M, et al. Diabetes Care. 2010;33: Lepore M, et al. Diabetes. 2000; 49:
96 There are challenges to insulin injection compliance US survey with 502 adults (T1 [23%],T2 [77%]) showed 1 : 77% have omitted insulin injection(s) 20% reported regular omission Barriers to compliance include 1,2 : - Perceived burden a lot of injections - Interference with daily activities - Injections are painful and embarrassing - Strict, complex treatment regimen Addressing interference with daily activities, injection pain, and embarrassment may contribute to improved treatment adherence 2 1. Peyrot M, et al. Diabetes Care. 2010;33: Rubin RR. Am J Med. 2005;118(Suppl3):27S 34S. 96
97 MDI Pump Patient Satisfaction: Pump vs. MDI Published 2005 Health-Related Quality of Life Assessment Lower is Better N= 197 Adults Type 1 or Type 2 Peyrot M, Rubin R. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:
98 ADVANCEMENTS IN PUMP THERAPY
99 Glucose mg/dl A NEW WAY TO TIGHTEN CONTROL The Paradigm REAL-Time insulin pump is integrated with continuous glucose monitoring. CGM reveals what fingersticks alone cannot Provides an update on your glucose levels every 5 minutes Fingersticks Alone Target Zone Continuous Glucose Monitoring 54 12AM 9AM 6PM 12MN Time of Day 99
100 BENEFITS INSULIN PUMP THERAPY: CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITORING FUNCTION Continuous Glucose Monitoring function Predictive alerts
101 BENEFITS INSULIN PUMP THERAPY: CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITORING FUNCTION Continuous Glucose Monitoring function Low glucose suspend function
102 Events per patient week AUC (mmol/lx min) LGS ASPIRE In-Home study Design In the ASPIRE In-Home study, the MiniMed sensor-augmented insulin pump with low suspend feature prevented more nocturnal hypoglycaemic events than an insulin pump without that feature. N=247, age 16 to 70 years Hypoglycemia Events per Patient-Week Mean AUC of Nocturnal Hypoglycaemia 6 30% reduction (p<0.001) % reduction (p<0.001) 5 32% reduction (p<0.001) Run-In Phase Study Phase Run-In Phase Study Phase 0 Threshold Suspend Control Threshold Suspend Control 0 Threshold Suspend Control Nocturnal Combined Day and Night Bergenstal RM,Klonoff DC, Bode BW, et al. Threshold-based insulin-pump interruption for reduction of hypoglycemia. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(3):
103 AFTER YOU HAVE HAD YOUR CRASH The airbag saves your life
104 PREVENTING THE ACCIDENT
105 LATEST MEDTRONIC DIABETES TECHNOLOGY: MINIMED 640G WITH Improved Design: Designed with you in mind Full color with auto brightness display Ergonomic design; ntuitive navigation Waterproof Greater Convenience: Easy to use Programmable treatment reminders Preset meal bolus Advanced Protection: Continuous Glucose Monitoring Technology Suspend BEFORE hypoglycemia Basal insulin AUTOMATICALLY resumes when glucose levels are approaching normal range
106
107 Mean and SD of Glucose (mg/dl) Pump suspension time Avg. pump suspension time t (min) CLINICAL EVIDENCE OF SmartGuard TECHNOLOLGY: PILGRIM Study 1 80% of hypoglycaemic events were avoided by use of SmartGuard (defined as SG <70mg/dL) SmartGuard achieved 42% less time spent low compared to Low Glucose Suspend P< Hypoglycemia Sensor Predicted Sensor Excercise Pump Suspension Pump Resumption & Meal Suspend before low Suspend on low Time (min) from pump suspension SmartGuard TM performance Mean SG ± SD at Suspend 92 ± 7.2 mg/dl Mean SG ± SD at Lowest value 77 ± 23 mg/dl Mean SG ± SD for Suspend Duration 90 ± 35 min 1. Danne T, Tsioli C, Kordonouri O, et al. The PILGRIM Study: In Silico Modeling of a Predictive Low Glucose Management System and Feasibility in Youth with Type1 Diabetes During Exercise. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics. 2014; 16(6):338:347.
Pumps & Sensors made easy. OPADA ALZOHAILI MD FACE Endocrinology Assistant Professor Wayne State University
 Pumps & Sensors made easy OPADA ALZOHAILI MD FACE Endocrinology Assistant Professor Wayne State University DeFronzo RA. Diabetes. 2009;58:773-795. Ominous Octet Relationship of b-cell Dysfunction and Development
Pumps & Sensors made easy OPADA ALZOHAILI MD FACE Endocrinology Assistant Professor Wayne State University DeFronzo RA. Diabetes. 2009;58:773-795. Ominous Octet Relationship of b-cell Dysfunction and Development
Report Reference Guide. THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES CareLink Report Reference Guide 1
 Report Reference Guide THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES CareLink Report Reference Guide 1 How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections.
Report Reference Guide THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES CareLink Report Reference Guide 1 How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections.
Report Reference Guide
 Report Reference Guide How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used to generate the sample reports was from sample patient
Report Reference Guide How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used to generate the sample reports was from sample patient
CareLink. software REPORT REFERENCE GUIDE. Management Software for Diabetes
 CareLink Management Software for Diabetes software REPORT REFERENCE GUIDE How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used
CareLink Management Software for Diabetes software REPORT REFERENCE GUIDE How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used
Science Behind Insulin Delivery
 Science Behind Insulin Delivery 1 Overview Objective The objective of this presentation is to demonstrate why insulin pump therapy is more effective than multiple daily shots in delivering superior outcomes
Science Behind Insulin Delivery 1 Overview Objective The objective of this presentation is to demonstrate why insulin pump therapy is more effective than multiple daily shots in delivering superior outcomes
THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES
 THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES Report Report Interpretation Reference Guide Guide 2007 Medtronic MiniMed. All rights reserved. 6025274-0U2 120707 CareLink Pro Report Reference Guide 0 p.2 Sensor
THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES Report Report Interpretation Reference Guide Guide 2007 Medtronic MiniMed. All rights reserved. 6025274-0U2 120707 CareLink Pro Report Reference Guide 0 p.2 Sensor
Diabetes II Insulin pumps; Continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) Ernest Asamoah, MD FACE FACP FRCP (Lond)
 Diabetes II Insulin pumps; Continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) Ernest Asamoah, MD FACE FACP FRCP (Lond) 9501366-011 20110401 Objectives Understand the need for insulin pumps and CGMS in managing
Diabetes II Insulin pumps; Continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) Ernest Asamoah, MD FACE FACP FRCP (Lond) 9501366-011 20110401 Objectives Understand the need for insulin pumps and CGMS in managing
Clinical Evidence for Insulin Pump Therapy
 Clinical Evidence for Insulin Pump Therapy 9501169-011 Objective Review the clinical evidence supporting the use of insulin pump therapy Key Points The benefits of CSII are: Improved metabolic control
Clinical Evidence for Insulin Pump Therapy 9501169-011 Objective Review the clinical evidence supporting the use of insulin pump therapy Key Points The benefits of CSII are: Improved metabolic control
THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES
 THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES Report Report Interpretation Reference Guide Guide 2009 Medtronic MiniMed. All rights reserved. 6025274-012_a CareLink Pro Report Reference Guide 0 p.2 Adherence
THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES Report Report Interpretation Reference Guide Guide 2009 Medtronic MiniMed. All rights reserved. 6025274-012_a CareLink Pro Report Reference Guide 0 p.2 Adherence
Insulin Pump Therapy in children. Prof. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCPCH(UK)
 Insulin Pump Therapy in children Prof. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCPCH(UK) aagha@kau.edu.sa Highlights Evolution of insulin pump Pumps mimics Pancreas Goals of diabetes care What lowers HbA1c Criteria for selection
Insulin Pump Therapy in children Prof. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCPCH(UK) aagha@kau.edu.sa Highlights Evolution of insulin pump Pumps mimics Pancreas Goals of diabetes care What lowers HbA1c Criteria for selection
Welcome to CareLink Pro
 Reference Guide Welcome to CareLink Pro This guide was developed to serve as a reference for obtaining patient data and reviewing CareLink Pro reports. Getting Started with CareLink Pro Adding New Patients
Reference Guide Welcome to CareLink Pro This guide was developed to serve as a reference for obtaining patient data and reviewing CareLink Pro reports. Getting Started with CareLink Pro Adding New Patients
What is a CGM? (Continuous Glucose Monitor) The Bionic Pancreas Is Coming
 The Bionic Pancreas Is Coming Montana Diabetes Professional Conference October 23, 2014 H. Peter Chase, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Colorado Barbara Davis Center Stanford: Bruce Buckingham,
The Bionic Pancreas Is Coming Montana Diabetes Professional Conference October 23, 2014 H. Peter Chase, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Colorado Barbara Davis Center Stanford: Bruce Buckingham,
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies
 1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Insulin pump use: ~ 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM < 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM 2007 FDA estimates ~375,000 insulin pumps for
1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Insulin pump use: ~ 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM < 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM 2007 FDA estimates ~375,000 insulin pumps for
PROTOCOL FOR HYBRID CLOSED LOOP TECHNOLOGY
 PROTOCOL FOR HYBRID CLOSED LOOP TECHNOLOGY Situations Requiring Special Consideration and Resource Documents Second Edition MiniMed 67G System Medical Education TABLE OF CONTENTS A PROTOCOL FOR HYBRID
PROTOCOL FOR HYBRID CLOSED LOOP TECHNOLOGY Situations Requiring Special Consideration and Resource Documents Second Edition MiniMed 67G System Medical Education TABLE OF CONTENTS A PROTOCOL FOR HYBRID
REPORT INTERPRETATION
 REPORT INTERPRETATION: Interpreting ipro Professional Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Reports and Making Therapy Adjustments TARGET AUDIENCE The audience for this section is physicians, mid-level practitioners,
REPORT INTERPRETATION: Interpreting ipro Professional Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Reports and Making Therapy Adjustments TARGET AUDIENCE The audience for this section is physicians, mid-level practitioners,
What is the role of insulin pumps in the modern day care of patients with Type 1 diabetes?
 What is the role of insulin pumps in the modern day care of patients with Type 1 diabetes? Dr. Fiona Wotherspoon Consultant in Diabetes and Endocrinology Dorset County Hospital Fiona.Wotherspoon@dchft.nhs.uk
What is the role of insulin pumps in the modern day care of patients with Type 1 diabetes? Dr. Fiona Wotherspoon Consultant in Diabetes and Endocrinology Dorset County Hospital Fiona.Wotherspoon@dchft.nhs.uk
DISCOVER THE POWER OF CONNECTION MINIMED 640G
 DISCOVER THE POWER OF CONNECTION MINIMED 640G INSULIN PUMP THERAPY CHANGING LIVES TODAY Have you just been diagnosed with insulin dependent diabetes? Perhaps you ve been on multiple daily injection therapy
DISCOVER THE POWER OF CONNECTION MINIMED 640G INSULIN PUMP THERAPY CHANGING LIVES TODAY Have you just been diagnosed with insulin dependent diabetes? Perhaps you ve been on multiple daily injection therapy
CARELINK PERSONAL ACTIONABLE INSIGHTS FOR BETTER DIABETES MANAGEMENT CARELINK REPORTS GUIDE
 CARELINK PERSONAL ACTIONABLE INSIGHTS FOR BETTER DIABETES MANAGEMENT CARELINK REPORTS GUIDE CARELINK PERSONAL ACTIONABLE INSIGHTS FOR BETTER DIABETES MANAGEMENT As part of your diabetes therapy you have
CARELINK PERSONAL ACTIONABLE INSIGHTS FOR BETTER DIABETES MANAGEMENT CARELINK REPORTS GUIDE CARELINK PERSONAL ACTIONABLE INSIGHTS FOR BETTER DIABETES MANAGEMENT As part of your diabetes therapy you have
PREVENTION OF NOCTURNAL HYPOGLYCEMIA USING PREDICTIVE LOW GLUCOSE SUSPEND (PLGS)
 PREVENTION OF NOCTURNAL HYPOGLYCEMIA USING PREDICTIVE LOW GLUCOSE SUSPEND (PLGS) Pathways for Future Treatment and Management of Diabetes H. Peter Chase, MD Carousel of Hope Symposium Beverly Hilton, Beverly
PREVENTION OF NOCTURNAL HYPOGLYCEMIA USING PREDICTIVE LOW GLUCOSE SUSPEND (PLGS) Pathways for Future Treatment and Management of Diabetes H. Peter Chase, MD Carousel of Hope Symposium Beverly Hilton, Beverly
Diabetes and Technology. Saturday, September 9, 2017 Aimee G sell, APRN, ANP-C, CDE
 Diabetes and Technology Saturday, September 9, 2017 Aimee G sell, APRN, ANP-C, CDE Disclosure Speaker s Bureau: Janssan Pharmaceuticals Current Technology V-Go by Valeritas Continuous Sensors (personal
Diabetes and Technology Saturday, September 9, 2017 Aimee G sell, APRN, ANP-C, CDE Disclosure Speaker s Bureau: Janssan Pharmaceuticals Current Technology V-Go by Valeritas Continuous Sensors (personal
Diabetes Technology Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Therapy And Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Adults: An Endocrine Society Clinical
 Diabetes Technology Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Therapy And Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Adults: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline Task Force Members Anne Peters, MD (Chair)
Diabetes Technology Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Therapy And Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Adults: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline Task Force Members Anne Peters, MD (Chair)
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies
 1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the US FDA estimated
1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the US FDA estimated
WOULD YOU LIKE TO REDUCE THE FEAR OF HYPOGLYCAEMIA FOR YOUR PATIENTS?
 WOULD YOU LIKE TO REDUCE THE FEAR OF HYPOGLYCAEMIA FOR YOUR PATIENTS? THE ONLY SYSTEM CLINICALLY PROVEN TO REDUCE HYPOGLYCAEMIA MINIMED 640G SYSTEM WITH SMARTGUARD TECHNOLOGY 1 HYPOGLYCAEMIA IS CHALLENGING
WOULD YOU LIKE TO REDUCE THE FEAR OF HYPOGLYCAEMIA FOR YOUR PATIENTS? THE ONLY SYSTEM CLINICALLY PROVEN TO REDUCE HYPOGLYCAEMIA MINIMED 640G SYSTEM WITH SMARTGUARD TECHNOLOGY 1 HYPOGLYCAEMIA IS CHALLENGING
THE ONLY SYSTEM^ CLINICALLY PROVEN TO REDUCE HYPOGLYCAEMIA
 THE ONLY SYSTEM^ CLINICALLY PROVEN TO REDUCE HYPOGLYCAEMIA MINIMED 640G system^ with SmartGuard technology HYPOGLYCAEMIA IS CHALLENGING FOR GLYCAEMIC CONTROL 1 AND quality of life 2 Achieving good glucose
THE ONLY SYSTEM^ CLINICALLY PROVEN TO REDUCE HYPOGLYCAEMIA MINIMED 640G system^ with SmartGuard technology HYPOGLYCAEMIA IS CHALLENGING FOR GLYCAEMIC CONTROL 1 AND quality of life 2 Achieving good glucose
DISCOVER THE POWER OF CONNECTION MINIMED 640G
 DISCOVER THE POWER OF CONNECTION MINIMED 640G INSULIN PUMP THERAPY CHANGING LIVES TODAY Has your child just been diagnosed with insulin dependent diabetes? Or perhaps they ve been on multiple daily injection
DISCOVER THE POWER OF CONNECTION MINIMED 640G INSULIN PUMP THERAPY CHANGING LIVES TODAY Has your child just been diagnosed with insulin dependent diabetes? Or perhaps they ve been on multiple daily injection
Hypoglycemia a barrier to normoglycemia Are long acting analogues and pumps the answer to the barrier??
 Hypoglycemia a barrier to normoglycemia Are long acting analogues and pumps the answer to the barrier?? Moshe Phillip Institute of Endocrinology and Diabetes National Center of Childhood Diabetes Schneider
Hypoglycemia a barrier to normoglycemia Are long acting analogues and pumps the answer to the barrier?? Moshe Phillip Institute of Endocrinology and Diabetes National Center of Childhood Diabetes Schneider
Today s Goals 10/6/2017. New Frontiers in Diabetes Technology. Disclosures
 New Frontiers in Diabetes Technology Marie E. McDonnell, MD Director, Brigham and Women's Diabetes Program Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Hypertension Brigham and Women s Hospital Today s Goals
New Frontiers in Diabetes Technology Marie E. McDonnell, MD Director, Brigham and Women's Diabetes Program Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Hypertension Brigham and Women s Hospital Today s Goals
Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring: From Application to Evaluation
 Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring: From Application to Evaluation Gary Scheiner MS, CDE Owner/Director, Integrated Diabetes Services 333 E. Lancaster Ave., Suite 24 Wynnewood, PA 1996 (877) 735-3648
Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring: From Application to Evaluation Gary Scheiner MS, CDE Owner/Director, Integrated Diabetes Services 333 E. Lancaster Ave., Suite 24 Wynnewood, PA 1996 (877) 735-3648
Medical Education. Personal Continuous Glucose Monitoring Protocol. Innovating for life.
 Personal Continuous Glucose Monitoring Protocol A Guide to Continuous Glucose Monitoring Integrated with Insulin Pump Therapy Includes Alert and Trend Management as well as Threshold Medical Education
Personal Continuous Glucose Monitoring Protocol A Guide to Continuous Glucose Monitoring Integrated with Insulin Pump Therapy Includes Alert and Trend Management as well as Threshold Medical Education
INSULIN THERAY دکتر رحیم وکیلی استاد غدد ومتابولیسم کودکان دانشگاه علوم پزشکی مشهد
 INSULIN THERAY DIABETES1 IN TYPE دکتر رحیم وکیلی استاد غدد ومتابولیسم کودکان دانشگاه علوم پزشکی مشهد Goals of management Manage symptoms Prevent acute and late complications Improve quality of life Avoid
INSULIN THERAY DIABETES1 IN TYPE دکتر رحیم وکیلی استاد غدد ومتابولیسم کودکان دانشگاه علوم پزشکی مشهد Goals of management Manage symptoms Prevent acute and late complications Improve quality of life Avoid
MINIMED 640G WITH SMARTGUARD GIVES YOU CONFIDENCE TO TAKE CONTROL OF YOUR DIABETES
 MINIMED 640G WITH SMARTGUARD GIVES YOU CONFIDENCE OF YOUR DIABETES HAVE YOU CONSIDERED THE REAL IMPACT HYPOS HAVE ON YOUR LIFE? AN ESTIMATED 1 HOUR EVERY DAY IS LOST TO THE MANAGEMENT OF 43% OF PEOPLE
MINIMED 640G WITH SMARTGUARD GIVES YOU CONFIDENCE OF YOUR DIABETES HAVE YOU CONSIDERED THE REAL IMPACT HYPOS HAVE ON YOUR LIFE? AN ESTIMATED 1 HOUR EVERY DAY IS LOST TO THE MANAGEMENT OF 43% OF PEOPLE
Performance-powered. The OneTouch. Ping insulin pump and meter-remote.
 Performance-powered. The OneTouch Ping insulin pump and meter-remote. I We don t just deliver insulin. We deliver outstanding clinical performance. P36337_OTP_DetAid_OmniPodUpdate_r12.indd 1 OneTouch Ping.
Performance-powered. The OneTouch Ping insulin pump and meter-remote. I We don t just deliver insulin. We deliver outstanding clinical performance. P36337_OTP_DetAid_OmniPodUpdate_r12.indd 1 OneTouch Ping.
Significant HbA1c reduction for type 2 diabetes, now clinically proven *
 Insulin Pump Significant reduction for type 2 diabetes, now clinically proven * OpT2mise: a landmark study, showing significant reduction of for T2 diabetes patients using pump * * Reznik Y. Cohen O. Aronson
Insulin Pump Significant reduction for type 2 diabetes, now clinically proven * OpT2mise: a landmark study, showing significant reduction of for T2 diabetes patients using pump * * Reznik Y. Cohen O. Aronson
WOULD YOU LIKE MORE CONFIDENCE IN YOUR HYPOGLYCAEMIC CONTROL? SMARTGUARD. PROVIDES PREDICTIVE PROTECTION
 WOULD YOU LIKE MORE CONFIDENCE IN YOUR HYPOGLYCAEMIC CONTROL? SMARTGUARD. PROVIDES PREDICTIVE PROTECTION 1,2 MINIMED 640G WITH SMARTGUARD HAVE YOU CONSIDERED THE REAL IMPACT HYPOGLYCAEMIA HAS ON YOUR LIFE?
WOULD YOU LIKE MORE CONFIDENCE IN YOUR HYPOGLYCAEMIC CONTROL? SMARTGUARD. PROVIDES PREDICTIVE PROTECTION 1,2 MINIMED 640G WITH SMARTGUARD HAVE YOU CONSIDERED THE REAL IMPACT HYPOGLYCAEMIA HAS ON YOUR LIFE?
Presented by Dr. Bruce Perkins, MD MPH Dr. Michael Riddell, PhD
 Type 1 Diabetes and Exercise: Optimizing the Medtronic MiniMed Veo Insulin Pump and Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) for Better Glucose Control 1,2 for Healthcare Professionals Presented by Dr. Bruce
Type 1 Diabetes and Exercise: Optimizing the Medtronic MiniMed Veo Insulin Pump and Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) for Better Glucose Control 1,2 for Healthcare Professionals Presented by Dr. Bruce
RELEASED. first steps. Icon Icon name What it means
 Icon Icon name What it means Connection The connection icon appears green when the Sensor feature is on and your transmitter is successfully communicating with your pump. The connection icon appears gray
Icon Icon name What it means Connection The connection icon appears green when the Sensor feature is on and your transmitter is successfully communicating with your pump. The connection icon appears gray
CGM: Continuous Glucose Monitoring Making Sense of It All AW: ANCO/GEND/1016/0117
 CGM: Continuous Glucose Monitoring Making Sense of It All Objectives Review how to do a time effective interpretation of CGM and insulin pump download data Review how medications, lifestyle, and current
CGM: Continuous Glucose Monitoring Making Sense of It All Objectives Review how to do a time effective interpretation of CGM and insulin pump download data Review how medications, lifestyle, and current
1. Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 1. Continuous Glucose Monitoring 1. Physiology of interstitial fluid glucose 2. Comparison of CGM and self-monitored blood glucose (SMBG) data 3. Insulin dosing indication in BGM vs. CGM & the FDA 4. Protection
1. Continuous Glucose Monitoring 1. Physiology of interstitial fluid glucose 2. Comparison of CGM and self-monitored blood glucose (SMBG) data 3. Insulin dosing indication in BGM vs. CGM & the FDA 4. Protection
DEMYSTIFYING INSULIN THERAPY
 DEMYSTIFYING INSULIN THERAPY ASHLYN SMITH, PA-C ENDOCRINOLOGY ASSOCIATES SCOTTSDALE, AZ SECRETARY, AMERICAN SOCIETY OF ENDOCRINE PHYSICIAN ASSISTANTS ARIZONA STATE ASSOCIATION OF PHYSICIAN ASSISTANTS SPRING
DEMYSTIFYING INSULIN THERAPY ASHLYN SMITH, PA-C ENDOCRINOLOGY ASSOCIATES SCOTTSDALE, AZ SECRETARY, AMERICAN SOCIETY OF ENDOCRINE PHYSICIAN ASSISTANTS ARIZONA STATE ASSOCIATION OF PHYSICIAN ASSISTANTS SPRING
Understanding the CareLink TM Therapy Management Dashboard Report
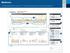 3 2 1 5 6 7 4 1 This is a great place to start recognizing trends. In this example you may see plenty of events that result in a low glucose trend. A low glucose is identified as a value less than 70mg/dL.
3 2 1 5 6 7 4 1 This is a great place to start recognizing trends. In this example you may see plenty of events that result in a low glucose trend. A low glucose is identified as a value less than 70mg/dL.
Insulin Pumps and Continuous Glucose Sensors- Embracing Technology. Susan Cavalier, BS, RN, CDE Manager, Diabetes Educator Sanford Diabetes Education
 Insulin Pumps and Continuous Glucose Sensors- Embracing Technology Susan Cavalier, BS, RN, CDE Manager, Diabetes Educator Sanford Diabetes Education Diabetes Management Tools in 1974 Insulin pump history
Insulin Pumps and Continuous Glucose Sensors- Embracing Technology Susan Cavalier, BS, RN, CDE Manager, Diabetes Educator Sanford Diabetes Education Diabetes Management Tools in 1974 Insulin pump history
This certificate-level program is non-sponsored.
 Program Name: Diabetes Education : A Comprehensive Review Module 5 Intensive Insulin Therapy Planning Committee: Michael Boivin, B. Pharm. Johanne Fortier, BSc.Sc, BPh.LPh, CDE Carlene Oleksyn, B.S.P.
Program Name: Diabetes Education : A Comprehensive Review Module 5 Intensive Insulin Therapy Planning Committee: Michael Boivin, B. Pharm. Johanne Fortier, BSc.Sc, BPh.LPh, CDE Carlene Oleksyn, B.S.P.
Artificial Pancreas Device Systems. Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes. pump. pump
 Protocol Artificial Pancreas Device Systems (10130) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/18 Next Review Date: 01/19 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/15, 03/16, 03/17, 01/18 Preauthorization is required.
Protocol Artificial Pancreas Device Systems (10130) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/18 Next Review Date: 01/19 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/15, 03/16, 03/17, 01/18 Preauthorization is required.
Paradigm/Guardian CGM Screens. CareLink Online Reports. Make Your Own Jackson Pollack. CGM by Jackson Pollack. How To Read CGM Screens/Reports
 CGM by Jackson Pollack One Pollack sold for $140 million in 1996! Make Your Own Jackson Pollack How To Read CGM Screens/Reports For only $1,000! Paradigm/Guardian CGM Screens On-Screen Reports 3 / 6 /
CGM by Jackson Pollack One Pollack sold for $140 million in 1996! Make Your Own Jackson Pollack How To Read CGM Screens/Reports For only $1,000! Paradigm/Guardian CGM Screens On-Screen Reports 3 / 6 /
Making the Most of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 Making the Most of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Gary Scheiner MS, CDE Owner & Clinical Director Integrated Diabetes Services LLC Wynnewood, PA AADE 2014 Diabetes Educator of the Year gary@integrateddiabetes.com
Making the Most of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Gary Scheiner MS, CDE Owner & Clinical Director Integrated Diabetes Services LLC Wynnewood, PA AADE 2014 Diabetes Educator of the Year gary@integrateddiabetes.com
Using the Bolus Wizard Calculator
 9501179-011 Using the Bolus Wizard Calculator Objective Describe the features and benefits of the Bolus Wizard Calculator Key Points The Bolus Wizard: Estimates high blood glucose corrections using the
9501179-011 Using the Bolus Wizard Calculator Objective Describe the features and benefits of the Bolus Wizard Calculator Key Points The Bolus Wizard: Estimates high blood glucose corrections using the
USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM
 USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM Instructions for the Experienced MiniMed 630G System User USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM: INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE EXPERIENCED USER Checklist for starting on your MiniMed 670G
USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM Instructions for the Experienced MiniMed 630G System User USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM: INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE EXPERIENCED USER Checklist for starting on your MiniMed 670G
Technology for Diabetes: 101 Basic Rules of the Road. Karen Hamon RN, BSN, CDE Stephen Stone MD, FAAP Neil H. White, MD, CDE
 Technology for Diabetes: 101 Basic Rules of the Road Karen Hamon RN, BSN, CDE Stephen Stone MD, FAAP Neil H. White, MD, CDE Quick Pump Facts! o Constant insulin supply o Pager-sized mini-computer worn
Technology for Diabetes: 101 Basic Rules of the Road Karen Hamon RN, BSN, CDE Stephen Stone MD, FAAP Neil H. White, MD, CDE Quick Pump Facts! o Constant insulin supply o Pager-sized mini-computer worn
Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 Continuous Glucose Monitoring What is Continuous Glucose Monitoring? Blood glucose meters measure glucose in your blood and glucose sensors measure glucose levels in the fluid around the cells They are
Continuous Glucose Monitoring What is Continuous Glucose Monitoring? Blood glucose meters measure glucose in your blood and glucose sensors measure glucose levels in the fluid around the cells They are
Artificial Pancreas Device Systems. Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes Individuals: With type 1 diabetes
 Protocol Artificial Pancreas Device Systems Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/18 Next Review Date: 01/20 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/15, 03/16, 03/17, 01/18, 05/18, 01/19 Preauthorization
Protocol Artificial Pancreas Device Systems Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/18 Next Review Date: 01/20 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/15, 03/16, 03/17, 01/18, 05/18, 01/19 Preauthorization
MINIMED 670G HYBRID CLOSED LOOP (HCL) IN THE FIELD
 MINIMED 670G HYBRID CLOSED LOOP (HCL) IN THE FIELD USE AND EXAMPLES Rich Flores, RD Diabet es Clinical Manger Northern Minnesota/ St. Cloud WARNING: Territory Medtronic performed an evaluation of the MiniMed
MINIMED 670G HYBRID CLOSED LOOP (HCL) IN THE FIELD USE AND EXAMPLES Rich Flores, RD Diabet es Clinical Manger Northern Minnesota/ St. Cloud WARNING: Territory Medtronic performed an evaluation of the MiniMed
CGM Use in Pregnancy & Unique Populations ELIZABETH O. BUSCHUR, MD THE OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY WEXNER MEDICAL CENTER
 CGM Use in Pregnancy & Unique Populations ELIZABETH O. BUSCHUR, MD THE OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY WEXNER MEDICAL CENTER Case 1: CGM use during pregnancy 29 yo G1P0000 at 10 5/7 weeks gestation presents to set
CGM Use in Pregnancy & Unique Populations ELIZABETH O. BUSCHUR, MD THE OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY WEXNER MEDICAL CENTER Case 1: CGM use during pregnancy 29 yo G1P0000 at 10 5/7 weeks gestation presents to set
WHAT CAN I DO TO REDUCE MY RISK OF DEVELOPING THE COMPLICATIONS OF TYPE 1 DIABETES?
 Christian In better control with his pump since 2012 WHAT CAN I DO TO REDUCE MY RISK OF DEVELOPING THE COMPLICATIONS OF TYPE 1 DIABETES? Many people with Type 1 diabetes worry about potential long-term
Christian In better control with his pump since 2012 WHAT CAN I DO TO REDUCE MY RISK OF DEVELOPING THE COMPLICATIONS OF TYPE 1 DIABETES? Many people with Type 1 diabetes worry about potential long-term
Diabetes Management: Current High Tech Innovations
 Diabetes Management: Current High Tech Innovations How Far We ve Come in the Last 40 Years William V. Tamborlane, MD Department of Pediatrics Yale School of Medicine Disclosures I am a consultant for:
Diabetes Management: Current High Tech Innovations How Far We ve Come in the Last 40 Years William V. Tamborlane, MD Department of Pediatrics Yale School of Medicine Disclosures I am a consultant for:
USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM. Instructions for the Experienced MiniMed 630G System User
 USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM Instructions for the Experienced MiniMed 630G System User This is a supplemental guide. For complete instructions and safety information, please see your MiniMed 670G System
USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM Instructions for the Experienced MiniMed 630G System User This is a supplemental guide. For complete instructions and safety information, please see your MiniMed 670G System
Interpreting the charts & graphs
 Report reference guide mg/dl The diasend solution Interpreting the charts & graphs diasend is a universal cloud-based diabetes data management system, that enables you to upload data from meters, pumps
Report reference guide mg/dl The diasend solution Interpreting the charts & graphs diasend is a universal cloud-based diabetes data management system, that enables you to upload data from meters, pumps
BREAKDOWN OF THE CARELINK REPORTS GETTING STARTED WITH CARELINK PERSONAL SOFTWARE
 BREAKDOWN OF THE CARELINK REPORTS GETTING STARTED WITH CARELINK PERSONAL SOFTWARE TABLE OF CONTENTS GETTING STARTED WITH CARELINK PERSONAL SOFTWARE Introducing CareLink Personal Software Before You Start...
BREAKDOWN OF THE CARELINK REPORTS GETTING STARTED WITH CARELINK PERSONAL SOFTWARE TABLE OF CONTENTS GETTING STARTED WITH CARELINK PERSONAL SOFTWARE Introducing CareLink Personal Software Before You Start...
UNDERSTANDING THE BASIC FEATURES AND MANAGEMENT IN THE SCHOOL SETTING CHRISTINE HERTLER RN BSN CDE & MARY MCCARTHY RN CDE
 UNDERSTANDING THE BASIC FEATURES AND MANAGEMENT IN THE SCHOOL SETTING CHRISTINE HERTLER RN BSN CDE & MARY MCCARTHY RN CDE The insulin pump Replaces injections Delivers insulin through a soft cannula
UNDERSTANDING THE BASIC FEATURES AND MANAGEMENT IN THE SCHOOL SETTING CHRISTINE HERTLER RN BSN CDE & MARY MCCARTHY RN CDE The insulin pump Replaces injections Delivers insulin through a soft cannula
Control of Glycemic Variability for Reducing Hypoglycemia Jae Hyeon Kim
 Control of Glycemic Variability for Reducing Hypoglycemia Jae Hyeon Kim Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Conflict of interest
Control of Glycemic Variability for Reducing Hypoglycemia Jae Hyeon Kim Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Conflict of interest
Understanding the CareLinkTM Sensor Meter Overview Report: Page 1
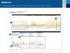 Understanding the CareLinkTM Sensor Meter Overview Report: Page 1 Sensor & Meter Overview (1 of 3) 4-Hour Glucose Sensor Overlay - Readings & Averages (mg/dl) 1 Glucose Sensor Overlay Bedtime to Wake-Up
Understanding the CareLinkTM Sensor Meter Overview Report: Page 1 Sensor & Meter Overview (1 of 3) 4-Hour Glucose Sensor Overlay - Readings & Averages (mg/dl) 1 Glucose Sensor Overlay Bedtime to Wake-Up
Injecting Insulin into Out Patient Practice
 Injecting Insulin into Out Patient Practice Kathleen Colleran, MD Associate Professor UNMHSC 4/22/10 Overview Natural history of Type 2 diabetes Reasons clinicians are reluctant to start insulin therapy
Injecting Insulin into Out Patient Practice Kathleen Colleran, MD Associate Professor UNMHSC 4/22/10 Overview Natural history of Type 2 diabetes Reasons clinicians are reluctant to start insulin therapy
University College Hospital. Blood glucose and HbA 1 c targets
 University College Hospital Blood glucose and HbA 1 c targets Children & Young People s Diabetes Service The diabetes team at UCLH aims to help every child and young person with Type 1 Diabetes to safely
University College Hospital Blood glucose and HbA 1 c targets Children & Young People s Diabetes Service The diabetes team at UCLH aims to help every child and young person with Type 1 Diabetes to safely
Comprehensive Diabetes Treatment
 Comprehensive Diabetes Treatment Joshua L. Cohen, M.D., F.A.C.P. Professor of Medicine Interim Director, Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism The George Washington University School of Medicine Diabetes
Comprehensive Diabetes Treatment Joshua L. Cohen, M.D., F.A.C.P. Professor of Medicine Interim Director, Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism The George Washington University School of Medicine Diabetes
INSPIRED BY GIVE HER MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs.
 INSPIRED BY GIVE HER MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs. * NOW APPROVED FOR AGES 7 AND UP. MORE TIME HERE TO USING
INSPIRED BY GIVE HER MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs. * NOW APPROVED FOR AGES 7 AND UP. MORE TIME HERE TO USING
New basal insulins Are they any better? Matthew C. Riddle, MD Professor of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Keystone Colorado 15 July 2011
 New basal insulins Are they any better? Matthew C. Riddle, MD Professor of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Keystone Colorado 15 July 2011 Presenter Disclosure I have received the following
New basal insulins Are they any better? Matthew C. Riddle, MD Professor of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Keystone Colorado 15 July 2011 Presenter Disclosure I have received the following
Anneli, Martina s daughter In better control with her pump since 2011 MY CHILD HAS TYPE 1 DIABETES
 Anneli, Martina s daughter In better control with her pump since 2011 MY CHILD HAS TYPE 1 DIABETES Many parents whose child is diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes wonder: Why is this happening to my child?
Anneli, Martina s daughter In better control with her pump since 2011 MY CHILD HAS TYPE 1 DIABETES Many parents whose child is diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes wonder: Why is this happening to my child?
Current Glucometers. Junior s s Glucose Log. All have advantages and disadvantages Answer 2
 Diabetes Dilemmas: Using Technology To Solve Clinical Conundrums Stephen E. Gitelman, MD UCSF A teenager with type 1 diabetes for 5 years comes into your office for a follow- up visit. You want to review
Diabetes Dilemmas: Using Technology To Solve Clinical Conundrums Stephen E. Gitelman, MD UCSF A teenager with type 1 diabetes for 5 years comes into your office for a follow- up visit. You want to review
Artificial Pancreas Device System (APDS)
 Medical Policy Manual Durable Medical Equipment, Policy No. 77 Artificial Pancreas Device System (APDS) Next Review: October 2019 Last Review: October 2018 Effective: November 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER
Medical Policy Manual Durable Medical Equipment, Policy No. 77 Artificial Pancreas Device System (APDS) Next Review: October 2019 Last Review: October 2018 Effective: November 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER
INSPIRED BY GIVE HIM MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs.
 INSPIRED BY GIVE HIM MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs. * NOW APPROVED FOR AGES 7 AND UP. Waterproof to a depth
INSPIRED BY GIVE HIM MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs. * NOW APPROVED FOR AGES 7 AND UP. Waterproof to a depth
1. What s the point of a network the case for research? 2. How to use CSII effectively
 1. What s the point of a network the case for research? 2. How to use CSII effectively John Pickup King s College London Faculty of Medicine Guy s Hospital, London What should an insulin pump network do?
1. What s the point of a network the case for research? 2. How to use CSII effectively John Pickup King s College London Faculty of Medicine Guy s Hospital, London What should an insulin pump network do?
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies
 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 1979 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% to 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the U.S. FDA
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 1979 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% to 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the U.S. FDA
Paolo Di Bartolo U.O di Diabetologia Dip. Malattie Digestive & Metaboliche AULS Prov. di Ravenna. Ipoglicemie e Monitoraggio Glicemico
 Paolo Di Bartolo U.O di Diabetologia Dip. Malattie Digestive & Metaboliche AULS Prov. di Ravenna Ipoglicemie e Monitoraggio Glicemico Management of Hypoglycaemia.if hypoglycemia is a problem, the principles
Paolo Di Bartolo U.O di Diabetologia Dip. Malattie Digestive & Metaboliche AULS Prov. di Ravenna Ipoglicemie e Monitoraggio Glicemico Management of Hypoglycaemia.if hypoglycemia is a problem, the principles
The Realities of Technology in Type 1 Diabetes
 The Realities of Technology in Type 1 Diabetes May 6, 2017 Rosanna Fiallo-scharer, MD Margaret Frederick, RN Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest to disclose I will discuss some unapproved treatments
The Realities of Technology in Type 1 Diabetes May 6, 2017 Rosanna Fiallo-scharer, MD Margaret Frederick, RN Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest to disclose I will discuss some unapproved treatments
How I use the latest technology to investigate and treat a person with Type 1 Diabetes. Dr Pratik Choudhary
 How I use the latest technology to investigate and treat a person with Type 1 Diabetes Dr Pratik Choudhary Disclosures Advisory board and speaker fees from Medtronic, Roche, Abbott and Johnson and Johnson,
How I use the latest technology to investigate and treat a person with Type 1 Diabetes Dr Pratik Choudhary Disclosures Advisory board and speaker fees from Medtronic, Roche, Abbott and Johnson and Johnson,
PATIENT TRAINING CHECKLIST MINIMED 670G SYSTEM
 Technical Training Insulin Pump Infusion Set: Insulin Pump Model: BASIC FEATURES Patient has demonstrated understanding of: Button Functions Home Screen Menu review Status Screens Battery type/insertion
Technical Training Insulin Pump Infusion Set: Insulin Pump Model: BASIC FEATURES Patient has demonstrated understanding of: Button Functions Home Screen Menu review Status Screens Battery type/insertion
Pump Therapy - Simple, Proven, and Well Accepted
 Pump Therapy - Simple, Proven, and Well Accepted Innovating for life. Pump therapy is simple for providers and patients Healthcare Providers Simple outpatient procedure: Low burden and cost to transition
Pump Therapy - Simple, Proven, and Well Accepted Innovating for life. Pump therapy is simple for providers and patients Healthcare Providers Simple outpatient procedure: Low burden and cost to transition
Insulin Pumps and Glucose Sensors in Diabetes Management
 Diabetes Update+ 2014 Congress Whistler, British Columbia Friday March 21, 2014ǀ 8:15 8:45 am Insulin Pumps and Glucose Sensors in Diabetes Management Bruce A Perkins MD MPH Division of Endocrinology Associate
Diabetes Update+ 2014 Congress Whistler, British Columbia Friday March 21, 2014ǀ 8:15 8:45 am Insulin Pumps and Glucose Sensors in Diabetes Management Bruce A Perkins MD MPH Division of Endocrinology Associate
Pump and Sensor Data Interpretation. Irl B. Hirsch, MD University of Washington School of Medicine
 Pump and Sensor Data Interpretation Irl B. Hirsch, MD University of Washington School of Medicine Dualities Research: Medtronic Diabetes Consulting: Abbott Diabetes Care, BD, Bigfoot, Roche Raise Your
Pump and Sensor Data Interpretation Irl B. Hirsch, MD University of Washington School of Medicine Dualities Research: Medtronic Diabetes Consulting: Abbott Diabetes Care, BD, Bigfoot, Roche Raise Your
The Growing Future of Diabetes: Insulin Pump Therapy in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes
 The Growing Future of Diabetes: Insulin Pump Therapy in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Sarah Dombrowski, PharmD, BCACP Pennsylvania Pharmacists Association 10/20/18 1 Objectives At the completion of this activity,
The Growing Future of Diabetes: Insulin Pump Therapy in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Sarah Dombrowski, PharmD, BCACP Pennsylvania Pharmacists Association 10/20/18 1 Objectives At the completion of this activity,
Agenda. Indications Different insulin preparations Insulin initiation Insulin intensification
 Insulin Therapy F. Hosseinpanah Obesity Research Center Research Institute for Endocrine sciences Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences November 11, 2017 Agenda Indications Different insulin preparations
Insulin Therapy F. Hosseinpanah Obesity Research Center Research Institute for Endocrine sciences Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences November 11, 2017 Agenda Indications Different insulin preparations
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE GUIDANCE EXECUTIVE (GE)
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE GUIDANCE EXECUTIVE (GE) Review of TA151 Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for the treatment of diabetes mellitus This guidance was issued in
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE GUIDANCE EXECUTIVE (GE) Review of TA151 Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for the treatment of diabetes mellitus This guidance was issued in
Evidence and Guidelines TECHNOLOGY 2016 Tina Kader, MD
 Evidence and Guidelines TECHNOLOGY 216 Tina Kader, MD Staff endocrinologist Jewish General Hospital Certified Diabetes Educator Montreal, Quebec AACE/ACE 215 Guidelines Glucose Monitoring: When, How, and
Evidence and Guidelines TECHNOLOGY 216 Tina Kader, MD Staff endocrinologist Jewish General Hospital Certified Diabetes Educator Montreal, Quebec AACE/ACE 215 Guidelines Glucose Monitoring: When, How, and
Diagnostics guidance Published: 12 February 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/dg21
 Integrated sensor-augmented pump therapy systems for managing blood glucose levels els in type 1 diabetes (the MiniMed Paradigm adigm Veo system and the Vibe and G4 PLATINUM CGM system) Diagnostics guidance
Integrated sensor-augmented pump therapy systems for managing blood glucose levels els in type 1 diabetes (the MiniMed Paradigm adigm Veo system and the Vibe and G4 PLATINUM CGM system) Diagnostics guidance
A Prospective Evaluation of Insulin Dosing Recommendations in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes at Near Normal Glucose Control: Bolus Dosing
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 1, Issue 1, January 2007 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLES A Prospective Evaluation of Insulin Dosing Recommendations in Patients with Type
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 1, Issue 1, January 2007 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLES A Prospective Evaluation of Insulin Dosing Recommendations in Patients with Type
Clinical Value and Evidence of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 Clinical Value and Evidence of Continuous Glucose Monitoring 9402313-012 Objective To review the clinical value and the recent clinical evidence for Professional and Personal CGM Key Points CGM reveals
Clinical Value and Evidence of Continuous Glucose Monitoring 9402313-012 Objective To review the clinical value and the recent clinical evidence for Professional and Personal CGM Key Points CGM reveals
Incorporating CGM Into Clinical Decision Making. Etie Moghissi, MD, FACE Clinical Associate Professor, David Geffen School of Medicine UCLA
 Incorporating CGM Into Clinical Decision Making Etie Moghissi, MD, FACE Clinical Associate Professor, David Geffen School of Medicine UCLA 1 Limitations of Current Glucose Monitoring Methods A1c Standard
Incorporating CGM Into Clinical Decision Making Etie Moghissi, MD, FACE Clinical Associate Professor, David Geffen School of Medicine UCLA 1 Limitations of Current Glucose Monitoring Methods A1c Standard
Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring Methods for Diabetes Mellitus: Comparative Effectiveness
 Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring Methods for Diabetes Mellitus: Comparative Effectiveness Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) www.ahrq.gov Outline of Material Introduction
Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring Methods for Diabetes Mellitus: Comparative Effectiveness Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) www.ahrq.gov Outline of Material Introduction
CAROLINAS CHAPTER/AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGISTS Annual Meeting HILTON HEAD ISLAND FRIDAY PRESENTATION
 CAROLINAS CHAPTER/AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGISTS 2016 Annual Meeting HILTON HEAD ISLAND FRIDAY PRESENTATION September 9-11, 2016 ~ Sonesta Resort ~ Hilton Head Island, SC This continuing
CAROLINAS CHAPTER/AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGISTS 2016 Annual Meeting HILTON HEAD ISLAND FRIDAY PRESENTATION September 9-11, 2016 ~ Sonesta Resort ~ Hilton Head Island, SC This continuing
Opinion 18 December 2013
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE Opinion 18 December 2013 LANTUS 100 units/ml, solution for injection in a vial B/1 vial of 10 ml (CIP: 34009 359 464 9 2)
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE Opinion 18 December 2013 LANTUS 100 units/ml, solution for injection in a vial B/1 vial of 10 ml (CIP: 34009 359 464 9 2)
Basics of Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Therapy. Lubna Mirza, MD Norman Endocrinology Associates 2018
 Basics of Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Therapy Lubna Mirza, MD Norman Endocrinology Associates 2018 Preamble Roughly 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients
Basics of Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Therapy Lubna Mirza, MD Norman Endocrinology Associates 2018 Preamble Roughly 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients
THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM SCHOOL NURSE GUIDE
 THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM SCHOOL NURSE GUIDE Indicated for type 1 patients 14 and over. Prescription required. WARNING: Medtronic performed an evaluation of the MiniMed 670G system and determined that it
THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM SCHOOL NURSE GUIDE Indicated for type 1 patients 14 and over. Prescription required. WARNING: Medtronic performed an evaluation of the MiniMed 670G system and determined that it
Emerging Automated Insulin Delivery Systems
 Emerging Automated Insulin Delivery Systems Richard M. Bergenstal, MD International Diabetes Center Park Nicollet & HealthPartners Minneapolis, MN Presenter Name 1 Dualities: Richard M. Bergenstal, MD
Emerging Automated Insulin Delivery Systems Richard M. Bergenstal, MD International Diabetes Center Park Nicollet & HealthPartners Minneapolis, MN Presenter Name 1 Dualities: Richard M. Bergenstal, MD
Advances in Technology in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus 2017 How far have we come-how far are we going? Is there a final frontier?
 Advances in Technology in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus 2017 How far have we come-how far are we going? Is there a final frontier? Alan B Schorr DO FAAIM FACE www.sugardoc.com abs@sugardoc.com Disclosures
Advances in Technology in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus 2017 How far have we come-how far are we going? Is there a final frontier? Alan B Schorr DO FAAIM FACE www.sugardoc.com abs@sugardoc.com Disclosures
Subject Index. Breastfeeding, self-monitoring of blood glucose 56
 Subject Index Animas Vibe 86, 130 Artificial pancreas clinical studies inpatient studies 175 180 outpatient studies outcome assessment 182, 183 technology 180, 181 telemedicine 182 components glucose sensor
Subject Index Animas Vibe 86, 130 Artificial pancreas clinical studies inpatient studies 175 180 outpatient studies outcome assessment 182, 183 technology 180, 181 telemedicine 182 components glucose sensor
Fine-tuning of The Dose of Insulin Pump
 Fine-tuning of The Dose of Insulin Pump The manual does not guarantee specific individual or specific applicability of the environment, there is no express or implied warranties. Contents of this manual
Fine-tuning of The Dose of Insulin Pump The manual does not guarantee specific individual or specific applicability of the environment, there is no express or implied warranties. Contents of this manual
Type 1 DM. CME Away India & Sri Lanka March 23 - April 7, 2018
 Type 1 DM CME Away India & Sri Lanka March 23 - April 7, 2018 Richard A. Bebb MD, ABIM, FRCPC Consultant Endocrinologist Medical Subspecialty Institute Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Copyright 2017 by Sea
Type 1 DM CME Away India & Sri Lanka March 23 - April 7, 2018 Richard A. Bebb MD, ABIM, FRCPC Consultant Endocrinologist Medical Subspecialty Institute Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Copyright 2017 by Sea
UNCOVERING THE BENEFITS OF THE ACCU- CHEK BOLUS ADVISOR MICHAEL PORTER CDE
 UNCOVERING THE BENEFITS OF THE ACCU- CHEK BOLUS ADVISOR MICHAEL PORTER CDE 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this session participants should be able to understand: The benefits of bolus advisors The
UNCOVERING THE BENEFITS OF THE ACCU- CHEK BOLUS ADVISOR MICHAEL PORTER CDE 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this session participants should be able to understand: The benefits of bolus advisors The
OneTouch Reveal web app Report Reference Guide
 OneTouch Reveal web app Report Reference Guide Your step-by-step guide to setting up and using the OneTouch Reveal web app OneTouch Verio meter OneTouch Verio Flex meter OneTouch Verio IQ meter OneTouch
OneTouch Reveal web app Report Reference Guide Your step-by-step guide to setting up and using the OneTouch Reveal web app OneTouch Verio meter OneTouch Verio Flex meter OneTouch Verio IQ meter OneTouch
Applications of Technologies to Your Patient. Irl B. Hirsch, MD Professor of Medicine University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle, Washington
 Applications of Technologies to Your Patient Irl B. Hirsch, MD Professor of Medicine University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle, Washington Disclosures Consultant: Abbott Diabetes Care, Roche
Applications of Technologies to Your Patient Irl B. Hirsch, MD Professor of Medicine University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle, Washington Disclosures Consultant: Abbott Diabetes Care, Roche
INSULIN INITIATION AND INTENSIFICATION WITH A FOCUS ON HYPOGLYCEMIA REDUCTION
 INSULIN INITIATION AND INTENSIFICATION WITH A FOCUS ON HYPOGLYCEMIA REDUCTION Jaiwant Rangi, MD, FACE Nov 10 th 2018 DISCLOSURES Speaker Novo Nordisk Sanofi-Aventis Boheringer Ingleheim Merck Abbvie Abbott
INSULIN INITIATION AND INTENSIFICATION WITH A FOCUS ON HYPOGLYCEMIA REDUCTION Jaiwant Rangi, MD, FACE Nov 10 th 2018 DISCLOSURES Speaker Novo Nordisk Sanofi-Aventis Boheringer Ingleheim Merck Abbvie Abbott
